
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Mar. Sci., 09 December 2024
Sec. Coastal Ocean Processes
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1464037
Introduction: The suspended sediment concentration (SSC) is an important consideration in marine engineering. Sediment movement characteristics can be studied by considering the fortnightly behavior of SSC. However, this consideration currently lacks accurate mathematical representation.
Method: In this study, a computationally efficient mathematical model capable of providing analytical solutions for predicting SSC based on resuspension, deposition, and advection was developed to further investigate the mathematical interpretation of fortnightly SSC behavior in coastal areas dominated by M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tides. The model decomposed the SSC into 35 quasi-harmonic terms as well as two terms with fortnightly period.
Result: The model was applied at five observation sites in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea, China, and validated to be able to reproduce the fortnightly variation of SSC. The results show that the primary fortnightly SSC term was generated by the combined action of M2 and S2 tidal currents and had a tidal frequency of 1.0159 °/h, which was equal to the difference between the frequencies of the two partial tides.
Discussion: The resuspension properties only affected the amplitude of the fortnightly SSC term but did not affect the phase. The deposition properties affected both amplitude and phase. The quasi-harmonic analysis indicates that in certain shallow sea areas with strong nonlinear tidal interactions, the amplitude of the M4 tidal elevation can influence the mean SSC, while the amplitude of the MS4 tidal elevation can affect the fortnightly SSC amplitude. As the simplified model is based on certain assumptions, the application conditions of the quasi-harmonic analytical solution include an approximate reciprocating flow pattern, a tidal range significantly smaller than the water depth. Our results provide a mathematical solution for the fortnightly evolution of suspended sediment.
Suspended sediment concentration (SSC) is an important consideration in many marine engineering applications, including harbor nourishment, marine pile stabilization and sand mining. SSC is commonly used as an indicator of changes in the marine environment. As most coastal areas are influenced by semi-diurnal and diurnal tides, many investigations have focused on the quarter-diurnal and semi-diurnal behavior of SSC. Moreover, fortnightly behavior also plays an important role in sediment movement. Notably, spring-neap variations can significantly affect sediment transport and the morphology of many coastal zones.
Key characteristics of SSC, such as mean values and periodic features, are mostly studied through field observations conducted over limited time periods. For instance, the mean SSC over a fortnightly tidal period, a critical parameter for estimating estuarine discharge (Vale and Sundby, 1987), has been extensively studied over various time periods (Gelfenbaum, 1983; Tattersall et al., 2003; Yang and Hamrick, 2003). Existing research on the fortnightly characteristics of the SSC has mainly focused on describing the phenomenon or a qualitative interpretation based on shear stress (Li et al., 2015; Toublanc et al., 2015; Du et al., 2021). However, the theoretical mean values and fortnightly characteristics of SSC cannot be reliably obtained from observations over a limited period, necessitating new measurements for each subsequent period. There remains a lack of an efficient and accurate mathematical expression to describe SSC for a specific period, which is essential for estimating SSC over longer time scales.
In the study of fortnightly characteristics of sediment movement, another common research method is numerical modeling. To date, many fully hydrodynamics-sediment coupled models have been established, such as POM (Wang, 2002), ECOMSed (HydroQual, Inc., 2002), FVCOM (Chen et al., 2006), ROMS (Warner et al., 2008), and Delft3D (Deltares, 2012). However, because the coupled model calculations require iterative solutions of differential equations, the computational efficiency is relatively low. Therefore, a model with an analytical solution is needed to efficiently compute the SSC.
In recent years, several studies have investigated the discrete influence of tidal constituents on suspended sediment (Buschman et al., 2013), with results indicating that both semi-diurnal and diurnal tidal signals are superimposed on the temporal variations in SSC (Xiong et al., 2018). While these studies primarily focused on analyzing the periodic changes in SSC, a comprehensive examination of the flow field variations associated with sediment transport was not fully explored. Additionally, research addressing the long-term periodic characteristics of flow fields remains relatively limited. Schoellhamer (2002) applied singular spectrum analysis to time series data from San Francisco Bay and reported that the physical processes contributing to the total variance of suspended sediment concentration (SSC) included diurnal, semidiurnal, and other higher-frequency tidal constituents (24%), as well as semimonthly tidal cycles (21%). As this method places less emphasis on the physical processes connecting hydrodynamics and sediment transport, its potential for developing a widely applicable model remains limited. Yu et al. (2012) used a quasi-harmonic analysis method for SSC in a sea area controlled by M2 (principal lunar semi-diurnal) and M4 (shallow water quarter diurnal) tidal currents. As the M4 tide is the overtide of the M2 tide, the long period (fortnight) SSC component could not decompose. Although quasi-harmonic analysis has previously been used as a routine method in tidal and tidal current analysis, the method is not typically employed for suspended sediment analysis.
In this study, a simplified one-dimensional (1D) case was used to demonstrate the feasibility of the quasi-harmonic analysis method for suspended sediment analysis in a coastal area mainly controlled by the M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tides. The analytical solution decomposed the SSC into 35 quasi-harmonic terms, and the result provides a mathematical solution for the fortnightly evolution of suspended sediment. This study aims to address the following objectives: (1) to develop a computationally efficient mathematical model for predicting SSC that circumvents the complexity and time demands associated with solving differential equations, and (2) to introduce a quasi-harmonic analysis method for SSC, incorporating the major tidal constituents in coastal areas, thereby enhancing generality and accuracy compared to existing Fourier and other spectral analysis methods.
In order to analyze the SSC, a 1D model has been developed that includes three processes: suspension, deposition and advection. The model can be used at a fixed observation site where the flow is characterized as a 1D system. The depth-averaged suspended sediment model was defined as follows:
where c is the suspended sediment concentration, the 〈 〉 operator represents depth-averaging, 〈c〉 is the depth-averaged suspended sediment concentration (DASSC), t is the time, and H is the depth. The flood current is assumed to be in a positive direction. U is the current velocity, x is the horizontal distance, and Qr and Qd are the simultaneous local resuspension and deposition, respectively. The horizontal diffusion term is neglected based on the existing literature (Bass et al., 2002; Stanev et al., 2007).
The horizontal advection term in Equation 1 can be decomposed as follows:
where 〈Udcd〉 represents the difference between the depth-averaged U · c and the product of the depth-averaged U and c. The second term on the right side of Equation 2 represents the nonlinear interaction between the vertical velocity and the SSC profiles. For simplicity, this term was not considered further, which is consistent with other depth-averaged models (Uncles and Stephens, 1989; Cheng and Wilson, 2008). Therefore, the advection term can be simplified as:
The resuspension terms in Equation 1 can be written according to Cheng and Wilson (2008):
where M is the erosion rate per unit time and unit area, ρ is the seawater density, CD is the drag coefficient, τc is the critical erosion shear stress, and M, ρ, and CD are assumed to be constant over time and space. Therefore, B is constant.
The deposition term can be determined using the following equation:
where cbed is the near-bed SSC and ws is the settling velocity, which is assumed to be constant. To simplify the terms, the ratio between the near-bed SSC and the DASSC is assumed to be constant (Yu et al., 2012). Hence, the deposition parameter D is also assumed to be constant.
The 1D depth-averaged continuity equation for flow is given by (Rodriguez et al., 2003; Yee-chung and Qingchao, 2004):
Hence, by combining Equations 2–6, the longitudinal 1D depth-averaged suspended sediment model can be simplified to:
The depth-averaged tidal current velocity (〈U〉) and water depth (H) can be obtained through quasi-harmonic analysis of observational data. The horizontal DASSC gradient ((∂〈c〉/∂x) is difficult to estimate and is unavailable in the literature. However, it was assumed to be constant in previous studies (Prandle, 1997; Bass et al., 2002; Hill et al., 2003; Yu et al., 2012). Accordingly, the horizontal DASSC gradient can be written as:
The advection and resuspension terms can then be expressed as a combination of several temporal harmonic terms, and Equation 7 can be written as:
where Ai, ωi, and ψi are the amplitude, frequency, and phase of the ith forcing harmonics, respectively. The general analytical solution is as follows:
where S is an integral constant. In a natural sea area, DASSC (〈c〉) reaches steady state and the first term on the right-hand side approaches zero.
