
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci. , 08 October 2024
Sec. Marine Affairs and Policy
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1471467
This article is part of the Research Topic Challenges and Solutions in Forecasting and Decision-Making in Marine Economy and Management View all 22 articles
 Xina Ji1
Xina Ji1 Xingong Ding2,3*
Xingong Ding2,3*Introduction: Coastal tourism has become an important pillar of economic growth in China's coastal regions, yet no quantitative research has analyzed the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution.
Methods: This study, within a multivariate framework, comprehensively examines the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution by employing various econometric techniques and focusing on four different types of marine pollutant discharges: chemical oxygen demand (COD), petroleum (PET), ammonia nitrogen (NHN), and total phosphorus (TP).
Results and discussion: Panel cointegration tests confirm a long-term relationship between coastal tourism and these four types of marine pollutant discharges. In the long run, coastal tourism has a significantly negative impact on COD, NHN, and TP. The results of Pooled Mean Group (PMG), Fully Modified Ordinary Least Squares (FMOLS), and Dynamic Ordinary Least Squares (DOLS) estimators show that for every 1% increase in coastal tourism revenue (TOUR), COD decreases by 0.734%, 0.536%, and 0.952% respectively; NHN decreases by 0.746%, 0.340%, and 1.633%; and TP decreases by 5.169%, 0.899%, and 0.334% respectively. However, the impact of coastal tourism on PET is not significant. The Dumitrescu-Hurlin (D-H) panel causality test results indicate different causality patterns between coastal tourism and various marine pollutant discharges. Specifically, there is a bidirectional causality between coastal tourism and COD, NHN, and a unidirectional causality between coastal tourism and PET, TP. Moreover, heterogeneity analysis reveals that coastal tourism does not significantly reduce all marine pollutant discharges in low-and middle-income coastal regions. Furthermore, compared to the central and southern coastal regions, the coastal tourism of northern regions has not significantly reduced marine pollution. This study can provide policymakers with references for developing coastal tourism and reducing marine pollutant discharges.
In regional economic development and citizens’ lives, the importance of tourism is increasingly prominent (Zhang and Xing, 2023). Coastal tourism, as a significant branch of tourism activities, has become an important pillar industry for the economic development of China’s coastal regions, owing to its superior resource endowment and proactive policy guidance (Liu et al., 2020; Ji and Wang, 2022; Wang et al., 2023). China boasts an 18,000-kilometer coastline, with many famous scenic spots and beautiful coastal landscapes along its coastal regions (Wang et al., 2022). In 2019, China’s coastal tourism industry maintained steady growth, achieving an added value of 1.757 trillion yuan for the year, accounting for 50.6% of the added value of major marine industries (MNRC, 2019). As the largest contributor to the added value of marine industries, coastal tourism has driven the development of the marine economy in China’s coastal regions. In the future, coastal tourism is expected to expand the recreational use of oceans and coasts, bringing more positive economic benefits to coastal regions (Yang et al., 2021).
With the continuous expansion and rapid development of coastal tourism in China, significant environmental pressures have inevitably emerged, leading to an increasing conflict between coastal tourism and the environment (Liu et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2022). Previous domestic and international studies have highlighted that coastal tourism has caused multiple forms of damage to coastal ecosystems and the environment. Specifically, excessive development in coastal regions has resulted in metal pollution on beaches (Vetrimurugan et al., 2017) and degradation of beach ecosystems (Buzzi et al., 2022). Activities such as snorkeling and diving disrupt and damage marine habitats (Beeharry et al., 2021), while littering by tourists harms the beach environment (Maione, 2021). The disposal of solid waste, such as plastics, indirectly damages ecosystems (Ronda et al., 2023). Additionally, the massive consumption of energy alters atmospheric greenhouse effects, contributing to climate change (Saenz-de-Miera and Rosselló, 2014; Robaina et al., 2020; Gao and Zhang, 2021). The increase in tourist numbers has also led to the deterioration of water quality in coastal regions (Nuzula et al., 2017; Kurniawan et al., 2023). Therefore, coastal regions are facing a significant challenge in balancing coastal tourism with environmental pollution, making exploring the relationship between the two particularly urgent.
The deterioration of the marine environment is closely related to various factors such as extensive economic development (Shao, 2020; Wang et al., 2020), technological innovation (Shao, 2020), urbanization (Xu and Zhang, 2022), industrial structure (Wang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2023), and human activities (Crain et al., 2009). However, coastal tourism, one of the frequent human activities, may also impact the marine environment, though this issue remains inconclusive and lacks systematic research. Some scholars have explored the potential impact of coastal tourism on the marine environment from a qualitative perspective. Kocasoy (1989) investigated the potential link between coastal tourism, marine pollution, and public health by surveying coastal tourist destinations in Turkey. The study pointed out that tourism is considered a major source of pollution in coastal regions. Beeharry et al. (2021) also analyzed the impact of coastal tourism activities on the marine environment in Mauritius through a questionnaire survey. The results showed a significant negative linear relationship between tourism activities and the marine environment. Specifically, operators of recreational activities and tourists believed that fuel-powered maritime activities caused significant harm to the ocean. Additionally, recreational tourism activities can disrupt natural marine habitats and lead to the loss of marine biodiversity, one of the most apparent negative impacts on the marine environment. Burak et al. (2004) conducted a comprehensive assessment of the effects of coastal tourism on Turkey’s coastal regions. Expanding economic activities such as tourism development and resort projects directly damaged coastal regions’ ecological environment and cultural assets. Zahedi (2008), through a review of research related to tourism and the environment, summarized the impacts of coastal tourism on the coastal environment. The study highlighted that eco-tourism in coastal areas does not necessarily benefit the ecosystem, as governments often prioritize economic development over environmental sustainability. Tourism’s uncontrolled and rapid growth poses a risk of gradual degradation to coastal ecosystems.
Exploring the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution from a qualitative perspective is not sufficiently comprehensive, making it essential to conduct quantitative analyses. Approximately 80% of pollutants in the marine environment originate from land-based activities such as industry, agriculture, and urbanization (Hildering et al., 2009). These land-based pollutants enter the ocean either through direct discharge or via rivers, posing significant threats to marine ecosystems (Liu et al., 2011; Zhao et al., 2020). For instance, organic pollutants can deplete dissolved oxygen in seawater through aerobic decomposition, endangering marine life (Lim et al., 2006). Additionally, marine eutrophication can lead to frequent red tides, ocean acidification, and hypoxia (Fan et al., 2019). Therefore, monitoring pollutant discharge in estuarine areas is crucial for effectively preventing marine pollution. In China, direct marine discharge outlet monitoring has revealed that the primary pollutants discharged into major estuarine areas include COD, PET, NHN, and TP (Chen and Qian, 2020). Based on the pollution levels and data availability of these pollutant discharges in the surrounding oceans of China, this study selects these four types of marine pollutant discharges to investigate whether and to what extent coastal tourism impacts marine pollution. To achieve this objective, we obtained data on the major pollutants from direct ocean discharge sources from the Bulletin of Marine Ecology and Environment Status of China and employed various econometric methods to quantitatively analyze the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution.
First, we conducted the CD test to examine whether there is cross-sectional dependence among all variables. The results rejected the null hypothesis at the 1% significance level, indicating that shocks in one province affect other provinces. Next, we applied panel unit root tests to assess the stationarity of the variables. The results showed that some variables were non-stationary at the level, but all variables became stationary after first-order differencing. Subsequently, we performed panel cointegration tests to determine whether there is a long-term relationship between the variables. The results indicated a long-term relationship between coastal tourism and the four types of marine pollutant discharges. Given the cointegration relationship among the variables, we further used PMG, FMOLS, and DOLS estimators to estimate the coefficients of the respective variables. The findings suggest that coastal tourism has a significant long-term negative impact on COD, NHN, and TP, implying that developing coastal tourism helps reduce these three pollutant discharges and mitigate marine pollution. However, coastal tourism did not significantly impact TP, primarily related to the main sources of petroleum pollutants in the ocean. Additionally, we applied the D-H panel causality test to analyze the causal relationships between these variables. The study revealed different causality patterns between coastal tourism and various marine pollutant discharges. We also considered the heterogeneity of the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution. The results indicated that coastal tourism in low- and middle-income coastal regions does not have a significant negative impact on all marine pollutant discharges as it does in high-income coastal regions. Furthermore, the heterogeneity analysis based on geographic regions showed that the northern coastal regions did not significantly reduce marine pollution. In contrast, the central and southern coastal regions demonstrated more favorable outcomes.
