- 1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Vel Tech Rangarajan Dr. Sagunthala R&D Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai, India
- 2School of Mechanical Engineering, Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
- 3Department of Machining, Assembly and Engineering Metrology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, VSB—Technical University of Ostrava, Ostrava, Czechia
- 4Department of Biosciences, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Chennai, India
- 5Department of Mechanical Engineering, Gazi University Faculty of Engineering, Ankara, Türkiye
- 6Department of Industrial Engineering, College of Engineering, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Friction drilling is an innovative method in hole-making for sheet metal applications, thin sheets of conventional structural alloy materials like copper, titanium, steel etc., even though there are other methods, such as thermal distortion for the welding of nuts, riveting of nuts, and threading. For the last hundred years, researchers have focused on studying the development of this technique to maintain strength, hole roughness, hole geometry, hardness etc. It is interested in finding solutions for wear, tool life, and plastic deformation.
Method: Friction drilling is also called a green hole-making process because this process uses the friction between the rotating tool and the workpiece. In this research, instead of regular HSS and Tungsten Carbide tools, the H13 tool steel is used, because the H13 steel tool has unique chemical compositions like chromium and molybdenum, which give high toughness, hot hardness, and wear resistance. Diamond-like-carbon (DLC) coating has been used in this research to enhance tool life and AZ31B magnesium alloy is used as the work material. Initially, in this research, the wear stability of the DLC-coated H13 tool was investigated, and later, the tool surface roughness and hole quality were verified.
Results and Discussion: The material loss observed for the DLC-coated H13 steel tool in the pin-on-disk test was 0.05 g. This investigation used two different diameter tools, namely 3 and 7 mm. Research has concluded that the 7 mm tool is better for friction drilling by seeing the roughness and hole quality. However, the conditions were that the spindle should rotate at 4,000 rpm and the feed rate of the tool to be at 200 mm/rev.
Introduction
The industries focused on reducing the weight of structures by using high-strength and lightweight materials, and the solution for the above issues was by decreasing the thickness of sheet metals (Eliseev and Kolubaev, 2021). Generally, for sheet metal joining, commonly used techniques are welding the nut, riveting the nut, and threading (Kumar and Jesudoss Hynes, 2019). The above three methods have disadvantages such as thermal distortion for the welding of nuts, twist, and jam during assembly for riveting nuts, and unreliable for threading. By comparison, researchers observed that the friction drilling method has many advantages, like secure hold (no twist), quick mounting, time, cost-saving, and increased safety. The solution for joining sheet metals is the friction drilling method, a non-traditional way of preparing holes in sheet metal (Albarbary et al., 2022; Alphonse et al., 2020a). The tool’s conical region pierces into the workpiece with the help of frictional heat generation caused by the combined force of higher spindle speed and feed rate (Kumar and Jesudoss Hynes, 2019). The excess material plunges through both sides of the material and is called bosh and bush. Bushing helps with threading and support; the bosh acts like a washer (Hynes et al., 2020; Raja and Rajasekaran, 2014). The following are the advantages of the friction drilling method bushing for thread formation: hardening of the bushing makes high thread strength, chipless process, environment-friendly, no lubrications are required, less roughness, and high-quality hole (Alphonse et al., 2020b; Alphonse et al., 2020c). The shape and height of the bushing depend on the spindle speed and feed rate (Dehghan et al., 2018). The researchers have continuously tried to choose appropriate process parameters (Rafi et al., 2010). Due to high-temperature involvement, researchers attempted to select suitable process parameters for improving the quality of holes (Deepak and Paulo Davim, 2019). The silent factors affecting the hole and bushing height quality are spindle speed, feed rate, tool material, and dimensions. Increases and decreases in parameters help improve the hole quality (Waleed et al., 2018). The literature shows that higher spindle speed and workpiece thickness affect surface roughness and bushing height. Higher spindle speed and lower feed rate will be acceptable for obtaining quality holes (El-Bahloul et al., 2015; Ozek and Demir, 2013). Friction drilling is a five-step process shown in Figure 1. Initially, the frictional force is generated into the work materials. The work material turns into a viscoelastic stage due to frictional force. In the first and second stages, the tool starts penetrating the work material. At the third and fourth stages, the work material softens, and the tool penetrates the material; the excess material forms as a bushing. In the last stage, the tool retracts, where bushing has formed two to three times the material thickness (Alphonse et al., 2020a; Alphonse et al., 2017).
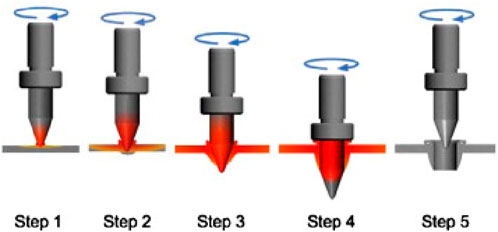
Figure 1. Friction drilling process (Özler, 2019).
In increasing the spindle speed, the hole quality and bushing height will increase. Preheating the work material with a range of 25°C to 300°C is an option for producing better quality holes and bushing height. The material gets softened, and the tool quickly plunges into the material to have a higher bushing height and good quality hole (Skovron et al., 2015). Another solution is predrilling; a 3 mm tool prepares the pre-hole for a 6 mm diameter hole. This technique also produces better-quality hole and bushing heights (Demir and Özek, 2014). Cracks and irregularities occurred in the bushing surfaces of a drilled hole, and these factors decreased with the help of predrilling (Su et al., 2018). Recent research shows that the H13 steel tool has unique properties like wear resistance and toughness. H13 steel tool enhances heat resistance because of its thermal conductivity (Rodríguez-Baracaldo et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2014). In another study (Cui et al., 2011), the abrasive wear was better even when the temperature was raised to 400 °C. It is essential to enhance the tool’s life; for this, the tool’s wear behaviour must be investigated. The pin-on-disk test ensures the wear loss of material coefficient of friction and the durability of the material (Leite et al., 2010; Solis Romero et al., 2013). Because of high temperatures, the material fails, especially in automobiles and other tribological applications. It is also essential to analyze the frictional performance (Natarajan et al., 2006; Bahrami et al., 2005; Patnaik et al., 2010). Diamond-like-Carbon (DLC) coating is well known for low wear as well as low coefficient of friction (COF) when it was compared with a few coatings like TiN and CrN (Wu et al., 2010a; Bhowmick et al., 2015). The DLC coating has unique properties like anti-corrosion, improved mechanical properties, etc. The DLC coating’s mechanical hardness is remarkable (Alphonse et al., 2022; Gustavsson et al., 2012). It is observed that the drilling quality and the tool life can be improved by depositing DLC coating into the cemented carbide material (Silva et al., 2015). The Diamond-Like-Carbon (DLC) coating was deposited on the surface of H13 steel using Plasma-assisted Chemical Vapour Deposition (PACVD). This method helps improve the hardness because of chemical reactions through ionization and plasma excitation (Alphonse et al., 2022; Vinoth et al., 2019). In this study, DLC coating has been adopted in the H13 steel tool to improve the wear resistance properties. DLC coating has opted for the tool material for the following reasons: chemical inertness, dense microstructure, and mechanical hardness (Wu et al., 2010b). Further, DLC coating can withstand higher temperatures (Ni et al., 2006) and resist wear.
