
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
METHODS article
Front. Mar. Sci., 07 November 2024
Sec. Ocean Observation
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1471695
This study introduces an innovative water depth estimation method for complex coastal environments, focusing on Yantian Port. By combining Random Forest algorithms with a Coordinate Attention mechanism, we address limitations of traditional bathymetric techniques in turbid waters. Our approach incorporates geographical coordinates, enhancing spatial accuracy and predictive capabilities of conventional models. The Random Forest Lon./Lat. model demonstrated exceptional performance, particularly in shallow water depth estimation, achieving superior accuracy metrics among all evaluated models. It boasted the lowest Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and highest coefficient of determination (R²), outperforming standard techniques like Stumpf and Log-Linear approaches. These findings highlight the potential of advanced machine learning in revolutionizing bathymetric mapping for intricate coastal zones, opening new possibilities for port management, coastal engineering, and environmental monitoring of coastal ecosystems. We recommend extending this research to diverse coastal regions to validate its broader applicability. Additionally, exploring the integration of additional geospatial features could further refine the model’s accuracy and computational efficiency. This study marks a significant advancement in bathymetric technology, offering improved solutions for accurate water depth estimation in challenging aquatic environments. As we continue to push boundaries in this field, the potential for enhanced coastal management and environmental stewardship grows, paving the way for more sustainable and informed decision-making in coastal zones worldwide.
Bathymetry, the measurement of water depth, is a critical component in coastal and marine management. Accurate bathymetric data is essential for a wide range of applications, including maritime navigation safety, coastal engineering, marine resource management, and ecological conservation (Liu et al., 2015; Li et al., 2021). Traditional bathymetry methods, such as ship-based echo sounding and LiDAR surveys, while highly accurate, are often time-consuming, expensive, and limited in spatial coverage (Vahtmae and Kutser, 2016). These limitations have driven the search for alternative methods that can provide efficient, cost-effective, and large-scale bathymetric mapping.
The advent of satellite remote sensing technology has revolutionized the field of bathymetry, offering unprecedented opportunities for wide-area water depth estimation (Li et al., 2019; Alevizos, 2020). Spectrally - derived bathymetry (SDB) leverages the relationship between water depth and the spectral properties of light as it interacts with the water column and seafloor (Agrafiotis, 2024). This approach enables rapid, repeatable, and cost-effective mapping of large nearshore areas, complementing traditional survey methods and providing valuable data for areas where in-situ measurements are challenging or impossible to obtain.
The development of SDB models has seen significant progress over the past few decades. Early approaches relied on empirical models, such as the band ratio method proposed by Stumpf et al (Stumpf et al., 2003). and the linear transform technique by Lyzenga (Lyzenga, 1978, 1985). These models, while simple and widely applicable, often struggle in complex coastal environments with variable water constituents and bottom types. To address these limitations, researchers developed semi-analytical models like the Quasi-Analytical Algorithm (QAA) (Lee et al., 1998; 1999; Lee and Carder, 2000, 2002; Le et al., 2009; Joshi and D’Sa, 2018), which attempt to account for the optical properties of water and its constituents. However, even these more sophisticated models face challenges in turbid or optically complex waters.
Recent advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence have opened new avenues for improving SDB accuracy and robustness (Misra et al., 2018; Benshila et al., 2020; Shen et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2023; Agrafiotis, 2024; Chan et al., 2024; Gupta et al., 2024; Qin et al., 2024). Machine learning algorithms, particularly Random Forest (RF), have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling non-linear relationships and complex environmental variables (Liu et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2021; Gülher and Alganci, 2023; Janowski et al., 2024). These data-driven approaches can capture intricate patterns between satellite-derived spectral information and water depth, often outperforming traditional empirical and semi-analytical models in diverse coastal settings.
The integration of spatial information into SDB models represents another significant development. Techniques such as geographically weighted regression (GWR) (Vinayaraj et al., 2016; Chybicki, 2018) and spatial attention mechanisms (Kim et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020) have been employed to account for the spatial heterogeneity of coastal environments. These approaches recognize that the relationship between spectral reflectance and water depth can vary spatially due to factors like water quality, bottom type, and local bathymetric features.
Multi-sensor and multi-temporal approaches have also gained traction in recent years (Sagawa et al., 2019; Lowell and Hermann, 2024). Researchers have explored the synergistic use of data from different satellite sensors, as well as the integration of satellite imagery with other data sources such as LiDAR (Ma et al., 2020). These multi-source approaches aim to leverage the strengths of different sensors and overcome the limitations of single-sensor methods.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain in deriving accurate bathymetry in complex coastal environments, particularly in areas with high turbidity, variable bottom types, or rapidly changing conditions. The port of Yantian, a major deep-water port in China, exemplifies these challenges (Wu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2024). Its complex underwater topography and dynamic water conditions make it an ideal test case for developing and evaluating advanced SDB methods.
In light of these challenges and recent developments, this study proposes a model to SDB that combines the strengths of Random Forest algorithms with a Coordinate Attention mechanism. This integration seeks to improve the model’s capacity to capture two key aspects: the intricate non-linear relationships between spectral data and water depth, and the inherent spatial dependencies in coastal bathymetry. The proposed method will be applied to the challenging environment of Yantian Port, with the goal of improving bathymetric mapping accuracy in complex coastal waters.
This study aims to advance satellite-derived bathymetry (SDB) techniques by developing an integrated Random Forest-Coordinate Attention model framework, specifically tailored for complex coastal environments like Yantian Port. The research objectives encompass training and validating the model using multispectral satellite imagery and in-situ depth measurements (Chen et al., 2019; Abdul Gafoor et al., 2022), comparing its performance against traditional SDB approaches (Huang et al., 2017; Garcia et al., 2020), and analyzing key factors influencing model performance, such as water turbidity, bottom type variability, and spatial heterogeneity (Li et al., 2017; Barnes et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018). By addressing these goals, this research seeks to contribute to the ongoing improvement of SDB techniques, with potential significant implications for port management, coastal engineering, and environmental monitoring worldwide. The study aims to offer a more accurate and efficient method for bathymetric mapping in complex coastal waters, thereby enhancing our understanding and management of these critical environments.
This study focuses on the coastal waters adjacent to Yantian Port in Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province (22°33’32”N, 114°17’24”E). Despite high maritime traffic, the area boasts exceptional water clarity, The overall terrain effect of the survey area is higher in the northwest and lower in the southeast. In the northwest of the survey area is the Marine police wharf (A), with a shallow water depth of about 1.5 meters on average. The water depth limit of the survey area is obvious, and the water depth on the side close to the embankment is shallow (area B, the average water depth is about 10 meters). There are obvious traces of artificial dredging channel, and some areas have shallow points, so there are hidden dangers and easy stranding of ships in safe navigation, which is ideal for bathymetric research.
Our analysis utilizes Sentinel-2 satellite imagery captured on December 12, 2021(S2B_MSIL1C_20211212T025119_N0500_R132_T50QKL_20221224T054712.SAFE). We processed these images to derive remote sensing reflectance (Rrs or Rw) using the advanced ACOLITE software (Python 20190326.0 version) (Lyzenga, 1985; Stumpf et al., 2003), developed by the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences. This software provides Rrs data (sr-1) across all visible and near-infrared bands, standardized to a 10-meter spatial resolution (Vanhellemont and Ruddick, 2016; Sagawa et al., 2019).
The bathymetric predictions incorporate multiple spectral reflectance bands from the Sentinel-2 imagery, specifically bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, and 10. To ensure consistency, all spectral images were resampled to a uniform 10 × 10 meter resolution (Arun Kumar, 2012). Additionally, we employed the S2 view feature in ACOLITE (Version 20210802.0) to minimize sun glint effects during the resampling process, as illustrated in Figure 1 (Arun Kumar, 2012).
