
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 05 March 2025
Sec. Food Microbiology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1531005
 Xin Luo
Xin Luo Ying Shen*
Ying Shen*Ham, a widely consumed and culturally significant food, undergoes fermentation and aging processes that contribute to its distinctive flavor and texture. These processes are influenced by a complex interplay of microbial communities, which vary by the production region. Understanding these microbial dynamics can provide insights into flavor development and quality improvements in ham. In this study, the microbial communities found in ham produced in three distinct regions were compared, revealing that bacteria have a more dominant role in shaping the overall microbiota than fungi. Notably, each type of ham exhibited a unique microbial profile, although those from similar regions shared more similar profiles. Specific bacterial biomarkers were identified for each regional ham: Lactobacillus and Tetragonococcus in Serrano prosciutto, Odoribacter, Alistipes, Staphylococcus, and Akkermansia in Jinhua prosciutto, and Pseudomonas, Blautia, and Bacteroides in Xuanwei prosciutto. The microbial network analysis identified closer associations between microorganisms in the domestically produced Chinese hams than in the Spanish ham, suggesting limited foreign microbial invasions that contributed to a richer, more stable flavor. These findings offer new insights into how microbial interactions shape the development of flavor and quality in ham and clarify future strategies for improving the production process by leveraging microbial communities.
Ham is a flavorful food with a rich history, cherished by the Chinese people and appreciated globally. During the 13th to 15th century, ham processing technology was introduced to Europe by Marco Polo, which profoundly influenced ham production outside of China and gave rise to diverse regional flavors (Zhou and Zhao, 2007). As ham processing continued to develop in various regions, foods with regional flavors gradually emerged, such as Serrano ham, Jinhua ham, and Xuanwei ham.
In the traditional ham-making process, fermentation is essential, and the process temperature, humidity, and strains of microorganisms collectively influence the taste of the final product (Bosse et al., 2018). Microorganisms, as the primary agents in the fermentation process, play a crucial role in flavor development (Yang et al., 2020). In traditional research, the composition of the microbial community in ham is mainly identified through microscopic observation and microbial cultivation, which can result in incomplete and inaccurate identification (Jiang et al., 2024). With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, amplicon sequencing offers expanded avenues for exploring microbial diversity. Commonly employed methods include 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacteria and Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) gene sequencing for fungi, which is extensively applied in environmental monitoring, gut microbiota studies, and other microbial ecology research (Morgan et al., 2017; Callahan et al., 2019). The existing research on the microbial community in ham showed that the bacterial composition of Norden ham is mainly dominated by Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Bacteroidetes, while Xuanwei ham is dominated by mold, Staphylococcus, and Micrococcus (Zhang, 2014; Zou et al., 2020). However, there is limited research comparing the microbial composition and internal microbial interactions among Xuanwei, Serrano, and Jinhua ham.
This study used next-generation sequencing technology to analyze the bacteria and fungi present in three commercially available hams, with the aim of clarifying the microbial composition, biomarkers, and interactions within their respective communities. These findings provide a systematic theoretical framework for understanding the formation of distinct flavors in these hams and enhancing their overall quality.
Slices of three types of vacuum-packed, ready-to-eat cured prosciutto were purchased from a market: Serrano prosciutto (SRP), Jinhua prosciutto (JHP), and Xuanwei prosciutto (XWP). The labels indicated that these hams originated from Spain; Jinhua, China; and Xuanwei, China, respectively, and had been cured for over a year. After purchasing, an appropriately sized sample obtained from the same area of each type of prosciutto was collected under a sterile hood and used as the basis for sequencing. Three samples of each type of ham were randomly selected for the experiment and stored at −80°C until used.
The samples were stored at −80°C and transported on dry ice. Total DNA was extracted using a DNA extraction kit, and the purity and concentration of the DNA were assessed using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and a NanoDrop One. The 16S rRNA gene V3–V4 variable region was amplified using the forward primer 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′ and the reverse primer 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′, and the rRNA gene ITS1 region was amplified using the forward primer 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ and the reverse primer 5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′. The PCR reaction program consisted of an initial denaturation at 98°C for 1 min; 30 cycles at 98°C for 10 s, 50°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 30 s; and a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. The PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel and purified using a DNA purification and recovery kit. The library was prepared using an NEB Next® Ultra™ II FS DNA PCR-free library prep kit and sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6,000 platform by Biomarker Technologies Co., Ltd., with paired-end sequencing (PE250, 250 bp).
After the data were obtained, Python scripts were used to split the library and remove barcode and primer sequences. Quality control of the raw data was performed using Trimmomatic (v0.33) (Bolger et al., 2014), and primer sequences were identified and removed using cutadapt (v1.9.1) (Martin, 2011). USEARCH was used for paired-end merging, and UCHIME (v 8.1) (Edgar et al., 2011; Edgar, 2013) was used to remove chimeras. Species annotation was performed and a feature table was generated using the Quantitative Insights into Microbial Ecology (v202202) pipeline (Bolyen et al., 2019).
After normalization, Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs) with a total abundance of <30 and <2 occurrences were removed. The α- and β-diversity indices were calculated using the vegan package (Oksanen et al., 2013) with the species annotation database Silva (v138.1) (Quast et al., 2013). Visualization was performed using RStudio (v4.0.3), and Venn diagrams and petal plots were generated by the VennDiagram package. Differences in the α-diversity between groups were tested using Wilcoxon tests with the ggsignif package, with p ≤ 0.05 indicating significant differences and p ≤ 0.01 indicating highly significant differences. LEfSe analysis was performed separately using the microeco R package (Liu C. et al., 2021).
