
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Microbiol. , 22 January 2025
Sec. Infectious Agents and Disease
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1515258
This article is part of the Research Topic Research Advances and Challenges in Emerging and Re-Emerging Viral Diseases View all 17 articles
Persistent infection with oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) types, such as HPV 16 or 18, is a major factor in cervical cancer development. However, only a small percentage of infected women develop cancer, indicating that other factors are involved. Emerging evidence links vaginal microbiota with HPV persistence and cancer progression. Alterations in microbial composition, function, and metabolic pathways may contribute to this process. Despite the potential of metagenomics to explore these interactions, studies on the vaginal microbiota’s role in cervical cancer are limited. This review systematically examines the relationship between cervical microbiota, HPV, and cervical cancer by analyzing studies from PubMed, EBSCO, and Scopus. We highlight how microbial diversity influences HPV persistence and cancer progression, noting that healthy women typically have lower microbiota diversity and higher Lactobacillus abundance compared to HPV-infected women, who exhibit increased Gardenella, Prevotella, Sneathia, Megasphaera, Streptococcus, and Fusobacterium spp., associated with dysbiosis. We discuss how microbial diversity is associated with HPV persistence and cancer progression, noting that studies suggest healthy women typically have lower microbiota diversity and higher Lactobacillus abundance, while HPV-infected women exhibit increased Gardnerella, Prevotella, Sneathia, Megasphaera, Streptococcus, and Fusobacterium spp., indicative of dysbiosis. Potential markers such as Gardnerella and Prevotella have been identified as potential microbiome biomarkers associated with HPV infection and cervical cancer progression. The review also discusses microbiome-related gene expression changes in cervical cancer patients. However, further research is needed to validate these findings and explore additional microbiome alterations in cancer progression.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide, particularly in women under 25 (Sharifian et al., 2023). Nearly 90% of women are exposed to HPV during their lifetime, but most infections resolve before viral integration into the host genome (Karpinets et al., 2022; Szymonowicz and Chen, 2020; Karpinets et al., 2020). However, about 10% persist, significantly increasing the risk of cervical cancer (Shulzhenko et al., 2014; Chang et al., 2023; Woodman et al., 2007). High-risk types like HPV 16 and 18 are the leading cause of cervical cancer and are associated with other cancers, such as those of the head and neck (Ure et al., 2022; Koshiol et al., 2008; Castellsagué, 2008; Banerjee et al., 2015; Chen et al., 2020; Condic et al., 2023; Arroyo Mühr et al., 2015; Feng et al., 2008; Zheng et al., 2023).
A dysbiotic cervicovaginal microbiome is more permissive to persistent HPV infection, facilitating viral oncogene expression and subsequent cervical dysplasia and cancer (Fang et al., 2022; Gilbert et al., 2018; Irfan et al., 2020). This dysbiosis is especially relevant among Hispanic women, whose microbiota is often low in Lactobacillus and resembles that of HPV-infected women, increasing their vulnerability to persistent infections (Tosado-Rodríguez et al., 2024; Vargas-Robles et al., 2023; Thyagarajan et al., 2020). A “nonoptimal” microbiota, characterized by reduced Lactobacillus species and overrepresented anaerobic bacteria and fungi, predisposes this group to cervical dysplasia and malignancy (Godoy-Vitorino et al., 2018; Vargas-Robles et al., 2023; Gosmann et al., 2017; Oliveira de Almeida et al., 2021; Raza et al., 2007). These findings highlight ethnic variability in microbiota composition and its influence on HPV persistence and cancer progression (Martínez et al., 2021).
Dysbiosis in the cervicovaginal microbiome, marked by decreased Lactobacillus and increased anaerobic bacteria, fosters a pro-inflammatory environment conducive to HPV persistence and cervical dysplasia (Mitra et al., 2016; Brotman et al., 2014; Doerflinger et al., 2014; Happel et al., 2020; Libertucci and Young, 2019; Marchesi and Ravel, 2015; Ogunrinola et al., 2020; Peebles et al., 2019; Rebersek, 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2021). Chronic inflammation driven by cytokines and immune cell recruitment further exacerbates epithelial damage, supporting oncogenesis (Mitra et al., 2015; Shannon et al., 2017; Libby et al., 2008). Microbiota dysbiosis also impairs mucosal barrier function, heightens local inflammation, and promotes conditions for viral persistence and genome integration—key steps in cervical carcinogenesis (Vyshenska et al., 2017; Baldridge et al., 2015; Schneider et al., 2022; Turnbaugh et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2017).
This review explores the association between microbiota, HPV, and cervical cancer by comparing microbial diversity in healthy and HPV-infected women. It highlights the increased prevalence of specific microorganisms in HPV-infected women, such as Sneathia spp., Prevotella, Megasphaera, Shuttleworthia, Streptococcus, Porphyromonas, and Fusobacterium spp., and discusses the functional implications of these microbiota shifts. Finally, this review identifies gaps in current research and suggests future directions.
We conducted a systematic review on the relationship between cervical microbiota, HPV, and cervical cancer, following PRISMA guidelines. The research question was framed using the PICOS framework. The population included women with HPV infection or cervical cancer, with interventions focusing on cervicovaginal microbiota composition. Outcomes assessed were HPV persistence, microbiota alterations, and cervical cancer progression, with comparators being women with normal microbiota and no HPV.
Advanced searches were conducted in PubMed, EBSCO, and Scopus using predefined search strings combining Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms and keywords with Boolean operators (AND, OR). For instance, the PubMed search string was: (“Human papillomavirus” OR “HPV”) AND (“cervical cancer” OR “cervical neoplasia”) AND (“microbiota” OR “microbiome” OR “vaginal microbiome”). Search strings were tailored for each database’s syntax.
References were independently screened to remove duplicates. Titles and abstracts were assessed using predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria required studies on microbiota in women with HPV or cervical cancer, published in English between 2010 and 2024. Exclusion criteria included ongoing studies, pre-prints, qualitative cross-sectional studies, duplicates, and null entries. Relevant details, including author, year, location, study design, patient number, age, and disease description, were extracted. Key findings on cervical microbiome, HPV infection, and cancer progression were analyzed.
To mitigate bias, the methodological quality of studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), with specific focus on selection, comparability, and outcome assessment domains. Discrepancies between reviewers were resolved through discussion with an external collaborator. A total of 62 papers were identified, with 22 removed as duplicates or irrelevant. Full-text reviews were conducted on 27 studies, of which 14 met the inclusion criteria. The results are outlined in the PRISMA diagram (Figure 1).
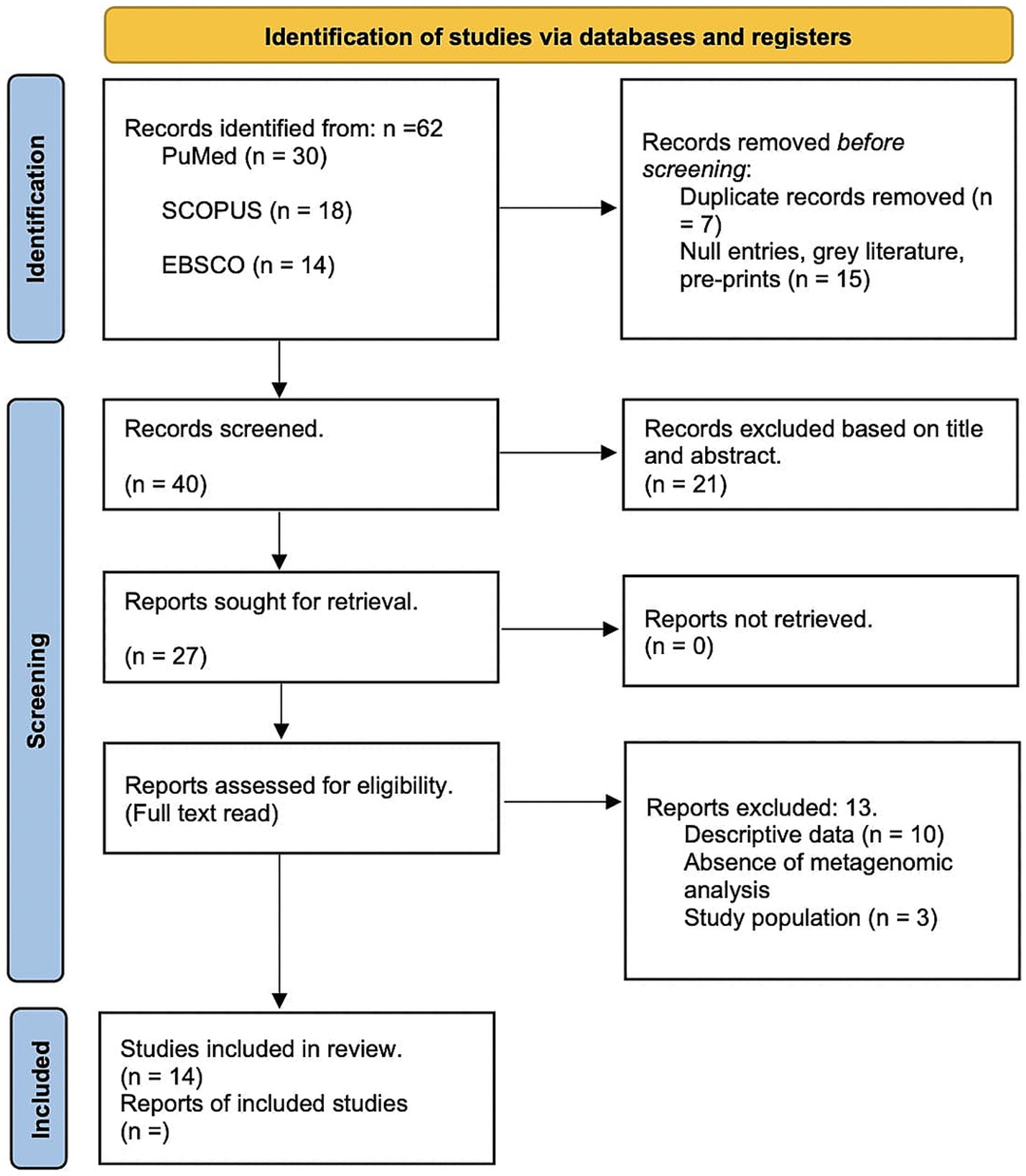
Figure 1. PRISMA Flow Diagram of Study Selection Process. This figure illustrates the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow chart detailing the systematic review process for assessing the relationship between cervical microbiota, HPV and cervical cancer progression. The diagram is divided into several sections representing different stages of the review process.
HPV is a small, non-enveloped, epitheliotropic icosahedral DNA virus (60 nm in diameter) in the subfamily Papillomaviridae and Firstpapillomavirinae. Virions have a single circular double-stranded histone-bound DNA molecule (~8 kb) with eight protein-coding genes (Sharifian et al., 2023). The viral genome has three regions (Figure 2), each contributing to HPV’s ability to infect, replicate, and contribute to carcinogenesis:
1. A noncoding regulatory long control region (LCR) with a promoter, enhancer, and silencer enabling the precise regulation of viral gene expression and replication.
2. A region for transformation and replication, encoding E1 to E7 proteins. The E6 and E7 oncoproteins are particularly significant because they disrupt critical cell cycle regulators, p53 and Rb, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation. E2, in contrast, plays a regulatory role by downregulating E6 and E7 expression, balancing the viral lifecycle (Brianti et al., 2017; Van Doorslaer et al., 2018).