In this study, the SSC was dominated by the M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal currents. The depth-averaged current is expressed as:
where u0 is the residual current; u1, u2, u3, u4, u5 and u6 are the amplitudes of M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal currents, respectively. ω1, ω2, ω3 and ω4 are the frequencies of M2, S2, O1, and K1 tidal currents, respectively. α1, α2, α3, α4, α5 and α6 are the phases of M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal currents, respectively. Similarly, the water depth can be written as:
where h0 is the average water depth; h1, h2, h3, h4, h5 and h6 are the amplitudes of M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal elevations, respectively. β1, β2, β3, β4, β5 and β6 are the phases of M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal elevations, respectively. For the convenience of comparing the magnitudes, Equations 11 and 12 can be written as:
The inverse of the water depth can be written as:
Combining Equations 7, 13, 14, and 15 and neglecting the higher-order (> 1) trivial terms, the analytical solution for DASSC is as follows:
When dominated by the M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal currents in most of the coastal areas, the DASSC consists of 35 quasi-harmonic terms (E1–E35). The frequencies, phases, and relative amplitudes of the quasi-harmonic terms are listed in Table 1. All trigonometric functions were calculated in radians. For the convenience of contrast with the tidal current quasi-harmonic constant, the frequency and phase in Table 1 are presented in degrees.
To verify the correctness of the analytical solution and to test its universality, the model was applied to 5 sites covering the Bohai Sea, the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea, and the observation data of tide, current and DASSC at each site were used for validation. The locations of the sites are shown in Figure 1, marked from north to south as C1 to C5. Simultaneously, 7- or 15-day tidal observations were conducted at nearby coastal tide gauge stations (H1 to H5), which are indicated in Figure 1. To illustrate the fortnightly characteristics of the suspended sediment response to tidal flow, the method is simplified to a one-dimensional model. The 5 applied and validated sites all approximate to a reciprocal flow state, which approximates to the basic assumptions of the solution.
The fixed point observations were all made from ship moorings. The Aanderaa RCM-9 current meter was used for current monitoring. Current velocity and direction were recorded every 2min and the data were extracted every 60min. The margin of error of the current observations was ±3cms−1. The tidal elevation was measured using a water-level indicator at both the coastal tide gauge stations and the suspended sediment monitoring sites, with a data extraction interval of 60min. The margin of error for the tidal height was ±0.1m. Suspended sediment was captured by a water sampler. The sampling interval was 60min. The suspended sediment samples were filtered, dried and weighed in the laboratory. The aperture of the filter membrane was 0.45µm. The SSC was measured by the filtration method. A blank membrane correction was performed to avoid errors caused by the weightlessness of the filtration membrane due to dissolution.
Field observations were conducted at sites with water depths ranging from 8 to 26 meters to measure currents and suspended sediment concentrations at various depths (surface, 0.2H, 0.4H, 0.6H, 0.8H, and bottom layers). At Site C1, located 14km offshore with a depth of 26m, observations were conducted from 15:00 on April 20 to 07:00 on April 22, 2023, under prevailing southerly winds (Beaufort force 2-5) with a maximum wave height of 0.3m. At Site C2, 23km offshore at a depth of 8m, measurements were taken during three tidal conditions: neap tide (12:00 on March 17 to 14:00 on March 18), middle tide (09:00 on March 20 to 11:00 on March 21), and spring tide (18:00 on March 24 to 20:00 on March 25, 2023), with wind speeds varying between 1.0 and 5.8ms−1 and shifting between east, northeast, and west. At Site C3, 5km offshore with a depth of 23.3m, observations were made during neap tide (08:00 on July 19 to 09:00 on July 20), middle tide (12:00 on July 22 to 13:00 on July 23), and spring tide (14:00 on July 25 to 15:00 on July 26, 2006), with wind speeds ranging from 2.3 to 3.2ms−1, all from a 30° direction. At Site C4, 27km offshore and 2.5km from Xiaoyang Island with a depth of 11.7m, measurements were conducted during spring tide (10:00 on November 19 to 11:00 on November 20) and neap tide (09:00 on November 26 to 10:00 on November 27, 2017), with northeast winds reaching 8.6ms−1 during the spring tide and 4.8ms−1 during the neap tide. Finally, at Site C5, located in the deep trench of the narrow Meizhou Bay with a depth of 23.9m, observations were made during the spring tide (19:00 on August 14 to 20:00 on August 15) and neap tide (00:00 on August 23 to 16:00 on August 24, 2007), with a maximum wind velocity of 9.0ms−1 from the south. Measurements at all sites included currents and suspended sediment samples collected at multiple depths. Wave and wind speed records during the observation periods indicate that wave action and wind-driven currents influenced the observations to some extent, potentially affecting seabed shear stress and SSC.
The quasi-harmonic constants for tidal elevation were calculated using 7- or 15-day tidal observations from tide gauge stations located along the coast near each site. The short-term tidal elevation data, synchronized with SSC observations at each site, were used to validate the model. The observed spring and neap tide currents (when available) were used for quasi-harmonic analysis, while the middle tide currents were utilized for validation. If the observations did not include a complete cycle of spring, middle, and neap tides, all available current measurements were used for the quasi-harmonic analysis.
The calibration results for tidal elevation and current show that the predicted harmonic constants generally reproduce the observed patterns, but with some degree of error. The observed highest and lowest tidal elevations were 0.46 and −0.33m at Site C1, 0.82 and −0.65m at Site C2, 1.75 and −1.64m at Site C3, 1.94 and −2.32m at Site C4, and 3.02 and −3.30m at Site C5. The predicted highest and lowest tidal elevations were 0.43 and −0.30m at Site C1, 0.85 and −0.54m at Site C2, 1.67 and −1.67m at Site C3, 1.90 and −1.97m at Site C4, and 3.28 and −3.20m at Site C5. The predicted tidal elevations at Sites C2 and C4 showed a larger relative error during neap tides compared to other sites, while Site C5 exhibited a 30min phase difference during the spring tide.
The observed maximum flood and ebb current velocities were 65 and 4.8ms−1 at Site C1, 50 and 51cms−1 at Site C2, 104 and 97cms−1 at Site C3, 159 and 169cms−1 at Site C4, and 91 and 84cms−1 at Site C5. The predicted maximum flood and ebb current velocities were 79 and 52cms−1 at Site C1, 39 and 42cms−1 at Site C2, 110 and 95cms−1 at Site C3, 170 and 175cms−1 at Site C4, and 94 and 70cms−1 at Site C5. The tidal current simulation results for Sites C3, C4, and C5 are better than for Sites C1 and C2, as the larger tidal range at C3, C4, and C5 results in stronger tidal currents. In contrast, the smaller tidal range at Sites C1 and C2 leads to weaker tidal currents, making them more susceptible to wind-driven currents during the observation period.
The results of the quasi-harmonic analysis of the tidal currents at Sites C1-C5 are listed in Table 2. The harmonic analysis results indicate that at Sites C1-C5, the M2 tidal constituent is the dominant one in all the partial tide currents. Except for Site C2, the S2 tidal constituent acts as the secondary dominant one at the other sites. Sites C1, C3, and C5 exhibit relatively strong residual currents. The characteristics of tidal currents in coastal regions are primarily composed of six tidal constituents: M2, S2, O1, K1, M4, and MS4. However, the tidal elevations observed at the five sites are predominantly made up of four tidal constituents: M2, S2, O1, and K1. The tidal components M4 and MS4 contribute less to the superposition of the tidal elevations. Therefore, the contributions of the quasi-harmonic terms E12, E13, E33, E34 and E35 to the DASSC would also be relatively small.