After normalization, ASVs with a total frequency of <0.2 were removed. Correlation analysis was performed based on Spearman’s rank correlation, and values with p > 0.05 and a correlation coefficient < 0.6 were eliminated. The interactions within bacterial and fungal microbiomes were analyzed separately. The interactions between the microbiomes were analyzed using the WGCNA (version 1.72.5), psych (version 2.4.6.26), and igraph (version 2.0.3) R packages (Langfelder and Horvath, 2008; Csardi, 2013; Revelle and Revelle, 2015). Gephi software (version 0.1.0) (Bastian et al., 2009) was used for visualization.
Microbial diversity is an important means of understanding the microbial community in food. The JHP group and XWP group had the highest number of bacteria in common but shared the lowest number of fungal types. The three groups shared 13 bacterial and 9 fungal microbial communities (Figures 1A,B). The Shannon and Chao1 diversity indices are important indicators for measuring microbial richness and evenness. The uniformity of the bacteria was highest in the JHP group, while the uniformity of the fungi was highest in the SRP group. The number of bacterial species was highest in the JHP group, and the uniformity of the fungi was highest in the XWP group (Figures 1C,D). The diversity analysis results of the data show that there were significant differences in bacteria and fungi among the different types of ham (Figures 1E,F).
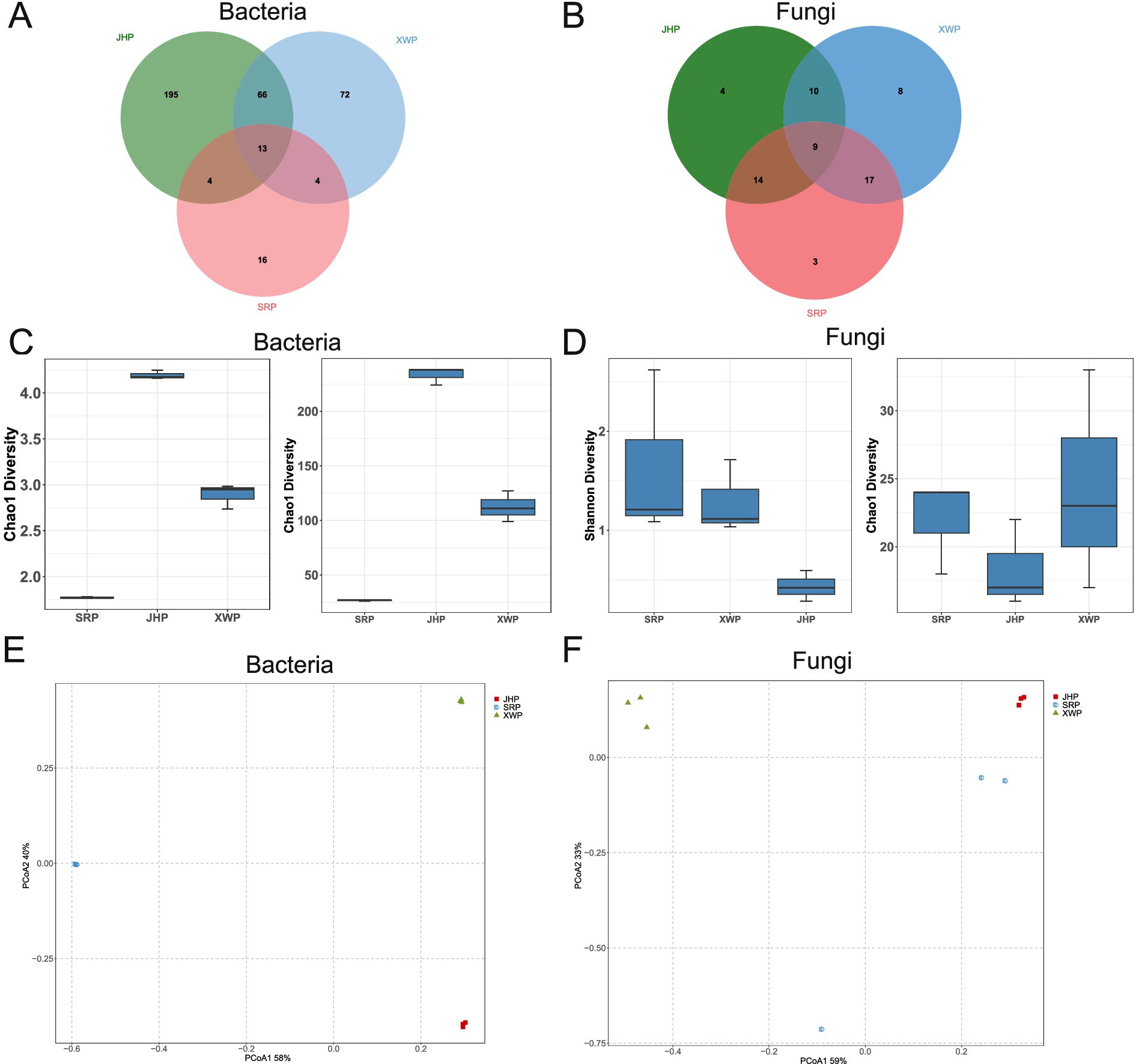
Figure 1. Diversity analysis of fungal and bacterial communities in different types of prosciuttos. (A,B) The shared and unique characteristics among bacteria (A) and fungi (B) in different groups. (C,D) Analysis of the α-diversity of bacteria (C) and fungi (D) in each group using Shannon and Chao1 indices. (E,F) Principal coordinates analysis based on Bray–Curtis distances of bacteria (E) and fungi (F) in the three types of ham.
