- 1School of Pharmacy, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 2Shanghai Key Laboratory for Molecular Engineering of Chiral Drugs, School of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 3Guangdong Key Laboratory for Research and Development of Natural Drugs, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan, China
Oceans boast a substantial microbial diversity, which is widely prevalent in seawater, marine sediments, and marine organisms. In contrast to terrestrial resources explored in traditional natural product research, the habitats of marine microorganisms are distinctly unique. Actinomycetes serve as a vital source of secondary metabolites, including antibiotics and other potent natural products like streptomycin and tetracycline. They have played a pivotal role in clinical treatments for significant diseases such as pathogenic bacterial infections. Nevertheless, the extensive use of antibiotics has led to a sharp increase in the variety and number of drug-resistant bacteria, notably multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) bacteria, in clinical settings, posing a grave threat to human survival. Consequently, there is an immediate need to discover structurally novel antibacterial natural products and develop new antibiotics. This mini review summarizes a total of 45 novel antibacterial natural products derived from marine actinomycetes, published in 2024. These products, including polyketides, alkaloids, macrolactams, and peptides, are highlighted in terms of their structures and biological activities. The objective of this article is to provide valuable insights for the research and development of novel antibiotics.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) bacteria has become a significant threat to global public health due to the overuse of antibiotics (Chin et al., 2018; Hu et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2019; Cui et al., 2020; Wang X. et al., 2020; Ding Q. et al., 2021; Wei et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021; Rasheed et al., 2024). The Lancet journal published a comprehensive analysis of the global impact of antimicrobial resistance (Murray et al., 2022). Analysis of data from 204 countries and regions revealed that antimicrobial resistance has become a major cause of death worldwide. In 2019, infections caused by antimicrobial resistance directly resulted in 1.27 million deaths and indirectly led to 4.95 million deaths, surpassing those from AIDS or malaria (Murray et al., 2022).
On the other hand, since the late 1990s, with the continuous exploitation of natural resources, discovering new bioactive natural products has become increasingly challenging (Demain, 2009; Spížek et al., 2010). Traditional strategies for the isolation and identification of natural products have led to the repeated isolation of numerous known compounds, making it increasingly difficult to discover new bioactive natural products. Over the past two decades, the number of antibiotics discovered by pharmaceutical companies has been declining (Zhang et al., 2022; Brüssow, 2024). There is an urgent need for humans to search for new natural products with novel structures, unique bioactivities, and mechanisms of action as lead compounds for new drug development (Cui et al., 2019; Ding et al., 2019; Li et al., 2019; Afrin et al., 2020; Zhang J. et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2024; Muhammad et al., 2024).
Compared to terrestrial biological resources, marine organisms inhabit vastly different environments (Liu et al., 2019; Zhong et al., 2020; Otero et al., 2023). The drastic differences in survival conditions (such as high pressure, high salinity, oligotrophic environments, lack of light, lack of oxygen, etc.) determine that marine organisms exhibit significant characteristics in metabolism, survival strategies, information transmission, and adaptation mechanisms (Surendhiran et al., 2021; Hamadou et al., 2023; Iqbal et al., 2024). Actinomycetes in marine organisms, as an important component, have always been one of the hotspots in natural product research (Jagannathan et al., 2021; Ryu et al., 2023). Eravacycline (Xerava®), a novel fluorocycline antibacterial agent, is a semisynthetic derivative of tetracycline from Streptomyces, which functions by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis (Huang P. Y. et al., 2024). In 2018, it was approved by the U.S.A. FDA and exhibits potent in vitro activity against Gram-positive and -negative strains expressing certain common tetracycline-specific acquired resistance mechanisms. In vitro, eravacycline demonstrates potent activity against a broad spectrum of clinically relevant Gram-positive and -negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
The actinomycetes genome typically contains a rich repertoire of biosynthetic gene clusters for secondary metabolites (Scherlach and Hertweck, 2021; Wen et al., 2024). The number of compounds we have discovered so far is far less than the number of compounds that microorganisms can produce, and a large number of potential secondary metabolites remain undiscovered (Zhang X. et al., 2020; Tianqiao et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). Searching for potential novel secondary metabolites and exploring lead molecules with significant pharmacological activities, marine actinomycete secondary metabolites, as important sources of new drug precursors, are gradually demonstrating significant research value and application potential (Donald et al., 2022; Gomez-Banderas, 2022; Ngamcharungchit et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024).
Based on data from PubMed, Elsevier, the American Chemical Society, and Google Scholar, this review comprehensively summarizes the sources, structures, and bioactivity progress of 45 novel antibacterial active natural products isolated from marine actinomycetes in 2024. According to their structural characteristics, these natural products are classified into four major categories, including polyketides (57.8%, 26/45), alkaloids (26.7%, 12/45), macrolactams (8.9%, 4/45), and peptides (6.7%, 3/45) (Figure 1A). These secondary metabolites are primarily isolated from actinomycetes across 6 different sources, including China (60%, 9/15), Korea (13.3%, 2/15), Thailand (6.7%, 1/15), United States (6.7%, 1/15), Japan (6.7%, 1/15) and Indian Ocean (6.7%, 1/15) (Figure 1B). Among these biological samples, 12 belong to the genus Streptomyces, accounting for 80%, highlighting the significance of Streptomyces in the discovery of novel antibacterial natural products (Figure 1C). Of particular note are the remarkable findings by Professor Jongheon Shin and Kibong Oh, researchers at Seoul National University, who discovered corynetoxin U17a (32). This compound demonstrated potent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.06 μg/mL (Lee et al., 2024). Table 1 outlines the names, sources of isolation, species, and MIC values of the antibacterial compounds identified.
