- 1Department of Fundamental Sciences and Techniques of Engineer, Chemical Engineering and Mineral Industries School, University of Ngaoundere, Ngaoundere, Cameroon
- 2Mechanics, Materials and Photonics Laboratory, National School of Agro-Industrial Sciences, University of Ngaoundere, Ngaoundere, Cameroon
- 3Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University of Ngaoundere, Ngaoundere, Cameroon
- 4Laboratory of Energy, Materials, Modeling and Methods, National Higher Polytechnic School of Douala, University of Douala, Douala, Cameroon
This article examines the residual reliability of composite materials, focusing on reinforced concrete subjected to buckling and post-buckling tests, a crucial topic in civil engineering. The main aim of the study is to assess how these loads affect mechanical properties, including compressive strength and elongation at break, while identifying associated failure mechanisms. A rigorous methodology was adopted, involving experimental tests on reinforced concrete samples, followed by microscopic analysis and comparison with literature data. The results reveal a significant decrease in compressive strength and modulus of elasticity with increasing loads and loading cycles. In addition, the study highlights a reduction in elongation at break, indicating a loss of ductility and stiffness of the material. Failure mechanisms observed include cracking and delamination, suggesting that the residual reliability of reinforced concrete is inferior to that of advanced composites. These findings underline the importance of appropriate design to ensure the durability of reinforced concrete structures, taking into account the impact of extreme loads and environmental conditions. This research contributes to a better understanding of the behavior of composite materials under critical conditions, providing recommendations for improving design and construction practices in civil engineering.
1 Context and importance of studying composite materials subjected to buckling and post-buckling tests
Composite materials, particularly reinforced concrete, play a crucial role in modern construction due to their superior mechanical properties, including high compressive and flexural strength, as well as durability against environmental conditions (Chawla, 2012). These materials typically consist of a matrix, often cement-based, and a reinforcement, usually steel, which together create a material exhibiting performance far superior to that of its individual components (Mehta and Monteiro, 2006; Neville, 2011).
However, under compressive loads, these composite materials may be subjected to buckling and post-buckling phenomena. Buckling occurs when the applied load exceeds a certain limit, leading to lateral deformation that can cause structural failure (Timoshenko and Gere, 2012; Ali et al., 2021; He et al., 2023; Mirzanamadi et al., 2024). Post-buckling, on the other hand, refers to the behavior of materials after they have reached their critical load, where further degradation may occur, severely affecting the load-bearing capacity of structures (Beznea and Chirica, 2011; Kachooee and Kafi, 2018; Wu et al., 2023; Mahdy et al., 2024).
The study of the residual reliability of these materials after buckling tests is essential to ensure structural safety. Reinforced concrete structures, often subjected to variable loads, must be able to withstand not only static loads but also dynamic loads due to environmental events such as earthquakes, high winds, or even accidental impacts (Yoo and Lee, 2011). In this sense, a thorough assessment of material reliability post-buckling can provide valuable insights into their long-term performance (Van Den Akker et al., 2020; Yue et al., 2022; Afzali, 2023).
Moreover, construction regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, imposing high demands for durability and safety (Standard, 2011). This makes it imperative to understand how composite materials react under extreme conditions to ensure that structures meet safety standards while remaining economically viable (Baley et al., 2024). Residual reliability, which evaluates a material’s ability to retain its properties after sustaining damage, is therefore a crucial area of research in modern structural engineering.
2 Synthesis of existing work on the reliability of composite materials under buckling and post-buckling loading
The study of composite materials under buckling and post-buckling loading is essential for ensuring safety and performance in various applications, including aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering (Ibrahim, 2015; Qiu et al., 2019; Kashani et al., 2013; Siddika et al., 2020; Gkournelos et al., 2021). Understanding the mechanisms of buckling, followed by analyzing post-buckling behavior, is crucial for designing reliable structures (Yoo and Lee, 2011).
2.1 Theoretical models of buckling
Buckling is a critical phenomenon that occurs when slender structures, such as columns, are subjected to compressive loads (Kubiak, 2013; Kołakowski and Teter, 2016; Emam and Lacarbonara, 2022; Atashipour et al., 2023). The initial concepts were established by Yoa and Pfeiffer (1983), who formulated the basic principles of column behavior under compression. The Euler equation for the critical buckling load is expressed as Equation 1:
where
2.2 Behavior of composite materials under buckling
Composite materials exhibit complex behavior under buckling due to their anisotropy. Tsai (2018) developed specific models to predict the buckling load of composites, considering fiber orientation and directional mechanical properties. This approach has been complemented by further work, such as that of Almeida et al. (2019) and Saiki (2024), who analyzed the effect of different fiber configurations.
2.3 Influence of defects on buckling
Salari-Sharif et al. (2018) examined the impact of manufacturing defects on buckling resistance. They showed that even small imperfections can significantly reduce the critical load (Little, 2003; Standard, 2005; Zio, 2016; Modarres and Groth, 2023). Integrating these defects into mechanical behavior models is essential for improving the accuracy of predictions. The effect of defects can be modeled by Equation 2.
Where
2.4 Post-buckling behavior
After critical loading, the behavior of composite materials evolves into a post-buckling phase. Vasiliev and Morozov (2013) studied this phase, indicating that load-bearing capacity can decrease non-linearly with increasing strain. The relationship between applied load
Where
2.5 Experimental and numerical approaches
Experimental work by Vasiliev and Morozov (2013) revealed that carbon/epoxy composites can suffer significant mechanical property losses of up to 40% after exposure to critical loads. These results underline the importance of assessing the residual reliability of composites after buckling. Residual load after buckling can be modeled by Equation 4.
Where PresidualPresidual is the residual load and
Advances in numerical methods, such as the finite element method (FEM), have also enabled the modeling of the behavior of composites under buckling and post-buckling with increased accuracy (Xu et al., 2013; Masood et al., 2021; Yıldırım and Ünal, 2024). Watt et al. (2006) incorporated environmental factors into their simulations, showing that conditions such as humidity and temperature can exacerbate the risk of buckling (Watt et al., 2006; Lal et al., 2011; Jaroszweski et al., 2019; Li et al., 2024).
2.6 Importance of residual reliability
The assessment of residual reliability has become a priority in the design of composite structures. Gioncu and Mazzolani (2013) emphasized that understanding failure mechanisms is essential for ensuring the durability of structures. Building codes also require more rigorous safety analyses to ensure that structures can withstand critical loads while maintaining their integrity (Standard, 2006; Neville, 2011; Arya, 2022).
In conclusion, the literature on buckling and post-buckling of composite materials has evolved significantly. Research has progressed from theoretical models to modern experimental and numerical approaches, allowing for a deeper understanding of failure mechanisms and residual reliability (Chawla, 2012; Gibson, 2007; Mehta and Monteiro, 2006; Neville, 2011). This knowledge is crucial for ensuring the performance and safety of composite structures under critical conditions (Bae et al., 2005; Lopes et al., 2012; Afzal et al., 2020). The reliability of composite materials, especially under critical loads, remains an active and essential research area for the development of safe and sustainable infrastructures (Hansen et al., 2011; Chawla, 2012).
3 Identification of gaps in current knowledge
Although extensive research has been conducted on the buckling and post-buckling of composite materials, several gaps remain, particularly concerning the assessment of residual reliability under critical loading conditions (Malhotra and Carino, 2003; Gjørv, 2011; Nojavan et al., 2017; Afzal et al., 2020). These studies indicate that while significant progress has been made in understanding the mechanical properties of composites, the evaluation of their performance after experiencing extreme loads is still insufficiently addressed.
3.1 Assessment of residual reliability
Residual reliability refers to a material’s ability to retain its performance after experiencing extreme loads or damage. According to Wu et al. (2019) and Podolak et al. (2021), while composite materials have been widely studied, little effort has been devoted to understanding their post-buckling behavior in terms of residual reliability. Most studies focus on initial mechanical properties and critical load, often neglecting the analysis of long-term performance after buckling events.
3.2 Lack of data on traditional materials
Another overlooked aspect is research on traditional composite materials, such as reinforced concrete. Mallick (2007) and Chawla (2012) highlight that most work concentrates on advanced composites, like carbon/epoxy composites, leaving aside materials that are widely used in construction. This creates an urgent need for specific research on the behavior of reinforced concrete under buckling and post-buckling, considering its unique characteristics such as ductility and compressive strength.
Bamboo-reinforced composite concrete is emerging as a promising alternative in modern construction, offering advantages in terms of durability, lightness and strength. Recent studies, such as that presented by Sreadha and Pany (2020), Sreadha and Pany (2021), highlight the superior mechanical performance of this material, as well as its potential for reducing the environmental impact of construction. This research opens up new avenues for the integration of composite materials in a variety of structural applications.
