- 1Machine Learning for Earth Sciences Laboratory, Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Dolgoprudny, Russia
- 2Shirshov Institute of Oceanology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
X-band marine radar captures the signal reflected from the sea surface. Theoretical studies indicate that the initial unfiltered signal contains meaningful information about wind wave parameters. Traditional methods of significant wave height (SWH) estimation rely on physical laws describing signal reflection from rough surfaces. However, recent studies suggest the feasibility of employing artificial neural networks (ANNs) for SWH approximation. Both classical and ANN based approaches necessitate costly in situ data. In this study, as a viable alternative, we propose generating synthetic radar images with specified wave parameters using Fourier-based approach and Pierson–Moskowitz wave spectrum. We generate synthetic images and use them for unsupervised learning approach to train a convolutional component of the reconstruction ANN. After that, we train the regression ANN based on the previous convolutional part to obtain SWH back from the synthetic images. Then, we apply preliminary trained weights for the regression model to train SWH approximation on the dataset of real sea clutter images. In this study, we demonstrate the increase in SWH estimation accuracy from radar images with preliminary training on synthetic data.
1 Introduction
X-band marine radars play an essential role in ship navigation and safety through obstacle detection (Huang et al., 2017). Besides their primary function, raw radar images capturing sea clutter contain substantive information (Young et al., 1985). Analysis of the spatial distribution of the reflected signal facilitates the derivation of parameters associated with wind waves and swell. Additionally, these radar images allow estimating such vital sea surface characteristics as significant wave height (SWH). Sea surface examination is strongly linked to ocean-atmosphere interaction and, consequently, to long-term climate reconstructions, such as Global Atlas of Ocean Waves1.
Given that the intensities of sea clutter radar images do not correspond directly to the ocean surface elevation on a one-to-one scale, a problem of accurate backscatter signal modeling is of great scientific interest. Such an elaborated model would give the opportunity to study sea surface with high temporal and spatial resolution (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004).
The classical approaches of SWH estimation include Fourier analysis and a linear dispersion relationship to recognize wave signals within the temporal series of radar data. One of the examples is the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR)-analysis-based method proposed by (Nieto-Borge et al., 2008). The method necessitates the incorporation of modulation transfer functions and calibration coefficients specific to individual radar antennas (Nieto-Borge et al., 1999), thereby constraining its generalizability. Despite this limitation, the classical methodology remains extensively applied for real-time estimation of ocean wave parameters, processing the back-scatter spectrum derived from radar images (Tilinina et al., 2022).
In addition to classical approaches, radar data processing includes methodologies that are potentially faster and highly independent of radar antenna specifications. Notably, certain publications show superior SWH estimation quality through contemporary artificial intelligence (AI)-based techniques (Vicen-Bueno et al., 2012), in comparison to classical methodologies. Within machine-learning paradigm, the functional relationships, such as artificial neural networks (ANNs), between radar images and corresponding SWH values are approximated through training on extensive datasets (Park et al., 2020). For this group of methods, the efficacy of regression quality can potentially be correlated with the size and the distribution of the training dataset (Long et al., 2017).
The authors of (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019) address the challenge of limited data by employing an algorithm for generating synthetic radar images with arbitrary SWH value. This methodology uses technique of generating realistic ocean surfaces, as detailed in (Mastin et al., 1987). While the methodology in (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019) does not incorporate image synthesis within a machine-learning framework, the ANN model and synthetic datasets can potentially enhance the overall SWH estimation from real X-band radar images.
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) show their efficacy in image recognition and feature extraction across various scientific domains, including geosciences. The notable instances are illustrated in (Choi et al., 2020; Kim et al., 2021), where CNNs are employed for real-time SWH estimation utilizing X-band radar images. The temporal convolutional network (TCN) is a variant of CNN architecture proposed in (Bai et al., 2018) for sequence processing. Based on it, (Huang et al., 2021) propose a TCN-based model to retrieve SWH from X-band marine radar images.
In summary, the recent progress in ANN and the emergence of modern machine-learning techniques have substantially diversified radar image processing methods. Nonetheless, the findings in this research domain present conflicting outcomes, and numerous questions persist. Consequently, evaluating current methodologies for radar image generation and SWH estimation remains a subject of ongoing scientific interest.
In this paper, we demonstrate the utilization of a preliminarily trained CNN for SWH estimation from real marine X-band radar images of sea clutter. Initially, we elaborate the methodology of generating a synthetic dataset of radar images. We train a model that reconstructs synthetic images in unsupervised learning approach. After that, we use preliminarily trained part of the reconstruction model to construct and train a regression model that approximates SWH from the synthetic image. Further, the pre-trained regression architecture is trained on a dataset of real radar images. We then compare the results of this pre-trained model with the quality of the simple SWH regression model.
In this study, we do not aim to develop a model that would accurately reproduce the radar signal from a given sea surface. Our goal is to increase the accuracy of the ANN-based model approximating SWH value from the radar image.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we provide the details of the real radar image dataset, the methodology of the artificial radar image synthesis. and the architectures of the applied ANNs, quality metrics and training and evaluation procedures. In Section 3, we provide the results of the elaborated model training. In Section 4, we analyze how SWH estimation quality increases with pre-training on synthetic dataset. Concluding remarks are made in Section 5.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Initial data
For this research, we adopt the data collection methodology outlined in (Tilinina et al., 2022). Our dataset comprises samples obtained during four research expeditions conducted in the Atlantic and Arctic oceans. These expeditions were undertaken by the Shirshov Institute of Oceanology of the Russian Academy of Sciences within the governmental program of regular ocean observations.
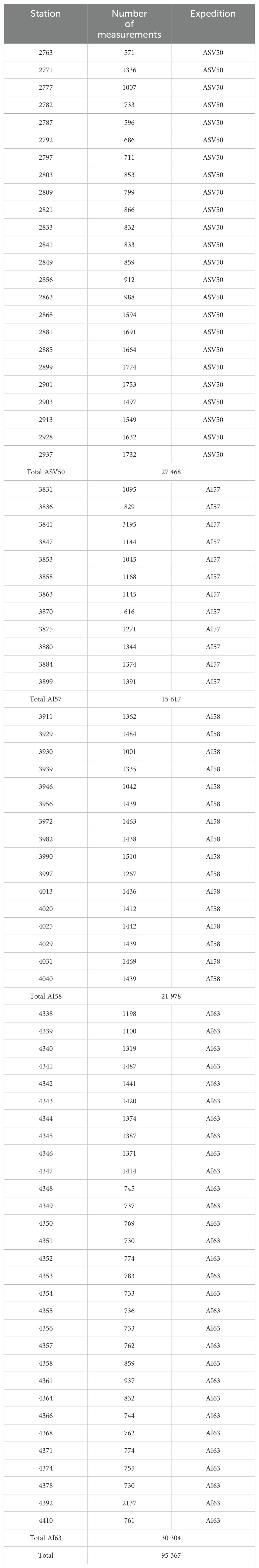
The routes of the expeditions encompass points with SeaVision radar images and/or Spotter buoys measurements2. Comprehensive details about the research expeditions can be found in Table 1.
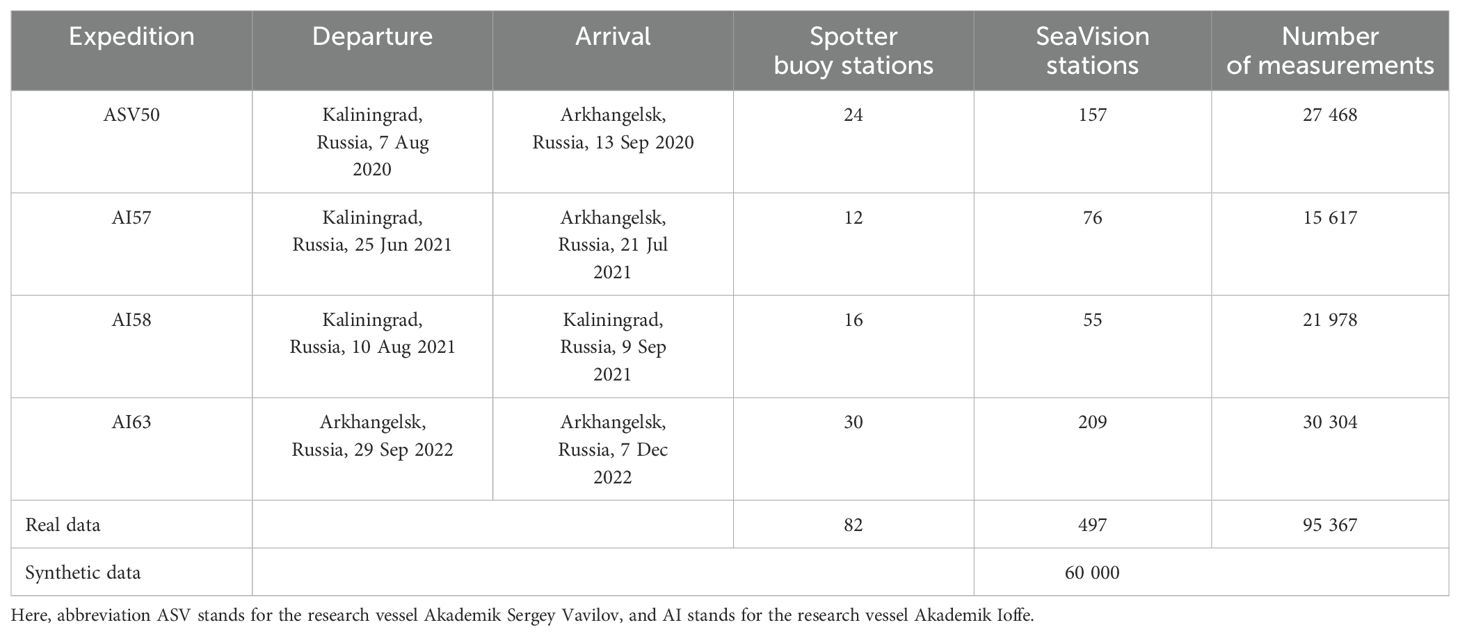
Table 1. Summary of undertaken scientific research marine cruises equipped with SeaVision and Spotter buoy for collecting real dataset of this study and summary of the synthetic dataset.
