
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Nanotechnol. , 22 October 2024
Sec. Nanomaterials
Volume 6 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnano.2024.1445269
Fluorine-doped zinc oxide (ZnO:F) thin films are valued for their potential as transparent conductive materials, particularly in optoelectronic applications. In this work, the deposition of highly conductive and transparent fluorine-doped ZnO thin films, deposited by chemical spray on glass substrates is reported. The effect of acetic (AcAc) in the initial fresh solution on Haacke’s Figure of Merit
Transparent thin films with low resistivity manufactured from semiconductor oxides have attracted the interest of the scientific community due to their promising applications for electronic and optoelectronic devices. Among the relevant characteristics of transparent conductive films (TCOs) are low electrical resistance and high optical transmittance, which can be evaluated by Haacke’s Figure of Merit
Haacke’s Figure of Merit is an indispensable indicator to evaluate transparent conductors (Veron et al., 2022) in typical applications such as transparent electrodes (Arora et al., 2022), transparent sensors (Gu et al., 2023), touch screens (Wu, 2020), photovoltaics (García-Mejía et al., 2024), and smart windows (DiGregorio et al., 2022). The traditional figure of merit (FoM) allows the evaluation of the quality and the efficiency of different transparent conductive materials to be compared, considering both electrical conductivity and optical transparency. On the other hand, Haacke’s (FoM) can be applied to optimize materials in the manufacturing of transparent conductors, ensuring maximum light transmission while maintaining high conductivity. (Dhar and Alford, 2012; Hubarevich et al., 2019).
In the literature, indium tin oxide (ITO) films have been extensively researched and commercialized due to their low electrical resistivity of
Anionic doping with fluorine or chlorine has demonstrated considerable advantages. When ZnO is doped with fluorine, both the electrical and optical properties of the material are enhanced. Fluorine doping introduces extra electrons into the ZnO lattice, which increases the electron concentration, thereby improving its conductivity (Jiamprasertboon et al., 2019; de la L Olvera et al., 2002). According to Hu and Gordon, (1991) the fact that fluorine and oxygen have close ionic radii (for
When it comes to cost-effective chemical deposition methods, careful attention is essential to produce high-quality ZnO:F films. Recent reports have highlighted improvements in ZnO films achieved through various manufacturing techniques (Hurma and Caglar, 2020). The ultrasonic spray pyrolysis (USP) technique presents different advantages over others that are more sophisticated, whether physical or chemical; among the most evident can be its simple setup and consequently low cost, ease of operation, and mainly provides the possibility of deposition of high-quality films in large areas. However, as with all deposition techniques, it also presents certain disadvantages, among which is the lack of thickness control, which depends largely on the configuration of the system and the external environmental conditions. Fluorine, which is highly volatile during synthesis, can be effectively incorporated by using high doping levels in the solution, up to 60 atomic percentage (at%). The composition of this solution is crucial for determining the properties of the resulting films. Specifically, the pH level, influenced by the presence of acetic acid (AcAc), has been shown to improve both the conductivity and optical properties of ZnO:F films (Kang and Park, 2018; Edinger et al., 2015). Research by Edinger et al. (2015) highlighted the positive impact of AcAc concentration in the precursor solution on the electrical characteristics of ZnO thin films produced via USP. Additionally, Jiao et al. (2011) reported that incorporating acetic acid during the USP synthesis of ZnO and ZnO:In films also enhanced their transport properties.
The production of high-quality ZnO:F thin films using chemical spray techniques faces a challenge due to the necessity of aging the starting solution for several weeks. Despite this limitation, the advantages of the spray method justify efforts to address the aging issue (Workie et al., 2023; Habas et al., 2010). The solution to this problem depends on the composition of the starting solution. Acetic acid facilitates the formation of complex species, which help to integrate fluorine ions into the ZnO lattice during the synthesis, as was previously reported for ZnO:F films made from aged solutions (Rodríguez-Báez et al., 2007). However, there has been no reported research on the impact of acetic acid in films produced with fresh solutions.
This work reports the beneficial effect of acetic acid concentration in the starting solution on Haacke’s Figure of Merit of ZnO and ZnO:F thin films deposited with a fresh solution. Additionally, the structural, electrical, and optical properties, as well as Haacke’s Figure of Merit of fluorine-doped ZnO and ZnO:F thin films, were studied.
ZnO and fluorine-doped ZnO (ZnO:F) films were deposited on glass substrates by the USP technique. A 0.2 M zinc acetate dihydrate [Zn (
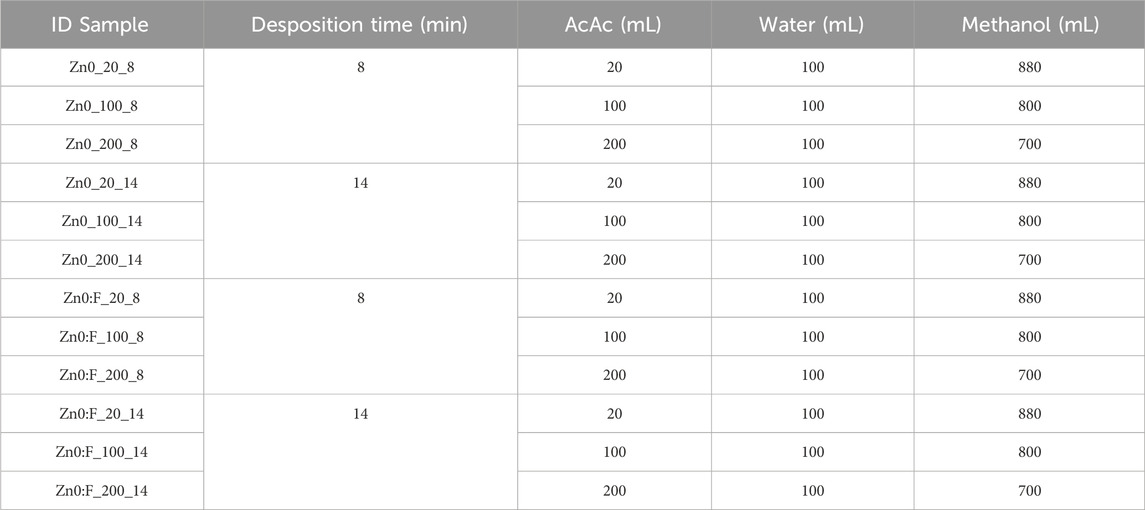
Table 1. Samples used and the proportions by volume of acetic acid:water:methanol for the preparation of the different starting solutions.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis of ZnO films was performed on PANa-lytical Xpert Pro equipment, Cu-K
where
The optical transmittance of these films was evaluated by using a UV-visible spectrometer Jasco, Model V-670. Spectra were recorded from 300 to 900 nm and using a scanning rate of 60 nm per minute. The optical band gap,
where
On the other hand, the surface morphology of thin films was observed using a scanning electron microscope FE-HRSEM Auriga 3916. ImageJ software was used to measure the grain size of each sample.
