- 1Faculty Jiaxing Key Laboratory of Industrial Internet Security, Jiaxing Vocational and Technical College, Jiaxing, China
- 2Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
- 3MODU System (S) Pte Ltd., Klang, Selangor, Malaysia
- 4Mathematics and Engineering, University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom
This study introduces a sophisticated intelligent predictive maintenance system for industrial conveyor belts powered by a random forest machine learning model. The random forest model was evaluated against established models such as logistic regression, neural networks, decision trees, and gradient boosting, demonstrating superior performance. The model achieved 100% accuracy in classifying gearbox lubricant levels and sprocket conditions, highlighting its potential for addressing critical challenges in predictive maintenance, such as avoiding unexpected downtime. However, further validation with larger datasets and varied operational environments is recommended to confirm robustness. This performance highlights its effectiveness in multiclass fault detection and overfitting mitigation, establishing a new standard in predictive maintenance technology. The system, enhanced by a comprehensive sensor array, not only adeptly captures but also intelligently analyzes critical operational data, providing proactive and data-driven insights for maintenance decision-making. This study not only affirms the dominance of the random forest model in predictive analytics but also underscores its pivotal role in optimizing maintenance strategies, enhancing operational efficiency, and ensuring the reliability of conveyor systems in industrial settings.
1 Introduction
Conveyor systems are indispensable in industrial manufacturing, especially in the age of Industrial 4.0 characterized by a focus on automation. These systems play a critical role in the infrastructure of the manufacturing sector, yet the maintenance of these systems often takes a back seat until failures result in operational downtime and reduced productivity (Wang et al., 2020). Maintenance approaches for conveyors, encompassing reactive and preventive strategies, demand significant effort and financial outlay (Creehan, 2005). For instance, routine checks and servicing of a conveyor’s drive unit necessitate shutting down the entire production line (Gebler et al., 2017), with technicians manually addressing the drive unit. This procedure can be notably burdensome and time-intensive, particularly for units positioned in challenging locations, such as on spiral or elevated chain conveyors. The ensuing production delays can amplify a company’s financial losses.
Predictive maintenance in conveyor belt systems entails unique challenges, including the difficulty of identifying the early signs of mechanical failure and the costly downtime associated with manual inspections. Traditional methods, such as scheduled preventive maintenance, often result in either over-maintenance or unexpected failures. By leveraging machine learning, this research aims to develop a system that accurately predicts failures and optimizes maintenance schedules, thereby reducing operational costs (Wu et al., 2023). The introduction of a system capable of monitoring and prognosticating the maintenance needs of conveyors could revolutionize maintenance procedures and enhance productivity (Yu, 2019; Kiangala and Wang, 2018). A variety of predictive maintenance methodologies based on machine learning have been developed for diverse types of machinery (Hosamo et al., 2022; Mathew et al., 2018; Žarković and Stojković, 2019; Gutschi et al., 2019). These predominantly employ algorithms categorized into regression, decision tree, and neural network-based models. predictive maintenance research has largely concentrated on belt conveyors (Liu et al., 2019; Medina et al., 2020; Kozhushko et al., 2020; Gupta et al., 2023; Szrek et al., 2020; Al-Kahwati et al., 2022), with the factors significantly impacting the performance of chain conveyors still largely unknown. Kiangala and Wang (2020) proposed a CNN model with on-the-fly training capabilities for identifying conveyor faults, although this model tends to suffer from data overfitting, which could impair prediction precision.
This research introduces an intelligent predictive maintenance system which utilizes random forest to address challenges associated with industrial conveyor belts. The system includes a conveyor monitoring setup with sensors that collect essential operational data to evaluate critical components like gearboxes and sprockets. By analyzing sensor data and conveyor behavior, this system predicts performance and optimizes maintenance schedules. This enables remote supervision of conveyor operations, including control panel visualizations, which removes the requirement for physical presence. Moreover, the data are processed by an AI model capable of detecting anomalies and faults in essential components. For example, should the lubricant oil level in the gearbox drop significantly, the system prompts a maintenance alert to avert irreversible damage to key components. The standout feature of this system is its predictive and remote monitoring capabilities, empowering maintenance teams or management to schedule maintenance at optimal intervals and oversee the conveyor system remotely, provided there is internet access.
2 Analytical foundations and machine learning in predictive maintenance
This section examines in detail the utilization of statistical correlation analysis and a suite of machine learning models in the realm of predictive maintenance, underscoring their crucial role in the assessment and diagnosis of the operational health of conveyor systems through the analysis of key components.
2.1 Preliminary data analysis through correlation tests
The foundational step in effective predictive maintenance involves a rigorous analysis of collected data, aimed at isolating significant sensor variables that are instrumental for the accurate assessment of the health of conveyor components (Bayoumi and McCaslin, 2017). The Pearson product moment correlation test and the Kendall rank correlation test are utilized due to their appropriateness for the continuous ordinal nature of the dataset (Khamis, 2008). Equation 1 represents the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient, a statistical metric that indicates the linear correlation between two variables. Equation 2 defines the Kendall rank correlation coefficient, reflecting the ordinal association between two variables.
Kendall rank correlation:
2.2 Exploration of machine learning models for predictive maintenance
Subsequent to the identification of significant variables through correlation tests, our research explores various machine learning models for predictive maintenance, with each model presenting unique attributes and capabilities.
2.2.1 Logistic regression
Logistic regression is employed for binary classification tasks to predict the probability of an outcome based on a set of predictors (LaValley, 2008). The model’s efficacy is tested using both forward and stepwise logistic regression techniques. The forward method starts with a minimal model and sequentially introduces variables, while the stepwise method includes an additional step of reassessing the significance of each variable at every stage.
2.2.2 Artificial neural networks (ANNs)
ANNs, inspired by biological neural networks, comprise interconnected layers of nodes. The model is designed with a single hidden layer, suitable for the data’s complexity, and utilizes the Softmax activation function to effectively address multi-class classification scenarios (Biswal and Sabareesh, 2015).
2.2.3 Decision tree
Decision tree is a model that uses a tree-like structure for decision-making in classification and regression tasks (Song and Lu, 2015). It is particularly adept at mapping potential outcomes based on sensor inputs. The model is configured with a maximum tree depth and is trained using the gain-split criterion.
2.2.4 Random forest
The Random forest model used in this study was configured with 500 trees and a maximum tree depth of ten. The Gini impurity criterion was employed to measure the quality of splits, and bootstrap sampling was applied to improve model generalization. The number of features considered at each split was set to the square root of the total number of features. These configurations were chosen for their ability to handle high-dimensional data and minimize overfitting, particularly in multiclass fault classification tasks. The model’s training involves setting specific numbers for trees, depth, and maximum leaf size, allowing it to adeptly handle complex data structures (Biau and Scornet, 2016; Ahmad et al., 2018; Sarker, 2021).
2.2.5 Gradient Boosting
Gradient boosting is an advanced ensemble learning technique that builds on decision trees (Friedman et al., 2000). It incrementally adds weak learners to form a strong predictive model, continuously improving its accuracy. The gradient boosting model is fine-tuned with parameters such as maximum depth and leaf size to optimize its performance for the dataset.