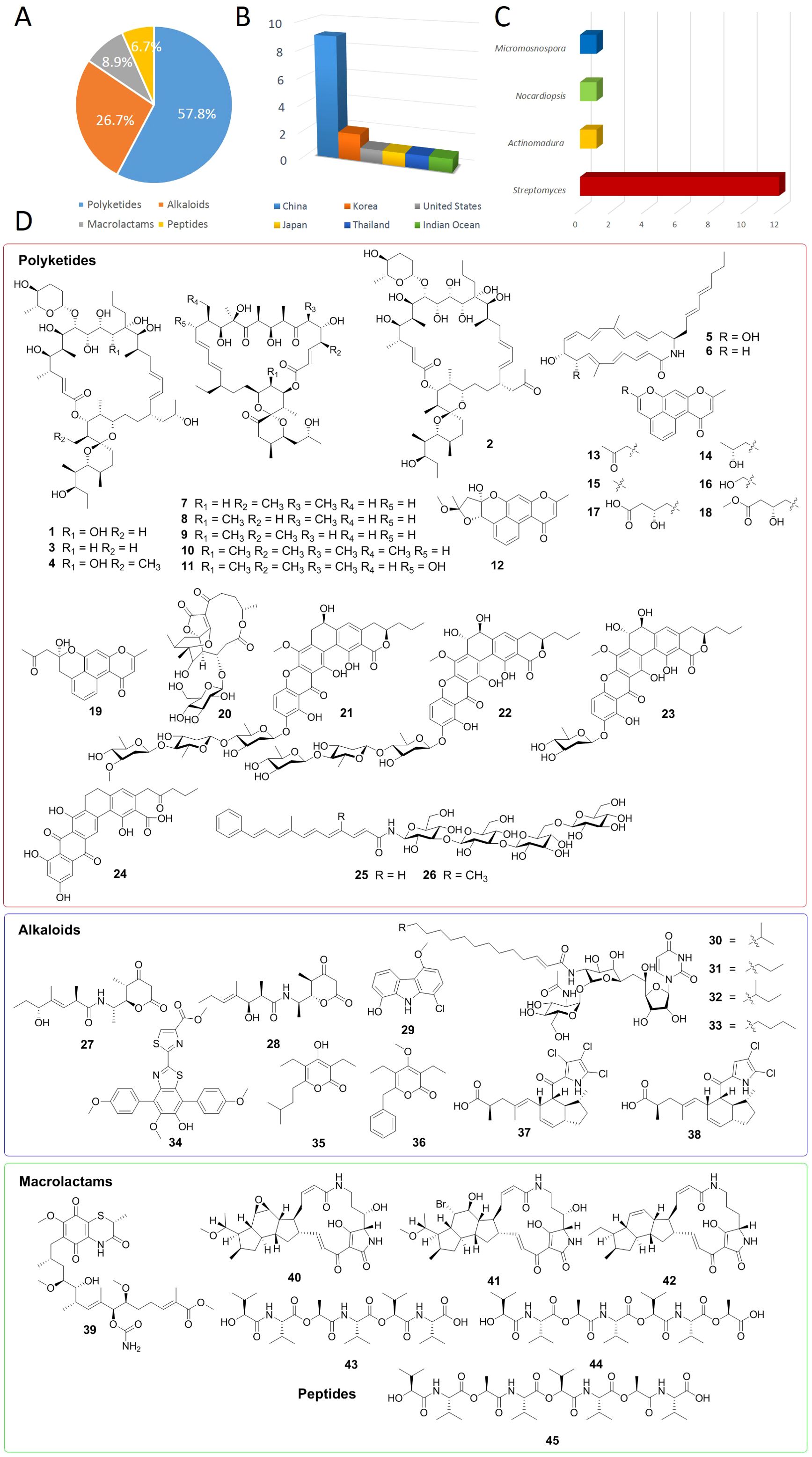
Figure 1. (A) Antibacterial compounds derived from marine actinomycetes according to structure types. (B) The different sources of marine actinomycetes. (C) The different genus of marine actinomycetes. (D) Chemical structures of compounds 1-45.
2 Polyketides
Among the secondary metabolites produced by microorganisms, polyketide compounds typically constitute the majority in statistical analysis due to their large quantity and diverse types of activities (Yang et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021; Yixuan et al., 2021). They primarily originate from the condensation of short-chain fatty acids by microorganisms. Additionally, the biosynthesis of polyketides can also involve modifications of the carbon chain produced at each step through processes such as oxidation and hydroxylation, leading to the generation of numerous distinct structures and a wide range of activities.
