- 1School of Information and Intelligent Engineering, Nantong College of Science and Technology, Nantong, China
- 2Faculty of Social, Business and Computer Sciences, Varna Free University, Varna, Bulgaria
Introduction: In cloud computing, a common idea to reduce operation costs and improve service quality is to study task scheduling algorithms.
Methods: To better allocate virtual machine resources, a virtual machine resource scheduling algorithm, Shapley value method–genetic algorithm (SVM-GA) is proposed. This algorithm uses the SVM to obtain the contribution values of each component of the virtual machine, refine the topological network, and achieve the optimal solution of scheduling by the genetic algorithm.
Results and Discussion: CloudSim simulation results indicate that SVM-GA has the lowest total task completion time when compared with existing intelligent optimization algorithms (such as the max–min algorithm, logistic regression algorithm, and differential evolution algorithm) with the same number of tasks, and the total task time is 25, 55, 81, 112, 145, and 175 s for 200, 400, 600, 800, 1,000, and 1,200 tasks, respectively. As the number of evolutionary generations increases, the ability of SVM-GA to reach the optimal solution of the model increases. In the simulated light load case, the SVM-GA migration time and Q10 migration count optimal solutions are slightly inferior to those of the logistic regression algorithm (3.02 s > 2.38 s; 1,129 times >999 times), but the migration energy consumption and service level agreement violation rate optimal solutions are superior. The SVM-GAA’s performance in the heavy load case is similar to that in the light load case. The experiments show the feasibility of the algorithm proposed in the study.
1 Introduction
Cloud computing, as a part of distributed computing, mainly decomposes huge data processing computing procedures into many subtle small procedures and then feeds back to users after obtaining the results by processing and analyzing the decomposition through a system composed of multiple servers. In the early days of cloud computing, the main task was to divide the small programs, solve the task release, and merge the calculation results. With development in network technology, cloud computing has now evolved into a hybrid application containing distributed computing, utility computing, parallel computing, network reserves, and hot backups of miscellaneous and virtualization technologies. Virtualization technology includes the virtual machine (VM) technology that is widely used to emulate other kinds of operating systems, build virtual operating environments and infrastructure frameworks, and reserve data for seamless and trouble-free data transfer and recovery. The most common applications are hard disk virtualization memory, construction of virtual private networks (VPN) in public networks, etc. The use of VM technology can allocate various resources in the cloud system according to the business or user needs, but its allocation results are not ideal. In addition, as increasing number of users upload data to the cloud platform, large-scale data cloud computing and parsing will often require higher energy usage, which means more CO2 will be generated in the process of data parsing in the cloud system, thus causing some impact on the environment. How to correctly and efficiently allocate virtual resources will affect the establishment of the VM scheduling policy. Building an energy-efficient and effective resource allocation VM scheduling model can not only improve the speed and accuracy of cloud computing but also protect the environment to a certain extent. Label noise and data decentralization also have a positive impact on cloud computing. To realize transmission fault diagnosis in the case of decentralized data, Yang et al. federated the semi-supervised transfer fault diagnosis method called targeted transfer learning through the distribution barycenter medium (TTL-DBM). The results indicated that TTL-DBM could obtain similar cross-domain features through the adaptation via the distribution medium and achieve higher diagnosis accuracy than other federated adaptation methods in the presence of data decentralization (Yang et al., 2024a). To enhance the generalization and accuracy of data standards, Yang et al. proposed a solution called label recovery and trajectory designable network (LRTDN). The results indicated that LRTDN could provide high diagnostic accuracy even if there were error annotations (Yang et al., 2024b). Based on this, the study proposes a Shapley value method–genetic algorithm (SVM-GA) for a VM scheduling model construction to reasonably allocate virtual resources. The proposed cloud computing task scheduling method aims to optimize task execution time, improve resource utilization, and reduce configuration overhead through the optimistic resource allocation strategy. This policy uses effective scheduling technology to consolidate dynamically configured VM on a small number of hosts to improve the overall system performance. The new model proposed in this study provides an effective solution for VM scheduling in the cloud environment, which helps realize efficient and energy-saving resource allocation. The main contributions of this research are as follows: (1) the global optimal allocation of virtual resources based on Shapley’s value method solves the defect of unreasonable resource allocation in traditional VM scheduling; (2) the genetic algorithm (GA) is introduced to further optimize the allocation scheme of system resources, which increases the global optimization ability of the model. Therefore, the proposed model has played a certain role in promoting the development of the VM industry.
