- 1School of Metallurgical and Ecological Engineering, University of Science and Technology Beijing (USTB), Beijing, China
- 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Special Melting and Preparation of High-End Metal Materials, Beijing, China
The oxygen content in high-silicon austenitic sulfuric acid-resistant stainless steels is one of the most detrimental parameters to their corrosion resistance. Based on the ion-molecular coexistence theory (IMCT), a thermodynamic model of the slag-steel reaction of austenitic stainless steel containing 5.0 wt% Si with CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 pentabasic slag was developed to investigate the deoxidation reaction and the oxygen control mechanism of the steel. The model was validated through experiments proposed in this study. The results of the slag-steel reaction indicated that the equilibrium oxygen content was determined by the greater of two factors: w[O]%, Si obtained from the [Si]-[O] equilibrium reaction controlled by the activity of SiO2 and w[O]%, Al obtained from the [Al]-[O] equilibrium reaction controlled by the activity of Al2O3. The system temperature and the basicity of slag are the most crucial among the multiple variables affecting the equilibrium oxygen content compared with Al2O3 and CaF2 in slag. However, achieving an ultra-low oxygen steel, both a basicity of slag greater than two and a low activity of Al2O3 in slag should be maintained. The total oxygen content in steel can reach a minimum value of 3.4 ppm when the slag composition encompasses w(CaF2)% = 29.38, w(CaO)% = 44.07, w(SiO2)% = 14.69, w(MgO)% = 9.89, w(Al2O3)% = 1.96. The high basicity of slag reduces the total oxygen content of stainless steel, whereas the influence of redox reactions between Si and Al results in a higher Al content in steel and the formation of more inclusions during solidification. Thus, the optimal Al2O3 content is less than 4% and the optimal basicity is 2.4 during the refining process.
Introduction
Austenitic stainless steels were used in chemical processing equipment due to their desirable corrosion properties, low alloy cost, and favorable mechanical properties over a narrow temperature and acid concentration range. Due to the advancement of the metallurgical science in recent years, high-alloy stainless steels with enhanced resistance to high temperatures in acidic environments have garnered considerable worldwide interest (ASM, 1990; Elhami et al., 2013). High-silicon austenitic stainless steel is a novel type of corrosion-resistant material (Pisarevskiy et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022b; Zhang et al., 2022c). Its structure provides increased strength and the ability to reduce the wall thickness in applications involving high pressures and temperatures. High-silicon stainless steels such as Saramet stainless steel and Sandvik SX stainless steel, typically contain between 4% and 7% Si (Hermas and Ogura, 1996; Burstein and Daymond, 2009; Zhang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022). Corrosion occurs at a rate of approximately 0.1 mm/a in concentrated sulfuric acid at temperatures greater than 130°C (Renner, 2001; Sequeira, 2019). Researchers agree that oxygen, the most prevailing harmful impurity, tends to deviate more severely in steel, and the precipitation of nonmetallic oxides impairs stainless steel corrosion performance (Zhang, 2006; Park and Kang, 2017). According to results of previous experiments (Szummer et al., 1993; Zheng et al., 2013), the presence of oxide inclusions on stainless steel surfaces could result in fewer spots in the passivation film when the boundary between the inclusions and the substrate was directly exposed to a non-favorable external environment. Pitting also occurs in inclusions, with oxides of Cr, Mn, Fe, and Al being more prone to pitting than the metal matrix. In addition, a number of studies (Jeon et al., 2014) have discovered that the increasing oxygen content of 27Cr-7Ni super duplex stainless steels resulted in the formation of large amounts of (Cr, Mn, Fe, and Al) oxides, reducing pitting resistance of the steels. Pits are formed as microcracks between inclusions, and the metal matrix grows larger. Several laboratory investigations (Li et al., 2021) have come to the same conclusion. In the cathodic environment of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC), a passive passivation film was formed on 316L stainless steel to prevent corrosion. Also, the film’s density, uniformity, and stability increased with the decrease in the oxygen content.
Studies were conducted to determine the ways to control the oxygen content in stainless steel refining processes so as to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel to sulfuric acid (Park and Todoroki, 2010; Louvis et al., 2011; Park and Kang, 2017). The researchers (Su et al., 2021) evaluated the impact of refining slag on inclusions in Nb-stabilized titanium-free Fe-18Cr ferritic stainless steels and discovered that a slag composed of CaO-SiO2-10w(Al2O3)%-10w(MgO)%-5w(CaF2)% and R (CaO/SiO2 mass ratio) of 3.5 yielded sufficient refining results. Thermodynamic modeling for predicting the stability diagram of inclusions in molten steel during slag inclusion reaction was developed (Ren et al., 2016). They also developed a method for optimizing the molten steel composition by optimizing slag inclusion reaction. To avoid the formation of MgO-Al2O3 spinel inclusions, the proposed method for treating Si-Mn sedimented 304 stainless steel was to treat it with a slag composed of 20% CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2. The laboratory slag-steel equilibrium experiments at 1,873 K (Zhang et al., 2022a) to evaluated the impact of the C/A ratio (CaO/Al2O3 mass ratio) of CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 on inclusions in Si-Mn deoxidized 430 stainless steel (Al-0.015 mass pct). As the slag basicity increased from 1.0 to 5.0, T [O] decreased from 70 to 38 ppm, the oxygen content in steel decreased from 13 to 8 ppm, and the inclusion density decreased from 16.0/m2 to 6.8/m2, except for an increase in the Al2O3 content of the inclusions. When the slag C/A ratio was increased from 0.7 to 2.5, the oxygen content of the steel decreased, as did the total weight, number density, and average diameter of inclusions in the steel.
Different components of slag have been shown to have varying effects on the deoxidation of numerous steel grades in slag-steel reactions (Duan et al., 2020). However, experimental studies evaluating the deoxidation of high-silicon austenitic stainless steels utilizing CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 pentabasic slag are lacking in rigor. A thermodynamic study and laboratory experiments were performed in this study to investigate the effect of CaO/SiO2, CaF2 and Al2O3 in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 on the deoxidation limit of austenitic stainless steel containing 5.0 wt% Si. The oxygen control mechanisms are also discussed in detail on the basis of the experimental data and thermodynamic models’ predictions. A technique for limiting ultra-low oxygen levels is being developed that could be applied effectively to industrial refining-stage operations.