Different types of ham are greatly affected by fermentation process parameters; thus, the microbial community is also greatly affected. Bacteria, as an important component of the microbial community, has a crucial role in the fermentation process. The ham in the SRP and JHP groups was dominated by Firmicutes, while the XWP group was primarily associated with Proteobacteria, indicating that different types of ham exhibit variations in microbial composition (Figure 2A). At the genus level, the species composition was further elucidated, with Lactobacillus and Tetragonococcus accounting for over 90% of the bacteria in the SRP group. In contrast, Tetragonococcus and the Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group were dominant in the JHP group. In the XWP group, however, Pseudomonas was the predominant genus (Figure 2B). These significant differences in composition contribute to the distinct flavors of the ham. Although there were notable differences in specific phyla and genera between groups, no significant differences were observed, which may be related to the number of samples (Figures 2C,D).
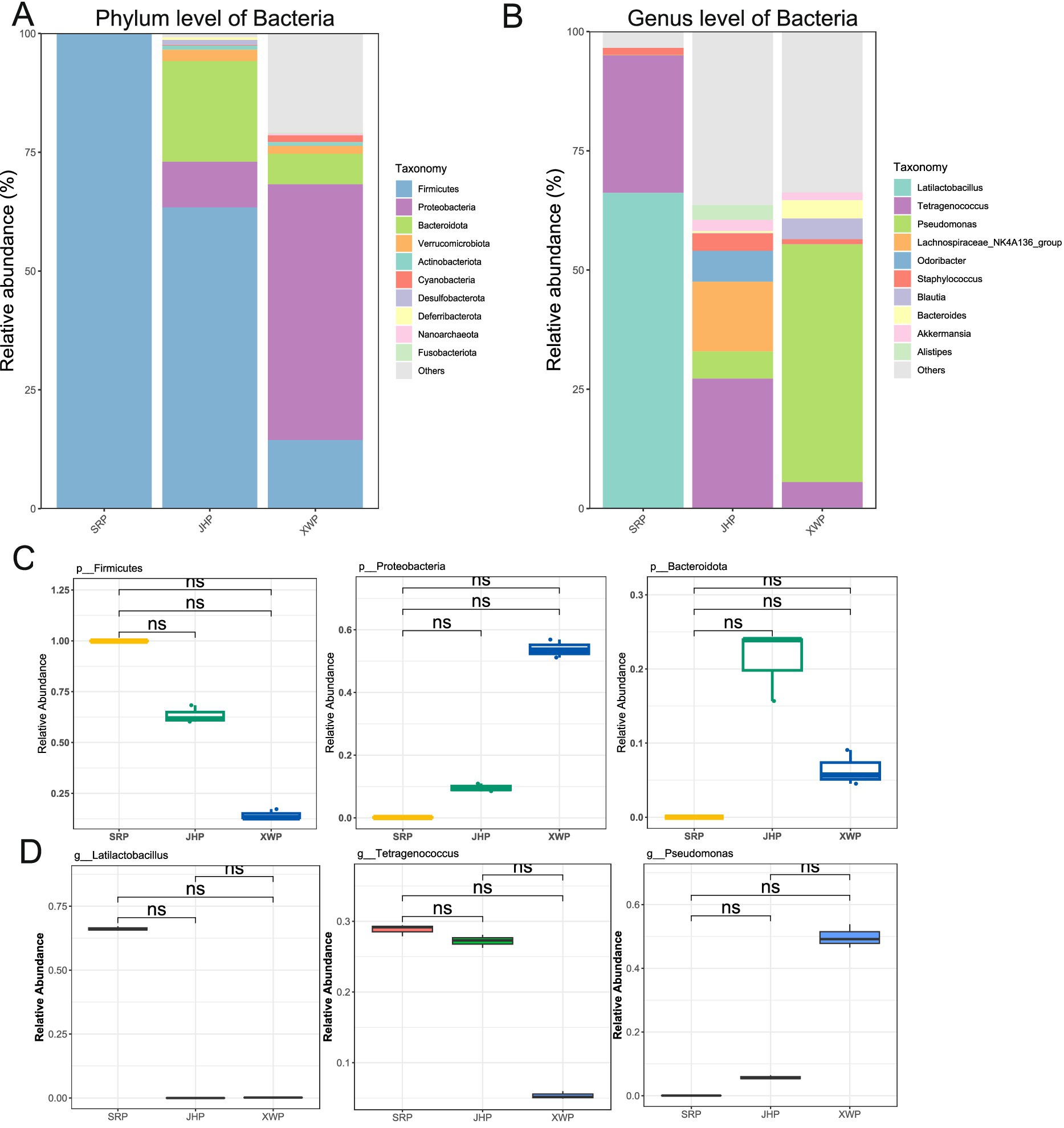
Figure 2. Analysis of the composition and abundance of bacteria at the phylum and genus levels among the three hams, and differences in the top three phyla and genera. (A,C) Analysis of the bacterial composition and ranking of the three different types of ham at the phylum level. (B,D) Analysis of differences in the bacterial composition and ranking of the three different types of ham at the genus level. Wilcoxon significance tests were performed between pairs.
