- 1Department of Climate Change, Energy, The Environment and Water, Australian Antarctic Division, Kingston, TAS, Australia
- 2Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies, University of Tasmania, Kingston, TAS, Australia
- 3Irvine Marine Fauna Research, Perth, WA, Australia
Data collection facilitated by remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) has proven to be revolutionary in many disciplines including for research in extreme environments. Here we assess current use and utility of small multirotor remotely piloted aircraft (RPAs) for the challenging role of facilitating ship-based cetacean research in Antarctica. While such aircraft are now used routinely in sheltered environments in and off Antarctica, a comprehensive literature review found that RPA-mediated cetacean research conducted from ships at sea and outside of the Antarctic Peninsula region was relatively uncommon. In order to determine the potential utility of ship-based multirotor RPA operations for cetacean research, we repeatedly deployed small RPAs during a multidisciplinary research voyage in maritime East Antarctica to collect scientific data contributing to an understanding of krill and krill predator interactions. RPA flight metrics (duration, height, length, speed, distance from ship, battery drainage, satellites acquired) were compared to ship underway environmental sampling data. At a mean duration of 12 minutes, these 139 RPA flights were relatively short yet adequate to achieve the science intended, namely a range of cetacean related data streams including photogrammetry, photo identification, behavioural observations and whale blow sampling in addition to water sampling and collection of general scenic imagery. RPA flight operations were constrained by wind speed but not by air temperature with flights undertaken throughout the full range of air temperatures experienced (down to –9.5°C) but not throughout the full range of wind speeds experienced. For a 12-minute flight duration, battery drainage was around 60% indicating that the RPAs were rarely pushed to their operational limit. There was little evidence that the cold impacted RPA lithium battery performance with estimated maximum flight time within approximately 10% of expected flight time for the RPA platforms most used. Whist small multirotor RPAs are rarely applied to cetacean related research in maritime East Antarctica, we demonstrate their value and potential to deliver data critical to address knowledge gaps that challenge the effective management of both krill and their predators.
1 Introduction
Remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) have proven revolutionary in a range of disciplines, especially where access to remote, extreme, hazardous and/or inaccessible environments is required (for example Di Stefano et al., 2018; Shahmoradi et al., 2020; Vargas Tamayo et al., 2020; Häusermann et al., 2023). Whilst RPAs have become integral to logistics (Xi et al., 2018), surveillance (Alvear et al., 2017), search and rescue (Lyu et al., 2023), media (Harvard et al., 2020) and other non-science applications (Mahadevan, 2010), their uptake within science disciplines has been particularly rapid due to the benefits and opportunities associated with the myriad of payload options (for example (Harris et al., 2019; Burgués and Marco, 2020; Butcher et al., 2021; Shelare et al., 2021). RPAs applied within a conservation and management context (Bersaglio et al., 2023) are proving to be an improved, faster and less invasive option than traditional methods (Howell et al., 2022; Alejandro et al., 2023; Hodgson et al., 2023) and particularly powerful for threatened species research (Gallego and Sarasola, 2021; Varela-Jaramillo et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023) or for marine species that are difficult to access (Barreto et al., 2021; Butcher et al., 2021; Hodgson et al., 2023).
Aerial observations to understand cetacean presence and behaviour has been a common scientific method employed since the whaling era (Carroll et al., 2014; Nowacek et al., 2016). Sighting surveys from planes and helicopters have been used globally to monitor cetacean species recovery (Stewart et al., 1987; Clark et al., 2010; Bannister, 2001; Herr et al., 2022b) with the logical potential for RPAs to generate a complementary data stream identified since at least 2008 (Schoonmaker et al., 2008). Subsequently, long range, fixed-wing RPAs have been used for line and strip transect surveys to derive cetacean abundance estimates (Hodgson et al., 2017) including in extreme environments (Aniceto et al., 2018) and also for research on Antarctic wildlife (Zmarz et al., 2018; Pfeifer et al., 2019; Pina and Vieira, 2022) and the physical Antarctic environment (Bello et al., 2022; Pina and Vieira, 2022). In addition to using RPAs to undertake aerial surveys (Angliss et al., 2018), RPAs and multirotor RPAs in particular, have been employed as a cetacean research tool to undertake photogrammetry (Durban et al., 2015; Christiansen et al., 2018), collect photo identification images (Koski et al., 2015; Ryan et al., 2022; Young et al., 2022), investigate energetics and kinematics (Christiansen et al., 2016; Werth et al., 2019), sample whale blow (Apprill et al., 2017; Pirotta et al., 2017), assess anthropogenic interactions (Ramp et al., 2021; Pirotta et al., 2022), sample faecal matter (Baird et al., 2022) and undertake behavioural observation (Torres et al., 2018; Fiori et al., 2020).
Whilst the majority of RPA-associated cetacean research occurs in relatively accessible regions, RPAs have also been used successfully in remote, polar regions (Johnston et al., 2022; Pallin et al., 2022), providing an alternative method to more efficiently facilitate the collection of data in locations that have historically added a degree of challenge (Hyun et al., 2020) to the study of a taxa that are already notoriously difficult to study (Nowacek et al., 2016). In Antarctica, the use of RPAs for cetacean research has increased in recent years (Durban et al., 2021; Bierlich et al., 2022; Pallin et al., 2022), primarily in the relatively sheltered regions of the Antarctic Peninsula where multirotor RPAs have been launched and recovered from small boats (around 6 m) to collect cetacean related data in nearshore waters. Larger (> 20 m), vessel based multirotor RPAs operations are less common but have successfully collected cetacean imagery and blow samples (Kennedy et al., 2020; Herr et al., 2022a, b). To the best of our knowledge, the use of fixed-wing RPAs for long range visual survey for cetaceans is yet to be described within the scientific literature for Antarctica but is likely imminent (Katsumata and Yoshida, 2023).
Both multirotor and fixed-wing RPAs provide an excellent opportunity to facilitate a contemporary understanding of cetacean abundance, distribution and habitat use in Antarctic waters particularly if flights can be conducted from large vessels and conducted simultaneously with other activities. Such data can be used for many purposes including: assessing the recovery of whale populations from past whaling activities; assessing the impacts of a rapidly changing environment; and informing the management of the Antarctic krill fishery. Antarctic baleen whales forage primarily on Antarctic krill, consuming large quantities of prey (Savoca et al., 2021). While most krill fishing effort is currently centred around the Antarctic Peninsula region, krill fishing recommenced off East Antarctica in 2016 (Kawaguchi and Nicol, 2020). The krill fishery in Antarctica is managed by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR). This international body implements a precautionary, ecosystem-based fisheries management approach, which aims to prevent adverse, irreversible long-term impacts from fishing activities on target species and the ecosystem. Ecosystem-based management requires an understanding of both krill and krill predators. Krill cannot be sustainably managed without considering the needs of krill predators through knowledge of their abundance, distribution, phenology, prey requirements and foraging behaviour. Vessel based RPAs provide an excellent opportunity to generate data that addresses knowledge gaps in East Antarctica and elsewhere.
Between January and March 2019, a multi-disciplinary marine science voyage (the ENRICH Voyage – Euphausiids and Nutrient Recycling In Cetacean Hotspots) was conducted off East Antarctica, from 64°S to 67°S and between 138°E and 154°W. During the voyage, the utility of small multirotor RPAs was assessed operationally and scientifically. Multirotor RPA flights were conducted for cetacean photogrammetry, photo-identification and blow sampling in order to contribute to the overarching aim of the voyage – to describe the characteristics of Antarctic krill swarms and determine whether these characteristics predict the distribution and behaviour of Antarctic predators, particularly Antarctic blue whales, and how these predators interact with krill in time and space. Here, we conduct a high-level review of cetacean research related RPA activities in Antarctica and specifically, we describe the multirotor RPA activities during the ENRICH voyage. We characterise the operating envelope of successful multirotor RPA use in maritime East Antarctica, highlighting the limitations, challenges and opportunities that RPA technology presents for future cetacean research.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Literature review
To determine how and where RPAs are currently used for research in Antarctica, we used Web of Science to search for scientific publications, applying the search to all possible fields using the combination of the keywords: ‘Antarctica’ OR ‘Antarctic’ AND ‘RPAS’ OR ‘UAV’ OR ‘UAS’ OR ‘unmanned aerial vehicle’ OR ‘unoccupied aerial vehicle’ OR ‘unmanned aerial system’ OR ‘unoccupied aerial system’ OR ‘remotely piloted aircraft’ OR ‘remotely piloted system’ OR ‘drone.’ We then applied the same search within Google Scholar to cross-check and detect additional references. We manually verified the adequacy of the references and removed false positives. The list of publications was current to 2023. Building on Pina and Vieira (2022), publications were classified according to the dominant thematic area presented in the publication: i) technology and development (including methods), ii) atmosphere, iii) cryosphere, iv) hydrosphere, v) terrestrial, vi) wildlife and vii) other (includes review and regulatory related papers). Within the ‘wildlife’ category we then specifically identified papers that described RPA use for cetacean research.
2.2 Multirotor RPA activities in East Antarctica
The 49-day ENRICH voyage departed from Hobart, Tasmania on the 19 January and returned to the same port on the 5 March 2019 aboard the Marine National Facility’s 93.9 m research vessel, RV Investigator1. The overarching aim of the research voyage was to describe the characteristics of Antarctic krill swarms and determine whether these characteristics predict the distribution and behaviour of Antarctic predators, particularly Antarctic blue whales, and how these predators interact with krill in time and space. Multi-disciplinary marine science was conducted off Antarctica from 64°S to 67°S and between 138°E and 154°W and included the use of a scientific multibeam echosounder (Simrad ME70) and a downward-facing split-beam echosounder (Simrad EK60) to measure the 3D geometry of krill swarms, target trawls to determine krill size and maturity stage composition, Integrated Growth Rate experiments to determine krill morphometric data and growth rates, sonobuoy deployments to undertake cetacean passive acoustic monitoring and real-time tracking, visual sightings for cetaceans and biogeochemistry deployments including CTDs (Conductivity Temperature Depth), Trace Metal Rosettes (TMRs), eXpendable BathyThermographs (XBTs) and drifters.
The ENRICH voyage also planned to use multiple small multirotor RPAs to undertake photogrammetry, photo-identification, whale ‘blow’ sampling, surface water sampling or to collect general whale and scenic imagery. Given the likely high number of RPA flights planned, the voyage also provided an opportunity to assess the feasibility and limitations of routinely using such aircraft for ship-based cetacean research in Antarctica.
Three multirotor RPAs: i) the DJI Inspire 2, ii) the DJI Phantom 4 Pro and iii) the DJI Phantom 4, were flown by a science team (two pilots flying the DJI Phantom 4 Pro and the DJI Phantom 4 to collect whale imagery and sample whale blow and water) and a documentary team (two pilots flying the DJI Inspire 2 to collect whale and scenic imagery) authorised under the Australian Antarctic Program Animal Ethics Committee and with Australian Government EPBC cetacean permit CP17-0004. All voyage activities were authorised under the Australian Government Antarctic Treaty (Environment Protection) Act. RPA pilots were licensed, holding an Australian Remote Pilots Licence (RePL), and operated under a Remotely Piloted Aircraft Operators Certificate (ReOC). The combined RPA flying experience of the documentary team included hundreds of hours flying in remote locations including Antarctica, flying to collect imagery of whales and operating from vessels at sea. The science team had also flown RPAs around whales and off of small boats with a combined RPA flying experience of < 100 hours at the time. RPA operation planning was informed by the Australian Antarctic Division’s Environmental Guidelines for operation of Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS) in Antarctica (v 1.1) as well as relevant permit conditions. At the time, the Australian Government Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA) advised that it had no jurisdiction over these Southern Ocean operations because they occurred outside the 12 nautical mile territorial limit.
