- 1Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (DOE), Richland, WA, United States
- 2Khoury College of Computer Sciences, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, United States
- 3Department of Bioengineering, College of Engineering, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, United States
The development of effective vaccines is crucial for combating current and emerging pathogens. Despite significant advances in the field of vaccine development there remain numerous challenges including the lack of standardized data reporting and curation practices, making it difficult to determine correlates of protection from experimental and clinical studies. Significant gaps in data and knowledge integration can hinder vaccine development which relies on a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between pathogens and the host immune system. In this review, we explore the current landscape of vaccine development, highlighting the computational challenges, limitations, and opportunities associated with integrating diverse data types for leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques in vaccine design. We discuss the role of natural language processing, semantic integration, and causal inference in extracting valuable insights from published literature and unstructured data sources, as well as the computational modeling of immune responses. Furthermore, we highlight specific challenges associated with uncertainty quantification in vaccine development and emphasize the importance of establishing standardized data formats and ontologies to facilitate the integration and analysis of heterogeneous data. Through data harmonization and integration, the development of safe and effective vaccines can be accelerated to improve public health outcomes. Looking to the future, we highlight the need for collaborative efforts among researchers, data scientists, and public health experts to realize the full potential of AI-assisted vaccine design and streamline the vaccine development process.
1 Introduction
The development of effective vaccines against pathogens is a critical priority for global health. The emergence of novel pathogens, such as SARS-CoV-2, present significant challenges to global health response strategies, highlighting the pressing need for accelerated vaccine development (1–3). Traditionally, vaccines have been developed and tested empirically by immunization with inactivated or live-attenuated microorganisms or toxins (4). While traditional approaches to vaccine development have been successful in the past, they often face challenges when dealing with rapidly evolving pathogens, especially those with high mutation rates. Traditional vaccine designs have several drawbacks including adverse reactions, safety concerns with undefined or proprietary preparations, reversion to virulence, and lengthy manufacturing timelines (5). The advent of next-generation vaccine technologies with defined antigens and delivery systems eliciting desired immune responses has revolutionized the field of vaccine design. The benefits of shifting from empiricism to rational vaccine design are already becoming apparent and offer new opportunities to address these challenges and advance our understanding of vaccine efficacy and durability (6).
State-of-the-art vaccine platform technologies, such as mRNA vaccines, viral vector-based vaccines, and structure-based antigen designs (7) have shown great potential as new vaccine candidate developments in protecting against emergent pathogens. These technologies have enabled the rapid design and production of vaccines for immediate short-term protection, as exemplified by the unprecedented speed at which COVID-19 vaccines were developed and deployed. Traditional approaches to vaccine platform selection and optimization are often time-consuming and resource-intensive, which cannot match the speed of pathogen mutation rates.
Due to the availability of exascale computing platforms, next generation hardware and advanced software infrastructure, artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML), and other computational tools are becoming increasingly important in vaccine development (8–10). These computing resources and tools can be leveraged to help identify potential vaccine targets, predict vaccine effectiveness, and optimize vaccine formulations. The combinatorial problem of vaccine design for selecting antigens, platforms, adjuvants, dosage, and scheduled delivery make it challenging to test all possible parameters experimentally. AI/ML solutions to determine optimal conditions could accelerate vaccine design and development and assist in experimental refinements. For instance, ML algorithms can analyze large datasets of pathogen sequences and identify conserved epitopes that can serve as vaccine targets (11). Computational models can also simulate immune responses based on different vaccine formulations, aiding in epitope selection of promising candidates.
While we refer to several recent reviews describing the prospects of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in speeding up research in vaccine design (12, 13), clinical trial design (14), and other applications of machine learning in vaccine design and development (11, 15), our review provides a comprehensive analysis of the data integration challenges and opportunities specific to vaccine development. We focus on the critical knowledge gaps in the application of next-generation vaccine technologies and computational tools and propose directions for future research to address these challenges. Importantly, He et al. highlight the importance of databases and data integration approaches supporting such AI and ML techniques (16). However, the use of ML and computational tools in vaccine development still present significant technical challenges (9, 17).
A major challenge is the aggregation of existing data and knowledge relevant for vaccine design to ensure accurate and reliable models are designed and trained using information from trustworthy resources. For example, there have been over 2,000 vaccine clinical trials registered in the U.S. alone over the past decades and there is important data scattered across different regional clinical registries globally. These data may provide insight into which factors contribute to successful vaccine design. As it is critical to understand why a vaccine was successful, systematically understanding why vaccine trials fail is pivotal for improving future research methodologies, ensuring efficient resource allocation, and enhancing public health preparedness. Lessons learned from these failures can lead to faster and more effective vaccine development in the future. This, however, requires a streamlined process for comprehensive data integration. More generally, vaccine development involves integrating data from various sources, including genomic, immunological, and clinical data, which can be heterogeneous, incomplete, or inconsistent (18, 19). Aggregating and harmonizing the contents of these resources to create a more refined and comprehensive knowledgebase is a challenging task and would require the development of novel standardized ontologies, data sharing protocols, and manual curation processes (20). Another challenge is the lack of standardized benchmarks and evaluation metrics for assessing the performance and accuracy of ML models in vaccine development (21).
Focusing on data integration, this review aims to identify and discuss critical knowledge gaps in the application of next-generation vaccine technologies and computational tools for the development of vaccines against emerging pathogens. We provide an overview of the current state of the art, highlight the challenges and limitations faced by the field, and propose directions for future research to address these challenges (Figure 1). Furthermore, we highlight the need for development of a novel knowledgebase that integrates diverse data sources to guide data-driven decision-making in vaccine development.
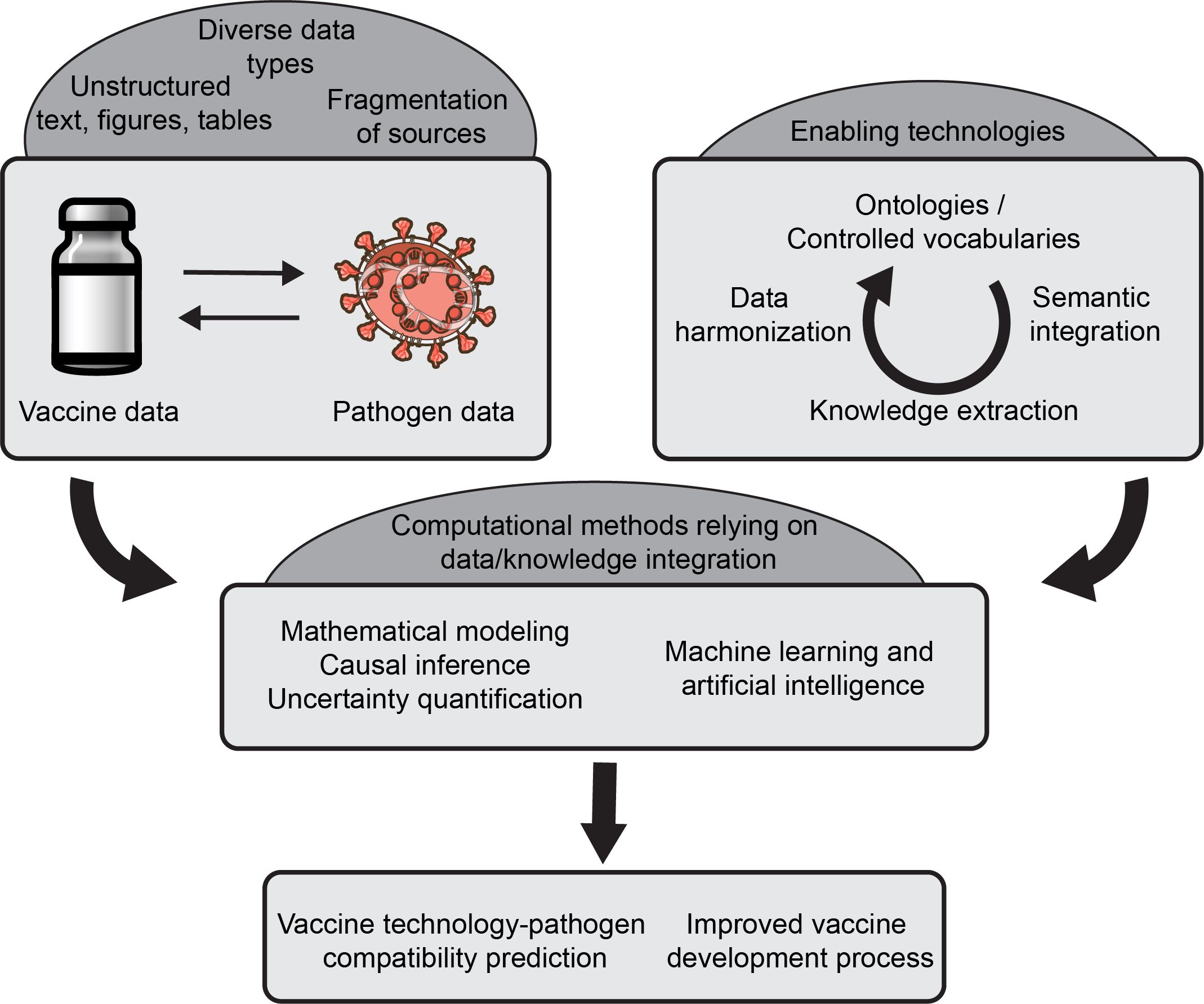
Figure 1. An overview of key computational methods for data integration supporting modern vaccine development. Leveraging existing data on vaccines and pathogens poses multiple challenges (top left) that can be addressed using methods for the automated extraction and integration of knowledge (top right). These enable the use of computational methods including machine learning and artificial intelligence (middle) to ultimately lead to better prediction of vaccine-pathogen compatibility and an improved vaccine development process.
2 Understanding vaccine development
Emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases have threatened public health throughout history and have persisted into modern times (22). Vaccines are an important tool in the prevention of disease outbreaks, epidemics, and pandemics. In fact, the development of safe and effective vaccines against infectious diseases has been one of the most impactful scientific advances to human health of the 21st century (23). However, recent climate, geodemographic, and technological shifts have altered the landscape of infectious disease risk. For example, trends in international airline travel had nearly doubled in the decade prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, increasing from two billion travelers in 2000 to over four billion travelers in 2019, leading to greater global connectivity in enabling pathogens to reach new environments and hosts (24). In addition to recent pathogenic transformation trends, there is an increased risk of infectious disease outbreaks because of delays in vaccine development and production. The vaccine lifecycle, from discovery to licensure, can cost billions of dollars and requires nearly a decade of approval processes for authorization with only an average ~6% success rate pre-pandemic (25).
A wide collection of vaccine platform technologies exists, from traditional vaccines to next-generation platforms (26, 27). Vaccine technology developments have significantly improved in eliciting targeted immune responses and have streamlined the processes enabling rapid scalability for the deployment of novel interventions. Emerging vaccine platform technologies include nucleic acid-based vaccines (28–30), recombinant vector vaccines (31, 32), whole-pathogen adapted vaccines (33–35), cellular vaccines (36), subunit vaccines (37, 38), engineered vaccines (39–41), and a suite of adjuvant-driven or synthetically derived vaccine combinations (42) leveraging the strengths of more than one platform technology (Figure 2). Vaccine platform technologies (43) are widely discussed but inconsistently classified as both the complexity of the technology and the scientific jargon used to describe these vaccines are disparate.
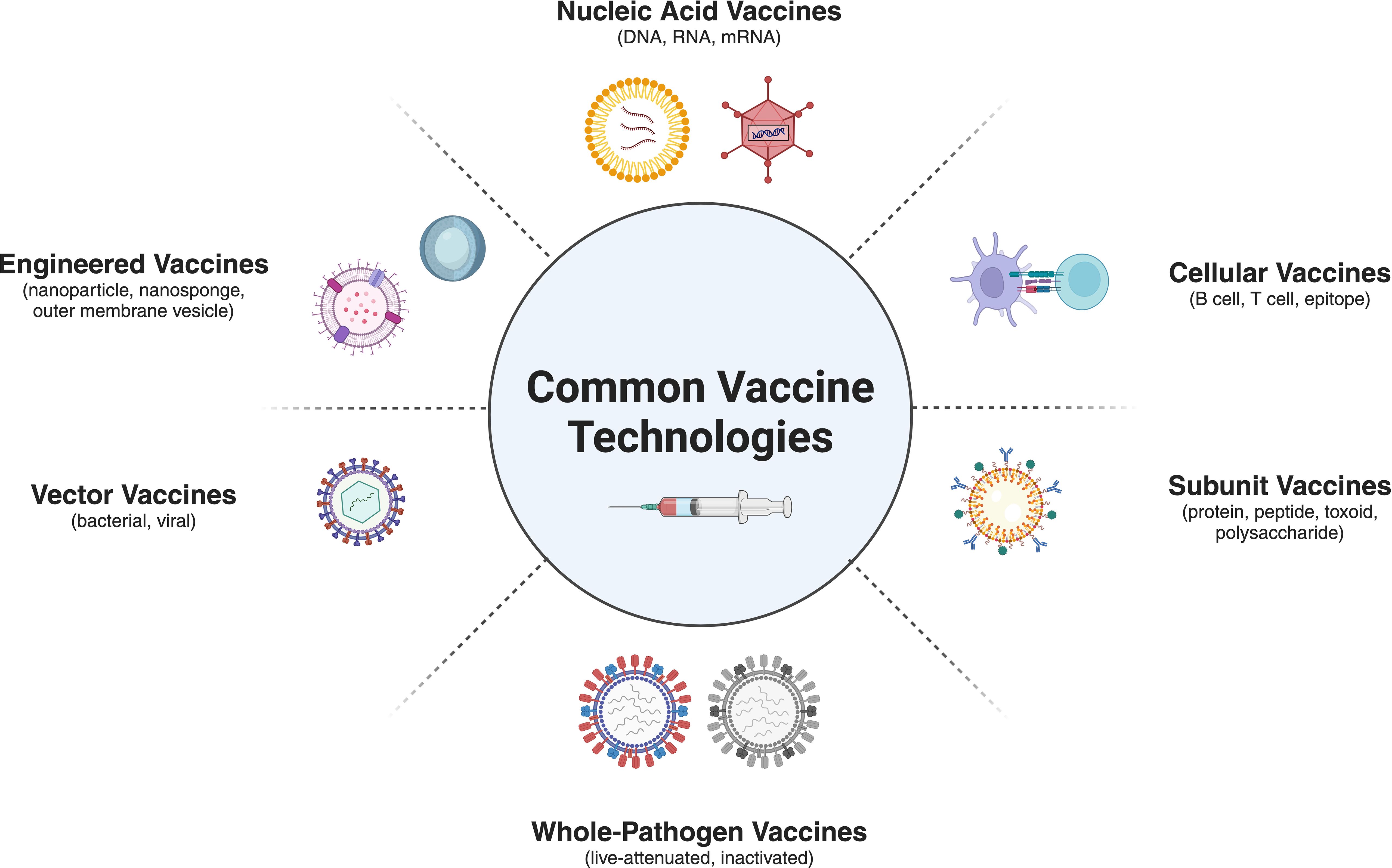
Figure 2. This figure showcases a variety of emerging vaccine platform technologies, including nucleic acid-based vaccines, whole pathogen vaccines, vector-based vaccines, engineered vaccine, cellular vaccines and nanoparticle-based delivery systems. The selection of an appropriate vaccine platform is a critical step in the vaccine development process and is guided by factors such as the nature of the pathogen, the desired immune response, and the target population. Each platform offers unique advantages in terms of safety, immunogenicity, and rapid manufacturing, enabling the development of targeted vaccines against a wide of pathogens. Created using BioRender.com.
