- 1School of Public Health, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou, China
- 2College of Health Science and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen, China
Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease worldwide, associated with systemic metabolic dysregulation. It can progress from simple hepatic steatosis (MAFL) to more severe conditions like Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). There is a critical lack of reliable non-invasive diagnostic methods and effective pharmaceutical treatments for MAFLD/MASH, emphasizing the need for further research. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale structures that play important roles in cell signaling by delivering bioactive molecules. However, there is a significant gap in literature regarding the roles of EVs from hosts, plants, and microbiota in MAFLD. This review explores the potential of EVs from various sources—host, plants, and microbiota—as biomarkers, therapeutic agents, drug carriers, and treatment targets for MAFLD. Firstly, the roles of host-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) in MAFLD, with a focus on cell-type specific EVs and their components—proteins, miRNAs, and lipids—for disease diagnosis and monitoring were discussed. Moreover, it highlighted the therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived EVs in reducing lipid accumulation and liver injury, and immune cell-derived EVs in mitigating inflammation and fibrosis. The review also discussed the use of host-derived EVs as drug carriers and therapeutic targets due to their ability to deliver bioactive molecules that impact disease mechanisms. Additionally, it summarized research on plant-derived EVs, which help reduce liver lipid accumulation, inflammation, and enhance gut barrier function in MAFLD. Also, the review explored microbial-derived EVs as novel therapeutic targets, particularly in relation to insulin resistance, liver inflammation, and dysfunction in MAFLD. Overall, by exploring the diverse roles of EVs from host, plant, and microbiota sources in MAFLD, this review offers valuable insights into their potential as non-invasive biomarkers and novel therapeutic strategies, which could pave the way for more effective diagnostic and treatment options for this increasingly prevalent liver disease. Notably, the challenges of translating EVs into clinical practice were also thoroughly discussed, aiming to provide possible directions and strategies for future research.
Background
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the leading cause of chronic liver conditions worldwide, impacting ~30% of the population and with a rising prevalence (1). The disease is primarily characterized by macrovesicular steatosis in ≥ 5% of hepatocytes without any secondary causes like alcohol or drug usage (2). Due to the link between NAFLD and systemic metabolic dysregulation, it has recently been proposed to rename NAFLD as Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) (3). Notably, MAFLD could advance from hepatic steatosis (fatty liver) alone, referred to as MAFL, to Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), a more severe inflammatory phase marked by liver cell injury with or without fibrosis, which could, in turn, evolve into liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) (4).
The exact mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of MAFLD remain incompletely understood. MAFLD primarily arises from nutritional excess, leading to the expansion of fat depots and ectopic fat accumulation (5). This process is exacerbated by macrophage infiltration into visceral adipose tissue, which fosters a pro-inflammatory environment and promotes insulin resistance (5)—a critical mechanism in MAFLD’s pathogenesis (6, 7). Insulin resistance disrupts normal lipolysis, resulting in increased fatty acid influx to the liver (7). This, combined with augmented de novo lipogenesis, exceeds the liver’s metabolic capacity, precipitating an imbalance in lipid metabolism that generates lipotoxic lipids (8, 9). Such lipotoxicity induces cellular stress, characterized by oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, activates inflammasomes, and leads to apoptotic cell death (8, 9). This inflammatory cascade not only drives hepatocyte injury but also stimulates tissue regeneration and fibrosis (8, 9). Pro-inflammatory and profibrotic macrophages are particularly implicated in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis (10). Furthermore, the intricate interplay of environmental and genetic factors plays a crucial role in MAFLD, with dietary influences being especially significant (11, 12). Current research has underscored the pivotal involvement of gut microbiota in the disease’s development (13, 14). Collectively, these insights reinforce the “multiple-hit hypothesis” of MAFLD, wherein a synergistic combination of factors contributes to its onset and progression toward more severe manifestations, such as MASH (5, 15, 16).
The primary treatment for MAFLD remains lifestyle modification aimed at achieving weight loss (17). This includes regular physical activity and dietary changes (18), such as adherence to a Mediterranean diet (19). However, many individuals find it challenging to sustain an exercise regimen, and cultural preferences may hinder acceptance of the Mediterranean diet (20). Bariatric surgery offers an alternative for managing MAFLD, particularly in cases of severe obesity (20), while liver transplantation remains a critical option for advanced stages of the disease (21). Nonetheless, these surgical interventions are associated with significant risks and potential complications (20, 21). Pharmacological therapies have emerged as promising alternatives. Agents such as statins, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists, farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists, and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have shown potential benefits in treating MAFLD (20, 22). However, their use is often complicated by different adverse effects, and large-scale clinical trial data supporting their efficacy and long-term safety in MAFLD and MASH remains limited (20, 23, 24). Resmetirom is a thyroid hormone receptor-beta (THR-β) agonist that was licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in March 2024 exclusively for the treatment of MASH (25). While it presents a novel therapeutic option, Resmetirom is also associated with several side effects (26). Consequently, the quest for safe and effective pharmacological therapies for MAFLD continues to be a pressing challenge.
MAFL can be diagnosed through a combination of imaging techniques and clinical characteristics, including the presence of metabolic comorbidities and abnormal laboratory findings. However, imaging cannot diagnose MASH; they can only help assess structural alterations in the liver and the extent of fibrosis. Currently, liver biopsy remains the “gold standard” for diagnosing MASH and assessing disease progression, including the degree of liver fibrosis (27, 28). Nevertheless, this histological evaluation carries inherent risks, including bleeding and, in rare instances, mortality (27, 28). Furthermore, histopathological assessments can be influenced by the limited representativeness of sampling sites and variability in interpretation among pathologists (27, 28). Additionally, liver biopsy presents challenges for the longitudinal monitoring of liver damage over time (28). As the development of MASH therapies advances, the need for non-invasive alternatives to liver biopsy has become critical, as these methods could identify patients in need of intervention and monitor treatment responses (27–30). In this context, liquid biopsies have demonstrated significant potential (29, 30). However, there is a significant shortage of reliable non-invasive diagnostic techniques for the diagnosis and progression of MAFLD. Thus, there is a pressing need to discover new non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis, staging, and prognosis of MAFLD, especially for MASH.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-enclosed structures secreted by prokaryotic, eukaryotic, and plant cells, and their release occurs in an evolutionarily conserved manner (31). These structures are commonly found in the Extracellular Matrix (ECM), various body fluids, and cell supernatants (32). Based on their size and biological mechanisms, EVs can be categorized into three groups: exosomes (30-150 nm), microvesicles (MVs, 100-1000 nm), and apoptotic bodies (ABs, 1-5 µm) (33). Initially, EVs were considered an avenue through which ordinary cells could handle and eliminate unwanted substances and regulate normal tissue balance, or conversely, as a way for cancer cells to support tumor advancement and spread (34, 35). Presently, EVs are acknowledged to be involved in cell-to-cell communication (36). They contain proteins, DNA, mRNA, microRNAs (miRNAs), and lipids from parent cells (37), through which their mediated signals can be transmitted (31). Active intercellular communication through EV secretion is crucial for maintaining normal physiological functions (38, 39), and EV-emitted abnormal signals are also associated with many disease states (40). In this regard, multiple studies have demonstrated the significant involvement of EVs in MAFLD progression (5, 41).
This review explores the roles of EVs originating from host cells, plant cells, and microbes in MAFLD (Figure 1). It emphasizes the promise of host-derived EVs as non-invasive biomarkers and therapeutic targets for MAFLD diagnosis and treatment, while also considering their use as drug carriers or therapeutic agents. Furthermore, the review discusses the therapeutic prospects of plant-derived EVs and the function of microbial-derived EVs as targets in MAFLD. This comprehensive tutorial review presents, for the first time, the diverse functions of EVs from various origins in relation to MAFLD.
However, the separation, standardization, and scale-up production of EVs still face numerous challenges (42, 43). The methods for isolating EVs are diverse, including ultracentrifugation, size exclusion chromatography, reagent-based separation kits, precipitation methods, as well as immunoaffinity and microfluidic-based separation techniques (44). However, these methods lack standardized protocols, leading to significant variability in the comparability of results across different experiments (42). Furthermore, the contents of EVs, such as proteins, RNA, and lipids, are highly heterogeneous and influenced by factors such as the cell type of origin, isolation technique, and storage conditions, making the prediction of EVs’ functionality and quality challenging (42, 45). More importantly, scaling up EV production to meet clinical demand presents technical and cost-related barriers, including standardization of cell culture, yield control, and purity assurance (42–45). Addressing these issues is crucial for the widespread application of EVs as therapeutic and diagnostic tools.
Host-derived EVs as potential biomarkers for MAFLD
Circulating cell type‐specific EVs as potential biomarkers for MAFLD
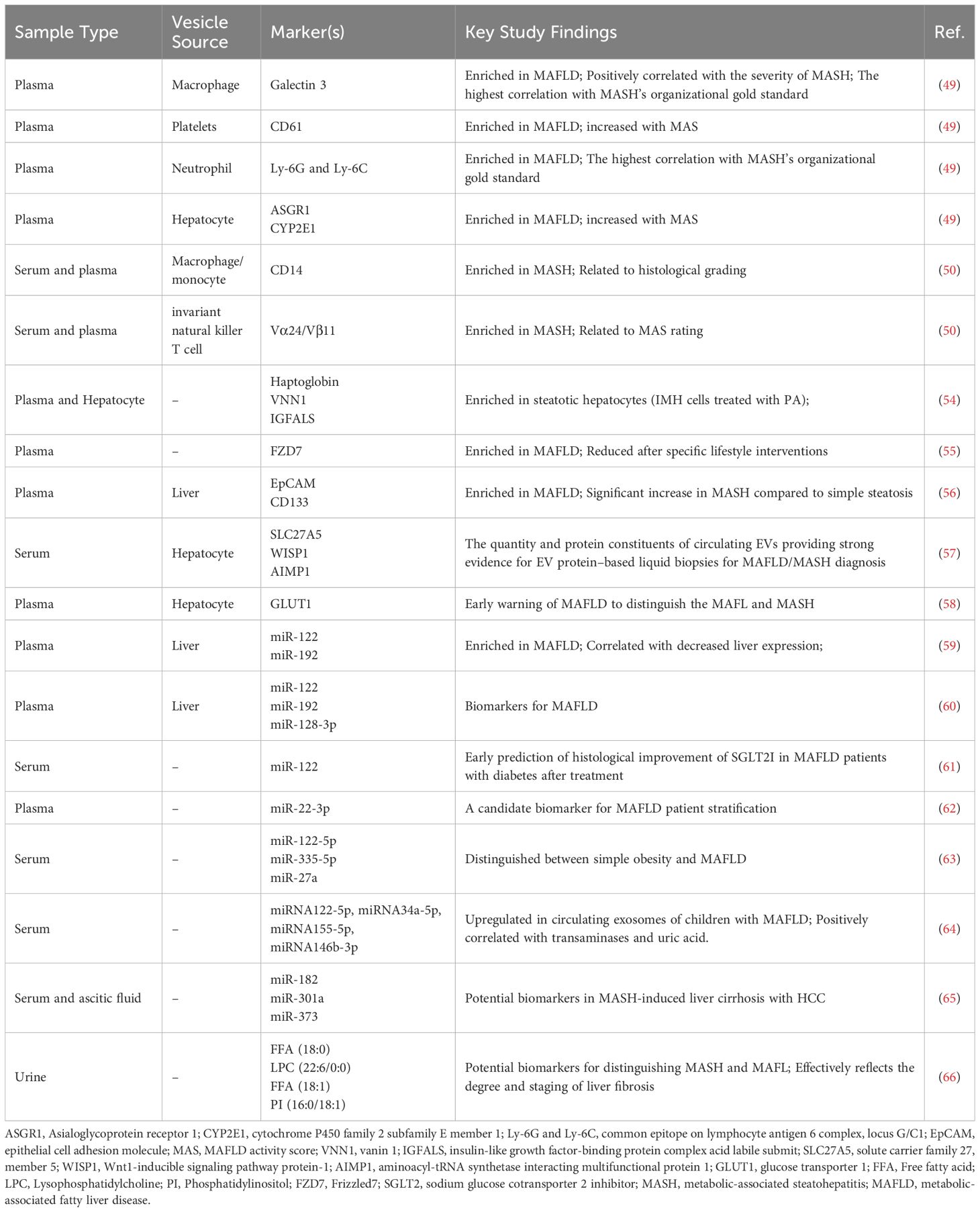
During the disease process, the majority of cells secrete EVs into the surrounding extracellular space (46). The variations in the quantity of EVs or changes in their contents could act as disease-specific indicators and are being explored as possible blood biomarkers (47). In the case of MAFLD, both the total quantity of circulating EVs and the number of EVs derived from specific cell types, such as hepatocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, have been found to increase with disease progression (48, 49). Using a Fat, Fructose, and Cholesterol (FFC) diet-induced MASH mouse model, Li et al. quantitatively analyzed cell-specific EVs and revealed that the concentrations of neutrophil-, macrophage-, and hepatocyte-derived EVs correlated well with MAFLD Activity Score (MAS) (49). Kornek’s team found that invariant Natural Killer T (iNKT) cell- and CD14+ cell-derived EVs were notably higher in the serum or plasma of MAFL/MASH patients than in healthy individuals and demonstrated clinical significance in relation to patients’ histological grading (50). Considering the close association of these cells with inflammation and fibrosis, and the fact that the pathogenesis and progression of MAFLD are characterized by liver inflammation and fibrosis, these cell type-specific extracellular vesicles may serve as specialized biomarkers, indicating the severity of inflammation in MAFL/MASH patients.