As the free parameters (k, B, and D) are difficult to measure or estimate, they were calibrated by fitting the predicted DASSC to the observed values. This calibration method has been widely used in previous studies (Bass et al., 2002; Yu et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2018). To calibrate the fortnightly SSC time series, SSC observations from the spring, middle, and neap tides were used for both calibration and validation. As the natural sediment is a mixture of multiple grain-size components, the parameters set in the model exhibited equivalent values. Therefore, the best-fit parameters may not represent the actual values due to the simplifications made in the model. This indicates that the calibrated resuspension and deposition parameters do not correspond to a specific representative grain size at the observation site but rather represent a generalized mixture of sediment grain sizes, especially at sites like C1 and C5, where sediment grain size distributions exhibit multiple peaks.
For the simplified horizontal gradient constant (k) in a sea area with approximately uniform sediment distribution, it can be constrained by the observed DASSC and the tidal excursion distance (Yu et al., 2012). The tidal excursion distance is calculated by integrating the hourly observed current velocities over a tidal cycle. The value of k is then constrained by the ratio of the maximum DASSC during the cycle to the tidal excursion distance. Accordingly, the limits for k were set at −7.81 × 10−6 to 7.81 × 10−6 kgm−4 for Site C1, −7.22 × 10−6 to 7.22 × 10−6 kgm−4 for Site C2, −9.40 × 10−5 to 9.40 × 10−5 kgm−4 for Site C4, and −1.33 × 10−5 to 1.33 × 10−5 kgm−4 for Site C5, respectively. Referring to the study by Zhu et al. (2018) in the area adjacent to Site C3, the sediment composition around Site C3 is nonuniform. A smaller k value cannot calibrate the predicted SSC to match the observed values, which mathematically supports that Site C3 is located in an area with nonuniform sediment distribution. Therefore, the k value for this site needs to be determined through SSC calibration.
The sediment grain size analysis results for each site are presented in Figure 2, indicating that the suspended sediment at all sites consists of both silt (φ = 4–8) and mud (φ > 8) components. Notably, at Site C4, bedload constitutes only 3.8% of the sediment, with the seabed sediment predominantly composed of suspended material. In contrast, Sites C1 and C3 are primarily characterized by larger bedload fractions. The resuspension parameter (B) could be constrained by the parameters in Equation 4. The sea-water density (ρ) was 1025kgm−3. Yu et al. (2012) suggested that the erosion rate in unit time and unit area (M) ranged from 1.0 × 10−5 to 5.0 × 10−3 kgm−2 s−1. In the study by Bricker et al. (2005), the drag coefficient (CD) ranged from 0.002 to 0.04. Based on the study by Zhu et al. (2018), the critical erosion shear stress (τc) for the silt-mud mixture ranged from 0.04 to 0.14Nm−2. Based on the ranges of M, CD, and τcobtained from previous studies, the range of the resuspension parameter (B) in Equation 4 can be constrained between 7.32 × 10−4 and 5.12 kgm−2 s−1. Therefore, B was constrained between 7.32 × 10−4 and 5.12kgsm−2. The range of the deposition parameter (D) in Equation 5 was difficult to constrain because the ratio between the near-bed SSC and DASSC is difficult to determine and is mainly influenced by sediment diameter. When flocculation settlement is not considered, a large diameter may result in a high settling velocity, which may cause a high ratio between near-bed SSC and DASSC. Therefore, a larger diameter may result in a higher deposition parameter.
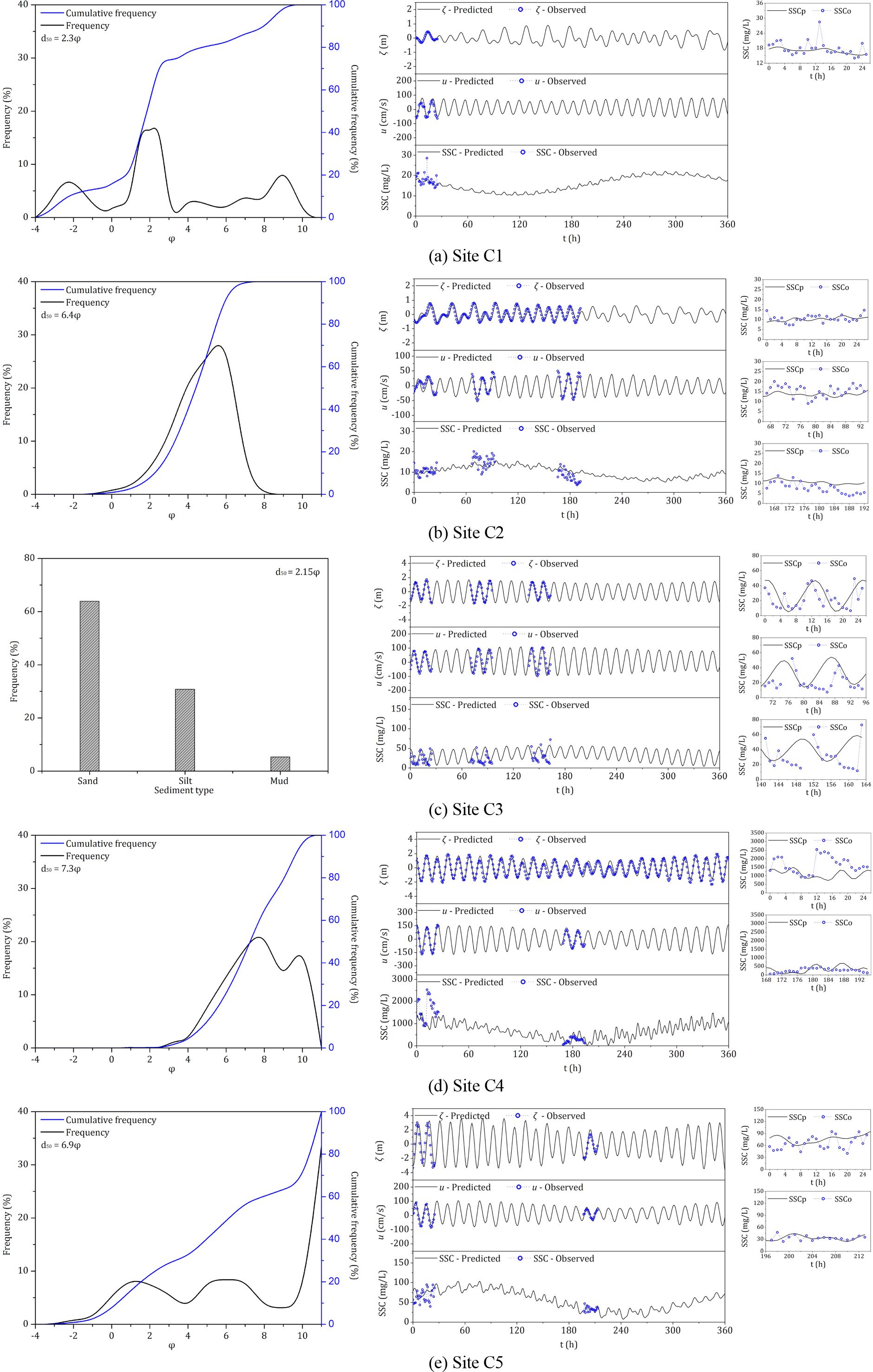
Figure 2. The grain size composition of seabed sediment (first column) and the results of the calibration for elevation, current, and SSC (second and third columns) at Sites (A) C1, (B) C2, (C) C3, (D) C4 and (E) C5. SSCp and SSCo represent the predicted and observed SSC, respectively.