Vaccine platform technology selection is only one part of a more comprehensive protective design. Additional protective vaccine design components (44) have various ingredients including active substances, antibiotics, adjuvants, preservatives, stabilizers, and other trace components (Figure 3) (30, 45). These protective ingredients often play an immunogenic role (structural, functional, or biological) in a given design product for subsequent downstream safety and immunogenicity interrogation (46, 47).
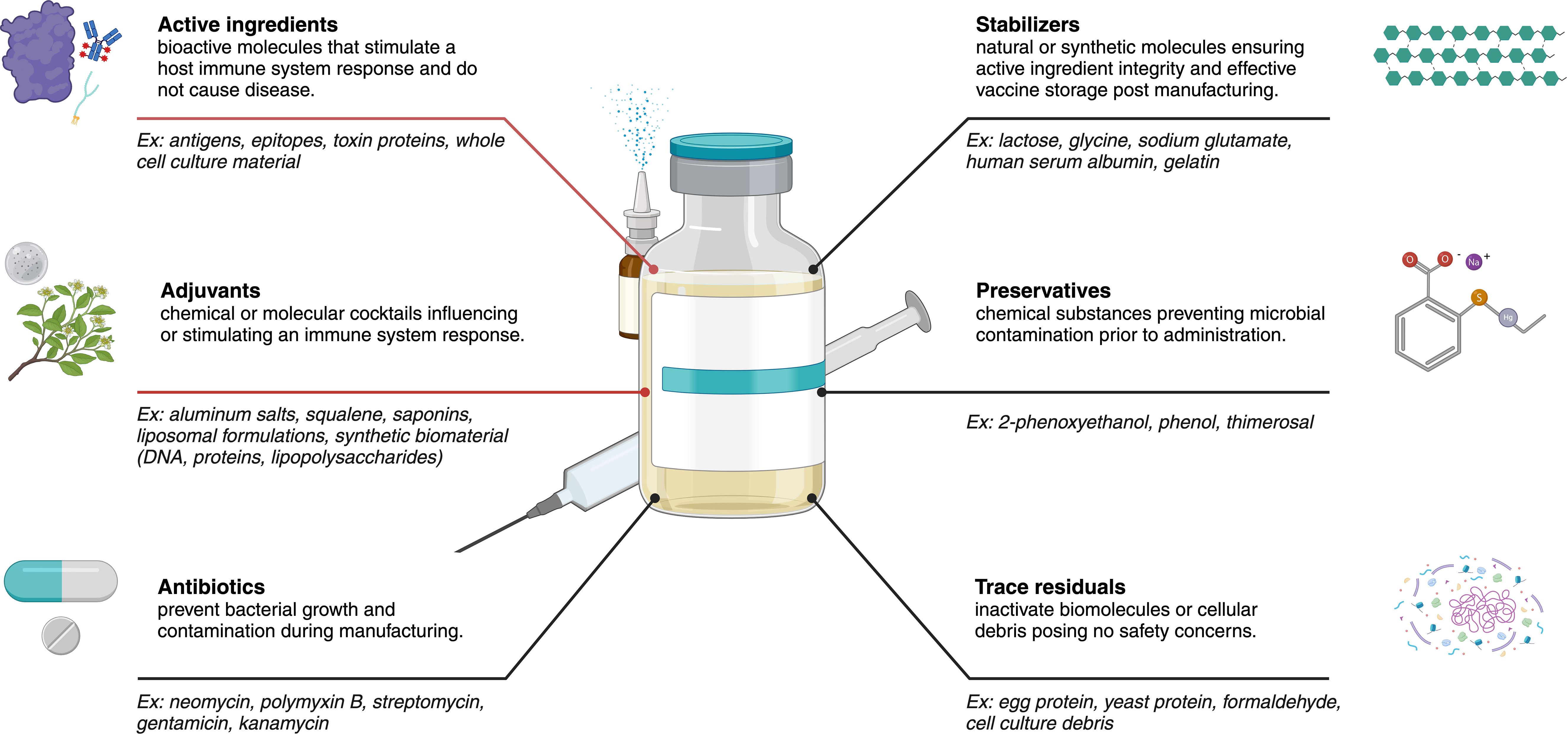
Figure 3. Common vaccine components (antigen, adjuvant, and delivery system) representing specific roles these ingredients play in the overall design of a given vaccine product for enhancing protection against an emerging infectious disease. Red lines indicate the two main contributors having a direct influence on vaccine efficacy and immune systems responses, where flexible combinations of these two ingredients enable improved vaccine efficacy and effectiveness depending on the optimal technology platform selected. The optimal combination of these components is crucial for developing safe and effective vaccines that elicit robust and long-lasting immune protection. Created using BioRender.com.
Recent advancements in vaccine development continue to improve vaccine manufacturing and accessibility for global distribution (48). However, despite recent efforts to improve vaccine product accessibility, there remains a large gap in vaccine product information, including metadata resources required for harmonizing cross-protective vaccine study information supporting new insights from ongoing interventional studies.
The limited union of metadata standards, reporting guidelines, and shared terminologies outlined by varying governmental and scientific resources (49, 50) make it challenging to accurately capture, extract, and integrate valuable knowledge required for protective insight discovery supporting new durable vaccine designs. The rate of disseminated research results reported in journal articles, corresponding to clinical trials registered to study outcomes, is limited. This creates large gaps in quality information tracking making it challenging to identify promising preclinical vs. clinical vaccine candidate development for rapid pandemic response (51–54).
3 Challenges and limitations of vaccine development
3.1 Pathogen genetics, mutation rates, and immune evasion strategies
The early stages of vaccine development rely heavily on computational tools for pathogen surveillance, DNA/RNA sequencing, protein repertoire prediction, and epitope prediction (55–57). These tools play a crucial role in identifying potential vaccine targets and designing effective immunization strategies against emerging pathogens. Emergent lethal human viruses pose many unique challenges for vaccine design and development due to their genetic diversity, mutation rates, and immune evasion strategies (21, 58, 59). The genetic variability of emerging pathogens can impede the identification of consistent vaccine targets and can lead to reduced vaccine efficacy and the need for frequent vaccine updates. For example, RNA viruses, such as influenza and HIV, rapidly mutate, making it challenging to identify vaccine targets (60, 61). Pathogens known for their high mutation rates often have shifting antigenic properties, heavily influencing target vaccine antigen selection and efficacy. These unpredictable mutations often lead to a loss of vaccine effectiveness over time and requires new vaccine formulations. For instance, influenza virus undergoes antigenic drift and shift, necessitating annual updates to ensure protection against circulating strains (62–65).
Vaccine development efforts are further complicated depending on immune evasion strategies that pathogens employ. Pathogens evade the host immune response by antigenic variation, immune system suppression, and the shielding of vulnerable epitopes. HIV, for example, employs multiple immune evasion strategies, including the rapid mutation of its surface proteins, the masking of conserved epitopes, and the depletion of CD4+ T cells, which are critical for mounting an effective immune response (66). To overcome these challenges, vaccine development strategies should focus on identifying conserved regions of the pathogen that are less susceptible to mutation and immune evasion. This can involve the use of structure-based antigen design to create immunogens that elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies, as well as the development of novel adjuvants and delivery systems to enhance the immune response. Bioinformatics tools and machine learning algorithms can aid in the identification of potential vaccine targets and the prediction of vaccine efficacy, by speeding up the research and discovery knowledge aggregation process and eliminating manual redundancy.
3.2 Computational approaches to modeling and predicting correlates of protection
Correlates of protection (CoPs) are biomarkers or immune responses that are statistically associated with protection against infection or disease. The identification, estimation, and modeling of correlates of protection plays a critical role in informing the design and evaluation of vaccines and serves as a benchmark for regulatory approval and public health policy. The immune response to infection or vaccination involves complex interactions among various cell types—dendritic cells, T cells, B cells—and the molecular signals they exchange, such as cytokines and chemokines (67). Determining correlates of protection therefore presents a significant challenge in the field of vaccine development (68–71) and requires principled statistical analysis based on an understanding of the underlying immunological mechanisms. The heterogeneity of data sources and the nuances of individual immune responses pose obstacles to the reliable evaluation of CoPs, making it a specialized and challenging aspect of vaccine research. This section provides an overview of the various computational approaches to modeling and predicting CoPs, including their evaluation from clinical study results, uncertainty quantification, and data model frameworks.
Evaluating CoPs from clinical study results involves aggregating data on study designs, immunological assays, host factors, and clinical endpoints. However, the lack of standardized data formats and reporting guidelines poses challenges for integrating and analyzing this information (70, 71). Shared representational frameworks and ontologies surrounding CoPs have not yet been established, posing reproducibility challenges for data integration and statistical analyses. There is still a significant knowledge gap in identifying CoP for many vaccines, however, some CoPs have been determined for certain vaccines, such as neutralizing antibody titers for influenza vaccines (72).
CoPs enable computational analyses that support running clinical trials in silico and help answer a variety of relevant questions for vaccine development, such as the extrapolation of results from animal studies to humans. For example, immunobridging analysis uses correlates of protection to predict the effect of existing vaccines in protecting against a known pathogen for a given host to give insight into the effect of a candidate vaccine against a novel pathogen in a potentially different host using a different CoP (73–76). While CoPs have historically been leveraged for these analyses by ad-hoc methods (77–80), recent theoretical formulations of causal inference have paved the way for new generic frameworks that can be readily applied for identifying CoPs and enabling their estimation in the face of known sources of uncertainty such as unobserved confounding, sample selection bias, external validity, missing data, measurement error, variability in individual responses, and immunobridging (81–86). The next generation of methods that can provide tight bounds on the estimates of vaccine efficacy in the presence of all these sources of uncertainty (87) has the potential for high impact in the design of vaccines and clinical trials. Recent statistical methods for assessment of immune correlates of protection from randomized, controlled, vaccine efficacy trials highlighting the importance of careful experimental design planning, pre-registration, and the application of a standardized statistical analysis plans improve access to results data supporting predictive analyses (88).
3.2.1 Uncertainty quantification analysis for vaccine development
Uncertainty quantification (UQ) plays a critical role in the modeling of vaccine efficacy and safety by providing a framework to assess the reliability of computational predictions. It helps in identifying the bounds within which the model’s predictions can be considered accurate, thereby guiding decision-making in vaccine development. However, quantifying uncertainty in vaccine development is challenging due to limited data, complex biological interactions, and the lack of negative data from failed vaccine candidates. In this section, we explore the role of UQ in vaccine development (89), the challenges faced, and how AI/ML tools can help in better understanding and mitigating these uncertainties.
Vaccine efficacy is typically assessed through clinical trials, where the vaccine’s ability to prevent disease or reduce its severity is evaluated. Safety is assessed through the monitoring of adverse events following immunization. Uncertainty in these models can arise from various sources, such as measurement errors, variability in individual responses, and the extrapolation of results from animal studies to humans (81). Quantifying these uncertainties helps in determining the confidence intervals around the predicted efficacy and safety outcomes, which is crucial for regulatory decision-making and risk-benefit assessments (90). Moreover, the lack of data from failed vaccine candidates in the public domain poses a significant challenge in UQ. Negative data refers to information about vaccine candidates in public domain that failed or were withdrawn at any stage of development. Understanding the reasons behind the failure of these candidates is crucial for improving future vaccine designs and optimizing resource allocation.
ML tools have emerged as powerful approaches for understanding and mitigating uncertainties in vaccine development. By integrating data from different stages of development, ML models can help identify the key factors influencing vaccine performance and provide more reliable predictions. However, it is essential to ensure that the data used for training these models is of high quality and that the models are validated using appropriate methods to avoid learning from noise. In this context, feature selection techniques can identify the most informative variables, reducing the dimensionality of the problem. By selecting relevant features, ML models can reduce the dimensionality of the problem and focus on the key factors influencing vaccine performance1.
Uncertainty propagation algorithms, such as Bayesian inference and Monte Carlo simulations, can quantify uncertainties associated with each component of the model (91). Surrogate modeling can approximate the behavior of vaccine models, allowing for efficient exploration of the parameter space (92). By training ML algorithms on a balanced dataset that includes both positive and negative examples, the models can learn to distinguish between successful and failed candidates more effectively (93).
3.2.2 Data model frameworks for representing correlates of protection
The discovery of CoPs is critical for accelerating vaccine development, however, the challenges associated with their validation are significant. A multidisciplinary approach that leverages computational tools, standardized frameworks, and integrated data is required to address these challenges and advance our understanding of vaccine-induced immunity. Here, we present a prospective data model for correlates of protection outlining common data collection information elements typically required in determining correlates of protection from statistical outcomes (Figure 4).