Circulating host-derived EV proteins as potential biomarkers for MAFLD
EVs derived from host cells closely resemble their source cells, enabling them to carry a diverse array of proteins, miRNAs, and lipids that facilitate intercellular communication (51). During the transition from a healthy to a diseased state, both the quantity of circulating EVs and their cargo, such as specific proteins, can reflect the pathological and physiological status of the originating cells (52, 53). Furthermore, EVs have been identified as emerging mediators of liver injury and inflammation in the context of MAFLD (48). Consequently, the specific proteins carried by these EVs represent promising candidates for biomarkers of MAFLD. Proteomics analysis of lipotoxic EVs derived from serum samples and hepatocytes of MASH patients revealed that haptoglobin, Vascular Non-Inflammatory Molecule-1 (Vanin 1), and the Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein Complex Acid Labile Subunit (IGF-BP ALS) could serve as biomarkers for detecting EVs originating from hepatocytes in MASH patients (54). Wnt/Frizzled receptor protein Frizzled 7 (FZD7) protein levels were upregulated in plasma exosomes derived from MAFLD patients, with lifestyle changes potentially downregulating FZD7, suggesting its promise as a new and effective biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of MAFLD (55). Circulating levels of EpCAM+ CD133+ EVs were significantly elevated during the transition from basic steatosis to steatohepatitis, which could be used as a non-invasive diagnostic marker for hepatitis, as well as in prognosis assessment and therapy monitoring (56). Research by Povero et al., identified Solute Carrier family 27, member 5 (SLC27A5) as a distinct indicator for circulating lipotoxic hepatocyte-originating EVs in MAFLD and MASH, whereas Asialoglycoprotein Receptor 1 (ASGR1) is a specific marker for hepatocyte-derived EVs in cirrhosis, and increased with disease progression (57). In addition, EV proteins such as WISP1, AIMP1, IL27RA, ICAM2, IL1β, STK16, and RGMA can reliably differentiate healthy controls from patients with precirrhotic and cirrhotic MASH (57). Zhang’s team reported that the proportion of Glucose Transporter 1 (GLUT1)-expressing serum hepatogenic exosomes was notably higher in MASH patients than in simple MAFL patients, with higher proportions in advanced MASH stages (58). These results indicate that EV proteins hold significant promise as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis and staging of MAFLD (as summarized in Table 1).
Circulating host-derived EV mi-RNAs as potential biomarkers for MAFLD
In addition to specific proteins, some miRNAs in liver-derived EVs could also be found in fatty liver disease and may act as non-invasive biomarkers for the disease. A previous study detected that circulating EVs in mice with MAFLD contained elevated levels of miR-122 and miR-192, which could act as indicators of liver injury (59). Furthermore, Newman et al. reported that miR-122, miR-192, and miR-128-3p in liver-specific ASGR1+ EVs could effectively discriminate between MAFL and MASH patients (60). Notably, serum exosomal miR-122 may also predict early histological improvements in MAFLD and diabetic patients treated with a Sodium Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitor (SGLT2I) (61). Castaño’s team demonstrated that MAFLD patients with higher miR-22-3p level exhibit elevated fasting insulin and glucose levels, along with a less favorable lipid profile (62). Distinct exosomal miRNA expression profiles were also observed in children with MAFLD, with specific miRNAs such as miR-122-5p, miR-335-5p, miR-27a, and miR-34a-5p being upregulated (63, 64), implying the potential of certain EV miRNAs as serum markers for MAFLD in children. Individuals with MASH-related liver cirrhosis and HCC exhibited higher expression levels of miR-182, miR-301a, and miR-373 in exosomes found in the serum and ascitic fluid than those with MASH-related liver cirrhosis but without HCC, suggesting that exosomal miRNAs could also be used as early diagnostic indicators for HCC (65). Therefore, circulating miRNA in EVs could also serve as potential biomarkers for stratification and therapy monitor of MAFLD (as summarized in Table 1).
Lipids in circulating host-derived EVs as potential biomarkers for MAFLD
Besides proteins and miRNAs, lipids are another class of bioactive components in EVs to mediate metabolic changes in recipient cells. Zhu et al. explored MAFLD biomarkers from the lipidomic perspective of urinary EVs and discovered that the four lipid molecules, namely Free Fatty Acid (FFA) (18:0), Lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) (22:6/0:0), FFA (18:1), and Phosphatidylinositol (PI) (16:0/18:1), could effectively distinguish between MASH from MAFL and reflect the degree and stage of liver fibrosis (66). Thus, lipids in EVs from the body fluids hold the promise to act as non-invasive biomarkers for MASH diagnosis and progression (as summarized in Figure 2 and Table 1).
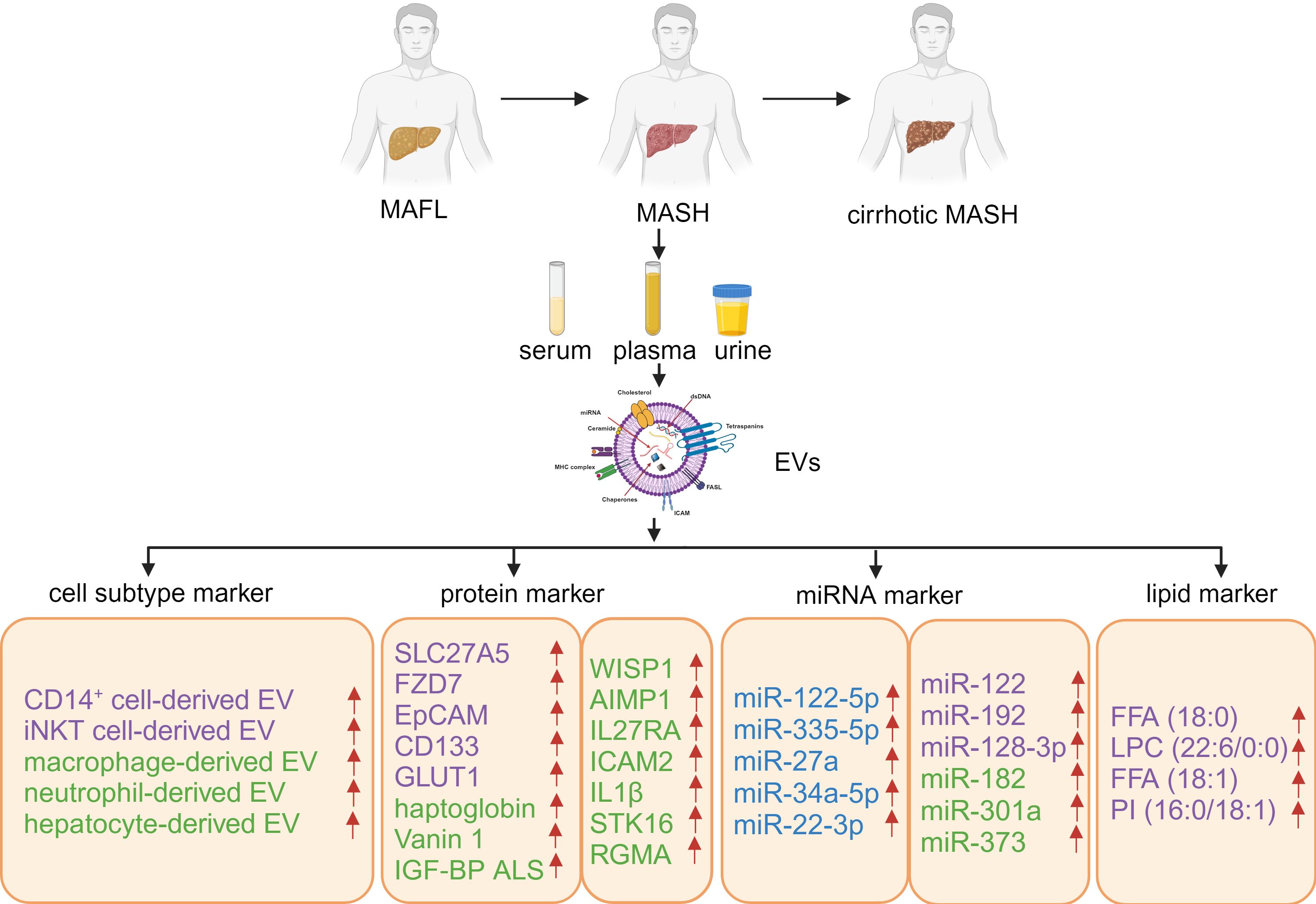
Figure 2. Host-derived EVs, containing specific proteins, miRNAs, and lipids, as biomarkers for MAFLD. The blue color indicates potential biomarkers for MAFL, the purple color represents potential biomarkers for the progression from MAFL to MASH, and the green color signifies potential biomarkers for MASH. Created with BioRender.com.
Host-derived EVs as therapeutic agents for MAFLD
Mesenchymal stem cells derived EVs as therapeutic agents for MAFLD
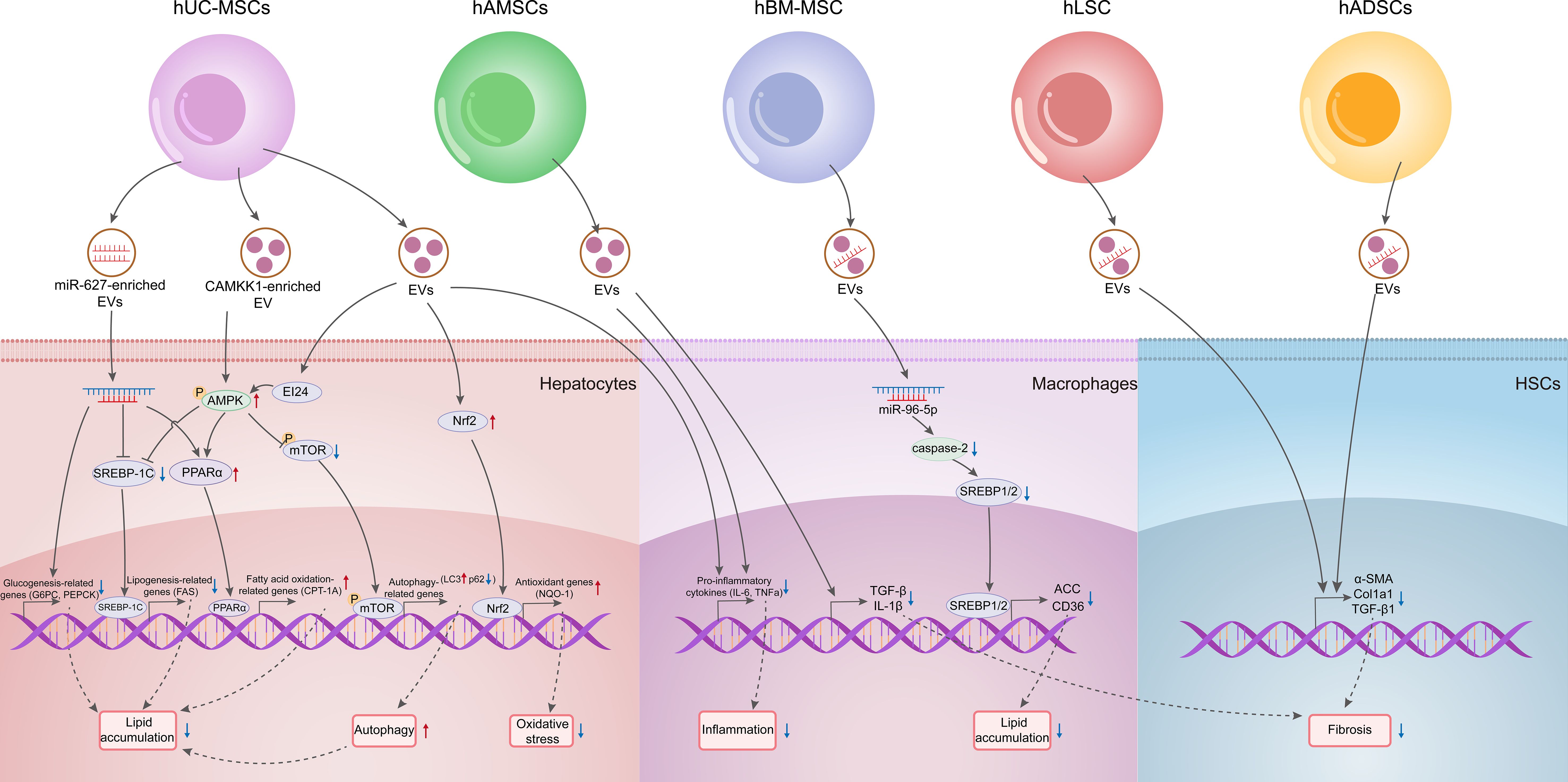
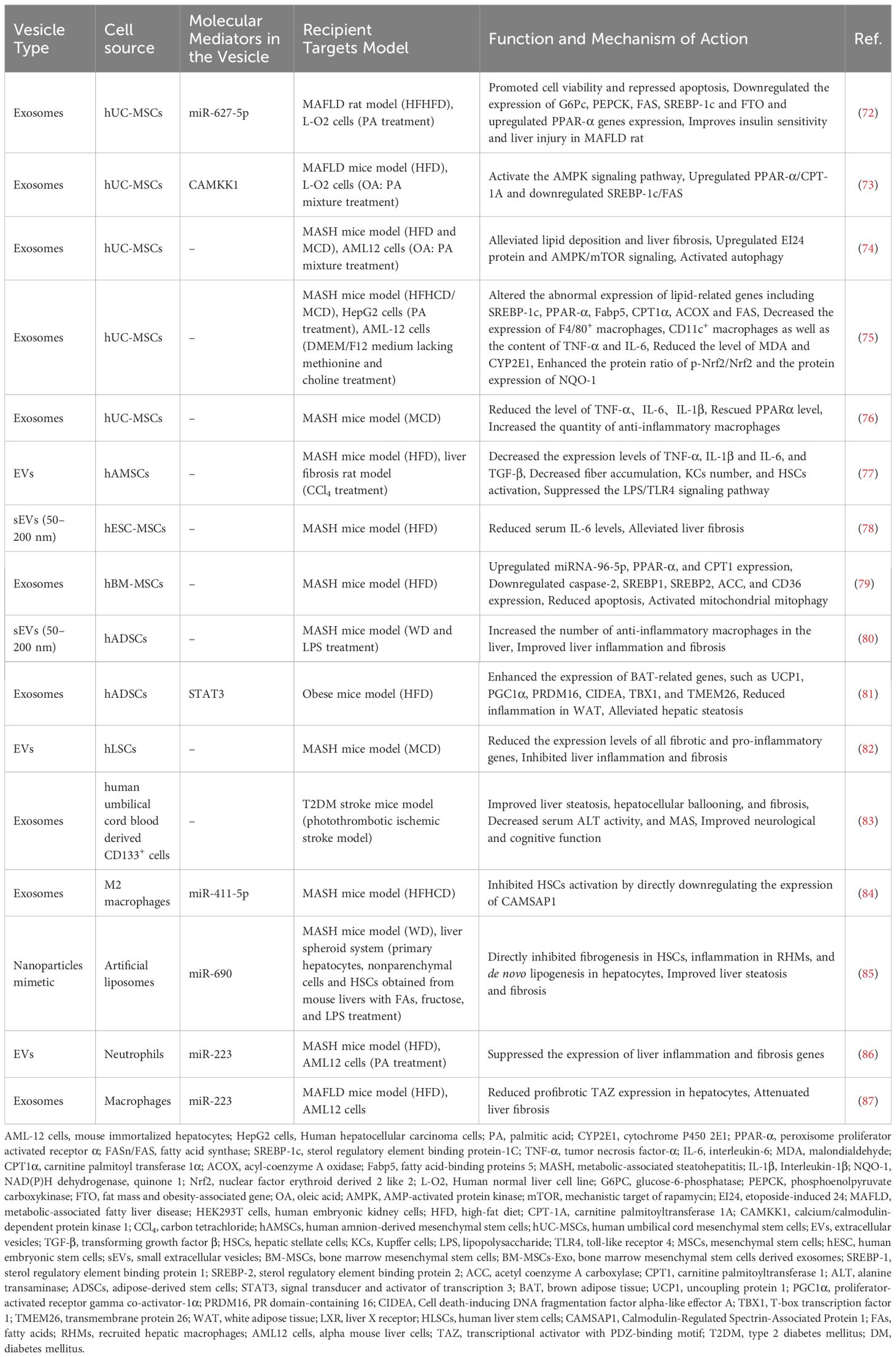
In addition to working as biomarkers, host-derived EVs can also hold promise as therapeutic agents for MAFLD. Stem cells are primarily derived from several distinct sources, including embryonic tissue; fetal tissues, such as the fetus, placenta (comprising the amniotic and chorionic membranes), amniotic fluid, and umbilical cord; as well as specific adult tissues, including adipose tissue, bone marrow, and blood (67). MSCs are multipotent progenitor cells with the potential for self-renewal and differentiation into mesenchymal lineages in vitro (68). Therapeutic applications of MSCs derived from various sources have been shown to be effective in treating neurological disorders, pulmonary dysfunction, metabolic and endocrine diseases, reproductive system disorders, skin burns, and cardiovascular diseases (68, 69). However, despite the safety demonstrated in preclinical and clinical studies, the long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapies necessitate validation through large-scale, randomized controlled Phase III clinical trials (68, 69). Notably, the therapeutic effects of these treatments are largely attributed to paracrine signaling rather than the prolonged survival and integration of transplanted cells (70). EVs can transfer bioactive molecules and facilitate intercellular communication, making them promising candidates for cell-free therapies (70, 71). Compared to stem cell treatments, EVs may provoke fewer immune responses, as they lack nuclei and most cellular organelles, thereby minimizing the risk of immune rejection (70, 71). Recent research has shown that miR-627-5p or Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase 1 (CAMKK1) enriched in human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hUC-MSCs)-derived exosomes downregulates gluconeogenesis- and lipogenesis-related genes whereas upregulates fatty acid oxidation-related genes, thereby improving glucose and lipid metabolism in vivo and in vitro (72, 73). Specifically, the exosomal miR-627-5p downregulated the expression of Glucose-6-Phosphatase (G6Pc), Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEPCK), Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS), Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein-1C (SREBP-1c) genes, and Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene (FTO) in PA-induced L-O2 cells, whereas it upregulated the expression of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor α (PPAR-α). Studies have also shown that hUC-MSCs and their exosomes alleviate lipid deposition and liver fibrosis in MASH mice through mechanisms involving the upregulation of Etoposide-Induced gene 24 (EI24) protein and AMPK/mTOR signaling as well as activation of autophagy (74). Exosomes released by hUC-MSCs were also shown to mitigate hepatocellular inflammation in Methionine-Choline Deficient (MCD) diet-induced MASH mice by downregulating pro-inflammatory macrophages and cytokines such as Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-α) and Interleukin 6 (IL-6), and facilitate the transition of macrophages into an anti-inflammatory state (75, 76). Moreover, hUC-MSC-derived exosomes exhibit antioxidation effects by activating the Nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (Nrf2)/NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, Quinone 1 (NQO-1) signaling pathway, which is crucial for MASH treatment (75).
