- 1Next Frontiers in Materials Lab, School of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 2Academic Development Unit, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 3Department of Materials Engineering, Sunyani Polytechnic Institute, Sunyani, Ghana
- 4College of Engineering, State University of New York (SUNY) Polytechnic Institute, Utica, NY, United States
- 5Department of mechanical Engineering, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Nairobi, Kenya
- 6School of Mechanical, Industrial and Aeronautical Engineering, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 7School of Architecture and Urban Planning, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 8Department of Mechanical Engineering, Academic City University, Accra, Ghana
The integration of sustainable additive manufacturing (AM) within the framework of African industrialization presents a promising avenue for economic advancement while addressing environmental concerns. This review explores the convergence of sustainable AM practices with the industrial landscape of Africa, highlighting potential benefits and challenges. Through efficient resource utilization and localized production capabilities, AM holds promise for enhancing industrial resilience, stimulating employment opportunities, and fostering innovation. However, the realization of these benefits necessitates navigating infrastructural limitations, technological disparities, and regulatory complexities. By critically examining sustainable AM strategies and their relevance to African contexts, this review aims to delineate actionable pathways for leveraging the transformative potential of AM. The role of AM in industrialization as expressed in the African Union Agenda 2063 are highlighted. This has the potential to increase the staggering ∼11% contribution of manufacturing to gross domestic product of Africa. Collaboration through the triple helix approach focusing on government, industry and academia is highly pivotal for the success of such nascent and ubiquitous AM technology which is able to address the sustainable development goals. Africa can leapfrog and harness sustainable AM as a catalyst for inclusive industrial development and sustainable growth across the continent. The implications of AM for an industrialised Africa and areas for future research direction are briefly discussed.
Introduction
Additive manufacturing (AM) involves creating structural and functional components from 3D models through a layer-by-layer deposition process (Rupp et al., 2022; Monteiro et al., 2022; Landi et al., 2022; Gao et al., 2021; Výtisk et al., 2022; Wang K. et al., 2022). This is in contrast to conventional subtractive methods where component parts are removed through machining (Egan et al., 2019; Jiang et al., 2020; Jiang, 2020; Roque et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2021). The shift from conventional approaches to AM technologies is beneficial from sustainability and economic viability standpoint. Although, the AM technology was initially associated with rapid prototyping (Gibson et al., 2015; Dimitrov et al., 2007; Poole and Phillips, 2015), it has evolved significantly offering enhanced efficiency in product development, reduced material wastage, improved product quality, and mass production across various classes of materials (Egan et al., 2019; Roque et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020; Wegner et al., 2022; Hagman and Svanborg, 2022; Patel et al., 2022; Psarommatis et al., 2023; Klenam et al., 2022). Furthermore, the precision and accuracy associated with products from AM make them suitable for customizing component parts seamlessly. The foundational concepts emerged in the early 1940s and 50s with significant progress made up to early 70s. The development of functional AM equipment in the 1980s and commercial application ushered in the new dawn of digital manufacturing. Thus, AM technologies are nascent and revolutionary technologies which will form the backbone of the economies of the future in an era of overwhelming complexities, tremendous competition and accelerated change.
The industrialization of Africa is incomplete without the adoption and implementation of AM technologies. Although, the technology is evolving and at its nascent stage, most African countries are yet to adopt and integrate it. This is partly due to low industrialization rates and infrastructure deficits. However, there is the need to leapfrog and gradually deploy the technology to meet the increasing demands of the manufacturing sector (Egan et al., 2019; Roque et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020; Wegner et al., 2022; Hagman and Svanborg, 2022; Patel et al., 2022; Psarommatis et al., 2023; Klenam et al., 2022). Currently, global trends show versatile use of AM technologies in aerospace (Egan et al., 2019; Roque et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020; Wegner et al., 2022; Hagman and Svanborg, 2022; Patel et al., 2022; Psarommatis et al., 2023; Klenam et al., 2022), consumer goods, industrial machinery, motor vehicle parts (Monteiro et al., 2022; Lim et al., 2012; Alami et al., 2023; Ashima et al., 2021; Isasi-Sanchez et al., 2020; Salifu et al., 2022; Najmon et al., 2019; Altıparmak and Xiao, 2021; Froes and Boyer, 2019; Oyesola et al., 2020; Oyesola et al., 2018), medical (Kumar et al., 2021; Arif et al., 2023; Jardini et al., 2014; Bose et al., 2018; Puppi and Chiellini, 2020; Lv et al., 2021; Badkoobeh et al., 2023; Safaei et al., 2021; Davoodi et al., 2020; Rezvani Ghomi et al., 2021; Bacha et al., 2019) and eco-friendly buildings (Bedarf et al., 2021; du Plessis et al., 2021; Salet et al., 2018; Tay et al., 2017; Kruger et al., 2020; Kruger et al., 2021) using locally sourced, low-cost materials. The ease of producing complex geometries and lightweight functional and structural components to near net shape contributes to increased use. In green buildings, AM techniques allow the use of cost-effective, recyclable materials like cob, bamboo, and hemp, offering natural insulation and aligning with sustainable practices such as low carbon footprint (Agnusdei and Del Prete, 2022; Balubaid and Alsaadi, 2023; Woodson, 2015). Since 2015, one of the leading market shares of AM is in aerospace with annual revenue of $7.3 billion and growth rate of ∼13%. This is attributed to being more efficient and economical than many subtractive (Bae et al., 2017; Newman et al., 2015; Manogharan et al., 2016; Watson and Taminger, 2018; Jayawardane et al., 2023), joining (Klenam et al., 2021; Kallee, 2010; Bagger and Olsen, 2005; Czerwinski, 2011; Padhy et al., 2015; Kirk Kanemaru et al., 2015; Li et al., 2021; Ogbonna et al., 2019), and forming processes (Bodunrin et al., 2023; Komane et al., 2023; Asumadu et al., 2023). Thus, leveraging AM technologies is pivotal for African nations to lead the sustainable industrial transformation, reshape supply chains, create sustainable jobs, and contribute to economic development in ways that address socioeconomic disparities (Agnusdei and Del Prete, 2022; Balubaid and Alsaadi, 2023; Woodson, 2015). The merits and upward global market trends of AM technologies provide the incentives to accelerate the adoption and gradual infrastructural investments to drive economic growth and development of Africa to the era of digital manufacturing.
Research on AM focuses on key areas such as material advancements (Egan et al., 2019; Roque et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020; Wegner et al., 2022; Hagman and Svanborg, 2022; Patel et al., 2022; Psarommatis et al., 2023; Klenam et al., 2022), optimization of design for complex geometries, and improving efficiency and precision. Increasing attention is given to sustainability, eco-friendly practices, recyclable materials, and energy-efficient processes. In Africa, research is emerging from countries like South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, Morocco, Egypt, and Tunisia (Klenam et al., 2022), but systematic studies on AM’s contribution to African industrialization remain limited.
This paper reviews AM technologies and their potential in Africa, assessing adoption rates, challenges, and opportunities. It highlights how AM aligns with African industrialization goals, economic benefits, job creation, and necessary infrastructure. The review explores the transformative potential of sustainable AM in driving equitable economic growth and suggests areas for future research and application in African manufacturing. The review examines Africa’s industrialization landscape and AM’s role, discusses emerging smart manufacturing technologies, and connects sustainable development goals (SDGs) with AM processes. It presents the market value of AM, offers case studies from African countries, and concludes with future research directions and a summary.
Approach and methodology
Approach
To ascertain the impact of emerging AM technologies on African industrialization, four key questions posed were:
• Is there any change in industrialization and manufacturing landscape of Africa?
• How can sustainable AM contribute to the African industrialization agenda?
• What are the main challenges faced by African countries in implementing sustainable AM technologies?
• How do current applications of AM in Africa align with SDGs?
Based on these questions, the objectives are to:
• Assess historical data to show any changes in industrialization and manufacturing landscape of Africa and its contribution to GDP.
• Identify emerging AM technologies and evaluate the challenges and barriers to their adoption in Africa.
• Evaluate the alignment of current AM applications in Africa with sustainable development goals.
These research questions and objectives guide the methodology of the review.
Methodology
An assessment of existing literature on sustainable AM technologies and its implications on African industrialization was done. This review is synthesized from carefully selected peer-reviewed conferences and journal articles using the Scopus database. All articles and conference proceedings included in this review were mainly in English. The search syntax was based on the title, abstract and keywords (TITLE–ABS–KEY) of articles. The overall search followed the order of “AND” and “OR” operators with the detailed search format in the Scopus database displayed as “(TITLE-ABS-KEY (“additive manufacturing*” OR “3D printing*”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“Africa*“O”sub-saharan Africa”)) AND (EXCLUDE (LANGUAGE,“German”) OR EXCLUDE (LANGUAGE,“Spanish”)) AND (LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD,“3D Printing”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD,“Additive Manufacturing”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD,“3D Printers”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACT KEYWORD) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “3-D Printing”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Three Dimensional Printing”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Engineering Education”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “3D-printing”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Industrial Research”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Sustainable Development”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Industry 4.0”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Africa”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Product Design”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Rapid Prototyping”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Additive Manufacturing Technology”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Digitalization”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “sub-Saharan Africa”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “South African Government”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Rapid Manufacturing”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Product Development”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Printing, Three-Dimensional”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Microstructure”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Innovation”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Fourth Industrial Revolution”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Digital Fabrication”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Computer Aided Design”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Case-studies”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Artificial Intelligence”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Printing Technologies”) OR LIMIT-TO (EXACTKEYWORD, “Powder Metallurgy”))”. A flowchart showing the approach and systematic thinking is provided in Figure 1.
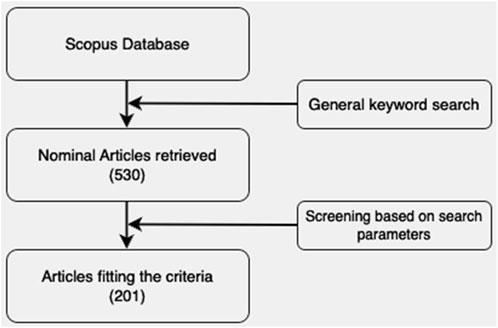
Figure 1. Representation of published data retrieved from Scopus Database focusing on AM or 3D printing publications done or collaborated with African scientists.
African industrialization and manufacturing landscape
The industrialization landscape in Africa is undergoing a major paradigm shift (Cilliers, 2018). Most African countries are gradually deviating from the conventional exportation of goods and services. Many of these countries are beginning to prioritize manufacturing to foster sustainable economic growth and development to an extent. Persistent challenges bedevilling the African industrialization efforts include lack of stable energy supply, exorbitant cost of energy, inadequate and poor transportation networks, insufficient funding and the low productivity sectors (Cilliers, 2018). However, the paradigm shift is in the form of structural change to increase the productivity sector towards manufacturing (Cilliers, 2018). Few of the emerging economies are Ethiopia, Rwanda, Ghana, Nigeria, Kenya and South Africa. These industrialization efforts are based on the triple helix concept involving government, industries and the higher education sector (Lerman et al., 2021; Leydesdorff, 2000; Leydesdorff, 2012). This is due to the bridging of the gap between academia and industry through the formation of various faculty–industry boards in many of these centres of higher learning (Lerman et al., 2021; Leydesdorff, 2012).
The direct impact on the manufacturing sector can be phenomenal. As income levels ascend and economies progress, the manufacturing sector experiences a discernible evolution, altering its contribution to overall economic dynamics. Conventionally, the contribution of the manufacturing sector, measured by its share of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), reaches its zenith, typically between 20%–35% (Manyika et al., 2013a). Subsequently, a noteworthy transition unfolds, characterized by the shifting consumption patterns and a concomitant surge in job creation within the service sector. In advanced economies and the global North, the focus of manufacturing is shifted towards promoting innovation, enhancing productivity, and facilitating international trade (Cilliers, 2018; Manyika et al., 2013a). This has been observed in increased use of data, automation and current state-of-the-art technologies and tools for enhanced efficiency (Manyika et al., 2013a). Conversely, in developing economies (global South) like Africa, manufacturing remains crucial, acting as an essential pathway from subsistence agriculture to increased incomes and improved standard of living. The manufacturing terrain in Africa is anticipated to undergo accelerated transformation amidst the advent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). This epoch holds promise for Africa, potentially catalysing a transition towards heightened levels of productivity and economic expansion. Nonetheless, the realization of these prospects necessitates a concerted effort on the part of African governments to spearhead initiatives, fostering partnerships and collaborative engagements with industrial stakeholders and institutions of higher education and research. This public–private collaborative framework, akin to a triple helix approach (Lerman et al., 2021; Leydesdorff, 2000; Leydesdorff, 2012), stands as imperative for maximizing the capacity of the continent to capitalize on emerging opportunities and steer the path towards sustainable growth trajectories.
An overview and trends of the African economy
Africa contends with approximately eight prominent challenges, encompassing healthcare deficiencies, educational inadequacies, water scarcity, energy insufficiencies, transportation complexities, widespread poverty, escalating unemployment, terrorism, governance deficiencies, and corruption (Klenam, 2019). These challenges, bearing significant weight on the economy, have profoundly impacted the economic trajectory of the continent. For instance, an analysis of income levels vis-à-vis global benchmarks reveals a disheartening narrative, as shown in Figure 2, albeit with marginal improvements since 1995 (Cilliers, 2018). Nevertheless, the income levels in Africa are among the lowest globally, underscoring the persistent prevalence of extreme poverty, tenacious and pervasive characteristic of underdevelopment.
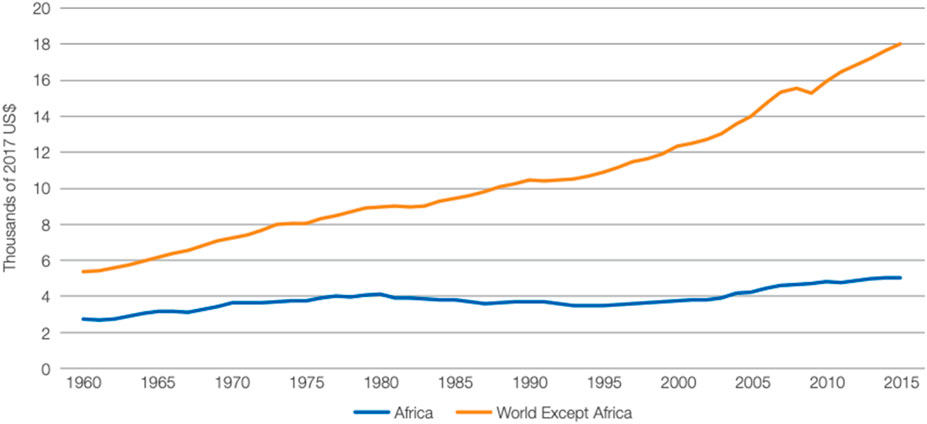
Figure 2. Comparison of average income levels of Africa with the rest of the world [World Bank data, (Cilliers, 2018)].
The wealth and prosperity of nations is largely and inextricably linked to industrialization. This is further entrenched and evident at the dawn of artificial intelligence, data analytics and advanced manufacturing. The advanced manufacturing landscape is contributing disproportionally to innovation, growth and export. This has been demonstrated by the Asian Tigers with concerted effort of transforming from low-productivity sector to high productivity and advanced manufacturing (Cilliers, 2018). Industrialization and advanced manufacturing are indispensable in the transition from subsistence agriculture to more robust, efficient, and high-value services. Furthermore, the knowledge spill over from manufacturing has significant potential for investment in advanced infrastructure and systems, thereby enhancing the productivity and profitability of agricultural operations (Cilliers, 2018). Consequently, such advancements are poised to stimulate growth within the manufacturing sector, thereby exerting a direct positive impact on wages and productivity within the agricultural sphere. This becomes particularly pertinent given the underdeveloped nature of the agricultural sector amidst the abundance of arable and fertile lands across the African continent.
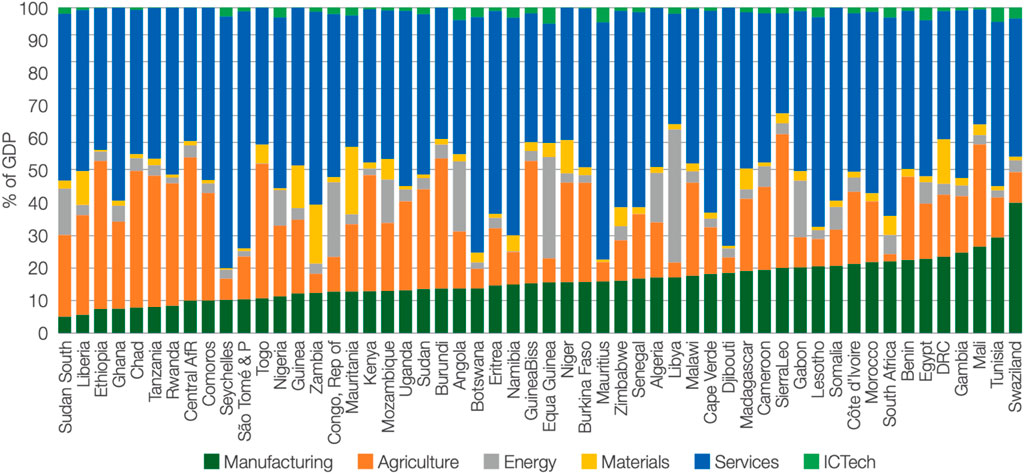
Manufacturing is crucial for the economies of developed and wealthy nations. This drives productivity and offering substantial employment with fair wages. Countries like the U.S., U.K., Italy, Germany, Japan, and France thrive due to strategic manufacturing investments. Recently, China has become a global manufacturing powerhouse, and emerging economies in Southeast Asia are similarly growing their industrial sectors to fuel economic growth. However, Africa’s structural transformation has faced setbacks since the 1970s economic downturn. Structural adjustment programs in the 1980s aimed at stability, but currency devaluation and trade liberalization hampered industrial growth. Nations like Ghana, Kenya, Mauritius, Nigeria, Ethiopia, Tanzania and Senegal shifted from low-productivity agriculture to urban services without significant manufacturing investment (Figure 3). This resulted in reduced manufacturing workforces, slowing growth, and lowering output per worker, hindering economic development. The manufacturing sector’s contribution to African GDP remains stagnant due to unresolved systemic challenges, with 2022 statistics (Figure 4) showing worsening situations.
