- 1Engelhardt Institute of Molecular Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
- 2Center for Precision Genome Editing and Genetic Technologies for Biomedicine, Engelhardt Institute of Molecular Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
- 3R-Pharm JSC, Medical Department, Moscow, Russia
- 4Sirius University of Science and Technology, Federal Territory Sirius, Krasnodarsky Krai, Russia
- 5Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Pharmacy, I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University, Moscow, Russia
- 6Department of Medical Elementology, Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), Moscow, Russia
Sterile inflammation has been increasingly recognized as a hallmark of non-infectious kidney diseases. Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines in injured kidney tissue promotes infiltration of immune cells serving to clear cell debris and facilitate tissue repair. However, excessive or prolonged inflammatory response has been associated with immune-mediated tissue damage, nephron loss, and development of renal fibrosis. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is a cytokine with pleiotropic effects including a major role in inflammation. IL-6 signals either via membrane-bound (classic signaling) or soluble receptor forms (trans-signaling) thus affecting distinct cell types and eliciting various metabolic, cytoprotective, or pro-inflammatory reactions. Antibodies neutralizing IL-6 or its receptor have been developed for therapy of autoimmune and chronic non-renal inflammatory diseases. Small molecule inhibitors of Janus kinases acting downstream of the IL-6 receptor, as well as recombinant soluble glycoprotein 130 variants suppressing the IL-6 trans-signaling add to the available therapeutic options. Animal data and accumulating clinical experience strongly suggest that suppression of IL-6 signaling pathways bears therapeutic potential in acute and chronic kidney diseases. The present work analyses the renoprotective potential of clinically relevant IL-6 signaling inhibitors in acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, and kidney transplantation with focus on current achievements and future prospects.
Principal interleukin-6 signaling
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a pivotal cytokine with pleiotropic cell biologic and physiologic functions ranging from immunomodulatory to metabolic effects. Structurally, IL-6 belongs to the four-helical cytokine family and shares homology with IL-11, ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), oncostatin M (OSM), cardiotrophin 1 (CT-1), cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC), IL-27, and IL-31, together referred to as the IL-6 cytokine family (1, 2). The IL-6 family members exert partially overlapping, as well as distinct effects with IL-6 being a major player in mediating inflammation. The cytokine promotes T-cell and B-cell immune responses via enlarging the pro-inflammatory T-helper 17 (Th17) and M1 macrophage subsets, boosting the antibody production by B-cells, and suppressing the anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells (Treg) and M2 macrophages (3–5). Along with the aggressive pro-inflammatory effect spectrum in immune cells, IL-6 exerts adaptive, cytoprotective, and proliferative effects in non-myeloid cells contributing to tissue repair but also provoking malignant cell growth (2, 6–8). Dysregulation of IL-6 signaling has been implicated in autoimmunity and immune-mediated organ damage during sterile inflammation (9).
IL-6 can be produced by T and B lymphocytes, fibroblasts, monocytes, keratinocytes, mesangial cells, endothelial cells, and subsets of epithelial cells (1). IL-6 expression in intact tissues is typically low but strongly induced during inflammation. Effects of the cytokine are mediated by three distinct signaling pathways referred to as the classic, the trans, and the trans-presentation or cluster modes (10). In the classic signaling, IL-6 first builds a dimer with the glycoprotein 80 (gp80) residing in the plasma membrane and constituting the membrane-bound IL-6 receptor alpha subunit (mIL-6R). The ensuing recruitment of the membrane-bound gp130 (mgp130) acting as the beta IL-6R subunit, followed by the assembly of two IL-6/IL-6R/mgp130 trimeric complexes into a functional hexamer initiate the signal transduction (11, 12). In view of the ubiquitous gp130 expression pattern, the classic signaling is restricted to the cell types possessing mIL-6R. This signaling mode has been primarily implicated in intact cell metabolism and functionality, whereas the pro-inflammatory cytokine effects are predominantly mediated by the trans-signaling (10, 13). The latter is enabled by the circulating soluble IL-6R form (sIL-6R) interacting with IL-6 followed by binding of the resulting IL-6/sIL-6R dimer with mgp130. Therefore, the trans-signaling mode does not depend on mIL-6R and exerts broad effects on all mgp130 expressing cells. The sIL-6R form originates from proteolytic cleavage of mIL-6R provided by metalloproteinases ADAM17 and ADAM10. Alternative IL-6R splicing may contribute to a minor extent to the sIL-6R generation in human (14). Shedding of IL-6R occurs mainly in neutrophils, monocytes, T helper cells, and hepatocytes and is enhanced during inflammation prompting initiation of the trans-signaling. Notably, a naturally occurring soluble gp130 variant (sgp130) acts as endogenous inhibitor of the trans-signaling by buffering the circulating IL-6/sIL-6R complexes and downregulating pro-inflammatory responses in normal conditions (14). In addition to the trans-signaling, sgp130 blunts the trans-presentation (cluster signaling), which is a paracrine interaction requiring a close spatial contact between a mgp130-expressing cell and a cell presenting preformed IL-6/mIL-6R complexes to the former (15). Specifically, the trans-presentation has been implicated in acquisition of the Th17 phenotype during neuroinflammation and development of cytotoxic CD8(+) T cells in the liver (16, 17). It is tempting to speculate that renal dendritic cells may mediate such effects on the infiltrating immune cells as well. Finally, an autocrine intracellular IL-6 signaling inaccessible to sgp130 has been identified ex vivo but its contribution to inflammatory processes in vivo requires further investigation (15). All IL-6 signaling modes share the downstream signal transducing pathway mediated by Janus Kinases (JAK) providing activating phosphorylation to the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) (1). The cellular response to IL-6 is further modulated by Suppressors of Cytokine Signaling (SOCs) that integrate distinct effects of pro- vs. anti-inflammatory cytokines downstream of STAT3 (18). Figure 1 depicts the IL-6 signaling pathways with a focus on the kidney.
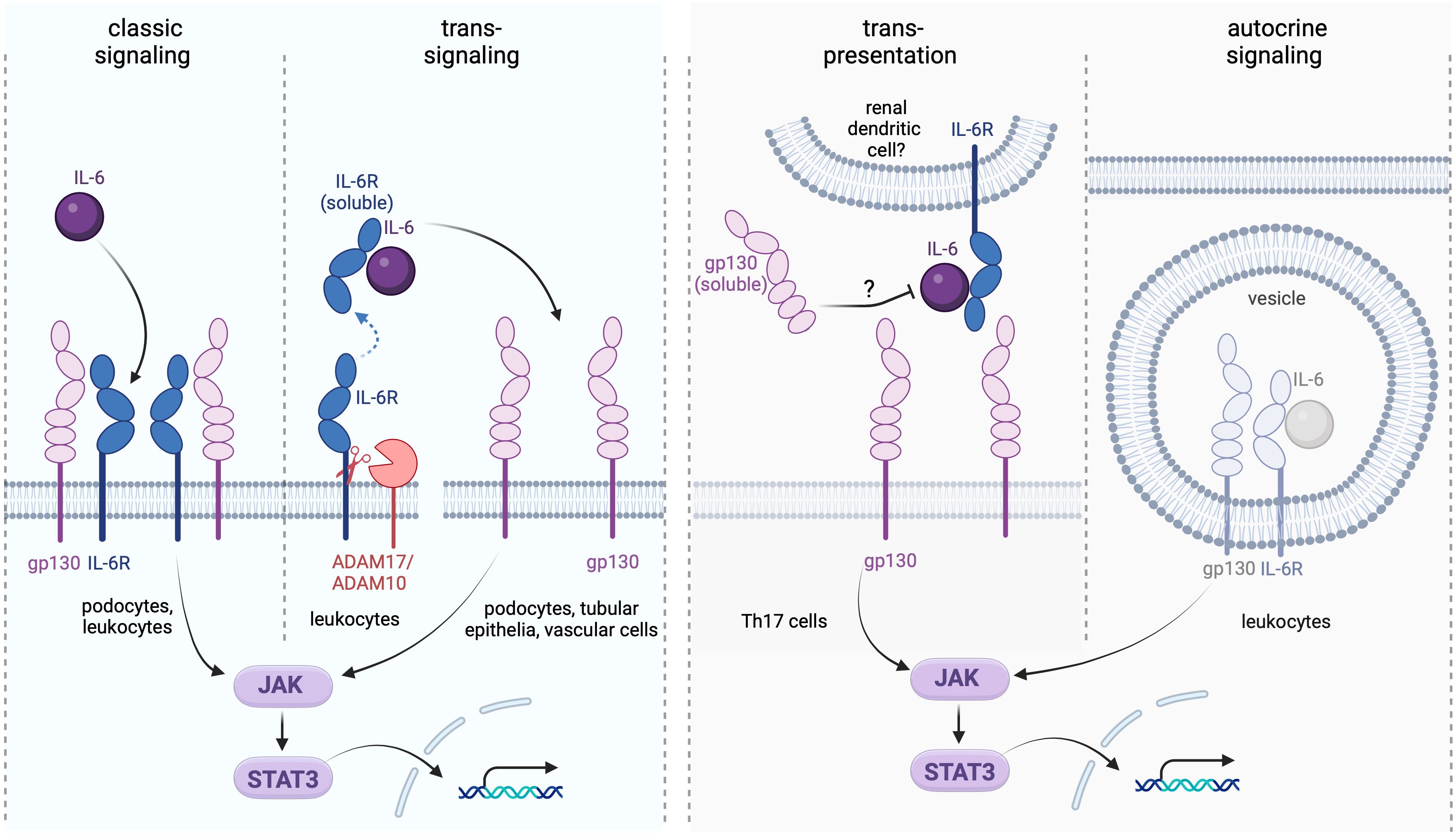
Figure 1. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling modes and their renal targets. The classic signaling takes place in podocytes expressing the membrane-bound IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) and may help maintaining the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier. The trans-signaling recruits the soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) generated by proteolytic cleavage involving the proteases ADAM17 and ADAM10. This type of signaling affects any kidney cell expressing gp130 independently on the presence of mIL-6R. The trans-presentation (cluster) mode may involve renal dendritic cells in local interactions with proinflammatory Th17 cells, in analogy to the reported trans-presentation setting in the brain tissue (16). The autocrine IL-6 signaling may occur intracellularly in cell types expressing IL-6, IL-6R, and gp130 simultaneously and likely contributes to pro-inflammatory immune cell reactions; although its role in the kidney requires further elucidation (15). While effects of the classic and trans-signaling pathways in the kidney have been well documented, the relevance of the trans-presentation and autocrine signaling modes in the renal physiology and pathophysiology remains speculative.