Four unique compounds (1-4), characterized by the presence of an L-rhodinose and spiroketal moiety, and featuring unusual continuous hydroxy groups within their macrolide structure, were isolated from a marine-derived Micromonospora sp. FIMYZ51 (Figure 1D) (Zhao W. et al., 2024). These compounds demonstrated strong antifungal properties against A. niger, with MIC values ranging from 0.5 to 2 μg/mL. Additionally, they exhibited varying levels of inhibitory activity against the pathogenic bacterium M. luteus, with MIC values from 0.0625 μg/mL to 1 μg/mL (Table 1). Separately, two heronamides (5 and 6) were isolated from a deep-sea Streptomyces sp. OUCT16-38 (Zhao Y. et al., 2024). When tested for antibacterial activity, both 5 and 6 showed significant growth inhibition against multidrug-resistant pathogens E. faecium and E. faecalis, with MIC values of 3.1 μg/mL (Table 1).
Metabolomic fingerprinting analysis, utilizing mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), of the marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. FXY-T5 resulted in the identification of five novel oligomycins: 24-lumooligomycin B (7), 4-lumooligomycin B (8), 6-lumooligomycin B (9), 40-homooligomycin B (10), and 15-hydroxy-oligomycin B (11) (Figure 1D) (Feng et al., 2024). Notably, 40-homooligomycin B (10) exhibited antifungal activity that was either stronger or comparable to that of positive controls, suggesting its potential as a biocontrol agent against plant pathogens such as C. musae and C. coccodes (Table 1). In a separate study, Xiaofei Huang and colleagues reported the discovery of eight new aromatic polyketides, naphpyrones A-H (12-19), from the heterologous expression strain Streptomyces coelicolor (Huang X. et al., 2024). Evaluation of their bioactivity showed that compounds 12 and 13 possessed antibacterial activity against S. aureus, with MIC values of 1 μg/mL and 4 μg/mL, respectively.
Glycoabyssomicin A (20), a novel abyssomicin variant incorporating a sugar moiety, was isolated from the deep-sea Streptomyces koyangensis SCSIO5802 through LC-MS-guided analysis (Zhu et al., 2024). When tested against a panel of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (including M. luteus, S. aureus, MRSA, and E. coli), it exhibited no antibacterial activity at a concentration of 10 μg per filter paper disc. During a screening of actinomycetes from mangrove rhizosphere sediment samples, a strain of Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 40068 demonstrated robust antibacterial activity. Further purification of its extract led to the identification of four new compounds, kebanmycins A-D (21-24) (Figure 1D) (Zhao M. et al., 2024). Among them, kebanmycin A (21) stood out for its potent antibacterial activity against S. aureus and MRSA, with an MIC value of 0.125 μg/mL, which is generally lower than that of the positive control vancomycin (MIC 1 μg/mL). Kebanmycin A’s (21) notable anti-MRSA efficacy makes it a promising candidate for further drug development targeting MRSA. Additionally, two new phenyl polyene metabolites, maduraflavacins A and B (25, 26), were isolated from a rare marine-derived actinomycete strain, Actinomadura glauciflava NA03286 (Figure 1D) (Zou et al., 2024). These compounds displayed weak antibacterial activity against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus and M. luteus, respectively (Table 1).
3 Alkaloids
Alkaloids are a class of nitrogen-containing alkaline organic compounds with complex and diverse chemical structures, occupying an important position among secondary metabolites (Liu et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2020; Zhang C. et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022; Xia et al., 2022). Alkaloids exhibit abundant physiological activities and pharmacological effects, such as antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor activities, making them a crucial resource for drug development and possessing potential value for the research and development of new drugs (Liu et al., 2021; Bhatti et al., 2022; Waseem et al., 2022; Mei et al., 2023; Yu et al., 2023).
During an investigation of Streptomyces sp. ZS-A65, which was isolated from marine sediments, two novel alpiniamide-type alkaloids were discovered: alpiniamides H and I (27, 28) (Figure 1D) (Pu et al., 2024). When tested for antibacterial activity against P. aeruginosa, compound 28 demonstrated robust antibiofilm activity, with an MIC of 87.5 μM (Table 1). Additionally, a new 9H-carbazole derivative, compound 29, was isolated from a solid fermented medium of the mangrove-derived Streptomyces strain OUCMDZ-5511, collected in Thailand, which was grown under fluoride stress conditions (Figure 1D) (Liu et al., 2024). Compound 29 exhibited antiquorum sensing activity against C. violaceum by reducing violacein production and inhibiting biofilm formation in a concentration-dependent manner, suggesting its potential as a novel quorum sensing inhibitor (Table 1). Furthermore, four tunicamycin class compounds, tunicamycin VII (30), tunicamycin VIII (31), corynetoxin U17a (32), and tunicamycin IX (33), were isolated from the culture broth of the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. MBTG32 (Figure 1D) (Lee et al., 2024). These compounds displayed potent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, particularly S. aureus, with MIC values ranging from 0.06 to 0.25 µg/mL (Table 1). The research also supported the notion that tunicamycins exert their antibacterial effects by inhibiting the MraY enzyme activity in S. aureus.