3.3 Modeling and simulation
Numerical modeling of buckling and post-buckling phenomena is also an area with existing gaps. While advanced models have been developed for specific composites, few studies have been conducted to incorporate environmental factors and manufacturing defects into the modeling of reinforced concrete. It is crucial to develop models that account for these factors to improve the accuracy of behavior predictions.
3.4 Standards and regulations
Current building codes emphasize durability and safety but often lack specific guidelines for assessing the residual reliability of composite materials under buckling. Gioncu and Mazzolani (2013) indicate that safety requirements should include buckling and post-buckling analyses, yet few standards provide clear procedures for this.
In summary, the gaps in current knowledge regarding the residual reliability of composite materials, particularly reinforced concrete, highlight the need for thorough research in this area. Special attention should be given to post-buckling assessment, integration of experimental data, and improvement of simulation models to develop more robust and accurate safety standards.
4 Methodology
4.1 Description of specimens used for testing
For this study, reinforced concrete specimens were designed and manufactured following rigorous construction standards. The concrete mix was composed of cement, aggregates, water, and additives to enhance mechanical properties and durability. The water-cement ratio was carefully controlled to ensure the desired strength.
The concrete was prepared with a water-cement ratio of 0.45, using 400 kg cement, 800 kg fine aggregate and 1,200 kg coarse aggregate per cubic meter.
The materials were mixed for 5 min in a concrete mixer, followed by vibration for 15 min to eliminate air bubbles.
The reinforcing bars used in the specimens have a diameter of 12 mm. These steel bars are essential for strengthening the concrete against tensile forces and bending moments.
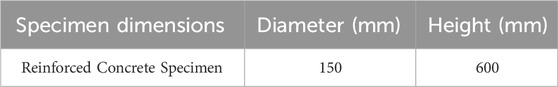
A total of 50 cylindrical specimens were prepared, each with a diameter of 150 mm and a height of 600 mm. These dimensions were chosen to ensure representative behavior under buckling conditions, as presented in Table 1.
The manufacturing process of the specimens followed these steps:
1. Mold Preparation: Steel molds were used to ensure precise dimensions.
2. Concrete Mixing: The components of the concrete were mixed according to a specific ratio, ensuring a uniform consistency.
3. Pouring: The concrete was poured into the molds and then vibrated to eliminate air bubbles and ensure proper compaction.
4. Curing: The specimens were kept under controlled conditions for 28 days to achieve maximum strength.
The prepared specimens were then subjected to buckling tests. The results were recorded to evaluate the critical load at which each specimen failed, as well as to analyze post-buckling behavior.
Figure 1 illustrates a reinforced concrete specimen prepared for the buckling tests.
The selected materials and specimens will provide reliable data on the behavior of reinforced concrete under buckling and post-buckling, which is essential for assessing its residual reliability.
5 Experimental protocols for buckling and post-buckling tests
5.1 Equipment used
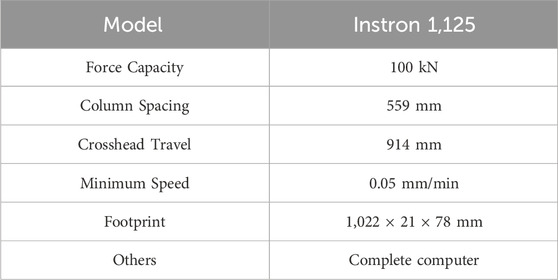
Compression tests on the specimens were conducted at ambient temperature and pressure, using an Instron universal compression/bending machine (available at the Mechanical Engineering laboratory of the University Institute of Technology, University of Ngaoundéré, Cameroon) (Figure 2), at a speed of 2 mm/min. The technical specifications of the compression machine are provided in Table 2.
5.2 Buckling test protocol
5.2.1 Preparation of specimens
Before the tests begin, each reinforced concrete specimen undergoes a thorough inspection to detect any visible defects, such as cracks or surface irregularities. These defects can alter the test results and compromise the integrity of the data.
The specimens are then classified based on the types of concrete used, such as ordinary concrete (C25/30) or high-performance concrete (C40/50), each having specific mechanical properties. For example, C40/50 concrete exhibits higher compressive strength, which is crucial for buckling tests.
Regarding steel, different grades of steel bars (e.g., S235, S355) are used as reinforcement. The mechanical properties of the steel, such as yield strength, tensile strength, and ductility, are also documented. For example, S355 steel has a yield strength of approximately 355 MPa, which is essential for ensuring the performance of the specimen under load.
Each specimen is then weighed to establish a mass reference, allowing for quality control and homogeneity of the concrete used. This step is crucial, as variations in mass can indicate issues with the mixing or implementation of the concrete.
Challenges encountered:
• Homogeneity of the Mix: Ensuring a homogeneous mix of concrete and steel is often a challenge. Variations in the distribution of aggregates or air bubbles can affect the final strength of the specimens.
• Control of Deformations: During preparation and curing, the concrete may undergo deformations due to environmental conditions (temperature, humidity), complicating the attainment of specimens that meet specifications.
• Alignment of Reinforcements: Proper alignment of the steel bars in the mold is crucial. Incorrect positioning can lead to unpredictable buckling points during tests.
• Securing Precautions: The specimens must be properly secured to prevent any movement or displacement during curing, which could compromise their integrity.
After preparation, the specimens are subjected to buckling tests, where it is essential to monitor not only the compressive strength but also the post-buckling behavior to better understand their residual reliability.
5.2.2 Test setup
The specimens are placed vertically in the compression machine, ensuring correct alignment to avoid non-uniform buckling effects. Shims may be used to ensure that the specimens are perfectly vertical. Strain sensors, such as extensometers, are installed at several points on the specimen to measure lateral and axial displacements during load application.
The general diagram illustrating the measurement mechanism is shown in Figure 3.
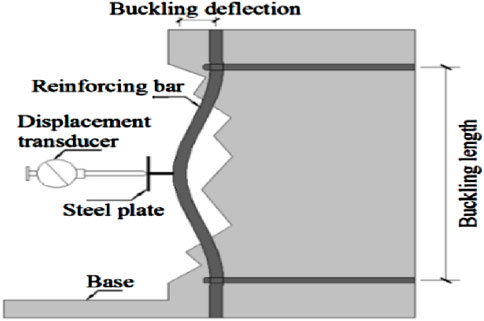
Figure 3. Mechanism for measuring lateral and axial displacements during load application (Yang et al., 2020).
5.2.3 Application of loads
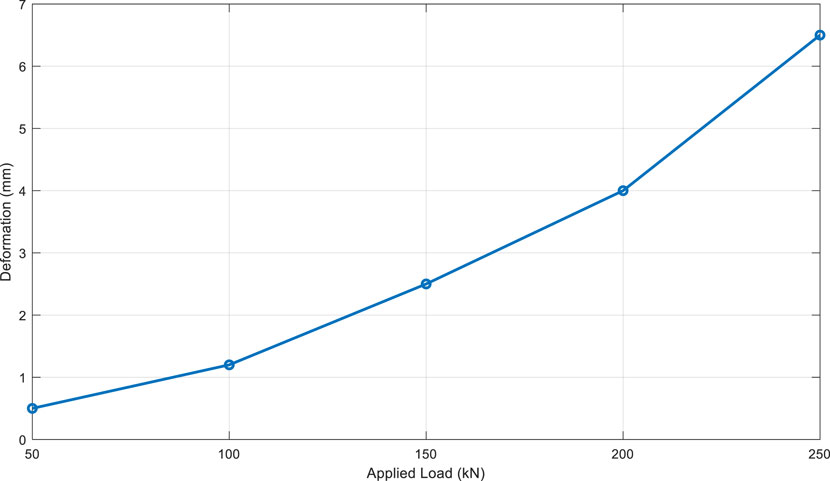
The compressive load is applied gradually. The rate of application is generally set at 1 MPa per minute to minimize the impact of dynamic loads and ensure that the material’s behavior is well observed. Continuous recordings of the applied loads and measured deformations are made during this phase. This allows for the plotting of the load-deformation curve, which is essential for subsequent analysis.
5.2.4 Evaluation criteria
Buckling is identified when the lateral deformation of the specimen exceeds a critical threshold. This threshold can be determined by theoretical calculation methods or preliminary tests. Visual observation is also used to detect any noticeable deviation from the specimen’s axis. At this stage, the maximum load to which the specimen was subjected is recorded, and the test is stopped to avoid further damage.