Clinically relevant inhibitors of IL-6 signaling
IL-6 signaling suppressing agents that have been approved or are in development for clinical use can be classified according to their modes of action. Monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-6 include clazakizumab, olokizumab, siltuximab and sirukumab. These antibodies suppress the classic and the trans-signaling pathways, whereas the trans-presentation (cluster) signaling remains active due to preforming of the IL-6/IL-6R complex inside the presenting cells (16). Only olokizumab is potentially able to suppress the cluster signaling along with the classic and trans-pathways due to specificity of the targeted IL-6 epitope (site III) prohibiting formation of functional hexamers from the two neighboring IL-6/IL-6R/gp130 complexes. To this end, olokizumab may bind with and inactivate the IL-6/IL-6R complex at the surface of the presenting cell thereby inhibiting the trans-presentation pathway (11, 19). Since the trans-presentation has been shown to promote development of Th17 and cytotoxic T cells (16), its suppression may add to the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of olokizumab. Furthermore, occupation of mgp130 with inactive olokizumab/IL-6/IL-6R complexes may to a certain extent attenuate effects of other IL-6 family cytokines signaling via mgp130. Monoclonal antibodies to IL-6R such as tocilizumab or sarilumab bind to both membrane-bound and soluble receptor form, thereby suppressing the classic and the trans-signaling pathways. In contrast to the former two groups, a modified soluble gp130 variant (olamkicept) binds with the circulating IL-6/sIL-6R complex thereby selectively inactivating the IL-6 trans-signaling (10). Since at least IL-11 signals via soluble receptors and gp130 as well, olamkicept suppresses the trans-signaling of both cytokines. Next generations of IL-6 trans-signaling inhibitors with improved selectivity for IL-6 over IL-11 and higher bioavailability have been developed and are in the preclinical testing (10). Finally, a number of small molecules acting downstream of IL-6R such as JAK inhibitors have been identified and clinically approved including abrocitinib, baricitinib, delgocitinib, fedratinib, filgotinib, oclacitinib, pacritinib, peficitinib, ruxolitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib (20). Figure 2 presents distinct mechanisms of IL-6 signaling targeted by the aforementioned agents.
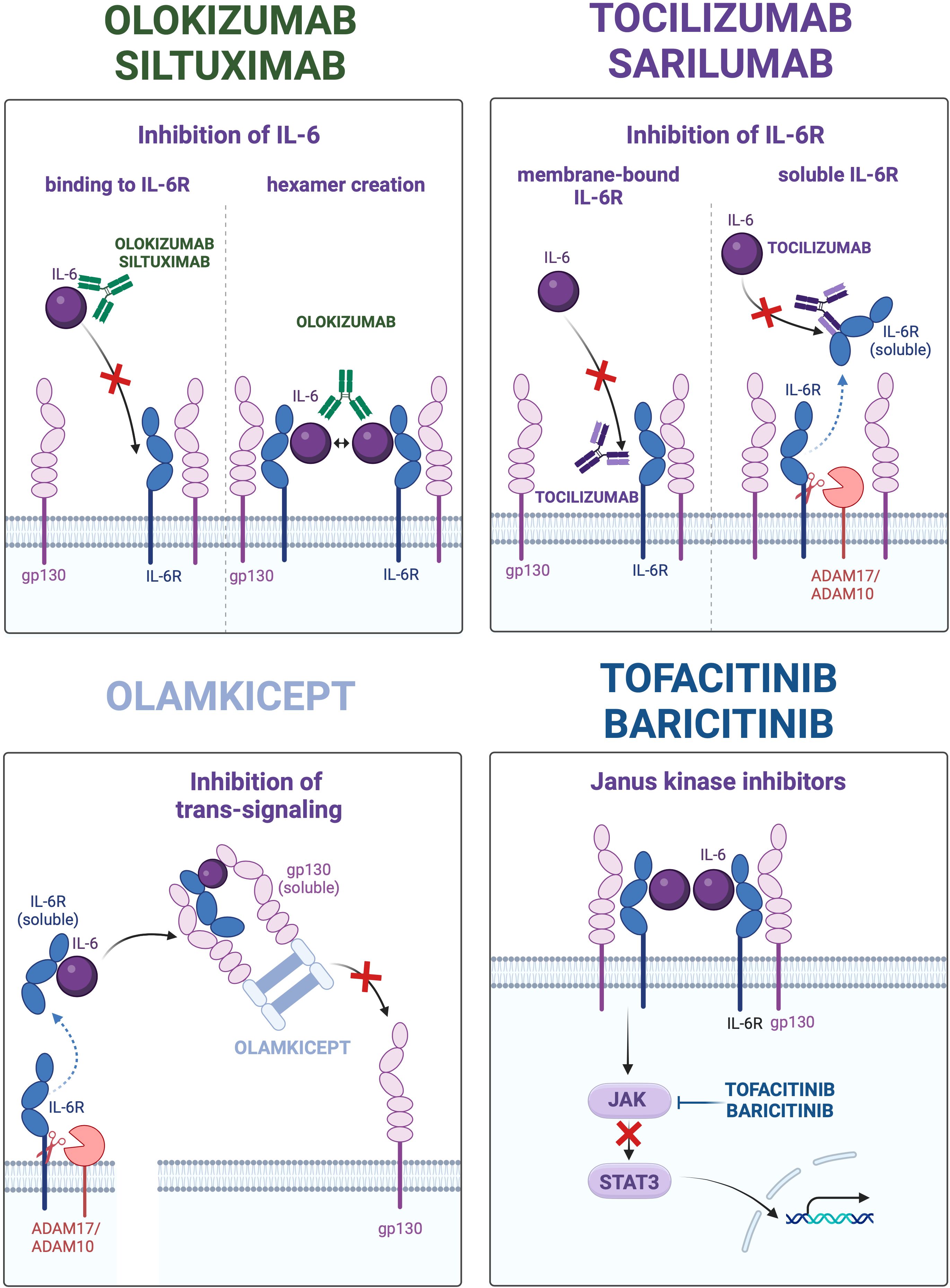
Figure 2. Distinct types of interleukin 6 (IL-6) signaling inhibition in therapeutic approaches. The four panels depict mechanisms of IL-6 signaling suppression utilized by monoclonal antibodies to IL-6 (left upper panel), monoclonal antibodies to IL-6 receptor (IL-6R; right upper panel), modified soluble glycoprotein 130 (gp130) variant (olamkicept; left lower panel), and small molecule inhibitors of Janus Kinases (JAK) – Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). The representative clinically relevant drugs are mentioned at respective panels.
Interleukin 6 in renal (patho)physiology
Renal expression and function of the IL-6 signaling components
Among kidney epithelial and vascular cells, expression of mIL-6R takes place only in podocytes and glomerular mesangial cells conferring them responsiveness to the classic IL-6 signaling mode (21, 22). No IL-6R shedding was detected in cultured human glomerular epithelial cells suggesting that podocytes or glomerular mesangial cells provide no significant contribution to circulating or urinary sIL-6R levels in vivo (21). Further experimental studies in cell culture and animal models demonstrated the IL-6-induced STAT3 activation in podocytes corroborating the functionality of mIL-6R in this cell type (21–24). The classic IL-6 signaling promotes proliferation of glomerular mesangial cells and mediates podocyte hypertrophy (25, 26). Therefore, IL-6 may contribute to the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier upon challenge and participate in glomerular hypertrophy and matrix expansion during pathophysiological hyperfiltration. Consistent with the latter assumption, blocking the JAK-STAT3 signaling downstream of IL-6 has been associated with protective effects in various experimental models of glomerular injury and kidney diseases (13, 22–24, 27). The cytokine is obviously dispensable for the intact embryonic kidney development, since pharmacologic IL-6 blockade or genetic IL-6 knockout produced no overt renal phenotype in mice (28). In contrast, embryonic overexposure to IL-6 during pregnancy due to maternal obesity has been implicated in reduction of kidney to body weight ratio in newborns (29). Likewise, administration of IL-6 to mice during gestation resulted in decreased kidney weight and suppression of nephrogenic zone, but facilitated glomerular maturation in pups suggesting that dysregulation of IL-6 signaling during embryonic kidney development may predispose to adult kidney pathology (29). Notably, enhanced circulating IL-6 levels frequently correlate with albuminuria, renal hypertrophy, tubular injury, and intestinal fibrosis suggesting that exaggerated stimulation by IL-6 may deplete the functional podocyte reserve and promote glomerular damage (30).
In contrast to mIL-6R that is expressed solely in glomeruli, production of IL-6 can take place virtually in all kidney epithelial and endothelial cells to a variable extent (21, 31–34). While immune cells are mainly responsible for circulating IL-6 levels under homeostatic conditions, the kidneys become a major cytokine source in pathophysiological situations associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) (35). Both injured kidney tissue and infiltrating immune cells significantly contribute to elevated local and systemic IL-6 levels in kidney disease (36). Experimental studies implicate IL-6 in mediating tubular damage since selective suppression of the downstream JAK-STAT3 signaling reduced acute kidney injury and alleviated diabetic kidney fibrosis in mice (37, 38). Furthermore, excessive IL-6 signaling may promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) thus enhancing risk of the clear-cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) (39). These pathophysiological effects are predominantly mediated by the trans-signaling. From the physiologic point of view, local production of the cytokine may be involved in functional and structural adaptations of glomerular and tubular epithelia to perturbations of water-, electrolyte- or protein load. The available data on distribution and functions of IL-6 and IL-6R in the kidney are summarized in the Table 1.