Utilizing the OSMAC strategy, researchers isolated and characterized one novel p-terphenyl and two new α-pyrone derivatives, specifically nocarterphenyl I (34) and nocardiopyrone D-E (35, 36), from the marine sediment-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. HDN154086 (Figure 1D) (Zhou et al., 2024). Notably, compound 34 features a rare 2,2’-bithiazole structure among natural products and exhibited promising antibacterial activity against B. subtilis and E. coli, with MIC values of 0.8 μM. 36 displayed notable antibacterial activity against MRSA when compared to the positive control ciprofloxacin (Table 1). In another study, Douglas Sweeney and colleagues employed pattern-based genome mining to explore the biosynthetic potential of the marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. CNY-716. This led to the discovery of the first halogenated pyrroloketoindane natural products, indanopyrrole A (37) and B (38) (Figure 1D) (Sweeney et al., 2024). Indanopyrrole A (37) demonstrated potent broad-spectrum antibiotic activity against clinically relevant pathogens, including E. coli (MIC = 4 μg/mL), MRSA (MIC = 2 μg/mL), and VRE (MIC = 2 μg/mL) (Table 1).
4 Macrolactams
Macrolactams are a class of large molecular cyclic compounds produced by microorganisms through secondary metabolic pathways, containing amide bonds and multiple ring structures (Hong et al., 2018; Wang P. et al., 2020; Ding L. et al., 2021). Macrolactams generally exhibit pharmacological activities such as antibacterial and antitumor effects, making them an important resource for drug development.
The ansamycin derivative, seco-geldanamycin B (39), was obtained through solid fermentation of the marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. ZYX-F-97 (Figure 1D) (Yi et al., 2024). This compound displayed moderate inhibitory effects against S. aureus and B. subtilis, with MIC values of 64 μg/mL (Table 1). Additionally, two novel polycyclic tetramate macrolactams (PTMs), hydroxycapsimycin (40) and brokamycin (41), were isolated alongside the known PTM ikarugamycin (42) from the culture broth of marine-derived Streptomyces sp. KKMA-0239 (Figure 1D) (Shigeno et al., 2024). Compound 40 showed weak activity against M. intracellulare, with an MIC of 50µg/mL. Compound 41 exhibited moderate activity against both M. intracellulare and drug-resistant M. avium, with MICs of 12.5 and 50 µg/ml, respectively. In comparison, ikarugamycin (42) demonstrated more potent antimicrobial activity than both 40 and 41 (Table 1).
5 Peptides
Peptides are primarily synthesized by microorganisms through non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) pathways, and these compounds typically possess complex structures and diverse biological activities (Xu et al., 2023). Peptides occupy an important position among microbial secondary metabolites, not only in terms of their large quantity but also their rich variety. They often exhibit pharmacological activities such as antibacterial, antitumor, and immunoregulatory effects, holding tremendous potential value and application prospects for new drug development (Xu et al., 2020; Liang et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2019; Wen et al., 2020; Wong et al., 2020; Chai et al., 2021).
From a marine sediment-derived strain of Streptomyces sp. ROA-065 (Figure 1D), researchers isolated three novel depsipeptides named homiamides A-C (43-45) (Ding et al., 2023). These compounds displayed weak antibacterial activities against both Gram-positive (B. subtilis, S. aureus) and Gram-negative (E. coli) bacteria, with MIC values ranging from 32 to 64 µg/mL (Table 1).
6 Conclusion
The escalating problem of global drug resistance has spurred intensive searches for novel antibacterial agents. Marine natural products have proven pivotal in drug discovery, forming the foundation for the early stages of generic drug development (Cao et al., 2016; Hussain et al., 2021; Shams Ul Hassan et al., 2021; Hassan et al., 2022; Carroll et al., 2024; Hassan et al., 2024). This review delves into 45 compounds reported in 2024 to possess antibacterial activity, sourced from marine actinomycetes. These compounds encompass polyketides, alkaloids, macrolactams, and peptides (Figure 1D; Table 1). The review outlines the origins, chemical structures, and biological activities of these compounds. In essence, the persistent emergence of drug-resistant bacteria poses a grave risk to human health. Marine microbial secondary metabolites present a promising avenue for discovering natural antibacterial agents characterized by unique structures, robust activities, and specific modes of action. Thus, the pursuit of novel antibacterial drugs from marine actinomycetes warrants particular focus.