The tidal current and tidal elevation at each site were calculated by applying the parameters of the tidal constituents obtained from the quasi-harmonic analysis into Equations 11 and 12. The DASSC was then computed using Equation 16. The best-fit values of k, B and D at each site are listed in Table 3, and the validation results are shown in Figure 2. Using the superposition of the 35 quasi-harmonic analytical terms decomposed in this study, the fortnightly variation of the DASSC can be essentially reproduced. The validation results also indicate that the simulation of SSC exhibits varying errors across different sites, particularly in the diurnal, semi-diurnal, and quarter-diurnal tidal cycles. Except for the neap tide period at Site C4 (Figure 2), the observed SSC during other observation periods exhibited greater amplitude variations in the semi-diurnal and quarter-diurnal cycles compared to the predicted values. This discrepancy is related to the use of a single sediment characteristic parameter to represent sediments that, in reality, consist of a mixture of grain sizes. Zhu et al. (2018) found that using multiple characteristic values to simulate mixed-grain sediments improves the accuracy of suspended sediment simulations. According to the Shields curve, silt particles have a lower initiation threshold compared to mud, and due to their larger grain size, they also have a higher settling velocity. Therefore, the amplitude of silt fluctuations is higher than that of muddy components, while the fluctuations in muddy suspended sediment concentrations tend to exhibit lower amplitudes around the mean value. Compared to the predicted SSC, the observed SSC contains more noise, particularly in cases of rapid short-term increases, such as the 13th-hour observation at Site C1 (Figure 2A). This noise appears to be associated with wave action during the sampling process. Additionally, the description of the dynamic conditions is based on quasi-harmonic analysis, which inherently introduces certain errors. The primary source of error in the tidal harmonic analysis arises from the limited data, as nearby 7- or 15-day tidal observations from coastal stations were used, which may not fully reflect the tidal conditions at the observation site. The tidal current harmonic analysis is mainly influenced by factors such as wind-driven currents. The prediction errors in tidal elevation and currents can subsequently affect the prediction of SSC, leading to further inaccuracies. Furthermore, in recent years, several studies have shown that coastal long waves can have a significant impact on sediment transport and erosion-deposition dynamics (Gao et al., 2021, 2023, 2024).
To evaluate the performance of the model, the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of SSC for each site was estimated, yielding RMSE values of 2.77, 3.04, 18.85, 576.82, and 16.18mgL−1 for Sites C1–C5, respectively. The mean observed SSC for these sites was 17.89, 11.23, 23.64, 951.49, and 52.62mgL−1, with maximum observed SSC values of 28.54, 20.10, 72.80, 2530.40, and 94.70mgL−1, respectively. The RMSE indicates that sites with relatively higher mean and maximum SSC tend to have larger errors. Site C2 has the lowest tidal current speed among the five sites, resulting in the lowest SSC. Consequently, the observed SSC is more affected by wave-induced noise. This is why Site C2 has a relatively low RMSE but does not capture the semi-diurnal and quarter-diurnal fluctuations observed in the SSC data as accurately (Figure 2B). At Site C3, suspended sediment samples were not collected at certain times, but sampling was complete during the spring tide. The predicted SSC at Site C3 shows a relatively higher RMSE compared to Sites C1 and C2; however, the SSC variation during the spring tide was well captured (Figure 2C). Since the horizontal DASSC gradient is simplified as a constant (k) in Equation 8, and the value of k at Site C3 is relatively high, this gradient simplification likely contributes to a more pronounced prediction error. Site C4 exhibits the strongest tidal currents, corresponding to the highest SSC (Figure 2D) and the largest RMSE. At Site C5, the neap tide showed the best reproduction of the observed suspended sediment values and variation trends (Figure 2E).
The quasi-hydrodynamic driving terms of the DASSC are not only the mathematical interpretation for the suspended sediment movement, but also have the realistic physical significance. By decomposing the DASSC into 35 quasi-harmonic terms, the influencing factors and their fluctuation frequencies are also decomposed.
E1 represents the mean DASSC over a whole fortnightly period. The parameters influencing the DASSC include the resuspension parameter, the deposition parameter, and the mean water depth. For DASSC, as it represents the vertically averaged concentration of suspended sediment in the water column, water depth influences it through vertical mixing processes. The mean water depth reflects the average mixing depth over the tidal cycle, thereby affecting the mean suspended sediment concentration throughout the entire tidal period. For the hydrodynamic conditions affecting the mean DASSC, the main influencing factors are the M2 tidal current, the residual current, the elevation of the M4 tidal constituent, the DASSC gradient, and the phases of M2 tidal current and the M4 tidal elevation. For observation Sites C1–C5, given that the amplitude of the M4 tidal elevation is considerably modest, the contribution of the M2 tidal current phase in conjunction with the M2 tidal elevation and phase did not show a significant impact. Due to the nonlinear interactions of tides, the amplitude of the M4 tide can be quite pronounced in certain regions, such as the shallow coastal areas at the head of Bohai Bay, China, reaching up to 25cm (Liu et al., 2020). As shown by the E1 term in Table 1, the relationship between the phase of the M2 tidal current and the phase of the M4 tidal elevation can also influence the average SSC during the fortnightly tidal cycle.
E16 and E35 exhibit fortnightly periodicity. Due to the minimal tidal elevation associated with the MS4 constituent at Sites C1-C5, the fortnightly dynamics of the DASSC are principally dictated by E16. Consequently, this pattern suggests that the fortnightly fluctuations of the DASSC are essentially the result of the frequency difference between the M2 and S2 tidal currents. In certain regions, such as the head of Bohai Bay, China, the amplitude of the MS4 tide can reach up to 20cm (Liu et al., 2020). As shown in Table 1, in such areas, the E35 term is expected to have a significant influence on the fortnightly variations in SSC.
E2 encapsulates the advective effects prompted by the M2 tidal current, along with the local resuspension driven by the combined shear forces exerted by the M2 tidal current and the residual current. The quasihydrodynamic terms E3-E7 correspond to the advection effects engendered by the S2, O1, K1, M4, and MS4 tidal currents, respectively. The oscillations in total water depth have a significant effect on the DASSC, which epitomizes the vertical mixing of suspended sediments. Consequently, the quasi-hydrodynamic terms E8-E13, together with E25-E35, describe the influence exerted by the variations in the mixing depth of locally resuspended sediments. Since this study employs a depth-averaged model (Equation 1), terms E8-E13 and E25-E35 reflect the effect of vertical mixing of suspended sediment.
As a limitation of the simplified 1D model used in this study, computational errors may arise when the method is applied at sites with rotating flow. Since erosion flux is influenced by the scalar square of current speed, while deposition flux is not affected by the direction of the current, the applicability of this method becomes limited at sites with relatively strong residual currents or significant SSC gradients. As shown in Table 1, this weakened applicability is primarily caused by the quasi-harmonic terms E1 and E2, indicating that predictions of the averaged DASSC and the semidiurnal characteristics may contain some inaccuracies.
The suspended sediment primarily consists of silt and mud, specifically the fraction where φ > 4. Based on the sediment grain size analysis from each site (Figure 2), the proportion of silt (excluding sandy components) in the suspended sediment follows the order of C2 > C4 > C1 > C5, while the proportion of mud shows the opposite trend. This corresponds to the descending order of the deposition parameter (D). This trend is explained by the fact that coarser particles have higher settling velocities.
Except for Site C4, Sites C1, C2, and C5 exhibit higher resuspension parameters (B) alongside higher deposition parameters (D). These findings are consistent with the results discussed in Zhu et al. (2018). At Site C4, the resuspension parameter (B) is significantly higher than at the other sites due to the smallest median grain size (7.3φ). Additionally, 96.2% of the seabed sediment is composed of suspended load (φ > 4), representing the highest proportion of suspended material. The high B value may also be related to the degree of soil consolidation. A consolidation lag at the interface critical stress, resulting in higher TSS (total suspended sediment concentration) during periods of decreasing stress, was reported by Sanford (2008), suggesting that the consolidation process occurs under conditions where the shear stress on the seabed is sufficiently low. Due to the stronger hydrodynamic conditions at Site C4, the soil is less prone to consolidation, leading to a higher resuspension capacity.