Thermodynamic model for deoxidation of high-silicon stainless steel
With the following assumptions, a model for the slag-steel reaction in the stainless steel refining process can be constructed based on the equilibrium thermodynamics of the slag-steel reaction: 1) Total mass of slag and molten steel are conserved during the reaction; 2) The activity of the components in steel and slag was determined using the ion-molecular coexistence theory (IMCT) (Zhang, 2007; Yang et al., 2009), and their activities in molten steel was determined using the 1% Henry standard state. The activity of the elements in molten steel was calculated using the Wagner model (Guo, 2013); 3) To simplify the calculation, the elements or components that may be present in the system are categorized into three groups: the elements in the steel not involved in the slag-steel reaction, the components in the slag not involved in the slag-steel reaction, and the elements or components involved in the slag-steel reaction.
The details and assumptions of the IMCT modelling were showed in previous studies (Duan et al., 2018). Only the deoxidation reactions in steel are considered, while dephosphorization and desulphurization were characterized separately, particularly in this model. The slag composition used for deoxidation was formulated as a pentabasic slag CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2. According to the basic principles of IMCT, the number of moles of the five components in 100 g slag is assigned as
The mass-action concentrations of the composite molecules
The mass action concentration of structural unit i and the ion pair (Me2+ + O2−) according to the definition of the mass action concentration of the structural unit, as shown in Eqs 2, 3, were calculated.
The Eq. 4 was derived based on the conservation of mass. Clearly, there were six independent variables in Eq. 4,
The activity
At the high temperatures of metallurgy, Eqs 5, 6 were actually in equilibrium because the metallurgical reaction has a rapid rate of reaction at a temperature of around 1,873 K, according to the Arrhenius equation (Laidler, 1984). Equilibrium constants for the above reactions are given by Eqs 7, 8.
The final dissolved oxygen content in the steel (i.e., the deoxidation limit) was related to the [Si]-[O] equilibrium and the [Al]-[O] equilibrium. The oxygen content in steel that was in equilibrium with SiO2 and Al2O3 in the slag were expressed as w[O]%, Si and w[O]%, Al, respectively. Based on Eqs 7, 8, the relationship between the equilibrium oxygen content in sulfuric acid-resistant stainless steel during refining and variables such as the activity
The activity of the element solute in the steel solution is standardized as a 1% solution,
Thermodynamic considerations
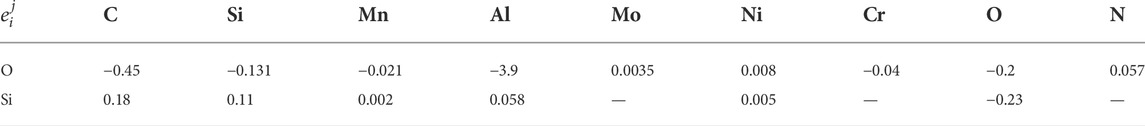
The effect of slag composition on oxygen in molten steel {w[Si]% = 5.0 mass pct and w[Al]% = 0.1 mass pct} at 1,873 K is discussed by Eqs 9, 10. The basicity (R) discussed in this study is the binary basicity (CaO/SiO2 mass ratio).
Effect of MgO content and binary basicity in slag on Si and Al deoxidation
It has been hypothesized that the basic oxides in the slag can react with all acidic oxides and form complex compounds, which would significantly reduce the activity of SiO2, Al2O3, etc., thus affecting the deoxidation reactions. When highlighting the role of MgO as a basicity supplement to CaO, it is necessary to analyze the impact of its content in the slag on the equilibrium oxygen content of the steel, as illustrated in Figure 1.
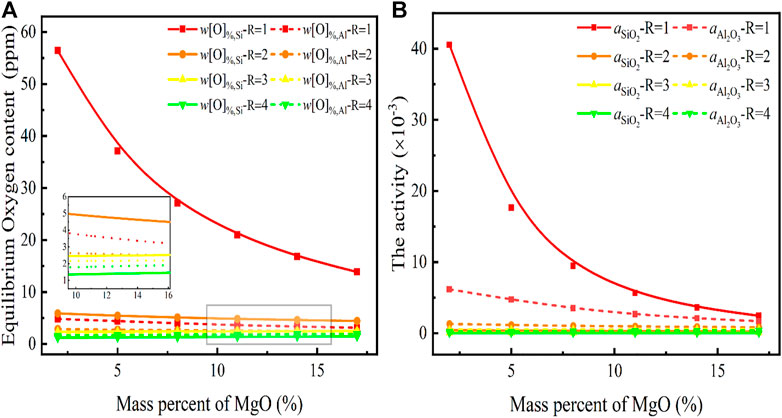
FIGURE 1. Relationship between basicity and MgO content in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 slag for (A) equilibrium oxygen content, (B)
Figure 1 indicates that the dependence of the determined equilibrium oxygen content on the MgO content and the basicity in the slag {w(CaF2)%: w(CaO)%: w(SiO2)%: w(Al2O3)%: w(MgO)% = 10:R:30:2: w(MgO)%}, where R in the slag is one, two, three, and four, respectively and w(MgO)% in the slag varies in the range of 5%–15%. In Figures 1A,B, the vertical coordinates represent the equilibrium oxygen content in steel and the activity of SiO2 and Al2O3 in the slag, respectively. The equilibrium w[O]%, Si at low basicity R = 1 decreases significantly with increasing MgO content, from 56.3 to 15.6 ppm, as shown in Figure 1A. In contrast, the equilibrium w[O]%, Al is less than 5 ppm and while there is a decreasing trend with increasing MgO content, no significant change occurs. The addition of MgO had little effect on either the equilibrium w[O]%, Si or w[O]%, Al content with increasing basicity, indicating that the deoxidation reaction of the high-silicon stainless steel is not affected by the MgO content in the slag system at high basicity.
As previously discussed in Eqs 5, 6, both Si and Al are strongly deoxygenated elements due to the presence of slag. However, they are also susceptible to the decomposition of SiO2 and Al2O3 in the slag when the reaction determining the oxygen content of the molten steel has not been yet known. As illustrated in Figures 1A,B, when the slag has a basicity of 1, the equilibrium w[O]%, Si is greater than the equilibrium w[O]%, Al and the activity of SiO2 is significantly greater than that of Al2O3. Al is significantly more capable of deoxidation than Si, yet in the presence of a CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 slag with basicity of 1, the final equilibrium oxygen in the steel depends on the equilibrium [Si]-[O] reaction dominated by SiO2 in the slag, which also reflects the essence of the slag-steel reaction.