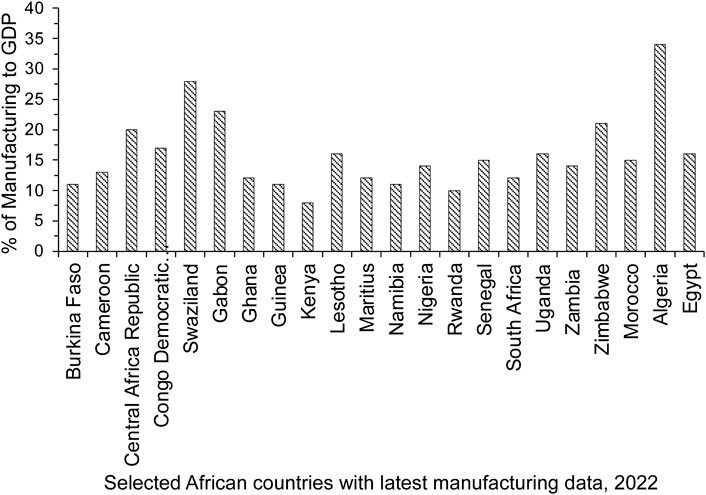
Figure 4. The contribution of manufacturing to the GDP of Africa of some selected countries based on 2022 data from the World Bank (Source: World Bank).
In 2015, the contribution of the manufacturing sector to African economies ranged from 5% to 30% of GDP (Figure 3). Smaller economies often showed stronger manufacturing sectors. Since the mid-1980s, this contribution has declined or stagnated. By 2015, Nigeria and South Africa, the continent’s largest economies, saw significant declines in manufacturing. In 2022, manufacturing contributed 14% to Nigeria’s GDP and 12% to South Africa’s, largely due to issues like power rationing and load shedding. Sub-Saharan Africa’s overall manufacturing contribution to GDP was 11% in 2022, with Algeria leading at 34% (Figure 4).
Retrofitting to “Afrofitting” the African manufacturing sector
Manufacturing in the Fourth Industrial Revolution will focus on sustainability through regional consumption. Similar strategies in Asia led to the rise of the Asian Tigers. From 2000 to 2010, countries like India, China, and Indonesia saw a ∼7.4% global manufacturing contribution, three times that of developed nations (Figure 5). Despite the data been ∼15 years old, the highlights are about the steady progress nations can achieve with well-planned and effectively executed programs with China being a case in point. China now ranks second globally, behind the U.S., whereas Indonesia moved from 20th to 13th, surpassing Canada and Spain.
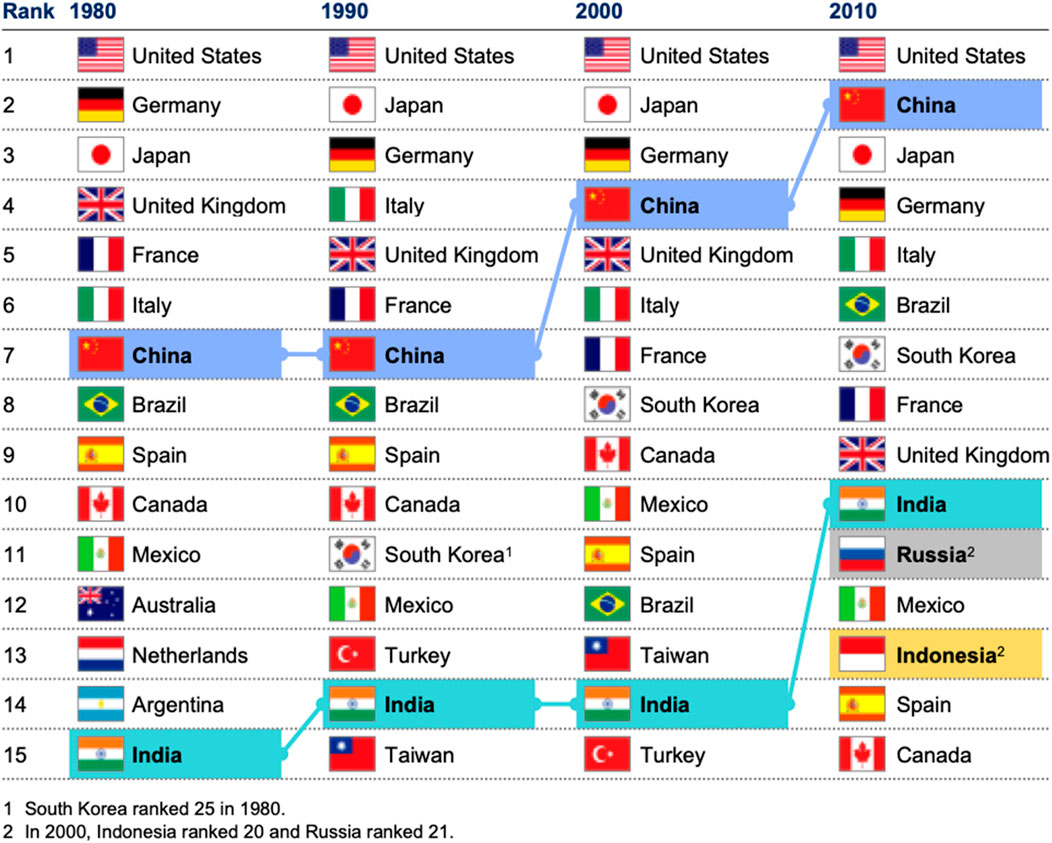

Figure 5. Top 15 manufacturing economies of the world with large developing economies steadily moving up (Manyika et al., 2013b).
Africa, while lagging economically, has the opportunity to industrialize through systematic policies and initiatives like the African Continental Free Trade Agreement (AfCFTA) (Ismail, 2017; Kambase and Akodia, 2022; Omphemetse, 2021). This single initiative has the potential to generate ∼$3.4 trillion for ∼1.3 billion Africans. By leveraging technologies like additive manufacturing, robotics, AI, and IoT (Malatji, 2024; Kalaba, 2020; Kere and Zongo, 2023; Lemma et al., 2022), Africa can accelerate growth exponentially. For instance, additive manufacturing enables rapid prototyping, customization, and decentralized production, benefiting African SMEs. Integrating digital technologies optimizes supply chains, streamlines production, and enhances market access. This could assist African manufacturers compete globally while adopting sustainable practices for a win-win scenario.
Sustainable advanced manufacturing, focused on resource efficiency, environmental responsibility, and social equity, is gaining momentum globally. African countries are embracing this by using renewable energy, reducing waste, and adopting eco-friendly production. Aligning industrialization with sustainability goals fosters inclusive growth, protects the environment, and builds resilient, competitive manufacturing ecosystems for long-term prosperity.
The concept of sustainable advanced manufacturing is gaining traction across the globe. This emphasizes resource efficiency, environmental responsibility, and social equity. African countries are increasingly adopting sustainable manufacturing practices, leveraging renewable energy sources, reducing waste generation, and implementing eco-friendly production processes. By aligning industrialization efforts with sustainability goals, African nations can foster inclusive growth, mitigate environmental degradation, and build resilient manufacturing ecosystems that contribute to long-term prosperity and competitiveness on the global stage.
Types of additive manufacturing–general overview
Additive manufacturing (AM) has over 40 years of continuous research, leading to seven classifications based on feedstock, energy source, and equipment per ISO/ASTM 52900 standards: vat polymerization, material jetting, binder jetting, material extrusion, powder bed fusion, sheet lamination, and direct energy deposition (Balubaid and Alsaadi, 2023; Adekanye S. A. et al., 2017; International Organization for Standardization, 2018; Mahamood et al., 2014; Kanishka and Acherjee, 2023; Frazier, 2014; Cooke et al., 2020; Haghnegahdar et al., 2022; Guo and Leu, 2013; Murr, 2015). Table 1 briefly summarizes these technologies, which vary in feedstock and mechanisms, offering diverse industrial applications. A recent addition is cold spray technology (Wu et al., 2021; Rojas et al., 2022; Li et al., 2018; Yin et al., 2018a; Fan et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2018b; Vaz et al., 2023; Zou, 2021), used for coating or bulk material design by accelerating metal or ceramic particles to form a cohesive layer through plastic deformation. Some of the advantages of AM processes are (Ford and Despeisse, 2016; Gebler et al., 2014):
• Cost-effective customization: Small batches of customizable parts are economically produced.
• Direct production: Parts are made directly from 3D CAD models, eliminating tools and moulds.
• Design flexibility: Digital designs are easily shared and modified for customization.
• Material efficiency: AM minimizes waste, supporting reuse and recycling.
• Complex geometries: Enables fabrication of intricate designs with high accuracy.
• Reduced defects: Fewer defects like porosity improve part quality.
• On-demand production: Reduces inventory risk and streamlines supply chains.
• Enhanced interaction: Encourages collaboration between producers, customers, and users.
Despite the benefits of AM process, key challenges that require further investigation and research include:
• Cost and speed: Production costs and speed need optimization to stay competitive.
• Design shift: Designers must adapt to AM’s unique capabilities, moving away from traditional methods.
• Perception: Overcoming the view that AM is only for prototyping is essential for broader adoption.
• Materials: Developing and standardizing AM materials is crucial to meet performance demands.
• Property validation: Ensuring mechanical and thermal properties meet standards is vital for real-world use.
• Multi-material systems: Advances in multi-material AM are needed for design flexibility.
• Automation: Automating AM systems boosts efficiency and scalability.
• Post-processing: Addressing surface imperfections and accuracy after printing is important.
• Support structures: Minimizing non-recyclable supports is key to sustainability.
• Intellectual property: Legal issues around copyright require attention.
• Skills gap: Training in AM techniques is critical to innovation.
• Collaboration: Effective coordination in AM projects is needed due to their complex nature.
• Competition: Staying agile in a rapidly evolving market is necessary for success.
Additive manufacturing (AM) begins with a 3D digital model, created using CAD and converted into formats like. AMF or. STL (Strong et al., 2018). The AM machine builds the object layer by layer, using materials such as resin, thermoplastics, or metal powders. This process minimizes waste and enables the creation of complex geometries not possible with traditional methods. Post-processing may be needed to remove supports and enhance accuracy.
Additive manufacturing (AM) offers significant advantages such as cost-effective customization, material efficiency, and the ability to produce complex geometries, but key challenges like optimizing costs, speed, material development, and post-processing must be addressed for broader adoption. As industries increasingly leverage digital designs and technologies like CAD/CAM, AM’s integration with sustainable practices and innovative solutions will be critical to its evolution, paving the way for more efficient, flexible, and scalable manufacturing processes in the future.
Emerging technologies and trends associated with AM
Emerging technologies and trends in additive manufacturing (AM) include the integration of traditional and AM processes to create hybrid manufacturing systems, cold spray technologies, advancements in multi-material and high-performance materials, and the adoption of digital manufacturing platforms driven by Industry 4.0 and 5.0. The rise of 4D printing, which adds a time-based dimension to 3D printing by enabling objects to change shape or function post-production, is also gaining momentum. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a key focus, with efforts to minimize waste and optimize energy usage in AM processes. These trends are revolutionizing industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in manufacturing. A brief overview of these emerging technologies is provided below, with suggested references for further reading.
Hybrid manufacturing
Hybrid manufacturing combines conventional manufacturing processes like subtractive methods with additive manufacturing (AM) technologies to enhance precision and efficiency (Nassehi et al., 2011; Zhu et al., 2013). Traditional subtractive processes, such as milling or machining, focus on material removal, which often results in significant waste. Transformative processes, like thermal treatment and metamorphic manufacturing (Daehn and Taub, 2018; Balasubramanian et al., 2001; Szadkowski, 1994; Doi et al., 2021), preserve mass while shaping components. Joining technologies are used to put multiple parts together, whereas subtractive technologies are used to disassemble components or cut pieces to near-net-shapes. Additive technologies involve material deposition to create robust structures, as seen in rapid prototyping and die casting. Hybrid processes merge one or more of these traditional approaches with AM, offering the best of both worlds by leveraging the precision of subtractive methods and the flexibility of additive techniques (Strong et al., 2018; Nassehi et al., 2011; Pérez et al., 2020).
Hybrid manufacturing has been in development for decades, largely driven by universities and research centres. This process enables near-net shape production via AM, followed by subtractive machining for final precision and surface finish (Strong et al., 2018; Pérez et al., 2020). Hybrid models integrate direct digital manufacturing (DDM) with traditional machine shops, promoting knowledge transfer and accelerating AM adoption (Webster et al., 2021). By combining technologies, hybrid manufacturing improves the performance and capacity of AM hubs, facilitating more advanced product development (Strong et al., 2018; Pérez et al., 2020). Examples of components produced using hybrid methods include brackets and turbine blades by companies like Alcoa and General Electric (Nassehi et al., 2011; Zhu et al., 2013).
Cold spray technologies
Cold spray is an emerging additive manufacturing (AM) technology that uses high-velocity metal or ceramic particles to build or coat parts without the need for heat (Walker, 2018; Srikanth et al., 2019; Wang Q. et al., 2021; Klenam et al., 2023), unlike techniques such as selective laser melting or fused deposition modeling. The high-velocity particles generate sufficient kinetic energy to bond materials, allowing for precise control over the shape, structure, and composition of the final product. Cold spray can deposit a wide range of materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics, with minimal heat-affected zones and distortions (Li et al., 2018; Champagne et al., 2015; Rahmati and Ghaei, 2014; Assadi et al., 2016; Moridi et al., 2014; Assadi et al., 2003; Su et al., 2019; Champagne and Helfritch, 2016). It also enables the fabrication of complex geometries and the repair or refurbishment of existing components with minimal material waste, making it a versatile and cost-effective method for industries like aerospace, automotive, and defense (Li et al., 2018; Yin et al., 2018b; Champagne and Helfritch, 2015; Cavaliere and Silvello, 2017; Astarita et al., 2016; Bagherifard and Guagliano, 2020).
Research on cold spray technologies can focus on several key areas, including optimizing particle velocity and deposition parameters to enhance bonding strength and material properties. Further exploration into the use of a broader range of materials, such as composites and advanced alloys, could expand its industrial applications. Studies on reducing surface roughness and improving dimensional accuracy in cold spray components are also critical for high-precision industries. Furthermore, there is the need to investigate long-term performance and durability of cold spray coatings under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments. This is vital for its adoption in aerospace, automotive and defense applications. Another possible research gap worth exploring is integrating cold spray with other additive manufacturing processes. This could provide various pathways to advance automation of the technology for efficiency and scalability.
Progress in advanced materials for AM processes
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) has rapidly evolved for the production of advanced materials (García-Collado et al., 2022; Forés-Garriga et al., 2023; Chen and Zheng, 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Hasanov et al., 2021; Hasanov et al., 2022; Nazir et al., 2023). These include multi-materials (García-Collado et al., 2022; Forés-Garriga et al., 2023; Chen and Zheng, 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Hasanov et al., 2021; Hasanov et al., 2022), metamaterials, functionally graded materials (Nazir et al., 2023), and complex concentrated alloys (Chen et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2021; Moorehead et al., 2020; Xiong, 2022; Melia et al., 2020; Ren et al., 2020; Pegues et al., 2020; Peng et al., 2021). The layer-by-layer process in multi-materials allows for the design and fabrication of components with varying properties, enabling customizable parts with distinct physical and mechanical characteristics. This method significantly reduces lead time for high-volume production. The process also mirrors natural systems where multiple material combinations coexist. Figure 6 illustrates examples of nature-inspired metamaterials and multi-materials, demonstrating synergy between material architecture, functionality, and performance (Liu et al., 2020; Hasanov et al., 2021; Nazir et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2019; Ravanbakhsh et al., 2021; Baca and Ahmad, 2020; Blanco et al., 2021a; Sarathchandra et al., 2018; Blanco et al., 2021b).

Figure 6. Typical example of nature–inspired structures for the design and additive manufacturing of cellular metamaterials and multi–materials (Nazir et al., 2023).
The main types of multi-materials used in additive manufacturing are shown in Figure 7. These include polymer-polymer, metal-metal, ceramic-ceramic materials, or combinations of each (García-Collado et al., 2022; Forés-Garriga et al., 2023; Chen and Zheng, 2018; Liu et al., 2020; Hasanov et al., 2021; Hasanov et al., 2022; Nazir et al., 2023). The additive manufacturing of dissimilar materials and its effects on the structural integrity of printed components offer advantages over conventional casting, welding, and forging processes (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024; Teawdeswan and Dong, 2024; Meyer et al., 2023; Willmott et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2023; Dzogbewu T. C. and de Beer D., 2023). It also opens up possibilities for further material exploration, with polymers and metals being widely studied. Commonly fabricated polymers include PLA, ABS, PEEK, and PET, focusing on properties like enhanced strength, stability, and performance. Metals and alloys used in multi-materials include Cu alloys, Ti alloys, Al alloys, and structural steels, with properties such as lightweighting, hardness, conductivity, wear resistance, strength-ductility synergy, and thermal performance (Nazir et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2019; Baca and Ahmad, 2020; Liu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024; Teawdeswan and Dong, 2024; Meyer et al., 2023; Willmott et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2023; Dzogbewu T. C. and de Beer D., 2023).
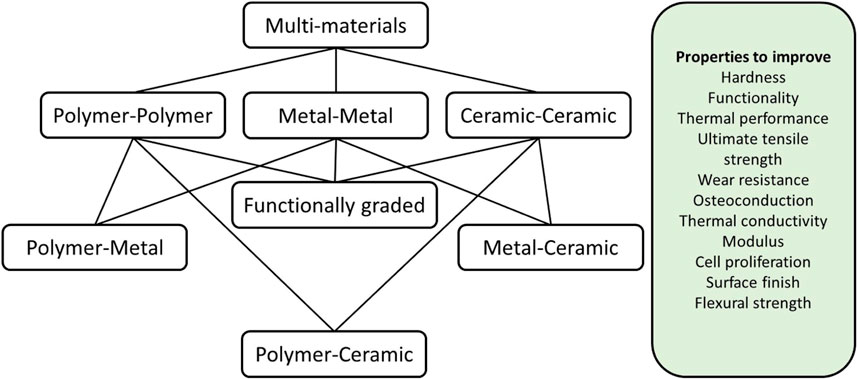
Figure 7. Typical multi–materials based on three main classes of engineering materials for additively manufactured products.
Functionally graded materials (FGMs) are engineered with gradual variations in composition, structure, and properties during manufacturing, aimed at creating heterogeneous components tailored for specific structural and functional needs. This approach allows the design of freeform components with performance-based gradual changes in composition, structure, and properties (Hasanov et al., 2022). FGMs are particularly explored to address mechanical property trade-offs, such as the strength-ductility balance in metallic materials. The typical additive manufacturing workflow for FGM design is shown in Figure 8. FGMs are mainly produced using fused filament fabrication, a type of material extrusion. Additive manufacturing enables precise control over spatial distribution and feedstock compositions through layer-by-layer deposition, offering full control over composition, structure, and property gradients (Hasanov et al., 2022).