Furthermore, for the electrical properties of the films, the resistivity,
Finally, the optical and electrical properties measured were used to calculate Haacke’s Figure of Merit
where
Figures 1, 2 present the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns for ZnO and ZnO:F films, respectively. All films exhibited a polycrystalline nature with the hexagonal wurtzite structure characteristic of ZnO, as identified by JCPDS card number 01-075-0576. The (002) plane showed preferential growth in the undoped ZnO samples, consistent with findings from other studies (Lee and Lin, 1996). In contrast, ZnO:F films produced from a fresh solution (Figure 2) showed contributions from the (002), (100), and (101) planes. This phenomenon occurs because incorporating fluorine (F) into ZnO alters its crystal structure. When fluorine atoms replace oxygen atoms within the lattice, it affects the formation energy and stability of the crystallographic planes. As a result, there is less growth preference along the (002) plane, which instead promotes increased growth in other directions like (100) and (101). This finding aligns with what was reported by (Anandhi et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2006).
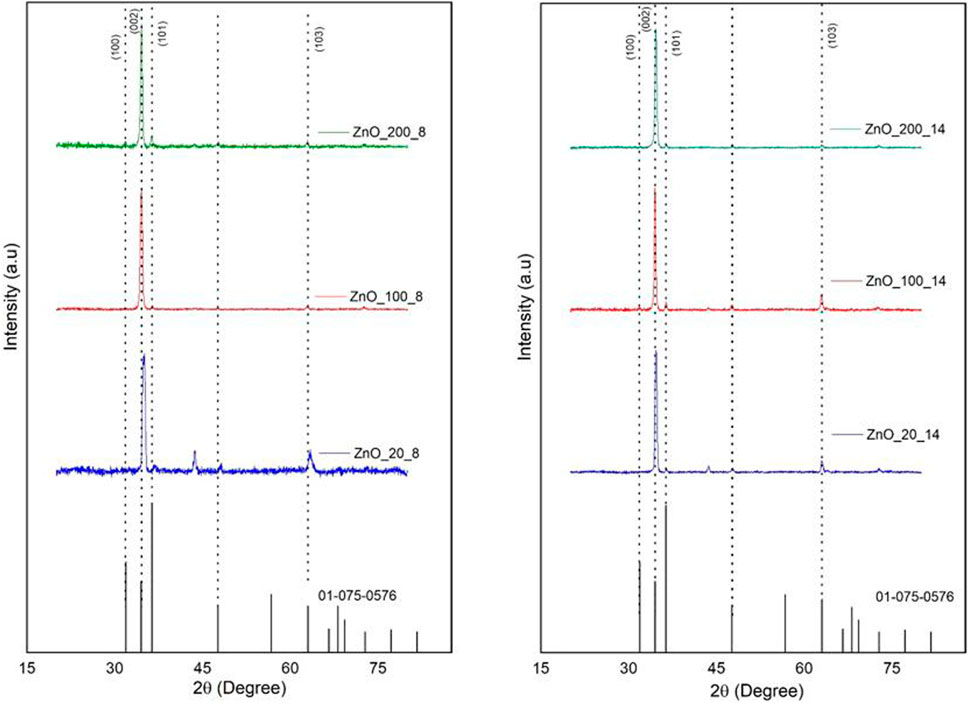
Figure 1. XRD spectra of the undoped ZnO thin films with different acetic acid quantity added in the precursor solution at different deposit times (8 and 14-min).
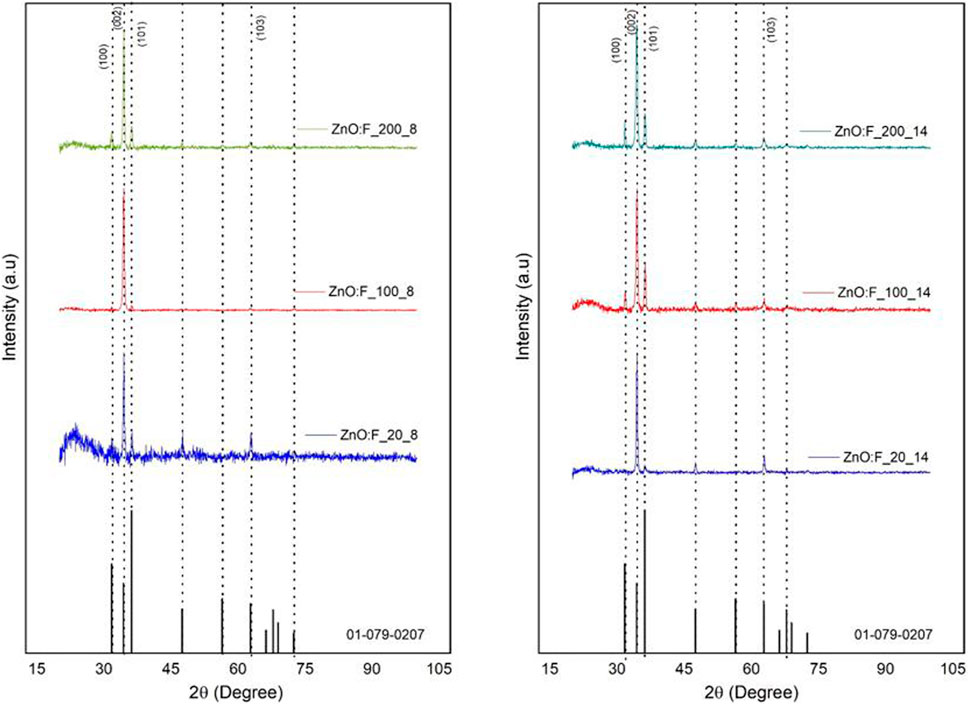
Figure 2. XRD spectra of the ZnO:F thin films with different acetic acid quantity added in the precursor solution at different deposit times (8 and 14-min).