2 Related works
The VM scheduling model in cloud computing has been a popular research object. Bo, Wan et al. proposed a cloud computing analytical model that simultaneously considers hot and cold start as well as hot and cold shutdown of VMs. The objective was to quantitatively predict and optimize the cost and performance of the cloud computing platform, which showed greater effectiveness (Wan et al., 2020). Similarly, Xu et al. developed a VM scheduling algorithm using gravitational effects to optimize the scheduling of VMs. Experimental results confirmed the algorithm’s ability to significantly reduce the energy consumption rate and VM migration time (Xu et al., 2019). Marri and Rajalakshmi proposed a multi-objective approach using the GA and the energy-aware model for task scheduling efficiency (Marri and Rajalakshmi, 2022). Karthikeyan and Soni proposed a hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm to satisfy the maximum resource utilization and wide utilization and cost, and the minimum total completion time required for the improved algorithm was obtained through simulation experiments (Karthikeyan and Soni, 2020). Naik et al. used Drosophila to integrate the cuckoo search algorithm to reduce the energy consumption of physical machines for migration (Naik et al., 2020). Wang et al. trained a neural network to predict the efficiency of a compressor and explain its behavior using the SVM (Wang J. Y. et al., 2022). Lin et al. used shapely weighted vectors to integrate expected linguistic preference relations and develop a binary linguistic ordered weighted quasi-average algorithm based on rank variance. The proposed algorithm had good efficacy in business investment problems (Lin et al., 2019). Wang et al. proposed a profit allocation method combining improved Shapley values and nucleolus methods to improve energy use efficiency to improve non-dominated ranking GA for the cooperative game model. Results indicated that this model saved 26.86% of computer resources and reduced carbon emissions by 39.42% compared to independent operations (Wang Y. L. et al., 2022). Malik et al. proposed a hybrid gray wolf and ant lion model for enhancing cloud computing, and the effectiveness of the algorithm was confirmed with the results of throughput and resource usage (Malik et al., 2022). Azzam et al. used GAs to construct a stable and continuous sensing panel recruitment system and proved the performance of the proposed system over the traditional individual recruitment system by realistic simulation (Azzam et al., 2018). Bhatnagar et al. integrated the GA and greedy algorithm to maximize the profit of a dating website and verified its effectiveness by realistic simulation tests (Bhatnagar et al., 2018). Dong et al. used an improved binary GA with feature granularity for important feature selection, proposed a GA-based granularity λ optimization algorithm, and derived experimental results by comparing other evolutionary algorithms and supervised algorithms, and the results indicated that it can provide higher accuracy using refined information (Dong et al., 2018). Elhoseny et al. proposed a Bessel curve-based method using the modified GA to plan dynamic domains for paths. Through experiments, the proposed method was shown to be effective in avoiding energy consumption of the robot in harsh environments (Elhoseny et al., 2018). Contaldi et al. used a parametric GA to learn Bayesian network structures in data samples and experimentally showed that the GA outperformed other advanced structure learners in large network structures and solved the data fragmentation problem with baseline permutation (Contaldi et al., 2019). Rovithakis et al. proposed a hybrid neural network combined with the GA as a feature extractor to select normal cells from those affected by acute lymphoblastic leukemia and experimentally proved its feasibility (Rovithakis et al., 2004).
Ma et al. proposed an online VM scheduling optimization scheme that combines energy consumption and cost, which optimizes VM allocation and migration from two aspects. The optimization plan mainly used Q-learning feedback to obtain the iterated Q-value to mark the optimal allocation order of the VM. Experimental results showed that the proposed scheme effectively saved 18.25% of physical machine energy consumption and 21.34% of execution costs (Ma et al., 2022). Rana et al. constructed an efficient VM scheduling method using a hybrid multi-objective whale algorithm. This method used differential calculation instead of the random solution generated by the whale algorithm, thereby enhancing the algorithm’s local search ability. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed model had certain advantages in balancing effect efficiency and cost (Rana et al., 2022). Memari et al. proposed a VM scheduling method based on taboo search. This method could balance hardware cost and response speed by comparing the execution time, latency, and cost functions, thereby making the scheduling strategy of the VM conform to the global optimum. The experimental results showed that the scheduling algorithm based on taboo search performed better than GA, particle swarm optimization algorithm, and simulated annealing algorithms on open-source datasets (Memari et al., 2022).
In summary, although these cloud computing VM scheduling algorithms are effective, they have certain limitations. The calculation of hot start and cold start models is complicated in big data processing, the practical application simulation of the gravitational effect algorithm is difficult, the convergence of GA is slow, the parameter adjustment of the particle swarm algorithm is difficult, the stability of the fruit fly algorithm is doubtful, the neural network and SVM are limited to deal with complex systems, and the binary language algorithm needs conversion to deal with non-binary input. The calculation of the improved Shapley value is complicated, the generalization ability of gray wolf and ant lion models is limited, the environmental adaptability of the GA is poor, the integration of genetic and greedy algorithms cannot protect privacy, the calculation cost of the improved binary GA is high, the Bessel curve method poses difficulties in path planning, and the parametric GA is inefficient in small networks. Hybrid neural networks and GAs are poor at generalization of non-standard data. The SVM and GA have good results in various scientific research fields, but there is not much relevant research regarding the VM scheduling model in cloud computing (Waziri and Yakasai, 2023; Smarandache, 2022). Therefore, the study proposes an improved GA using Shapley value enforcement to construct a VM scheduling model for better allocation of VM resources. The new model proposed in this study provides an effective solution for VM scheduling in the cloud environment, which helps realize efficient and energy-saving resource allocation.