3. A region encoding capsid proteins L1 and L2, essential for virion assembly (Brianti et al., 2017; Van Doorslaer et al., 2018).
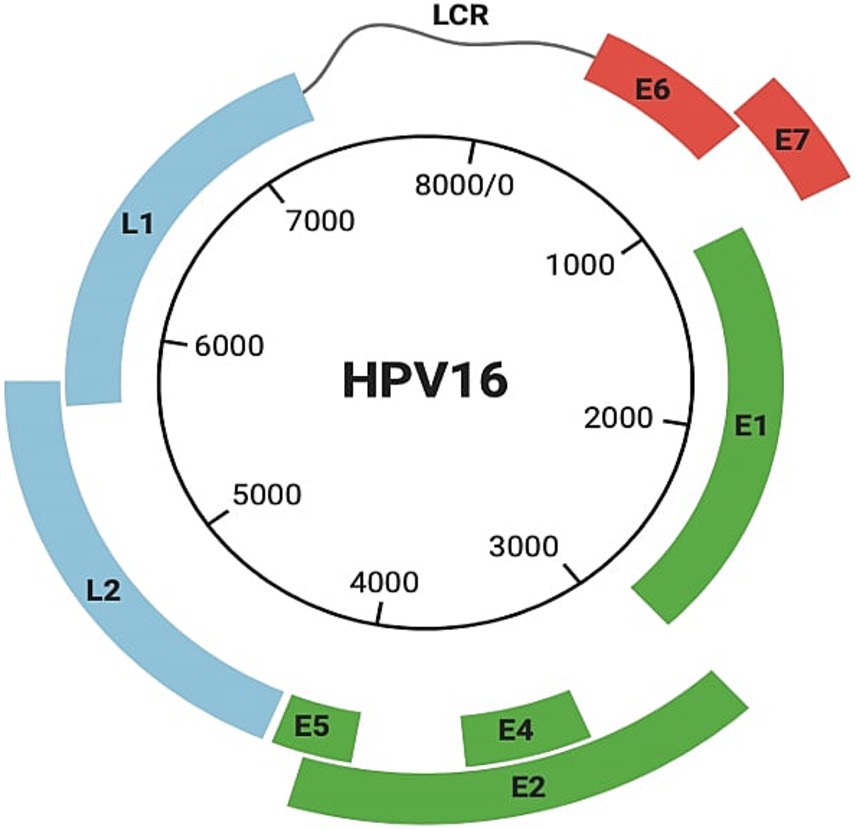
Figure 2. Structure of HPV 16. It includes the noncoding regulatory long control region (LCR), a region containing genes (E1–E7) responsible for transformation and replication, including E6 and E7, and a region encoding capsid proteins L1 and L2.
HPV diversity includes 223 different types, with new types continually identified (Bzhalava et al., 2014; de Villiers et al., 2004). Of these, 14 types are high oncogenic risk (HR), including HPV 16 and 18 which are the most frequently associated with cervical carcinogenesis (de Sanjose et al., 2010; Muñoz et al., 2003). Around 71% of cervical carcinoma cases globally involve HPV16 or HPV18, though the prevalence of other genotypes varies by region. For instance, while HPV16 dominates in Europe, HPV52 and HPV58 are more prevalent in parts of Asia, highlighting the geographical variability in HPV genotype distribution and its implications for tailored vaccination strategies (Ye et al., 2024).
Cervical carcinoma is the fourth most prevalent cancer and leading cause of cancer-related mortality among women globally (Fang et al., 2022; Weill Cornell Medicine, n.d.). In 2020, there were 604,127 new cases and 341,831 deaths worldwide (Sharifian et al., 2023; Chang et al., 2023; Siegel et al., 2020). Mortality rates can reach up to 88% in severe cases, particularly in developing countries (Banerjee et al., 2015; Arbyn et al., 2011).
Cervical cancer involves uncontrolled cell proliferation in the cervix, which connects the uterus to the vagina (National Cancer Institute, 2023). It is classified into five stages (Figure 3):
• Stage 0: Cervical dysplasia, with irregular cells on the cervix surface.
• Stage 1: Cancer confined to the cervix, with tumors 3 mm to 4 cm in diameter.
• Stage 2: Cancer extends beyond the cervix and uterus to the upper two-thirds of the vagina.
• Stage 3: Tumor invades the lower third of the vagina, pelvic walls, and lymph nodes.
• Stage 4: Advanced cancer, with metastasis to distant organs such as the bladder, rectum, liver, lungs, or distant lymph nodes (National Cancer Institute, 2022; American Cancer Society, 2020).
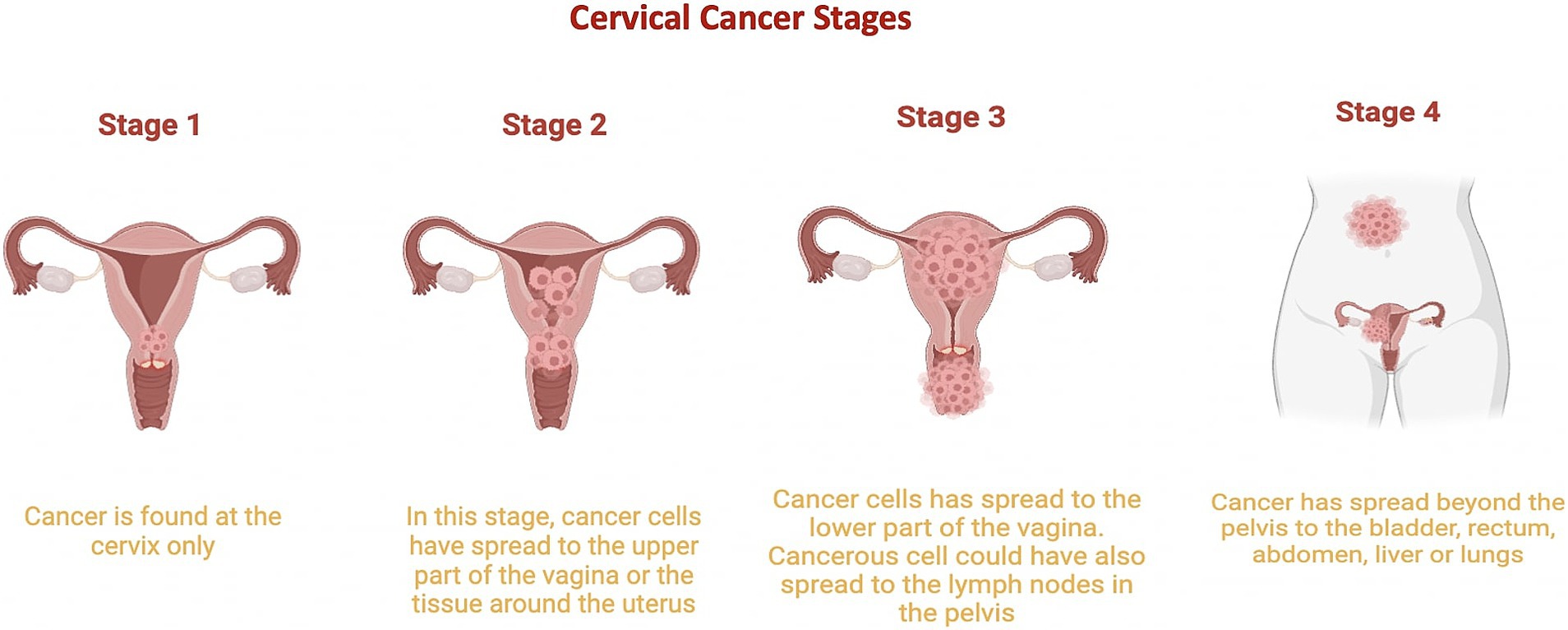
Figure 3. Cervical Cancer Stages. This graphic illustrates the progression of cervical cancer from stage 1, where it is limited to the cervix, to stage 2, where it begins to spread to other regions of the uterus. Stage 3 is characterized by the cancer reaching the lower part of the vagina, and stage 4 shows cancer spreading to other parts of the body. Stage 0 is not included in this depiction.
The progression of cervical cancer is closely tied to persistent HPV infection, particularly with high-risk types such as HPV 16 and 18. Persistent HPV infections can lead to cervical dysplasia (Stage 0), a precursor to invasive cervical cancer. As the infection persists, viral oncogenes E6 and E7 disrupt tumor suppressors p53 and Rb, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation and enabling the transition from precancerous lesions to invasive stages (Figure 3; Doorbar et al., 2012; Crosbie et al., 2013).
Microbiota refers to the range of commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic microorganisms found in multicellular organisms. Each part of the human body has a specific microbiota playing a key role in health, such as the intestinal or vaginal microbiota (Sharifian et al., 2023). The disruption of microbiota homeostasis increases vulnerability to viral infections (Avilés-Jiménez et al., 2017; Schwabe and Jobin, 2013). Changes in the abundance of certain microorganisms, their functional abilities and the changes caused in the metabolic pathways are factors that can contribute to cancer progression (Shin et al., 2015; Heintz-Buschart and Wilmes, 2018; Deng et al., 2021). Yet, the exact mechanisms of how microbiota disruptions lead to diseases are still unknown (Condic et al., 2023).
The role of the microbiome in cancer development has gained recognition, now considered one of the emerging hallmarks of cancer (Hanahan, 2022; Ekström et al., 2013). Microbial communities influence processes like inflammation, immune evasion, and metabolic reprogramming.
The vaginal microbiota thrives in an anaerobic habitat, receiving nutrients like glucose and oxygen (Linhares et al., 2011). It is also dynamic, influenced by age, menstrual cycle, sexual activity, stress, and pregnancy (Chen et al., 2021; Culhane et al., 2002; Noyes et al., 2018; Aagaard et al., 2012). Vaginal dysbiosis, the most common disorder among reproductive-age women, involves irregular microbial growth, increased diversity, and imbalance, leading to higher infection susceptibility (Sharifian et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2021; Javed et al., 2019; Eschenbach, 1993) with symptoms such as elevated vaginal pH, irritation and discharge (Torcia, 2019; Brotman et al., 2014). Dysbiosis contributes to cervical cancer development through epithelial barrier disruption, metabolic dysregulation, abnormal cell proliferation, genome instability, chronic inflammation, and angiogenesis (Sharifian et al., 2023; Castanheira et al., 2021; Mitra et al., 2016).
Microbial metabolism plays a crucial role in modulating the cervicovaginal microenvironment and promoting carcinogenesis. Dysbiotic microbiota alter metabolite production, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which typically support vaginal health but can promote inflammation under dysbiosis (Tjalsma et al., 2012; Bokulich et al., 2022). Elevated SCFA levels activate pro-inflammatory pathways like NF-κB, increasing cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, creating a pro-carcinogenic environment (Mitra et al., 2016).
Inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, elevated during dysbiosis, recruit immune cells that release reactive oxygen species (ROS), causing oxidative stress and DNA damage. This facilitates HPV genome integration, overexpressing E6 and E7 oncoproteins, which drive cellular proliferation and inhibit apoptosis (Schmitt et al., 1994; Sharifian et al., 2023).
Pathways such as glycan biosynthesis and amino acid metabolism, enriched in dysbiotic microbiomes, further promote cancer progression. Glycan biosynthesis weakens the epithelial barrier, increasing pathogen invasion (Fang et al., 2022), while amino acid metabolism supports pathogenic bacteria growth, exacerbating inflammation and HPV persistence (Usyk et al., 2020).