The comparative analysis in Table 1 vividly illustrates the unique attributes and contributions of each machine learning model in the context of predictive maintenance for conveyor systems. Logistic regression and decision tree are lauded for their simplicity and interpretability, while ANN is distinguished for its prowess in managing non-linear complexities. Gradient boosting is recognized for its capacity to iteratively refine prediction accuracy. However, it is the random forest algorithm that conspicuously excels, attributed to its superior robustness against overfitting, remarkable predictive accuracy, and an inherent mechanism for feature importance estimation. Collectively, these attributes position random forest as a substantial contributor to operational efficiency and downtime reduction in industrial conveyor applications, thereby reaffirming its pivotal role in a comprehensive and multi-faceted predictive maintenance strategy.
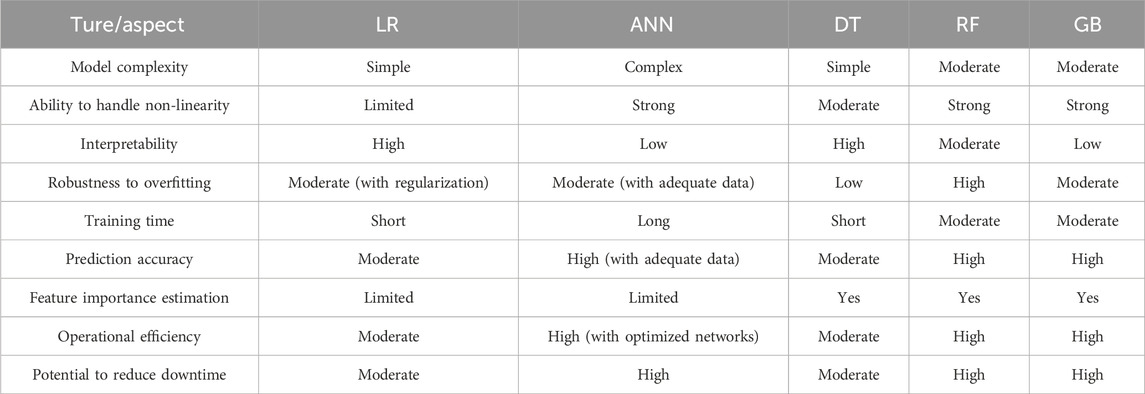
Table 1. Comparative analysis of machine learning models for predictive maintenance in conveyor systems.
3 Methodology
3.1 System description and setup
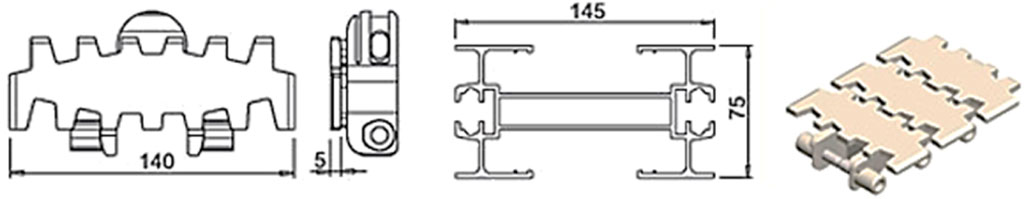
The industrial chain conveyor at the MODU facility, with its unique design and dimensions, is depicted in Figure 1. The conveyor has an elliptical track layout, materials, and dimensions, including the specifics of the ML2 plastic chain and the three-phase asynchronous AC motor. Its primary components are the gearbox, sprocket, and chain, and their design and critical importance is shown in Figures 2, 3. The common failure points include the depletion of gearbox lubricant and the wear of sprocket teeth, which set the stage for a predictive maintenance approach.
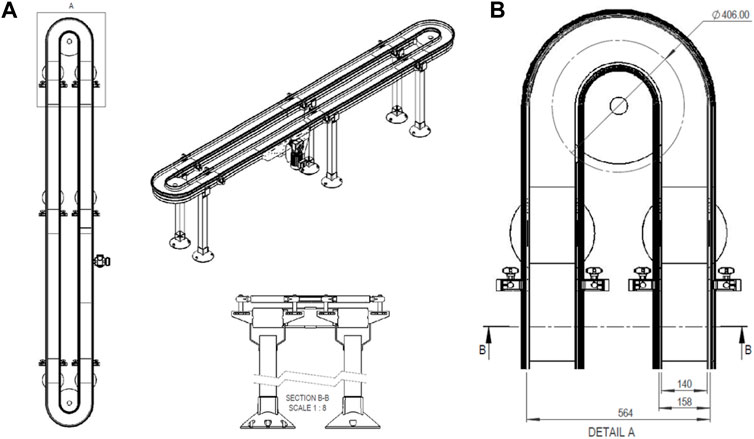
Figure 1. Design of the chain conveyor. (A) Design of the chain conveyor on site. (B) Dimension of the ML2 plastic conveyor chain.
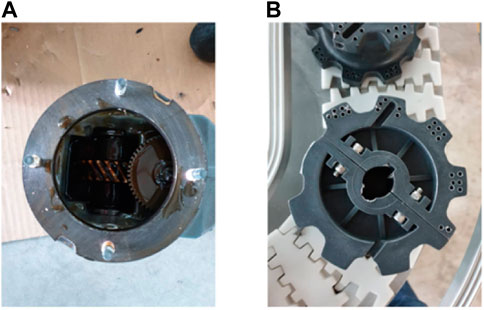
Figure 3. Critical components of the industrial chain conveyor. (A) Gearbox (amount of lubricant oil). (B) Sprocket teeth condition.
3.2 Predictive maintenance system architecture
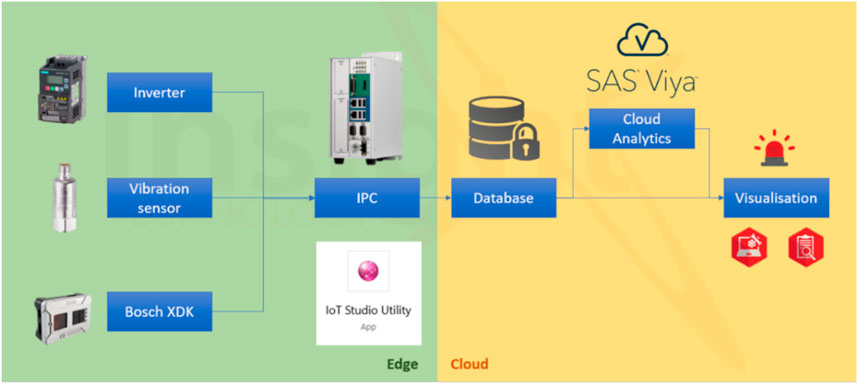
The structure of the predictive maintenance (PdM) system is illustrated in Figure 4. The integration, placement, and role of each sensor device—the Schneider inverter, IFM vibration sensor, and Bosch XDK sensor—are shown in Figure 5. The system features a data collection process, frequent collection, a communication protocol (MQTT), and storage (SAS H2 database). An Automation Industrial Computer NIFE 200 is the central controller and IoT gateway, seamlessly integrating sensor data into the predictive maintenance framework.
