- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Department of Stroke Center, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 3Hematology Department, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 4Department of Clinical Laboratory, Weihai Haida Hospital, Weihai, Shandong, China
- 5Jinan Biomedical Industry Academy of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong, China
Introduction: Despite improvements in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), some patients still suffer from functional impairments, indicating the poor understanding of pathophysiologic process of AIS. Inflammation plays an important role in the pathophysiology of AIS. The purpose of the study was to investigate the peripheral inflammation in different subtypes of AIS.
Methods: Here, retrospective data from AIS with large vessel occlusion (LVO) and small vessel occlusion (SVO), and healthy controls, were initially analyzed. Then, flow cytometry was performed to evaluate the levels of peripheral naïve and memory T-cells. Finally, we characterized the T cell receptors (TCR) repertoire using high-throughput sequencing.
Results: Elevated levels of leukocytes, neutrophils, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and decreased levels of lymphocytes were found in LVO group than that in SVO group, which were correlated with the severity of LVO. In addition, higher percentages of both effector memory (Tem) and central memory (Tcm) T cells, and lower percentage of naïve T cells in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, were found in LVO group than that in SVO and healthy groups. Moreover, impaired TCR diversity, and different abundances of V-J gene combinations and amino acid sequences, were found in LVO as compared with healthy group, which would be potential biomarkers for LVO diagnosis.
Discussion: In conclusion, AIS with LVO can rapidly induce peripheral immune response, which provides new insight into the understanding of pathophysiology of AIS.
Introduction
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is one of the leading causes of mortality and disability worldwide (1). It occurs due to brain ischemia resulting from the thrombosis of cerebral blood vessels (2), which can be mainly caused by large artery atherosclerosis (LAA) and small artery occlusion (SAO) according to the Trial of Org 10,172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) classification (3). Although the outcomes of AIS have dramatically improved due to the effectiveness of endovascular therapy, these treatments are highly time-dependent and only a few patients with AIS could receive effective treatment in time (4). Most importantly, several strategies with regarding to AIS therapy have not been successfully translated into clinical application to date (5). These indicate that the pathological and physiological process contributing to neurological injury following AIS have not yet been fully understood.
Increasing evidence confirms that the activation of immune response is a crucial contributor to the pathophysiology of AIS (6, 7). Peripheral immune cells, such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes, play important roles in the progression of AIS (8). In addition, the high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a potential predictor of poor functional outcome in patients with AIS (9). However, the changes of the peripheral components in different subtypes of AIS remains unclear.
The levels of lymphocytes were confirmed to be correlated with the outcome of AIS. Decreased number of lymphocytes was associated with worse pathological complete response rate of stroke (10), while increased proportion of lymphocytes had beneficial effects in AIS (11, 12). Among all the lymphocytes, T cells have been extensively studied because of their potency in both innate and adaptive immune responses (13). They are divided into CD4+ helper T cells, CD8+ toxic T cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs) according to the different surface markers (14, 15), which play different regulatory roles in the pathophysiological process of AIS depending on their functional characteristics. The reduction of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells within 24 h after AIS leads to a decrease in the infarct size. In contrast, Tregs have protective effect on lowering infarct area and improving neurological function (16, 17). In addition, studies have shown that T cells could promote the deterioration of functional damage in the early stage but improve prognosis in the later stage of AIS, suggesting the different roles of T cell subsets in AIS (18, 19). Moreover, immune cell infiltration analysis suggested that T cell subsets with relevant genes can be identified as the diagnostic biomarkers in AIS (20). Therefore, it is essential to investigate the functions of different T cell subsets in AIS, which will provide new insights into the pathophysiological mechanisms of AIS. Recent years, a new group of T cells with CD45 surface markers has been discovered, which can be divided into two new subgroups: CD45RA+ naïve T cells and CD45RO+ memory T cells (21). Previous studies have confirmed the involvement of CD45 subsets in different diseases, such as sepsis and T-cell lymphoma (21, 22). However, it is still unknown whether CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ T cells are involved in the progression of AIS.
T cells initiate their major functions through T cell receptors (TCRs), which are produced by somatic DNA recombination of multiple gene segments (23). The diversity is generated by the random rearrangement of the variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) segments of TCR genes, which are central components of the adaptive immune system. TCR sequences are individual and have complex genetics due to VDJ recombination (24). Analysis of the TCR repertoire can provide a better understand of immune-mediated responses to infections, malignancies, and immunological disorders, including neuroinflammatory diseases. Based on technological advances in high-throughput sequencing (HTS), millions of TCR sequences can be used to assess clonal expansion and diversity in the peripheral blood of the multiple sclerosis (MS) patients (25, 26). The unique sequences will be valuable biomarkers for immune-mediated disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response. Although a few studies have focused on TCR or characteristics of TCR repertoires in brain or peripheral blood of AIS (27–29), these studies did not distinguish the changes of TCR characteristic in the subtypes of AIS.
In the present study, we initially analyzed the circulating data retrospectively in patients with AIS, which were divided into large-vessel occlusion (LVO) and small-vessel occlusion (SVO) by imaging methods. Then, peripheral blood samples of patients with LVO and SVO were collected to detect proportional changes of CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ T cells. Finally, the TCR repertoire was analyzed to identify the unique immune response in AIS with LVO.
Materials and methods
Research ethics
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University (No. SZR2021-006-01) and The Second Hospital of Shandong University (No. KYLL-2021 (KJ)P-0300).
Study population
Retrospective data from 368 patients with AIS (≥18 years old), recruited from both Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University (n = 312) and The Second Hospital of Shandong University (n = 56) between September 2022 to December 2023, were analyzed for peripheral clinical characteristics. The AIS patients were divided into large vessel occlusion (LVO, n = 161) and small vessel occlusion (SVO, n = 207) using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography angiography (CTA), brain magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and/or digital subtraction angiography (DSA) (30). Exclusion criteria: (1) only received MRI without further brain imaging; (2) had severe other disease, such as liver or kidney dysfunction, cardiac impairment; (3) had severe inflammatory conditions. The age- and sex-matched healthy participations (n = 167), which were confirmed to have no cerebrovascular disease or other sever conditions in the physical Examination Department of The Second Hospital of Shandong University over the same period, were included as the control group.
Clinical data collection
Venous blood samples were collected within the first 24 h of stroke onset. Blood glucose, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), and counts of leukocyte, neutrophile, and lymphocyte as well as the proportion of neutrophile and lymphocyte, were analyzed. The NLR was calculated as the ratio of the absolute neutrophile counts to the absolute lymphocyte counts. The stroke severity at onset was evaluated using National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) (31).
Flow cytometry analysis
To determine the phenotype of T cells, 18 patients with LVO and 17 patients with SVO, aged from 32 to 82 years, were recruited from both Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University (LVO, n = 8) and The Second Hospital of Shandong University (SVO, n = 17; LVO, n = 10) from May to December 2023. Peripheral anticoagulant blood samples from patients were obtained within 24 h of AIS onset at the Department of Clinical Laboratory. The samples of 22 healthy controls were collected at the same time. The whole blood of each sample was mixed gently and transferred into five groups (100 μL/tube): (1) labeled with APC-conjugated mouse anti-human CD3 (#317318, Biolegend, San Diego, CA, United States) and FITC-conjugated mouse anti-human CD56 (#304604, Biolegend) antibody; (2) labeled with APC-conjugated mouse anti-human CD3, FITC-conjugated mouse anti-human CD4 (#300506, Biolegend), and PE-conjugated mouse anti-human CD8 (#344706, Biolegend) antibody; (3) labeled with PE-conjugated mouse anti-human CD4 (#300508, Biolegend), PerCP-conjugated mouse anti-human CD45RA (#304156, Biolegend), FITC-conjugated mouse anti-human CD45RO (#304204, Biolegend), and APC-conjugated mouse anti-human CCR7 (#353214, Biolegend) antibody; (4) labeled with PE-conjugated mouse anti-human CD8, PerCP-conjugated mouse anti-human CD45RA, FITC-conjugated mouse anti-human CD45RO, and APC-conjugated mouse anti-human CCR7 antibody; (5) the isotype control tube labeled with APC/FITC/PE/PerCP rat anti-human IgG antibody (#410712, #410720, #410707, #410710, Biolegend). Five microliter of each antibody was added into the corresponding tube and incubated for 20 min. Then, 1 mL erythrocyte lysing buffer (#555899, BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, United States) was added and incubated at 37°C for 5 min. After centrifugation for 5 min, the cells were resuspended and washed with 1 mL phosphate buffer solution (PBS). Finally, after being suspended with 0.5 mL PBS, the cells were detected by flow cytometry (FACS Aria III; BD Biosciences). The gating strategy applied for the enumeration of T cells is shown in Supplementary Figure S1. Peripheral whole blood cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, and red blood cells, can be divided into different populations based on cell size and granularity, as measured by forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) characteristics, respectively. Lymphocyte were gated on the basis of FSC and SSC characteristics for the following research. The cells were analyzed by using FlowJo VX10 software (TreeStar, Ashland, OR, United States).
HTS of TCR repertoire
Peripheral blood samples were collected into EDTA vacutainer tubes at volumes more than 2 mL. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from whole blood samples using Ficoll density-gradient separation lysis (LTS1077-1, TBD, Tianjin, China) according to the instructor. Total RNA was extracted from PBMCs using RNAsimple Total RNA Kit (#DP419, Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). RNA concentration was evaluated using a NanoDrop ND-2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, United Kingdom). cDNA synthesis and multiplex PCR amplification of the complementary-determining region 3 (CDR3) in the TCR β-chain were performed together using the Immune Repertoire Library Preparation Kit (Geneway, Jinan, China) following a protocol described in a previous study (32). TCR libraries were sequenced on DNBSEQ-T7 platform (MGI, Shenzhen, China), generating paired-end short reads with 150 bp in length.