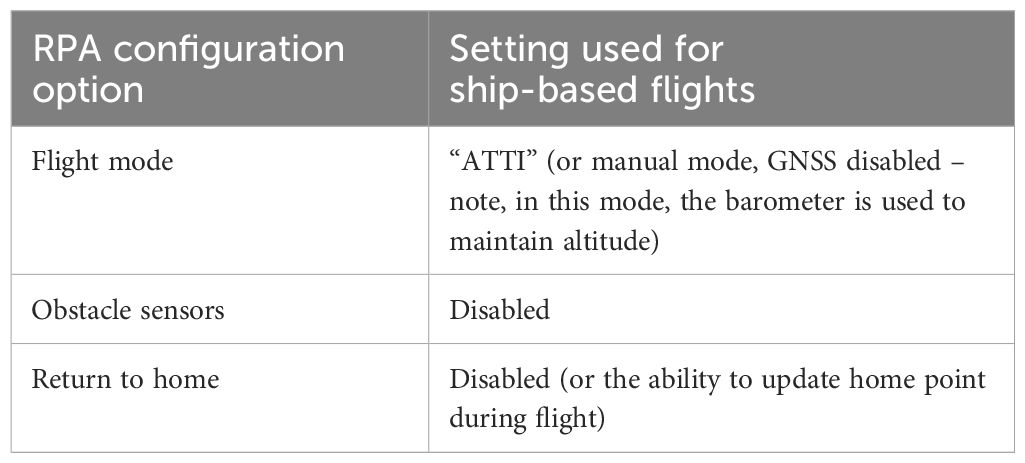
RPAs were flown in “ATTI” mode (Attitude Mode – a DJI-specific mode that allows drone flight without the use of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) or Vision Position Systems) to remove conflict between the onboard magnetic compass, GNSS information, and autopilot logic caused by proximity to the south magnetic pole. RPAs were launched from the RV Investigator on days where whales were sighted within a suitable distance (~ < 1500m) of the vessel, mean wind speeds were less than 15 knots (27.8 kmh−1) and with permission from the Bridge Officer and the Chief Scientist. RPAs were hand launched from the foredeck of deck 2 (the bow; from a location approximately 10.1 m above the water line at the time), which was roped off from other crew and scientists and cleared of ice daily. The RPA was held by the co-pilot, equipped with appropriate PPE (clear face-shield, safety glasses and gloves), with arms raised, 2 m above the deck level therefore launching from a height of approximately 12 m above sea level (registered as 0 m by the RPA). RPA launch sequences were announced over the ship intercom to ensure no unauthorised personnel entered the foredeck area. When the RPA achieved flight, it was released to hover and then flown in the direction of the whales(s) whilst the pilot (focused on the screen and keeping the whale(s) in the frame) maintained communications with the co-pilot (focused on the whale(s) and the position of the RPA) and vessel crew/Bridge on the whales(s) location and activities. When the RPA was in position above the whale(s), it collected vertical aerial pictures/video using a camera mounted vertically under the RPA. A live video link, providing the pilot with a live feed from the camera was used to correct the position of the RPA and confirm that photos/video of adequate quality were obtained. The RPA was then flown back to the research vessel with retrieval initiated following communication with the Bridge and crew. The co-pilot, equipped with appropriate PPE (clear face-shield, safety glasses and gloves), positioned with hands outstretched, retrieved the RPA by holding the landing gear once the RPA was in range. RPA flights were conducted in strict coordination with whale scientists onboard the vessel, including via feedback with whale observers on whether RPA operations were impacting whale behaviour and in order to keep track of whales in the area. The minimum approach distance to the whale varied depending on the research objective but was never less than 5m.
To characterise the environmental operating envelope of RPA use on this voyage, we derived RPA flight metrics (duration, height, length, speed, distance from ship, battery drainage, satellites acquired, flight turnaround times) and underway environmental sampling data collected concurrently by the RV Investigator including GPS location, air temperature and wind speed in addition to Beaufort scale as estimated by the whale observation team. We also derived additional environmental parameters known to impact RPA navigation and flight control including the geomagnetic Kp index (to characterise geomagnetic activity; Matzka et al., 2021), distance to the south magnetic pole, and magnetic declination and inclination (magneticField function in R package: oce). RPA flight metrics were obtained by decoding the RPA flight log files with both Flight Reader (https://www.flightreader.com/) and Airdata UAV (https://airdata.com/). All data manipulation and visualisations were undertaken in R 4.3.2 (R Core Team, 2023).
3 Results
3.1 Literature review
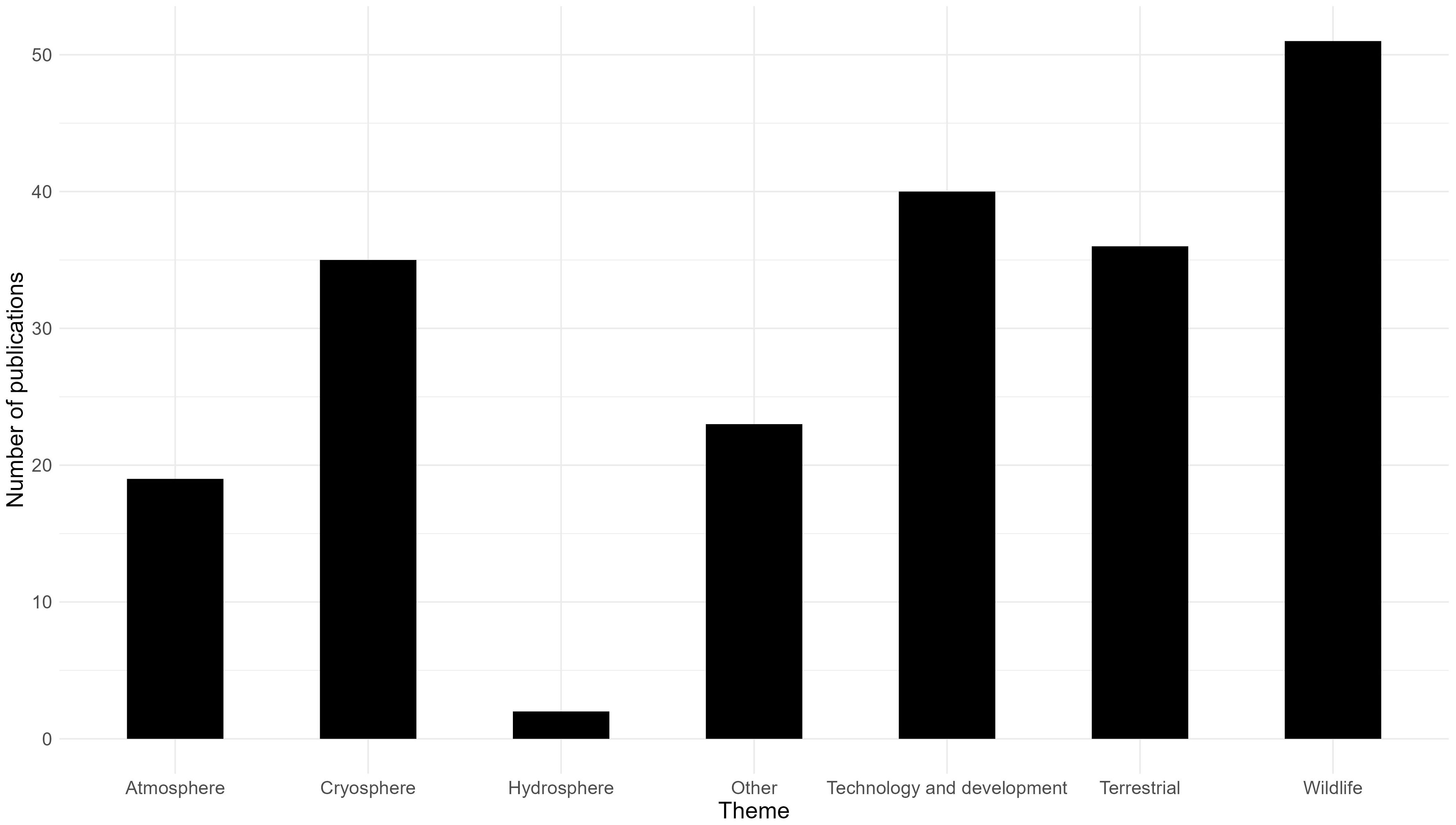
The literature review generated 206 peer-reviewed publications published between 2004 and 2023 in various forms including journal articles (n = 174), conference proceedings (n = 29), book sections (n = 2) and a report (n = 1) demonstrating RPA use in Antarctica including location, RPA type and scientific application and including 18 review articles. For these Antarctic related references, the dominant application was ‘wildlife’ followed by ‘technology and development’ (Figure 1). Amongst the wildlife publications, thirteen were specifically cetacean related focussing on a range of species including Antarctic minke, humpback, killer, sei, fin and southern right whales. One additional article was cetacean related however described the detection of whale bones via land survey and another additional article was a review (see Supplementary Material). Given that the intention of the literature review undertaken was to gain an understanding of RPA operations around cetaceans in Antarctica, we note an additional five technical reports (not peer reviewed) that described at-sea vessel-based RPA operations around cetaceans in Antarctica. All references are detailed in the Supplementary Material.
Across the thirteen peer reviewed publications and the five technical reports, six different multirotor RPA models were used, with fourteen references reporting the use of more than one RPA model. The commercially available DJI Phantom (n=11) and Inspire (n=9) models were the most commonly used followed by the LemHex-44 (n=7), the FreeFly Alta 6 (n=7), the APH-22 (n=3) and the Swellpro Splashdrone (n=1). Excluding the single review publication and another publication detailing the mapping of whale bones on land, the majority of RPA activities were undertaken in nearshore waters of the Antarctic Peninsula region (n=10) and off islands (n=5; Auckland Islands, Falkland Islands, Elephant Island, South Georgia; Figure 2.) Flying UAVs off of small boats (around 6m) was common practice (n=9 references), especially along the Antarctica Peninsula (n=8 references). RPAs were also flown off a range of larger vessels including ~20m (n=2 vessels), ~40m (n=1 vessel), ~70m (n=1 vessel) and ~120m (n=1 vessel) in length. Relatively few vessel-based RPA operations for cetacean science were reported for the East Antarctic sector (n=2 between 0°E – 30°E, n=2 at the Auckland Islands). Only one reference provided operational details regarding RPA use (Dawson et al., 2017) but this did not extend to defining the environmental conditions under which flights occurred.
