- Hubei Key Laboratory of Quality Control of Characteristic Fruits and Vegetables, College of Life Science and Technology, Hubei Engineering University, Xiaogan, China
Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) is one of the most effective tools for studying gene expression. Inonotus obliquus is a rare and edible medicinal fungus. Selecting an appropriate reference gene is crucial for researching its gene function. In this study, we selected 11 potential reference genes of Inonotus obliquus. Subsequently, we applied GeNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper algorithms to evaluate the expression stability of these 11 reference genes. Under varying carbon sources, VPS exhibited good stability and was suitable as an internal reference gene. Under different nitrogen sources, RPB2 was the most stable reference gene. For varying growth factors, PP2A was the most stable reference gene. At different pH levels, UBQ showed the highest stability. Under different temperature conditions, RPL4 was the most stable. In different strains, RPL2 was the most stable reference gene, while VAS demonstrated the greatest stability across different growth stages. Overall, VPS was the most recommended reference gene for the entire sample set. This study provides a foundation for the further application of RT-qPCR in the gene expression analysis of Inonotus obliquus.
Introduction
Inonotus obliquus, also known as betula antler, Ganoderma sibirica, betula mushroom, or Betula Antler, is a valuable medicinal fungus from the Inonotus genus within the Polyporaceae family (Song et al., 2013; Zhong et al., 2009). This fungus contains various bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, obliquin, oxidized triterpenoids, steroids, polyphenols, and low molecular weight components (Chen et al., 2015). Among these, the polysaccharide component is considered one of the primary active substances. Numerous studies have demonstrated that the fruiting body, mycelium, and fermentation broth polysaccharides of I. obliquus possess pharmacological activities such as anti-tumor effects, diabetes treatment, immune regulation, antiviral properties, antioxidant activity, and anti-fatigue effects (Lu et al., 2021).
Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) is a highly sensitive, specific, and accurate DNA amplification system that is widely used in gene expression studies (Chowrasia et al., 2019; Hu et al., 2022). However, the results of RT-qPCR analyses can be influenced by factors such as RNA extraction quality, reverse transcription efficiency, and amplification efficiency. In particular, selecting appropriate reference genes is crucial for the successful application of qRT-PCR in gene expression analysis (Lin et al., 2014). The use of stably expressed reference genes can significantly reduce external interference. Studies have shown that no absolutely stable reference gene exists, and the expression stability of any reference gene is subject to certain limitations. Therefore, to ensure accurate and reliable results, it is essential to screen suitable reference genes according to the specific treatment conditions used in RT-qPCR experiments (Chen et al., 2023).
Materials and methods
Sampling culture conditions