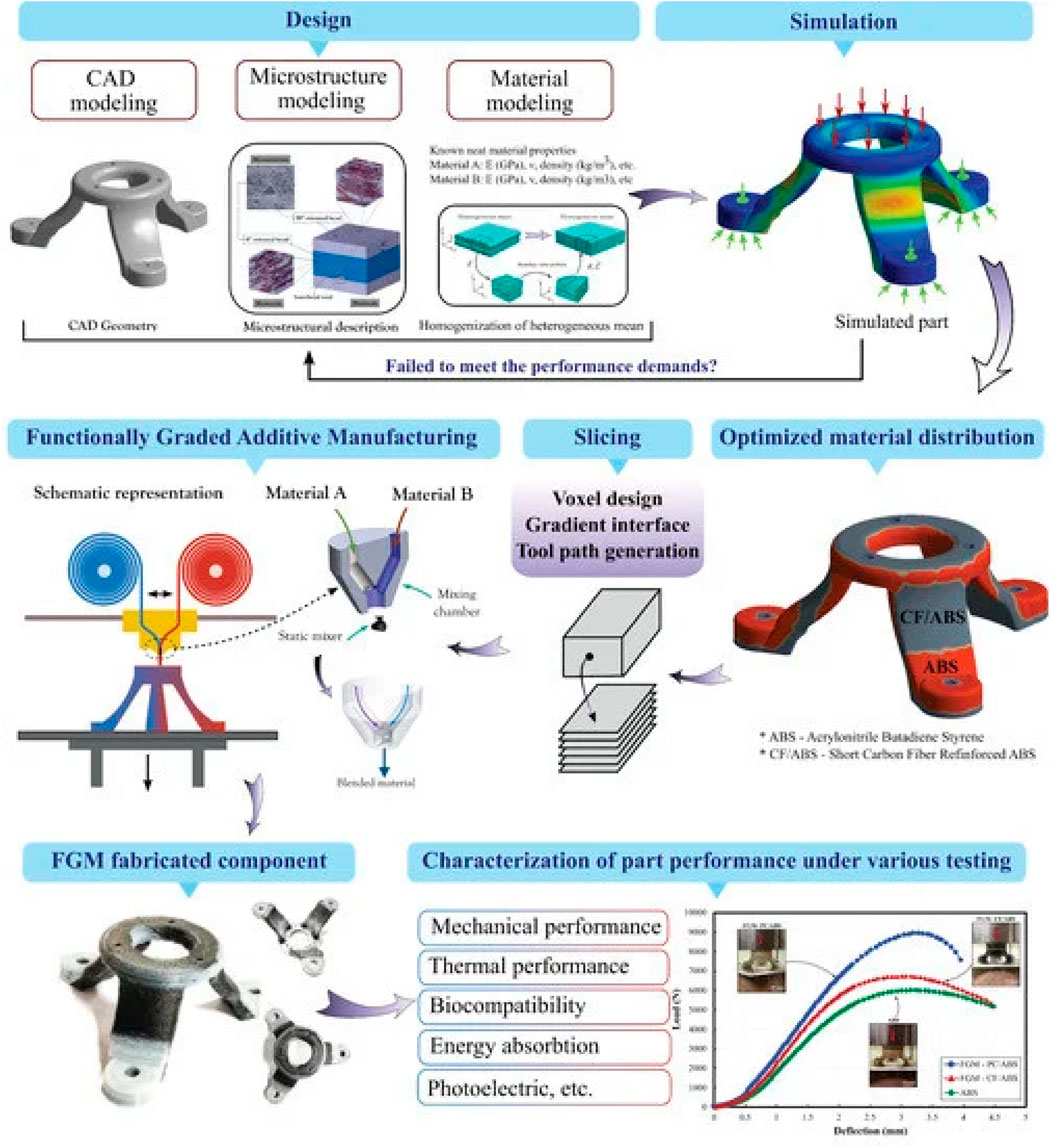
Figure 8. Schematic diagram showing the workflow of 3D printing of functionally graded material (Hasanov et al., 2022).
Industries 4.0 and 5.0 driving digital manufacturing
The shift from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0 significantly impacts additive manufacturing (AM) (Gibson et al., 2015; Daehn and Taub, 2018; Hopkinson et al., 2006a; Hopkinson et al., 2006b; Zhang et al., 2020). Industry 4.0 integrates cyber-physical systems, IoT, and cloud computing to optimize manufacturing, increase flexibility, and enable real-time control (Rupp et al., 2022; Gibson et al., 2015; Wang W.-Y. et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022). In AM, smart factories use interconnected systems for automated workflows and data-driven decisions. Industry 5.0 introduces human-machine collaboration and AI-driven automation, pushing towards metamorphic manufacturing (Daehn and Taub, 2018). This fusion of human creativity and machine intelligence will drive innovation, customization, and sustainability, positioning AM as a key player in the evolving digital manufacturing landscape.
The concept of 4D printing
Four D printing is an evolution of 3D printing with the dimension of time, enabling structures to change shape or function in response to environmental stimuli (Mohammadi et al., 2024; Haleem et al., 2018). It has gained attention in fields like biomedicine (Cui et al., 2020; Ramezani and Mohd Ripin, 2023; Antezana et al., 2023), materials science (Antezana et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2021; Kuang et al., 2019), and robotics (Adam et al., 2021; Zolfagharian et al., 2022), with recent advances expanding its capabilities.
In biomedicine, 4D printing shows potential in tissue engineering and drug delivery systems. Self-folding structures mimic natural tissues (Cui et al., 2020; Ramezani and Mohd Ripin, 2023; Antezana et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023), while shape-memory polymers create adaptive implants that respond to physiological changes (Ramezani and Mohd Ripin, 2023), offering personalized medical solutions (Antezana et al., 2023).
Advances in materials like liquid crystal elastomers and new fabrication techniques (Guo et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2021) have broadened its applications. In robotics, 4D printing enables soft robots that adapt to their environment (Zhang et al., 2021; Zolfagharian et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023), useful for tasks like search-and-rescue or medical devices. As the technology matures, 4D printing is set to revolutionize manufacturing, healthcare, and robotics by developing adaptive, responsive materials and structures. While there have been significant advances in materials, processes, and applications, there are still challenges and opportunities for future research, particularly in the areas of biomedical applications, and the development of machine learning approaches for 4D printing.
Sustainable development goals and additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing (AM) is closely aligned with the sustainable development goals (SDGs), directly impacting 13 of the 17 SDGs (Figure 9) and Africa Agenda 2063. AM supports drivers for its adoption across industries by promoting education, quality control, lightweighting for environmental benefits, alternative energy, and recyclability, contributing to environmental, societal, and economic sustainability (Figure 10) (Machado et al., 2019; Hegab et al., 2023). Furthermore, sustainable industrial ecosystems and accelerators are key to Africa’s Industrialization Agenda 2026, fostering innovation and technological growth through resilient infrastructure and strategic partnerships. These accelerators support business development, infrastructure, networks, and financial assistance, helping transition ideas to market (Caccamo and Beckman, 2022; Aljalahma and Slof, 2022; Kaur et al., 2024; Riesener et al., 2019; Pustovrh et al., 2020). They bridge the gap between academia and industry, driving innovation and the adoption of digital manufacturing, where AM plays a leading role (Lerman et al., 2021; Leydesdorff, 2000; Leydesdorff, 2012).
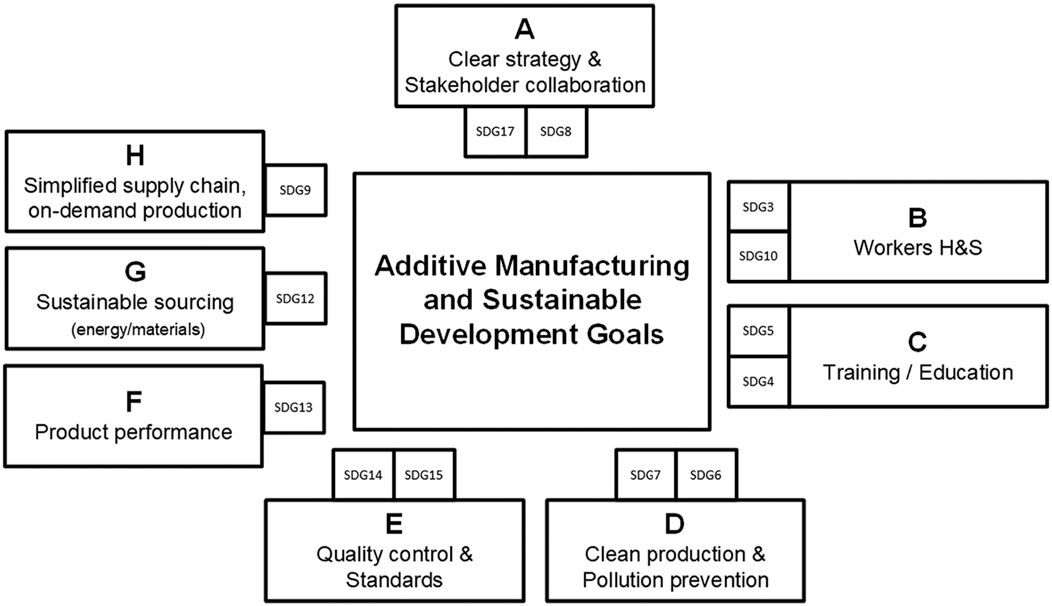
Figure 10. Interplay of additive manufacturing with sustainable development goals (Machado et al., 2019; Hegab et al., 2023).
Sustainable practices in additive manufacturing–an overview
Sustainable practices in AM represent a paradigm shift in advanced manufacturing, focusing on resource efficiency, eco-friendly material selection, energy-efficient technologies, waste minimization, and recycling (Arif et al., 2023; Woodson, 2015; De Beer, 2010; Jiang and Fu, 2020; Al Jahdaly et al., 2022; Raabe, 2023; Olivetti and Cullen, 1979). AM supports localized production, eliminating extensive supply chains and infrastructure, empowering local communities, and reducing lead times and currency fluctuation impacts. This decentralized approach could thrive in Africa’s informal economy, with digital inventories replacing physical warehouses. Table 2 outlines critical evaluation criteria for ensuring sustainability in AM technologies (Gebler et al., 2014).
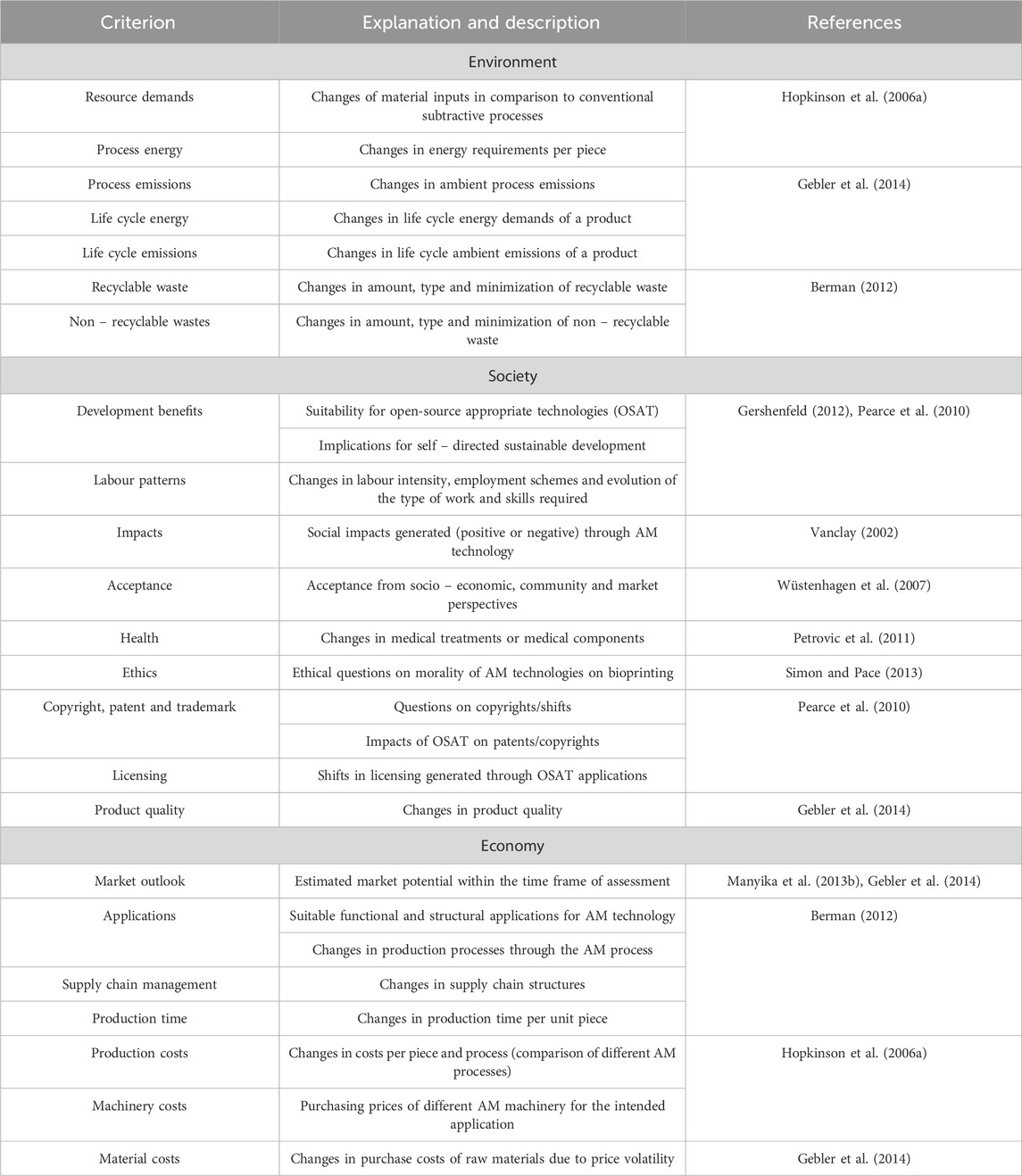
Table 2. Criteria and explanation for the sustainable evaluation of AM technologies and intended implications (Gebler et al., 2014).
Additive manufacturing fosters innovation, aligning with SDG 9 as a pillar of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, driving technological and material advancements (Klenam et al., 2022; Assadi et al., 2016; Bandyopadhyay et al., 2022). Eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient printing methods, and optimized process parameters reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints, contributing to global sustainability efforts (Machado et al., 2019; Hegab et al., 2023). AM also supports resilient infrastructure by enabling rapid prototyping and the production of spare parts, crucial during supply chain disruptions, such as during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The use of bio-based and recycled materials in AM aligns with circular economy principles, reducing reliance on traditional raw materials and promoting waste minimization (Arif et al., 2023; Woodson, 2015; De Beer, 2010; Jiang and Fu, 2020; Al Jahdaly et al., 2022; Raabe, 2023; Olivetti and Cullen, 1979). AM technologies contribute to environmentally friendly approaches by addressing natural resource consumption, waste generation, and pollution remediation, emphasizing sustainability in the environment, society, and economy (Agnusdei and Del Prete, 2022; Jayawardane et al., 2023; Gebler et al., 2014; Hegab et al., 2023; Olivetti and Cullen, 1979; Cann et al., 2020; Raabe et al., 2019; Joshi and Sheikh, 2015).
Material selection and localized sourcing
Traditional manufacturing consumes 35%–40% of engineered materials globally, with the metal industry contributing 12% of CO2 emissions (Gao et al., 2021; Daraban et al., 2019). Subtractive manufacturing leads to significant material wastage and emits greenhouse gases, which are unsustainable in today’s resource-constrained era (Balubaid and Alsaadi, 2023; Raabe, 2023; Olivetti and Cullen, 1979; Cann et al., 2020; Radlbeck and Mensinger, 2011; Gordon et al., 2006; Thakur et al., 2018). Additive manufacturing offers a sustainable alternative by focusing on eco-friendly materials and localized sourcing (De Beer, 2010; Raabe, 2023; World Economic Forum, 2015). Sustainable material selection prioritizes recyclability, biodegradability, low toxicity, and minimal waste, helping to mitigate environmental impacts (Gao et al., 2021; Daraban et al., 2019).
Using biodegradable polymers, recycled plastics, bio-based composites, and impurity-tolerant alloys in AM reduces reliance on petroleum-based materials and lowers carbon emissions (Raabe, 2023; Raabe et al., 2019). Recycled materials for 3D printing can cut the demand for virgin resources and reduce production costs. Locally sourced materials for AM further decrease transportation-related emissions and strengthen regional economies, promoting job creation and resilient supply chains (Oyesola et al., 2018; Agnusdei and Del Prete, 2022; Balubaid and Alsaadi, 2023; Raabe, 2023; Cann et al., 2020; Raabe et al., 2019; Joshi and Sheikh, 2015; Radlbeck and Mensinger, 2011; Gordon et al., 2006; Thakur et al., 2018).
Sustainable practices in AM, particularly in material selection and sourcing, promote environmental stewardship, resource efficiency, and technological innovation (Agnusdei and Del Prete, 2022; Raabe, 2023; Vanclay, 2002; Wüstenhagen et al., 2007; Petrovic et al., 2011; Radlbeck and Mensinger, 2011; Gordon et al., 2006; Thakur et al., 2018; Wang Y. et al., 2021). As industries adopt these practices, eco-friendly materials will continue to advance sustainability and resilience in manufacturing.
Energy efficiency
Current industrial manufacturing consumes 15% of global energy (Gao et al., 2021; Daraban et al., 2019). Energy efficiency in AM is crucial for sustainable production, particularly in regions like Africa, where energy sources are often unreliable. Technologies such as power bed fusion (PBF), which uses laser melting and sintering, and fused deposition modeling (FDM) are known for its low power requirements (Monteiro et al., 2022; Gao et al., 2021; Wang K. et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2020). This offers energy-efficient alternatives to most conventional methods. These processes also reduce the need for energy-intensive post-processing.
The integration of renewable energy into 3D printing is expanding, with solar-powered AM systems used in off-grid and remote communities (O’Neill and Mehmanparast, 2024; Wang Y. et al., 2021; Zhakeyev et al., 2017; Dzogbewu T. C. and de Beer D. J., 2023; Strack, 2019). Africa, rich in renewable resources, is well-positioned to benefit from these developments, promoting energy independence, reducing environmental impacts, and supporting economic growth. This could also help curb rural-to-urban migration by decentralizing manufacturing capabilities. In conclusion, energy-efficient AM technologies, combined with renewable energy, have the potential to drive sustainable industrialization in Africa (Meurisse et al., 2018).
Waste reduction and recycling towards sustainable circular economy
Waste in engineering design, primarily from conventional manufacturing, has significant environmental impacts. Additive manufacturing (AM), with its circular economy approach, reduces waste by up to 90% and promotes recycling across industries (Mohammed et al., 2022; Jiang et al., 2019a; Di and Yang, 2022; Jiang et al., 2019b; Byard et al., 2019; Dhiman et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2018). Generally, the strategies of the circular economy supporting additive manufacturing with identifiable benefits are given in Table 3 (Hegab et al., 2023; Spirio et al., 2024). The precision and on-demand fabrication with AM technologies minimize material waste, as seen in stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), and metal AM methods like selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. These processes optimize material use, converting machining waste into feedstocks for further 3D printing (Dhiman et al., 2021). In fusion deposition modeling (FDM), recycled thermoplastics like PET and ABS are repurposed into feedstock, diverting plastic waste from landfills and incineration (Hegab et al., 2023; Mohammed et al., 2022; Spirio et al., 2024; Al Rashid and Koç, 2023). This closed-loop recycling approach embodies the principles of a circular economy and supports sustainability within AM practices (Di and Yang, 2022). These advancements signify a shift toward resource-efficient and eco-friendly manufacturing.