Sequencing data preprocessing
The sequencing data were stored in FASTQ format, in which raw reads were demultiplexed according to the sequences of index primers corresponding to different samples. The low-quality sequences were discarded for quality control. The remainders were mapped into V, D, and J gene segments of TCR β-chain using the MiXCR software (version 3.0.6) with default parameters for sequencing alignment and clonotype assembly (33). TCR reference gene data were downloaded from the IMGT database1. The frequency of each TCR β-clonotype was further converted into rpm (reads per million) for standardization. The diversity of samples was evaluated based on D50 Diversity index and UT index. The diversity from the cumulative 50% of the total CDR3 detected in the sample was measured using the D50 index (34). The UT index was ranged from 0 to 1, and it was calculated based on the previous study (35).
Statistical analyses
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software (Version VIII, La Jolla, CA, United States) or R software (version 4.0.2). Continuous data were presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). In contrast, categorical variables were presented as numbers and percentages. In the analysis of retrospective data and flow cytometry, the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal–Wallis test was used for comparisons between more than two groups based on data distribution and homogeneity. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test was used when the data showed normal distribution and variance homogeneity, otherwise Kruskal–Wallis test was applied. For continuous variables in the TCR repertoire, Student’s t-test was used for comparison between two groups, and the correlation between NIHSS and levels of peripheral blood cells, or between NIHSS and TCR clonotypes expression, was assessed using Pearson’s test. The Chi-Square test or Fisher’s exact test was used to analyze categorical variables. p < 0.05 was considered the threshold for statistical significance.
Results
Participation clinical characteristics
To determine the peripheral immune responses in different subtypes of AIS, we initially analyzed the retrospective data from patients with LVO, SVO, and healthy controls. The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1 and Supplementary File 1. No significant differences were found among the three groups in baseline characteristics including age and gender. As risk factors of AIS, lower levels of HDL cholesterol, and high levels of both blood glucose and triglyceride were found in patients with LVO and SVO groups than in healthy controls (p < 0.0001). No significant change was found in levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol after AIS.
The laboratory parameters in patients with LVO and SVO were significantly different from those of healthy controls (Figure 1 and Supplementary File 1). The leukocyte count in the patients’ groups was higher than that in the healthy control group (Figure 1A, p < 0.0001), which was mainly due to an elevated neutrophile count (Figure 1B, p < 0.0001). In contrast, the lymphocyte count decreased in patients with AIS compared to the healthy control group (Figure 1C, p < 0.0001). An increased ratio of neutrophile to leukocyte and a decreased ratio of lymphocyte to leukocyte were also observed in patients with AIS (Figures 1D,E, p < 0.0001). As NLR has been reported to be a useful marker of inflammation, we also compared NLR in the three groups. Consistent with the previous study, NLR was higher in patients than that in healthy controls (Figure 1F, p < 0.0001). Interestingly, we found higher counts of leukocyte (Figure 1A, p < 0.0001) and neutrophile (Figure 1B, p < 0.0001), and elevated ratio of neutrophile to leukocyte (Figure 1D, p < 0.0001) and NLR (Figure 1F, p < 0.0001) in LVO group than that in SVO group. In contrast, lymphocyte count (Figure 1C, p = 0.0003) and ratio of lymphocyte to leukocyte (Figure 1E, p < 0.0001) in LVO group were decreased as compared with that in SVO group. These results suggest that AIS with LVO can rapidly induce more severe immune response in the peripheral blood.
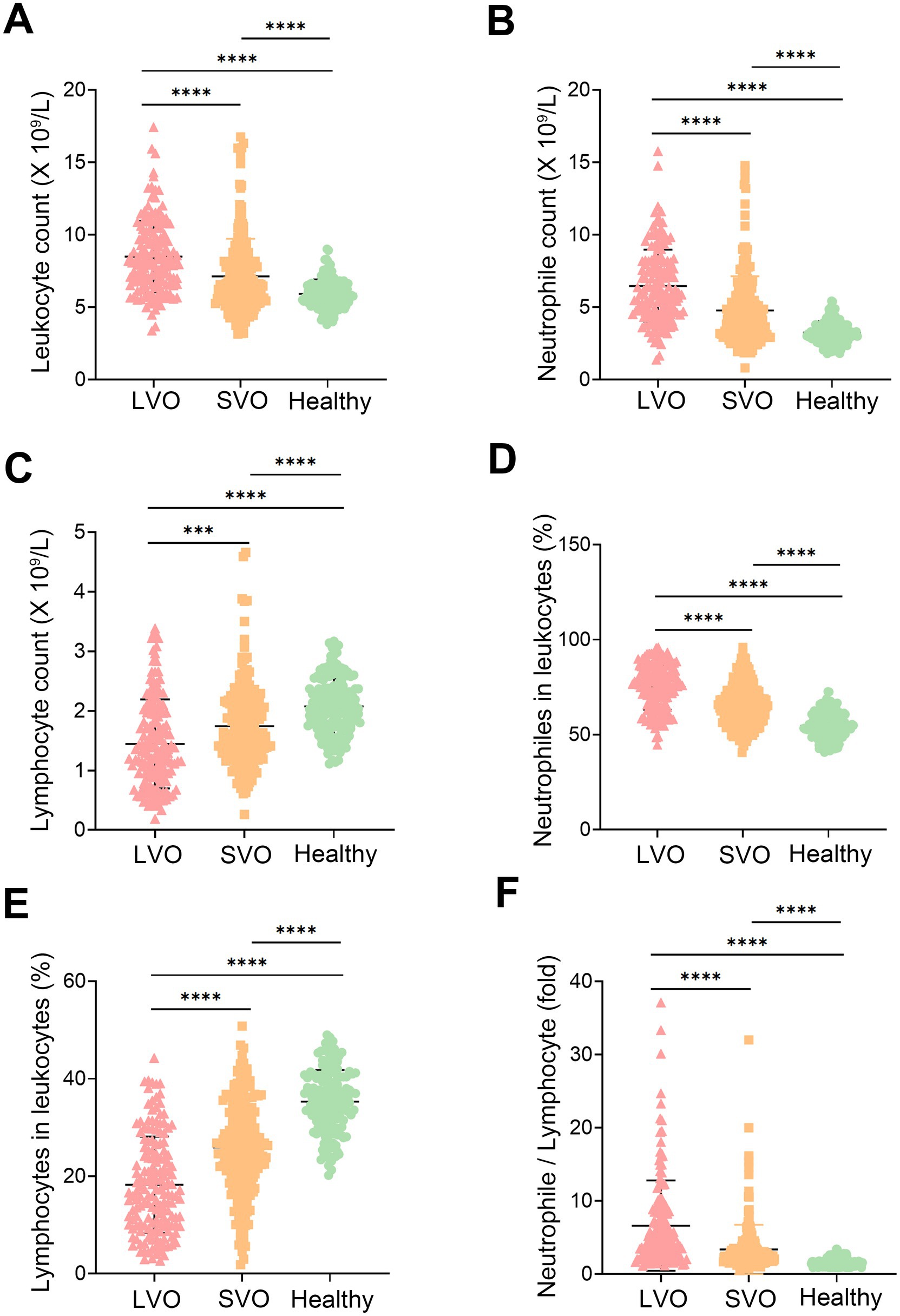
Figure 1. Participation characteristics. Leukocyte (A), neutrophile (B), and lymphocyte (C) counts in the peripheral blood of AIS with LVO and SVO, and healthy controls. The ratio of neutrophiles (D) and lymphocytes (E) to leukocytes in the peripheral blood of AIS with LVO and SVO, and healthy controls. (F) The ratio of neutrophile to lymphocyte in the peripheral blood of AIS with LVO and SVO, and healthy controls. (***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).
Correlation between peripheral blood cells and NIHSS
To determine whether there was a relationship between the expression levels of peripheral blood cells and the severity of AIS, we analyzed the correlation between the peripheral laboratory data and NIHSS in LVO group and SVO group, respectively. As shown in Figure 2 and Supplementary File 1, the counts of leukocytes (Figure 2A, r = 0.1686, p = 0.0331) and neutrophiles (Figure 2B, r = 0.2236, p = 0.0045), and the percentage of neutrophiles (Figure 2D, r = 0.2979, p = 0.0001) as well as NLR (Figure 2F, r = 0.2286, p = 0.0036) were positively correlated with NIHSS in the LVO group. In contrast, both the count and percentage of lymphocytes were inversely correlated with NIHSS in the LVO group (Figure 2C, r = −0.2207, p = 0.005; Figure 2E, r = −0.2592, p = 0.0009). However, no relationship was found between the levels of peripheral blood cells and NIHSS in the SVO group (data not shown). These results suggest that the expression levels of peripheral immune cells can more specifically reflect the severity of patients with AIS caused by LVO.