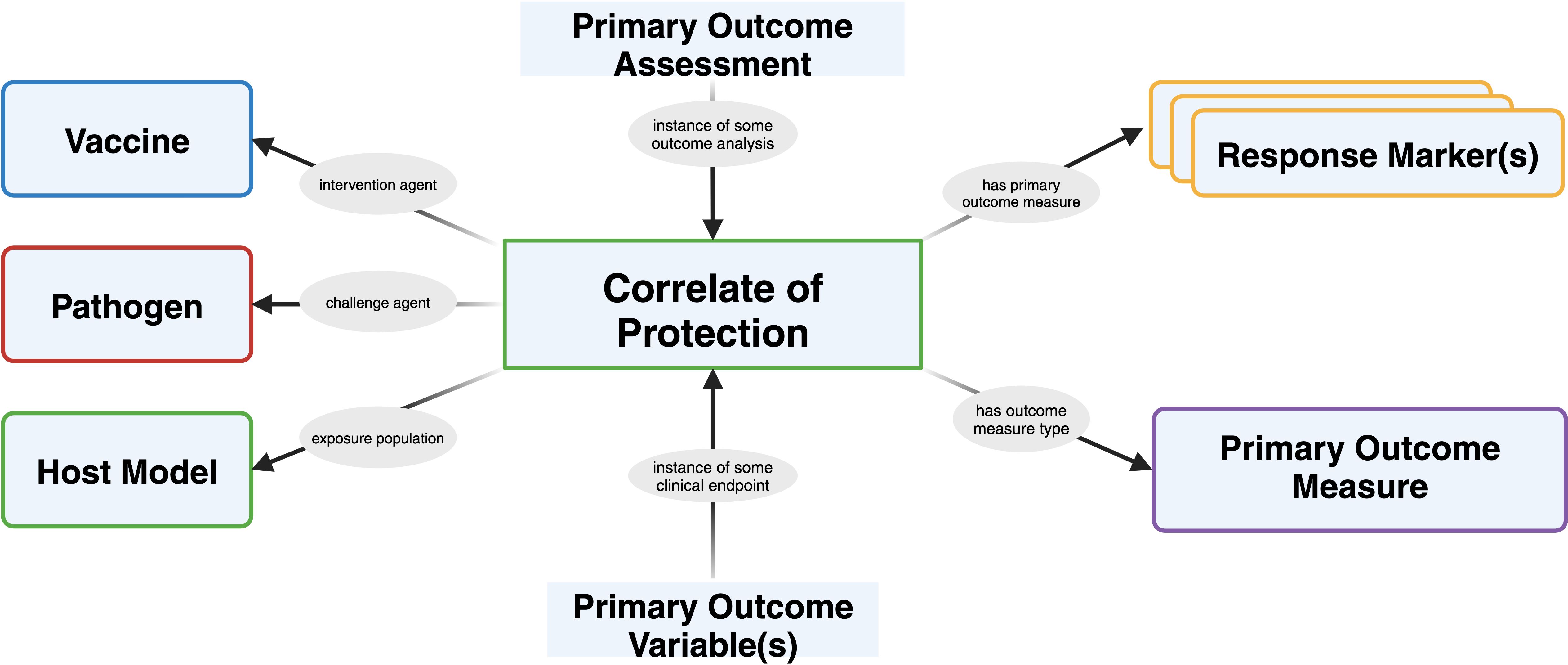
Figure 4. Generalized correlate of protection schema resulting from clinical trial results data and information for evaluating correlate of protection analyses. The schema integrates data from various sources such as clinical trials, including immunological assays, host factors, and clinical endpoints, to identify the key immune parameters that correlate with protection. Understanding the CoPs are essential for evaluating vaccine efficacy, optimizing vaccine design, and predicting the durability of vaccine-induced immunity. Created using BioRender.com.
Correlates of protection are semi-structured and provided mainly in literary sources (94) and reference textbooks (68), but are discussed inconsistently across sources and stem from different statistical analyses. Information reporting on immune signatures and CoPs are often spread across multiple sections of a single publication or across different publications. The data model for immune signatures (see Figure 4) and CoP may vary depending on the specific research questions being addressed. This lack of a universal data model makes it difficult to compare and integrate data from different studies, limiting the ability to draw comprehensive conclusions about vaccine efficacy and safety (95). Moreover, the development of advanced text mining systems that can effectively extract and integrate information from multiple sources is crucial. We discuss the challenge of scaling a common language around correlates of protection for vaccine development in the next section.
Nomenclature presents several additional challenges. For example, different types of CoPs are described using different and sometimes overlapping nomenclature such as “surrogates of protection” and “correlates of risk”, and there currently exists no taxonomical resource for CoP-related terms. Further, several different kinds of vocabularies are required to identify entities that appear as part of CoPs. The Vaccine Ontology (VO) (96) is an existing ontology that aims to represent vaccine-related information, including immune responses. However, the current VO lacks comprehensive coverage of immune response terms and relationships. Extending the VO to include a more detailed representation of immune cell types, cytokines, and signaling pathways involved in vaccine-induced immunity would greatly enhance its utility for computational modeling. Additionally, aligning immune response terms with existing ontologies, such as the Gene Ontology (GO) (97) and the Cell Ontology (CL) (98), would facilitate data integration and knowledge discovery. For example, the Infection Disease Ontology for Malaria (IDOMAL) (99) demonstrates how ontologies can be used to integrate and analyze heterogeneous data related to a specific infectious disease.
Similarly, the confluence of data and knowledge supports the development of bespoke machine learning workflows as well as the application of generic workflows. Classical machine learning and computational modeling approaches have shown initial promise in predicting vaccine effectiveness and discovering novel CoPs by leveraging immune response data (76). For example, machine learning approaches have been used to predict the immunogenicity of influenza vaccines based on the analysis of gene expression profiles and antibody titers (100).
In summary, computational approaches to modeling and predicting CoPs are essential for accelerating vaccine development and improving public health outcomes. By using clinical study results, uncertainty quantification methods, data model frameworks, and machine learning techniques, researchers can identify reliable CoPs, optimize vaccine design, and predict vaccine efficacy.
3.3 Data harmonization and knowledge integration challenges
Data and relevant information describing vaccine development and immunization is distributed across dozens of distinct resources (Figure 5). Computational methods would generally benefit from drawing on many if not all available resources. Here we provide an overview of existing resources ranging from controlled vocabularies and ontologies to databases on vaccine characteristic and immune responses. We also point out important gaps and limitations associated with the current state of these resources.
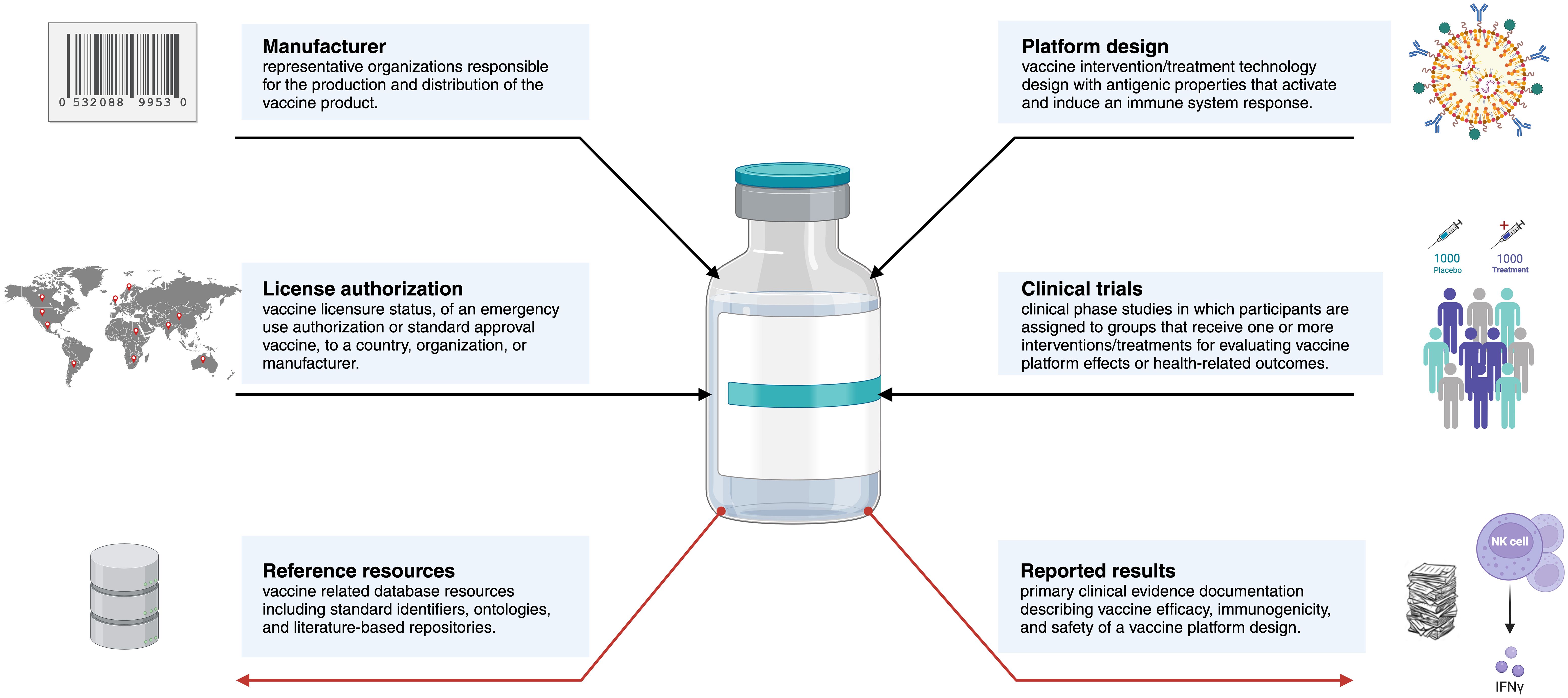
Figure 5. A conceptual diagram of key concepts and relationships surrounding vaccines. Red arrows indicate comprehensive methods are required for extraction and integration of these resources. Accurate curation and mapping of these vaccine products across knowledge resources is a critical step in the experimental data and knowledge harmonization for downstream query. Created using BioRender.com.
3.3.1 Resources for identifying critical vaccine relationship information
The storage and management of scientific data involves identifying concepts in an unambiguous way. Concepts relevant for vaccine development include, for instance, organisms (hosts or pathogens), vaccine products and technologies, cell types, genes, proteins, biological processes, and several other entity types. Concept identification is typically achieved by using unique identifiers that remain distinct from colloquial names and synonyms. Identifiers are assigned to concepts by controlled vocabularies, taxonomies and ontologies (101). In addition to standardizing the identification of relevant concepts, resolver resources construct links to web pages that describe each concept (102, 103). For example, the NCBI Taxonomy database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/taxonomy) has assigned an identification number 28450 to Burkholderia pseudomallei. This identifier can be resolved using the compact URI (CURIE) identifier schema standard (104, 105) as ncbitaxon:28450. Unique namespace prefixes, such as ncbitaxon assigned by the local data provider, can be persistently mapped from literature references to HTML webpage locations being described by this taxon identifier using CURIE resolver services by Identifiers.org (https://identifiers.org/taxonomy:28450) or the Bioregistry (https://bioregistry.io/ncbitaxon:28450).
Below, we summarize the landscape of such identifier and terminology resources for several concept types relevant to vaccine development.
3.3.1.1 Vaccine naming and persistent identification
There exist several ontologies and related resources that catalogue and assign identifiers to vaccines. These resources provide a detailed hierarchical classification of vaccines, such as by their platform design, the pathogen against which they immunize, and the disease against which they inoculate. The most detailed of such is the Vaccine Ontology (96). Several more general resources also include vaccines such as Medial Subject Headings (MeSH) (106), the National Cancer Institute Thesaurus (NCIT) (107), the Unified Medical Language System (UMLS) (108), the Computer Retrieval of Information on Science Projects (CRISP) Thesaurus (109), Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) (110), Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) (111), and Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine - Clinical Terms (SNOMED-CT) (112).
Additionally, several organizations maintain their own unique identification systems for vaccines, such as the United States Food and Drug Administration’s Submission Tracking Number (identifier prefix: STN), the United States Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s vaccine administered) code set (identifier prefix: CVX), the American Medical Association’s Current Procedural Terminology (identifier prefix: CPT), the European Medicines Evaluation Agency (identifier prefix: EMA) product number, and the World Health Organization Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification (identifier prefix: ATC) codes (113–120). These resources are typically used to identify vaccines in reference to primary study metadata, such as clinical trials protocols and statistical plans, sponsor authorization and licensing identifiers, and product tracking numbers. Despite the existence of these resources, ensuring the persistence of identifiers and harmonized naming, standards pose a large challenge in this area (121, 122).
The broad array of agency-specific product information systems and coded identifiers make it difficult to verify and integrate identification elements across resources by country. One specific challenge is that not all data sources employ similar guidelines or best practices for assignment of resolvable identifiers and naming conventions.
3.3.1.2 Vaccine ingredients and common components
The Vaccine Ontology curates terms representing components of vaccines, such as adjuvants, antigens, emulsifiers, preservatives, solvents, and stabilizers. Many of these terms are linked to chemicals in the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) Ontology (123) and other related chemical identification resources. The Vaccine Adjuvant Compendium (https://vac.niaid.nih.gov) curates similar terms (124, 125), and provides additional context linking to immune signatures, pre-clinical, and clinical information. Unstructured text information exists in various ad-hoc formats that do not use identifiers, such as the FDA vaccine insert packets and CDC CVX code labels describing excipients. Better standardization across these sources would enable principled analysis of the role vaccine components might play in efficacy and safety.
3.3.1.3 Vaccine host-pathogen taxonomy
The NCBI Taxonomy repository provides a comprehensive and detailed hierarchical classification of organism-specific lineages across all clades of life (126). It is particularly useful for annotating host and pathogen organisms as well as vaccine targeted organisms based on genomic sequence identification. However, genomic database collections do not always track and assign persistent identifiers to pathogenic variants of interest. This can create critical gaps for assembling vaccine-pathogen relationships connected to variant-specific sequence identities during outbreaks and pandemics (127).
Variant tracking, depending on the mutation rate of the pathogen of interest, often requires full descriptive reporting standards when publishing experiments or observations for correctly identifying variant protection. New ontologies, such as the Coronavirus Infectious Disease Ontology (CIDO) (128), have begun to incorporate agency-specific terminology for well-known SARS-CoV-2 pathogenic variants. For example, CIDO has included new terms for common SARS-CoV-2 variant names based on the GISAID (129, 130), PANGO (131–133), and WHO classification systems (134), facilitating keeping track of circulating pathogen lineage metadata information. Accurate and up-to-date tracking of emerging pathogen variants of interest (VOI) and variants of concern (VOC) is crucial for future vaccine development success and characterization of linked protective outcomes such as vaccine efficacy and protective durability (135).
Other relevant ontologies include the Infectious Disease Ontology (IDO) collection which is connected to widely used more general disease ontologies (136). Though, currently incomplete, IDO has established a roadmap for providing curated terms for resolving pathogenic strain information in the future.
3.3.1.4 Vaccine antigen selection
Vaccines can contain portions of nucleotide or peptide sequences bearing a variety of roles such as being an antigen, conjugate, or vector. Biologically-relevant genomic sequence variance and antigen coded sequence mutations are known to heavily influence vaccine design efficacy (28, 137). Explicit vaccine sequence information is valuable for downstream analysis but is also often not defined nor referenced explicitly from publications, clinical trials, or other documents describing experimental approaches to new vaccine development. Antigens often correspond to a well-defined gene sequence, either identified through gene nomenclature resources such as Entrez Gene Database, protein nomenclature resources such as UniProt, or when available complete genome reference databases such as GenBank and related sequence-based database extensions (138–141). Other lookup resources specific to antigen search and discovery include the Immune Epitope Database and the VDJdb curated database of T-cell receptors with known antigen specificity (142, 143).
3.3.1.5 Vaccine adverse events and discourse
Structured information on vaccine adverse events is key to assessing vaccine safety. Several related resources curate identifiers and names for adverse events, such as the Ontology of Adverse Events (OAE), Ontology for Vaccine Adverse Events (OVAE), Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), and the Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) framework (144–147). Similarly, the Symptom Ontology and the Human Phenotype (HP) Ontology cover partially overlapping concepts that appear in adverse event resources and can be linked in many cases (148–150). Finally, there are resources dedicated to standardizing public discourse on vaccine effects such as the Vaccine Misinformation Ontology (VAXMO) (151).
It is important to note that extracting useful information from social media posts about vaccines is challenging due to the prevalence of misinformation and disinformation. Distinguishing genuine adverse event reports from false or misleading information remains a significant hurdle, even with the inclusion of image evidence or the use of advanced AI systems. Researchers and public health officials must exercise caution when relying on social media data for vaccine safety monitoring and develop robust methods to validate the information obtained.