Except for different strain assays, I. obliquus JL01 was used as the material in all experiments. We set up six experiments under different culture conditions, varying the treatments while keeping the basic culture conditions constant. The nitrogen sources included peptone, soybean powder, beef paste, and yeast powder. The carbon sources included glucose, sucrose, maltose, and soluble starch. The growth factors varied among Vitamin B1 (VB1), Vitamin B2 (VB2), and Vitamin B6 (VB6). The culture temperatures were set at 25, 28, and 31°C. The pH values were 4, 5, 6, and 7. We used HE, JL01, and MAFF420256 strains, which are distantly related (Guo and Wang, 2020). HE originated in Russia, JL01 originated in China and MAFF420256 originated in Japan. For the culture stage assay, we first sampled the culture at 15 days. Subsequently, we collected samples every 2 days for a total of 14 sampling points. The base liquid medium consisted of the following components: glucose 2%, peptone 1%, KH2PO4 0.3 mg%, MgSO4 0.15 mg%, VB1 0.1 mg%, with a pH of 5.0. After 15 days of culture, we collected samples and performed three biological replicates.
Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
For total RNA extraction from I. obliquus samples cultured under different treatments, we used the Ultrapure RNA kit (Cat. CW0581) and followed the kit’s specific instructions. We assessed the RNA concentration and purity using a micronucleic acid protein analyzer Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, USA) and 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The RNA served as the basis for subsequent cDNA synthesis. We used the Hifair III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Cat. 11139ES60) from Yeasen Biotechnology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. to synthesize cDNA. Additionally, to evaluate primer amplification efficiency, we extracted RNA from I. obliquus cultured in the basic medium and reverse-transcribed it for use.
Primer design and specific testing
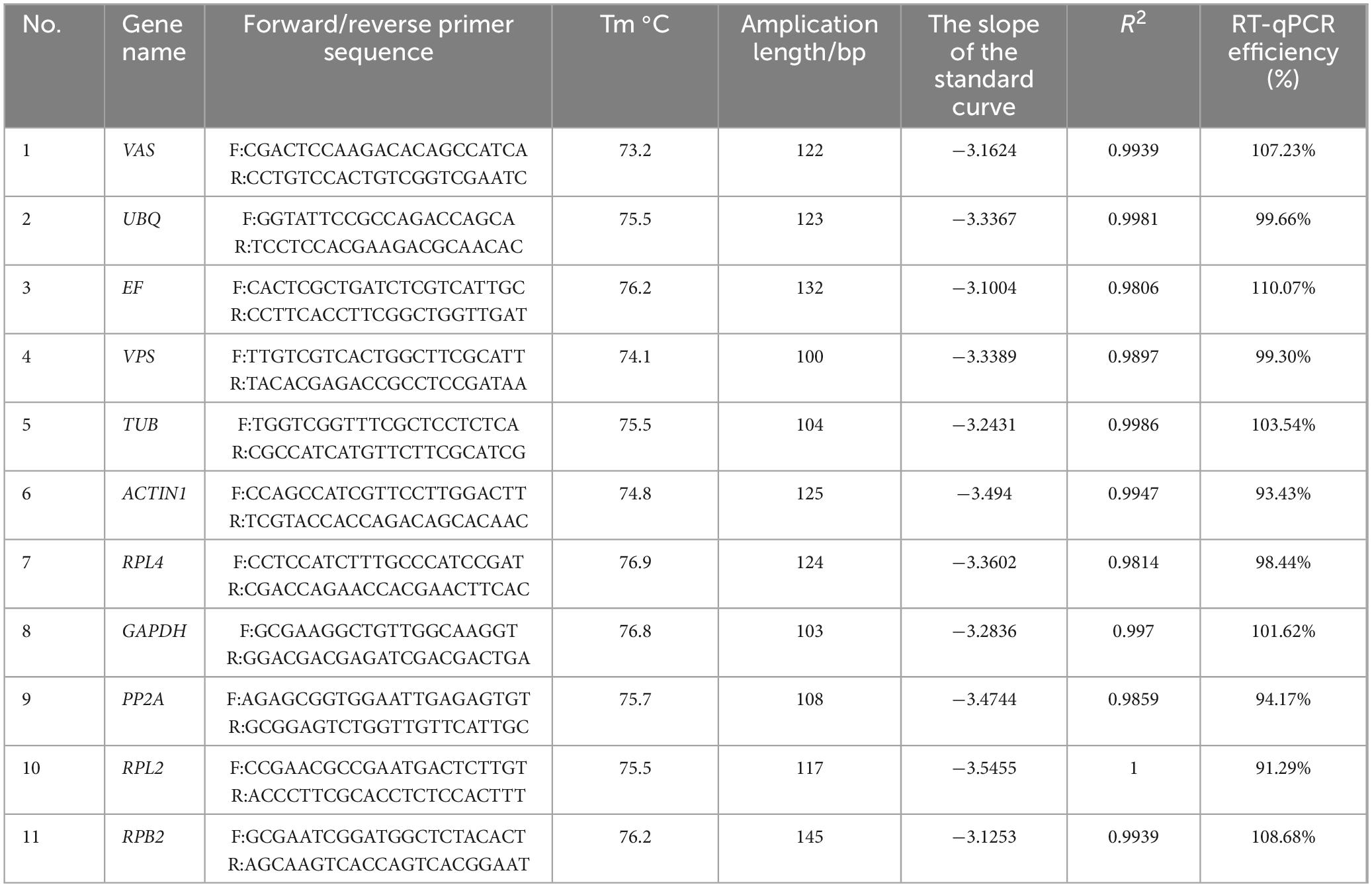
The I. obliquus genome has been sequenced and its information was stored in our laboratory. In this study, we chose 11 reference genes from various functional categories: UBQ, RPL2, PP2A, VAS, EF, ACTIN1, GAPDH, VPS, RPL4, RPB2, and TUB, which are widely used in other edible or medicinal fungi. We designed primers for these candidate reference genes using Primer Premier 6.0, following the design principles for RT-qPCR primers. We then verified the specificity of these primers and the amplified products using ordinary PCR.
Detection of primer amplification efficiency
We diluted cDNA obtained by reverse transcription into five gradients: 100, 10, 1, 0.1, and 0.01 ng/ul, with each gradient representing a tenfold dilution. We used these five concentrations as templates to perform RT-qPCR on the 11 candidate reference genes, with three biological replicates for each gradient. After conducting RT-qPCR, we plotted the standard curve and calculated the amplification efficiency (E) and correlation coefficient (R2) based on the slope of the primer pair’s standard curve (Wan et al., 2011).
Quantitative real-time PCR
We used the ViiA7 real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR system to measure the expression levels of each reference gene. The reaction system consisted of 20 μL, including 10 μL of Hieff qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (Low Rox Plus), 0.4 μL each of forward and reverse primers, 8.2 μL of ddH2O, and 1 μL of cDNA. We prepared the reaction system and performed the reaction on the ViiA7 real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument. The reaction conditions were: 94°C for 5 min; followed by 40 cycles of 94°C for 10 s, 60°C for 20 s, and 72°C for 20 s. We set up three biological replicates for each sample.