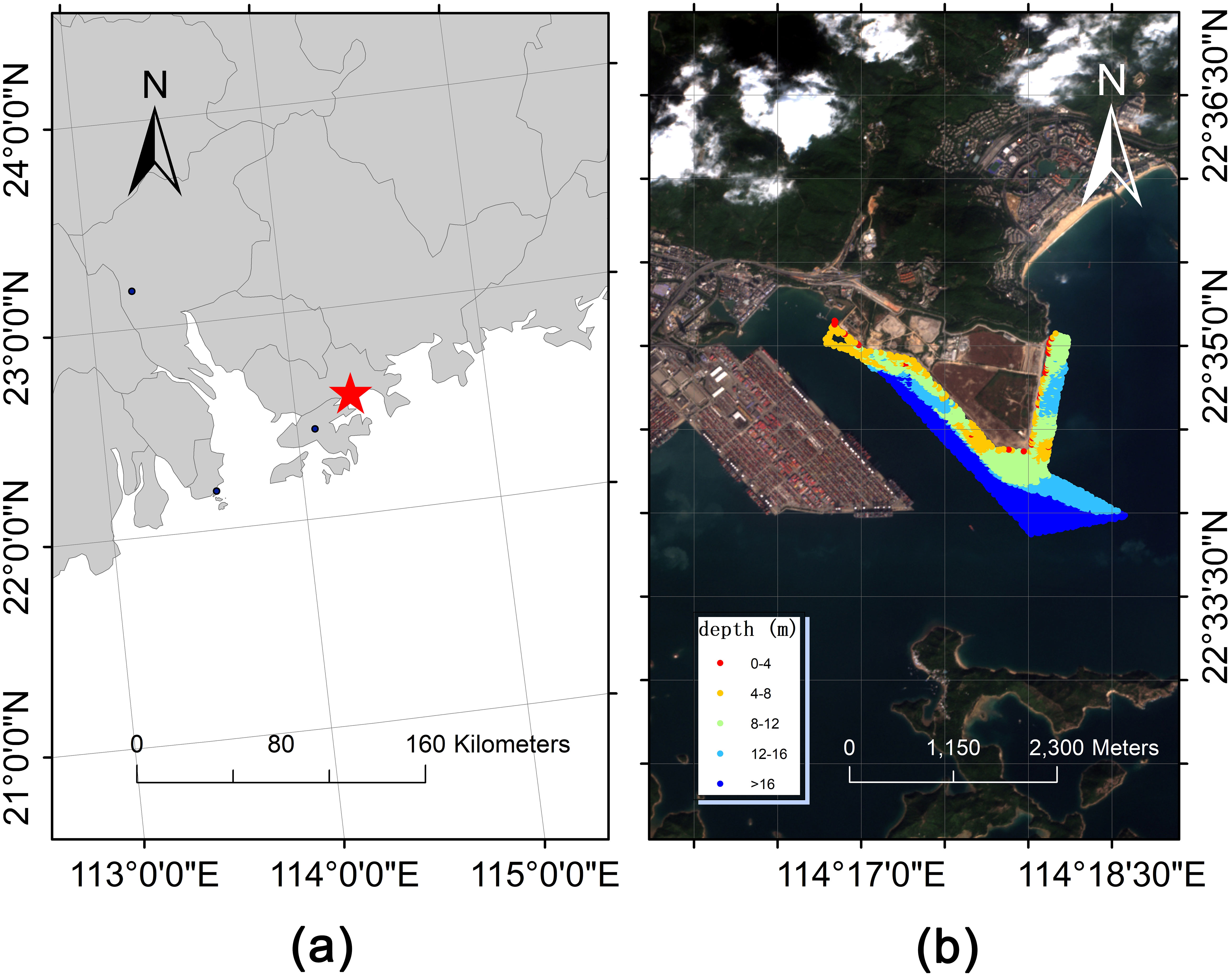
Figure 1. (A) The geographical location of the study area; (B) Data collection area where different colors represent variations of in situ depth data.
This comprehensive approach to data acquisition and processing provides a robust foundation for our bathymetric analysis, leveraging state-of-the-art satellite technology and software to achieve high-resolution depth estimations in the complex coastal environment of Yantian Port.
In-situ depth measurements were conducted on December 10-11, 2021, in the waters adjacent to Yantian Port. We employed the WBMS multibeam echo sounder system from NORBIT, Norway, which can achieve a distance resolution of less than 10 mm under optimal conditions. The system was mounted on a vessel for ship-based measurements. During the survey, wind speeds ranged from 2-3 on the Beaufort scale, with wave heights between 0.1-0.3 m, meeting the basic requirements for satellite-derived bathymetry. The survey meet the Code for Survey of Water Transport Engineering (JTS131-2012),Global Positioning System (GPS) Measurement Specification (GB/T18314-2009),Technical Requirements for Multi-beam Bathymetry System (JT/T 790-2010).
To facilitate our research, we selected 3 million uniformly distributed data points within the study area. From this dataset, we extracted 4,000 points for the training set, ensuring both uniform spatial distribution and even representation across depth ranges. Similarly, we selected 1,000 points for the test set to validate the bathymetry retrievals. This sampling strategy ensures comprehensive coverage of the study area and robust evaluation of our bathymetric model performance.
The Stumpf model is a widely used remote sensing technique for estimating water depth (Stumpf et al., 2003). It analyzes water column light attenuation using satellite imagery to derive bathymetric data. The model employs a band ratio technique to compensate for variations in water clarity and light conditions. The depth estimation formula is:
Where Z is the estimated depth, R(λi) and R(λj) are radiances at two wavelengths, n is 1000, and m1 and m0 are empirically determined coefficients.
The Log-Linear model assumes a linear relationship between the natural logarithm of water-leaving radiance and depth (Lyzenga, 1978, 1985; Lyzenga et al., 2006). It is expressed as:
Where L(λ i) and L(λ j) are measured radiances, L∞(λ i) and L∞(λ j) represent radiance in very deep water, and a1, a2, and a3 are coefficients.
Random Forest is an ensemble learning algorithm combining decision trees through bagging and random subspace methods (Breiman, 2001; Liu et al., 2015; Kumudham and Rajendran, 2018).
It excels at handling complex, nonlinear relationships between water depth and image reflectance without relying on physical models or optical parameters (Liaw and Wiener, 2002).The Random Forest method is an ensemble learning algorithm that constructs multiple decision trees and outputs the mode of the classes (for classification problems) or the mean prediction (for regression problems) of the individual trees. In our study, we used 100 trees in the Random Forest model. The hyperparameters used for the shown results include 42 for the maximum depth of the tree, 10 for the minimum number of samples required to split an internal node, and 5 for the minimum number of samples required to be at a leaf node. These hyperparameters were tuned using grid search with cross-validation to optimize the model performance.
This study introduces the innovative RF-Lat./Lon algorithm, a significant advancement in bathymetric mapping for complex coastal environments. By integrating a coordinate attention mechanism into the Random Forest framework, this approach addresses the challenges of bathymetry by satellites in turbid port waters.
The RF-Lat./Lon algorithm enhances traditional Random Forest techniques by incorporating geographical coordinates as key features alongside spectral reflectance data. This novel approach allows the model to leverage spatial context, resulting in more accurate depth estimations across diverse aquatic landscapes.
At its foundation, the algorithm leverages an ensemble of decision trees, each trained on diverse subsets of input data. The coordinate attention mechanism dynamically allocates varying weights to geographical locations throughout the learning process, empowering the model to adapt to local conditions and nuances in underwater topography.
Key advantages of the RF-Lat./Lon approach include superior accuracy in turbid waters, robustness in handling outliers and missing data, adaptability to different coastal environments, and computational efficiency for large-scale mapping projects.
The assessment of bathymetric accuracy relies on several crucial performance metrics that are fundamental to evaluating the precision of depth estimations. Key among these are Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Relative Error (MRE), and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) (Brando et al., 2009). These metrics play a vital role in quantifying the accuracy of depth measurements. The formulas for calculating these metrics are as follows:
We employ several performance metrics to assess bathymetric accuracy:
Where Zi represents actual depths and Z’i denotes predicted depths.
Our study employs a comprehensive two-stage methodology for accurate bathymetry mapping in complex coastal environments. This approach optimizes data utilization and develops a reliable framework for processing remote sensing data, with a particular focus on evaluating the effectiveness of our proposed RF-Lon./Lat. model.
In the first stage, we lay the groundwork for accurate depth estimation through careful data selection and preprocessing. This involves selecting remote sensing images with minimal cloud cover and clear water conditions to ensure optimal visibility. Atmospheric correction is applied to mitigate atmospheric effects and enhance the quality of reflectance data for subsequent analysis. Preliminary water depth estimation is then performed using various bathymetry algorithms on the corrected reflectance data, generating initial depth estimates as a foundation for further refinement. Additionally, tidal correction is accounted for to maintain consistency in depth estimates, with necessary adjustments based on reliable tidal data sources.
In the second stage, we focus on data transformation, model training, and performance assessment. Satellite data is converted into a tabular format and integrated with spectral information and in-situ measurements. Traditional bathymetry models are developed as a baseline, followed by the training of the RF-Lon./Lat. model, which incorporates spectral band values and geographical coordinates. Depth predictions are generated using both traditional and RF models, and tidal corrections are applied to ensure accuracy across different temporal conditions. Finally, model performance is evaluated using metrics such as MAE, RMSE, and R², comparing the effectiveness of the RF-Lon./Lat. model against traditional approaches.
Figure 2 provides a visual representation of our bathymetric method, illustrating the flow of data and processes through both stages. This diagram highlights the sequential nature of our approach, from initial data preparation to final model evaluation.
By structuring our methodology into these two distinct yet interconnected stages, we ensure a thorough and systematic approach to bathymetry mapping. This framework allows for efficient processing of remote sensing data while providing a robust platform for assessing the improvements offered by our RF-Lon./Lat. model in depth estimation accuracy.
In the realm of coastal management and marine navigation, achieving precise bathymetric mapping remains a formidable challenge, particularly in complex aquatic environments. This study conducts a comprehensive evaluation of cutting-edge water depth estimation models, focusing on their application in the dynamic setting of Yantian Port. By leveraging high-resolution Sentinel-2 satellite data across multiple spectral bands, we aim to push the boundaries of bathymetric accuracy and precision.
Our methodology is grounded in a robust random sampling technique, ensuring the capture of unbiased and spatially diverse datasets. This approach provides a solid foundation for our comparative analysis, allowing us to explore the full spectrum of bathymetric variations within the study area. Consequently, we enhance the reliability of our results and ensure their applicability across a wide range of coastal environments.
The study examines four distinct models, each representing a different approach to water depth estimation. These include the traditional Stumpf model, the Log-Linear approach, the Random Forest (RF) model, and the innovative Random Forest with Longitude/Latitude (RF-Lon./Lat.) method, which integrates geospatial context into the estimation process.
To ensure a thorough evaluation, we employ three key performance metrics: the coefficient of determination (R²), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). These metrics offer complementary insights, allowing us to assess not only the accuracy of each model but also its precision and overall reliability in real-world applications.