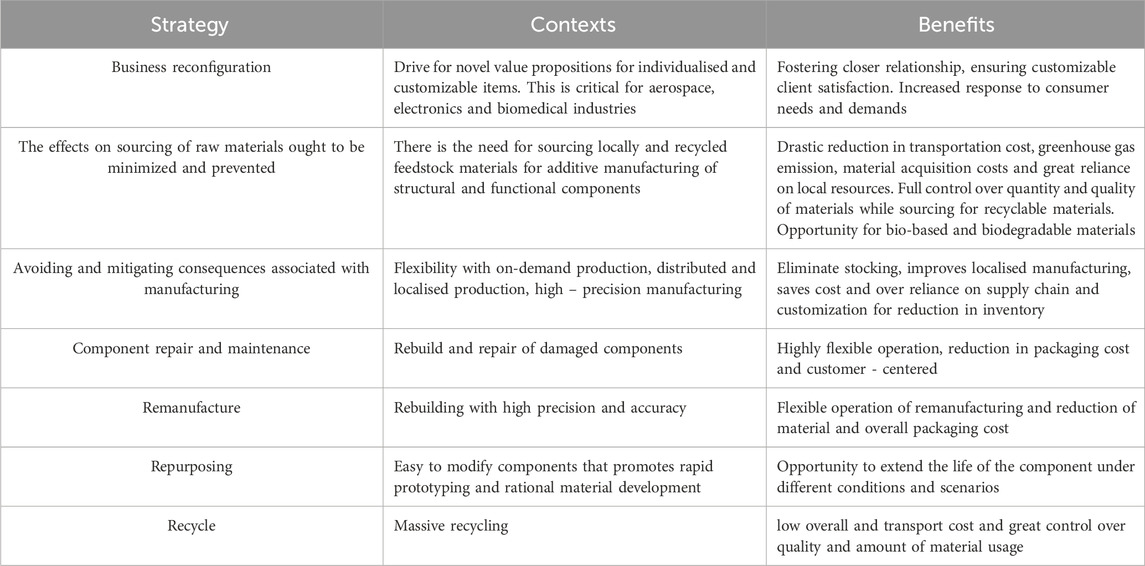
Table 3. Circular economic strategies and benefits of sustainable practices in AM (Hegab et al., 2023; Kravchenko et al., 2020).
Life cycle analysis and assessment in AM technologies–an overview
Life cycle analysis (LCA) is a crucial framework for assessing the environmental impact of additive manufacturing (AM) technologies (Landi et al., 2022; Výtisk et al., 2022; Kokare et al., 2023). It examines the full life cycle of AM processes, including raw material extraction, energy use during printing, post-processing, logistics, and disposal or recycling. Table 4 compares the production and life cycle costs of AM and conventional manufacturing (CM), showing advantages of AM. By applying LCA, environmental impacts can be identified, and sustainability strategies developed. In resource-scarce regions like Africa, LCA supports informed decisions and policies tailored to local needs, as illustrated in Figure 11 (Kokare et al., 2023).
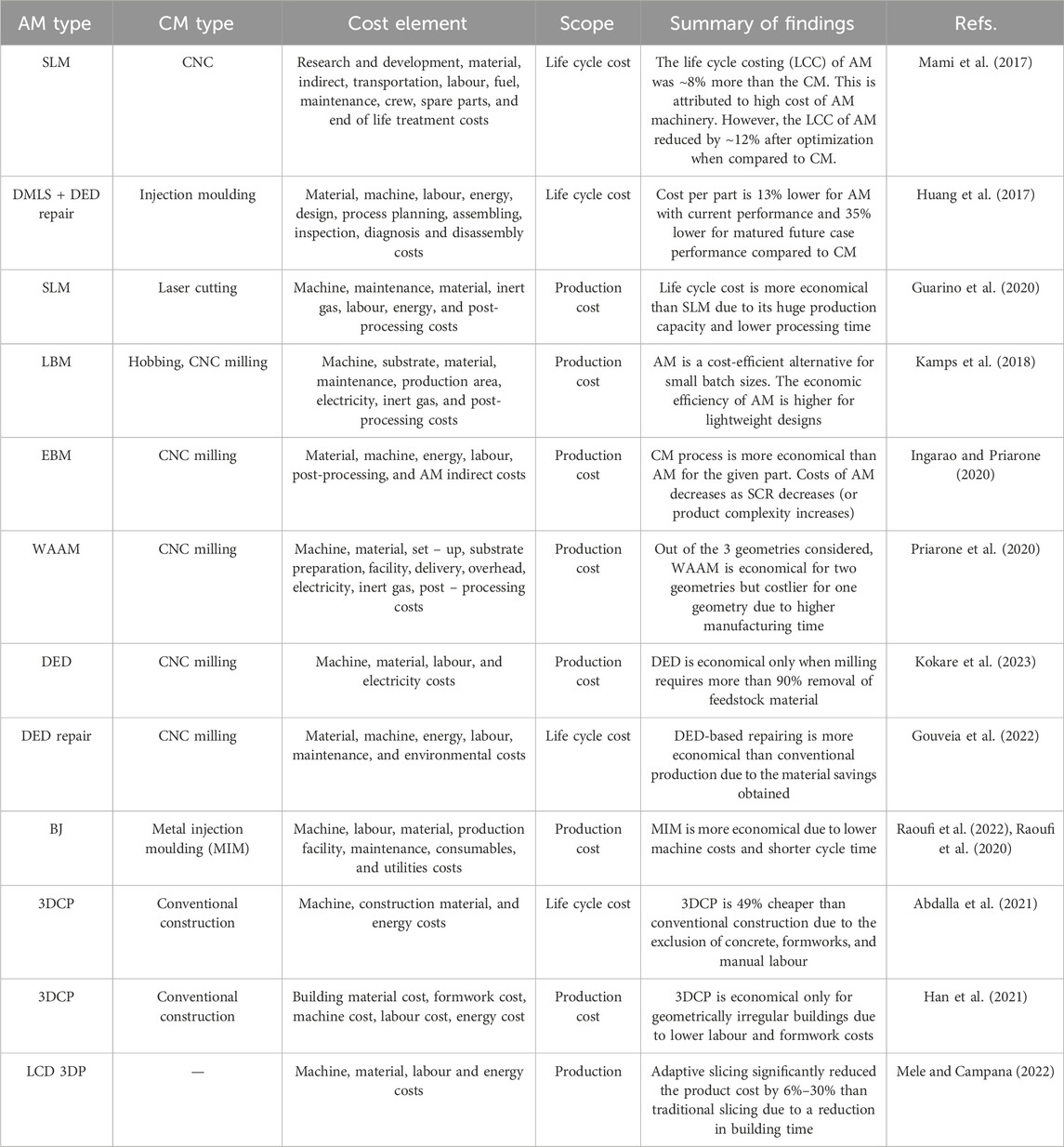
Table 4. Studies focusing on life cycle assessment comparing AM and CM structural and functional components (Kokare et al., 2023).
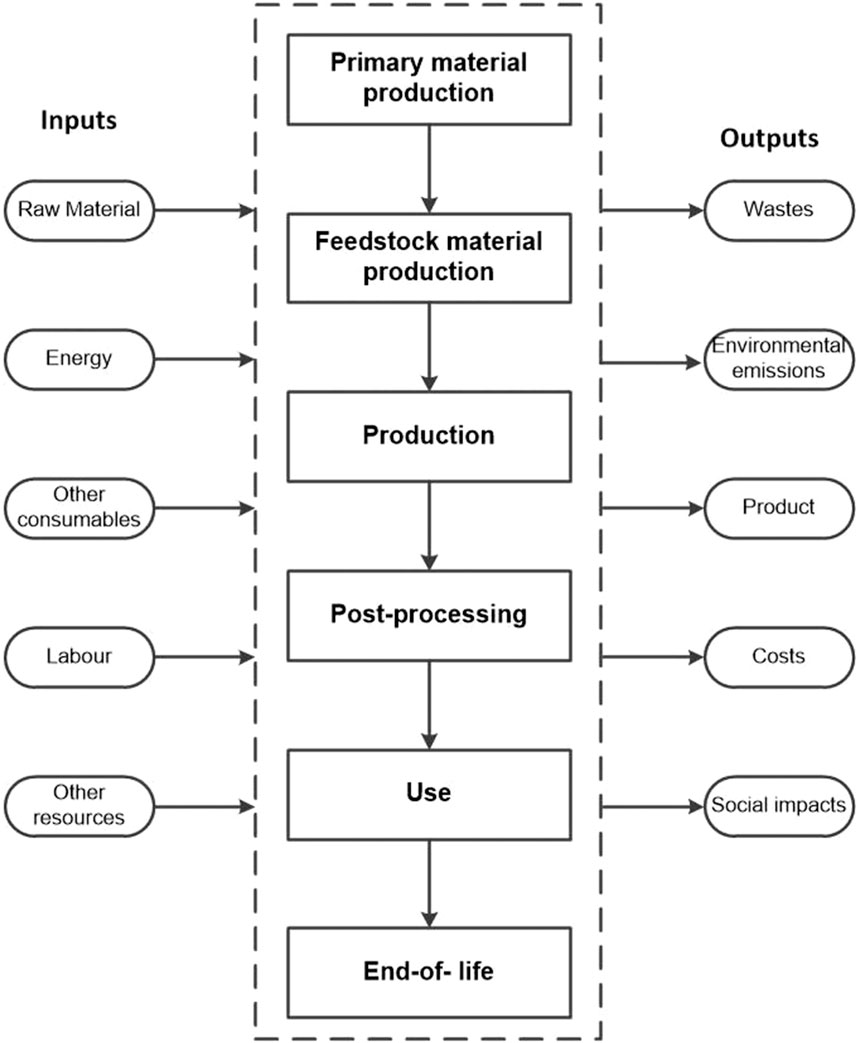
Figure 11. Life cycle assessment of a 3D printed component (Kokare et al., 2023).
Generally, LCA helps optimize AM processes and materials for sustainability, pinpointing opportunities for resource efficiency, waste reduction, and energy conservation. This approach strengthens both environmental and economic outcomes. In Africa, where AM supports localized production, LCA can help reduce carbon footprints and improve resource utilization. Research should focus on comprehensive LCA studies to identify critical stages for improvement and promote closed-loop material systems, essential for a circular economy in AM. Sustainable materials and practices in AM align with responsible manufacturing and the broader sustainability goals throughout the lifecycle of components.
Estimated market value of AM by 2050
The market share of additive manufacturing has been increasing exponentially since 2010 (Kolade et al., 2022). Globally, additively manufactured products have increased in value from $ 2.3 billion in 2012 to ∼$3.07 billion in 2013 and then ∼$13.78 billion in 2020. This value is expected to hit $62.79 billion by 2028. A compound growth of ∼26.4% has been recorded annually on average since the global adoption of AM and its related technologies in 1989. The market value is expected to increase with an estimated global market value of $550 billion by 2050. The increasing exponential growth is attributed to the merits of the technology as discussed earlier. It is also one the eight pillars and technological adjacencies of the Fourth Industrial revolution (4IR).
African industries that can benefit from integrating AM technologies
Additive manufacturing (AM) holds immense potential for African industries such as oil and gas, healthcare, aerospace, defense, automotive, consumer goods, and energy. In the oil and gas sector, AM can streamline operations by enabling on-demand production of critical components, reducing reliance on traditional supply chains and minimizing downtime (Klenam et al., 2022; Barambu Umar, 2023). The ability to customize parts also offers significant cost savings and operational improvements.
In healthcare, AM played a crucial role during the COVID-19 pandemic, producing essential medical equipment like PPE and ventilators. AM allows for rapid prototyping and customization of medical devices, improving patient care (Dzogbewu T. C. and de Beer D., 2023; Dzogbewu T. C. and de Beer D. J., 2023; Dzogbewu et al., 2022). South Africa’s development of customized biomedical implants highlights the potential for better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs (du Preez and de Beer, 2015; Preez et al., 2020; du Preez and de Beer, 2006; Stefaniak et al., 2021; de Beer et al., 2016).
In manufacturing, AM enables the production of complex geometries and customized products, increasing competitiveness and job creation, particularly for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) (Muvunzi et al., 2022). Promoting collaboration between universities, industry, and government, along with national frameworks, can guide the adoption of AM and drive innovation (du Preez and de Beer, 2015; Preez et al., 2020; du Preez and de Beer, 2006; de Beer et al., 2016). By addressing infrastructure challenges and offering financial incentives, African industries can fully harness benefits of AM for industrial growth, sustainability, and economic advancement. The applications of AM also extend to aerospace, defense, automotive, and energy sectors, where it accelerates prototyping and low-volume production of complex parts. In consumer goods, 3D printing enables cost-effective customization and continuous product improvement, particularly in the footwear industry, where it eliminates costly moulds and supports small-batch production. Across sectors, AM enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and fosters innovation.
Case studies on potential AM adoption by African countries and relevant sector
The adoption and acceptance of additive manufacturing (AM) in Africa are gaining traction. This is mainly driven by increased awareness, infrastructural support, and the commitment of key stakeholders from the public and private sectors. In terms of curriculum design for most schools across the continent, 3D printing tools have been used to compliment the training of students, support teaching, create artefacts and assistive devices for hands–on training and for outreach programs (Ford and Minshall, 2019) and awareness creation (Mhlongo et al., 2023). The technology is being applied to address unique local challenges, fostering economic growth.
Several case studies highlight the use of AM technologies in African countries, though many remain undocumented or proprietary. These examples are not exhaustive, but representative nations were selected from four economic blocs based on economic size and adoption of 4IR technologies. In the Southern African Development Community (SADC), South Africa stands out for its leadership in AM, driven by research institutions, industry partnerships, and government legislation. In West Africa, Nigeria, the largest economy in ECOWAS, is implementing AM in its growing spare parts and luxury goods sectors, supported by research initiatives. During the 2019–2021 COVID-19 pandemic, AM was used to design and develop personal protective equipment, ventilator components, testing swabs, hands-free door openers, medical devices, respirator masks, and filters. These efforts mitigated supply chain disruptions and enabled rapid local production to meet urgent medical needs, with universities, companies, and grassroots organizations leveraging 3D printing to quickly and affordably produce essential items. AM’s effectiveness during the pandemic was due to its ability to reduce dependence on disrupted international supply chains and offer cost-efficient production, particularly for countries with limited resources. Its flexibility allowed for rapid prototyping and customization to meet specific needs while bridging gaps in Africa’s underdeveloped manufacturing infrastructure. By fostering collaboration and promoting innovation, AM built resilience across communities, and its material efficiency supported sustainability by reducing waste, making it an ideal solution for addressing medical supply shortages in Africa and globally during the crisis. Building on these gains, many African countries are expanding and utilizing the infrastructure developed during the pandemic, with the potential to integrate it into mainstream manufacturing. This could strengthen economic growth and support the realization of Africa Union Agenda 2063.
South Africa
Additive manufacturing (AM) technologies were introduced in South Africa in the early 90s (Dzogbewu et al., 2022; du Preez and de Beer, 2015; de Beer et al., 2016; du Plessis et al., 2019a; Campbell et al., 2011; Kunniger, 2015; Alabi, 2019). However, the adoption has been rapid approximately a decade after the global commercialization of the technology. South Africa, being one of the more industrialized African economies had manufacturing sector contributing ∼19% to its GDP prior to her independence. Therefore, the adopting of the technology was well intentioned and motivated (Dzogbewu et al., 2022; de Beer et al., 2016; Campbell et al., 2011). The Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) acquired the first AM system (3D Systems SLA 250) in 1991. By 1998, various public and private institutions had procured a total of seven AM systems. The invention of personal and desktop 3D printers saw an astronomical increase in 3D printers from ∼90 in 2005 to ∼1,500 in 2010 and over 3,500 in 2015. About 87% of the facilities were entry levels. This momentum led to the establishment of the Rapid Product Development Association of South Africa (RAPDASA) in the early 2000s and the creation of a National Additive Manufacturing Strategic Roadmap in 2013. Significant budget allocations between 2010 and 2016 supported the use of AM technologies for aerospace and biomedical component design and manufacturing. These efforts facilitated the adoption of AM by local businesses and high-value industry sectors. The CSIR Centre of Competence was then established to promote the development, industrialization, commercialization, and acquisition of world-class AM infrastructure, guided by globally accepted best practices (de Beer et al., 2016). The adoption of AM aligns with the strategic goals of economic efficiency and environmental sustainability while positioning South Africa as an industrial hub of the continent.
Four priority areas for advancing AM technologies were set out by the South African government (Dzogbewu et al., 2022; de Beer et al., 2016). The priority areas were joint effort by subject matter experts from governments agencies to inform policy, education establishment and research councils to support innovation and industry players to for implementation and commercialization (de Beer et al., 2016). The priority areas are: (1) The need for qualified AM or 3D printing technologies for final manufacturing of high–earn value goods in aerospace and medical industry; (2) integration of AM technologies in traditional manufacturing markets; (3) the development of new technologies and designing of new functional and structural materials; and (4) development of support programmes geared toward small, medium and micro enterprises (SMME). The priority areas contextualised and provided an inclusive framework for the triple helix approach for all industry players (Lerman et al., 2021; Leydesdorff, 2000; Leydesdorff, 2012; Kolade et al., 2022).
Additive manufacturing technologies have gradually been integrated into the South African manufacturing sector. This is due to increasing research from universities, research centres and private-public partnership. Thus, in 2023, South Africa had the highest research throughput with over 60% of publications on the continent (Klenam et al., 2022). Pioneering works were done by the Central University of Technology. The aerospace industry has produced specialized parts for lightweight applications (du Plessis et al., 2019a; Blakey-Milner et al., 2021). The Aeroswift Project, a private-public partnership led to the design of the world’s largest and fastest Ti-based additive manufacturing systems (Dzogbewu et al., 2022; Campbell et al., 2011; Kunniger, 2015; du Plessis et al., 2019b). This is testament to digital and high-tech manufacturing capabilities of South Africa to transform the aerospace sector. The biomedical industry is actively using AM for the design and manufacture of prosthetics and implants. For instance, Anton Du Plessis, from Stellenbosch University has been phenomenal in the field of biomimicry and bioinspired additive manufacturing (du Plessis et al., 2021; du Plessis et al., 2019b; du Plessis et al., 2016). Their team has been one of the first to procure X-ray micro computed tomography and other state-of-the-art characterization techniques for processing-structural-property investigated of 3D printed functional and structural materials (du Plessis et al., 2021; Kruger et al., 2021; du Plessis et al., 2019b; du Plessis et al., 2016; du Plessis and le Roux, 2018; du Plessis et al., 2020). Similarly, the automotive and railway industries are also producing mechanical component parts with the technology on small scale in various industrial parks in Johannesburg, Durban and Cape Town (Toth et al., 2022). The Physical Metallurgy Group at Mintek, subsidiary of the South African Department of Mineral Resource (DMR) in Johannesburg procured Amazement rePowder Ultrasonic atomizer and a General Electric metal 3D printing facilities in 2023. This is in with the mineral beneficiation and value addition to the South African mineral wealth under the auspices of the DRM. Thus, South Africa is mainly steady progress to leverage from advanced materials development, robotics and manufacturing, one of the pillars of the Fourth Industrial revolution.