For clarity, a “station” refers to an instance where the ship is adrift, thereby creating optimal conditions for data acquisition. Table 1 outlines the departure and arrival ports, as well as the number of stations where data from both the Spotter buoy and the SeaVision radar were collected.
The selection of locations for sea wave observation was based on local weather conditions and temporal constraints. In total, there around 95 000 SeaVision images and 62 hours of simultaneous Spotter buoy in situ measurements were collected. It is noteworthy (Table 1) that the number of Spotter buoy stations differs from the number of SeaVision stations. This discrepancy arises because the engineering support required for operations at the buoy stations is significantly more complex compared to the SeaVision operations, resulting in some SeaVision stations lacking corresponding buoy measurements. In this study, however, we focus exclusively on the subset of data comprising synchronous observations from both the Spotter buoy and the SeaVision radar, as summarized in Table 1. The summary of the station data is in Table 2.
Spotter wave buoy measures vertical and horizontal displacements of the ocean surface with 2.5 Hz sampling frequency providing highly accurate measurements of wind wave characteristics (Raghukumar et al., 2019) and collecting the training dataset of SWH.
Random sea-surface elevation can be modeled as a stationary Gaussian process, wherein the statistical properties are defined by spectral moments. For instance, the surface elevation variance corresponds to the zeroth moment. To determine the wave spectrum, Welch’s method is employed, utilizing a 600-second Hann window. From the zeroth spectral moment, SWH is calculated.
To compute the current value of SWH, the ten minutes of buoy data are analyzed, comprising approximately 1546 records, so that every time interval corresponds in time to the radar image coinciding with the center of the interval. The spectrum is calculated using a Hann window of equivalent width. This window is then incrementally shifted forward by one record at a time until the analysis encompasses the most recent ten minutes of data.
SeaVision radar creates one sea clutter image every two seconds. Research vessels ASV and AI are equipped with JRC JMA-9110-6XA and JMA-9122-6XA X-band radars, respectively. These radars have the same principal characteristics, such as the frequency of 9.41 GHz, a 6-foot antenna with a horizontal directional resolution of 1.2°, and almost identical shortest pulse lengths of 0.08 µs and 0.07 µs, respectively. Images are stored externally along with the GPS coordinates, speed over the ground (SOG), and course over the ground (COG). These files are later combined and converted into NetCDF format for post-processing. Radar antenna characteristics with the detailed description of the image collection process can be found in (Tilinina et al., 2022).
The center of the resulting sea clutter image coincides with the location of the radar antenna. Raw images with the spatial resolution of 1.875 m cover >7 km radius around the ship. The image exhibits a signal with diverse structures and intensities attributed to local wind direction, vessel rotation, and reflections of electromagnetic signal from the rough ocean surface (Lyzenga and Walker, 2015).
There is a “blind” zone near the center due to signal reflection from the vessel. To mitigate this effect, we exclude the part of the image within a 300 m radius around the ship. After visual examination of radar images, we observe that the reflected signal becomes less distinct with increasing distance from the radar antenna. As a result, we choose a radius of ≈2000 m to ensure the highest possible significant variability observed in radar data. Consequently, first, we restrict our analysis to the 300–2000 m range for further processing.
The important step of the data pre-processing is a choice of the optimal 180° sector containing the most informative wave signal. The technique used in this research extracts the most contrasting area from the entire radar image to provide the most clearly identified wind waves. For every station, the sector with the largest temporal standard deviation is the optimal sector. In this study, considering spatial resolution of 1.875 m, we choose the outer radius of the meaningful area as ≈1920 m (1024 pixels). Hence, we work with pre-processed 1024×2048 pixels images in contradistinction to 384×384 pixels images in (Tilinina et al., 2022).
Then, we linearly transform the values of the back-scattered radar signal image so that for every specific image, the minimum value is 0 and the maximum is 255. For further purposes, we use only masked real 1024×2048 pixels images. Namely, we replace the pixels outside 300–1920 m radius area with zeros. The example of the pre-processed radar image is shown in Figure 1.
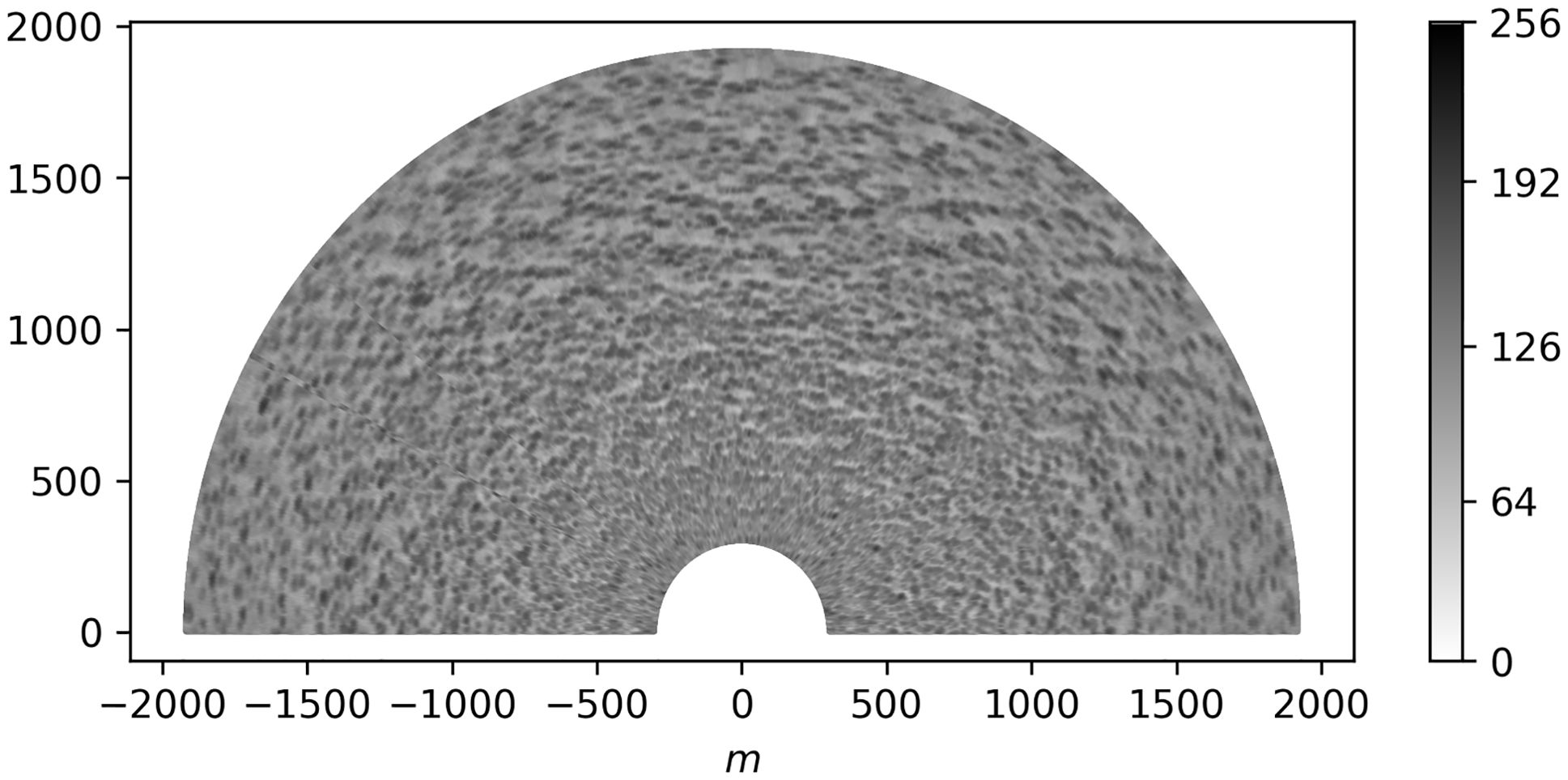
Figure 1. The example of the pre-processed radar image from AI57 marine research mission of Shirshov Institute of Oceanology of Russian Academy of Sciences. The position of a radar antenna is in (0,0) point.
2.2 Synthesis of realistic sea surface
We develop the methodology of generating synthetic radar images (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019) based on realistic ocean scenes (Mastin et al., 1987). The authors of (Mastin et al., 1987) elaborated a technique that presents fully developed sea with an empirical modified Pierson–Moskowitz sea power spectrum (Pierson and Moskowitz, 1964).
As proposed in (Mastin et al., 1987), we first generate a 2088×2088 pixels array with the noise values uniformly distributed from −0.5 to 0.5. We choose the image size that is bigger than 2048 pixels to further exclude possible edge effects. The result of this step is a white-noise image (see Figure 2A).