On the other hand, Edinger et al. (2015) demonstrated that the concentration of acetic acid in the initial solution influences the structural, optical, and, notably, transport properties of chemically sprayed undoped ZnO thin films. Jiao et al. (2011) also reported that the concentration of acetic acid affects sprayed ZnO films, causing a shift in the preferred crystalline planes, changes in morphology from flake to triangle, and enhanced electrical transport. Smith, (2000) suggests that these changes in sprayed ZnO films occur because the precursors do not easily integrate into the growing film, resulting in a deposit primarily composed of flat equilibrium faces. In contrast, small and neutral complex molecules are more likely to form non-equilibrium faces. Finally, these non-equilibrium faces, which are polar, can be stabilized during film growth if the surrounding atmosphere contains polar gases that can adsorb onto these faces and slow down their growth (Smith, 2000; Smith and Rodriguez-Clemente, 1999). In our study, the observed change in the preferred crystal growth planes in ZnO films is likely due to the varying concentrations of acetic acid during the synthesis process.
Table 2 shows the crystallite sizes calculated by using Equation 1, as well as the FWHM and
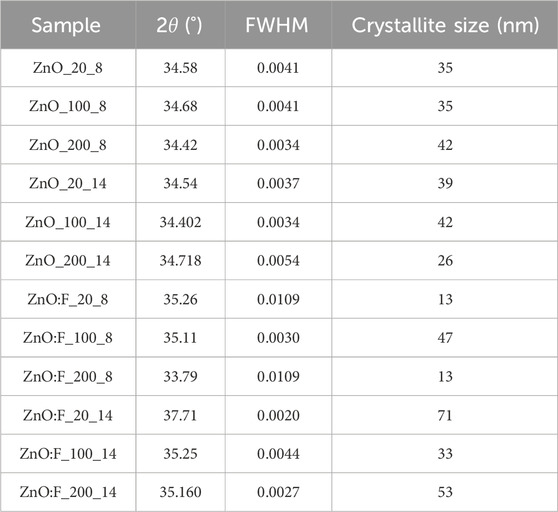
Table 2. Crystallite sizes of plane (002) of ZnO and ZnO:F films according to Equation 1.
Figures 3, 4 show the optical transmittance spectra of synthesized thin films of ZnO and ZnO:F, respectively. In the case of ZnO films (Figure 3) it can be observed that the transmittance of the films decreases as the acetic acid content increases. This is attributed to the carbon content in the film for the AcAc excess due to the selective adsorption of acetic acid on specific surface facets of ZnO, such as (001) planes reported previously (Smith and Rodriguez-Clemente, 1999; Hagendorfer et al., 2014). In addition, as the acetic acid increases in the starting solution, the free carrier absorption into the ZnO also increases, as is shown in the electrical properties below, which in turn means that the corresponding transmittance decreases. Namely, it negatively affects the optical properties. The average transmittance at 550 nm for ZnO films ranged between 60% and 90%, as was expected. On the other hand, in the thin films of ZnO:F (Figure 4), the transmittance at 550 nm varied between 77% and 98%, which is an appropriate value for transparent conductive electrodes (Edwards et al., 2004; Elsokary et al., 2024; Hwang and Lee, 2024). It is worth mentioning that at 310–320 nm, the absorption values significantly increased, indicating the fundamental absorption region of ZnO (Elmas et al., 2019).
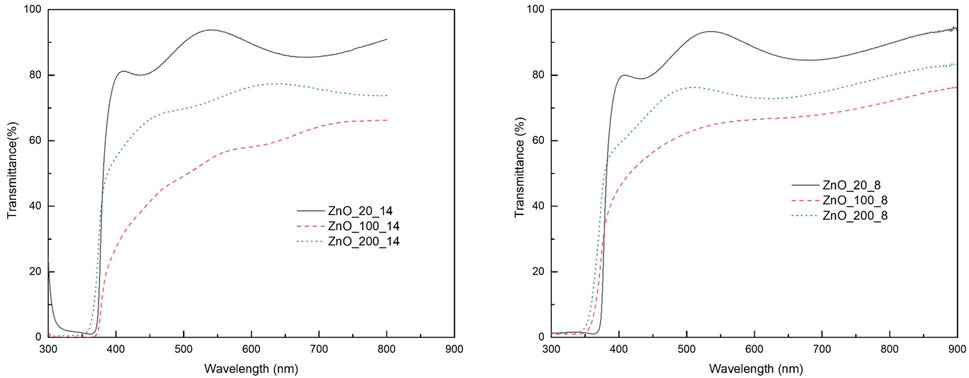
Figure 3. Optical transmittance for ZnO films deposited at different concentrations of acetic acid and deposition times.
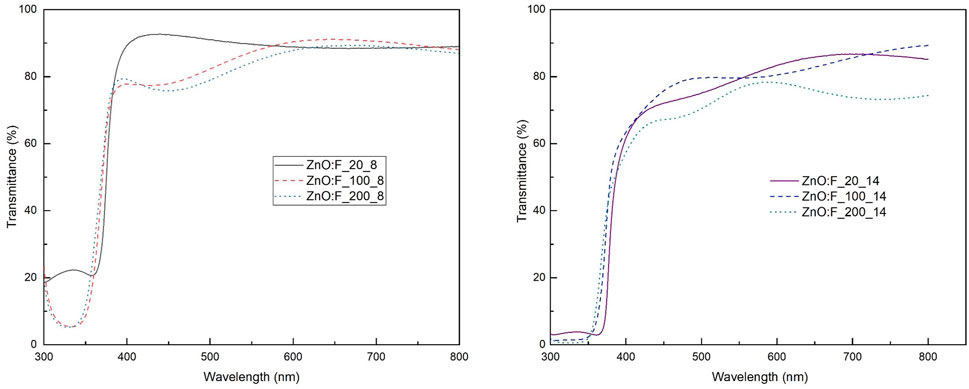
Figure 4. Optical transmittance for ZnO:F films deposited at different concentrations of acetic acid and deposition times.
Table 3 shows the transmittance at 550 nm and the bandgap calculated by Equation 2 of each sample. In general, the bandgap of ZnO and ZnO:F films increases with the rising content of acetic acid. For ZnO films, the highest value is 3.34 eV, while for ZnO:F films, the bandgap decreases with higher acetic acid content, reaching the lowest value of 3.20 eV.