This study makes significant contributions to the existing literature in three key areas. First, we are among the first to employ econometric methods to quantitatively analyze the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution, providing robust empirical support for exploring the relationship between the two. Second, we delve into whether this relationship varies across different types of marine pollutant discharges, offering a new perspective on the impact of coastal tourism on various pollutant discharges. Finally, this study examines the heterogeneity of the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution by categorizing coastal regions based on income levels and geographical location. By identifying these differences, our research provides scientific evidence for local governments and relevant authorities to formulate more precise and effective environmental policies and development plans, helping to address marine pollution issues better.
This study aims to explore the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution. We analyzed of 11 coastal regions in China, including Zhejiang, Tianjin, Shanghai, Shandong, Liaoning, Jiangsu, Hebei, Hainan, Guangxi, Guangdong, and Fujian. These coastal regions cover 1.302 million square kilometers, accounting for 13.57% of China’s total land area (Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China, n.d.). In 2019, the total population of these coastal regions was 613.22 million, representing 45.02% of China’s total population. The combined GDP of these regions amounted to 52,193.677 billion yuan, accounting for 52.97% of China’s total GDP (NBSC, 2020). This highlights the critical role coastal regions play in China’s overall development and global economic competitiveness (Wang et al., 2020). Additionally, in 2019, the total wastewater discharge from direct ocean discharge sources in China’s coastal regions reached as high as 8.011 billion tons (MNRC, 2019). Therefore, to better promote the coordinated development between coastal tourism and the marine ecological environment in coastal regions, this study selected these 11 coastal regions as the research sample for in-depth analysis. The study areas are shown in Figure 1.
This study covers the period from 2006 to 2019. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic spread rapidly. The Ministry of Culture and Tourism of China issued a notice on January 26, 2020, suspending all tourism activities to address the pandemic. This measure directly led to a severe blow to China’s tourism industry, causing a sharp decline in tourism revenue (Wu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022; Ran et al., 2023). Due to the impact of COVID-19, data from 2020 onwards are difficult to reflect the normal state of economic activities. Therefore, considering data availability and consistency in statistical standards, this study analyzes data from 2006 to 2019.
The dependent variable in this study is marine pollution, measured using the discharges of four major pollutants directly discharged into the ocean from coastal regions in China. Land-based pollution is the primary source of marine pollution (Hildering et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2020), and monitoring direct marine discharge outlets allows for a more intuitive and effective assessment of the degree of marine pollution. In China’s marine pollution context, the main pollutants directly discharged into the ocean include COD, PET, NHN and TP (Yuan and Xiang, 2018; Chen and Qian, 2020). The discharge data for these pollutants have been widely used in various research analyses (Zhang et al., 2017; Yuan and Xiang, 2018; Chen and Qian, 2020; Peng et al., 2023). Although the Bulletin of Marine Ecology and Environment Status of China also covers various pollution sources such as riverine sources, deposition of atmospheric pollutants, and marine litter and microplastics, these were not included in this study due to data availability and discontinuity in time series.
This study considers coastal tourism revenue as an independent variable. Referring to Liu et al. (2017), we used the ratio of total tourism revenue to GDP in coastal cities as a proxy variable for coastal tourism. To ensure the accuracy and rigor of the research, we compiled and aggregated the total tourism revenue data from coastal cities in 11 coastal provinces, representing the coastal tourism revenue of each province. The data is sourced from the China Statistical Yearbook.
This study employs four control variables. First, the Gross Ocean Product (GOP) represents the final output of marine economic activities in coastal regions within a certain period. It is obtained by summing the added value of three types of marine industries and effectively reflects the level of marine economic development in coastal regions. Referring to Shao et al. (2021), we used per capita GOP with data from the China Marine Statistical Yearbook. The population variable is derived by summing the populations of coastal cities within each coastal province with data from the China Statistical Yearbook. Strict environmental regulations can effectively control pollutant discharges and improve marine environmental quality (Sun et al., 2023). Therefore, this study uses the proportion of industrial pollution control investment to GDP as the environmental regulation variable, following Liu et al. (2021). Technological innovation can alleviate the ecological pressure on the marine environment (Shao, 2020; Ren and Ji, 2021). Based on the study by Su et al. (2021), we used the number of personnel engaged in scientific and technological activities in marine R&D institutions as the technological innovation variable, with data from the China Marine Statistical Yearbook. To ensure comparability and robustness in the panel data analysis, all variables used in this study have been ln-transformed to mitigate the impact of different dimensions. Table 1 presents the variable sources and descriptions, while Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics.
This study employs the STIRPAT model (Stochastic Impacts by Regression on Population, Affluence, and Technology) developed by Dietz and Rosa (1994) and York et al. (2004) to determine the selection of variables. This model is widely used to assess the impact of driving forces on ecological environmental changes and can estimate the causal effects represented by the model coefficients (Wei, 2011). The basic formula of the STIRPAT model is:
where I represents the environmental impact caused by humans, P denotes the population size, A stands for affluence, T signifies the level of technology. And a represents the model’s constant coefficient, b, c, and d denote the underestimated parameters, and signifies the error term. After taking the logarithm of the model, it can be rewritten as:
The STIRPAT model allows for the estimation of various coefficients as parameters and the appropriate decomposition of each factor. However, the basic model no longer meets the complex demands of modern research. Therefore, based on the characteristics and content of the study, we can incorporate additional factors into the basic STIRPAT model to explore their impact on environmental stress (Wang et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2021). To comprehensively analyze the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution, this study expands the basic STIRPAT model, drawing on and referencing previous literature to meet the design requirements of this research. Referring to Liddle (2014); Koçak et al. (2020) and Ahmad and Ma (2022), we incorporated coastal tourism as an affluence factor into the STIRPAT model. Following Liu et al. (2019) and Song et al. (2020), we include environmental regulation variables in the model. The dependent variables of this study are four types of marine pollutant discharges. Therefore, the expanded formula is as follows:
In the four models mentioned above, the dependent variables are four types of marine pollutant discharges: COD, PET, NHN, and TP. The independent variable is coastal tourism revenue (TOUR), and the control variables include Environmental Regulation (ER), GOP, Technological Innovation (TECH), and Total Population (POP). The parameters , , and represent the coefficients for the corresponding variables in each of the four models, respectively. The variable t denotes time, and i represents the provinces. The terms , , and represent the error terms in each of the four models, respectively.
Due to spillover effects, spatial effects, or unobserved common factors, cross-sectional dependence may exist in panel data models, leading to estimation errors (Liddle, 2012; Rahman et al., 2021). In the context of China’s macroeconomic development and regional connections, there are close links between provinces. When one province experiences a shock, it inevitably impacts other provinces. Therefore, to prevent biases in the statistical analysis of panel data in this study, we use the CD test proposed by Pesaran (2004) to examine whether there is cross-sectional dependence in the panel data. Conducting the CD test is a necessary step before panel data analysis. This test analyzes whether there is cross-sectional dependence in the error terms by eliminating the mean during the computation process (Khan et al., 2019). Typically, the null hypothesis is that the error terms in the panel data are cross-sectionally independent (Saqib and Benhmad, 2021). It is worth noting that this test can effectively identify cross-sectional dependence in the data even when the dependence is weak and can handle non-normally distributed random errors (Perone, 2024). The equation for the CD test used in this study is as follows:
N represents the cross-sectional units, T denotes the time dimension, and i and j respectively stand for the elements of the connection matrix. The represents the pairwise correlation of the residuals obtained from OLS estimation. Even when the sample size N and time T are small, the CD test can still provide robust and accurate results for small samples (Islam et al., 2022; Perone, 2024). To ensure the accuracy of subsequent analysis results, this study employs tools and techniques that can yield robust results even in the presence of cross-sectional dependence.