5.3 Post-buckling test protocol
5.3.1 Continuation of loading
After observing buckling, the protocol requires that loading continues to evaluate the post-buckling behavior of the specimen. This additional loading is applied until the deformation reaches a predefined value, typically set at 2.5%. This phase is crucial for understanding how the material reacts after buckling, as it provides information on the residual capacity of the specimen.
5.3.2 Monitoring and measurement
During this phase, the strain sensors continue to record the displacements of the specimen. Data is collected at regular intervals to analyze in detail the relationship between the applied load and the deformation. A video system may be used to capture the behavior of the specimen in real time, allowing for visual analysis of deformations and any cracks that may appear under increased loads.
5.3.3 Result analysis
The results obtained during the post-buckling test are essential for assessing the residual reliability of the material. The analysis focuses on the residual load that the specimen can support after buckling and the type of deformation observed. Comparisons can be made with the data obtained during the buckling test to determine the impact of buckling on the mechanical properties of reinforced concrete.
6 Methods for assessing residual reliability
The assessment of the residual reliability of reinforced concrete specimens after buckling and post-buckling tests relies on several analytical and experimental methods (Kashani et al., 2013; Bai et al., 2016; Yang et al., 2018; Huang et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2023; Martins et al., 2024). These methods allow for the characterization of the material’s mechanical properties and the identification of failure mechanisms.
6.1 Compressive strength
Compressive strength is one of the most fundamental measures for assessing the reliability of a material. It is determined by the standard test ASTM C39/C39M. The compressive strength
Where
6.2 Modulus of elasticity
The modulus of elasticity is a key measure of the stiffness of concrete. It is evaluated according to the ASTM C469/C469M standard. The modulus of elasticity
Where
6.3 Elongation at break
Elongation at break is an indicator of the ductility of concrete. This measurement is performed according to the ASTM C496/C496M standard. Elongation at break is calculated using Equation 7.
Where
6.4 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation
The use of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) allows for the examination of the microstructure of concrete after testing. This method provides detailed images that help identify cracks, delaminations, and other forms of degradation. SEM observations can reveal crucial information about damage mechanisms, such as Equation 8:
Where
6.5 Data analysis
The data collected during the tests are analyzed to identify trends and relationships between the various measured properties. Statistical techniques may be applied to assess the significance of the differences observed in mechanical properties before and after the tests.
7 Results and discussions
7.1 Experimental data obtained from buckling and post-buckling tests
7.1.1 Results of buckling and post-buckling tests
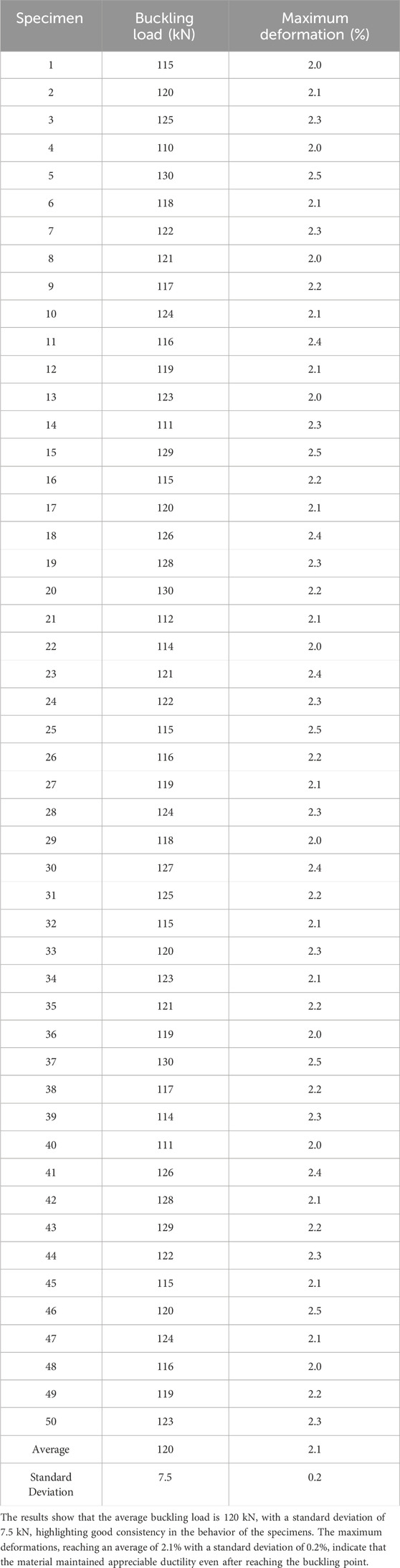
The results of the buckling and post-buckling tests provide essential information on the behavior of reinforced concrete specimens under extreme loads. The collected data is presented in Table 3, which summarizes the results for 50 specimens.
7.2 Analysis of results
The analysis of the results reveals that reinforced concrete presents a balanced combination of strength and ductility, which is essential for structural applications. The ability of the specimens to withstand an average buckling load of 120 kN, coupled with maximum deformations of 2.1%, demonstrates the material’s robust performance under extreme loads.
The standard deviation of 7.5 kN for the buckling load indicates homogeneity in the quality of the concrete, which is crucial for ensuring the reliability of structures. The observed variations in buckling loads are relatively low, suggesting that the concrete mix and manufacturing process were well controlled. This reinforces confidence in the use of reinforced concrete for critical constructions, where material consistency is paramount.
The measured ductility, with an average of 2.1%, is particularly significant. This property allows reinforced concrete to deform without rupture, which is crucial during events such as earthquakes or sudden loads. The ability to absorb such deformations contributes to the safety of structures by allowing energy dissipation before catastrophic failure.
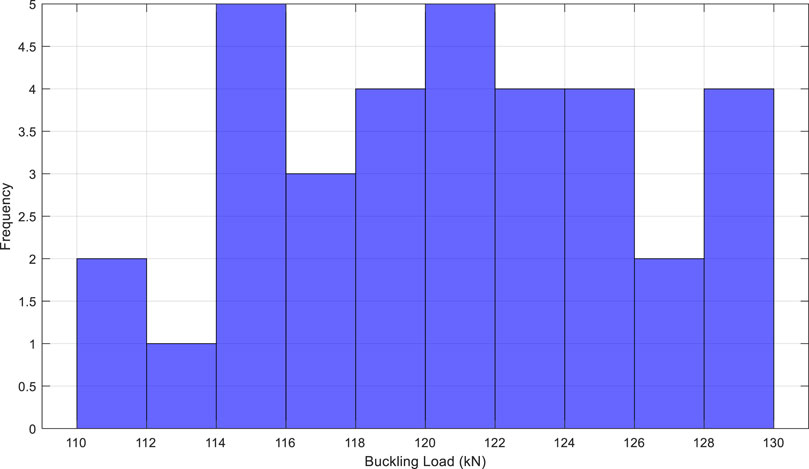
The analysis of the data shows that the majority of the specimens had buckling loads between 115 kN and 130 kN, as shown by the histogram in Figure 4.
This histogram reveals a normalized distribution, reinforcing the idea that the material is homogeneous and reliable. Such a distribution is desirable in practical applications, as it indicates that all specimens behave similarly under loads.
In conclusion, the results of the buckling and post-buckling tests indicate that reinforced concrete presents a good balance between strength and ductility, essential characteristics for ensuring the safety and durability of structures. These data provide a solid foundation for further studies and the development of recommendations for the use of reinforced concrete in critical structural applications.
8 Analyze the evolution of residual reliability based on different studied parameters
The analysis of the residual properties of reinforced concrete specimens revealed significant trends related to compressive strength, elastic modulus, and elongation at rupture. This section presents detailed results that illustrate the impact of applied load and the number of loading cycles.