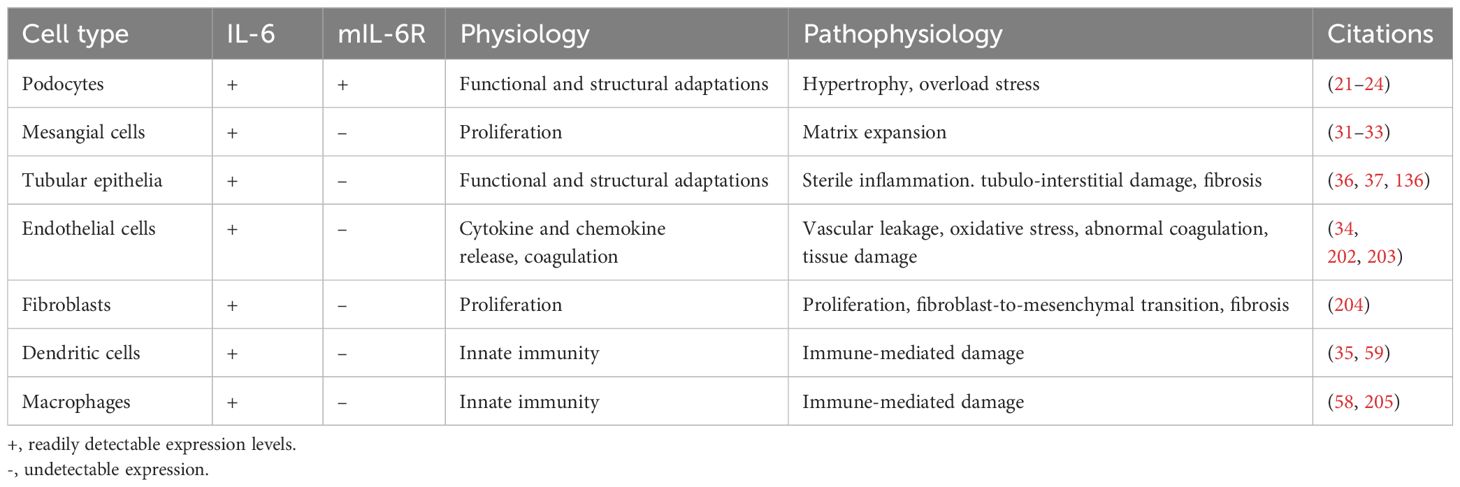
Table 1. Expression, physiologic functions, and pathophysiologic implications of interleukin-6 signaling in kidney cells.
Expression of gp130 appears to be ubiquitous in the kidney since the classic or trans IL-6 signaling modes were readily detected in renal cell cultures or animal models of kidney diseases (35). Finally, SOCs interfering with IL-6-induced STAT3 activation are broadly expressed across the kidney epithelia as well (27).
Effects of IL-6 on the kidney function and hemodynamics
Blood filtration is critical to the body homeostasis. To fulfil this task, renal blood perfusion is maintained at constantly high levels (20-25% of cardiac output) by means of autonomous regulation and systemic feedback (40). Experiments in IL-6 knockout mice suggested only minor effects of the cytokine on the intact renal blood flow and glomerular hemodynamics (41). Nevertheless, hormones regulating renal hemodynamics and function such as angiotensin II (AngII) or vasopressin induce changes in IL-6 expression suggesting that the cytokine may mediate some endocrine signaling events (42, 43). Kidney disorders frequently induce or aggravate hypertension and vice versa (44). IL-6 levels have been associated with elevated blood pressure in humans and in experimental animal models (41, 45–49). Increase in physiologic blood pressure in response to physical stress involves IL-6 signaling as well (48). The cytokine may enhance the blood pressure via synergism with the Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS) since IL-6 deletion blunted the angiotensin II (AngII)-induced hypertension in mice (41, 45, 50). Surprisingly, vasoconstrictive response to AngII was largely preserved in IL-6 knockout mice suggesting non-vascular mechanisms (41). AngII is not only a potent vasoconstrictor but also stimulates tubular salt reabsorption via induction of the aldosterone biosynthesis in the adrenal glands. However, IL-6 knockout mice were not protected against the aldosterone-dependent hypertension (46). Alternatively, pro-hypertensive and pro-fibrotic effects of IL-6 may be mediated by immune cells with pathogenic phenotypes accumulating in the kidney tissue, as suggested by beneficial effects of IL-6 blockade in rats with salt-sensitive hypertension (51). Although details linking IL-6 to the blood pressure remain to be clarified (43, 52, 53), the cytokine has been increasingly recognized as a key player connecting chronic inflammation to hypertension (47, 54, 55).
IL-6 signaling in the immune-mediated kidney damage
Sterile inflammation is a common pathogenetic feature of acute and chronic non-infectious kidney diseases (56, 57). Kidney injury leads to release of multiple membrane, intracellular, and nuclear compounds from dying cells (urate, ATP, heat-shock proteins, cyclophilins, lipoproteins, histones, etc.) serving as Danger-Associated–Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) and inducing infiltration of immune cells into the kidney tissue independent of primary etiology (58). This process is mediated by dendritic cells and macrophages, which abundantly express Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR) and release proinflammatory cytokines including IL-6 in response to DAMPs (58–60). The IL-6 induction in immune cells is likely potentiated by paracrine interactions with injured renal cells producing IL-6 as well (36). Therefore, along with protective functions such as clearance of cellular debris and antigen presentation, macrophages contribute to sustained intrarenal exposure to IL-6 via a positive paracrine feedback. Pathophysiologic roles of macrophages in acute and chronic kidney damage are well established (58, 60, 61), whereas the impact of macrophage-derived IL-6 on the development, course, and resolution of kidney disease is less clear. The extent of macrophage invasion and acquisition of distinct macrophage phenotypes in the kidney tissue appear to be critical for the outcome of Acute Kidney Injury (62). Depletion of macrophages before the AKI event has been shown to alleviate kidney damage and promote repair of the kidney tissue in the ischemia-reperfusion AKI mouse model. At the same time, suppression of macrophages several days after the AKI event delayed the tubular repair (62). Suppression of proinflammatory, cytokine-releasing M1 macrophages and promoting their switch to the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype was shown to reduce inflammation and promote repair of kidney tissue in AKI models (63). Importantly, optimal AKI resolution minimizes the risk of late interstitial fibrosis and transition to CKD. However, translation of experimental data to human disease is complicated by differences in details of immune responses between the human and murine species (64). Examination of macrophage phenotypes in kidney biopsies from patients with acute tubular injury revealed enrichment in both HLA-DR+ M1 macrophages and CD163+ M2 macrophages (65). Furthermore, increased macrophage density in kidney biopsies correlates with the severity of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and progression to the End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) (66). Renal M1 macrophages secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, which, in turn, switches the differentiation balance of peripheral blood monocytes from dendritic cells to macrophages (35, 67). It is tempting to speculate that M1 macrophage-derived IL-6 is implicated in pathogenesis of AKI and CKD. An enhanced number of the IL-17-producing T helper (Th17) cells along with reduction in the regulatory T cells (Treg) have been further recognized as crucial pathogenetic events in the immune-mediated kidney damage (68, 69). Although TGF-β regulates T-cell-mediated tolerance and immunity through both Treg and Th17 cells, excessive IL-6 availability shifts the CD4-positive T cell differentiation toward Th17 rather than Treg thereby inducing a pathogenic pro-inflammatory imbalance between the two T-cell phenotypes (5).
Components of IL-6 signaling as kidney disease biomarkers
The serum levels of IL-6 in healthy adults are typically below 5 pg/ml (1-5 pg/ml) being in the lower detection range for the most commercial assays (9). In contrast, circulating levels of sIL-6R (40-75 ng/mL) and sgp130 are much higher (250-400 ng/ml). Calculations based on the molecular weights of IL-6 (~20 kDa), sIL-6R (~55 kDa), and sgp130 (~100 kDa), their circulating levels, and mutual binding affinities imply a limited buffering capacity for suppression of the trans-signaling by sgp130. Thus, initiation of the trans-signaling mainly depends on changes in circulating IL-6 and sIL-6R concentrations (9). Moreover, the balance between circulating IL-6, sIL-6R, and sgp130 may favor either the classic or trans-signaling pathways, as well as permit both signaling modes simultaneously (70). Accordingly, IL-6, sIL-6R, and sgp130 have been receiving growing attention as potential serum or urinary biomarkers in kidney pathology. Several aspects need to be taken into consideration for interpretation of their predictive and prognostic values. The clearance of circulating IL-6 and sIL-6R occurs mainly via their filtration into the urine. Due to the relatively small molecular weights both IL-6 (~20 kDa) and sIL-6R (~55 kDa) pass through the glomerular filtration barrier. In contrast, the IL-6/sIL-6R complex with the molecular weight over 70 kDa, as well as sgp130 (~100 kDa) or the IL-6/sIL-6R/sgp130 complex are mostly retained in the blood assuming the intact glomerular filtration barrier. Therefore, urine of a healthy individual is expected to contain low to moderate levels of IL-6 and sIL-6R. Due to the urine concentration process, the urinary levels of IL-6 and sIL-6R may exceed their plasma concentrations, despite proximal reabsorption of filtered protein. Kidney diseases are frequently associated with impaired glomerular function resulting in proteinuria. Considering the concomitant induction of IL-6 expression in the injured kidney tissue along with impaired proximal protein reabsorption due to tubular damage, significant increases of circulating and especially urinary IL-6 and sIL-6R are typically detected in renal patients even by the reduced GFR. Glomerular damage may, in turn, enhance the urinary IL-6 excretion while reducing its serum levels due to proteinuria. Taken together, urinary IL-6 levels have shown predictive value in adult and pediatric kidney diseases (30, 71). More systematic clinical studies are required to standardize the diagnostic implementation of urinary IL-6 tests in various kidney pathology.
IL-6 signaling in acute kidney injury
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) or Acute Renal Failure (ARF) is defined as a sudden loss of kidney function occurring within a short time frame of several hours to several days and leading to insufficient waste filtration from the blood. AKI complicates renal and non-renal diseases in approximately 5% of hospital admissions and 30% of intensive care unit (ICU) admissions being a major cause of morbidity and mortality in hospitalized patients (72). AKI may result from an acute hemodynamical or toxic kidney damage or reflect a decompensation in various chronic kidney disorders. Inadequate AKI resolution may lead to persistent morphological and functional kidney damage with ensuing transition to CKD or ESRD (72). Approximately 40% of patients with renal disease develop acute tubular necrosis manifesting as AKI with ensuing nephron loss. In this light, prediction, early recognition and targeted etiologic and pathogenetic therapy of AKI is of high clinical relevance (72).