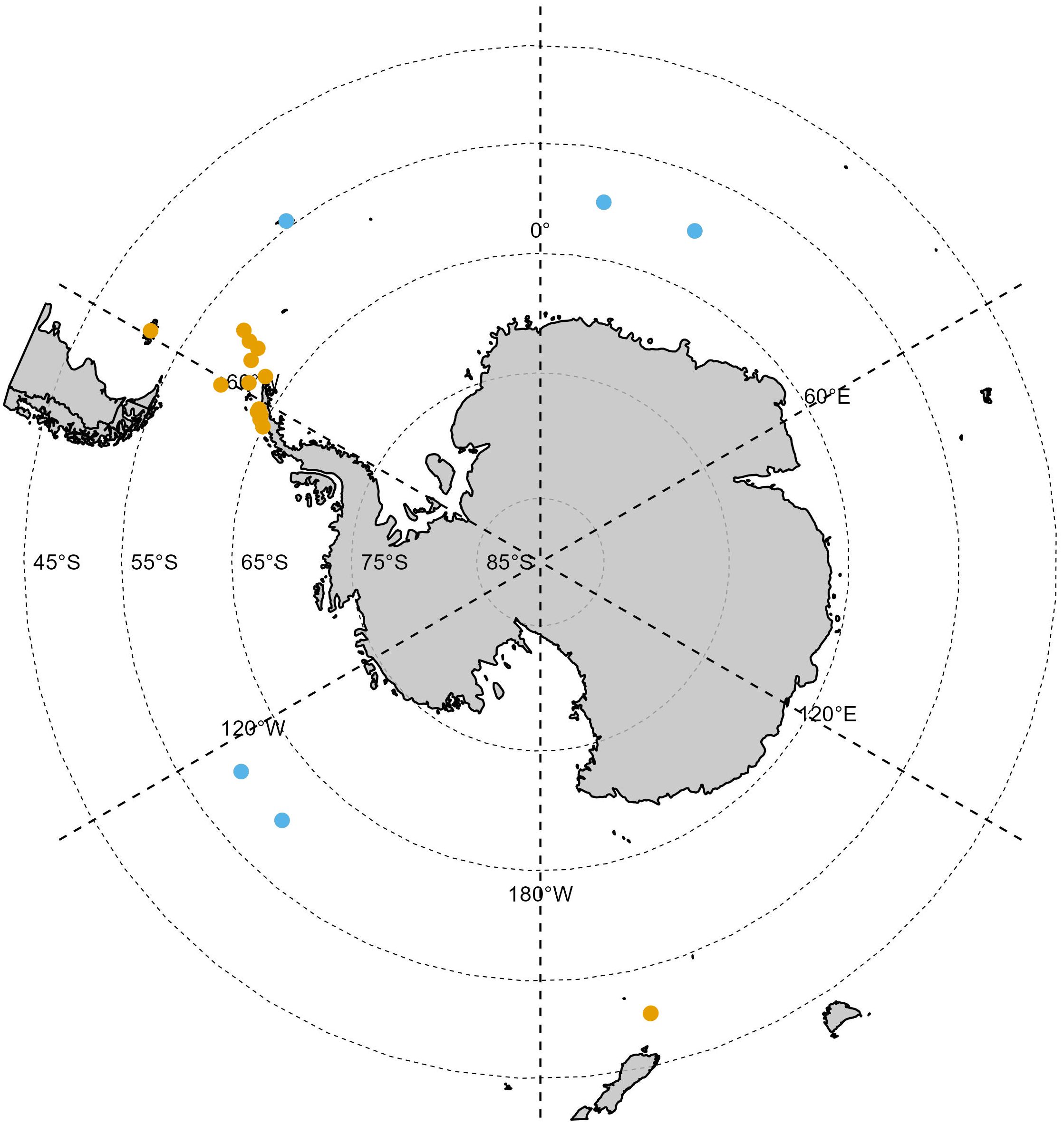
Figure 2. The general geographic location of multirotor RPA use around cetaceans in Antarctica and at subantarctic islands between 2004 and 2023. Orange locations represent RPA operations described in peer-reviewed publications, blue locations represent RPA operations described in technical reports. See Supplementary Material for list of references.
3.2 Multirotor RPA activities in maritime East Antarctica
On the Antarctic ENRICH voyage, 139 multirotor RPA flights were undertaken between the 25th January 2019 and the 25th February 2019 using a DJI Inspire 2 (n=119), DJI Phantom 4 (n=15) or a DJI Phantom 4 Pro (n= 5) using the operational settings described in Table 1. Flights occurred over the open water of maritime east Antarctica in the region bounded by 138.5°E – 152.6°E and 63.3°S – 66.3°S (Figure 3). The RPAs were used for whale photogrammetry, whale blow sampling, whale photo identification, surface water sampling for trace metal analysis, visual survey of whale behaviour and the collection of whale imagery for a documentary. During these flights, data was collected on Antarctic blue whales, fin whales and humpback whales. Data streams derived from RPA flights included photo identification (n = 12 Antarctic blue whales), photogrammetry (n = 7 Antarctic blue whales, n = 1 fin whale, n = 3 humpback whales) and observations of feeding behaviour (n = 2 Antarctic blue whales, n = 2 fin whales, n = 2 humpback whale groups). Additionally, a single Antarctic blue whale blow sample was taken, and six flights were conducted to collect surface water samples (n=17) for trace metal analysis. Four flights collected 11 samples of surface seawater near two icebergs (< 300 m and ~50 m distance from the ship) and two flights collected 6 samples close to the ship to undertake a quality control analysis of the influence of the ship on trace metal samples. RPA flights occurred on 17 separate days over the 32-day period with 1 to 19 flights occurring in any day.
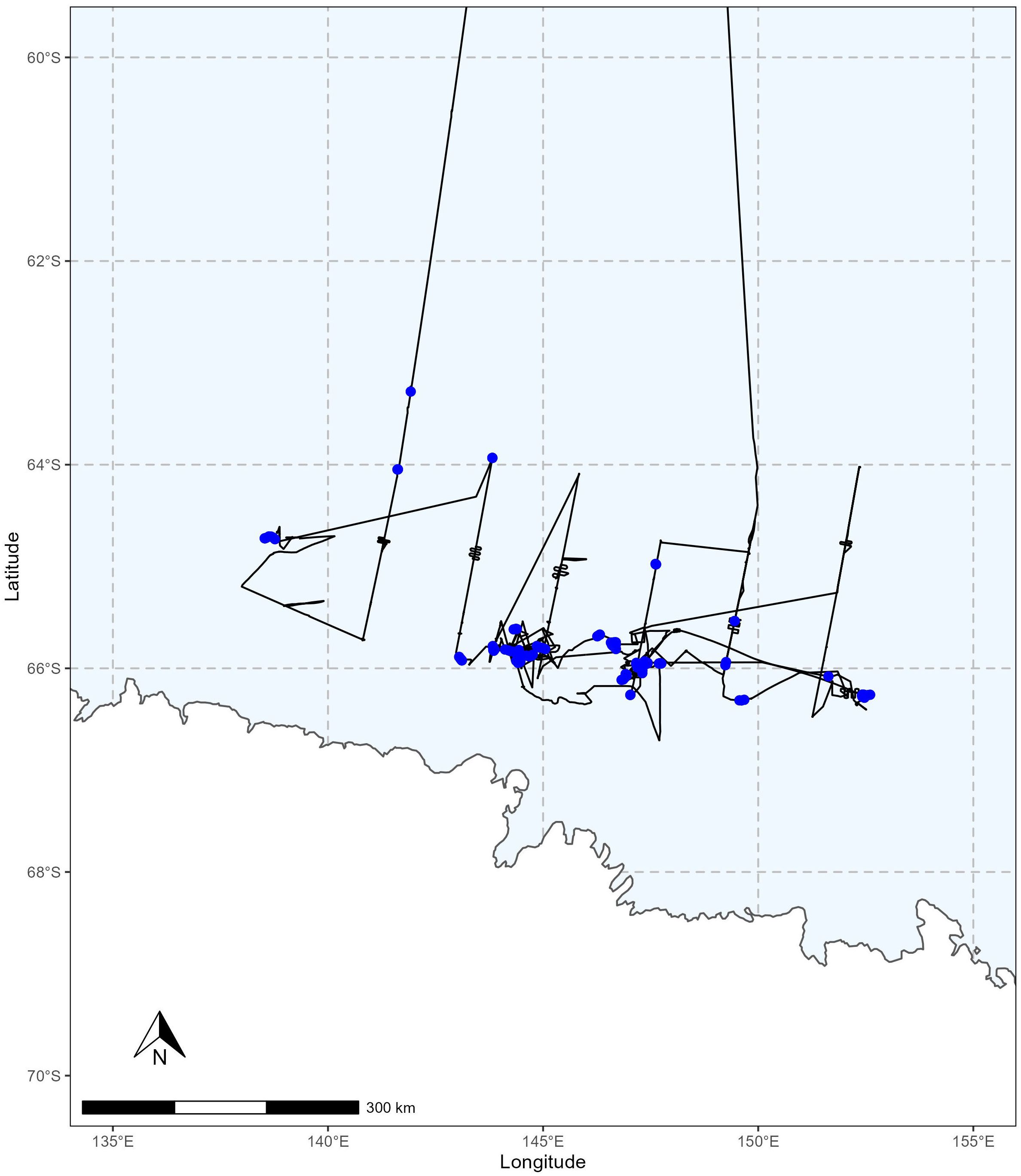
Figure 3. Map detailing the area of RPA operations throughout the ENRICH voyage. 139 flights (blue points) occurred along the ship track line (black line). The Antarctic continent is included in white to the south of the RPA operations.
Flights were on average 12 minutes in duration (range: 3 min to 18 min), covering an average distance of 4.6 km (range: 0.5 km to 8.2 km) and flown at an average flight speed of 6.5 ms−1/12.6 knots (median speed of 4.5 ms−1/8.7 knots). The average flight height achieved was around 29 m/95 ft (median flight height approximately 30 m/98 ft; maximum flight height: approximately 71 m m/233 ft). The DJI Inspire 2 was flown at a slightly greater height (median: 32 m/105 ft) than the DJI Phantom 4 (median: 21 m/69 ft) and DJI Phantom 4 Pro (median: 20 m/66 ft), largely due to differences in camera lens capabilities and flight objectives. The average amount of battery drained per flight was 60% (median: 66%; in the case of the DJI Inspire 2, battery drainage value was averaged across both batteries). Being a larger RPA, the amount of battery drained was consistently higher for the DJI Inspire 2 than the DJI Phantom 4 and the DJI Phantom 4 Pro, however, battery drainage rates were similar at around 4% per minute (Figure 4). Estimates derived from the regression line equations describing the relationship between battery drainage and flight duration for each RPA platform indicated that at 100% battery drainage, flight durations would be around 21.8 min for the DJI Inspire 2 (manufacturer specifications indicated an expected flight duration of 23 to 27 minutes), 25.5 min for the DJI Phantom 4 (manufacturer specifications indicated an expected flight duration of 28 minutes) and 23.3 min for the DJI Phantom 4 Pro (manufacturer specifications indicated an expected flight duration of 30 minutes) platforms.