To summarize, the friction drilling process uses frictional heat to soften work materials which makes it possible to create holes. This method is highly useful for manufacturing industries where sheet metal is used extensively. The significant benefits of this process are hole quality and material versatility. The biggest challenges faced are tool wear, process parameter selection and tool design. The tool life is low, because of high temperature. To improve the life of the tool DLC coating has been adopted in this research. Industries prefer lightweight materials for the building of body parts, in this view AZ31B magnesium alloy has been used for the study. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) is noteworthy because of its low friction and hardness properties. The natural diamond present in the DLC coating helps to resist deformation and abrasion while machining. This helps in improving the life span of the tool, moreover at the tool-workpiece interface heat generated will be minimized because of the low friction coefficient of DLC also preventing thermal degradation and reducing thermal stresses. H13 steel tool is used widely by the manufacturing industry because of its exceptional performance. Because of the higher composition of chromium and molybdenum, this tool is called as hot work steel, which can resistance to thermal fatigue and significant hardness, also this particular steel can with higher temperatures. The properties of the H13 tool collectively contribute to the widespread in industries for robust and high-performance tools. The study aims to find a better-coated tool for the industry to improve production at low cost. The characteristics of tool wear and hole quality were investigated for a DLC-coated H13 tool. In addition, the surface morphology of the tool as well as the work piece was analyzed in the study.
Experimental methodology
A tribometer is used to measure tribological properties between two different surfaces. The pin-on-disk used for testing wear characteristics is shown in Figures 2A, B. The DLC-coated H13 specimen is prepared with 32 mm length and 8 mm diameter dimensions.
Based on the wear study results, a DLC-coated H13 friction drilling tool was prepared. The machining is further processed for friction drilling with the help of a Vertical Machining Centre (VMC) machine. Figure 3A and b show a friction drilling tool and material ready for the process, where AZ31B is on the fixture and DLC-coated H13 tool steel is on the spindle head.
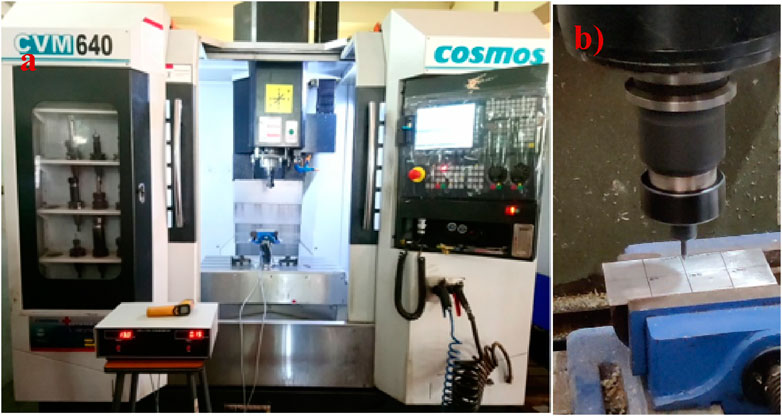

Figure 3. (A) Vertical Machining Center (VMC) (Alphonse et al., 2020a), (B) AZ31B is on the fixture and DLC-coated H13 tool steel is on the spindle head.
The VMC machine can handle the spindle speed range from 2,000 rpm to 10,000 rpm (Bayraktar and Afyon, 2020). The friction drilling process rotates the spindle at 3,000 rpm, 4,000 rpm, and feed rates of 50 mm/rev, 150 mm/rev, and 200 mm/rev. Results concluded that the sliding behaviour of the DLC-coated material would be smooth, and shearing stress and contact pressure would be less (Heinrichs et al., 2012). The work material used for the process is magnesium alloy AZ31B. Recently, magnesium alloy has found a place in the applications of automobile, aerospace, electronics, and marine industries (Sunil et al., 2016). The properties of magnesium alloy are low density, high specific strength, and the ability to weld, machine, and cast (Kakiuchi et al., 2011).
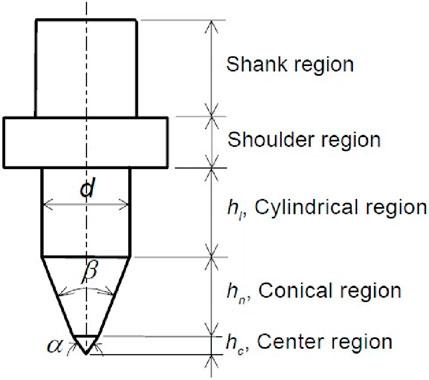
The geometry of the friction tool is shown in Figure 4. Here, the shank region is used to hold the tool into the chuck of the VMC machine. The shoulder region restricts further tool movement and prepares the bosh, the maximum projection received during tool movement. In the third stage of friction drilling, the tool’s cylindrical portion helps improve the drilled hole surface finish. The hole quality decided in the initial stage of friction drilling, centre region, and conical region helps the tool smooth movement into the work material.
Researchers need to focus on selecting process parameters that affect the hole quality. Proper selection of parameters has been made only through ongoing studies of works of literature (Alphonse et al., 2017; Ahmed and Singh, 2017). The tool processes parameters like the diameter of the tool, centre region (α), and conical region (β), and input parameters like spindle speed and feed rate are essential in getting a proper surface quality hole. The process parameter is shown in Table 1 based on the industry expertise.