Ischemia-reperfusion injury and inflammation of the kidney tissue have been linked with induction of IL-6 expression in AKI patients and experimental animal models (73–75). The damaged kidney is the major source for circulating IL-6 originating both from injured kidney cells and infiltrating immune cells (76). At the same time, the ability of the proximal tubule to reabsorb and metabolize filtrated small proteins including IL-6 is reduced in AKI. Enhanced IL-6 production and impaired renal metabolism of the cytokine lead to substantially elevated urinary IL-6 levels in AKI patients despite the reduced filtration of circulating IL-6 into the urine due to decreased GFR (71). Local IL-6 induction in response to tissue injury followed by reciprocal systemic induction of the cytokine expression in a wide range of white blood cells increase the renal exposure to IL-6 primarily via the trans-signaling mode mediated by sIL-6R (77). Despite numerous reports of enhanced serum or urinary IL-6 levels in association with AKI (71, 78–82), data on simultaneous detection of IL-6 and sIL-6R in serum or urine is rather scarce and mostly derived from kidney transplant recipients experiencing acute graft rejection (83). Synchronized detection of IL-6 and sIL-6R in patients with or at risk of AKI are mandatory for improved understanding of relevant IL-6 signaling modes in this condition. Although IL-6 is primarily viewed as a proinflammatory cytokine promoting renal damage, cell-protective and regenerative effects of IL-6 during kidney injury have been documented as well (77, 84). In fact, boosting the trans IL-6 signaling using a IL-6:sIL-6R fusion protein (hyper-IL-6) exerted marked renoprotective effects in two distinct mouse models of AKI induced either by HgCl2 or ischemia-reperfusion (77, 84). These results raise the opportunity of protective rather than pathophysiologic role of IL-6 induction in the injured kidney and challenge the eligibility of pharmacologic IL-6 signaling blockade in AKI patients. Somewhat confusing is the fact that genetic IL-6 deletion protected against HgCl2-induced AKI and IgA-mediated kidney damage in mouse models (77, 85). Furthermore, transgenic IL-6 overexpression led to progressive kidney injury resembling the terminal stages of multiple myeloma (myeloma kidney) (86). The aforementioned discrepancies in IL-6 effects may be related with predominant activation of either the classic or the trans-signaling modes, as well as with distinct immunologic status in IL-6 deficient mice vs. wild-type or IL-6 overexpressing mice subjected to AKI. The immune-mediated damage plays a major role in AKI (62). Suppression of the M1 macrophage-dependent acute pro-inflammatory response was beneficial in AKI mouse models (63), whereas the anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages were shown to mediate the kidney repair in the late AKI phase (62). Likewise, increases in circulating and renal Th17 cells have been associated with AKI in humans and rodent models (87), whereas Tregs exert renoprotective effects (88). Since IL-6 promotes the maturation of M1 macrophages and Th17 cells (35), blockade of the cytokine may bear renoprotective potential in the pre-AKI or initial AKI phases. As increased urinary and, to a lesser extent, serum IL-6 levels predict AKI (71, 78, 79), a test for urinary IL-6 may be considered as an indicator for the administration of IL-6 pathway inhibitors to prevent or alleviate the disease.
IL-6 signaling in chronic kidney disease
The diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) relies on one of the following criteria persisting longer than 3 months: reduction of GFR below 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, albuminuria of at least 30 mg per 24 hours, or other abnormalities reflecting functional kidney injury or structural kidney damage (hematuria, polycystic or dysplastic kidneys et cetera) (89). Affecting over 850 million people worldwide, CKD has been increasingly recognized as a global public health challenge and a major non-communicable human disease (90). CKD frequently develops during progression of the Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) (91). Apart from the diabetes mellitus, etiology of CKD comprises various risk factors including unresolved or recurrent AKI, hereditary kidney diseases, congenital anomalies of the urogenital system, autoimmune disorders, hypertension, and obesity (44). Despite various primary causes, progression of CKD is driven by shared pathophysiologic mechanisms associated with tissue hypoxia, oxidative and metabolic stress, chronic inflammation, and fibrosis. Moreover, CKD must be viewed as a systemic disease implicating innate immunity, neuroendocrine control, as well as the cardiovascular, digestive, and respiratory organ systems (92). Maladaptive interactions between kidney and immune cells along with chronic metabolic stress of kidney epithelia are the pathophysiologic hallmarks of CKD progression (60, 68, 69, 93). In this light, dysregulation of IL-6 signaling has been typically observed in CKD patients and animal models. However, etiologic factors substantially affect the diagnostic and prognostic IL-6 significance with the apparently strongest correlation between IL-6 levels and progression to CKD in patients with autoimmune kidney disorders and less clear situation in patients with the Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) (35, 94–98).
Autoimmune kidney diseases
Autoimmune kidney diseases comprise the lupus nephritis (LN), anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic associated (ANCA) vasculitis, anti-glomerular basement disease (also known as Goodpasture’s disease), IgA nephropathy (IgAN), and membranous nephritis (MN) (99). The autoimmunity-mediated renal diseases are caused by loss of self-tolerance to certain own proteins becoming autoantigens and provoking immune-mediated kidney damage, typically manifesting by glomerulonephritis (GN). The autoantigens may be of renal or non-renal origin, the latter accumulate in glomeruli due to the physiologically high renal blood supply and the perm-selective blood filtration. IL-6 has been implicated in pathophysiology of distinct autoimmune GN forms either as a diagnostic marker or a pathogenetic factor (100). Since IL-6 blocking agents are increasingly used to retard progress of inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and Castleman’s disease, the amount of clinical information on their effects in patients with autoimmune renal disorders is continuously growing (101, 102).
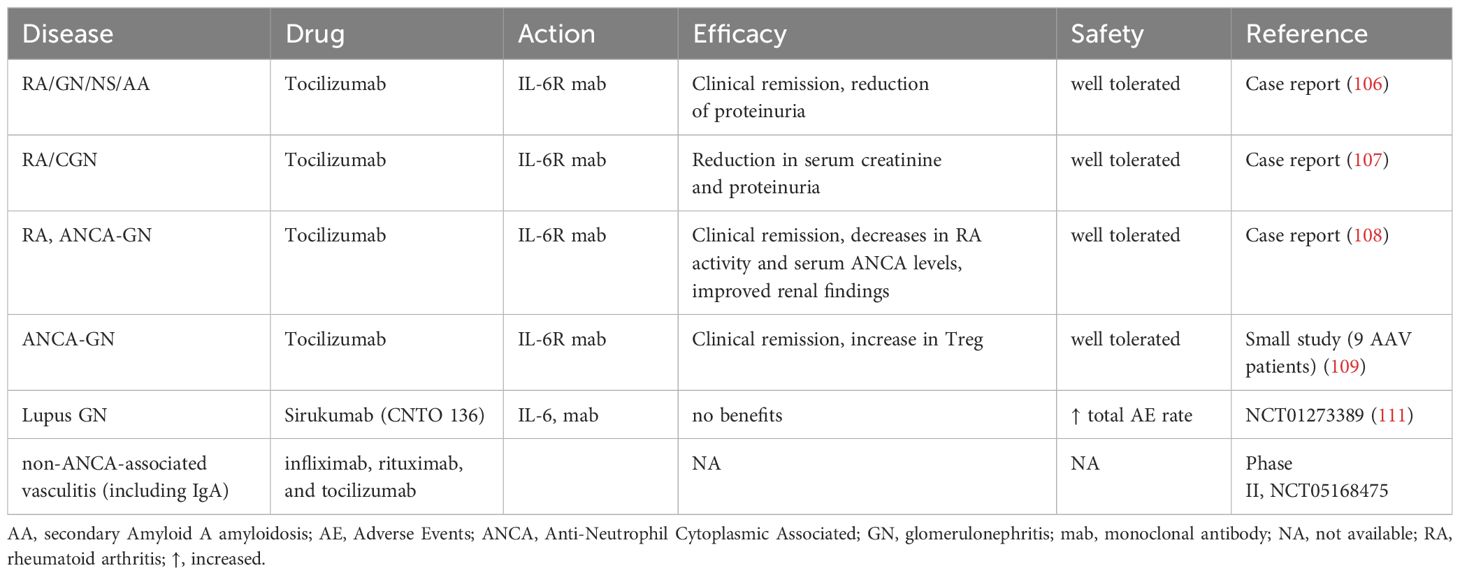
RA may be complicated by nephropathy basically displaying GN with or without nephrotic syndrome (NS). Notably, renal complications in RA patients may be caused not only by the immune-mediated kidney damage itself but by side effects of antirheumatic drugs as well (103). Although the incidence of RA-associated nephropathy with progression to CKD has substantially declined after the clinical introduction of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), renal complications in RA patients remain a problem deserving attention (103). Safety and tolerability of distinct IL-6 signaling inhibitors in RA patients with renal insufficiency have been generally established (104). Nevertheless, systematic studies addressing effects of IL-6 inhibition on the incidence or course of renal complications in RA patients are still scarce and mostly limited to case reports. In this context, several case reports describe beneficial effects of the IL-6R blocker tocilizumab on the renal function in patients with RA-associated GN, mainly due to secondary amyloidosis (105–107). Tocilizumab has further shown nephroprotective effects in patients developing ANCA vasculitis and GN with or without RA in the background (108, 109). The underlying mechanisms are likely related with the systemic anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of tocilizumab rather than being kidney-specific (110). Since IL-6 has been implicated in the pathophysiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), effects of IL-6 blockade used to treat the disease have been studied in patients with Lupus GN as well. Disappointingly, treatment of SLE patients with an IL-6 inhibitor sirukumab revealed no obvious benefits in those developing Lupus GN but was associated with significantly increased adverse effect incidence (111). Finally, IL-6 is believed to promote IgAN (94, 112). Consequently, blockade of IL-6 signaling in patients with IgAN is viewed as an emerging therapeutic option but a supporting clinical evidence is barely available to date. Clinical experience with IL-6 signaling inhibitors in the autoimmune kidney diseases are summarized in the Table 2A. Principally, inhibition of IL-6 signaling pathways appears to prevent or retard the autoimmune kidney diseases. The underlying mechanisms mainly rely on general anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects such as the normalization of T cell and macrophage balance by suppressing the pro-inflammatory Th17 and M1, while facilitating the anti-inflammatory Treg and M2 phenotypes (64, 109). The extent of nephroprotection may vary depending on the IL-6 intervention level (IL-6, IL-6R, or JAK/STAT3). Convincing clinical benefits have been currently obtained only for the IL-6R blocker tocilizumab in patients with RA-related or ANCA-associated nephropathy, whereas information on other drugs and indications is still insufficient for evidence-based conclusions.