Based on the comparison of the optical basicity, (ΛCaO > ΛMgO), it can be deduced that the ability of CaO to bind SiO2 is stronger than the ability of MgO, resulting in an increase in the basicity characterized by CaO to 2. In this situation, the MgO content can no longer affect and rapid decreases in the oxygen content of the steel to about 5 ppm and in the activity of SiO2 in the slag to an extremely low level occur, which also reflects the dependence of the equilibrium oxygen reduction in steel by the strong deoxidizing element Si on the basicity characterized by the strong basic CaO, the equilibrium w[O]%, Al is less than the equilibrium w[O]%, Si, which is always kept below 5 ppm. On the other hand, even at a basicity of 1, the equilibrium w[O]%, Al obtained from Al deoxidation is always low because the activity of Al2O3 is not affected by the basicity and MgO.
Effect of Al2O3 content and binary basicity in slag on Si and Al deoxidation
Owing to the fact that the product of Al deoxidation is Al2O3, the Al2O3 content in the slag becomes a critical factor that affects deoxidation and it is essential to consider how the Al2O3 in the slag may affect the oxygen in the final steel equilibrium. The slag composition is: w(CaF2) %: w(Cao)%:w(SiO2) %:w(Al2O3) %:w(MgO)% = 30: R: w(Al2O3) %%:10, where the Al2O3 content is chosen as 2%, 6%, and 10%, respectively and the basicity is varied from 0 to 10, the equilibrium w[O]%, Si and w[O]%, Al of Eqs 7, 8 are calculated, as shown in Figure 2. Unlike the effect of MgO on the oxygen in molten steel, basicity can be classified into three categories.
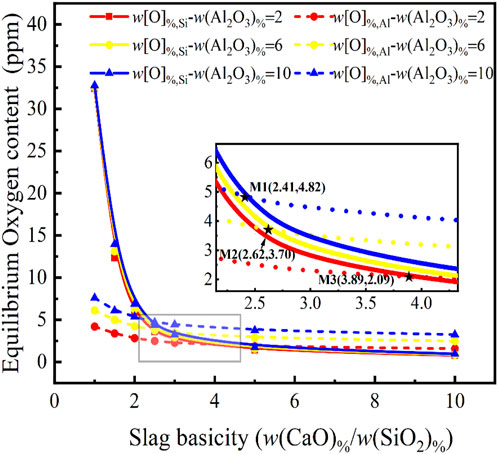
FIGURE 2. Relationship between basicity in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 slag and Al2O3 content on the equilibrium oxygen content at 1,873 K for a certain molten steel composition {w[Si]% = 5.0, w[Al]% = 0.1}.
When the Al2O3 content is 10%, the basicity of 2.41 becomes the key parameter in determining the oxygen control mechanism. When the basicity is less than 2.41, the oxygen in the molten steel depends on the w[O]%, Si obtained from the [Si]-[O] equilibrium, and the equilibrium w[O]%, Si content tends to decrease as the basicity increases. When the basicity is greater than 2.41, the oxygen in the molten steel depends on the calculated value of the equilibrium w[O]%, Al. At this point, the oxygen content can be as low as below 4.82 ppm. When the Al2O3 content is 6%–10%, the basicity equal to 2.62 becomes the key parameter for the equilibrium w[O]%, Si and the equilibrium w[O]%, Al. The oxygen control mechanism is similar to the previous situation, and the oxygen content can be as low as below 3.7 ppm. When the Al2O3 content is 2%–6%, the basicity of 3.89 becomes the key parameter in determining the equilibrium w[O]%, Si and the equilibrium w[O]%, Al. In additional, the oxygen content of molten steel tends to decrease slightly as the basicity increases. Although the oxygen content can be as low as 2.09 ppm, further reductions are extremely difficult.
It can be concluded that while the Al2O3 content of the slag has little effect on the equilibrium oxygen content of the steel above 4.8 ppm, the Al2O3 content of the slag becomes critical for ultra-low oxygen steels at less than 4.8 ppm, which requires not only a higher basicity (>2.41), but also a tightly controlled Al2O3 content in the slag.
Effect of CaF2 content in slag on the oxygen content of the molten steel
Although CaF2 is typically added to steel slag as a viscosity regulator and catalyst to improve deoxidation kinetics, less research on its effect on the thermodynamics of the deoxidation reaction has been conducted. The composition of the slag was fixed at 2 w(Al2O3) % and 10 w(MgO)%, with the structure of w(CaF2) %:w(CaO)%:w(SiO2) %:w(Al2O3) %:w(MgO)% = w(CaF2) %:R:2:10. The equilibrium oxygen content of Eqs 7, 8 {w [O]%, Si, w[O]%, Al} were calculated for 20, 30 and 40 w(CaF2) % in the slag for the variation of the slag basicity from 0 to 10, as shown in Figure 3.
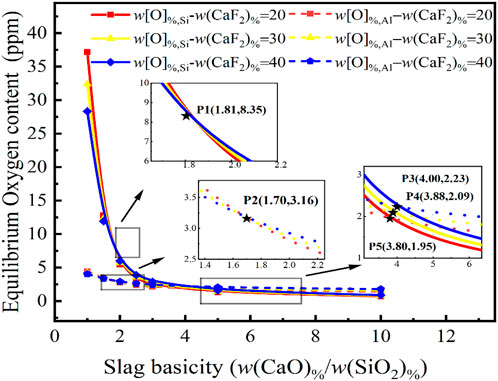
FIGURE 3. Relationship between basicity in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 slag and CaF2 content on the equilibrium oxygen content at 1,873 K for a certain molten steel composition {w[Si]% = 5.0, w[Al]% = 0.1}.