Vaginal microbes are classified into 5 community status types (CST) based on the predominance of certain species. The CST classification system was originally proposed by Ravel et al. (2011), identifying CST-I, CST-II, CST-III, and CST-V are dominated by Lactobacillus species: L. crispatus, L. gasseri, L. iners, and L. jensenii, respectively. CST-IV is divided into CST IV-A, with modest Lactobacillus presence, and CST IV-B, dominated by anaerobes like Atopobium, Prevotella, Parvimonas, Gardnerella, and Megasphera (Chen et al., 2021; Sharifian et al., 2023; Kyrgiou et al., 2017; Romero et al., 2014; Table 1). Recently, the CST classification has been refined using VALENCIA software, which identifies CSTs based on amplicon sequencing data and provides a more standardized approach to classifying vaginal microbial communities. Unlike the original framework, VALENCIA offers greater granularity, particularly within CST-IV, by identifying subtypes dominated by specific anaerobes, thus enabling a more detailed understanding of dysbiotic states (Gajer et al., 2012; France et al., 2020).
Recent years have seen a revolution in studying microbiota and their connection to cancer with the advent of metagenomics (Banerjee et al., 2015). Metagenomics examines the functions, structures, and interactions of microorganisms by analyzing entire nucleotide sequences from bulk samples (Banerjee et al., 2015). Previously, microbiota studies relied on traditional bacterial culture methods, which were limited because most microorganisms cannot be cultured in laboratories (Fang et al., 2022; Arokiyaraj et al., 2018; Wei et al., 2021). Using whole metagenomic sequencing, researchers can sequence the entire DNA within a sample, increasing the depth and specificity of identified species and providing insights into gene function and metabolic pathways (Fang et al., 2022; Shah et al., 2018; Biegert et al., 2021). This approach has enabled associations between the predominance of certain microorganisms in the vaginal microbiome and the development of cervical cancer (Luan et al., 2020).
It is well established that healthy women tend to show lower microbiota diversity and a higher presence of Lactobacillus spp. compared to women with bacterial vaginosis. For instance, Chen et al. (2021) review article highlights the differences in the vaginal microbiome between healthy women and those with bacterial vaginosis showing that in healthy women, the vaginal microbiome is predominantly composed of Lactobacillus spp. For this, they compiled information by conducting a thorough literature search, selecting relevant studies based on predefined criteria, extracting, and analyzing key data, and integrating findings to provide a comprehensive review of the female vaginal microbiome. Studies claim that healthy cervical microbiota is characterized by the presence of Lactobacillus spp. whereas an increase in Gardnerella vaginalis, Prevotella bivia, and Atopobium vaginae, is significantly associated with the development of dysbiosis (Muzny et al., 2018). One caveat of the study is that results rely on self-collected samples could introduce variability in sample quality and timing. Additionally, the study focused on a specific population, African American women who have sex with women, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other groups. Fredricks et al. (2007) also argue that the presence of certain bacteria, such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, and BV-associated bacterium-1, was strongly associated with bacterial vaginosis. It is, however, important to notice that in the study they used targeted PCR assays for the detection of vaginal bacteria in vaginal samples collected from women diagnosed with vaginal dysbiosis which could lead to some bacteria missing from the essay. Finally, the study by Srinivasan et al. (2012) found significant differences in the bacterial communities of healthy women compared to those with bacterial vaginosis. Using high-resolution phylogenetic analyses, the study identified that women with vaginosis had a higher diversity of bacterial species, predominantly anaerobes such as Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, and Mobiluncus.
Healthy cervical microbiota is overrepresented with Lactobacillus spp. since they can withstand infections by producing bacteriocin, biosurfactants, and lactic acid (Banerjee et al., 2015; Fang et al., 2022; Witkin and Linhares, 2017). For example, a study in Brazil sequenced cervical samples from over 500 women from five different regions and found that Lactobacillus, specifically L. crispatus, is the dominant species in HPV-negative women. They argue Lactobacillus spp. are crucial for maintaining vaginal health by producing lactic acid and maintaining a low pH environment (Marconi et al., 2020). Yet, it is important to acknowledge that, the study focused on taxonomic composition without delving into the functional implications of the microbiota, which could provide deeper insights into the health impacts of microbiota changes. The study by Chen et al. (2021) demonstrated, using 16S rRNA gene sequencing, that in healthy women, the vaginal microbiome is predominantly composed of Lactobacillus spp., including species such as Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus iners. These bacteria produce antimicrobial compounds like lactic acid and bacteriocins, which maintain a low vaginal pH and inhibit pathogen colonization. In contrast, the cervical microbiota of women with vaginal dysbiosis, caused by HPV, is characterized by a marked reduction in Lactobacillus spp. and an increase in anaerobic bacteria, including Gardnerella vaginalis, which forms biofilms and shelters other bacterial vaginosis-associated microbes. One study’s limitation is that it acknowledges the high heterogeneity across different studies, making it challenging to generalize findings to other settings. This study also does not delve deeply into the functional implications of the microbiome composition changes which could further explain the importance of Lactobacillus spp. in healthy women. Furthermore, a study culturing HeLa cells treated with culture supernatants of Lactobacillus crispatus showed a significantly decreased the expression of the HPV E6 oncogene, creating an anti-proliferative state (Motevaseli et al., 2016). However, the study’s findings are based on in vitro experiments, which may not fully replicate in vivo conditions and only focused on a few autophagy genes, leaving out potential impacts on other relevant pathways or genes. Results are also specific to HeLa cells and may not be generalizable to other cell types.
While Lactobacillus dominance is generally protective for vaginal health, specific species play varied roles. Lactobacillus crispatus is the most protective, producing high levels of lactic acid to maintain low vaginal pH, inhibit pathogens, and strengthen the epithelial barrier (Petrova et al., 2017; Borges et al., 2022). Its production of bacteriocins and hydrogen peroxide further enhances its protective effects.
Conversely, Lactobacillus iners is associated with transitional microbiota states. It adapts to dysbiotic environments and may contribute to inflammation through its enzyme and metabolite production, potentially promoting HPV persistence and cervical dysplasia (Vaneechoutte, 2017; van der Veer et al., 2017). Lactobacillus jensenii and Lactobacillus gasseri have intermediate roles, with lower acid production and less pronounced pathogen inhibition compared to L. crispatus.
Based on this information it is not surprising that CST-I and CST-II are common in HPV-negative women, while CST-IV dominates during HPV infection and cervical cancer development (Table 2; Chen et al., 2021; Brotman et al., 2014; Shannon et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2020). CST-IV is associated with persistent HPV due to G. vaginalis secreting vaginolysin, causing cellular lysis and dysbiosis (Sharifian et al., 2023; Nowak et al., 2018). CST-III characterized by a dominant presence of L. iners is prevalent among HPV-positive women because this bacteria can survive in varying pH ranges and inhibits pathogen colonization (Sharifian et al., 2023; Romero et al., 2014; Macklaim et al., 2013; Macklaim et al., 2011). L. iners also produces inerolysin, a cytotoxin that creates pores, facilitating HPV entry into the vaginal epithelium (Sharifian et al., 2023; Pleckaityte, 2020; Curty et al., 2019).
As HPV infection progresses, the abundance of Lactobacillus spp. decreases and is accompanied by a sharp increase in diversity of anaerobic bacteria such as Sneathia spp. and Fusobacterium spp. (Aitmanaitė et al., 2023; Audirac-Chalifour et al., 2016; Łaniewski et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2021; Tango et al., 2020). For example, the study by Lee et al. (2013) showed that HPV-positive women had a more diverse vaginal microbiota compared to HPV-negative women in a Korean twin cohort. The dominant bacterial genera in HPV-negative women were Lactobacillus species, whereas HPV-positive women exhibited higher proportions of anaerobic bacteria such as Gardnerella, Atopobium, and Prevotella. While these findings provide valuable insights into the microbiota-HPV connection, the study was conducted exclusively on a Korean cohort, which limits the generalizability of the results to other populations, as each population has unique microbiota characteristics influenced by genetic, environmental, and cultural factors. Nonetheless, it serves as an important reference for understanding the relationship between HPV status and microbiota diversity. Some subgroup analyses, such as those involving postmenopausal women, had relatively small sample sizes, affecting the robustness of the conclusions.
The presence of Gardnerella could be used as a potential marker for HPV infection and cancer progression. Some studies argue that Gardnerella is mainly found in women infected with HPV and cervical cancer (Lee et al., 2013). In fact, a study by So et al. (2020) that investigated the changes in vaginal microbiota during cervical carcinogenesis in women with HPV infection indicated that women with cervical cancer showed an increase in anaerobic bacteria such as Atopobium, and Prevotella and specially Gardnerella. However, they sampled only 50 women with only 10 of them being healthy. Thus, the relatively small sample size may affect the generalizability of the findings. According to a study by Chen et al. (2020), Gardnerella was present in HPV-negative women, although at lower levels compared to HPV-positive women. This highlights that the presence and abundance of Gardnerella and other anaerobic bacteria increase significantly in women with HPV infection and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia progression. A study by Tango et al. (2020) also indicates that Gardnerella can be present in HPV-negative women, but its abundance significantly increases in HPV-positive individuals and those with cervical cancer. While Gardnerella is frequently associated with HPV infection and cervical cancer (Brotman et al., 2014; Mitra et al., 2016), its reliability as a biomarker is limited due to low specificity and its presence in other dysbiotic conditions like bacterial vaginosis. Rather than serving as a standalone marker, Gardnerella is better understood as part of a dysbiotic microbial community contributing to disease progression. Further studies are needed to quantify its sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values for clinical use.
Prevotella is another genus frequently linked to cervical cancer progression, as it provides nutrients to other dysbiosis-related bacteria, making the host more vulnerable to HPV infections (Sharifian et al., 2023; Pybus and Onderdonk, 1997; Chao et al., 2020). Sharifian et al. (2023) reported that increased vaginal microbiota diversity, particularly a higher presence of anaerobic bacteria such as Prevotella, is associated with HPV infection and progression to cervical cancer. However, Prevotella is also commonly found in other dysbiotic conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis and pelvic inflammatory disease, raising questions about its specific role in cervical carcinogenesis (Mitra et al., 2016; Brotman et al., 2014). Pybus and Onderdonk (1997) demonstrated a symbiotic relationship between Gardnerella vaginalis and Prevotella bivia, where ammonia produced by P. bivia supports the growth of G. vaginalis. This interaction may contribute to bacterial vaginosis pathogenesis by promoting an environment conducive to overgrowth of BV-associated bacteria, which could indirectly influence HPV persistence and disease progression.
In addition to Gardnerella and Prevotella, other anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria, such as Sneathia, Megasphaera, Streptococcus, and Fusobacterium spp., play significant roles in HPV persistence and cervical cancer development. Sneathia spp. have been consistently associated with cervical dysplasia and cancer, likely due to their ability to induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and damage epithelial barriers, creating a microenvironment conducive to HPV persistence and integration into the host genome (Mitchell et al., 2015; Brotman et al., 2014). Similarly, Megasphaera spp. are known to produce metabolites that disrupt vaginal pH and promote immune evasion, facilitating viral persistence and progression to neoplasia (Mitra et al., 2016). Fusobacterium spp., commonly implicated in other cancers such as colorectal cancer, have also been identified in cervical dysplasia and cancer. They may contribute to carcinogenesis through chronic inflammation, production of genotoxic metabolites, and interactions with host immune cells that suppress anti-tumor responses (Kostic et al., 2013; Shannon et al., 2017). Additionally, while Streptococcus spp. are not traditionally associated with vaginal dysbiosis, certain pathogenic strains have been linked to HPV persistence through their potential to enhance inflammation and alter mucosal immunity, further supporting a permissive environment for viral oncogenesis (Gillet et al., 2011).
