
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mech. Eng., 18 February 2025
Sec. Mechatronics
Volume 11 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmech.2025.1436338
This article is part of the Research TopicGlobal Excellence in Mechatronics: North AmericaView all 4 articles
Lane-keeping systems are a major part of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). Existing lane detection algorithms are based on either Computer Vision (CV) models or deep learning techniques which are often vulnerable to unfamiliar routes, lane marking conditions, night-time driving, weather conditions, etc. To improve lane detection accuracy under various challenging conditions, we propose a framework that utilizes several lane detection models with different features to obtain a robust algorithm. The proposed Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE) algorithm works with two cameras, one front camera and one rear camera. The front camera is used for lane offset estimates whereas the rear camera serves as a time-delayed reference for the estimated lane offsets. The offsets from front camera CV models (two) are used as inputs to the MMAE algorithm which compares the offset computed by the rear camera CV model (time-delayed) as the reference. The proposed MMAE algorithm then estimates the probability of lane offsets to match the time-delayed reference model lane offset and selects the offset with higher probability of matching with reference model. The offset from the time-delayed reference model cannot be used for the real-time lane keeping control system since it would produce erroneous steering output due to the time lag in offset estimated by the real camera model. Thus, the MMAE estimated offset offers a more accurate lane offset and hence used in a PID steering controller for the lane keeping system. The proposed algorithm is then deployed in an AirSim simulation environment for performance evaluation. The simulation results show that the proposed MMAE algorithm performed robustly even when one of the models performed poorly. The proposed lane detection algorithm was able to identify the poorly performing model and switch to the other model to ensure better lane detection performance.
The lane-keeping assist systems (LKAS) are an integral part of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) as well as autonomous vehicles (AV). LKAS actively controls the steering to keep the vehicle in lane with appropriate amount of steering. On the other hand, the passive system, called lane departure systems (LDS), do not actively control the steering, rather it only alerts the driver when the vehicle veers away from the current lane with no active turn signal (Liu et al., 2007).
The LKAS system is generally made up of two units, a lane detection unit, and a steering controller unit. As the steering-assist technology is mature and widely used, this unit is less likely to fail. The lane detection unit in a LKAS uses cameras and is subject to failure due to inadequate identification of lane markings due to fading, a portion of the lane marking lines being covered with dirt/debris or snow, etc. A significant amount of research has been carried out into developing robust algorithms for LKAS to improve its performance. In addition to the failure mode of the lane detection unit as stated earlier, other challenging road conditions such as rain/snow or wet roadways, and interference of camera views due to other road vehicles and lead to poor performance of the LKAS. To develop solutions addressing these failure conditions, it is important to understand how the lane detection algorithm estimates the offset between vehicle and lane centers. It uses a single camera or multiple cameras that capture the images of the road ahead and then locates the lane marker positions as well as their curvatures through computer vision/machine learning (ML) based algorithms (Muril et al., 2020). Figure 1 shows an overall schematic of a LKAS using the camera images as an input to a CV or ML based algorithm to first detect the offset between vehicle center and lane center and then control the steering.
Computer vision and machine learning are two important methodologies adopted in self-driving technology. However, these methodologies are subject to poor performance when unseen or noisy situations arise, resulting in erroneous lane detection with potentially catastrophic consequences. Because of such limitations, self-driving vehicles require the driver to always be ready to take back control as the situations may demand. Thus, an efficient and accurate lane detection unit is required in an AV that can handle any uncertainty or fault in the subsystems.
Zakaria et al. (2023) published a systematic review on lane detection in Autonomous vehicles. In their study, they mentioned that ADAS systems heavily rely on accurate lane detection to ensure safety. The article reviewed 102 publications from 2018 to 2021 to analyze the most effective methods for detecting road lanes. The research identifies the use of both traditional geometric modeling and modern Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques, particularly deep learning, which has gained increasing attention in recent years. Some studies have combined deep learning with machine learning or classical methods, showing promising results. The paper also examines the datasets and equipment used in training detection systems and suggests that future research should focus on improving accuracy, speed, and performance under challenging conditions.
Zhang et al. (2009) presented a methodology to identify road boundaries. They used two distinct methodologies: the first method utilized image segmentation, while the second used the Hough transform and vanishing point methodologies. The paper claimed to achieve reasonably good performance in identifying the road boundaries. Li J. et al. (2016) presented a deep neural network based lane detection methodology that utilized both a convolutional neural network (CNN) and a recurrent neural network (RNN) for improved performance in the absence of lane markings. In a more recent study, Haque et al. (2019) presented a lane detection methodology based on computer vision. Their methodology included calibration, cropping, combined thresholding, perspective transformation, and sliding window search to find the lane markers. Kim et al. (2021) presented an LKAS based on a convolutional mixture density network (CMDN) that could handle parameter uncertainty. The system’s main outputs, namely the vehicle’s lateral position error and the yaw error included uncertainties that were estimated. These uncertainties were used by the control system to generate a steering command based on the reliability of the lateral position and yaw angle errors. Although this methodology offered better performance over the conventional lane keeping controller (without reinforcement learning), the algorithm was tested only for the scenarios of rain and fog.
Deng et al. (2023) proposed an adaptive cross-scale ROI fusion network (ACSNet), which improves feature extraction by adaptively selecting important anchors and fusing them across scales. This allowed for better detection of lanes in challenging conditions by integrating diverse features. Additionally, a Three-dimensional Coordinate Attention Mechanism (TDCA) was introduced to enhance feature extraction by exploring relationships across rows, columns, and spatial dimensions. Experimental results show that ACSNet performs well on public datasets, CULane and Tusimple, demonstrating improved lane detection capabilities.