Our analysis results, visualized in Figure 3, reveal striking variations in depth estimation accuracy across the different algorithms. The traditional models demonstrate poor suitability for the complex aquatic environment of Yantian Port, while the Random Forest model marks a significant leap forward in performance. However, the true breakthrough comes with the exceptional performance of the novel RF-Lon./Lat. model, which outperforms all others in the study.
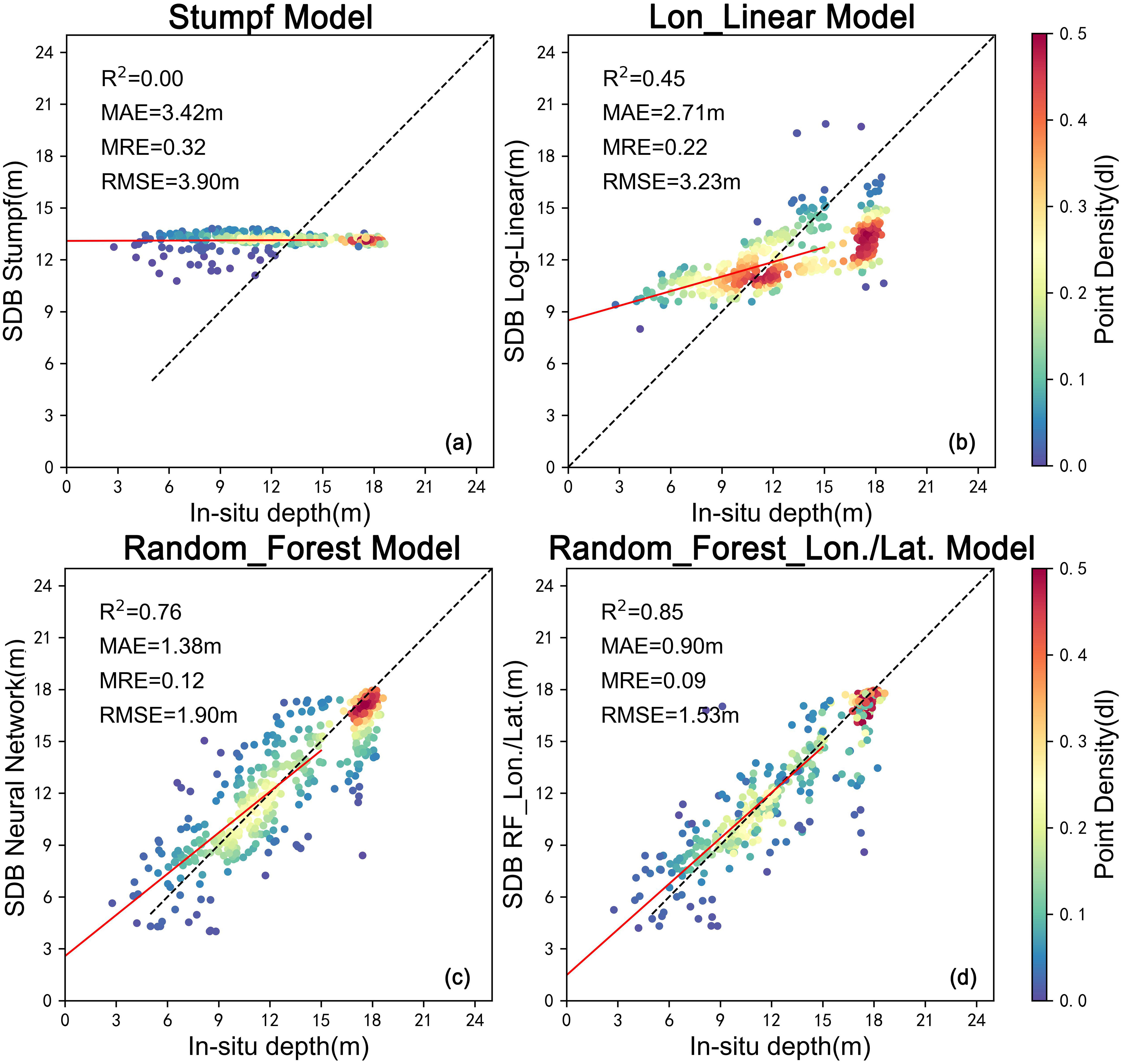
Figure 3. Comparative analysis of bathymetric estimation methods. (A) Stumpf Model: Traditional spectral ratio technique; (B) Log-Linear Model: Enhanced spectral interpretation method; (C) Random Forest Model: Machine learning approach utilizing spectral data; (D) Random Forest with Longitude/Latitude (RF-Lon./Lat.): Advanced algorithm incorporating geospatial context.
To provide a tangible visualization of these results, we generate water depth maps using each model, as depicted in Figure 4. The stark contrast between the outputs is immediately apparent, with the RF-Lon./Lat. model offering the most refined and realistic representation of the underwater landscape.
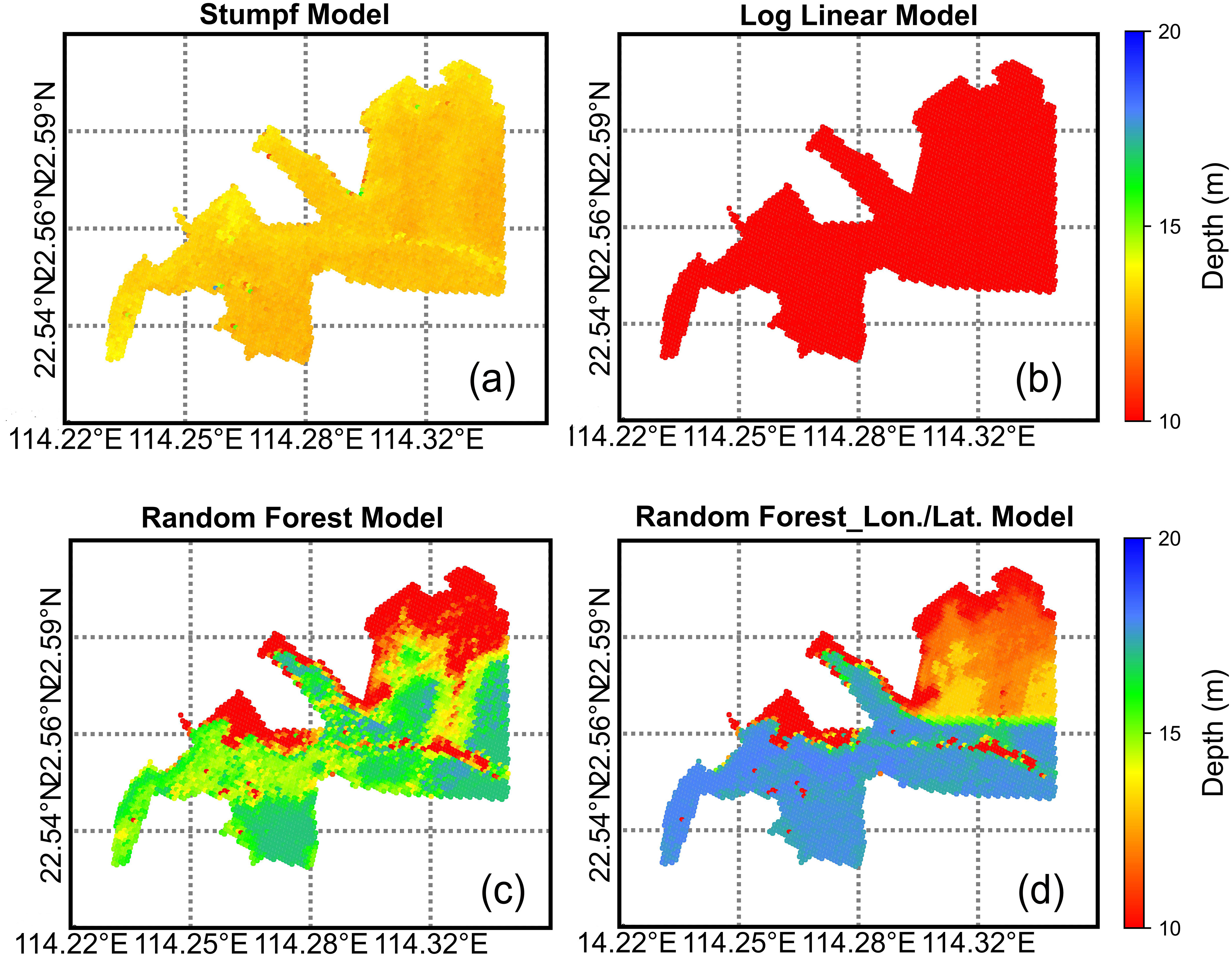
Figure 4. Bathymetric maps of yantian port using various estimation techniques. (A) Stumpf Model: Classic spectral ratio approach; (B) Log-Linear Model: Advanced spectral interpretation technique; (C) Random Forest Model: Machine learning algorithm utilizing spectral data; (D) Random Forest with Longitude/Latitude (RF-Lon./Lat.): Innovative method integrating geospatial context.
The RF-Lon./Lat. model’s superior performance has significant implications for bathymetric mapping. By effectively merging geospatial context with powerful nonlinear modeling capabilities, this approach presents a promising solution for precise and efficient water depth estimation in turbid waters and port areas. Its success in the challenging environment of Yantian Port indicates potential for wide applicability across complex coastal regions globally.