Data analysis
To identify suitable internal reference genes for I. obliquus, we used three common software programs: GeNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper, to process the data based on CT values (Supplementary Table 1). We also utilized the web tool RefFinder (Xie et al., 2023)1 to integrate and validate the results. Using these different data analysis methods, we evaluated the stability of the 11 candidate reference genes. We then selected the most stable reference genes across seven experimental groups, which included different nitrogen sources, carbon sources, growth factors, pH levels, temperatures, strains, and developmental stages of mycelia, all under liquid culture conditions.
Results and discussion
Selection and identification of the candidate reference genes
Based on previous studies (Xu et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2022), we selected 11 candidate reference genes for screening ACTIN1, β-tubulin (TUB), protein phosphatase 2A regulatory B subunit (PP2A), ribosomal protein L2 (RPL2), ribosomal protein L4 (RPL4), elongation factor 1-gamma (EF), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II second-largest subunit (RPB2), ubiquitin (UBQ), vacuolar ATP synthase (VAS), and vacuolar protein sorting (VPS).
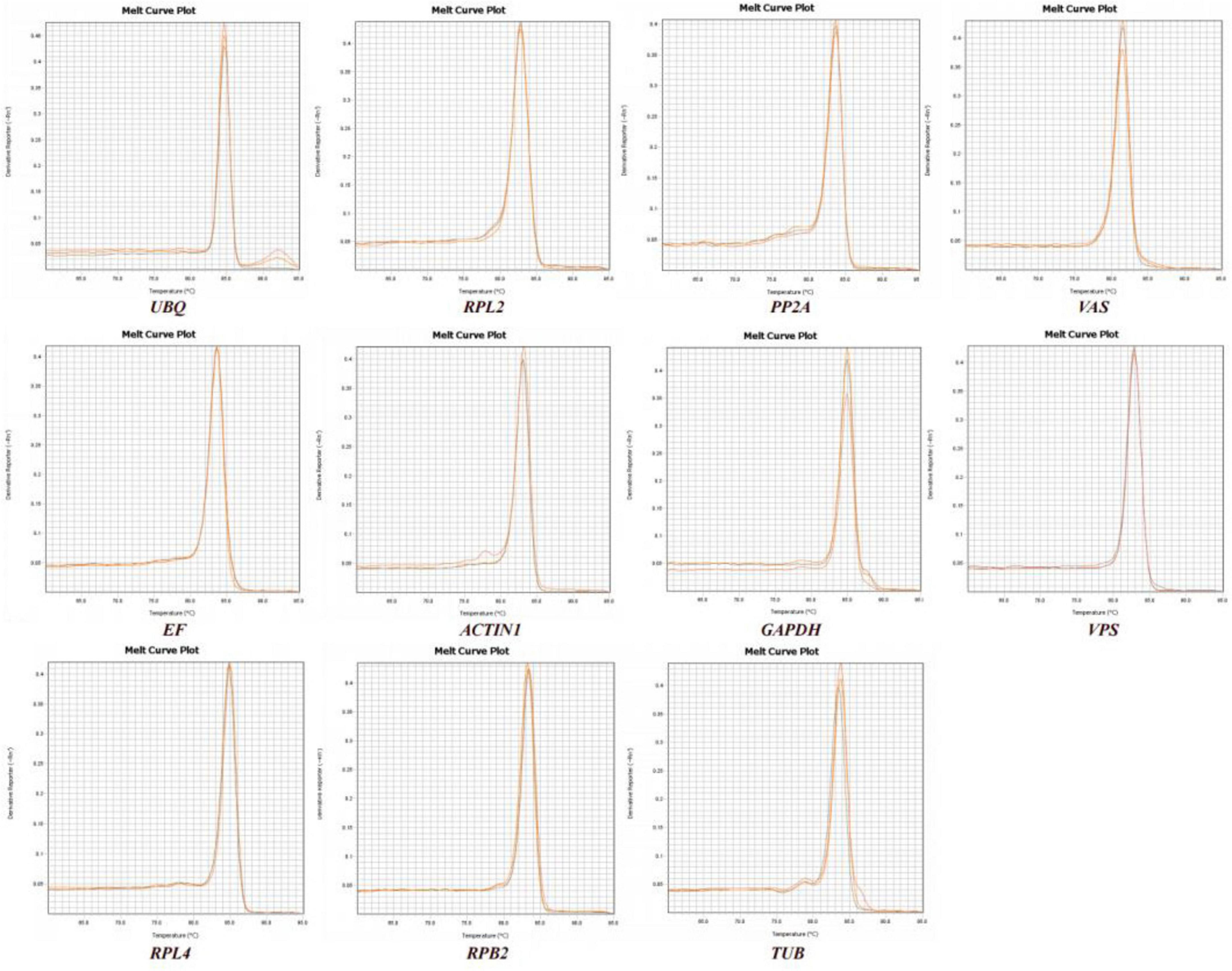
We observed the PCR amplification product bands for these 11 candidate reference gene primers using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The electrophoretic images confirmed that the amplified product fragment sizes were correct, with single bands, and no non-specific amplification or primer dimerization (Figure 1). The qRT-PCR results showed that the melting curves for each candidate reference gene primer were unimodal (Figure 2). The amplification efficiency of the 11 candidate reference genes ranged from 91.29 to 110.07%, with correlation coefficients (R2) between 0.9806 and 1. Primer information is provided in Table 1.
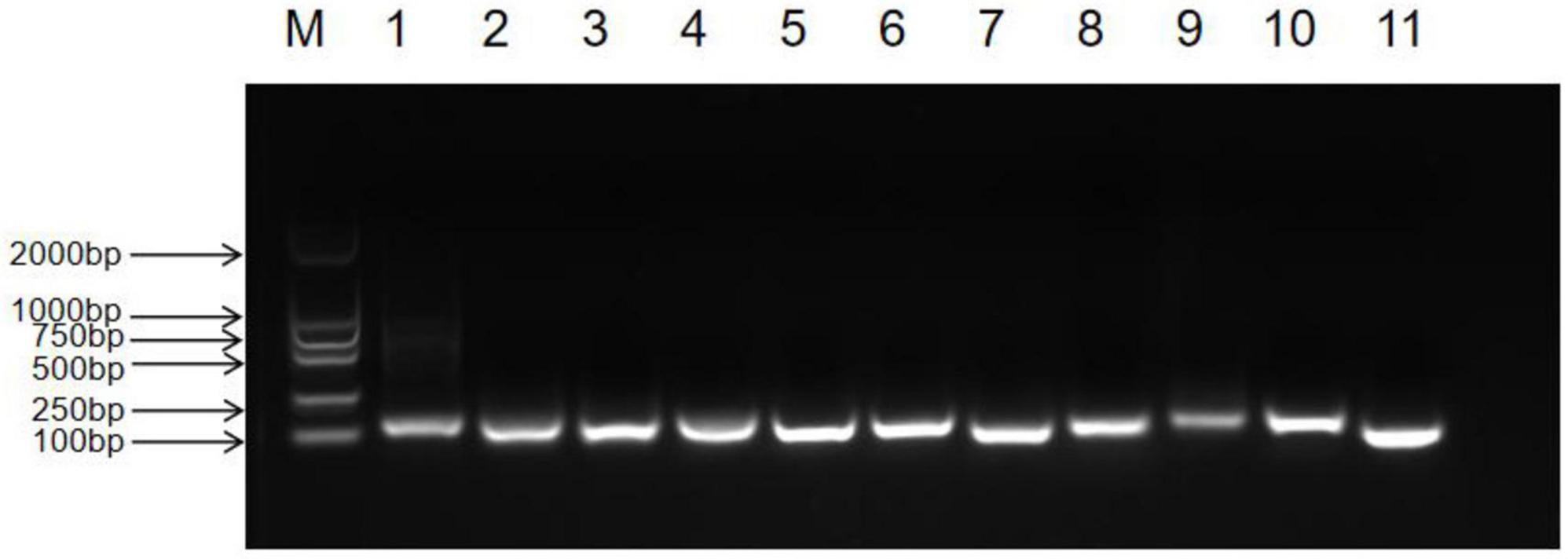
Figure 1. Detection of common PCR products for 11 candidate reference genes in Inonotus obliquus via agarose gel electrophoresis (M: DL2000 marker, 1: UBQ, 2: RPL2, 3: PP2A, 4: VAS, 5: EF, 6: ACTIN1, 7: GAPDH, 8: VPS, 9: RPL4, 10: RPB2, 11: TUB).
Expression profile of reference genes
We predicted the expression levels of the 11 candidate reference genes using the CT values obtained from all samples. A lower CT value indicates higher expression abundance. Figure 3 shows the distribution of CT values for these 11 reference genes across all groups. The results indicate that the CT values of the 11 reference genes under different treatments ranged from 15.55 to 29.32. Among these, the expression variation of UBQ in all samples was the highest (13.76). The expression variation of VAS was the second highest (12.288), and the expression variation of EF was the third highest (10.128). In contrast, VPS had the lowest CT value variation (5.49). Overall, other variations in transcript levels were moderate, which were sequentially sorted as GAPDH (8.84), RPL2 (8.77), ACTIN1 (7.08), RPL4 (6.67), PP2A (5.87), RPB2 (5.69), TUB (5.53). Based on these findings, VPS is the most recommended reference gene for the entire sample set (Figure 3).