Results and discussions
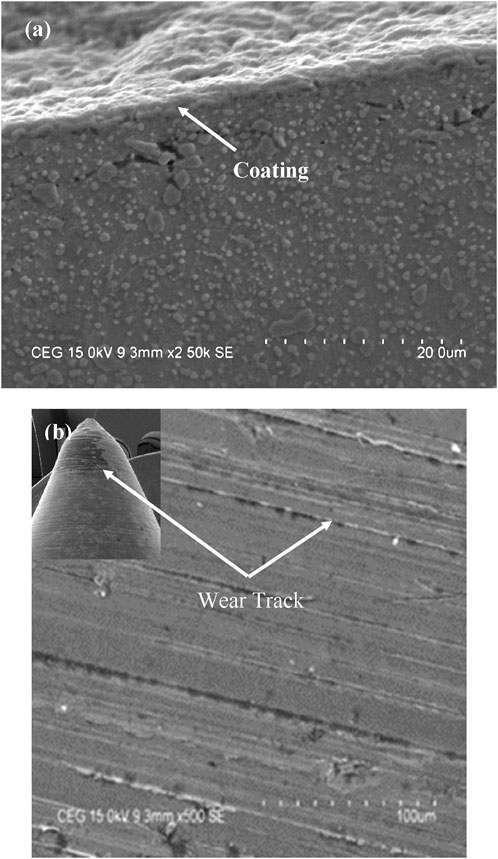
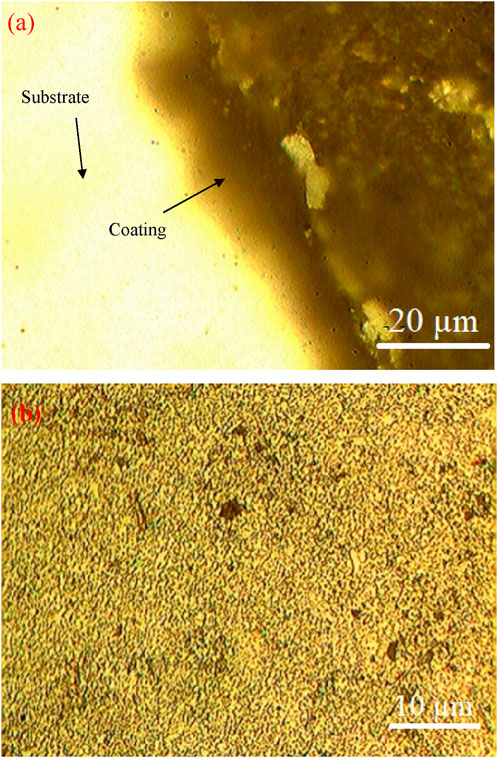
Figures 5A, B shows the microstructure image of DLC coating and H13 sample. The image was captured after hardening; in this state, the material consists of tempered martensite, austenite, and rich carbides, and the presence of carbides helps improve wear properties. The hardness of H13 steel was observed after tempering at 51–52 HRC; this is because of the transformation of martensite after the quenching process. Figure 3 observed the coating deposited over the substrate; the thickness was about 8 µm.
The Pin-on-Disc (POD) test was carried out; the parameters used for evaluation were sliding distance, sliding velocity, load, and temperature. In this research, the most attention has been given to the parameter temperature (30°C–250 C) because the tool works at high temperatures. EN31 metal was used as a disk with a hardness of 63 HRC. Figure 5 shows the results of the wear test. The weight loss of the sample during the 600-s run of POD is demonstrated in Figure 6. The temperature applied was about 250°C, and the material loss happened much less initially till 450 s; later, beyond 450 s, material loss starts in the coating. It is concluded from Figure 6 that the DLC-coated H13 material best suits friction drilling in terms of material loss because the friction drilling tool works a maximum of 3 s for a hole at a temperature maximum of 300°C.
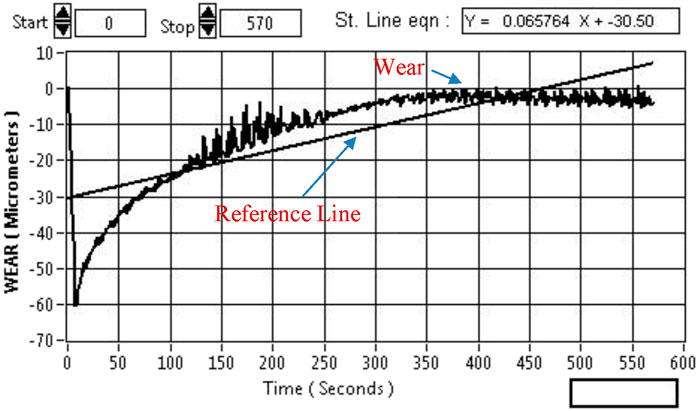
Figure 6. The result obtained from pin-on-disc wear testing machine, wear loss of DLC Coated H13 Steel.
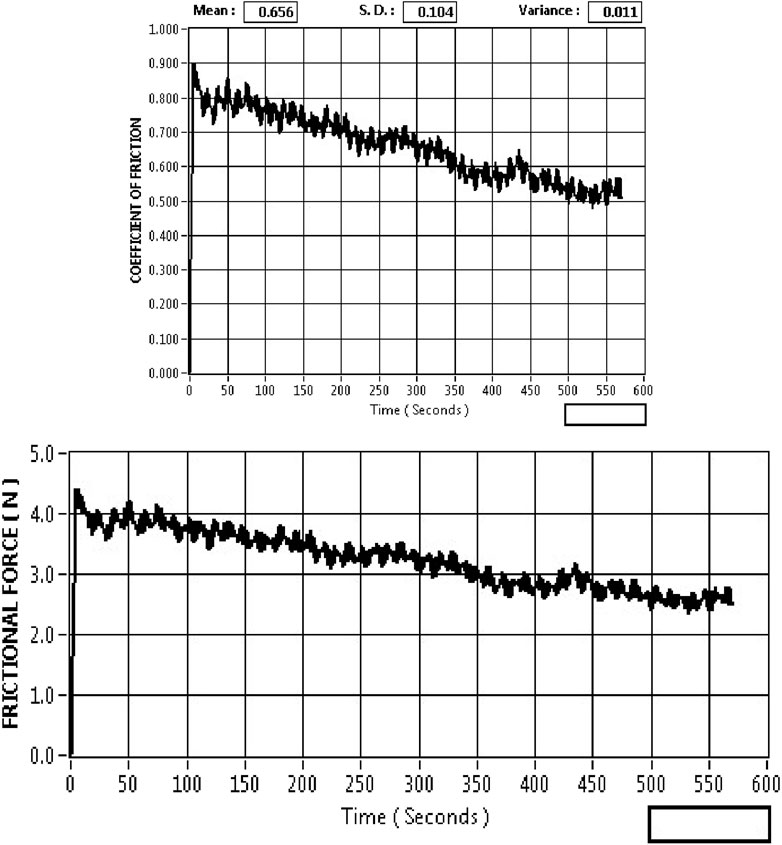
The results observed for the coefficient of friction (CoF) and friction force (FF) for the DLC-coated H13 steel tool are shown in Figure 7. The wear rate depends on CoF; the bonding of DLC coating with H13 steel is rigid, and this tends to have lesser CoF, which is shown in the Figure 7. Depending upon the loading, the coefficient of friction can be varied; also, owing to the application point, the frictional force has decreased gradually at lesser load conditions.