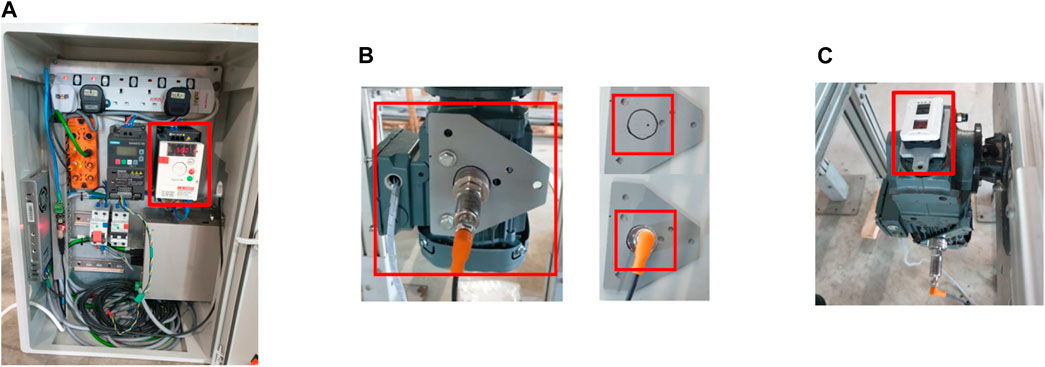
Figure 5. Installation of sensor devices. (A) Inverter in MODU smart box. (B) IFM VVB001 mounted on motor. (C) Bosch XDK mounted on top of the gearbox.
3.3 Experimental methodology and data analysis
3.3.1 Experimental setup
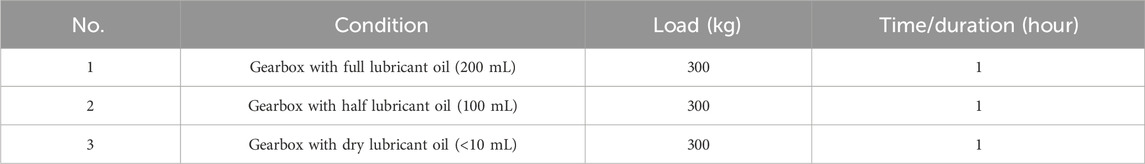
Two experiments were conducted to evaluate the operational performance of the conveyor under varying conditions commonly encountered in industrial settings. The focus on gearbox lubricant levels and sprocket teeth conditions reflects frequent industry challenges, where irregular maintenance can lead to significant downtimes and costs. These conditions were experimentally simulated (Tables 2, 3) to directly address the practical reliability issues faced by conveyor systems. The experimental conditions, operational procedures, and data collection methodology ensure the consistency and reliability of the data collected, as summarized by flowchart in Figure 6.
3.3.2 Data analysis and predictive modeling
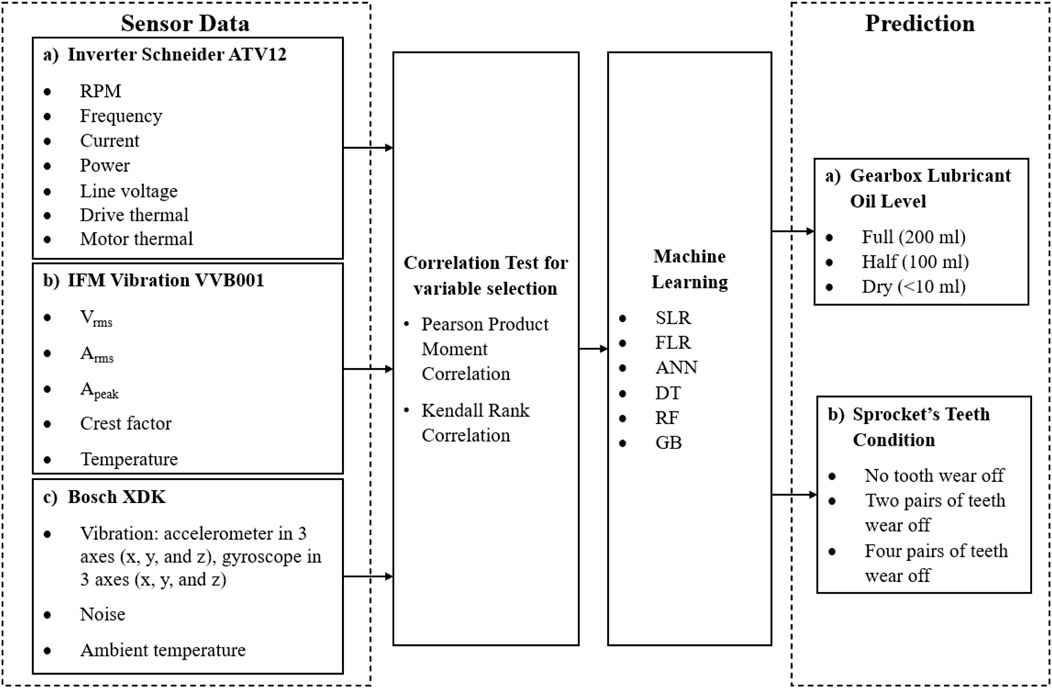
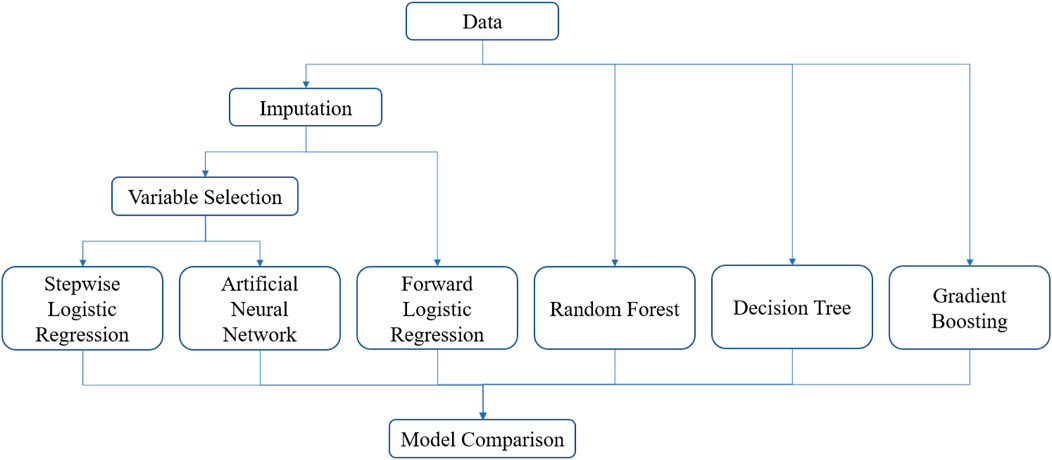
The data analysis techniques employed including Pearson product moment and Kendall rank correlation tests to identify significant variables linked to conveyor failures. The development, training, and rigorous validation of various machine learning models (SLR, FLR, ANN, DT, GB, and RF) incorporate cross-validation and ensemble techniques to mitigate overfitting, thus ensuring robust model performance. These validation techniques are critical in evaluating capability of the models to effectively generalize unseen data, enhancing the reliability and applicability of the predictive maintenance strategies. The model evaluation criteria and the process of determining the most effective predictive model are detailed in the model training process (Figure 7).