In addition to hUC-MSCs, several other types of MSCs have demonstrated therapeutically potentials for MAFLD treatment. Human Amnion Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hAMSCs)-derived EVs have been shown to decrease the number of Kupffer Cells (KCs) and inhibit Hepatic Stellate Cell (HSC) activation in the livers of MASH rats and lower the mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, and Transforming Growth Factor beta (TGF-β) (77). Small EVs (sEVs, 50-200 nm) from human Embryonic Stem Cell-derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells (hESC-MSCs) also alleviate liver fibrosis in MASH mouse model (78). In a High Fat Diet (HFD)-induced MASH model, treatment with human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hBM-MSCs) or their derived exosomes (hBM-MSCs-Exo) upregulated miR-96-5p and downregulated caspase-2, leading to reduced expression of lipid synthesis (SREBP1/2, ACC) and uptake (CD36) genes. hBM-MSCs or hBM-MSCs-Exo also enhanced fatty acid oxidation genes, activated mitochondrial autophagy, and reduced apoptosis, contributing to MASH remission (79). Additionally, injection of human Adipose tissue-derived Stem Cells (hADSCs) or their sEVs increased anti-inflammatory macrophages in the livers of MASH model mice, thus improving inflammation and fibrosis (80). Zhao et al. reported that long-term HFD feeding extensively suppressed the expression of Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT)-associated genes such as Uncoupling Protein 1 (UCP1), and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ Coactivator α (PGC-1α) in epididymal White Adipose Tissue (WAT), while hADSCs significantly reversed these changes. Moreover, hADSC-derived exosomes reprogrammed adipose macrophages from the pro-inflammatory M1 to the anti-inflammatory M2 subtype, reducing WAT inflammation in HFD mice (81). Exosomes derived from human Liver Stem Cell (hLSC)-derived EVs enhanced liver functionality in MASH mice by downregulating genes associated with fibrosis and inflammation (82). Furthermore, exosomes obtained via intravenous administration of early Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) sourced from umbilical cord blood markedly improved hepatic steatosis, hepatocellular ballooning, and fibrosis, accompanied by decreased serum Alanine Transaminase (ALT) activity and MAS in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) mice with stroke (83).
Collectively, these findings indicate that MSC-derived EVs can mitigate lipid accumulation in liver cells by enhancing lipid oxidation, inhibiting lipid synthesis, and promoting autophagy, while also improving liver damage in MASH through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Thus, MSC-derived EVs exhibit considerable promise for treating MAFLD (as summarized in Figure 3 and Table 2).
Immune cell-derived EVs as therapeutic agents for MAFLD
Since MALFD is also immunologically relevant, some immune cell-derived EVs can communicate with liver cells via certain miRNAs enriched in them, ameliorating liver fibrosis and inflammation in fatty liver mouse models. For instance, exosomal miR-411-5p from M2 macrophages has been shown to inhibit HSC activation in a MASH mouse model by targeting and suppressing the gene Calmodulin regulated Spectrin-Associated Protein 1 (CAMSAP1) (84). Furthermore, KCs can generate their own miR-690 and transfer it to liver cells, thereby recruiting hepatic macrophages, and HSCs via exosome release. Notably, miR-690 could directly suppress fibrogenesis, inflammatory responses, and de novo lipogenesis in HSCs, hepatic macrophages, and hepatocytes, respectively, improving liver steatosis and fibrosis in MASH mice (85). Additionally, in HFD-fed mice and PA-treated AML12 hepatocytes, hepatocytes could internalize miR-223-enriched EVs (primarily originating from neutrophils) via the interaction between the Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDLR) on hepatocytes and Apolipoprotein E (APOE) on the surface of neutrophil-derived EVs, suppressing liver inflammatory and fibrotic gene expression (86). Hou et al. discovered that HFD-fed mice with a myeloid-specific knockout of IL-6 receptor A (IL6Ra) showed reduced hepatic miR-223 expression and increased transcriptional activation of Tafazzin (TAZ), a miR-223 target gene, which exacerbated liver fibrosis. However, treatment with IL-6 prompts macrophages to secrete miR-223-enriched exosomes, reducing the expression of TAZ in liver cells via exosomal transfer, ultimately contributing to the attenuation of liver fibrosis in mice induced by HFD (87). Overall, immune cell-derived exosomes, enriched with specific miRNAs, play a crucial role in communicating with liver cells to alleviate liver fibrosis and inflammation in MASH (as summarized in Table 2).
Host-derived EVs as drug delivery vehicles for MAFLD
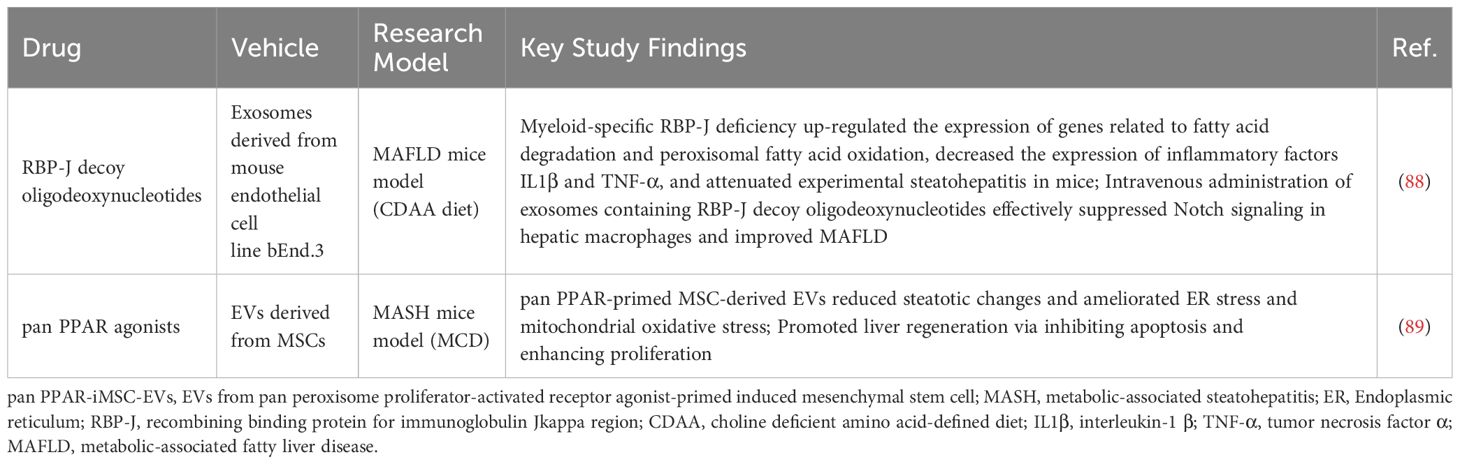
Due to their self-derived nature and high compatibility with the host, host-derived EVs could be suitable drug carriers for MAFLD treatment (as summarized in Table 3). Research by Ding et al. demonstrated that inhibiting RNA-binding Protein J region (RBP-J) in myeloid cells reduces Notch signaling, leading to decreased inflammatory cytokine production and enhanced fatty acid metabolism in the livers of mice on a Choline Deficient Amino Acid (CDAA) diet, which ultimately alleviates liver inflammation in steatohepatitis models. They also found that intravenous administration of exosomes containing RBP-J decoy oligodeoxynucleotides effectively suppressed Notch signaling in hepatic macrophages, significantly improving MAFLD (88). Additionally, Kim’s study revealed that pan Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (pan PPAR) agonists -primed MSC-derived EVs possess beneficial properties such as organ uptake, anti-steatotic effects, and tissue repair capabilities, which could greatly enhance MASH treatment (89). Therefore, using EVs as drug delivery carriers offers new opportunities for innovative MAFLD/MASH therapies.
Host-derived EVs as therapeutic targets for MAFLD
Hepatocytes-derived EVs as therapeutic targets for MAFLD
Hepatocytes constitute the main cell type in the liver, comprising approximately 80% of the total hepatic cell population (90). The primary contributing factor to MAFLD is overnutrition, which leads to the enlargement of adipose depots and the deposition of ectopic fat in the liver (5). Excessive lipid accumulation in hepatocytes leads to lipotoxicity, initiating a series of harmful events such as oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ER stress, which eventually result in hepatocyte death (5). EVs released from lipotoxic hepatocytes mediate intercellular communication with target cells, such as macrophages, monocytes, and HSCs, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of MAFLD.
Recent studies indicate that EVs released from lipotoxic hepatocytes communicate with macrophages to promote the liver’s inflammatory response and the progression of MAFLD. For example, in the MCD diet-induced MASH mouse model, exosomes enriched in miR-34a released by lipotoxic hepatocytes promotes liver inflammation by activating Kupffer cells (91). Similarly, exosomal miR-192-5p released by hepatocytes in rats with MASH activates pro-inflammatory macrophages via the Rictor/Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway, which contributes to liver inflammation (92). Cholesterol-induced lysosomal dysfunction increases exosome release from Huh7 cells, which then polarizes pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages, thus triggering inflammation in a miR-122-5p-dependent manner (93).
PA can induce lipotoxicity in hepatocytes and is a widely used in vitro model for MAFLD. PA induces the release of lipotoxic EVs by activating Inositol Requiring Enzyme 1 alpha (IRE1α) (48). Activated IRE1α produces X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), which further stimulates the expression of Serine Palmitoyltransferase (SPT) genes, thus initiating ceramide production and EVs secretion (94). Then lipotoxic EVs generate sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) with C16:0 ceramide as a substrate, thus activating macrophage chemotaxis and promoting hepatic inflammation (48, 94), which could be attenuated by inhibitors of sphingosine kinases, antagonists of S1P receptors (95), as well as the antagonist of S1P (96).
Mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) was identified as another critical signaling molecule involved in the release of EVs from hepatocytes under lipotoxic conditions. PA or its metabolite LPC treatment induces the secretion of EVs enriched in the potent chemokine CXCL10 from Huh7 cells and primary mouse hepatocytes (PMHs) by activating the MLK3-STAT1 pathway (97), which in turn induce macrophage chemotaxis into the liver, leading to liver inflammation in FFC diet-induced MASH mice (98).
Notably, the Death Receptor 5 (DR5) pro-apoptotic signaling pathway is also implicated in lipotoxicity-induced release of EVs from hepatocytes. PA stimulates the DR5-Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand (TRAIL)-caspase/Rho Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Protein Kinase 1 (ROCK1) apoptotic signaling pathway, leading hepatocytes to generate lipotoxic EVs, which in turn promote an inflammatory response in macrophages, while the ROCK1 inhibitor fasudil reduces serum levels of EVs and improves MASH (99).