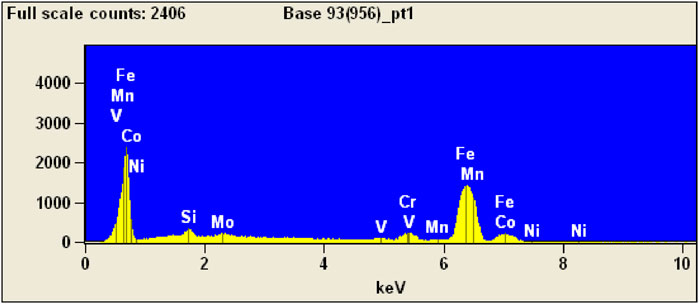
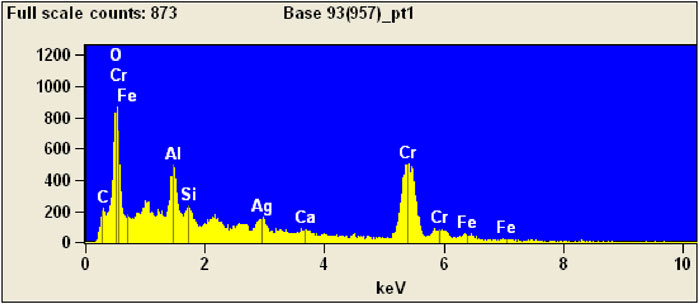
The detailed analysis of the composition of surface morphology before and after wear is shown in Figure 8. In Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), the smooth surface can be viewed in Fig. As can be observed, the coating deposition of 8 µm on the substrate can also see the strong bonding between the surface and coating. The coating thickness was uniformly over the surface, which may prevent direct contact with the substrate. A few wear tracks can be observed on the surface, but no failure of the surface has been visible on the surface of the coated H13 steel tool. Figures 9, 10 show the EDAX composition and morphology of the H13 steel tool and DLC coating. The EDS result shows a high ferrous content in H13 steel, about 78.45%, which helps with hardening, strength, and toughness. The presence of DLC coating makes the material much harder, and ferrous added into the substrate, the chromium and molybdenum content of 3.82% and 2.8%, respectively, helps improve the wear resistance. In DLC coating, chromium, and carbon content were 49.64% and 16.35%, respectively, which helps improve the wear resistance and toughness of the material.
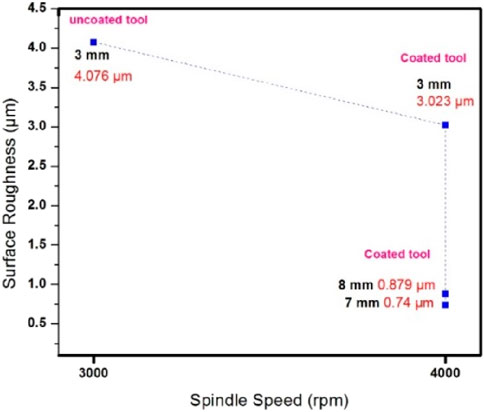
The DLC-coated H13 steel tool attains a maximum surface finish. The experimental study was completed with 3 mm, 7 mm, and 8 mm tools. Figure 11 shows the roughness of drilled holes at 3,000 rpm, 4,000 rpm, 50 mm/rev, 150 mm/rev, and 200 mm/rev. The roughness observed was less for a lightweight material (AZ31B).
The surface profile and smoothness are measured, to understand the surface properties. Ra is the roughness parameter indicated to evaluate the numerical average between the peak valley across the worn surface. Experiments start with a 3 mm diameter friction-drilling tool. The roughness observed for the AZ31B material was 5.4 µm. It also observed that when the feed rate increases, the roughness reduces. The observed results concluded that the coated H13 steel tool roughness was less than the uncoated tool. In general, the roughness reduces with the increase in feed rate. In the second stage of the friction drilling process, by knowing the importance of the coated drilling tool, 3 mm was compared with 7 mm and 8 mm.
From Figure 12, it came to be understood that with an increase in the diameter of the tool, the roughness decreases. When the feed rate increases, the roughness of the drilled hole reduces because the friction drilling process works on heat. The experiment was further carried out with 7 mm and 8 mm tools. The roughness observed for the 7 mm and 8 mm tools is 0.74 µm and 0.879 µm, respectively.
From Figure 12, it is known that spindle speed reduces wear. The difference in wear between 3,000 rpm and 4,000 rpm is 1.053 µm. Figure 13 shows the surface roughness comparison between the 3 mm and 7 mm tools. The cylindrical portion of the tool helps to improve the surface quality, and the 7 mm tool is better. It also observed that a higher spindle speed and feed rate of 4,000 rpm and 200 mm/rev would be a better option for the friction drilling process.
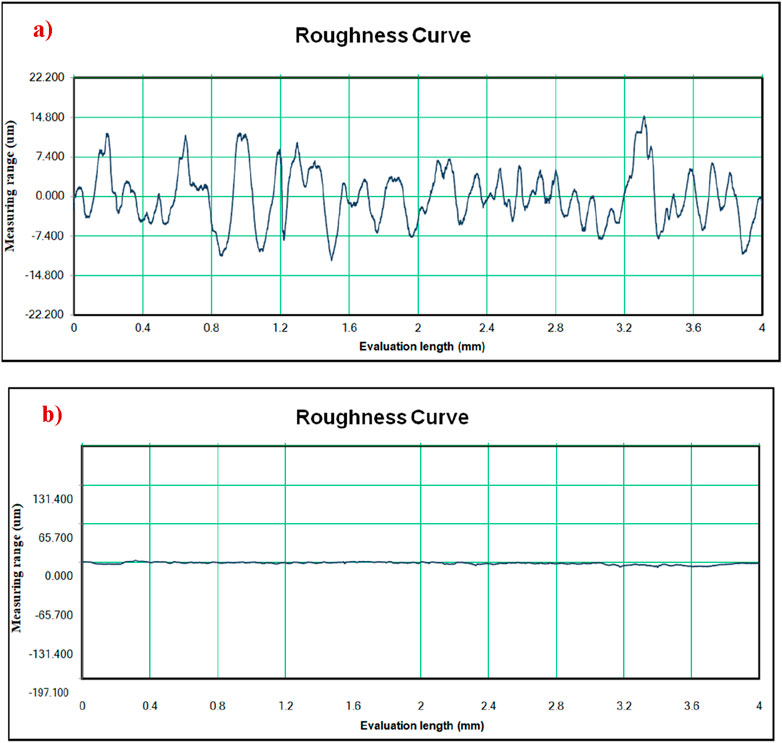
Figure 13. Surface roughness comparison between best and worst surface of AZ31B alloy (A) 3,000 rpm, 50 mm/rev, 3 mm, 5.321 µm, (B) 4,000 rpm, 200 mm/rev, 7 mm, 0.74 µm.