Before conducting the cointegration tests, we need to check whether all variables have unit roots. To ensure the robustness of the test results, this study employs both first-generation and second-generation panel unit root tests. Since first-generation panel unit root tests are not suitable for situations with cross-sectional dependence, which may lead to spurious regression (Iqbal et al., 2023), we use the second-generation panel unit root test, the CIPS test proposed by Pesaran (2007), to address this issue. The CIPS test can detect and eliminate cross-sectional dependence in our panel data (Bangake and Eggoh, 2011). The null hypothesis of the CIPS test is that all variables in the panel data are non-stationary (Bildirici, 2017), and its equation is expressed as follows:
Among them, represents the variables, represents the deterministic components, represents the significance level, and represents the error term. The statistical equation for the CIPS test is as follows, where represents the t-statistic of .
The panel cointegration test is used to examine whether there is a long-term convergence relationship between two or more non-stationary time series variables (Muye and Muye, 2017). The panel cointegration tests by Kao (1999) and Pedroni (1999) are commonly used methods, but they require cross-sectional independence. If cross-sectional dependence exists, it can lead to biased results (Islam et al., 2022). In contrast, the Westerlund and Edgerton (2007) and the Westerlund ECM cointegration tests can avoid this issue. This study focuses on the Westerlund ECM cointegration test, and its error correction equation is presented as follows:
Among them, represents the coefficient of the error correction term. To test for cointegration among the variables, there are two sets of statistical data: two panel statistics and two group-mean statistics. The and statistics are used to determine the existence of cointegration in a cross-sectional unit. The equations for these statistics are as follows:
The and statistics are used to determine the existence of cointegration across the entire panel. The equations for these statistics are as follows:
Pesaran et al. (1999) developed the PMG estimator to estimate the short-term and long-term impact coefficients between variables. The unique feature of PMG is that it allows for different intercepts, short-term coefficients, and error variances across different groups, while assuming that the long-term coefficients are the same across all cross-sections (Cetin et al., 2022; Saidmamatov et al., 2023). This characteristic limit the homogeneity of long-term relationships among provinces in panel data while allowing for heterogeneity in short-term relationships (Iqbal et al., 2023). Compared to DOLS and FMOLS, a significant advantage of PMG is its ability to assess short-term dynamics in the model. Moreover, PMG is applicable regardless of whether the variables used in the analysis are I(0) or I(1) (Hongxing et al., 2021).
The PMG estimator assumes that all variables in the model have a long-term relationship. Additionally, PMG is based on the ARDL model, where is the lag order of the dependent variable, and is the lag order of the independent variables. Therefore, the equation for PMG in the form of error correction mechanism is expressed as follows:
Where , represents the error correction term, defines the speed of adjustment, represents the long-term coefficients, and represent the short-term coefficients for the dependent and independent variables, respectively, and is the error term.
When there is a cointegration relationship among the variables in the panel series, issues of autocorrelation and endogeneity can lead to biased coefficients obtained by OLS estimation. FMOLS and DOLS estimators can correct these biases, ensuring the accuracy of the estimates. Additionally, these two estimators can maintain the robustness of the results even with small sample sizes (Rahman et al., 2021).
The FMOLS estimator, as proposed by Pedroni (2000), uses a non-parametric approach by integrating semi-parametric corrections into the OLS estimation to address biases caused by endogeneity and serial correlation. The equation for the FMOLS estimator is expressed as follows:
represents the parameter estimated using FMOLS for each individual in the panel data. The equation for the corresponding t-statistic is expressed as follows:
The DOLS estimator, as developed by Kao and Chiang (2000), uses a parametric approach by incorporating the lagged and lead values of the explanatory variables to eliminate issues of endogeneity and serial correlation. Monte Carlo simulations have shown that, compared to OLS and FMOLS, the parameter estimation bias of DOLS is smaller (Khan et al., 2019; Rahman et al., 2021). The equation for the DOLS estimator is expressed as follows:
Where, and represent the number of lagged and lead terms, respectively.
The above panel estimators do not fully confirm the causality and its direction between the variables. Therefore, we adopt the panel causality test by Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) to evaluate the causality between coastal tourism and four types of marine pollutant discharges. The unique advantage of the D-H causality test is that it performs well even in the presence of cross-sectional dependence among provinces, making it widely regarded as an advanced version of the Granger causality test (Iqbal et al., 2023). The equation for the D-H panel causality test is expressed as follows:
Where, represents the autoregressive parameters, and represents the regression coefficients. The null hypothesis of the D-H causality test is that there is no causality across all cross-sections, while the alternative hypothesis is that there is at least one causal relationship in the panel data.
To explore the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution, a series of pre-analysis tests, including the CD test, panel unit root tests, and panel cointegration tests, need to be conducted.
First, the results of the CD test in Table 3 indicate that the null hypothesis of no cross-sectional dependency is rejected for all variables at the 1% significance level, supporting the alternative hypothesis of the existence of cross-sectional dependency among the variables. This suggests that there is cross-sectional dependence and interrelation among the variables within the same period, which further ensures the reliability of subsequent tests and analysis results.
The unit root test requires that the data be stationary at level or first-order difference. Due to the limitations of each testing method, we employed both first-generation unit root tests, including LLC, IPS, ADF-Fisher, and PP-Fisher, as well as the second-generation unit root test, CIPS. The null hypothesis for all five different types of unit root tests is that all panels contain a unit root. The results of the unit root tests in Table 4 show that some variables are non-stationary at the level. However, after taking the first-order differencing, all variables reject the null hypothesis of having a unit root, indicating that all variables are stationary after the first-order differencing.
This study uses the Pedroni (1999), Kao (1999), Westerlund and Edgerton (2007), and Westerlund ECM cointegration tests to examine whether there is a long-term relationship between the analyzed variables in the four models. The null hypothesis for all four cointegration tests is the absence of a cointegration relationship. Table 5 reports the results of the cointegration tests. The results of the Pedroni (1999) cointegration test show that for different dependent variables in the four models, the null hypothesis of no cointegration relationship is rejected at the 1% significance level. The panel cointegration test results of Kao (1999) similarly indicate that the null hypothesis is rejected for all four models, supporting the alternative hypothesis of the existence of a panel cointegration relationship. The cointegration test results of Westerlund and Edgerton (2007) reveal a long-term relationship among the estimated variables in the four models. In the Westerlund ECM cointegration test, the null hypothesis of the Gt and Ga statistics is that there is no cointegration relationship for all cross-sectional units, while the null hypothesis of the Pt and Pa statistics is that there is no cointegration relationship for the entire panel. The results indicate that there is a cointegration relationship in the four models, both for the entire panel and for individual cross-sectional units. In summary, all four cointegration tests demonstrate the existence of a long-term equilibrium relationship among the analyzed variables in these four models.
The panel cointegration test can determine whether there is a long-term relationship between variables. However, it cannot ascertain the specific coefficients of the variables in the long-term relationship. Therefore, we employed the PMG, FMOLS, and DOLS estimators to estimate the corresponding variable coefficients. These three estimators require that the variables are stationary after first-order differencing and that the variables have a cointegration relationship. After meeting these conditions, this study aims to estimate the long-term impact coefficient of coastal tourism on marine pollution. The PMG estimator can estimate short-term and long-term coefficients in the model, while the FMOLS and DOLS estimators rigorously examine the long-term effects. The coefficient estimates for each variable across the four models are presented in Table 6. Most of the estimators show similar results regarding the signs and statistical significance of the coefficients.