Autophagy plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of MAFLD by regulating lipid metabolism, mitigating inflammation, and responding to cellular stress (100). Inhibition of autophagy through knockdown of autophagy-related gene 5 (ATG5) in murine hepatocytes AML12 cells resulted in the secretion of pro-inflammatory exosomes, enhancing Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and TNFα co-treatment-induced liver inflammation and injury (101). These studies indicate that lipotoxic hepatocyte-derived EVs engage in close communication with macrophages, driving hepatic inflammation and disease progression.
HSCs play a key role in liver fibrosis, and recent studies have strongly linked the communication between HSCs and EVs derived from lipotoxic hepatocytes with the progression of MAFLD. In patients with MASH exhibiting F3-F4 fibrosis, activated HSCs and myofibroblasts exhibited a marked upregulation of the pro-fibrotic molecule, Cell Communication Network Factor 2 (CCN2), which subsequently potentiated HSC activation and aggravated liver fibrosis (102). In vitro studies indicated that lipotoxic hepatocytes-EVs induced by PA could be efficiently internalized by HSCs, leading to HSCs activation and subsequent liver fibrosis through inducing CCN2 (102). PA treatment also alters the miRNA expression profiles in hepatocyte-derived exosomes, which promotes HSCs activation by targeting PPAR-γ expression or Phosphatase and Tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced Kinase 1 (PINK1), thereby accelerating liver fibrosis progression (103–105). Besides PA, CoCl2-triggered chemical and intermittent hypoxia can also enhance the release of EVs from fatty acid-exposed HepG2 cells, triggering a pro-fibrotic response in human HSCs, and led to a higher release of circulating EVs in a CDAA diet-induced MASH model, thereby exacerbating hepatic fibrosis (106).
The lipotoxic EVs released by hepatocytes can also induce monocyte adhesion. In a mouse model of MASH induced by an FFC diet, integrin β1 (ITGβ1) present in lipotoxic EVs mediates monocyte adhesion to liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, thereby exacerbating hepatic inflammation (107). Notably, treatment with an ITGβ1 antibody significantly mitigates liver damage and fibrosis (107), indicating that it could be a promising therapeutic option to alleviate liver damage in MASH.
Considering the liver inflammation or HSC activation induced by EVs derived from lipotoxic hepatocytes, several pharmacological agents have been identified as potential treatments for MAFLD by reducing the release of EVs from these cells. Treatment of hepatocyte-derived EVs with ezetimibe modulates communication between hepatocytes and macrophages by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome-IL-1β pathway, suggesting the potential of ezetimibe as a treatment for steatohepatitis (108). IL-22 therapy showed promise in MASH by mitigating the inflammatory effects of mitochondrial DNA-enriched hepatocyte-derived EVs (109). Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) and DNA Methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) reduced fibrogenic Th17 cell activity and fibrosis by downregulating angiocrine factors in hepatocytes-derived EVs (110). Elafin was found to upregulate miR-181b-5p and miR-219-5p in serum exosomes from livers of HFD-fed mice, which led to increased leptin expression in adipose tissue, alleviating hepatic steatosis (111). In addition, new-generation insulin-sensitizing thiazolidinediones or Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier 2 (MPC2) knockdown in hepatocytes inhibited HSC activation by reducing hepatocyte exosome secretion (112).
In summary, EVs from hepatocytes play a pivotal role in driving inflammation and fibrosis in fatty liver disease by activating macrophages/HSCs/monocytes and promoting inflammatory pathways (as summarized in Table 4). Therefore, they can be considered as therapeutic targets for MAFLD.
Adipocytes-derived EVs as therapeutic targets for MAFLD
In addition to their role in secreting EVs, hepatocytes also act as recipient cells, taking up EVs from other tissues, including adipocytes, thus influencing disease progression. Metabolic disorders, such as obesity and insulin resistance, are acknowledged as significant risk factors for MAFLD (113, 114). For example, exosomes from subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue (SAAT) of obese patients reduce insulin-stimulated Akt phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle cells and mouse hepatocytes, diminishing insulin sensitivity (115, 116). EVs enriched with IL-6, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1), and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), originating from the adipocytes of patients with aneurysmal aortic disease, have been shown to induce systemic insulin resistance and correlate positively with liver enzyme levels (116). Similarly, exosome-like vesicles (ELVs) from the adipose tissue of obese mice impair glucose uptake and promote insulin resistance both in vivo and in vitro (117). According to these studies, adipocyte-derived EVs play a significant role in inducing insulin resistance, which is pivotal in the pathogenesis of MAFLD.
EVs secreted by adipocytes can also promotes MAFLD by disturbing lipid metabolism in the liver. For example, adipocyte-derived exosomal LINC01705 increases lipid accumulation in high glucose-induced HepG2 cells via miR-552-3p/LXR axis modulation (118). In the MASH mouse model, adipose-derived exosomes enriched in miR-103 are taken up by hepatocytes, leading to autophagy inhibition and exacerbation of MASH, which could be reversed by miR-103 antagonist (119). Aerobic exercise has been shown to alleviate steatohepatitis in HFD-fed mice by downregulating specific miRNAs in WAT-derived EVs and improving liver steatosis scores (120). Aldo-keto reductase 1B7 (Akr1b7) is an enzyme that regulates lipid synthesis and plays a key role in hepatic lipid metabolism (121). Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-induced exosomes secreted by adipocytes promote the transition from liver steatosis to MASH by transporting exosomal Akr1b7 to hepatocytes (122). The adipokine resistin triggers liver steatosis by inducing ERS, while melatonin counteracted this effect by decreasing resistin delivery via adipocyte-derived exosomes (123). Exosomes derived from visceral adipose tissue (VAT) in obese patients can also be taken up by HSCs, disrupting the TGF-β pathway and contributing to the development of MAFLD (124). These studies indicate that adipocyte-derived EVs can carry various biomolecules that induce insulin resistance and lipid accumulation in hepatocytes, as well as disrupt the TGF-β signaling pathway, thereby influencing the onset and progression of MAFLD. Therefore, adipocyte-derived EVs may represent viable therapeutic targets for MAFLD.
Intestine cell-derived EVs as therapeutic targets for MAFLD
The “gut-liver” axis plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of MAFLD by regulating the gut microbiota, intestinal barrier, secreted signaling molecules, and immune responses, thereby influencing hepatic lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses (125, 126). Patients with MAFLD often suffer from gut microbiota dysbiosis, which disrupts the integrity of the intestinal barrier, resulting in increased permeability (127). This disruption of intestinal barrier function can lead to an increased release of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) like lipopolysaccharide (LPS) into the circulation and be transported to the liver where it actives toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and induces inflammation (128). As signaling molecules, EVs could mediates the crosstalk between the gut and the liver. The disruption of intestinal barrier function can lead to an increased release of EVs, and the composition of bioactive molecules they carry, such as LPS, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, will also change in MAFLD (129). Fizanne et al. reported that fecal EVs from MAFLD and MASH patients had a lower mean protein quantity and a greater content of LPS. Furthermore, MASH fecal EVs enhanced intestinal cell permeability and promoted the activation of LX2 cells (130). Research by Kumar et al. indicates that exosomes from the intestines of germ-free mice treated with antibiotics exhibit distinct lipid compositions between lean (L-Exo) and HFD-induced obese (H-Exo) groups, with L-Exo primarily containing phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and H-Exo rich in phosphatidylcholine (PC). Specifically, the content of PC from the intestines of obese mice increases, whereas the content of PE content decreases (131). Analysis of fecal samples from five healthy volunteers and seven patients with Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) revealed that the number of EVs in the fecal samples of T2D patients was significantly higher (approximately 4.5×1013 particles/g feces) compared to those of healthy individuals (2×1013 particles/g feces). Additionally, the concentration of PC in EVs was also significantly increased (approximately 10%) in T2D patients, compared to that in healthy individuals, which was around 0.35% (131). This suggests that the diet-dependent increase in exosomal PC has clinical relevance. Intestine-derived EVs can be detected by biosensors in distant target tissues, such as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR). As a ligand-activated transcription factor, AhR can be activated by small molecules derived from diet, microbes, metabolism, and pollutants, playing complex regulatory roles in cellular physiology and pathology. When intestine-derived EVs are taken up by hepatocytes, the PC in H-Exo activates AhR as a ligand. The activated AhR then crosstalk with transcription factors to rewire hepatocyte metabolism and reprogram the cellular transcriptome. For instance, it inhibits the expression of key genes in the insulin signaling pathway, such as IRS-2, PI3K, and Akt, leading to insulin resistance. Additionally, the activation of AhR also affects the expression of fatty acid synthase and cholesterol synthase in the liver, altering the lipid composition of the liver. PC in H-Exo also activates AhR in adipocytes and skeletal muscle cells, inhibiting the expression of IRS-2 and further exacerbating insulin resistance. Moreover, H-Exo could be taken up by macrophages and promotes the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-6, which further exacerbates liver inflammation (131). Overall, these findings suggest that intestine-derived EVs could serve as potential therapeutic targets for metabolic disease such as T2D and MAFLD.
Immune cell-derived EVs as therapeutic targets for MAFLD
Immune cells also influence the progression of MAFLD by releasing EVs. Circulating microparticles (MPs) derived from activated and apoptotic T cells are increased in patients with active hepatitis C, which could be taken up by HSC in an ICAM-1-dependent manner and leads to activation of ERK1/2 and subsequent upregulation of fibrolytic matrix metalloprotease (MMP) genes and downregulation of procollagen α1(I) gene (132). In addition, exosomes from adipose tissue macrophages in obese mice decrease Akt phosphorylation and downstream GLUT4 in hepatocytes, and also suppress PPARγ in a miR-155 manner, finally impacting insulin sensitivity (133).
Taken together, EVs carry miRNAs, lipids and other biomolecules, allowing for communication between hepatocytes and other cell types and emerging as promising therapeutic targets for the management of MAFLD (as summarized in Figure 4).
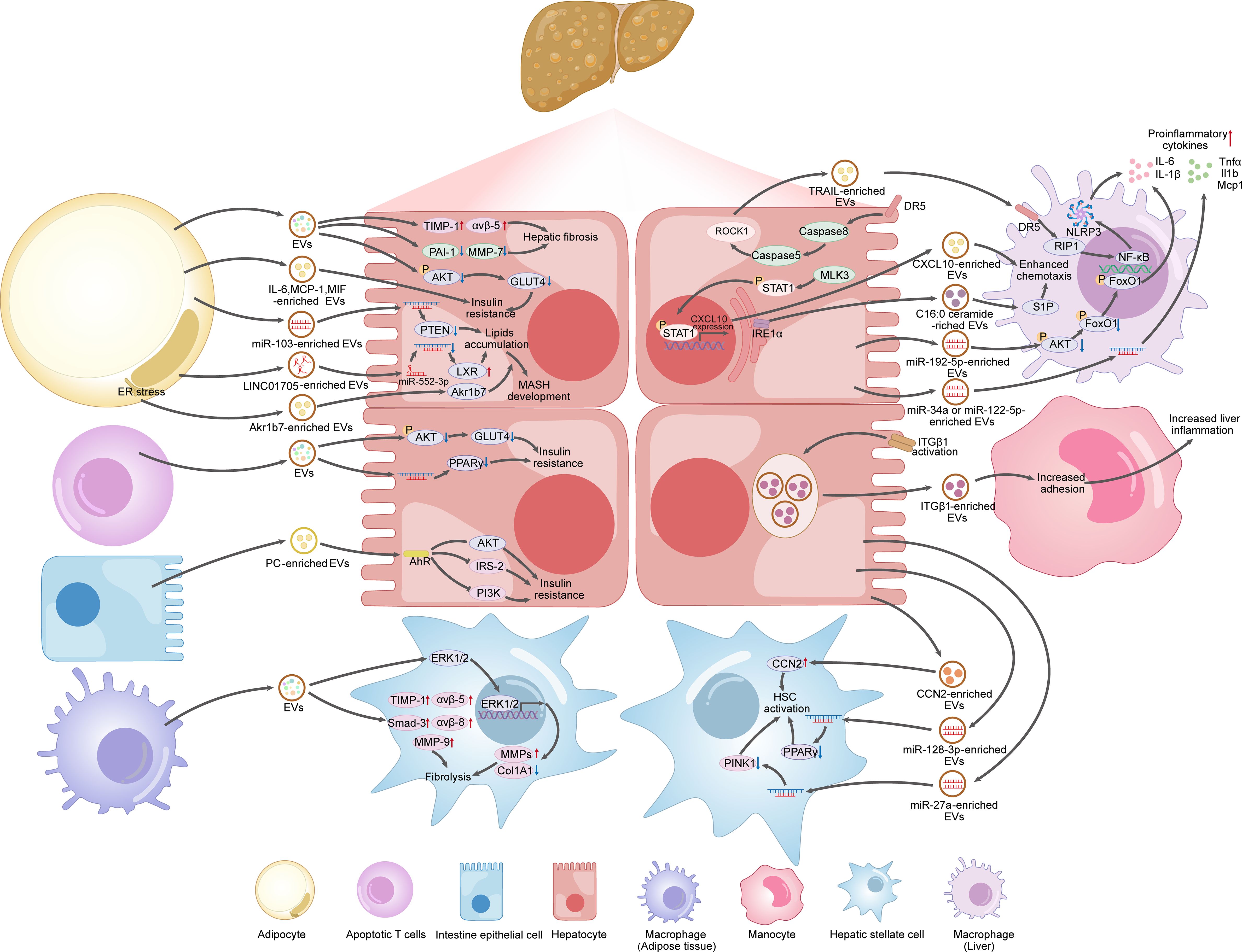
Figure 4. EVs produced by hepatocytes, adipocytes, intestine cells, immune cells, as potential therapeutic targets for MAFLD.