8.1 Compressive strength
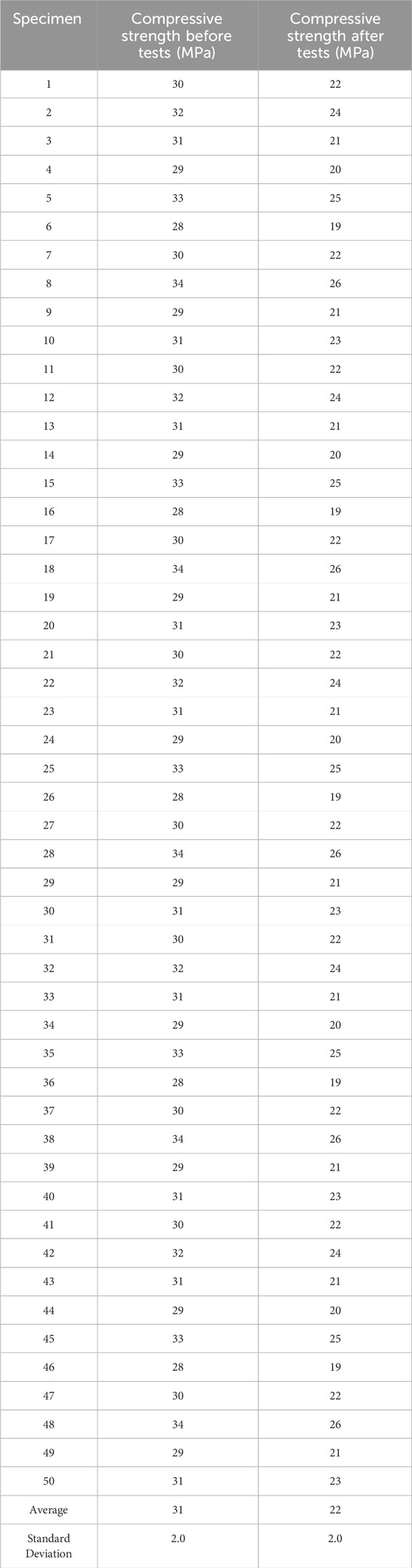
The results of the compressive strength tests are presented in Table 4. The measurements taken before and after the tests show a marked decrease in strength.
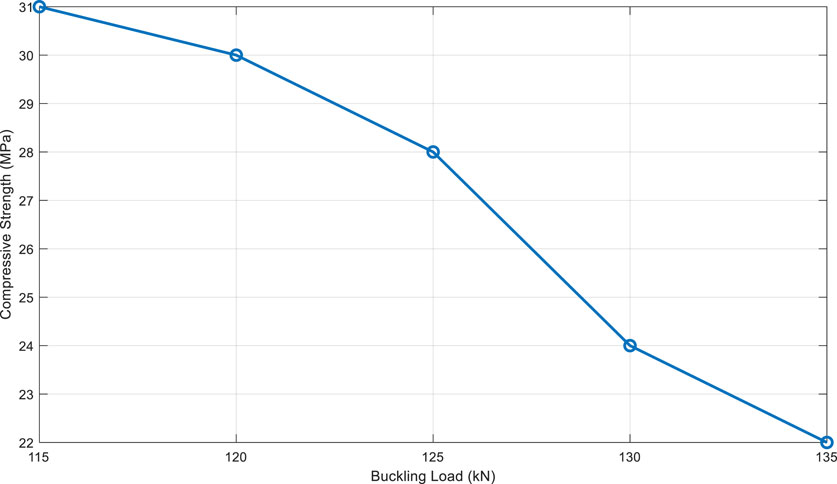
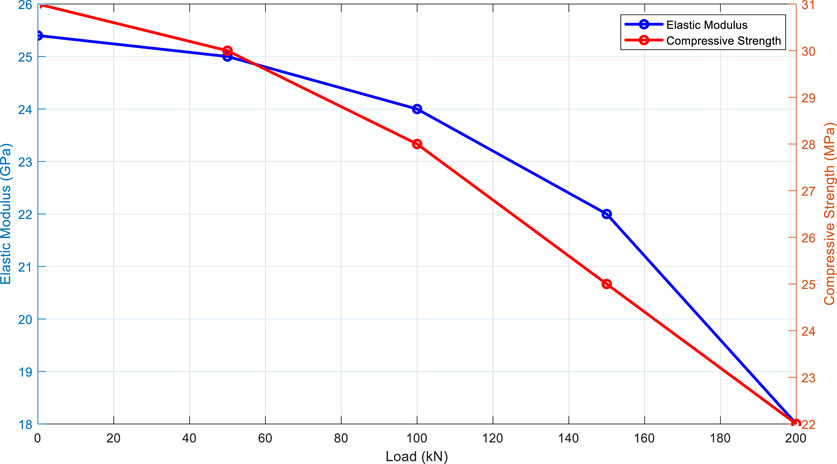
The average compressive strength decreased from 31 MPa to 22 MPa, representing a reduction of 29%. Specimens subjected to higher loads exhibited lower residual performance, as shown in Figure 5, which illustrates the relationship between buckling load and residual compressive strength.
This figure indicates that higher buckling loads result in lower residual strength, highlighting the impact of load levels on the material’s durability.
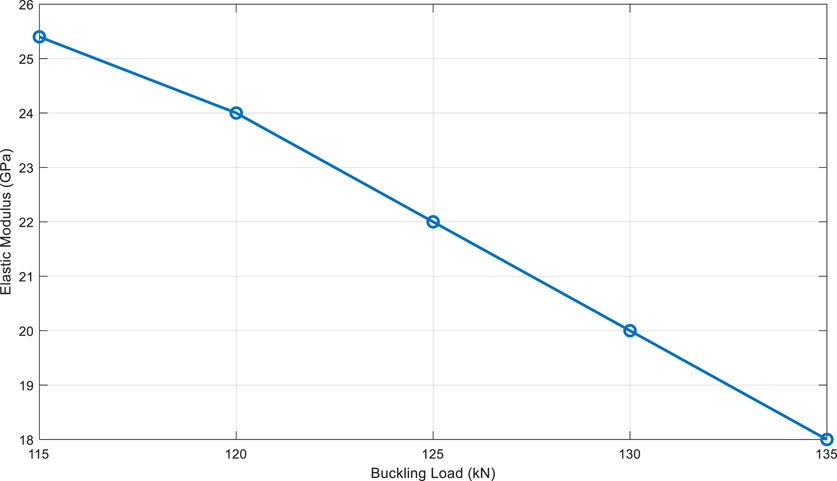
8.2 Elastic modulus
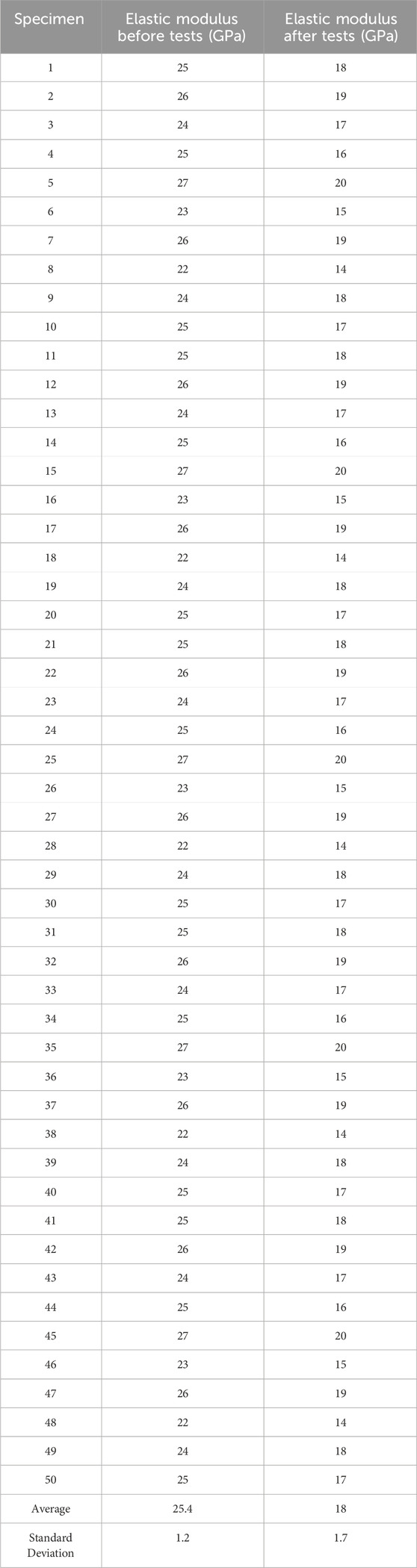
The results for the elastic modulus are presented in Table 5.
The elastic modulus decreased from 25.4 GPa to 18 GPa, representing a loss of 29%. As illustrated in Figure 6, this reduction is more pronounced for specimens that underwent higher buckling loads.
This figure shows that the elastic modulus decreases with increasing load, indicating a loss of material rigidity.
The durability of the material was evaluated through a series of mechanical tests designed to assess its performance under varying load conditions. Specifically, the compressive strength of the reinforced concrete samples was measured before and after applying incremental loads. By monitoring the changes in the elastic modulus during these tests, we were able to determine how the material’s rigidity and structural integrity were affected by the applied stress.
Additionally, fatigue tests were conducted, where the samples were subjected to repeated loading cycles to observe how they behaved over time. This approach allowed us to identify any signs of microcracking or permanent deformation, which are critical indicators of potential failure. Furthermore, microscopic analyses were performed to examine internal defects and the development of cracks within the material, providing insights into the mechanisms of degradation. Overall, these evaluations helped us understand the material’s resilience and its ability to maintain performance under stress, thus providing a comprehensive assessment of its durability.