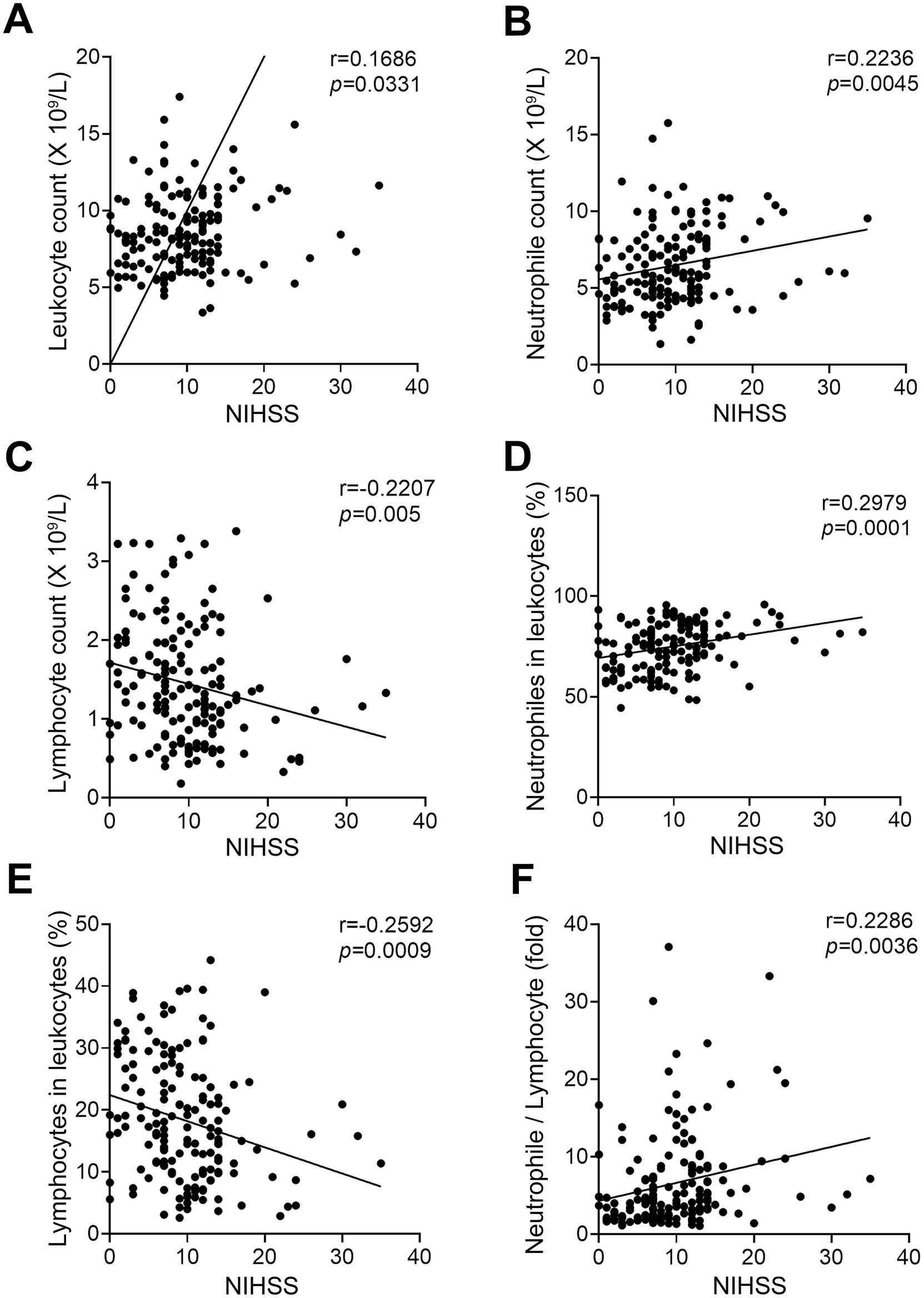
Figure 2. Correlation between NIHSS and circulating blood cells in patients of AIS with LVO. The correlation between NIHSS and leukocyte (A), neutrophile (B), and lymphocyte (C) counts. The correlation between NIHSS and the ratio of neutrophiles (D) and lymphocytes (E) to leukocytes. (F) The correlation between NIHSS and the ratio of neutrophile to lymphocyte.
Phenotype analysis of peripheral T cells
T cells play essential roles in immune response. To detect the peripheral phenotype of T cells in AIS with different subtypes, flow cytometry analysis was performed. As shown in Figure 3 and Supplementary File 2, although the total number of peripheral lymphocytes was significantly reduced in patients with AIS, the proportion of CD4+ T cells was higher in the LVO group than in the SVO and healthy control groups (Figure 3A, p < 0.001). In contrast, the proportion of NK cells decreased in the LVO group as compared with the SVO group (Figure 3B, p < 0.05) and control group (Figure 3B, p < 0.001). No significant difference was found between the SVO group and control group. These results indicate that AIS with LVO can rapidly enhance the adaptive immune response mediated by T cells.
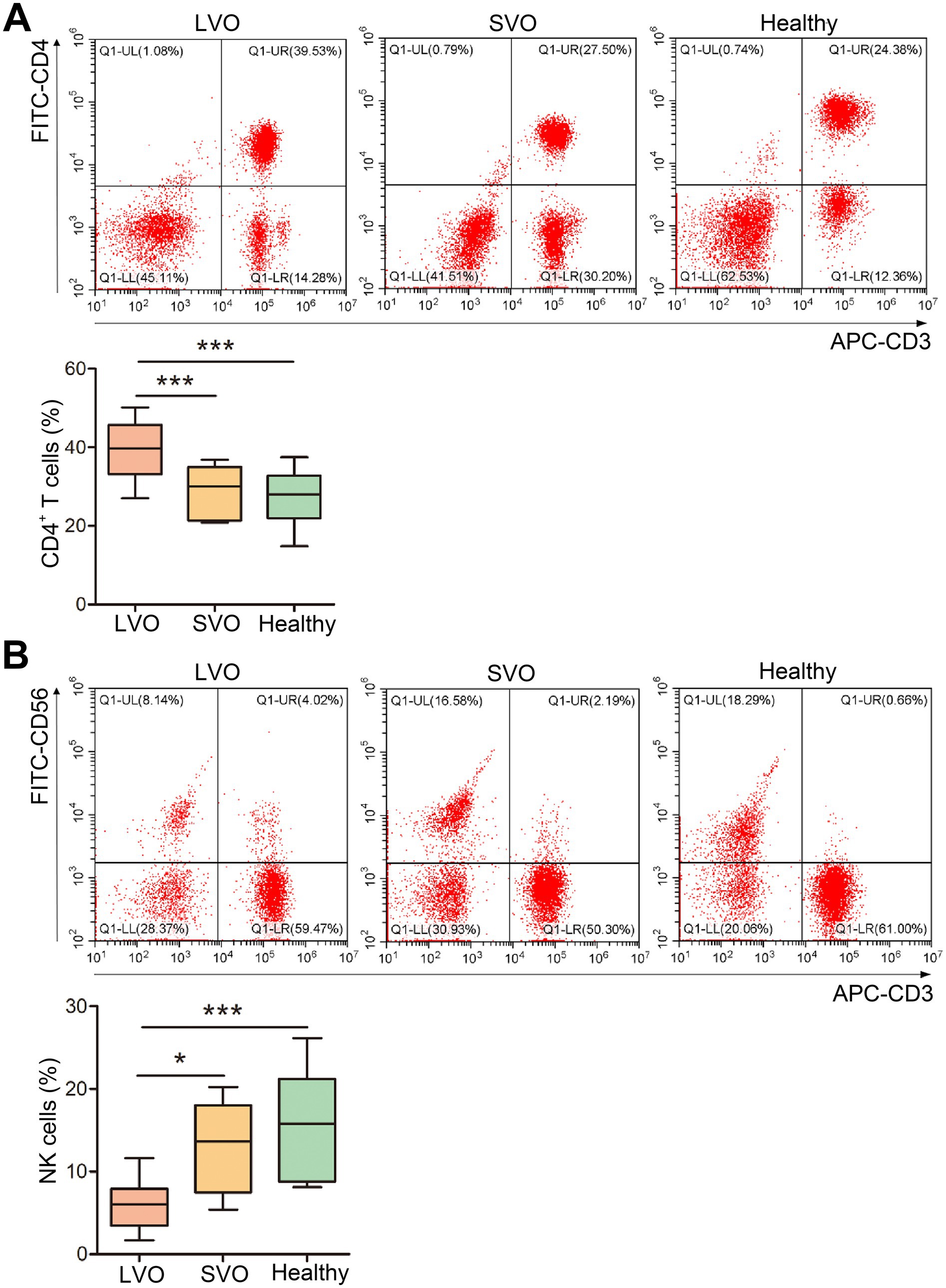
Figure 3. Changes in T-cell subtypes. (A) The percentage of CD4+ T cells was determined by flow cytometry. (B) The percentage of NK cells was determined using flow cytometry (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001).
To further analyze the immune response after AIS, naïve, effector memory T (Tem), and central memory T (Tcm) of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were, respectively, detected in LVO and SVO subtypes. As shown in Figure 4 and Supplementary File 2, the percentage of CD45RA+CCR7+ in CD4+ (naïve CD4+) T cells decreased (Figure 4A, p < 0.01), while the percentage of CD45RO+CCR7+ (Tcm, Figure 4B, p < 0.001) and CD45RO+CCR7− (Tem, Figure 4B, p < 0.001) in CD4+ T cells increased in LVO group as compared with SVO and control groups, suggesting a decrease in naïve CD4+ T cells and an increase in Tcm and Tem CD4+ T cells after AIS with LVO. Although no significant difference was found in the percentage of total CD8+ T cells, similar changes were found in CD45RA+CCR7+ (Figure 5A, p < 0.01, Supplementary File 2), CD45RO+CCR7+ (Figure 5B, p < 0.001), and CD45RO+CCR7− (Figure 5B, p < 0.01) in CD8+ T cells, as in CD4+ T cells of patients with LVO. No significant difference was found between the SVO and healthy control groups in naive, Tcm, and Tem cells. These results suggest that only AIS with LVO can stimulate the transformation of T cells into memory T cells.