3.3.1.6 Vaccine-related ontology integration and gaps
The proliferation and heterogeneity of vaccine resources presents several challenges during data integration. We have given an overview of a number of resources relevant to vaccine data, still, multiple further ontologies can be found in databases that catalogue biomedical identifier resources including the Bioregistry and BioPortal (152, 153). The usage and integration of these resources, however, remains challenging. First, retrieval presents a major issue as resources appear in a variety of formats. For example, most organization-specific identification systems require web-scraping and are difficult to process. Further, several resources have licenses that are restrictive in terms of usage allowed (e.g., UMLS) or are proprietary (e.g., CPT) which makes their reuse difficult (154). Second, reconciliation is challenging, as nomenclature is not always consistent nor detailed enough to resolve ambiguities. Precise and comprehensive semantic mappings are required to reconcile ontologies and related resources at scale, which also poses several problems with respect to the availability and completeness of mappings as well as the methods necessary to accomplish this. Finally, completeness is an important issue, as even the combination of all resources does not cover all vaccines, vaccine candidates, and vaccine platforms. This can be addressed in some cases by contributing or suggesting to the maintainers of the resource to include new terms. For example, the Vaccine Ontology is a part of the Open Biological and Biomedical Ontologies (OBO) Foundry, a set of community-maintained ontologies with shared curation and community guidelines (155). In other cases, it may be required to develop new ontologies or nomenclature resources.
3.3.2 Data integration methods to support machine learning
Modern life science knowledge discovery requires the integration of data and knowledge from heterogeneous, multi-modal data sources (156, 157). Data integration is becoming increasingly important to support AI/ML which leverage such heterogeneous, multi-modal data. Integration, however, is limited by variations in both structured and unstructured data formats where common data models and standards would be needed (158–160). In this section, we review current methods and best practices for data integration, highlight how they have been applied in vaccinology, and highlight upcoming challenges and opportunities for the domain. Specifically, we cover existing standards, the landscape of existing knowledge sources, and opportunities for applying natural language processing (NLP) and large language models.
Knowledge, often in the form of relationships between entities described in the previous section, are often scattered across many structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information resources. Fragmentation of structured data contained in specific vaccine related knowledgebases such as the U.S Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Federal Drug Administration (FDA), WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP), ClinicalTrials.gov, Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), etc. (113, 115, 161, 162), along with reported outcomes sparingly shared in resulting journal articles, are a challenge to track down and connect outcome and study phase progress. More specifically, there are a variety of disparate data formats and standards across published experimental studies on pathogens and vaccine platforms. Structured biomedical data and clinical study knowledge can appear in several formats. Simple relationships between concepts can be encoded as semantic triples consisting of a subject, a predicate and an object, possibly further augmented by additional properties (163). Representing complex knowledge such as correlates of protection requires a more detailed data model for accurately capturing the necessary biological entities and the relationships they represent.
A handful of databases contain host-pathogen data aggregated from literature in a structured form. Efforts from the Human Immunology Project Consortium (HIPC) database (https://immunespace.org/), the Host-Pathogen Interaction Prediction (HPIP) analysis framework, and the COVID-19 Prevention Network (CoVPN) consortium network website (https://preventcovid.org/) (164–167) collect and curate relevant information, but there is currently no comprehensive resource containing detailed immune signature identifications and CoP statistical results.
The NIH 2023 data sharing policy (https://grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/notice-files/NOT-OD-21-013.html) is expected to have a significant impact on the availability of raw data in public repositories. This increased access to data will facilitate the development and validation of computational tools and data integration methods for vaccine research. The policy mandates that all NIH-funded research generate publicly accessible data, which will enable researchers to more easily combine and analyze data from multiple sources. This, in turn, will accelerate the identification of novel vaccine targets, the optimization of vaccine formulations, and the assessment of vaccine safety and efficacy.
3.3.2.1 Host-pathogen infection, disease, and clinical outcome data
Relationships of vaccines to pathogens, host organisms, and diseases constitute the backbone of vaccine-related knowledge. However, this information is highly fragmented, sparse, and available at varying levels of granularity. For example, connections between vaccines and the organisms they immunize against can be found in a combination of structured sources like VO, VIOLIN (168), and the Cov19VaxKB (169) combined with unstructured sources published by organizations like the CDC, FDA, and EMA. The VO and VIOLIN database provide explicit annotations on vaccines’ host organism(s), which are typically implicit in other resources. Connections between vaccines and diseases can also be extracted from a combination of direct structured annotations in VO and VIOLIN, through inference on clinical trial resources, inferred through the Disease Ontology’s has material basis in annotations, and from unstructured sources from the CDC, FDA, and EMA.
Vaccine side effects and adverse outcomes are available from multiple resources. VAERS accumulates adverse event reports, which requires statistical interpretation and only covers a small number of vaccines. Further, it does not use controlled vocabularies and therefore needs preprocessing (grounding). Additional processing has been done to match VAERS to the Adverse Event Ontology (AEO) (170). VAERS has also been analyzed with other natural language processing systems for text classification to medical officer review (171). VIOLIN contains side effect information in unstructured text that can be extracted with NLP. Side effects can also be extracted from the FDA’s label inserts for vaccines (172). NLP has been shown to be an effective method approach for vaccine event extraction (173, 174), while ML methods have been shown to be an effective approach for side effect prediction-based methods using electronic health records (175).
Despite the availability of these sources and inference methods, it’s necessary to do additional manual curation to achieve full coverage of the vaccine landscape. Methods that measure entity co-occurrence, such as those based on NLP, could provide an initial assessment of the landscape accelerating manual curation.
3.3.2.2 Clinical trials data
Clinical trials data is distributed across a large number of country- and region-specific registries (176). The principal clinical trial registry used in the United States, ClinicalTrials.gov, contains the most granular information on study results (177). The World Health Organization (WHO) aggregates multiple clinical trial registries into a unified data store and provides cross-references when the same trial is registered in multiple primary registries (178). However, there exist several challenges in using the collection of these registries due to differing data availability, data standards, and curation practices used in each of the constituent clinical trial registries. For example, some registries contain a dedicated field for the phase of a clinical trial, some contain it within free text describing the trial, and some do not include it at all. Further, to connect information between trials and other resources, concepts need to be standardized to controlled vocabularies or ontologies. ClinicalTrials.gov uses MeSH to accomplish this for its trials’ conditions and interventions, but there remain significant gaps in standardizing these and other fields.
Examples of successful data harmonization efforts and their benefits more generally include population, intervention, comparison, and outcome (PICO) framework (179). The development and adaptation of external data standards such as Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) (https://www.cdisc.org) and BRIDG (https://bridgmodel.nci.nih.gov) is one avenue towards standardizing data before it enters registries. Alternatively, several complementary approaches have demonstrated progress towards establishing data models and information extraction pipelines covering several aspects of clinical trial registries, including for outcomes (180), for funding sources (181), for endpoints (179), and for related regulatory documentation (182). Similar efforts to support precision medicine have resulted in clinically-enriched knowledge graphs (183, 184). Because many fields within clinical trial registries are stored as free text, there remain several opportunities for developing further data models and extraction pipeline for additional aspects, such as cohort recruitment and exclusion, intervention administration, reasons for stopping trials, and other fields.
3.3.2.3 Vaccine licensing data
Vaccine regulatory information is crucial for informing the development of new vaccines. However, the vaccine regulatory landscape is complex due to the process of approval (e.g., standard vs. emergency use authorization), the variety of license statuses (active, inactive, withdrawn, etc.), and the number of regional- and country-specific agencies that review and grant authorization. These complexities create challenges in data harmonization efforts across license tracking statuses and reporting resources.
The FDA includes detailed documentation about the review of each vaccine including its clinical review memo, approval letters, and other supporting documents. For example, the approved BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine COMIRNATY is described by the FDA in https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/comirnaty (185). Similarly, the emergency use authorized Novavax vaccine is described by the FDA in https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/coronavirus-covid-19-cber-regulated-biologics/novavax-covid-19-vaccine-adjuvanted (186). Despite providing detailed vaccine insert documentation for individual vaccines, the FDA does not provide a single source for aggregating versioned documentation of current approvals, emergency use authorizations, or withdrawals in a stable user-friendly location. The CDC’s CVX code resource provides an aggregated overview of active, inactive, and never active vaccines in the USA, but does not link to FDA approval identifiers for harmonizing release versioning. The EMA provides a single aggregated document on all reviewed medicines, including vaccines, but varies in the language used to describe these statuses.
Additionally, several third-party resources exist that aggregate or curate vaccine licensing information. For example, the Vaccine Ontology contains annotations for USA-licensed vaccines. VIOLIN stores licenses in a semi-structured way. Finally, the COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker (https://covid19.trackvaccines.org) contains detailed licensing information for SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, covering the entire complexity of the licensing landscape, but it is limited by pathogen, requires web scraping and data standardization, and its maintenance has been discontinued as of December 2022.
There remain several ongoing challenges in leveraging vaccine licensing information. First, there is the limited availability of vaccine information by distributor, which is currently scattered across unstructured sources and agencies in many regions, stored in proprietary resources inaccessible to the general research community. Second, is the variability and inconsistency of the terminology used in referencing, naming, or describing of vaccine information. Controlled vocabularies, such as the NCI Thesaurus (NCIT) collection (http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo/ncit.owl) have an incomplete classification of licensing that could serve as a basis for extension to a vocabulary that could help standardize across agencies and regions (see https://bioregistry.io/ncit:C118405). Further, common terms such as emergency use authorization (EUA) have different context- and agency-dependent meaning. Finally, capturing license information is confounded by the dynamical nature of licenses which can change over time, motivating the development of a more sophisticated data model for capturing the lifecycle of a given vaccine.
3.3.2.4 Vaccine platform complexity
Vaccine design is a complex process that involves the selection of appropriate platforms, adjuvants, and antigens. Vaccine platforms are the backbone of vaccine development, providing the foundation for the delivery of antigens and the stimulation of the immune system. However, the complexity and diversity of vaccine platforms make ontologizing a challenging task. Many vaccines build on aspects of multiple platforms, and the lack of standardized ways to annotate these platforms hinders data integration and analysis. Adjuvants are essential components of many vaccines, enhancing the immune response and improving vaccine efficacy (47, 187). Antigens are the key components of vaccines that trigger the immune response and confer protection against pathogens. The lack of standardized ontologies and annotation systems for vaccine platforms, adjuvants, and antigens presents significant challenges in vaccine design and data integration. Collaborative efforts to develop and implement standardized ontologies, along with the integration of vaccine data from multiple sources, are essential for advancing vaccine research and development. By leveraging the power of ontologies, unique and persistent identifiers, with results data for integration we can accelerate the design of safe and effective vaccines and improve public health outcomes.
3.3.3 Vaccine platform data curation knowledge gaps
As discussed above, significant knowledge gaps exist in the curation of data on vaccine platforms, stemming from language and reporting inconsistencies, the lack of standardized datasets, and variable data reporting requirements. These gaps hinder the ability to rapidly develop and adapt vaccines to new pathogens, as exemplified by the challenges faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. The use of human-readable formats, such as unstructured text in scientific articles, makes it difficult to extract and integrate data across different studies. Additionally, the inconsistent use of terminology between experimental and computational domains creates barriers to data harmonization and analysis (188). Publicly available datasets on vaccine efficacy and safety often suffer from incompleteness and lack of standardization. Relevant information, such as adjuvant formulations and dosing schedules, is often reported in an ad-hoc manner and scattered across different sources, including clinical trial registries, journal articles, and regulatory documents (189).
Efforts to promote the use of machine-readable formats, such as standardized data tables and structured metadata, can improve the efficiency and accuracy of data curation. The development of tools and platforms for automated data extraction and integration, leveraging natural language processing and machine learning techniques, can help overcome the challenges posed by unstructured and heterogeneous data sources.
3.3.4 Community standards, data sharing, and reporting
There exists a confluence of community data standards, model formats, and reporting guidelines that support the curation and organization of knowledge from primary sources (190). Many such curated resources are adopting external data standards to improve their reusability. For example, the molecular interaction and pathway modeling community have several standard data exchange language formats for encoding curated artifacts, including BEL, BioPAX, and SBML standards (191–193). The clinical data modeling community has also produced several standards for encoding clinical data, including the CDISC, the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model (OMOP-CDM), and the HL7/FHIR (194–196).
Concurrently, several general principles, guidelines, and community standards resources have emerged to support curators (197). Popular implementations include the FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, reusable) data principles, TRUST (transparency, responsibility, user focus, sustainability and technology) principles, CARE principles (CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance), FAIR for Research Software (FAIR4RS), O3 (open data, open code, open infrastructure) guidelines, the Research Data Alliance COVID-19 working Group (RDA COVID-19) standards collection, and structured data extaction APIs such as Google Colab (https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/tutorials/extract_structured_data) (198–203).
Frameworks that automate the assembly of biomedical knowledge can support building new databases and knowledge graphs that can be queried from a combination of programing languages, dialog systems, and more recently, through the interface of large language models. This includes schemas such as the Biolink Model, BioCypher, Phenotype Knowledge Translator (PheKnowLator), GA4GH Phenopackets, and ISA-FHIR (204–208). Other approaches towards knowledge assembly based on the semantic web (209, 210) and linked open data (211, 212) allow for information to be federated from many distinct sources following shared data modeling practices. A well-known example is the UniProt RDF platform and SIB linked data (213–215).
3.4 Automated tools for knowledge extraction from literature
A key challenge of data integration in this space (and life sciences more broadly) is that most data is fragmented across scientific publications in an unstructured form such as text, figures, and tables. Peer-reviewed publications relevant to vaccine mechanisms are accessible via PubMed and PubMed Central, as well as publisher-specific repositories, however, most content is not available in a full-text form. Some targeted projects such as LitCovid provide SARS-CoV-specific publications but are limited to only a subset of all relevant literature (216). Given access to literature content, natural language processing techniques can extract data from text in a structured form. Natural language processing systems typically approach extraction from scientific publications by first recognizing key concepts in text, a process called named entity recognition (NER), then extracting relationships between concepts (called relation extraction) (217). Traditionally, NLP systems have used rule-based extraction approaches whereby patterns corresponding to relations of interest are matched to trigger extraction logic from text (218). More recently, machine learned, transformer-based algorithms have become prevalent. These models (including PubmedBERT (219) and BioBERT (220)) are generic to processing biomedical text and can be fine-tuned for specific extraction tasks. Finally, the latest generation of large language models – both proprietary (e.g., ChatGPT, https://chatgpt.com) and open source (e.g., Bloom (221)) – can be used for interpreting and extracting data from publications without fine tuning, rather, using custom prompts with instructions and examples, sometimes called in-context learning (222). We highlight prior work on NLP applied in the domain of vaccine mechanisms in Table 1.