In conclusion, this comparative analysis contributes valuable insights to the rapidly evolving field of machine learning applications in bathymetric mapping. By demonstrating the superior accuracy of the RF-Lon./Lat. model, we have paved the way for enhanced water depth estimation techniques that can address the complex challenges of modern coastal environments. As we continue to refine and expand upon these methods, the future of bathymetric mapping looks increasingly precise, efficient, and adaptable to the diverse needs of marine and coastal stakeholders worldwide. This advancement not only promises to revolutionize port management and navigation safety but also holds the potential to significantly impact fields such as coastal conservation, climate change research, and sustainable marine resource management.
This study aims to develop a novel water depth inversion method by combining Random Forest algorithms with a Coordinate Attention mechanism to address the challenges of satellite-derived bathymetry in complex coastal environments. Our main research question is: How can we improve the accuracy and reliability of water depth estimation in turbid waters and complex topographic conditions? Through a case study in Yantian Port, we validated the effectiveness of the proposed method and compared it with traditional approaches. The following will discuss in detail the main findings of the study, their interpretations, and significance.
In the dynamic realm of oceanography and marine resource management, precise water depth estimation remains a critical challenge (Richardson et al., 2024). This study presents a groundbreaking analysis of four distinct bathymetric models, each employing a unique approach to depth estimation. As Table 1 shows, our investigation encompasses the traditional Stumpf model, the Log-Linear approach, the advanced Random Forest (RF) technique, and our innovative Random Forest with Longitude/Latitude (RF-Lon./Lat.) method. By meticulously examining their performance across various depth ranges, we aim to provide valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of each approach, ultimately advancing bathymetric mapping techniques. Our key findings include: The RF-Lon./Lat. model significantly outperforms traditional methods in overall performance, especially in shallow water areas (0-20 meters).The introduction of geographic coordinates as input variables greatly improves spatial accuracy. The method effectively captures complex non-linear relationships while considering spatial heterogeneity. The new method shows lower RMSE and higher R² values across different depth ranges.
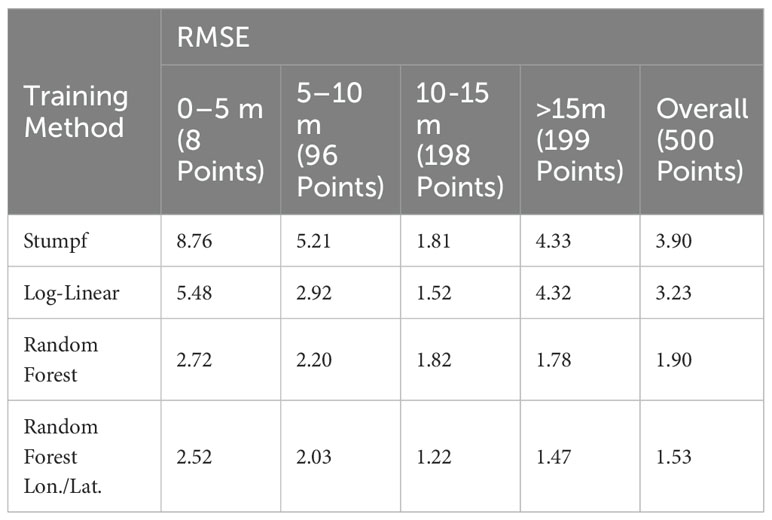
Table 1. A comparison of the RMSE errors for different water depths and different bathymetry methods.
Our methodology leverages high-resolution satellite imagery combined with precise in-situ measurements, enabling a comprehensive assessment of model accuracy across different depth intervals. We employ a suite of performance metrics, including Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and detailed error distribution analysis, offering a nuanced understanding of each model’s behavior in diverse coastal environments.
The investigation reveals intriguing patterns in model performance across depth ranges. In shallow waters (5-10m), the Log-Linear model demonstrates remarkable accuracy, surpassing more complex models. This success underscores the importance of considering depth-specific methodologies in bathymetric studies and challenges the assumption that more complex models always yield better results.
As we explore mid-range depths (10-15m), a significant shift in model efficacy becomes apparent. The RF-Lon./Lat. model emerges as the clear frontrunner, outperforming other approaches. This superior performance indicates its potential for revolutionizing bathymetric mapping in coastal areas where traditional methods often struggle.
In deeper waters (>15m), all models exhibit improved performance, reflecting the relative stability of optical properties in these regions. However, the RF-Lon./Lat. model maintains its edge, achieving the lowest RMSE. This pattern underscores the adaptability of machine learning approaches to varying depth conditions and highlights the particular strength of the RF-Lon./Lat. model in deeper coastal waters.
As Figure 5 shows, a detailed analysis of residual error distributions provides further insights. The Stumpf model exhibits a symmetrical pattern centered around zero, suggesting balanced over- and underestimation. The Log-Linear model displays a positive skew, indicating a tendency to overestimate depths. In contrast, the RF model demonstrates a more concentrated distribution near zero, albeit with a slight negative skew. The RF-Lon./Lat. model showcases the narrowest and most symmetric error distribution, indicating exceptional precision across various bathymetric conditions.
These findings have profound implications for bathymetric mapping. The consistent superiority of the RF-Lon./Lat. model, particularly in mid-range and deep waters, presents a promising avenue for improving depth estimations in complex coastal environments. Its ability to maintain high precision across various depth ranges demonstrates the power of integrating geographical context into machine learning approaches.
Moreover, the depth-specific performance variations observed underscore the importance of tailored approaches in bathymetric studies. While the Log-Linear model excels in shallow waters, its performance declines in deeper areas. Conversely, the RF and RF-Lon./Lat. models maintain relatively consistent accuracy across all depth ranges, with the latter showing exceptional prowess in deeper waters.
These insights open up exciting new avenues for future research. The success of the RF-Lon./Lat. model suggests potential for further improvements through the integration of additional geospatial features. Future studies could explore incorporating variables such as coastal morphology, sediment characteristics, or hydrodynamic patterns to refine depth estimations further. Additionally, developing hybrid models that combine the strengths of different approaches for various depth ranges could lead to even more accurate and comprehensive bathymetric maps.
In conclusion, this comprehensive analysis not only highlights the varying strengths of different bathymetric models but also points towards a promising future in water depth estimation techniques. The remarkable performance of the RF-Lon./Lat. model across diverse depth ranges paves the way for more accurate and reliable bathymetric mapping in coastal environments. As we continue to refine these methods, the potential for improving our understanding and management of marine ecosystems grows exponentially, offering exciting prospects for fields ranging from coastal engineering to marine conservation and climate change research.
While our proposed Random Forest and RF-Lon./Lat. models excel in water depth inversion within the 20 m range of the study area, it’s crucial to address the inherent uncertainties and challenges of remote sensing-based bathymetric mapping in Yantian Port’s complex environment. These factors influence depth retrieval accuracy and have broader implications for applying such techniques in similar dynamic aquatic systems.
Yantian Port presents unique challenges for bathymetric modeling. Its turbid waters exhibit significant variability in optical properties due to fluctuations in sediment load and water quality. This variability can disrupt established relationships between water depth and spectral reflectance, potentially compromising depth estimations. Frequent cloud cover and precipitation often impede high-quality remote sensing data acquisition, affecting both model training and validation.
Data processing introduces additional uncertainties. The atmospheric correction module may not completely eliminate all atmospheric effects from satellite imagery. Residual errors can propagate through the analysis, influencing retrieved reflectance values. Imprecisions in geometric correction can lead to misalignments between remote sensing data and in-situ measurements, further complicating depth retrieval.
The port’s dynamic nature presents challenges in data synchronization. Tidal variations, if not adequately accounted for, can introduce significant discrepancies between measured and estimated depths. This temporal mismatch underscores the need for robust tidal correction methodologies in tidal-influenced waterways.
The accuracy of water depth retrieval is significantly influenced by the underlying assumptions and parameter selections in inversion models. Despite their sophistication, these models rely on simplifications of intricate physical processes and may not fully encapsulate all factors affecting water depth in such a dynamic environment (Al Najar et al., 2023).
To address these challenges and enhance bathymetric mapping reliability in Yantian Port, several avenues for improvement emerge. Developing robust atmospheric correction techniques tailored to turbid coastal environments is crucial. Integrating real-time water quality monitoring data can account for temporal variations in optical properties. Exploring multi-temporal and multi-sensor data fusion can mitigate cloud cover impact and improve data availability. Implementing advanced machine learning algorithms capable of adapting to dynamic conditions and capturing complex, non-linear relationships is essential. Incorporating high-resolution digital elevation models and hydrodynamic simulations can improve tidal corrections and account for morphological changes. Additionally, developing uncertainty quantification frameworks can provide confidence intervals for depth estimations.
However, this study also has some limitations: The generalizability of the model still needs to be validated in a wider range of coastal environments. The inversion accuracy for extremely shallow water areas (<5m) still needs improvement. The model’s adaptability to highly turbid or rapidly changing water conditions requires further research.
In conclusion, while our proposed models represent a significant advancement in Yantian Port’s bathymetric mapping, the path forward requires a holistic approach addressing multifaceted uncertainties. By refining methodologies, integrating diverse data sources, and developing sophisticated modeling techniques, we can enhance water depth retrieval accuracy and reliability. Such improvements will benefit navigation and port management and provide valuable insights for bathymetric mapping in similar challenging aquatic environments worldwide.