Diabetic kidney disease
The Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) develops in approximately 40% of individuals with diabetes of either type 1 (T1D) or type 2 (T2D) and is the dominant cause for the Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) (91, 113). The pathophysiologic mechanisms of diabetic kidney damage combine microvascular injury, glomerular hyperfiltration, toxic effects of hyperglycemia, and associated comorbidities such as hypertension or dyslipidemia (91). The resulting nephron loss and sterile inflammation of renal tissue evoke invasion of immune cells and immune-mediated damage. Proinflammatory cytokines have been principally implicated in cardiometabolic diseases including diabetes (98). In this context, several lines of evidence suggested a pathogenetic role of IL-6 in diabetes and DKD (30).
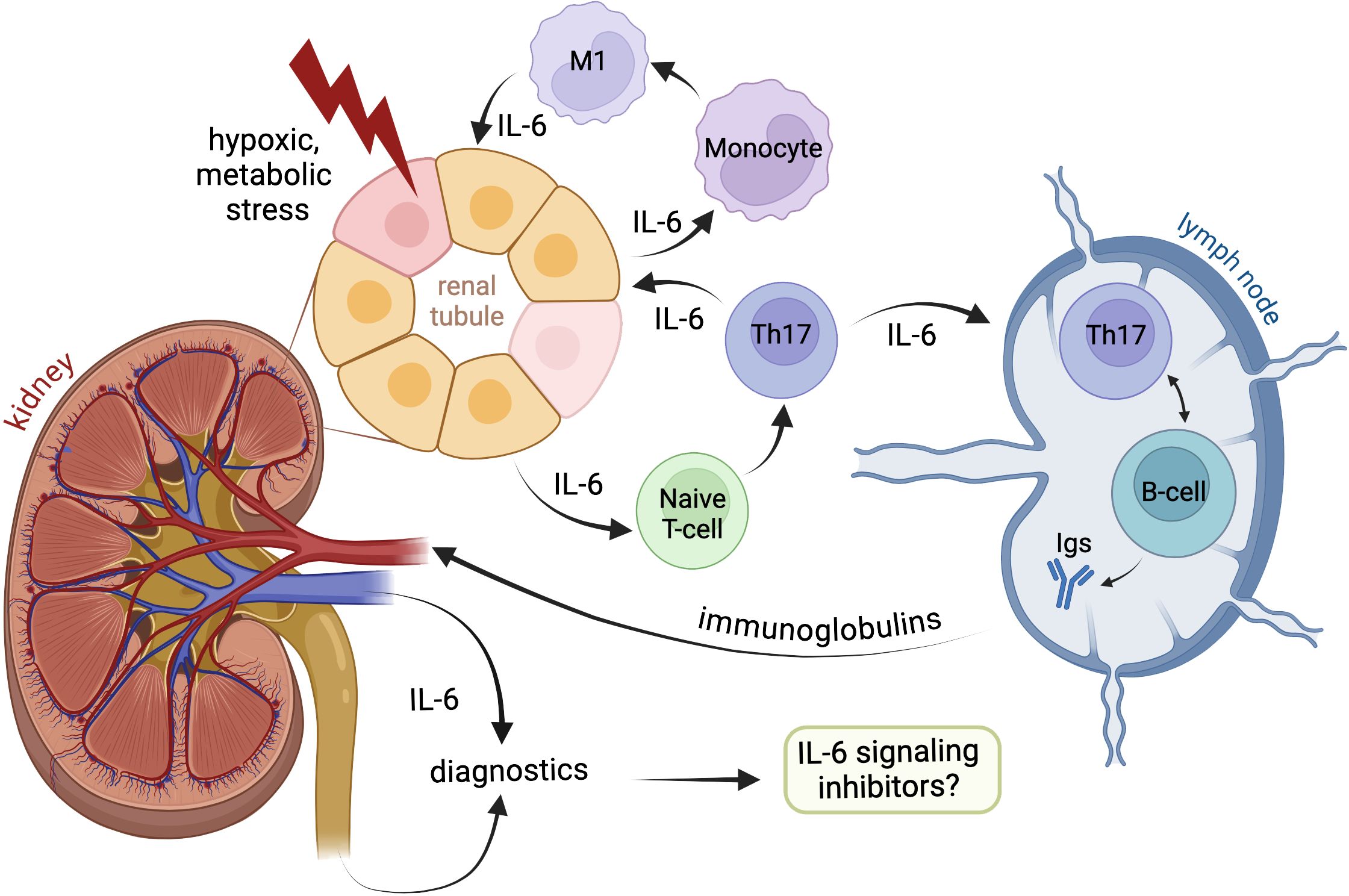
IL-6 is a cytokine with pleiotropic functions including central and peripheral effects on the glucose homeostasis (114). IL-6 and leptin share signaling mechanisms that suppress feeding and improve glucose tolerance. Central activation of the IL-6 trans-signaling has been reported to improve glucose metabolism in mouse models of obesity (114). Similar to leptin, central IL-6 action may be mediated via activation of oxytocinergic neurons located in in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (115, 116). In contrast to the reported obesity-associated leptin resistance, central IL-6 trans-signaling appears to be stimulated in obesity (114). The hypothalamic neurons may transduce effects of IL-6 on the systemic glucose metabolism by modulation of the sympathetic/parasympathetic tone or via the hypothalamic-pituitary hormonal axis. Apart from that, IL-6-dependent stimulation of insulin secretion may involve gastrointestinal hormones such as the glucagon-like peptide 1 (117). In peripheral tissues, IL-6 promotes insulin-dependent glucose utilization in skeletal muscles along with lipolysis in the fat tissue (118–120). In the liver, however, the cytokine induces insulin resistance reflected by blunted synthesis but enhanced degradation of glycogen, as well as facilitated gluconeogenesis (121). All these effects of the cytokine are part of catabolic metabolism serving to improve energy mobilization in response to challenge. The physiologic “antidiabetic” effects of the cytokine need to be taken into consideration for understanding its role in diabetes and DKD. Nevertheless, prolonged stimulation of the IL-6 signaling during chronic systemic inflammation coincides with development of insulin resistance (122). Moderately enhanced plasma IL-6 levels have been frequently reported in T2D patients but the pathophysiological meaning of this finding remains debatable (123–125). Thorough matching the T2D patients with the respective control patients for age, weight, sex, and BMI revealed no significant differences in plasma IL-6 levels suggesting that the fat mass but not impaired insulin responsiveness underlies the elevated IL-6 plasma levels in diabetic patients (126). Indeed, IL-6 mRNA expression was demonstrated in human subcutaneous adipose tissue and elevated IL-6 mRNA levels measured in individuals with insulin resistance (127, 128). While molecular pathways connecting IL-6 to insulin resistance in the adipose tissue remain elusive, stimulation of IL-6 synthesis may reflect a compensatory response to impaired glucose metabolism (122). Therefore, the fat tissue constitutes a large source of circulating IL-6 in patients with diabetes and metabolic syndrome independently on the kidney involvement (124). DKD adds the kidney as another major site of IL-6 production, since the extent of kidney damage appears to correlate with increased renal IL-6 mRNA expression in DKD patients (97). Furthermore, enhanced circulating or urinary IL-6 levels have been associated with the risk of kidney disease progression in T1D and T2D patients (96, 129, 130). The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms are strongly related to the immune-mediated kidney damage induced by infiltrating Th17 lymphocytes and M1 macrophages (64, 67–69). The invasion of immune cells might be provoked by IL-6 release from injured kidney cells, followed by mutual paracrine stimulation of proinflammatory cytokine release promoting kidney damage and fibrosis. Once initiated, this vicious pathogenetic circle may become largely independent on circulating IL-6 levels due to amplified local IL-6 synthesis and release in the kidney tissue (Figure 3). Notably, monocyte-derived macrophages from newly diagnosed untreated T2D patients showed upregulated activity of the nucleotide binding and oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3)-inflammasomes along with the stimulated proinflammatory cytokine expression profile (131). Apart from immune cells, activation of NLRP3-inflammasomes has been reported in kidney epithelial and endothelial cells from diabetic humans and mice. Moreover, experimental evidence strongly implicates activation of NLRP3-inflammasome in non-immune kidney cells upon DKD (132). NLRP3-inflammasomes lead to maturation of IL-1β and IL-18, whereas IL-6 is a known downstream target of IL-1β with potential synergistic proinflammatory effects (133, 134). In line with this, the IL-6R inhibitor tocilizumab retarded DKD in a mouse model of obesity- and diabetes-induced DKD (db/db mice) mainly via suppressed activation of NLRP3-inflammasomes and blunted immune-mediated kidney damage (135). In contrast, genetic IL-6 deletion in mice provided no protection against the obesity-induced renal impairment but aggravated nephrotoxic effects of high fat diet-induced instead (136). Notably, IL-6 knockout mice develop mature-onset obesity implicating IL-6 as an essential player in the carbohydrate and lipid metabolism (137). Accordingly, administration of IL-6 pathway inhibitors to treat autoimmune diseases was associated with increased body weight and body mass index (BMI) in humans (138). At the same time, IL-6R blockade has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic patients receiving tocilizumab for management of rheumatoid arthritis (139). The aforementioned discrepancies may reflect a disbalance between the central and peripheral IL-6 signaling in diabetes. With respect to the relevant IL-6 signaling modes, data from DKD patients, mouse models, and cell culture involve both the classic and the trans IL-6 signaling in diabetic kidney injury (13, 123). Further dissection between central and peripheral effects of the cytokine and distinct signaling modes is mandatory to carefully assess the therapeutic potential of IL-6 inhibiting agents in diabetes and DKD.