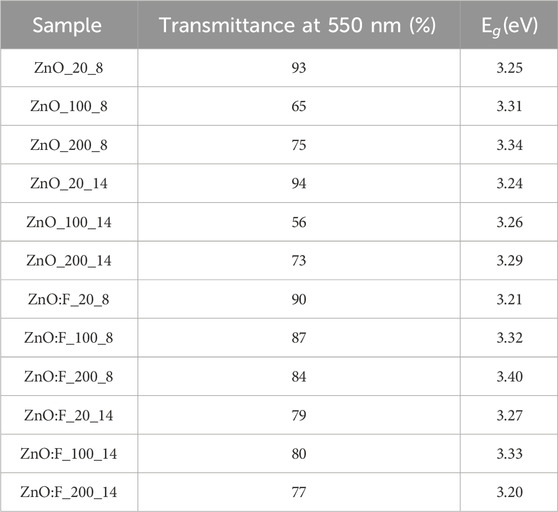
Table 3. Optical properties of ZnO and ZnO:F films with AcAc variation according to Equation 2.
Figures 5, 6 show SEM micrographs of thin films of ZnO and ZnO:F, respectively. The films exhibited the following characteristics: uniformity, good adhesion, absence of cracks, and absent pores. Furthermore, Table 4 shows the average grain size measured by ImageJ software for doped and undoped films. The acidity and fluoride content significantly influence the morphology of the films in terms of shape and size distribution. In fact, for undoped ZnO films, only hexagonal-shaped grains with a narrow size distribution were observed (Figure 5). In addition, in Figure 6 it can be observed the ZnO:F films morphology, it was found that as the acetic acid content increases, the grain size also increases. This effect has been reported by Jiao et al. (2011). According to (Chen et al., 2015), the incorporation of acetic acid caused the grains to grow and eventually develop into pyramid shapes, enhancing both surface roughness and the ability to scatter light. Larger quantities of acetic acid resulted in the formation of well-defined pyramidal grains with six uniform side facets, leading to highly rough surfaces with significant light-trapping capabilities. Edinger et al. (2015) demonstrate that adjusting the acetic acid concentration in the precursor solution can effectively control the morphological characteristics of ZnO thin films produced by spray pyrolysis, which is vital for enhancing their performance in applications such as photovoltaics and transparent conductive oxides.
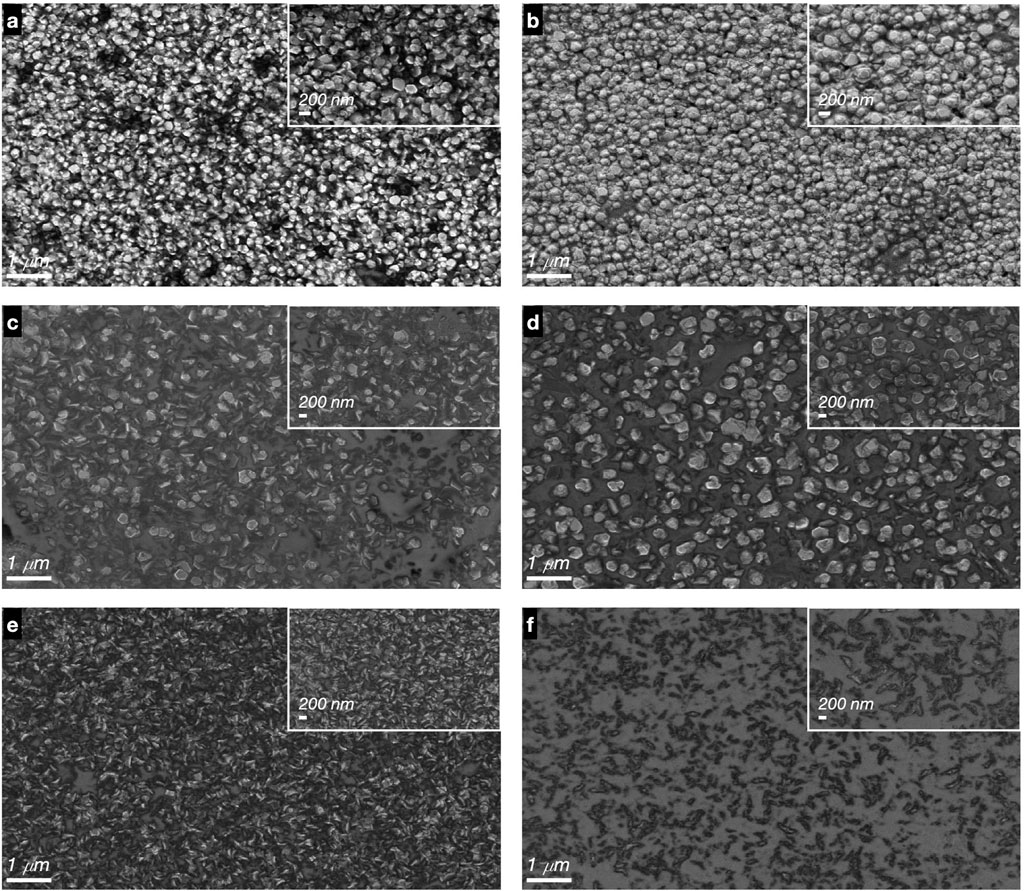
Figure 5. SEM images of undoped ZnO with different acetic acid added in the precursor solution. (A) ZnO_20_8, (B) ZnO_20_14, (C) ZnO_100_8, (D) ZnO_100_14, (E) ZnO_200_8, (F) ZnO_200_14.