In this section, we present the results of cross-validation using different sets of water depth inversion points and compare the performance of various algorithms, including Deep learning and Support Vector Machines (SVM). This approach ensures that our models are robust and generalizable across different datasets and conditions.
Figures 6A, B depict the performance of the RF model using a randomly selected training sample of 500 points. The predicted depth exhibits significant deviation from the actual depth, as evidenced by an R² value approaching 0, indicating poor predictive capability. The elevated root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) further underscore the substantial disparity between predicted and actual depths. In Figures 6C, D, we augment the training dataset to training 800 samples using the same prediction dataset. The findings reveal a marginal enhancement in precision, accompanied by slight reductions in RMSE and MAE values. However, the overall predictive performance remains suboptimal, as indicated by the diminished R² value. This suggests that increased sample size benefits the SVM model significantly and renders it better suited for this type of data. This suggests that while increasing the sample size is beneficial, the model still struggles to capture the underlying complexity of the dataset.
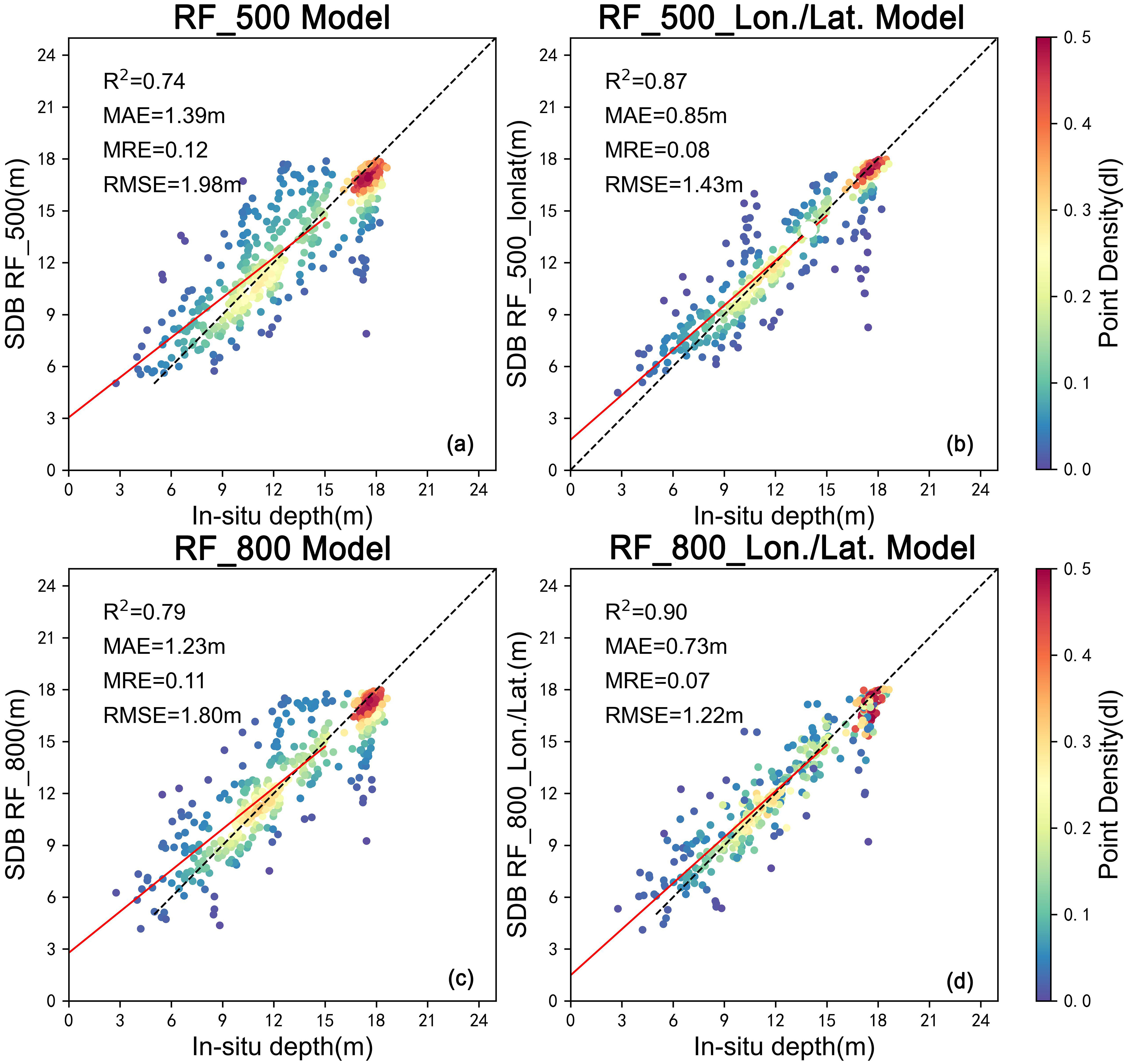
Figure 6. Cross-validation with different water depth inversion points and different algorithms. (A) RF Prediction with 500 Training Samples. (B) RF Prediction with 500 Training Samples (Lon./Lat.); (C) RF Prediction with 800 Training Samples. (D) RF Prediction with 800 Training Samples (Lon./Lat.).
Figures 7A, B illustrate the Deep Learning Model’s performance using 500 samples. Compared to the Random Forest (RF) approach, this model demonstrates a closer alignment with actual in-situ depths, as evidenced by higher R² values, despite higher RMSE and MAE. The point density plots reveal tighter clustering around the 1:1 line, suggesting the Deep Learning Model’s enhanced ability to predict water depths accurately.

Figure 7. Cross-validation with different water depth inversion points and different algorithms. (A) Deep_learning Model Prediction with 500 Samples; (B) Deep_learning Model Prediction with 500 Samples(Lon./Lat.); (C) Support Vector Machine Prediction with 500 Samples; (D) Support Vector Machine Prediction with 500 Samples(Lon./Lat.).
Figures 7C, D showcase the Support Vector Machine (SVM) model’s results, also trained with 500 samples. Performance metrics indicate further improvement, characterized by reduced RMSE and MAE. While R² values remain modest, they surpass those obtained from the RF results. This improvement underscores the potential of advanced machine learning techniques in enhancing water depth inversion accuracy.
A comparative analysis between RF and RF with Longitude/Latitude (RF-Lon./Lat.) across varying sample sizes yields valuable insights. The standard RF models struggle to capture the intricacies of water depth inversion data, whereas RF-Lon./Lat. shows greater promise by delivering improved predictive accuracy and reliability. Increasing the training sample size enhances the performance of both models; however, the RF-Lon./Lat. consistently outperforms both Deep Learning and SVM models, indicating its superior suitability for this specific task. The incorporation of geographical coordinates in the RF-Lon./Lat. model provides a significant advantage, allowing it to better account for spatial variations in depth patterns. The consistent superiority of RF-Lon./Lat. across different sample sizes suggests its robustness and potential for broader application in diverse coastal environments. While not explicitly mentioned, the RF-Lon./Lat. model likely offers a good balance between predictive power and computational efficiency, making it an attractive option for large-scale bathymetric mapping projects.
The findings of this study have significant implications for coastal management and marine science. The improved accuracy in water depth measurement can: a) Enhance navigational safety and optimize port operations. b) Provide more reliable data support for coastal infrastructure development. c) Promote the protection and study of marine ecosystems. d) Provide more precise baseline data for climate change impact studies.
While this study presents significant advancements in satellite-derived bathymetry for complex coastal environments, it is important to acknowledge several limitations that may affect the interpretation and generalizability of our results.
Firstly, the sample size, although substantial, represents only a fraction of the total water area in Yantian Port. This limitation potentially impacts the model’s stability and generalizability, particularly in complex coastal environments where depth variations can be significant over short distances. The restricted sample size may lead to underrepresentation of certain depth ranges or bottom types, potentially biasing the model’s performance. Future studies should aim to increase the sample size and ensure a more comprehensive coverage of the study area to enhance the robustness of the bathymetric models.
Secondly, temporal and seasonal constraints pose another significant limitation. Due to resource and time restrictions, our data collection was confined to a single time period, which may not capture the full range of environmental conditions that affect water depth and optical properties in Yantian Port. Tidal variations, seasonal changes in water turbidity, and fluctuations in suspended sediment loads can significantly influence the relationship between spectral reflectance and water depth. To address this limitation, future research should consider multi-temporal data collection strategies, incorporating measurements across different seasons and tidal conditions. This approach would enhance the model’s ability to account for temporal variability and improve its applicability across diverse environmental conditions.
Thirdly, methodological limitations were observed, particularly in the performance of our Random Forest model in extremely shallow waters (depths< 5 meters). The reduced accuracy in these areas may be attributed to the complex optical properties of shallow waters, where factors such as bottom reflectance and suspended particles have a more pronounced effect on spectral signatures. While the introduction of geographic coordinates as input variables improved overall spatial accuracy, this approach may be less effective in areas with rapid terrain changes. Future research could explore the integration of additional environmental parameters or the development of depth-specific models to improve accuracy in challenging shallow water environments.
Fourthly, spectral limitations of our approach should be noted. The current model primarily utilizes visible and near-infrared bands from Sentinel-2 imagery. This reliance on a limited spectral range may underutilize information available in other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, such as shortwave infrared bands, which could provide additional insights into water column properties and bottom types. Moreover, the model’s performance in highly turbid waters or rapidly changing environmental conditions remains to be thoroughly tested. Future studies could explore the integration of additional spectral bands or the fusion of data from multiple sensors to enhance the model’s capability in diverse water conditions.