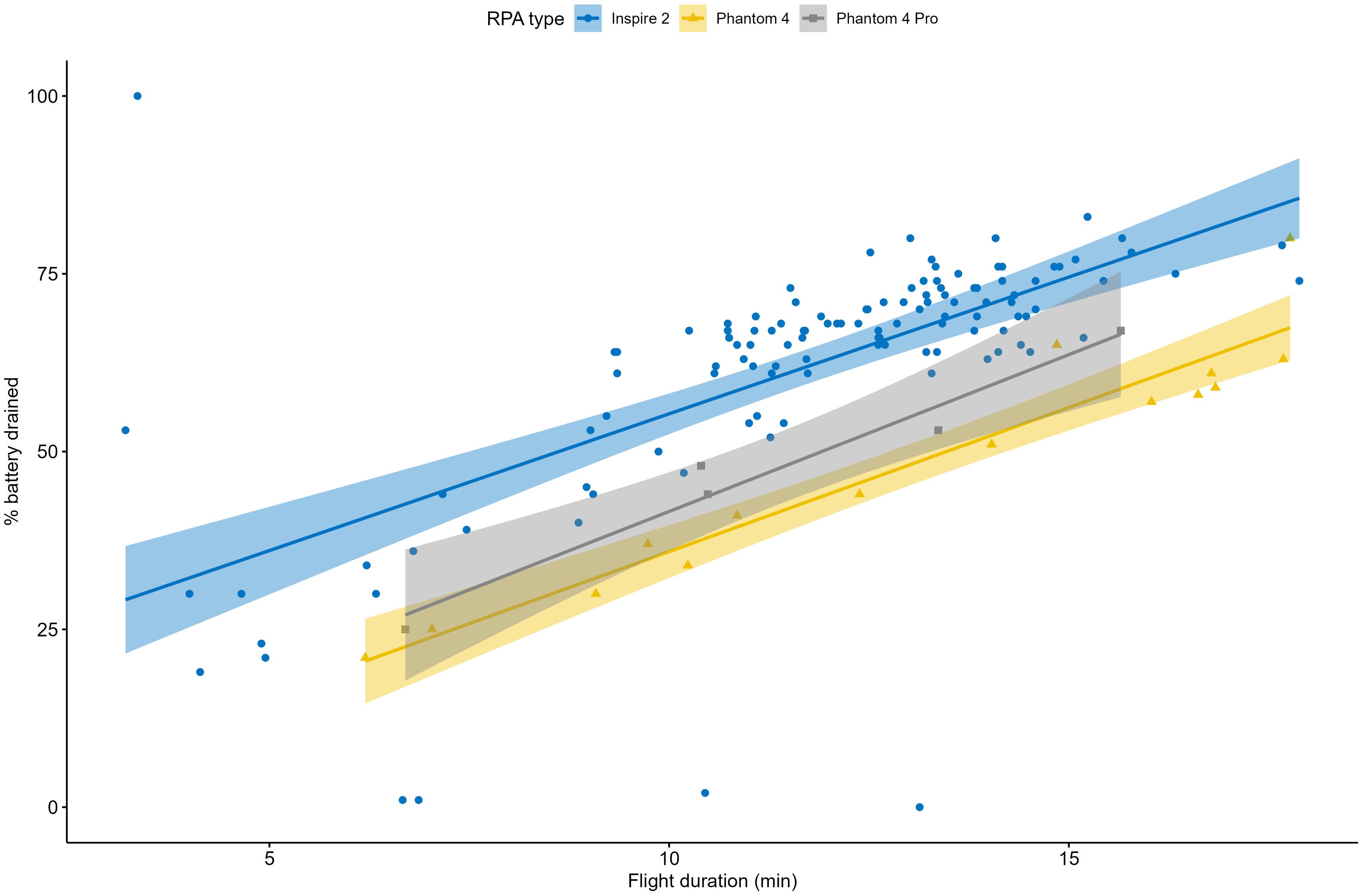
Figure 4. Battery drainage (%) in relation to flight duration (minutes) for the three RPA types used (DJI Inspire 2 – blue line, DJI Phantom 4 – orange line, DJI Phantom 4 Pro – grey line). Regression lines are included and shaded areas are the 95% confidence interval.
A minimum of 14 and a maximum of 22 satellites were acquired for each of the 139 RPA flights. Compass calibration issues for the DJI Phantom 4 platforms were regularly noted by pilots during the 32-day period of flying. There was no evidence of strong geomagnetic activity during that time as evidenced by Kp index values (the activity level classification for geomagnetic storms) between 0 and 4 (mean = 1.3, median = 1). Flights were on average 506 km from the south magnetic pole (range 147 km to 816 km) where magnetic inclination (the angle made with the horizontal by Earth’s magnetic field lines; range −90° at the south magnetic pole to 90° at the north magnetic pole) and declination (the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth’s surface) were on average, −88° (range: −86° to −89°) and 100° (57° to 115°) respectively.
The ship was underway throughout RPA flights, travelling at an average speed of 3.3 knots (median: 3.1 knots, range: 0 knots to 9.2 knots). Maximum distance from the ship did not exceed 2.2 km (median: 880 m). The larger maximum flight distance from the ship values are predominantly driven by the DJI Inspire 2 flights. The DJI Inspire 2 median maximum flight distance from the ship was 996 m (maximum: 2.2 km), the DJI Phantom 4 median maximum flight distance from the ship was 298 m (maximum: 1.2 km) and the DJI Phantom 4 Pro median maximum flight distance from the ship was 194 m (maximum 509 m).
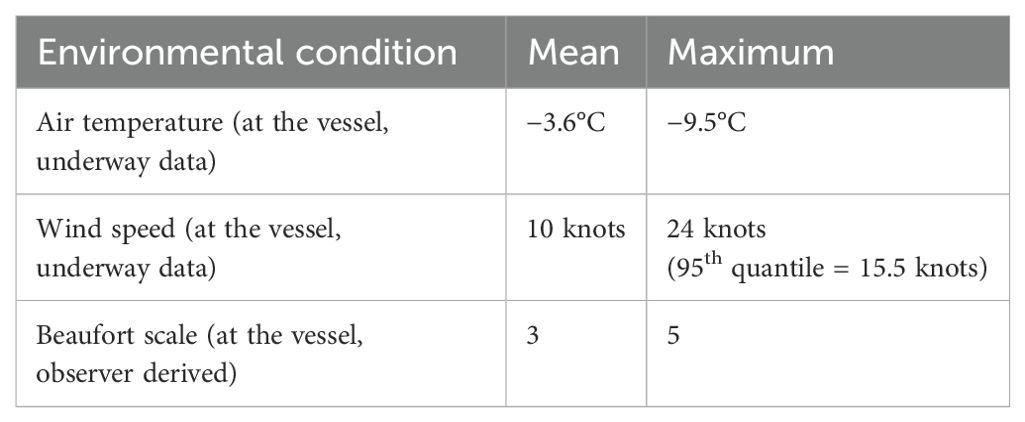
The average air temperature across the 139 flights was −3.6°C (median: −3.0°C; Table 2). The air temperature encountered across the 32-day period throughout which flights occurred did not limit flying operations: the coldest air temperature recorded was −9.7°C and the coldest air temperature encountered during RPA flights was −9.5°C (Figure 5).
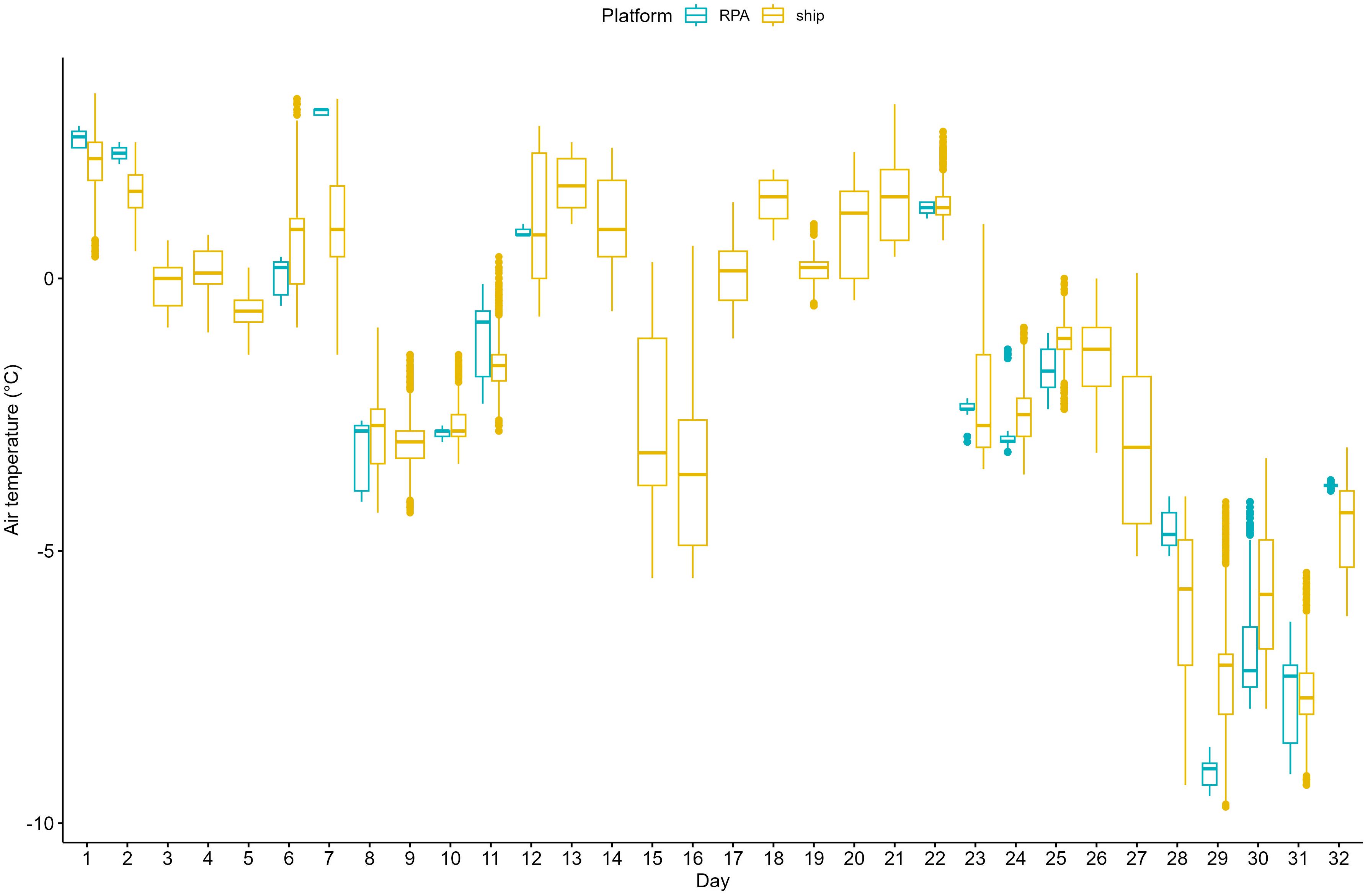
Figure 5. Boxplot detailing the daily air temperature (°C) encountered, derived from ship underway data (yellow), and air temperature encountered during RPA flights (blue). Day 1 is January 25, 2019 (UTC).
The wind speed recorded during UAV flights ranged from 0.1 knots to 23.9 knots, but on average, was 10 knots (median: 10.3 knots; Table 2). Wind speeds of up to 55.6 knots were encountered during the 32-day period throughout which flights occurred with a median wind speed of 13.5 knots. Higher wind speeds limited RPA use with the RPA clearly not operated throughout the full range of wind speeds encountered (Figure 6). Flights did not occur above Beaufort scale 5 with 52% of flights occurring at Beaufort scale 3 (Table 2).