Nigeria
Manufacturing sector and the infusion of nascent technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution are inseparable (Klenam et al., 2022; Inoma et al., 2020; Adefuye et al., 2019). The manufacturing sector in Nigeria is grouped under eight major industries since 2015. This includes oil refining, cement production, food, beverage and tobacco, fashion (textiles, apparel and footwear), wood and wood products, pulp, paper and paper products, chemical and pharmaceutical products, and non-metallic products. The AM technologies are applicable in these sectors of manufacturing in Nigeria and can drive a rapid economic transformation (Inoma et al., 2020; Adefuye et al., 2019; Adekunle and Alhassan, 2022; Ishengoma and Mtaho, 2014; Olomu et al., 2023). This is essential to the increasing fortunes and contribution of manufacturing to the GDP of the Nigerian economy (Inoma et al., 2020; Adefuye et al., 2019; Adekunle and Alhassan, 2022; Adekanye A. et al., 2017). Leveraging AM technologies in dental and medical industries, footwear, jewellery and automotive industries has the capacity to position Nigeria as an industrial hub on the continent.
Additive manufacturing is increasingly being used to produce automotive parts in Nigeria (Klenam et al., 2022; Inoma et al., 2020; Adefuye et al., 2019; Adekunle and Alhassan, 2022). Typical example is the use of both AM and subtractive technologies to produce gears. For the two approaches, in terms of lead time, energy savings and overall cost, AM technologies were better than the subtractive technologies (Adekunle and Alhassan, 2022). The use of AM for rapid prototyping of components for aerospace and automotive parts are also on the rise. This results in drastic reduction in time-to-market of products with less use of tooling and massive infrastructure for most factories. Thus, AM technologies provide innovation pathways for manufacturing structural and functional components with ease, contributing to the African industrialization agenda. This is why AM technologies are touted the future of modern manufacturing.
The inclusion of AM technologies in high education sector in Nigeria has increased (Mhlongo et al., 2023; Inoma et al., 2020). This is to address the skills shortfall in the Nigerian economy and then provide an education that is forward thinking, experiential and extensional. The linkage between AM based courses and the perception, attitude and knowledge of the undergraduate and postgraduates are on the rise (Inoma et al., 2020). The use of AM technologies drives awareness and boost industry participation. It has also been effective in enhancing the learning of difficult concepts of students in engineering (Mhlongo et al., 2023). By using 3D printing, models are designed and produced based on specific concepts to enhance understanding of three-dimensional perspectives of ideas (Ford and Minshall, 2019).
Egypt
The Egyptian Strategy for Development provides the pathway for the infusion of AM technologies into the manufacturing sector (Geneidy et al., 2019; Saleem et al., 2023; Bibb and McKnight, 2022; El-Mahdy et al., 2021; McKnight et al., 2015; Abbady et al., 2022; El-din et al., 2021). The Egypt Vision 2030 aimed to invest heavily in areas that drives the technologies of the future and to ensure Egypt is in the top 30 heavily industrialized countries of the world. The prospects of AM in the construction industry, educational establishment, preservation of cultural heritage by replicating historical artifacts and recycling of wastes toward green manufacturing is being examined for overall contribution to manufacturing (Geneidy et al., 2019; Saleem et al., 2023; Bibb and McKnight, 2022; El-Mahdy et al., 2021; McKnight et al., 2015; Abbady et al., 2022; El-din et al., 2021; Nigro et al., 2024).
Archiving and replicating historical artefacts have been critical to Egyptian rich cultural heritage (Saleem et al., 2023; Bibb and McKnight, 2022). The Factum Foundation used 3D scanning and printing technologies to create and printed replicas of artefacts such as the “Tomb of Tutankhamun” and other historical relics (Saleem et al., 2023; Bibb and McKnight, 2022). Thus, original historical artefacts are preserved, and the 3D models are then used for exhibition and educational purposes.
Additive manufacturing is widely being used in the Egyptian construction industry (Geneidy et al., 2019; El-din et al., 2021). This is mainly due to merits such as increased design flexibility, use of in-situ materials, different types of raw materials, reduced used of resource with negligible waste, eco–and environmentally–friendly, low-cost construction method, reduced workforce, low transportation costs and low-cost mass customization route (El-din et al., 2021).
There is increasing application of AM techniques in surgical and dentistry in the medical fraternity in Egypt (Hafez et al., 2015; Hafez, 2012). It has successfully been used for producing splints, surgical guides, templates and cutting tools in orthopaedic and maxillofacial surgery processes (Hafez et al., 2015). In some instance, patient-specific and tailored templates for total knee arthroplasty have been 3D printed (Hafez, 2012). To curb the increasing demand for donors for various vital organs for transplant, 3D printed organs have been successfully implanted in urology (Soliman et al., 2015) and cardiology (El-Sherbiny and Yacoub, 2013). Typical example is the successful bladder transplant in Egypt (Soliman et al., 2015). For cardiology, various hydrogels have been used as scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering (El-Sherbiny and Yacoub, 2013). As of 2013, the major AM and other 3D prototyping machinery available in Egypt is summarized in Table 5.
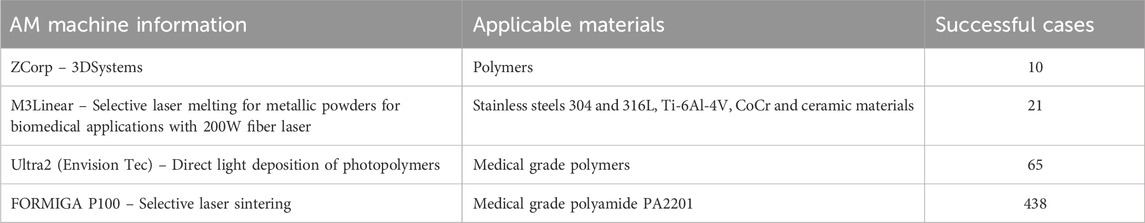
Table 5. Additive manufacturing machines and successful medical cases done in Egypt (Hafez et al., 2015).
Kenya
Kenya is one of the progressive African nations embracing technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Some of these technologies have been deployed in SMMEs and various industries which is in line with the Kenya Vision 2030 (Cairns et al., 2022; Rodrigues et al., 2024). A critical driver of these initiatives is underpinned by the Nairobi Integrated Urban Development Master Plan (NIUPLAN) which provides the roadmap for an industrialised and knowledge economy. We are in the knowledge and information age where there is tremendous, extensive and rapid disruptive technological transformation.
In Kenya, additive manufacturing (AM) has been applied across various sectors, demonstrating its transformative potential (Mounde and Arisi Alex, 2019). One notable case study is in the medical industry, where 3D printing has been used to produce affordable prosthetics, improving accessibility for amputees (du Plessis et al., 2019a). Some of the leading institutions and startup deploying innovative and customizable prosthetics are the Victoria Hand Project started working in 2020 with St. Luke’s Orthopaedic and Trauma Hospital (https://www.victoriahandproject.com/kenya) and 3D LifePrints. Furthermore, a vein finder was produced and manufactured from 3D printing for an infant (Ishengoma and Mtaho, 2014). These biomedical products or devices are being produced timeously, low-cost and easily accessible to individuals with disabilities thereby improving the quality of life.
The AM technologies is gaining traction in the educational sector (Cairns et al., 2022; Mounde and Arisi Alex, 2019; Peter et al., 2022). Thus, universities are integrating AM into their curricula, for advance manufacturing, design and fabrication of prototypes, fostering innovation and practical skills (Kolade et al., 2022). The integration is organized around Fabrication laboratories in most universities in Africa (Ishengoma and Mtaho, 2014; Leminen, 2015). This is mainly through the public-private partnership and collaboration with global institutions from the global North. Typical example is the Semiconductor Technologies Limited, one of the leading microchip and nanotechnology materials development company in Dedan Kimati University of Technology in Nyeri in Kenya. By using AM technologies and partnership from the Global North and East, they are carrying out cutting edge research and commercialization of high-earn products with wide range applications in various industries (Caccamo and Beckman, 2022; Riesener et al., 2019; Pustovrh et al., 2020). Face shields and masks were 3D printed during the Covid – 19 pandemic. This is a typical example of the triple helix approach to innovation (Kolade et al., 2022; Leminen, 2015).
The automotive and construction industries have benefited with application of AM technologies (Bedarf et al., 2021; Tay et al., 2017; Sakin and Kiroglu, 2017; Kanyilmaz et al., 2021; Sikora et al., 2021). There is continuous use of 3D printing by local startups to manufacture vehicle parts to reduce costs and lead times (Kolade et al., 2022). Additionally, the construction sector has seen advancements through AM, with projects exploring the use of 3D-printed components for eco-friendly housing. Lastly, agricultural equipment manufacturers are leveraging AM to produce customized tools and spare parts, enhancing productivity and sustainability in farming practices. Although these case studies are on-going in the public and private space in Kenya, most of them are not documented and not available to the public.
Critical assessment of the four research questions and the linkage to sustainable African development is summarized in Table 6. The first one highlighted the manufacturing landscape of the continent and how the excesses can be minimized. The role of sustainable AM in the industrialization of the continent is also discussed in light with the available literature, highlighting current trends and implications for future research direction. Some of the recent challenges of implementing sustainable AM approaches were identified and possible solutions to overcome them proffered.
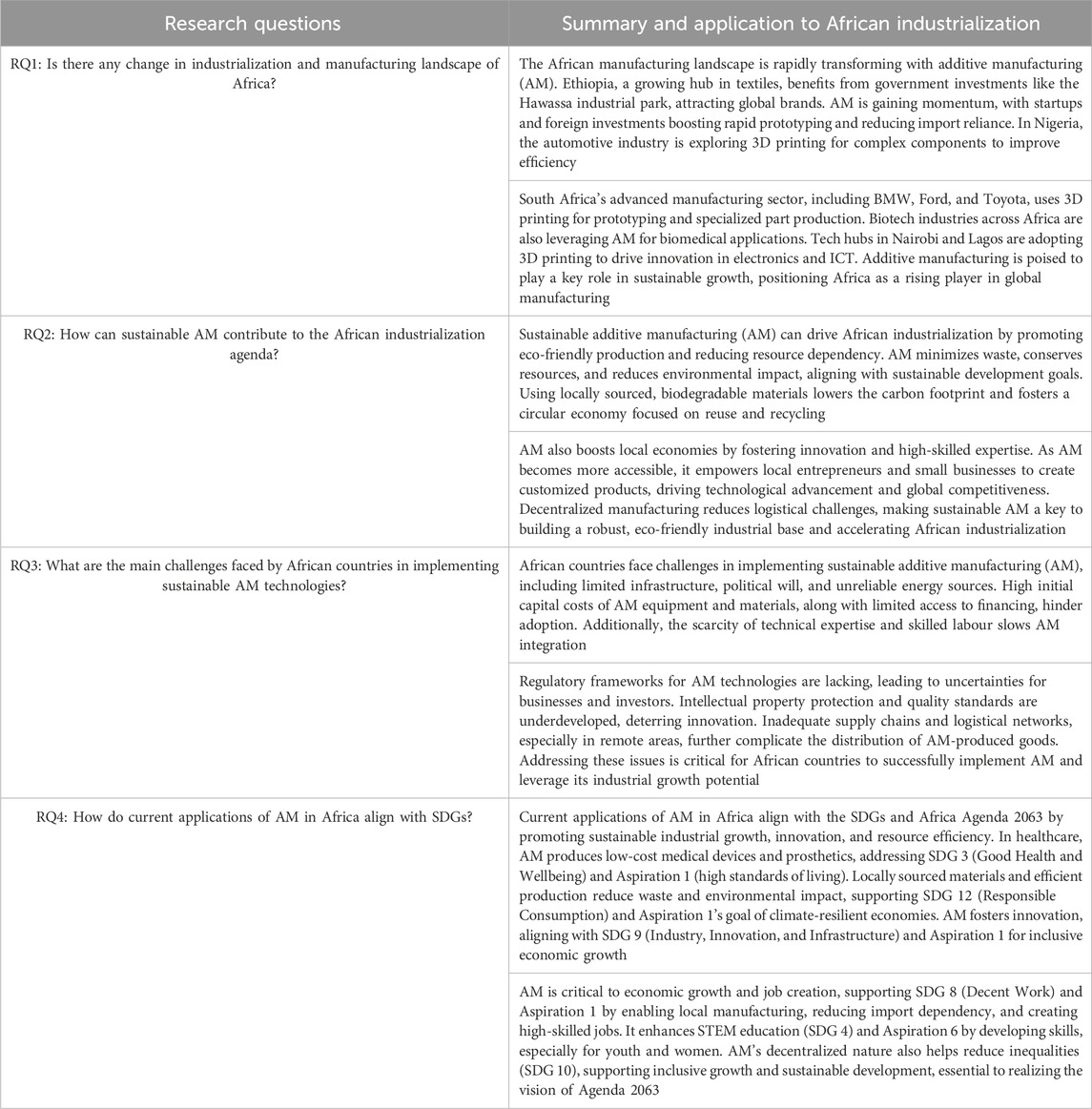
Table 6. The research questions and summary of concluding remarks towards an AM-driven African industrialization.
Future research opportunities and challenges for Africa industrialization
There is increasing research and innovation in the science and engineering of additive manufacturing. However, there are still pertinent issues that require further investigation. These issues ranged from interfacing computational tools with experimentation in additive manufacturing. Some of the main areas are focused on additive manufacturing that is complimented and enabled by machine learning design. Areas such as 3D printing–assisted topological optimization, ML–assisted process monitoring with diagnosis and prognosis for the design of additive manufacturing, process parameter optimization, defect detection and characterization in additively manufactured products. There is the need to develop physics–based models for robust design of additively manufactured products. All these ML–based techniques offer more opportunities and gaps that require careful and pragmatic steps for better structural and functional components to be designed from the 3D printing processes.
Practical recommendations for leveraging additive manufacturing (AM) to drive industrialization in Africa include:
• Investment in Infrastructure: Governments should invest in AM infrastructure, such as research centres and technology hubs. Organizing investments around African economic blocs can reduce costs, while revamping existing projects can offer quick returns.
• Promotion of R&D: Foster collaboration between academia, industry, and government to support AM research tailored to African needs, with funding and partnerships focusing on sectors like healthcare, energy, and agriculture.
• Capacity Building: Implement training programs to develop a skilled AM workforce, focusing on design, machine operation, and materials science, with universities and technical schools playing key roles.
• Support for SMMEs: Provide incentives, technical assistance, and access to AM facilities for small and medium-sized enterprises, encouraging AM integration through favourable government procurement policies.
• Regulatory Frameworks: Develop clear regulations and standards to ensure quality, safety, and sustainability in AM, aligning with international standards for global interoperability.
• Local Materials & Sustainability: Promote the use of locally sourced materials and sustainable practices in AM to minimize environmental impact, encouraging research into recycled and renewable resources.
• Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Facilitate collaboration between governments, the private sector, and research institutions to drive AM adoption, knowledge transfer, and infrastructure investment.
By adopting these strategies, African countries can unlock AM’s potential to drive industrialization, stimulate economic growth, and address key societal challenges.
Summary and concluding remarks
The economic growth of Africa is through value addition to its natural resources and skilled workforce. This partly hinges on vibrant manufacturing sector, which is currently at staggering 11% of the GDP of Africa. A vibrant manufacturing sector should implement sustainable additive manufacturing (AM) to the mix to drive economic growth, foster innovation, and promote sustainability across the continent. With its ability to produce customizable parts with minimal material wastage, AM offers a cost-effective solution for addressing the diverse manufacturing needs of Africa. By leveraging the capabilities of AM, African countries can overcome traditional barriers to industrialization, such as limited access to capital-intensive machinery, energy demands and infrastructure. Moreover, AM enables the fabrication of complex geometries and intricate designs, empowering local industries to compete on a global scale and catalyse the development of indigenous manufacturing capabilities.
The successful implementation of sustainable AM practices in Africa requires concerted efforts from governments, industries, and educational institutions. Investment in research and development, infrastructure development, and skills training is essential to harness the full potential of AM technologies. Additionally, collaboration with international partners and the adoption of best practices in sustainable manufacturing will be instrumental in driving the continental industrialization agenda forward. By embracing sustainable AM practices, Africa can not only accelerate its industrialization journey but also address pressing societal challenges, promote inclusive growth, and build a resilient and sustainable future for now and posterity.
Case studies of the adoption of AM in leading countries in Africa are highlighted. South Africa currently leads the adoption, acceptance and integration of AM processes into the manufacturing sector. Other countries include Nigeria, Kenya and Egypt. The industries integrating AM includes aerospace, energy, health, education and construction sector. Although these sectors show promise, there is the need for increased awareness on the continent for rapid industrialization and realization of the Africa Agenda 2063 and the sustainable development goals. It is instructive to note that technologies such as AM and those of the Fourth Industrial Revolution will be play critical role in the development of the Africa we need. This will provide the pathway to leapfrog and speed up the industrialization process and overhaul the reliance on traditional manufacturing processes which are becoming unsustainable and expensive.
Author contributions
DK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Methodology. TA: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MB: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JO: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. RG: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. SM: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. FM: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. WS: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbady, H. E. M. A., Klinkenberg, E. T. M., De Moel, L., Nicolai, N., Van Der Stelt, M., Verhulst, A. C., et al. (2022). 3D-printed prostheses in developing countries: a systematic review. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 46, 19–30. doi:10.1097/pxr.0000000000000057
Abdalla, H., Fattah, K. P., Abdallah, M., and Tamimi, A. K. (2021). Environmental footprint and economics of a full-scale 3D-printed house. Sustain 13 (21), 11978. doi:10.3390/su132111978
Adam, G., Benouhiba, A., Rabenorosoa, K., Clévy, C., and Cappelleri, D. J. (2021). 4D printing: enabling technology for microrobotics applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3. doi:10.1002/aisy.202000216
Adefuye, O. A., Raji, N. A., Adedeji, K. A., Fadipe, O. L., and Olowu, B. (2019). Additive manufacturing and sand casting foundries practices in in Nigeria. Eng. Technol. Res. J. 4, 55–63. doi:10.47545/etrj.2019.4.1.049
Adekanye, A., Mahamood, R. M., Akinlabi, E. T., and Owolabi, M. G., Additive manufacturing: the future of manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. Prihodnost Manuf. (2017a). 51(5):709–715. doi:10.17222/mit.2016.261
Adekanye, S. A., Mahamood, R. M., Akinlabi, E. T., and Owolabi, M. G. (2017b). Additive manufacturing: the future of manufacturing. Mater. Technol. 51, 709–715. doi:10.17222/mit.2016.261
Adekunle, S. O., Alhassan, A. M., Disina, M. U., and Balogun, S. A. (2022). Additive manufacturing technology, a strategy for transformation of Nigerian manufacturing sector. J. Sci. Innovation Technol. Res. 26 (9), 211–218.