Author contributions
CP: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SH: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review & editing. MI: Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SY: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. HJ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Validation, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by NSFC (No. 82404465), the Senior Talent Foundation of Jiangsu University (5501290012), the Chugai Foundation for Innovative Drug Discovery Science: C-FINDs (2025-CF-01). The work was supported by NSFC (81973191), project supported by the Modern Plateau Plant Medicine Research Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SA1700208).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Afrin S., Haneefa S. M., Fernandez-Cabezudo M. J., Giampieri F., Al-Ramadi B. K., Battino M. (2020). Therapeutic and preventive properties of honey and its bioactive compounds in cancer: An evidence-based review. Nutr. Res. Rev. 33, 50–76. doi: 10.1017/S0954422419000192
Bhatti S. A., Hussain M. H., Mohsin M. Z., Mohsin A., Zaman W. Q., Guo M., et al. (2022). Evaluation of the antimicrobial effects of Capsicum, Nigella sativa, Musa paradisiaca L., and Citrus limetta: A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6, 1043823. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.1043823
Brüssow H. (2024). The antibiotic resistance crisis and the development of new antibiotics. Microbial Biotechnol. 17, e14510. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14510
Cao J., Wang J., Wang S., Xu X. (2016). Porphyra species: a mini-review of its pharmacological and nutritional properties. J. medicinal Food 19, 111–119. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2015.3426
Carroll A. R., Copp B. R., Grkovic T., Keyzers R. A., Prinsep M. R. (2024). Marine natural products. Natural Product Rep. 41, 162–207. doi: 10.1039/D3NP00061C
Chai T. T., Xiao J., Dass S. M., Teoh J. Y., Ee K. Y., Ng W. J., et al. (2021). Identification of antioxidant peptides derived from tropical jackfruit seed and investigation of the stability profiles. Food Chem. 340, 127876. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127876
Chen M., Xiao J., El-Seedi H. R., Woźniak K. S., Daglia M., Little P. J., et al. (2024). Kaempferol and atherosclerosis: From mechanism to medicine. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 2157–2175. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2121261
Chin P. S., Ang G. Y., Yu C. Y., Tan E. L., Tee K. K., Yin W. F., et al. (2018). Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and genetic diversity of Listeria spp. isolated from raw chicken meat and chicken-related products in Malaysia. J. Food Prot. 81, 284–289. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-186
Cui H., Zhang C., Li C., Lin L. (2019). Preparation and antibacterial activity of Litsea cubeba essential oil/dandelion polysaccharide nanofiber. Ind. Crops Products 140, 111739. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111739
Cui H., Zhang C., Li C., Lin L. (2020). Inhibition mechanism of cardamom essential oil on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Lwt 122, 109057. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109057
Demain A. L. (2009). Antibiotics: natural products essential to human health. Medicinal Res. Rev. 29, 821–842. doi: 10.1002/med.20154
Ding Q., Jiang H., Chen Y., Luo L., He R., Ma H., et al. (2019). Influence of nitrogen protection on the extraction yield and antioxidant activities of polyphenols by ultrasonic-assisted extraction from rapeseed meal. J. Food Process Eng. 42, e13104. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.13104
Ding Q., Sheikh A. R., Chen Q., Hu Y., Sun N., Su X., et al. (2023). Understanding the mechanism for the structure-activity relationship of food-derived ACEI peptides. Food Rev. Int. 39, 1751–1769. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2021.1936005
Ding Q., Sheikh A. R., Gu X., Li J., Xia K., Sun N., et al. (2021). Chinese propolis: ultrasound-assisted enhanced ethanolic extraction, volatile components analysis, antioxidant and antibacterial activity comparison. Food Sci. Nutr. 9, 313–330. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1997
Ding L., Zhang S. D., Haidar A. K., Bajimaya M., Guo Y., Larsen T. O., et al. (2021). Polycyclic tetramate macrolactams—a group of natural bioactive metallophores. Front. Chem. 9, 772858. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.772858
Donald L., Pipite A., Subramani R., Owen J., Keyzers R. A., Taufa T. (2022). Streptomyces: Still the biggest producer of new natural secondary metabolites, a current perspective. Microbiol. Res. 13, 418–465. doi: 10.3390/microbiolres13030031
Feng X. Y., Li J. H., Li R. J., Yuan S. Z., Sun Y. J., Peng X. P., et al. (2024). Structures, biosynthesis, and bioactivity of oligomycins from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. FXY-T5. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 1082–1095. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c06307
Gomez-Banderas J. (2022). Marine natural products: A promising source of environmentally friendly antifouling agents for the maritime industries. Front. Mar. Sci. 9, 858757. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.858757
Hamadou A. H., Zhang J., Chen C., Xu J., Xu B. (2023). Vitamin C and β-carotene co-loaded in marine and egg nanoliposomes. J. Food Eng. 340, 111315. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111315
Hassan S. S. U., Abdel-Daim M. M., Behl T., Bungau S. (2022). Natural products for chronic diseases: a ray of hope. Molecules 27, 5573. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175573
Hassan S. S. U., Wu J., Li T., Ye X., Rehman A., Yan S., et al. (2024). Unlocking marine microbial treasures: new PBP2a-targeted antibiotics elicited by metals and enhanced by RSM-driven transcriptomics and chemoinformatics. Microbial Cell factories 23, 303. doi: 10.1186/s12934-024-02573-0