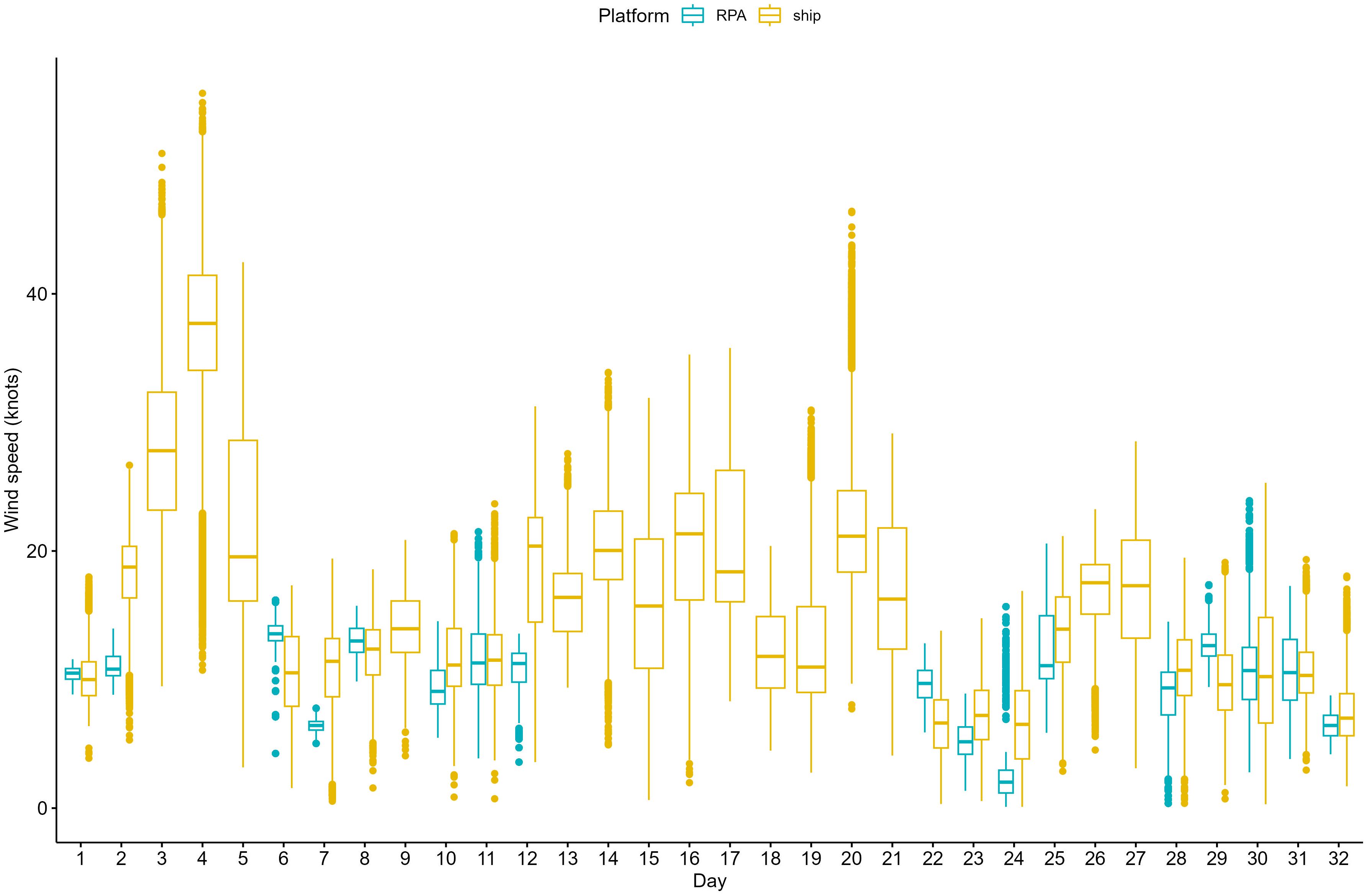
Figure 6. Boxplot detailing the daily wind speed (knots) encountered, derived from ship underway data (yellow) and wind speed encountered during RPA flights (blue). Day 1 is January 25, 2019.
The average time between RPA flight end and the initiation of the subsequent RPA flight following battery exchange or other RPA configuration requirements was 19 minutes (median: 16 minutes) but could be as low as 5 minutes (Figure 7).
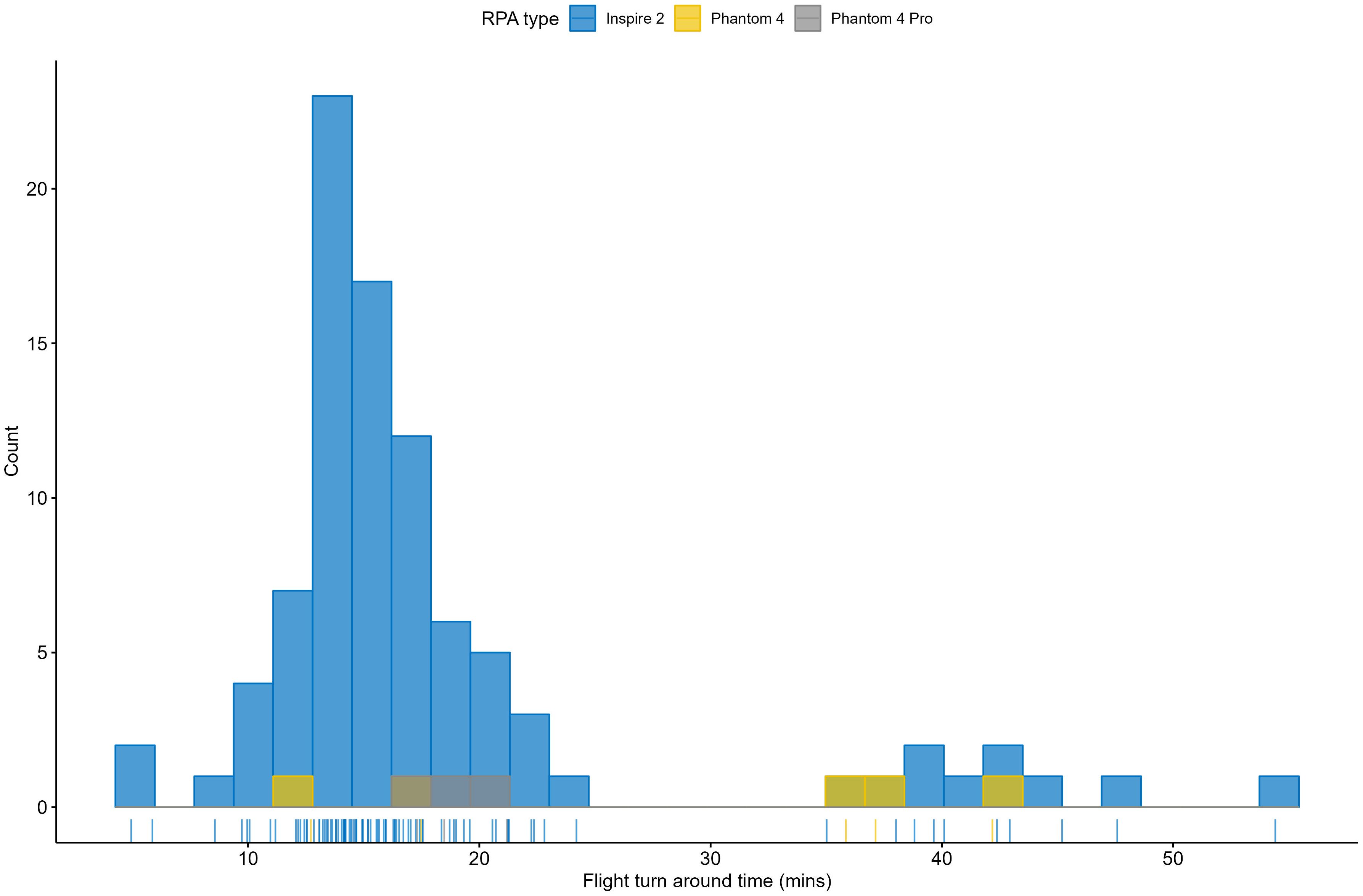
Figure 7. Turnaround times (the time between RPA flight end and the initiation of the subsequent RPA flight; in minutes) for the three RPA types (DJI Inspire 2 – blue, DJI Phantom 4 – orange, DJI Phantom 4 Pro – grey).
Finally, RPAs were flown without incident. No RPA was lost and no collisions occurred despite RPAs flying in close proximity to the ship superstructure. No injuries occurred due to hand capture and release. RPAs were recalled once to avoid an aggregation of birds roosting on an iceberg.
4 Discussion
We demonstrate the successful use of ship-based small multirotor RPAs for cetacean research in maritime Antarctica. This research was carried out as a component of a multidisciplinary research voyage to study Antarctic krill and the distribution and behaviour of their predators with a particular focus on critically endangered Antarctic blue whales. The successful RPA flights generated data related to photogrammetry, photo identification and feeding behaviour of Antarctic blue whales, fin whales and humpback whales.
The literature review found that RPAs have been used extensively across most scientific disciplines for Antarctic based research with wildlife research via multirotor RPAs the dominant application. Publications describing the use of RPAs on ships to study wildlife at sea in Antarctica were relatively uncommon (in comparison to nearshore waters of the Antarctic Peninsula and islands) with the review highlighting, in particular, how rare Antarctic ship-based cetacean related research via multirotor RPA is in the East Antarctic sector. RPA flights for wildlife and cetacean research tended to be focused around the nearshore and protected waters of the Antarctic Peninsula and Antarctic or subantarctic islands. Whilst this highlights a gap in the geographic range of RPA related cetacean research effort, it is not unsurprising given the high concentration of Antarctic stations and tourist vessels, sheltered waters and high krill biomass located consistently and continuously throughout the nearshore waters of the Antarctic Peninsula (Atkinson et al., 2017; Green et al., 2023). The high biomass of krill in the region is the basis of the Antarctic krill fishery with the overlap between fishing effort and krill predators (e.g. Weinstein et al., 2017) necessitating the focus on collection of relevant scientific data. Amongst this literature, the base for RPA operations described was often a small boat launched from land or tourist vessel, via a day trip-type scenario following whale sightings (for example, Durban et al., 2021; Bierlich et al., 2022). Outside of this region, the offshore distribution of cetaceans such as Antarctic blue whales (see Andrews-Goff et al., 2022; Miller et al., 2024) imposes logistical constraints on the field operations designed to study them and this day-trip model via small boat launch is logistically and operationally challenging with increased safety risk. Some of these challenges can clearly be overcome via the use of RPAs at sea, launched from a research vessel and hence the importance of characterising and reporting ship-based operations of multirotor RPAs in Antarctica. Under the search terms applied, we found no publications that discussed, in detail, the operational use (pre-flight settings, RPA operating procedures and environmental operating conditions) of RPAs off large vessels to study cetaceans in Antarctica.
The vessel-based RPA flights undertaken on the ENRICH voyage were constrained by wind speed but not by air temperature. Flights were undertaken throughout the full range of air temperatures experienced (down to –9.5°C) but not throughout the full range of wind speeds experienced. Over the 32-day period when RPAs were operated, wind speeds reached > 2 times the strength of wind speeds occurring throughout the RPA flights undertaken. Flights were undertaken up to Beaufort scale 5 indicating a wave height of up to approximately 3m was acceptable for safe RPA operations from the foredeck.