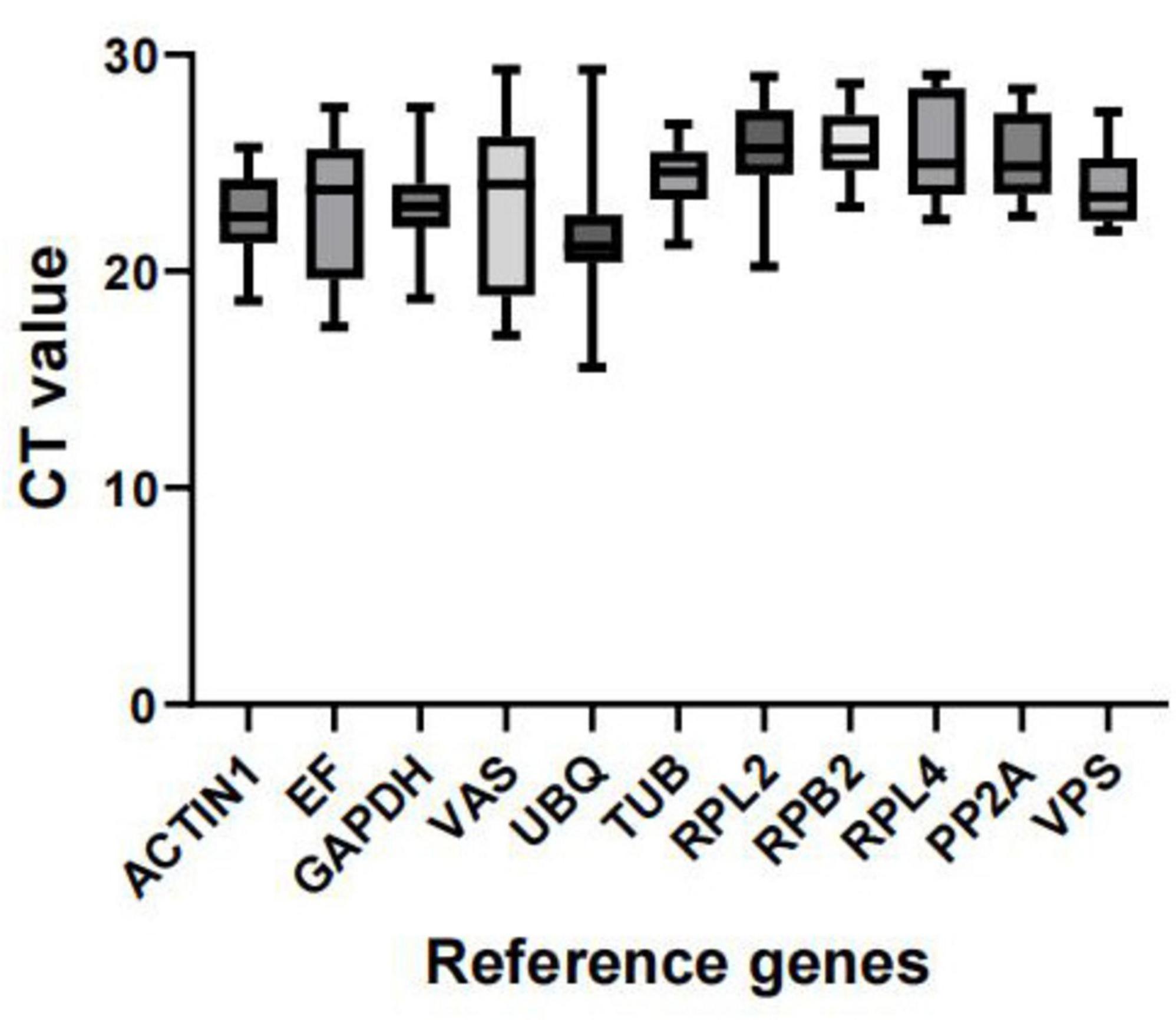
Figure 3. Distribution of Ct values for candidate reference genes. Expression data are displayed as Ct values for each reference gene in all samples. The line across the box depicts the median. The box indicates the 25th and 75th percentiles and the caps represent the maximum and minimum values.
Validation of the expression stability of reference genes
To identify the most stable reference genes, we used three programs—Genorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper—to assess gene expression stability from different perspectives. Genorm analyzed and compared the stability value (M) of reference genes across various samples to determine the most suitable candidates. A lower M value indicates higher stability, and an M value of less than 1.5 suggests that the gene can be used as a stable reference gene (Vandesompele et al., 2002).
With the exception of UBQ, which showed an M value of 2.061 in the different strains group, all other M values across all groups were less than 1.5. Under different carbon sources, EF and GAPDH had the lowest M values. For different nitrogen sources, RPB2 and VPS had the lowest M values. Similarly, RPB2 and VPS were the most stable when different growth factors were added. Under varying pH conditions, UBQ and TUB showed the lowest M values. For different temperatures, VPS and VAS had the lowest M values. During different growth stages, VAS and PP2A were the most stable. Finally, under different strain conditions, RPL2 and VPS had the lowest M values (Figure 4).