For the PMG estimator, the error correction coefficients for the four models are -0.772, -1.207, -0.579, and -0.421, respectively, all significant at the 1% level. This indicates that when other variables deviate from the long-term equilibrium, the error term will pull the deviation back towards the long-term equilibrium state at an annual rate of 0.772, 1.207, 0.579, and 0.421, respectively. In the short term, the impact of coastal tourism on these four types of marine pollution discharges is not significant, as marine pollution is a cumulative process that does not manifest its effects in the short term. Additionally, the control variables do not have a significant short-term impact on marine pollution.
The regression results of Model 1 indicate that, according to the PMG, FMOLS, and DOLS estimators, TOUR has a significantly negative long-term impact on COD, with a 1% increase in TOUR leading to a reduction in COD by 0.734%, 0.536%, and 0.952%, respectively. Conversely, GOP positively impacts on COD, with a 1% increase in GOP resulting in an increase in COD by 0.346%, 4.004%, and 1.030%, respectively. Additionally, TECH shows a significantly negative impact on COD. In the results of Model 2, TOUR does not significantly affect PET for any of the three estimators, though TECH among the control variables exhibits a suppressive effect on PET. The results of Model 3 demonstrate that TOUR reduces NHN, with a 1% increase in TOUR leading to a reduction in NHN by 0.746%, 0.340%, and 1.633%, respectively. While POP positively impacts NHN, increases in TECH and GOP contribute to reductions in NHN. Similarly, the results of Model 4 reveal that TOUR has a significantly negative impact on TP across all three estimators, with a 1% increase in TOUR leading to a reduction in TP by 5.169%, 0.899%, and 0.334%, respectively. In contrast, both GOP and POP have positive effects on TP.
The previous section explored the cointegration relationships between the variables and the estimation of the associated coefficients, but it did not consider the direction of causality between the variables. The panel causality test by Dumitrescu and Hurlin (2012) effectively investigates the direction of causality between variables. In Table 7, we can see that TOUR exhibits a bidirectional causal relationship with COD and NHN, while it shows a unidirectional causal relationship with PET and TP. Regarding the control variables, ER has a unidirectional causal relationship with TP and no causal relationship with the other three pollutant discharges. GOP has a unidirectional causal relationship with COD, NHN, and TP, but a bidirectional causal relationship with PET. TECH shows no causal relationship with COD, PET, or TP, but only has a unidirectional causal relationship with NHN. POP has a unidirectional causal relationship with all four pollutant discharges.
This section will explore heterogeneity analysis based on income levels and geographic regions, with the specific regional divisions presented in Table 8. Compared to the PMG estimator, FMOLS remains applicable even in small sample sizes (Rahman et al., 2021). Additionally, FMOLS is a parametric method that corrects for endogeneity and serial correlation errors to obtain results, whereas DOLS is merely a parametric approach (Doğanalp et al., 2023). Therefore, due to the accuracy and robustness of FMOLS, we used this estimator for the heterogeneity analysis.
The results of the heterogeneity analysis are presented in Figure 2. Overall, TOUR exhibits significant heterogeneity in its impact on various pollutant discharges across different income levels and geographic regions. Specifically, while TOUR has a significantly negative effect on COD across high-, middle-, and low-income coastal regions, the magnitude of the coefficients varies considerably. For high- and middle-income coastal regions, a 1% increase in TOUR reduces COD by 1.467% and 1.672%, respectively. However, for low-income coastal regions, COD decreases by only 0.277%. Additionally, there are noticeable differences in TOUR’s impact on COD across different geographic regions, with the largest coefficient observed in the southern coastal regions, followed by the central coastal regions, and the smallest effect in the northern coastal regions, where the coefficient is only 0.179. TOUR’s impact on PET remains largely insignificant across different income levels and geographic regions, consistent with the previous regression results. The only exception is that TOUR significantly negatively affects PET in high-income coastal regions. TOUR’s impact on NHN is also negative across provinces of varying income levels. However, it is noteworthy that a 1% increase in TOUR in low-income coastal regions leads to only a 0.061% reduction in NHN. Moreover, TOUR has no significant effect on NHN in the northern coastal regions, while the southern coastal regions show the largest coefficient. TOUR does not significantly impact TP in middle- and low-income coastal regions but shows a significantly negative effect in high-income coastal regions. From a geographic perspective, TOUR has no significant impact on TP in the northern coastal regions. In contrast, in the central and southern coastal regions, a 1% increase in TOUR reduces TP by 0.273% and 0.296%, respectively.
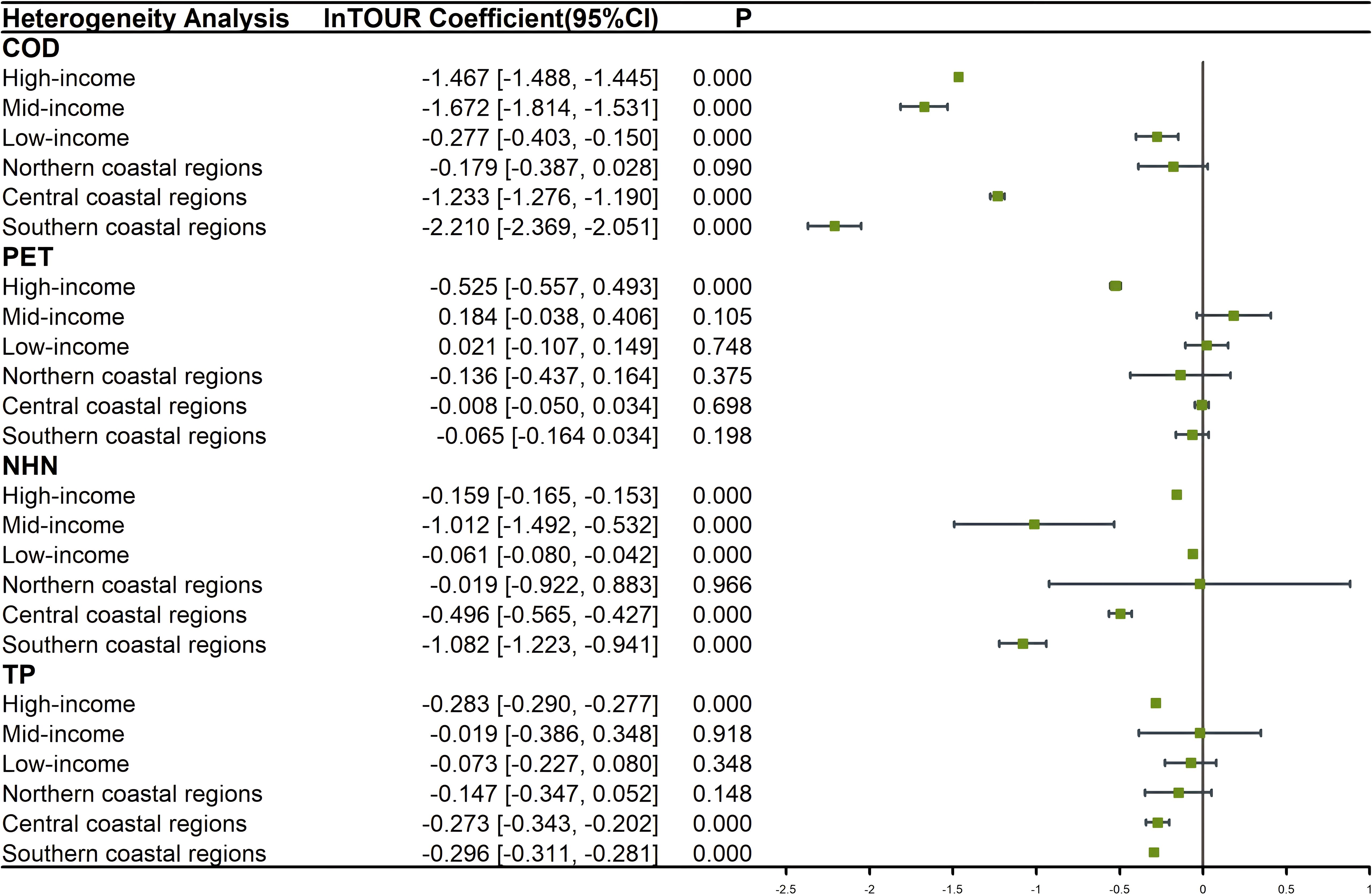
Figure 2. Results of heterogeneity analysis based on income level and geographical regional comparison.