In a study, Bisht et al. (2022) proposed a method for lane detection and tracking based on integration of Hough transform and inter-frame clustering. In this research, they showed how using a Kalman filter and integration of a model with the detection system can add inertia to avoid drastic failures in lane detection algorithm. Their algorithm resulted in 84.17% correct rate on Caltech-dataset which is a substantial improvement compared to previous studies.
Al Noman et al. (2023) investigated computer vision-based lane detection using gradient and hue lightness saturation (HLS) thresholding. They used a sliding window searching method to find the lane markers and the final algorithm has a 96% accuracy with a 0.64% false positive rate on a dataset of 975 frames.
Sultana et al. (2023) proposed a real-time lane detection and tracking method to detect lane marking in challenging conditions. They utilized comprehensive intensity threshold range (CITR), angle-based geometric constraint (AGC) and length-based geometric constraint (LGC) followed by Hough Transform, and range of horizontal lane position (RHLP) to identify the lane markings. Existing datasets were used to evaluate the performance of their proposed algorithm which showed higher accuracy of detection.
Ye et al. (2024) proposed a lane detection model, which unlike traditional lane detections, focuses on simpler road markings, PortLaneNet addresses complexities such as intricate ground markings, tire crane lane lines, and diverse regional lines. The model introduces the Scene Prior Perception Module, which uses pre-training and prior knowledge from similar scenes in container terminals to improve accuracy.
Maddiralla and Subramanian (2024) presented the Lane Detection with Convolutional Attention Mechanism (LD-CAM) model, aimed at improving lane detection in autonomous vehicles (AVs) under challenging conditions such as poor roads, curves, damaged lanes, and extreme weather. While existing deep learning models perform well on well-maintained roads and in favorable weather, they struggle with these extreme conditions. The LD-CAM model includes an encoder to extract features, an enhanced convolution block attention module (E-CBAM) to refine feature quality, and a decoder that ensures no information loss in the output.
Dahl et at (2023) showed that using prediction uncertainty in advanced driver assistance systems improves the system’s robustness and accuracy in detecting potential driving errors. In their study, they implemented four threat detection methods where each method uses different strategies for leveraging uncertainty information, where the goal is to ensure that the intervention decision is based on trustworthy predictions.
Sang and Norris (2024) proposed a fuzzy logic-based adaptive self-tuned algorithm with high generalizability across diverse weather conditions for robust lane detection. The algorithm included edge identification and line detection modules, enabling image adjustments in response to challenging weather conditions. The proposed tracking function utilizes previous detection results to fine-tune the selected Range of Interest (ROI), optimizing both accuracy and processing time. By incorporating these adaptive features into common geometric-based frameworks, the algorithm achieves higher detection rates compared to previous studies during challenging weather conditions. As can be seen from the most recent literature, classical algorithms based on image processing are the most used and well-researched algorithms for lane detection due to their computational advantages over the AI/ML based algorithms. However, classical CV based algorithms may not perform well in challenging and uncertain road conditions.
In some studies, researchers have used some baseline models to estimate the uncertainty of machine learning based models, but they have not utilized these uncertainties to integrate multiple models in MMAE, filtering or any model integration framework. On the other hand, the experiments in this study will show that different detections models have different weaknesses and strengths which makes MMAE a suitable approach for integration of them.
The purpose of this study is to improve the robustness of the LKAS system by limiting the effects of the uncertainties due to road marking degradations as well as weather conditions. In this work, we present an MMAE based lane detection algorithm that uses two computer vision-based models, the output of which is used in a PID controller to implement the LKAS on the vehicle. Here, the implemented models are evaluated by an observer to estimate any uncertainties and the probability of each model matching an uncertainty threshold at each time step is computed. Thus, only the output for the model that offered the least amount of uncertainty is passed on to the steering controller.
• There is no study in the literature which integrates multiple detection models in an integration framework to get the most out of each model.
• In this research, we investigated a Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE) framework to further improve the accuracy and robustness of lane detection by integrating multiple classical algorithms in order to get the best out of these algorithms.
• The focus of this work is not to improve the individual base algorithms selected for this research. Rather, the focus is on how the MMAE framework can help multiple lane detection algorithms to cover each one’s weaknesses under various driving and environmental conditions and thus improve the overall lane detection accuracy.
The remainer of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the MMAE based lane detection algorithm which is the main contribution in this paper. Section 3 shows the simulation results for several challenging road conditions. It is followed by Section 4 capturing the findings of the paper (concluding remarks). Section 5 captures the improvements that are planned as future work.
As mentioned earlier, two different computer vision-based models are integrated in a MMAE framework (Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation) in this work. MMAE technique is a probabilistic methodology that utilizes multiple estimation models and tries to match the system with a model that best fits the real-time data output from the system. It has been successfully applied in many estimation and detection applications. Barrios et al. (2006) applied Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation System (MMAE) algorithms to integrate GPS measurements to improve efficiency and performance. Quinlan and Middleton (2010) presented a multi-modal Kalman filter involving multiple models. They compared their results with those obtained using a particle filter approach which showed improvements in the presence of ambiguous information. Takens’ data-driven modeling methodology was combined with Kalman filtering by Hamilton et al. (2016) which reconstructed the model dynamics from observed system delays. Kalman filtering was used to update the model with new observations. They claimed that their approach might have performed better in the presence of modeling errors. Rahman et al. (2017) utilized an MMAE framework to detect Li-Ion battery fault conditions and showed that this methodology was able to successfully detect various battery conditions such as overcharging, over-discharging, etc.