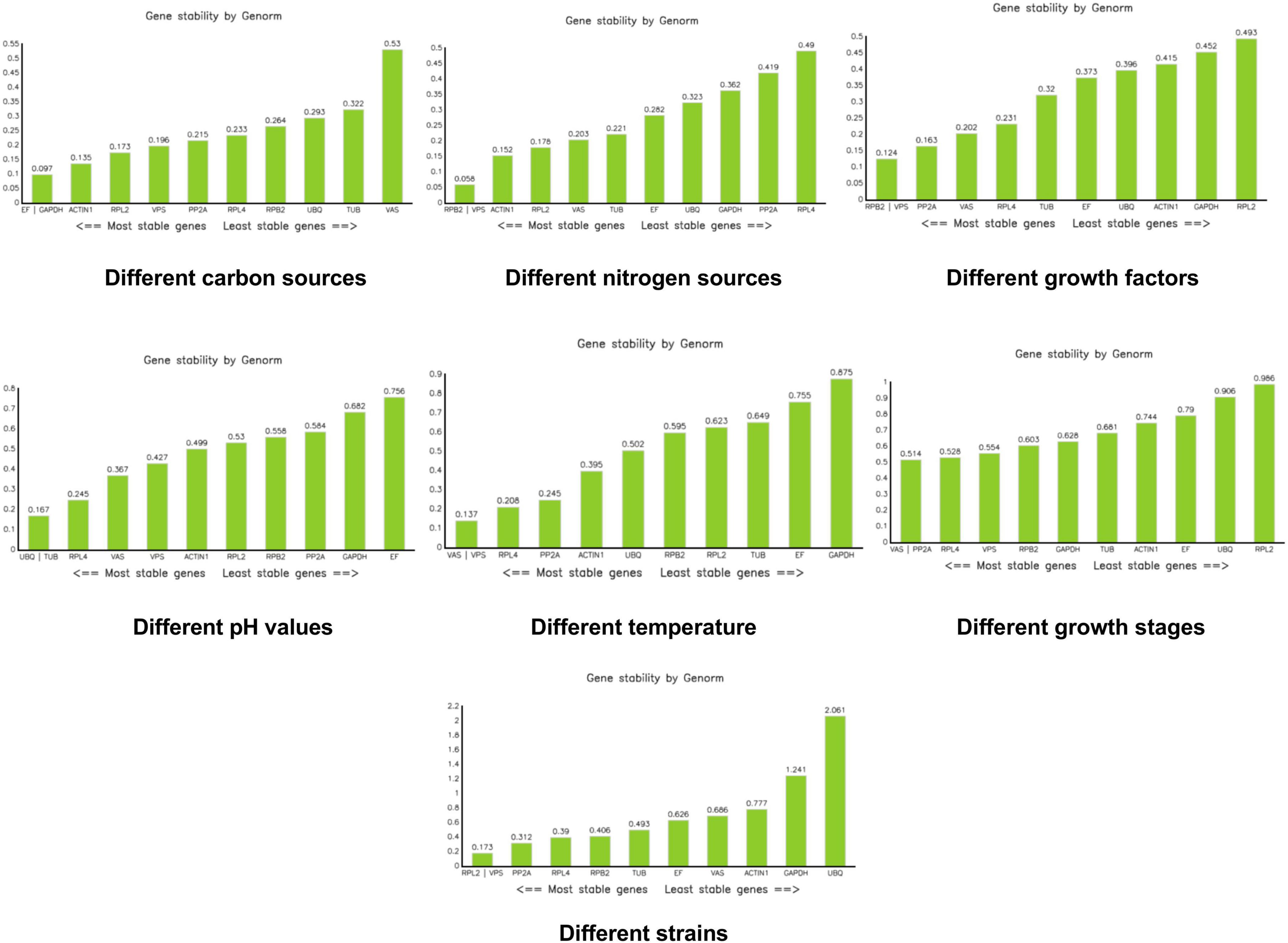
Figure 4. Analysis of stability values for the reference genes under different treatments using the Genorm software.
NormFinder software calculates the expression stability value of reference genes and identifies the most suitable reference gene based on this stability value. The gene with the smallest expression stability value is considered the most suitable. NormFinder evaluates gene stability using the stability value (S); a smaller S indicates better stability of the gene (Andersen et al., 2004). According to NormFinder results, RPL4, VPS, and RPB2 were the most stable reference genes under different carbon sources. Under different nitrogen sources, RPB2, VPS, and VAS were the most stable. PP2A was identified as the most stable reference gene under different growth factors. UBQ and VPS were the most stable reference genes under different pH conditions. RPL4 was the most stable reference gene at different temperatures. VAS emerged as the most stable reference gene during different growth stages. EF was the most stable reference gene across the different strains (Figure 5).
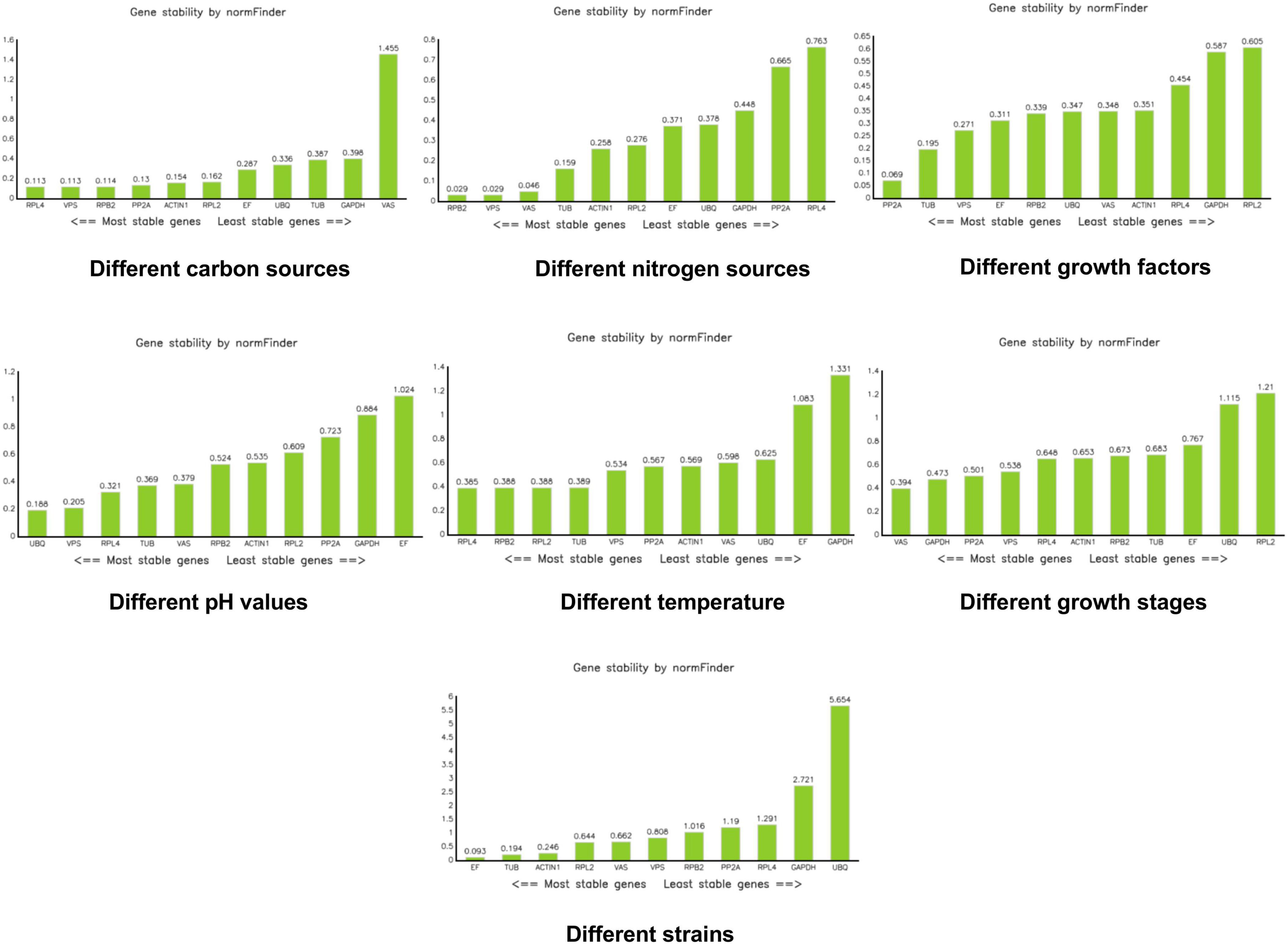
Figure 5. Analysis of stability values for the reference genes under different treatments using the NormFinder software.