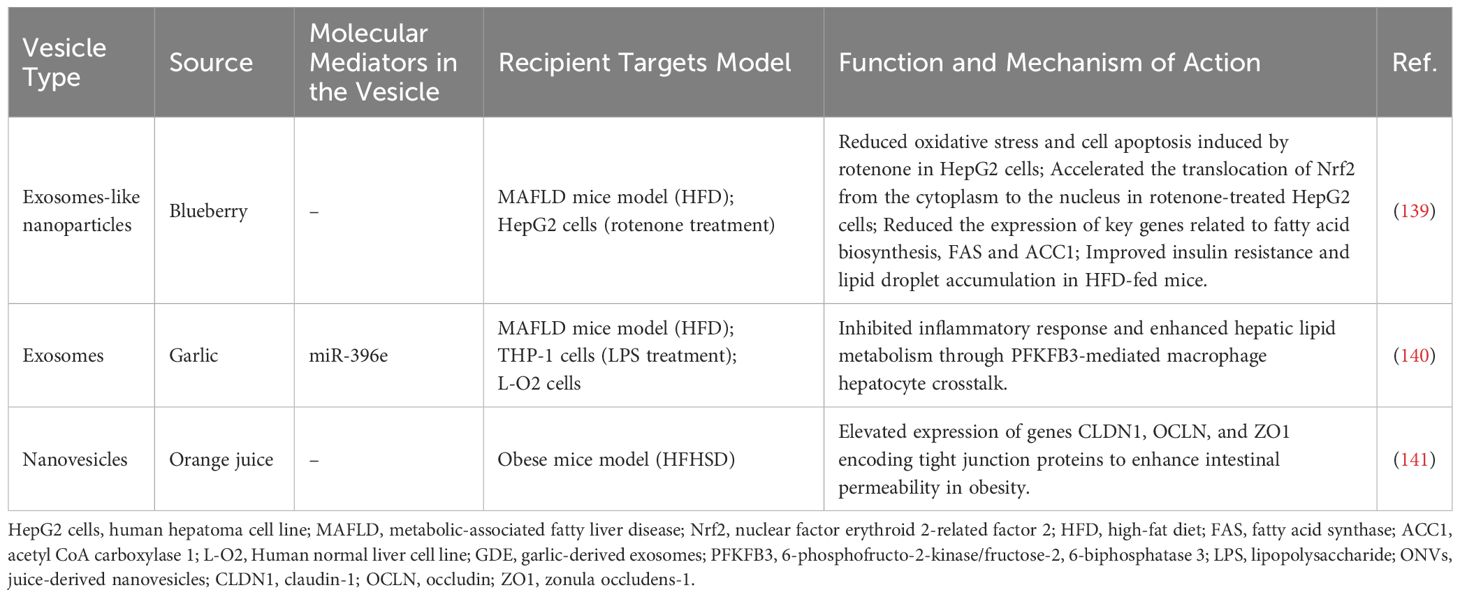
Plant-derived EVs as therapeutic agents for MAFLD
Current research primarily focuses on host-derived EVs, but studies on plant-derived EVs are also emerging. Halperin et al. first identified EVs from plant cells of carrots in 1967 (134). Plant-derived EVs influence intracellular physiological processes through their bioactive molecules, exhibiting pharmacological activities such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, immune regulation, and promoting regeneration (135–137). Their excellent biocompatibility further underscores their potential as drug delivery systems, highlighting significant prospects in disease treatment (135–138). Recent findings suggest that plant-derived EVs can improve liver dysfunction in MAFLD by modulating key enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism, glucose metabolism, and oxidative stress, indicating their potential as therapeutic agents for MAFLD. For example, Blueberry-derived Exosomes-Like Nanoparticles (BELNs) reduce oxidative stress in HepG2 cells by inhibiting Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) generation and restoring mitochondrial membrane potential and improve insulin sensitivity in HFD-fed mice by downregulating fatty acid biosynthesis genes (139). Studies have demonstrated that Garlic-Derived Exosomes (GDE) effectively suppress inflammation in macrophages and improve liver dysfunction in HFD-fed mice, with miR-396e in GDE playing a crucial role in mediating interactions between macrophages and hepatocytes by targeting 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) (140). In comparison to mice subjected to a high-fat high-sugar diet (HFHSD), Berger et al. found that genes encoding tight junction proteins Claudin-1 (CLDN1), Occludin (OCLN), and Zonula occludens-1 (ZO1) are upregulated in the jejunum of mice treated with orange juice-derived EVs, indicating that these EVs can enhance intestinal permeability in obesity (141). Ammonia borane is a hydrogen donor that can produce hydrogen with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, anti-fibrotic, and antimicrobial effects (142–144). Wang et al. discovered that oral administration of ginger-derived EVs loaded with ammonia borane alleviate insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in a mouse model with T2DM accompanied by MAFLD (145). These studies suggest that plant-derived EVs can reduce liver lipid accumulation and inflammation, thereby alleviating liver dysfunction (as summarized Table 5). Additionally, plant-derived EVs can also improve intestinal barrier function and serve as carriers for drug delivery. These beneficial effects make them viable therapeutic agents for the treatment and prevention of MAFLD.
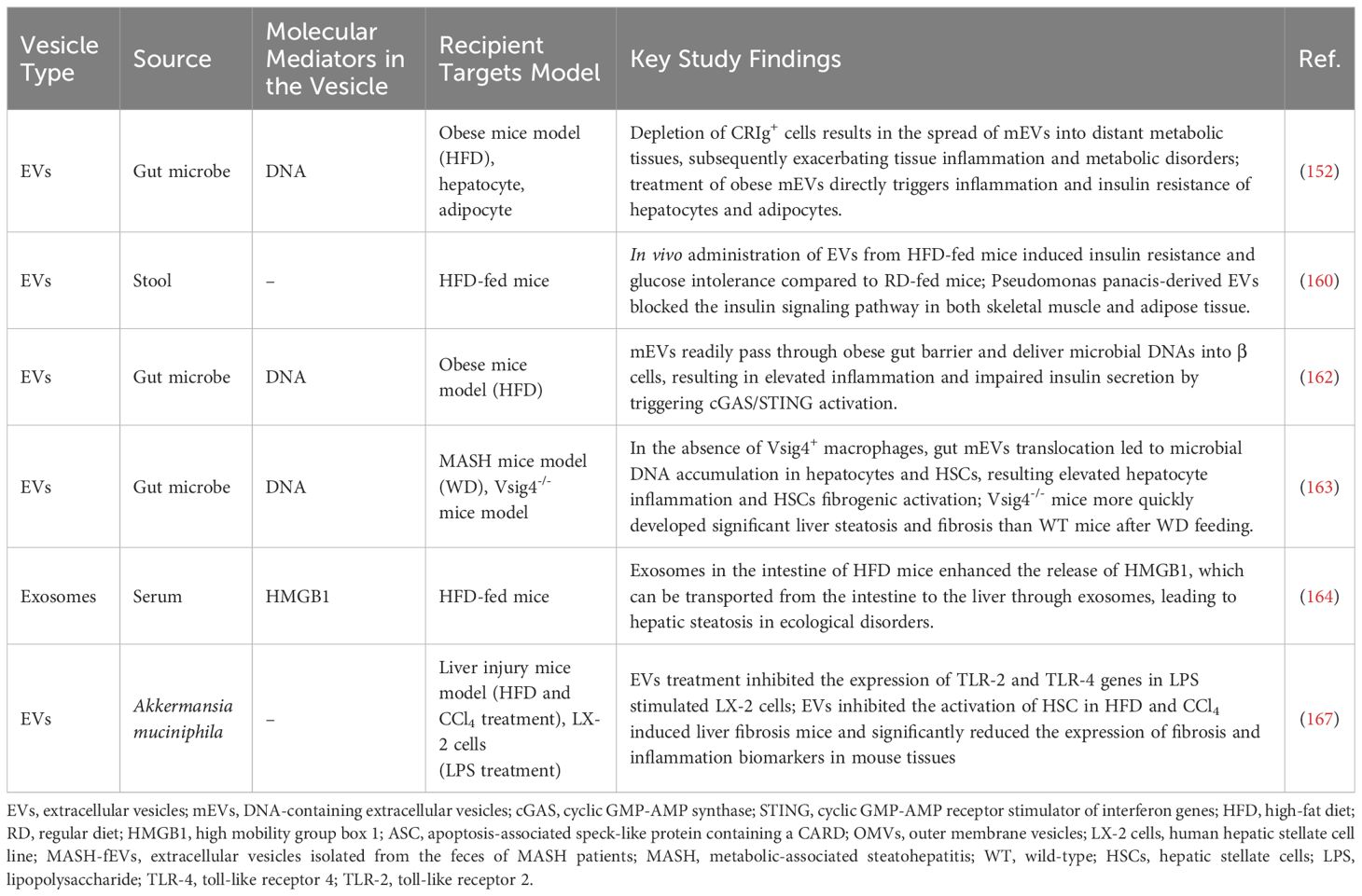
Microbial-derived EVs as therapeutic targets for MAFLD
Emerging evidence underscores the critical role of intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in the development of metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and MAFLD (146, 147). As these diseases progress, disruption of the intestinal barrier often facilitates the translocation of microbial metabolites into the bloodstream, affecting distant organs (146, 148). Besides metabolites, microbial DNA is also found to be enriched in the circulation and linked to metabolic disorders and tissue inflammation in obese individuals and animal models (149–151). Research demonstrated that the bacterial DNA originates from their EVs (152). mEVs were first identified by Work et al. in 1966 in Escherichia coli (153). Subsequent studies observed the production and release of mEVs from a diverse range of microbial species in the host circulation (154, 155). mEVs are generated from the outer membrane of bacteria and play a significant role in host-microbe communication (156). They perform various functions in host interactions, including transporting virulence factors that enhance pathogenicity and facilitate immune evasion, transferring DNA to influence host gene expression, carrying nutrient-related proteins for resource acquisition in nutrient-limited environments, facilitating intra- and interspecies communication among bacteria, and enabling rapid membrane remodeling for environmental adaptation (157). Furthermore, mEVs and host cell-derived EVs exhibit distinct surface markers (157, 158). Host-derived EVs are characterized by specific markers such as CD63, CD81, and CD9, while mEVs contain unique outer membrane proteins, including OprO, OprF, and OprB (157, 158). During the onset of metabolic diseases, impaired intestinal barrier facilitates the leakage of mEVs into the circulation, allowing them to communicate with target organs of the host (159–161). Recent research indicates a link between mEVs and MAFLD, suggesting their potential as therapeutic targets for MAFLD (as summarized in Table 6). Intestinal mEVs derived from HFD-fed mice, particularly those originating from Pseudomonas panacis, could readily cross the intestinal barrier and be taken up by insulin-responsive tissues such as the liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle, disrupting insulin signaling and inducing insulin resistance (160). mEVs from MAFLD mice can also deliver microbial DNA to pancreatic β cells, hepatocytes, and HSCs, leading to impaired insulin secretion, enhanced hepatic inflammation, and exacerbation of liver fibrosis through the activation of the cGAS/STING pathway (152, 162, 163). The clearance of microbials and mEVs from circulation relies on the V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4 positive (Vsig4+) or Complement receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily positive (CRIg+) macrophages in the liver through a C3-dependent opsonization mechanism (152, 162, 163). However, the proportion of these cell populations decreases during the development of MAFLD/MASH, leading to microbial DNA accumulation and subsequent detrimental effects in target cells (152, 162, 163).
In HFD-induced MAFLD mouse models with disrupted gut microbiota, levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) are significantly elevated in the intestinal tissue, enabling its transfer via mEVs from the compromised intestinal barrier to the liver, where it activates Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4), ultimately resulting in hepatic inflammation and liver dysfunction (164, 165). However, treatment of LPS-stimulated HSCs with both live and pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila, a symbiotic bacterium that colonizes the intestinal mucosa and improves intestinal health and metabolic status (166), along with its EVs, significantly reduced the expression of TLR-2 and TLR-4 genes, and ameliorated liver inflammation and fibrosis, with EVs showing the most effective recovery of HSCs (167). This research highlights a novel approach to treating liver inflammation and fibrosis using EVs from specific probiotics.
In summary, MAFLD is characterized by compromised intestinal barrier and a significant reduction in the population of Vsig4+ and CRIg+ macrophages, which allows mEVs to transport bacterial DNA or pro-inflammatory cytokines to distant target cells, including hepatocytes, HSCs, adipocytes, pancreatic β cells, and skeletal muscle cells, thereby leading to insulin resistance, liver inflammation and dysfunction. Notably, certain probiotic-derived mEVs exhibit protective effects against this condition. Therefore, mEVs present promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of MAFLD (as summarized in Figure 5).
Conclusions and future perspectives
As an important part of nanomedicines, EVs transport a diverse array of cellular cargo, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which could be internalized by target cells. This internalization facilitates the transfer of bioinformation that reflects the condition of the donor cell to the recipient cell, occurring in both healthy and pathological contexts, such as liver disease. Recent review articles have emphasized the critical roles of EVs in the pathogenesis of MAFLD and MASH (168–172), underscoring their potential as biomarkers (168, 171–173), therapeutic targets (170), and innovative treatment strategies (168, 171, 172). Lu et al. summarized the contribution of EVs to the pathogenesis of alcoholic fatty liver disease and MAFLD (169). Jiang et al. explored the mechanistic pathways through which EVs influence various biological processes, such as metabolic dysregulation, immune dysfunction, gut microbial imbalances, and fibrotic progression in MAFLD, highlighting their promise as non-invasive biomarkers and therapeutic modalities (168). Wang et al. examined the role of EVs in MASH pathogenesis, providing evidence for the therapeutic potential of stem cell-derived EVs and their use as clinical biomarkers for diagnosis, staging, and prognosis (171). Zhu et al. focused on the biological functions and underlying mechanisms of EVs in fibrotic diseases, further delineating their role as both biomarkers and therapeutic agents (172). Garcia et al. proposed a strategy to identify EV surface proteins as diagnostic biomarkers for MAFLD (173). Wu et al. discussed the origin, characteristics, cargo, and functional roles of EVs within the context of MAFLD, emphasizing their potential as novel therapeutic targets (170). This review is the first to comprehensively explore the diverse functions of EVs from hosts, plants, and microbes in MAFLD, offering a detailed synthesis of current evidence. Notably, we underscored the substantial potential of host-derived EVs as non-invasive biomarkers, therapeutic agents, therapeutic targets, and drug delivery systems for MAFLD. Additionally, we discussed the emerging therapeutic applications of plant-derived EVs in MAFLD prevention and treatment, as well as the promise of microbiota-derived EVs as an innovative therapeutic approach for MAFLD. Mechanistically, host-derived EVs influence the progression of MAFLD by mediating intercellular communication through bioactive molecules carried from the parental cells under disease conditions. Therefore, targeting these EVs presents a potential strategy for intervening in disease progression. EVs derived from MSCs and immune cells can also facilitate intercellular communication through their cargo, primarily alleviating MAFLD by modulating lipid metabolism, reducing inflammation, and mitigating fibrosis. Plant-derived EVs not only alleviate hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation but also reduce MAFLD severity by enhancing intestinal barrier function. Furthermore, microbial-derived EVs contribute to the progression of MAFLD by inducing insulin resistance, liver inflammation, and liver dysfunction. EVs derived from these three distinct sources exert their effects on MAFLD through different mechanisms, which may be attributed to differences in their composition, including both the cargo and surface markers. The physiological and pathological states of the originating cells may also influence the content and biomarkers of the EVs produced (158). Given the variation in the expression of cell surface receptors by EVs, their effects on recipient cells may also differ (158). Furthermore, this heterogeneity may be influenced by the originating organ or tissue of the EVs (174). For example, host-derived EVs are characterized by molecular markers such as CD63, CD81, and CD9 (158), whereas microbial-derived EVs contain unique outer membrane proteins such as OprO, OprF, and OprB (157).