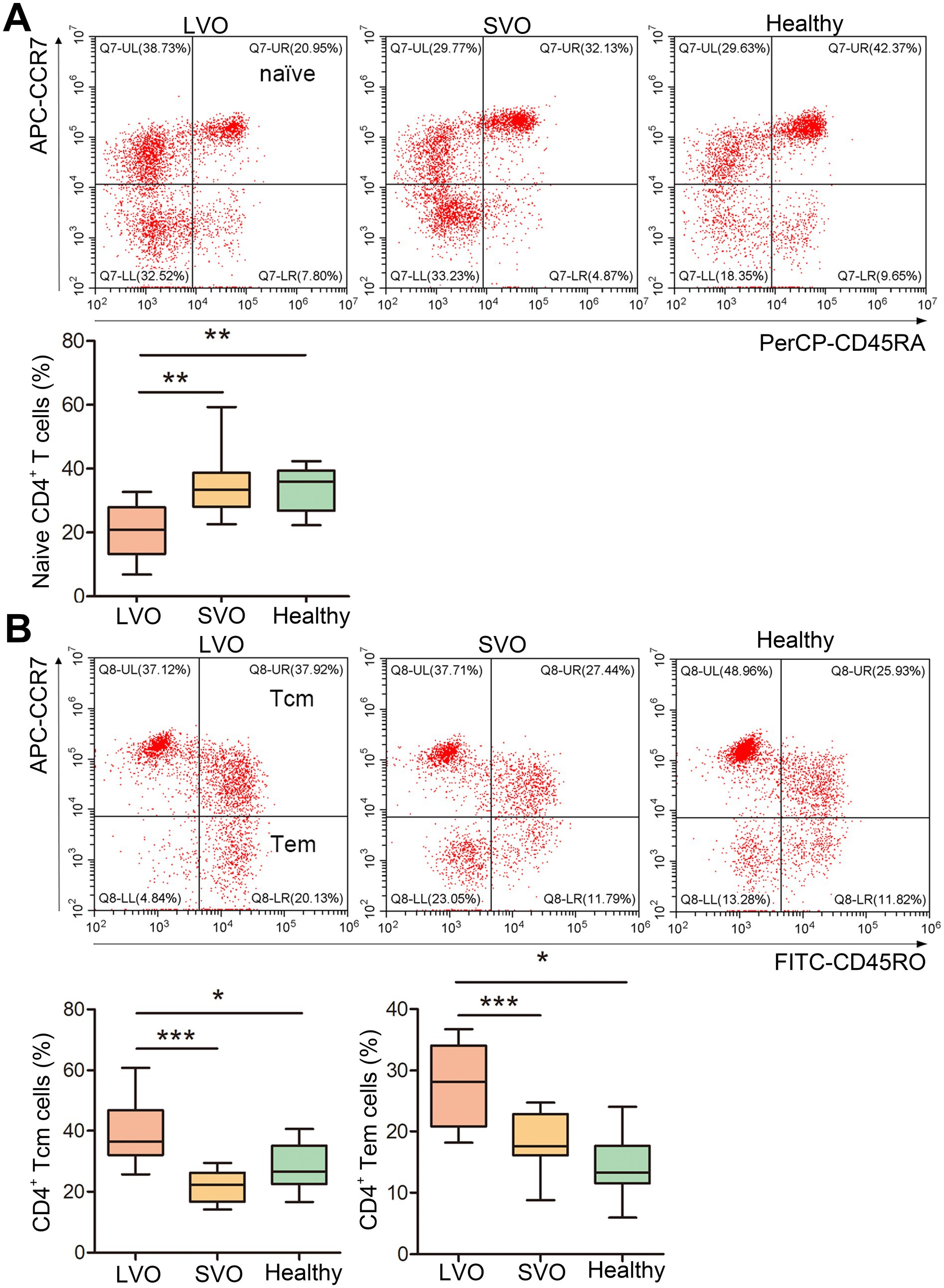
Figure 4. Changes in naïve, Tcm, and Tem CD4+ T cells. (A) The percentage of naïve CD4+ T cells was determined by detecting CD45RA+CCR7+ cells among the CD4+ T cells. (B) The percentage of Tcm CD4+ T cells was investigated by detecting CD45RO+CCR7+ cells among the CD4+ T cells. The percentage of Tem CD4+ T cells was investigated by detecting CD45RO+CCR7− cells in CD4+ T cells. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).

Figure 5. Changes in naïve, Tcm, and Tem levels in CD8+ T cells. (A) The percentage of naïve CD8+ T cells was investigated by detecting CD45RA+CCR7+ cells among CD8+ T cells. (B) The percentage of Tcm CD8+ T cells was investigated by detecting CD45RO+CCR7+ cells among CD8+ T cells. The percentage of Tem CD8+ T cells was investigated by detecting CD45RO+CCR7− cells in CD8+ T cells. (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
The characteristics of TCR repertoires in AIS patients with LVO
Given the changes of T cells above, we sought to further determine the T cells’ characteristics of LVO. As no changes were found in T cells between SVO group and healthy control group, PBMCs were isolated from peripheral blood and TCR repertoire sequencing analysis were performed in AIS patients with LVO and healthy controls. We assessed TCR sequences and identified V-J combinations at the transcription level. The results showed that the number of V-J combinations (Figure 6A, p = 0.0028) and the TCR sequences in CDR3 (Figure 6B, p = 0.0018, Supplementary File 3) were more abundant in AIS with LVO group than in control group. Notably, consistent with the increased memory T cells, these results indicate a dramatic increase in immunological activity in the number of immunological items during the pathological process of AIS with LVO.
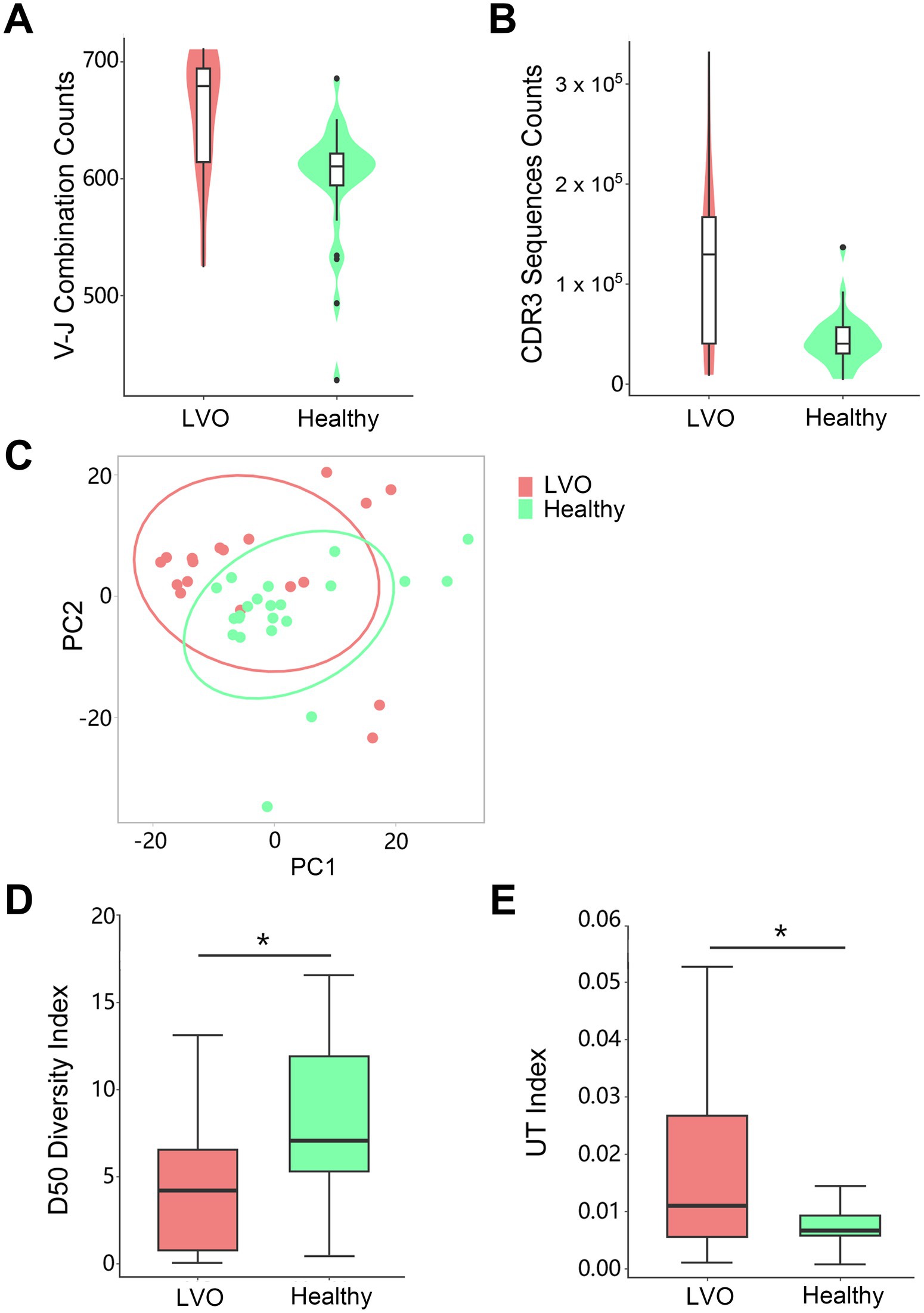
Figure 6. Quantity and diversity of the TCR repertoire: the number of unique V-J combinations (A) and counts of unique CDR3 sequences (B) were determined. (C) Principal component analysis of the AIS with LVO (red) and healthy groups (green). X-axis and Y-axis represent principal component 1 (PC1) and principal component 2 (PC2), respectively. The D50 Diversity Index (D) and UT Index (E) show the diversity of the TCR repertoire in the AIS with LVO and healthy groups. The violin chart and box plot show the data distribution with the minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum (*p < 0.05).