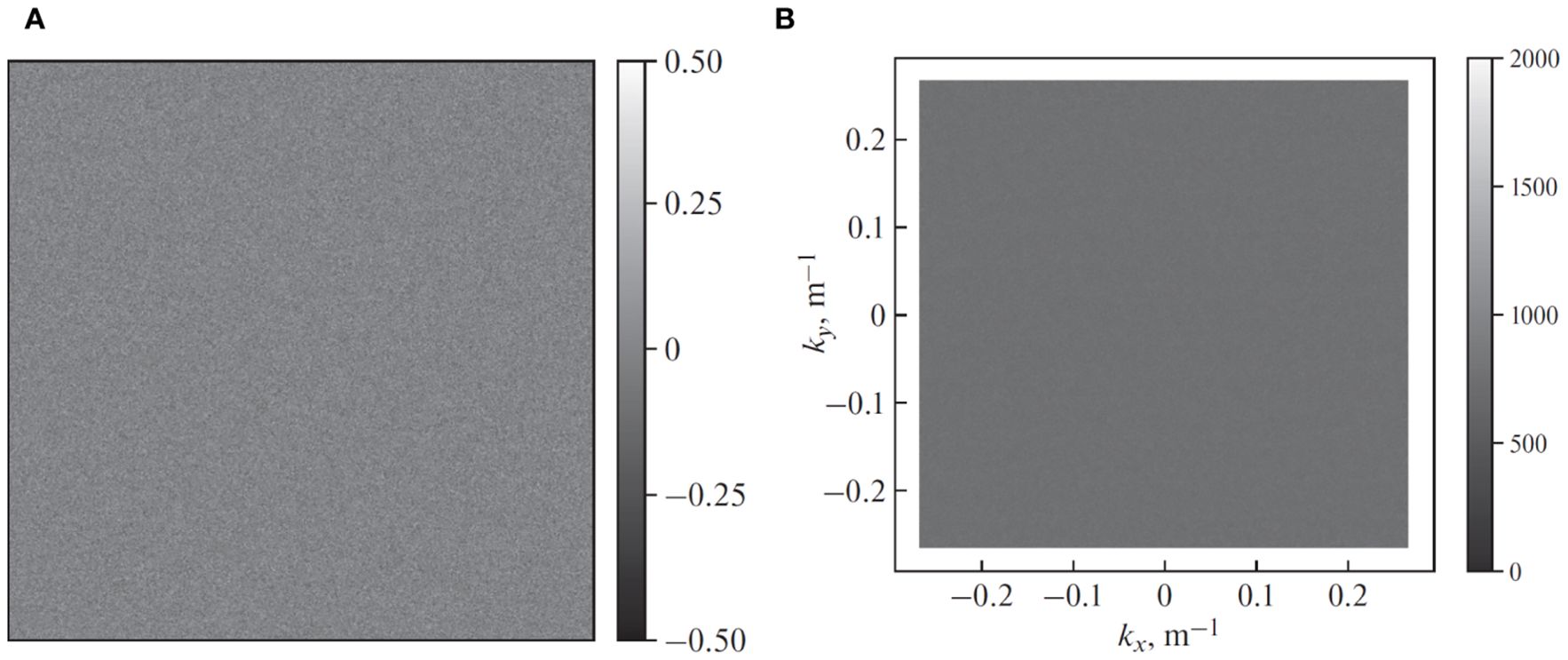
Figure 2. The first stage of the sea surface synthesis. (A) White noise. (B) Fourier-transformed white noise.
The spatial resolution is 1.875 m, equal to that of the real radar images. This parameter allows us to perform a two-dimensional forward Fourier transform of the white-noise image to generate an array of complex numbers. The magnitude of these complex Fourier components is shown in Figure 2B. The coordinate axes in Figure 2B are orthogonal components kx and ky [m−1] of spatial frequency vector.
The methodology of creating a synthetic sea surface is based on the following theory. In this research, we consider a simple case of fully developed wind waves, characterized by a wave power spectrum constant in time. Under these assumption, W. Pierson and L. Moskowitz (Pierson and Moskowitz, 1964) empirically approximated the mathematical form of the downwind power spectrum FPM(f):
where f is the temporal frequency [Hz], fm is the peak temporal frequency [Hz], α = 0.0081 is the Phillips constant, and g is the mean gravitational acceleration [m/s2].
The form of the fully-developed wind spectrum (1) depends solely on a single parameter fm that indicates the frequency of the spectrum maximum. It was also discovered in (Pierson and Moskowitz, 1964) that fm is a function of 10 m surface wind speed U10 with the constant mean gravitational acceleration g:
SWH is usually defined as an average measurement of the largest 33% of waves3: , where is the total number of measured waves, is a height of the -th wave from the largest 33%. For a given power spectrum , we can equivalently calculate significant wave height4: . Thus, from (2), for Pierson–Moskowitz spectrum (1), we obtain:
Hence, we completely determine the shape of the one-dimensional downwind fully developed wave spectrum (1) with either U10 or SWH (3).
The two-dimensional wave power spectrum F(f,φ) was proposed in (Hasselmann et al., 1980) as an extension of (1) taking into account wind direction:
where FPM(f) is one-dimensional Pierson-Moskowitz spectrum from (1), D(f,φ) is a normalized directional multiplier at angle φ from the downwind direction, and is the gamma function. The empirical parameters in (5) are defined by (Mastin et al., 1987): and is equal to 4.06 for and –2.34 for .
The example of the normalized filter FPM(f)D(f,φ) for U10 = 15 m/s for the frequency domain of Figure 2B is shown in Figure 3A. To transform the white-noise spectrum into the two-dimensional Pierson–Moskowitz spectrum (4), we multiply the magnitudes of the Fourier components of the initial white-noise image by (1) and (5).
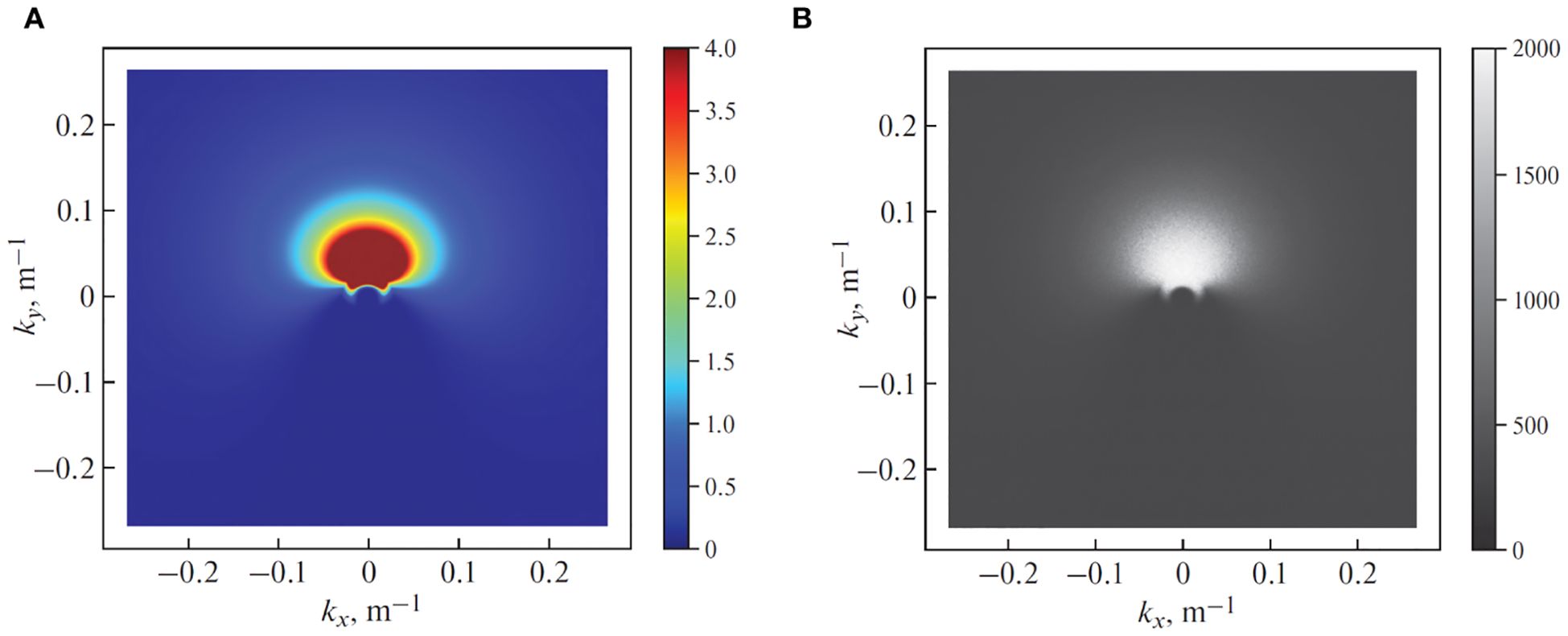
Figure 3. The second stage of the sea surface synthesis. (A) Two-dimensional spectral filter (U10 = 15 m/s) for white-noise Fourier components. (B) Filtered magnitudes of white-noise Fourier components.
The resulting spectrum creates a narrower profile near fm(2) in the downwind direction, forms a bimodal spectrum shape for φ ≈ 90° from the downwind direction, and suppresses the long-crested peak frequency components, while retaining non-peak frequencies (Mastin et al., 1987). The filtered magnitudes of the white-noise Fourier components from Figure 2B are shown in Figure 3B.
Subsequently, we combine the filtered magnitudes with the original phase of the white-noise complex Fourier components, and apply the inverse Fourier transform, as described in (Mastin et al., 1987). The result of this procedure is a 2088×2088 pixels array of complex numbers. The desired synthetic sea surface is a real part of this array. We illustrate the full-domain realistic sea surface and its central part in Figure 4.