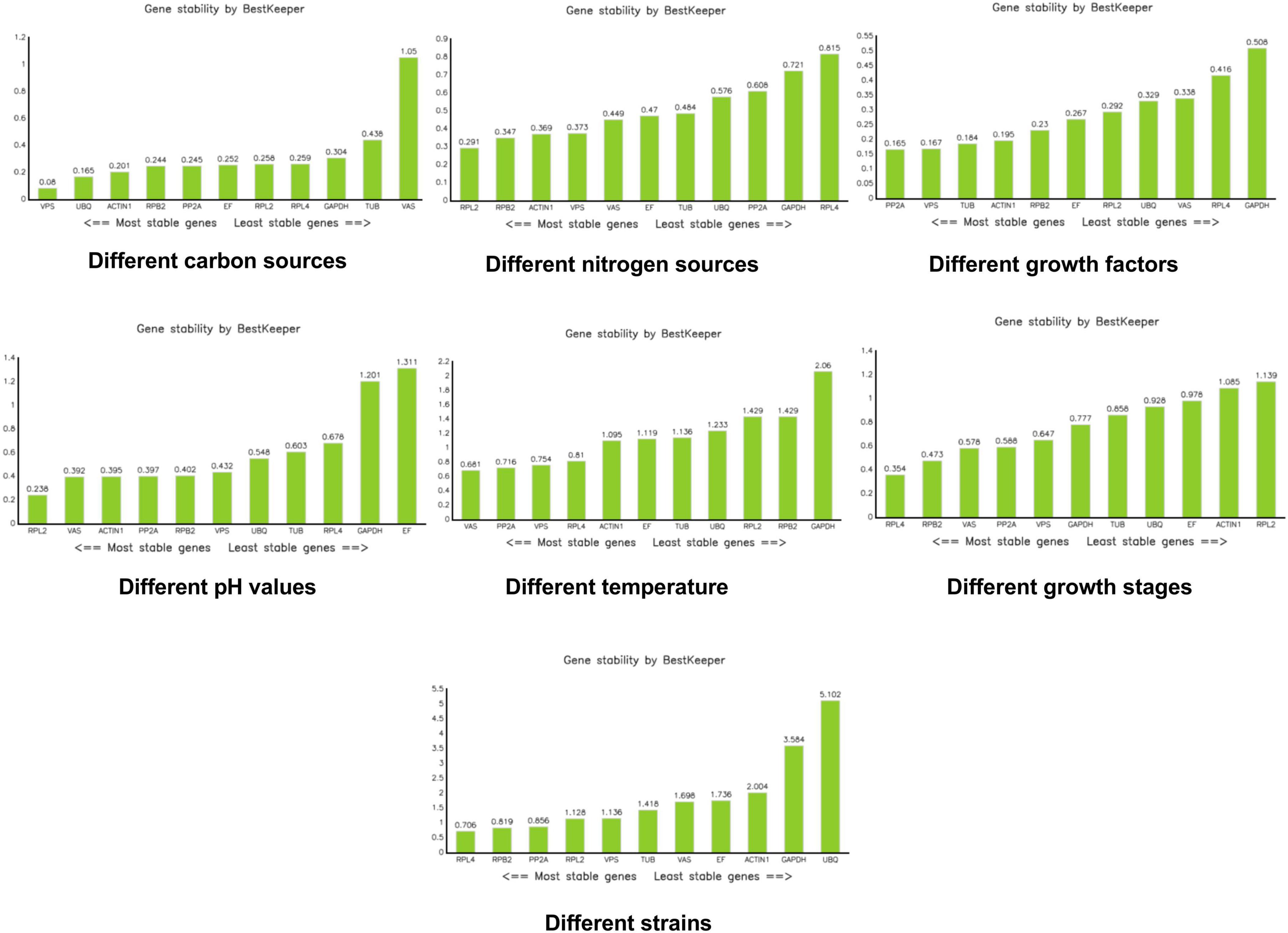
BestKeeper assesses the stability of candidate reference genes by calculating the CT coefficient of variation (CV), standard deviation (SD), and correlation coefficient (r). Generally, a larger correlation coefficient, along with a smaller standard deviation and coefficient of variation, indicates more stable gene expression. An SD value greater than 1 suggests that the gene is unstable, while an SD value less than 1, coupled with a smaller CV, indicates higher stability of the internal reference gene (Pfaffl et al., 2004). According to BestKeeper, VPS was the most stable reference gene under different carbon sources. RPL2 was the most stable reference gene under different nitrogen sources. PP2A and VPS were the most stable reference genes under different growth factors. RPL2 was also the most stable reference gene under different pH conditions. For different temperatures, VAS, PP2A, VPS, and RPL4 were considered the most stable. RPL4 emerged as the most stable reference gene during different growth stages. Under different mycelial conditions, RPL4, RPB2, and PP2A were identified as the most stable reference genes (Figure 6).