Hong Y. Q., Guo X., Chen G. H., Zhou J. W., Zou X. M., Liao X., et al. (2018). Determination of five macrolide antibiotic residues in milk by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography with field amplified sample stacking. J. Food Saf. 38, e12382. doi: 10.1111/jfs.2018.38.issue-1
Hu W., Li C., Dai J., Cui H., Lin L. (2019). Antibacterial activity and mechanism of Litsea cubeba essential oil against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Ind. Crops Products 130, 34–41. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.12.078
Huang P. Y., Hsu C. K., Tang H. J., Lai C. C. (2024). Eravacycline: a comprehensive review of in vitro activity, clinical efficacy, and real-world applications. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 22, 387–398. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2024.2351552
Huang X., Xu X., Zhou L., Ma C., Wang W., Li C., et al. (2024). Naphpyrones A–H, antibacterial aromatic polyketides isolated from the Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2)/spi1 Δ spi H3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 73, 541–548. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c09101
Hussain H., Mamadalieva N. Z., Ali I., Green I. R., Wang D., Zou L., et al. (2021). Fungal glycosides: structure and biological function. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 110, 611–651. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.02.029
Iqbal M. W., Riaz T., Mahmood S., Bilal M., Manzoor M. F., Qamar S. A., et al. (2024). Fucoidan-based nanomaterial and its multifunctional role for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 354–380. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2106182
Jagannathan S. V., Manemann E. M., Rowe S. E., Callender M. C., Soto W. (2021). Marine actinomycetes, new sources of biotechnological products. Mar. Drugs 19, 365. doi: 10.3390/md19070365
Lee J., Hwang J. Y., Oh D., Oh D. C., Park H. G., Shin J., et al. (2024). Tunicamycins from marine-derived Streptomyces bacillaris inhibit MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase in Staphylococcus aureus. Mar. Drugs 22, 293. doi: 10.3390/md22070293
Li B. Y., Xu X. Y., Gan R. Y., Sun Q. C., Meng J. M., Shang A., et al. (2019). Targeting gut microbiota for the prevention and management of diabetes mellitus by dietary natural products. Foods 8, 440. doi: 10.3390/foods8100440
Li S., Yang B., Tan G. Y., Ouyang L. M., Qiu S., Wang W., et al. (2021). Polyketide pesticides from actinomycetes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 69, 299–307. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.05.006
Liang Q., Chalamaiah M., Ren X., Ma H., Wu J. (2018). Identification of new anti-inflammatory peptides from zein hydrolysate after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and transport in Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 1114–1120. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04562
Lin L., Agyemang K., Abdel-Samie M. A. S., Cui H. (2019). Antibacterial mechanism of Tetrapleura tetraptera extract against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus and its application in pork. J. Food Saf. 39, e12693. doi: 10.1111/jfs.12693
Liu Y., Liu J., Yan P., Kachanuban K., Liu P., Jia A., et al. (2024). Carbazole and quinazolinone derivatives from a fluoride-tolerant Streptomyces strain OUCMDZ-5511. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 6424–6431. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00780
Liu J., Wan J., Du W., Wang D., Wen C., Wei Y., et al. (2021). In vivo functional verification of four related genes involved in the 1-deoxynojirimycin biosynthetic pathway in mulberry leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 10989–10998. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03932
Liu J., Wan J., Wang D., Wen C., Wei Y., Ouyang Z. (2020). Comparative transcriptome analysis of key reductase genes involved in the 1-deoxynojirimycin biosynthetic pathway in mulberry leaves and cloning, prokaryotic expression, and functional analysis of MaSDR 1 and MaSDR 2. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 12345–12357. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04832
Liu Y., Zhang D., Liu G. M., Chen Q., Lu Z. (2019). Ameliorative effect of dieckol-enriched extraction from Laminaria japonica on hepatic steatosis induced by a high-fat diet via β-oxidation pathway in ICR mice. J. Funct. Foods 58, 44–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.04.051
Mei S., Ding J., Chen X. (2023). Identification of differential volatile and non-volatile compounds in coffee leaves prepared from different tea processing steps using HS-SPME/GC–MS and HPLC-Orbitrap-MS/MS and investigation of the binding mechanism of key phytochemicals with olfactory and taste receptors using molecular docking. Food Res. Int. 168, 112760. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112760
Muhammad N., Uddin N., Liu Z., Yang M., Liu M. (2024). Research progress and biosynthetic mechanisms of nutritional compounds obtained from various organs during the developmental stages of a medicinal plant (Chinese Jujube). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 79, 744–758. doi: 10.1007/s11130-024-01225-3
Murray C. J., Ikuta K. S., Sharara F., Swetschinski L., Aguilar G. R., Gray A., et al. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 399, 629–655. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
Ngamcharungchit C., Chaimusik N., Panbangred W., Euanorasetr J., Intra B. (2023). Bioactive metabolites from terrestrial and marine actinomycetes. Molecules 28, 5915. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155915
Otero P., Carpena M., Garcia-Oliveira P., Echave J., Soria-Lopez A., García-Pérez P., et al. (2023). Seaweed polysaccharides: Emerging extraction technologies, chemical modifications and bioactive properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63, 1901–1929. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1969534