Agnusdei, L., and Del Prete, A., (2022). Additive manufacturing for sustainability: a systematic literature review. Sustain. Futur. 4 doi:10.1016/j.sftr.2022.100098
Alabi, M. O. (2019). Framework for effective additive manufacturing education at South African universities. South Africa: North-West University.
Alami, A. H., Ghani Olabi, A., Alashkar, A., Alasad, S., Aljaghoub, H., Rezk, H., et al. (2023). Additive manufacturing in the aerospace and automotive industries: recent trends and role in achieving sustainable development goals. Ain Shams Eng. J. 14, 102516. doi:10.1016/j.asej.2023.102516
Al Jahdaly, B. A., Maghraby, Y. R., Ibrahim, A. H., Shouier, K. R., Alturki, A. M., and El-Shabasy, R. M. (2022). Role of green chemistry in sustainable corrosion inhibition: a review on recent developments. Mater. Today Sustain. 20, 100242. doi:10.1016/j.mtsust.2022.100242
Aljalahma, J., and Slof, J. (2022). An updated systematic review of business accelerators: functions, operation, and gaps in the existing literature. J. Open Innovation Technol. Mark. Complex. 8, 214. doi:10.3390/joitmc8040214
Al Rashid, A., and Koç, M. (2023). Additive manufacturing for sustainability and circular economy: needs, challenges, and opportunities for 3D printing of recycled polymeric waste. Mater. Today Sustain. 24, 100529. doi:10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100529
Altıparmak, S. C., and Xiao, B. (2021). A market assessment of additive manufacturing potential for the aerospace industry. J. Manuf. Process 68, 728–738. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.072
Antezana, P. E., Municoy, S., Ostapchuk, G., Catalano, P. N., Hardy, J. G., Evelson, P. A., et al. (2023). 4D printing: the development of responsive materials using 3D-printing technology. Pharmaceutics 15, 2743. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15122743
Arif, Z. U., Khalid, M. Y., Noroozi, R., Hossain, M., Shi, H. T. H., Tariq, A., et al. (2023). Additive manufacturing of sustainable biomaterials for biomedical applications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 18, 100812. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100812
Ashima, R., Haleem, A., Bahl, S., Javaid, M., Mahla, S. K., and Singh, S. (2021). Automation and manufacturing of smart materials in additive manufacturing technologies using Internet of Things towards the adoption of industry 4.0. Mater Today Proc. 45, 5081–5088. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.583
Assadi, H., Gärtner, F., Stoltenhoff, T., and Kreye, H. (2003). Bonding mechanism in cold gas spraying. Acta Mater 51, 4379–4394. doi:10.1016/s1359-6454(03)00274-x
Assadi, H., Kreye, H., Gärtner, F., and Klassen, T. (2016). Cold spraying – a materials perspective. Acta Mater 116, 382–407. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2016.06.034
Astarita, A., Coticelli, F., and Prisco, U. (2016). Repairing of an engine block through the cold gas dynamic spray technology. Mater. Res. 19, 1226–1231. doi:10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0109
Asumadu, T. K., Mensah-Darkwa, K., Gikunoo, E., Klenam, D. E. P., Vandadi, M., Rahbar, N., et al. (2023). Strain gradient plasticity phenomenon in surface treated plain carbon steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 871, 144806. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2023.144806
Baca, D., and Ahmad, R. (2020). The impact on the mechanical properties of multi-material polymers fabricated with a single mixing nozzle and multi-nozzle systems via fused deposition modeling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 106, 4509–4520. doi:10.1007/s00170-020-04937-3
Bacha, A., Sabry, A. H., and Benhra, J. (2019). Fault diagnosis in the field of additive manufacturing (3D printing) using bayesian networks. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 15, 110–123. doi:10.3991/ijoe.v15i03.9375
Badkoobeh, F., Mostaan, H., Rafiei, M., Bakhsheshi-Rad, H. R., RamaKrishna, S., and Chen, X. (2023). Additive manufacturing of biodegradable magnesium-based materials: design strategies, properties, and biomedical applications. J. Magnesium Alloys 11, 801–839. doi:10.1016/j.jma.2022.12.001
Bae, E.-J., Jeong, I.-D., Kim, W.-C., and Kim, J.-H. (2017). A comparative study of additive and subtractive manufacturing for dental restorations. The J. of Pros. Den. 118 (2), 187–193. doi:10.1016/j.prosdent.2016.11.004
Bagger, C., and Olsen, F. O. (2005). Review of laser hybrid welding. J. Laser Appl. 17, 2–14. doi:10.2351/1.1848532
Bagherifard, S., and Guagliano, M. (2020). Fatigue performance of cold spray deposits: coating, repair and additive manufacturing cases. Int. J. Fatigue 139, 105744. doi:10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105744
Balasubramanian, S., Brennan, R. W., and Norrie, D. H. (2001). An architecture for metamorphic control of holonic manufacturing systems. Comput. Ind. 46, 13–31. doi:10.1016/s0166-3615(01)00101-4
Balubaid, M., and Alsaadi, N. (2023). Achieving sustainability in manufacturing through additive manufacturing: an analysis of its enablers. Sustainability 15 (12), 9504. doi:10.3390/su15129504
Bandyopadhyay, A., Traxel, K. D., Lang, M., Juhasz, M., Eliaz, N., and Bose, S. (2022). Alloy design via additive manufacturing: advantages, challenges, applications and perspectives. Mater. Today 52, 207–224. doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2021.11.026
Barambu Umar, A.-A. (2023). Framework for adoption of metal additive manufacturing in the oil and gas industry in Africa. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol., 1–10. doi:10.47363/jeast/2023(5)196
Bedarf, P., Dutto, A., Zanini, M., and Dillenburger, B. (2021). Foam 3D printing for construction: a review of applications, materials, and processes. Autom. Constr. 130, 103861. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103861
Berman, B. (2012). 3-D printing: the new industrial revolution. Bus. Horiz. 55, 155–162. doi:10.1016/j.bushor.2011.11.003
Bibb, R., and McKnight, L. (2022). Identification of bird taxa species in ancient Egyptian mummies: Part 2, a qualitative evaluation of the utility of CT scanning and 3D printing. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 46, 103668. doi:10.1016/j.jasrep.2022.103668
Blakey-Milner, B., Gradl, P., Snedden, G., Brooks, M., Pitot, J., Lopez, E., et al. (2021). Metal additive manufacturing in aerospace: a review. Mater Des. 209, 110008. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2021.110008
Blanco, D., Rubio, E. M., Marín, M. M., and Davim, J. P. (2021a). in Procedia CIRP (Elsevier B.V.), 196–201.
Blanco, D., Rubio, E. M., Marín, M. M., and Davim, J. P. (2021b). Advanced materials and multi-materials applied in aeronautical and automotive fields: a systematic review approach. Procedia CIRP 99, 196–201. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2021.03.027
Bodunrin, M., Obiko, J., and Klenam, D. (2023). On the uniaxial compression testing of metallic alloys at high strain rates: an assessment of DEFORM-3D simulation. Appl. Sci. 13 (4), 2686. doi:10.3390/app13042686
Bose, S., Ke, D., Sahasrabudhe, H., and Bandyopadhyay, A. (2018). Additive manufacturing of biomaterials. Prog. Mater Sci. 93, 45–111. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.08.003
Byard, D. J., Woern, A. L., Oakley, R. B., Fiedler, M. J., Snabes, S. L., and Pearce, J. M. (2019). Green fab lab applications of large-area waste polymer-based additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 27, 515–525. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.006
Caccamo, M., and Beckman, S. (2022). Leveraging accelerator spaces to foster knowledge communities. Technovation 113, 102421. doi:10.1016/j.technovation.2021.102421
Cairns, R., Onyango, J., Stirling, A., and Johnstone, P. (2022). Imagining urban transformation in Kenya. Environ. Sci. Policy 135, 86–95. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2022.04.016
Campbell, R. I., De Beer, D. J., and Pei, E. (2011). Additive manufacturing in South Africa: building on the foundations. Rapid Prototyp. J. 17, 156–162. doi:10.1108/13552541111113907
Cann, J. L., De Luca, A., Dunand, D. C., Dye, D., Miracle, D. B., Oh, H. S., et al. (2020). Sustainability through alloy design: challenges and opportunities. Prog. Mater Sci. 117, 100722. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100722
Cavaliere, P., and Silvello, A. (2017). Crack repair in aerospace aluminum alloy panels by cold spray. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 26, 661–670. doi:10.1007/s11666-017-0534-9
Champagne, V., and Helfritch, D. (2015). Critical Assessment 11: structural repairs by cold spray. Mater. Sci. Technol. (United Kingdom) 31, 627–634. doi:10.1179/1743284714y.0000000723
Champagne, V., and Helfritch, D. (2016). The unique abilities of cold spray deposition. Int. Mater. Rev. 61, 437–455. doi:10.1080/09506608.2016.1194948
Champagne, V., Nardi, A., and Cote, D. (2015). Materials characterization of advanced cold-spray aluminum alloys. Int. J. Powder Metallurgy 51, 37–47.
Chen, D., and Zheng, X. (2018). Multi-material additive manufacturing of metamaterials with giant, tailorable negative Poisson’s ratios. Sci. Rep. 8, 9139. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-26980-7
Chen, Y., Li, B., Chen, B., and Xuan, F. (2023). High-cycle fatigue induced twinning in CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy processed by laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 61, 103319. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2022.103319
Cilliers, J. (2018). Made in Africa – Manufacturing and the fourth industrial revolution, Africa in the World Report, 8, 1–32.
Cooke, S., Ahmadi, K., Willerth, S., and Herring, R. (2020). Metal additive manufacturing: technology, metallurgy and modelling. J. Manuf. Process 57, 978–1003. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.07.025
Cui, C., Kim, D. O., Pack, M. Y., Han, B., Han, L., Sun, Y., et al. (2020). 4D printing of self-folding and cell-encapsulating 3D microstructures as scaffolds for tissue-engineering applications. Biofabrication 12, 045018. doi:10.1088/1758-5090/aba502
Daehn, G. S., and Taub, A. (2018). Metamorphic manufacturing: the third wave in digital manufacturing. Manuf. Lett. 15, 86–88. doi:10.1016/j.mfglet.2018.02.014
Daraban, A. E. O., Negrea, C. S., Artimon, F. G. P., Angelescu, D., Popan, G., Gheorghe, S. I., et al. (2019). A deep look at metal additive manufacturing recycling and use tools for sustainability performance. Sustain. Switz. 11 (19), 5494. doi:10.3390/su11195494
Davoodi, E., Fayazfar, H., Liravi, F., Jabari, E., and Toyserkani, E. (2020). Drop-on-demand high-speed 3D printing of flexible milled carbon fiber/silicone composite sensors for wearable biomonitoring devices. Addit. Manuf. 32, 101016. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2019.101016
De Beer, D. J., Annals of DAAAM and proceedings of the international DAAAM symposium 21 (2010). 1539–1540.
de Beer, D., du Preez, W., Greyling, H., Prinsloo, F., Sciammarella, F., Trollip, N., et al. (2016). A South African additive manufacturing Strategy. Johannesburg.
Dhiman, S., Joshi, R. S., Singh, S., Gill, S. S., Singh, H., Kumar, R., et al. (2021). A framework for effective and clean conversion of machining waste into metal powder feedstock for additive manufacturing. Clean. Eng. Technol. 4, 100151. doi:10.1016/j.clet.2021.100151
Di, L., and Yang, Y. (2022). Towards closed-loop material flow in additive manufacturing: recyclability analysis of thermoplastic waste. J. Clean. Prod. 362, 132427. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132427
Dimitrov, D., Schreve, K., Taylor, A., and Vincent, B. (2007). Rapid prototyping driven design and realisation of large components. Rapid Prototyp. J. 13, 85–91. doi:10.1108/13552540710736768
Doi, K., Yamauchi, Y., Kijima, S., and Yamashita, M. (2021). Search by a metamorphic robotic system in a finite 2D square Grid. Inf. Comput. 285, 104695. doi:10.1016/j.ic.2021.104695
du Plessis, A., Babafemi, A. J., Paul, S. C., Panda, B., Tran, J. P., and Broeckhoven, C. (2021). Biomimicry for 3D concrete printing: a review and perspective. Addit. Manuf. 38, 101823. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2020.101823
du Plessis, A., Broeckhoven, C., Yadroitsava, I., Yadroitsev, I., Hands, C. H., Kunju, R., et al. (2019a). Beautiful and functional: a review of biomimetic design in additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 27, 408–427. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.033
du Plessis, A., and le Roux, S. G. (2018). Standardized X-ray tomography testing of additively manufactured parts: a round robin test. Addit. Manuf. 24, 125–136. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2018.09.014
du Plessis, A., le Roux, S. G., and Guelpa, A. (2016). Comparison of medical and industrial X-ray computed tomography for non-destructive testing. Case Stud. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 6, 17–25. doi:10.1016/j.csndt.2016.07.001
du Plessis, A., le Roux, S. G., and Tshibalanganda, M. (2019b). Advancing X-ray micro computed tomography in Africa: going far, together. Sci. Afr. 3, e00061. doi:10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00061
du Plessis, A., Yadroitsava, I., and Yadroitsev, I. (2020). Effects of defects on mechanical properties in metal additive manufacturing: a review focusing on X-ray tomography insights. Mater Des. 187, 108385. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108385
du Preez, W. B., and de Beer, D. J. (2006). in Proceedings of the all Africa technology diffusion conference. Boksburg, South Africa.
du Preez, W. B., and de Beer, D. J. (2015). Implementing the south african additive manufacturing technology roadmap – the role of an additive manufacturing centre of competence. J. Industrial Eng. 26, 85–92. doi:10.7166/26-2-1179
Dzogbewu, T. C., and de Beer, D. (2023a). Powder bed fusion of multimaterials. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 7, 15. doi:10.3390/jmmp7010015
Dzogbewu, T. C., and de Beer, D. J. (2023b). Additive manufacturing of selected ecofriendly energy devices. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 18. doi:10.1080/17452759.2023.2276245
Dzogbewu, T. C., Fianko, S. K., Amoah, N., Afrifa Jnr, S., and de Beer, D. (2022). Additive manufacturing in South Africa: critical success factors. Heliyon 8, e11852. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11852
Egan, P., Wang, X., Greutert, H., Shea, K., Wuertz-Kozak, K., and Ferguson, S. (2019). Mechanical and biological characterization of 3D printed lattices. Addit. Manuf. 6, 73–81. doi:10.1089/3dp.2018.0125
El-Mahdy, D., Gabr, H. S., and Abdelmohsen, S. (2021). SaltBlock as a 3D printed sustainable construction material in hot arid climates. J. Build. Eng. 43, 103134. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103134
El-Sherbiny, I. M., and Yacoub, M. H. (2013). Hydrogel scaffolds for tissue engineering: progress and challenges. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2013, 38. doi:10.5339/gcsp.2013.38
Fan, N., Cizek, J., Huang, C., Xie, X., Chlup, Z., Jenkins, R., et al. (2020). A new strategy for strengthening additively manufactured cold spray deposits through in-process densification. Addit. Manuf. 36, 101626. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2020.101626
Ford, S., and Despeisse, M. (2016). Additive manufacturing and sustainability: an exploratory study of the advantages and challenges. J. Clean. Prod. 137, 1573–1587. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.04.150
Ford, S., and Minshall, T. (2019). Invited review article: where and how 3D printing is used in teaching and education. Addit. Manuf. 25, 131–150. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2018.10.028
Forés-Garriga, A., Gómez-Gras, G., and Pérez, M. A. (2023). Additively manufactured three-dimensional lightweight cellular solids: experimental and numerical analysis. Mater Des. 226, 111641. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111641
Frazier, W. E. (2014). Metal additive manufacturing: a review. J. Mater Eng. Perform. 23, 1917–1928. doi:10.1007/s11665-014-0958-z
Gao, C., Wolff, S., and Wang, S. (2021). Eco-friendly additive manufacturing of metals: energy efficiency and life cycle analysis. J. Manuf. Syst. 60, 459–472. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.06.011
Gao, Z., Yin, J., Liu, P., Li, Q., Zhang, R., Yang, H., et al. (2023). Simultaneous multi-material embedded printing for 3D heterogeneous structures. Int. J. Extreme Manuf. 5, 035001. doi:10.1088/2631-7990/acd285
García-Collado, A., Blanco, J. M., Gupta, M. K., and Dorado-Vicente, R. (2022). Advances in polymers based Multi-Material Additive-Manufacturing Techniques: state-of-art review on properties and applications. Addit. Manuf. 50, 102577. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2021.102577
Gebler, M., Schoot Uiterkamp, A. J. M., and Visser, C. (2014). A global sustainability perspective on 3D printing technologies. Energy Policy 74, 158–167. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2014.08.033
Geneidy, O., Ismaeel, W. S. E., and Abbas, A. (2019). A critical review for applying three-dimensional concrete wall printing technology in Egypt. Archit. Sci. Rev. 62, 438–452. doi:10.1080/00038628.2019.1596066
Gershenfeld, N. (2012). How to make almost anything - the digital fabrication revolution. Foreign Policy 91, 42–57.
Gibson, I., Rosen, D., and Brent, S. (2015). Additive manufacturing technologies:3D printing, rapid prototyping, and direct digital manufacturing. 2nd Editio. New York: Springer Science+Business Media.