3 Construction of the virtual machine scheduling model in the context of cloud computing
3.1 The virtual machine scheduling model constructed using the Shapley value method
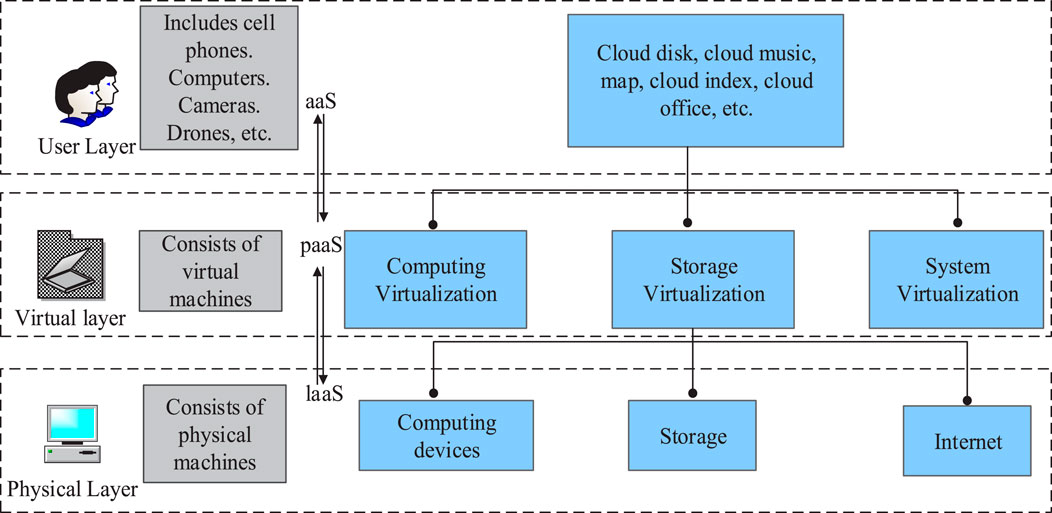
In simple terms, the cloud computing structure mainly includes three layers: the user, virtual, and physical layer. Different layers realize different functions, and according to the type of services required at each layer, they can be divided into software, platform, and infrastructure (Abdulqadir et al., 2021). Through the above three levels of services, cloud computing achieves the customization of overall information services and the integration of the underlying logical resources and basic software applications. The research directions for establishing energy-saving models are mainly two kinds of energy consumption modeling and resource scheduling strategies, among which, because the energy-saving integration scheme in the cloud environment is more significant for research, the research focuses on building a study of virtual and physical layers in cloud computing. The structure levels and functions related to cloud computing are shown in Figure 1.
In Figure 1, infrastructure as a service (IaaS) integrates various hardware resources into a resource pool, which covers memory, hard disk, and CPU. IaaS users request resources in terms of VMs, and users have greater freedom, but multiple VMs work together with greater difficulty. Considering that the energy-saving technology of the system in the context of cloud computing is mainly realized by reasonably allocating the server locations where VMs are located, the study uses the SVM to implement weight allocation for physical machines in the virtual layer and evaluates the gap between a series of performances of individual physical machines from the reserve space to computing power according to the size of the weight values.
The SVM distributes benefits based on the degree of contribution and its capacity to calculate the contribution value of each participant in the cooperative game process. This is consistent with the context of the use of the SVM algorithm, which is composed of multiple subcomponents that collectively perform the calculations and operations necessary for the system to function (Chen et al., 2023). Therefore, the SVM is used to determine the importance of the relevant subcomponents in a single physical machine. The related process is shown as follows:
The set of physical machines is
Here,
Once the contribution value of the set of physical machines is calculated, the exact value of
It is supposed that in the topological network structure of the VM placement problem, the
In Equation 3,
After obtaining the mathematical representation of the VM allocation model, the specific contribution value of the physical machine is calculated
Here,
In the topological network structure model, each physical computer has the same number of neighboring nodes for the total contribution value PM, and different nodes have different weights; the formula for the node contribution value in large-scale networks is summarized in Equation 5.
Here,
By using the above function expression, the contribution value of a single node to the whole physical machine is obtained, and the virtual resources can be allocated according to the relevant contribution weight. However, in a cloud environment, there is a problem of overloading a computing node, so some VMs need to be migrated to another node. To reduce the negative impact of the additional resources occupied by an overloaded computing node during the migration process and to facilitate the practical operation, the study chose to reduce the total band migration VM memory. The involved VM migration energy consumption is shown in Equation 6.
In Equation 6,
3.2 Genetic algorithm-based optimization strategy for virtual machine scheduling
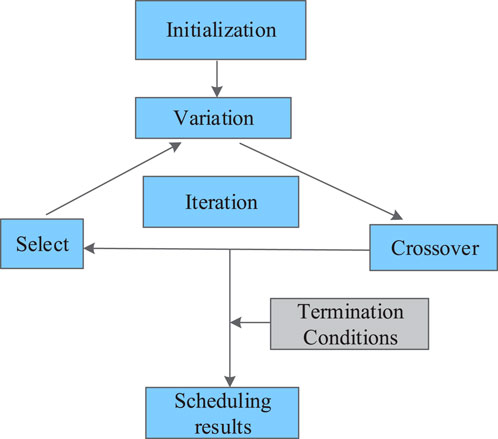
Since the best solution cannot be found when the number of physical machines is large for VM migration scheduling in the cloud environment, the intelligent optimization algorithm can derive the relative optimal solution as the solution. The GA, as a computational model that simulates Darwinian biological evolution by combining natural selection and genetic mechanism, can obtain optimal solutions and evolve continuously through computer simulation of natural evolution, thus obtaining better optimization results in a short time. The GA has been widely used in combinatorial optimization, machine learning, signal processing, adaptive control, and artificial life. Therefore, the study selected the GA as an improvement algorithm, the individuals with high contribution values obtained based on the SVM were selected as parents, and the relative optimal solution was finally iterated after cross-selection to derive the scheduling results of the VM. The whole operation flow is shown in Figure 3.