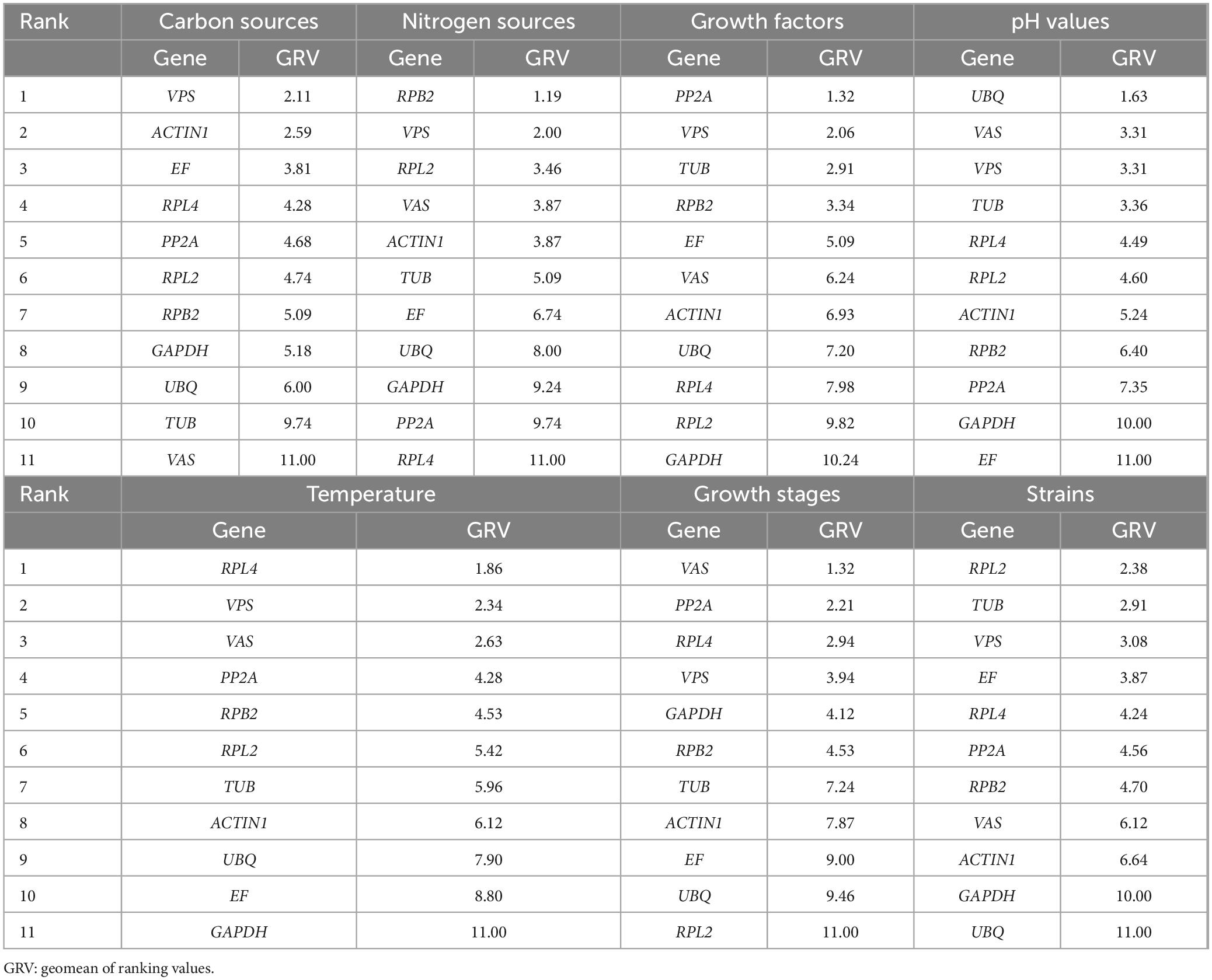
Sorting by different procedures is essential for accurate evaluation. RefFinder, a comprehensive web-based tool, evaluates internal reference genes for RT-qPCR. According to RefFinder’s output, the stability of internal reference genes varied under different treatment conditions. VPS demonstrated good stability across different carbon source cultures. RPB2 was the most stable reference gene under different nitrogen sources. PP2A was the most stable reference gene when different growth factors were used. UBQ showed the highest stability under various pH conditions. RPL4 emerged as the most stable reference gene at different temperatures. RPL2 was the most stable reference gene among different strains. VAS proved to be the most stable reference gene during different growth stages (Table 2).
I. obliquus is a rare and edible medicinal fungus due to its rich triterpenoids, polysaccharides, and sterols. It has anti-cancer, hypoglycemic, anti-oxidation, and anti-inflammation effects. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms of its medicinal components. Here, qRT-PCR was used to study the expression of genes related to the formation of medicinal components in I. obliquus, which is helpful for further study of the molecular mechanism of the formation of medicinal ingredients. However, there is a lack of reports on the systematic screening of reference genes in I. obliquus. Different nutrients in mediums and culture conditions are very important for the formation of medicinal ingredients. Different strains at different stages of development would exhibit different medicinal ingredients. Therefore, stable reference genes are needed to explore and reveal the molecular mechanism of genes related to medicinal ingredients under these various conditions. Our experiments show that no single reference gene is suitable for all situations. However, for each culture condition, we recommend and exclude some reference genes.
Under various carbon source conditions, results obtained by the three kinds of software Genorm, Normfinder, and bestkeeper are inconsistent, but the stability of VAS in the bestkeeper analysis is > 1. In the carbon source experiment, we do not recommend the use of VAS. Results of the integrated analysis are consistent with those of bestkeeper, both of which recommending VPS. Moreover, its M value is 0.196 in the Genorm analysis and 0.113 in the NormFinder analysis, indicating relative stability. Therefore, we believe that VPS is the most stable under different carbon source conditions. Under different nitrogen source conditions, RPB2 is the most stable in the Genorm and NormFinder analyses. In the bestkeeper analysis, the stability of RPB2 is 0.347, which is also relatively stable. Results of the integration analysis pointed to PPB2, which is consistent with the results of Genorm and NormFinder. When in a medium containing different growth factors, such as VB1, VB2, and VB6, the reference genes RPB2 and VPS are the most stable according to the Genorm analysis, whereas PP2A and VPS are shown to be the most stable in the NormFinder, bestkeeper, and integrated analyses. Hence, we believe PP2A and VPS are all stable, with the most stable one being PP2A. In various pH values, UBQ is recommended by Genorm, NormFinder, and integrated analyses. GAPDH and EF are the least stable, with a stability > 1. They were deemed to be unsuitable reference genes in various pH. In different temperatures, VAS, VPS, and RPL4 all indicate good stability. However, GAPDH, RPB2, RPL2, UBQ, TUB, EF, and ACTIN1 all indicate worse stability at > 1 according to the bestkeeper analysis. During growth development, VAS and PP2A are the best per the Genorm and integrated analyses. RPL2 and ACTIN1 are not recommended by according to the bestkeeper analysis. Between these different strains, RPL2, VPS, and RPL4 all show superior stability, but RPL2 is recommended in the first instance.