Pu F., Fang J., Li W., Zhang B., Hong X., Xu L., et al. (2024). New alpiniamide-type polyketide with antibiofilm activities from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. ZS-A65. Chem. Biodiversity 21, e202400029. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202400029
Rasheed H. A., Rehman A., Karim A., Al-Asmari F., Cui H., Lin L. (2024). A comprehensive insight into plant-derived extracts/bioactives: Exploring their antimicrobial mechanisms and potential for high-performance food applications. Food Bioscience 59, 104035. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104035
Ryu D., Hillman P. F., Akinniyi G., Nam S. J., Yang I. (2023). Marine mudflat actinomycetes as a novel natural products source. Front. Mar. Sci. 10, 1297446. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1297446
Scherlach K., Hertweck C. (2021). Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential. Nat. Commun. 12, 3864. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24133-5
Shams Ul Hassan S., Ishaq M., Zhang W. D., Jin H. Z. (2021). An overview of the mechanisms of marine fungi-derived anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor agents and their novel role in drug targeting. Curr. Pharm. design 27, 2605–2614. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200728142244
Shigeno S., Kadowaki M., Nagai K., Hosoda K., Terahara T., Nishimura T., et al. (2024). New polycyclic tetramate macrolactams with antimycobacterial activity produced by marine-derived Streptomyces sp. KKMA-0239. J. Antibiotics 77, 265–271. doi: 10.1038/s41429-024-00710-w
Spížek J., Novotná J., Řezanka T., Demain A. L. (2010). Do we need new antibiotics? The search for new targets and new compounds. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37, 1241–1248. doi: 10.1007/s10295-010-0849-8
Sun X., Zhang D., Zhao L., Shi B., Xiao J., Liu X., et al. (2020). Antagonistic interaction of phenols and alkaloids in Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum) pericarp. Ind. Crops Products 152, 112551. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112551
Surendhiran D., Li C., Cui H., Lin L. (2021). Marine algae as efficacious bioresources housing antimicrobial compounds for preserving foods-A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 358, 109416. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109416
Sweeney D., Bogdanov A., Chase A. B., Castro-Falcón G., Trinidad-Javier A., Dahesh S., et al. (2024). Pattern-based genome mining guides discovery of the antibiotic indanopyrrole A from a marine Streptomycete. J. Natural Products 87, 2768–2778. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.4c00934
Tianqiao S., Xiong Z., You Z., Dong L., Jiaoling Y., Junjie Y., et al. (2021). Genome-wide identification of Zn2Cys6 class fungal-specific transcription factors (ZnFTFs) and functional analysis of UvZnFTF1 in ustilaginoidea virens. Rice Sci. 28, 567–578. doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.03.001
Wang F., Bao Y., Zhang C., Zhan L., Khan W., Siddiqua S., et al. (2022). Bioactive components and anti-diabetic properties of Moringa oleifera Lam. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 62, 3873–3897. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1870099
Wang P., Wang D., Zhang R., Wang Y., Kong F., Fu P., et al. (2020). Novel macrolactams from a deep-sea-derived Streptomyces species. Mar. Drugs 19, 13. doi: 10.3390/md19010013
Wang X., Yang Y., Huycke M. M. (2020). Risks associated with enterococci as probiotics. Food Res. Int. 129, 108788. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108788
Waseem M., Akhtar S., Ahmad N., Ismail T., Lazarte C. E., Hussain M., et al. (2022). Effect of microwave heat processing on nutritional indices, antinutrients, and sensory attributes of potato powder-supplemented flatbread. J. Food Qual. 2022, 2103884. doi: 10.1155/2022/2103884
Wei Z., Shan C., Zhang L., Wang Y., Xia X., Liu X., et al. (2021). A novel subtilin-like lantibiotics subtilin JS-4 produced by Bacillus subtilis JS-4, and its antibacterial mechanism against Listeria monocytogenes. LWT 142, 110993. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.110993
Wen X., Wang L., Li J., Chen Y., Zhuo D., Anjago W. M., et al. (2024). Staurosporine-producing Streptomyces sp. strain 11× 1 cell-free culture filtrates control diseases caused by the oomycete plant pathogens Pythium myriotylum and Phytophthora sojae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 34, 123–147. doi: 10.1080/09583157.2023.2301646
Wen C., Zhang J., Feng Y., Duan Y., Ma H., Zhang H. (2020). Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from watermelon seed protein hydrolysates and their cytoprotective effects on H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Food Chem. 327, 127059. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127059
Wong F. C., Xiao J., Wang S., Ee K. Y., Chai T. T. (2020). Advances on the antioxidant peptides from edible plant sources. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 99, 44–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.012
Xia G., Li Y., Tao H., Zhang L., Zhang J., Yang H., et al. (2022). Inactivation mechanism of catalytic infrared against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its decontamination application on dry green Sichuan pepper (Zanthoxylum schinifolium). Food Control 132, 108483. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108483
Xu Z., Chen H., Fan F., Shi P., Cheng S., Tu M., et al. (2020). Pharmacokinetics and transport of an osteogenic dodecapeptide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 9961–9967. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02779
Xu D., Zhang Z., Yao L., Wu L., Zhu Y., Zhao M., et al. (2023). Advances in the adenylation domain: discovery of diverse non-ribosomal peptides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 107, 4187–4197. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12585-2