Coastal tourism has a negative impact on the discharge of pollutants such as COD, NHN, and TP, indicating that the development of coastal tourism contributes to the reduction of marine pollution. By enhancing economic benefits and raising environmental awareness, coastal tourism reduces pollutant discharge into the ocean on two levels, thereby effectively improving and protecting the marine environment (Song, 2016). Specifically, on the one hand, coastal tourism generates significant fiscal revenue for both local communities and governments, which can be used to protect and manage sensitive marine environments (Davenport and Davenport, 2006; Liu et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). For example, revenue from tickets for marine recreational activities such as yachting, sailing, diving, snorkeling, and water parks, as well as franchise fees paid by companies involved in these activities, provide ample financial support for government efforts in marine environment management and pollution control. On the other hand, coastal tourism effectively raises public environmental awareness (Chen et al., 2023). Through frequent interaction with the ocean and beaches, tourists gradually recognize the importance of marine environmental protection, value marine resources more highly, and actively participate in conservation efforts. For residents, coastal tourism not only brings economic benefits but also encourages them to consciously maintain the environment and actively promote environmental awareness, creating a positive cycle of marine environment protection. However, coastal tourism has no significant impact on PET, suggesting that the development of coastal tourism has not effectively reduced PET into the ocean. With the growing global demand for oil, activities related to oil extraction, refining, and maritime transportation are becoming increasingly frequent. During these processes, leakage incidents from oil wells, pipelines, drilling platforms, or transport tankers are common, leading to an increase in oil spills, which directly cause severe harm to the marine environment (Barakat et al., 1999; Xue et al., 2015). Because coastal tourism has limited direct influence on these PET-related activities, it has not significantly impacted PET.
Stricter environmental regulations and increased investment in pollution control, although considered effective in improving marine environmental quality and reducing pollutant discharges, do not significantly or consistently impact the discharge of the four types of marine pollutants, according to our research findings. This indicates that China’s investment in marine environmental pollution control remains insufficient, and there is a need for greater investment in marine environmental management in coastal regions in the future. This conclusion aligns with the findings of Liu et al. (2022). The study also found that the GOP has a positive impact on COD and TP, indicating that the development of China’s marine economy has exacerbated the discharge of these pollutants, consistent with the findings of Peng et al. (2020). Conversely, the impact of GOP on PET and NHN is mostly significantly negative, suggesting that the development of the marine economy has, to some extent, alleviated the environmental pressure caused by these pollutant discharges, a result consistent with Shao (2020). Furthermore, the research shows that marine technological innovation exhibits a strong negative correlation with marine pollution when using FMOLS and DOLS estimators, indicating that technological innovation positively reduces marine pollution. Promoting technological innovation can facilitate low-pollution production, thereby helping to improve marine pollution. This conclusion is consistent with the findings of Wang et al. (2019) and Shao (2020). Regarding the population variable, most results show a positive correlation between population size and marine pollution. This suggests that as the population of coastal cities grows, pollutant discharges also increase, placing greater pressure on the marine environment, the conclusion consistent with the findings of Li et al. (2019).
The following bidirectional causal relationships exist between coastal tourism and COD, NHN. A decline in environmental quality directly reduces tourist destinations’ attractiveness, while tourism’s economic benefits provide local governments with more funds for environmental protection and pollution control (Zhang and Gao, 2016). Regarding PET and TP, there is a unidirectional causal relationship with coastal tourism, indicating that the development of coastal tourism impacts their discharge into the ocean. This finding is consistent with the study by Ahmad and Ma (2022). Regarding environmental regulation, we found a unidirectional causal relationship only with TP, suggesting that increased investment in governance can effectively reduce marine pollution by improving pollutant treatment facilities and promoting ecological restoration (Zeng et al., 2019; Chen and Qian, 2020). However, there is no causal relationship between environmental regulation and the other three marine pollutant discharges, indicating that current environmental governance efforts are insufficient to control the discharges of these pollutants effectively (Liu et al., 2022). There is a bidirectional causal relationship between GOP and PET, suggesting that marine economic activities affect pollutant discharges, while changes in the marine environment, in turn, influence the development of the marine economy (Li et al., 2023). For example, maritime transport, aquaculture, and energy development increase marine pollution, while the deterioration of the marine environment leads to sea-level rise, ecosystem destruction, and energy depletion, thereby impacting economic development. Additionally, there are unidirectional causal relationships between GOP and the other three pollutant discharges, with many studies providing ample evidence that marine economic development has a direct or indirect significant impact on marine pollution (Shao, 2020; Ren and Ji, 2021; Shao et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021). There is a unidirectional causal relationship between marine technological innovation and NHN, indicating that technological advancements are important in reducing marine pollution (Shao, 2020; Zheng et al., 2020). For instance, improvements in pollutant treatment technology, ecological restoration technology, and clean energy technology can more efficiently control and manage marine pollution. Finally, there is a unidirectional causal relationship between coastal population and these marine pollutant discharges, indicating that as population size increases, pollution issues worsen, placing greater pressure on the marine environment (Li et al., 2019).
In high-income coastal regions, coastal tourism has a significant long-term negative impact on marine pollution. These regions typically possess more abundant financial resources, enabling them to implement more effective measures for controlling marine pollution. The economic benefits generated by coastal tourism can be effectively channeled into protecting and managing the marine environment, thereby reducing marine pollution issues over the long term. In contrast, the impact of coastal tourism on marine pollution in middle- and low-income coastal regions is inconsistent and does not uniformly exert a negative influence on all types of marine pollutant discharges. Due to the relatively limited financial resources and environmental management capabilities in middle- and low-income coastal regions, marine environmental protection facilities are often not at a high level. Additionally, environmental awareness regarding marine protection in these regions is relatively weak. As a result, the effectiveness of coastal tourism in reducing marine pollution in these regions is less evident than in high-income coastal regions.
In the northern coastal regions, coastal tourism development has not significantly reduced marine pollution. Liaoning, Hebei, Tianjin, and Shandong are key industrial provinces in China, playing a crucial role in heavy industries such as steel, machinery, and manufacturing. Due to the large number of pollutants typically emitted by industrial activities, the environmental management revenue generated by coastal tourism is insufficient to offset the negative impact of industrial pollution on the marine environment in these areas. In contrast, coastal tourism has been more effective in reducing marine pollutant discharges in the central and southern coastal regions, with the southern coastal regions standing out. Provinces like Fujian and Guangdong have more mature coastal tourism industries, which generate more significant economic benefits. With more abundant financial resources, the southern coastal regions can invest more in constructing marine environmental protection facilities and pollution control, thereby significantly reducing pollutant discharges and improving the quality of the marine environment. Furthermore, environmental awareness is stronger in the southern coastal regions, where greater emphasis is placed on sustainable development, and environmental pollution is more strictly and effectively regulated. Additionally, the southern coastal regions are at the forefront nationwide in applying environmental and clean energy technologies, which help to more efficiently treat pollutants and reduce the discharge of harmful substances into the ocean. In comparison, the central coastal regions have relatively lower technological levels in this regard, resulting in less effective pollutant reduction efforts than in the southern coastal regions.
This study utilizes data on four different types of marine pollutant discharges from 11 coastal provinces in China from 2006 to 2019 to quantitatively analyze the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution. The research findings can be summarized into the following three points.