As shown in Figure 3, the initialization parameters of the VM scheduling model are determined first. This is because VM migration usually involves service level agreement (SLA) violation rate, migration time, migration energy consumption, number of migrations, and migration index downtime. Since this paper determines the values of
The migration time,
Here,
Because the number of VMs is
To further improve the scheduling efficiency of the VM for cloud computing tasks, adaptive operators are used to complete the scheduling of cloud computing tasks in the GA. A large crossover probability of the GA will destroy individuals with better genes to a larger extent, and it will lead to a long time for non-convergence of the algorithm. However, a small crossover probability has the problem of slow search process for optimal solutions. Similarly, if the variation probability is large, the genetic short hair degenerates into a random search algorithm; if it is small, the algorithm will fall into a local optimal situation. To solve the above problems and also consider the individual fitness, the traditional mathematical expressions of crossover probability and variation probability are improved to derive Equations 8, 9.
The mathematical expression for the probability of variation is shown in Equation 8.
In Equation 8,
The mathematical expression for the probability of variation is shown in Equation 9.
In Equation 9,
The improved variation probability is shown in Equation 11.
The above improvements ensure that the individuals close to the maximum fitness value in the population do not cross over at the early stage of evolution, which in turn reduces the probability of the algorithm having a locally optimal solution. At the later stage of evolution,
Here,
Consider the improved GA for the load balancing degree problem; to measure the standard deviation of the running time of each computing resource task, the load balancing degree is calculated by Equation 13.
In Equation 13,
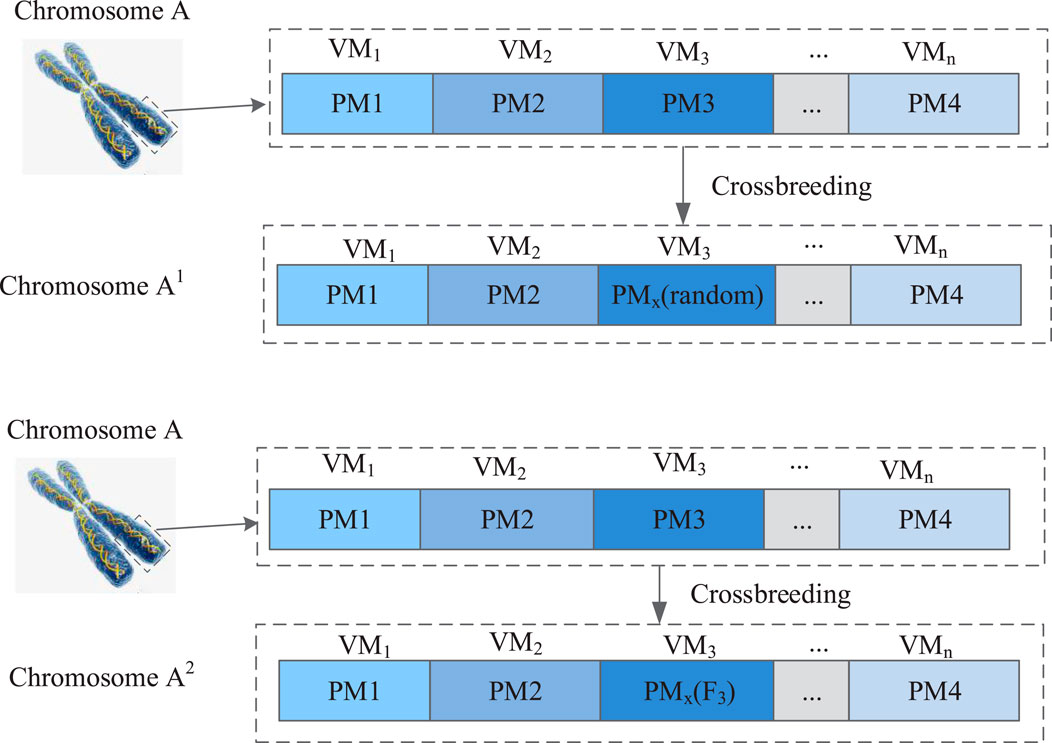
Based on mutated chromosomes, different physical machines can appear in a certain pattern, and the probability of target physical machines undergoing mutation can also be derived. The mutation process is shown in Figure 5.
As shown in Figure 5, a certain chromosome undergoes a mutation without introducing a mutated gene, resulting in only one sub-chromosome. The introduction of mutated genes allows for the acquisition of additional chromosomes while preserving the number of sub-chromosomes, resulting in the acquisition of two sub-chromosomes. The above selection–crossover–variation steps are repeated until the set number of iterations is reached, the relatively most superior gene is output, and the scheduling results of the VM are obtained.