Fungi, as an important component of microbial communities, also contribute to the formation of flavors. Overall, Ascomycota was the main fungal phylum among the three types of ham (Figure 3A). At the genus level, Debarytomyces was predominant, and there were differences in the composition and abundance of fungi in the three types of ham. The formation of flavor by fungi may be due to changes in the proportions of the fungal composition (Figures 3C,D).
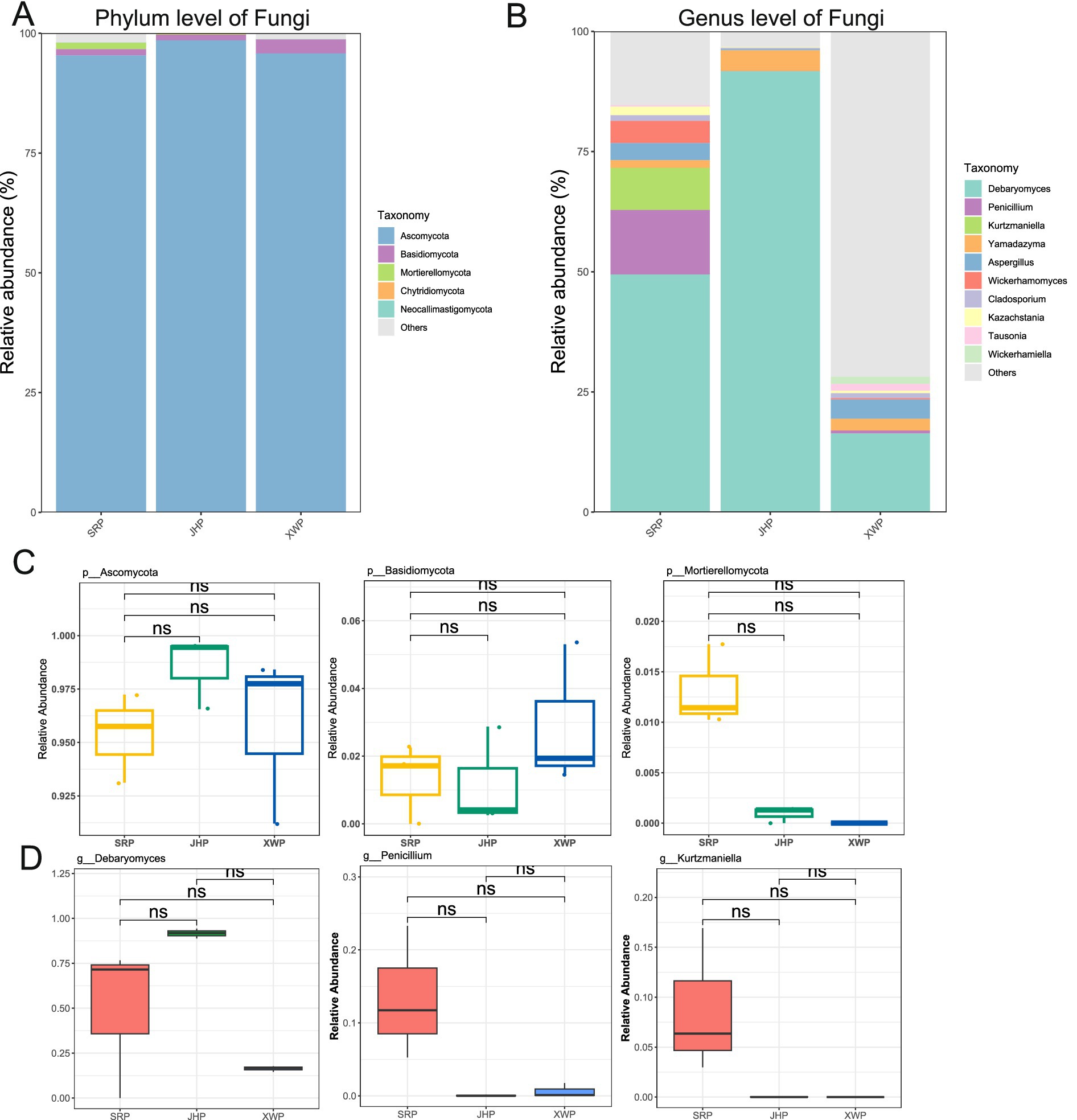
Figure 3. Analysis of the composition and abundance of fungi at the phylum and genus levels, and phyla and genera among the three hams. (A,C) Analysis of the fungal composition and ranking of the three different types of ham at the phylum level. (B,D) Analysis of the fungal composition and ranking of the three types of ham at the genus level. Wilcoxon significance tests were performed between pairs.
Biomarker screening based on LEfSe is an important analytical method for analyzing the formation of ham flavor among different types of ham. Within the bacterial community, the SRP group included genera from the Firmicutes, specifically Lactobacillus and Tetragonococcus, as biomarkers (Figures 4A,B). The JHP group included members of Bacteroidota, such as Odorobacter, Alistipes, Staphylococcus, Akkermansia, Halomonas, and the xylanophyllum group, as biomarkers. In the XWP group, Pseudomonas, Blautia, and Bacteroides from Proteobacteria were identified as key biomarkers. The biomarker screening of fungi revealed that the SRP group was characterized by the genera Kurtzmaniella, Wickerhamomyces, and Mortierella as biomarkers, whereas the XWP group was characterized by the genera Wickerhammomyces and Cyberlindnera. These different microorganisms provide the possibility for unique flavor formation in the different hams (Figures 4C,D).