Site C3 differs significantly from the other sites, with a lower suspended sediment content (36.1%) and a higher bedload proportion (63.9%), indicating predominantly bedload transport (Figure 2). However, it still shows relatively high SSC, indicating that horizontal transport contributes significantly to the suspended sediment load, resulting in a relatively high value of k. Additionally, referencing the study by Zhu et al. (2018) of the area adjacent to Site C3, the location of Site C3 appears to be part of a strong tidal channel. However, the proximity of the site to a silty-muddy bay on the northwest side suggests the presence of a strong SSC gradient and conditions conducive to the advection process.
The amplitudes of each quasi-harmonic term at Sites C1-C5 are shown in Figure 3. In the present study, E1 (representing the mean value of DASSC) consistently exhibits a dominant presence at all observation sites. Observations at sites C1, C2, C4, and C5 indicate that the term E16, which signifies the fortnightly behavior of DASSC, manifests a relatively higher magnitude. Mathematically, the increased amplitude of E16 is partly due to its lower frequency. Physically, this is a consequence of the resonance arising from the close frequencies of the tidal constituents M2 and S2. Equation 16 and Table 1 demonstrate that the amplitude of E16 is directly proportional to the resuspension parameter B and the product of the M2 and S2 tidal current velocities, while inversely proportional to water depth. Furthermore, a smaller deposition parameter D can result in a higher E16 amplitude. Given the complexity of the factors influencing the E16 amplitude, a direct comparison across different sites or regions is not straightforward. The calculated E16 amplitudes for Sites C1–C5 are 5.05, 3.76, 7.65, 385.14, and 33.65 mgL-1, respectively. Site C4, which exhibits significantly higher M2 and S2 tidal current velocities, also has a substantially greater E16 amplitude compared to the other sites.
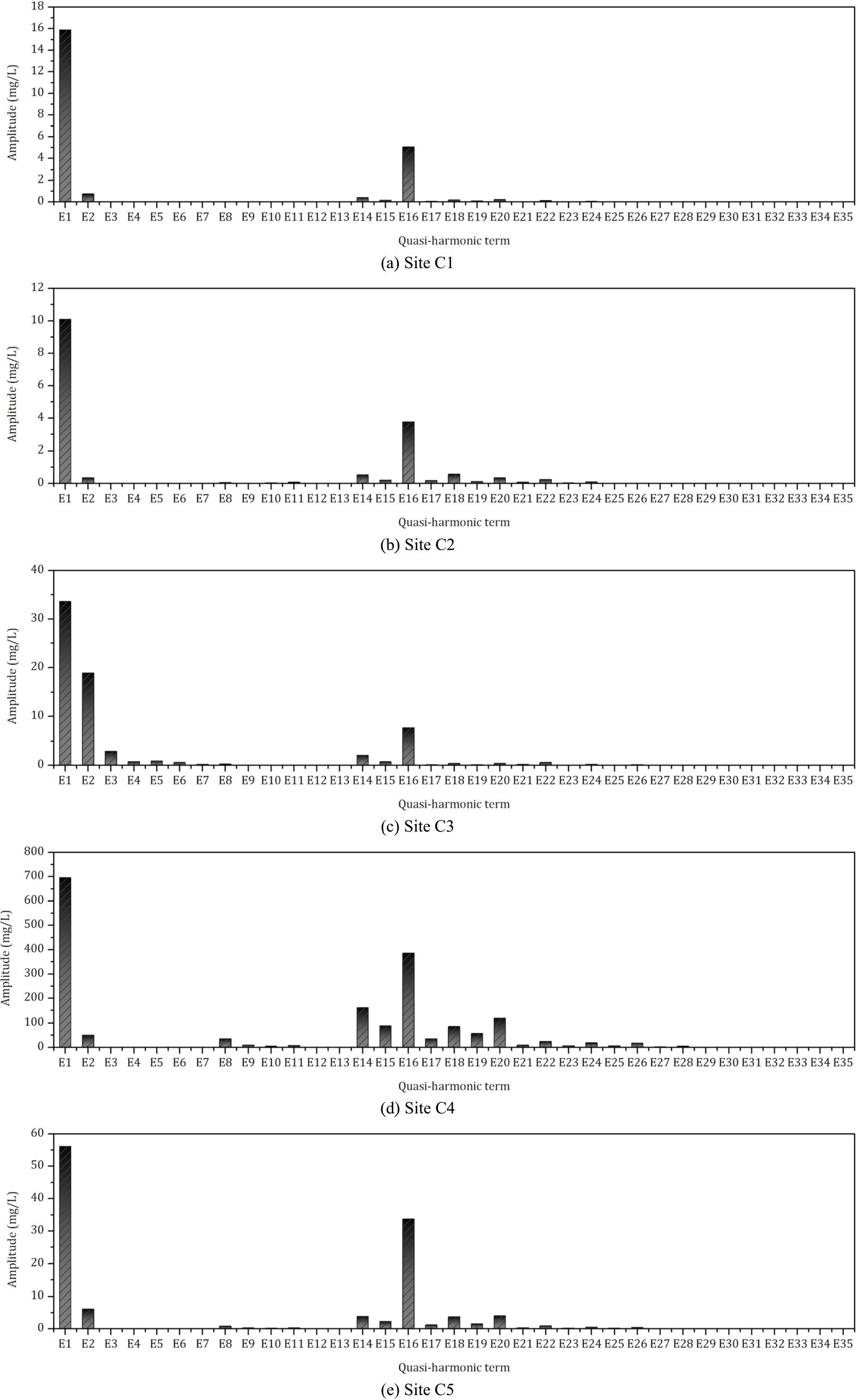
Figure 3. Comparison of the amplitudes of each quasi-harmonic terms at observation Sites (A) C1, (B) C2, (C) C3, (D) C4 and (E) C5.
The terms E2, E14, E15, E18, E20, and E22 are characterized by a relatively high magnitude, suggesting that the seabed shear stresses induced by the superposition of M2 with its interactions with S2, O1, K1, M4, and the residual current, coupled with the consequent local resuspension of sediments, are the predominant factors in the diurnal, semidiurnal, and quarter-diurnal variations of DASSC within the marine environment. E14 and E15 have similar frequencies (57.9682°/h for E14 and 58.9841°/h for E15). As M2 is the dominant tidal constituent across all sites, with M2 tidal current velocities exceeding those of S2, E14 is generally higher than E15 at all sites. E18, E20, and E22 have lower frequencies compared to E14 and E15 (13.9430°/h for E18, 15.5854°/h for E20, and 28.9841°/h for E22). As a result, even though the tidal current velocities for K1, O1, and M4 are relatively lower, their lower frequencies, as described by Equation 16, allow them to potentially reach magnitudes comparable to E14 and E15, particularly at Sites C2 and C5. The superposition of the quasi-harmonic terms of DASSC at Sites C1-C5 is depicted in Figure 4. Physically, the tidal range has a direct influence on the current velocity. Areas with a smaller tidal range, such as Site C1 and C2 (Figure 2), exhibit relatively weaker fluctuations in the diurnal, semidiurnal, and quarter-diurnal components of DASSC (as illustrated in Figure 4). Conversely, in regions with a larger tidal range, the short-period fluctuations (relative to the fortnightly cycle) are also more pronounced. A larger tidal range suggests that the amplitudes of terms E8–E13 and E25–E35 may be higher. Additionally, this increased range can result in stronger tidal currents, implying greater fluctuation amplitudes for terms E2–E7 and E14–E24.