Despite the growing interest in EVs as biomarkers and therapeutic agents, their clinical application remains challenging due to several key limitations. First, current methods for EV isolation, capture, and analysis are not standardized, making it difficult to ensure the purity, activity, and stability of EVs across different cell types (175, 176). There is a critical need for protocols that adhere to good manufacturing practices to ensure product quality and cost-efficiency, as existing methods can be time-consuming or expensive (177). Another issue concerns the low delivery efficiency of the produced EVs. For instance, intravenously injected EVs are prone to clearance by the mononuclear phagocyte system (42), which calls for the development of liver-targeting strategies, such as integrin modification. Safety is another concern, particularly regarding the immunogenicity of microbial-derived EVs, which may activate TLR pathways and require thorough safety evaluations. Furthermore, regulatory hurdles persist, as there is no standardized process for EV production or clear guidelines for assessing their safety (42, 178). Given these challenges, improved collaboration is needed between EV researchers, nanomedicine experts, regulatory bodies, and clinical institutions to advance the clinical translation of EVs. Due to challenges such as the purity of isolated EVs, production scalability, and targeted delivery, the lack of clinical trials remains a significant limitation in the application of EVs. Nonetheless, the body of related research is continuously growing, providing a foundation for the future clinical application of EVs in MAFLD management.
Author contributions
JF: Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – original draft. SB: Writing – original draft. QA: Writing – original draft. CL: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.82060829 and No. 82204759), the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (23JRRA1720), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (No. JCYJ20240813113239051), and the Common University Innovation Team Project of Guangdong (Grant No. 2021KCXTD041).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers who participated in the review and AJEditor (https://china.aje.com/) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript, and the Scientific Image and Illustration Software Biorender (https://www.biorender.com/) in figure preparation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
Akr1b7: Aldo-keto-reductase 1B7
APOE: Apolipoprotein E
ASGR1: Asialoglycoprotein Receptor 1
Atg5: Autophagy-related 5
BELNs: Blueberry-derived exosomes-like nanoparticles
BAT: Brown Adipose Tissue
CAMKK1: Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase 1
CCN2: Cell Communication Network Factor 2
CDAA: Choline Deficient Amino Acid
DNMT1: DNA Methyltransferase 1
ECM: Extracellular Matrix
ELVs: Exosome-Like Vesicles
EPCs: Endothelial Progenitor Cells
ERS: Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
EVs: Extracellular Vesicles
FAS: Fatty Acid Synthase
FFA: Free Fatty Acid
FFC: Fat, Fructose, and Cholesterol
FTO: Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene
GDE: Garlic-Derived Exosomes
GLUT1: Glucose Transporter 1
G6Pc: Glucose-6-Phosphatase
HCC: Hepatocellular Carcinoma
HDAC2: Histone Deacetylase 2
HFD: High Fat Diet
hAMSCs: Human Amnion Mesenchymal Stem Cells
hESC-MSCs: Human Embryonic Stem Cell-derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal cells
hADSCs: Human Adipose Tissue-derived Stem Cells
hBM-MSCs: Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells
hLSC: Human Liver Stem Cell
HMGB1: High-Mobility Group Box 1
HSC: Hepatic Stellate Cell
hUC-MSCs: human Umbilical Cord MSCs
IGF-BP ALS: Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein Complex Acid Labile Subunit
IL-1β: Interleukin-1β
IL6Ra: IL-6 receptor A
iNKT: invariant Natural Killer T
ITGβ1: Integrin β1
KCs: Kupffer Cells
LDLR: Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor
LPC: Lipopolysaccharide
LPS: Lysophosphatidylcholine
MAFLD: Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
MCD: Methionine-Choline Deficient
MCP-1: Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1
MMP: Matrix Metalloproteinase
MPs: Microparticles
MPC2: Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier 2
MSCs: Mesenchymal Stem Cells
NAFLD: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
MAS: MAFLD Activity Score
MASH: Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis
PA: Palmitic Acid
pan PPAR: pan Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor
PE: Phosphatidylethanolamine
PEPCK: Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase
PMHs: Primary Mouse Hepatocytes
PPAR-α: Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor α
ROCK1: Rho Associated Coiled-Coil Containing Protein Kinase 1
ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species
SAAT: Subcutaneous Abdominal Adipose Tissue
SGLT2I: Sodium Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitor
SREBP-1c: Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein-1C
S1P: Sphingosine 1-Phosphate
TAZ: Transcriptional Activation with PDZ-binding Motif
TRAIL: Tumor Necrosis Factor Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand
T2DM: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
T2D: Type 2 Diabetes
UCP1: Uncoupling Protein 1
Vanin 1: Vascular Non-Inflammatory Molecule-1
VAT: Visceral Adipose Tissue
WAT: White Adipose Tissue
References
1. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, Paik JM, Henry A, Van Dongen C, Henry L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology. (2023) 77:1335–47. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000004
2. Maurice J, Manousou P. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Med (Lond). (2018) 18:245–50. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.18-3-245
3. Song SJ, Lai JC, Wong GL, Wong VW, Yip TC. Can we use old NAFLD data under the new MASLD definition? J Hepatol. (2023) 80:e54–e56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.07.021
4. Singh S, Allen AM, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, Murad MH, Loomba R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2015) 13:643–654.e641-649, quiz e639-640. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.04.014
5. Powell EE, Wong VW, Rinella M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Lancet. (2021) 397:2212–24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32511-3
6. Watt MJ, Miotto PM, De Nardo W, Montgomery MK. The liver as an endocrine organ-linking NAFLD and insulin resistance. Endocr Rev. (2019) 40:1367–93. doi: 10.1210/er.2019-00034
7. Haas JT, Francque S, Staels B. Pathophysiology and mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annu Rev Physiol. (2016) 78:181–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105331
8. Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. (2018) 24:908–22. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9
9. Sanyal AJ. Past, present and future perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:377–86. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0144-8
10. Lefere S, Tacke F. Macrophages in obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Crosstalk with metabolism. JHEP Rep. (2019) 1:30–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2019.02.004
11. Wree A, Broderick L, Canbay A, Hoffman HM, Feldstein AE. From NAFLD to NASH to cirrhosis-new insights into disease mechanisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2013) 10:627–36. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.149
12. Chalasani N, Guo X, Loomba R, Goodarzi MO, Haritunians T, Kwon S, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants associated with histologic features of nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2010) 139:1567–1576, 1576.e1561-1566. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.07.057
13. Xu X, Poulsen KL, Wu L, Liu S, Miyata T, Song Q, et al. Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:287. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01119-3
14. Chen J, Vitetta L. Gut microbiota metabolites in NAFLD pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5214. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155214
15. Habibullah M, Jemmieh K, Ouda A, Haider MZ, Malki MI, Elzouki AN. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a selective review of pathogenesis, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1291501. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1291501
16. Loomba R, Friedman SL, Shulman GI. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell. (2021) 184:2537–64. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.015
17. European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. (2016) 64:1388–402. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.004
18. Younossi ZM, Corey KE, Lim JK. AGA clinical practice update on lifestyle modification using diet and exercise to achieve weight loss in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: expert review. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:912–8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.051
19. Xiao Y, Zhang X, Yi D, Qiu F, Wu L, Tang Y, et al. Mediterranean diet affects the metabolic outcome of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Front Nutr. (2023) 10:1225946. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1225946
20. Sun J, Jin X, Li Y. Current strategies for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease treatment (Review). Int J Mol Med. (2024) 54. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5412
21. Lonardo A, Mantovani A, Petta S, Carraro A, Byrne CD, Targher G. Metabolic mechanisms for and treatment of NAFLD or NASH occurring after liver transplantation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2022) 18:638–50. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00711-5
22. Mantovani A, Byrne CD, Targher G. Efficacy of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 7:367–78. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00261-2
23. Dai Y, He H, Li S, Yang L, Wang X, Liu Z, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:622589. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.622589
24. Raj H, Durgia H, Palui R, Kamalanathan S, Selvarajan S, Kar SS, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. World J Diabetes. (2019) 10:114–32. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i2.114
25. Ledford H. First US drug approved for a liver disease surging around the world. Nature. (2024). doi: 10.1038/d41586-024-00747-9
26. Suvarna R, Shetty S, Pappachan JM. Efficacy and safety of Resmetirom, a selective thyroid hormone receptor-β agonist, in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:19790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70242-8
27. Sanyal AJ, Shankar SS, Calle RA, Samir AE, Sirlin CB, Sherlock SP, et al. Non-invasive biomarkers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: the FNIH NIMBLE project. Nat Med. (2022) 28:430–2. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01652-8
28. Wong VW, Adams LA, de Lédinghen V, Wong GL, Sookoian S. Noninvasive biomarkers in NAFLD and NASH - current progress and future promise. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 15:461–78. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0014-9
29. Castagneto-Gissey L, Bornstein SR, Mingrone G. Can liquid biopsies for MASH help increase the penetration of metabolic surgery? A narrative review. Metabolism. (2024) 151:155721. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155721
30. Ugonabo O, Udoh US, Rajan PK, Reeves H, Arcand C, Nakafuku Y, et al. The current status of the liver liquid biopsy in MASH related HCC: overview and future directions. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:1369. doi: 10.3390/biom13091369
31. Yáñez-Mó M, Siljander PR, Andreu Z, Zavec AB, Borràs FE, Buzas EI, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. (2015) 4:27066. doi: 10.3402/jev.v4.27066
32. Yang Q, Liu J, Wu B, Wang X, Jiang Y, Zhu D. Role of extracellular vesicles in osteosarcoma. Int J Med Sci. (2022) 19:1216–26. doi: 10.7150/ijms.74137
33. Zijlstra A, Di Vizio D. Size matters in nanoscale communication. Nat Cell Biol. (2018) 20:228–30. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0049-8
34. Ostenfeld MS, Jeppesen DK, Laurberg JR, Boysen AT, Bramsen JB, Primdal-Bengtson B, et al. Cellular disposal of miR23b by RAB27-dependent exosome release is linked to acquisition of metastatic properties. Cancer Res. (2014) 74:5758–71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3512
35. Pan BT, Teng K, Wu C, Adam M, Johnstone RM. Electron microscopic evidence for externalization of the transferrin receptor in vesicular form in sheep reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. (1985) 101:942–8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.942
36. van Niel G, Carter DRF, Clayton A, Lambert DW, Raposo G, Vader P. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 23:369–82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00460-3
37. Fujita Y, Yoshioka Y, Ochiya T. Extracellular vesicle transfer of cancer pathogenic components. Cancer Sci. (2016) 107:385–90. doi: 10.1111/cas.2016.107.issue-4
38. Yates AG, Pink RC, Erdbrügger U, Siljander PR, Dellar ER, Pantazi P, et al. In sickness and in health: The functional role of extracellular vesicles in physiology and pathology in vivo: Part I: Health and Normal Physiology: Part I: Health and Normal Physiology. J Extracell Vesicles. (2022) 11:e12151. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12151
39. Roefs MT, Sluijter JPG, Vader P. Extracellular vesicle-associated proteins in tissue repair. Trends Cell Biol. (2020) 30:990–1013. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.09.009
40. Yates AG, Pink RC, Erdbrügger U, Siljander PR, Dellar ER, Pantazi P, et al. In sickness and in health: The functional role of extracellular vesicles in physiology and pathology in vivo: Part II: Pathology: Part II: Pathology. J Extracell Vesicles. (2022) 11:e12190. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12190
41. Ipsen DH, Tveden-Nyborg P. Extracellular vesicles as drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: small particles with big impact. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:93. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9010093
42. Buschmann D, Mussack V, Byrd JB. Separation, characterization, and standardization of extracellular vesicles for drug delivery applications. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. (2021) 174:348–68. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.04.027
43. Kumar MA, Baba SK, Sadida HQ, Marzooqi SA, Jerobin J, Altemani FH, et al. Extracellular vesicles as tools and targets in therapy for diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:27. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01735-1
44. De Sousa KP, Rossi I, Abdullahi M, Ramirez MI, Stratton D, Inal JM. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles and future directions in diagnosis and therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. (2023) 15:e1835. doi: 10.1002/wnan.v15.1
45. Du S, Guan Y, Xie A, Yan Z, Gao S, Li W, et al. Extracellular vesicles: a rising star for therapeutics and drug delivery. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:231. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01973-5
46. Szabo G, Momen-Heravi F. Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 14:455–66. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.71
47. Hirsova P, Ibrahim SH, Verma VK, Morton LA, Shah VH, LaRusso NF, et al. Extracellular vesicles in liver pathobiology: Small particles with big impact. Hepatology. (2016) 64:2219–33. doi: 10.1002/hep.28814
48. Kakazu E, Mauer AS, Yin M, Malhi H. Hepatocytes release ceramide-enriched pro-inflammatory extracellular vesicles in an IRE1α-dependent manner. J Lipid Res. (2016) 57:233–45. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M063412
49. Li J, Liu H, Mauer AS, Lucien F, Raiter A, Bandla H, et al. Characterization of cellular sources and circulating levels of extracellular vesicles in a dietary murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol Commun. (2019) 3:1235–49. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1404
50. Kornek M, Lynch M, Mehta SH, Lai M, Exley M, Afdhal NH, et al. Circulating microparticles as disease-specific biomarkers of severity of inflammation in patients with hepatitis C or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2012) 143:448–58. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.031
51. Maas SLN, Breakefield XO, Weaver AM. Extracellular vesicles: unique intercellular delivery vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. (2017) 27:172–88. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2016.11.003
52. Goetzl EJ, Mustapic M, Kapogiannis D, Eitan E, Lobach IV, Goetzl L, et al. Cargo proteins of plasma astrocyte-derived exosomes in Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. (2016) 30:3853–9. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600756R
53. Nakao Y, Amrollahi P, Parthasarathy G, Mauer AS, Sehrawat TS, Vanderboom P, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles are a biomarker for NAFLD resolution and response to weight loss surgery. Nanomedicine. (2021) 36:102430. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2021.102430
54. Nakao Y, Fukushima M, Mauer AS, Liao CY, Ferris A, Dasgupta D, et al. A comparative proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles associated with lipotoxicity. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:735001. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.735001
55. Scavo MP, Depalo N, Rizzi F, Carrieri L, Serino G, Franco I, et al. Exosomal FZD-7 expression is modulated by different lifestyle interventions in patients with NAFLD. Nutrients. (2022) 14:1133. doi: 10.3390/nu14061133
56. Muñoz-Hernández R, Gato S, Gil-Gómez A, Aller R, Rojas A, Morán L, et al. Role of EpCAM+ CD133+ extracellular vesicles in steatosis to steatohepatitis transition in NAFLD. Liver Int. (2023) 43:1909–19. doi: 10.1111/liv.15604
57. Povero D, Yamashita H, Ren W, Subramanian MG, Myers RP, Eguchi A, et al. Characterization and proteome of circulating extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers for NASH. Hepatol Commun. (2020) 4:1263–78. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1556
58. Zhang W, Zhang J, Shi H, Liu F, Yu H, Shi H. Exosome GLUT1 derived from hepatocyte identifies the risk of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Hepatol Int. (2023) 17:1170–81. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10520-1
59. Povero D, Eguchi A, Li H, Johnson CD, PapouChado BG, Wree A, et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles with specific proteome and liver microRNAs are potential biomarkers for liver injury in experimental fatty liver disease. PloS One. (2014) 9:e113651. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113651
60. Newman LA, Useckaite Z, Johnson J, Sorich MJ, Hopkins AM, Rowland A. Selective isolation of liver-derived extracellular vesicles redefines performance of miRNA biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomedicines. (2022) 10:195. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010195
61. Akuta N, Kawamura Y, Watanabe C, Nishimura A, Okubo M, Mori Y, et al. Impact of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor on histological features and glucose metabolism of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease complicated by diabetes mellitus. Hepatol Res. (2019) 49:531–9. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13304
62. Castaño C, Novials A, Párrizas M. Exosomes from short-term high-fat or high-sucrose fed mice induce hepatic steatosis through different pathways. Cells. (2022) 12:169. doi: 10.3390/cells12010169
63. Zhang JW, Pan HT. microRNA profiles of serum exosomes derived from children with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Genes Genomics. (2022) 44:879–88. doi: 10.1007/s13258-021-01150-8
64. Zhou X, Huang K, Jia J, Ni Y, Yuan J, Liang X, et al. Exosomal miRNAs profile in children's nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the correlation with transaminase and uric acid. Ann Nutr Metab. (2020) 76:44–53. doi: 10.1159/000506665
65. Muhammad Yusuf AN, Raja Ali RA, Muhammad Nawawi KN, Mokhtar NM. Potential biomarkers in NASH-induced liver cirrhosis with hepatocellular carcinoma: A preliminary work on roles of exosomal miR-182, miR-301a, and miR-373. Malays J Pathol. (2020) 42:377–84.