In addition, we performed a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) on the V-J combination frequency profile. As shown in the Figure 6C and Supplementary File 3, there was a significant difference between AIS patients with LVO and healthy controls in the sample cluster. In summary, we constructed a phenotype of LVO with immunological tendencies compared to healthy controls. TCR expression profiles were subsequently analyzed to assess the systemic immune responses mediated by T cells.
Next, we estimated the diversity of TCR clonotypes in each sample by calculating the D50 Diversity and UT index, irrelevant to the variation of sample sequencing depth. A lower D50 Diversity index was observed in AIS patients with LVO than in healthy controls (Figure 6D, p = 0.0498). In contrast, the UT index was higher in AIS patients with LVO than in healthy controls (Figure 6E, p = 0.02, Supplementary File 3), indicating that AIS with LVO could decrease the diversity of TCR profiles as compared with healthy controls.
Diversity of TCR repertoires and usage frequency of V-J gene combinations in AIS patients with LVO
We further performed a characteristic analysis to reveal the specificity of TCR sequence abundance in AIS patients with LVO and healthy controls. As shown in Figures 7A,B, the whole tree-map represented the average immune status of samples based on the abundance of CDR3 sequences. Each chip represented one CDR3 sequence’s abundance. The larger of the color chip, the higher abundance of this sequence. Meanwhile, large color chips led to a decrease in the quantity of chips, which indicated the reduction of diversity. We found more large-colored chips in AIS patients with LVO (Figure 7A) than in controls (Figure 7B and Supplementary File 4), which also illustrated the high-abundance sequences and poor TCR diversity in LVO patients.
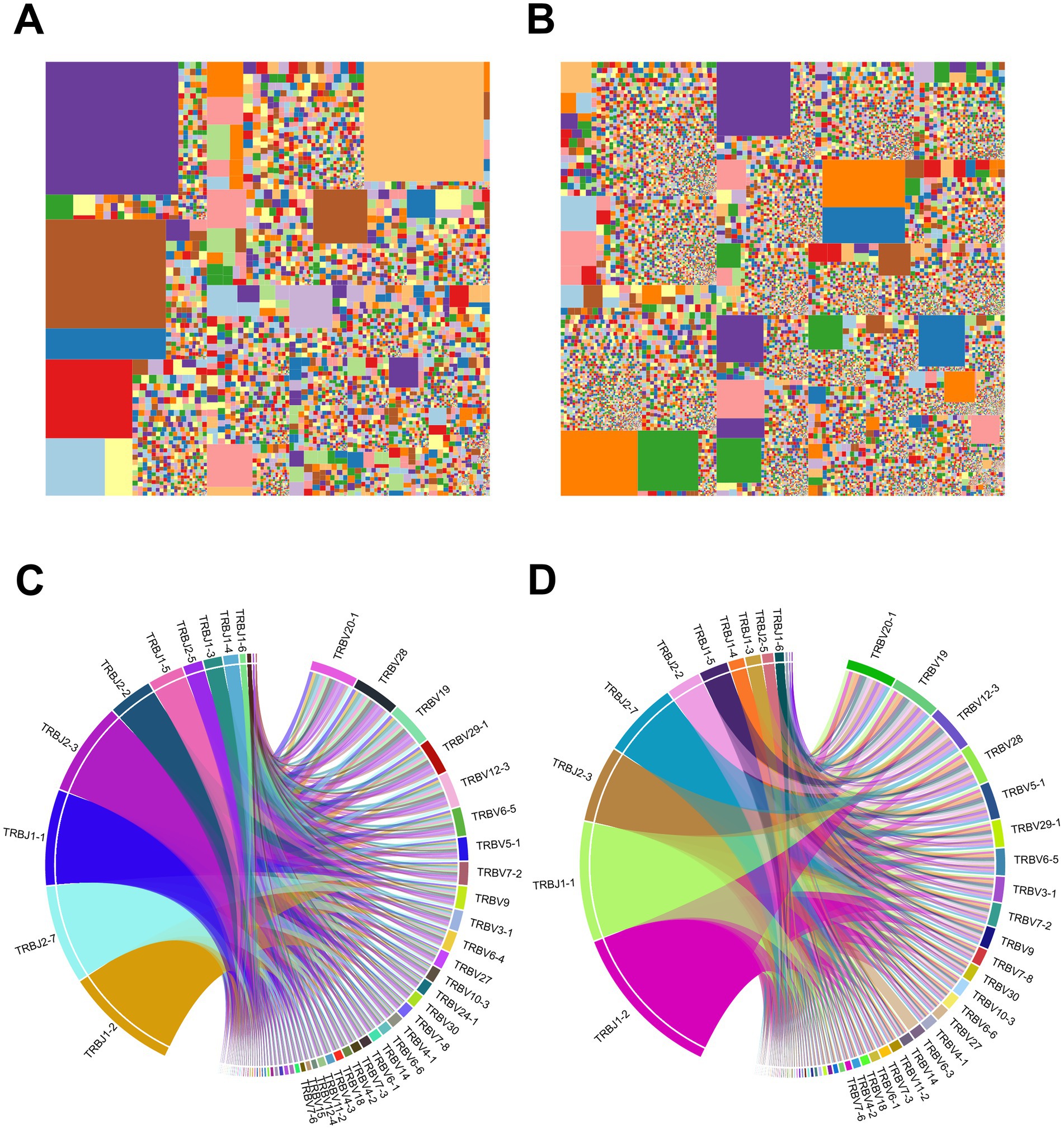
Figure 7. Samples’ immunological characteristics. (A,B) TCR sequence abundance and usage frequency of V-J combinations in patients with LVO. Tree-map of module CDR3 sequence abundance in samples from the AIS with LVO group (A) and healthy group (B). (C,D) Circos plots of the V-J gene combination usage frequency in samples from the AIS with LVO group (C) and healthy group (D). The left half-circle indicates the J gene and the right half-circle indicates the V gene. The length of sectors represents the relative usage frequency of the V genes or the J genes.
As the most variable components of TCR sequence, V and J segments play a crucial role in targeting a wide range of pathogenic process and the combination of V-J segments are the primary focus of many TCR-related studies. The comparison of V-J segments could reveal their contributions to the progression of AIS, and help to explain the differences in immune status between different groups. Furthermore, Circos plots was used to show the usage of V-J gene combinations. In the Circos plots, the length of the sectors represents the relative usage frequency of the V or J genes, while the width of the links connecting the V and J genes represents the relative usage frequency of the V-J combinations. Nevertheless, patients with LVO (Figure 7C) showed the similar average frequency of the use of V-J gene combinations as healthy controls (Figure 7D and Supplementary File 4). These results further indicated that the TCR diversities in AIS patients with LVO were induced by the high abundance of VDR3 sequences.
Different abundances of V-J gene combinations in AIS patients with LVO
We then determined the different abundance of V-J gene combinations in AIS patients with LVO from healthy controls. A total of 63V and 14J gene segments were identified in all samples. Compared with the control group, a significantly lower percentage of TRBV4-1 and TRBV5-1, and a higher percentage of TRBV5-3, TRBV5-6, TRBV6-1, TRBV7-3, TRBV10-1, TRBV12-1, TRBV12-4, TRBV13, TRBV23-1, and TRBV25-1 were found in the AIS with LVO group (Figure 8A, p < 0.05, p < 0.01). Moreover, a significantly lower percentage of TRBJ1-2 and TRBJ2-2, but a higher percentage of TRBJ1-4, TRBJ2-1, and TRBJ2-6 were found in the AIS with LVO group than the healthy group (Figure 8B, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, Supplementary File 5). These results indicated that LVO induced different abundance of V-J gene combinations.