As can be seen, the oxygen content has a weak dependence on the CaF2 content of the slag and the trends of the curves for the equilibrium w[O]%, Al and the equilibrium w[O]%, Si are almost identical. It is noteworthy that as the basicity increases to 1.81, the equilibrium w[O]%, Si = 8.35 ppm. At a basicity of less than 1.81, the relationship between CaF2 content and equilibrium w[O]%, Si content is positively correlated. When the basicity exceeds 1.81, however, the relationship between the CaF2 content and the equilibrium w[O]%, Si content is negative. A similar occurrence exists for the equilibrium w[O]%, Al curve, but since the steel grade is a high-silicon content sulfuric acid-resistant stainless steel, the oxygen content in the molten steel is controlled by the activity of SiO2 in the slag. According to the calculations of the IMCT model, an increase or reduction in CaF2 concentration will have a minimal effect on the equilibrium w[O]%, Si and the equilibrium w[O]%, Al but the predominant influence will still be basicity. When the oxygen content of molten steel needs to be stripped to around 2.09 ppm, the CaF2 content has a minimal effect on the equilibrium oxygen content at a basicity of 3.8–4.0, with the oxygen content varying between 1.95 and 2.23 ppm. However, the oxygen control mechanism changes with the basicity and CaF2 content, as shown at points P3, P4, and P5 in Figure 3.
Overall, the thermodynamic influence of CaF2 content in slag on deoxidation in the steel is extremely limited and other effects arising from steelmaking have been studied in the literature. However, the equilibrium w[O]%, Al is always less than 5 ppm over the full composition range of CaF2 and the equilibrium w[O]%, Si content also varies little, indicating that it is difficult to meet the requirements of ultra-low oxygen smelting of stainless steel by only adjusting the CaF2 content in the slag.
Effect of smelting temperature on the oxygen content of the molten steel
Temperature is an important parameter in the smelting process. With a fixed steel melt with w[Si]% = 5.0, w[Al]% = 0.1 and a slag of w(MgO)% = 10, w(CaF2)% = 10, w(Al2O3)% = 2, investigating the relationship between the steel and CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 slag as a function of basicity in the temperature range of 1,673–1,973 K (1,400°C–1,700°C) was necessary. The evolution of the equilibrium oxygen content in steel of the slag for w(CaF2) %:w(CaO)%:w(SiO2) %:w(Al2O3) %:w(MgO)% = 30:R:2:10 has been discussed. Similarly, the activity of SiO2 and Al2O3 in the slag calculated using the IMCT model, and Eqs 7, 8 to calculate the equilibrium w[O]%, Si and the equilibrium w[O]%, Al, respectively, are shown in Figure 4. It can be seen that there are several patterns as follows. The oxygen content in molten steel depends on the equilibrium w[O]%, Si obtained from the [Si]-[O] equilibrium regulated by the activity of SiO2 in the slags, which grows non-linearly with increasing temperature when the basicity is one in the lower range. When the basicity is greater than or equal to two or three, the overall oxygen content of the steel in equilibrium with the activity of SiO2 and Al2O3 is low, and the temperature has little effect, but the oxygen content is still determined by the [Si]-[O] equilibrium derived from the [Si]-[O] equilibrium controlled by the activity of SiO2 in the slags.
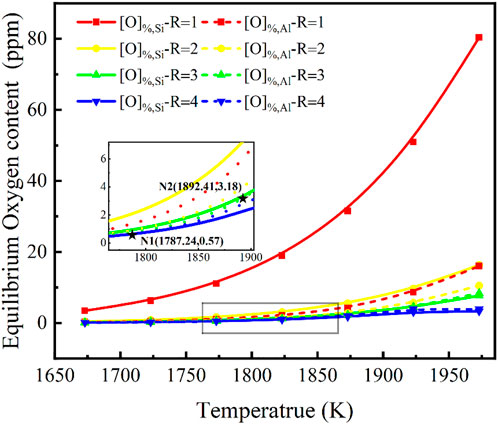
FIGURE 4. Relationship between basicity in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 slag and temperature on the equilibrium oxygen content for a certain steel composition {w[Si]% = 5.0, w[Al]% = 0.1}.
As the basicity increases and the temperature expands, oxygen content changes from being controlled by the activity of SiO2 in the slag to being controlled by w[O]%, Al from the activity of Al2O3 in equilibrium with [Al]-[O]. When the temperature is less than 1787.24 K, oxygen content remains controlled by the activity of SiO2 in the slag, as shown at point N1 in Figure 4. In contrast, at a basicity of three, at temperatures greater than 1892.41 K, the oxygen content in the molten steel changes from a mechanism controlled by the activity of SiO2 in the slag to w[O]%, Al obtained by the activity of Al2O3 in equilibrium with [Al]-[O]. It must be noted that at this point the oxygen content varies between 0.57 and 3.18 ppm, which is difficult to achieve in actual smelting, but is significant in that an oxygen control mechanism has been found.
Experimental verification
Experimental apparatus and methods
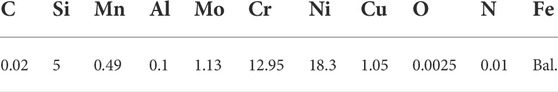
By combining the composition ratios, samples of austenitic stainless steel containing 5.0 wt% Si based on stainless steel XDS-2 were made in a vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace under a high purity argon environment using MgO crucibles. Table 1 shows the chemical compositions, while Table 4 shows the chemical composition of the slag and chemical composition of steel in the experimental results. The effects of basicity on oxygen content can be compared using S1, S2, and S3. The effects of Al2O3 content on oxygen content can be compared using S2, S6, and S7. The effects of CaF2 content on oxygen content can be compared using S2, S4, and S5. Slag contains a sufficient amount of magnesium oxide to prevent erosion of the magnesium oxide crucible.
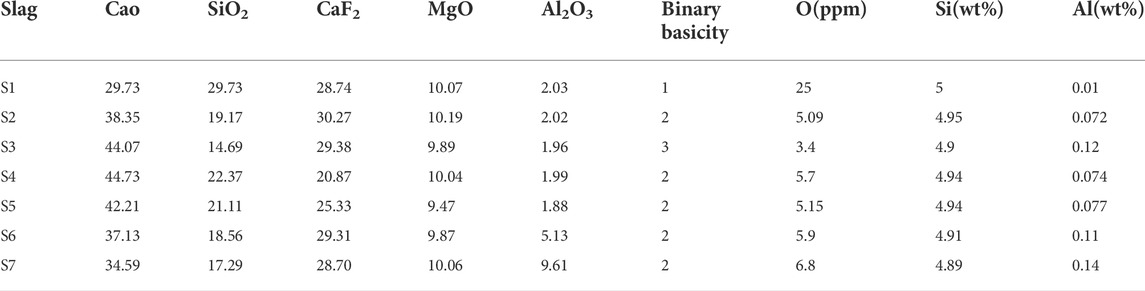
TABLE 4. Chemical composition of slags used in the study (wt%) and chemical composition of steel in the experimental ingots.