66. Zhu Q, Li H, Ao Z, Xu H, Luo J, Kaurich C, et al. Lipidomic identification of urinary extracellular vesicles for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis diagnosis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2022) 20:349. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01540-4
67. Bacakova L, Zarubova J, Travnickova M, Musilkova J, Pajorova J, Slepicka P, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - a review. Biotechnol Adv. (2018) 36:1111–26. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.03.011
68. Zhidu S, Ying T, Rui J, Chao Z. Translational potential of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative therapies for human diseases: challenges and opportunities. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2024) 15:266. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03885-z
69. Hoang DM, Pham PT, Bach TQ, Ngo ATL, Nguyen QT, Phan TTK, et al. Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:272. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01134-4
70. Jarrige M, Frank E, Herardot E, Martineau S, Darle A, Benabides M, et al. The future of regenerative medicine: cell therapy using pluripotent stem cells and acellular therapies based on extracellular vesicles. Cells. (2021) 10:240. doi: 10.3390/cells10020240
71. Alqurashi H, Ortega Asencio I, Lambert DW. The emerging potential of extracellular vesicles in cell-free tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. (2021) 27:530–8. doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2020.0222
72. Cheng L, Yu P, Li F, Jiang X, Jiao X, Shen Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell-exosomal miR-627-5p ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by repressing FTO expression. Hum Cell. (2021) 34:1697–708. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00593-1
73. Yang F, Wu Y, Chen Y, Xi J, Chu Y, Jin J, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate liver steatosis by promoting fatty acid oxidation and reducing fatty acid synthesis. JHEP Rep. (2023) 5:100746. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100746
74. Liang C, Gao S, Gao J, Xu Y, Li Q. Comparison of effects of HucMSCs, exosomes, and conditioned medium on NASH. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:18431. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45828-3
75. Kang Y, Song Y, Luo Y, Song J, Li C, Yang S, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via Nrf2/NQO-1 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 192:25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.037
76. Shi Y, Yang X, Wang S, Wu Y, Zheng L, Tang Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes protect against MCD-induced NASH in a mouse model. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13:517. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03201-7
77. Ohara M, Ohnishi S, Hosono H, Yamamoto K, Yuyama K, Nakamura H, et al. Extracellular vesicles from amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Stem Cells Int. (2018) 2018:3212643. doi: 10.1155/2018/3212643
78. Zhang B, Zhang B, Lai RC, Sim WK, Lam KP, Lim SK. MSC-sEV treatment polarizes pro-fibrotic M2 macrophages without exacerbating liver fibrosis in NASH. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8092. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098092
79. El-Derany MO, AbdelHamid SG. Upregulation of miR-96-5p by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes alleviate non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Emphasis on caspase-2 signaling inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. (2021) 190:114624. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114624
80. Watanabe T, Tsuchiya A, Takeuchi S, Nojiri S, Yoshida T, Ogawa M, et al. Development of a non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model with rapid accumulation of fibrosis, and its treatment using mesenchymal stem cells and their small extracellular vesicles. Regener Ther. (2020) 14:252–61. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2020.03.012
81. Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, Bai Y, Li Z, Zhang H, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and beiging in white adipose tissue. Diabetes. (2018) 67:235–47. doi: 10.2337/db17-0356
82. Bruno S, Pasquino C, Herrera Sanchez MB, Tapparo M, Figliolini F, Grange C, et al. HLSC-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate liver fibrosis and inflammation in a murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol Ther. (2020) 28:479–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.10.016
83. Venkat P, Gao H, Findeis EL, Chen Z, Zacharek A, Landschoot-Ward J, et al. Therapeutic effects of CD133 + Exosomes on liver function after stroke in type 2 diabetic mice. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1061485. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1061485
84. Wan Z, Yang X, Liu X, Sun Y, Yu P, Xu F, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-411-5p impedes the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting CAMSAP1 in NASH model. iScience. (2022) 25:104597. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104597
85. Gao H, Jin Z, Bandyopadhyay G, Cunha ERK, Liu X, Zhao H, et al. MiR-690 treatment causes decreased fibrosis and steatosis and restores specific Kupffer cell functions in NASH. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:978–990.e974. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.05.008
86. He Y, Rodrigues RM, Wang X, Seo W, Ma J, Hwang S, et al. Neutrophil-to-hepatocyte communication via LDLR-dependent miR-223-enriched extracellular vesicle transfer ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:e141513. doi: 10.1172/JCI141513
87. Hou X, Yin S, Ren R, Liu S, Yong L, Liu Y, et al. Myeloid-cell-specific IL-6 signaling promotes microRNA-223-enriched exosome production to attenuate NAFLD-associated fibrosis. Hepatology. (2021) 74:116–32. doi: 10.1002/hep.31658
88. Ding J, Xu M, Du W, Fang ZQ, Xu H, Liu JJ, et al. Myeloid-specific blockade of Notch signaling ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:1941–54. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.80122
89. Kim J, Lee SK, Jeong SY, Cho HJ, Park J, Kim TM, et al. Cargo proteins in extracellular vesicles: potential for novel therapeutics in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2021) 19:372. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01120-y
90. Zhang WJ, Li KY, Huang BH, Wang H, Wan SG, Zhou SC. The hepatocyte in the innate immunity. Virology. (2022) 576:111–6. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2022.09.011
91. Xu Y, Zhu Y, Hu S, Pan X, Bawa FC, Wang HH, et al. Hepatocyte miR-34a is a key regulator in the development and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Metab. (2021) 51:101244. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101244
92. Liu XL, Pan Q, Cao HX, Xin FZ, Zhao ZH, Yang RX, et al. Lipotoxic hepatocyte-derived exosomal microRNA 192-5p activates macrophages through rictor/akt/forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. (2020) 72:454–69. doi: 10.1002/hep.31050
93. Zhao Z, Zhong L, Li P, He K, Qiu C, Zhao L, et al. Cholesterol impairs hepatocyte lysosomal function causing M1 polarization of macrophages via exosomal miR-122-5p. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 387:111738. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111738
94. Dasgupta D, Nakao Y, Mauer AS, Thompson JM, Sehrawat TS, Liao CY, et al. IRE1A stimulates hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles that promote inflammation in mice with steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 159:1487–1503.e1417. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.031
95. Liao CY, Song MJ, Gao Y, Mauer AS, Revzin A, Malhi H. Hepatocyte-derived lipotoxic extracellular vesicle sphingosine 1-phosphate induces macrophage chemotaxis. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2980. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02980
96. Mauer AS, Hirsova P, Maiers JL, Shah VH, Malhi H. Inhibition of sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling ameliorates murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2017) 312:G300–g313. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00222.2016
97. Ibrahim SH, Hirsova P, Tomita K, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW, Harrison SA, et al. Mixed lineage kinase 3 mediates release of C-X-C motif ligand 10-bearing chemotactic extracellular vesicles from lipotoxic hepatocytes. Hepatology. (2016) 63:731–44. doi: 10.1002/hep.28252
98. Tomita K, Freeman BL, Bronk SF, LeBrasseur NK, White TA, Hirsova P, et al. CXCL10-Mediates Macrophage, but not Other Innate Immune Cells-Associated Inflammation in Murine Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:28786. doi: 10.1038/srep28786
99. Hirsova P, Ibrahim SH, Krishnan A, Verma VK, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW, et al. Lipid-induced signaling causes release of inflammatory extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:956–67. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.12.037
100. Zhang S, Peng X, Yang S, Li X, Huang M, Wei S, et al. The regulation, function, and role of lipophagy, a form of selective autophagy, in metabolic disorders. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:132. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04593-3
101. Shen Y, Malik SA, Amir M, Kumar P, Cingolani F, Wen J, et al. Decreased hepatocyte autophagy leads to synergistic IL-1β and TNF mouse liver injury and inflammation. Hepatology. (2020) 72:595–608. doi: 10.1002/hep.31209
102. Li X, Chen R, Kemper S, Brigstock DR. Production, exacerbating effect, and EV-mediated transcription of hepatic CCN2 in NASH: implications for diagnosis and therapy of NASH fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12823. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612823
103. Povero D, Panera N, Eguchi A, Johnson CD, PapouChado BG, de Araujo Horcel L, et al. Lipid-induced hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles regulate hepatic stellate cell via microRNAs targeting PPAR-γ. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2015) 1:646–663.e644. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.07.007
104. Lee YS, Kim SY, Ko E, Lee JH, Yi HS, Yoo YJ, et al. Exosomes derived from palmitic acid-treated hepatocytes induce fibrotic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:3710. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03389-2
105. Luo X, Xu ZX, Wu JC, Luo SZ, Xu MY. Hepatocyte-derived exosomal miR-27a activates hepatic stellate cells through the inhibition of PINK1-mediated mitophagy in MAFLD. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2021) 26:1241–54. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.022
106. Hernández A, Reyes D, Geng Y, Arab JP, Cabrera D, Sepulveda R, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from fat-laden hepatocytes undergoing chemical hypoxia promote a pro-fibrotic phenotype in hepatic stellate cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2020) 1866:165857. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165857
107. Guo Q, Furuta K, Lucien F, Gutierrez Sanchez LH, Hirsova P, Krishnan A, et al. Integrin β(1)-enriched extracellular vesicles mediate monocyte adhesion and promote liver inflammation in murine NASH. J Hepatol. (2019) 71:1193–205. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.07.019
108. Kim SH, Kim G, Han DH, Lee M, Kim I, Kim B, et al. Ezetimibe ameliorates steatohepatitis via AMP activated protein kinase-TFEB-mediated activation of autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Autophagy. (2017) 13:1767–81. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1356977
109. Hwang S, He Y, Xiang X, Seo W, Kim SJ, Ma J, et al. Interleukin-22 ameliorates neutrophil-driven nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through multiple targets. Hepatology. (2020) 72:412–29. doi: 10.1002/hep.31031
110. Zhang H, Ma Y, Cheng X, Wu D, Huang X, Chen B, et al. Targeting epigenetically maladapted vascular niche alleviates liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13:eabd1206. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd1206
111. Wang J, Ortiz C, Fontenot L, Mukhopadhyay R, Xie Y, Law IKM, et al. Elafin inhibits obesity, hyperglycemia, and liver steatosis in high-fat diet-treated male mice. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:12785. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69634-3
112. McCommis KS, Hodges WT, Brunt EM, Nalbantoglu I, McDonald WG, Holley C, et al. Targeting the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier attenuates fibrosis in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. (2017) 65:1543–56. doi: 10.1002/hep.29025
113. Li M, Chi X, Wang Y, Setrerrahmane S, Xie W, Xu H. Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:216. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01073-0
114. Gutiérrez-Cuevas J, Santos A, Armendariz-Borunda J. Pathophysiological molecular mechanisms of obesity: A link between MAFLD and NASH with cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:11629. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111629
115. Fuchs A, Samovski D, Smith GI, Cifarelli V, Farabi SS, Yoshino J, et al. Associations among adipose tissue immunology, inflammation, exosomes and insulin sensitivity in people with obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2021) 161:968–981.e912. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.05.008
116. Kranendonk ME, Visseren FL, van Herwaarden JA, Nolte-'t-Hoen EN, de Jager W, Wauben MH, et al. Effect of extracellular vesicles of human adipose tissue on insulin signaling in liver and muscle cells. Obes (Silver Spring). (2014) 22:2216–23. doi: 10.1002/oby.20847
117. Deng ZB, Poliakov A, Hardy RW, Clements R, Liu C, Liu Y, et al. Adipose tissue exosome-like vesicles mediate activation of macrophage-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes. (2009) 58:2498–505. doi: 10.2337/db09-0216
118. Lin A, He W. LINC01705 derived from adipocyte exosomes regulates hepatocyte lipid accumulation via an miR-552-3p/LXR axis. J Diabetes Investig. (2023) 14:1160–71. doi: 10.1111/jdi.v14.10
119. Lu MM, Ren Y, Zhou YW, Xu LL, Zhang MM, Ding LP, et al. Antagonizing adipose tissue-derived exosome miR-103-hepatocyte phosphatase and tensin homolog pathway alleviates autophagy in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A trans-cellular crosstalk. World J Gastroenterol. (2023) 29:4528–41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i29.4528
120. de Mendonça M, Rocha KC, de Sousa É, Pereira BMV, Oyama LM, Rodrigues AC. Aerobic exercise training regulates serum extracellular vesicle miRNAs linked to obesity to promote their beneficial effects in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 319:E579–e591. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00172.2020