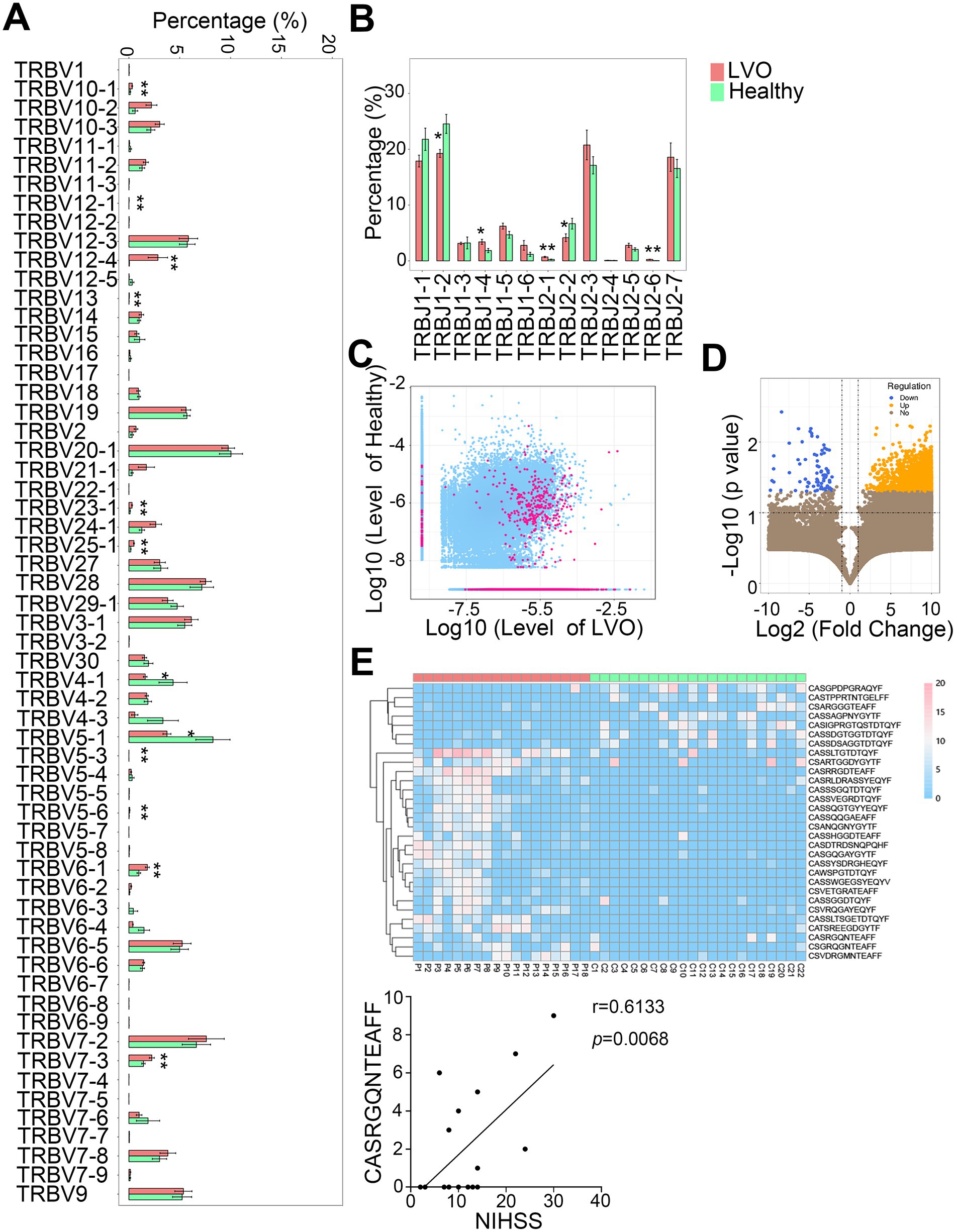
Figure 8. Differential abundances of the V and J gene segments and CDR3 sequences between the AIS with LVO and healthy groups. The relative abundance of V gene (A) and J gene (B) in the two groups. (C) Scatter plot showing differential abundance of CDR3 sequences in LVO and healthy groups (red, different CDR3 sequences; blue, CDR3 sequences with no significant difference). The X- and Y-axis represents the log-transformed mean of the relative abundance of the healthy and LVO group, respectively. (D) The volcano map shows the different clones between the LVO and healthy groups (yellow with increased abundance and blue with decreased abundance). The X- and Y-axes represent the log transformed p-value and fold changes, respectively. (E) Thirty differentially expressed amino acid clonotypes are shown as a heatmap. The X- and Y-axis represent samples and expression levels of CDR3 sequences, respectively. (F) The correlation between NIHSS and the unique amino acid clonotype (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
We further analyzed the abundance of CDR3 sequences between AIS with LVO and healthy groups. There were 734 upregulated and 49 downregulated amino acid clonotypes between the AIS with LVO and healthy group (Figures 8C,D). In addition, 30 differentially expressed amino acid clonotypes, were found in at least 10 samples (Figure 8E). Among these clonotypes, the expression levels of one amino acid clonotypes (CASRGQNTEAFF) was found to be positively correlated with NIHSS (Figure 8F, r = 0.6133, p = 0.0068), suggesting that the expression level of this amino acid clonotypes was related to the severity of AIS with LVO.
The prediction model for AIS with LVO
As the different abundance of TCR sequences between the AIS with LVO group and healthy group, we next want to build a diagnostic model to predict AIS with LVO. We firstly aligned the top 50 abundant CDR3 sequences with the indicated length to create a motif diagram. The results showed a significant difference in the motifs between the AIS with LVO group (Figure 9A) and the healthy group (Figure 9B). This suggests that selecting a suitable amino acid sequence can distinguish AIS patients with LVO from healthy controls.
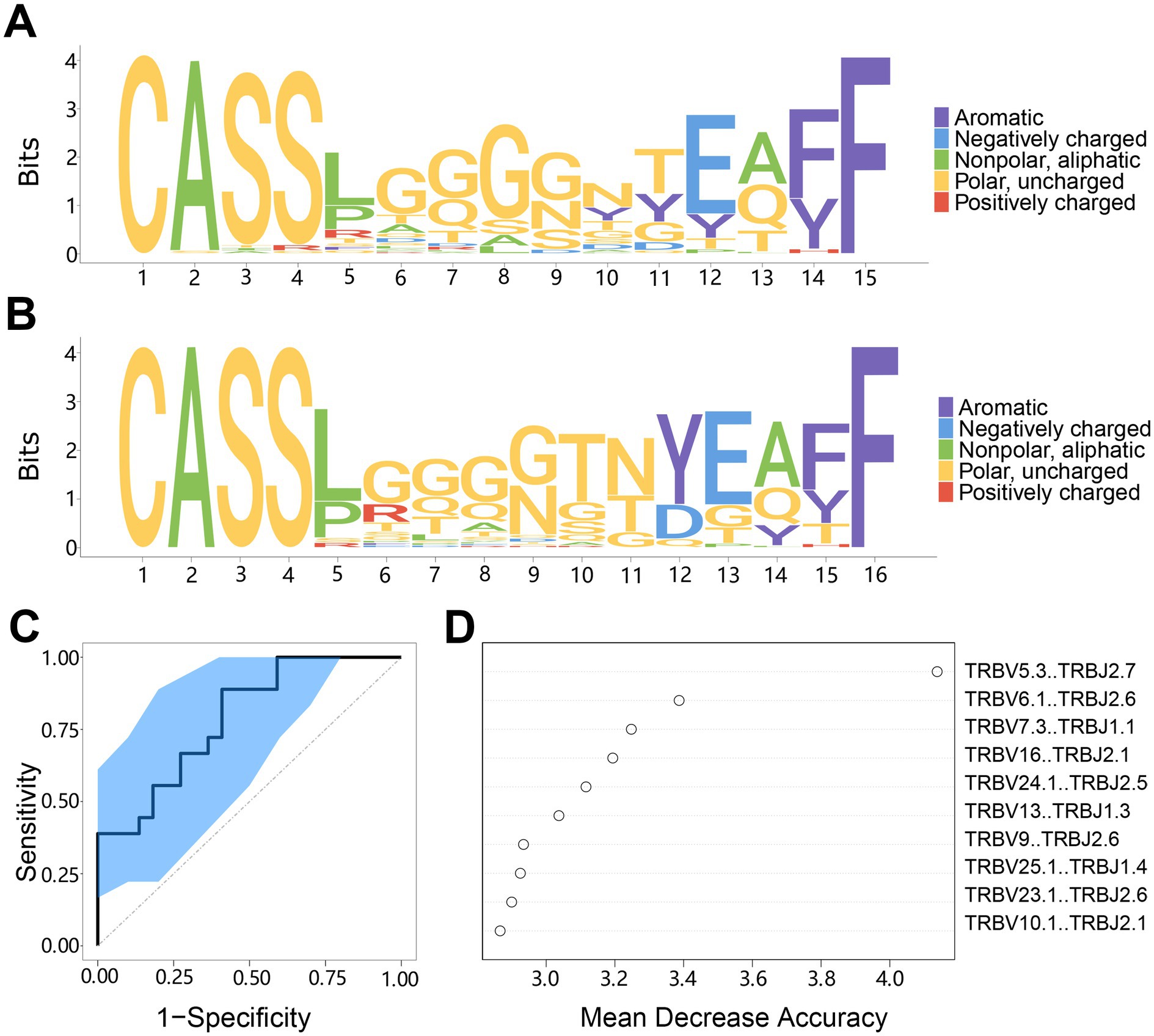
Figure 9. The motif specificity of TCR repertoires and prediction model system for AIS with LVO. (A) Motif diagram of the CDR3 sequences in AIS with LVO group. (B) Motif diagram of the CDR3 sequences in the healthy group. (C) ROC curve showing the classification effect of the LVO prediction model. The ordinate is the true-positive rate (sensitivity), and the abscissa is the false-positive rate (1-specificity). (D) The top 10 segments of V-J combinations that influenced the model effect. The mean decrease in accuracy is a rating index, and its value positively correlates with the effect on the model.
Then, we created a model using the random forest method to predict AIS with LVO based on differences in TCR repertoire characteristics. We changed the settings from 0.2 to 0.3 to improve the accuracy, while lowering the fault tolerance rate to stabilize the classification function of the model. We then evaluated the model classification effect in predicting AIS patients with LVO. The results showed that the distribution of the ROC curve was relatively smooth, and the leave-one-out cross-validation produced an area under the curve (AUC, 95%CI: 0.519–0.981, Figure 9C). Additionally, we evaluated the V-J combinations that affected the model assessment effect and discovered 10 combinations that made the largest contributions to the model (Figure 9D). These results indicate that the model can distinguish between patients with LVO and healthy controls, which provides the possibility of developing TCR biomarkers for the early diagnosis of AIS with LVO.