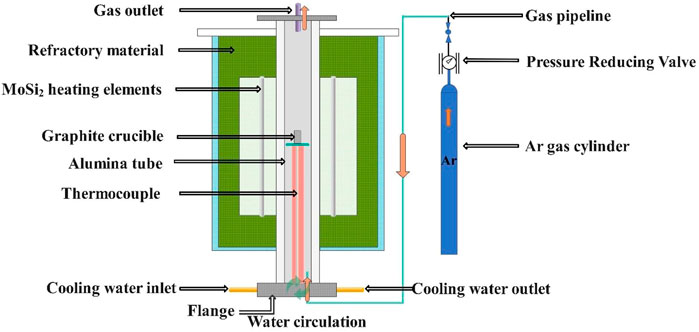
The experiments were carried out in a vertical resistance heated aluminum tube furnace with MoSi2 heating elements. A schematic diagram of the resistance furnace used in this study as shown in Figure 5. A proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller coupled to a type B reference thermocouple was used to control the temperature of the heating furnace. Prior to the experiment, another type B thermocouple was used to calibrate the temperature to 1873 K (1,600°C). The experimental steps are obtained: 1) Preparation of slag in a graphite crucible (outer diameter: 50 mm, inner diameter: 44 mm, H: 88 mm). CaF2, CaO, MgO, Al2O3, and SiO2 reagent grade powders (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.) were used as slag ingredients, mixed thoroughly and placed in a graphite crucible in a tube furnace as shown in Figure 5, protected by a high purity argon atmosphere, and the temperature was raised to 1,873 K and maintained for 30 min to ensure a homogeneous composition. A sample of the liquid slag system is quenched and ground on a copper plate to form a synthetic slag for use; 2) 160 g of acid-resistant stainless steel containing with 40 g of the above synthetic slag was placed in a MgO crucible and placed in the constant temperature zone of the resistance furnace for the experiment. To avoid oxidation of the steel, high-purity AR was rushed into the reaction zone at a constant flow rate of 1 L/min. After heating the experimental sample to 1,873 K under an argon atmosphere, the slag-steel reaction was reached by holding for 1 h. Afterwards, the entire crucible containing the experimental liquid sample was quickly removed from the furnace and quenched in ice water. Approximately 1 g of each sample was removed from these reaction products prior to the oxygen and nitrogen hydrogen analyzer (TCH600, LECO, United States) analyzing their oxygen content and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) analyzing their silicon and aluminum content. The oxygen content of the ingot was determined based on the average of the three samples of metal taken during each test run.
Results and discussion
Effect of slag composition on deoxidation of high-Silicon stainless steels at 1,873 K
The slag-steel equilibrium experiments for a certain steel composition in Table 1, carried out at 1,873 K under different slag compositions designed as shown in Table 4. A comparison between the thermodynamic model predicted values and experimental values are given in Figure 6.
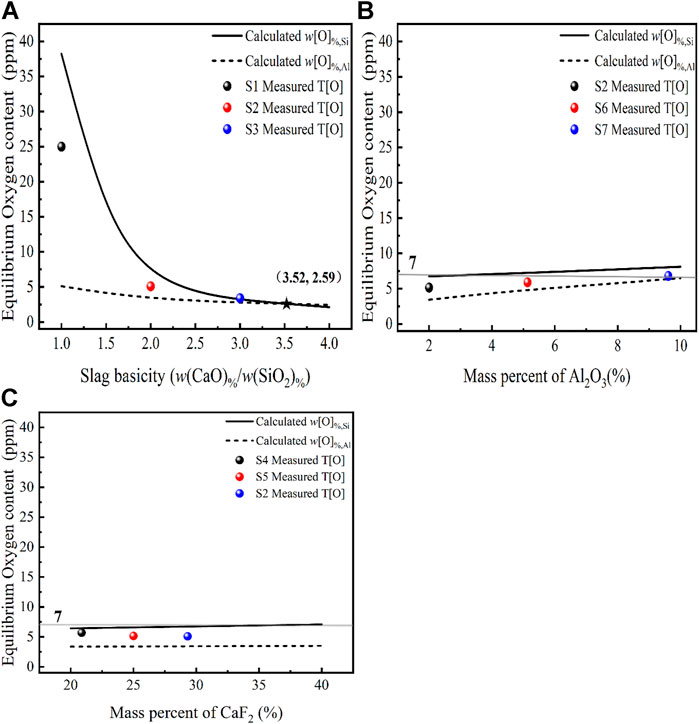
FIGURE 6. Effect of different slag compositions at 1,873 K (A) CaO, (B) Al2O3, (C) CaF2 on the oxygen content in steel [model predictions (lines), experimental data (dots) and T[O] = 7 ppm (gray line)].