Co-infections with other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Trichomonas vaginalis, have been shown to exacerbate HPV infection and persistence, potentially contributing to cervical cancer progression. These pathogens induce chronic inflammation and disrupt the epithelial barrier, creating an environment conducive to HPV replication and persistence (Gillet et al., 2011; Moscicki et al., 2012). For example, Chlamydia trachomatis has been associated with increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which may impair HPV clearance and promote oncogenesis (Moscicki et al., 2012). While not the focus of this review, understanding the interplay between HPV and co-infecting STIs highlights the importance of addressing these co-factors in cervical cancer prevention strategies.
Women who receive the HPV vaccine are largely protected from cancer caused by high-risk HPV strains. Limited evidence suggests that vaccination does not directly alter the cervicovaginal microbiota but may indirectly affect it by reducing HPV-induced dysbiosis. For example, studies have shown that HPV infection is associated with shifts in microbiota composition, including reduced Lactobacillus dominance and increased anaerobic bacteria such as Gardnerella and Prevotella (Mitra et al., 2016; Brotman et al., 2014). By preventing HPV infection, vaccination may help maintain a more stable and protective microbiota.
Metagenomic studies also allow us to explore the functional profile of genes annotated during the sequencing analysis. For example, Kwon et al. (2019) used the KEGG database for pathway annotation and the HUMAnN2 pipeline to map microbial genes to metabolic pathways, identifying enriched pathways in cervical cancer patients compared to healthy women. These included bacterial invasion, biofilm formation, and inflammatory responses, highlighting how altered microbiota promotes bacterial persistence, immune evasion, and chronic inflammation, all contributing to carcinogenesis (Table 3; Figure 4). However, it is important to note that these findings do not establish causality, as microbiota alterations may also result from carcinogenesis rather than act as a direct causal factor.
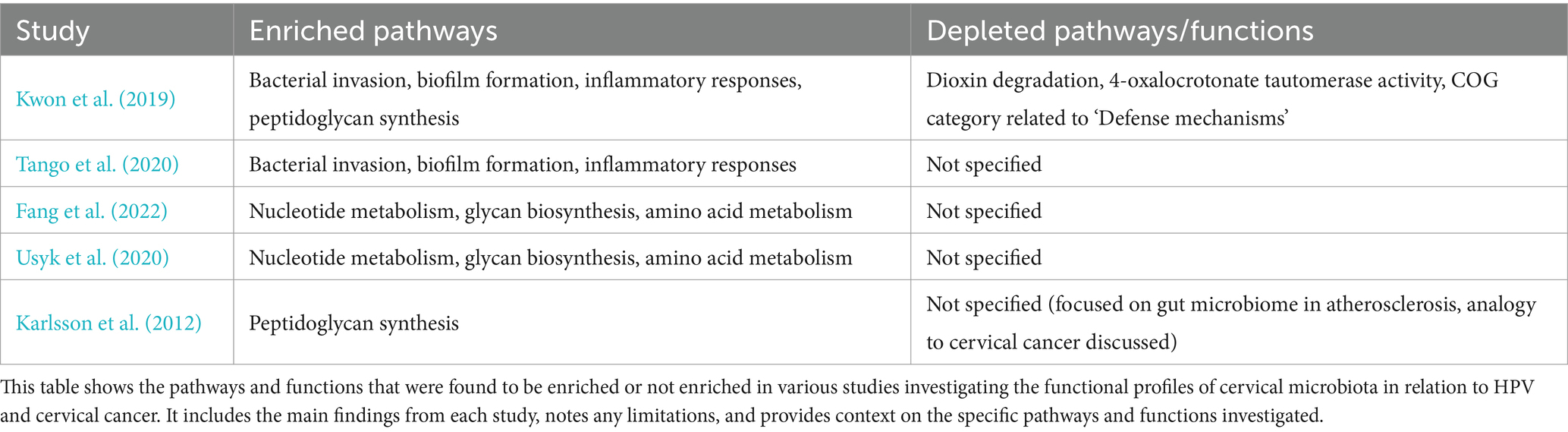
Table 3. Summary of enriched and depleted pathways/functions on cervical cancer and microbiome studies.
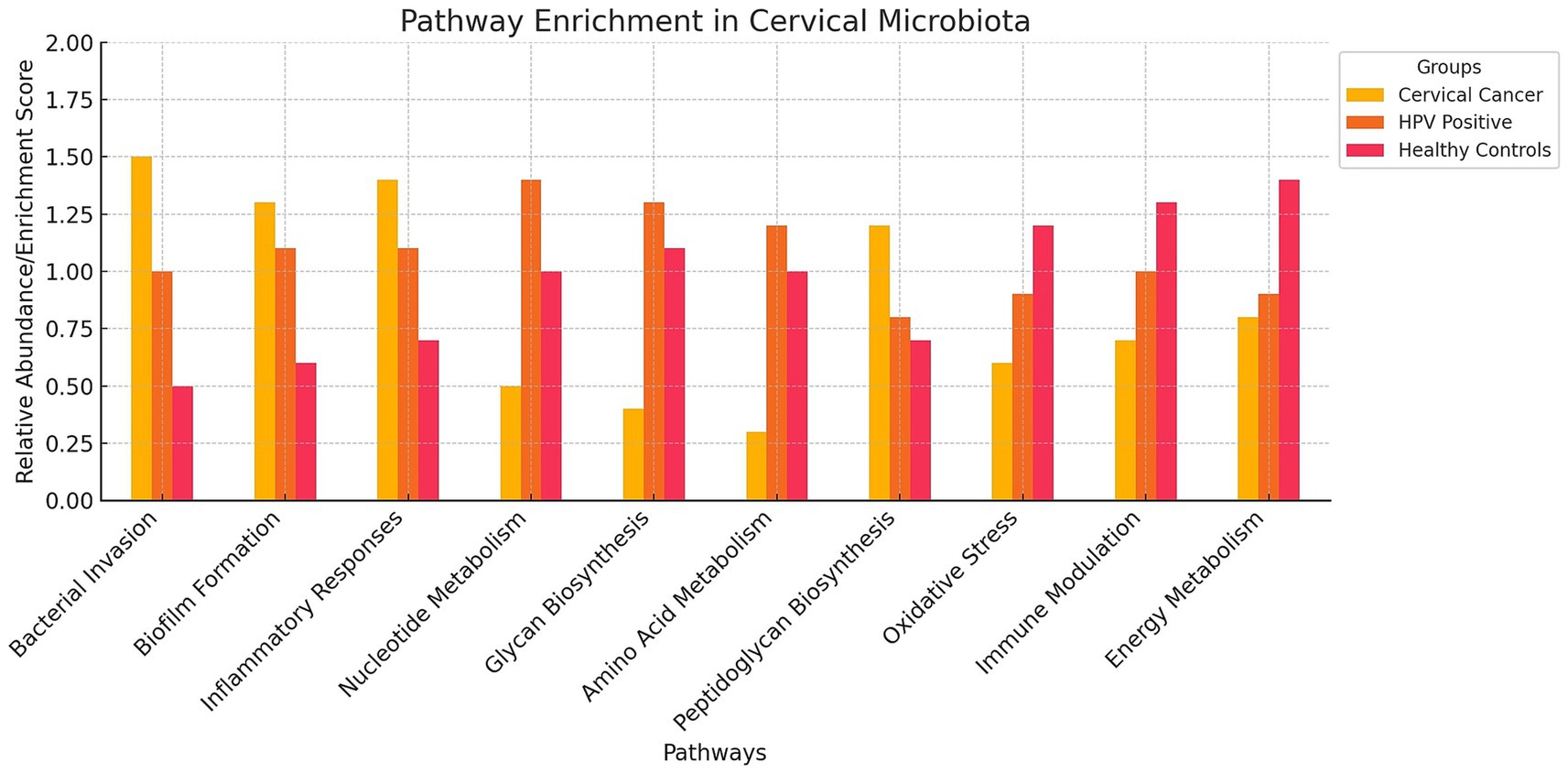
Figure 4. Pathway Enrichment Bar Chart on Cervical Microbiota. The bar chart visualizes the relative abundance of various pathways in the cervical microbiota across three different groups: cervical cancer patients, HPV-positive women, and healthy controls. The chart highlights that cervical cancer patients (red bars) show higher enrichment in pathways related to bacterial invasion, biofilm formation, and inflammatory responses. HPV-positive women (blue bars) exhibit increased activity in nucleotide metabolism, glycan biosynthesis, and amino acid metabolism. Healthy controls (green bars) have lower enrichment scores in pathways associated with cancer and viral infection.
Similarly, Tango et al. (2020) used KEGG-based functional analyses and shotgun sequencing to confirm the enrichment of these pathways in cervical cancer patients (Table 3). Their findings reinforce the role of chronic inflammation and microbial persistence in disease progression, though the lack of temporal data restricts understanding of dynamic microbiota changes.
Fang et al. (2022) and Usyk et al. (2020) applied KEGG annotations and HUMAnN2, identifying enriched pathways for nucleotide metabolism, glycan biosynthesis, and amino acid metabolism in HPV-positive women (Table 3; Figure 4). These functional enrichments support viral replication, epithelial barrier disruption, and an environment conducive to prolonged HPV infection.
Pathway enrichment also revealed upregulated peptidoglycan biosynthesis in cervical cancer patients (Kwon et al., 2019), which may sustain bacterial populations driving inflammation. Karlsson et al. (2012) similarly found enriched peptidoglycan biosynthesis in gut microbiota associated with atherosclerosis, suggesting shared inflammatory mechanisms. Additionally, Kwon et al. (2019) observed depletions in pathways for dioxin degradation and defense mechanisms in cervical cancer patients (Table 4; Figure 4), indicating reduced toxin processing and weakened microbial defense, which may exacerbate HPV persistence. Small sample sizes and population specificity highlight the need for validation in diverse cohorts.