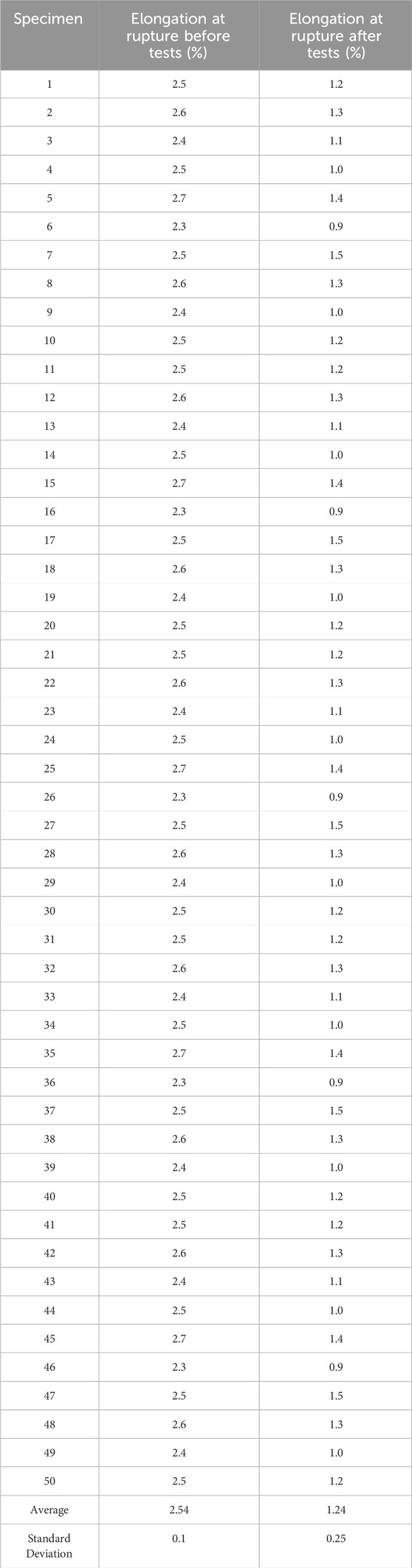
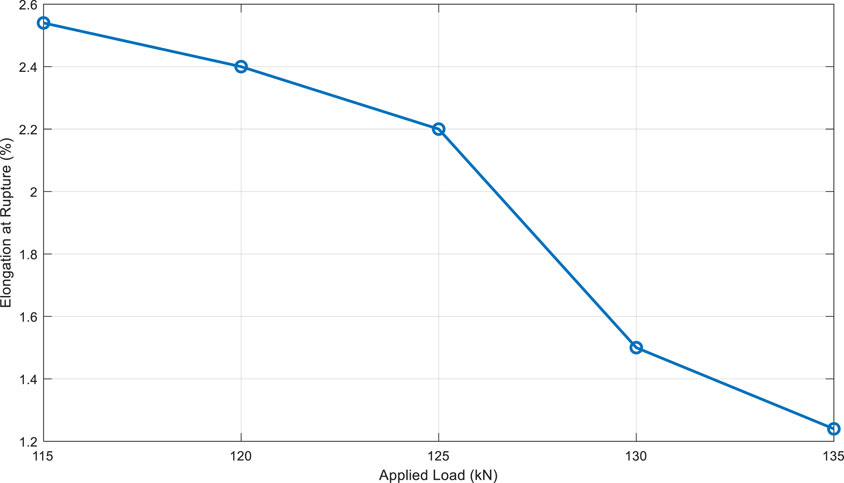
8.3 Elongation at rupture
The results regarding elongation at rupture are presented in Table 6.
Elongation at rupture decreased from 2.54% to 1.24%, representing a reduction of 51%. Figure 7 illustrates this trend, highlighting the relationship between applied load and elongation at rupture.
This figure shows that specimens subjected to higher loads exhibit lower elongation at rupture, indicating increased brittleness.
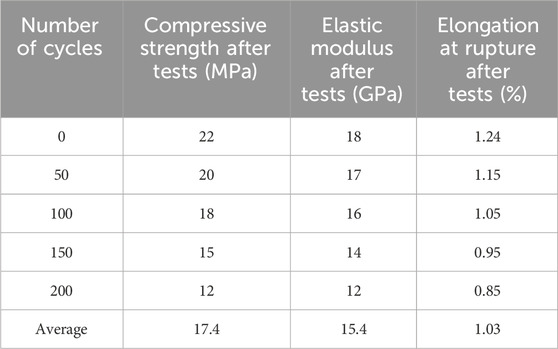
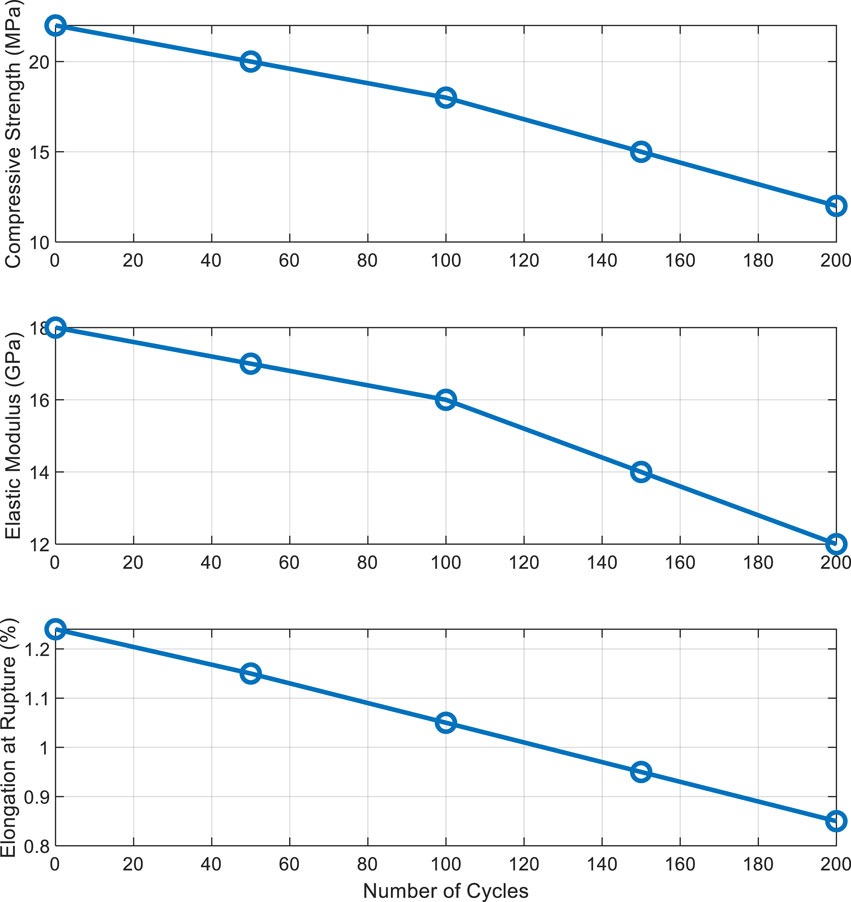
8.4 Impact of number of loading cycles
The impact of the number of loading cycles on residual properties was also examined. The results are presented in Table 7.
The data show a progressive reduction in compressive strength, elastic modulus, and elongation at rupture with the increase in the number of cycles. Figure 8 illustrates this trend.
This figure indicates that as the number of cycles increases, mechanical properties degrade, emphasizing the importance of fatigue in evaluating material reliability.
In conclusion, the results clearly demonstrate that the residual reliability of reinforced concrete is strongly influenced by the applied load and the number of loading cycles. The significant decrease in compressive strength, elastic modulus, and elongation at rupture highlights the necessity for thorough material evaluations to ensure durability in critical applications. These data will serve as a reference for future recommendations on the use of reinforced concrete in structures subjected to varying loads.
9 Physical mechanisms behind observed behaviors
The microscopic observations revealed that the primary damage mechanisms were concrete cracking, local buckling of the reinforcements, and debonding between the concrete and steel. These phenomena intensified with increasing load and the number of cycles, explaining the progressive decline in residual reliability.