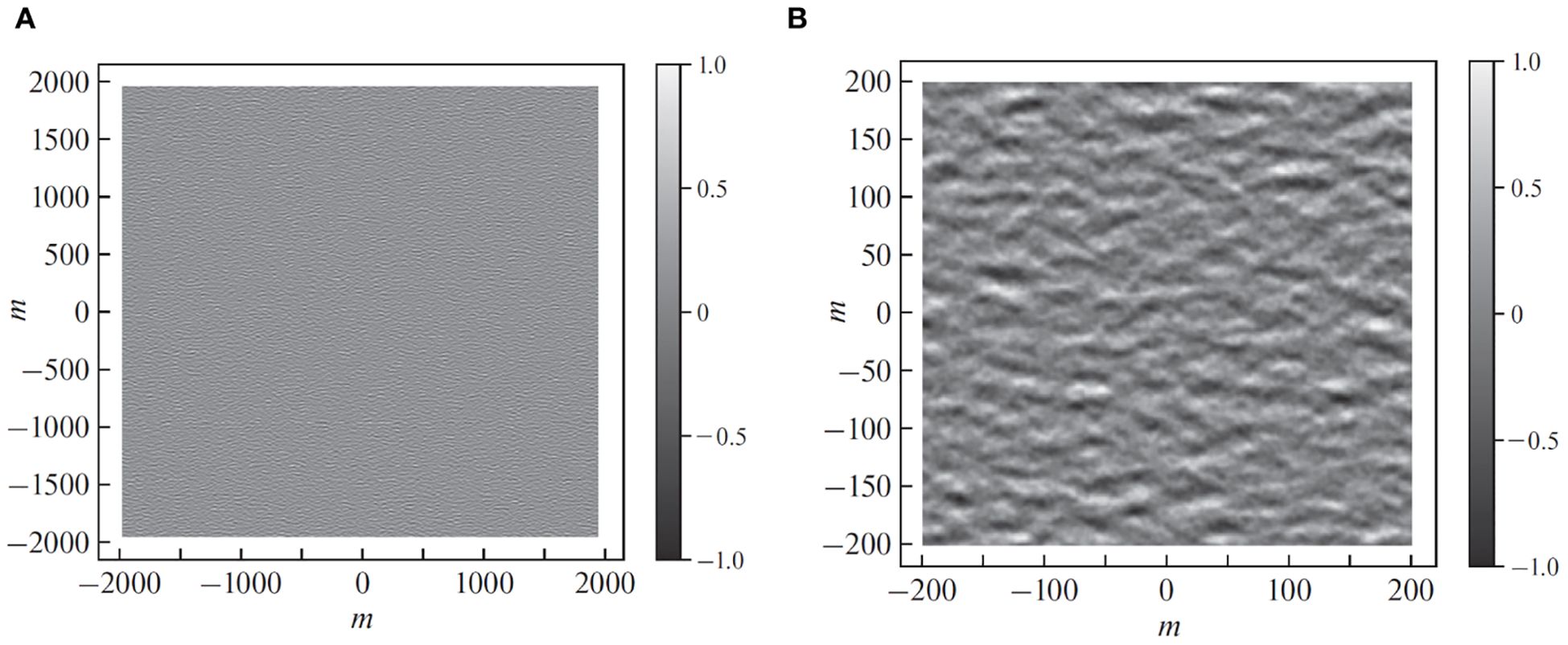
Figure 4. The synthetic sea surface created by processing the white-noise image from Figure 2A. (A) Full image. (B) 200 m × 200 m area.
2.3 Synthesis of radar images
Here we describe transformation of the synthetic sea surfaces obtained in 2.2 into synthetic X-band radar images.
As (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004) claim, sea clutter primarily arises due to backscatter through Bragg resonance with ocean waves that have wavelengths similar to the transmitted electromagnetic waves. Longer waves become visible in radar images because they modulate the sea clutter signals with three effects: hydrodynamic modulation, tilt modulation, and shadowing (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004). Hydrodynamic modulation transforms the energy of the smaller ripples due to their interaction with longer waves. Tilt modulation results from changes in the effective incidence angle along the slope of the long waves. Shadowing involves the partial shadowing of the sea surface by higher waves (Plant and Keller, 1990; Wetzel, 1990; Lee et al., 1995; Nieto-Borge et al., 2004).
The numerical simulations show that when the wave field is homogeneous in space and stationary in time, hydrodynamic modulation is negligible (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004). Moreover, local wind velocity modulation is pre-filtered from the received radar signal (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019).
Although it is proved that geometrical shadowing serves as a first-order approximation of the backscattering phenomenon, while tilt modulation have a relatively minor impact on the imaging mechanism compared to geometric shadowing at grazing incidence (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004; Wijaya and van Groesen, 2016), in this study we consider both geometrical effects omitting only hydrodynamic and local wind velocity modulations.
Thus, for simplification purposes, we propose that two main effects that influence the X-band signal reflected from the sea surface are geometrical shadowing (Gangeskar, 2014; Wijaya and van Groesen, 2016; Ludeno and Serafino, 2019) and simplified tilt modulation (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019).
As in (Wijaya and van Groesen, 2016), we believe it is important to note that the following algorithm that transforms the synthetic sea surface into the X-band radar image presented in this paper pertain to “idealized” scenarios, specifically, linear seas that are not influenced by local or global wind effects.
Simplifications mentioned above are based mainly on the fact that we use synthetic radar images solely for pre-training but not for the final ANN-based regression model. Hence, we do not claim complete realism for the generated radar images, in accordance with the elaborated papers (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004; Wijaya and van Groesen, 2016; Ludeno and Serafino, 2019).
We further follow the transformation technique proposed by (Nieto-Borge et al., 2004) with the subsequent modifications (Gangeskar, 2014; Wijaya and van Groesen, 2016; Ludeno and Serafino, 2019).
Briefly, in this study, the shadowing effect refers to the geometrical optics approximation. In certain areas, the sea surface obstructs the reflection of radar rays from adjacent areas, leading to the shadowing of nearby waves. Consequently, the radar antenna receives no meaningful signal from the shadowed parts of the sea surface (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019). Obviously, this phenomenon depends on the grazing angle that is determined by the relationship between the radar antenna height Za and the distance x to the antenna (Figure 5).
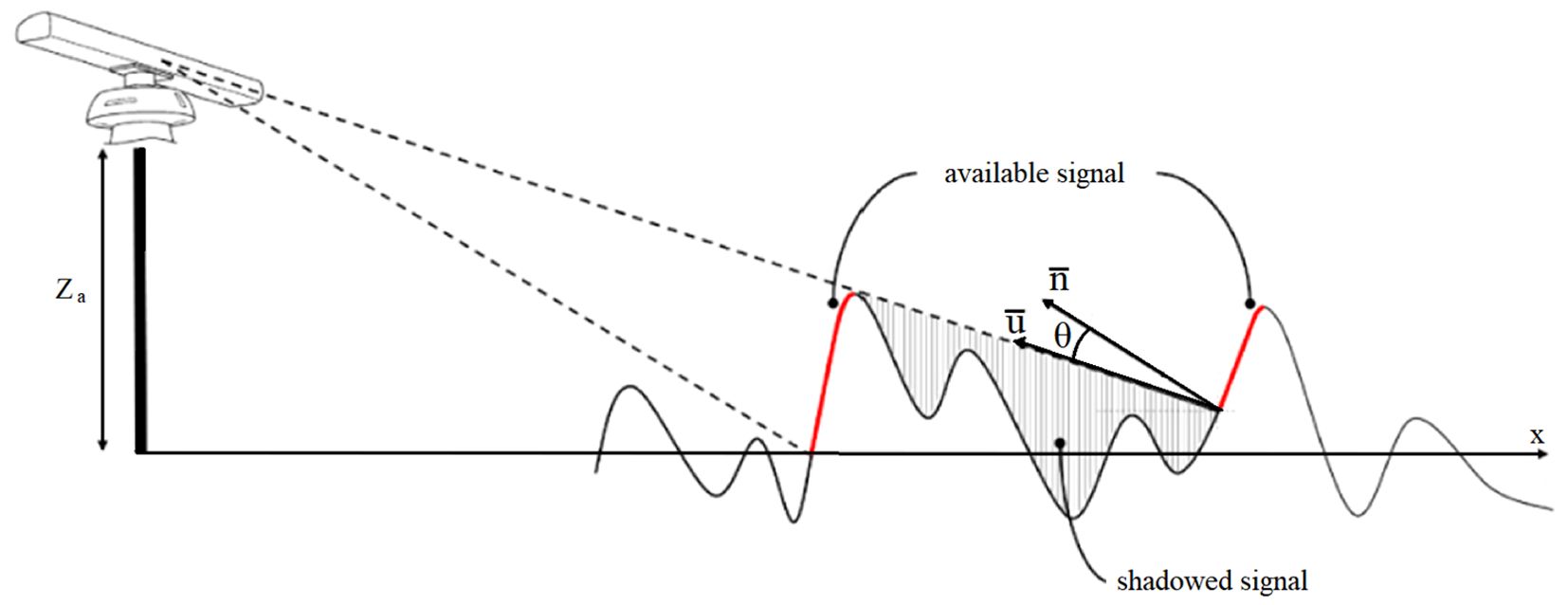
Figure 5. Geometrical scheme of shadowing and tilt modulation effects based on (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019).
In the real radar images, the shadowed area is not equal to zero, so the data in these areas are modelled as Gaussian white noise (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019).
For tilt modulation, the steepness of the observed surface slope affects the power amplitude received by the radar antenna (Ludeno and Serafino, 2019). Thus, for non-shadowed areas, the received back-scattered signal is proportional to cosθ, where θ is the angle between the radar ray and the vector normal to the wave surface (Figure 5).
Summarizing, we present the following algorithm that transforms the synthetic sea surface into the X-band radar image. For every synthetic sea surface:
1. Distance mask: we determine the masked points – the points with the distance to the radar more than 1920 m or less than 300 m.
2. Shadowing: we determine the points that are not available for a radar ray.
3. Tilt modulation: for every non-shadowed point we determine the angle θ between the radar ray and the vector normal to the wave surface.
4. For every non-shadowed point the amplitude of the back-scattered signal is cosθ.
5. We compute the minimum and the maximum values of the back-scattered amplitude among the non-shadowed points.
6. Normalization: we linearly transform the amplitude values so that the new minimum value is 0 and the new maximum value is 255.
7. Noise: for shadowed and masked points we set the amplitude values as random numbers distributed uniformly from 0 to 255.
8. We choose the half of the array that corresponds to the downwind direction.
The example of the resulting synthetic X-band radar image with the size of 1024×2048 pixels is shown without the mask in Figure 6A and with the mask in Figure 6B.