Recent advancements in LLMs, such as ChatGPT, have shown promising results in various scientific domains, including single-cell RNA-seq analysis (252). In addition to using LLMs for data extraction tasks, as outlined above, LLMs may be used directly as a source of integrated vaccine knowledge. However, due to the nature of LLMs capturing relationships in text implicitly through learned weights, it is challenging to connect responses generated by LLMs to primary evidence from literature or other sources. Therefore, further investigation is needed to assess the extent to which these models can provide accurate and reliable information in this context.
Correctly identifying and extracting data information from semi-structured tables, graphs, and figures has proven to be challenging for NLP and other automated approaches. NLP methods present generic- and domain-specific challenges. Some are a result of the complexity of language itself, for example, anaphora (references to previously mentioned concepts via pronouns) and synonyms both impact the ability for rule-based systems to recognize concepts correctly. Similarly, imprecise language (e.g., varying specificity of vaccine terms) and ambiguity (e.g., “NLP vaccine” nomenclature) are difficult for even newer systems to overcome. As LLMs and other machine-learned techniques become more prevalent, the need for reproducible and reliable workflows becomes important as the same inputs are no longer guaranteed to give the same outputs, and the issue of hallucination can affect the accuracy of results. Hallucination, in the context of LLMs refers to the generation of false or misleading information that is not grounded in the input data or the model’s training. This can lead to inaccurate or unreliable outputs, which is a significant concern when applying these models to scientific research. Finally, a practical issue for all NLP methodologies is the limited availability of full-text content since important data or tables often do not appear in the abstract (253).
We identify several opportunities for the application of NLP in the future. First, it can be used to generate more detailed indexes of vaccines and other concepts of interest in the literature to make it easier to query, enable preliminary analyses such as the assessment of relative entropy (254), and provides a foundation for further extraction and curation activities. Accordingly, there is an opportunity for using NLP to assist in automated or semi-automated relation extraction, for example, between vaccines and their target pathogens, diseases, and other features mentioned above. This presents an opportunity both in the biomedical literature as well as semi-structured datasets that contain free text fields such as those appearing in clinical trial registries and adverse event databases. Finally, we see an opportunity to use LLM-based workflows such as SPIRES (255) or Kor (256).
4 Conclusion
The development of safe and effective vaccines is a critical public health priority, and the integration of diverse data and knowledge and the application of AI and ML techniques hold immense promise for accelerating this process. The process of developing safe and effective vaccines is fraught with challenges, ranging from the rapid mutation of pathogens to the lack of standardized data integration and curation practices. By leveraging data from various sources, including platform data, pathogen data, and published knowledge, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence vaccine efficacy and safety as shown in Figure 1.
This review highlights the current landscape of vaccine development, and the opportunities associated with integrating diverse data types to enable AI and ML techniques. We have discussed the role of semantic integration, causal inference and natural language processing, in extracting valuable insights from published literature and unstructured data sources. Furthermore, we have emphasized the importance of establishing standardized data formats and ontologies to facilitate seamless integration and analysis of heterogeneous data. However, to fully harness the potential of AI/ML and computational tools in vaccine development, it is crucial to address the lack of data and knowledge interoperability across various domains. This lack of integration hinders the development of comprehensive models and limits the ability to derive meaningful insights from the available data. To overcome the challenges associated with data and knowledge integration in vaccine development, we propose the following future directions and implementation strategies:
● Establishing standardized ontologies/data formats. Developing standardized ontologies and data formats specific to vaccine development can facilitate the integration of data from various sources, such as host-pathogen interactions, clinical trials, and vaccine design. This will enable more efficient data sharing and analysis across different research institutions.
● Promoting data sharing and collaboration. Encouraging a culture of data sharing and collaboration among researchers, industry partners, and public health organizations can help break down silos and facilitate the integration of knowledge across different domains. This can be achieved through the creation of open-access databases, data-sharing platforms, and collaborative research networks.
● Advancing AI/ML algorithms for data integration. Investing in the development of advanced AI/ML algorithms specifically designed for integrating heterogeneous data from disparate sources can help overcome the challenges associated with data harmonization. These algorithms should be able to handle the complexity and variability of vaccine and platform related data and provide meaningful insights to guide vaccine development.
● Integrating real-world evidence. Integrating real-world evidence, such as post-marketing surveillance data and electronic health records, with traditional vaccine development data can provide a more comprehensive understanding of vaccine safety and effectiveness. Such efforts require the development of robust data infrastructure and the application of AI/ML techniques to analyze and derive insights from these diverse data sources.
● Fostering interdisciplinary collaboration. Encouraging collaboration among experts from various fields, such as immunology, virology, data science, and computer science, can help bridge the gaps in knowledge and facilitate the development of innovative solutions to address the challenges in vaccine development.
In conclusion, realizing the full potential of AI/ML and computational tools in vaccine development will require a concerted effort from all stakeholders, including researchers, funding agencies, industry partners, government organizations, and academic institutions. By investing in the development of standardized ontologies and data formats, promoting data sharing and collaboration, advancing AI/ML algorithms for data integration, integrating real-world evidence, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, we can accelerate the development of safe and effective vaccines and improve global public health outcomes.
Author contributions
LA: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CH: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JT: Writing – review & editing. AM: Writing – review & editing. KK: Writing – review & editing. NA-C: Writing – review & editing. ZS: Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – review & editing. BG: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NK: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency under the Rapid Assessment of Platform Technologies to Expedite Response (RAPTER) program (Award No. HDTRA1242031). The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy or position of the US Department of Defense or the US Government. The authors thank Dr. Traci Pals for her support of this work. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory is a multi-program national laboratory.
Acknowledgments
We thank all those who contributed to this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Graham BS. Rapid COVID-19 vaccine development. Science. (2020) 368:945–6. doi: 10.1126/science.abb8923
2. Lurie N, Saville M, Hatchett R, Halton J. Developing covid-19 vaccines at pandemic speed. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382:1969–73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp2005630
3. Yue J, Liu Y, Zhao M, Bi X, Li G, Liang W. The R&D landscape for infectious disease vaccines. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2023) 22:867–8. doi: 10.1038/d41573-023-00119-4
4. Sharma M, Krammer F, García-Sastre A, Tripathi S. Moving from empirical to rational vaccine design in the “Omics” Era. Vaccines. (2019) 7:89. doi: 10.3390/vaccines7030089
5. Rappuoli R, Mandl CW, Black S, De Gregorio E. Vaccines for the twenty-first century society. Nat Rev Immunol. (2011) 11:865–72. doi: 10.1038/nri3085
6. De Gregorio E, Rappuoli R. From empiricism to rational design: a personal perspective of the evolution of vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol. (2014) 14:505–14. doi: 10.1038/nri3694
7. Kim DN, McNaughton AD, Kumar N. Leveraging artificial intelligence to expedite antibody design and enhance antibody–antigen interactions. Bioengineering. (2024) 11:185. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020185
8. Ong E, Wong MU, Huffman A, He Y. COVID-19 coronavirus vaccine design using reverse vaccinology and machine learning. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1581. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01581
9. Sunita, Sajid A, Singh Y, Shukla P. Computational tools for modern vaccine development. Hum Vaccines Immunother. (2020) 16:723–35. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1670035
10. Kaushik R, Kant R, Christodoulides M. Artificial intelligence in accelerating vaccine development - current and future perspectives. Front Bacteriol. (2023) 2:1258159. doi: 10.3389/fbrio.2023.1258159
11. Bravi B. Development and use of machine learning algorithms in vaccine target selection. NPJ Vaccines. (2024) 9:15. doi: 10.1038/s41541-023-00795-8
12. Russo G, Reche P, Pennisi M, Pappalardo F. The combination of artificial intelligence and systems biology for intelligent vaccine design. Expert Opin Drug Discovery. (2020) 15:1267–81. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1791076
13. Hederman AP, Ackerman ME. Leveraging deep learning to improve vaccine design. Trends Immunol. (2023) 44:333–44. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2023.03.002
14. Harrer S, Shah P, Antony B, Hu J. Artificial intelligence for clinical trial design. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 40:577–91. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.05.005
15. Hu RS, Hesham AEL, Zou Q. Machine learning and its applications for protozoal pathogens and protozoal infectious diseases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:882995. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.882995
16. He Y, Rappuoli R, De Groot AS, Chen RT. Emerging vaccine informatics. BioMed Res Int. (2011) 2010:e218590. doi: 10.1155/2010/218590
17. Bali A, Bali N. Role of artificial intelligence in fast-track drug discovery and vaccine development for COVID-19. Nov AI Data Sci Adv Sustain Era COVID-19. (2022), 201–29. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9069021/.
18. Pappalardo F, Flower D, Russo G, Pennisi M, Motta S. Computational modelling approaches to vaccinology. Pharmacol Res. (2015) 92:40–5. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2014.08.006
19. Sansone SA, Rocca-Serra P, Field D, Maguire E, Taylor C, Hofmann O, et al. Toward interoperable bioscience data. Nat Genet. (2012) 44:121–6. doi: 10.1038/ng.1054
20. Vilanova C, Tanner K, Dorado-Morales P, Villaescusa P, Chugani D, Frías A, et al. Standards not that standard. J Biol Eng. (2015) 9:17. doi: 10.1186/s13036-015-0017-9
21. Lipsitch M, Dean NE. Understanding COVID-19 vaccine efficacy. Science. (2020) 370:763–5. doi: 10.1126/science.abe5938
22. Piret J, Boivin G. Pandemics throughout history. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:631736. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.631736
23. Rodrigues CMC, Plotkin SA. Impact of vaccines; health, economic and social perspectives. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:1526. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01526
24. Baker RE, Mahmud AS, Miller IF, Rajeev M, Rasambainarivo F, Rice BL, et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2022) 20:193–205. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00639-z
25. Gouglas D, Thanh Le T, Henderson K, Kaloudis A, Danielsen T, Hammersland NC, et al. Estimating the cost of vaccine development against epidemic infectious diseases: a cost minimisation study. Lancet Glob Health. (2018) 6:e1386–96. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30346-2
26. Pollard AJ, Bijker EM. A guide to vaccinology: from basic principles to new developments. Nat Rev Immunol. (2021) 21:83–100. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-00479-7
27. Pecetta S, Ahmed SS, Ellis R, Rappuoli R. Chapter 67 - Technologies for Making New Vaccines. In: Orenstein W, Offit P, Edwards KM, Plotkin S, editors. Plotkin’s Vaccines, Eighth Edition. Elsevier, Philadelphia (2023). p. 1350–1373.e9. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-79058-1.00067-0
28. Zhang L, More KR, Ojha A, Jackson CB, Quinlan BD, Li H, et al. Effect of mRNA-LNP components of two globally-marketed COVID-19 vaccines on efficacy and stability. NPJ Vaccines. (2023) 8:156. doi: 10.1038/s41541-023-00751-6
29. Liu Y, Ye Q. Nucleic Acid Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines. (2022) 10:1849. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111849
30. Ghattas M, Dwivedi G, Lavertu M, Alameh MG. Vaccine technologies and platforms for infectious diseases: current progress, challenges, and opportunities. Vaccines. (2021) 9:1490. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121490
31. Wang S, Liang B, Wang W, Li L, Feng N, Zhao Y, et al. Viral vectored vaccines: design, development, preventive and therapeutic applications in human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:149. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01408-5
32. Lafontaine ER, Chen Z, Huertas-Diaz MC, Dyke JS, Jelesijevic TP, Michel F, et al. The autotransporter protein BatA is a protective antigen against lethal aerosol infection with Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia pseudomallei. Vaccine X. (2019) 1:100002. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2018.100002
33. Kantele A, Riekkinen M, Jokiranta TS, Pakkanen SH, Pietilä JP, Patjas A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of ETVAX®, an oral inactivated vaccine against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: a double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial amongst Finnish travellers to Benin, West Africa. J Travel Med. (2023) 30:taad045. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taad045
34. Chuong C, Cereghino CN, Rai P, Bates TA, Oberer M, Weger-Lucarelli J. Enhanced attenuation of chikungunya vaccines expressing antiviral cytokines. NPJ Vaccines. (2024) 9:59. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00843-x
35. Chiuppesi F, Zaia JA, Gutierrez-Franco MA, Ortega-Francisco S, Ly M, Kha M, et al. Synthetic modified vaccinia Ankara vaccines confer cross-reactive and protective immunity against mpox virus. Commun Med. (2024) 4:19. doi: 10.1038/s43856-024-00443-9
36. Khan MS, Khan IM, Ahmad SU, Rahman I, Khan MZ, Khan MSZ, et al. Immunoinformatics design of B and T-cell epitope-based SARS-CoV-2 peptide vaccination. Front Immunol. (2023) 13. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1001430
37. Bayani F, Hashkavaei NS, Arjmand S, Rezaei S, Uskoković V, Alijanianzadeh M, et al. An overview of the vaccine platforms to combat COVID-19 with a focus on the subunit vaccines. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. (2023) 178:32–49. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2023.02.004
38. Schmidt LK, Orne CE, Shaffer TL, Wilson SM, Khakhum N, Torres AG, et al. Development of melioidosis subunit vaccines using an enzymatically inactive burkholderia pseudomallei ahpC. Infect Immun. (2022) 90:e0022222. doi: 10.1128/iai.00222-22
39. Bezbaruah R, Chavda VP, Nongrang L, Alom S, Deka K, Kalita T, et al. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems for vaccines. Vaccines. (2022) 10:1946. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111946
40. Wang S, Wang D, Duan Y, Zhou Z, Gao W, Zhang L. Cellular nanosponges for biological neutralization. Adv Mater. (2022) 34:e2107719. doi: 10.1002/adma.202107719
41. Lieberman LA. Outer membrane vesicles: A bacterial-derived vaccination system. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1029146. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1029146
42. Quakkelaar ED, Melief CJM. Experience with synthetic vaccines for cancer and persistent virus infections in nonhuman primates and patients. Adv Immunol. (2012) 114:77–106. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396548-6.00004-4
43. Vaccine Types. NIAID: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (2019). Available at: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/vaccine-types (Accessed February 3, 2025).
44. Dreher-Lesnick SM, Finn TM. Chapter 8 - Vaccine Additives and Manufacturing Residuals in Vaccines Licensed in the United States. In: Orenstein W, Offit P, Edwards KM, Plotkin S, editors. Plotkin’s Vaccines, Eighth Edition. Elsevier, Philadelphia (2023). p. 91–99.e2. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-79058-1.00008-6
45. Chaudhury S, Duncan EH, Atre T, Storme CK, Beck K, Kaba SA, et al. Identification of immune signatures of novel adjuvant formulations using machine learning. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:17508. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35452-x
46. U.S. Vaccine Safety - Overview, History, and How It Works. CDC (2024). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/ensuringsafety/history/index.htmlanchor_1593624850886.