4 Simulation experimental results of the virtual machine scheduling model constructed using SVM-GA
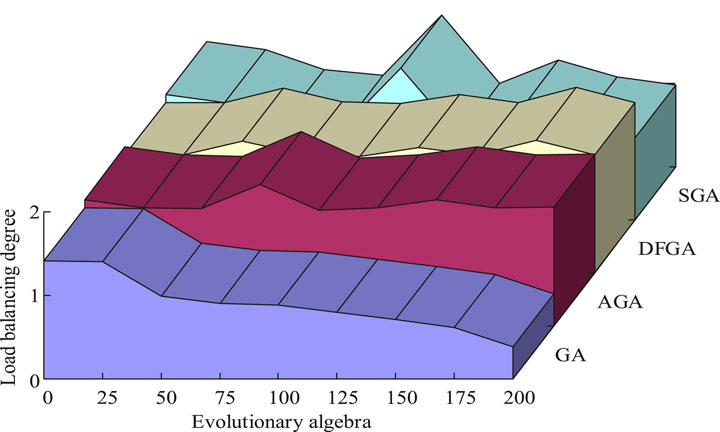
Load balance refers to the standard deviation of the running time for each computing resource to complete a given task. Smaller standard deviation implies that each computing resource completes the task closer to the average running time, leading to a more balanced load. Such load balance results in a higher individual adaptation value and the likelihood of selection into the next generation increases accordingly. In the GA, the population size is set to 100, the crossover probability is 0.8, the mutation probability is 0.05, and the number of iterations is 200. The selection strategy is the roulette method, the crossover strategy is single-point crossover, and the mutation strategy is random variation. For SVM-GA, the weight of migration time, SLA violation rate, and migration energy consumption in fitness function are 0.5, 0.3, and 0.2, respectively. Therefore, the improved GA is compared with the simple GA (SGA), adaptive GA (AGA), and dual AGA (DAGA), and the results are shown in Figure 6.
In Figure 6, the load balance of the optimized algorithm shows a decreasing trend with the increase in evolutionary generations, while for the other three GAs, the load balance degree fluctuates up and down with the increase in evolutionary generations. According to the experimental results of load balancing, compared with the control algorithm, the improved algorithm has higher stability, and the load balancing degree does not fluctuate with the increase of evolutionary generations. The improved GA has the smallest load balance degree value at 200 evolutionary generations, the individual fitness value is higher, and the individuals with excellent genes are more likely to be selected as parents for inheritance. The study was then conducted in the CloudSim cloud computing environment simulation platform.
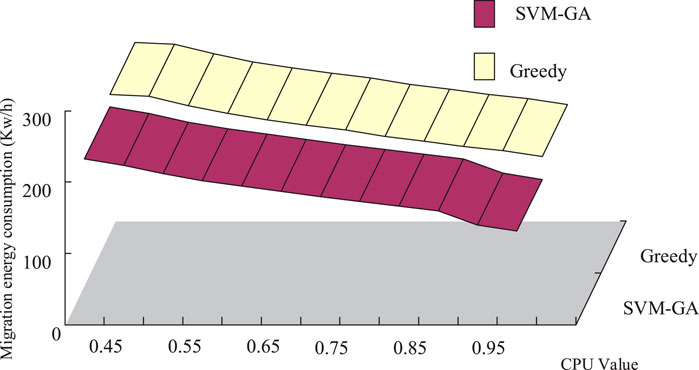
To investigate the effect of different CPU thresholds on the algorithm migration energy consumption, CPU thresholds are set as variables to compare the impact of SVM-GA and greedy algorithm load energy consumption under different CPU variables. The experimental data source is 800 servers, where the number of VMs and the number of tasks are the same. The experimental results are shown in Figure 7.
As can be seen in Figure 7, the migration energy consumption of the SVM-GA was lower than that of the greedy algorithm at either CPU value, indicating that the method proposed in the study was energy-efficient. Subsequent experiments were designed to verify other performances of the SVM-GA algorithm, and the data sources used were anonymous workload traces from Google clusters and PlantLab VMs. Two different types of computational nodes were created, with the relevant parameters shown in Table 1.
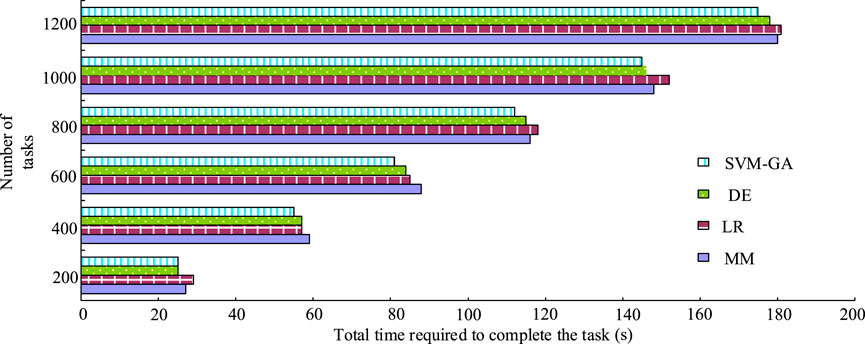
In cloud computing task scheduling, the optimal scheduling solution was generally obtained by using the scheduling algorithm to find the optimal solution of the optimization objective, which was generally reflected by the total time taken to complete a certain task, and the less the total time consumed by the task, the better the performance of the scheduling algorithm in general. Therefore, experiments were designed to compare the total task completion time obtained by SVM-GA, max–min algorithm (MM), logistic regression (LR), and differential evolution (DE). The completion time and the results are shown in Figure 8.