1. Coastal tourism has a significant negative impact on COD, NHN, and TP, indicating that the development of coastal tourism can reduce the discharge of these three types of pollutants into the ocean. This effect can be attributed to the economic benefits brought by coastal tourism to coastal regions, and the heightened public awareness of environmental protection. However, the impact of coastal tourism on PET is not significant, as it is related to the primary sources of petroleum pollution in the marine environment.
2. The control variables show varying degrees of significant correlation with marine pollution. Environmental regulation does not significantly and consistently impact marine pollution, indicating that China’s investment in marine environmental pollution management is still insufficient. The influence of GOP on different pollutant discharges varies; while its development alleviates the environmental pressure from some pollutant discharges, it also exacerbates the emission of other pollutants. Marine technological innovation exhibits a strong negative correlation with marine pollution, suggesting that technological advancements contribute to reducing marine pollution. In contrast, the impact of population size on marine pollution is positive, as population growth leads to an increase in pollutant discharges.
3. The heterogeneity analysis based on income level differences reveals that in high-income coastal regions, coastal tourism has a significant negative impact on marine pollution. However, in middle- and low-income coastal regions, coastal tourism does not significantly reduce all types of marine pollutant discharges. This indicates that, due to the limited economic development and financial resources in middle- and low-income coastal regions, marine pollution control and environmental protection have not yet reached high standards. The heterogeneity analysis based on geographic region comparison shows that coastal tourism in the northern coastal regions has not significantly reduced marine pollution. The primary reason is that these provinces are key industrial bases where industrial activities cause substantial pollution to the marine environment. Although coastal tourism generates revenue for environmental management, it is insufficient to offset the negative impacts of industrial activities on the marine environment. In contrast, coastal tourism in the central and southern coastal regions demonstrates a more significant effect in reducing marine pollutant discharges.
Based on the above research findings, we propose the following policy recommendations.
1. To vigorously develop coastal tourism and achieve sustainable development, the government should provide sufficient financial support to coastal regions. This could be done by establishing special funds primarily for infrastructure construction, initiating ecological protection projects, and improving environmental protection facilities. In addition, appropriate policy incentives would also help promote the simultaneous development of coastal tourism and marine environmental improvement. For example, financial subsidies could be offered to enterprises implementing environmental protection measures or reducing pollution, encouraging more coastal businesses to participate in environmental protection efforts. At the same time, raising public environmental awareness is crucial. Local governments and relevant departments should enhance environmental awareness and education within businesses and communities, increasing the environmental consciousness of employees and residents. To achieve broader awareness, media, environmental education programs, and promotional activities can be utilized to enhance public environmental consciousness, encouraging them to actively participate in marine environmental protection and minimize the negative impact on the marine environment during tourism activities.
2. Despite the varying impacts of environmental regulations on different marine pollutant discharges, strengthening and optimizing the enforcement of these regulations remains the most direct and effective means of protecting the marine environment. To achieve this, the government should consider implementing differentiated environmental regulatory measures tailored to specific pollutant discharges, thereby enhancing the precision and effectiveness of related policies. Furthermore, increasing financial investment in marine environmental protection and management is particularly critical, especially in heavily polluted areas, as it can significantly improve local marine ecosystems. Simultaneously, promoting the green development of the marine economy will facilitate industrial upgrading and effectively reduce the proportion of high-pollution industries. The government should also emphasize marine technological innovation by supporting and advancing the research and application of new marine technologies, particularly in pollution control and environmental monitoring. This approach will provide more advanced and effective tools for protecting the marine environment.
3. Compared to high-income coastal regions, the development of coastal tourism in middle- and low-income coastal regions has not yet effectively alleviated marine pollutant discharges. Governments and relevant departments in these regions should actively seek financial support from provincial governments, national bodies, or international environmental organizations. These funds can be utilized not only for implementing marine environmental protection projects and building environmental protection facilities but also for technological research and development to improve the efficiency of marine pollution control. Moreover, the coastal tourism resources in middle- and low-income coastal regions remain underdeveloped. Governments should consider vigorously promoting marine eco-tourism projects, making full use of local natural resources. This approach would help increase local revenue and promote local efforts to protect the marine environment. Additionally, northern coastal regions should focus on adjusting and upgrading their industrial structures. The government can guide the region’s industries to transition from high-pollution heavy industries to low-pollution sectors such as high-tech and coastal tourism. This transition would increase tourism revenue while reducing the negative impact on the marine environment, achieving a win-win situation for economic development and ecological benefits.
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: China Marine Ecological Environment Status Bulletin; China Statistical Yearbook; China Marine Statistical Yearbook.
XJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors would like to thank the Editors and the reviewers for the useful and constructive comments.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ahmad N., Ma X. (2022). How does tourism development affect environmental pollution? Tour. Econ. 28, 1453–1479. doi: 10.1177/13548166211000480
Bangake C., Eggoh J. C. (2011). The Feldstein–Horioka puzzle in African countries: A panel cointegration analysis. Econ. Model. 28, 939–947. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2010.11.011
Barakat A. O., Mostafa A. R., RullkÖtter J., Rahman Hegazi A. (1999). Application of a multimolecular marker approach to fingerprint petroleum pollution in the marine environment. Mar. pollut. Bull. 38, 535–544. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(98)00110-6
Beeharry Y., Bekaroo G., Bussoopun D., Bokhoree C., Phillips M. R. (2021). Perspectives of leisure operators and tourists on the environmental impacts of coastal tourism activities: a case study of Mauritius. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23, 10702–10726. doi: 10.1007/s10668-020-01080-7
Bildirici M. (2017). CO 2 emissions and militarization in G7 countries: panel cointegration and trivariate causality approaches. Environ. Dev. Econ. 22, 771–791. doi: 10.1017/S1355770X1700016X
Burak S., Doğan E., Gazioğlu C. (2004). Impact of urbanization and tourism on coastal environment. Ocean Coast. Manag 47, 515–527. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2004.07.007
Buzzi N. S., Menéndez M. C., Truchet D. M., Delgado A. L., Severini M. D. F. (2022). An overview on metal pollution on touristic sandy beaches: Is the COVID-19 pandemic an opportunity to improve coastal management? Mar. pollut. Bull. 174, 113275. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113275
Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China. (n.d.). Available online at: https://www.gov.cn/. (Accessed August 12, 2024).
Cetin M. A., Bakirtas I., Yildiz N. (2022). Does agriculture-induced environmental Kuznets curve exist in developing countries? Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 29, 34019–34037. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18065-2
Chen J., Huang Y., Wu E. Q., Ip R., Wang K. (2023). How does rural tourism experience affect green consumption in terms of memorable rural-based tourism experiences, connectedness to nature and environmental awareness? J. Hosp. Tour. Manage. 54, 166–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jhtm.2022.12.006
Chen X., Qian W. (2020). Effect of marine environmental regulation on the industrial structure adjustment of manufacturing industry: An empirical analysis of China’s eleven coastal provinces. Mar. Policy 113, 103797. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2019.103797
Crain C. M., Halpern B. S., Beck M. W., Kappel C. V. (2009). Understanding and managing human threats to the coastal marine environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1162, 39–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04496.x
Davenport J., Davenport J. L. (2006). The impact of tourism and personal leisure transport on coastal environments: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 67, 280–292. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2005.11.026
Dietz T., Rosa E. A. (1994). Rethinking the environmental impacts of population, affluence and technology. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 1, 277–300.