The oxygen content in the molten steel was investigated at 1,873 K in relation to different slag basicity (1–4). The three laboratory-scale deoxidation experimental results for the slag systems S1, S2, and S3 in equilibrium with the molten steel are shown in Figure 6A. The measured total oxygen content follows the same trend as the equilibrium oxygen content in the deoxidation model, which gradually decreases as the basicity increases. Comparing the relationship between the measured T[O], the calculated w[O]%, Si and w[O]%, Al, respectively, we find that the conclusion reached coincide with the thermodynamic analysis of the equilibrium oxygen content in the molten steel in relation to the mechanism of oxygen control of the reaction, i.e., the calculated equilibrium oxygen content of the higher deoxidation reaction determines the magnitude of the equilibrium oxygen content of the molten steel. This is demonstrated by the fact that when
Figure 6B shows a comparison of the calculated and measured oxygen content with different Al2O3 content at 1873 K with a basicity of two for the slag systems S2, S6, and S7. It can be seen that the prediction models w[O]%, Al, w[O]%, Si and the experimentally measured oxygen content all vary with the activity of the slag component Al2O3. At R = 2 and the Al2O3 content increases from 2 to 10, the
Figure 6C shows a comparison of the oxygen content of the steel solution with the experimentally measured oxygen content when the CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 content of the slag CaF2 is varied at 1,873 K with a fixed basicity of two for the slag systems S2, S4, and S5. It can be seen that varying the CaF2 content does not have much effect on the deoxidation of stainless steel, while the trend is consistent with the thermodynamic simulation results. The researcher (Park and Park, 2016) found that at 1,873 K, the removal of inclusions increased with increasing CaF2 content in the CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 pentabasic slag, while the effect of CaF2 was negligible when the CaF2 content was greater than 20%. The researchers submit information from ladle treatment operations that shows that the presence of CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-TiO2-SiO2 in slag has no effect on the amount and kind of inclusions (Andersson and Sichen, 2009). In summary, the main factor determining the equilibrium oxygen content in the steel is the basicity, and the basicity determines to some extent the changes in the oxygen control mechanism.
Effect of slag composition on w[Al]%, w[Si]% in high-silicon stainless steels at 1,873 K
In sulfuric acid-resistant stainless steel, Si plays an important alloying element in determining the corrosion resistance index and Al is an important element in oxygen control when the oxygen content is very low. When setting up different slag components to remove oxygen from steel, the relevant elements between slag and steel will react and whether this will have an effect on the w[Si]%, w[Al]% of the steel also needs to be studied. For steel slag reactions as follows:
By substituting the steel temperature
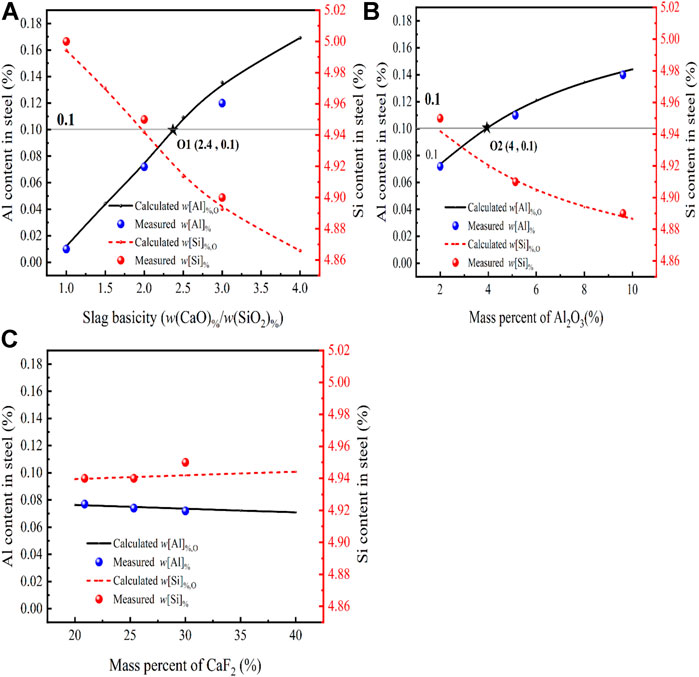
FIGURE 7. Effect of different slag compositions at 1,873 K (A) CaO, (B) Al2O3, (C) CaF2 on the Si and Al content in steel [model predictions (lines), experimental data (dots) and the initial w[Al]% (gray line)].
From Figure 7A, it can be seen the relationship between the calculated equilibrium w[Al]%, w[Si]% of the slag at different basicities (1–4) and their measured values. When the basicity varies from 1 to 3, the calculated Al content is positively correlated with the change in basicity, while the calculated Si content is negatively correlated with the change in basicity. The measured Al content in the steel increased from 0.012 to 0.12 and the measured Si content decreased from 5 to 4.87. This is because
FIGURE 8. Model predictions of the relationship between (A) CaO, (B) Al2O3, (C) CaF2 and
Figure 7B presents a comparison between the w[Al]%, w[Si]% calculated by the thermodynamic model and the measured content for different Al2O3 content in CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 of the slag at 1,873 K and the basicity of 2. When the deoxidation reaction reaches the equilibrium, the w[Al]% in the molten steel increases as the Al2O3 content in the slag increases, this is because at R = 2 and the Al2O3 content increases from 2 to 10, and there is a significant change in the slag,
Figure 7C Shows the effect of CaF2 content in the slag on the w[Al]% and w[Si]% of the slag as calculated by the thermodynamic model at 1,873 K for the basicity of two and compared with the measured ones. By comparing the increase in basicity and Al2O3 content, it can be seen that as the CaF2 content in the slag increases from 20% to 40%, the w[Al]%, w[Si]% in the steel shows an opposite trend, with the value of w[Al]% decreasing from 0.078 to 0.072 and the w[Si]% increasing from 4.94 to 4.95 at equilibrium in the molten steel. 2The increase in CaF2 content in the slag caused a decrease in
Effect of temperature on w[Al]%, w[Si]% in high-silicon stainless steels
For the S2 slag system, the evolution of the temperature dependence between the equilibrium oxygen content and the Aluminum and Silicon content in the steel was studied in the range 1,773–1,873 K, as shown in Figure 9. In Figure 9A, the conclusion obtained experimentally are consistent with the thermodynamic model calculations. At the basicity of 2, the oxygen content in the steel depends on the w[O]%, Si obtained from [Si]-[O] equilibrium controlled by the activity of SiO2 in the slag. When the temperature was increased from 1,623 to 1,873 K, the equilibrium w[O]%, Si and the equilibrium w[Al]% both increased non-linearly, and the measured T[O] in the steel increased from 2.5 to 5.15 ppm, which also verified the conclusion that lower temperatures are favorable for deoxidation within a certain range.