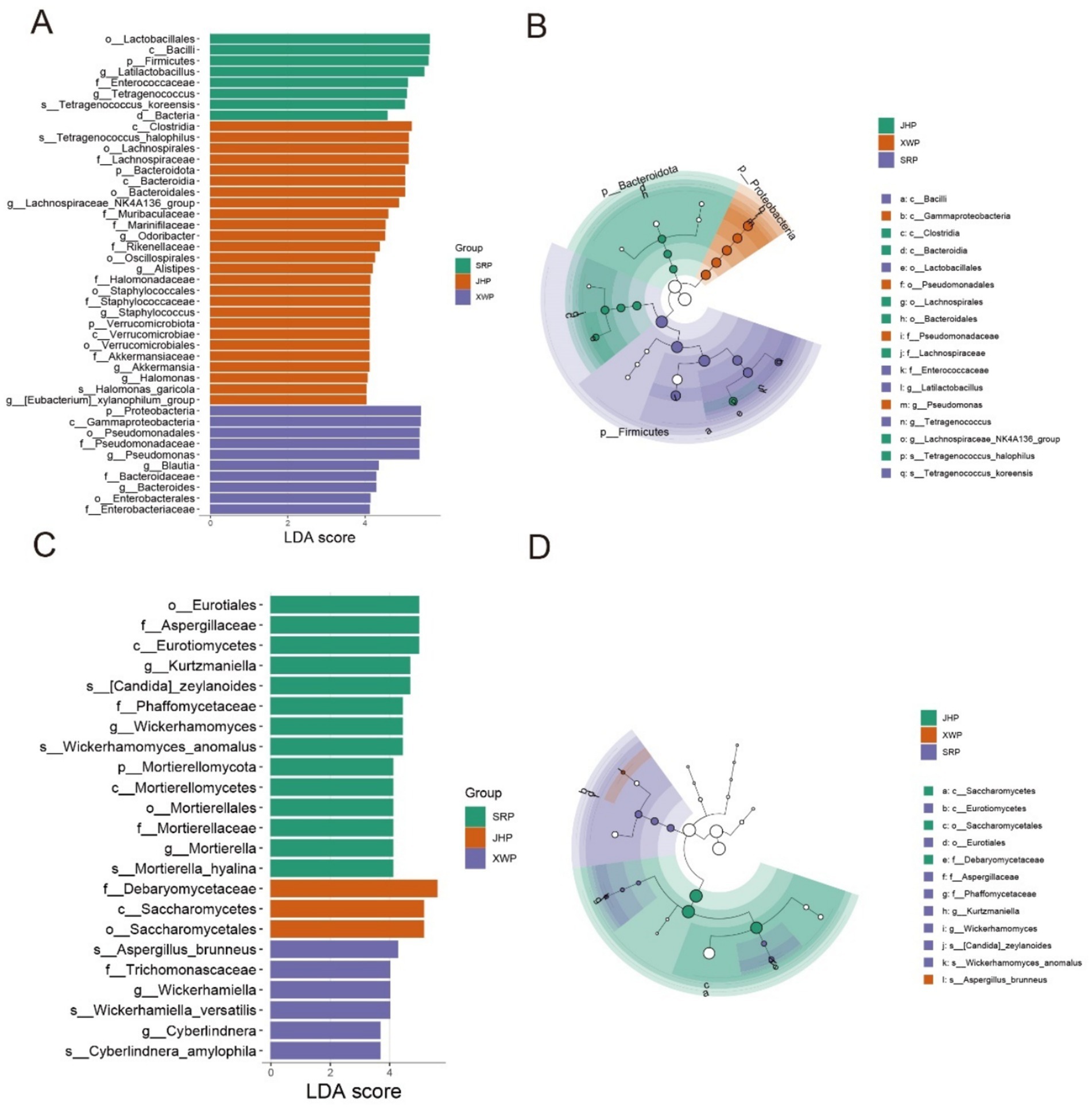
Figure 4. Biomarker screening of fungi and bacteria in different hams. (A,B) Biomarkers based on Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) > 4 in different bacterial taxa of the three hams and the associated cladogram. (C,D) Biomarkers based on LDA > 3 in different fungal taxa of the three hams and the associated cladogram.
The microbial communities were predominantly composed of bacteria and fungi. Investigating the interactions within these communities can offer valuable insight into the microecological dynamics. Our focus extended beyond the interactions between fungal and bacterial communities in each type of ham to include the relationships between individual fungi and bacteria. Overall, the bacteria had a substantial influence on the microbial community, whereas fungi exerted less of an impact on the overall microbial community structure. The SRP microorganisms had the lowest number and complexity of interactions among the three types of ham, whereas the microbial communities in XWP showed the strongest correlations. In addition, the fungi and bacteria in JHP and XWP exhibited close relationships to form a complex network of interactions (Figure 5). In summary, the three types of ham had developed their own distinct microbial networks, with the notable differences between SRP and the other two hams likely attributed to local customs and environmental factors.