Lastly, the generalizability of our results to other coastal areas presents a significant limitation. The model’s performance is based on the specific environmental conditions of Yantian Port, and its direct application to other coastal regions may be limited. Different geographical locations often present unique combinations of hydrological, geological, and ecological characteristics that can significantly affect the relationship between spectral reflectance and water depth. The model’s applicability in temperate or polar regions, open seas, or complex ecosystems such as coral reefs remains unverified. To address this limitation, future research should focus on testing and adapting the model across a wide range of coastal environments, including different climate zones, water types, and bottom conditions. This broader validation would not only enhance the model’s versatility but also contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing satellite-derived bathymetry in diverse coastal settings.
In conclusion, this analysis highlights the RF-Lon./Lat. model’s effectiveness in water depth inversion. Its ability to outperform both traditional machine learning approaches (SVM) and more complex deep learning models underscores the importance of incorporating spatial context in bathymetric mapping. These findings pave the way for more accurate and efficient depth estimation techniques in coastal and marine environments, with potential applications ranging from navigation safety to ecosystem monitoring and coastal management.
Bathymetry by satellites in turbid environments, particularly in harbor areas, presents a complex challenge. While traditional methods like the Stumpf and Log-Linear models have been widely used, their performance often falters in waters with high suspended particulate matter. To address this limitation, we propose an innovative approach that integrates geographic information with these conventional techniques.
Our methodology introduces longitude and latitude as key input variables, enhancing spatial accuracy and precision in depth estimation. This novel approach aims to capture the nuanced spatial heterogeneity inherent in the relationship between water reflectance and depth.
The study focuses on Rushikonda Beach, a picturesque c-shaped bay on India’s east coast. We conducted comprehensive field data collection, including high-precision water depth measurements using a multi-beam echo sounder, accurate positional data gathered via differential GPS, and multispectral reflectance data from the Sentinel-2 satellite.
By synthesizing these diverse data sources, we developed a robust water depth inversion model. The integration of geographic information methods during model training allowed us to account for spatial variations in the reflectance-depth relationship effectively.
At the core of our approach is a Random Forest algorithm enhanced with a coordinate attention mechanism. This sophisticated technique enables the capture of complex, nonlinear relationships between water reflectance and depth. The incorporation of longitude and latitude information significantly improves the model’s spatial accuracy and enhances the overall precision of water depth inversion in turbid environments.
This innovative methodology represents a significant advancement in bathymetric mapping for challenging aquatic environments. By leveraging both traditional optical techniques and modern machine learning approaches, our model offers a more comprehensive and accurate solution to the long-standing challenge of depth estimation in turbid waters.
The implications of this research extend beyond Rushikonda Beach, potentially revolutionizing bathymetric surveys in various complex coastal and harbor environments worldwide. As we continue to refine this approach, it promises to enhance our understanding of underwater topography, crucial for maritime safety, coastal management, and environmental monitoring.
As Figure 8 shows, the experimental results reveal the superior performance of the Random Forest model incorporating spatial information in the turbid environment of Rushikonda Beach, a picturesque c-shaped bay on India’s east coast. This advanced approach significantly outperforms traditional Stumpf and Log-Linear models across various depth ranges.
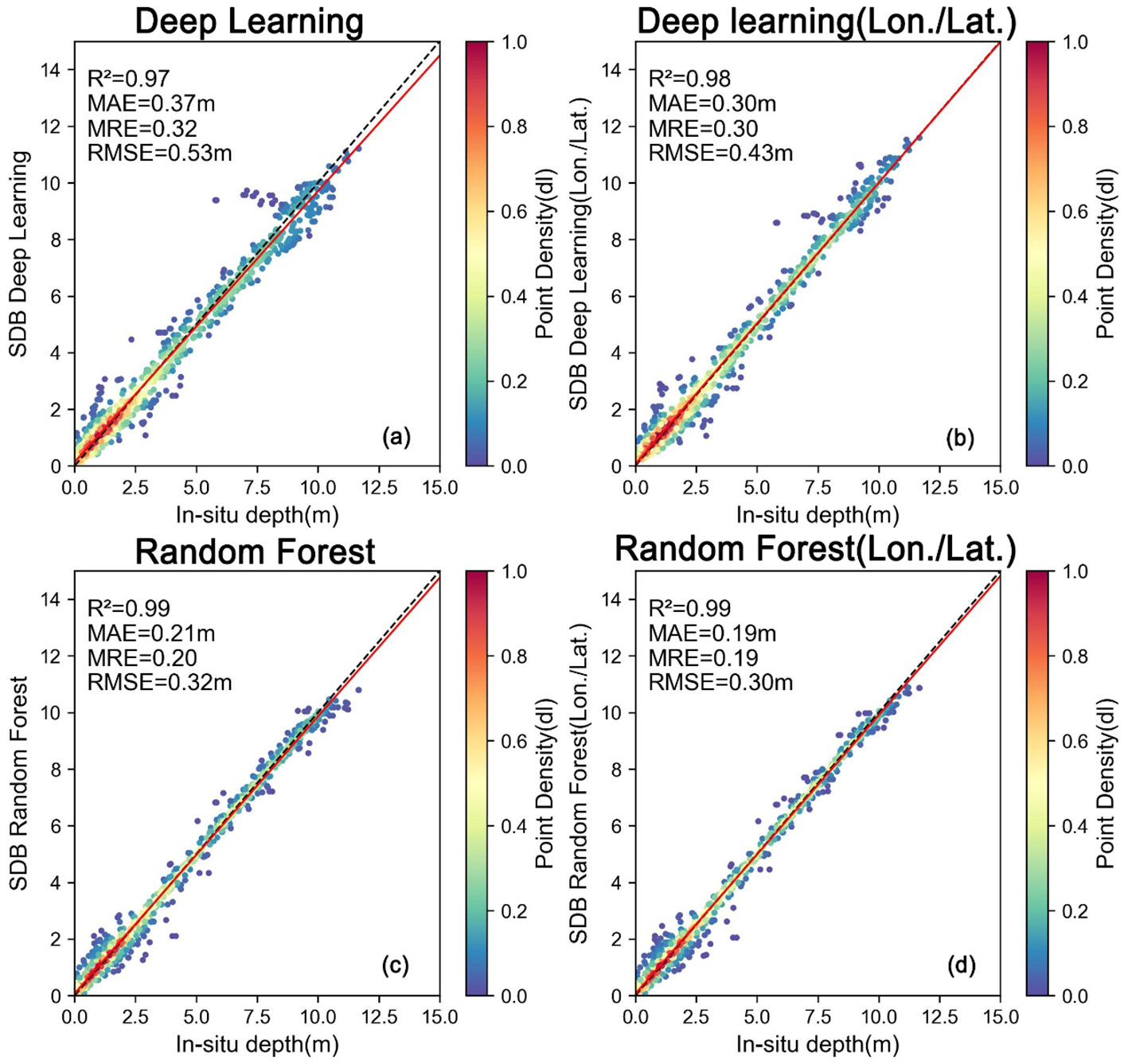
Figure 8. Comparative analysis of bathymetric estimation techniques. (A) Stumpf Model: Traditional spectral ratio approach; (B) Log-Linear Model: Enhanced spectral interpretation method; (C) Random Forest Model: Machine learning technique utilizing spectral data; (D) Random Forest with Longitude/Latitude: Advanced algorithm integrating geospatial context.
Key findings include:Lower Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and higher R² values across different water depth ranges and particularly notable improvements in accuracy within the shallow water range (0-20 meters).
The enhanced performance of this spatial-aware Random Forest model represents a significant advancement in water depth inversion techniques for turbid environments. As Figure 9 shows, its success not only improves the accuracy of bathymetric mapping but also offers valuable support for coastal management and navigational safety.