This work was inspired based on the successful application of MMAE in fault condition detection which can be leveraged to detect a poorly performing lane detection model under certain road/environmental/lighting conditions and then replace that model with a better model from a set of models stored in this framework. Thus, this work proposes an MMAE-based lane detection system for different driving scenarios including uncertain road/environmental/lighting conditions for possible improvements in predicting vehicle location with respect to the lane markings.
A high-level schematic of the proposed algorithm is illustrated in Figure 2 which shows how the MMAE based lane detection algorithm works as a part of the LKAS system. Here the front camera images are fed to both computer vision models which generates the offsets between the vehicle center and lane center. These offsets are then used by the MMAE algorithm along with the rear camera reference model to determine which front camera model matches better with the reference model. A more detailed illustration of the lane detection models (model #1 and #2) used in this research is shown in Figure 3. Here Model 1 is similar to the one presented in Pagale et al. (2023) while Model 2 is similar to model shown in Gaskey (2023). Sobel edge detector algorithm is described in Ozgunalp (2017).
To evaluate how these two models perform, they were tested in different driving scenarios. It was observed that one model performed better than the other under these driving conditions/scenarios, mainly due to the uncertainties in road or weather conditions (e.g., the estimated lane offset error was greater than the allowable threshold). These performance issues can be attributed to: (i) the unresolvable issues, e.g., lane marking covered by snow; (ii) the resolvable issues that can be addressed by adjustments in the models, e.g., missing parts of a lane marking line, a sharp change in lane curvature, a highly contrasting shadow of a building on the street, or a rain-soaked wet road. It should be noted that this study only considered a few challenging experiments to outline the weaknesses and strengths of the presented models to show how MMAE based algorithms can improve the overall detection accuracy if a single model fails. However, in a scenario where both models fail to measure the lane offset accurately, the MMAE algorithm will likely not perform well either. Additional lane detection models integrated in the MMAE framework may offer a solution in such a case as discussed further in the future work section. In this study, we considered resolvable model failures only. Figure 4A shows the performance of two lane detection models considered in this work on a sample image with a wet street. It shows that the second model offered a better result with relatively more accurate lane detection. It is likely that the first model was unable to identify the lane probably due to the light reflections on the street.
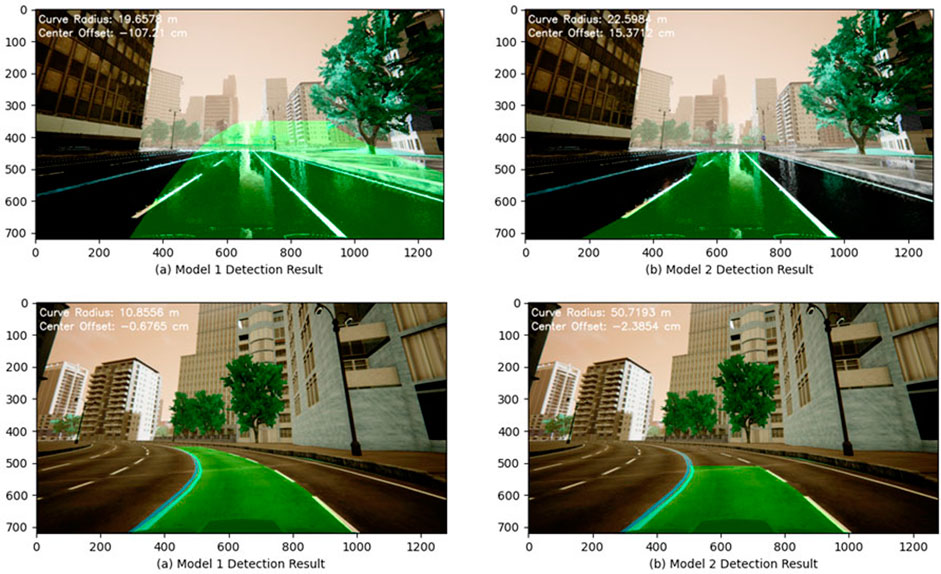
Figure 4. (A) The performance of two different lane detection models on a wet street. (B) The performance of two different lane detection models in a sharp turn.
Figure 4B shows the case where the vehicle is making a sharp turn. The second model, having a smaller region of interest (ROI), was not able to detect the lane completely. On the other hand, the first model exhibited a robust performance. Further comparison of these two models showed each model had some advantages and disadvantages based on the driving scenarios. Thus, it makes a good case to integrate these two models via MMAE framework in order to achieve a more robust detection by leveraging their advantages in different driving scenarios. Here MMAE methodology will be used to combine these two models.
Both the front and rear cameras are used in implementing the proposed lane detection algorithm. The front camera is used to provide the input video feed for both models while the rear camera is used as a reference. As illustrated in Figure 3, two different models for lane detection using front camera images are based on computer vision techniques. The first model is more straightforward than the second model, but its ROI is larger and has a better performance in long-distance detection. The second model is more advanced; however, it has a smaller ROI and offers more robust lane detection in shorter range.
To evaluate computer vision models and implement the proposed MMAE based lane detection algorithm in simulation, AirSim (Shah et al., 2018) simulation environment has been used in this study. The City release of AirSim has a limited number of roads and buildings in a virtual urban area. We placed two cameras on the vehicle, the first camera being located on the front middle of the vehicle’s roof while the second one is located at the bottom of the rear windshield of the vehicle. The selected vehicle in the simulation was an SUV called PhysXCar. Figure 5 shows the location of the front and back cameras on the vehicle.