As shown in Figure 8, as the number of tasks increased, the time required to complete the total task increased for all four algorithms, but the SVM-GA algorithm took 25, 55, 81, 112, 145, and 175 s to complete the total task when the number of tasks was 200, 400, 600, 800, 1,000, and 1,200, respectively. The load balancing obtained by the four algorithms iscompared, and the results are shown in Figure 9.
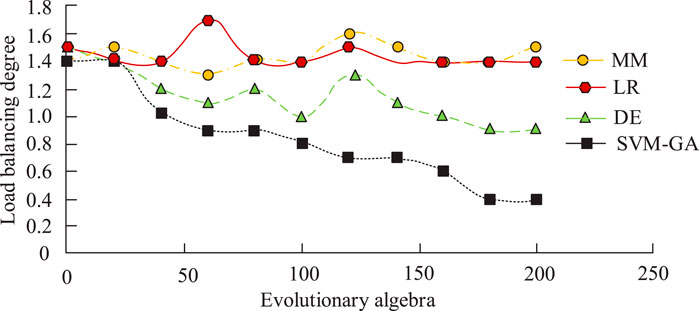
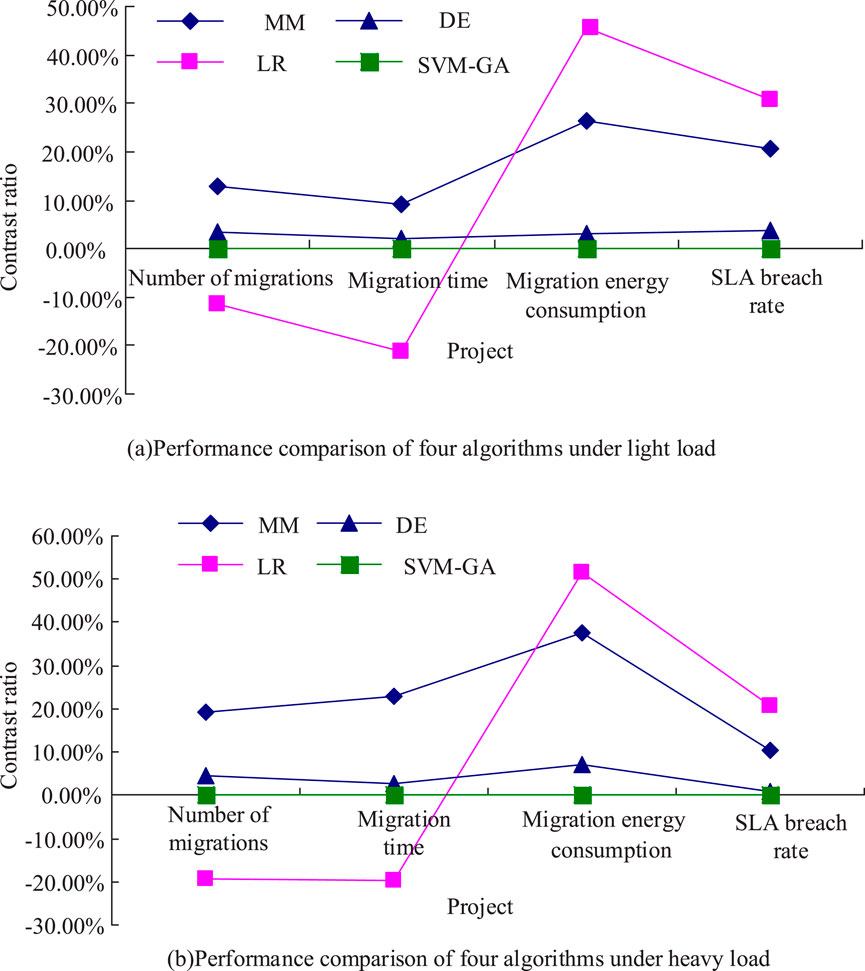
As shown in Figure 9, as the number of evolutionary generations increased, the overall load balance of the four algorithms fluctuated slightly up and down, and it was difficult to find a specific pattern for the change of load balance of MM, LR, and DE algorithms, while the decrease fluctuation of load balance of the SVM-GA method was not very large. The solution reached by SVM-GA became increasingly excellent and reached convergence at 160–200 evolutionary generations. As shown in Figure 9, the proposed model had high stability and a fast convergence rate, thus verifying the advanced nature of the proposed model. It set up 100 workload traces and 50 minimum Google cluster traces to simulate light user requirements and 50 load-max GCTVs to simulate heavy user requirements with constant 100 workload traces. Experiments were set up to examine the SLA violation rate, migration time, migration energy consumption, and number of migrations for VM migration. The results obtained by the improved algorithm were used as a benchmark to compare the results obtained by MM, LR, and DE, respectively, to verify the algorithm performance, and the experimental results are shown in Figure 10.