Doğanalp N., Ozsolak B., Aslan A., Ozsolak B., Aslan A. (2021). The effects of energy poverty on economic growth: a panel data analysis for BRICS countries. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res 28 (36), 50167–50178. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14185-x
Dumitrescu E.-I., Hurlin C. (2012). Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Econ. Model. 29, 1450–1460. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2012.02.014
Fan W., Zhao R., Yao Z., Xiao C., Pan Y., Chen Y., et al. (2019). Nutrient removal from Chinese coastal waters by large-scale seaweed aquaculture using artificial upwelling. Water 11, 1754. doi: 10.3390/w11091754
Gao J., Zhang L. (2021). Exploring the dynamic linkages between tourism growth and environmental pollution: new evidence from the Mediterranean countries. Curr. Issues Tour. 24, 49–65. doi: 10.1080/13683500.2019.1688767
Hildering A., Keessen A. M., Van Rijswick H. F. M. W. (2009). Tackling pollution of the Mediterranean Sea from land-based sources by an integrated ecosystem approach and the use of the combined international and European legal regimes. Utrecht Law Rev. 5, 80. doi: 10.18352/ulr.96
Hongxing Y., Abban O. J., Boadi A. D., Ankomah-Asare E. T. (2021). Exploring the relationship between economic growth, energy consumption, urbanization, trade, and CO2 emissions: a PMG-ARDL panel data analysis on regional classification along 81 BRI economies. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 28, 66366–66388. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15660-1
Iqbal A., Tang X., Rasool S. F. (2023). Investigating the nexus between CO2 emissions, renewable energy consumption, FDI, exports and economic growth: evidence from BRICS countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 25, 2234–2263. doi: 10.1007/s10668-022-02128-6
Islam M., Ali M., Ceh B., Singh S., Khan M. K., Dagar V. (2022). Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption driven sustainable development in ASEAN countries: do financial development and institutional quality matter? Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 29, 34231–34247. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18488-x
Ji J., Wang D. (2022). Regional differences, dynamic evolution, and driving factors of tourism development in Chinese coastal cities. Ocean Coast. Manage. 226, 106262. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106262
Kao C. (1999). Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J. Econom. 90, 1–44. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4076(98)00023-2
Kao C., Chiang M.-H. (2000). On the estimation and inference of a cointegrated regression in panel data, in: Advances in Econometrics. Emerald (MCB UP). Bingley, 179–222. doi: 10.1016/S0731-9053(00)15007-8
Khan M. T. I., Yaseen M. R., Ali Q. (2019). Nexus between financial development, tourism, renewable energy, and greenhouse gas emission in high-income countries: A continent-wise analysis. Energy Econ. 83, 293–310. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2019.07.018
Koçak E., Ulucak R., Ulucak Z.Ş. (2020). The impact of tourism developments on CO2 emissions: An advanced panel data estimation. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 33, 100611. doi: 10.1016/j.tmp.2019.100611
Kocasoy G. (1989). The relationship between coastal tourism, sea pollution and public health: A case study from Turkey. Environmentalist 9, 245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02241824
Kurniawan F., Adrianto L., Bengen D. G., Prasetyo L. B. (2023). Hypothetical effects assessment of tourism on coastal water quality in the Marine Tourism Park of the Gili Matra Islands, Indonesia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 25, 7959–7985. doi: 10.1007/s10668-022-02382-8
Li K., Fang L., He L. (2019). How population and energy price affect China’s environmental pollution? Energy Policy 129, 386–396. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.02.020
Li C., Zhang Y., Chen Z., Wang X., Yue M., Liu J., et al. (2023). Systematic and dynamic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on marine economic development, air pollution and energy consumption: A case study of China’s coastal regions. Ocean Coast. Manage. 244, 106774. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2023.106774
Liddle B. (2012). The importance of energy quality in energy intensive manufacturing: Evidence from panel cointegration and panel FMOLS. Energy Econ. 34, 1819–1825. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2012.07.013
Liddle B. (2014). Impact of population, age structure, and urbanization on carbon emissions/energy consumption: evidence from macro-level, cross-country analyses. Popul. Environ. 35, 286–304. doi: 10.1007/s11111-013-0198-4
Lim H.-S., Diaz R. J., Hong J.-S., Schaffner L. C. (2006). Hypoxia and benthic community recovery in Korean coastal waters. Mar. pollut. Bull. 52, 1517–1526. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.05.013
Liu J., An K., Jang S. S. (2020). A model of tourists’ civilized behaviors: Toward sustainable coastal tourism in China. J. Destin. Mark. Manag 16, 100437. doi: 10.1016/j.jdmm.2020.100437
Liu F., Huang Y., Zhang L., Li G. (2022). Marine environmental pollution, aquatic products trade and marine fishery Economy——An empirical analysis based on simultaneous equation model. Ocean Coast. Manage. 222, 106096. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106096
Liu S., Lou S., Kuang C., Huang W., Chen W., Zhang J., et al. (2011). Water quality assessment by pollution-index method in the coastal waters of Hebei Province in western Bohai Sea. China. Mar. pollut. Bull. 62, 2220–2229. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.06.021
Liu S., Peng B., Liu Q., Fan C. (2019). Economic-related CO 2 emissions analysis of Ordos Basin based on a refined STIRPAT model. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 9, 1064–1080. doi: 10.1002/ghg.1920
Liu J., Zhang J., Fu Z. (2017). Tourism eco-efficiency of Chinese coastal cities – Analysis based on the DEA-Tobit model. Ocean Coast. Manage. 148, 164–170. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2017.08.003
Liu P., Zhu B., Yang M. (2021). Has marine technology innovation promoted the high-quality development of the marine economy? ——Evidence from coastal regions in China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 209, 105695. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105695
Maione C. (2021). Quantifying plastics waste accumulations on coastal tourism sites in Zanzibar, Tanzania. Mar. pollut. Bull. 168, 112418. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112418
MNRC (2019). Bulletin of Marine Ecology and Environment Status of China 2019 (Ministry of Natural Resources of China). Available at: https://www.mnr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/.
Muye I. M., Muye I. Y. (2017). Testing for causality among globalization, institution and financial development: Further evidence from three economic blocs. Borsa Istanb. Rev. 17, 117–132. doi: 10.1016/j.bir.2016.10.001
NBSC. (2020). China Statistical Yearbook 2020 (National Bureau of Statistics of China). Available at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/.
Nuzula N. I., Armono H. D., Rosyid D. M. (2017). The impact of coastal tourism activities on water quality at Baluran National Park. PTEK The Journal for Technology and Science. 28, 59–62.
Pedroni P. (1999). Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 61, 653–670. doi: 10.1111/obes.1999.61.issue-S1
Pedroni P. (2000). Fully modified OLS for heterogeneous cointegrated panels, in: Advances in Econometrics. Emerald (MCB UP). Bingley, 93–130. doi: 10.1016/S0731-9053(00)15004-2
Peng L., Deng X., Li Z. (2023). An extended input-output analysis of links between industrial production and water pollutant discharge in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Clean. Prod. 390, 136115. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136115
Peng D., Yang Q., Yang H.-J., Liu H., Zhu Y., Mu Y. (2020). Analysis on the relationship between fisheries economic growth and marine environmental pollution in China’s coastal regions. Sci. Total Environ. 713, 136641. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136641
Perone G. (2024). The relationship between renewable energy production and CO2 emissions in 27 OECD countries: A panel cointegration and Granger non-causality approach. J. Clean. Prod. 434, 139655. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139655
Pesaran M. H. (2004). General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. Cambridge Working Papers. Economics 1240, 1. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.572504
Pesaran M. H. (2007). A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J. Appl. Econom. 22, 265–312. doi: 10.1002/jae.951
Pesaran M. H., Shin Y., Smith R. P. (1999). Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. Journal of the American Statistical Association 94, 621–634. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.572504
Rahman M. M., Nepal R., Alam K. (2021). Impacts of human capital, exports, economic growth and energy consumption on CO2 emissions of a cross-sectionally dependent panel: Evidence from the newly industrialized countries (NICs). Environ. Sci. Policy 121, 24–36. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2021.03.017
Ran Q., Wang X., Wang D., Yan H. (2023). Inbound tourism economy for coastal areas of China: differences and influencing factors. J. Coast. Res. 39, 750–762. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-22-00105.1
Ren W., Ji J. (2021). How do environmental regulation and technological innovation affect the sustainable development of marine economy: New evidence from China’s coastal provinces and cities. Mar. Policy 128, 104468. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104468
Robaina M., Madaleno M., Silva S., Eusébio C., Carneiro M. J., Gama C., et al. (2020). The relationship between tourism and air quality in five European countries. Econ. Anal. Policy 67, 261–272. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2020.07.012
Ronda A. C., Menéndez M. C., Tombesi N., Álvarez M., Tomba J. P., Silva L. I., et al. (2023). Microplastic levels on sandy beaches: Are the effects of tourism and coastal recreation really important? Chemosphere 316, 137842. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137842
Saenz-de-Miera O., Rosselló J. (2014). Modeling tourism impacts on air pollution: The case study of PM10 in Mallorca. Tour. Manage. 40, 273–281. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2013.06.012
Saidmamatov O., Tetreault N., Bekjanov D., Khodjaniyazov E., Ibadullaev E., Sobirov Y., et al. (2023). The nexus between agriculture, water, energy and environmental degradation in central Asia—Empirical evidence using panel data models. Energies 16, 3206. doi: 10.3390/en16073206
Saqib M., Benhmad F. (2021). Does ecological footprint matter for the shape of the environmental Kuznets curve? Evidence from European countries. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 28, 13634–13648. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11517-1
Shao Q. (2020). Nonlinear effects of marine economic growth and technological innovation on marine pollution: Panel threshold analysis for China’s 11 coastal regions. Mar. Policy 121, 104110. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104110
Shao Q., Guo J., Kang P. (2021). Environmental response to growth in the marine economy and urbanization: A heterogeneity analysis of 11 Chinese coastal regions using a panel vector autoregressive model. Mar. Policy 124, 104350. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104350
Song D. (2016). Countermeasure study on sustainable utilization of tourism resources and tourism environmental pollution in coastal areas of the pearl river delta, China. Nat. Environ. pollut. Technol. 15, 873.