The setting.json file of AirSim contains the configuration of the environment. This file, as well as the other codes, are stored in a GitHub repo (Fakhari, 2023). The configuration of the cameras provided in Table 1. The field of view (FOV) for the front camera was 120° while that of the back camera was selected as 150°. The pitch of the front camera was set at 10° while that of the back camera was −20°. In AirSim, the vehicle coordinates are fixed at the center of the vehicle and follows NED coordinate convention where X-axis is always pointing toward the front of the vehicle. The selected camera FOV and pitch angles of the cameras are obtained via trial and error to ensure the best possible results in terms of lane detection. Figure 6 shows the street views in the AirSim simulation environment as captured by the front and rear cameras.
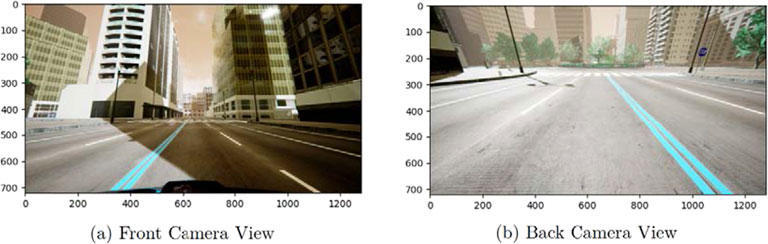
Figure 6. The perspective views of the cameras in the simulation environment. (A) Front camera view; (B) Rear camera view.
As indicated earlier, two different lane detection algorithms based on computer vision have been used here. The lane detection results on sample roads for these two models are shown in Figures 7, 8. In model #1, the camera image is first cropped with ROI extraction, the image binarization if performed next, and a birds-eye view of the image is then obtained. Hough transform is then used on the image to locate the line markings. Finally, the center point of the lane nearest to the vehicle center (first row of the image) is used to compute the offset or error. Figure 7 shows the simulation results of the lane detection performance using model #1, showing high level of accuracy.
In model #2, once the camera calibration is done, the image is cropped, and ROI is extracted. For making the binary, the thresholding is done using Sobel, Saturation, and Hue thresholding. Then the binary image is used in a sliding windows algorithm to detect the lines in each row of sliding windows. The lane marking lines are then found by fitting a second-order curve to these lines. Finally, the offset of the vehicle and lane centers was calculated. Figure 8 illustrates the performance of the lane detection using this model which exhibits good accuracy.
As stated earlier, the rear camera is used to estimate the lane offset in the back of the vehicle and is considered as a reference model in the MMAE algorithm to evaluate the two models that used the front camera images. The rear camera images were fed into yet a third algorithm to detect the lane-offset in the back of the vehicle. This third algorithm is an implementation of a well-known and tested CLRNet based algorithm by Zheng et al. (2022) on a rear short-range camera. Tests on this trained network show a very accurate result on the offset detection for the rear camera when compared to the ground truth.
As mentioned in the previous sections, a modified MMAE algorithm is developed in this study to evaluate two computer vision models that use the front camera images as inputs. The estimated offsets from model #1 and model #2 are used as inputs to the proposed MMAE algorithm. Unlike the conventional MMAE algorithms, in this study there are no mathematical observers available to evaluate the performance of front camera models. Thus, the estimated offset using the rear camera images is used as the reference for calculating the probabilities of failure of each of the models that used front camera images. It is noted that the third model (that used rear camera images) showed very good lane detection performance in a wide range of road and weather conditions in a priori simulations. The residuals of each of the models (i.e., model #1 or #2) are the subtraction of the model offset from the reference model offset. We note that the reference model is one step behind since it uses rear camera images. Therefore, the residual was defined as the difference between the offsets of the front camera models at step n-1 and the offsets of the rear camera model at step n. Let’s denote the offset of the vehicle and lane centers as z. Similar to the state estimation, the purpose here is to estimate the offset using multiple models. The offset z can be calculated as shown in Equation 1:
where f is the lane detection function which can be any of the proposed models or the reference (rear camera) model, and z is the measured offset. The residual (offset error) for calculation of conditional probability can be defined using Equation 2 below:
where
Equation 3 merely illustrated that the sum of all probabilities equals to unity. The above probabilities can be computed using Equation 4 for the
where
where l is the measurement dimension, which is 1 here and,
where
where C is the output vector [1 0] and P is state covariance matrix of white dynamics noise which is assumed to be an identity matrix at the initial step, and R is the covariance of the measurement noise which is considered to be
Let’s assume that ek as the offset of the vehicle and lane centers as outputted by the proposed MMAE algorithm at each time step k, and the output of the controller is the steering command at time step k is sk which is the input to the vehicle model in the simulation environment. The discrete PID formulation for time step k can be written as in Equation 9 below:
where k is the current time step; KP, KI, and KD are the Proportional, Integral and Derivative (PID) gains, respectively. The test simulation runs indicated that two different sets of gains, one for straight roads and one for curvy roads offered better lane keeping performance. Table 2 shows the tuned PID gains for this controller, which were obtained by trial and error.