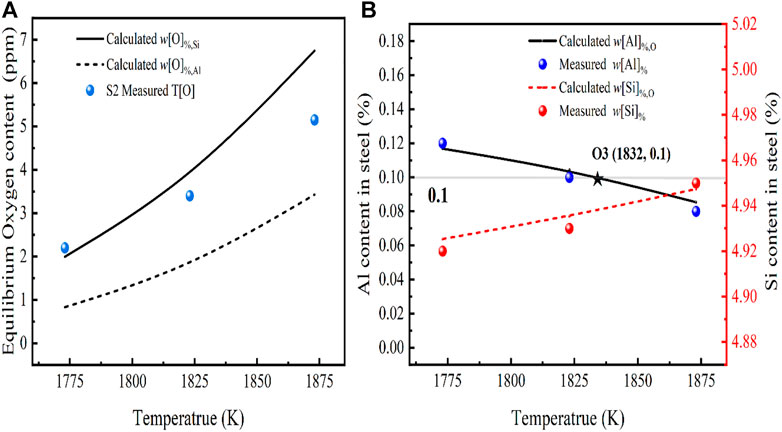
FIGURE 9. Effect of temperature on (A) oxygen, (B) silicon and aluminium content in steel (model predictions (lines) and experimental-data (dots)).
Experimental results show that an increase in temperature increases the equilibrium w[O]% of the molten steel and at the same time leads to a decrease in the w[Al] % of the molten steel, as shown in Figure 9B. It must be noted that the equilibrium w[Al]% line has an intersection with the iso-concentration line {initial w[Al]% = 0.1 in the molten steel} at O3, indicating that a decrease in the w[Al]% of the molten steel occurs at temperatures greater than 1,832 K. Therefore, in order to prevent the oxidation of Al in the molten steel and to promote the deoxidation reaction, the smelting temperature of high-Si stainless steel should be controlled at around 1,832 K.
Conclusion
In this paper, the thermodynamic analysis of the slag-metal equilibrium reactions, that is, austenitic stainless steels containing 5.0 wt% Si with CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 type slags at different temperature is systematically investigated. The oxygen control mechanism of the deoxidation reaction was investigated in conjunction with the thermodynamic model. Our findings are summarized below.
1) In the slag reaction of the high-Si (5% Si) austenitic stainless steels, the equilibrium oxygen content in the molten steel depends on the deoxidation reaction corresponding to the higher oxygen content obtained as controlled by the activity of the slag group elements. In CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-SiO2 type slags, the basicity has the greatest influence on the activity of the group elements, so that the basicity mainly determines the equilibrium oxygen content in the steel and the oxygen control mechanism.
2) When the basicity is less than two, the oxygen content in the molten steel depends on the [Si]-[O] equilibrium obtained from the activity of SiO2 in the slag, but when the basicity is greater than two, the oxygen control mechanism changes according to the other components of the slag system, and to obtain ultra-low oxygen steel, not only a larger basicity is required, but also control of the Al2O3 content in the slag.
3) When 1,873 K, R (CaO/SiO2 mass ratio) of 2, w(Al2O3)% varies in a certain range (0%–10%), the total oxygen content of stainless steel containing 5.0 wt% Si is less than 7 ppm. When the slag composition includes w(CaO)% = 44.07, w(SiO2)% = 14.69, w(MgO)% = 9.89, w(Al2O3)% = 1.96, the total oxygen content in the steel can achieve a minimum of 3.4 ppm.
4) Under certain slag conditions, the equilibrium Al content decreases with increasing temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen content and equilibrium silicon content increase with increasing temperature. High basicity slag is beneficial to reduce the total oxygen in stainless steel, but will increase the Al content in stainless steel, which may promote the formation of inclusions of Al2O3 and increase the deformability of inclusions. To control the Al content in stainless steel, the basicity should be kept to 2.4 and the w(Al2O3)% to four where possible.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
GD was in charge of the numerical simulation, data analysis, and the first writing of the paper. HD assisted with the research, supplied research equipment, and reviewed the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmats.2022.937288/full#supplementary-material
References
Andersson, E., and Sichen, D. (2009). The effect of CaF2 in the slag in ladle refining. steel Res. Int. 80 (8), 544–551.
ASM (1990). ASM handbook vol. 2: Properties and selection: Nonferrous alloys and special purpose materials. 10 Ed. ASM Int, America, Unknown.
Burstein, G., and Daymond, B. (2009). The remarkable passivity of austenitic stainless steel in sulphuric acid solution and the effect of repetitive temperature cycling. Corros. Sci. 51 (10), 2249–2252. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2009.07.010
Duan, S.-c., Li, C., Guo, X.-l., Guo, H.-j., Guo, J., and Yang, W.-s. (2018). A thermodynamic model for calculating manganese distribution ratio between CaO–SiO2–MgO–FeO–MnO–Al2O3–TiO2–CaF2 ironmaking slags and carbon saturated hot metal based on the IMCT. Ironmak. Steelmak. 45 (7), 655–664. doi:10.1080/03019233.2017.1318547
Duan, S.-C., Shi, X., Zhang, M.-C., Li, B., Yang, W.-S., Wang, F., et al. (2020). Effect of slag composition on the deoxidation and desulfurization of Inconel 718 superalloy by ESR type slag without deoxidizer addition. Metall. Mat. Trans. B 51 (1), 353–364. doi:10.1007/s11663-019-01729-3
Elhami, S., Razfar, M., Farahnakian, M., and Rasti, A. (2013). Application of GONNS to predict constrained optimum surface roughness in face milling of high-silicon austenitic stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 66 (5), 975–986. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4382-y
Hermas, A., and Ogura, K. (1996). Effects of alloying additions on the spontaneous passivation of stainless steels containing copper at different temperatures. Electrochimica acta 41 (10), 1601–1609. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(95)00411-4
Jeon, S.-H., Hur, D. H., Kim, H.-J., and Park, Y.-S. (2014). Influence of oxygen content on the inclusion formation and pitting corrosion resistance of hyper duplex stainless steels. Mat. Trans. 55, 1872–1877. doi:10.2320/matertrans.m2014164
Karasev, A., and Suito, H. (1999). Quantitative evaluation of inclusion in deoxidation of Fe-10 mass pct Ni alloy with Si, Ti, Al, Zr, and Ce. Metall. Materi. Trans. B 30 (2), 249–257. doi:10.1007/s11663-999-0054-1
Laidler, K. J. (1984). The development of the Arrhenius equation. J. Chem. Educ. 61 (6), 494. doi:10.1021/ed061p494
Li, D., Chen, D., and Liang, P. (2021). Influence of oxygen content on the corrosion behaviour of 316 L stainless steel in the simulated cathodic environment of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Alloys Compd. 873, 159695. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159695
Louvis, E., Fox, P., and Sutcliffe, C. J. (2011). Selective laser melting of aluminium components. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211 (2), 275–284. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.09.019
Pak, J.-J., Jeong, Y.-S., Tae, S.-J., Kim, D.-S., and Lee, Y.-Y. (2005). Thermodynamics of titanium and nitrogen in an Fe-Ni melt. Metall. Materi. Trans. B 36 (4), 489–493. doi:10.1007/s11663-005-0040-1
Park, J. H., and Kang, Y. (2017). Inclusions in stainless steels− a review. Steel Res. Int. 88 (12), 1700130. doi:10.1002/srin.201700130
Park, J. H., and Todoroki, H. (2010). Control of MgO· Al2O3 spinel inclusions in stainless steels. ISIJ Int. 50 (10), 1333–1346. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.50.1333
Park, J. S., and Park, J. H. (2016). Effect of physicochemical properties of slag and flux on the removal rate of oxide inclusion from molten steel. Metall. Materi. Trans. B 47 (6), 3225–3230. doi:10.1007/s11663-016-0789-4
Pisarevskiy, L., Korostelev, A., and Filippov, G. (2021). Thermal aging of high-strength corrosion-resistant austenitic stainless steel and its thermal stability. Metallurgist 65 (3), 265–276. doi:10.1007/s11015-021-01156-3
Ren, Y., Zhang, L., Fang, W., Shao, S., Yang, J., and Mao, W. (2016). Effect of slag composition on inclusions in Si-deoxidized 18Cr-8Ni stainless steels. Metall. Materi. Trans. B 47 (2), 1024–1034. doi:10.1007/s11663-015-0554-0
Renner, M. H. (2001). Metallic materials for concentrated sulfuric acid service. CORROSION 2001, Houston, Texas. OnePetro.