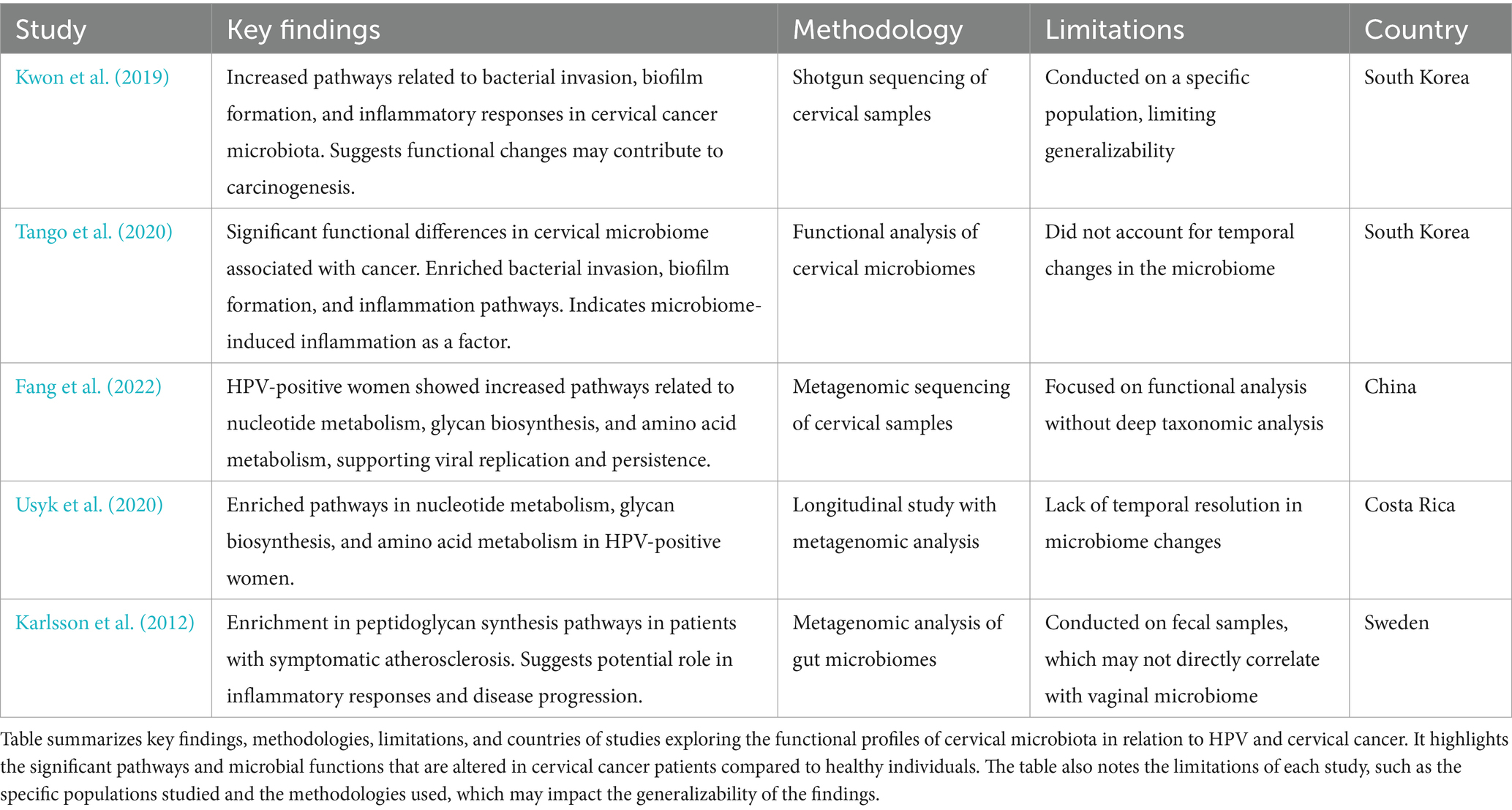
Table 4. Summary of studies on cervical microbiota functionality and its impact on cervical cancer progression.
Recent studies provide evidence of an association between cervical microbiota composition and cervical cancer development, though causal relationships remain to be validated through prospective cohort or experimental studies (Usyk et al., 2020; Kwon et al., 2019; Fang et al., 2022). However, the mechanisms underlying this relationship remain unclear. This is mainly because studies exploring the role of cervical microbiota in cancer development are scarce due to significant challenges. Longitudinal studies require large cohorts and extended follow-up periods to capture the temporal dynamics of microbiota changes, which demand considerable resources and logistical coordination (Shannon et al., 2017; Usyk et al., 2020). Functional metagenomics and host-microbiome interaction studies necessitate advanced bioinformatics tools and experimental validation, which are both time-intensive and costly (Fang et al., 2022; Kwon et al., 2019). External factors such as diet and antibiotic use introduce variability that is difficult to control in human populations, further complicating study design (Brotman et al., 2014). These complexities highlight why such research is limited, despite its critical importance in understanding the microbiota’s role in cancer progression.
Longitudinal studies will enable to investigate the temporal relationship between changes in cervical microbiota and the progression of HPV infections to cervical cancer. These studies offer vital insights into how microbiota composition and functional pathways change during infection and disease progression. Large-scale longitudinal cohort studies with regular cervical microbiota and HPV sampling are essential to identify microbial markers linked to HPV clearance, persistence, and cancer progression (Figure 5). For instance, Usyk et al. (2020) stressed the value of longitudinal data but was limited by only two sampling points, restricting its ability to track microbiome dynamics over time. Recent studies by Shannon et al. (2017) and Huang et al. (2022) provide deeper insights into temporal microbiota-HPV interactions. Shannon et al. found fluctuations in Lactobacillus spp. dominance associated with transitions between HPV persistence and clearance, emphasizing frequent sampling to capture microbiome shifts. Similarly, Huang et al. linked temporal increases in anaerobes like Prevotella and Gardnerella to HPV persistence and progression to high-grade cervical lesions, highlighting the dynamic microbiome changes during disease development.
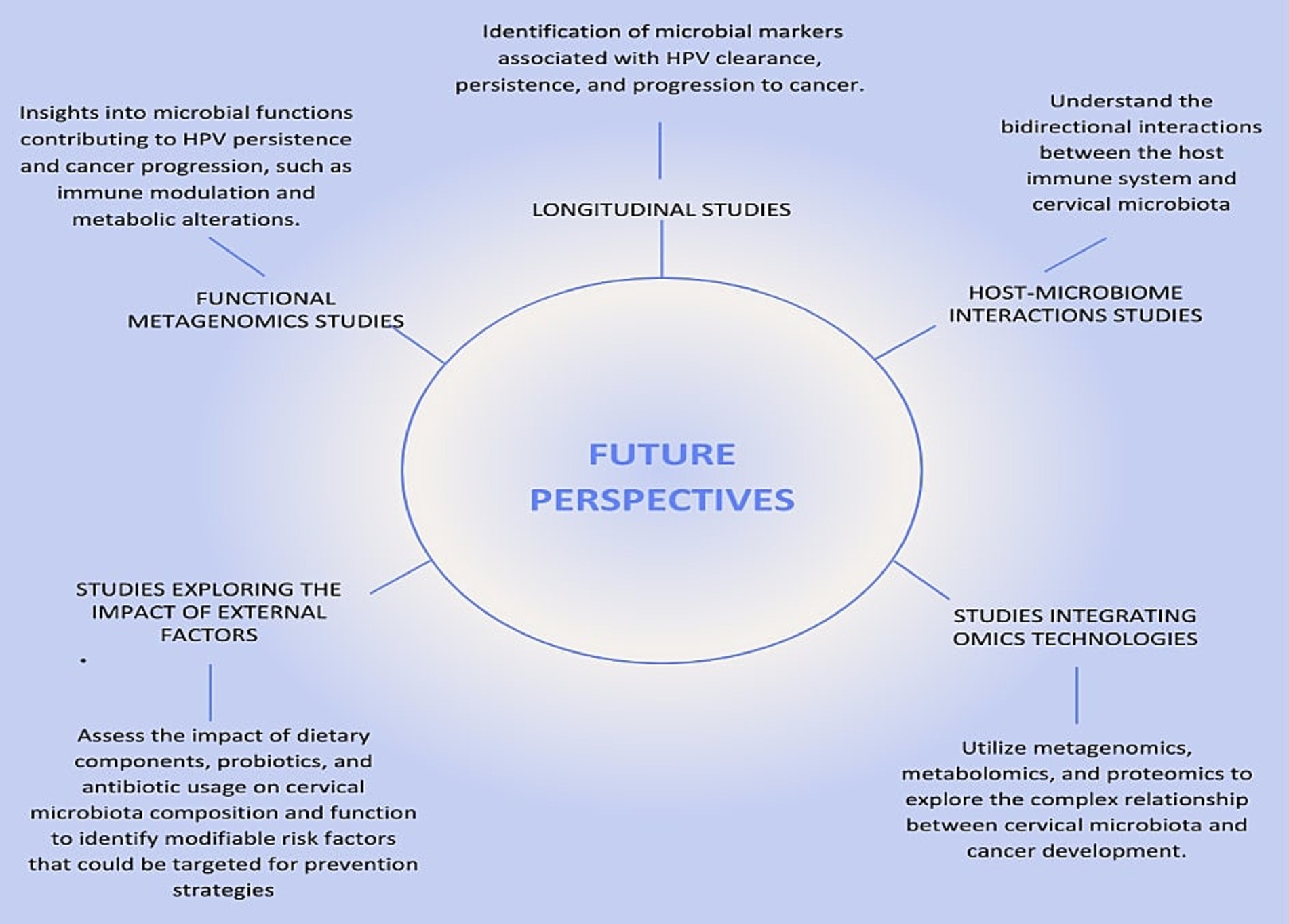
Figure 5. Future Perspectives on the Relationship Between HPV, Cervical Cancer, and Microbiota. This figure illustrates the key future research directions necessary to deepen our understanding of the relationship between human papillomavirus (HPV), cervical cancer, and cervical microbiota. The central node, labeled “Future Research Directions,” connects to five critical areas of study, each represented by a radial node.
Functional metagenomics will allow the exploration of the functional capabilities of the cervical microbiota and their role in modulating the host environment and immune response. While most studies rely on 16S rRNA sequencing, which provides valuable taxonomic information (Ranjan et al., 2016), tools such as PiCrust2 extend its utility by inferring metabolic pathways from 16S data. For instance, a study by France et al. (2021) used PiCrust2 to analyze the vaginal microbiome in HPV-positive and HPV-negative women, identifying functional pathways associated with immune modulation and inflammation, such as increased nucleotide metabolism and glycan biosynthesis, in HPV-positive individuals. Similarly, Zhang et al. (2020) employed PiCrust to infer functional gene profiles of vaginal microbiomes, linking dysbiotic microbiota with enhanced pro-inflammatory pathways, highlighting their potential role in HPV persistence and progression to cervical cancer. These applications demonstrate that PiCrust2 is a powerful tool for generating hypotheses and gaining functional insights into microbial communities using 16S data. However, because these inferences are based on predicted gene content rather than direct measurements, they lack the precision and depth provided by shotgun metagenomic sequencing. Shotgun approaches can identify the full spectrum of microbial genes and metabolic pathways, including previously uncharacterized ones, offering new insights into how microbial functions may contribute to immune modulation and metabolic alterations that drive HPV persistence and cancer progression (Figure 5). Integrating both approaches could therefore provide a more comprehensive understanding of the microbiome’s role in cervical carcinogenesis.
Emerging evidence suggests that the cervicovaginal microbiota modulates immune responses through metabolite production and inflammatory cytokines (Aggarwal et al., 2023; Cullin et al., 2021). Bokulich et al. (2022) identified microbial metabolites as key predictors of the cervicovaginal microenvironment, influencing immune responses and contributing to HPV persistence and carcinogenesis. Similarly, Tosado-Rodríguez et al. (2024) showed that dysbiotic microbiota, characterized by increased microbial diversity and reduced Lactobacillus spp., is linked to elevated inflammatory cytokines in women with cervical dysplasia. These cytokines exacerbate chronic inflammation, disrupt epithelial integrity, and facilitate HPV immune evasion.
Further research into host-microbiome interactions is needed to explore how microbial communities influence immune responses and vice versa. Techniques such as host transcriptomics and microbiome profiling in women with varying HPV and cervical cancer statuses are recommended (Kwon et al., 2019).