47. Zhao T, Cai Y, Jiang Y, He X, Wei Y, Yu Y, et al. Vaccine adjuvants: mechanisms and platforms. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:283. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01557-7
48. Wang D, Bjørnstad ON, Lei T, Sun Y, Huo J, Hao Q, et al. Supply chains create global benefits from improved vaccine accessibility. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:1569. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37075-x
49. Rahmadhan MAWP, Handayani PW. Challenges of vaccination information system implementation: A systematic literature review. Hum Vaccines Immunother. (2023) 19:2257054. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2257054
50. Block J. Is the US’s vaccine adverse event reporting system broken? BMJ. (2023) 383:2582. doi: 10.1136/bmj.p2582
51. McCarthy M. Results in journals often fail to match those on ClinicalTrials.gov, study finds. BMJ. (2014) 348:g2503. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g2503
52. Hartung DM, Zarin DA, Guise JM, McDonagh M, Paynter R, Helfand M. Reporting discrepancies between the ClinicalTrials.gov results database and peer-reviewed publications. Ann Intern Med. (2014) 160:477–83. doi: 10.7326/M13-0480
53. DeVito NJ, Morley J, Smith JA, Drysdale H, Goldacre B, Heneghan C. Availability of results of clinical trials registered on EU Clinical Trials Register: cross sectional audit study. BMJ Med. (2024) 3:e000738. doi: 10.1136/bmjmed-2023-000738
54. Salholz-Hillel M, Pugh-Jones M, Hildebrand N, Schult TA, Schwietering J, Grabitz P, et al. Dissemination of Registered COVID-19 Clinical Trials (DIRECCT): a cross-sectional study. BMC Med. (2023) 21:475. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03161-6
55. Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, Molenkamp R, Meijer A, Chu DK, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. (2021) 25:2000045. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.5.210204e
56. Narykov O, Srinivasan S, Korkin D. Computational protein modeling and the next viral pandemic. Nat Methods. (2021) 18:444–5. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01144-0
57. Hwang W, Lei W, Katritsis NM, MacMahon M, Chapman K, Han N. Current and prospective computational approaches and challenges for developing COVID-19 vaccines. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. (2021) 172:249–74. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.02.004
58. Cui J, Li F, Shi ZL. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2019) 17:181–92. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0118-9
59. Volz E, Hill V, McCrone JT, Price A, Jorgensen D, O’Toole Á, et al. Evaluating the effects of SARS-coV-2 spike mutation D614G on transmissibility and pathogenicity. Cell. (2021) 184:64–75.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.020
60. Duffy S. Why are RNA virus mutation rates so damn high? PloS Biol. (2018) 16:e3000003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000003
61. Korber B, Fischer WM, Gnanakaran S, Yoon H, Theiler J, Abfalterer W, et al. Tracking changes in SARS-coV-2 spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell. (2020) 182:812–827.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.043
62. Koel BF, Burke DF, Bestebroer TM, van der Vliet S, Zondag GCM, Vervaet G, et al. Substitutions near the receptor binding site determine major antigenic change during influenza virus evolution. Science. (2013) 342:976–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1244730
63. Yewdell JW. Antigenic drift: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity. (2021) 54:2681–7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.016
64. Chen Z, Bancej C, Lee L, Champredon D. Antigenic drift and epidemiological severity of seasonal influenza in Canada. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:15625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19996-7
65. Murray GGR, Balmer AJ, Herbert J, Hadjirin NF, Kemp CL, Matuszewska M, et al. Mutation rate dynamics reflect ecological change in an emerging zoonotic pathogen. PloS Genet. (2021) 17:e1009864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009864
66. Wei X, Decker JM, Wang S, Hui H, Kappes JC, Wu X, et al. Antibody neutralization and escape by HIV-1. Nature. (2003) 422:307–12. doi: 10.1038/nature01470
67. Arunachalam PS, Wimmers F, Mok CKP, Perera RAPM, Scott M, Hagan T, et al. Systems biological assessment of immunity to mild versus severe COVID-19 infection in humans. Science. (2020) 369:1210–20. doi: 10.1126/science.abc6261
68. Plotkin Sa B, Gilbert P. Chapter 4 - Correlates of Protection. In: Orenstein W, Offit P, Edwards KM, Plotkin S, editors. Plotkin’s Vaccines, Eighth Edition. Elsevier, Philadelphia (2023). p. 45–51.e5. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-79058-1.00004-9
69. Organization WH. Correlates of vaccine-induced protection: methods and implications (2013). Available online at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/84288 (Accessed February 3, 2025).
70. Thorlund K, Smith D, Linsell C, White N, Butler C, Boulware D, et al. The importance of appropriate selection of clinical endpoints in outpatient COVID-19 clinical trials. Commun Med. (2023) 3:53. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00281-1
71. Ciani O, Manyara AM, Davies P, Stewart D, Weir CJ, Young AE, et al. A framework for the definition and interpretation of the use of surrogate endpoints in interventional trials. EClinicalMedicine. (2023) 65:102283. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102283
72. Verschoor CP, Singh P, Russell ML, Bowdish DME, Brewer A, Cyr L, et al. Correction: microneutralization assay titres correlate with protection against seasonal influenza H1N1 and H3N2 in children. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0163830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163830
73. Ramasamy MN, Kelly EJ, Seegobin S, Dargan PI, Payne R, Libri V, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of AZD2816, a beta (B.1.351) variant COVID-19 vaccine, and AZD1222 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19) as third-dose boosters for previously vaccinated adults: a multicentre, randomised, partly double-blinded, phase 2/3 non-inferiority immunobridging study in the UK and Poland. Lancet Microbe. (2023) 4:e863–74. doi: 10.1016/s2666-5247(23)00177-5
74. Benkeser D, Montefiori DC, McDermott AB, Fong Y, Janes HE, Deng W, et al. Comparing antibody assays as correlates of protection against COVID-19 in the COVE mRNA-1273 vaccine efficacy trial. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15:eade9078. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ade9078
75. Bockstal V, Leyssen M, Heerwegh D, Spiessens B, Robinson C, Stoop JN, et al. Non-human primate to human immunobridging demonstrates a protective effect of Ad26.ZEBOV, MVA-BN-Filo vaccine against Ebola. NPJ Vaccines. (2022) 7:156. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00564-z
76. Khoury DS, Schlub TE, Cromer D, Steain M, Fong Y, Gilbert PB, et al. Correlates of protection, thresholds of protection, and immunobridging among persons with SARS-coV-2 infection. Emerg Infect Dis. (2023) 29:381–8. doi: 10.3201/eid2902.221422
77. Joffe M. Principal stratification and attribution prohibition: good ideas taken too far. Int J Biostat. (2011) 7:Article 35. doi: 10.2202/1557-4679.1367
78. Pearl J. Principal stratification–a goal or a tool? Int J Biostat. (2011) 7:20. doi: 10.2202/1557-4679.1322
79. Gilbert PB, Hudgens MG, Wolfson J. Commentary on “Principal stratification - a goal or a tool?” by Judea Pearl. Int J Biostat. (2011) 7:Article 36. doi: 10.2202/1557-4679.1341
80. Frangakis CE, Rubin DB. Principal stratification in causal inference. Biometrics. (2002) 58:21–9. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2002.00021.x
81. Logunov DY, Dolzhikova IV, Shcheblyakov DV, Tukhvatulin AI, Zubkova OV, Dzharullaeva AS, et al. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. Lancet Lond Engl. (2021) 397:671–81. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00234-8
82. Correa J, Lee S, Bareinboim E. Nested Counterfactual Identification from Arbitrary Surrogate Experiments. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates, Inc (2021). p. 6856–67. Available at: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/hash/36bedb6eb7152f39b16328448942822b-Abstract.html.
83. Nabi R, Bhattacharya R, Shpitser I. ICML'20: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Article No.: 663, 7153–63.
84. Sherman E, Shpitser I. Identification and estimation of causal effects from dependent data. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. (2018) 2018:9446–57. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30643365.
85. Tikka S, Karvanen J. Surrogate outcomes and transportability. Int J Approx Reason. (2019) 108:21–37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2019.02.007
86. Lee S, Correa J, Bareinboim E. General Identifiability with Arbitrary Surrogate Experiments. Columbia University (2019). Available at: https://causalai.net/r46.pdf.
87. Duarte G, Finkelstein N, Knox D, Mummolo J, Shpitser I. An automated approach to causal inference in discrete settings. arXiv. (2021). doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2109.13471
88. Gilbert PB, Fong Y, Hejazi NS, Kenny A, Huang Y, Carone M, et al. Four statistical frameworks for assessing an immune correlate of protection (surrogate endpoint) from a randomized, controlled, vaccine efficacy trial. Vaccine. (2024) 42:2181–90. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.02.071
89. Olivares A, Staffetti E. Uncertainty quantification of a mathematical model of COVID-19 transmission dynamics with mass vaccination strategy. Chaos Solitons Fractals. (2021) 146:110895. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110895
90. Lu Y, Chen T, Hao N, Van Rechem C, Chen J, Fu T. Uncertainty quantification and interpretability for clinical trial approval prediction. Health Data Sci. (2024) 4:0126. doi: 10.34133/hds.0126
91. Krastev S, Krajden O, Vang ZM, Juárez FPG, Solomonova E, Goldenberg M, et al. Navigating the uncertainty: A novel taxonomy of vaccine hesitancy in the context of COVID-19. PloS One. (2023) 18:e0295912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295912
92. Wang C, Qiang X, Xu M, Wu T. Recent advances in surrogate modeling methods for uncertainty quantification and propagation. Symmetry. (2022) 14:1219. doi: 10.3390/sym14061219
93. Zech JR, Badgeley MA, Liu M, Costa AB, Titano JJ, Oermann EK. Variable generalization performance of a deep learning model to detect pneumonia in chest radiographs: A cross-sectional study. PloS Med. (2018) 15:e1002683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002683
94. Gilbert PB, Montefiori DC, McDermott AB, Fong Y, Benkeser D, Deng W, et al. Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science. (2022) 375:43–50. doi: 10.1126/science.abm3425
95. Poland GA, Kennedy RB, McKinney BA, Ovsyannikova IG, Lambert ND, Jacobson RM, et al. Vaccinomics, adversomics, and the immune response network theory: Individualized vaccinology in the 21st century. Semin Immunol. (2013) 25:89–103. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.04.007
96. Lin Y, He Y. Ontology representation and analysis of vaccine formulation and administration and their effects on vaccine immune responses. J BioMed Semant. (2012) 3:17. doi: 10.1186/2041-1480-3-17
97. Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. (2000) 25:25–9. doi: 10.1038/75556
98. Diehl AD, Meehan TF, Bradford YM, Brush MH, Dahdul WM, Dougall DS, et al. The Cell Ontology 2016: enhanced content, modularization, and ontology interoperability. J BioMed Semant. (2016) 7:44. doi: 10.1186/s13326-016-0088-7
99. Topalis P, Mitraka E, Dritsou V, Dialynas E, Louis C. IDOMAL: the malaria ontology revisited. J BioMed Semant. (2013) 4:16. doi: 10.1186/2041-1480-4-16
100. Hou J, Wang S, Jia M, Li D, Liu Y, Li Z, et al. A systems vaccinology approach reveals temporal transcriptomic changes of immune responses to the yellow fever 17D vaccine. J Immunol Baltim Md 1950. (2017) 199:1476–89. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700083
101. Bodenreider O. Biomedical ontologies in action: role in knowledge management, data integration and decision support. Yearb Med Inform. (2008) 17(01):67–79. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1638585
102. Hoyt CT, Balk M, Callahan TJ, Domingo-Fernández D, Haendel MA, Hegde HB, et al. Unifying the identification of biomedical entities with the Bioregistry. Sci Data. (2022) 9:714. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01807-3
103. Juty N, Le Novère N, Laibe C. Identifiers.org and MIRIAM Registry: community resources to provide persistent identification. Nucleic Acids Res. (2012) 40:D580–586. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1097
104. Wimalaratne SM, Juty N, Kunze J, Janée G, McMurry JA, Beard N, et al. Uniform resolution of compact identifiers for biomedical data. Sci Data. (2018) 5:180029. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2018.29
105. FAIRsharing. CURIE (2024). Available at: https://fairsharing.org/FAIRsharing.af21db (Accessed February 3, 2025).
106. Rogers FB. Medical subject headings. Bull Med Libr Assoc. (1963) 51:114–6. Available online at: https://bioregistry.io/pubmed:13982385 (Accessed February 25, 2025).
107. de Coronado S, Haber MW, Sioutos N, Tuttle MS, Wright LW. NCI Thesaurus: using science-based terminology to integrate cancer research results. Stud Health Technol Inform. (2004) 107:33–7.
108. McCray AT. An upper-level ontology for the biomedical domain. Comp Funct Genomics. (2003) 4:80–4. doi: 10.1002/cfg.v4:1
109. Bair AH, Brown LP, Pugh LC, Borucki LC, Spatz DL. Taking a bite out of CRISP. Strategies on using and conducting searches in the Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects database. Comput Nurs. (1996) 14:218–24; quiz 225–6. doi: 10.1097/00024665-199607000-00010
110. Brown EG, Wood L, Wood S. The medical dictionary for regulatory activities (MedDRA). Drug Saf. (1999) 20:109–17. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199920020-00002
111. Baorto DM, Cimino JJ, Parvin CA, Kahn MG. Combining laboratory data sets from multiple institutions using the logical observation identifier names and codes (LOINC). Int J Med Inf. (1998) 51:29–37. doi: 10.1016/S1386-5056(98)00089-6
112. Lu DFF, Eichmann D, Konicek D, Park HT, Ucharattana P, Delaney C. Standardized nursing language in the systematized nomenclature of medicine clinical terms: A cross-mapping validation method. Comput Inform Nurs CIN. (2006) 24:288–96. doi: 10.1097/00024665-200609000-00011
113. Research C for BE and. Vaccines Licensed for Use in the United States. FDA (2022). Available at: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/vaccines/vaccines-licensed-use-united-states (Accessed February 3, 2025).
114. Research C for BE and. FDA. FDA. Labeling for CBER-Regulated Products (2023). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/development-approval-process-cber/labeling-cber-regulated-products (Accessed February 3, 2025).
115. IIS | Code Sets | CVX | Vaccines. CDC (2018). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/programs/iis/code-sets.html (Accessed February 3, 2025).
116. Thorwarth WT. CPT: an open system that describes all that you do. J Am Coll Radiol JACR. (2008) 5:555–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2007.10.004
117. American Medical Association. CPT® (Current Procedural Terminology) (2024). Available online at: https://www.ama-assn.org/amaone/cpt-current-procedural-terminology (Accessed February 3, 2025).
118. Product-information requirements. European Medicines Agency (2024). Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/marketing-authorisation/product-information-requirements (Accessed February 3, 2025).
119. Marketing authorisation. European Medicines Agency (2024). Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/marketing-authorisation (Accessed February 3, 2025).
120. Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification (2024). Available online at: https://www.who.int/tools/atc-ddd-toolkit/atc-classification (Accessed February 3, 2025).
121. Seo Y, Pacifici E. Elements of regulatory dissonance: examining FDA and EMA product labeling of new vaccines (2006-2018). Vaccine. (2020) 38:7485–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.09.067
122. Teixeira T, Kweder SL, Saint-Raymond A. Are the european medicines agency, US food and drug administration, and other international regulators talking to each other? Clin Pharmacol Ther. (2020) 107:507–13. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1617
123. Hastings J, Owen G, Dekker A, Ennis M, Kale N, Muthukrishnan V, et al. ChEBI in 2016: Improved services and an expanding collection of metabolites. Nucleic Acids Res. (2016) 44:D1214–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1031
124. Vaccine Reports and Strategic Plans. NIAID: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (2021). Available at: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/vaccine-reports-strategic-plans (Accessed February 3, 2025).