Figures 13, 14 show the surface roughness comparison of H13 tools. The surface roughness observed that the 7 mm tool roughness was 3.321 µm while the 8 mm tool for the study was 2.668 µm. Further, the result will be based on surface morphological analysis.
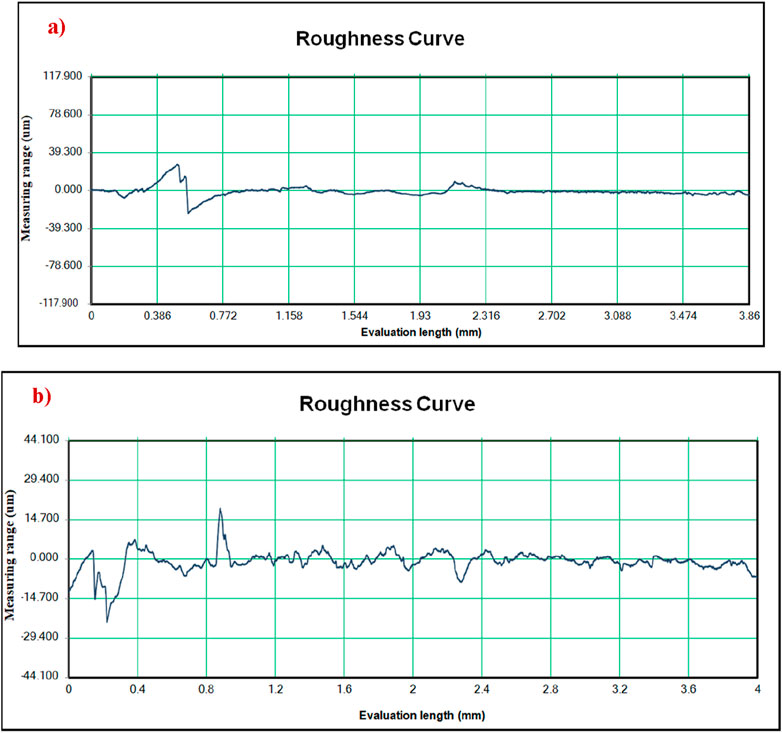
Figure 14. Surface roughness comparison between best and worst surface of H13 Steel Tool (A) 7 mm tool Ra: 3.321 µm, (B) 8 mm tool Ra: 2.668 µm.
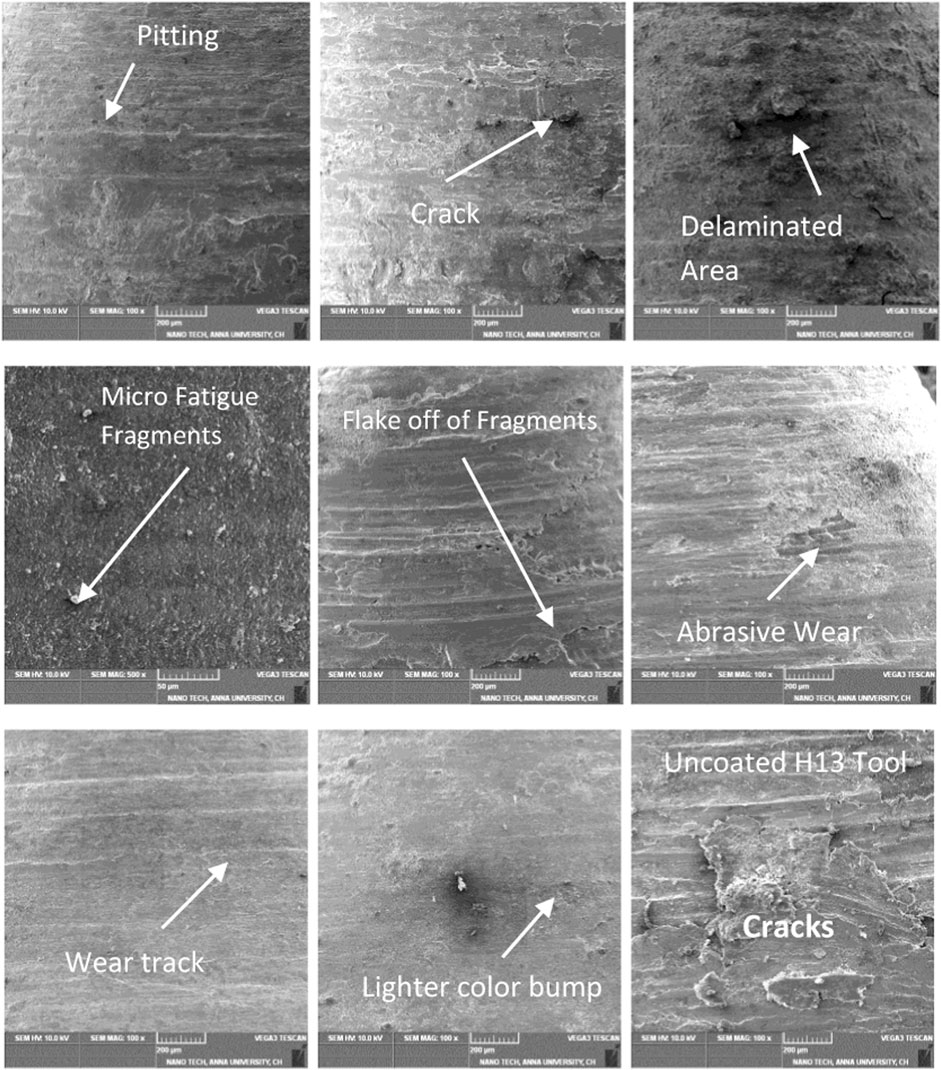
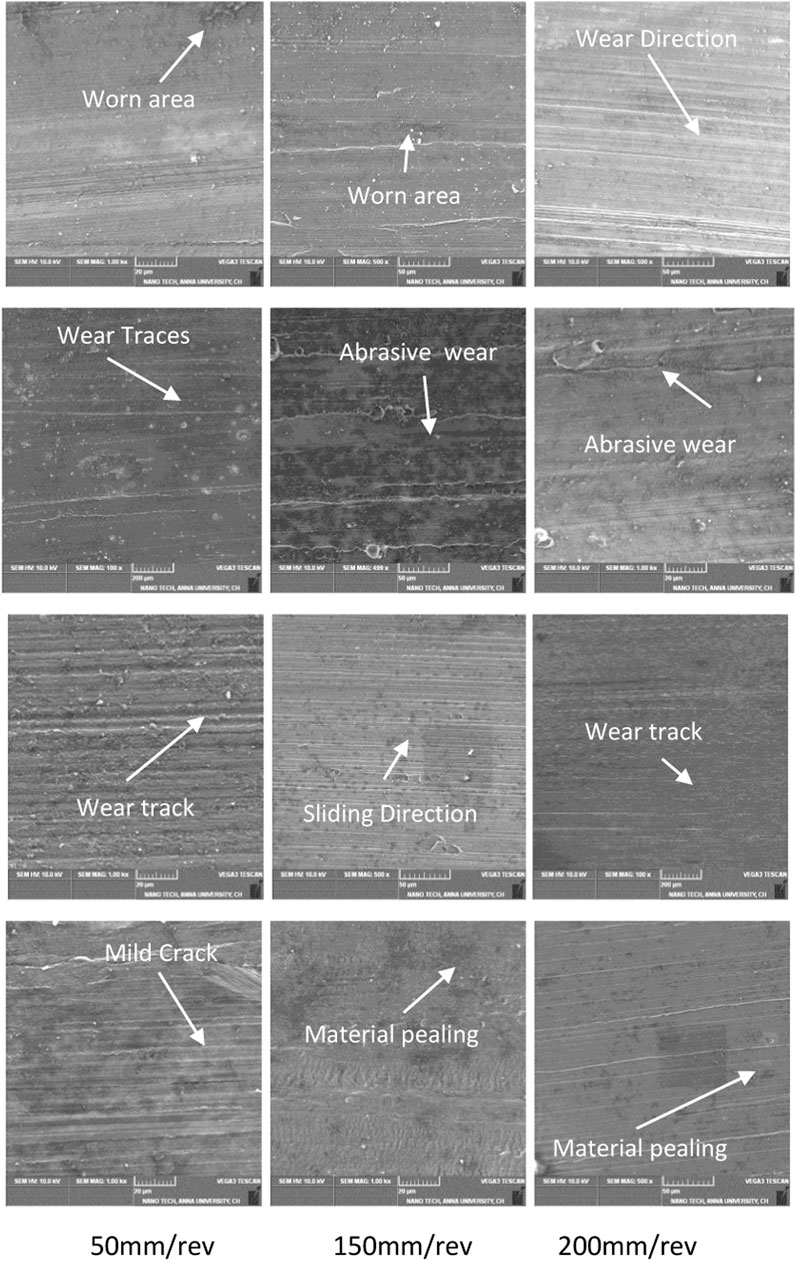
Surface Morphological images of the Friction Drilling Tool under different Conditions are shown in Figure 15. Figures 15A–C show SEM images of the 3 mm tool. The surface quality is observed when the spindle rotates at 3,000 rpm and feed rate of 50 mm/rev, 150 mm/rev, and 200 mm/rev, respectively. Delamination, cracks, and pitting are observed in a few places on the surfaces. Although the wear intensity is high, the coating exits in a few places, as seen in Figure 15A. For further verification of the 3 mm tool, the speed of the spindle increases to 4,000 rpm. Figures 15D–F have SEM images of the 3 mm tool. The feed rate was 50 mm/rev, 150 mm/rev, and 200 mm/rev, respectively.
Micro fatigue fragments and lighter colour bumps were observed in Figure 15D, whereas in Figure 15E, fragments were flake-off in multiple places in the image. In addition, delaminated areas and abrasive wear are also seen in Figure 15F. The 3 mm tool has more disadvantages when compared with other tools. Because of the tool’s cylindrical portion, the hole quality improves by clearing excess material on the surfaces. 