Discussion
Although endovascular therapy is effective for AIS, some patients still suffer from permanent disability. From the retrospective data, we firstly found that the changes of peripheral blood cells were correlated with the severity of AIS with LVO but not SVO. Using flow cytometry, we found that AIS with LVO enhanced the peripheral adaptive immune response by increasing the percentage of Tcm and Tem cells. Furthermore, TCR repertoire sequencing analysis showed that TCR diversity was impaired in patients with LVO, although the number of V-J combinations and CDR3 sequences increased. Together with the flow cytometry results, these findings suggest that AIS with LVO could induce an adaptive immune response, accompanied by a lack of comprehensive immunological activity, owing to the specific immune response to disease. Importantly, we found different abundances of V-J gene combinations and amino acid clonotypes between the AIS with LVO and control groups, which could be used as diagnostic biomarkers for AIS. This study will provide new insights into the pathophysiological process of AIS.
Human and animal studies have confirmed that AIS can lead to immediate activation of local immune cells and prompt mobilization of peripheral immune cells in the first hours and up to days after stroke (8, 36). Although studies have confirmed that the peripheral neutrophiles and NLR are closely related to the prognosis of AIS, few studies have focused on their roles on different subtypes of AIS. Our results confirmed that the changes of peripheral immune cells were more obvious in the LVO group than that in SVO group. In addition, these changes have a correlation with NIHSS in the LVO but not SVO group, suggesting that the peripheral immune changes can more specifically related to the severity of AIS patients with LVO. To our knowledge, this is the first study showing the relationship between the peripheral components and different AIS subtypes, which will be useful for the understanding of the roles of peripheral immune response in different AIS subtypes.
Studies have shown that innate immune cells were initially activated, followed by T cells activation after AIS (37). In addition, the relative levels of CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ T cells can reveal the systematic immune response and are associated with the pathophysiology and prognosis of multiple disease, such as pancreatic and non-small cell lung cancer (21, 38). In our study, although the lymphocyte count decreased in patients with AIS, the reduced ratio of CD45RA+CCR7+ (naïve) T cells, and increased ratio of CD45RO+CCR7+ T (Tcm) and CD45+CCR7− T (Tem) cells, further confirmed that the adaptive immune response could be rapidly stimulated in patients with LVO by stimulating the transformation of T cells into memory T cells. Together with the high NLR, the percentage of naïve, Tcm, and Tem can more specifically reflect the immunological condition after AIS with LVO. This is the first study to evaluate naïve, Tcm, and Tem of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in peripheral blood of patients with different AIS subtypes.
Considering the critical roles of the immune response, we performed an analysis to quantify and compare the TCR repertoire in PBMCs samples. Analysis of TCR repertoire has been used to characterize various diseases. For instance, the impaired TCR diversity and significant differences in V-J segments in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) make the TCR repertoire profile a potential biomarker of SLE (32, 39). Here, we clearly demonstrated that AIS with LVO induced rapid impairment of TCR diversity and the enrichment or reduction of specific V-J combinations in the PBMCs. As the TCR repertoire investigates CDR3, and each CDR3 sequence is a unique label, it can track T cell composition (40). Together with the varied percentage of T cell subsets, the decreased percentage of naïve T cells and segments of TRBV4-1, TRBV5-1, TRBJ1-2, and TRBJ2-2 sequences, as well as the increased percentage of Tcm and Tem cells and segments of TRBV5-3, TRBV6-1, TRBV7-3, TRBV10-1, TRBV13, TRBV23-1, TRBV25-1, TRBJ2-1, and TRBJ2-6 might indicate changes in these sequences in the relevant T cell subsets. In addition, we also found the correlation between amino acid sequence and the severity of AIS with LVO. The combined application of the percentage of Tcm/Tem cells with different abundances of V-J gene combinations and specific amino acid clonotypes could better reflect the body’s immune status in the patients with LVO.
We also found a range of amino acid clonotypes which can be used as a signature for the trained prediction model due to the altered TCR profile. Despite the limited sample size, our model efficiently discriminated AIS patients with LVO from healthy controls, indicating its potential as a biomarker for the diagnosis of AIS with LVO. Currently, the diagnosis of AIS relies mainly on the evaluations of clinical and neuroimaging features, including computed tomography (CT), MRI, and digital DSA (41). However, in the early stage of infarction, mild or no abnormal changes can be found on CT and MRI, because of the low sensitivity of these imaging modalities (42). Although DSA is the gold standard for diagnosing AIS, the expensive cost and invasive operation make its universal application impossible. In addition, all the examinations above require radiation exposure and are not feasible for patients with special circumstances, such as those with a pacemaker or emotional instability. Most importantly, these treatments take a long time and can easily delay the optimal treatment time. Therefore, several studies have been conducted to investigate the rapid diagnostic biomarkers of AIS, including glucose, iron, ferritin, homocysteine, insulin, P-selectin, matrix metalloproteinase-9, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, platelets, glial fibrillary acidic protein, TNF-α, and proenkephalin-A (43–48). However, these biomarkers are not widely used for diagnosing AIS, because of significant individual differences. Moreover, the inflammation-related biomarkers, such as C-reactive protein and interleukin (IL)-6, play a crucial role in predicting AIS (49). Still, they were limited to be used as diagnostic tools because of their similar changes in other inflammatory and infectious processes (50). Taken together, as the rapid changes of TCR repertoire sequences in AIS patients with LVO and the correlation between the CDR3 sequence and LVO severity, our study will provide important assistance for the diagnosis of AIS with LVO. These changes of unique amino acids may be the potential biomarkers for the rapid diagnosis of AIS with LVO.
Conclusion
In this study, we provided evidence of a change in the peripheral blood cells, the percentage of Tcm/Tem cells, and a predictive role of the TCR repertoire in the AIS with LVO. We found that the LVO group had increased leukocytes, neutrophils and NLR, and decreased lymphocytes as compared to the SVO group, which correlated with the severity of LVO. TCR diversity was impaired in the LVO group, with unique V-J gene combinations, indicating potential biomarkers for LVO diagnosis. Overall, AIS with LVO rapidly triggers a peripheral immune response and our findings will help further understanding of the pathophysiological mechanism of AIS with LVO.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA1171875.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Jinan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University (No. SZR2021-006-01) and The Second Hospital of Shandong University (No. KYLL-2021(KJ)P-0300). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LM: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft. BS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. CF: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. RJ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant number ZR2021MH044 and ZR2023MH353), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81701169), the Postdoctoral Innovation Project of Shandong Province (grant number SDCX-ZG-202302030), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number 2019 M652398), and the Jinan Clinical Medicine Science and Technology Innovation Plan (grant number 202328062).