Sequeira, C. A. (2019). High temperature corrosion: Fundamentals and engineering. John Wiley & Sons.
Su, L., Xu, J., Li, G., and Zhu, C. (2021). Influences of deoxidation and VOD slag on the behavior of inclusions in Fe–21Cr ferrite stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 15, 1949–1958. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.011
Szummer, A., Janik-Czachor, M., and Hofmann, S. (1993). Discontinuity of the passivating film at nonmetallic inclusions in stainless steels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 34 (2), 181–183. doi:10.1016/0254-0584(93)90210-d
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Yu, L., Cui, K., Fu, T., and Mao, H. (2022). Effective separation and recovery of valuable metals from waste Ni-based batteries: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 439, 135767. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.135767
Wang, Q., Wang, L., Zhai, J., Li, J., and Chou, K.-C. (2017). Evolution of inclusions in Fe-13Cr treated by CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-based top slag. Metall. Materi. Trans. B 48 (1), 564–572. doi:10.1007/s11663-016-0852-1
Xu, J., Huang, F., Wang, X., and Jing, C. (2016). Influence of silicon on desulfurization of Al‐killed steel by CaO–Al2O3 slag contained FeO and MnO. Steel Res. Int. 87 (12), 1694–1701. doi:10.1002/srin.201600053
Yang, X.-m., Jiao, J.-s., Ding, R.-c., Shi, C.-b., and Guo, H.-j. (2009). A thermodynamic model for calculating sulphur distribution ratio between CaO–SiO2–MgO–Al2O3 ironmaking slags and carbon saturated hot metal based on the ion and molecule coexistence theory. ISIJ Int. 49 (12), 1828–1837. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.49.1828
Yoshikawa, T., and Morita, K. (2007). Influence of alloying elements on the thermodynamic properties of titanium in molten steel. Metall. Materi. Trans. B 38 (4), 671–680. doi:10.1007/s11663-007-9075-9
Zhang, H., Peng, Y., Zhang, S., Liu, C., Cheng, R., and Ni, H. (2022a). Effects of refining slag on transformation and removal of inclusions in type 430 stainless steel. Metall. Mat. Trans. B 53, 702–715. doi:10.1007/s11663-021-02420-2
Zhang, J. (1988). Calculation model of mass action concentrations CaO-SiO2 slag system. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 10 (4), 412.
Zhang, J. (2007). Computational thermodynamics of metallurgical melts and solutions. Beijing: The Publishing House of Metallurgical Industry, 245.
Zhang, L. (2006). State of the art in the control of inclusions in tire cord steels‐a review. steel Res. Int. 77 (3), 158–169. doi:10.1002/srin.200606370
Zhang, Y., Fu, T., Cui, K., Shen, F., Wang, J., Yu, L., et al. (2021). Evolution of surface morphology, roughness and texture of tungsten disilicide coatings on tungsten substrate. Vacuum 191, 110297. doi:10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110297
Zhang, Y., Fu, T., Yu, L., Shen, F., Wang, J., and Cui, K. (2022b). Improving oxidation resistance of TZM alloy by deposited Si–MoSi2 composite coating with high silicon concentration. Ceram. Int. 48, 20895–20904. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.080
Zhang, Y., Yu, L., Fu, T., Wang, J., Shen, F., and Cui, K. (2022c). Microstructure evolution and growth mechanism of Si-MoSi2 composite coatings on TZM (Mo-0.5 Ti-0.1 Zr-0.02 C) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 894, 162403. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162403
Keywords: deoxidation, austenitic stainless steel, slag-steel interface reaction, slag optimization, thermodynamic model
Citation: Dou G, Guo H, Guo J, Li S, Yan Y and Wang Z (2022) Investigation of deoxidation of high-silicon austenitic sulfuric acid-resistant stainless steel. Front. Mater. 9:937288. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2022.937288
Received: 06 May 2022; Accepted: 02 August 2022;
Published: 24 October 2022.
Edited by:
Qifeng Shu, University of Oulu, FinlandReviewed by:
Yingyi Zhang, Anhui University of Technology, ChinaArtur Mariano De Sousa Malafaia, Universidade Federal de São João del-Rei, Brazil
Copyright © 2022 Dou, Guo, Guo, Li, Yan and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hanjie Guo, Z3VvaGFuamllQHVzdGIuZWR1LmNu; Jing Guo, Z3VvamluZ0B1c3RiLmVkdS5jbg==
 Guanxiong Dou
Guanxiong Dou