Figure 9 shows the developed control system for the proposed MMAE based LKAS. As illustrated here, the simulation environment at each time-step provides front and rear camera images. The front camera images are used in models #1 and #2 for lane detection and offset calculation while the rear camera image is used in the third model for estimating the reference offset. The output offsets from both front camera models and the reference offset are used in the MMAE algorithm to compute the probability of each model to match with the reference model (Likelihood Function) using Equation 4, considering one step delay for the offset of models since the reference model (looking back) can only evaluate the past offset. The likelihood function outputs the probabilities of the two lane detection models matching the reference model, p1 and p2, respectively. Then a decision-making unit outputs the model offset with higher probability. It is to be noted that since the reference model (offset output from the rear camera MMAE model) works better than the two main models due to its proximity and direct view of the road behind the car and therefore has much fewer possible failures. However, it cannot be used for direct steering control since the lane keeping steering command should be based on future offset (ahead of the ego vehicle) not the past offset as computed by the rear camera CV model. The output offset from the decision block is then subtracted from the target offset (which is zero) and sent as the input to the PID controller to generate a proper steering command for the next time step. The simulated vehicle uses this steering command to steer the car to ensure zero offset error. The vehicle’s throttle is set at the maximum value until the vehicle reaches 15 m/s which is the maximum allowed speed in the simulation.
As illustrated in Section 2, model #1 does not work well in cases with sharp contrast shadows on the street. Figure 10 shows the simulation view of a test to show this weakness of model #1. However, it should be noted that model #1 showed a good performance on curvy roads with good lighting. Figure 11 shows the calculated offset (distance between the center of the lane and vehicle) by model #1 which has a significant noise. The shadow on the street can be attributed to this noise.
The evaluation of the second model illustrated that the model failed for the cases with sharp turns. However, the resulting noise for this model in the shadow scenario was acceptable and this model was sufficiently accurate in this scenario. Thus, we have designed different case studies to evaluate the performance of the proposed MMAE-based algorithm. Figure 12 shows the model matching probabilities of the proposed lane detection algorithm for case study #1, having a sharp contrast shadow on the street. The shadow extends to the first quarter of the street, and in the corresponding time-steps (0–25), the proposed algorithm reveals that model #1 is not working properly and decided to switch to model #2 since the probability of this model output matching the reference model output is much higher. After the vehicle passed through the shadow (timesteps 30–80), both models showed robust performance. As a result, the algorithm had several switches between these two models.
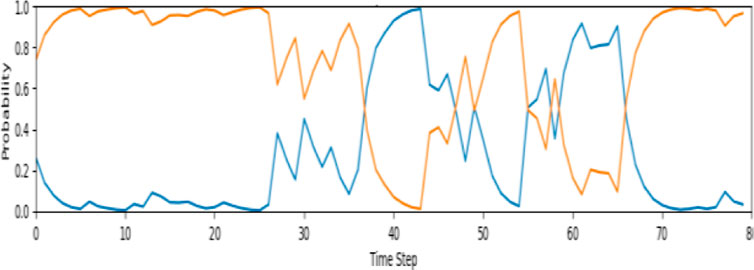
Figure 12. The probabilities of the proposed model for case study #1 (Blue–Model 1 and Orange–Model 2).
Figure 13 illustrates the performance of the proposed MMAE in case study #2 (a sharp turn). As mentioned earlier, model #2 does not work well in sharp turns. As expected, the proposed algorithm detected this behavior and switched to model #1 between time step 10 and 70 (when the road curvature ends). Thus, for the above two cases, the proposed MMAE based LKAS was able to detect failure in each model under varying road scenarios and switch to the better performing model to attain robust lane detection.
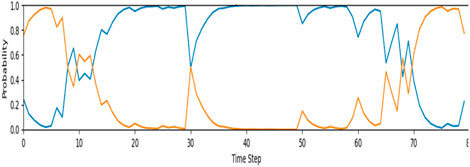
Figure 13. The probabilities of the proposed model for case study #2 (Blue–Model 1 and Orange–Model 2).
Enhancements to the reference (rear camera) model were made to further improve its robustness. The reference model, which uses rear camera images to compute the offsets to be compared with each of the other models via MMAE, could encounter diminished performance during the lane detections. If the reference model fails to produce the correct value of the offset for evaluating the front camera models, the calculated probabilities would have significant errors. To mitigate this issue, first, the failure of the reference model is defined. If the output offset of the reference model changes suddenly by more than a certain threshold, it would be concluded that the reference model has failed. The value of this threshold is found by trial-and-error methods. Once such a failure is detected, the reference model offset value can be corrected by averaging the calculated value with an extrapolation of previous values. A threshold of 20 cm is found to be optimal. Figure 14 shows the results of the proposed MMAE based lane detection algorithm with a corrected reference model output offset having a jump threshold of 20 cm. The failures of the reference model (the red jumps) are detected by the algorithm and corrected. The lane-keeping result of this case study (a turn with wet ground) was robust, and the vehicle was controlled effectively to stay within the lane. As seen from the figures, the first model exhibited large errors (failures) between time steps 9 and 15, and the proposed MMAE algorithm was able to detect this failure and switch to better performing model #2.
Table 3 shows the results of models and observer offsets against the ground truth offset and their errors as well for case study #2. Accordingly, model #1 had a root mean square error (RMSE) of 21.12 cm, and model #2 had an RMSE of 47.29 cm which shows model #1 is more desirable in a sharp turn scenario. In addition, the error of final offset as the output of MMAE had an RMSE of 20.40 cm which has a lower RMSE than both models. This shows that the proposed algorithm based on two models could attain better performance than each model with a correct switch between models based on their uncertainties. The reported steering command is calculated based on the final offset error using a PID controller which is fed to the simulation environment as a number between −1 and 1. The observer offset which is used for finding the probability of each model had an RMSE of 13.87 cm and showed a reliable performance with a maximum error of 25.16 cm.

Table 3. The results of models and observer offsets and their corresponding errors against ground truth for case #2.