2.4 Dataset of synthetic images
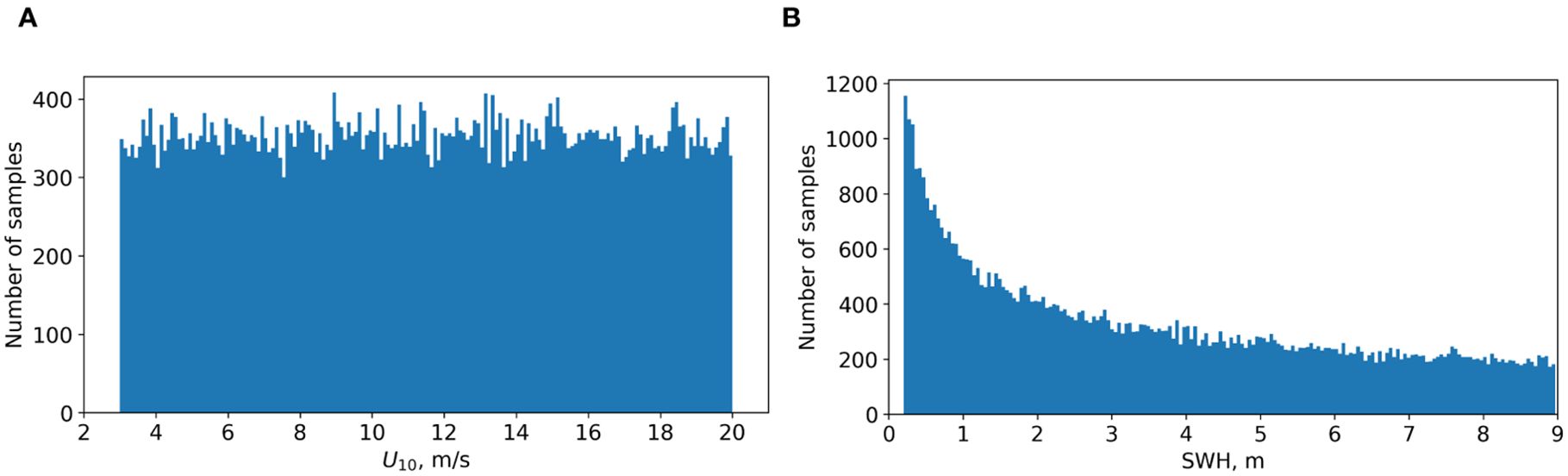
To generate a set of synthetic images, we first generate 60 000 values of U10 speed distributed uniformly in the range from 3 m/s to 20 m/s. We include extremely low and extremely high wind speed values to provide proper learning quality in comparison with the real wind wave conditions. For fully-developed sea, SWH value is a quadratic function of U10 (3) leading to a bigger share of lower SWH values. The distributions of U10 and SWH are shown in Figure 7.
After that, for every wind speed value we generate a corresponding sea surface, as described in 2.2, and then convert it to a synthetic radar image, according to 2.3. We compute the grazing angles with the radar antenna height Za= 20 m. This procedure results in 60 000 samples of synthetic radar images (Table 1).
2.5 Data pre-processing
In this research, we apply convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Consistent with standard practice, we linearly normalize both input data and the target SWH values. Namely, for every pixel of the real and synthetic radar images, the normalized radar image pixel . This procedure limits pixel values between –0.5 and 0.5. We also adjust SWH to approximately have a zero mean and a variance equal to one: After normalization, for the masked areas of the image (white areas in Figure 6B), we set the zero value.
CNNs lack inherent rotation invariance, necessitating diverse training data with varied spatial feature orientations (Chidester et al., 2018). In this study, the orientation of spatial features may not exhibit high diversity. Consequently, we employ two-dimensional data augmentation for the real SeaVision and synthetic radar semicircles, namely, random rotation with an angle ranging from −5° to 5°. This approach encourages the CNN-based model to acquire rotation invariance through training on augmented data, thereby enhancing the generalization ability of the CNN.
2.6 ANN models
In this study, we apply convolutional neural networks (CNNs), i.e., parametric mappings where the model parameters are optimized through sequential application of a fixed-size convolutional kernel to two-dimensional input data (Rezvov et al., 2022).
The high depth of CNNs is anticipated to enhance the predictive output quality. However, the large number of layers introduces training instability in the back-propagation algorithm, leading to learning inefficiency due to the vanishing gradients. This effect results from the accumulation of excessively small gradients for model parameters. Consequently, the product of the gradient vector and the learning rate coefficient tends toward zero, causing the parameters to remain constant during each optimization step.
An effective approach to address the issue of learning instability involves the incorporation of connections that bypass the intermediate layers of the model. These skip connections serve to diminish the likelihood of accumulating small gradients. A notable example is the implementation of residual connections, wherein the output of an intermediate layer is added to the output of a subsequent level.
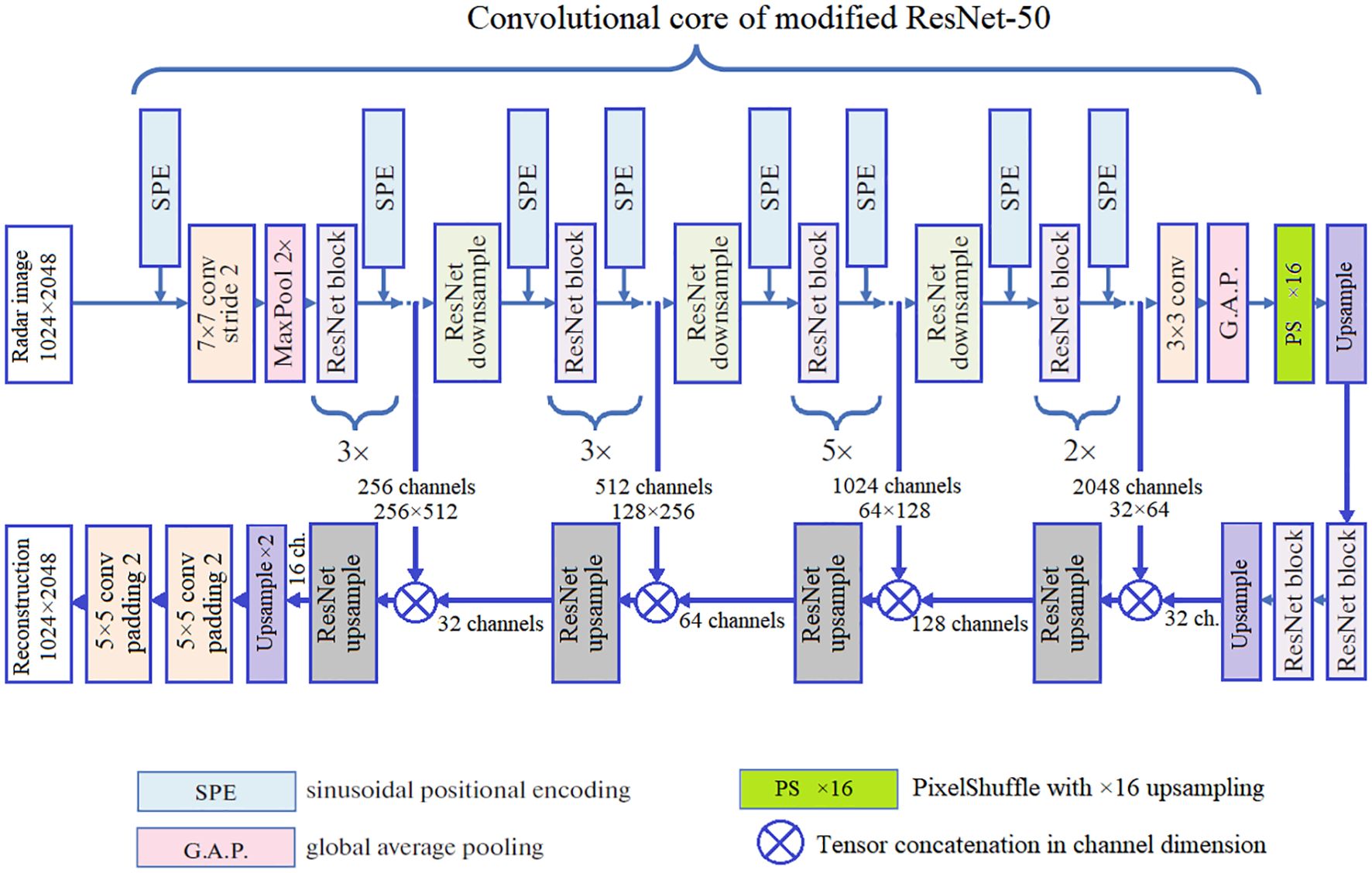
In this paper, we build two CNN architectures based on the model for processing SeaVision radar images as it is described in (Krinitskiy et al., 2023). The basic architecture is the modified ResNet50 combining the advantages of deep CNNs and residual connections.
The convolutional core of the modification adheres to the original ResNet architecture, with the addition of sinusoidal positional encoding of various wavelengths to enable the CNN to capture the wavelengths peculiar to real SeaVision images (Krinitskiy et al., 2023). Two-dimensional positional encoding introduces additional channels with generated harmonic maps featuring various wavelengths and directions. Specifically, there are cosine- and sine-based positional encoding channels that vary in both horizontal and vertical directions. These maps are concatenated with the output of the ResNet blocks so that the subsequent ResNet block processes activation maps from the previous layers along with the positional encoding channels. It is worth noting that for modified ResNet50, positional encoding maps are injected into the activation maps after each ResNet building block.
2.6.1 Unsupervised reconstruction model
The first architecture elaborated for this research is the reconstruction CNN model with the structure similar to U-Net (Ronneberger et al., 2015). U-Net is based on a typical contracting network augmented with consecutive upsampling blocks. Hence, U-Net architecture consists of two parts: the contracting path from the input to the bottleneck, and the expansive path from the bottleneck to the output. The upsampling blocks of the model contain a large number of feature channels to effectively propagate context information to higher resolution layers.