Song X., Geng Y., Li K., Zhang X., Wu F., Pan H., et al. (2020). Does environmental infrastructure investment contribute to emissions reduction? A case of China. Front. Energy 14, 57–70. doi: 10.1007/s11708-019-0654-7
Su C.-W., Song Y., Umar M. (2021). Financial aspects of marine economic growth: From the perspective of coastal provinces and regions in China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 204, 105550. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105550
Sun J., Zhai N., Miao J., Mu H., Li W. (2023). How do heterogeneous environmental regulations affect the sustainable development of marine green economy? Empirical evidence from China’s coastal areas. Ocean Coast. Manage. 232, 106448. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106448
Vetrimurugan E., Shruti V. C., Jonathan M. P., Roy P. D., Kunene N. W., Villegas L. E. C. (2017). Metal concentration in the tourist beaches of South Durban: An industrial hub of South Africa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 117, 538–546. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.02.036
Wang C., Meng X., Siriwardana M., Pham T. (2022). The impact of COVID-19 on the Chinese tourism industry. Tour. Econ. 28 (1), 131–152. doi: 10.1177/13548166211041209
Wang Y., Sun C., Zou W. (2021). Study on the interactive relationship between marine economic growth and marine environmental pressure in China. Environ. Resour. Econ. 79, 117–133. doi: 10.1007/s10640-021-00555-z
Wang P., Wang J., Zhang J., Ma X., Zhou L., Sun Y. (2022). Spatial-temporal changes in ecosystem services and social-ecological drivers in a typical coastal tourism city: A case study of Sanya, China. Ecol. Indic. 145, 109607. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109607
Wang C., Wang F., Zhang X., Yang Y., Su Y., Ye Y., et al. (2017). Examining the driving factors of energy related carbon emissions using the extended STIRPAT model based on IPAT identity in Xinjiang. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 67, 51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.09.006
Wang S., Xing L., Chen H. (2020). Impact of marine industrial structure on environmental efficiency. Manage. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 31, 111–129. doi: 10.1108/MEQ-06-2019-0119
Wang Z., Yuan F., Han Z. (2019). Convergence and management policy of marine resource utilization efficiency in coastal regions of China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 178, 104854. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2019.104854
Wang Q., Zhang C., Li R. (2023). Does environmental regulation improve marine carbon efficiency? The role of marine industrial structure. Mar. pollut. Bull. 188, 114669. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114669
Wang P., Zhang J., Ma J., Guo L., Yang L., Ma X., et al. (2023). What impacts ecosystem services in tropical coastal tourism cities? A comparative case study of Haikou and Sanya, China. J. Environ. Manage. 342, 118227. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118227
Wang Z., Zhao L., Wang Y. (2020). An empirical correlation mechanism of economic growth and marine pollution: A case study of 11 coastal provinces and cities in China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 198, 105380. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2020.105380
Wei T. (2011). What STIRPAT tells about effects of population and affluence on the environment? Ecol. Econ. 72, 70–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2011.10.015
Westerlund J., Edgerton D. L. (2007). New improved tests for cointegration with structural breaks. Journal of time series Analysis 28, 188–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9892.2006.00504.x
Wu W., Lee C.-C., Xing W., Ho S.-J. (2021). The impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on Chinese-listed tourism stocks. Financ. Innov. 7, 22. doi: 10.1186/s40854-021-00240-6
Wu R., Wang J., Wang S., Feng K. (2021). The drivers of declining CO2 emissions trends in developed nations using an extended STIRPAT model: A historical and prospective analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 149, 111328. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111328
Xu W., Zhang Z. (2022). Impact of coastal urbanization on marine pollution: evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 19, 10718. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191710718
Xue J., Yu Y., Bai Y., Wang L., Wu Y. (2015). Marine oil-degrading microorganisms and biodegradation process of petroleum hydrocarbon in marine environments: A review. Curr. Microbiol. 71, 220–228. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0825-7
Yang W., Cai F., Liu J., Zhu J., Qi H., Liu Z. (2021). Beach economy of a coastal tourist city in China: A case study of Xiamen. Ocean Coast. Manage. 211, 105798. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105798
York R., Rosa E. A., Dietz T. (2004). The ecological footprint intensity of national economies. J. Ind. Ecol. 8, 139–154. doi: 10.1162/1088198043630487
Yuan B., Xiang Q. (2018). Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: Based on an extended CDM model. J. Clean. Prod. 176, 895–908. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.034
Zahedi S. (2008). “Tourism impact on coastal environment,” in Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions VII (WIT Press, The New Forest, UK), 45–57. doi: 10.2495/CENV080051
Zeng J., Liu T., Feiock R., Li F. (2019). The impacts of China’s provincial energy policies on major air pollutants: A spatial econometric analysis. Energy Policy 132, 392–403. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.05.052
Zhang L., Gao J. (2016). Exploring the effects of international tourism on China’s economic growth, energy consumption and environmental pollution: Evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 53, 225–234. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.08.040
Zhang C., Wang Y., Song X., Kubota J., He Y., Tojo J., et al. (2017). An integrated specification for the nexus of water pollution and economic growth in China: Panel cointegration, long-run causality and environmental Kuznets curve. Sci. Total Environ. 609, 319–328. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.107
Zhang G., Xing L. (2023). Research on tourism economic effect under the threshold of new-type urbanization in coastal cities of China: From the perspective of development economics. Ocean Coast. Manage. 239, 106587. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2023.106587
Zhao Y., Song Y., Cui J., Gan S., Yang X., Wu R., et al. (2020). Assessment of water quality evolution in the pearl river estuary (South Guangzhou) from 2008 to 2017. Water 12, 59. doi: 10.3390/w12010059
Keywords: coastal tourism, marine pollution, pollutant discharges, quantitatively analyze, long-term relationship
Citation: Ji X and Ding X (2024) Analysis on the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution: an empirical analysis of China’s 11 coastal regions. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1471467. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1471467
Received: 27 July 2024; Accepted: 20 September 2024;
Published: 08 October 2024.
Edited by:
Xuemei Li, Ocean University of China, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Ji and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xingong Ding, ZGluZ3hpbmdvbmdAYmJndS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.