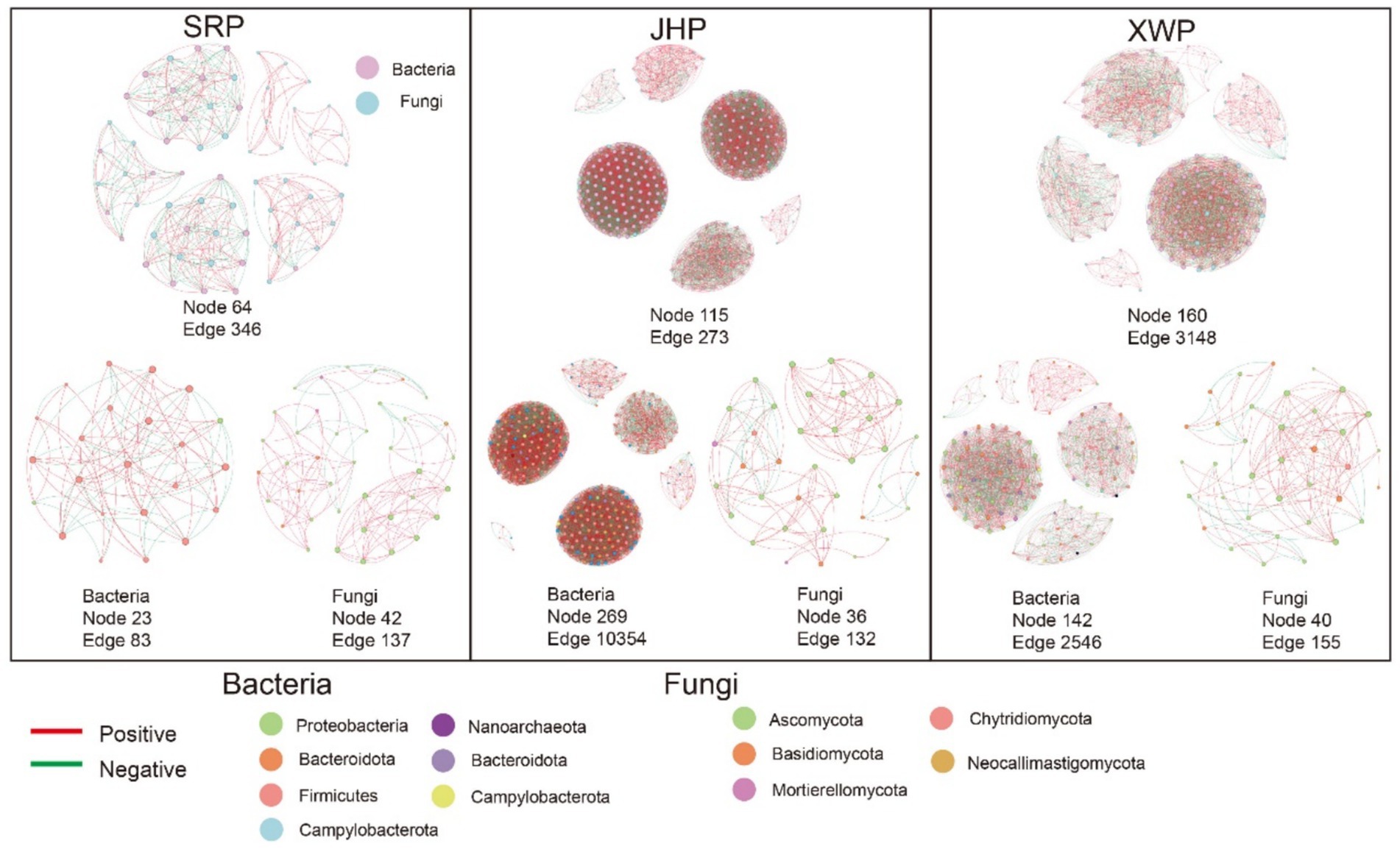
Figure 5. Network analysis based on Spearman correlation. Network interactions between fungi and bacteria were determined between each group and within the fungal and bacterial communities (r > 0.6, p < 0.05).
Ham, a product reliant on microbial fermentation during its production, owes its flavor profile to the composition and interaction of microorganisms (Chen et al., 2021). In this study, there were relatively few shared bacteria and fungi taxa among the different hams, although JHP and XWP shared more types of bacteria, which may be related to their similar regional characteristics. In this study, it was observed that the diversity and richness of bacteria were significantly higher than that of fungi (Figures 1C,D), consistent with findings from research on Panxian, Xuanen, Sanchuan, and Sabah ham (Mu et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2020; Deng et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2023). Thus, irrespective of the method of ham production, it was evident that bacteria predominantly governed the fermentation process, with fungi playing a lesser role. SRP, a ham produced in Europe, exhibited the lowest levels of diversity and richness compared with the other groups, yet it had higher levels of fungi, suggesting a close association with the region. Principal coordinates analysis results showed significant differences among the three types of ham, which illustrated the influence of regional characteristics on the fermentation community of ham and the subsequent flavor characteristics.
At the phylum level of bacterial, Firmicutes and Proteobacteria were predominate in all three types of ham, with SRP and JHP particularly dominated by Firmicutes, consistent with the findings of Wang et al. (2021) on the bacterial composition of Norden ham. By contrast, XWP was predominantly inhabited by Proteobacteria, possibly due to the distinct humid and hot environment of that region. During the fermentation process, numerous beneficial and pathogenic bacteria emerged. In SRP, Lactobacillus and Tetragonococcus dominated the fermentation, whereas Tetragonococcus was predominant in JHP and Pseudomonas in XWP. The microbial composition strongly correlated with the fermentation region and process (Li et al., 2011). Pseudomonas includes many opportunistic pathogenic bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which can cause diseases such as pneumonia and sepsis (Jurado-Martín et al., 2021). Therefore, individuals who are infected or immunocompromised should be cautious about consuming XWP to reduce the risk of infections.