4 Results of predictive maintenance analysis: Assessing gearbox lubricant and sprocket teeth conditions in conveyor belts
4.1 Experiment 1—gearbox lubricant oil condition
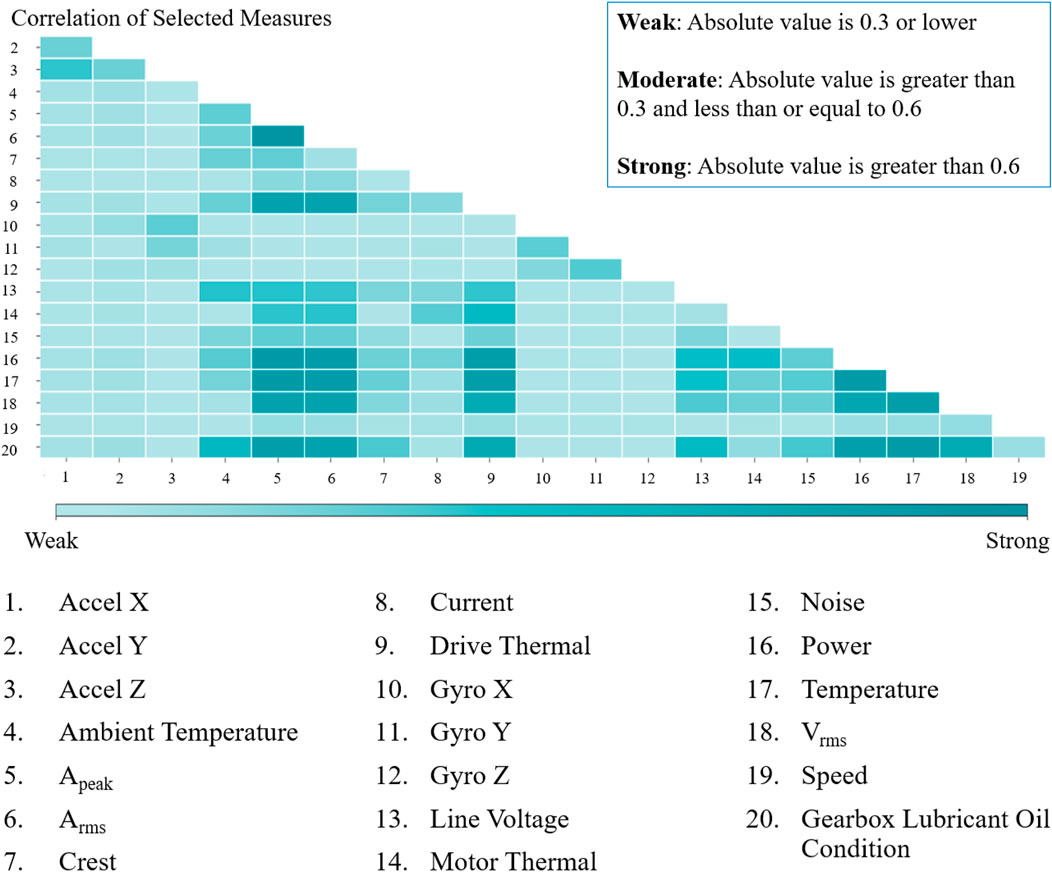
The Pearson product moment correlation test revealed a robust correlation between the gearbox’s lubricant oil level and various parameters, including temperature readings from the vibration sensor, Apeak, Arms, Vrms, power, and drive thermal (Figure 8). Concurrently, the analysis showed a moderate correlation between the gearbox’s lubricant oil level and the temperature data collected by the Bosch XDK sensor, alongside line voltage, noise, and crest—a relationship further elucidated in Figure 9.
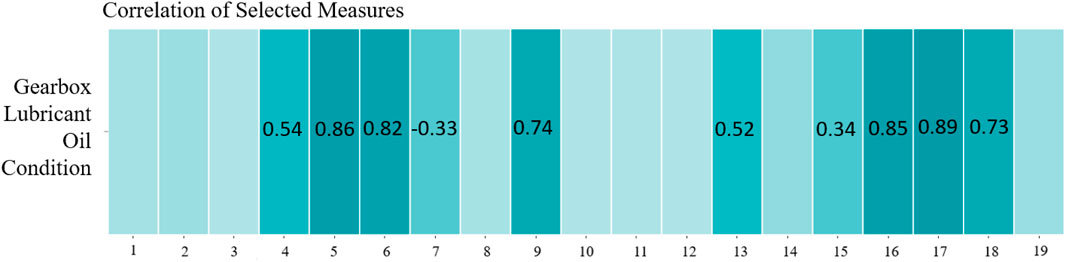
Figure 9. Pearson product moment correlation test for the gearbox lubricant oil condition (zoom into correlation between output variable with all input variables).