The updated MMAE based LKAS algorithm was validated in three more case studies. The first one (case study #3) is in a mild turn with high contrast shades as well as speed bumpers. Figure 15 shows a view of this test environment and Figure 16 shows the result of the updated MMAE LKAS for this case study. As can be seen, the system was able to keep the vehicle inside the lane. In the first 10 timesteps of this scenario, there are two challenges facing the system: the first one is the high contrast shadow in front of the front camera and the second one is the speed bump seen by the rear camera. The speed bump failed the observer/estimator model. The high contrast shadow also resulted in a failure for model #1 in timestep 5–7 which was handled by the MMAE with switching to model #2. The calculated offset for model #1 at timestep 5 had a huge jump and the probability of this model reduced close to zero. This failure in model #1 was predictable since model #1 is vulnerable to barriers as was mentioned earlier and the simulation result validated the improved performance of proposed MMAE in such situations.
Case study #4 is in a straight street with high-contrast shadows. Figure 17 shows a view of this test environment in AirSim where half of the roadway is in the shade and the second half is under sunlight. Figure 18 shows the result of MMAE LKAS for this case study which has a stable result. Again, the proposed LKAS system was able to keep the vehicle inside the lane in this test and perform robustly. The observer worked well in this scenario: model #1 worked with a higher probability for the first half of the test and had a lower residual; however, in the second half this model acted noisily and the MMAE LKAS decided to switch to model #2 and the probability of this model remained higher except for the last few seconds. Table 4 presents the ground truth evaluation of case study #4. According to this table, the RMSE error of model #1 is 48.62 cm and the RMSE of model #2 is 45.33 cm during 80 timesteps. The final offset which was calculated by the proposed MMAE has a RMSE of 41.43 cm which has a 14.8% better performance than model #1 only system and 8.3% better performance than model #2 only system. The observer also had an RMSE of 23.35 cm. The maximum ground truth offset [Left, Right] pair of the vehicle from the center of the lane for this case is [13.45, 25.82]; however, models #1, #2, and the final model found this pair as [−66.06, 42.43], [−57.70, 19.30] and [−51.06, 42.43], respectively. For the errors, models #1, #2, and the final model have the maximum error of 83.7, 79.88, and 70.06 cm which shows that the MMAE could also reduce the global error as well as the RSME for the final model.

Table 4. The results of models and observer offsets and their corresponding errors against ground truth for case #4.
Case study #5 is in a turn with wet ground and rainy weather as shown in Figure 19. Figure 20 shows the results of MMAE LKAS for this case study. As illustrated, the proposed system performed robustly, and the vehicle was kept in the lane by the controller. Here, the observer had a failure at timestep 5, but it was resolved quickly, and the vehicle remained in the lane. The video of the result of this case study is available and attached to the supplementary materials.
In this research, two computer vision-based lane detection models are utilized in a multiple-model adaptive estimation framework to improve their performance. The proposed system is investigated against multiple case studies in a simulation environment to validate the robustness and the performance of the framework. This study investigated the improvements by an uncertainty-aware adaptive model combination in various case studies, which can be considered as an enhancement over Li C. et al. (2016) and former studies on the fusion of data using multiple cameras. It should be noted that compared to sensor fusion, MMAE does not use an extra sensor modality for enhancing the result and stabilizing the estimation, rather it improves the robustness in the algorithm level with adding no extra information in the sensor level. Case study #1 is used for fundamental tests and improvements to the MMAE framework. In case study #2, the results showed that the proposed MMAE could significantly improve the performance of the first and second models. In fact, these two models that were designed and investigated in previous studies could reach an RMSE of 21.12 cm and 47.29 cm in this case study. However, the proposed MMAE could attain an RMSE of 20.4 cm by an optimum combination of these two models. On the other hand, the proposed MMAE reduced the maximum offset error from 145.19 cm (which resulted in the failure of model #2 in this case study) to 55.02 cm. Similar to the result of Li et al. (2019) study that investigated a multi-sensor fusion approach, in the current study the utilization of multiple models could help the final MMAE controller to switch from a failing model to the more accurate model based on calculated uncertainties. In fact, Li et al. (2019) study showed that the fusion of IMU and GPS sensors into the camera could cover the camera failures. It should be noted that in the current study, only cameras are used as sensors, and the focus is on improvements by the combination of lane detection algorithms (models). Case study #3 which was designed to evaluate the performance of the observer itself showed that the observer could have some failures at a few timesteps. However, these failures did not result in a test failure and the proposed MMAE LKAS was able to keep the vehicle in the lane due to the short duration of observer failure. However, the weaknesses of the observer are detected in case studies #3 and #5 and they are discussed in the section for future improvements. In case study #4, the proposed framework could reduce the RMSE by 14.8% compared to a single model detection system which was investigated in previous studies. Besides, the RMSE maximum error (which could result in a lane departure) was reduced by 12.94 cm. This improvement is significant compared to similar studies. In Xiong et al. (2020) study, a multiple camera fusion for a similar scenario (ordinary urban roads) resulted in a 5%–50% accuracy improvement compared to a single camera lane detection system. They also used a similar lane detection model as model #2 in this study. This comparison shows that employing multiple lane detection models/algorithms not only could be as beneficial as having multiple sensors (cameras, IMUs, GPS) but it is also less computationally expensive.