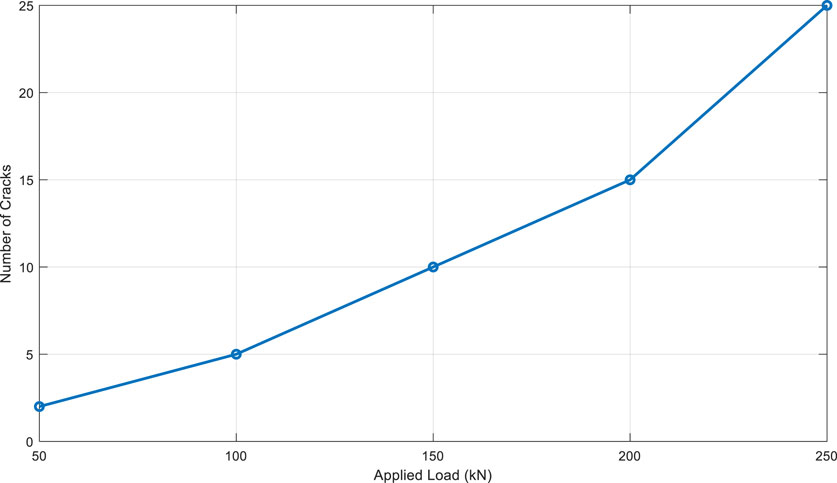
9.1 Concrete cracking
Concrete is inherently brittle, and when subjected to high compressive stresses, it tends to crack. As shown in Figure 9, the relationship between the applied load and the number of cracks formed indicates a significant increase in cracking with higher loads.
This figure illustrates that as the load increases beyond a certain threshold, the number of visible cracks in the concrete increases dramatically. This cracking contributes to a reduction in structural integrity, leading to lower compressive strength and elastic modulus, as seen in the results presented in Tables 4, 5.
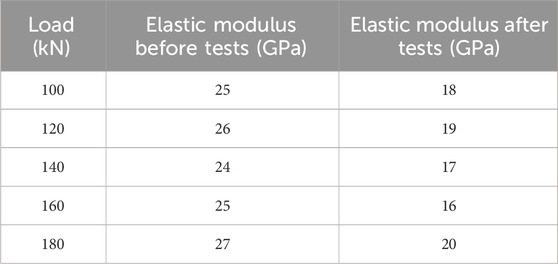
9.2 Local buckling of reinforcements
The local buckling of reinforcements occurs when the applied load exceeds the critical load that the reinforcement can withstand. Table 8 summarizes the impact of different loads on the elastic modulus of the specimens. As the buckling occurs, the effective load-carrying capacity of the reinforcement is diminished.
As shown in Table 8, the elastic modulus significantly decreases after testing under higher loads, indicating that local buckling has occurred. This reduction in elastic modulus correlates with a loss of stiffness, further contributing to the degradation of mechanical properties.
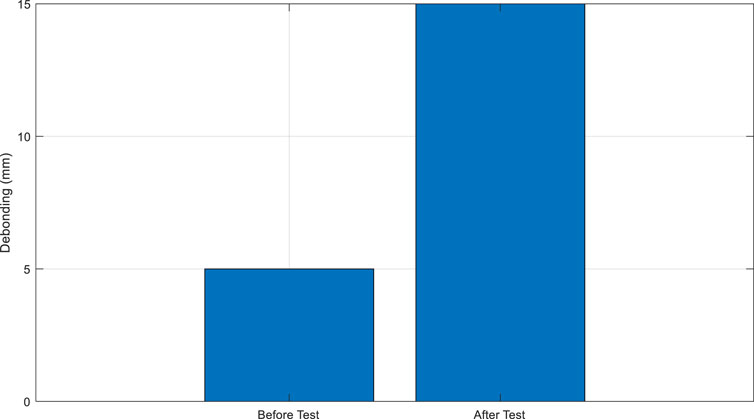
9.3 Debonding between concrete and steel
Debonding is another critical failure mechanism that occurs at the interface between concrete and steel reinforcement, often exacerbated by cyclic loading. Figure 10 illustrates the interface condition before and after cyclic loading.
The figure show noticeable deterioration of the bond, which leads to a reduction in the load transfer efficiency between the concrete and the steel reinforcements. This debonding can be particularly detrimental in structures subjected to dynamic loads, as it compromises the composite action intended in reinforced concrete systems.
9.4 Summary of observed behaviors
The cumulative effects of these mechanisms—cracking, buckling, and debonding—result in a significant decline in the residual reliability of the concrete specimens. Figure 11 provides a visual summary of the overall impact of various loading conditions on the mechanical properties of the specimens.
This figure summarizes the trends observed across different mechanical tests, highlighting the interrelationship between load levels, cycle counts, and the degradation of material properties.
In summary, the physical mechanisms underlying the observed behaviors in reinforced concrete under load include concrete cracking, local buckling of reinforcements, and debonding at the concrete-steel interface. These mechanisms not only explain the decline in mechanical properties, as shown in the tables and figures, but also emphasize the importance of understanding these processes for predicting the durability and reliability of concrete structures under varying loads. Continued research and monitoring are essential for developing strategies to mitigate these issues and enhance the performance of reinforced concrete in practical applications.
10 Comparison of results with literature data
The results obtained in this study reveal trends that are consistent with existing literature on the behavior of composite materials subjected to buckling and post-buckling loads. For instance, previous research by Yoo and Lee (2011) and Kashani et al. (2013) has documented similar degradation patterns in reinforced concrete when exposed to extreme loads. These studies reported reductions in compressive strength and modulus of elasticity that align with the findings of this study, thereby reinforcing the understanding of how cyclic loading impacts the mechanical properties of reinforced concrete.
However, this study provides crucial new data indicating that the absolute values of the residual properties of reinforced concrete are significantly lower than those documented for advanced composites, such as carbon or glass fiber composites. For instance, Vasiliev and Morozov (2013) observed that carbon/epoxy composites could retain a higher percentage of their load-bearing capacity after buckling, suggesting superior resilience compared to reinforced concrete.
This disparity underscores the heterogeneous and less performant nature of reinforced concrete, which is critical for engineering applications. While reinforced concrete is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and availability, these findings highlight the limitations of its mechanical properties under critical loading conditions. The identification of specific failure mechanisms, such as cracking and delamination, further contributes to this body of knowledge, as these mechanisms have been less frequently documented in previous studies.
In summary, the new data presented in this study not only confirm existing knowledge but also provide a more nuanced understanding of the performance limitations of reinforced concrete. This underscores the imperative for more rigorous design practices and further research into alternative materials or composite reinforcements that could enhance the durability and reliability of concrete structures under severe loading scenarios.
10.1 Comparison of mechanical properties
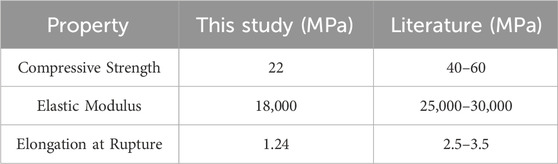
The measured mechanical properties, such as the elastic modulus and compressive strength, were evaluated from the experimental results. Table 9 presents a comparison of the average values obtained in this study with those found in the literature.
The values obtained in this study show that the compressive strength and elastic modulus of reinforced concrete are significantly lower than those of advanced composites. This can be attributed to the complex microstructure and inherent variability of concrete, which impact its performance under load.
Specifically, the irregular arrangement of aggregates and the bonding characteristics between the cement matrix and reinforcement lead to a less uniform stress distribution. Additionally, the presence of microcracks and voids in the concrete can initiate failure mechanisms under high loads, resulting in reduced strength and stiffness. Comparatively, advanced composites, such as carbon or glass fiber-reinforced materials, benefit from a more consistent microstructure and superior tensile strength, allowing them to maintain better mechanical properties under similar loading conditions. This disparity highlights the need for careful consideration of design and material selection in applications where high load-bearing capacity and durability are critical, emphasizing the importance of understanding the limitations of reinforced concrete in structural engineering.
10.2 Impact of buckling
Figure 12 illustrates the results of the buckling test, showing the relationship between the applied load and the deformation of the reinforced concrete samples.
This figure demonstrates that, unlike advanced composites that exhibit better resistance to buckling, the reinforced concrete samples show significant deformation at lower loads. This confirms observations in the literature regarding the vulnerability of reinforced concrete to buckling.
10.3 Analysis of residual properties
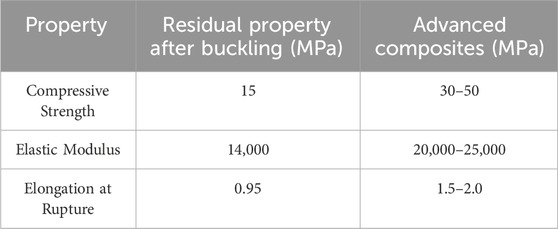
The residual properties of the samples after buckling tests were also evaluated. Table 10 presents the results of the residual properties compared to advanced composites.