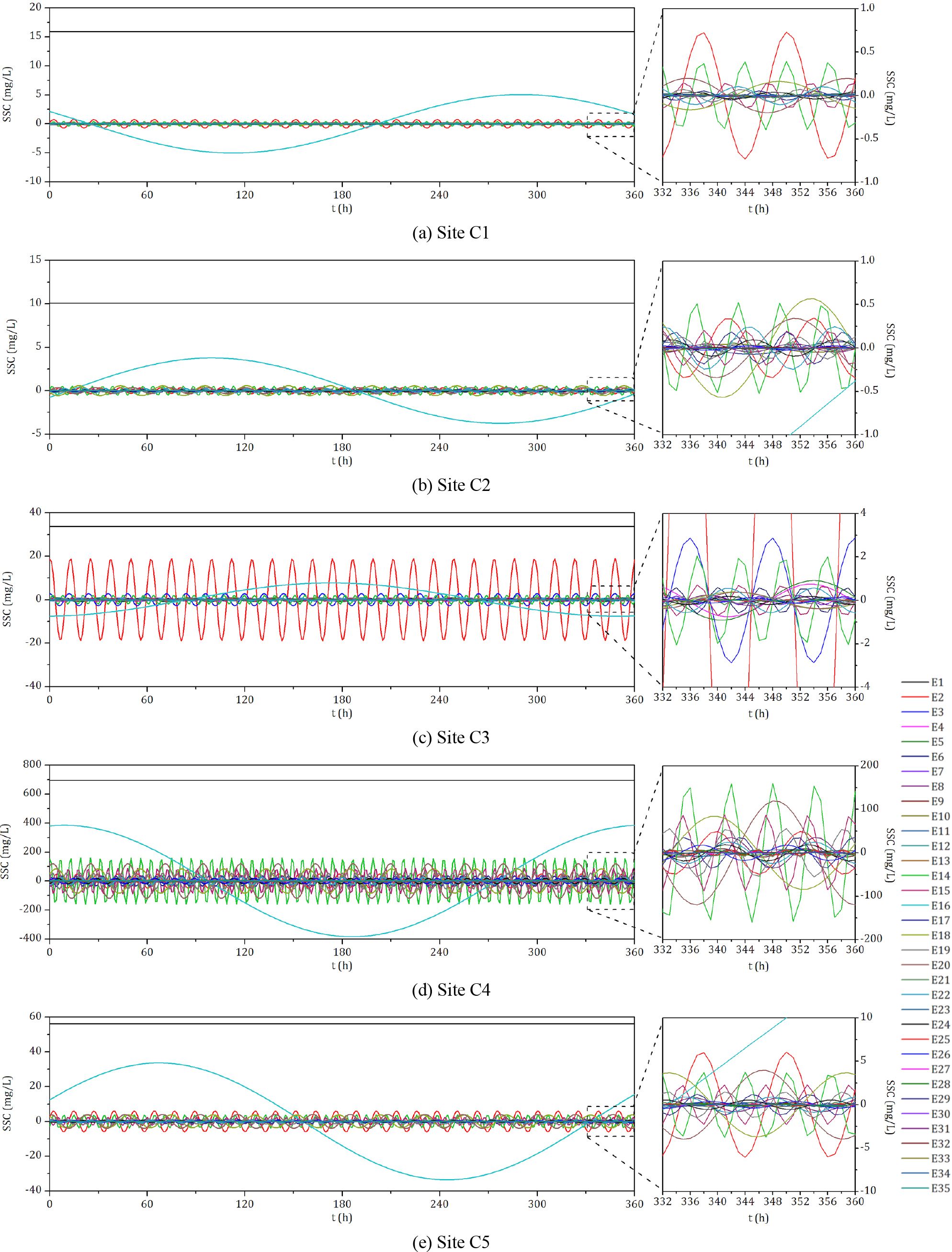
Figure 4. Superposed state of quasi-harmonic analysis terms at observation Sites (A) C1, (B) C2, (C) C3, (D) C4 and (E) C5.
Site C1 is distinguished by a relatively strong residual current (as shown in Table 2). At Site C1, besides the term E1 (representing the mean DASSC) and the long-period (fortnightly cycle) term E16, the amplitude of E2 is the highest, indicating that the residual current has a significant impact on the DASSC. A notable characteristic induced by the residual current is the asymmetry of the DASSC peaks within a semidiurnal tidal cycle, where the peaks of adjacent quarter-diurnal periods exhibit a considerable discrepancy.
In some regions, the direction and speed of the residual current can vary due to seasonal factors (such as wind and differences in freshwater discharge during wet and dry seasons in estuaries). For example, this has been reported in the Scheldt in Belgium and The Netherlands by Regnier et al. (1998). The effect of the residual current on the asymmetry is shown in Figure 5. A reverse residual current (u0 = −13cms−1) and no residual current (u0 = 0cms−1) were assumed to be comparable with the best-fit residual current (u0 = 13cms−1). This hypothetical approach aims to explore how potential seasonal changes in the direction and speed of the residual current might alter the characteristics of SSC. Without the residual current, the asymmetry of the contiguous DASSC peaks in the two contiguous quarter-diurnal periods was extremely weak. As E2 is mainly generated by the combined shear forces of the M2 tidal and the residual currents, an extremely low residual current may not strengthen the flood or ebb currents or the shear forces on the seabed. As the frequency and initial phase of E2 are twice the frequency and initial phase of E14, E2 is positively superimposed on the first peak of E14 in a semi-diurnal period and reversely superimposed on the second peak of E14. Further, if the residual current is assumed to be reversed, E2 is reversely superimposed on the first E14 peak and positively superimposed on the second E14 peak. Therefore, the direction and velocity of the residual current influence the order of the high- and low-DASSC peaks in the semi-diurnal period and the extent of peak asymmetry.
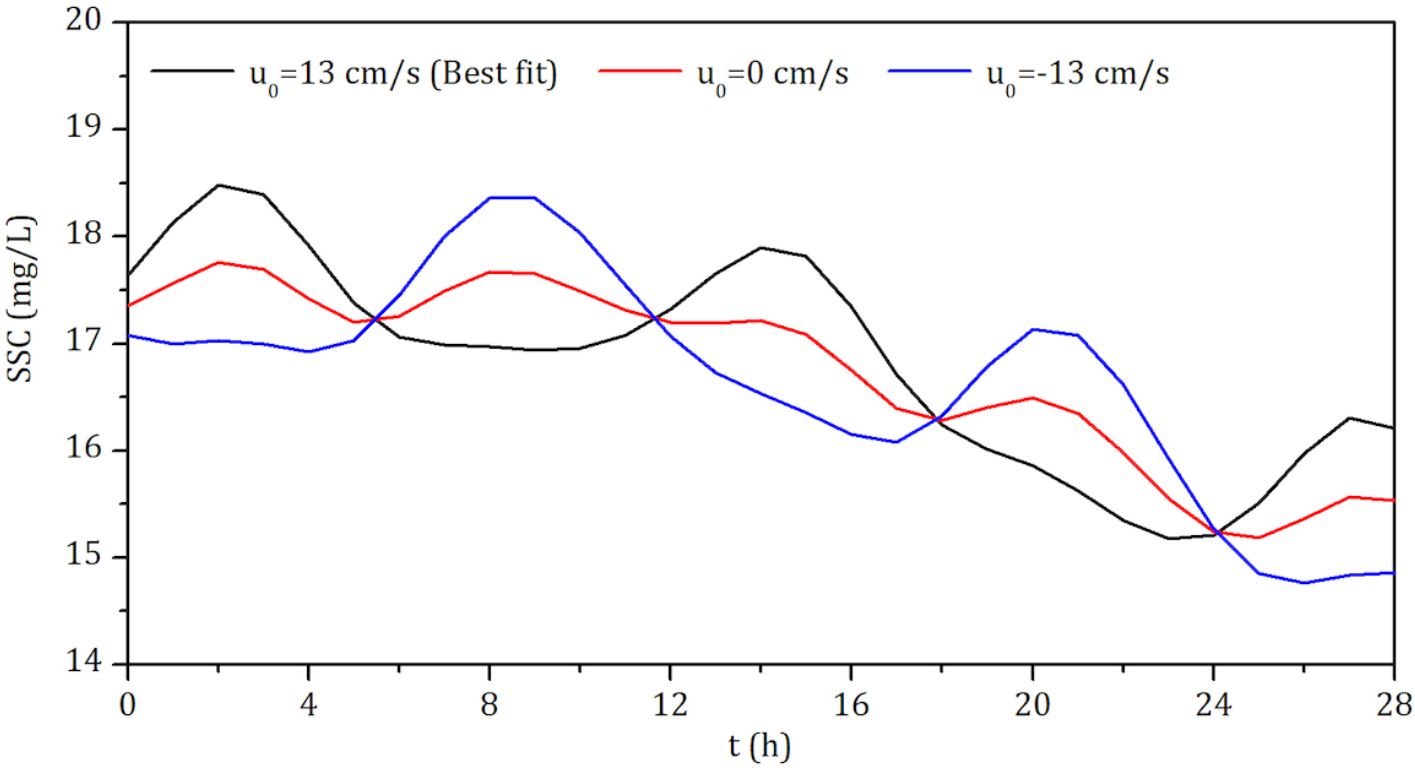
Figure 5. The effects of the best-fit residual current (u0 = 13cms−1), an artificially assumed reverse residual current (u0 = −13cms−1), and no residual current (u0 = 0cms−1) on the temporal evolution of DASSC at Site C1. Without a residual current, the asymmetry between consecutive DASSC peaks in two adjacent quarter-diurnal periods is minimal. A reverse residual current can shift the relative magnitudes of consecutive DASSC peaks, depending on whether it aligns with the flood or ebb tide.