Gordon, R. B., Bertram, M., and Graedel, T. E. (2006). Metal stocks and sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 1209–1214. doi:10.1073/pnas.0509498103
Gouveia, J. R., Pinto, S. M., Campos, S., Matos, J. R., Sobral, J., Esteves, S., et al. (2022). Life cycle assessment and cost analysis of additive manufacturing repair processes in the mold industry. Sustain. Switz. 14, 2105. doi:10.3390/su14042105
Guarino, S., Ponticelli, G. S., and Venettacci, S. (2020). Environmental assessment of Selective Laser Melting compared with Laser Cutting of 316L stainless steel: a case study for flat washers’ production. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 31, 525–538. doi:10.1016/j.cirpj.2020.08.004
Guo, N., and Leu, M. C. (2013). Additive manufacturing: technology, applications and research needs. Front. Mech. Eng. 8, 215–243. doi:10.1007/s11465-013-0248-8
Guo, S., Cui, H., Agarwal, T., and Zhang, L. G. (2024). Nanomaterials in 4D Printing: Expanding the Frontiers of Advanced Manufacturing. Small 20 (2307750), 1–31. doi:10.1002/smll.202307750
Hafez, M. A. (2012). The use of computer-assisted orthopaedic surgery in complex cases of hip and knee arthroplasty: experience from a developing country. Biomed. Tech. 57, 301–306. doi:10.1515/bmt-2011-0097
Hafez, M. A., Abdelghany, K., and Hamza, H. (2015). Highlighting the medical applications of 3D printing in Egypt. Ann. Transl. Med. 3, 359. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.12.01
Haghnegahdar, L., Joshi, S. S., and Dahotre, N. B. (2022). From IoT-based cloud manufacturing approach to intelligent additive manufacturing: industrial Internet of Things—an overview. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 119, 1461–1478. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-08436-x
Hagman, C., and Svanborg, P., (2022). Additive manufacturing of a removable partial prosthesis in titanium using binder jetting technology: a brief research report. Front. Manuf. Technol. 2 doi:10.3389/fmtec.2022.863593
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., and Vaishya, R. (2018). 4D printing and its applications in Orthopaedics. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 9, 275–276. doi:10.1016/j.jcot.2018.08.016
Han, Y., Yang, Z., Ding, T., and Xiao, J. (2021). Environmental and economic assessment on 3D printed buildings with recycled concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 278, 123884. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123884
Hasanov, S., Alkunte, S., Rajeshirke, M., Gupta, A., Huseynov, O., Fidan, I., et al. (2022). Review on additive manufacturing of multi-material parts: progress and challenges. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 6, 4. doi:10.3390/jmmp6010004
Hasanov, S., Gupta, A., Alifui-Segbaya, F., and Fidan, I. (2021). Hierarchical homogenization and experimental evaluation of functionally graded materials manufactured by the fused filament fabrication process. Compos Struct. 275, 114488. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114488
Hopkinson, N., Hague, R., and Dickens, P. (2006a). Rapid manufacturing: an industrial revolution for the digital age. John Wiley and Sons.
Hopkinson, N., Hague, R. J. M., and Dickens, P. M. (2006b). Rapid manufacturing: an industrial revolution for the digital age. West Sussex: John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Huang, R., Riddle, M. E., Graziano, D., Das, S., Nimbalkar, S., Cresko, J., et al. (2017). Environmental and economic implications of distributed additive manufacturing: the case of injection mold tooling. J. Ind. Ecol. 21, S130–S143. doi:10.1111/jiec.12641
Ingarao, G., and Priarone, P. C. (2020). A comparative assessment of energy demand and life cycle costs for additive- and subtractive-based manufacturing approaches. J. Manuf. Process 56, 1219–1229. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.06.009
Inoma, A. O., Ibhadode, O. O., and Ibhadode, A. A. O. (2020). The perception and deployment of 3D printing in the Nigerian educational sector for science and engineering programs. Sci. Afr. 10, e00641. doi:10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00641
International Organization for Standardization, Additive manufacturing—general principles—terminology. (2018). Available at: Https://Www.Iso.Org/Obp/Ui/#iso:Std:Iso-Astm:52900.Dis:Ed-2:V1:En.
Isasi-Sanchez, L., Morcillo-Bellido, J., Ortiz-Gonzalez, J. I., and Duran-Heras, A. (2020). Synergic sustainability implications of additive manufacturing in automotive spare parts: a case analysis. Sustain 12 (20), 8461. doi:10.3390/su12208461
Ishengoma, F. R., and Mtaho, A. B. (2014). 3D printing: developing countries perspectives. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 104, 30–34. doi:10.5120/18249-9329
Ismail, F. A. (2017). Advancing regional integration in Africa through the continental free trade area (CFTA). Law Dev. Rev. 10, 119–146. doi:10.1515/ldr-2017-0003
Jardini, A. L., Larosa, M. A., Filho, R. M., Zavaglia, C. A. D. C., Bernardes, L. F., Lambert, C. S., et al. (2014). Cranial reconstruction: 3D biomodel and custom-built implant created using additive manufacturing. J. Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg. 42, 1877–1884. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2014.07.006
Jayawardane, H., Davies, I. J., Gamage, J. R., John, M., and Biswas, W. K., Sustainability perspectives – a review of additive and subtractive manufacturing, 2 (2023). 100015, doi:10.1016/j.smse.2023.100015
Jiang, J. (2020). A novel fabrication strategy for additive manufacturing processes. J. Clean. Prod. 272, 122916. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122916
Jiang, J., and Fu, Y. F. (2020). A short survey of sustainable material extrusion additive manufacturing. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 21, 123–132. doi:10.1080/14484846.2020.1825045
Jiang, J., Xiong, Y., Zhang, Z., and Rosen, D. W. (2022). Machine learning integrated design for additive manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 33, 1073–1086. doi:10.1007/s10845-020-01715-6
Jiang, J., Xu, X., and Stringer, J. (2019a). Optimization of process planning for reducing material waste in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 59, 317–325. doi:10.1016/j.rcim.2019.05.007
Jiang, J., Xu, X., and Stringer, J. (2019b). Optimisation of multi-part production in additive manufacturing for reducing support waste. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 14, 219–228. doi:10.1080/17452759.2019.1585555
Jiang, J., Xu, X., Xiong, Y., Tang, Y., Dong, G., and Kim, S. (2020). A novel strategy for multi-part production in additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 109, 1237–1248. doi:10.1007/s00170-020-05734-8
Joshi, S. C., and Sheikh, A. A. (2015). 3D printing in aerospace and its long-term sustainability. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 10, 175–185. doi:10.1080/17452759.2015.1111519
Kalaba, M. (2020). South Africa’s Carbon Tax: Balancing Climate Action and Economic Development. South African Institute of International Affairs. JSTOR, 1–21.
Kambase, N. N., and Akodia, J. A. (2022). The dos and don’ts of the african continental free trade agreement pose the Ghana’s maritime industry vis-A-vis its national industrialization drive. World J. Eng. Technol. 10, 843–874. doi:10.4236/wjet.2022.104055
Kamps, T., Lutter-Guenther, M., Seidel, C., Gutowski, T., and Reinhart, G. (2018). Cost- and energy-efficient manufacture of gears by laser beam melting. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 21, 47–60. doi:10.1016/j.cirpj.2018.01.002
Kanishka, K., and Acherjee, B. (2023). Revolutionizing manufacturing: a comprehensive overview of additive manufacturing processes, materials, developments, and challenges. J. Manuf. Process 107, 574–619. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.10.024
Kanyilmaz, A., Demir, A. G., Chierici, M., Berto, F., Gardner, L., Kandukuri, S. Y., et al. (2021). Role of metal 3D printing to increase quality and resource-efficiency in the construction sector. Addit. Manuf. 50, 102541. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2021.102541
Kaur, M., Ahmad, W., Hari, K. S., and Kattumuri, R. (2024). FinTech entrepreneurial ecosystem in India: role of incubators and accelerators. Glob. Finance J. 60, 100933. doi:10.1016/j.gfj.2024.100933
Kere, S., and Zongo, A. (2023). Digital technologies and intra-African trade. Int. Econ. 173, 359–383. doi:10.1016/j.inteco.2023.01.005
Kim, Y.-K. K., Baek, M.-S. S., Yang, S., and Lee, K.-A. A. (2021). In-situ formed oxide enables extraordinary high-cycle fatigue resistance in additively manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Addit. Manuf. 38, 101832. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2020.101832
Kirk Kanemaru, S., Sasaki, T., Sato, T., Era, T., and Tanaka, M. (2015). Study for the mechanism of TIG-MIG hybrid welding process. Weld. World 59, 261–268. doi:10.1007/s40194-014-0205-0
Klenam, D., Asumadu, T., Bodunrin, M., Vandadi, M., Bond, T., van der Merwe, J., et al. (2023). Cold spray coatings of complex concentrated alloys: critical assessment of milestones, challenges, and opportunities. Coatings 13 (3), 538. doi:10.3390/coatings13030538
Klenam, D. E. P. (2019). Composition refinement of medium carbon-low alloy steels to improve wear and corrosion resistance for rail axle applications. Johannesburg, South Africa: University of the Witwatersrand.
Klenam, D. E. P., Bamisaye, O. S., Williams, I. E., van der Merwe, J. W., and Bodunrin, M. O. (2022). Global perspective and African outlook on additive manufacturing research − an overview. Manuf. Rev. 9 (35), 1–38. doi:10.1051/mfreview/2022033
Klenam, D. E. P., Ogunwande, G. S., Omotosho, T., Ozah, B., Maledi, N. B., Hango, S. I., et al. (2021). Welding of magnesium and its alloys: An overview of methods and process parameters and their effects on mechanical behaviour and structural integrity of the welds. Manuf. Rev. 8 (29), 1–31. doi:10.1051/mfreview/2021028
Kokare, S., Oliveira, J. P., and Godina, R. (2023). Life cycle assessment of additive manufacturing processes: a review. J. Manuf. Syst. 68, 536–559. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2023.05.007
Kolade, O., Adegbile, A., and Sarpong, D. (2022). Technol. Soc. 69, 101960. doi:10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101960
Komane, T., Maledi, N., Klenam, D., van der Merwe, J., and Bodunrin, M. (2023). Flow behavior and microstructure of hot-worked Fe-30.9Mn-4.9Al-4.5Cr-0.4C and Fe-21.3Mn-7.6Al-4.3Cr-1C low-density stainless steels. Appl. Sci. 13, 1–18. doi:10.3390/app13042310
Kravchenko, M., Pigosso, D. C. A., and McAloone, T. C. (2020). in Proceedings of the NordDesign 2020 conference, NordDesign 2020, the design society.
Kruger, J., Cicione, A., Bester, F., van den Heever, M., Cho, S., Walls, R., et al. (2020). Facilitating ductile failure of 3D printed concrete elements in fire. Springer International Publishing.
Kruger, J., du Plessis, A., and van Zijl, G. (2021). An investigation into the porosity of extrusion-based 3D printed concrete. Addit. Manuf. 37, 101740. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2020.101740
Kuang, X., Wu, J., Chen, K., Zhao, Z., Ding, Z., Hu, F., et al. (2019). Grayscale digital light processing 3D printing for highly functionally graded materials. Sci. Adv. 5, eaav5790–9. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aav5790
Kumar, R., Kumar, M., and Chohan, J. S. (2021). The role of additive manufacturing for biomedical applications: a critical review. J. Manuf. Process 64, 828–850. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.02.022
Kunniger, D. (2015). Diffusion of additive manufacturing in gauteng South Africa. Pretoria, South Africa: University of Pretoria.
Landi, D., Zefinetti, F. C., Spreafico, C., and Regazzoni, D. (2022). in Procedia CIRP (Elsevier B.V.), 700–705.
Leminen, S. (2015). Living labs as open innovation networks-networks, roles and innovation outcomes, doctoral thesis. Espoo, Finland: Aalto University.
Lemma, A., Mendez-Parra, M., and Naliaka, L., The AfCFTA: unlocking the potential of the digital economy in Africa. (2022).
Lerman, L. V., Gerstlberger, W., Ferreira Lima, M., and Frank, A. G. (2021). Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 71, 101854. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2020.101854
Leydesdorff, L. (2000). The triple helix: an evolutionary model of innovations. Res. Policy 29, 243–255. doi:10.1016/s0048-7333(99)00063-3
Li, J., Meng, X., Wan, L., and Huang, Y. (2021). Welding of high entropy alloys: progresses, challenges and perspectives. J. Manuf. Process 68, 293–331. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.042
Li, W., Yang, K., Yin, S., Yang, X., Xu, Y., and Lupoi, R. (2018). Solid-state additive manufacturing and repairing by cold spraying: a review. J. Mater Sci. Technol. 34, 440–457. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2017.09.015
Lim, S., Buswell, R. A., Le, T. T., Austin, S. A., Gibb, A. G. F., and Thorpe, T. (2012). Developments in construction-scale additive manufacturing processes. Autom. Constr. 21, 262–268. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2011.06.010
Liu, F., Li, T., Jiang, X., Jia, Z., Xu, Z., and Wang, L. (2020). The effect of material mixing on interfacial stiffness and strength of multi-material additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 36, 101502. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2020.101502
Liu, L., Wang, D., Han, C., Li, Y., Wang, T., Wei, Y., et al. (2024). Additive manufacturing of multi-materials with interfacial component gradient by in-situ powder mixing and laser powder bed fusion. J. Alloys Compd. 978, 173508. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2024.173508
Liu, Y., Xu, H., Liu, D., and Wang, L. (2022). A digital twin-based sim-to-real transfer for deep reinforcement learning-enabled industrial robot grasping. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 78, 102365. doi:10.1016/j.rcim.2022.102365
Lv, Y., Wang, B., Liu, G., Tang, Y., Lu, E., Xie, K., et al. (2021). Metal material, properties and design methods of porous biomedical scaffolds for additive manufacturing: a review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 641130. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.641130
Machado, C. G., Despeisse, M., Winroth, M., and Ribeiro da Silva, E. H. D. (2019). in Procedia CIRP (Elsevier B.V.), 482–487.
Mahamood, R. M., Akinlabi, E. T., Shukla, M., and Pityana, S. (2014). Revolutionary additive manufacturing: an overview. Lasers Eng. (Old City Pub.) 10, 161–178.
Malatji, M. (2024). Accelerating the African continental free trade area through optimization of digital supply chains. Eng. Rep. 6. doi:10.1002/eng2.12711
Mami, F., Revéret, J. P., Fallaha, S., and Margni, M. (2017). Evaluating eco-efficiency of 3D printing in the aeronautic industry. J. Ind. Ecol. 21, S37–S48. doi:10.1111/jiec.12693
Manogharan, G., Wysk, R. A., and Harrysson, O. L. A. (2016). Additive manufacturing–integrated hybrid manufacturing and subtractive processes: economic model and analysis. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 29, 473–488. doi:10.1080/0951192x.2015.1067920
Manyika, J., Chui, M., Bughin, J., Dobbs, R., Bisson, P., and Marrs, A. (2013b). Disruptive technologies: advances that will transform life, business, and the global economy: San Francisco: McKinsey Global Institute, 1–176. Available at: www.mckinsey.com/mgi.
Manyika, J., George, K., and Rassey, L. (2013a). Get ready for the new era of global manufacturing. Harv Bus. Rev. Available at: https://hbr.org/2013/01/get-ready-for-the-new-era-of-g.
McKnight, L. M., Adams, J. E., Chamberlain, A., Atherton-Woolham, S. D., and Bibb, R. (2015). Application of clinical imaging and 3D printing to the identification of anomalies in an ancient Egyptian animal mummy. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 3, 328–332. doi:10.1016/j.jasrep.2015.06.028
Mele, M., and Campana, G. (2022). Advancing towards sustainability in liquid crystal display 3D printing via adaptive slicing. Sustain Prod. Consum. 30, 488–505. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2021.12.024
Melia, M. A., Whetten, S. R., Puckett, R., Jones, M., Heiden, M. J., Argibay, N., et al. (2020). High-throughput additive manufacturing and characterization of refractory high entropy alloys. Appl. Mater Today 19, 100560. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100560
Meurisse, A., Makaya, A., Willsch, C., and Sperl, M. (2018). Solar 3D printing of lunar regolith. Acta Astronaut. 152, 800–810. doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.06.063
Meyer, I., Oel, M., Ehlers, T., and Lachmayer, R. (2023). Additive manufacturing of multi-material parts – design guidelines for manufacturing of 316L/CuCrZr in laser powder bed fusion. Heliyon 9, e18301. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18301
Mhlongo, S., Mbatha, K., Ramatsetse, B., and Dlamini, R. (2023). Challenges, opportunities, and prospects of adopting and using smart digital technologies in learning environments: an iterative review. Heliyon 9, e16348. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16348
Mohammadi, M., Kouzani, A. Z., Bodaghi, M., Long, J., Khoo, S. Y., Xiang, Y., et al. (2024). Sustainable robotic joints 4D printing with variable stiffness using reinforcement learning. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 85, 102636. doi:10.1016/j.rcim.2023.102636
Mohammed, M., Wilson, D., Gomez-Kervin, E., Petsiuk, A., Dick, R., and Pearce, J. M. (2022). Sustainability and feasibility assessment of distributed E-waste recycling using additive manufacturing in a Bi-continental context. Addit. Manuf. 50, 102548. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2021.102548
Monteiro, H., Carmona-Aparicio, G., Lei, I., and Despeisse, M. (2022). Energy and material efficiency strategies enabled by metal additive manufacturing – a review for the aeronautic and aerospace sectors. Energy Rep. 8, 298–305. doi:10.1016/j.egyr.2022.01.035
Moorehead, M., Bertsch, K., Niezgoda, M., Parkin, C., Elbakhshwan, M., Sridharan, K., et al. (2020). High-throughput synthesis of Mo-Nb-Ta-W high-entropy alloys via additive manufacturing. Mater Des. 187, 108358. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108358
Moridi, A., Hassani-Gangaraj, S. M., Guagliano, M., and Dao, M. (2014). Cold spray coating: review of material systems and future perspectives. Surf. Eng. 30, 369–395. doi:10.1179/1743294414y.0000000270
Mounde, A., and Arisi Alex, M. (2019). Adaption of 3D printing for manufacturing in Kenya. Kenya: Innovation Research Symposium, University of Nairobi.
Murr, L. E. (2015). Metallurgy of additive manufacturing: examples from electron beam melting. Addit. Manuf. 5, 40–53. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2014.12.002
Muvunzi, R., Mpofu, K., Khodja, M., and Daniyan, I. (2022). International journal of manufacturing, materials, and mechanical engineering. 12 1 21. doi:10.4018/ijmmme.302912
Najmon, J. C., Raeisi, S., and Tovar, A. (2019). in Additive manufacturing for the aerospace industry (Elsevier Inc.), 7–31.
Nassehi, A., Newman, S., Dhokia, V., Zhu, Z., and Asrai, R. I. (2011). in Enhancing Manufacturing Competitiveness and Economic Sustainability: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Changeable, Agile, Reconfigurable and Virtual Production (Montreal: Springer), 52–56.