7 mm and 8 mm tools have better results and solutions. Figures 15G, H show the SEM images of the 7 mm and 8 mm tools. The wear was significantly less when compared with other tools. Only a few pitting areas are visible in the figure’s SEM images. The surface area of the material could be smoother in this condition. Figure 15I shows the uncoated tool for comparison due to non-coating. The surface metals easily peel on the surface, and it also observed more wear tracks on the metal.
Surface Morphological images of AZ31B Magnesium alloy at different Conditions are shown in Figure 16. In Figures 16A–C, the surface area of AZ31B at a feed rate of 50 mm/rev, 150 mm/rev, and 200 mm/rev is shown respectively after the machining process. Here, a 3 mm tool at a spindle speed of 3,000 rpm has been compared. In a few places, the material starts to wear and highlights the material surface. In the image, there are significant marks for wear. For confirmation, the spindle speed is changed to 4,000 rpm at a feed rate of 50 mm/rev, 150 mm/rev, and 200 mm/rev, respectively, as shown in Figures 16D–F. The surface area of AZ31B significantly improved, but abrasive wear is visible in a few places. When the excess material plunges during machining, abrasive wear occurs on the surfaces of the workpiece. To avoid this, improve the diameter of the tool.
Figures 16G–F 7 mm friction drilling tool was used for the study because of 4,000 rpm, and the roughness observed was good. To prove the spindle speed and diameter, 4,000 rpm and 7 mm were kept constant for friction drilling operation. This research noticed that wear was significantly less when compared with a 3 mm tool. Only a few wear lines are visible on the surface of the material. However, using an 8 mm friction drilling tool with a spindle speed of 4,000 rpm causes less damage to the material. Only mild cracks are visible in the material. Figures 16J, K were good, but in a few places, material peeling was present in a few places in Figure 16L.