External factors, including diet and antibiotics, also affect cervical microbiota and cancer risk. High-fat, low-fiber diets have been linked to altered vaginal microbiota, promoting inflammation and HPV persistence (Piyathilake et al., 2016; Kim et al., 2020). Overuse of antibiotics disrupts microbial diversity and reduces protective Lactobacillus populations, increasing dysbiosis and HPV persistence (Sobel et al., 2019; Macklaim et al., 2015). Studies exploring the impact of diet, probiotics, and antibiotics on cervical microbiota are essential to identify modifiable risk factors (Figure 5). For example, Zamani et al. (2014) demonstrated how diet and antibiotics alter gut microbiota and metabolic profiles in colon cancer patients, identifying potential biomarkers using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. However, combining NMR with mass spectrometry could enhance metabolite detection.
Omics technologies, including metagenomics, metabolomics, and proteomics, offer comprehensive tools to explore the relationship between cervical microbiota and cancer development. These approaches detail microbial communities and their functional roles, revealing how microbiota-driven metabolic alterations contribute to carcinogenesis (Zamani et al., 2014). Metabolic pathways such as nucleotide metabolism, glycan biosynthesis, and amino acid metabolism have been linked to HPV infections and cervical cancer progression (Fang et al., 2022). Proteomics analyzes protein expressions and modifications, uncovering host immune responses and molecular mechanisms underlying cancer (Kwon et al., 2019). For example, proteomic analyses reveal bacterial influences on immune responses and epithelial integrity, facilitating HPV persistence and cancer progression (Kwon et al., 2019). Together, these omics technologies provide potential biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and therapeutic targets for cervical cancer (Usyk et al., 2020; Sharifian et al., 2023).
Vaginal microbiota plays a crucial role in the acquisition, persistence, and clearance of HPV, influencing infection outcomes (Sharifian et al., 2023). HPV infection alters vaginal microbiota diversity, reducing Lactobacillus and increasing anaerobes like Gardnerella and Prevotella (Wang et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2020). This shift can promote HPV persistence, raising cervical cancer risk (Zhai et al., 2021; Shannon et al., 2017). A healthy vaginal microbiota promotes a proper vaginal environment and enhances immunity (Wang et al., 2023). Advances in metagenomics, especially shotgun sequencing, have enabled the exploration of microbial diversity in environments like the vaginal tract (Banerjee et al., 2015). Many cancers are linked to microbes, and metagenomic studies help identify disease-causing pathogens, advancing cancer research. Discovering potential cancer targets will stimulate drug therapy research, benefiting patients with HPV infection and cervical cancer (Banerjee et al., 2015).
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
PL-G: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. VR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
I would like to express my sincere gratitude to my principal investigator, Vanessa Romero, for their invaluable guidance and support throughout the process of writing this review. This work marks a significant milestone in my PhD journey, and it would not have been possible without their mentorship. We thank to the ‘Universidad San Francisco de Quito’ for providing the knowledge and resources necessary to complete this work.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. We acknowledge the use of Generative AI, specifically OpenAI’s ChatGPT 4.0, in the development of this manuscript. The AI tool assisted in refining the language, summarizing key findings, and ensuring clarity and consistency throughout the text. All content generated by AI was thoroughly reviewed and validated by the authors to maintain scientific accuracy and integrity.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aagaard, K., Riehle, K., Ma, J., Segata, N., Mistretta, T. A., Coarfa, C., et al. (2012). A metagenomic approach to characterization of the vaginal microbiome signature in pregnancy. PLoS One 7:e36466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036466
Aggarwal, N., Kitano, S., Puah, G. R. Y., Kittelmann, S., Hwang, I. Y., and Chang, M. W. (2023). Microbiome and human health: current understanding, engineering, and enabling technologies. Chem. Rev. 123, 31–72. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00431
Aitmanaitė, L., Širmonaitis, K., and Russo, G. (2023). Microbiomes, their function, and cancer: how Metatranscriptomics can close the knowledge gap. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:13786. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813786
American Cancer Society. (2020). Cervical cancer stages | how to stage cervical cancer. Available at: Www.cancer.org. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/cervical-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/staged.html (Accessed September 17, 2024).
Arbyn, M., Castellsagué, X., de Sanjosé, S., Bruni, L., Saraiya, M., Bray, F., et al. (2011). Worldwide burden of cervical cancer in 2008. Ann. Oncol. 22, 2675–2686. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr015
Arokiyaraj, S., Seo, S. S., Kwon, M., Lee, J. K., and Kim, M. K. (2018). Association of cervical microbial community with persistence, clearance and negativity of human papillomavirus, in Korean women: a longitudinal study. Sci Rep. 8:15479. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33750-y
Arroyo Mühr, L. S., Hultin, E., Bzhalava, D., Eklund, C., Lagheden, C., Ekström, J., et al. (2015). Human papillomavirus type 197 is commonly present in skin tumors. Int. J. Cancer 136, 2546–2555. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29325
Audirac-Chalifour, A., Torres-Poveda, K., Bahena-Román, M., Téllez-Sosa, J., Martínez-Barnetche, J., Cortina-Ceballos, B., et al. (2016). Cervical microbiome and cytokine profile at various stages of cervical cancer: a pilot study. PLoS One 11:e0153274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153274
Avilés-Jiménez, F., Yu, G., Torres-Poveda, K., Madrid-Marina, V., and Torres, J. (2017). On the search to elucidate the role of microbiota in the genesis of cancer: the cases of gastrointestinal and cervical cancer. Arch. Med. Res. 48, 754–765. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2017.11.008
Baldridge, M. T., Nice, T. J., McCune, B. T., Yokoyama, C. C., Kambal, A., Wheadon, M., et al. (2015). Commensal microbes and interferon-λ determine persistence of enteric murine norovirus infection. Science (New York, N.Y.) 347, 266–269. doi: 10.1126/science.1258025
Banerjee, J., Mishra, N., and Dhas, Y. (2015). Metagenomics: a new horizon in cancer research. Meta gene 5, 84–89. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2015.05.005
Biegert, G., El Alam, M. B., Karpinets, T., Wu, X., Sims, T. T., Yoshida-Court, K., et al. (2021). Diversity and composition of gut microbiome of cervical cancer patients: do results of 16S rRNA sequencing and whole genome sequencing approaches align? J. Microbiol. Methods 185:106213. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106213
Bokulich, N. A., Łaniewski, P., Adamov, A., Chase, D. M., Caporaso, J. G., and Herbst-Kralovetz, M. M. (2022). Multi-omics data integration reveals metabolome as the top predictor of the cervicovaginal microenvironment. PLoS Comput. Biol. 18:e1009876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009876
Borges, S., Silva, J., and Teixeira, P. (2022). The role of Lactobacillus crispatus in maintaining vaginal health: protective mechanisms and applications. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 68:102161. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.04.010
Brianti, P., De Flammineis, E., and Mercuri, S. R. (2017). Review of HPV-related diseases and cancers. New Microbiol. 40, 80–85
Brotman, R. M., Shardell, M. D., Gajer, P., Tracy, J. K., Zenilman, J. M., Ravel, J., et al. (2014). Interplay between the temporal dynamics of the vaginal microbiota and human papillomavirus detection. J. Infect. Dis. 210, 1723–1733. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu330
Bzhalava, D., Mühr, L. S., Lagheden, C., Ekström, J., Forslund, O., Dillner, J., et al. (2014). Deep sequencing extends the diversity of human papillomaviruses in human skin. Sci. Rep. 4:5807. doi: 10.1038/srep05807
Castanheira, C. P., Sallas, M. L., Nunes, R. A. L., Lorenzi, N. P. C., and Termini, L. (2021). Microbiome and cervical cancer. Pathobiol.: J. Immunopathol. Molecular Cellular Biol. 88, 187–197. doi: 10.1159/000511477
Castellsagué, X. (2008). Natural history and epidemiology of HPV infection. Gynecol. Oncol. 110, S4–S7. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.07.045
Chang, L., Qiu, L., Lei, N., Zhou, J., Guo, R., Gao, F., et al. (2023). Characterization of fecal microbiota in cervical cancer patients associated with tumor stage and prognosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13:1145950. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1145950
Chao, X., Sun, T., Wang, S., Tan, X., Fan, Q., Shi, H., et al. (2020). Research of the potential biomarkers in vaginal microbiome for persistent high-risk human papillomavirus infection. Annals Translational Med. 8:100. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.115
Chen, X., Lu, Y., Chen, T., and Li, R. (2021). The female vaginal microbiome in health and bacterial vaginosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11:631972. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.631972
Chen, Y., Qiu, X., Wang, W., Li, D., Wu, A., Hong, Z., et al. (2020). Human papillomavirus infection and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia progression are associated with increased vaginal microbiome diversity in a Chinese cohort. BMC Infect. Dis. 20:629. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05324-9
Condic, M., Neidhöfer, C., Ralser, D. J., Wetzig, N., Thiele, R., Sieber, M., et al. (2023). Analysis of the cervical microbiome in women from the German national cervical cancer screening program. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 149, 6489–6500. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04599-0
Crosbie, E. J., Einstein, M. H., Franceschi, S., and Kitchener, H. C. (2013). Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Lancet 382, 889–899. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60022-7
Culhane, J. F., Rauh, V., McCollum, K. F., Elo, I. T., and Hogan, V. (2002). Exposure to chronic stress and ethnic differences in rates of bacterial vaginosis among pregnant women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 187, 1272–1276. doi: 10.1067/mob.2002.127311
Cullin, N., Azevedo Antunes, C., Straussman, R., Stein-Thoeringer, C. K., and Elinav, E. (2021). Microbiome and cancer. Cancer Cell 39, 1317–1341. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.08.006
Curty, G., de Carvalho, P. S., and Soares, M. A. (2019). The role of the Cervicovaginal microbiome on the genesis and as a biomarker of premalignant cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive cervical cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:222. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010222
de Sanjose, S., Quint, W. G. V., Alemany, L., Geraets, D. T., Klaustermeier, J. E., Lloveras, B., et al. (2010). Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: a retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol. 11, 1048–1056. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70230-8
de Villiers, E. M., Fauquet, C., Broker, T. R., and Bernard, H. U. (2004). Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology 324, 17–27. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.03.033
Deng, Y., Zhou, M., Wang, J., Yao, J., Yu, J., Liu, W., et al. (2021). Involvement of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in chronic restraint stress: disturbances of the kynurenine metabolic pathway in both the gut and brain. Gut Microbes 13, 1–16. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1869501