To ensure accuracy and reliability of experimental results, RT-qPCR requires the selection of stable reference genes to control for non-specific variation between samples (Ma et al., 2013). Previous studies have indicated that no single stable internal reference gene is universally suitable for all experimental conditions. Many commonly used reference genes exhibit significant variability under different treatments (Lü et al., 2018). Thus, our results systematically ascertain more appropriate reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis in I. obliquus. We also conclude that each setting requires a specific set of reference genes, providing a basis for the systematic study of molecular mechanisms under different experimental conditions.
Conclusion
In this study, we employed qRT-PCR technology alongside BestKeeper, NormFinder, and GeNorm software to evaluate the expression stability of 11 candidate reference genes across different strains, growth stages, and culture conditions. Comprehensive ranking revealed the following results: under different carbon sources, VPS demonstrated good stability and is suitable as an internal reference gene. When varying nitrogen sources, RPB2 proved to be the most stable reference gene. For different growth factors, PP2A was identified as the most stable reference gene. At different pH values, UBQ was the most stable reference gene. RPL4 was the most stable reference gene at different temperatures. Among different strains, RPL2 was the most stable reference gene. Lastly, VAS showed the highest stability across different growth stages. This study offers valuable insights for enhancing the accuracy of functional gene expression analysis in I. obliquus.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
LL: Writing – original draft. XG: Writing – review and editing. SW: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by Hubei Engineering University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1500043/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Andersen, C. L., Jensen, J. L., and Ørntoft, T. F. (2004). Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 64, 5245–5250. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Chen, X., Qiu, Z. S., Su, X. Y., Xu, Y., Cao, L. S., Yang, Z. D., et al. (2023). Screening of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in Endoclita signifier Walker larvae. J. Environ. Entomol. 1016–1026.
Chen, Y. Y., Huang, Y. R., Cui, Z. M., and Liu, J. J. (2015). Purification, characterization and biological activity of a novel polysaccharide from Inonotus obliquus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 79, 587–594. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.05.016
Chowrasia, S., Kaur, H., Mujib, A., and Mondal, T. K. (2019). Evaluation of Oryza coarctata candidate reference genes under different abiotic stresses. Biol. Plant 308:110878.
Guo, X. F., and Wang, S. M. (2020). Phylogenetic study of Inonotus obliquus (Chaga) based on internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) of ribosomal DNA. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 85, 387–393.
Hu, A., Yang, X., Zhu, J., Wang, X., Wu, H., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for RT–qPCR analysis of Nitraria sibirica under various abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 22:592. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03988-w
Lin, Y., Zhang, C., Lan, H., Gao, S., Liu, H., Liu, J., et al. (2014). Validation of potential reference genes for qPCR in maize across abiotic stresses, hormone treatments, and tissue types. PLoS One 9:e95445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095445
Lü, J., Chen, S., Guo, M., Ye, C., Qiu, B., Wu, J., et al. (2018). Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of the ladybird beetle Henosepilachna vigintioctomaculata. Front. Physiol. 9:1614. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01614
Lu, Y. P., Jia, Y. N., Xue, Z. H., Li, N. N., Liu, J. Y., and Chen, H. X. (2021). Recent developments in Inonotus obliquus (Chaga mushroom) Polysaccharides: Isolation, structural characteristics, biological activities and application. Polymers 13:1441. doi: 10.3390/polym13091441
Ma, S., Niu, H., Liu, C., Zhang, J., Hou, C., and Wang, D. (2013). Expression stabilities of candidate reference genes for RT-qPCR under different stress conditions in soybean. PLoS One 8:e75271. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075271
Pfaffl, M. W., Tichopad, A., Prgomet, C., and Neuvians, T. P. (2004). Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper–Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 26, 509–515. doi: 10.1023/b:bile.0000019559.84305.47
Song, F. Q., Liu, Y., Kong, X. S., Chang, W., and Song, G. (2013). Progress on understanding the anticancer mechanisms of medicinal mushroom: Inonotus obliquus. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 14, 1571–1578. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.3.1571
Vandesompele, J., De Preter, K., Pattyn, F., Poppe, B., Van Roy, N., De Paepe, A., et al. (2002). Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Wan, H., Yuan, W., Ruan, M., Ye, Q., Wang, R., Li, Z., et al. (2011). Identification of reference genes for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR normalization in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 416, 24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.105
Xie, F., Wang, J., and Zhang, B. (2023). RefFinder: A web-based tool for comprehensively analyzing and identifying reference genes. Funct. Integr. Genomics. 23:125.
Xu, J., Xu, Z., Zhu, Y., Luo, H., Qian, J., Ji, A., et al. (2014). Identification and evaluation of reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization in Ganoderma lucidum. Curr. Microbiol. 68, 120–126. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0442-2
Yang, Y., Xu, X., Jing, Z., Ye, J., Li, H., Li, X., et al. (2022). Genome-wide screening and stability verification of the robust internal control genes for RT-qPCR in Filamentous Fungi. J. Fungi (Basel). 8:952. doi: 10.3390/jof8090952
Keywords: Inonotus obliquus, reference gene, RT-qPCR, gene expression, medicinal fungus
Citation: Li L, Guo X and Wang S (2025) Selection and evaluation of reference genes for qRT-PCR in Inonotus obliquus. Front. Microbiol. 16:1500043. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1500043
Received: 22 September 2024; Accepted: 09 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Kunal R. Jain, Sardar Patel University, IndiaReviewed by:
Sezer Okay, Hacettepe University, TürkiyeIrina Ivshina, Institute of Ecology and Genetics of Microorganisms (RAS), Russia
Copyright © 2025 Li, Guo and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaofan Guo, MTg1NTQ4NzkyQHFxLmNvbQ==; Shouming Wang, c213YW5nMDIwNkAxNjMuY29t
 Lulu Li
Lulu Li Shouming Wang
Shouming Wang