Whilst it is well established that temperatures below 0°C impact lithium battery performance resulting in significant power loss (Wang et al., 2016), the cold impacted battery performance to only a small degree, if at all. Estimated maximum flight time was within approximately 10% of expected flight time (as derived from manufacturer specifications for conditions above 0°C) for both the DJI Inspire 2 and DJI Phantom 4 and within 22% of expected flight time for the DJI Phantom 4 Pro (though few flights were undertaken on this platform). However, the RPA flights undertaken were relatively short at an average duration of 12 minutes. If RPA flights were longer, cold would likely begin to play a limiting role on operations primarily through the influence of cold on the comfort and dexterity of the RPA pilot rather than via the influence of cold on the battery given the existence of self-heating battery systems (Wang et al., 2016) and the ability to insulate batteries from extreme external temperatures (Häusermann et al., 2023). Often RPA flights occurred when the vessel was underway, at times flying out to around 2 km from the vessel but mostly much closer at just under 900 m from the vessel.
Whilst the RPA flights undertaken were relatively short in duration, they could be frequent given short turnaround times so often were adequate to achieve the science intended, namely photogrammetry, photo identification, behavioural observation, whale blow sampling, and water sampling. For a 12-minute flight duration, battery drainage was around 60% indicating that the RPAs were rarely pushed to their operational limit. Instead, RPAs were returned to the vessel for battery or payload exchange in line with whale surfacing behaviour and down times informed and coordinated by ongoing communications between pilots and whale observers. However, even if pushed to their operational limit to achieve flight times of up to approximately 30 minutes (as indicated by the manufacturer), the range achieved by these commercial multirotor RPAs is unlikely to enable extensive visual surveys which are so critical to an understanding of cetacean abundance and distribution. Long range, fixed wing drones that can be launched and retrieved from the deck of the ship are not only logistically and methodologically capable of undertaking these types of surveys (Hodgson et al., 2017) but can access areas that vessels cannot, such as regions of heavy ice inhabited by some Antarctic cetacean species (for example, Double et al., 2015; Herr et al., 2019; El-Gabbas et al., 2024).
RPAs were operated by both a science team and a documentary team throughout the voyage. The documentary team applied their extensive flying experience to the operation of the larger DJI Inspire 2 which was also relatively more robust to wind, able to undertake longer flights and easier to see at a distance due to its large size and darker colour than the other RPA platforms. The science team, flying off a large vessel and in Antarctica for the first time, were flying the smaller white DJI Phantom 4 RPAs which could also be difficult to see in the cloudy conditions that dominated despite the addition of colourful tape and flashing LEDs. The documentary team flying the DJI Inspire 2 therefore undertook around 80% of all flights. This demonstrates the opportunity that proficient pilots across disciplines offer for the collection of scientific data but also the need to consider RPA specifications relative to the operating environment.
The RPAs employed during the research voyage, like all RPAs, used GNSS signals to aid navigation and positioning. There are four GNSS with global coverage: GPS, GLONASS, BDS, and Galileo (Zheng et al., 2022). GNSS signal availability is governed by the altitude of satellite orbit, the inclination angle of the satellite and the Earth ground-level ‘field of view’ width of the signal transmitter attached to the satellite with the spacing, altitude and attitude of satellites all critical components when minimising error (Sheridan, 2020). For all GNSS, coverage of high latitudes is low (relative to equatorial regions) and this is especially true for GPS at latitudes > 75° due to satellite flight orbital inclination and altitude resulting in poor observation geometry. For all GNSS, at least four satellites are required for a full position fix and time or altitude fix. All RPA flights acquired at least 14 satellites despite all deployments occurring at high latitudes. The RPAs used both GPS and GLONASS, a GNSS combination resulting in the best estimate accuracy at high latitudes (Zheng et al., 2022). High precision and accuracy GNSS technologies have become available since this voyage occurred (Hodgson, 2020) and provide further confidence that high latitude RPA operations can occur with low position and navigation error.
The voyage’s proximity to the south magnetic pole meant there was high magnetic declination angles and steep magnetic inclination angles which can affect multirotor RPAs, which rely heavily on the magnetic compass and magnetometer for flight control. Initial testing of the ability to fly the RPAs in P-mode (GNSS positioning mode) determined that sometimes the software prevented launches and flight control at times was unreliable. Pilots also suspected that the large steel structure of the vessel was interfering with the RPA compass. All RPA flights, therefore, were undertaken in ATTI-mode (manual mode). The influence of the south magnetic pole and associated magnetic declination/inclination are unlikely to be an ongoing issue for contemporary flights using RPAs with dual GNSS to override the compass function. Flying RPAs in manual flight modes continues to be recommended for high latitude operations to mitigate the influence of high magnetic declination and steep magnetic inclination on the compass.
Other considerations when flying small multirotor RPAs off a ship include ensuring that the ship superstructure is not positioned in between the flight controller and the RPA (which could happen if a whale travels behind the ship, for example) or risk loss of connection between the RPA and flight controller. Pilots should also consider disabling obstacle avoidance sensors when flying from vessels that have complex and cluttered deck space or emit signals such as Automatic Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast (for ships that also carry aircraft such as helicopters). Finally, for vessel-based RPA operations when the vessel is underway, the return to home feature should either be disabled or updated regularly to avoid early automatic return of the RPA (due to on board calculations indicating battery power is too low relative to distance from home) or return of the RPA to the take-off/home location that no longer aligns with the actual vessel location.
Prior to the voyage, the Australian Government’s Civil Aviation Safety Authority (CASA) advised that they did not have jurisdiction over the RPA operations planned outside of Australian territory. Operations of Australian RPA outside of Australian territory must comply with Australia’s international obligations. The international convention covering RPA use in international waters is the Convention on International Civil Aviation (the Chicago Convention), which Australia signed in 1944. Australian RPA operations must comply with the standards and recommended practices set out in annexes to the Chicago Convention. Currently, there is work underway to achieve the safe, secure and efficient integration of RPAs into global aviation frameworks so, temporarily, RPA operations in east Antarctic waters (12 nautical mile Australian Antarctic Territory coastline) will not be authorised by CASA. Contemporary flight management via CASA is likely to be far more stringent than that applied in 2019. Flights occurring typically within 500m of the pilot where the pilot maintains visual contact with the RPA without relying on any visual aids are classified as a visual line of sight (VLOS) operations. Extended visual line of sight operations (EVLOS) occur when the RPA is flown beyond the pilot’s visual line of sight. EVLOS operations generally involve at least one visual observer placed within VLOS of the RPA or using a device, such as binoculars, to observe the RPA and general operating area. The flights we describe here are likely on the cusp of EVLOS and contemporary requirements for research such as this would include submission of documented practices and procedures to CASA, additional flying hours, proof of operational concept under VLOS conditions and a pilot proficiency check (Civil Aviation Safety Regulations, 1998).
Regardless of the regulatory setting and requirements associated with EVLOS operations, the ability to undertake RPA operations to study the largest of krill predators, taking advantage of a somewhat reliable surfacing behaviour (Calderan et al., 2023) and swimming speeds equivalent to RPA flight speed (Andrews-Goff et al., 2022) clearly presents significant opportunities to facilitate research in a hostile, remote environment. The research on the ENRICH voyage was undertaken with the specific goal to characterise Antarctic krill swarms, determine whether these characteristics predict the distribution and behaviour of Antarctic predators, particularly Antarctic blue whales, and characterise the predator–prey interactions. The RPAs employed collected vision associated with feeding and photogrammetry. Whilst there are alternative methods to collect similar data (for example, biologging tags; Cade et al., 2022), the data that can be derived from these feeding events observed are a step towards characterising prey field interactions and feeding kinematics (Goldbogen et al., 2017) and did not require dedicated ship time and additional personnel to launch a small boat for tag deployment. The ability for photogrammetry to provide critical information on health via body condition assessment is well proven (for example, Bierlich et al., 2022) and an expected outcome from this research also.
However, it is exceedingly clear that RPAs are a platform that can offer more than the collection of visual data alone. For cetaceans, RPAs have been used to deploy biologging tags using a gravity drop system (Wiley et al., 2023) with further innovation to develop a drone-based platform for biopsy sampling and type C (Andrews et al., 2019) small implantable satellite tag deployment underway (Andrews-Goff et al., 2024). Combining the use of biopsy samples (for an assessment of foraging strategy, pregnancy status and stock identity), with RPA derived imagery (to determine body condition) and satellite tag deployment (to ascertain foraging behaviour along with spatial and temporal occupancy of Antarctic feeding grounds) will provide entirely novel opportunities to study cetaceans.
RPA derived data streams can provide the basis of a robust monitoring program in the face of a changing climate, and address key knowledge gaps for management bodies such as CCAMLR and the International Whaling Commission (IWC). Critical to the sustainable management of krill is the adoption of a precautionary and ecosystem approach to fisheries management, which accounts for the predation needs of krill predators (Kelly et al., 2017, 2018). Data informed estimates of krill consumption rates (derived from metrics such as temporal and spatial occupancy and foraging performance) by cetaceans is critical to CCAMLR’s ecosystem fisheries management approach.
This paper describes the extensive use of small, ship-based, multirotor RPAs for cetacean research in Antarctica. The RPAs delivered a range of cetacean related data streams including photogrammetry, photo identification, behavioural observations and whale blow sampling in addition to water sampling and collection of general scenic imagery. Despite the harsh environmental conditions encountered with air temperatures routinely well below 0°C and high winds, the RPAs performed exceptionally well to deliver the desired scientific outcomes safely within short, wide-ranging flights. In the period since these flights occurred, both the regulatory space and RPA development have advanced, and future research opportunities will benefit from improved battery and flight performance while accounting for more stringent flight management requirements. Regardless, the potential for RPAs to deliver critical data to address the knowledge gaps that challenge effective management of both krill, and their predators cannot be overstated. Harnessing the ability of these platforms to passively collect data and actively deploy sampling devices will be revolutionary for cetacean research globally, especially in isolated and remote regions such as maritime Antarctica.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: Australian Antarctic Data Centre: https://doi.org/10.26179/zs9v-ak70 or https://data.aad.gov.au/metadata/AAS_4101_RPA_ops_summ.
Ethics statement
This research was reviewed and approved by the Australian Antarctic Ethics Committee under Australian Antarctic Science Project 4101 and complied with all relevant permits including the Australian Government Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act Cetacean Permit (C12-0006, 2017-004) and the Australian Government Antarctic Treaty (Environment Protection) Act provided specifically for Australian Antarctic Science Project 4101 as part of the 2019 Investigator Voyage.
Author contributions
VA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LI: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was made possible with the support of numerous Australian Antarctic Science (AAS) Projects with gracious and excellent support from personnel at the Australian Antarctic Division. These projects include: AAS Project 4101: Antarctic baleen whale habitat utilisation and linkages to environmental characteristics; AAS Project 4102: Population abundance, trend, structure and distribution of the endangered Antarctic blue whale; AAS Project 4512: Ensuring sustainable management of the krill fishery in waters off the Australian Antarctic Territory; AAS Project 4600: Conservation and management of Australian and Antarctic whalespost-exploitation status, distribution, foraging ecology and their role in the Southern Ocean ecosystem; AAS Project 4636: Sustainable Management of Antarctic Krill and Conservation of the Krill-based Ecosystem. Thanks to the CSIRO Marine National Facility (MNF) for its support in the form of sea time on RV Investigator, support personnel, scientific equipment and data management.