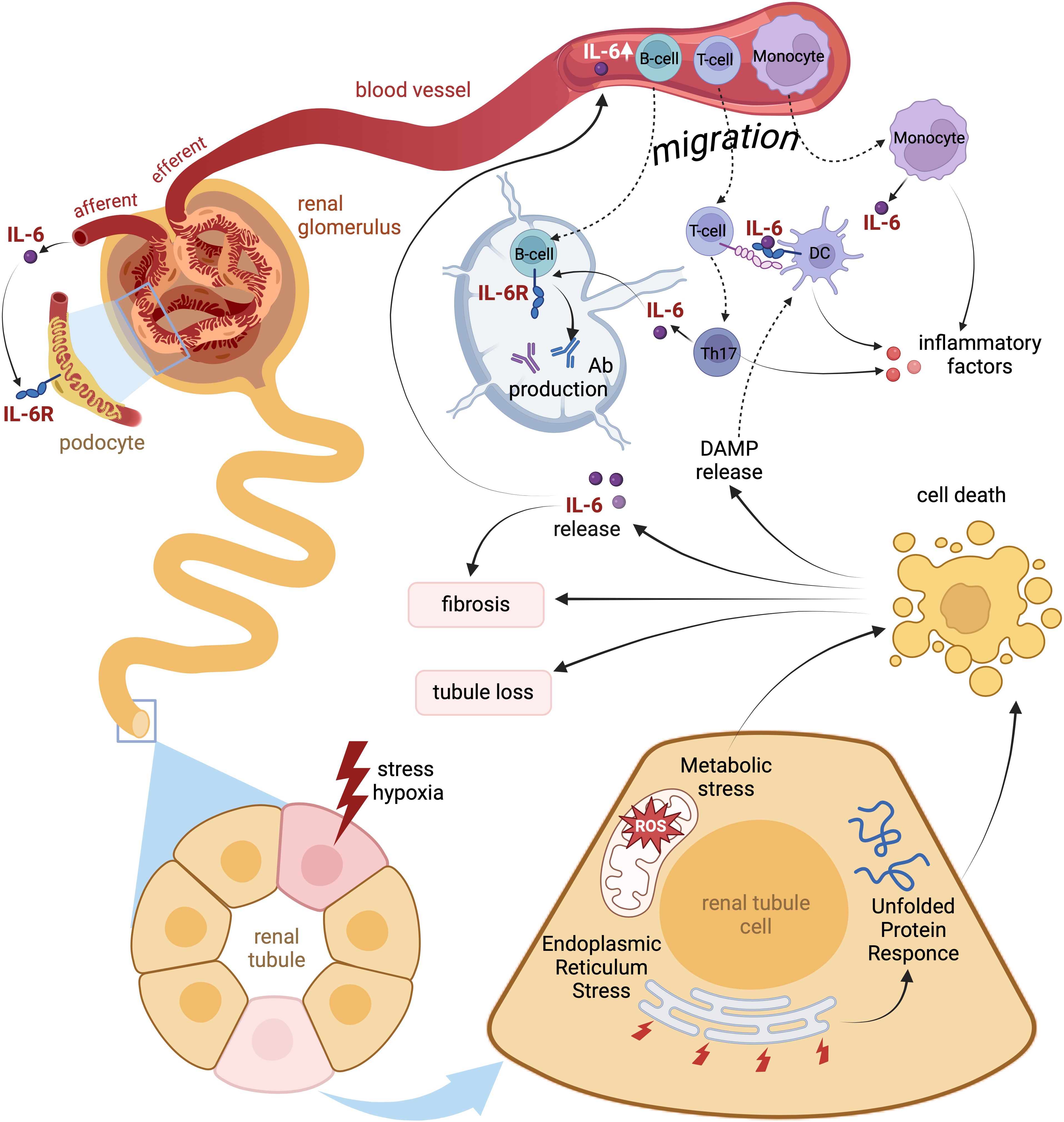
Figure 3. Local and systemic pathophysiologic effects of IL-6 signaling during kidney injury. Acute or chronic hypoxic and metabolic stress of renal tissue breaks intact energy and protein homeostasis in kidney epithelia causing endoplasmic reticulum stress with unfolded protein response. Injured cells signal via enhanced IL-6 secretion thus attracting local immune cells. Decompensation of cell protective adaptations lead to apoptosis of renal tubular cells and release of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMP) further enhancing the local immune response. Both IL-6 and DAMP induce invasion of T-cells and monocytes followed by predominant acquisition of pro-inflammatory Th17 and M1 phenotypes. The infiltrating immune cells produce IL-6 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines thus adding to local sterile inflammation of renal tissue. Later migration of antigen-presenting cells exposed to DAMP to lymphatic nodes may trigger production of autoantibodies by B-cells. Finally, the inflamed kidney tissue delivers substantial amounts of IL-6 into the blood thus provoking systemic inflammation.
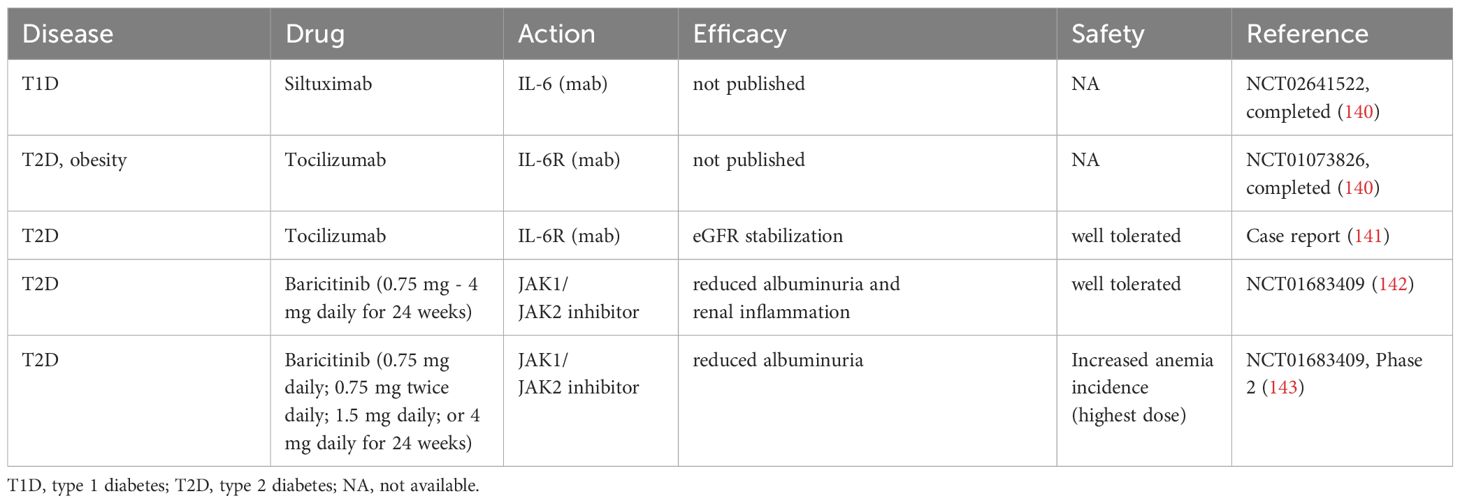
Despite growing number of animal studies suggesting beneficial effects of IL-6 suppression in DKD and CKD, clinical experience with inhibitors of IL-6 pathways in diabetic patients are rather limited and less conclusive (Table 2B). Two kidney-focused clinical trials testing either suppression of IL-6 with siltuximab (NCT02641522) in T1D patients or inhibition of IL-6R with tocilizumab in patients suffering from T2D and obesity (NCT01073826) were conducted but the results and conclusions are pending (140). A case report documented rescue of the renal function in a patient with DKD receiving tocilizumab (141). Administration of baricitinib in T2D patients to suppress JAK downstream of IL-6R showed acceptable safety and a moderate improvement of the kidney function reflected by reduced albuminuria (142, 143). While potential benefits of systemic IL-6 inhibition in DKD patients require further investigation, selective renal targeting of the IL-6 signaling to suppress immune cell invasion and local maturation of Th17 cells and M1 macrophages may open a new therapeutic avenue for improved management of DKD and CKD.