The data indicate that the residual properties of reinforced concrete degrade more significantly after buckling compared to advanced composites, which retain a larger portion of their initial properties. This emphasizes the importance of material design in structural applications.
In conclusion, the results of this study align with trends observed in the literature, but the absolute properties of reinforced concrete remain inferior to those of advanced composites. These differences can be attributed to the heterogeneous and less performant nature of reinforced concrete, as well as its sensitivity to buckling and failure phenomena. A deep understanding of these mechanisms is essential for improving the performance of reinforced concrete in critical structural applications. Future research should focus on developing hybrid composite materials that could combine the advantages of concrete and advanced materials to enhance the reliability and durability of structures.
11 Conclusion and perspectives
11.1 Summary of main conclusions of the study
This study has provided valuable insights into the performance of reinforced concrete subjected to buckling and post-buckling loads, revealing critical findings regarding the degradation of its mechanical properties. The experimental tests demonstrated a significant decrease in compressive strength and modulus of elasticity as the applied loads and number of cycles increased. These findings are consistent with previous studies, such as those by Yoo and Lee (2011) and Kashani et al. (2013), which also reported similar degradation patterns under extreme loading conditions.
Microscopic observations identified key failure mechanisms, including cracking, local buckling of the reinforcement, and delamination between concrete and steel, all of which contribute to this degradation. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) observations provided crucial visual evidence of these damage mechanisms, as illustrated in Figure 13.
This image reveals the extent of cracks and delamination, underscoring the complex behavior of reinforced concrete under stress.
Overall, these results indicate that the residual reliability of reinforced concrete is lower than that of advanced composites, emphasizing the necessity for rigorous design practices to ensure the durability and safety of reinforced concrete structures under extreme loading conditions. This study contributes to a deeper understanding of the limitations of reinforced concrete and its behavior under complex stresses, aligning with the conclusions drawn in earlier research (e.g., Gioncu and Mazzolani, 2013).
11.2 Original contributions of the article
This article makes a significant contribution by offering detailed experimental data on the residual reliability of reinforced concrete under buckling and post-buckling tests—an area that has often been overlooked in the literature. By identifying specific failure mechanisms and contrasting the results with those of advanced composite materials, this study enhances our understanding of the inherent limitations of reinforced concrete. Additionally, it proposes a rigorous methodology for assessing residual reliability, which includes tailored experimental protocols and advanced analytical methods. This approach could serve as a benchmark for future research and encourage the development of more robust testing standards for composite materials. The findings also highlight the importance of a multidisciplinary approach that integrates knowledge from material science, mechanics, and structural engineering.
11.3 Future research perspectives
Future research should focus on innovative strategies to enhance the performance of reinforced concrete, such as the integration of hybrid composite materials that leverage the strengths of both concrete and advanced composites. Investigating the effects of various treatments and additives, including synthetic fibers or polymers, on the failure resistance and ductility of concrete would be particularly relevant. Furthermore, the development of new testing protocols that simulate realistic and diverse loading conditions—including thermal and environmental effects—could yield valuable insights into the long-term durability of structures.
Finally, a comprehensive investigation of fatigue mechanisms in reinforced concrete, taking into account the long-term impacts of repeated loading cycles, could facilitate the design of more durable and reliable structures. Addressing these contemporary challenges in civil engineering will be crucial for meeting evolving building codes and ensuring public safety.
12 List of terminologies
• Compressive strength before testing: The ability of a specimen to withstand compressive forces before testing
• Compressive strength after testing: The ability of a specimen to withstand compressive forces after testing
• Elastic modulus before testing: A measure of a material’s stiffness before any load is applied
• Elastic modulus after testing: A measure of a material’s stiffness after it has undergone testing
• Elongation at break before testing: The maximum deformation of a specimen before rupture, measured prior to testing
• Elongation at break after testing: The maximum deformation of a specimen before rupture, measured after testing
• Residual property after buckling: The mechanical characteristics of a material after it has experienced buckling
• Advanced composites: Composite materials with superior mechanical properties, used in demanding applications
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AN: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. UN: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing–original draft. FO: Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the reviewers for their time and effort. Their constructive comments and helpful suggestions helped me to clarify the research contributions of the main paper and to improve its quality.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
P, Applied Load (kN); E, Modulus of Elasticity (GPa); σ, Compressive Strength (MPa); δ, Deformation (%); α, Degradation coefficient.
References
Afzal, M., Liu, Y., Cheng, J. C., and Gan, V. J. (2020). Reinforced concrete structural design optimization: a critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 260, 120623. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120623
Afzali, M. (2023). Nonlinear numerical analysis of thermal buckling and post-buckling of rectangular FG plates with temperature-dependent properties using CUF.
Agarwal, B. D., Broutman, L. J., and Chandrashekhara, K. (2017). Analysis and performance of fiber composites. John Wiley and Sons.
Ali, Z. A., Kadhim, A. A., Al-Khayat, R. H., and Al-Waily, M. (2021). Review influence of loads upon delamination buckling in composite structures. J. Mech. Eng. Res. Dev. 44 (3), 392–406.
Almeida Jr, J. H. S., Bittrich, L., Jansen, E., Tita, V., and Spickenheuer, A. (2019). Buckling optimization of composite cylinders for axial compression: a design methodology considering a variable-axial fiber layout. Compos. Struct. 222, 110928. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.110928
Arya, C. (2022). Design of structural elements: concrete, steelwork, masonry and timber designs to eurocodes. Taylor & Francis Group. doi:10.1201/9781003208037
Atashipour, S. R., Challamel, N., and Girhammar, U. A. (2023). On buckling of layered composite heavy columns—effect of interlayer bonding imperfection. Int. J. Solids Struct. 260, 112030. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2022.112030
Bae, S., Mieses, A. M., and Bayrak, O. (2005). Inelastic buckling of reinforcing bars. J. Struct. Eng. 131 (2), 314–321. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2005)131:2(314)
Bai, Y., Lin, X., and Mou, B. (2016). Numerical modeling on post-local buckling behavior of circular and square concrete-filled steel tubular beam columns. Int. J. Steel Struct. 16, 531–546. doi:10.1007/s13296-016-6022-0
Baley, C., Davies, P., Troalen, W., Chamley, A., Dinham-Price, I., Marchandise, A., et al. (2024). Sustainable polymer composite marine structures: developments and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 145, 101307. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2024.101307
Beznea, E. F., and Chirica, I. (2011). “Buckling and post-buckling analysis of composite plates,” in Advances in composite mater. Ecodesign and Analysis, 383–408.
Chawla, K. K. (2012). Composite materials: science and engineering. Springer Science and Business Media.
Emam, S., and Lacarbonara, W. (2022). A review on buckling and postbuckling of thin elastic beams. Eur. J. Mechanics-A/Solids 92, 104449. doi:10.1016/j.euromechsol.2021.104449
Gibson, R. F. (2007). Principles of composite material mechanics. Taylor & Francis Group. doi:10.1201/9781420014242
Gjørv, O. E. (2011). Durability of concrete structures. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 36, 151–172. doi:10.1007/s13369-010-0033-5
Gkournelos, P. D., Triantafillou, T. C., and Bournas, D. A. (2021). Seismic upgrading of existing reinforced concrete buildings: a state-of-the-art review. Eng. Struct. 240, 112273. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112273
Hansen, L. O., Young, R. S., Hinami, K., Leung, A., and Williams, M. V. (2011). Interventions to reduce 30-day rehospitalization: a systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 155 (8), 520–528. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00008
He, L., Li, Z., Xie, Y., Liu, Y., and Liu, M. (2023). Buckling failure mechanism and critical buckling load prediction method of super-long piles in soft-clay ground in deep water. Ocean. Eng. 276, 114216. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114216
Huang, Z., Li, D., Uy, B., Thai, H. T., and Hou, C. (2019). Local and post-local buckling of fabricated high-strength steel and composite columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 154, 235–249. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.12.004
Ibrahim, R. A. (2015). Overview of structural life assessment and reliability, part i: basic ingredients of fracture mechanics. J. Ship Prod. Des. 31 (01), 1–42. doi:10.5957/jspd.2015.31.1.1
Jaroszweski, D., Fu, Q., and Easton, J. (2019). A data model for heat-related rail buckling: implications for operations, maintenance and long-term adaptation in Proceedings of the 12th world congress on railway research (Tokyo, Japan), 28.