Conclusion
This article proposes DLC coating for the H13 Steel tool; industries prefer friction drilling tools for which can machine harder materials. The method is preferred based on creating high-quality holes with very minimal material wastage, reduced tool wear and the energy consumed is very low. The study analysed the coating which can provide better tool life. Initially, wear analysis was performed in the DLC-coated H13 tool, and has arrived to observe very less coating removal from the coated surface. The DLC coatings were deposited on the H13 friction drilling tool for machining the AZ31B magnesium alloy. From this study, the following conclusions were drawn.
• DLC coating deposited 8 µm thickness on H13 steel and has strong adhesion. With the help of a wear test, it was observed to reduce the sliding distance for better wear tracks on the surface.
• DLC coating improves the hardness and wear behaviour, which was observed using SEM and EDAX. The chromium and molybdenum content of 3.82% and 2.8%, respectively, helps improve the wear resistance. The wear rate depends on CoF; the bonding of DLC coating with H13 steel is stronger, and this tends to have lesser CoF.
• The surface quality of the coated H13 steel tool is better than the uncoated tool because of the unique characteristics of the DLC coating. The study determined that a 7 mm coated tool is the best option having less roughness of 0.74 µm for friction drilling, moreover, the 8 mm coated tool also has less roughness of 0.879 µm respectively. The study showed that with the increase in the diameter of the tool, the surface quality also improved.
• The surface quality of the hole is varied with an increase or decrease in tool dimension. It is concluded that a 7 mm and 8 mm diameter tool is better for a friction drilling tool.
• The study noted that surface roughness was significantly less when the spindle speed and feed rate increased speed. The best option observed for the 7 mm tool was 0.74 µm for the friction drilling tool when the spindle rotates at 4000 rpm and a feed rate of 200 mm/rev. Finally, DLC coating can be a better solution for friction drilling tool applications.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. VR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. EN: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Resources, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. AA: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors extend their appreciation to King Saud University for funding this work through Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP 2024R164), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. This article was co-funded by the European Union under the REFRESH—Research Excellence For REgion Sustainability and High-tech Industries project number CZ.10.03.01/00/22_003/0000048 via the Operational Programme Just Transition and has been done in connection with project Students Grant Competition SP2024/087 “Specific Research of Sustainable Manufacturing Technologies” financed by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports and Faculty of Mechanical Engineering VŠB-TUO. The article has been done in connection with the project Students Grant Competition SP2024/087 “Specific Research of Sustainable Manufacturing Technologies” financed by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports and Faculty of Mechanical Engineering VŠB-TUO.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmed, W. W., and Singh, R. V. S. (2017). Artificial intelligence modelling of process parameters on friction drilling of metal matrix composites. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 7, 109–113.
Albarbary, Y. E., Afify, R., Mansour, E. H., Mahmoud, T. S., and Khedr, M. (2022). The effect of pre-drilling on the characteristics of friction drilled A356 cast aluminum alloy. J. Manuf. Process 82, 646–656. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.08.040
Alphonse, M., Bupesh Raja, V. K., and Gupta, M. (2022). Effect of coating type on tribological response of H13 tool steel. Surf. Rev. Lett. 29 (6). doi:10.1142/S0218625X22500743
Alphonse, M., Bupesh Raja, V. K., Logesh, K., and MuruguNachippan, N. (2017). Evolution and recent trends in friction drilling technique and the application of thermography. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater SciEng 197 (1), 012058. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/197/1/012058
Alphonse, M., Raja, V. K. B., and Gupta, M. (2020b). Investigation on tribological behavior during friction drilling process - a review. Tribol. Industry 42 (2), 200–213. doi:10.24874/ti.655.02.19.03
Alphonse, M., Raja, V. K. B., and Gupta, M. (2020c). Materials Today: proceedings Optimization of plasma nitrided, liquid nitrided and PVD TiN coated H13-D2 friction drilling tool on AZ31B magnesium alloy. Mater Today Proc., 2–10. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.791
Alphonse, M., Raja, V. K. B., Gupta, M., and Logesh, K. (2020a). Optimization of coated friction drilling tool for an FML composite. Mater. Manuf. Process., 1–10. doi:10.1080/10426914.2020.1832684
Bahrami, A., Anijdan, S. H. M., Golozar, M. A., Shamanian, M., and Varahram, N. (2005). Effects of conventional heat treatment on wear resistance of AISI H13 tool steel. Wear 258 (5–6), 846–851. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2004.09.008
Bayraktar, Ş., and Afyon, F. (2020). Machinability properties of Al–7Si, Al–7Si–4Zn and Al–7Si–4Zn–3Cu alloys. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42 (4), 187. doi:10.1007/s40430-020-02281-x
Bhowmick, S., Banerji, A., and Alpas, A. T. (2015). Tribological behaviour of W-DLC against an aluminium alloy subjected to lubricated sliding. Tribol. Industry 37 (3), 277–283.
Cui, X. H., Wang, S. Q., Wei, M. X., and Yang, Z. R. (2011). Wear characteristics and mechanisms of h13 steel with various tempered structures. J. Mater Eng. Perform. 20 (6), 1055–1062. doi:10.1007/s11665-010-9723-0
Deepak, D., and Paulo Davim, J. (2019). Multi-response optimization of process parameters in AWJ machining of hybrid GFRP composite by grey relational method. Procedia Manuf. 35, 1211–1221. doi:10.1016/j.promfg.2019.07.021
Dehghan, S., Ismail, M. I. S., Ariffin, M. K. A., and Baharudin, B. T. H. T. (2018). Experimental investigation on friction drilling of titanium alloy. Eng. Solid Mech. 6, 135–142. doi:10.5267/j.esm.2018.2.002
Demir, Z., and Özek, C. (2014). Investigate the effect of pre-drilling in friction drilling of A7075-T651. Mater. Manuf. Process. 29 (5), 593–599. doi:10.1080/10426914.2014.892986
El-Bahloul, S. A., El-Shourbagy, H. E., and El-Midany, T. T. (2015). Optimization of thermal friction drilling process based on taguchi method and fuzzy logic technique. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Appl. 4 (2), 54–59. doi:10.7753/IJSEA0402.1006
Eliseev, A., and Kolubaev, E. (2021). Friction drilling: a review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 116, 1391–1409. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-07544-y
Gustavsson, F., Forsberg, P., Renman, V., and Jacobson, S. (2012). Formation of tribologically beneficial layer on counter surface with smart chemical design of DLC coating in fuel contact. Tribol. - Mater. Surfaces and Interfaces 6 (3), 102–108. doi:10.1179/1751584X12Y.0000000013
Heinrichs, J., Olsson, M., and Jacobson, S. (2012). Mechanisms of material transfer studied in situ in the SEM:. Wear 292–293, 49–60. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2012.05.033
Hynes, N. R. J., Muthu, M., Rakesh, N., and Gurubaran, C. K. (2020). Numerical analysis in friction drilling of AISI1020 steel and AA 6061 T6 alloy. Recent Adv. Environ. Earth Sci. Econ., 145–149.