As the frequency and initial phase of E2 are twice those of E14, E2 is positively superimposed on the first peak of E14 in a semi-diurnal period and inversely superimposed on the second peak of E14. Further, if the residual current is assumed to be reversed, E2 is inversely superimposed on the first E14 peak and positively superimposed on the second E14 peak. Therefore, the direction and velocity of the residual current influence the order of the high- and low-DASSC peaks in the semi-diurnal period and the extent of peak asymmetry.
Equation 16 indicates that the resuspension parameter B influences only the amplitude of the fortnightly DASSC term, whereas both the amplitude and phase are affected by the deposition parameter D. The phase lag between the DASSC and tidal currents over short periods (semidiurnal and quarterdiurnal) has been widely discussed in the literature (Cheng and Wilson, 2008; Yu et al., 2011; Zhu et al., 2018). The phase lag of E16 in Equation 16 indicates that there is a phase lag exists between the fortnightly DASSC quasi-harmonic term and the fortnightly evolution of the tidal current superimposed on M2 and S2. The fortnightly behavior lag was also reported in the observational data by Azhikodan and Yokoyama (2018). They explained that due to the time lag between the tidal flow and SSC, the SSC did not decrease during spring-to-intermediate tides, even though the current velocity and shear stress started to decrease. The SSC began to decrease during intermediate-to-neap tides and was considerably lower once the neap tide occurred. Since Site C1 had the least observational data compared to the other sites, and the predicted SSC for Sites C3 and C5 showed better agreement with the observed SSC trends than Sites C2 and C4, the observed SSC at Sites C3 and C5 was used to analyze the lag characteristics of the fortnightly tidal feature relative to the tidal current velocities. Using the D values for Sites C3 and C5 from Table 3 in Equation 16, the time lag between the SSC peak (E16 term) and the peak tidal current was calculated to be 10 and 14 hours, respectively. Additionally, at Sites C3 and C5, the highest SSC during the spring tide occurred 10 and 13 hours after the maximum current velocity, respectively.
Based on sediment characteristics (Figure 2), the general range of B can be determined. Initially, an empirical value of B is selected based on the seabed type. However, the first parameter to be calibrated is D, as it influences not only the amplitude but also both the long-period fortnightly variations and the short-period quarter-diurnal and semi-diurnal fluctuations. The calibration of k is completed last. In regions with relatively uniform sediment distribution, the value of k is typically small, while in non-uniform areas, it is larger and must be calibrated to match the observed SSC.
Based on the characteristics of the effects of parameters B and D on DASSC as described previously, the calibration of B and D is concurrently constrained by the phase and amplitude of both the fortnightly and semidiurnal cycles. Consequently, there are few viable combinations of parameters B and D. Figure 6 presents the unique pair of B and D parameters that align the predictions of the model with the observed spring-neap DASSC variations. Upon further comparison, the best-fit parameter set is capable of reproducing the amplitudes observed in both fortnightly and semidiurnal cycles, whereas the comparative parameter set yields underestimated amplitudes in semidiurnal cycles. Hence, the calibration results for parameters B and D have a degree of uniqueness and are considered reliable.
The controllability of the calibration results for the parameter B indicates that quasi-harmonic analysis, with its analytically solvable efficiency, can be utilized to estimate parameters that are difficult to measure, thus providing input conditions for numerical models based on systems of differential equations, such as FVCOM (Chen et al., 2006, 2012). In Equation 4, the erosion rate per unit time and unit area (M) is challenging to observe or calculate. However, through the quasi-harmonic analysis employed in the present study, parameter B can be calibrated. Subsequently, the drag coefficient (CD) can be calibrated using a hydrodynamic model, and the critical shear stress for erosion (τc) can be estimated via the Shields curve (Shields, 1936; Dou, 1999), thereby enabling the estimation of M.
In estuarine and coastal areas dominated by M2, S2, O1, K1, M4 and MS4 tidal currents, a computationally efficient mathematical model capable of providing analytical solutions for predicting SSC based on resuspension, deposition, and advection was established. The DASSC was decomposed into 35 quasiharmonic terms, including a primary fortnightly term generated by the combined action of the M2 and S2 currents. The fortnightly term had a frequency of 1.0159° h−1, which is the difference between the frequencies of the M2 and S2 tides.
Although the observational sites in this study did not detect a significant influence of shallow water tides on the fortnightly variations of SSC, the quasi-harmonic analysis results indicate that in certain narrow bay heads, due to nonlinear tidal interactions, the relationship between the phase of the M4 tidal elevation and the phase of the M2 tidal current can significantly impact the mean SSC during the fortnightly cycle, as well as the amplitude of the M4 tidal elevation. Furthermore, the MS4 tidal elevation can affect the amplitude of fortnightly SSC fluctuations.
The conditions of application of the quasi-harmonic analytical solution are as follows: (1) The difference in the direction of ebb and flow is close to 180°. (2) The wave action is weak. (3) M2 is the main component of the tides and tidal currents. (4) Half of the tidal range is much lower than the water depth. In regions where tidal currents exhibit rotary flow characteristics, the effectiveness of this method is constrained by the direction of the residual current and the concentration gradient. Specifically, if the residual current is strong or the concentration gradient is large, and if their directions deviate significantly from the main flow directions during flood and ebb tides, the predicted suspended sediment concentration using this method may yield relatively larger errors.
The two peaks of the DASSC in the two contiguous quarter-diurnal periods in this study were asymmetric during the semi-diurnal period. The direction and velocity of the residual current influenced the order of the high and low DASSC peaks in the semi-diurnal period and the magnitude of the peak asymmetry, respectively.
The resuspension properties of the sediment only affect the amplitude of the fortnightly DASSC term and do not affect the phase. The deposition properties affected both the amplitude and the phase of the fortnightly DASSC term.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
ZZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. BL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. BC: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. BY: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WC: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HX: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2023YFC3007900), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Contract No. ZR2022QD042), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52301345).