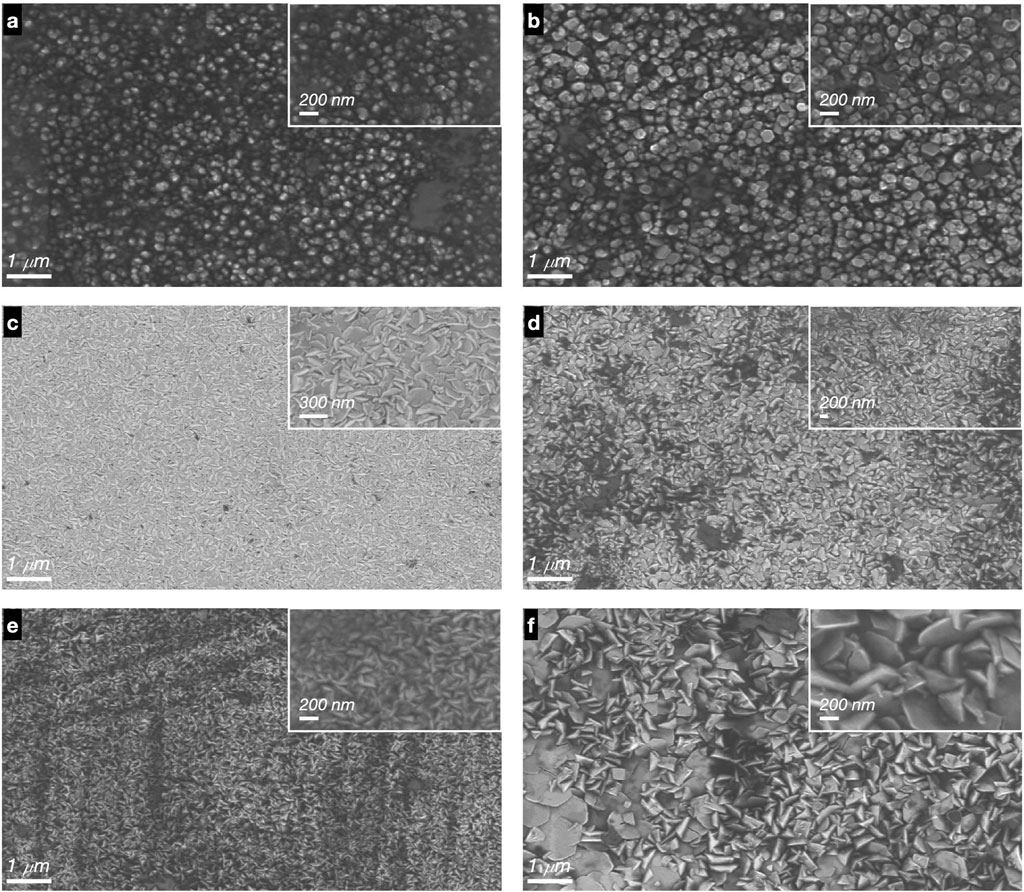
Figure 6. SEM images of ZnO:F with different acetic acid added in the precursor solution. (A) ZnO:F_20_8, (B) ZnO:F_20_14, (C) ZnO:F_100_8, (D) ZnO:F_100_14, (E) ZnO:F_200_8, (F) ZnO:F_200_14.
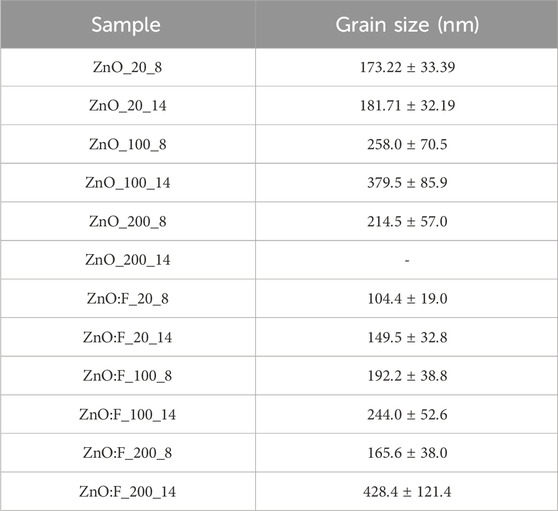
Table 4. Average grain size of the ZnO and ZnO:F films deposited with different concentrations of acetic acid and with deposition times of 8 and 14-min.
The presence of AcAc in the precursor solution is necessary to avoid zinc hydroxide compounds and favor zinc acetate complexes, as has been shown by Caillaud et al. (1993), who also reported significant growth rates around 2
The resistivity and effective mobility of ZnO and ZnO:F thin films as a function of acetic acid content in the starting solution are presented in Table 5. Figures 7, 8 show the resistivity vs. mobility graphs of both films. It can be observed that the electrical properties of ZnO:F films improved as the acetic acid content increased. It is worth mentioning that the resistivity, carrier concentration, and mobility for the lowest acetic acid content are not shown in Table 5 because they were out of range during the measurements.
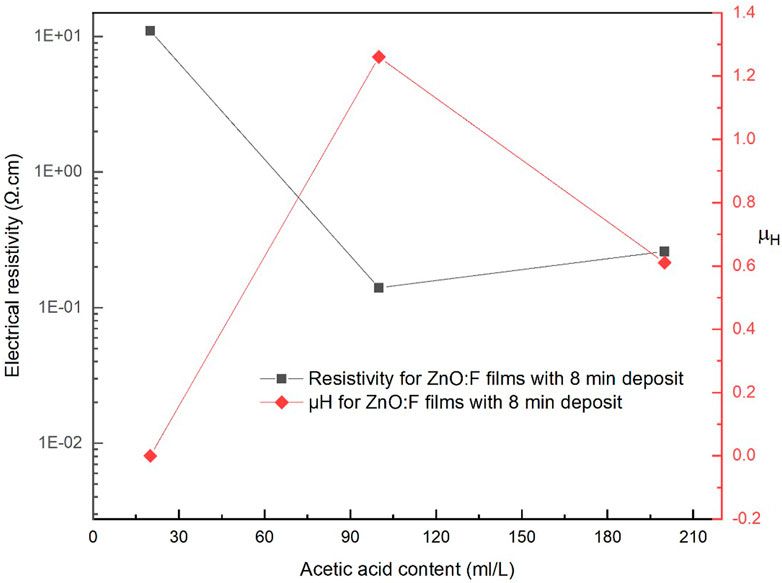
Figure 7. Electrical resistivity and Hall mobility as a function of the acetic acid content for ZnO:F thin films deposited at 8-min.