End-stage renal disease
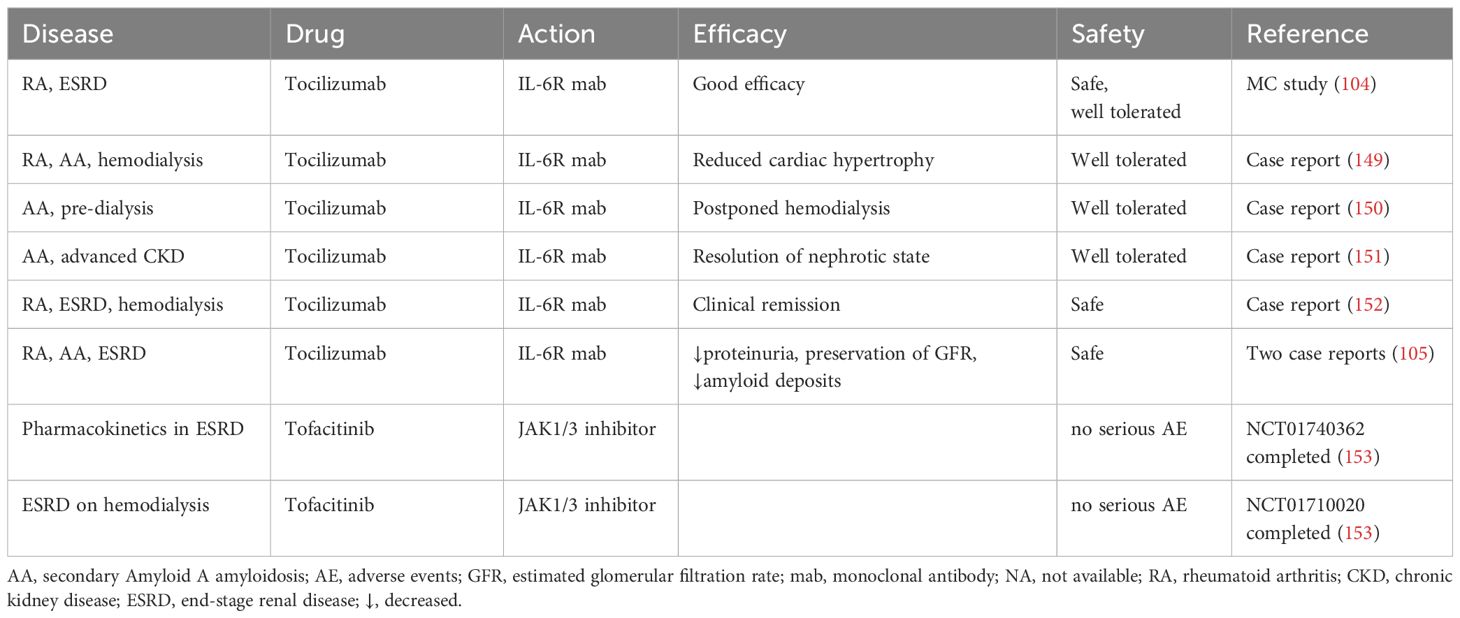
ESRD is a terminal step of kidney insufficiency with GFR below 15 mL/min, which is a life-threatening condition requiring Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) in form of hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or kidney transplantation. The main causes of ESRD in developed countries comprises DKD, hypertension, primary and secondary systemic vasculitis, polycystic kidney disease, obstructive nephropathy or vesicoureteral reflux, renal amyloidosis, and drug nephrotoxicity (144). Irreversible kidney injury in ESRD is associated with systemic inflammation provoking multiple dysfunctions of internal organs, skeletal muscles, and integumentary tissues with risk of ensuing cardiorenal syndrome, hepatorenal syndrome, respiratory disorders, cerebrovascular pathology, muscle atrophy, and cahexia (145). Proinflammatory cytokines including IL-6 have been implicated in progression of CKD to ESRD (129). Circulating IL-6 levels are markedly increased in ESRD patients, both newly diagnosed or receiving hemodialysis (146). The reported highest IL-6 concentrations in patients with ESRD ranged within 60-150 pg/ml thus manyfold exceeding moderately increased IL-6 levels in DKD (mostly below 10 pg/ml) (130, 146). Persisting elevation of plasma IL-6 levels has been proven as a hallmark of CKD aggravation and a predictor of overall and cardiovascular mortality in pre-dialysis and hemodialysis CKD patients (147). Notably IL-6 emerges as a more reliable prognostic marker of CKD outcomes than the C-reactive protein, albumin, or tumor necrosis factor (147). Since ESRD provokes systemic inflammation, the resulting injury of other organs and tissues may provide multiple sources for enhanced circulating IL-6 levels in addition to the damaged kidneys. Pharmacologic suppression of the IL-6 signaling to attenuate systemic inflammation and the CKD/ERSD-associated cardiovascular burden appears rational in this setting (148). Although the clinical experience with IL-6 inhibitors in ESRD patients is scarce and mostly limited to the IL-6R blocker tocilizumab, an acceptable safety level and beneficial effects on the renal and cardiovascular outcomes were consistently reported in pre-dialysis or hemodialysis patients (105, 149–152). Administration of the JAK-inhibitor tofacitinib to patients with mild to severe renal insufficiency demonstrated satisfactory pharmacokinetics suggesting that tofacitinib may be used in ESRD patients as well (Table 2C) (153).
Kidney transplantation
Kidney transplantation represents the most vulnerable condition for the renal injury. The transplanted kidney subjected to the ischemia–reperfusion injury reacts to hypoxic and metabolic stress by agile IL-6 production, thereby eliciting or aggravating own rejection via cellular and humoral alloimmune responses (154). Enhanced urinary IL-6 or sIL-6R levels have been increasingly recognized as early diagnostic markers of graft rejection associated with poor prognosis (3, 83, 155–160). The transplanted kidney appears to be the main source of increased circulating and urinary IL-6 originating primarily from tubular epithelial cells, monocytes and macrophages (161, 162). The impact of kidney-derived IL-6 on the graft survival has been studied in experimental transplantation models using wild-type (WT) and IL-6-deficient mice (163). The serum IL-6 levels in mice receiving WT kidney transplantation were substantially higher compared to IL-6-deficient kidney recipients, the latter were even comparable to the levels detected in sham-operated mice. Accordingly, grafts from IL-6 knockout mice demonstrated prolonged rejection-free time suggesting major contribution of graft-derived IL-6 to the development of transplant rejection (163). Furthermore, IL-6 interfered with Treg activity against the effector T cell responses and impaired graft acceptance in non-renal murine transplant models (164, 165).
Clinically, increased urinary or serum IL-6 levels coincide with inflammation, acute rejection, and chronic rejection of renal allografts (155–157). High serum IL-6 levels have been strongly associated with ensuing transplant rejection among renal allograft recipients undergoing tolerance induction using a mixed chimerism strategy (166). Moreover, increased urinary IL-6 levels accompany delayed graft function and resolve in a tight correlation with functional improvement of the transplant (158). The underlying mechanisms are complex and include stimulation of the pro-inflammatory Th17 cells, suppression of the anti-inflammatory Treg cells, enhanced production of alloantibodies, as well as local pro-inflammatory tissue reactions (154).
A growing body of experimental and clinical evidence points to significant therapeutic potential of IL-6 signaling inhibitors in prevention and treatment of acute and chronic renal graft rejection (3). Phenotyping of IL-6 knockout mice revealed a highly favorable T cell profile with the strongly reduced to absent Th17 response by the dominating FoxP3+ Treg phenotype promoting immune tolerance (167). Although the differentiation of naïve T cells into Th17 does not solely depend on IL-6 and can be alternatively achieved by combined effects of IL-21, tumor growth factor beta (TGF-β) and IL-23 (168–171), sustained IL-6 signaling plays an essential role in maintaining Th17 cell identity while suppressing Treg cells (172). Blockade of IL-6R using tocilizumab to treat RA led to sustained increase in circulating Treg levels during the therapy suggesting that IL-6 inhibition may improve the Th17/Treg balance in kidney transplantation as well (173, 174). In contrast to Treg cells, tocilizumab-induced changes in the percentage of Th17 cells were less conclusive. Cytokines and factors other than IL-6 may help maintain the Th17 response, as described above (167, 175). However, suppression of the IL-6 signaling retards the acquisition of Th17 pathogenic phenotype (176). Effects of IL-6 inhibition on the Th17/Treg balance in the setting of kidney transplantation have not been systematically investigated so far, although the available data suggests favorable effects (177, 178). Moreover, increased circulating Treg levels and clinical benefits were observed in patients receiving IL-6R blockade by tocilizumab for management of autoimmune disorders at risk or during manifestation of autoimmunity-mediated renal disease (106, 107, 109). Ongoing studies on therapeutic potential of the IL-6R inhibitor tocilizumab to promote immunologic tolerance in combination with recipient Treg cells (NCT03867617) or to rescue Treg functionality during co-stimulation blockade with belatacept (NCT04066114) may translate the experimental findings to the clinic (179).
The current clinical experience with IL-6 signaling inhibitors in kidney transplant recipients has been primarily derived from tocilizumab and clazakizumab employed as a strategy to manage the humoral alloimmune response, i.e. either for human leukocyte antigen (HLA) desensitization before transplantation or treatment of chronic antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) after the transplantation (177, 180–182). In general, IL-6 inhibition using tocilizumab or clazakizumab was associated with reduction of donor-specific antibody titers (DSA, anti-HLA) (177, 180, 182–185), stabilization or improvement of kidney function (177, 183, 184, 186, 187), reduction of proteinuria (186), and benefits for kidney morphology (183, 186–188). Notably, reduction in eGFR correlated with decrease in DSA titers and resolution of histological abnormalities in patients receiving clazakizumab suggesting that benefits of IL-6 inhibition are significantly mediated by suppression of B cell activity (183). Despite noticeable number of side effects, mainly infections and diverticulitis, clazakizumab was generally well tolerated by kidney transplant recipients receiving concomitant immunosuppression (177, 182, 183). The efficacy of tocilizumab appears less conclusive according to several reports (181, 189–191). However, no direct comparison between the two drugs was conducted so far and the question of preferential IL-6 vs. IL-6R targeting for better graft outcomes remains open.
Further clinical experience was obtained with JAK/STAT3 inhibitors such as tofacitinib acting downstream of IL-6R (153, 192, 193). Notably, tofacitinib provided sufficient immunosuppression levels as monotherapy, comparable to the efficacy of calcineurin inhibitors being currently the first-line immunosuppressive regiment in transplant recipients worldwide. At the same time, use of tofacitinib was associated with higher general and serious infection rate requiring further studies and protocol adjustmens (193). In any case, the observed strong immunosuppressive efficacy of tofacitinib suggests similar therapeutic potential of IL-6 or IL-6R inhibitors in partial or complete substitution of highly nephrotoxic calcineurin inhibitors (194).
The available clinical experience with IL-6 signaling inhibitors in kidney transplantation is summarized in the Table 2D. Since the kidney is the most frequently transplanted organ, data on targeting the IL-6 signaling in non-renal transplant recipients are still limited but could be carefully interpreted as corroborating the therapeutic potential of IL-6 inhibition as well (NCT03644667 ongoing) (195, 196).