Acknowledgments
The ENRICH research voyage would not have been possible without the tenacity, hard work and support of many. In particular, we thank Karen Westwood for project management and Natalie Kelly for being the driving force behind the survey design and voyage Science Plan. We greatly appreciate the hard work and support of our AAD colleagues in the Science Branch, Science Technical Support, Operations, the Executive, Science Planning and Coordination, Human Resources, Media and Public Affairs, IT, the Polar Medicine Unit and the Australian Antarctic Data Centre. We thank Captain Adrian Koolhof and his crew, Lisa Woodward, Linda Gaskell and MNF staff. We would like to particularly acknowledge the significant contribution of both Alexander Vail and James Cox whose expert RPA abilities enabled the collection of much of the data discussed here and to who we are most grateful. Sincere thanks to all the scientists on board who worked long hours in often tough conditions to maximise what was achieved. Many thanks to Dr Brian Miller and Dr Elanor Bell for their feedback on earlier versions of this manuscript and to Dr Doug Thost for running his expert eye over the technical RPA components, in particular. Huge thank you also to Simon Wotherspoon who assisted with analyses to finalise the quality control of the original data set. Thank you to the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2024.1473471/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
- ^ https://www.csiro.au/en/about/facilities-collections/MNF/Research-vessel-Equipment-Data/RV-Investigator/Specifications
References
Alejandro C.-C., Francesco S., Lucio P., Emiliano V., Roberto G. V. (2023). Faster and better: comparison between traditional and drone monitoring in a cryptic species, the purple heron Ardea purpurea. Acta Ornithologica 57, 134–142. doi: 10.3161/00016454AO2022.57.2.002
Alvear O., Zema N. R., Natalizio E., Calafate C. T. (2017). Using UAV-based systems to monitor air pollution in areas with poor accessibility. J. Adv. Transp. 2017. doi: 10.1155/2017/8204353
Andrews R. D., Baird R. W., Calambokidis J., Goertz C. E. C., Gulland F. M. D., Heide-Jorgensen M. P., et al. (2019). Best practice guidelines for cetacean tagging. J. Cetacean Res. Manage. 20, 27–66. doi: 10.47536/jcrm.v20i1.237
Andrews-Goff V., Bell E. M., Miller B. S., Wotherspoon S. J., Double M. C. (2022). Satellite tag derived data from two Antarctic blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus intermedia) tagged in the east Antarctic sector of the Southern Ocean. Biodiversity Data J. 10, e94228. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.10.e94228
Andrews-Goff V., Double M., Zerbini A., Williams G., Harcourt R., Kelly N., et al. (2024). “PROJECT 26. Remote aerial deployment and sampling: development of a new sampling platform for large cetaceans,” in IWC-SORP Research Fund: 2024 progress reports from funded projects, Paper presented to the Scientific Committee of the International Whaling Commission: SC/69B/SH/06Rev1: 24-28. (Cambridge, UK: International Whaling Commission)
Angliss R. P., Ferguson M. C., Hall P., Helker V., Kennedy A., Sformo T. (2018). Comparing manned to unmanned aerial surveys for cetacean monitoring in the Arctic: methods and operational results. J. Unmanned Vehicle Syst. 6, 109–127. doi: 10.1139/juvs-2018-0001
Aniceto A. S., Biuw M., Lindstrøm U., Solbø S. A., Broms F., Carroll J. (2018). Monitoring marine mammals using unmanned aerial vehicles: quantifying detection certainty. Ecosphere 9, e02122. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.2018.9.issue-3
Apprill A., Miller C. A., Moore M. J., Durban J. W., Fearnbach H., Barrett-Lennard L. G. (2017). Extensive core microbiome in drone-captured whale blow supports a framework for health monitoring. Msystems 2. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00119-17
Atkinson A., Hill S. L., Pakhomov E. A., Siegel V., Anadon R., Chiba S., et al. (2017). KRILLBASE: a circumpolar database of Antarctic krill and salp numerical densities 1926–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 9, 193–210. doi: 10.5194/essd-9-193-2017
Baird R. W., Lerma J. K., Cornforth C. J., Wood K. A. (2022). An unexpected benefit from drone-assisted fecal sample collection: picking up subsurface poop after it floats to the surface. Aquat. Mammals 48, 565–567. doi: 10.1578/AM.48.6.2022.565
Bannister J. (2001). Status of southern right whales off Australia. J. Cetacean Res. Manage. (special issue) 2, 103–110. doi: 10.47536/jcrm.vi.273
Barreto J., Cajaíba L., Teixeira J. B., Nascimento L., Giacomo A., Barcelos N., et al. (2021). Drone-monitoring: improving the detectability of threatened marine megafauna. Drones 5, 14. doi: 10.3390/drones5010014
Bello A. B., Navarro F., Raposo J., Miranda M., Zazo A., Álvarez M. (2022). Fixed-wing UAV flight operation under harsh weather conditions: A case study in Livingston island glaciers, Antarctica. Drones 6, 384. doi: 10.3390/drones6120384
Bersaglio B., Enns C., Goldman M., Lunstrum L., Millner N. (2023). Grounding drones in political ecology: understanding the complexities and power relations of drone use in conservation. Global Soc. Challenges J. 2, 47–67. doi: 10.1332/HNEK4485
Bierlich K. C., Hewitt J., Schick R. S., Pallin L., Dale J., Friedlaender A. S., et al. (2022). Seasonal gain in body condition of foraging humpback whales along the Western Antarctic Peninsula. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1036860
Burgués J., Marco S. (2020). Environmental chemical sensing using small drones: A review. Sci. total Environ. 748, 141172. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141172
Butcher P. A., Colefax A. P., Gorkin III RA, Kajiura S. M., López N. A., Mourier J., et al. (2021). The drone revolution of shark science: A review. Drones 5, 8. doi: 10.3390/drones5010008
Cade D. E., Kahane-Rapport S. R., Wallis B., Goldbogen J. A., Friedlaender A. S. (2022). Evidence for size-selective predation by Antarctic humpback whales. Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.747788
Calderan S. V., Leaper R., Andrews-Goff V., Miller B. S., Olson P. A., Reyes M. V. R., et al. (2023). Surfacing rates, swim speeds, and patterns of movement of Antarctic blue whales. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1087967
Carroll G., Hedley S., Bannister J., Ensor P., Harcourt R. (2014). No evidence for recovery in the population of sperm whale bulls off Western Australia, 30 years post-whaling. Endangered Species Res. 24, 33–43. doi: 10.3354/esr00584
Christiansen F., Dujon A. M., Sprogis K. R., Arnould J. P. Y., Bejder L. (2016). Noninvasive unmanned aerial vehicle provides estimates of the energetic cost of reproduction in humpback whales. Ecosphere 7 (10), e01468. doi: 10.1002/ecs2.1468
Christiansen F., Vivier F., Charlton C., Ward R., Amerson A., Burnell S., et al. (2018). Maternal body size and condition determine calf growth rates in southern right whales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 592, 267–281. doi: 10.3354/meps12522
Civil Aviation Safety Regulations. (1998). Statutory Rules No. 237, 1998 made under the Civil Aviation Act 1988. Australian Government. Available at: https://www.legislation.gov.au/F1998B00220/latest/text.
Clark C. W., Brown M. W., Corkeron P. (2010). Visual and acoustic surveys for North Atlantic right whales, Eubalaena glacialis, in Cape Cod Bay, Massachusetts 2001–2005: management implications. Mar. Mammal Sci. 26, 837–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-7692.2010.00376.x
Dawson S. M., Bowman M. H., Leunissen E., Sirguey P. (2017). Inexpensive aerial photogrammetry for studies of whales and large marine animals. Front. Mar. Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00366
Di Stefano G., Romeo G., Mazzini A., Iarocci A., Hadi S., Pelphrey S. (2018). The Lusi drone: A multidisciplinary tool to access extreme environments. Mar. Pet. Geol. 90, 26–37. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.006
Double M. C., Miller B. S., Leaper R., Olson P., Cox M. J., Miller E., et al. (2015). “Cruise report on blue whale research from the NZ/Aus Antarctic ecosystems voyage 2015 of the Southern Ocean research partnership,” in Paper SC/66a/SH/7 presented to the IWC Scientific Committee. (Cambridge, UK: International Whaling Commission).
Durban J. W., Fearnbach H., Barrett-Lennard L. G., Perryman W. L., Leroi D. J. (2015). Photogrammetry of killer whales using a small hexacopter launched at sea. J. Unmanned Vehicle Syst. 3, 131–135. doi: 10.1139/juvs-2015-0020
Durban J., Fearnbach H., Paredes A., Hickmott L., LeRoi D. (2021). Size and body condition of sympatric killer whale ecotypes around the Antarctic Peninsula. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 677, 209–217. doi: 10.3354/meps13866
El-Gabbas A., Thomisch K., Van Opzeeland I., Burkhardt E., Boebel O. (2024). Dynamic species distribution models of Antarctic blue whales in the Weddell Sea using visual sighting and passive acoustic monitoring data. Diversity Distributions 30, 87–105. doi: 10.1111/ddi.13790
Fiori L., Martinez E., Orams M. B., Bollard B. (2020). Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to assess humpback whale behavioral responses to swim-with interactions in Vava'u, Kingdom of Tonga. J. Sustain. Tourism 28, 1743–1761. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1758706
Gallego D., Sarasola J. H. (2021). Using drones to reduce human disturbance while monitoring breeding status of an endangered raptor. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 7, 550–561. doi: 10.1002/rse2.v7.3
Goldbogen J. A., Cade D. E., Calambokidis J., Friedlaender A. S., Potvin J., Segre P. S., et al. (2017). How baleen whales feed: the biomechanics of engulfment and filtration. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 9, 367–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-122414-033905
Green D. B., Titaud O., Bestley S., Corney S. P., Hindell M. A., Trebilco R., et al. (2023). KRILLPODYM: a mechanistic, spatially resolved model of Antarctic krill distribution and abundance. Front. Mar. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1218003
Harris J. M., Nelson J. A., Rieucau G., Broussard III WP (2019). Use of drones in fishery science. Trans. Am. Fisheries Soc. 148, 687–697. doi: 10.1002/tafs.2019.148.issue-4
Harvard J., Hyvönen M., Wadbring I. (2020). Journalism from above: drones and the media in critical perspective. Media Communication 8, 60–63. doi: 10.17645/mac.v8i3.3442
Häusermann D., Bodry S., Wiesemüller F., Miriyev A., Siegrist S., Fu F., et al. (2023). FireDrone: multi-environment thermally agnostic aerial robot. Adv. Intell. Syst. 5, 2300101. doi: 10.1002/aisy.202300101
Herr H., Hickmott L., Viquerat S., Panigada S. (2022a). First evidence for fin whale migration into the Pacific from Antarctic feeding grounds at Elephant Island. R. Soc. Open Sci. 9, 220721. doi: 10.1098/rsos.220721
Herr H., Kelly N., Dorschel B., Huntemann M., Kock K.-H., Lehnert L. S., et al. (2019). Aerial surveys for Antarctic minke whales (Balaenoptera bonaerensis) reveal sea ice dependent distribution patterns. Ecol. Evol. 9, 5664–5682. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2019.9.issue-10
Herr H., Viquerat S., Devas F., Lees A., Wells L., Gregory B., et al. (2022b). Return of large fin whale feeding aggregations to historical whaling grounds in the Southern Ocean. Sci. Rep. 12, 9458. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13798-7
Hodgson M. E. (2020). On the accuracy of low-cost dual-frequency GNSS network receivers and reference data. GIScience Remote Sens. 57, 907–923. doi: 10.1080/15481603.2020.1822588
Hodgson A. J., Kelly N., Peel D. (2023). Drone images afford more detections of marine wildlife than real-time observers during simultaneous large-scale surveys. PeerJ 11, e16186. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16186
Hodgson A., Peel D., Kelly N. (2017). Unmanned aerial vehicles for surveying marine fauna: assessing detection probability. Ecol. Appl. 27, 1253–1267. doi: 10.1002/eap.2017.27.issue-4
Howell L. G., Clulow J., Jordan N. R., Beranek C. T., Ryan S. A., Roff A., et al. (2022). Drone thermal imaging technology provides a cost-effective tool for landscape-scale monitoring of a cryptic forest-dwelling species across all population densities. Wildlife Res. 49, 66–78. doi: 10.1071/WR21034
Hyun C.-U., Park M., Lee W. Y. (2020). Remotely piloted aircraft system (RPAS)-based wildlife detection: A review and case studies in maritime Antarctica. Animals 10, 2387. doi: 10.3390/ani10122387
Johnston D. R., Rayment W., Dawson S. M. (2022). Morphometrics and body condition of southern right whales on the calving grounds at Port Ross, Auckland Islands. Mamm. Biol. 102, 1525–1536. doi: 10.1007/s42991-021-00175-6
Katsumata T., Yoshida T. (2023). Development progress of a long-range vertical takeoff and landing UAV for the improvement of ship-based cetacean sighting surveys. Cetacean Population Stud. 4, 45–47. doi: 10.34331/cpops.2022O001
Kawaguchi S., Nicol S. (2020). "Krill fishery," in Fisheries and aquaculture: Volume 9. Eds. G. Lovrich and M. Thiel (New York: Oxford Academic). doi: 10.1093/oso/9780190865627.003.0006 (accessed 17 Sept. 2024).