The main distinction and the principal concept of U-Net is the presence of the specific skip connections that transmit activation maps from the intermediate layers of the contracting path to the intermediate layers of the expansive path. In other words, the high-resolution features from the contracting path are added to the upsampled output on the expansive path to facilitate localization. Subsequently, a consecutive convolution layer is capable of learning to generate a more precise output based on this information (Ronneberger et al., 2015).
For this research, we develop a U-Net architecture with the contracting path based on the convolutional core of modified ResNet50 (the upper half of Figure 8). The input of the model is supposed to be a two-dimensional array with 1024×2048 size. Four skip connections and a bottleneck pass the multilevel features into the expansive path of the model (the lower half of Figure 8). It leads to the output with the input size. With the equal size of the input and the output, the model architecture is aimed at unsupervised reconstruction of the input array.
As Figure 8 shows, the expansive part of the model consists of upsampling ResNet blocks with the additional upsampling layers if necessary. On the expansive path, we coordinate the spatial size of the block outputs with the outputs of the skip connections to properly concatenate the tensors before the subsequent ResNet block or layer. The number of channels for the concatenated activation maps and the output size of the skip connections are shown in Figure 8.
2.6.2 Regression model
The second architecture built for this study is the regression CNN model designed to approximate the scalar target SWH value through processing 1024×2048 radar images. Unlike the regression model from (Krinitskiy et al., 2023) with the same input and output objects, we base our model on the reconstruction architecture described in 2.6.1 including the skip connections (see Figure 9).
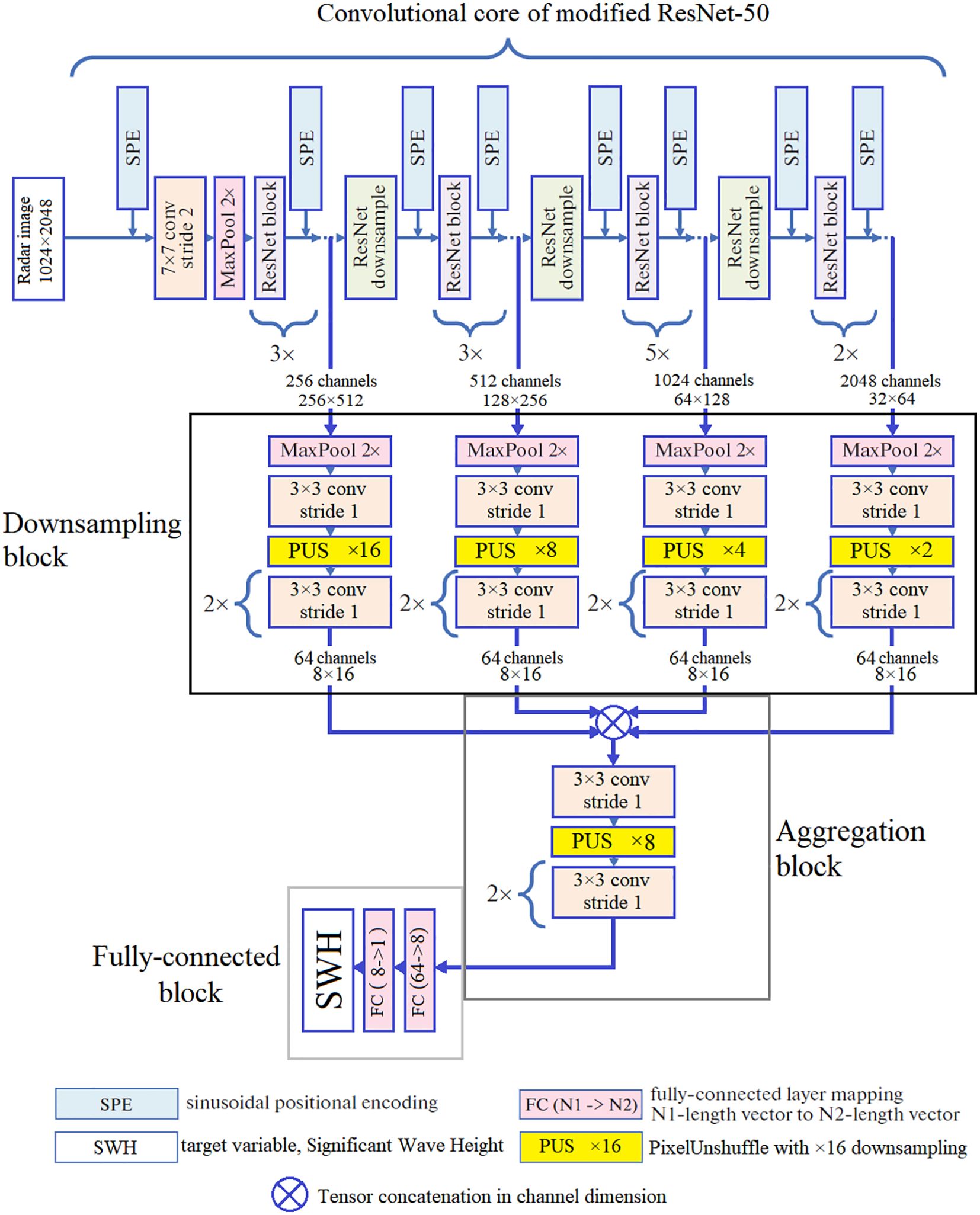
Figure 9. High-level architecture of the regression CNN model based on modified ResNet50 and feature aggregation.
As Figure 9 shows, our regression model consists of four fundamental parts. The first part is the convolutional core of modified ResNet50. We preserve four contracting paths to pass the outputs of the intermediate layers to the downsampling blocks. Every parallel downsampling block consists of a pooling layer, a convolutional layer, a pixel unshuffling layer and two consecutive convolutions. The task of the downscaling part of the model is to bring four activation maps of the skip connections to the same size. In the third part of the architecture, the features from the previous block are aggregated through channel concatenation. The aggregated activation map is passed to the downsampling block resulting in vector of size 64. The fully-connected subnet following the aggregation part contains two sequential fully-connected layers of the widths 64 and 8. The terminating layer is of the width 1 since in this study, we approximate SWH scalar.
2.7 Quality metrics
Various quality metrics are employed to assess and monitor the learning process of the models. For the unsupervised reconstruction model, the simplest quality metric utilized is the root mean-squared error, denoted as RMSErec. This form of reconstruction error quantifies the disparity between the input data and the data obtained after the U-Net compresses and decompresses the input. The RMSErec metric provides an evaluation of the noise introduced to the input as it passes through the bottleneck and the skip connections.
If we denote our reconstruction model as R and a batch of input images as y, then an output batch is y∗ = R(y). We compute RMSErec summarizing only by unmasked points to exclude non-meaningful areas of radar images. The number of points in the input batch is N, and the result is:
In (6), and are the identical elements of the input and the output tensors. We summarize the difference between the input and the output point-by-point. The indices i, j and k denote points in ranges of respective spatial dimensions and a batch size, respectively, taking into account distance mask.
The inadequacy of RMSE in detecting visually altered defective regions in images with consistent intensity values has been demonstrated in (Bergmann et al., 2019). In this research, we adopt a perceptual quality metric grounded in structural similarity, which assesses the inter-dependencies among local image regions. Unlike RMSE, which compares pixel values, structural similarity takes into account contrast and structural information. The computation of the structural similarity index measure (SSIM) is outlined as follows:
where µ is the pixel sample mean of y, µ∗ is the pixel sample mean of y∗, σ2 is the variance of y, σ∗2 is the variance of y∗, σyy∗ is the cross-correlation of y and y∗. C1 and C2 are constant values equal to 0.012 and 0.032, respectively.
In this paper, we compute the Structural Similarity Index (SSIM) between two windows, each sized 128×128 pixels, applied to both the input and the output images. The SSIM values range between −1 and 1, where a higher SSIM signifies greater similarity.
In case of the regression model, only root mean-squared error RMSESWH is utilized since the output of this CNN is a vector containing significant wave height values with a length equal to the batch size BS:
where SWH is a target value measured by Spotter buoy (see 2.1) or determined by the synthetic ocean surface (see 2.2), SWH∗ is the output value of the regression model, and k denotes a dataset element of a batch with the size BS.
2.8 Training and evaluation
The training process of artificial neural networks is known for its sensitivity to various details, and the selection of a training algorithm and hyperparameters plays a critical role in determining the quality of the resulting model. Currently, the Adam optimizer (Kingma and Ba, 2017) stands out as the most stable and widely employed training algorithm, utilizing a momentum approach to estimate lower-order moments of the loss function gradients. In our study, we leverage the Adam optimization procedure.
In the optimization algorithms, the batch size and the learning rate hold particular significance. Due to the substantial dimensions of SeaVision radar images, substantial variations in batch size were impractical. Instead, we selected the largest feasible batch size for our computer hardware (batch_size = 2) to mitigate noise in CNN gradient estimates.
Adhering to best practices, we fine-tuned the learning rate schedule not only to attain high quality in SWH regression but also to enhance robust generalization skills. Generalization is evaluated by scrutinizing the disparity between the quality estimated on the training and validation subsets, where a small gap signifies good generalization and a large gap indicates poor generalization.
Aligned with recent research findings, we implemented the specialized learning rate schedule (Ding, 2021; Loshchilov and Hutter, 2017). This cyclical schedule encompasses a cosine-shaped decrease in the learning rate throughout the training process. We incorporate a multiplicative form of increase in the simulated annealing period with each cosine cycle. We also employ exponential decay of the simulated annealing magnitude with each cosine cycle, utilizing the multiplicative form.
In this research, training consists of three principal consecutive steps. For all the steps, we use normalized values as it was described in 2.3.
On Step 1, we train the reconstruction model using the dataset of synthetic images described in 2.4. The dataset comprising 60 000 synthetic radar images is randomly divided into two segments: a training dataset (50 000 images) and a validation dataset (10 000 images).