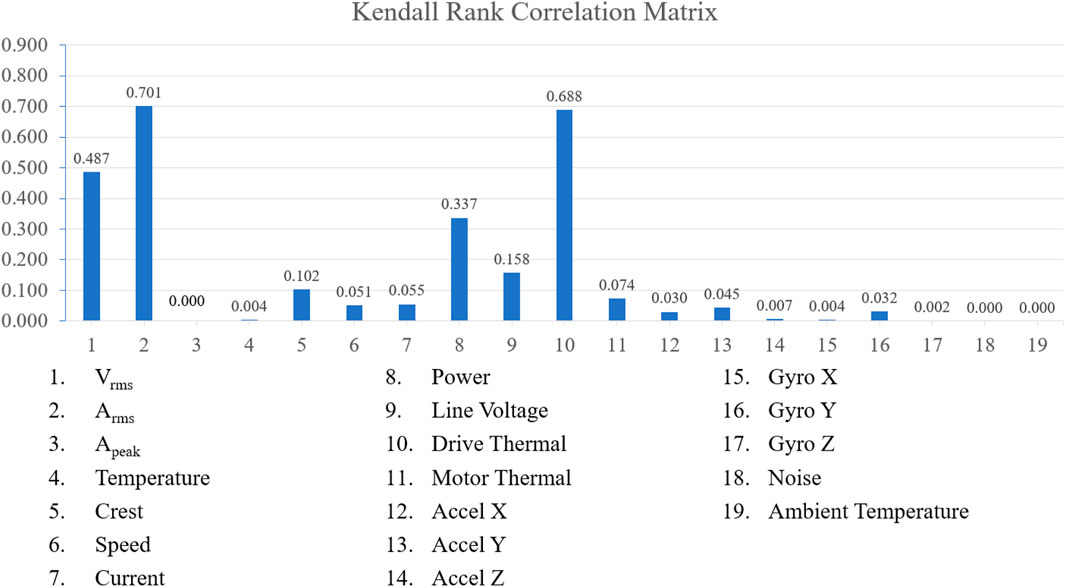
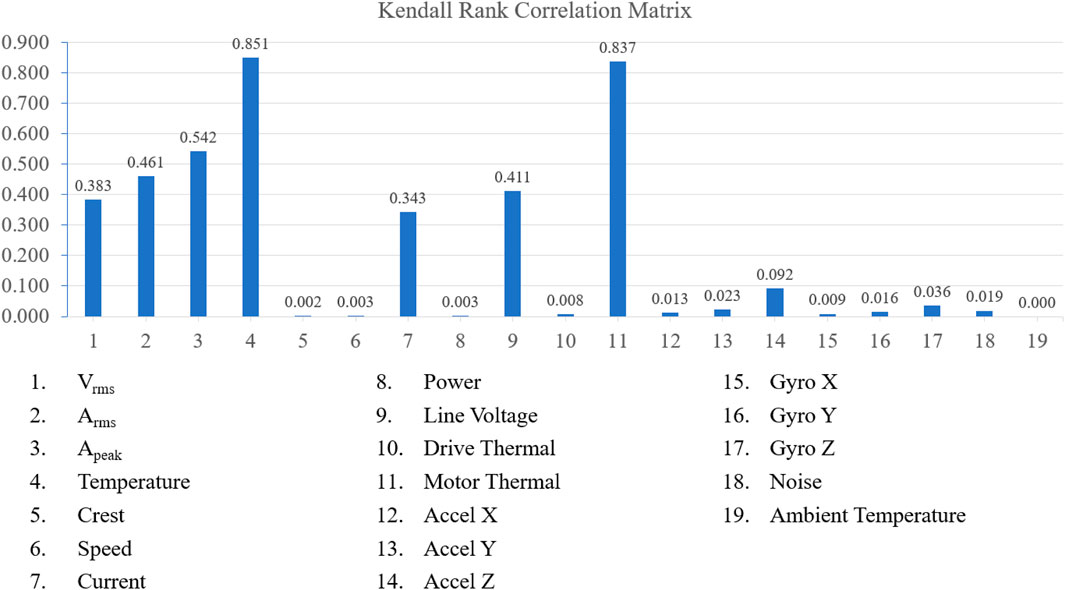
Conversely, the Kendall rank correlation test demonstrated a pronounced correlation between the lubricant oil condition in the gearbox and both Arms and drive thermal. Additionally, this test indicated a moderate correlation with Vrms and power, detailed in Figure 10.
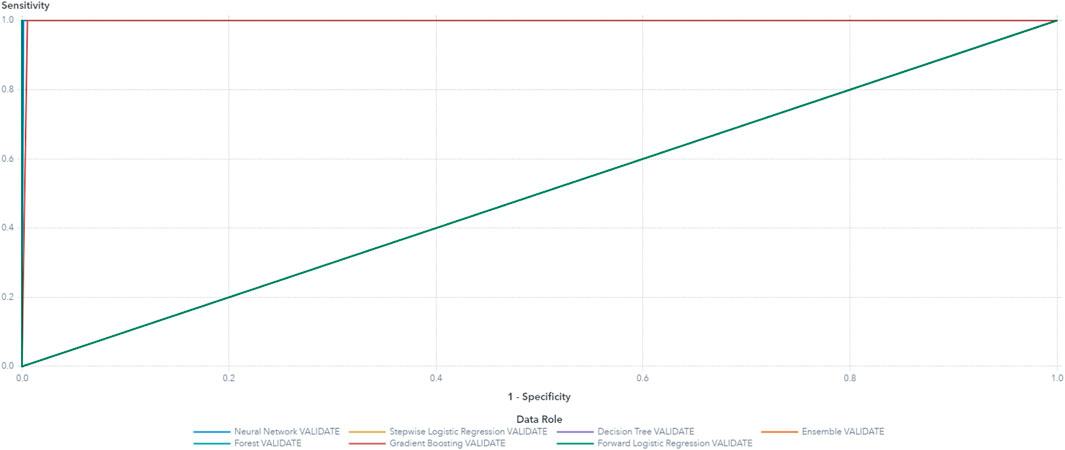
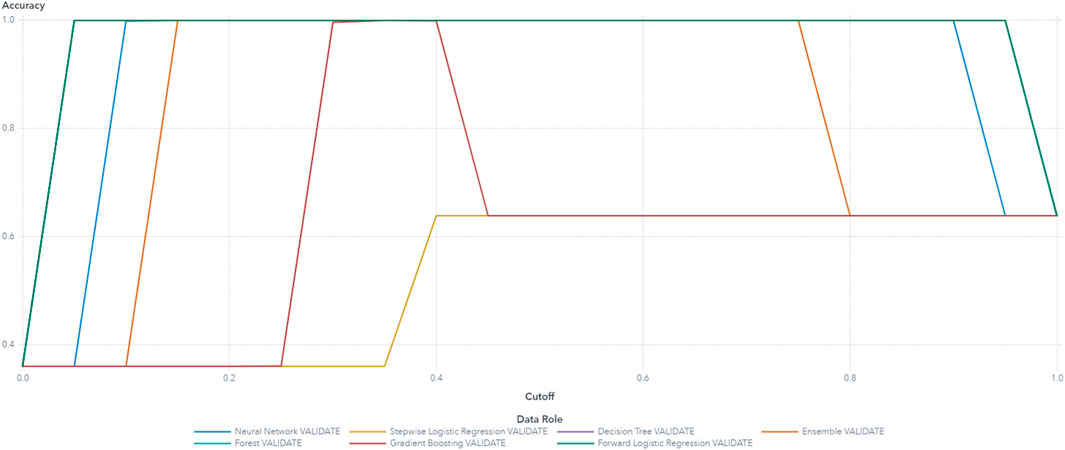
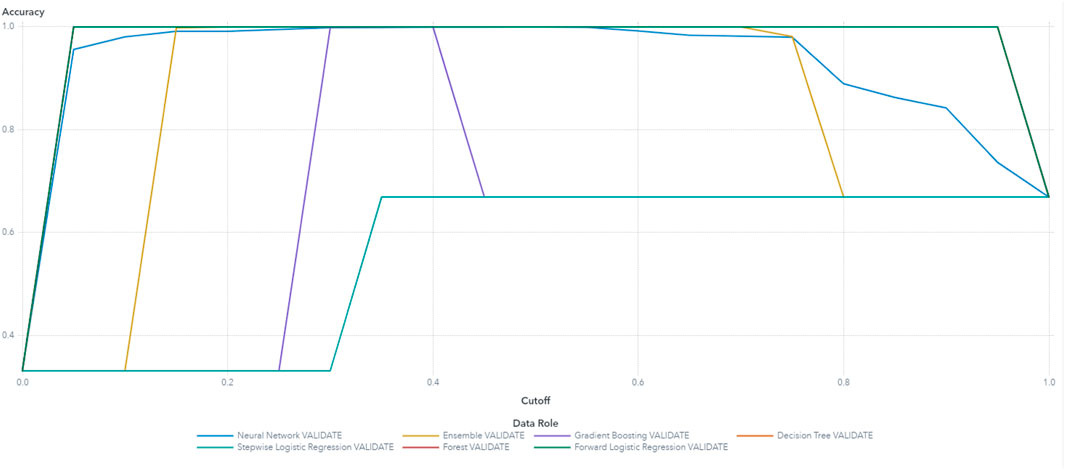
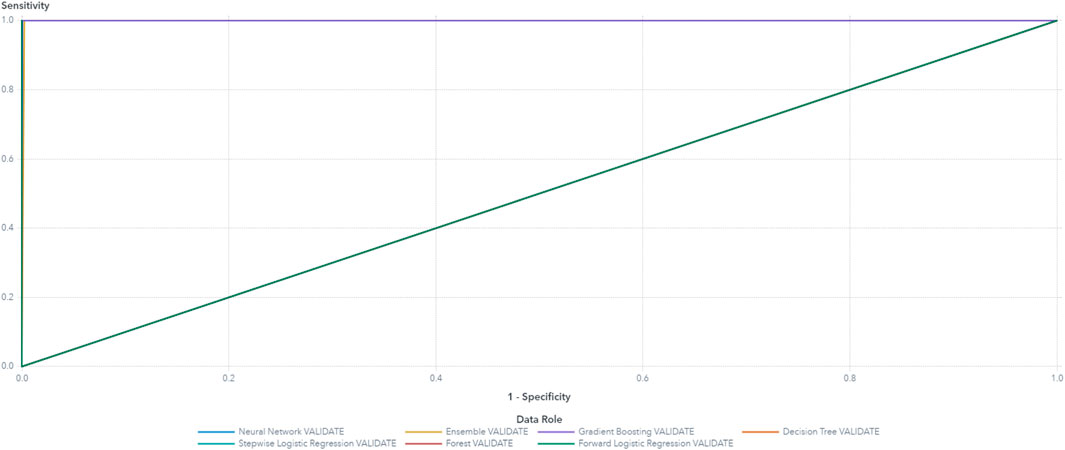
Based on these results, the final variables selected for the machine learning model building are Arms, drive thermal, Vrms, and power. The random forest model demonstrated superior performance, achieving the highest accuracy and the lowest average squared error compared to other models such as decision tree, logistic regression, and gradient boosting. The random forest model’s accuracy reached 100%, significantly outperforming decision tree and logistic regression, which achieved 90% and 88%, respectively. These results were validated through ten-fold cross-validation, with a standard deviation in accuracy of less than 0.02, further highlighting the robustness and generalizability of random forest. The use of multiple models, including random forest, also aids in assessing model robustness and reducing the risk of overfitting (Table 4). The high performance model possessed low average squared error and high accuracy of classification. The accuracy and ROC plots are illustrated in Figures 11, 13 respectively. Figure 12 illustrates the accuracy through the proportion correctly classified versus cutoff point. Figure 13 shows the true positive rate (sensitivity) versus the false positive rate (specificity) for all possible cut-off values. The diagnostic test of the model showed a near-perfect test