Kachooee, A., and Kafi, M. A. (2018). A suggested method for improving post buckling behavior of concentric braces based on experimental and numerical studies. Structures 14, 333–347. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2018.04.003
Kashani, M. M., Crewe, A. J., and Alexander, N. A. (2013). Nonlinear stress–strain behaviour of corrosion-damaged reinforcing bars including inelastic buckling. Eng. Struct. 48, 417–429. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.09.034
Kołakowski, Z., and Teter, A. (2016). Coupled static and dynamic buckling modelling of thin-walled structures in elastic range review of selected problems. Acta Mech. Automatica 10 (2), 141–149. doi:10.1515/ama-2016-0023
Kubiak, T. (2013). Static and dynamic buckling of thin-walled plate structures. Heidelberg: Springer International Publishing, 27–47. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-00654-3
Lal, A., Singh, B. N., and Kale, S. (2011). Stochastic post buckling analysis of laminated composite cylindrical shell panel subjected to hygrothermomechanical loading. Compos. Struct. 93 (4), 1187–1200. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2010.11.005
Li, M., Dai, Q., Su, P., and You, Z. (2024). Buckling prediction based on joint opening and safe temperature estimation in jointed plain concrete pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 444, 137630. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.137630
Little, R. G. (2003). Toward more robust infrastructure: observations on improving the resilience and reliability of critical systems in 36th annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences. Proceedings of the IEEE (IEEE), 9. doi:10.1109/HICSS.2003.1173880
Lopes, A. V., Lopes, S. M., and do Carmo, R. N. (2012). Effects of the compressive reinforcement buckling on the ductility of RC beams in bending. Eng. Struct. 37, 14–23. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.12.038
Mahdy, W. M., Wang, L., Liu, F., and Zhao, L. (2024). The competition between buckling and stress failure of degraded composite cylindrical shell under combined axial compression and external pressure loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 199, 111731. doi:10.1016/j.tws.2024.111731
Malhotra, V. M., and Carino, N. J. (2003). Handbook on nondestructive testing of concrete. Taylor & Francis Group.
Mallick, P. K. (2007). Fiber-Reinforced Composites. Materials, manufacturing, and design. CRC Press. doi:10.1201/9781420005981
Martins, A. D., Teixeira, Â. P., Correia, J. R., Silvestre, N., and e Sá, M. F. (2024). Reliability-based code calibration of local buckling strength design of pultruded GFRP I-and H-section columns. Eng. Struct. 318, 118687. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.118687
Masood, S. N., Gaddikeri, K. M., and Viswamurthy, S. R. (2021). Experimental and finite element numerical studies on the post-buckling behavior of composite stiffened panels. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 28 (16), 1677–1690. doi:10.1080/15376494.2019.1701151
Mirzanamadi, R., Nyberg, E., Torstensson, P., and Andersson-Sköld, Y. (2024). Lateral track buckling in Sweden: insights from operators and infrastructure managers. Civil. Eng 5 (1), 136–149. doi:10.3390/civileng5010007
Modarres, M., and Groth, K. (2023). Reliability and risk analysis. CRC Press. doi:10.1201/9781003307495
Nojavan, A., Schultz, A. E., and Chao, S. H. (2017). Analytical study of in-plane buckling of longitudinal bars in reinforced concrete columns under extreme earthquake loading. Eng. Struct. 134, 48–60. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.12.003
Podolak, P., Droździel, M., Czapski, P., Kubiak, T., and Bieniaś, J. (2021). The failure mode variation in post-buckled GFRP columns with different stacking sequences-Experimental damage analysis and numerical prediction. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 210, 106747. doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106747
Qiu, D., Peng, L., Lai, X., Ni, M., and Lehnert, W. (2019). Mechanical failure and mitigation strategies for the membrane in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 113, 109289. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2019.109289
Saiki, L. E. D. C. (2024). On the impact of delamination on composite structures: comprehensive modal, static, and buckling analysis. Available at: https://repositorio.unifei.edu.br/jspui/handle/123456789/4117.
Salari-Sharif, L., Godfrey, S. W., Tootkaboni, M., and Valdevit, L. (2018). The effect of manufacturing defects on compressive strength of ultralight hollow microlattices: a data-driven study. Addit. Manuf. 19, 51–61. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2017.11.003
Siddika, A., Al Mamun, M. A., Ferdous, W., and Alyousef, R. (2020). Performances, challenges and opportunities in strengthening reinforced concrete structures by using FRPs–A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Fail. Anal. 111, 104480. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104480
Sreadha, A. R., and Pany, C. (2020). Review on fabrication of bamboo composite materials reinforced concrete. J. Sci. Technol. (JST) 5 (3), 258–279. doi:10.46243/jst.2020.v5.i3.pp258-279
Sreadha, A. R., and Pany, C. (2021). Static, free vibration and buckling analysis of composite panels; a review. Adv. J. Graduate Res. 9 (1), 21–45. doi:10.21467/ajgr.9.1.21-45
Standard, A. A. (2011). Building code requirements for structural concrete (ACI 318-11). American Concrete Institute.
Van Den Akker, B. P., Donadon, M. V., Loendersloot, R., de Oliveira, L. A., and Arbelo, M. A. (2020). The influence of hygrothermal aging on the fatigue behavior and residual strength of post-buckled co-bonded stiffened panels subjected to compressive loading. Compos. Part B Eng. 194, 108023. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108023
Vasiliev, V. V., and Morozov, E. V. (2013). Advanced mechanics of composite materials and structural elements. Newnes.
Watt, M. S., Moore, J. R., Facon, J. P., Downes, G. M., Clinton, P. W., Coker, G., et al. (2006). Modelling environmental variation in Young’s modulus for Pinus radiata and implications for determination of critical buckling height. Ann. Bot. 98 (4), 765–775. doi:10.1093/aob/mcl161
Wu, B., Pagani, A., Filippi, M., Chen, W. Q., and Carrera, E. (2019). Accurate stress fields of post-buckled laminated composite beams accounting for various kinematics. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 111, 60–71. doi:10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2019.02.002
Wu, Q., Hu, S., Tang, X., Liu, X., Chen, Z., and Xiong, J. (2023). Compressive buckling and post-buckling behaviors of J-type composite stiffened panel before and after impact load. Compos. Struct. 304, 116339. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116339
Xu, J., Zhao, Q., and Qiao, P. (2013). A critical review on buckling and post-buckling analysis of composite structures. Front. Aerosp. Eng. 2 (3), 157–168.
Yan, D., Pezzulla, M., and Reis, P. M. (2020). Buckling of pressurized spherical shells containing a through-thickness defect. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 138, 103923. doi:10.1016/j.jmps.2020.103923
Yang, C., Yu, Z. X., Sun, Y. P., Zhao, L., and Zhao, H. (2018). Axial residual capacity of circular concrete-filled steel tube stub columns considering local buckling. Adv. Steel Constr. 14 (3), 496–513. doi:10.18057/IJASC.2018.14.3.11
Yang, H., Sun, P., and Deng, Y. (2020). Experiment investigation of the influence of reinforcing bar buckling on seismic behavior of RC columns. Eng. Struct. 220, 110923. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2020.110923
Yao, G., Chen, Y., Yang, Y., Ma, X., and Men, W. (2023). Investigation on buckling performance of prefabricated light steel frame materials under the action of random defects during construction. Materials 16 (16), 5666. doi:10.3390/ma16165666
Yıldırım, E. G., and Ünal, R. (2024). A review on post–buckling behaviors of composites: crippling phenomenon. J. Aeronautics Space Technol. 17 (1), 1–28.
Yoa, C. H., and Pfeiffer, P. A. (1983). Elastic stability of curved members. J. Struct. Eng. 109 (12), 2922–2940. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1983)109:12(2922)
Yue, N., Broer, A., Briand, W., Rébillat, M., Loutas, T., and Zarouchas, D. (2022). Assessing stiffness degradation of stiffened composite panels in post-buckling compression-compression fatigue using guided waves. Compos. Struct. 293, 115751. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115751
Keywords: reinforced concrete, residual reliability, buckling, post-buckling, mechanical properties, failure, advanced composites, compressive strength
Citation: Ngnassi Djami AB, Nguelcheu UN and Offole F (2024) Residual reliability of a composite material subjected to buckling and post-buckling tests: the case of reinforced concrete. Front. Mech. Eng. 10:1526724. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1526724
Received: 12 November 2024; Accepted: 04 December 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Li Li, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Chitaranjan Pany, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, IndiaAman Garg, The Northcap University, India
Copyright © 2024 Ngnassi Djami, Nguelcheu and Offole. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Aslain Brisco Ngnassi Djami, bmduYXNzYnJpc0B5YWhvby5mcg==
 Aslain Brisco Ngnassi Djami
Aslain Brisco Ngnassi Djami Ulrich Ngnassi Nguelcheu3
Ulrich Ngnassi Nguelcheu3