The composition of fungi remained relatively consistent, with notable variations primarily involving Debaryomyces, a probiotic fermentation yeast (Breuer and Harms, 2006; Angulo et al., 2020). This genus had a consistent fermentative role across the various types of ham, and its proportions potentially correlated with the stage of fermentation. LEfse analysis is a key method for biomarker screening, and Lactobacillus, a dominant microorganism in fermentation, is also an important probiotic (Petrova et al., 2017). Tetragonococcus is also a common microorganism involved in fermentation (Wei et al., 2023). The JHP group included a significant number of beneficial gut microbiota, such as Lachnospiraceae, Odoribacter, and Alistipes, which are involved in bile acid metabolism and immune regulation (Parker et al., 2020; Ghosh et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2023). However, it also harbored certain pathogenic bacteria, such as Staphylococcus, which was potentially linked to the fermentation process. Therefore, consumption of this type of ham should be approached with caution, especially with consideration of the health status of consumers. Blautia was identified as a biomarker in the XWP group and is recognized for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a potentially beneficial component of the gut microbiota (Liu X. et al., 2021). Pseudomonas, however, as a potential pathogen, necessitates thorough disinfection measures during cooking. In the fungal community, fermentation fungi such as Kurtzmaniella and Wickerhamomyces dominated in SRP, while Wickerhamiella and Cyberlindnera were dominant in XWP. These distinct fermentation groups have an important role in shaping the unique flavor profiles of each type of ham. Therefore, choosing the appropriate ham for consumption can have beneficial effects on gut microbiota.
Microbial interaction networks are crucial for investigating the interactions among diverse microorganisms within microbial ecosystems (Hassani et al., 2018). The interactions among bacteria shape the overall microbial interaction network and are likely attributed to the diverse functions bacteria perform during the fermentation process (Ma et al., 2022). This phenomenon is closely linked to food spoilage during fermentation. As depicted in Figure 5, notable differences in microbial interactions were present between JHP and XWP hams, two locally produced hams in China, compared with the SRP ham. Specifically, the bacterial relationships in the Chinese-produced hams exhibited closer associations, with tightly interconnected microorganisms that maintain functional stability and resist the proliferation of spoilage bacteria (Chen et al., 2022). This contributes to stabilizing the fermentation process and enhancing the taste of food. Furthermore, varying import and export standards among different countries can also contribute to the occurrence of this phenomenon.
In conclusion, ham, a widely consumed food globally, was analyzed in this study to compare the microbial communities present in hams from three distinct regions with distinct flavors. The analysis revealed that the bacterial abundance in the microbial community surpassed that of fungi. In addition, ham samples from similar regions shared a higher number of microorganisms. Each of the three types of ham exhibited unique microbial communities with significant differences among them. Notably, Lactobacillus and Tetragonococcus from the Firmicutes phylum were identified as biomarkers for the SRP group. In the JHP group, biomarkers included Odorobacter, Alistipes, Staphylococcus, Akkermansia, and others from the Bacteroidota phylum. The biomarkers of the XWP group were Pseudomonas, Blautia, and Bacteroides from Proteobacteria. Microbial network analysis revealed that bacteria had a more dominant role in the overall microbiota than fungi. The two domestically produced microbial networks in the hams from China showed greater similarity, with tighter associations between microorganisms. These findings may offer insights into the development of rich flavors, the reduction of foreign microbial invasions, and the stability of taste. This study provides a novel microbial perspective on the formation of specific microbial communities in ham, with implications for future quality improvements.
All of the data supporting this study are available in the NCBl repository, accession number is PRJNA1227238.
XL: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YS: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Doctoral Research Startup Fund of Guizhou Academy of Sciences [Qiankeyuan R (2022) no. 03].
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Angulo, M., Reyes-Becerril, M., Medina-Córdova, N., Tovar-Ramírez, D., and Angulo, C. (2020). Probiotic and nutritional effects of Debaryomyces hansenii on animals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 7689–7699. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10780-z
Bastian, M., Heymann, S., and Jacomy, M. (2009). Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 3, 361–362. doi: 10.1609/icwsm.v3i1.13937
Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M., and Usadel, B. (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114–2120. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bolyen, E., Rideout, J. R., Dillon, M. R., Bokulich, N. A., Abnet, C. C., al-Ghalith, G., et al. (2019). Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 852–857. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Bosse, R., Müller, A., Gibis, M., Weiss, A., Schmidt, H., and Weiss, J. (2018). Recent advances in cured raw ham manufacture. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 58, 610–630. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1208634
Breuer, U., and Harms, H. (2006). Debaryomyces hansenii—an extremophilic yeast with biotechnological potential. Yeast 23, 415–437. doi: 10.1002/yea.1374
Callahan, B. J., Wong, J., Heiner, C., Oh, S., Theriot, C. M., Gulati, A. S., et al. (2019). High-throughput amplicon sequencing of the full-length 16S rRNA gene with single-nucleotide resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:e103. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz569
Chen, W., Wang, J., Chen, X., Meng, Z., Xu, R., Duoji, D., et al. (2022). Soil microbial network complexity predicts ecosystem function along elevation gradients on the Tibetan plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 172:108766. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2022.108766
Chen, L., Wang, Z., Ji, L., Zhang, J., Zhao, Z., Zhang, R., et al. (2021). Flavor composition and microbial community structure of Mianning ham. Front. Microbiol. 11:623775. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.623775
Csardi, M. G. (2013). Package ‘igraph’: Last accessed. Available at: https://igraph.org/r/pdf/1.2.6/igraph.pdf
Deng, X., Li, J., He, L., Zhang, Y., Huang, G., Bao, X., et al. (2021). Microbial community succession pattern on the surface of Xuanen ham during fermentation. Food Ferment. Ind. 47, 34–42. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.025561