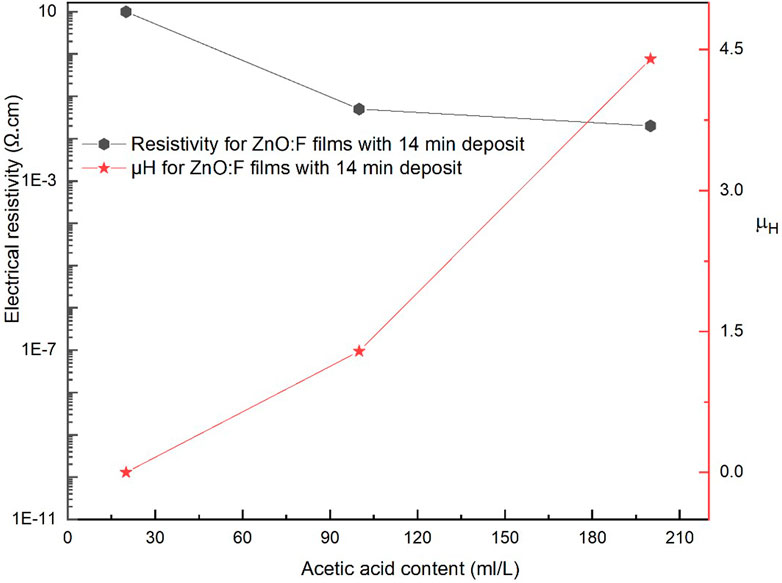
Figure 8. Electrical resistivity and Hall mobility as a function of the acetic acid content for ZnO:F thin films deposited at 14-min.
On the other hand, both ZnO and ZnO:F films deposited from solutions with a low acetic acid content (20 mL
The Haacke’s Figure of Merit for each sample was determined using Equation 3. Figures 9, 10 illustrate the variation of
The primary objective of this work was the manufacture of high-quality TCOs based on semiconductor oxides. The mechanisms developed to achieve high conductivity and transmittance in the visible spectrum begin with two types of deposition techniques: the physical methods involvs high vacuum processing (Chen et al., 2021) and economical chemical methods suitable for large-scale production (Chen et al., 2015). Regarding chemical techniques, which often struggle to attain high Figure of Merit values, the strategy focuses on a comprehensive study of the key variables that influence transport properties. Each chemical method has specific variables that impact the characteristics of the films (Maldonado et al., 2005). For instance, in chemical spray processes, reports highlight the importance of the starting solution composition in ZnO thin films. Given the lack of studies on F-doped ZnO and the role of acetic acid, this work proposes a thorough investigation to explore the effects of both low and excess AcAc concentrations in the starting solution. Hence, this research has demonstrated the positive effect of acetic acid in enhancing transport properties, which subsequently improves the Figure of Merit.
The AcAc addition in the starting solution enhanced zinc acetate precursor dissolution, and it avoided a milky finish that decreased the transmittance of ZnO films. A complete study of chemical species in solution and the effect of inorganic acids and AcAc content in solution on growth rates has been reported in the case of the deposition of ZnO by pyrosol technique (Caillaud et al., 1993). It has been shown that a pH solution in the range of four to five leads to an optimum growth rate. According to Caillaud et al. (1993) from zinc acetate dissolved in water, the acid variation gives rise to the following chemical species:
Under normal conditions, it has been established that for pH in the range of 3.5–4.3, where the acetate complexes are the major species, the ZnO growth rate reaches maximum values. The ZnO growth rate decreases for pH values less than 3.6. Therefore, the zinc acetate complex
Simultaneously, the decomposition of ammonium fluoride occurs according to the Equation 4 (Agashe and Major, 1996):
The decomposition temperature of ammonium fluoride is below 100°C. Therefore, it occurs almost instantaneously and forms an HF cloud in the vicinity of the growing ZnO:F film.
The boiling point of AcAc, methanol, and water are 117.9°C, 65°C, and 100°C, respectively. During the synthesis process, a rise in the temperature of the traveling drop occurs abruptly, from room temperature to 450°C (Sears and Gee, 1988). A decrease in the volume of the drops occurs due to the quick boiling of solvents, which can cause instantaneous precipitation of zinc hydroxides, diffusion on the substrates, and rapid ZnO formation with characteristics determined from solution composition.
The excess AcAc in the starting solution generates an acid cloud during the pyrolytic decomposition that drags down on the hot substrate surface due to the nitrogen flow. The high reactivity of F can form a
In the case of low AcAc content, film formation proceeds at a low rate due to significant pH variation, which leads to a decrease of
It should be noted that the results obtained in this work are compared with previous reports where the effect of varying the acetic acid concentration on the synthesis of ZnO and ZnO:F films is also studied. For instance, Harun et al. (2017) discussed the influence of AcAc on the preparation of ZnO thin films by the sol-gel method, with a focus on optoelectronic applications; they observed that the acetic acid concentration affects both the morphology and the optical and electrical properties of the films and they determined the AcAc concentration at which crystallization is enhanced and resistivity of the films is reduced. On the other hand, Shikha et al. (2015) made a similar analysis where variations in grain size and surface texture are highlighted, which impact visible light transmittance and conductivity. However, in this work we address how the AcAc concentration is impacted by the USP method which is considered more suitable for large-scale applications since it is faster and cheaper than the sol-gel method, since the latter involves the use of high-purity precursors such as metal alkoxides which tend to be more expensive and also involves several processing steps, which increases manufacturing time and costs. In contrast, USP is a continuous and more direct process, allowing for greater efficiency (Kaneva et al., 2012).
Finally, the obtained results suggest that this method for synthesis of ZnO and ZnO:F thin films can be useful in the production of Transparent Conductive Oxides. Moreover, this methodology presents an advantage over other reported methods by using a fresh starting solution making the process more efficient and cost-effective, besides it avoids the aging of the solution, which can delay the production of these films.
In conclusion, this work has demonstrated that the ultrasonic chemical spray technique can be used to produce highly transparent and conductive thin films of ZnO and ZnO:F. The variation in acetic acid content in the starting solution has been shown to play a key role in the modulation of electrical, morphological, and optical characteristics of the films. It was found that ZnO:F films with the lowest resistivity value (0.016
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
GB-B: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. AM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. MO: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. JZ-J: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The publication of this article was funded by the Secretaría de Investigación y Posgrado of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional with the project number 20242831.