Case study #5 which is the most challenging scenario with wet ground, curvy road, and low light path, resulted in the same way and despite a single model system that failed to keep the vehicle in the lane for this scenario the proposed MMAE LKAS was able to keep the vehicle in the lane using the exact same models. In fact, the proposed MMAE based model is validated via the case studies which show the fact that each lane detection model could have some failures under challenging situations, and the redundancy of multiple models and a robust likelihood function was able to select the better performing model where one of the models failed temporarily.
As Figure 21 illustrates, the final model (the gray line) was calculated by model #1 (the blue line) until step 36 since it had a be performance; however, after this step, the residual error of model #1 increases, and the final model switched to model #2 (the orange line). In fact, except for step 40 (the final offset which is calculated by MMAE), in all the other steps the gray line is below the two blue and orange lines which show the final model of MMAE worked always better than a single model performance. In summary, the proposed MMAE results compared to former studies show that each lane detection system has potential improvements. In fact, the system can be improved by adding new sensors such as IMU or GPS or it can be improved by adding more cameras and CV models, as well as a fusion of the output data from added sensors. The results of this study showed that employing multiple lane detection models together in the MMAE framework could improve the overall performance of the system up to 15% without any computational overhead. The proposed MMAE framework can also be integrated with multiple sensor fusion that were investigated in previous studies.
In this paper, we proposed a novel MMAE based LKAS system that leverages two computer vision-based models with distinctive features for lane detection using the front camera images. These two models were investigated in several case studies, and the diverse sources of failure were detected. A third model based on the rear camera with superior lane detection accuracy and reliability was used as a reference model for the two front camera-based CV models. The proposed MMAE based algorithm estimated the conditional probabilities of each model and selected the correct model for the best possible lane detection performance. The lane offset value from the selected model was then used as the input error for the PID controller to control the steering angle in the AirSim simulation environment. The simulation results show that the proposed MMAE-based LKAS system performed better than each of the base models. Overall, the results for all case studies show that the proposed algorithm performed robustly in correctly estimating the lane offset and was able to improve lane detection in sharp turns, lanes with missing lane markers, wet road, and streets with high contrast shadows. A comparison of results with other studies that used sensor fusion for enhancements showed that the proposed MMAE-based algorithm can improve the accuracy and robustness of the lane detection system to the level similar to or better than these sensor fusion-based algorithms.
In this research, comprehensive road/environmental conditions in AirSim simulation environment were not made. Hence, the inclusion of additional CV models that deal with more comprehensive scenarios would enhance the MMAE LKAS performance in future studies. Additionally, the PID controller could be replaced with an MPC based controller to provide improved lane keeping performance. Furthermore, it could be worth investigating an RNN to develop a prediction-based model for detecting the center line in case of failure in the observers.
Also, this work is a proof-of-concept for the proposed MMAE-based lane detection algorithm which was validated using computer simulation. It is highly desirable to implement the proposed algorithm in a real vehicle and perform validation testing under different road/environmental/lighting conditions. It should be noted that the proposed LKAS would fail when both lane detection algorithms included in the MMAE framework fail to estimate lane offset simultaneously. This would be a case of multi-point failure (as opposed to single point failure which is a common assumption in fault tolerant control literature) which is less likely to occur. As future work, the proposed MMAE based framework can be further enhanced by including several other models that would work in conjunction with the two models considered here and thus would significantly reduce the chances of simultaneous failure, thus improving overall lane detection reliability and accuracy. In addition, the full framework can be designed uncertainty aware such that when all models fail to attain a reasonable reliability, the detection system would send a fault code to the control system.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
IF: Methodology, Software, Investigation, Validation, Writing–original draft. SA: Conceptualization, Supervision, Resources, Funding acquisition, Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author IF was employed by MicroVision, Inc.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Al Noman, M. A., Zhai, L., Almukhtar, F. H., Rahaman, M. F., Omarov, B., Ray, S., et al. (2023). A computer vision-based lane detection technique using gradient threshold and hue-lightness-saturation value for an autonomous vehicle. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 13 (1), 347. doi:10.11591/ijece.v13i1.pp347-357
Barrios, C., Himberg, H., Motai, Y., and Sadek, A. (2006). Multiple model framework of adaptive extended Kalman filtering for predicting vehicle location. 2006 IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Conf., 1053–1059. doi:10.1109/itsc.2006.1707361
Bisht, S., Sukumar, N., and Sumathi, P. (2022). Integration of Hough transform and inter-frame clustering for road lane detection and tracking. 2022 IEEE Int. Instrum. Meas. Technol. Conf. (I2MTC), 1–6. doi:10.1109/i2mtc48687.2022.9806621
Dahl, J., De Campos, G., and Fredriksson, J. (2023). Prediction-uncertainty-aware threat detection for ADAS: a case study on lane-keeping assistance. IEEE Trans. Intelligent Veh. 8, 2914–2925. doi:10.1109/tiv.2023.3253555
Deng, L., Liu, X., Jiang, M., Li, Z., Ma, J., and Li, H. (2023). Lane detection based on adaptive cross-scale region of interest fusion. Electronics 12 (24), 4911. doi:10.3390/electronics12244911
Fakhari, I. (2023). imanf94/LaneDetection-MMAE: lane keeping and lane detection algorithm based on multiple model adaptive estimation of different computer vision models. Available at: https://github.com/imanf94/LaneDetection-MMAE (Accessed August 29, 2024).
Gaskey, O. (2023). OanaGaskey/advanced-lane-detection: computer vision algorithm to compute road curvature and lane vehicle offset using OpenCV image processing, camera calibration, perspective transform, color masks, sobels and polynomial fit. Available at: https://github.com/OanaGaskey/Advanced-Lane-Detection (Accessed: August 29, 2024).