Author HX was employed by Qingdao Marine Equipment Inspection & Testing Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Azhikodan G., Yokoyama K. (2018). Sediment transport and fluid mud layer formation in the macro-tidal chikugo river estuary during a fortnightly tidal cycle. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 202, 232–245. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.01.002
Bass S. J., Aldridge J. N., McCave I. N., Vincent C. E. (2002). Phase relationships between fine sediment suspensions and tidal currents in coastal seas. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 107, 14. doi: 10.1029/2001JC001269
Bricker J. D., Inagaki S., Monismith S. G. (2005). Bed drag coefficient variability under wind waves in a tidal estuary. J. Hydraulic Eng. 131, 497–508. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:6(497)
Buschman F., van der Vegt M., Hoitink A., Hoekstra P. (2013). Water and suspended sediment division at a stratified tidal junction. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 118, 1459–1472. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v118.3
Chen C., Beardsley R., Cowles G. (2006). An unstructured grid, finite-volume coastal ocean model (fvcom) system. Oceanography 19, 78–89. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2006.92
Chen C., Beardsley R. C., Cowles G. W., Qi J., Lai Z., Gao G, et al. (2012). An unstructured grid, finite-volume community ocean model: FVCOM user manual, New Bedford, Mass. SMAST/UMASSD-13-0701. (New Bedford, Mass: Sea Grant College Program).
Cheng P., Wilson R. E. (2008). Modeling sediment suspensions in an idealized tidal embayment: importance of tidal asymmetry and settling lag. Estuaries coasts 31, 828–842. doi: 10.1007/s12237-008-9081-4
Deltares (2012). User Manual for Delft3D-Flow: Simulation of Multi-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Flows and Transport Phenomena, Including Sediments (Delft, Netherlands: Deltares).
Du Y., Lin H., He S., Wang D., Wang Y. P., Zhang J. (2021). Tide-induced variability and mechanisms of surface suspended sediment in the Zhoushan archipelago along the southeastern coast of China based on Goci data. Remote Sens. 13, 929. doi: 10.3390/rs13050929
Gao J., Hou L., Liu Y., Shi H. (2024). Influences of bragg reflection on harbor resonance triggered by irregular wave groups. Ocean Eng. 305, 117941. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117941
Gao J., Ma X., Dong G., Chen H., Liu Q., Zang J. (2021). Investigation on the effects of bragg reflection on harbor oscillations. Coast. Eng. 170, 103977. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2021.103977
Gao J., Shi H., Zang J., Liu Y. (2023). Mechanism analysis on the mitigation of harbor resonance by periodic undulating topography. Ocean Eng. 281, 114923. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114923
Gelfenbaum G. (1983). Suspended-sediment response to semidiurnal and fortnightly tidal variations in a mesotidal estuary: Columbia river, U. S. A. Mar. Geol. 52, 39–57. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(83)90020-8
Hill D., Jones S., Prandle D. (2003). Derivation of sediment resuspension rates from acoustic backscatter time-series in tidal waters. Continent. Shelf Res. 23, 19–40. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00170-X
HydroQual, Inc (2002). A Primer for ECOMSED, User Manual (Mahwah, New Jersey, USA: HydroQual, Inc.).
Li Z., Li M. Z., Dai Z., Zhao F., Li J. (2015). Intratidal and neap-spring variations of suspended sediment concentrations and sediment transport processes in the north branch of the Changjiang estuary. Acta oceanol. Sin. 34, 137–147. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0605-z
Liu H., Zhang Z., Kang H., Yin B. (2020). “Numerical simulation of the shallow water tides in bohai sea,” in IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Vol. 453. 012009 (Bristol, England, UK: IOP Publishing).
Prandle D. (1997). Tidal characteristics of suspended sediment concentrations. J. hydraulic Eng. 123, 341–350. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1997)123:4(341)
Regnier P., Mouchet A., Wollast R., Ronday F. (1998). A discussion of methods for estimating residual fluxes in strong tidal estuaries. Continent. Shelf Res. 18, 1543–1571. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(98)00071-5
Rodriguez A., Brea D., Farías D., Bravo H. R., Castelló E., Hillman G., et al. (2003). Hydraulic analyses for a new bridge over the Parana river, Argentina. Int. J. sediment Res. 18, 166–175. doi: 10.1029/2005JC003045
Sanford L. P. (2008). Modeling a dynamically varying mixed sediment bed with erosion, deposition, bioturbation, consolidation, and armoring. Comput. Geosci. 34, 1263–1283. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2008.02.011
Schoellhamer D. H. (2002). Variability of suspended-sediment concentration at tidal to annual time scales in San Francisco bay, USA. Continent. Shelf Res. 22, 1857–1866. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00042-0
Shields A. (1936). Anwendung der Aehnlichkeitsmechanik und der Turbulenzforschung auf die Geschiebebewegung (Berlin: Preussischen Versuchsanstalt fur Wasserbau). Technical report.
Stanev E. V., Brink-Spalink G., Wolff J.-O. (2007). Sediment dynamics in tidally dominated environments controlled by transport and turbulence: A case study for the east Frisian Wadden sea. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 112.
Tattersall G., Elliott A., Lynn N. (2003). Suspended sediment concentrations in the Tamar estuary. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 57, 679–688. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00408-0
Toublanc F., Brenon I., Coulombier T., Le Moine O. (2015). Fortnightly tidal asymmetry inversions and perspectives on sediment dynamics in a macrotidal estuary (Charente, France). Continent. Shelf Res. 94, 42–54. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.12.009
Uncles R. J., Stephens J. A. (1989). Distributions of suspended sediment at high water in a macrotidal estuary. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 94, 14395–14405. doi: 10.1029/JC094iC10p14395
Vale C., Sundby B. (1987). Suspended sediment fluctuations in the Tagus estuary on semi-diurnal and fortnightly time scales. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 25, 495–508. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(87)90110-7
Wang X. H. (2002). Tide-induced sediment resuspension and the bottom boundary layer in an idealized estuary with a muddy bed. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 32, 3113–3131. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2002)032<3113:TISRAT>2.0.CO;2
Warner J. C., Sherwood C. R., Signell R. P., Harris C. K., Arango H. G. (2008). Development of a three-dimensional, regional, coupled wave, current, and sediment-transport model. Comput. geosci. 34, 1284–1306. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2008.02.012
Xiong J., Wang X. H., Wang Y. P., Chen J., Shi B., Gao J., et al. (2018). Reprint of mechanisms of maintaining high suspended sediment concentration over tide-dominated offshore shoals in the southern yellow sea. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 206, 2–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.03.019
Yang Z. Q., Hamrick M. J. (2003). Variational inverse parameter estimation in a cohesive sediment transport model: an adjoint approach. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans 108, 3005. doi: 10.1029/2002JC001423
Yee-chung J., Qingchao G. (2004). “Modelling erosion and deposition by 1d depth-averaged moment equations,” in Proceedings of the Ninth International Sumposium on River Sedimentation. Beijing China: Tsinghua University Press.
Yu Q., Flemming B. W., Gao S. (2011). Tide-induced vertical suspended sediment concentration profiles: phase lag and amplitude attenuation. Ocean Dynam. 61, 403–410. doi: 10.1007/s10236-010-0335-x
Yu Q., Wang Y. P., Flemming B., Gao S. (2012). Tide-induced suspended sediment transport: Depth-averaged concentrations and horizontal residual fluxes. Continent. Shelf Res. 34, 53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.11.015
Keywords: suspended sediment, fortnightly characteristics, quasi-harmonic analysis, mathematical solution, numerical model
Citation: Zhu Z, Liang B, Chen B, Yang B, Chi W, Xu H and Hu Z (2024) Quasi-harmonic analysis of fortnightly suspended sediment response to semi-diurnal tidal currents. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1464037. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1464037
Received: 13 July 2024; Accepted: 18 November 2024;
Published: 09 December 2024.
Edited by:
Alejandro Jose Souza, Center for Research and Advanced Studies - Mérida Unit, MexicoReviewed by:
Aldo Sottolichio, Université de Bordeaux, FranceCopyright © 2024 Zhu, Liang, Chen, Yang, Chi, Xu and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bo Yang, yangbo1011@ouc.edu.cn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.