125. Vaccine Adjuvant Research Programs. NIAID: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (2022). Available at: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/research/vaccine-adjuvant-research-programs (Accessed February 3, 2025).
126. Schoch CL, Ciufo S, Domrachev M, Hotton CL, Kannan S, Khovanskaya R, et al. NCBI Taxonomy: a comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database J Biol Database Curation. (2020) 2020:baaa062. doi: 10.1093/database/baaa062
127. Caetano-Anollés G, Claverie JM, Nasir A. A critical analysis of the current state of virus taxonomy. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1240993
128. He Y, Yu H, Huffman A, Lin AY, Natale DA, Beverley J, et al. A comprehensive update on CIDO: the community-based coronavirus infectious disease ontology. J BioMed Semant. (2022) 13:25. doi: 10.1186/s13326-022-00279-z
129. Gangavarapu K, Latif AA, Mullen JL, Alkuzweny M, Hufbauer E, Tsueng G, et al. Outbreak.info genomic reports: scalable and dynamic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations. Nat Methods. (2023) 20:512–22. doi: 10.1038/s41592-023-01769-3
130. Khare S, Gurry C, Freitas L, Schultz MB, Bach G, Diallo A, et al. Gisaid’s role in pandemic response. China CDC Wkly. (2021) 3:1049–51. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2021.255
131. Rambaut A, Holmes EC, O’Toole Á, Hill V, McCrone JT, Ruis C, et al. A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology. Nat Microbiol. (2020) 5:1403–7. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0770-5
132. O’Toole Á, Hill V, Pybus OG, Watts A, Bogoch II, Khan K, et al. Tracking the international spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages B.1.1.7 and B.1.351/501Y-V2 with grinch. Wellcome Open Res. (2021) 6:121. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres
133. O’Toole Á, Scher E, Underwood A, Jackson B, Hill V, McCrone JT, et al. Assignment of epidemiological lineages in an emerging pandemic using the pangolin tool. Virus Evol. (2021) 7:veab064. doi: 10.1093/ve/veab064/6315289
134. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants (2024). Available online at: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (Accessed February 3, 2025).
135. Vashishtha VM, Kumar P. The durability of vaccine-induced protection: an overview. Expert Rev Vaccines. (2024) 23:389–408. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2024.2331065
136. Babcock S, Beverley J, Cowell LG, Smith B. The infectious disease ontology in the age of COVID-19. J BioMed Semant. (2021) 12:13. doi: 10.1186/s13326-021-00245-1
137. Szabó GT, Mahiny AJ, Vlatkovic I. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Platforms and current developments. Mol Ther. (2022) 30:1850–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.02.016
138. Brown GR, Hem V, Katz KS, Ovetsky M, Wallin C, Ermolaeva O, et al. Gene: a gene-centered information resource at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. (2015) 43:D36–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1055
139. UniProt Consortium. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:D523–31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1052
140. Sayers EW, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, Ostell J, Pruitt KD, Karsch-Mizrachi I. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. (2020) 48:D84–6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz956
141. Schäffer AA, Hatcher EL, Yankie L, Shonkwiler L, Brister JR, Karsch-Mizrachi I, et al. VADR: validation and annotation of virus sequence submissions to GenBank. BMC Bioinf. (2020) 21:211. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3537-3
142. Salimi N, Fleri W, Peters B, Sette A. The immune epitope database: a historical retrospective of the first decade. Immunology. (2012) 137:117–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03611.x
143. Goncharov M, Bagaev D, Shcherbinin D, Zvyagin I, Bolotin D, Thomas PG, et al. VDJdb in the pandemic era: a compendium of T cell receptors specific for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Methods. (2022) 19:1017–9. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01578-0
144. He Y, Sarntivijai S, Lin Y, Xiang Z, Guo A, Zhang S, et al. OAE: the ontology of adverse events. J BioMed Semant. (2014) 5:29. doi: 10.1186/2041-1480-5-29
145. Marcos E, Zhao B, He Y. The Ontology of Vaccine Adverse Events (OVAE) and its usage in representing and analyzing adverse events associated with US-licensed human vaccines. J BioMed Semant. (2013) 4:40. doi: 10.1186/2041-1480-4-40
146. Wong MU, Racz R, Ong E, He Y. Towards precision informatics of pharmacovigilance: OAE-CTCAE mapping and OAE-based representation and analysis of adverse events in patients treated with cancer drugs. AMIA Annu Symp Proc AMIA Symp. (2017) 2017:1793–801. Available online at: https://bioregistry.io/pubmed:29854250 (Accessed February 25, 2025).
147. Svingen T, Villeneuve DL, Knapen D, Panagiotou EM, Draskau MK, Damdimopoulou P, et al. A pragmatic approach to adverse outcome pathway development and evaluation. Toxicol Sci. (2021) 184:183–90. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfab113
148. Schriml LM, Munro JB, Schor M, Olley D, McCracken C, Felix V, et al. The human disease ontology 2022 update. Nucleic Acids Res. (2022) 50:D1255–61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1063
149. Schriml LM, Arze C, Nadendla S, Ganapathy A, Felix V, Mahurkar A, et al. GeMInA, Genomic Metadata for Infectious Agents, a geospatial surveillance pathogen database. Nucleic Acids Res. (2010) 38:D754–764. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp832
150. Gargano MA, Matentzoglu N, Coleman B, Addo-Lartey EB, Anagnostopoulos AV, Anderton J, et al. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2024: phenotypes around the world. Nucleic Acids Res. (2024) 52:D1333–46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1005
151. Amith M, Tao C. Representing vaccine misinformation using ontologies. J BioMed Semant. (2018) 9:22. doi: 10.1186/s13326-018-0190-0
152. Whetzel PL, Noy NF, Shah NH, Alexander PR, Nyulas C, Tudorache T, et al. BioPortal: enhanced functionality via new Web services from the National Center for Biomedical Ontology to access and use ontologies in software applications. Nucleic Acids Res. (2011) 39:W541–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr469
153. Hoyt CT, Balk M, Callahan TJ, Domingo-Fernández D, Haendel MA, Hegde HB, et al. Unifying the identification of biomedical entities with the Bioregistry. Sci Data. (2022) 9:714. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01807-3
154. Unified Medical Language System (UMLS). U.S. National Library of Medicine (2024). Available at: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/index.html (Accessed February 3, 2025).
155. Jackson R, Matentzoglu N, Overton JA, Vita R, Balhoff JP, Buttigieg PL, et al. OBO Foundry in 2021: operationalizing open data principles to evaluate ontologies. Database J Biol Database Curation. (2021) 2021:baab069. doi: 10.1093/database/baab069
156. Bianchi S, Burla A, Conti C, Farkash A, Kent C, Maman Y, et al. Biomedical data integration - capturing similarities while preserving disparities. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc Annu Int Conf. (2009) 2009:4654–7. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5332650
157. Almeida JR, Pazos A, Oliveira JL. Clinical data integration strategies for multicenter studies. In: Camarinha-Matos LM, Ferrada F, editors. Technological innovation for connected cyber physical spaces: 14th IFIP WG 55/SOCOLNET doctoral conference on computing, electrical and industrial systems, doceis 2023, caparica, Portugal, july 5–7, 2023, proceedings. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2023). p. 175–90. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-36007-7_13
158. Martínez-García M, Hernández-Lemus E. Data integration challenges for machine learning in precision medicine. Front Med. (2021) 8:784455. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.784455
159. Müller A, Christmann LS, Kohler S, Eils R, Prasser F. Machine learning for medical data integration. Stud Health Technol Inform. (2023) 302:691–5. doi: 10.3233/SHTI230241
160. Huerta EA, Blaiszik B, Brinson LC, Bouchard KE, Diaz D, Doglioni C, et al. FAIR for AI: An interdisciplinary and international community building perspective. Sci Data. (2023) 10:487. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02298-6
161. ICTRP search portal (2024). Available online at: https://www.who.int/clinical-trials-registry-platform/the-ictrp-search-portal (Accessed February 3, 2025).
162. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) (2024). Available online at: https://vaers.hhs.gov/ (Accessed February 3, 2025).
163. Waagmeester A, Stupp G, Burgstaller-Muehlbacher S, Good BM, Griffith M, Griffith OL, et al. Wikidata as a knowledge graph for the life sciences. eLife. (2020) 9:e52614. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52614
164. Smith KC, Chawla DG, Dhillon BK, Ji Z, Vita R, van der Leest EC, et al. A curated collection of human vaccination response signatures. Sci Data. (2022) 9:678. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01558-1
165. Diray-Arce J, Miller HER, Henrich E, Gerritsen B, Mulè MP, Fourati S, et al. The Immune Signatures data resource, a compendium of systems vaccinology datasets. Sci Data. (2022) 9:635. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01714-7
166. Yu H, Li L, Huffman A, Beverley J, Hur J, Merrell E, et al. A new framework for host-pathogen interaction research. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1066733. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1066733
167. Mena Lora AJ, Long JE, Huang Y, Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Follmann D, et al. Rapid development of an integrated network infrastructure to conduct phase 3 COVID-19 vaccine trials. JAMA Netw Open. (2023) 6:e2251974. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.51974
168. He Y, Racz R, Sayers S, Lin Y, Todd T, Hur J, et al. Updates on the web-based VIOLIN vaccine database and analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res. (2014) 42:D1124–1132. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1133
169. Huang PC, Goru R, Huffman A, Yu Lin A, Cooke MF, He Y. Cov19VaxKB: A web-based integrative COVID-19 vaccine knowledge base. Vaccine X. (2021) 10:100139. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2021.100139
170. Zhao B, Zhao L. Mining adverse events in large frequency tables with ontology, with an application to the vaccine adverse event reporting system. Stat Med. (2023) 42:1512–24. doi: 10.1002/sim.v42.10
171. Botsis T, Nguyen MD, Woo EJ, Markatou M, Ball R. Text mining for the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System: medical text classification using informative feature selection. J Am Med Inform Assoc. (2011) 18:631–8. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2010-000022
172. Tanaka Y, Chen HY, Belloni P, Gisladottir U, Kefeli J, Patterson J, et al. OnSIDES (ON-label SIDE effectS resource) Database: Extracting Adverse Drug Events from Drug Labels using Natural Language Processing Models. medRxiv. (2023). doi: 10.1101/2024.03.22.24304724
173. Adverse Drug Events Discovery Using Natural Language Processing - inovex GmbH (2024). Available online at: https://www.inovex.de/de/blog/adverse-drug-events-discovery-nlp/ (Accessed February 3, 2025).
174. Improving Drug Safety With Adverse Event Detection Using NLP (2024). Available online at: https://www.databricks.com/blog/2022/01/17/improving-drug-safety-with-adverse-event-detection-using-nlp.html (Accessed February 3, 2025).
175. Wang J, Qian C, Cui S, Glass L, Ma F. Towards Federated COVID-19 Vaccine Side Effect Prediction. In: Amini MR, Canu S, Fischer A, Guns T, Kralj Novak P, Tsoumakas G, editors. Machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases: european conference, ECML PKDD 2022, grenoble, France, september 19–23, 2022, proceedings, part VI. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham (2023). p. 437–52. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26422-1_27
176. Bioregistry. Clinical Trial Registries (2024). Available online at: https://bioregistry.io/collection/0000012 (Accessed February 3, 2025).
177. How to Read Study Results. ClinicalTrials.gov (2024). Available at: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study-basics/how-to-read-study-results (Accessed February 3, 2025).
178. Primary registries (2024). Available online at: https://www.who.int/clinical-trials-registry-platform/network/primary-registries (Accessed February 3, 2025).
179. Shi X, Du J. Constructing a finer-grained representation of clinical trial results from ClinicalTrials.gov. Sci Data. (2024) 11:41. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02869-7
180. Chen Z, Peng B, Ioannidis VN, Li M, Karypis G, Ning X. A knowledge graph of clinical trials ([Formula: see text]). Sci Rep. (2022) 12:4724. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08454-z
181. Hassanzadeh O, Miller RJ. Automatic Curation of Clinical Trials Data in LinkedCT. In: Arenas M, Corcho O, Simperl E, Strohmaier M, d’Aquin M, Srinivas K, et al, editors. The Semantic Web - ISWC 2015. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2015). p. 270–8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25010-6_16
182. Goldacre B, Gray J. OpenTrials: towards a collaborative open database of all available information on all clinical trials. Trials. (2016) 17:164. doi: 10.1186/s13063-016-1290-8
183. Quan X, Cai W, Xi C, Wang C, Yan L. AIMedGraph: a comprehensive multi-relational knowledge graph for precision medicine. Database. (2023) 2023:baad006. doi: 10.1093/database/baad006/7059703
184. Gong L, Whirl-Carrillo M, Klein TE. PharmGKB, an integrated resource of pharmacogenomic knowledge. Curr Protoc. (2021) 1:e226. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.226
185. FDA. U.S Food & Drug Administration. COMIRNATY (2023). Available online at: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/comirnaty (Accessed February 3, 2025).
186. Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine, Adjuvanted. FDA (2024). Available at: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/coronavirus-covid-19-cber-regulated-biologics/novavax-covid-19-vaccine-adjuvanted (Accessed February 3, 2025).
187. Adjuvants and Vaccines | Vaccine Safety. CDC (2022). Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/concerns/adjuvants.html (Accessed February 3, 2025).
188. Haendel MA, Chute CG, Robinson PN. Classification, ontology, and precision medicine. N Engl J Med. (2018) 379:1452–62. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1615014
189. Anderson ML, Peterson ED. Compliance with results reporting at ClinicalTrials.gov. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:2370–1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsa1409364
190. International Society for Biocuration. Biocuration: Distilling data into knowledge. PloS Biol. (2018) 16:e2002846. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2002846
191. Slater T. Recent advances in modeling languages for pathway maps and computable biological networks. Drug Discovery Today. (2014) 19:193–8. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.12.011
192. Demir E, Cary MP, Paley S, Fukuda K, Lemer C, Vastrik I, et al. The BioPAX community standard for pathway data sharing. Nat Biotechnol. (2010) 28:935–42. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1666
193. Hucka M, Bergmann FT, Chaouiya C, Dräger A, Hoops S, Keating SM, et al. The systems biology markup language (SBML): language specification for level 3 version 2 core release 2. J Integr Bioinforma. (2019) 16:20190021. doi: 10.1515/jib-2019-0021
194. Standards. CDISC (2024). Available at: https://www.cdisc.org/standards (Accessed February 3, 2025).
195. Hallinan CM, Ward R, Hart GK, Sullivan C, Pratt N, Ng AP, et al. Seamless EMR data access: Integrated governance, digital health and the OMOP-CDM. BMJ Health Care Inform. (2024) 31:e100953. doi: 10.1136/bmjhci-2023-100953
196. Index - FHIR v5.0.0 (2024). Available online at: https://hl7.org/fhir/index.html (Accessed February 3, 2025).
197. Sansone SA, McQuilton P, Rocca-Serra P, Gonzalez-Beltran A, Izzo M, Lister AL, et al. FAIRsharing as a community approach to standards, repositories and policies. Nat Biotechnol. (2019) 37:358–67. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0080-8
198. Wilkinson MD, Dumontier M, Aalbersberg IJJ, Appleton G, Axton M, Baak A, et al. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci Data. (2016) 3:160018. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.18
199. Lin D, Crabtree J, Dillo I, Downs RR, Edmunds R, Giaretta D, et al. The TRUST Principles for digital repositories. Sci Data. (2020) 7:144. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0486-7
200. Applying the “CARE Principles for Indigenous Data Governance” to ecology and biodiversity research (2024). Available online at.