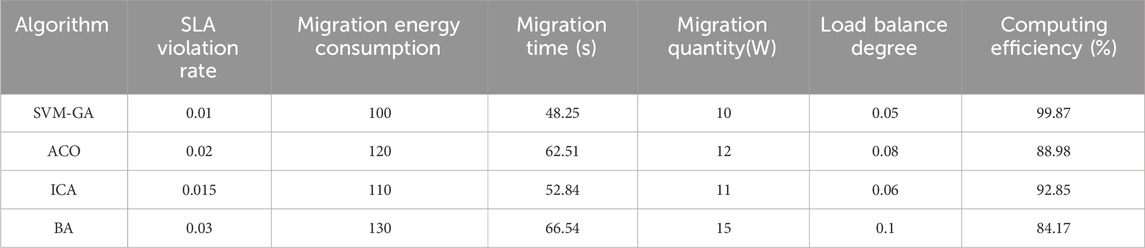
As shown in Figure 10, the optimization results of migration time and migration count items obtained by LR under light load were lower than the reference benchmark, and the relative values of migration count and migration time obtained by LR were −11.55% and −21.09%, respectively. In contrast, the migration energy consumption and SLA violation rate of the three traditional intelligent algorithms were above those of the SVM-GA. The migration time and number of migrations were similar to the light load case, and the best solution was obtained by LR, followed by SVM-GA. The relative values of migration number and migration time for the heavy migration load case were −19.24% and −19.64%, respectively. For migration energy consumption and SLA violation rate, MM, DE, and LR yielded results above those of SVM-GA, indicating that SVM-GA worked best. To further prove the superiority of SVM-GA in the field of cloud computing task scheduling, SVM-GA was combined with the most advanced ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm in the current field. The bat algorithm (BA) was compared with independent component analysis (ICA). The comparison results are shown in Table 2.
In Table 2, SVM-GA had the lowest violation rate, indicating that it is more reliable in meeting SLAs. The migration energy consumption was the lowest, which showed its superiority in energy-saving. The shortest migration time meant that it was more efficient when migrating VMS. The lowest number of migrations indicated that it had done a better job of reducing unnecessary migrations. The highest load balance indicated that it was more balanced in resource allocation. It was the most computationally efficient method, indicating that it was faster at completing tasks. It can be seen that SVM-GA has significant advantages in cloud computing task scheduling, especially in improving energy efficiency and satisfying SLAs.
5 Conclusion
To obtain the optimal resource allocation policy and realize the effective allocation of VM resources in the cloud computing environment, a VM scheduling model using Shapley value improved GA was proposed. The results showed that the total task time of the proposed SVM-GA algorithm was 25 s, 55 s, 81 s, 112 s, 145 s, and 175 s compared with MM, LR, and DE algorithms for the number of tasks of 200, 400, 600, 800, 1,000, and 1,200, respectively. The load balancing degree comparison of the above four algorithms in the VM scheduling model showed that the ability of SVM-GA to solve the optimal solution increased as evolutionary generations increased, and the algorithm converged at 160 to 200 evolutionary generations. The migration time of SVM-GA under light load was 3.02 s, the number of migrations was 1,129, the migration energy consumption was 30.02 kW/h, and the SLA violation rate was 8.53%. The energy consumption of SVM-GA (30.02Kw/h) < DE (30.99 kW/h) < MM (37.95 kW/h) < LR (43.76 kW/h). The violation rate index was 8.53%, which is smaller than that of DE (8.85%), MM (10.28%), and LR (11.14%). The SVM-GA performance under heavy load was similar to that under the light load, and the values of all four metrics increased. The SVM-GA migration time under heavy load was 5.83 s, the number of migrations was 1,863, the migration energy consumption was 57.32 kW/h, and the SLA violation rate was 23.33%. The experiments show that the VM scheduling model strategy has some merits and can better establish an energy-saving model to allocate virtual resources. However, there are still areas worth improving in terms of migration time and the number of migrations.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LC: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, and writing–original draft. YN: investigation, methodology, validation, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by the Nantong Basic Science Research Project in 2022: Research on Multi-Enterprise Collaborative Scheduling System Based on Cloud Platform (JCZ2022046) and the General project of philosophy and social science research in Jiangsu universities: The construction and practical research of the full education data management framework in higher vocational colleges under the background of big data (No. 2022SJYB 1815).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdulqadir, H. R., Zeebaree, S. R. M., Shukur, H. M., Sadeeq, M. M., Salim, B. W., Salih, A. A., et al. (2021). A study of moving from cloud computing to fog computing. Qubahan Acad. J. 1 (2), 60–70. doi:10.48161/qaj.v1n2a49
Azzam, R., Mizouni, R., Otrok, H., Singh, S., and Ouali, A. (2018). A stability-based group recruitment system for continuous mobile crowd sensing. Comput. Commun. 119, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2018.01.012
Bhatnagar, A., Gambhir, V., and Thakur, M. K. (2018). A new perspective to stable marriage problem in profit maximization of matrimonial websites. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 14 (4), 961–979. doi:10.3745/JIPS.02.0092
Chen, H., Covert, I. C., Lundberg, S. M., and Lee, S. I. (2023). Algorithms to estimate Shapley value feature attributions. Nat. Mach. Intell. 5 (6), 590–601. doi:10.1038/s42256-023-00657-x