Edgar, R. C. (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10, 996–998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604
Edgar, R. C., Haas, B. J., Clemente, J. C., Quince, C., and Knight, R. (2011). UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27, 2194–2200. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Ghosh, T. S., Shanahan, F., and O'Toole, P. W. (2022). The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 19, 565–584. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00605-x
Hassani, M. A., Durán, P., and Hacquard, S. (2018). Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont. Microbiome 6:58. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0445-0
Jiang, X., Peng, Z., and Zhang, J. (2024). Starting with screening strains to construct synthetic microbial communities (SynComs) for traditional food fermentation. Food Res. Int. 190:114557. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114557
Jurado-Martín, I., Sainz-Mejías, M., and McClean, S. (2021). Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An audacious pathogen with an adaptable arsenal of virulence factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:3128. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063128
Langfelder, P., and Horvath, S. (2008). WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinf. 9:559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Li, X.-R., Ma, E.-B., Yan, L.-Z., Meng, H., du, X. W., Zhang, S.-W., et al. (2011). Bacterial and fungal diversity in the traditional Chinese liquor fermentation process. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 146, 31–37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.030
Lin, J., Song, C., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Quan, W., and Shu, X. (2023). Comparative analysis of microbial diversity of five dry-cured hams in Yunnan. China Food Addit. 34, 233–241. doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2023.10.030
Liu, C., Cui, Y., Li, X., and Yao, M. (2021). Microeco: An R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 97:fiaa255. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiaa255
Liu, X., Mao, B., Gu, J., Wu, J., Cui, S., Wang, G., et al. (2021). Blautia-a new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 13, 1–21. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1875796
Ma, S., Luo, H., Zhao, D., Qiao, Z., Zheng, J., An, M., et al. (2022). Environmental factors and interactions among microorganisms drive microbial community succession during fermentation of Nongxiangxing daqu. Bioresour. Technol. 345:126549. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126549
Martin, M. (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 17:10. doi: 10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Morgan, H. H., du Toit, M., and Setati, M. E. (2017). The grapevine and wine microbiome: insights from high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 8:820. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00820
Mu, Y., Su, W., and Mu, Y. (2019). Analysis of microbial diversity and key volatile flavor compounds of Panxian dry-cured ham. Food Res Dev 40, 77–85. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.15.013
Oksanen, J., Blanchet, F. G., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., Minchin, P. R., O'Hara, R. B., et al. (2013). Package ‘vegan’: Community ecology package, version. Available at: https://mirror.ibcp.fr/pub/CRAN/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf
Parker, B. J., Wearsch, P. A., Veloo, A. C. M., and Rodriguez-Palacios, A. (2020). The genus alistipes: gut bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, cancer, and mental health. Front. Immunol. 11:906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00906
Petrova, M. I., Reid, G., Vaneechoutte, M., and Lebeer, S. (2017). Lactobacillus iners: friend or foe? Trends Microbiol. 25, 182–191. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.11.007
Quast, C., Pruesse, E., Yilmaz, P., Gerken, J., Schweer, T., Yarza, P., et al. (2013). The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D590–D596. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1219
Revelle, W., and Revelle, M. W. (2015). Package ‘psych’: The comprehensive R archive network. Available at: https://cran.rstudio.org/web/packages/psych/psych.pdf
Wang, X., Shi, Q., Liu, B., Lei, Y., Tang, H., Zhang, S., et al. (2021). Bacterial dynamics during the processing of Nuodeng dry-cured ham. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 42, 83–98. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020030129
Wei, G., Chitrakar, B., Regenstein, J. M., Sang, Y., and Zhou, P. (2023). Microbiology, flavor formation, and bioactivity of fermented soybean curd (furu): a review. Food Res. Int. 163:112183. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112183
Yan, C., Huang, S.-H., Ding, H.-F., Kwek, E., Liu, J.-H., Chen, Z.-X., et al. (2023). Adverse effect of oxidized cholesterol exposure on colitis is mediated by modulation of gut microbiota. J. Hazard. Mater. 459:132057. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132057
Yang, Y., Hu, W., Xia, Y., Mu, Z., Tao, L., Song, X., et al. (2020). Flavor formation in Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): impacts of the flavor-active microorganisms, raw materials, and fermentation technology. Front. Microbiol. 11:580247. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.580247
Zhang, P. (2014). Effects of salt dosage on quality changes in Sichuan bacon during processing and storage. [master’s thesis]. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University.
Zhang, Y., Shu, X., Huang, X., Lv, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Applying 16S rDNA sequencing to analyze the microbial diversity on the surface and in the interior of Saba ham, a traditional Chinese fermented meat product. Meat Res. 34, 26–32. doi: 10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-20200803-184
Zhou, G. H., and Zhao, G. M. (2007). Biochemical changes during processing of traditional Jinhua ham. Meat Sci. 77, 114–120. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2007.03.028
Keywords: packaged sliced dry-cured hams, Serrano prosciutto, Jinhua prosciutto, Xuanwei prosciutto, microbial composition
Citation: Luo X and Shen Y (2025) Comparative analysis of the microbial composition of three packaged sliced dry-cured hams from a Chinese market. Front. Microbiol. 16:1531005. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1531005
Received: 19 November 2024; Accepted: 13 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Javier Carballo, University of Vigo, SpainReviewed by:
Iftikhar Younis Mallhi, Minhaj University Lahore, PakistanCopyright © 2025 Luo and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ying Shen, c2hlbnlpbmdAZ3phdGEuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.