in which the ROC curve was almost vertical from (0,0) to (0,1) and horizontal to (1,1). Figure 15 indicates a decent separation from random classification, especially for the random forest model. As a result of the analysis, random forest was selected as the superior model based on its outcomes of highest accuracy and lowest average squared error. Although the random forest model achieved the best overall performance, the decision tree model was more interpretable, making it suitable for cases where model transparency is critical, despite its lower accuracy and higher susceptibility to overfitting. Logistic regression, while computationally efficient, struggled with the complexity of multiclass classification in this predictive maintenance task, showing lower accuracy than random forest. These results emphasize the trade-offs between model accuracy, interpretability, and computational cost in predictive maintenance tasks.
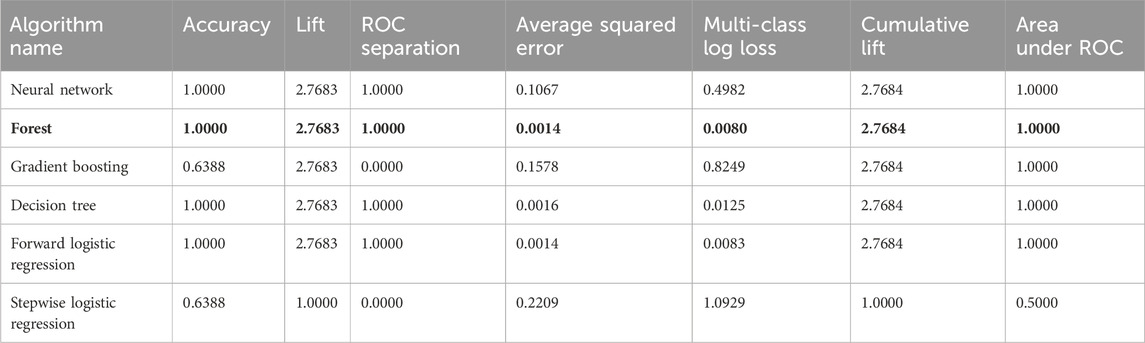
Table 4. Outcome and accuracy of machine learning models for classifying the gearbox lubricant oil condition.
4.2 Experiment 2: Sprocket teeth condition
In Experiment 2, the Pearson product moment correlation test revealed a significant correlation between the sprocket teeth condition and several parameters, notably the temperature readings from the vibration sensor, motor thermal, drive thermal, temperature data from the Bosch XDK sensor, and Apeak (Figure 13). Simultaneously, the test indicated a moderate correlation of the sprocket’s teeth condition with Arms, line voltage, Vrms, and current, with these relationships detailed in Figure 14.
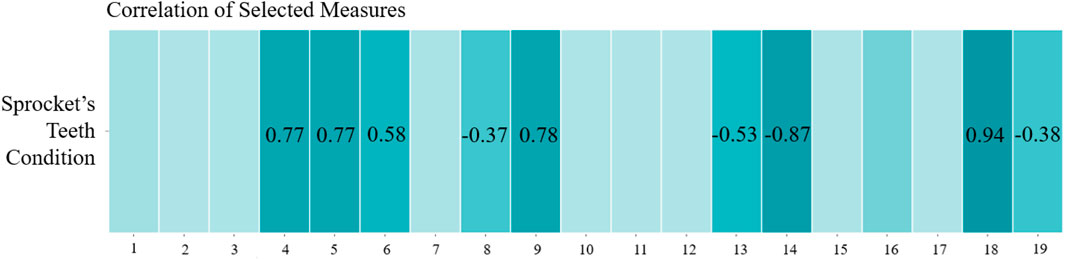
Figure 14. Pearson product moment correlation test for sprocket teeth condition (zoom into correlation between the output variable with all input variables).