Contaldi, C., Vafaee, F., and Nelson, P. C. (2019). Bayesian network hybrid learning using an elite-guided genetic algorithm. Artif. Intell. Rev. 52 (1), 245–272. doi:10.1007/s10462-018-9615-5
Dong, H. B., Li, T., Ding, R., and Sun, J. (2018). A novel hybrid genetic algorithm with granular information for feature selection and optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 65, 33–46. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2017.12.048
Elhoseny, M., Tharwat, A., and Hassanien, A. E. (2018). Bezier curve based path planning in a dynamic field using modified genetic algorithm. J. Comput. Sci. 25, 339–350. doi:10.1016/j.jocs.2017.08.004
Karthikeyan, P., and Soni, R. (2020). A hybrid PSO optimised virtual machine scheduling algorithm in cloud computing. Int. J. Bus. Inf. Syst. 34 (4), 536–559. doi:10.1504/ijbis.2020.109028
Lin, J., Zhang, Q., and Meng, F. Y. (2019). A novel algorithm for group decision making based on continuous optimal aggregation operator and Shapley Value. Int. J. Uncertain. Fuzziness Knowledge-Based Syst. 27 (6), 969–1002. doi:10.1142/s0218488519500430
Ma, X., Xu, H., Gao, H., Bian, M., and Hussain, W. (2022). Real-time virtual machine scheduling in industry iot network: a reinforcement learning method. IEEE Trans. Industrial Inf. 19 (2), 2129–2139. doi:10.1109/tii.2022.3211622
Malik, M. K., Singh, A., and Swaroop, A. (2022). A planned scheduling process of cloud computing by an effectivejob allocation and fault-tolerant mechanism. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 13 (2), 1153–1171. doi:10.1007/s12652-021-03537-7
Marri, N. P., and Rajalakshmi, N. R. (2022). MOEAGAC: an energy aware model with genetic algorithm for efficient scheduling in cloud computing. Int. J. Intelligent Comput. Cybern. 15 (2), 318–329. doi:10.1108/ijicc-07-2021-0134
Memari, P., Mohammadi, S. S., and Jolai, F. (2022). A latency-aware task scheduling algorithm for allocating virtual machines in a cost-effective and time-sensitive fog-cloud architecture. J. Supercomput. 78 (1), 93–122. doi:10.1007/s11227-021-03868-4
Naik, B. B., Singh, B., and Samaddar, A. B. (2020). FHCS: hybridised optimisation for virtual machine migration and task scheduling in cloud data center. IET Commun. 14 (12), 1942–1948. doi:10.1049/iet-com.2019.1149
Rana, N., Abd Latiff, M. S., Abdulhamid, S. M., Abdulhamid, S. I. M., and Misra, S. (2022). A hybrid whale optimization algorithm with differential evolution optimization for multi-objective virtual machine scheduling in cloud computing. Eng. Optim. 54 (12), 1999–2016. doi:10.1080/0305215x.2021.1969560
Rovithakis, G. A., Maniadakis, M., and Zervakis, M. (2004). A hybrid neural network/genetic algorithm approach to optimizing feature extraction for signal classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part B 34 (1), 695–703. doi:10.1109/tsmcb.2003.811293
Smarandache, F. (2022). Plithogeny, plithogenic set, logic, probability and statistics: a short review. J. Comput. Cognitive Eng. 1 (2), 47–50. doi:10.47852/bonviewjcce2202191
Wan, B., Dang, J. L., Li, Z. T., Gong, H., Zhang, F., and Oh, S. (2020). Modeling analysis and cost-performance ratio optimization of virtual machine scheduling in cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distributed Syst. A Publ. IEEE Comput. Soc. 31 (7), 1518–1532. doi:10.1109/tpds.2020.2968913
Wang, J. Y., He, X., Wang, B. T., and Zheng, X. (2022). Shapley additive explanations of multigeometrical variable coupling effect in transonic compressor. Trans. ASME 144 (4), 041015–041020. doi:10.1115/1.4053322
Wang, Y. L., Liu, Z., Cai, C. C., Xue, L., Ma, Y., Shen, H., et al. (2022). Research on the optimization method of integrated energy system operation with multi-subject game. Energy 245, 123305. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.123305
Waziri, T. A., and Yakasai, B. M. (2023). Assessment of some proposed replacement models involving moderate fix-up. J. Comput. Cognitive Eng. 2 (1), 28–37. doi:10.47852/bonviewjcce2202150
Xu, X. L., Zhang, Q. T., Maneas, S., Sotiriadis, S., Gavan, C., and Bessis, N. (2019). VMSAGE: a virtual machine scheduling algorithm based on the gravitational effect for green Cloud computing. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory Int. J. Fed. Eur. Simul. Soc. 93, 87–103. doi:10.1016/j.simpat.2018.10.006
Yang, B., Lei, Y., Li, X., and Li, N. (2024a). Targeted transfer learning through distribution barycenter medium for intelligent fault diagnosis of machines with data decentralization. Expert Syst. Appl. 244, 122997. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122997
Keywords: Shapley value, virtual machine, cloud computing, genetic algorithm, topological network, energy saving model
Citation: Chen L and Niu Y (2024) Improved genetic algorithm based on Shapley value for a virtual machine scheduling model in cloud computing. Front. Mech. Eng. 10:1390413. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1390413
Received: 23 February 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 11 December 2024.
Edited by:
Mohamed Arezki Mellal, University of Boumerdés, AlgeriaCopyright © 2024 Chen and Niu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lili Chen, emx2Y2NsbEAxMjYuY29t
 Lili Chen
Lili Chen Yuxia Niu1
Yuxia Niu1