The authors thanks Dr. Jorge Roque (SEM analysis) from CINVESTAV, Miguel Angel Luna-Arias (electrical measurements), and M.C. Adolfo Tavira-Fuentes (X-Ray characterization) for technical support. Gabriela Bobadilla Barrón also acknowledges the financial support received from CONAHCYT through a doctoral scholarship.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnano.2024.1445269/full#supplementary-material
Agashe, C., and Major, S. (1996). Effect of heavy doping in sno 2: F films. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 2965–2969. doi:10.1007/bf00356009
Altamirano-Juárez, D. C., Torres-Delgado, G., Jiménez-Sandoval, S., Jiménez-Sandoval, O., and Castanedo-Pérez, R. (2004). Low-resistivity zno: F: Al transparent thin films. Sol. energy Mater. Sol. cells 82, 35–43. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2004.01.003
Anandhi, R., Mohan, R., Swaminathan, K., and Ravichandran, K. (2012). Influence of aging time of the starting solution on the physical properties of fluorine doped zinc oxide films deposited by a simplified spray pyrolysis technique. Superlattices Microstruct. 51, 680–689. doi:10.1016/j.spmi.2012.02.006
Arora, I., Natarajan, V., and Sharma, P. K. (2022). Structural correlations for increased fom in pb doped zn2sno4 nanostructured films for applications as transparent electrode. J. Alloys Compd. 900, 163531. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163531
Caillaud, F., Smith, A., and Baumard, J.-F. (1993). Effect of ph of the solution on the deposition of zinc oxide films by spray pyrolysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 998–1002. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1993.tb05325.x
Chávez-Vargas, E., Jayaraman, V., Karthik, T., Olvera, M. d. l. L., Vega-Pérez, J., Jiménez-González, A., et al. (2018). Effect of doping concentration, solvent proportions and solution aging on the figure of merit of chemically sprayed zno: F thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 15821–15828. doi:10.1007/s10854-018-9373-9
Chen, S., Wilson, R. M., and Binions, R. (2015). Synthesis of highly surface-textured zno thin films by aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 5794–5797. doi:10.1039/c5ta00446b
Chen, Y.-C., Hsu, P.-C., Xu, L., and Juang, J.-Y. (2021). Simultaneous enhancement of electrical conductivity, uniformity, and near-infrared transmittance via laser annealing on zno:ga films deposited by atmospheric pressure plasma jet. J. Alloys Compd. 857, 157697. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157697
Dhar, A., and Alford, T. (2012). Optimization of nb2o5/ag/nb2o5 multilayers as transparent composite electrode on flexible substrate with high figure of merit. J. Appl. Phys. 112. doi:10.1063/1.4767662
de la L Olvera, M., Maldonado, A., and Asomoza, R. (2002). Zno: F thin films deposited by chemical spray: effect of the fluorine concentration in the starting solution. Sol. energy Mater. Sol. cells 73, 425–433. doi:10.1016/s0927-0248(02)00211-8
DiGregorio, S. J., Miller, C. E., Prince, K. J., Hildreth, O. J., and Wheeler, L. M. (2022). All-atmospheric fabrication of Ag–Cu core–shell nanowire transparent electrodes with Haacke figure of merit >600 × 10–3 Ω−1. Sci. Rep. 12, 20962. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25080-x
Edinger, S., Bekacz, J., Richter, M., Hamid, R., Wibowo, R., Peić, A., et al. (2015). Influence of the acetic acid concentration on the growth of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis of aqueous solutions. Thin Solid Films 594, 238–244. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2015.04.027
Edwards, P. P., Porch, A., Jones, M. O., Morgan, D. V., and Perks, R. M. (2004). Basic materials physics of transparent conducting oxides. Dalton Trans., 2995–3002. doi:10.1039/b408864f
Elmas, S., Pat, S., Mohammadigharehbagh, R., Musaoğlu, C., Özgür, M., Demirkol, U., et al. (2019). Determination of physical properties of graphene doped zno (zno:gr) nanocomposite thin films deposited by a thermionic vacuum arc technique. Phys. B Condens. Matter 557, 27–33. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2018.12.039
Elsokary, A., Soliman, M., Abulfotuh, F., Ebrahim, S., Sadat-Shafai, T., and Karim, M. (2024). Fabrication of composite transparent conductive electrodes based on silver nanowires. Sci. Rep. 14, 3045. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-53286-8
García-Mejía, M., Sastré-Hernández, J., Aguilar-Hernández, J., Becerril-Silva, M., Mendoza-Pérez, R., and Cruz-Orea, A. (2024). In2s3 thin films with potential use as window layers in photovoltaic devices. Phys. Scr. 99, 025911. doi:10.1088/1402-4896/ad186f
Gu, Y., Qiu, Z., Zhu, S., Lu, H., Peng, L., Zhang, G., et al. (2023). Patternable and transferable silver nanowire conductors via plasma-enhanced cryo-transferring process towards highly stretchable and transparent capacitive touch sensor array. Nano Res. 16, 11303–11311. doi:10.1007/s12274-023-5832-6
Haacke, G. (1976). New figure of merit for transparent conductors. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 4086–4089. doi:10.1063/1.323240
Habas, S. E., Platt, H. A., van Hest, M. F., and Ginley, D. S. (2010). Low-cost inorganic solar cells: from ink to printed device. Chem. Rev. 110, 6571–6594. doi:10.1021/cr100191d
Hagendorfer, H., Lienau, K., Nishiwaki, S., Fella, C. M., Kranz, L., Uhl, A. R., et al. (2014). Highly transparent and conductive zno: Al thin films from a low temperature aqueous solution approach. Adv. Mater 26, 632–636. doi:10.1002/adma.201303186
Harun, K., Hussain, F., Purwanto, A., Sahraoui, B., Zawadzka, A., and Mohamad, A. A. (2017). Sol-gel synthesized zno for optoelectronics applications: a characterization review. Mater. Res. Express. 4. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/aa9e82
Hu, J., and Gordon, R. G. (1991). Textured fluorine-doped zno films by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition and their use in amorphous silicon solar cells. Sol. cells 30, 437–450. doi:10.1016/0379-6787(91)90076-2
Hubarevich, A., Marus, M., Mukha, Y., Wang, K., Smirnov, A., and Sun, X. (2019). Optoelectronic performance of agnw transparent conductive films with different width-to-height ratios and a figure of merit embodying an optical haze. AIP Adv. 9. doi:10.1063/1.5081986
Hurma, T., and Caglar, M. (2020). Effect of anionic fluorine incorporation on structural, optical and electrical properties of zno nanocrystalline films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 110, 104949. doi:10.1016/j.mssp.2020.104949
Hwang, J. Y., and Lee, S. Y. (2024). Comprehensive effect on the development of multifunctional low emissive and transparent conductive amorphous-sizo/ag/amorphous-sizo multilayer structure. Opt. Mater. 154, 115650. doi:10.1016/j.optmat.2024.115650