Kakiuchi, T., Uematsu, Y., Teratani, T., and Harada, Y. (2011). Effect of film elastic modulus on fatigue behaviour of DLC- coated wrought magnesium alloy AZ61. ProcediaEng 10, 1087–1090. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2011.04.179
Kumar, R., and Jesudoss Hynes, N. R. (2019). Thermal drilling processing on sheet metals: a review. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2 (3), 193–205. doi:10.1016/j.ijlmm.2019.08.003
Leite, B., Figueroa, M. V., Gallo, C. A., Corujeira, S., Rovani, A. C., Mei, P. R., et al. (2010). Wear mechanisms and microstructure of pulsed plasma nitrided AISI H13 tool steel. Wear 269 (5-6), 466–472. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2010.04.037
Natarajan, N., Vijayarangan, S., and Rajendran, I. (2006). Wear behaviour of A356/25SiCp aluminium matrix composites sliding against automobile friction material. Wear 261 (8-9), 812–822. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2006.01.011
Ni, W., Cheng, Y., Weiner, A. M., and Perry, T. A. (2006). Tribological behavior of diamond-like-carbon (DLC) coatings against aluminum alloys at elevated temperatures. Surf. Coatings Technol. 201, 3229–3234. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.06.045
Ozek, C., and Demir, Z. (2013). Investigate the surface roughness and bushing shape in friction drilling of a7075-t651 and st 37 steel. TEM J. 2 (2), 170–180.
Özler, L. (2019). The influence of variable feed rate on bushing and surface roughness in friction drilling. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 41 (8), 308–309. doi:10.1007/s40430-019-1812-x
Patnaik, A., Satapathy, A., Chand, N., Barkoula, N. M., and Biswas, S. (2010). Solid particle erosion wear characteristics of fiber and particulate filled polymer composites: a review. Wear 268 (1), 249–263. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2009.07.021
Rafi, H. K., Ram, G. D. J., Phanikumar, G., and Rao, K. P. (2010). Friction surfaced tool steel (H13) coatings on low carbon steel: a study on the effects of process parameters on coating characteristics and integrity. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205 (1), 232–242. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.06.052
Raja, V. K. B., and Rajasekaran, R. (2014). An overview of non traditional drilling process. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 9, 23145–23153.
Rodríguez-Baracaldo, R., Benito, J. A., Puchi-Cabrera, E. S., and Staia, M. H. (2007). High temperature wear resistance of (TiAl)N PVD coating on untreated and gas nitrided AISI H13 steel with different heat treatments. Wear 262 (3-4), 380–389. doi:10.1016/j.wear.2006.06.010
Silva, W. M., Jesus, L. M., Carneiro, J. R., Souza, P. S., Martins, P. S., and Trava-airoldi, V. J. (2015). Performance of carbide tools coated with DLC in the drilling of SAE 323 aluminum alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 284 (25), 404–409. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.09.061
Skovron, J. D., Rohan Prasad, R., Ulutan, D., Mears, L., Detwiler, D., Paolini, D., et al. (2015). Effect of thermal assistance on the joint quality of Al6063-t5a during flow drill screwdriving. J. ManufSciEng 137 (5), 1–8. doi:10.1115/1.4031242
Solis Romero, J., Medina Flores, A., Roblero Aguilar, O., and Oseguera Peña, J. (2013). Tribological evaluation of plasma nitride H13 steel. Superf. Vacio 26 (4), 131–138.
Su, K., Welo, T., and Wang, J. (2018). Improving friction drilling and joining through controlled material flow. ProcediaManuf 26, 663–670. doi:10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.077
Sunil, B. R., Kumar, G. P., Patle, H., and Dumpala, R. (2016). Magnesium based surface metal matrix composites by friction stir processing. J. Magnesium Alloys 4, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.jma.2016.02.001
Vinoth, I. S., Detwal, S., Umasankar, V., and Sarma, A. (2019). Tribological studies of automotive piston ring by diamond-like carbon coating. Tribol. - Mater. Surfaces and Interfaces 13 (1), 31–38. doi:10.1080/17515831.2019.1569852
Waleed, W. A., Chathriyan, A., and Vimal, R. S. S. (2018). Experimental investigation on the influence of process parameters in thermal drilling of metal Matrix Composites. FME Trans. 46 (2), 171–176. doi:10.5937/fmet1802171W
Wang, F., Zhao, J., Li, A., and Zhang, H. (2014). Effects of cutting conditions on microhardness and microstructure in high-speed milling of h13 tool steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 73 (1-4), 137–146. doi:10.1007/s00170-014-5812-9
Wu, G., Dai, W., Zheng, H., and Wang, A. (2010b). Improving wear resistance and corrosion resistance of AZ31 magnesium alloy by DLC/AlN/Al coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205 (7), 2067–2073. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.08.103
Keywords: wear, friction drilling, diamond-like-carbon (DLC), H13 steel tool, AZ31B alloy
Citation: Alphonse M, Raja VKB, Cepova L, Salunkhe S, Nasr EA and Abdelgawad AE (2024) Tribological and investigation study of a dlc-coated H13 friction drilling tool on AZ31B magnesium alloy. Front. Mech. Eng. 10:1470507. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1470507
Received: 25 July 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 09 October 2024.
Edited by:
Stanisław Legutko, Poznań University of Technology, PolandReviewed by:
Munish Gupta, Shandong University, ChinaJán Dižo, University of Žilina, Slovakia
Krzysztof Nadolny, Koszalin University of Technology, Poland
Copyright © 2024 Alphonse, Raja, Cepova, Salunkhe, Nasr and Abdelgawad. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: V. K. Bupesh Raja, YnVwZXNoLnYua0BnbWFpbC5jb20=; Sachin Salunkhe, c2FjaGluc2FsdW5raGVAZ2F6aS5lZHUudHI=
 Mathew Alphonse
Mathew Alphonse V. K. Bupesh Raja
V. K. Bupesh Raja Lenka Cepova
Lenka Cepova Sachin Salunkhe
Sachin Salunkhe Emad Abouel Nasr6
Emad Abouel Nasr6