In machine learning, it is customary to assess the performance of a model by computing quality metrics on a validation subset obtained through random sampling from the original set of labeled examples. This methodology presupposes that the examples are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.). The random partition ensures a uniform distribution of modeled surface wind wave conditions across the datasets. Moreover, the distribution of SWH values is similar for both datasets.
We train the reconstruction model using the mean-squared error between an input and an output images summing only over unmasked points. The length of training is 80 epochs. We change the first cosine cycle from learning_rate = 7.5×10−5 to learning_rate = 1×10−8.
On Step 2, we train the regression model using the same dataset of synthetic images described in 2.4. The number of images for training and evaluation is the same as for Step 1. Nevertheless, we change the random split of the dataset to prevent overfitting.
Step 2 consists of two stages: 21 and 22. For both stages of Step 2, the input of the model is the masked radar image. We train the regression model using the mean-squared error between an output value and a target SWH.
For Stage 21, we initialize the weights of the convolutional modified ResNet50 core and the skip connections with the weights from the pre-trained reconstruction model as described for Step 1. After that, we train only downsampling block, feature aggregation and fully-connected layers. The convolutional core weights are frozen.
After 20 epochs, we start Stage 22, training the whole regression model. Epoch 1 of Stage 22 is inintialized with the weights of the full regression model after epoch 20 of Stage 21. The length of Stage 22 training is 40 epochs. We change the cosine cycles from learning_rate = 7.5×10−5 to learning_rate = 1×10−8.
On Step 3, we train the regression model using the dataset of real SeaVision synthetic images described in 2.1.
In studies concerning the application of statistical models, particularly ANNs, for the analysis of remote sensing data, it is crucial to account for the auto-correlation inherent in the observational time series dataset. Owing to the inherent evolution of underlying physical phenomena, consecutive observations may demonstrate substantial auto-correlation, thereby influencing the accuracy of the model (Krinitskiy et al., 2023).
It is imperative to refrain from systematically incorporating consecutive examples into the training and testing sets. In this research, we tackle the challenge of strongly correlated successive examples by adopting station-wise random sampling, a strategy from (Krinitskiy et al., 2023). This approach avoids the systematic sampling of successive examples into the training and validation subsets, ensuring a reliable assessment of our model’s quality.
In other words, to prevent overfitting and potential data leakage, we train, validate and test the model distinct stations. If the station is included in the training dataset, it is excluded from the validation and testing datasets.
Another significant challenge in statistical modeling is the problem of covariate shift, which occurs when there is a degradation in model performance during evaluation due to a discrepancy between the distribution of the testing data and that of the training data. For an accurate assessment of model quality, it is crucial that the testing and validation datasets adhere to the same distribution as the training dataset. In this study, we use a straightforward sampling strategy designed to promote, though not ensure, alignment of the target value distributions across the training, validation, and testing subsets. This approach involves station-wise sampling that is stratified according to mean SWH (Krinitskiy et al., 2023).
Step 3 consists of three stages: 31, 32 and 33. The input of the model is the masked radar image. We train the regression model using the mean-squared error between an output value and a target Spotter buoy SWH.
For Stage 31, we initialize the weights of the full model with the weights from the pre-trained regression model after Stage 22. Then, we train only fully-connected block for 10 epochs. After that, on Stage 32 we start training fully-connected block, feature aggregation and downsampling block while the covolutional core weights are frozen. After 40 epochs of Stage 32, we start Stage 33, training the full regression model. The length of Stage 33 training is 20 epochs. We change the cosine cycles from learning_rate= 7.5 × 10−5 to learning_rate = 1 × 10−8 for stages 31 and 32, and from learning_rate = 3.75×10−5 to learning_rate = 2×10−5 for stage 33.
3 Results
In this section, we present the results of training the SWH estimation model on SeaVision radar imagery including pre-training steps on synthetic radar images.
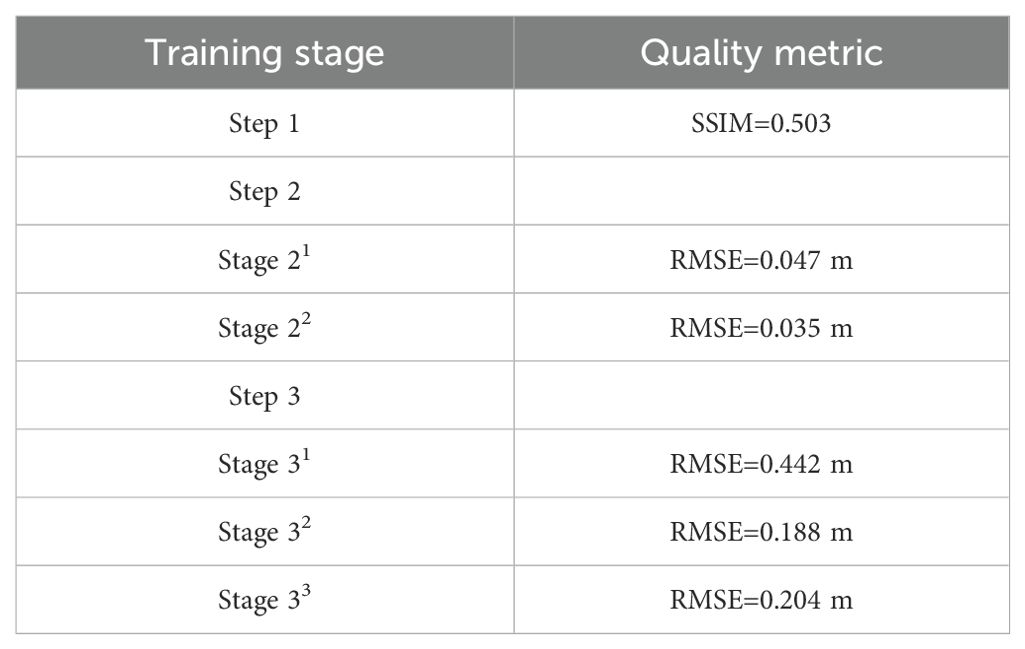
First, the unsupervised reconstruction training shows relatively high (i.e., relatively good) Structural Similarity Index value SSIM = 0.503 on validation dataset. This result means that the reconstruction model is able to extract the multi-level features from the synthetic radar images. The convolutional core passes the extracted and processed features through the skip connections. This detail of the architecture allows subsequent use of Step 1 weights for Step 2.
The regression model trained on the synthetic dataset (Step 2) demonstrates root mean-squared values RMSESWH= 0.047 m after Stage 21 and RMSESWH= 0.035 m after Stage 22 on validation dataset. The monotonous decrease in RMSE value proves the necessity of gradual unfreezing of pre-trained weights for smooth transition from the previous step. These values of RMSESWH are too good to be true in case of real ocean data, however, one may consider them as the measure of success in case of synthetic dataset. These low (i.e., good) values of RMSESWH indicate that the neural network is capable of handling the variety of imagery similar to radar-captured sea clutter images.
Finally, the regression model trained on the real dataset (Step 3) shows root mean-squared error values RMSESWH= 0.442 m after Stage 31, RMSESWH= 0.188 m after Stage 32 and RMSESWH= 0.204 m after Stage 33 on validation dataset.
The results are summarized in Table 3.
We compare the final results in our study with the simple modified ResNet50 without pre-training (Krinitskiy et al., 2023). As one may see, pre-training with synthetic data and architecture modifications proposed in our study significantly improve the quality of SWH approximation in terms of root mean-squared error from RMSESWH= 0.48 m reported in (Krinitskiy et al., 2023) to RMSESWH= 0.204 m.
4 Discussion
This study initially proposes the efficacy of neural-network regression methods for determining SWH from sea clutter imagery acquired by a navigation X-band radar. However, in situ data collection is both costly and limited in its ability to offer a diverse range of ocean wave conditions.
The synthesis of radar images effectively addresses the issue of insufficient data. Moreover, the generation of diverse synthetic sea surface conditions allows for simulating radar images with specific hyperparameters essential for the research. Synthetic images contribute to the expansion of the dataset, rendering it in a more uniform manner.
We present an enhanced approach for generating a synthetic sea surface and synthetic radar images under the condition of a fully-developed sea. We suppose this method promising as it allows for the utilization of various power spectra of wind waves. The resulting images exhibit realism for visual perception.
Recent studies demonstrate proficiency in the task of SWH approximation, particularly in cases of low wind speed. To enhance CNN generalization capabilities, we developed two different architectures capable of proper preliminary training to conduct experiments involving the unsupervised reconstruction and the regression model on an elaborated synthetic dataset.
The results of the unsupervised reconstruction illustrate that the U-Net-like model with skip connections and ResNet blocks is capable of capturing the harmonic structure of wind waves.
Our findings indicate that the reconstruction model reproduces the fine structure of ocean wind waves. Despite the fact that the MSE training loss, which is sensitive to point-by-point distortions, tends to smooth images and eliminate small-scale features, SSIM quality metric is relatively high. At the same time, the pre-trained regression model shows good results for both synthetic and real datasets.
It is precisely the small-scale structure of a radar image that encompasses crucial information about wave lengths and heights. Consequently, we suppose that the convolutional core of the reconstruction and regression models does not lose wave information and successfully extracts multi-scale features from the radar images. As a result, the pre-trained model shows better SWH approximation quality than the simple modified ResNet50 without pre-training (Krinitskiy et al., 2023).
5 Conclusions and outlook
In this study, we demonstrate the capability of a convolutional neural network (CNN) proposed in this paper of approximating significant wave height (SWH) with the quality superior to the one reported in recent studies exploiting CNNs for this task (Krinitskiy et al., 2023). The superiority is achieved through the preliminary training of our CNN within the subsequent stages of (a) unsupervised autoencoder-like training and (b) further supervised pre-training with a synthetic target similar to the real SWH. We demonstrate significant improvement of the SWH estimation quality in terms of root mean-squared error, compared to the results reported recently in a similar CNN-involving setting (Krinitskiy et al., 2023).