Jiamprasertboon, A., Dixon, S. C., Sathasivam, S., Powell, M. J., Lu, Y., Siritanon, T., et al. (2019). Low-cost one-step fabrication of highly conductive zno: Cl transparent thin films with tunable photocatalytic properties via aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1, 1408–1417. doi:10.1021/acsaelm.9b00190
Jiao, B., Zhang, X., Wei, C., Sun, J., Huang, Q., and Zhao, Y. (2011). Effect of acetic acid on zno: in transparent conductive oxide prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 520, 1323–1329. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2011.04.152
Kaneva, N., Stambolova, I., Blaskov, V., Dimitriev, Y., Bojinova, A., and Dushkin, C. (2012). A comparative study on the photocatalytic efficiency of zno thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis and sol-gel method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 207, 5–10. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.10.020
Kang, K.-M., and Park, H.-H. (2018). Effect of atomic layer deposition temperature on the growth orientation, morphology, and electrical, optical, and band-structural properties of zno and fluorine-doped zno thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 377–385. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b08943
Kim, I., Lee, K.-S., Lee, T. S., Jeong, J.-h., Cheong, B.-k., Baik, Y.-J., et al. (2006). Effect of fluorine addition on transparent and conducting al doped zno films. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 063701. doi:10.1063/1.2347715
Lee, C., and Lin, L. (1996). Characteristics of spray pyrolytic zno thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 92, 163–166. doi:10.1016/0169-4332(95)00223-5
Maldonado, A., Guillén-Santiago, A., Olvera, M. d. l. L., Castanedo-Pérez, R., and Torres-Delgado, G. (2005). The role of the fluorine concentration and substrate temperature on the electrical, optical, morphological and structural properties of chemically sprayed zno: F thin films. Mater. Lett. 59, 1146–1151. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2004.12.006
Mallick, A., and Basak, D. (2018). Revisiting the electrical and optical transmission properties of co-doped zno thin films as n-type tcos. Prog. Mater. Sci. 96, 86–110. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.03.004
Peelaers, H., Kioupakis, E., and Walle, C. (2012). Fundamental limits on optical transparency of transparent conducting oxides: free-carrier absorption in sno2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100. doi:10.1063/1.3671162
Perednis, D., and Gauckler, L. J. (2005). Thin film deposition using spray pyrolysis. J. electroceramics 14, 103–111. doi:10.1007/s10832-005-0870-x
Rodríguez-Báez, J., Maldonado, A., Castañeda, L., Delgado, G. T., Castanedo-Pérez, R., and Olvera, M. d. l. L. (2007). On the effect of acetic acid on physical properties of chemically sprayed fluorine-doped zno thin films. Thin Solid Films 515, 8689–8694. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2007.03.132
Sanchez-Juarez, A., Tiburcio-Silver, A., Ortiz, A., Zironi, E., and Rickards, J. (1998). Electrical and optical properties of fluorine-doped zno thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Thin Solid Films 333, 196–202. doi:10.1016/s0040-6090(98)00851-7
Sears, W., and Gee, M. A. (1988). Mechanics of film formation during the spray pyrolysis of tin oxide. Thin solid films 165, 265–277. doi:10.1016/0040-6090(88)90698-0
Shikha, D., Mehta, V., Sood, S., and Sharma, J. (2015). Structural and optical properties of zno thin films deposited by sol–gel method: effect of stabilizer concentration. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 4902–4907. doi:10.1007/s10854-015-3000-9
Smith, A. (2000). Pyrosol deposition of zno and sno2 based thin films: the interplay between solution chemistry, growth rate and film morphology. Thin Solid Films 376, 47–55. doi:10.1016/s0040-6090(00)01403-6
Smith, A., and Rodriguez-Clemente, R. (1999). Morphological differences in zno films deposited by the pyrosol technique: effect of hcl. Thin Solid Films 345, 192–196. doi:10.1016/s0040-6090(99)00167-4
Vallejo, W., Cantillo, A., Salazar, B., Diaz-Uribe, C., Ramos, W., Romero, E., et al. (2020). Comparative study of zno thin films doped with transition metals (cu and co) for methylene blue photodegradation under visible irradiation. Catalysts 10, 528. doi:10.3390/catal10050528
Veron, F., Pasquet, I., Thimont, Y., Barnabé, A., and Tailhades, P. (2022). Improved performance of transparent p-type conductors cucro2:mg delafossite thin films through easy and low cost laser annealing. Mater. Lett. 313, 131795. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2022.131795
Workie, A. B., Ningsih, H. S., and Shih, S.-J. (2023). An comprehensive review on the spray pyrolysis technique: historical context, operational factors, classifications, and product applications. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 170, 105915. doi:10.1016/j.jaap.2023.105915
Wu, C.-C. (2020). Ultra-high transparent sandwich structure with a silicon dioxide passivation layer prepared on a colorless polyimide substrate for a flexible capacitive touch screen panel. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 207, 110350. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2019.110350
Xian, G., Zheng, T., Tao, Y., and Pan, Z. (2024). Hydrothermal growth and orientation of lafeo3 epitaxial films. Materials 17, 2758. doi:10.3390/ma17112758
Xin, M. (2021). Growth temperature on zno: Al thin films morphology and optical properties. Surf. Eng. 37, 1476–1483. doi:10.1080/02670844.2021.1976021
Yoon, K. H., and Cho, J. Y. (2000). Photoluminescence characteristics of zinc oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Res. Bull. 35, 39–46. doi:10.1016/s0025-5408(00)00183-5
Keywords: zinc oxide films, fluorine-doped zinc oxide films, ultrasonic spray pyrolysis, transparent conductive films, Haacke´s Figure of Merit
Citation: Bobadilla-Barrón G, Maldonado A, Olvera MdlL and Zamora-Justo JA (2024) Effect of solutions acidity on Haacke’s Figure of Merit of ZnO and ZnO:F thin films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Front. Nanotechnol. 6:1445269. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2024.1445269
Received: 07 June 2024; Accepted: 08 October 2024;
Published: 22 October 2024.
Edited by:
Elias Emeka Elemike, Federal University of Petroleum Resource Effurun, NigeriaReviewed by:
Nishtha Lukhmana, University of Georgia, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Bobadilla-Barrón, Maldonado, Olvera and Zamora-Justo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: J. A. Zamora-Justo, anphbW9yYWpAaXBuLm14
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.