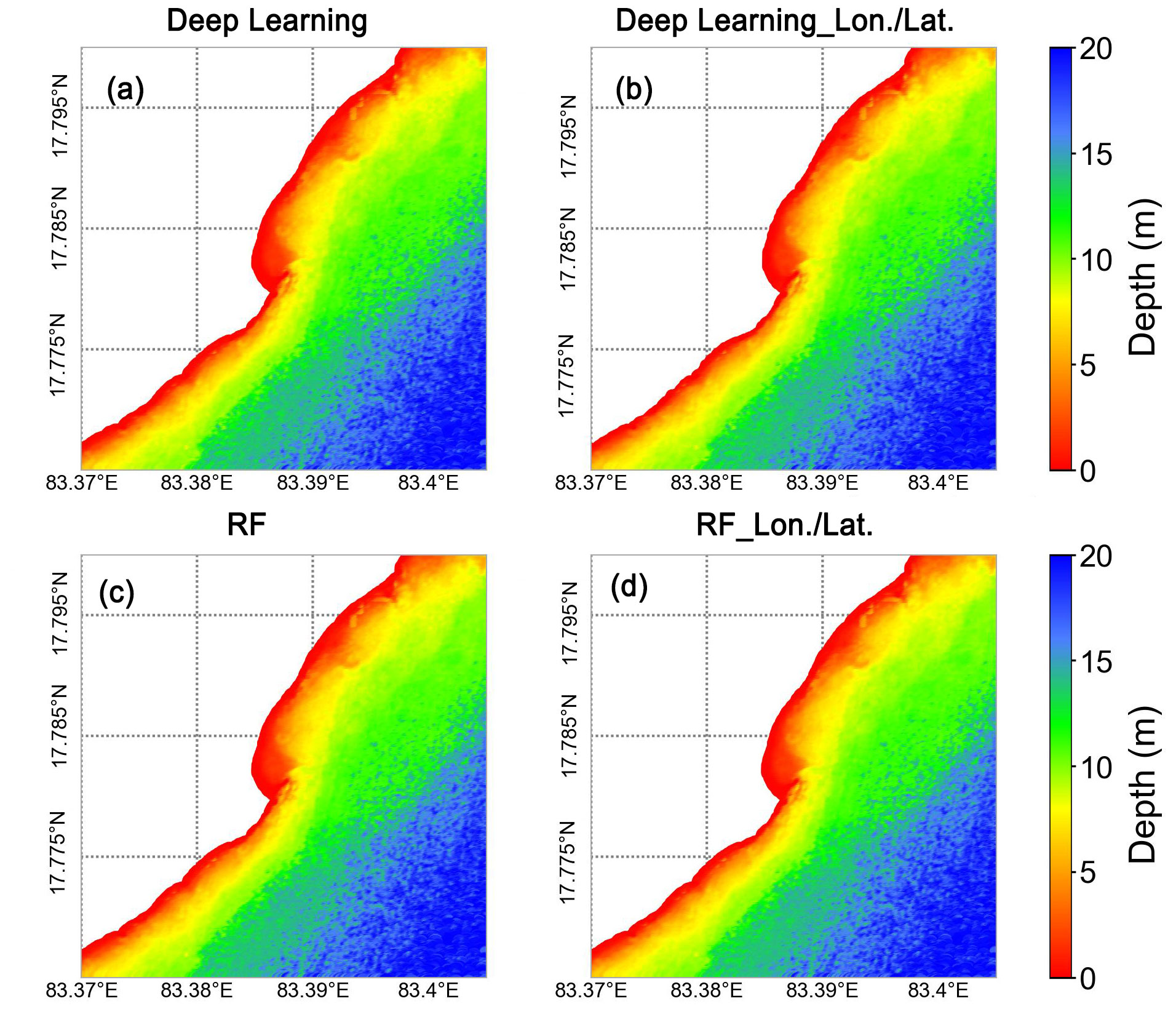
Figure 9. Bathymetric correlation analysis in rushikonda beach. (A) Stumpf Model: Classical spectral ratio technique; (B) Log-Linear Model: Advanced spectral interpretation approach; (C) Random Forest Model: Machine learning algorithm utilizing spectral data; (D) Random Forest with Longitude/Latitude: Innovative method integrating geospatial context.
This innovative method addresses longstanding challenges in estimating water depths in complex coastal areas, where traditional approaches often fall short. By effectively integrating spatial information, the model demonstrates its ability to capture the nuanced relationships between water reflectance, depth, and geographical location.
As Figure 9 shows, the implications of this research extend beyond Rushikonda Beach, potentially revolutionizing bathymetric surveys in various turbid coastal and harbor environments worldwide. As we continue to refine this approach, it promises to enhance our understanding of underwater topography, crucial for sustainable coastal development, maritime operations, and environmental monitoring.
Our research demonstrates the significant potential of advanced machine learning techniques in complex harbor waters, particularly through the application of the Random Forest algorithm enhanced with coordinate attention. This innovative approach markedly improves the accuracy of water depth inversion, outperforming traditional methods in challenging turbid environments. By integrating geographical coordinates into the model and utilizing a Random Forest algorithm with coordinate attention, we’ve been able to capture complex non-linear relationships between water reflectance and depth, resulting in significant accuracy improvements, especially in shallow water ranges.
These advancements not only showcase the capabilities of machine learning in bathymetric mapping but also provide valuable references for future applications in similar coastal environments. The method’s success in Nanshan Port suggests its potential adaptability to other complex aquatic systems worldwide. As we continue to accumulate data and optimize the model, this approach holds broad application prospects beyond water depth inversion, including water quality assessment in coastal and inland water bodies, atmospheric research, and coastal zone management.
The success of this geospatially-enhanced Random Forest model opens new avenues for interdisciplinary research, bridging the gap between remote sensing, machine learning, and coastal sciences. By providing more accurate and reliable bathymetric data, this method contributes significantly to maritime safety, coastal planning, and environmental conservation efforts. As we refine this technique, its impact on our understanding and management of complex aquatic environments continues to grow, promising advancements in both scientific knowledge and practical applications in coastal and marine sectors.
Our RF-Lon./Lat. model represents a significant advancement in satellite-derived bathymetry (SDB) for complex coastal environments. By integrating geographical coordinates through a Coordinate Attention mechanism, our approach transcends traditional methods that rely solely on spectral information. This innovation addresses critical gaps in existing SDB techniques, particularly in turbid and topographically complex waters where conventional methods often fall short. The model’s superior performance, especially in shallow water ranges (0-20 meters), offers unprecedented accuracy for coastal mapping and monitoring.
The practical implications of this technology are far-reaching. By providing more precise bathymetric data, our method has the potential to significantly improve navigational safety, optimize port operations, and support environmental monitoring efforts. It can inform coastal infrastructure development, enhance marine habitat protection, and contribute valuable data to climate change impact studies. The adaptability of our approach to local conditions and its ability to capture nuanced spatial heterogeneity set it apart from current technologies.
Our dual-stage methodology offers a comprehensive solution that balances data quality, model sophistication, and practical applicability. This not only enhances the accuracy of depth estimations but also provides a scalable framework for future bathymetric studies in diverse aquatic settings. The computational efficiency of our approach, coupled with its robust performance across different depth ranges, makes it particularly suitable for large-scale bathymetric mapping projects.
As we continue to refine and apply the RF-Lat./Lon algorithm, its potential to revolutionize our understanding and management of coastal ecosystems is substantial. By effectively combining advanced machine learning capabilities with spatial context, our model paves the way for more precise and reliable bathymetric data. This innovative approach marks a new era in maritime and coastal science, offering unprecedented precision and insight in bathymetric mapping, and has the potential to transform fields such as coastal management, maritime safety, and marine ecosystem conservation.
This study introduces an innovative water depth inversion method, combining Random Forest algorithms with a Coordinate Attention mechanism. Applied to the complex environment of Nanshan Port, our approach addresses limitations of traditional bathymetric techniques in turbid, topographically diverse waters.
By integrating geographic coordinates as key input variables, we significantly enhanced spatial accuracy in depth estimation. The Random Forest Lon./Lat. model demonstrated superior performance, particularly in shallow waters (0-20 meters), achieving the lowest RMSE and highest R² values among tested methods.
Our approach effectively captures complex nonlinear relationships between spectral reflectance and coastal water depth, while accounting for spatial heterogeneity and local variations in water quality and bottom type. This results in robust and reliable depth estimates even in challenging aquatic environments.
The study advances satellite-derived bathymetry (SDB) and offers valuable insights for port management, coastal engineering, and environmental monitoring. Future research directions may include applying this method to a wider range of coastal environment types to verify its universality, exploring the fusion of multi-source remote sensing data (such as SAR, hyperspectral) to further improve accuracy, developing adaptive coordinate attention mechanisms to optimize the depth inversion process in different environments, studying the combination of this method with water quality parameter inversion to obtain more comprehensive coastal environmental information.
As we continue to accumulate data and optimize the model, we anticipate further improvements in bathymetric mapping accuracy and efficiency. This research paves the way for enhanced understanding and management of critical aquatic environments, with wide-ranging applications in maritime safety, coastal conservation, and sustainable resource management.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
SF: Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. ZC: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WS: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the 2023 Hainan Province “South China Sea New Star” Science and Technology Innovation Talent Platform Project (NHXXRCXM202316), in part by Hainan Natural Science Foundation of China (No.424QN253,No.620RC602), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61966013), in part by High-quality Undergraduate Education Improvement Plan -2023 School-level Four New Research and Practice Project - Island coastal Zone Ecology and Computer Vision Teaching Practice Platform, in part by the Teaching Reform Research Project, Hainan Normal University, hsjg2023-07, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61991454, in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2023YFC3107605, in part by the Oceanic Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University under Grant SL2022ZD206, and in part by the Scientific Research Fund of Second Institute of Oceanography, MNR under Grant SL2302.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdul Gafoor F., Al-Shehhi M. R., Cho C.-S., Ghedira H. (2022). Gradient boosting and linear regression for estimating coastal bathymetry based on sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. 14, 5037. doi: 10.3390/rs14195037
Agrafiotis P. (2024). “MAGICBATHYNET: A multimodal remote sensing dataset for bathymetry prediction and pixel-based classification in shallow waters,” in IGARSS 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 249–253.
Alevizos E. (2020). A combined machine learning and residual analysis approach for improved retrieval of shallow bathymetry from hyperspectral imagery and sparse ground truth data. Remote Sens. 12, 3489. doi: 10.3390/rs12213489
Al Najar M., Thoumyre G., Bergsma E. W., Almar R., Benshila R., Wilson D. G. (2023). Satellite derived bathymetry using deep learning. Mach. Learn. 1-24. doi: 10.1007/s10994-021-05977-w
Arun Kumar V. (2012). Numerical modelling of coastal and nearshore processes in the vicinity of shoreline harbours with special reference to visakhapatnam coast India.