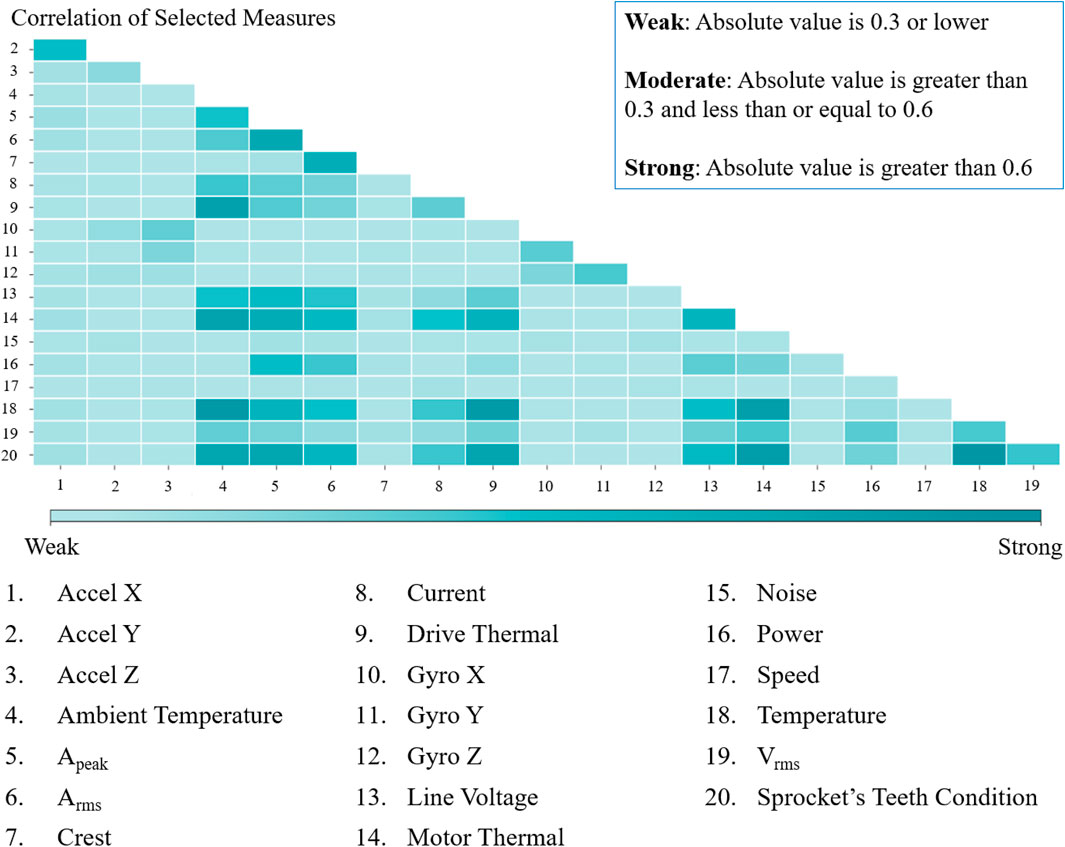
Concurrently, the Kendall rank correlation test revealed a substantial correlation between the sprocket teeth condition and both the temperature data from the vibration sensor and motor thermal. Moreover, this analysis highlighted a moderate correlation with Apeak, Arms, line voltage, Vrms, and current—relationships comprehensively illustrated in Figure 15.
The final variables selected for machine learning model building were temperature data from the vibration sensor, motor thermal, Apeak, Arms, line voltage, Vrms, and current. The outcome and accuracy of the six machine learning models are summarized in Table 5. The accuracy and ROC plots are illustrated in Figures 16, 17, respectively. From the evaluation of machine learning models, the decision tree and random forest recorded the same outcome of highest accuracy and lowest average squared error. Random forest was selected as the best model based on its feature of randomized feature selection and ability to better generalize the data, which is believed to perform better during deployment.
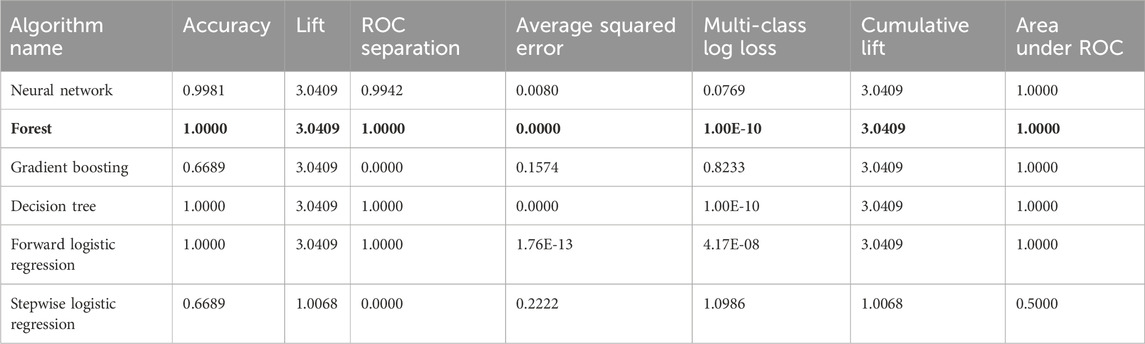
Table 5. Outcome and accuracy of machine learning models for classifying the sprocket teeth condition.
5 Conclusion
This study aimed to devise an intelligent predictive maintenance system based on random forest to address the intricate challenges associated with industrial conveyor belt systems. Through meticulous experimentation and analysis, the research successfully highlighted the efficacy of a random forest machine learning model over five other models for accurately classifying the gearbox lubricant oil level and sprocket condition of a chain conveyor. The superior performance of the random forest model can be attributed to its proficiency in multiclass fault detection, versatility in handling both categorical and continuous data, and its utilization of majority voting or averaging techniques in prediction outputs; these significantly curtail over-fitting and thereby augment final prediction accuracy.
The study pinpointed power, temperature, and vibration as the main predictors among 19 evaluated parameters, demonstrating consistency across different experimental setups. These predictors emerged as the most significant indicators of the health of two critical components in an industrial chain conveyor system—the gearbox and the sprocket. Notably, the predictive accuracy for the examined conditions reached a remarkable 100% based on the validation portion of the collected data. However, this high level of accuracy warrants cautious interpretation, as it may be influenced by the sample size of the collected data. Consequently, further experiments with extended data collection periods are recommended to validate and reinforce the robustness of the random forest machine learning model.
Moreover, variations in configurations and models of machine learning might introduce slight deviations in the results, suggesting an avenue for exploring the impact of different machine learning frameworks. Despite these considerations, the random forest model distinctly stood out, achieving 100% accuracy in the classification of the health condition of conveyor critical components.
In conclusion, this research significantly contributes to the field of predictive maintenance for industrial conveyor belts. By integrating intelligent machine learning techniques, specifically the random forest model, it provides a potent and reliable tool for monitoring and preemptively addressing the operational challenges of conveyor systems. The findings underscore the potential of machine learning in transforming maintenance strategies, paving the way for enhanced operational efficiency and reliability in industrial settings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MW: formal analysis, methodology, and writing–original draft. KG: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, resources, validation, and writing–original draft. KC: conceptualization, data curation, software, and writing–review and editing. YK: conceptualization, formal analysis, and writing–review and editing. MD: investigation, software, validation, and writing–review and editing. CY: conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, and writing–review and editing. ES: formal analysis, funding acquisition, resources, and writing–review and editing. HW: writing–review and editing. YZ: writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Research Grant [4C428]; Collaborative Research in Engineering, Science, and Technology (CREST) R&D grant [T20C2-18].