Hamilton, F., Berry, T., and Sauer, T. (2016). Ensemble Kalman filtering without a model. Phys. Rev. X 6 (1), 011021. doi:10.1103/physrevx.6.011021
Haque, M. R., Islam, M. M., Alam, K. S., Iqbal, H., and Shaik, M. E. (2019). A computer vision based lane detection approach. Int. J. Image, Graph. Signal Process. 10 (3), 27.
Kim, M., Seo, J., Lee, M., and Choi, J. (2021). Vision-based uncertainty-aware lane keeping strategy using deep reinforcement learning. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 143 (8), 084503. doi:10.1115/1.4050396
Li, C., Dai, B., Wang, R., Fang, Y., Yuan, X., and Wu, T. (2016). Multi-lane detection based on omnidirectional camera using anisotropic steerable filters. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 10 (5), 298–307. doi:10.1049/iet-its.2015.0144
Li, J., Mei, X., Prokhorov, D., and Tao, D. (2016). Deep neural network for structural prediction and lane detection in traffic scene. IEEE Trans. neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28 (3), 690–703. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2016.2522428
Li, Y., Zhang, W., Ji, X., Ren, C., and Wu, J. (2019). Research on lane a compensation method based on multi-sensor fusion. Sensors 19 (7), 1584. doi:10.3390/s19071584
Liu, J. F., Wu, J. H., and Su, Y. F. (2007). Development of an interactive lane keeping control system for vehicle. 2007 IEEE Veh. power Propuls. Conf., 702–706. doi:10.1109/vppc.2007.4544214
Maddiralla, V., and Subramanian, S. (2024). Effective lane detection on complex roads with convolutional attention mechanism in autonomous vehicles. Sci. Rep. 14, 19193. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-70116-z
Muril, M. J., Aziz, N. H. A., Ghani, H. A., and Ab Aziz, N. A. (2020). A review on deep learning and nondeep learning approach for lane detection system. 2020 IEEE 8th Conf. Syst. Process Control (ICSPC), 162–166. doi:10.1109/icspc50992.2020.9305788
Ozgunalp, U. (2017). Combination of the symmetrical local threshold and the sobel edge detector for lane feature extraction. 2017 9th Int. Conf. Comput. Intell. Commun. Netw. (CICN), 24–28. doi:10.1109/cicn.2017.8319349
Pagale, M., Mulik, S., Purohit, R., Thakare, A., Hanchate, R., and Jadhav, S. (2023). Design and implementation of lane detection using Hough transformation. 2023 2nd Int. Conf. Appl. Artif. Intell. Comput. (ICAAIC), 927–932. doi:10.1109/icaaic56838.2023.10141315
Quinlan, M. J., and Middleton, R. H. (2010). Multiple model kalman filters: a localization technique for robocup soccer. RoboCup 2009 Robot. Soccer World Cup XIII 13, 276–287. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-11876-0_24
Rahman, M. A., Anwar, S., and Izadian, A. (2017). Electrochemical model-based condition monitoring via experimentally identified li-ion battery model and HPPC. Energies 10 (9), 1266. doi:10.3390/en10091266
Sang, I.-C., and Norris, W. R. (2024). A robust lane detection algorithm adaptable to challenging weather conditions. IEEE Access 12, 11185–11195. doi:10.1109/access.2024.3354975
Shah, S., Dey, D., Lovett, C., and Kapoor, A. (2018). Airsim: high-fidelity visual and physical simulation for autonomous vehicles. Field Serv. Robotics Results 11th Int. Conf., 621–635. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-67361-5_40
Sultana, S., Ahmed, B., Paul, M., Islam, M. R., and Ahmad, S. (2023). Vision-based robust lane detection and tracking in challenging conditions. IEEE Access 11, 67938–67955. doi:10.1109/access.2023.3292128
Xiong, H., Yu, D., Liu, J., Huang, H., Xu, Q., Wang, J., et al. (2020). Fast and robust approaches for lane detection using multi-camera fusion in complex scenes. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 14 (12), 1582–1593. doi:10.1049/iet-its.2019.0399
Ye, H., Kang, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, W., and Zhang, X. (2024). PortLaneNet: a scene-aware model for robust lane detection in container terminal environments. World Electr. Veh. J. 15 (5), 176. doi:10.3390/wevj15050176
Zakaria, N. J., Shapiai, M. I., Ghani, R. A., Yasin, M. N. M., Ibrahim, M. Z., and Wahid, N. (2023). Lane detection in autonomous vehicles: a systematic review. IEEE Access 11, 3729–3765. doi:10.1109/access.2023.3234442
Zhang, G., Zheng, N., Cui, C., Yan, Y., and Yuan, Z. (2009). An efficient road detection method in noisy urban environment. 2009 IEEE Intell. Veh. Symp., 556–561. doi:10.1109/ivs.2009.5164338
Keywords: lane-keeping assist systems (LKAS), computer vision (CV), Kalman filter, multiple model adaptive estimation (MMAE), lane detection (LD)
Citation: Fakhari I and Anwar S (2025) Computer vision model based robust lane detection using multiple model adaptive estimation methodology. Front. Mech. Eng. 11:1436338. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2025.1436338
Received: 21 May 2024; Accepted: 15 January 2025;
Published: 18 February 2025.
Edited by:
Mohamed Arezki Mellal, University of Boumerdés, AlgeriaReviewed by:
Wei Feng, Panzhihua University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Fakhari and Anwar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sohel Anwar, c2Fud2FyQHB1cmR1ZS5lZHU=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.