Barnes B. B., Garcia R., Hu C., Lee Z. (2018). Multi-band spectral matching inversion algorithm to derive water column properties in optically shallow waters: An optimization of parameterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 204, 424–438. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.10.013
Benshila R., Thoumyre G., Najar M. A., Abessolo G., Almar R., Bergsma E., et al. (2020). A deep learning approach for estimation of the nearshore bathymetry. J. Coast. Res. 95, 1011–1015. doi: 10.2112/si95-197.1
Brando V. E., Anstee J. M., Wettle M., Dekker A. G., Phinn S. R., Roelfsema C. (2009). A physics based retrieval and quality assessment of bathymetry from suboptimal hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 113, 755–770. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.12.003
Chan T. O., Zhang S., Xia L., Luo M., Wu J., Awange J. (2024). A novel reflectance transformation and convolutional neural network framework for generating bathymetric data for long rivers: A case study on the Bei River in South China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 127, 103682. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2024.103682
Chen B., Yang Y., Xu D., Huang E. (2019). A dual band algorithm for shallow water depth retrieval from high spatial resolution imagery with no ground truth. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 151, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.02.012
Chybicki A. (2018). Three-dimensional geographically weighted inverse regression (3GWR) model for satellite derived bathymetry using Sentinel-2 observations. Mar. Geodesy 41, 1–23. doi: 10.1080/01490419.2017.1373173
Garcia R. A., Lee Z., Barnes B. B., Hu C., Dierssen H. M., Hochberg E. J. (2020). Benthic classification and IOP retrievals in shallow water environments using MERIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 249. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.112015
Gülher E., Alganci U. (2023). Satellite-derived bathymetry mapping on horseshoe island, antarctic peninsula, with open-source satellite images: evaluation of atmospheric correction methods and empirical models. Remote Sens. 15, 2568. doi: 10.3390/rs15102568
Gupta G. K., Bhat R. V., Balan M. S. (2024). Improving satellite-derived bathymetry estimation with a joint classification–regression model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 21, 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3367731
Huang R., Yu K., Wang Y., Wang J., Mu L., Wang W. (2017). Bathymetry of the coral reefs of weizhou island based on multispectral satellite images. Remote Sens. 9, 750. doi: 10.3390/rs9070750
Janowski Ł., Skarlatos D., Agrafiotis P., Tysiąc P., Pydyn A., Popek M., et al. (2024). High resolution optical and acoustic remote sensing datasets of the Puck Lagoon. Sci. Data 11, 360. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03199-y
Joshi I. D., D’Sa E. J. (2018). An estuarine-tuned quasi-analytical algorithm (QAA-V): assessment and application to satellite estimates of SPM in Galveston Bay following Hurricane Harvey. Biogeosciences 15, 4065–4086. doi: 10.5194/bg-15-4065-2018
Kim J. S., Baek D., Seo I. W., Shin J. (2019). Retrieving shallow stream bathymetry from UAV-assisted RGB imagery using a geospatial regression method. Geomorphology 341, 102–114. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.05.016
Kumudham R., Rajendran V. (2018). Classification performance assessment in side scan sonar image while underwater target object recognition using random forest classifier and support vector machine. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 7, 21–30. doi: 10.14419/ijet.v7i2.21.12448
Le C. F., Li Y. M., Zha Y., Sun D., Yin B. (2009). Validation of a quasi-analytical algorithm for highly turbid eutrophic water of Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 47, 2492–2500. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2015658
Lee Z., Carder K. L. (2000). “Hyperspectral remote sensing of shallow water environments: A review,” in Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of the Ocean. Eds. Frouin R. J., Kawamura H., Kishino M., 83–94.
Lee Z., Carder K. L. (2002). Effect of spectral band numbers on the retrieval of water column and bottom properties from ocean color data. Appl. Optics 41, 2191–2201. doi: 10.1364/AO.41.002191
Lee Z. P., Carder K. L., Mobley C. D., Steward R. G., Patch J. S. (1998). Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters. I. A semianalytical model. Appl. Optics 37, 6329–6338. doi: 10.1364/ao.37.006329
Lee Z. P., Carder K. L., Mobley C. D., Steward R. G., Patch J. S. (1999). Hyperspectral remote sensing for shallow waters: 2. Deriving bottom depths and water properties by optimization. Appl. Optics 38, 3831–3843. doi: 10.1364/ao.38.003831
Li J., Knapp D. E., Lyons M., Roelfsema C., Phinn S., Schill S. R., et al. (2021). Automated global shallow water bathymetry mapping using google earth engine. Remote Sens. 13, 1469. doi: 10.3390/rs13081469
Li J., Knapp D. E., Schill S. R., Roelfsema C., Phinn S., Silman M., et al. (2019). Adaptive bathymetry estimation for shallow coastal waters using Planet Dove satellites. Remote Sens. Environ. 232. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111302
Li X., Wu Z., Shen W. (2024). Addressing challenges in port depth analysis: integrating machine learning and spatial information for accurate remote sensing of turbid waters. Sensors (Basel) 24. doi: 10.3390/s24123802
Li J., Yu Q., Tian Y. Q., Becker B. L. (2017). Remote sensing estimation of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in optically shallow waters. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 128, 98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.03.015
Li J., Yu Q., Tian Y. Q., Becker B. L., Siqueira P., Torbick N. (2018). Spatio-temporal variations of CDOM in shallow inland waters from a semi-analytical inversion of Landsat-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 218, 189–200. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.09.014
Liu Y., Tang D., Deng R., Cao B., Chen Q., Zhang R., et al. (2020). An adaptive blended algorithm approach for deriving bathymetry from multispectral imagery. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 14, 801–817. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.4609443
Lowell K., Hermann J. (2024). Accuracy of bathymetric depth change maps using multi-temporal images and machine learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 12, 1401. doi: 10.3390/jmse12081401
Lyzenga D. R. (1978). Passive remote sensing techniques for mapping water depth and bottom features. Appl. Optics 17, 379–383. doi: 10.1364/AO.17.000379
Lyzenga D. R. (1985). Shallow-water bathymetry using combined lidar and passive multispectral scanner data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 6, 115–125. doi: 10.1080/01431168508948428
Lyzenga D. R., Malinas N. R., Tanis F. J. (2006). Multispectral bathymetry using a simple physically based algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 44, 2251–2259. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2006.872909
Ma Y., Xu N., Liu Z., Yang B., Yang F., Wang X. H., et al. (2020). Satellite-derived bathymetry using the ICESat-2 lidar and Sentinel-2 imagery datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 250, 112047. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2020.112047
Misra A., Vojinovic Z., Ramakrishnan B., Luijendijk A., Ranasinghe R. (2018). Shallow water bathymetry mapping using Support Vector Machine (SVM) technique and multispectral imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 39, 4431–4450. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2017.1421796
Qin X., Wu Z., Luo X., Shang J., Zhao D., Zhou J., et al. (2024). MuSRFM: Multiple scale resolution fusion based precise and robust satellite derived bathymetry model for island nearshore shallow water regions using sentinel-2 multi-spectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 218, 150–169. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.09.007
Richardson G., Foreman N., Knudby A., Wu Y., Lin Y. (2024). Global deep learning model for delineation of optically shallow and optically deep water in Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 311, 114302. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114302
Sagawa T., Yamashita Y., Okumura T., Yamanokuchi T. (2019). Satellite derived bathymetry using machine learning and multi-temporal satellite images. Remote Sens. 11, 1155. doi: 10.3390/rs11101155
Shen W., Chen M., Wu Z., Wang J. (2023). Shallow water bathymetry retrieval based on an improved deep learning method using GF-6 multispectral imagery in nanshan port waters. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3310166
Stumpf R. P., Holderied K., Sinclair M. (2003). Determination of water depth with high-resolution satellite imagery over variable bottom types. Limnol Oceanography 48, 547–556. doi: 10.4319/lo.2003.48.1_part_2.0547
Vahtmae E., Kutser T. (2016). Airborne mapping of shallow water bathymetry in the optically complex waters of the Baltic Sea. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 10, 25012. doi: 10.1117/1.Jrs.10.025012
Vanhellemont Q., Ruddick K. (2016). “Acolite for Sentinel-2: Aquatic applications of MSI imagery”, in Proceedings of the 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic.
Vinayaraj P., Raghavan V., Masumoto S. (2016). Satellite-derived bathymetry using adaptive geographically weighted regression model. Mar. Geodesy 39, 458–478. doi: 10.1080/01490419.2016.1245227
Wu Z., Mao Z., Shen W. (2021). Integrating multiple datasets and machine learning algorithms for satellite-based bathymetry in seaports. Remote Sens. 13, 4328. doi: 10.3390/rs13214328
Keywords: water depth inversion, random forest, coordinate attention, bathymetric mapping, turbid waters
Citation: Fang S, Wu Z, Wu S, Chen Z, Shen W and Mao Z (2024) Enhancing Water depth inversion accuracy in turbid coastal environments using random forest and coordinate attention mechanisms. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1471695. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1471695
Received: 28 July 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 07 November 2024.
Edited by:
Panagiotis Agrafiotis, Technical University of Berlin, GermanyReviewed by:
Lukasz Janowski, Gdynia Maritime University, PolandCopyright © 2024 Fang, Wu, Wu, Chen, Shen and Mao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhongqiang Wu, d3V6aG9uZ3FpYW5nMjAwOEBxcS5jb20=; Shulei Wu, d3NsQGhhaW5udS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.