Synthetic dataset simulating radar-acquired sea clutter imagery with corresponding SWH values that we used in our pre-training may provide additional improvements for an utilized ANN due to the control over the distribution of both wind speed and corresponding SWH values.
Nevertheless, the application of synthetic images has a number of restrictions for SWH regression problem. The synthetic dataset based on fully developed sea assumption is not able to reproduce a variety of different real conditions, such as rain or obstacles on sea surface. Thus, the synthetic images do not exhibit the same statistical and physics-reflecting properties as those in the real dataset. Moreover, the proposed algorithm is not applicable fundamentally for generating sea surface under low wind conditions. Such conditions require taking into account additional physical phenomena that distort the wave spectrum.
In the future, we plan to add more real radar images collected from different locations into the ANN to further improve the regression model quality. Different advanced methods of synthetic dataset generation are also to be explored. Furthermore, we should examine various ANN architectures for SWH regression problem.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: the PANGAEA repository https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.939620.
Author contributions
VR: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. VG: Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MB: Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AS: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. NT: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded under the Agreement No. 075-03-2024-117 dated January 17, 2024. The development of the scheme for synthetic data generation was supported by the program PRIORITY 2030 of Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
- ^ Gulev, S. (2014) Global Atlas of Ocean Waves. Available at: http://www.sail.msk.ru/atlas/ (Accessed: 21 December 2023).
- ^ Sofar Ocean (2023) Spotter Buoy by Sofar. Available at: https://www.sofarocean.com/products/spotter (Accessed: 22 December 2023).
- ^ National Weather Service (2023) Significant Wave Height. Available at: https://www.weather.gov/mfl/waves (Accessed: 22 December 2023).
- ^ National Data Buoy Center (2023) How are significant wave height, dominant period, average period, and wave steepness calculated? Available at: https://www.ndbc.noaa.gov/faq/wavecalc.shtml (Accessed: 22 December 2023).
References
Bai S., Kolter J. Z., Koltun V. (2018). An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling [online] [Preprint]. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1803.01271. (Accessed September 17, 2024)
Bergmann P., Löwe S., Fauser M., Sattlegger D., Steger C. (2019). “Improving unsupervised defect segmentation by applying structural similarity to autoencoders,” 14th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2019). Prague, Czech Republic, February 25-27, 2019. Setúbal, Portugal: SciTePress, 372–380. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1807.02011
Chidester B., Do M. N., Ma J. (2018). Rotation equivariance and invariance in convolutional neural networks [online] [Preprint]. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1805.12301. (Accessed September 17, 2024)
Choi H., Park M., Son G., Jeong J., Park J., Mo K., et al. (2020). Real-time significant wave height estimation from raw ocean images based on 2D and 3D deep neural networks. Ocean Eng. 201, 107129. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107129
Ding Y. (2021). “The impact of learning rate decay and periodical learning rate restart on artificial neural network,” in Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Electronics Engineering, New York, NY, USA. 6–14 (Thailand. New York, N.Y.:Association for Computing Machinery). doi: 10.1145/3460268.3460270
Gangeskar R. (2014). An algorithm for estimation of wave height from shadowing in X-band radar sea surface images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 52, 3373–3381. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2272701
Hasselmann D. E., Dunckel M., Ewing J. A. (1980). Directional Wave Spectra Observed during JONSWAP 1973. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 10, 1264–1280. doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(1980)010<1264:DWSODJ>2.0.CO;2
Huang W., Liu X., Gill E. W. (2017). Ocean wind and wave measurements using x-band marine radar: A comprehensive review. Remote Sens. 9 (12), 1261. doi: 10.3390/rs9121261
Huang W., Yang Z., Chen X. (2021). Wave Height Estimation From X-Band Nautical Radar Images Using Temporal Convolutional Network. IEEE J. Selected Topics Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 14, 11395–11405. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3124969
Kim H., Ahn K., Oh C. (2021). Estimation of Significant Wave Heights from X-Band Radar Based on ANN Using CNN Rainfall Classifier. J. Korean Soc. Coast. Ocean Eng. 33, 101–109. doi: 10.9765/KSCOE.2021.33.3.101
Kingma D. P., Ba J. (2017). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980. (Accessed September 17, 2024)
Krinitskiy M., Golikov V., Anikin N., Suslov A., Gavrikov A., Tilinina N. (2023). Estimating Significant Wave Height from X-Band Navigation Radar Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Moscow Univ. Phys. Bull. 78, S128–S137. doi: 10.3103/S0027134923070159
Lee P. H. Y., Barter J. D., Beach K. L., Hindman C. L., Lake B. M., Rungaldier H., et al. (1995). X-band microwave backscattering from ocean waves. J. Geophysical Res.: Oceans 100, 2591–2611. doi: 10.1029/94JC02741
Long Y., Gong Y., Xiao Z., Liu Q. (2017). Accurate object localization in remote sensing images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 55, 2486–2498. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2645610
Loshchilov I., Hutter F. (2017). SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts [online] [Preprint]. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1608.03983. (Accessed September 17, 2024)
Ludeno G., Serafino F. (2019). Estimation of the significant wave height from marine radar images without external reference. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 7 (12), 432. doi: 10.3390/jmse7120432
Lyzenga D. R., Walker D. T. (2015). A simple model for marine radar images of the ocean surface. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 12, 2389–2392. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2478390
Mastin G. A., Watterberg P. A., Mareda J. F. (1987). Fourier synthesis of ocean scenes. IEEE Comput. Graphics Appl. 7, 16–23. doi: 10.1109/MCG.1987.276961
Nieto-Borge J. C., Hessner K., Jarabo-Amores P., de la Mata-Moya D. (2008). Signal-to-noise ratio analysis to estimate ocean wave heights from X-band marine radar image time series. IET Radar Sonar Navigation 2, 35–41(6). doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20070027
Nieto-Borge J. C., Hessner K., Reichert K. (1999). “Estimation of the significant wave height with X-band nautical radars,” 18th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering. St. John’s, Newfoundland, Canada, July 11-16, 1999. New York, N.Y.: American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Nieto-Borge J. C., Rodriguez G. R., Hessner K., González P. I. (2004). Inversion of marine radar images for surface wave analysis. J. Atmospheric Oceanic Technol. 21, 1291–1300. doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2004)021<1291:IOMRIF>2.0.CO;2
Park J., Ahn K., Oh C., Chang Y. S. (2020). Estimation of Significant Wave Heights from X-Band Radar Using Artificial Neural Network. J. Korean Soc. Coast. Ocean Eng. 32, 561–568. doi: 10.9765/KSCOE.2020.32.6.561
Pierson W. J., Moskowitz L. (1964). A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S. A. Kitaigorodskii. J. Geophysical Res. 69, 5181–5190. doi: 10.1029/JZ069i024p05181
Plant W. J., Keller W. C. (1990). Evidence of Bragg scattering in microwave Doppler spectra of sea return. J. Geophysical Res.: Oceans 95, 16299–16310. doi: 10.1029/JC095iC09p16299
Raghukumar K., Chang G., Spada F., Jones C., Janssen T., Gans A. (2019). Performance Characteristics of “Spotter,” a Newly Developed Real-Time Wave Measurement Buoy. J. Atmospheric Oceanic Technol. 36, 1127–1141. doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-18-0151.1
Rezvov V., Krinitskiy M., Gulev S. (2022). Approximation of high-resolution surface wind speed in the North Atlantic using discriminative and generative neural models based on RAS-NAAD 40-year hindcast. Proceedings of Science. 2022, 23 doi: 10.22323/1.429.0023
Ronneberger O., Fischer P., Brox T. (2015). U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation, in: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, eds. Navab N., Hornegger J., Wells W., Frangi A. (Cham: Springer), 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Tilinina N., Ivonin D., Gavrikov A., Sharmar V., Gulev S., Suslov A., et al. (2022). Wind waves in the North Atlantic from ship navigational radar: SeaVision development and its validation with the Spotter wave buoy and WaveWatch III. Earth System Sci. Data 14, 3615–3633. doi: 10.5194/essd-14-3615-2022
Vicen-Bueno R., Lido-Muela C., Nieto-Borge J. (2012). Estimate of significant wave height from non-coherent marine radar images by multilayer perceptrons. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 84. doi: 10.1186/1687-6180-2012-84
Wetzel L. B. (1990). “Electromagnetic Scattering from the Sea at Low Grazing Angles,” in Surface Waves and Fluxes. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, vol 8., eds. Geernaert G. L., Plant W. L. (Dordrecht: Springer), 109–171. doi: 10.1007/978-94-009-0627-3_3
Wijaya A., van Groesen E. (2016). Determination of the significant wave height from shadowing in synthetic radar images. Ocean Eng. 114, 204–215. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2016.01.011
Keywords: wind waves, X-band marine radar, significant wave height, synthetic radar images, machine learning, deep learning, convolutional neural networks, unsupervised preliminary training
Citation: Rezvov V, Krinitskiy M, Gavrikov A, Golikov V, Borisov M, Suslov A and Tilinina N (2024) Improving data-driven estimation of significant wave height through preliminary training on synthetic X-band radar sea clutter imagery. Front. Mar. Sci. 11:1363135. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1363135
Received: 29 December 2023; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 27 September 2024.
Edited by:
Jochen Horstmann, Helmholtz Centre for Materials and Coastal Research (HZG), GermanyReviewed by:
Yong Wan, China University of Petroleum (East China), ChinaLei Gao, Ryerson University, Canada
Ruben Carrasco, Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres (HZ), Germany
Copyright © 2024 Rezvov, Krinitskiy, Gavrikov, Golikov, Borisov, Suslov and Tilinina. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vadim Rezvov, cmV6dm92LnZ5dUBwaHlzdGVjaC5zdQ==
 Vadim Rezvov
Vadim Rezvov Mikhail Krinitskiy
Mikhail Krinitskiy Alexander Gavrikov2
Alexander Gavrikov2 Alexander Suslov
Alexander Suslov