Acknowledgments
Gratitude is extended to MODU System (S) Pte Ltd. for supplying the conveyor system and to SAS for the provision of the data analytic platform.
Conflict of interest
Author KC was employed by MODU System (S) Pte Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmad, M. W., Reynolds, J., and Rezgui, Y. (2018). Predictive modelling for solar thermal energy systems: a comparison of support vector regression, random forest, extra trees and regression trees. J. Clean. Prod. 203, 810–821. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.207
Al-Kahwati, K., Birk, W., Nilsfors, E. F., and Nilsen, R. (2022). Experiences of a digital twin based predictive maintenance solution for belt conveyor systems. PHM Soc. Eur. Conf. 7 (1), 1–8. doi:10.36001/phme.2022.v7i1.3355
Bayoumi, A., and McCaslin, R. (2017). Internet of things – a predictive maintenance tool for general machinery, petrochemicals and water treatment. Petrochem. Water Treat., 137–146. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-48725-0_14
Biau, G., and Scornet, E. (2016). A random forest guided tour. Test 25 (2), 197–227. doi:10.1007/s11749-016-0481-7
Biswal, S., and Sabareesh, G. R. (2015). “Design and development of a wind turbine test rig for condition monitoring studies,” in 2015 international conference on industrial instrumentation and control, ICIC 2015, 891–896. doi:10.1109/IIC.2015.7150869
Creehan, K. D. (2005). Establishing optimal maintenance practices in a traditional manufacturing environment. J. Chin. Inst. Industrial Eng. 22 (1), 11–18. doi:10.1080/10170660509509272
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., and Tibshirani, R. (2000). Additive logistic regression: a statistical view of boosting (With discussion and a rejoinder by the authors). Ann. Statistics 28 (2), 337–407. doi:10.1214/aos/1016218223
Gebler, O. F., Hicks, B., Harrison, A., and Barker, M. (2017). “Investigating the diagnostic capabilities of monitored system parameters to support improvements in conveyor operation and maintenance,” in Wccm 2017 - 1st world congress on condition monitoring 2017. Available at: http://www.bindt.org/events/First-World-Congress-on-Condition-Monitoring-WCCM-2017/.
Gupta, V., Mitra, R., Koenig, F., Kumar, M., and Tiwari, M. K. (2023). Predictive maintenance of baggage handling conveyors using IoT. Comput. and Industrial Eng. 177, 109033. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2023.109033
Gutschi, C., Furian, N., Suschnigg, J., Neubacher, D., and Voessner, S. (2019). Log-based predictive maintenance in discrete parts manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 79, 528–533. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2019.02.098
Hosamo, H. H., Svennevig, P. R., Svidt, K., Han, D., and Nielsen, H. K. (2022). A Digital Twin predictive maintenance framework of air handling units based on automatic fault detection and diagnostics. Energy Build. 261, 111988. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.111988
Khamis, H. (2008). Measures of association: how to choose? J. Diagnostic Med. Sonogr. 24 (3), 155–162. doi:10.1177/8756479308317006
Kiangala, K. S., and Wang, Z. (2018). Initiating predictive maintenance for a conveyor motor in a bottling plant using industry 4.0 concepts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 97 (9–12), 3251–3271. doi:10.1007/s00170-018-2093-8
Kiangala, K. S., and Wang, Z. (2020). An effective predictive maintenance framework for conveyor motors using dual time-series imaging and convolutional neural network in an industry 4.0 environment. IEEE Access 8, 121033–121049. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006788
Kozhushko, G. G., Yampolsky, D. A., and Lukashuk, M. D. (2020). Analysis of forced vibrations of conveyor belts. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 709 (3), 033022. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/709/3/033022
LaValley, M. P. (2008). Logistic regression. Circulation 117 (18), 2395–2399. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.682658
Liu, X., He, D., Lodewijks, G., Pang, Y., and Mei, J. (2019). Integrated decision making for predictive maintenance of belt conveyor systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 188, 347–351. doi:10.1016/j.ress.2019.03.047
Mathew, V., Toby, T., Singh, V., Rao, B. M., and Kumar, M. G. (2018). “Prediction of Remaining Useful Lifetime (RUL) of turbofan engine using machine learning,” in IEEE international conference on circuits and systems, ICCS 2017, 306–311. doi:10.1109/ICCS1.2017.8326010
Medina, R., Macancela, J. C., Lucero, P., Cabrera, D., Sánchez, R. V., and Cerrada, M. (2020). Gear and bearing fault classification under different load and speed by using Poincaré plot features and SVM. J. Intelligent Manuf. 33, 1031–1055. doi:10.1007/s10845-020-01712-9
Sarker, I. H. (2021). Machine learning: algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2 (3), 160. doi:10.1007/s42979-021-00592-x
Song, Y., and Lu, Y. (2015). Decision tree methods: applications for classification and prediction. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 27 (2), 130–135. doi:10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.215044
Szrek, J., Wodecki, J., Błazej, R., and Zimroz, R. (2020). An inspection robot for belt conveyor maintenance in underground mine-infrared thermography for overheated idlers detection. Appl. Sci. Switz. 10 (14), 4984–5017. doi:10.3390/app10144984
Wang, P. Y., Liu, W. C., Liu, N., and You, Y. P. (2020). Digital twin-driven system for roller conveyor line: design and control. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 11 (11), 5419–5431. doi:10.1007/s12652-020-01898-z
Wu, M., Yeong, C. F., Su, E. L. M., Holderbaum, W., and Yang, C. (2023). A review on energy efficiency in autonomous mobile robots. Robotic Intell. Automation 43, 648–668. doi:10.1108/RIA-05-2023-0060
Yu, X. (2019). Machine learning based predictive maintenance and regression based control of a servo motor for industrial conveyor belts. Berlin: Technische Universität. Master Thesis.
Keywords: predictive maintenance, conveyor belt systems, random forest, machine learning, operational efficiency, comparative analysis, algorithm evaluation
Citation: Wu M, Goh KW, Chaw KH, Koh YS, Dares M, Yeong CF, Su ELM, William H and Zhang Y (2024) An intelligent predictive maintenance system based on random forest for addressing industrial conveyor belt challenges. Front. Mech. Eng. 10:1383202. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1383202
Received: 07 February 2024; Accepted: 29 October 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Mohamed Arezki Mellal, University of Boumerdés, AlgeriaReviewed by:
Xiang Zhang, Zhejiang University of Finance and Economics, ChinaŞekip Esat Hayber, Bursa Uludağ University, Türkiye
Yih Hwa Ho, Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka, Malaysia
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Goh, Chaw, Koh, Dares, Yeong, Su, William and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eileen L. M. Su, ZWlsZWVuc3VAdXRtLm15
†Present address: Che Fai Yeong, DF Automation & Robotics Sdn Bhd, Johor, Malaysia
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Mingyu Wu
Mingyu Wu Kai Woon Goh2‡
Kai Woon Goh2‡ Eileen L. M. Su
Eileen L. M. Su Holderbaum William
Holderbaum William