Yang Q., Solairaj D., Apaliya M. T., Abdelhai M., Zhu M., Yan Y., et al. (2020). Protein expression profile and transcriptome characterization of Penicillium expansum induced by Meyerozyma guilliermondii. J. Food Qual. 2020, 8056767. doi: 10.1155/2020/8056767
Yi K. X., Xie Q. Y., Ma Q. Y., Yang L., Dai H. F., Zhao Y. X., et al. (2024). Diverse ansamycin derivatives from the marine-derived Streptomyces sp. ZYX-F-97 and their antibacterial activities. Fitoterapia 173, 105814. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105814
Yixuan L., Qaria M. A., Sivasamy S., Jianzhong S., Daochen Z. (2021). Curcumin production and bioavailability: a comprehensive review of curcumin extraction, synthesis, biotransformation and delivery systems. Ind. Crops Products 172, 114050. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114050
Yu Z., Xia M., Lan J., Yang L., Wang Z., Wang R., et al. (2023). A comprehensive review on the ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and quality control of the genus Lycium in China. Food Funct. 14, 2998–3025. doi: 10.1039/D2FO03791B
Zhang H., Ahima J., Yang Q., Zhao L., Zhang X., Zheng X. (2021). A review on citrinin: Its occurrence, risk implications, analytical techniques, biosynthesis, physiochemical properties and control. Food Res. Int. 141, 110075. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.110075
Zhang Y., Hao R., Chen J., Li S., Huang K., Cao H., et al. (2024). Health benefits of saponins and its mechanisms: perspectives from absorption, metabolism, and interaction with gut. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 9311–9332. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2212063
Zhang Y., Hassan M. M., Rong Y., Liu R., Li H., Ouyang Q., et al. (2022). A solid-phase capture probe based on upconvertion nanoparticles and inner filter effect for the determination of ampicillin in food. Food Chem. 386, 132739. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132739
Zhang J., Wen C., Li C., Duan Y., Zhang H., Ma H. (2019). Antioxidant peptide fractions isolated from wheat germ protein with subcritical water extraction and its transport across Caco-2 cells. J. Food Sci. 84, 2139–2146. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14720
Zhang J., Wen C., Zhang H., Duan Y., Ma H. (2020). Recent advances in the extraction of bioactive compounds with subcritical water: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 95, 183–195. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.11.018
Zhang X., Wu F., Gu N., Yan X., Wang K., Dhanasekaran S., et al. (2020). Postharvest biological control of Rhizopus rot and the mechanisms involved in induced disease resistance of peaches by Pichia membranefaciens. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 163, 111146. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111146
Zhang C., Yu X., Shi X., Han Y., Guo Z., Liu Y. (2020). Development of carbon quantum dot–labeled antibody fluorescence immunoassays for the detection of morphine in hot pot soup base. Food Analytical Methods 13, 1042–1049. doi: 10.1007/s12161-020-01700-y
Zhao Y., Chen H., Yue L., Dong Y., Su D., Lyu J., et al. (2024). Heronamides with unreported skeletons from deep-sea Streptomyces: discovery and biosynthesis. Organic Chem. Front. 11, 1175–1183. doi: 10.1039/D3QO01837G
Zhao W., Jiang H., Ge Y., Zhou C., Ma Y., Zhou J., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial spiroketal macrolides and dichloro-diketopiperazine from Micromonospora sp. FIMYZ51. Fitoterapia 175, 105946. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.105946
Zhao M., Zhang W., Yang C., Zhang L., Huang H., Zhu Y., et al. (2024). Discovery of kebanmycins with antibacterial and cytotoxic activities from the mangrove-derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 40068. J. Natural Products 87, 1591–1600. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.4c00232
Zhong R., Wan X., Wang D., Zhao C., Liu D., Gao L., et al. (2020). Polysaccharides from marine Enteromorpha: structure and function. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 99, 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.030
Zhou L., Chang Y., Yang S., Huang X., Wang J., Jiang C., et al. (2024). Antibacterial p-terphenyl and α−pyrone derivates isolated from the marine-derived actinomycete Nocardiopsis sp. HDN154086. J. Antibiotics 77, 201–205. doi: 10.1038/s41429-023-00698-9
Zhu Y., Li C., Cui H., Lin L. (2021). Encapsulation strategies to enhance the antibacterial properties of essential oils in food system. Food Control 123, 107856. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107856
Zhu X., Wang S., Song Y., Chen T., Yan Y. (2024). LC-MS guided discovery of a new type of abyssomicin, glycoabyssomicin A, from a deep-sea derived Streptomyces. Natural Product Res., 1–6. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2024.2417839
Keywords: marine actinomycetes, antibacterial activity, polyketides, alkaloids, macrolactams
Citation: Pan C, Hassan SSu, Ishaq M, Yan S and Jin H (2025) Marine actinomycetes: a hidden treasure trove for antibacterial discovery. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1558320. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1558320
Received: 10 January 2025; Accepted: 29 January 2025;
Published: 13 February 2025.
Edited by:
Guillermin Agüero-Chapin, University of Porto, PortugalReviewed by:
Carlos Jimenez, University of A Coruña, SpainCopyright © 2025 Pan, Hassan, Ishaq, Yan and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Syed Shams ul Hassan, U2hhbXMxMzI3QHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; Shikai Yan, U2hreWFuQDEyNi5jb20=; Huizi Jin, S2ltaHpAc2p0dS5lZHUuY24=
 Chengqian Pan
Chengqian Pan Syed Shams ul Hassan
Syed Shams ul Hassan Muhammad Ishaq
Muhammad Ishaq Shikai Yan
Shikai Yan Huizi Jin
Huizi Jin