121. Volat FE, Pointud JC, Pastel E, Morio B, Sion B, Hamard G, et al. Depressed levels of prostaglandin F2α in mice lacking Akr1b7 increase basal adiposity and predispose to diet-induced obesity. Diabetes. (2012) 61:2796–806. doi: 10.2337/db11-1297
122. Gu H, Yang K, Shen Z, Jia K, Liu P, Pan M, et al. ER stress-induced adipocytes secrete-aldo-keto reductase 1B7-containing exosomes that cause nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. (2021) 163:220–33. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.011
123. Rong B, Feng R, Liu C, Wu Q, Sun C. Reduced delivery of epididymal adipocyte-derived exosomal resistin is essential for melatonin ameliorating hepatic steatosis in mice. J Pineal Res. (2019) 66:e12561. doi: 10.1111/jpi.2019.66.issue-4
124. Koeck ES, Iordanskaia T, Sevilla S, Ferrante SC, Hubal MJ, Freishtat RJ, et al. Adipocyte exosomes induce transforming growth factor beta pathway dysregulation in hepatocytes: a novel paradigm for obesity-related liver disease. J Surg Res. (2014) 192:268–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.06.050
125. Tilg H, Adolph TE, Trauner M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:1700–18. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.09.017
126. Wu J, Wang K, Wang X, Pang Y, Jiang C. The role of the gut microbiome and its metabolites in metabolic diseases. Protein Cell. (2021) 12:360–73. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00814-7
127. Chen P, Stärkel P, Turner JR, Ho SB, Schnabl B. Dysbiosis-induced intestinal inflammation activates tumor necrosis factor receptor I and mediates alcoholic liver disease in mice. Hepatology. (2015) 61:883–94. doi: 10.1002/hep.27489
128. Albillos A, de Gottardi A, Rescigno M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol. (2020) 72:558–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.003
129. Ou Z, Situ B, Huang X, Xue Y, He X, Li Q, et al. Single-particle analysis of circulating bacterial extracellular vesicles reveals their biogenesis, changes in blood and links to intestinal barrier. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12:e12395. doi: 10.1002/jev2.v12.12
130. Fizanne L, Villard A, Benabbou N, Recoquillon S, Soleti R, Delage E, et al. Faeces-derived extracellular vesicles participate in the onset of barrier dysfunction leading to liver diseases. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12:e12303. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12303
131. Kumar A, Sundaram K, Mu J, Dryden GW, Sriwastva MK, Lei C, et al. High-fat diet-induced upregulation of exosomal phosphatidylcholine contributes to insulin resistance. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:213. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20500-w
132. Kornek M, Popov Y, Libermann TA, Afdhal NH, Schuppan D. Human T cell microparticles circulate in blood of hepatitis patients and induce fibrolytic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. (2011) 53:230–42. doi: 10.1002/hep.23999
133. Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y, Birmingham A, Seo JB, et al. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal miRNAs can modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell. (2017) 171:372–384.e312. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.08.035
134. Halperin W, Jensen WA. Ultrastructural changes during growth and embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. J Ultrastruct Res. (1967) 18:428–43. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5320(67)80128-X
135. Lo KJ, Wang MH, Ho CT, Pan MH. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: A new revolutionization of modern healthy diets and biomedical applications. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:2853–78. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c06867
136. Dad HA, Gu TW, Zhu AQ, Huang LQ, Peng LH. Plant exosome-like nanovesicles: emerging therapeutics and drug delivery nanoplatforms. Mol Ther. (2021) 29:13–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.11.030
137. Lian MQ, Chng WH, Liang J, Yeo HQ, Lee CK, Belaid M, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications. J Extracell Vesicles. (2022) 11:e12283. doi: 10.1002/jev2.v11.12
138. Kim J, Li S, Zhang S, Wang J. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. (2022) 17:53–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2021.05.006
139. Zhao WJ, Bian YP, Wang QH, Yin F, Yin L, Zhang YL, et al. Blueberry-derived exosomes-like nanoparticles ameliorate nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by attenuating mitochondrial oxidative stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2022) 43:645–58. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00681-w
140. Liu J, Li W, Bian Y, Jiang X, Zhu F, Yin F, et al. Garlic-derived exosomes regulate PFKFB3 expression to relieve liver dysfunction in high-fat diet-fed mice via macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk. Phytomedicine. (2023) 112:154679. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154679
141. Berger E, Colosetti P, Jalabert A, Meugnier E, Wiklander OPB, Jouhet J, et al. Use of nanovesicles from orange juice to reverse diet-induced gut modifications in diet-induced obese mice. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. (2020) 18:880–92. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.08.009
142. Zhang W, Zhou Y, Fan Y, Cao R, Xu Y, Weng Z, et al. Metal-organic-framework-based hydrogen-release platform for multieffective helicobacter pylori targeting therapy and intestinal flora protective capabilities. Adv Mater. (2022) 34:e2105738. doi: 10.1002/adma.202105738
143. Zhang Y, Tan S, Xu J, Wang T. Hydrogen therapy in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: from bench to bedside. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 47:1–10. doi: 10.1159/000489737
144. Jin Z, Sun Y, Yang T, Tan L, Lv P, Xu Q, et al. Nanocapsule-mediated sustained H(2) release in the gut ameliorates metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Biomaterials. (2021) 276:121030. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121030
145. Wang X, Tian R, Liang C, Jia Y, Zhao L, Xie Q, et al. Biomimetic nanoplatform with microbiome modulation and antioxidant functions ameliorating insulin resistance and pancreatic β-cell dysfunction for T2DM management. Biomaterials. (2024) 313:122804. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122804
146. Fan Y, Pedersen O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2021) 19:55–71. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0433-9
147. de Vos WM, Tilg H, Van Hul M, Cani PD. Gut microbiome and health: mechanistic insights. Gut. (2022) 71:1020–32. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326789
148. Krautkramer KA, Fan J, Bäckhed F. Gut microbial metabolites as multi-kingdom intermediates. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2021) 19:77–94. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0438-4
149. Lelouvier B, Servant F, Païssé S, Brunet AC, Benyahya S, Serino M, et al. Changes in blood microbiota profiles associated with liver fibrosis in obese patients: A pilot analysis. Hepatology. (2016) 64:2015–27. doi: 10.1002/hep.28829
150. Amar J, Chabo C, Waget A, Klopp P, Vachoux C, Bermúdez-Humarán LG, et al. Intestinal mucosal adherence and translocation of commensal bacteria at the early onset of type 2 diabetes: molecular mechanisms and probiotic treatment. EMBO Mol Med. (2011) 3:559–72. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100159
151. Ortiz S, Zapater P, Estrada JL, Enriquez P, Rey M, Abad A, et al. Bacterial DNA translocation holds increased insulin resistance and systemic inflammatory levels in morbid obese patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2014) 99:2575–83. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-4483
152. Luo Z, Ji Y, Gao H, Gomes Dos Reis FC, Bandyopadhyay G, Jin Z, et al. CRIg(+) macrophages prevent gut microbial DNA-containing extracellular vesicle-induced tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:863–74. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.042
153. Work E, Knox KW, Vesk M. The chemistry and electron microscopy of an extracellular lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (1966) 133:438–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52382.x
154. Chelakkot C, Choi Y, Kim DK, Park HT, Ghim J, Kwon Y, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions. Exp Mol Med. (2018) 50:e450. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.282
155. Liu Y, Defourny KAY, Smid EJ, Abee T. Gram-positive bacterial extracellular vesicles and their impact on health and disease. Front Microbiol. (2018) 9:1502. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01502
156. Alberti G, Mazzola M, Gagliardo C, Pitruzzella A, Fucarini A, Giammanco M, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. BioMed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. (2021) 165:233–40. doi: 10.5507/bp.2021.042
157. McMillan HM, Kuehn MJ. The extracellular vesicle generation paradox: a bacterial point of view. EMBO J. (2021) 40:e108174. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108174
158. Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. (2020) 367:eaau6977. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6977
159. Jin X, Yu CH, Lv GC, Li YM. Increased intestinal permeability in pathogenesis and progress of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. (2007) 13:1732–6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i11.1732
160. Choi Y, Kwon Y, Kim DK, Jeon J, Jang SC, Wang T, et al. Gut microbe-derived extracellular vesicles induce insulin resistance, thereby impairing glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:15878. doi: 10.1038/srep15878
161. Pabst O, Hornef MW, Schaap FG, Cerovic V, Clavel T, Bruns T. Gut-liver axis: barriers and functional circuits. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 20:447–61. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00771-6
162. Gao H, Luo Z, Ji Y, Tang K, Jin Z, Ly C, et al. Accumulation of microbial DNAs promotes to islet inflammation and β cell abnormalities in obesity in mice. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:565. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28239-2
163. Luo Z, Ji Y, Zhang D, Gao H, Jin Z, Yang M, et al. Microbial DNA enrichment promotes liver steatosis and fibrosis in the course of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Acta Physiol (Oxf). (2022) 235:e13827. doi: 10.1111/apha.v235.3
164. Chen Y, Sun H, Bai Y, Zhi F. Gut dysbiosis-derived exosomes trigger hepatic steatosis by transiting HMGB1 from intestinal to liver in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 509:767–72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.180
165. Li L, Chen L, Hu L, Liu Y, Sun HY, Tang J, et al. Nuclear factor high-mobility group box1 mediating the activation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in hepatocytes in the early stage of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Hepatology. (2011) 54:1620–30. doi: 10.1002/hep.24552
166. Cani PD, Depommier C, Derrien M, Everard A, de Vos WM. Akkermansia muciniphila: paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 19:625–37. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00631-9
167. Keshavarz Azizi Raftar S, Ashrafian F, Yadegar A, Lari A, Moradi HR, Shahriary A, et al. The Protective Effects of Live and Pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila and Its Extracellular Vesicles against HFD/CCl4-Induced Liver Injury. Microbiol Spectr. (2021) 9:e0048421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00484-21
168. Jiang W, Xu Y, Chen JC, Lee YH, Hu Y, Liu CH, et al. Role of extracellular vesicles in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1196831. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1196831
169. Lu X, Song M, Gao N. Extracellular vesicles and fatty liver. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2023) 1418:129–41. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-1443-2_9
170. Wu Z, Xia M, Salas SS, Trillos-Almanza MC, Aguilar MM, Arroyave-Ospina JC, et al. Extracellular vesicles in metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease: mechanisms, diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Explor Digestive Diseases. (2022) 1:4–20. doi: 10.37349/edd
171. Wang Q, Tang X, Wang Y, Zhang D, Li X, Liu S. The role of extracellular vesicles in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Emerging mechanisms, potential therapeutics and biomarkers. J Adv Res. (2024). doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.03.009
172. Zhu J, Wang S, Yang D, Xu W, Qian H. Extracellular vesicles: emerging roles, biomarkers and therapeutic strategies in fibrotic diseases. J Nanobiotechnology. (2023) 21:164. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01921-3
173. Garcia NA, Mellergaard M, Gonzalez-King H, Salomon C, Handberg A. Comprehensive strategy for identifying extracellular vesicle surface proteins as biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:13326. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713326
174. Wen SW, Lima LG, Lobb RJ, Norris EL, Hastie ML, Krumeich S, et al. Breast cancer-derived exosomes reflect the cell-of-origin phenotype. Proteomics. (2019) 19:e1800180. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201800180
175. Vo N, Tran C, Tran NHB, Nguyen NT, Nguyen T, Ho DTK, et al. A novel multi-stage enrichment workflow and comprehensive characterization for HEK293F-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13:e12454. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12454
176. Miceli RT, Chen TY, Nose Y, Tichkule S, Brown B, Fullard JF, et al. Extracellular vesicles, RNA sequencing, and bioinformatic analyses: Challenges, solutions, and recommendations. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13:e70005. doi: 10.1002/jev2.v13.12
177. Syromiatnikova V, Prokopeva A, Gomzikova M. Methods of the large-scale production of extracellular vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:10522. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810522
Keywords: metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), extracellular vesicles (EVs), host-derived EVs, plant-derived EVs, microbial-derived EVs, biomarkers, therapeutic agents, therapeutic targets
Citation: Wang J, Bao S, An Q, Li C and Feng J (2025) Roles of extracellular vesicles from different origins in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: progress and perspectives. Front. Immunol. 16:1544012. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1544012
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 19 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Dhanu Gupta, Karolinska University Laboratory, SwedenReviewed by:
Divya P. Kumar, JSS Academy of Higher Education and Research, IndiaOleksandr Kamyshnyi, Ternopil State Medical University, Ukraine
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Bao, An, Li and Feng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Feng, fengjuan@sztu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jing Wang1†
Jing Wang1†