202. Hoyt CT, Gyori BM. Open code, open data, and open infrastructure to promote the sustainability of curated scientific resources. Sci Data. (2024) 11:547. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03406-w
203. FAIRsharing | RDACovid19WG (2024). Available online at: https://fairsharing.org/3540 (Accessed February 3, 2025).
204. Biolink Model: A universal schema for knowledge graphs in clinical, biomedical, and translational science (2024). Available online at.
205. Lobentanzer S, Aloy P, Baumbach J, Bohar B, Carey VJ, Charoentong P, et al. Democratizing knowledge representation with BioCypher. Nat Biotechnol. (2023) 41:1056–9. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-01848-y
206. Callahan TJ, Tripodi IJ, Stefanski AL, Cappelletti L, Taneja SB, Wyrwa JM, et al. An open-source knowledge graph ecosystem for the life sciences. arXiv. (2024). doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2307.05727
207. Jacobsen JOB, Baudis M, Baynam GS, Beckmann JS, Beltran S, Buske OJ, et al. The GA4GH Phenopacket schema defines a computable representation of clinical data. Nat Biotechnol. (2022) 40:817–20. doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01357-4
208. Klopfenstein SAI, Sass J, Vorisek CN, Jorczik F, Schmidt CO, Löbe M, et al. Bringing communities together: mapping the investigation-study-assay-model (ISA) to fast healthcare interoperability resources (FHIR). Stud Health Technol Inform. (2024) 310:18–22. doi: 10.3233/shti230919
209. Vidal ME, Jozashoori S, Sakor A. Semantic Data Integration Techniques for Transforming Big Biomedical Data into Actionable Knowledge. In: 2019 IEEE 32nd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS). IEEE (2019). p. 563–6. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8787394/.
210. Haque AKMB, Arifuzzaman BM, Siddik SAN, Kalam A, Shahjahan TS, Saleena TS, et al. Semantic web in healthcare: A systematic literature review of application, research gap, and future research avenues. Int J Clin Pract. (2022) 2022:6807484. doi: 10.1155/2022/6807484
211. Kamdar MR, Fernández JD, Polleres A, Tudorache T, Musen MA. Enabling Web-scale data integration in biomedicine through Linked Open Data. NPJ Digit Med. (2019) 2:90. doi: 10.1038/s41746-019-0162-5
212. Kamdar MR, Musen MA. An empirical meta-analysis of the life sciences linked open data on the web. Sci Data. (2021) 8:24. doi: 10.1038/s41597-021-00797-y
213. Redaschi N, Consortium U. UniProt in RDF: tackling data integration and distributed annotation with the semantic web. Nat Preced. (2009). doi: 10.1038/npre.2009.3193.1
214. UniProt Consortium. Uniprot: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:D523–31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1052
215. SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics RDF Group Members. The SIB swiss institute of bioinformatics semantic web of data. Nucleic Acids Res. (2024) 52:D44–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad902
216. Chen Q, Allot A, Leaman R, Wei CH, Aghaarabi E, Guerrerio JJ, et al. LitCovid in 2022: an information resource for the COVID-19 literature. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:D1512–8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1005
217. Huang MS, Han JC, Lin PY, You YT, Tsai RTH, Hsu WL. Surveying biomedical relation extraction: a critical examination of current datasets and the proposal of a new resource. Brief Bioinform. (2024) 25:bbae132. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae132/7644532
218. Valenzuela-Escárcega MA, Babur Ö, Hahn-Powell G, Bell D, Hicks T, Noriega-Atala E, et al. Large-scale automated machine reading discovers new cancer-driving mechanisms. Database. (2018) 2018:bay098. doi: 10.1093/database/bay098
219. Gu Y, Tinn R, Cheng H, Lucas M, Usuyama N, Liu X, et al. Domain-specific language model pretraining for biomedical natural language processing. ACM Trans Comput Healthc. (2022) 3:1–23. doi: 10.1145/3458754
220. Lee J, Yoon W, Kim S, Kim D, Kim S, So CH, et al. BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics. (2020) 36:1234–40. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz682
221. Workshop B, Scao TL, Fan A, Akiki C, Pavlick E, et al. BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model (2022). doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2211.05100
222. Joachimiak MP, Caufield JH, Harris NL, Kim H, Mungall CJ. Gene Set Summarization using Large Language Models. arXiv. (2023). doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2305.13338
223. Dong G, Bate A, Haguinet F, Westman G, Dürlich L, Hviid A, et al. Optimizing signal management in a vaccine adverse event reporting system: A proof-of-concept with COVID-19 vaccines using signs, symptoms, and natural language processing. Drug Saf. (2024) 47:173–82. doi: 10.1007/s40264-023-01381-6
224. Geronikolou SA, Takan I, Pavlopoulou A, Mantzourani M, Chrousos GP. Thrombocytopenia in COVID−19 and vaccine−induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia. Int J Mol Med. (2022) 49(3):35. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5090
225. Botsis T, Foster M, Kreimeyer K, Pandey A, Forshee R. Monitoring biomedical literature for post-market safety purposes by analyzing networks of text-based coded information. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc AMIA Summit Transl Sci. (2017) 2017:66–75. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28815108.
226. Kreimeyer K, Menschik D, Winiecki S, Paul W, Barash F, Woo EJ, et al. Using probabilistic record linkage of structured and unstructured data to identify duplicate cases in spontaneous adverse event reporting systems. Drug Saf. (2017) 40:571–82. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0523-4
227. Botsis T, Woo EJ, Ball R. The contribution of the vaccine adverse event text mining system to the classification of possible Guillain-Barré syndrome reports. Appl Clin Inform. (2013) 4:88–99. doi: 10.4338/ACI-2012-11-RA-0049
228. Botsis T, Buttolph T, Nguyen MD, Winiecki S, Woo EJ, Ball R. Vaccine adverse event text mining system for extracting features from vaccine safety reports. J Am Med Inform Assoc. (2012) 19:1011–8. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-000881
229. Canaparo M, Ronchieri E, Scarso L. A natural language processing approach for analyzing COVID-19 vaccination response in multi-language and geo-localized tweets. Healthc Anal N Y N. (2023) 3:100172. doi: 10.1016/j.health.2023.100172
230. Ye J, Hai J, Wang Z, Wei C, Song J. Leveraging natural language processing and geospatial time series model to analyze COVID-19 vaccination sentiment dynamics on Tweets. JAMIA Open. (2023) 6:ooad023. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooad023
231. Chen C, Zhu J. Quantifying health policy uncertainty in China using newspapers: text mining study. J Med Internet Res. (2023) 25:e46589. doi: 10.2196/46589
232. Alhumoud S, Al Wazrah A, Alhussain L, Alrushud L, Aldosari A, Altammami RN, et al. ASAVACT: Arabic sentiment analysis for vaccine-related COVID-19 tweets using deep learning. PeerJ Comput Sci. (2023) 9:e1507. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1507
233. Verma M, Moudgil N, Goel G, Pardeshi P, Joseph J, Kumar N, et al. People’s perceptions on COVID-19 vaccination: an analysis of twitter discourse from four countries. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:14281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41478-7
234. Mori Y, Miyatake N, Suzuki H, Mori Y, Okada S, Tanimoto K. Comparison of impressions of COVID-19 vaccination and influenza vaccination in Japan by analyzing social media using text mining. Vaccines. (2023) 11:1327. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11081327
235. Hur J, Ozgür A, Xiang Z, He Y. Identification of fever and vaccine-associated gene interaction networks using ontology-based literature mining. J BioMed Semant. (2012) 3:18. doi: 10.1186/2041-1480-3-18
236. Newton AJH, Chartash D, Kleinstein SH, McDougal RA. A pipeline for the retrieval and extraction of domain-specific information with application to COVID-19 immune signatures. BMC Bioinf. (2023) 24:292. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05397-8
237. Leonardelli L, Lofano G, Selvaggio G, Parolo S, Giampiccolo S, Tomasoni D, et al. Literature mining and mechanistic graphical modelling to improve mRNA vaccine platforms. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:738388. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.738388
238. Cosbi. A QSP approach based on a graphical model to improve mRNA vaccine platforms (2024). Available online at: https://www.cosbi.eu/case-studies/a-qsp-approach-based-on-a-graphical-model-to-improve-mrna-vaccine-platforms (Accessed February 3, 2025).
239. Messan KS, Sulima PP, Ghosh D, Nye J. The research foundation for COVID-19 vaccine development. Front Res Metr Anal. (2023) 8:1078971. doi: 10.3389/frma.2023.1078971
240. Caucheteur D, May Pendlington Z, Roncaglia P, Gobeill J, Mottin L, Matentzoglu N, et al. COVoc and COVTriage: novel resources to support literature triage. Bioinformatics. (2023) 39(1):btac800. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btac800
241. Chen Q, Allot A, Leaman R, Islamaj R, Du J, Fang L, et al. Multi-label classification for biomedical literature: an overview of the BioCreative VII LitCovid Track for COVID-19 literature topic annotations. Database J Biol Database Curation. (2022) 2022:baac069. doi: 10.1093/database/baac069
242. Vora B, Kuruvilla D, Kim C, Wu M, Shemesh CS, Roth GA. Applying Natural Language Processing to ClinicalTrials.gov: mRNA cancer vaccine case study. Clin Transl Sci. (2023) 16:2417–20. doi: 10.1111/cts.13648
243. Weissenbacher D, O’Connor K, Klein A, Golder S, Flores I, Elyaderani A, et al. Text mining biomedical literature to identify extremely unbalanced data for digital epidemiology and systematic reviews: dataset and methods for a SARS-CoV-2 genomic epidemiology study. medRxiv. (2023). doi: 10.1101/2023.07.29.23293370
244. Urru S, Sciannameo V, Lanera C, Salaris S, Gregori D, Berchialla P. A topic trend analysis on COVID-19 literature. Digit Health. (2022) 8:20552076221133696. doi: 10.1177/20552076221133696
245. Leung YT, Khalvati F. Exploring COVID-19-related stressors: topic modeling study. J Med Internet Res. (2022) 24:e37142. doi: 10.2196/37142
246. Hur J, Xiang Z, Feldman EL, He Y. Ontology-based Brucella vaccine literature indexing and systematic analysis of gene-vaccine association network. BMC Immunol. (2011) 12:49. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-49
247. Nath SK, Pankajakshan P, Sharma T, Kumari P, Shinde S, Garg N, et al. A data-driven approach to construct a molecular map of trypanosoma cruzi to identify drugs and vaccine targets. Vaccines. (2023) 11:267. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020267
248. Li J, Gao J, Feng B, Jing Y. PlagueKD: a knowledge graph-based plague knowledge database. Database J Biol Database Curation. (2022) 2022:baac100. doi: 10.1093/database/baac100
249. Ammar N, Olusanya OA, Melton C, Chinthala L, Huang X, White BM, et al. Digital personal health coaching platform for promoting human papillomavirus infection vaccinations and cancer prevention: knowledge graph-based recommendation system. JMIR Form Res. (2023) 7:e50210. doi: 10.2196/50210
250. Amith M, Lin RZ, Cui L, Wang D, Zhu A, Xiong G, et al. Conversational ontology operator: patient-centric vaccine dialogue management engine for spoken conversational agents. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2020) 20:259. doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-01267-y
251. Hu Y, Keloth VK, Raja K, Chen Y, Xu H. Towards precise PICO extraction from abstracts of randomized controlled trials using a section-specific learning approach. Bioinformatics. (2023) 39(9):btad542. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btad542
252. Hou W, Ji Z. Assessing GPT-4 for cell type annotation in single-cell RNA-seq analysis. Nat Methods. (2024) 21:1462 5. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02235-4
253. Penning de Vries BBL, van Smeden M, Rosendaal FR, Groenwold RHH. Title, abstract, and keyword searching resulted in poor recovery of articles in systematic reviews of epidemiologic practice. J Clin Epidemiol. (2020) 121:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2020.01.009
254. Younesi E, Toldo L, Müller B, Friedrich CM, Novac N, Scheer A, et al. Mining biomarker information in biomedical literature. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. (2012) 12:148. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-12-148
255. Caufield JH, Hegde H, Emonet V, Harris NL, Joachimiak MP, Matentzoglu N, et al. Structured prompt interrogation and recursive extraction of semantics (SPIRES): A method for populating knowledge bases using zero-shot learning. arXiv. (2023) 40. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae104
256. Kor — 😼 Kor 1.0.1 (2024). Available online at: https://eyurtsev.github.io/kor/ (Accessed February 3, 2025).
Keywords: vaccine platform technologies, correlates of protection, machine learning, artificial intelligence, large language models, computational methods, data harmonization, knowledge extraction
Citation: Anderson LN, Hoyt CT, Zucker JD, McNaughton AD, Teuton JR, Karis K, Arokium-Christian NN, Warley JT, Stromberg ZR, Gyori BM and Kumar N (2025) Computational tools and data integration to accelerate vaccine development: challenges, opportunities, and future directions. Front. Immunol. 16:1502484. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1502484
Received: 26 September 2024; Accepted: 23 January 2025;
Published: 07 March 2025.
Edited by:
Jessica Kubicek-Sutherland, Los Alamos National Laboratory (DOE), United StatesReviewed by:
Arijit Bhattacharya, Adamas University, IndiaEmily Coates, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2025 Anderson, Hoyt, Zucker, McNaughton, Teuton, Karis, Arokium-Christian, Warley, Stromberg, Gyori and Kumar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Benjamin M. Gyori, Yi5neW9yaUBub3J0aGVhc3Rlcm4uZWR1; Neeraj Kumar, TmVlcmFqLkt1bWFyQHBubmwuZ292
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Lindsey N. Anderson
Lindsey N. Anderson Charles Tapley Hoyt
Charles Tapley Hoyt Jeremy D. Zucker
Jeremy D. Zucker Andrew D. McNaughton
Andrew D. McNaughton Jeremy R. Teuton1
Jeremy R. Teuton1 Klas Karis
Klas Karis Zachary R. Stromberg
Zachary R. Stromberg Benjamin M. Gyori
Benjamin M. Gyori Neeraj Kumar
Neeraj Kumar