Nazir, A., Gokcekaya, O., Md Masum Billah, K., Ertugrul, O., Jiang, J., Sun, J., et al. (2023). Multi-material additive manufacturing: a systematic review of design, properties, applications, challenges, and 3D printing of materials and cellular metamaterials. Mater Des. 226, 111661. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111661
Newman, S. T., Zhu, Z., Dhokia, V., and Shokrani, A. (2015). Process planning for additive and subtractive manufacturing technologies. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 64, 467–470. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2015.04.109
Nigro, L., Montanari, D., Sabatini, S., De Giuseppe, M., Benedettucci, F. M., Lucibello, S., et al. (2024). Caress the pharaoh. The tactile reproduction of ramses II's “mummy” in the sapienza university museum of the near East, Egypt and mediterranean. J. Cult. Herit. 67, 158–163. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2024.02.010
Ogbonna, O. S., Akinlabi, S. A., Madushele, N., Mashinini, P. M., and Abioye, A. A. (2019). Application of MIG and TIG welding in automobile industry. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1378, 042065. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1378/4/042065
Olivetti, E. A., and Cullen, J. M. (1979). Toward a sustainable materials system. Science 360, 1396–1398. doi:10.1126/science.aat6821
Olomu, M. O., Binuyo, G. O., and Oyebisi, T. O. (2023). The adoption and impact of Internet-based technological innovations on the performance of the industrial cluster firms. J. Econ. Technol. 1, 164–178. doi:10.1016/j.ject.2023.11.004
Omphemetse, S. S. (2021). The advent of the african continental free trade agreement as a tool for development. Foreign Trade Rev. 56, 216–224. doi:10.1177/0015732521995171
O’Neill, F., and Mehmanparast, A. (2024). A review of additive manufacturing capabilities for potential application in offshore renewable energy structures. Forces Mech. 14, 100255. doi:10.1016/j.finmec.2024.100255
Oyesola, M., Mathe, N., Mpofu, K., and Fatoba, S. (2018). Sustainability of Additive Manufacturing for the South African aerospace industry: a business model for laser technology production, commercialization and market prospects. Procedia CIRP 72, 1530–1535. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2018.03.072
Oyesola, M. O., Mpofu, K., Mathe, N. R., and Daniyan, I. A. (2020). Hybrid-additive manufacturing cost model: a sustainable through-life engineering support for maintenance repair overhaul in the aerospace. Procedia Manuf. 49, 199–205. doi:10.1016/j.promfg.2020.07.019
Padhy, G. K., Wu, C. S., and Gao, S. (2015). Auxiliary energy assisted friction stir welding – status review. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 20, 631–649. doi:10.1179/1362171815y.0000000048
Patel, P., Defersha, F., and Yang, S. (2022). Resilience analysis of additive manufacturing-enabled supply chains: an exploratory study. Front. Manuf. Technol. 2. doi:10.3389/fmtec.2022.884164
Pearce, J. M., Blair, M., Laciak, J., Andrews, R., Nosrat, A., and Zelenika-Zovko, I. (2010). 3-D printing of open source appropriate technologies for self-directed sustainable development. J. Sustain Dev. 3, 17–29. doi:10.5539/jsd.v3n4p17
Pegues, J. W., Melia, M. A., Puckett, R., Whetten, S. R., Argibay, N., and Kustas, A. B. (2020). Exploring additive manufacturing as a high-throughput screening tool for multiphase high entropy alloys. Addit. Manuf. 37, 101598. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2020.101598
Peng, S., Mooraj, S., Feng, R., Liu, L., Ren, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2021). Additive manufacturing of three-dimensional (3D)-architected CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy with great energy absorption. Scr Mater 190, 46–51. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.028
Peng, T., Kellens, K., Tang, R., Chen, C., and Chen, G. (2018). Sustainability of additive manufacturing: an overview on its energy demand and environmental impact. Addit. Manuf. 21, 694–704. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2018.04.022
Petrovic, V., Vicente Haro Gonzalez, J., Jordá Ferrando, O., Delgado Gordillo, J., Ramon Blasco Puchades, J., and Portoles Grinan, L. (2011). Additive layered manufacturing: sectors of industrial application shown through case studies. Int. J. Prod. Res. 49, 1061–1079. doi:10.1080/00207540903479786
Poole, S., and Phillips, R. (2015). in Proceedings of the 2015 Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa and Robotics and Mechatronics International Conference, PRASA-RobMech 2015, 189–194.
Preez, W. B., De Beer, D. J., and Booysen, G. J. (2020). Establishing a quality management system for production of certified customised titanium medical implants through additive manufacturing. MRS Adv. 5, 1387–1396. doi:10.1557/adv.2020.192
Priarone, P. C., Pagone, E., Martina, F., Catalano, A. R., and Settineri, L. (2020). Multi-criteria environmental and economic impact assessment of wire arc additive manufacturing. CIRP Ann. 69, 37–40. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2020.04.010
Psarommatis, F., Fraile, F., Mendonca, J. P., Meyer, O., Lazaro, O., and Kiritsis, D., (2023). Zero defect manufacturing in the era of industry 4.0 for achieving sustainable and resilient manufacturing. Front. Manuf. Technol. 3 doi:10.3389/fmtec.2023.1124624
Puppi, D., and Chiellini, F. (2020). Biodegradable polymers for biomedical additive manufacturing. Appl. Mater Today 20, 100700. doi:10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100700
Pustovrh, A., Rangus, K., and Drnovšek, M. (2020). The role of open innovation in developing an entrepreneurial support ecosystem. Technol. Forecast Soc. Change 152, 119892. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119892
Raabe, D. (2023). The materials science behind sustainable metals and alloys. Chem. Rev. 123, 2436–2608. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00799
Raabe, D., Tasan, C. C., and Olivetti, E. A. (2019). Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals. Nature 575, 64–74. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1702-5
Radlbeck, C., and Mensinger, M. (2011). Sustainability of steel structures. IABSE Symp. Rep. 96, 243–249. doi:10.2749/222137809796088756
Rahmati, S., and Ghaei, A. (2014). The use of particle/substrate material models in simulation of cold-gas dynamic-spray process. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 23, 530–540. doi:10.1007/s11666-013-0051-4
Ramezani, M., and Mohd Ripin, Z. (2023). 4D printing in biomedical engineering: advancements, challenges, and future directions. J. Funct. Biomater. 14, 347. doi:10.3390/jfb14070347
Raoufi, K., Haapala, K. R., Etheridge, T., Manoharan, S., and Paul, B. K. (2022). Cost and environmental impact assessment of stainless steel microscale chemical reactor components using conventional and additive manufacturing processes. J. Manuf. Syst. 62, 202–217. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.11.017
Raoufi, K., Manoharan, S., Etheridge, T., Paul, B. K., and Haapala, K. R. (2020). Cost and environmental impact assessment of stainless steel microreactor plates using binder jetting and metal injection molding processes. Procedia Manuf. 48, 311–319. doi:10.1016/j.promfg.2020.05.052
Ravanbakhsh, H., Karamzadeh, V., Bao, G., Mongeau, L., Juncker, D., and Zhang, Y. S. (2021). Emerging technologies in multi-material bioprinting. Adv. Mater. 33, e2104730. doi:10.1002/adma.202104730
Ren, J., Zhang, A., and Wang, X. (2020). Traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 155, 104743. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104743
Rezvani Ghomi, E., Khosravi, F., Neisiany, R. E., Singh, S., and Ramakrishna, S. (2021). Future of additive manufacturing in healthcare. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 17, 100255. doi:10.1016/j.cobme.2020.100255
Rodrigues, V., Breda, Z., and Rodrigues, C. (2024). The implications of industry 4.0 for the tourism sector: a systematic literature review. Heliyon 10, e31590. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31590
Rojas, D. F., Li, H., Orhan, O. K., Shao, C., Hogan, J. D., and Ponga, M. (2022). Mechanical and microstructural properties of a CoCrFe0.75NiMo0.3Nb0.125 high-entropy alloy additively manufactured via cold-spray. J. Alloys Compd. 893, 162309. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162309
Roque, R., Barbosa, G. F., and Guastaldi, A. C. (2021). Design and 3D bioprinting of interconnected porous scaffolds for bone regeneration. An additive manufacturing approach. J. Manuf. Process 64, 655–663. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.01.057
Rupp, M., Buck, M., Klink, R., Merkel, M., and Harrison, D. K. (2022). Additive manufacturing of steel for digital spare parts – a perspective on carbon emissions for decentral production. Clean. Environ. Syst. 4, 100069. doi:10.1016/j.cesys.2021.100069
Safaei, K., Abedi, H., Nematollahi, M., Kordizadeh, F., Dabbaghi, H., Bayati, P., et al. (2021). Additive manufacturing of NiTi shape memory alloy for biomedical applications: review of the LPBF process ecosystem. Jom 73, 3771–3786. doi:10.1007/s11837-021-04937-y
Sakin, M., and Kiroglu, Y. C. (2017). 3D printing of buildings: construction of the sustainable houses of the future by BIM. Energy Procedia 134, 702–711. doi:10.1016/j.egypro.2017.09.562
Saleem, S. N., Seddik, S.A. el R., and el-Halwagy, M. (2023). Scanning and three-dimensional-printing using computed tomography of the “Golden Boy” mummy. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9, 1028377. doi:10.3389/fmed.2022.1028377
Salet, T. A. M., Ahmed, Z. Y., Bos, F. P., and Laagland, H. L. M. (2018). Design of a 3D printed concrete bridge by testing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 13, 222–236. doi:10.1080/17452759.2018.1476064
Salifu, S., Desai, D., Ogunbiyi, O., and Mwale, K. (2022). Recent development in the additive manufacturing of polymer-based composites for automotive structures—a review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 119, 6877–6891. doi:10.1007/s00170-021-08569-z
Sarathchandra, D. T., Kanmani Subbu, S., and Venkaiah, N. (2018). Functionally graded materials and processing techniques: an art of review. 5, 21328, 21334. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.536
Sikora, P., Chung, S. Y., Liard, M., Lootens, D., Dorn, T., Kamm, P. H., et al. (2021). The effects of nanosilica on the fresh and hardened properties of 3D printable mortars. Constr. Build. Mater 281, 122574. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122574
Soliman, Y., Feibus, A. H., and Baum, N. (2015). 3D printing and its urologic applications. Rev. Urol. 17, 20–24. doi:10.3909/riu0656
Spirio, A., Arrigo, R., Frache, A., Tuccinardi, L., and Tuffi, R. (2024). Plastic waste recycling in additive manufacturing: recovery of polypropylene from WEEE for the production of 3D printing filaments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 112474. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2024.112474
Srikanth, A., Mohammed Thalib Basha, G., and Venkateshwarlu, B. (2019). A brief review on cold spray coating process. Mater Today Proc. 22, 1390–1397. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.482
Stefaniak, A. B., Du Preez, S., and Du Plessis, J. L. (2021). Additive manufacturing for occupational hygiene: a comprehensive review of processes, emissions, and exposures. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 24, 173–222. doi:10.1080/10937404.2021.1936319
Strack, G. (2019). Additive manufacturing approaches for biological power generation. Curr. Opin. Electrochem 17, 167–173. doi:10.1016/j.coelec.2019.06.002
Strong, D., Kay, M., Conner, B., Wakefield, T., and Manogharan, G. (2018). Hybrid manufacturing – integrating traditional manufacturers with additive manufacturing (AM) supply chain. Addit. Manuf. 21, 159–173. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2018.03.010
Su, J., jie Kang, J., Yue, W., zheng Ma, G., qiang Fu, Z., na Zhu, L., et al. (2019). Review of cold spraying and its use for metallic glass coatings. Mater. Sci. Technol. (United Kingdom) 35, 1908–1923. doi:10.1080/02670836.2019.1654240
Szadkowski, J. (1994). Simplicity concept in structural optimization for the metamorphic manufacturing system. IFAC Proc. Vol. 27, 431–435. doi:10.1016/s1474-6670(17)46062-9
Tay, Y. W. D., Panda, B., Paul, S. C., Noor Mohamed, N. A., Tan, M. J., and Leong, K. F. (2017). 3D printing trends in building and construction industry: a review. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 12, 261–276. doi:10.1080/17452759.2017.1326724
Teawdeswan, L., and Dong, G. (2024). Inverse design of multi-material gyroid structures made by additive manufacturing. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 262, 108734. doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108734
Thakur, S., Chaudhary, J., Sharma, B., Verma, A., Tamulevicius, S., and Thakur, V. K. (2018). Sustainability of bioplastics: opportunities and challenges. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain Chem. 13, 68–75. doi:10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.04.013
Toth, A. D., Padayachee, J., Mahlatji, T., and Vilakazi, S. (2022). Report on case studies of additive manufacturing in the South African railway industry. Sci. Afr. 16, e01219. doi:10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01219
Vanclay, F. (2002). Conceptualising social impacts. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 22, 183–211. doi:10.1016/s0195-9255(01)00105-6
Vaz, R. F., Garfias, A., Albaladejo, V., Sanchez, J., and Cano, I. G. (2023). A review of advances in cold spray additive manufacturing. Coatings 13, 267. doi:10.3390/coatings13020267
Výtisk, J., Honus, S., Kočí, V., Pagáč, M., Hajnyš, J., Vujanovic, M., et al. (2022). Comparative study by life cycle assessment of an air ejector and orifice plate for experimental measuring stand manufactured by conventional manufacturing and additive manufacturing. Sus. mat. and tech. 32 doi:10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00431
Walker, M. (2018). Microstructure and bonding mechanisms in cold spray coatings. Mater. Sci. Technol. (United Kingdom) 34, 2057–2077. doi:10.1080/02670836.2018.1475444
Wang, K., Song, Y., Sheng, H., Xu, J., Zhang, S., and Qin, J. (2022a). Energy efficiency design for eco-friendly additive manufacturing based on multimodal attention fusion. J. Manuf. Process 79, 720–730. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.05.010
Wang, Q., Han, P., Yin, S., Niu, W. J., Zhai, L., Li, X., et al. (2021a). Current research status on cold sprayed amorphous alloy coatings: a review. Coatings 11, 1–21. doi:10.3390/coatings11020206
Wang, W.-Y., Yin, J., Chai, Z., Chen, X., Zhao, W., Lu, J., et al. (2022b). in Journal of materials informatics (Alhambra, United States: OAE Publishing Inc).
Wang, Y., Ahmed, A., Azam, A., Bing, D., Shan, Z., Zhang, Z., et al. (2021b). Applications of additive manufacturing (AM) in sustainable energy generation and battle against COVID-19 pandemic: the knowledge evolution of 3D printing. J. Manuf. Syst. 60, 709–733. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.07.023
Watson, J. K., and Taminger, K. M. B. (2018). A decision-support model for selecting additive manufacturing versus subtractive manufacturing based on energy consumption. J. Clean. Prod. 176, 1316–1322. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.12.009
Webster, S., Lin, H., Carter, F. M., Ehmann, K., and Cao, J. (2021). Physical mechanisms in hybrid additive manufacturing: a process design framework. J. Mater Process Technol. 291, 117048. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117048
Wegner, M., Hartwich, T. S., Heyden, E., Schwan, L., Schwenke, J., Wortmann, N., et al. (2022). New Trends in Aviation and Medical Technology Enabled by Additive Manufacturing. Front. Manuf. Technol. 2, 919738. doi:10.3389/fmtec.2022.919738
Willmott, J. D., Bibb, R. J., Johnson, A. A., and Paterson, A. M. (2023). Three-dimension dithering and its effect on the interfacial strength of multi-material and emulated multi-material additive manufacturing processes. Addit. Manuf. 78, 103837. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2023.103837
Woodson, T. S. (2015). 3D printing for sustainable industrial transformation. Development 58, 571–576. doi:10.1057/s41301-016-0044-y
Wu, H., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Liao, H., Raoelison, R. N., and Deng, S. (2021). New process implementation to enhance cold spray-based additive manufacturing. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 30, 1284–1293. doi:10.1007/s11666-021-01205-y
Wüstenhagen, R., Wolsink, M., and Bürer, M. J. (2007). Social acceptance of renewable energy innovation: an introduction to the concept. Energy Policy 35, 2683–2691. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2006.12.001
Xiong, W. (2022). Additive manufacturing as a tool for high-throughput experimentation. J. Mater. Inf. 2, 1–10. doi:10.20517/jmi.2022.19
Xu, J., Wang, K., Sheng, H., Gao, M., Zhang, S., and Tan, J. (2020). Energy efficiency optimization for ecological 3D printing based on adaptive multi-layer customization. J. Clean. Prod. 245, 118826. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118826
Yin, S., Cavaliere, P., Aldwell, B., Jenkins, R., Liao, H., Li, W., et al. (2018b). Cold spray additive manufacturing and repair: fundamentals and applications. Addit. Manuf. 21, 628–650. doi:10.1016/j.addma.2018.04.017
Yin, S., Jenkins, R., Yan, X., and Lupoi, R. (2018a). Microstructure and mechanical anisotropy of additively manufactured cold spray copper deposits. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 734, 67–76. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.096
Zhakeyev, A., Wang, P., Zhang, L., Shu, W., Wang, H., and Xuan, J. (2017). Additive manufacturing: unlocking the evolution of energy materials. Adv. Sci. 4, 1700187. doi:10.1002/advs.201700187
Zhang, B., Li, H., Cheng, J., Ye, H., Sakhaei, A. H., Yuan, C., et al. (2021). Mechanically robust and UV-curable shape-memory polymers for digital light processing based 4D printing. Adv. Mater. 33, e2101298. doi:10.1002/adma.202101298
Zhang, C., Chen, F., Huang, Z., Jia, M., Chen, G., Ye, Y., et al. (2019). Additive manufacturing of functionally graded materials: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 764, 138209. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2019.138209
Zhang, L., Chen, X., Zhou, W., Cheng, T., Chen, L., and Guo, Z. (2020). Digital twins for additive manufacturing: a state-of-the-art review. Appl. Sci. 10 (23), 8350. doi:10.3390/app10238350
Zhang, W., Sasnauskas, A., Coban, A., Marola, S., Casati, R., Yin, S., et al. (2024). Powder sheets additive manufacturing: principles and capabilities for multi-material printing. Addit. Manuf. Lett. 8, 100187. doi:10.1016/j.addlet.2023.100187
Zhang, Y., Raza, A., Xue, Y. Q., Yang, G., Hayat, U., Yu, J., et al. (2023). Water-responsive 4D printing based on self-assembly of hydrophobic protein “Zein” for the control of degradation rate and drug release. Bioact. Mater 23, 343–352. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.11.009
Zhu, Z., Dhokia, V. G., Nassehi, A., and Newman, S. T. (2013). A review of hybrid manufacturing processes – state of the art and future perspectives. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 26, 596–615. doi:10.1080/0951192x.2012.749530
Zolfagharian, A., Bodaghi, M., and Le Duigou, A. (2022). Editorial: 4D printing and 3D printing in robotics, sensors, and actuators manufacturing. Front. Robot. AI 9. doi:10.3389/frobt.2022.1110571
Keywords: additive manufacturing, sustainability, African industrialization, sustainable development goals, economic development
Citation: Klenam D, Asumadu T, Bodunrin M, Obiko J, Genga R, Maape S, McBagonluri F and Soboyejo W (2025) Toward sustainable industrialization in Africa: the potential of additive manufacturing – an overview. Front. Manuf. Technol. 4:1410653. doi: 10.3389/fmtec.2024.1410653
Received: 01 April 2024; Accepted: 11 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Kingsley Ukoba, University of Johannesburg, South AfricaReviewed by:
António Abreu, Lisbon Higher Institute of Engineering (ISEL), PortugalTomasz J. Nitkiewicz, Częstochowa University of Technology, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Klenam, Asumadu, Bodunrin, Obiko, Genga, Maape, McBagonluri and Soboyejo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Desmond Klenam, ZGVzbW9uZC5rbGVuYW1Ad2l0cy5hYy56YQ==
 Desmond Klenam
Desmond Klenam Tabiri Asumadu
Tabiri Asumadu Michael Bodunrin
Michael Bodunrin Japheth Obiko
Japheth Obiko Rodney Genga
Rodney Genga Sechaba Maape7
Sechaba Maape7 Wole Soboyejo
Wole Soboyejo