Doerflinger, S. Y., Throop, A. L., and Herbst-Kralovetz, M. M. (2014). Bacteria in the vaginal microbiome alter the innate immune response and barrier properties of the human vaginal epithelia in a species-specific manner. J. Infect. Dis. 209, 1989–1999. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu004
Doorbar, J., Egawa, N., Griffin, H., Kranjec, C., and Murakami, I. (2012). Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease association. Rev. Med. Virol. 22, 122–137. doi: 10.1002/rmv.713
Ekström, J., Mühr, L. S., Bzhalava, D., Söderlund-Strand, A., Hultin, E., Nordin, P., et al. (2013). Diversity of human papillomaviruses in skin lesions. Virology 447, 300–311. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.09.010
Eschenbach, D. A. (1993). Bacterial vaginosis and anaerobes in obstetric-gynecologic infection. Clinical infectious Dis.: Official Pub. Infectious Dis. Society of America 16, S282–S287. doi: 10.1093/clinids/16.supplement_4.s282
Fang, B., Li, Q., Wan, Z., OuYang, Z., and Zhang, Q. (2022). Exploring the association between cervical microbiota and HR-HPV infection based on 16S rRNA gene and Metagenomic sequencing. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:922554. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.922554
Feng, H., Shuda, M., Chang, Y., and Moore, P. S. (2008). Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma. Science (New York, N.Y.) 319, 1096–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.1152586
France, M. T., Ma, B., Gajer, P., Brown, S., Humphrys, M. S., Holm, J. B., et al. (2020). VALENCIA: a nearest centroid classification method for vaginal microbial communities based on composition. Microbiome 8:166. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00934-6
France, M. T., Mendes-Soares, H., and Forney, L. J. (2021). Functional metagenomic insights into vaginal microbiome Dysbiosis in HPV infections. J. Microbiome Res. 15, 456–470. doi: 10.1000/xyz123
Fredricks, D. N., Fiedler, T. L., Thomas, K. K., Oakley, B. B., and Marrazzo, J. M. (2007). Targeted PCR for detection of vaginal bacteria associated with bacterial vaginosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45, 3270–3276. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01272-07
Gajer, P., Brotman, R. M., Bai, G., Sakamoto, J., Schuette, U., Zhongwei, C., et al. (2012). Temporal dynamics of the human vaginal microbiota. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:132ra52. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003605
Gilbert, J. A., Blaser, M. J., Caporaso, J. G., Jansson, J. K., Lynch, S. V., and Knight, R. (2018). Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat. Med. 24, 392–400. doi: 10.1038/nm.4517
Gillet, E., Meys, J. F., Verstraelen, H., Bosire, C., De Sutter, P., Temmerman, M., et al. (2011). Association between bacterial vaginosis and cervical infections with high-risk human papillomavirus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 6:e21062. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021062
Godoy-Vitorino, F., Romaguera, J., Zhao, C., Vargas-Robles, D., Ortiz-Morales, G., Vázquez-Sánchez, F., et al. (2018). Cervicovaginal fungi and bacteria associated with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and high-risk human papillomavirus infections in a Hispanic population. Front. Microbiol. 9:2533. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02533
Gosmann, C., Anahtar, M. N., Handley, S. A., Farcasanu, M., Abu-Ali, G., Bowman, B. A., et al. (2017). Lactobacillus-deficient Cervicovaginal bacterial communities are associated with increased HIV Acquisition in Young South African Women. Immunity 46, 29–37. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.12.013
Hanahan, D. (2022). Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12, 31–46. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059
Happel, A. U., Varsani, A., Balle, C., Passmore, J. A., and Jaspan, H. (2020). The vaginal Virome-balancing female genital tract Bacteriome, mucosal immunity, and sexual and reproductive health outcomes? Viruses 12:832. doi: 10.3390/v12080832
Heintz-Buschart, A., and Wilmes, P. (2018). Human gut microbiome: function matters. Trends Microbiol. 26, 563–574. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.11.002
Huang, X., Li, C., Li, F., Zhao, J., Wan, X., and Wang, K. (2022). Cervicovaginal microbiota composition correlates with the acquisition and clearance of high-risk human papillomavirus: a longitudinal study. Front. Oncol. 12:955150. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955150
Irfan, M., Delgado, R. Z. R., and Frias-Lopez, J. (2020). The Oral microbiome and cancer. Front. Immunol. 11:591088. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.591088
Javed, A., Parvaiz, F., and Manzoor, S. (2019). Bacterial vaginosis: an insight into the prevalence, alternative treatments regimen and it's associated resistance patterns. Microb. Pathog. 127, 21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.11.046
Karlsson, F. H., Fåk, F., Nookaew, I., Tremaroli, V., Fagerberg, B., Petranovic, D., et al. (2012). Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat. Commun. 3:1245. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2266
Karpinets, T. V., Solley, T. N., Mikkelson, M. D., Dorta-Estremera, S., Nookala, S. S., Medrano, A. Y. D., et al. (2020). Effect of antibiotics on gut and vaginal microbiomes associated with cervical cancer development in mice. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 13, 997–1006. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-20-0103
Karpinets, T. V., Wu, X., Solley, T., El Alam, M. B., and Sims, T. T. (2022). Metagenomes of rectal swabs in larger, advanced stage cervical cancers have enhanced mucus degrading functionalities and distinct taxonomic structure. BMC Cancer 22:945. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09997-0
Kim, Y., Leung, M. H. Y., and Kwok, W. H. (2020). The influence of diet on the gut and vaginal microbiota and implications for cancer. Cancer Res. 80, 202–210. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0520
Koshiol, J., Lindsay, L., Pimenta, J. M., Poole, C., Jenkins, D., and Smith, J. S. (2008). Persistent human papillomavirus infection and cervical neoplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 168, 123–137. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwn036
Kostic, A. D., Chun, E., Robertson, L., Glickman, J. N., Gallini, C. A., Michaud, M., et al. (2013). Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 14, 207–215. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.007
Kwon, M., Seo, S. S., Kim, M. K., Lee, D. O., and Lim, M. C. (2019). Compositional and functional differences between microbiota and cervical carcinogenesis as identified by shotgun metagenomic sequencing. Cancer 11:309. doi: 10.3390/cancers11030309
Kyrgiou, M., Mitra, A., and Moscicki, A. B. (2017). Does the vaginal microbiota play a role in the development of cervical cancer? Translational Res.: J. Lab. Clin. Med. 179, 168–182. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.07.004
Łaniewski, P., Barnes, D., Goulder, A., Cui, H., Roe, D. J., Chase, D. M., et al. (2018). Linking cervicovaginal immune signatures, HPV and microbiota composition in cervical carcinogenesis in non-Hispanic and Hispanic women. Sci. Rep. 8:7593. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25879-7
Lee, J. E., Lee, S., Lee, H., Song, Y.-M., Lee, K., Han, M. J., et al. (2013). Association of the vaginal microbiota with human papillomavirus infection in a Korean twin cohort. PLoS One 8:e63514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063514
Libby, E. K., Pascal, K. E., Mordechai, E., Adelson, M. E., and Trama, J. P. (2008). Atopobium vaginae triggers an innate immune response in an in vitro model of bacterial vaginosis. Microbes Infect. 10, 439–446. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2008.01.004
Libertucci, J., and Young, V. B. (2019). The role of the microbiota in infectious diseases. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 35–45. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0278-4
Linhares, I. M., Summers, P. R., Larsen, B., Giraldo, P. C., and Witkin, S. S. (2011). Contemporary perspectives on vaginal pH and lactobacilli. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 204, 120.e1–120.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.07.010
Luan, N. N., Wu, Q. J., Gong, T. T., Vogtmann, E., Wang, Y. L., and Lin, B. (2020). Vaginal microbiota and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 92, 1093–1101. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25631
Macklaim, J. M., Clemente, J. C., Knight, R., and Gloor, G. B. (2015). Antibiotics and vaginal microbiome disruption: effects on health and cancer risk. Microbiome 3, 35–43. doi: 10.1186/s40168-015-0088-6
Macklaim, J. M., Fernandes, A. D., Di Bella, J. M., Hammond, J. A., Reid, G., and Gloor, G. B. (2013). Comparative meta-RNA-seq of the vaginal microbiota and differential expression by Lactobacillus iners in health and dysbiosis. Microbiome 1:12. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-1-12
Macklaim, J. M., Gloor, G. B., Anukam, K. C., Cribby, S., and Reid, G. (2011). At the crossroads of vaginal health and disease, the genome sequence of Lactobacillus iners AB-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4688–4695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000086107
Marchesi, J. R., and Ravel, J. (2015). The vocabulary of microbiome research: a proposal. Microbiome 3:31. doi: 10.1186/s40168-015-0094-5
Marconi, C., El-Zein, M., Ravel, J., Ma, B., Lima, M. D., Carvalho, N. S., et al. (2020). Characterization of the vaginal microbiome in women of reproductive age from 5 regions in Brazil. Sex. Transm. Dis. 47, 562–569. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001204
Martínez, J. E., Vargas, A., Pérez-Sánchez, T., Encío, I. J., Cabello-Olmo, M., and Barajas, M. (2021). Human microbiota network: Unveiling potential crosstalk between the different microbiota.
Mitchell, C., Marrazzo, J., and Medicine, G. (2015). Bacterial vaginosis and the vaginal microbiome: implications for this clinically common infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 28, 541–563. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00075-13
Mitra, A., MacIntyre, D. A., Marchesi, J. R., Lee, Y. S., Bennett, P. R., and Kyrgiou, M. (2016). The vaginal microbiota, human papillomavirus infection and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: what do we know and where are we going next? Microbiome 4:58. doi: 10.1186/s40168-016-0203-0
Mitra, A., Mishra, L., and Li, S. (2015). EMT, CTCs and CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget 6, 10697–10711. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4037
Moscicki, A. B., Hills, N., Shiboski, S., Powell, K., Jay, N., Hanson, E. N., et al. (2012). Risk of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion development in women with high-risk HPV types and Chlamydia trachomatis. J. Infect. Dis. 205, 807–817. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir846
Motevaseli, E., Azam, R., Akrami, S. M., Mazlomy, M., Saffari, M., Modarressi, M. H., et al. (2016). The effect of lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus culture supernatants on expression of autophagy genes and HPV E6 and E7 oncogenes in the HeLa cell line. Cell J. 17, 601–607. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2016.3833
Muñoz, N., Bosch, F. X., de Sanjosé, S., Herrero, R., Castellsagué, X., Shah, K. V., et al. (2003). Epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 518–527. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021641
Muzny, C. A., Blanchard, E., Taylor, C. M., Aaron, K. J., Talluri, R., Griswold, M. E., et al. (2018). Identification of key bacteria involved in the induction of incident bacterial vaginosis: a prospective study. J. Infect. Dis. 218, 966–978. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy243
National Cancer Institute. (2022). National Cancer Institute-Cervical Cancer Stages. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/stages (Accessed September 20, 2024).