Kelly N., Cox M., Emmerson L., Kawaguchi S., Raymond B., Southwell C., et al. (2017). “Towards an ecological risk assessment of krill fishing in East Antarctica (CCAMLR Divisions 58.4.1 and 58.4.2),” in Ecosystem Monitoring and Management Working Group, CCAMLR, WG-EMM-17/20. (Hobart, Tasmania, Australia: Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources), 32pp.
Kelly N., Emmerson L., Kawaguchi S., Southwell C., Welsford D. (2018). “An ecological risk assessment of current conversation measures for krill fishing in East Antarctica,” in Ecosystem Monitoring and Management Working Group, CCAMLR, WG-EMM-18/37. (Hobart, Tasmania, Australia: Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources), 27pp.
Kennedy A. S., Carroll E. L., Baker C. S., Bassoi M., Buss D., Collins M. A., et al. (2020). “Whales return to the epicentre of whaling? Preliminary results from the 2020 cetacean survey at South Georgia (Islas Georgias del Sur),” in Paper presented to the Scientific Committee of the International Whaling Commission: SC/68B/CMP/22. (Cambridge, UK: International Whaling Commission).
Koski W. R., Gamage G., Davis A. R., Mathews T., LeBlanc B., Ferguson S. H. (2015). Evaluation of UAS for photographic re-identification of bowhead whales, Balaena mysticetus. J. Unmanned Vehicle Syst. 3, 22–29. doi: 10.1139/juvs-2014-0014
Lyu M., Zhao Y., Huang C., Huang H. (2023). Unmanned aerial vehicles for search and rescue: A survey. Remote Sens. 15, 3266. doi: 10.3390/rs15133266
Mahadevan P. (2010). The military utility of drones. CSS Analyses Secur. Policy 78, 1–3. doi: 10.3929/ethz-a-006253833
Matzka J., Bronkalla O., Tornow K., Elger K., Stolle C. (2021). Geomagnetic Kp index. V. 1.0 (GFZ Data Services). doi: 10.5880/Kp.0001
Miller B. S., Andrews-Goff V., Barlow J., Bell E., Calderan S., Double M. C., et al. (2024). Antarctic sonobuoy surveys for blue whales from 2006-2021 reveal contemporary distribution, changes over time, and paths to further our understanding of their distribution and biology. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1324816
Nowacek D. P., Christiansen F., Bejder L., Goldbogen J. A., Friedlaender A. S. (2016). Studying cetacean behaviour: new technological approaches and conservation applications. Anim. Behav. 120, 235–244. doi: 10.1016/j.anbehav.2016.07.019
Pallin L., Bierlich K. C., Durban J., Fearnbach H., Savenko O., Baker C. S., et al. (2022). Demography of an ice-obligate mysticete in a region of rapid environmental change. R. Soc. Open Sci. 9, 220724. doi: 10.1098/rsos.220724
Pfeifer C., Barbosa A., Mustafa O., Peter H.-U., Rümmler M.-C., Brenning A. (2019). Using fixed-wing UAV for detecting and mapping the distribution and abundance of penguins on the South Shetlands Islands, Antarctica. Drones 3, 39. doi: 10.3390/drones3020039
Pina P., Vieira G. (2022). UAVs for science in Antarctica. Remote Sens. 14, 1610. doi: 10.3390/rs14071610
Pirotta V., Hocking D. P., Iggleden J., Harcourt R. (2022). Drone observations of marine life and human-wildlife interactions off Sydney, Australia. Drones 6 (3), 75. doi: 10.3390/drones6030075
Pirotta V., Smith A., Ostrowski M., Russell D., Jonsen I. D., Grech A., et al. (2017). An economical custom-built drone for assessing whale health. Front. Mar. Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00425
Ramp C., Gaspard D., Gavrilchuk K., Unger M., Schleimer A., Delarue J., et al. (2021). Up in the air: drone images reveal underestimation of entanglement rates in large rorqual whales. Endangered Species Res. 44, 33–44. doi: 10.3354/esr01084
R Core Team (2023). R: A language and environment for statistical computing (Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing). Available at: https://www.R-project.org/.
Ryan K. P., Ferguson S. H., Koski W. R., Young B. G., Roth J. D., Watt C. A. (2022). Use of drones for the creation and development of a photographic identification catalogue for an endangered whale population. Arctic Sci. 8 (4), 1191–1201.doi: 10.1139/as-2021-0047
Savoca M. S., Czapanskiy M. F., Kahane-Rapport S. R., Gough W. T., Fahlbusch J. A., Bierlich K. C., et al. (2021). Baleen whale prey consumption based on high-resolution foraging measurements. Nature 599, 85–90. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03991-5
Schoonmaker J., Wells T., Gilbert G., Podobna Y., Petrosyuk I., Dirbas J. (2008). “Spectral detection and monitoring of marine mammals,” in Proc. SPIE 6946, Airborne Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance (ISR) Systems and Applications V, 694606 (14 April 2008). doi: 10.1117/12.777740
Shahmoradi J., Mirzaeinia A., Roghanchi P., Hassanalian M. (2020). “Monitoring of inaccessible areas in GPS-denied underground mines using a fully autonomous encased safety inspection drone,” in AIAA 2020-1961. AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum. January 2020.
Shelare S. D., Aglawe K. R., Waghmare S. N., Belkhode P. N. (2021). Advances in water sample collections with a drone – a review. Materials Today: Proc. 47, 4490–4494. doi: /10.1016/j.matpr.2021.05.327
Sheridan I. (2020). Drones and global navigation satellite systems: Current evidence from polar scientists. R. Soc. Open Sci. 7, 191494. doi: 10.1098/rsos.191494
Stewart B. S., Karl S. A., Yochem P. K., Leatherwood S., Laake J. L. (1987). Aerial surveys for cetaceans in the former Akutan, Alaska, whaling grounds. Arctic 40, 33–42. doi: 10.14430/arctic1744
Torres L. G., Nieukirk S. L., Lemos L., Chandler T. E. (2018). Drone up! Quantifying whale behavior from a new perspective improves observational capacity. Front. Mar. Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00319
Varela-Jaramillo A., Rivas-Torres G., Guayasamin J. M., Steinfartz S., MacLeod A. (2023). A pilot study to estimate the population size of endangered Galápagos marine iguanas using drones. Front. Zool. 20, 4. doi: 10.1186/s12983-022-00478-5
Vargas Tamayo L., Thron C., Fendji J. L. K. E., Thomas S.-K., Förster A. (2020). Cost-minimizing system design for surveillance of large, inaccessible agricultural areas using drones of limited range. Sustainability 12, 8878. doi: 10.3390/su12218878
Wang C.-Y., Zhang G., Ge S., Xu T., Ji Y., Yang X.-G., et al. (2016). Lithium-ion battery structure that self-heats at low temperatures. Nature 529, 515–518. doi: 10.1038/nature16502
Weinstein B. G., Double M., Gales N., Johnston D. W., Friedlaender A. S. (2017). Identifying overlap between humpback whale foraging grounds and the Antarctic krill fishery. Biol. Conserv. 210, 184–191. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2017.04.014
Werth A. J., Kosma M. M., Chenoweth E. M., Straley J. M. (2019). New views of humpback whale flow dynamics and oral morphology during prey engulfment. Mar. Mammal Sci. 35, 1556–1578. doi: 10.1111/mms.12614
Wiley D. N., Zadra C. J., Friedlaender A. S., Parks S. E., Pensarosa A., Rogan A., et al. (2023). Deployment of biologging tags on free swimming large whales using uncrewed aerial systems. R. Soc. Open Sci. 10, 221376. doi: 10.1098/rsos.221376
Xi Z., Lou Z., Sun Y., Li X., Yang Q., Yan W. (2018). “A vision-based inspection strategy for large-scale photovoltaic farms using an autonomous UAV,” in 2018 17th International Symposium on Distributed Computing and Applications for Business Engineering and Science (DCABES), Wuxi, China, pp. 200–203. doi: 10.1109/DCABES.2018.00059.
Young B. G., Koski W. R., Kilabuk R., Watt C. A., Ryan K. P., Ferguson S. H. (2022). Collaborative field research using drones for whale photo-identification studies in Cumberland Sound, Nunavut. Drone Syst. Appl. 10, 256–265. doi: 10.1139/dsa-2021-0026
Zhang H., Turvey S. T., Pandey S. P., Song X., Sun Z., Wang N. (2023). Commercial drones can provide accurate and effective monitoring of the world's rarest primate. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 9, 775–786. doi: 10.1002/rse2.341
Zheng Y., Zheng F., Yang C., Nie G., Li S. (2022). Analyses of GLONASS and GPS+GLONASS precise positioning performance in different latitude regions. Remote Sens. 14, 4640. doi: 10.3390/rs14184640
Keywords: drone, whale, Antarctic blue whale, Southern Ocean, multirotor
Citation: Andrews-Goff V, Smith JN, Irvine LG and Double MC (2024) Ship-based RPA operations for cetacean research in Antarctica: progress, opportunities and challenges. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1473471. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1473471
Received: 31 July 2024; Accepted: 04 September 2024;
Published: 30 September 2024.
Edited by:
Kunio T. Takahashi, National Institute of Polar Research, JapanReviewed by:
Taiki Katsumata, The Insitute of Cetacean Research, JapanYu Kanaji, Japan Fisheries Research and Education Agency (FRA), Japan
Copyright © 2024 Andrews-Goff, Smith, Irvine and Double. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Virginia Andrews-Goff, VmlyZ2luaWEuQW5kcmV3cy1Hb2ZmQGFhZC5nb3YuYXU=
 Virginia Andrews-Goff
Virginia Andrews-Goff Joshua N. Smith
Joshua N. Smith Lyn G. Irvine
Lyn G. Irvine Michael C. Double1
Michael C. Double1