Acknowledgments
All the authors contributed to this study. We thank the participants for contributions to this study. We also want to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for the English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2024.1512720/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Katan, M, and Luft, A. Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol. (2018) 38:208–11. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1649503
2. Phipps, MS, and Cronin, CA. Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ. (2020) 368:l6983. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l6983
3. Adams, HP Jr, Bendixen, BH, Kappelle, LJ, Biller, J, Love, BB, Gordon, DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of org 10172 in acute stroke treatment. Stroke. (1993) 24:35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.24.1.35
4. Yeo, LL, Paliwal, P, Teoh, HL, Seet, RC, Chan, BP, Liang, S, et al. Timing of recanalization after intravenous thrombolysis and functional outcomes after acute ischemic stroke. JAMA Neurol. (2013) 70:353–8. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamaneurol.547
5. Gao, Y, Chen, T, Lei, X, Li, Y, Dai, X, Cao, Y, et al. Neuroprotective effects of polydatin against mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in the rat cerebral cortex following ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. (2016) 14:5481–8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5936
6. Karakaya, S, Karadag, I, Ozdilekcan, C, Durmusoglu, E, Ates, O, and Cakmak Oksuzoglu, OB. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as an Indicator to predict decreased carbon monoxide diffusion of the lung in patients with testicular Cancer. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. (2022) 32:369–72. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2022.03.369
7. Fury, W, Park, KW, Wu, Z, Kim, E, Woo, MS, Bai, Y, et al. Sustained increases in immune transcripts and immune cell trafficking during the recovery of experimental brain ischemia. Stroke. (2020) 51:2514–25. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029440
8. An, C, Shi, Y, Li, P, Hu, X, Gan, Y, Stetler, RA, et al. Molecular dialogs between the ischemic brain and the peripheral immune system: dualistic roles in injury and repair. Prog Neurobiol. (2014) 115:6–24. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.12.002
9. Sadeghi, F, Sarkady, F, Zsori, KS, Szegedi, I, Orban-Kalmandi, R, Szekely, EG, et al. High neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and low lymphocyte-monocyte ratio combination after thrombolysis is a potential predictor of poor functional outcome of acute ischemic stroke. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:1221. doi: 10.3390/jpm12081221
10. Iadecola, C, and Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med. (2011) 17:796–808. doi: 10.1038/nm.2399
11. Ortega, SB, Torres, VO, Latchney, SE, Whoolery, CW, Noorbhai, IZ, Poinsatte, K, et al. B cells migrate into remote brain areas and support neurogenesis and functional recovery after focal stroke in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2020) 117:4983–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913292117
12. Chen, Y, Bodhankar, S, Murphy, SJ, Vandenbark, AA, Alkayed, NJ, and Offner, H. Intrastriatal B-cell administration limits infarct size after stroke in B-cell deficient mice. Metab Brain Dis. (2012) 27:487–93. doi: 10.1007/s11011-012-9317-7
13. Gill, D, and Veltkamp, R. Dynamics of T cell responses after stroke. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2016) 26:26–32. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2015.09.009
14. Kim, J, Song, TJ, Park, JH, Lee, HS, Nam, CM, Nam, HS, et al. Different prognostic value of white blood cell subtypes in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Atherosclerosis. (2012) 222:464–7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.02.042
15. Liesz, A, Zhou, W, Na, SY, Hammerling, GJ, Garbi, N, Karcher, S, et al. Boosting regulatory T cells limits neuroinflammation in permanent cortical stroke. J Neurosci. (2013) 33:17350–62. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4901-12.2013
16. Liesz, A, Suri-Payer, E, Veltkamp, C, Doerr, H, Sommer, C, Rivest, S, et al. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat Med. (2009) 15:192–9. doi: 10.1038/nm.1927
17. Liesz, A, Zhou, W, Mracsko, E, Karcher, S, Bauer, H, Schwarting, S, et al. Inhibition of lymphocyte trafficking shields the brain against deleterious neuroinflammation after stroke. Brain. (2011) 134:704–20. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr008
18. Magnus, T, Wiendl, H, and Kleinschnitz, C. Immune mechanisms of stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. (2012) 25:334–40. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e328352ede6
19. Jayaraj, RL, Azimullah, S, Beiram, R, Jalal, FY, and Rosenberg, GA. Neuroinflammation: friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. (2019) 16:142. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1516-2
20. Li, Q, Tian, Y, Niu, J, Guo, E, Lu, Y, Dang, C, et al. Identification of diagnostic signatures for ischemic stroke by machine learning algorithm. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2024) 33:107564. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2024.107564
21. Yang, W, Jia, X, Su, Y, and Li, Q. Immunophenotypic characterization of CD45RO+ and CD45RA+ T cell subsets in peripheral blood of peripheral T cell lymphoma patients. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2014) 70:993–7. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0008-3
22. Ahmed, MGT, Limmer, A, and Hartmann, M. CD45RA and CD45RO are regulated in a cell-type specific manner in inflammation and Sepsis. Cells. (2023) 12:1873. doi: 10.3390/cells12141873
23. Davis, MM, and Bjorkman, PJ. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. (1988) 334:395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0
24. Attaf, M, Huseby, E, and Sewell, AK. Alphabeta T cell receptors as predictors of health and disease. Cell Mol Immunol. (2015) 12:391–9. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.134
25. Rosati, E, Dowds, CM, Liaskou, E, Henriksen, EKK, Karlsen, TH, and Franke, A. Overview of methodologies for T-cell receptor repertoire analysis. BMC Biotechnol. (2017) 17:61. doi: 10.1186/s12896-017-0379-9
26. Alves Sousa, AP, Johnson, KR, Ohayon, J, Zhu, J, Muraro, PA, and Jacobson, S. Comprehensive analysis of TCR-β repertoire in patients with neurological immune-mediated disorders. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:344. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36274-7
27. Ritzel, RM, Crapser, J, Patel, AR, Verma, R, Grenier, JM, Chauhan, A, et al. Age-associated resident memory CD8 T cells in the central nervous system are primed to potentiate inflammation after ischemic brain injury. J Immunol. (2016) 196:3318–30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502021
28. Schulze, J, Gellrich, J, Kirsch, M, Dressel, A, and Vogelgesang, A. Central nervous system-infiltrating T lymphocytes in stroke are activated via their TCR (T-cell receptor) but lack CD25 expression. Stroke. (2021) 52:2939–47. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032763
29. Zong, Y, Liu, Y, Wang, J, Rastegar-Kashkooli, Y, Fu, P, Chen, S, et al. The characteristics of T-cell receptor repertoire in relation to systemic immune response of patients with ischemic stroke. J Neurochem. (2024). doi: 10.1111/jnc.16246
30. Goyal, M, Demchuk, AM, Menon, BK, Eesa, M, Rempel, JL, Thornton, J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:1019–30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1414905
31. Lyden, P, Brott, T, Tilley, B, Welch, KM, Mascha, EJ, Levine, S, et al. Improved reliability of the NIH stroke scale using video training. NINDS TPA stroke study group. Stroke. (1994) 25:2220–6. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.25.11.2220
32. Ye, X, Wang, Z, Ye, Q, Zhang, J, Huang, P, Song, J, et al. High-throughput sequencing-based analysis of T cell repertoire in lupus nephritis. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1618. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01618
33. Bolotin, DA, Poslavsky, S, Mitrophanov, I, Shugay, M, Mamedov, IZ, Putintseva, EV, et al. MiXCR: software for comprehensive adaptive immunity profiling. Nat Methods. (2015) 12:380–1. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3364
34. Hou, D, Ying, T, Wang, L, Chen, C, Lu, S, Wang, Q, et al. Immune repertoire diversity correlated with mortality in avian influenza a (H7N9) virus infected patients. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:33843. doi: 10.1038/srep33843
35. Lin, KR, Deng, FW, Jin, YB, Chen, XP, Pan, YM, Cui, JH, et al. T cell receptor repertoire profiling predicts the prognosis of HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. (2018) 7:3755–62. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1610
36. Price, CJ, Menon, DK, Peters, AM, Ballinger, JR, Barber, RW, Balan, KK, et al. Cerebral neutrophil recruitment, histology, and outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. (2004) 35:1659–64. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000130592.71028.92
37. Wang, YR, Cui, WQ, Wu, HY, Xu, XD, and Xu, XQ. The role of T cells in acute ischemic stroke. Brain Res Bull. (2023) 196:20–33. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.03.005
38. Hang, J, Huang, J, Zhou, S, Wu, L, Zhu, Y, Zhu, L, et al. The clinical implication of CD45RA(+) naive T cells and CD45RO(+) memory T cells in advanced pancreatic cancer: a proxy for tumor biology and outcome prediction. Cancer Med. (2019) 8:1326–35. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1988
39. Liu, X, Zhang, W, Zhao, M, Fu, L, Liu, L, Wu, J, et al. T cell receptor beta repertoires as novel diagnostic markers for systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2019) 78:1070–8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215442
40. Wang, X, Muzaffar, J, Kirtane, K, Song, F, Johnson, M, Schell, MJ, et al. T cell repertoire in peripheral blood as a potential biomarker for predicting response to concurrent cetuximab and nivolumab in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. (2022) 10:e004512. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004512
41. Shen, J, Li, X, Li, Y, and Wu, B. Comparative accuracy of CT perfusion in diagnosing acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review of 27 trials. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0176622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176622
42. Mair, G, Alzahrani, A, Lindley, RI, Sandercock, PAG, and Wardlaw, JM. Feasibility and diagnostic accuracy of using brain attenuation changes on CT to estimate time of ischemic stroke onset. Neuroradiology. (2021) 63:869–78. doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02591-w
43. Doehner, W, von Haehling, S, Suhr, J, Ebner, N, Schuster, A, Nagel, E, et al. Elevated plasma levels of neuropeptide proenkephalin a predict mortality and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2012) 60:346–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.04.024
44. Hasan, N, McColgan, P, Bentley, P, Edwards, RJ, and Sharma, P. Towards the identification of blood biomarkers for acute stroke in humans: a comprehensive systematic review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2012) 74:230–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04212.x
45. Lehmann, MF, Kallaur, AP, Oliveira, SR, Alfieri, DF, Delongui, F, de Sousa, PJ, et al. Inflammatory and metabolic markers and short-time outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke in relation to TOAST subtypes. Metab Brain Dis. (2015) 30:1417–28. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9731-8
46. Schiff, L, Hadker, N, Weiser, S, and Rausch, C. A literature review of the feasibility of glial fibrillary acidic protein as a biomarker for stroke and traumatic brain injury. Mol Diagn Ther. (2012) 16:79–92. doi: 10.1007/BF03256432
47. Vila, N, Castillo, J, Davalos, A, and Chamorro, A. Proinflammatory cytokines and early neurological worsening in ischemic stroke. Stroke. (2000) 31:2325–9. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.31.10.2325
48. Basic Kes, V, Simundic, AM, Nikolac, N, Topic, E, and Demarin, V. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke and their relation to early neurological deficit and stroke outcome. Clin Biochem. (2008) 41:1330–4. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.08.080
49. Ji, X, Tian, L, Yao, S, Han, F, Niu, S, and Qu, C. A systematic review of body fluids biomarkers associated with early neurological deterioration following acute ischemic stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:918473. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.918473
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke, large vessel occlusion, T cell receptors repertoire, CD45, T cell
Citation: Ma L, Sun B, Fan C, Xiao J, Geng M, Liu J, Jiang R, Jiang Y and Liu D (2024) Characteristics of peripheral immune response induced by large-vessel occlusion in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 15:1512720. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1512720
Edited by:
Timo Uphaus, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, GermanyReviewed by:
Wei Wei, University Medical Center Göttingen, GermanyHongjian Pu, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2024 Ma, Sun, Fan, Xiao, Geng, Liu, Jiang, Jiang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dianwei Liu, ZGlhbndlaTE5ODJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yang Jiang, eWFuZ2ppYW5nQGVtYWlsLnNkdS5lZHUuY24=
 Ling Ma
Ling Ma Bin Sun2
Bin Sun2 Runze Jiang
Runze Jiang Yang Jiang
Yang Jiang Dianwei Liu
Dianwei Liu