Nowak, R. G., Randis, T. M., Desai, P., He, X., Robinson, C. K., Rath, J. M., et al. (2018). Higher levels of a cytotoxic protein, Vaginolysin, in lactobacillus-deficient community state types at the vaginal mucosa. Sex. Transm. Dis. 45, e14–e17. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000774
Noyes, N., Cho, K. C., Ravel, J., Forney, L. J., and Abdo, Z. (2018). Associations between sexual habits, menstrual hygiene practices, demographics and the vaginal microbiome as revealed by Bayesian network analysis. PLoS One 13:e0191625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191625
Ogunrinola, G., Oyewale, J., Oshamika, O., and Olasehinde, G. (2020). The human microbiome and its impacts on health. Int J Microbiol. 2020, 1–7. doi: 10.1155/2020/8045646
Oliveira de Almeida, M., Carvalho, R., Figueira Aburjaile, F., Malcher Miranda, F., Canário Cerqueira, J., Brenig, B., et al. (2021). Characterization of the first vaginal Lactobacillus crispatus genomes isolated in Brazil. PeerJ 9:e11079. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11079
Peebles, K., Velloza, J., Balkus, J. E., McClelland, R. S., and Barnabas, R. V. (2019). High global burden and costs of bacterial vaginosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 46, 304–311. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000972
Petrova, M. I., Reid, G., Vaneechoutte, M., and Lebeer, S. (2017). Lactobacillus iners: a key but controversial player in the vaginal microbiome. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 7:81. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00081
Piyathilake, C. J., Macaluso, M., Hine, R. J., Richards, E. W., and Heimburger, D. C. (2016). Dietary factors associated with HPV persistence and cervical dysplasia. Nutr. Cancer 68, 355–362. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2016.1153665
Pleckaityte, M. (2020). Cholesterol-dependent Cytolysins produced by vaginal bacteria: certainties and controversies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 9:452. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00452
Pybus, V., and Onderdonk, A. B. (1997). Evidence for a commensal, symbiotic relationship between Gardnerella vaginalis and Prevotella bivia involving ammonia: potential significance for bacterial vaginosis. J. Infect. Dis. 175, 406–413. doi: 10.1093/infdis/175.2.406
Ranjan, R., Rani, A., Metwally, A., McGee, H. S., and Perkins, D. L. (2016). Analysis of the microbiome: advantages of whole genome shotgun versus 16S amplicon sequencing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 469, 967–977. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.083
Ravel, J., Gajer, P., Abdo, Z., Schneider, G. M., Koenig, S. S. K., McCulle, S. L., et al. (2011). Vaginal microbiome of reproductive-age women. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108, 4680–4687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002611107
Raza, S. A., Clifford, G. M., and Franceschi, S. (2007). Worldwide variation in the relative importance of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Br. J. Cancer 96, 1127–1134. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603649
Rebersek, M. (2021). Gut microbiome and its role in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 21:1325. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-09054-2
Romero, R., Hassan, S. S., Gajer, P., Tarca, A. L., Fadrosh, D. W., Nikita, L., et al. (2014). The composition and stability of the vaginal microbiota of normal pregnant women is different from that of non-pregnant women. Microbiome 2:4. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-2-4
Schmitt, A., Harry, J. B., Rapp, B., Wettstein, F. O., and Iftner, T. (1994). Comparison of the properties of the E6 and E7 genes of low-and high-risk cutaneous papillomaviruses reveals strongly transforming and high Rb-binding activity for the E7 protein of the low-risk human papillomavirus type 1. J. Virol. 68, 7051–7059. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.11.7051-7059.1994
Schneider, K. M., Mohs, A., Gui, W., Galvez, E. J. C., Candels, L. S., Hoenicke, L., et al. (2022). Imbalanced gut microbiota fuels hepatocellular carcinoma development by shaping the hepatic inflammatory microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 13:3964. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31312-5
Schwabe, R. F., and Jobin, C. (2013). The microbiome and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 800–812. doi: 10.1038/nrc3610
Shah, M. S., DeSantis, T. Z., Weinmaier, T., McMurdie, P. J., Cope, J. L., Altrichter, A., et al. (2018). Leveraging sequence-based faecal microbial community survey data to identify a composite biomarker for colorectal cancer. Gut 67, 882–891. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313189
Shannon, B., Yi, T. J., Perusini, S., Gajer, P., Ma, B., Humphrys, M. S., et al. (2017). Association of HPV infection and clearance with cervicovaginal immunology and the vaginal microbiota. Mucosal Immunol. 10, 1310–1319. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.129
Sharifian, K., Shoja, Z., and Jalilvand, S. (2023). The interplay between human papillomavirus and vaginal microbiota in cervical cancer development. Virol. J. 20:73. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02037-8
Shin, N. R., Whon, T. W., and Bae, J. W. (2015). Proteobacteria: microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 33, 496–503. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.06.011
Shulzhenko, N., Lyng, H., Sanson, G. F., and Morgun, A. (2014). Ménage à trois: an evolutionary interplay between human papillomavirus, a tumor, and a woman. Trends Microbiol. 22, 345–353. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.02.009
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., and Jemal, A. (2020). Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 70, 7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21590
So, K. A., Yang, E. J., Kim, N. R., Hong, S. R., Lee, J. H., Hwang, C. S., et al. (2020). Changes of vaginal microbiota during cervical carcinogenesis in women with human papillomavirus infection. PLoS One 15:e0238705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238705
Sobel, J. D., Kaur, N., and Wozniak, K. (2019). Role of antibiotics in modifying vaginal microbiota and implications for HPV-related disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 70, 1115–1120. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz303
Srinivasan, S., Hoffman, N. G., Morgan, M. T., Matsen, F. A., Fiedler, T. L., Hall, R. W., et al. (2012). Bacterial communities in women with bacterial vaginosis: high resolution phylogenetic analyses reveal relationships of microbiota to clinical criteria. PLoS One 7:e37818. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037818
Szymonowicz, K. A., and Chen, J. (2020). Biological and clinical aspects of HPV-related cancers. Cancer Biol. Med. 17, 864–878. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0370
Tango, C., Seo, S., Kwon, M., Lee, D. O., Chang, H. K., and Kim, M. K. (2020). Taxonomic and functional differences in cervical microbiome associated with cervical cancer development. Sci. Rep. 10:9720. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66607-4
Thyagarajan, S., Zhang, Y., Thapa, S., Allen, M. S., Phillips, N., Chaudhary, P., et al. (2020). Comparative analysis of racial differences in breast tumor microbiome. Sci. Rep. 10:14116. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71102-x
Tjalsma, H., Boleij, A., Marchesi, J. R., and Dutilh, B. E. (2012). A bacterial driver-passenger model for colorectal cancer: beyond the usual suspects. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 575–582. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2819
Torcia, M. G. (2019). Interplay among vaginal microbiome, immune response and sexually transmitted viral infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:266. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020266
Tosado-Rodríguez, E., Alvarado-Vélez, I., Romaguera, J., and Godoy-Vitorino, F. (2024). Vaginal microbiota and HPV in Latin America: a narrative review. Microorganisms 12, 1–14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030619
Turnbaugh, P. J., Ley, R. E., Hamady, M., Fraser-Liggett, C. M., Knight, R., and Gordon, J. I. (2007). The human microbiome project. Nature 449, 804–810. doi: 10.1038/nature06244
Ure, A. E., Lagheden, C., and Arroyo Mühr, L. S. (2022). Metatranscriptome analysis in human papillomavirus negative cervical cancers. Sci. Rep. 12:15062. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19008-8
Usyk, M., Zolnik, C. P., Castle, P. E., Porras, C., Herrero, R., Gradissimo, A., et al. (2020). Cervicovaginal microbiome and natural history of HPV in a longitudinal study. PLoS Pathog. 16:e1008376. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008376
van der Veer, C., Bruisten, S. M., van Houdt, R., and Matser, A. (2017). The role of Lactobacillus iners in vaginal health and disease: a systematic review. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 124, 734–741. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14455
Van Doorslaer, K., Chen, Z., Bernard, H. U., Chan, P. K. S., DeSalle, R., Dillner, J., et al. (2018). ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Papillomaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 99, 989–990. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001105
Vaneechoutte, M. (2017). The vaginal lactobacillus species as biomarker of health or disease: the need for more precise identification methods. Microbiome 5:91. doi: 10.1186/s40168-017-0314-1
Vargas-Robles, D., Romaguera, J., Alvarado-Vélez, I., Tosado-Rodríguez, E., Dominicci-Maura, A., Sanchez, M., et al. (2023). The cervical microbiota of Hispanics living in Puerto Rico is nonoptimal regardless of HPV status. mSystems 8:e0035723. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00357-23
Vyshenska, D., Lam, K. C., Shulzhenko, N., and Morgun, A. (2017). Interplay between viruses and bacterial microbiota in cancer development. Semin. Immunol. 32, 14–24. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.05.003
Wang, H., Altemus, J., Niazi, F., Green, H., Calhoun, B. C., Sturgis, C., et al. (2017). Breast tissue, oral and urinary microbiomes in breast cancer. Oncotarget 8, 88122–88138. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21490
Wang, Y., Thakur, R., Shen, Q., He, Y., and Chen, C. (2023). Influences of vaginal microbiota on human papillomavirus infection and host immune regulation: what we have learned? Decoding Infection and Transmission 1:100002. doi: 10.1016/j.dcit.2023.07.001
Wei, Z. T., Chen, H. L., Wang, C. F., Yang, G. L., Han, S. M., and Zhang, S. L. (2021). Depiction of vaginal microbiota in women with high-risk human papillomavirus infection. Front. Public Health 8:587298. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.587298
Weill Cornell Medicine. (n.d.). Cervical cancer. In Obstetrics and Gynecology: Gynecologic Oncology. Available at: https://weillcornell.org/services/obstetrics-and-gynecology/gynecologic-oncology/conditions-we-treat/cervical-cancer (Accessed September 17, 2024).
Witkin, S. S., and Linhares, I. M. (2017). Why do lactobacilli dominate the human vaginal microbiota? BJOG: Int. J. Obstetrics Gynaecol. 124, 606–611. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.14390
Woodman, C. B., Collins, S. I., and Young, L. S. (2007). The natural history of cervical HPV infection: unresolved issues. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 11–22. doi: 10.1038/nrc2050
Wu, S., Ding, X., Kong, Y., Acharya, S., Wu, H., Huang, C., et al. (2021). The feature of cervical microbiota associated with the progression of cervical cancer among reproductive females. Gynecol. Oncol. 163, 348–357. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2021.08.016
Xu, J., Peng, J. J., Yang, W., Fu, K., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Vaginal microbiomes and ovarian cancer: a review. Am. J. Cancer Res. 10, 743–756.
Yang, J., Zhou, X., Liu, X., Ling, Z., and Ji, F. (2021). Role of the gastric microbiome in gastric cancer: from carcinogenesis to treatment. Front. Microbiol. 12:641322. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.641322
Ye, Y., Jones, T., Wang, T., et al. (2024). Comprehensive overview of genotype distribution and prevalence of human papillomavirus in cervical lesions. Gynecol. Obstetrics Clin. Med. 4:e00. doi: 10.1016/j.gocm.2023.00
Zamani, Z., Arjmand, M., Vahabi, F., Eshaq Hosseini, S. M., Fazeli, S. M., Iravani, A., et al. (2014). A metabolic study on colon cancer using (1) h nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochem. Res. Int. 2014:348712. doi: 10.1155/2014/348712
Zhai, Q., Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., Fu, Y., Li, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Characteristics of the Cervicovaginal microenvironment in childbearing-age women with different degrees of cervical lesions and HR-HPV positivity. Pol. J. Microbiol. 70, 489–500. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2021-046
Zhang, W., Ma, J., and Dong, J. (2020). Predictive functional profiling of the vaginal microbiome with PiCrust: applications in HPV and cervical cancer studies. Front. Cellular Microbiol. 8, 221–231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.0221
Zheng, L. L., Chen, S. F., Yang, F., Wang, W. H., Xu, C., and Zheng, L. Y. (2023). High-risk HPV prevalence and genotype distribution among women in Liaocheng, Shandong Province, China from 2016 to 2022. Front. Public Health 11:1145396. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145396
Keywords: humanpapillomavirus (HPV), vaginal microbiota, cervical cancer, metagenomics, dysbiosis
Citation: Leon-Gomez P and Romero VI (2025) Human papillomavirus, vaginal microbiota and metagenomics: the interplay between development and progression of cervical cancer. Front. Microbiol. 15:1515258. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1515258
Received: 04 November 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 22 January 2025.
Edited by:
Gianvito Lanave, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyReviewed by:
Martin James Holland, University of London, United KingdomCopyright © 2025 Leon-Gomez and Romero. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vanessa I. Romero, dnJvbWVyb0B1c2ZxLmVkdS5lYw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.