Choice of proper IL-6 signaling inhibitors in kidney diseases
IL-6 induction affects pathophysiology of major non-infectious kidney disorders including renal complication of autoimmune diseases, AKI, CKD, and rejection of renal allografts. Accumulating clinical experience points to therapeutic potential of IL-6 suppression in renal patients but diagnostic criteria and treatment protocols for administration of different IL-6 signaling inhibitor types need to be established. Complete or partial silencing of IL-6 signaling can be principally achieved by inhibition of IL-6, IL-6R, gp130, or the downstream JAK/STAT3 pathway (1). While IL-6 expression is strongly induced during inflammation, parallel changes in the mIL-6R or mgp130 expression levels are rather mild. Use of IL-6-neutralizing antibodies appears plausible in this context (10). In contrast, initially high doses of antibodies targeting IL-6R would be required for saturating inhibition of its membrane-bound and soluble variants. Finally, pharmacologic suppression of gp130 is not reasonable since many cytokines share gp130 for signaling events and gp130-knockout mice exhibit multiorgan pathology (197). Similarly, small-molecule inhibitors of JAKs target not only IL-6 but other cytokines recruiting the JAK/STAT3 pathway (1, 10). Based on these considerations, flexible dosage adjustment of IL-6-neutralizing antibodies may represent a viable approach towards a personalized therapeutic effect in various kidney diseases.
Selective suppression of distinct IL-6 signaling pathways may provide further therapeutic benefits. Among the three IL-6 signaling routes, the trans-signaling has been generally established as the major mediator of pro-inflammatory and pathophysiologic effects. Identification of sgp130 as an endogenous trans-signaling inhibitor forced development of recombinant sgp130 variants for therapeutic purposes (10). The first generated sgp130 variant olamkicept comprises six extracellular domains of gp130 fused to an Fc-part of an IgG antibody (sgp130Fc) and is intended for selective suppression of the IL-6 trans-signaling pathway, while permitting the classic mode. Clinical testing of olamkicept as an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent started in 2012 and delivered promising results so far (10, 198, 199). A certain cross reactivity of olamkicept with the IL-11 trans signaling was resolved by later refinements in drug design resulting in sgp130 variants with predominant to exclusive selectivity for IL-6 over IL-11 (200). Therefore, olamkicept and its next generation drugs may efficiently buffer the trans-signaling events in kidney diseases as well. Moreover, sgp130 analogues have been shown to suppress the cluster IL-6 signaling along with the trans-signaling pathway (15). Although the pathophysiological impact of the cluster (trans-presentation) signaling in kidney diseases has not been clearly established, it is tempting to speculate that this signaling mode may promote the priming of Th17 cells by the renal dendritic cells (16). Notably, due to intracellular preformation of IL-6:IL-6R complexes by presenting cells, the cluster signaling appears to be resistant to IL-6 neutralizing antibodies, with a probable exception of olokizumab. Olokizumab blocks the functional hexamer assembly by occupying the relevant binding site in IL-6 (site III) thereby being able to suppress the signaling even after successful presentation of the IL-6:IL-6R complex to a mgp130-expressing cell. The ability of olokizumab to inhibit the cluster-signaling needs further experimental verification to explore its potential as a pan-inhibitor of all IL-6 signaling modes.
Despite promising therapeutic potential of IL-6 inhibiting drugs in kidney diseases, the translation to the nephrological field is delayed by the relative scarcity of clinical information from renal patients and the absence of clear guidelines, respectively. Nevertheless, IL-6 inhibiting agents have been increasingly implemented for prevention and treatment of kidney transplant rejection and retardation of autoimmune kidney diseases. The great majority of clinical data was obtained using the IL-6R neutralizing antibody tocilizumab (105, 188). Nevertheless, we believe that available monoclonal antibodies to IL-6 bear comparable or even superior therapeutic potential. More clinical studies are mandatory to establish further IL-6 inhibiting agents to combat the acute and chronic allo- and autoimmune reactions. Use of new agents selectively suppressing trans-signaling, such as olamkicept, needs further characterization due to expected clinical benefits. Apart from the kidney transplantation setting, ESRD would obviously profit from IL-6 inhibitors as well. Since ESRD leads to systemic inflammation and multiorgan damage, suppression of IL-6 signaling is justified (145). Any type of IL-6 inhibiting agents would potentially be applicable but further clinical investigation is needed to our opinion. More complex is the situation with DKD, since IL-6 may have certain “antidiabetic” effects (114). Furthermore, podocytes may profit from the classic IL-6 signaling but the trans-signaling aggravates glomerular inflammation (201). Therefore, selective suppression of the trans-signaling using olamkicept may be considered as the primary choice but this speculation requires experimental support. Along the same line, olokizumab may provide benefits due to its putative ability to suppress the cluster-signaling, which may reduce the immune-mediated kidney damage. However, effects of distinct IL-6 inhibiting agents including olamkicept and olokizumab in DKD require further detailed investigation. The same applies to AKI, the understanding of the cytokine effects in the AKI pathophysiology including the injury and repair phases need to be improved and different IL-6 inhibitors tested.
Taken together, IL-6 has been increasingly recognized as a major player in kidney pathophysiology due to its role in sterile inflammation and immune-mediated damage. IL-6 inhibiting therapy has entered the nephrological care with clinically proven benefits for renal transplant recipients and emerging perspective in a wide range of kidney diseases. In addition, IL-6 inhibitors are expected to reduce risk of inflammation-associated cardio-vascular complications of kidney diseases. Therefore, introduction of IL-6 signaling inhibitors into clinical nephrology bears great potential to reduce the morbidity and mortality related to kidney disease. Improved understanding of the interplay between different IL-6 signaling modes in kidney diseases along with accumulation of clinical experience with IL-6 inhibiting drugs in renal patients will define concrete therapeutic avenues.
Author contributions
EG: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MD: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Visualization, Writing – original draft. KM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research on IL-6-inhibition as a therapeutic approach was supported by grant #19-75-30032 from the Russian Science Foundation (Figure 1), and the pathophysiologic effects of IL-6 signaling the kidney was studied with the support of grant #075-15-2019-1660 from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (Figure 3).
Acknowledgments
Figures were created with BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
MS and DB are employed by R-Pharm JSC.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rose-John S. Interleukin-6 family cytokines. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2018) 10:a028415. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028415
2. Jones SA, Jenkins BJ. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. (2018) 18:773–89. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0066-7
3. Chandran S, Tang Q. Impact of interleukin-6 on T cells in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. (2022) 22:18–27. doi: 10.1111/ajt.17209
4. Maeda K, Mehta H, Drevets DA, Coggeshall KM. IL-6 increases B-cell IgG production in a feed-forward proinflammatory mechanism to skew hematopoiesis and elevate myeloid production. Blood. (2010) 115:4699–706. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-230631
5. Korn T, Hiltensperger M. Role of IL-6 in the commitment of T cell subsets. Cytokine. (2021) 146:155654.
6. Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida D, Yu G-Y, Vallabhapurapu S, et al. IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell. (2009) 15:103–13. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.001
7. Guo R, Jiang M, Wang G, Li B, Jia X, Ai Y, et al. IL6 supports long-term expansion of hepatocytes in vitro. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:7345. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35167-8
8. Wang X-P, Schunck M, Kallen K-J, Neumann C, Trautwein C, Rose-John S, et al. The interleukin-6 cytokine system regulates epidermal permeability barrier homeostasis. J Invest Dermatol. (2004) 123:124–31. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22736.x
9. McElvaney OJ, Curley GF, Rose-John S, McElvaney NG. Interleukin-6: obstacles to targeting a complex cytokine in critical illness. Lancet Respir Med. (2021) 9:643–54. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00103-X
10. Rose-John S, Jenkins BJ, Garbers C, Moll JM, Scheller J. Targeting IL-6 trans-signalling: past, present and future prospects. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:666–81. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00856-y
11. Boulanger MJ, Chow D, Brevnova EE, Garcia KC. Hexameric structure and assembly of the interleukin-6/IL-6 α-Receptor/gp130 complex. Science. (2003) 300:2101–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1083901
12. Taga T, Kishimoto T. GP 130 AND THE INTERLEUKIN-6 FAMILY OF CYTOKINES. Annu Rev Immunol. (1997) 15:797–819. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.797
13. Lei C, Su H, Ye C, Tang H, Gao P, Wan C, et al. The classic signalling and trans-signalling of interleukin-6 are both injurious in podocyte under high glucose exposure. J Cell Mol Medi. (2018) 22:251–60. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13314
14. Schumertl T, Lokau J, Rose-John S, Garbers C. Function and proteolytic generation of the soluble interleukin-6 receptor in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Cell Res. (2022) 1869:119143. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.119143
15. Lamertz L, Rummel F, Polz R, Baran P, Hansen S, Waetzig GH, et al. Soluble gp130 prevents interleukin-6 and interleukin-11 cluster signaling but not intracellular autocrine responses. Sci Signal. (2018) 11:eaar7388. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aar7388
16. Heink S, Yogev N, Garbers C, Herwerth M, Aly L, Gasperi C, et al. Trans-presentation of IL-6 by dendritic cells is required for the priming of pathogenic TH17 cells. Nat Immunol. (2017) 18:74–85. doi: 10.1038/ni.3632
17. Böttcher JP, Schanz O, Garbers C, Zaremba A, Hegenbarth S, Kurts C, et al. IL-6 trans-Signaling-Dependent rapid development of cytotoxic CD8+ T cell function. Cell Rep. (2014) 8:1318–27. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.008
18. Yoshimura A, Naka T, Kubo M. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:454–65. doi: 10.1038/nri2093
19. Shaw S, Bourne T, Meier C, Carrington B, Gelinas R, Henry A, et al. Discovery and characterization of olokizumab: A humanized antibody targeting interleukin-6 and neutralizing gp130-signaling. mAbs. (2014) 6:773–781. doi: 10.4161/mabs.28612
20. Shawky AM, Almalki FA, Abdalla AN, Abdelazeem AH, Gouda AM. A comprehensive overview of globally approved JAK inhibitors. Pharmaceutics. (2022) 14:1001. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14051001
21. Moutabarrik A, Nakanishi I, Ishibashi M. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-6 receptor are expressed by cultured glomerular epithelial cells. Scand J Immunol. (1994) 40:181–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03448.x
22. Dai Y, Gu L, Yuan W, Yu Q, Ni Z, Ross MJ, et al. Podocyte-specific deletion of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 attenuates nephrotoxic serum–induced glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. (2013) 84:950–61. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.197
23. Feng X, Lu T-C, Chuang PY, Fang W, Ratnam K, Xiong H, et al. Reduction of Stat3 activity attenuates HIV-induced kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:2138–46. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008080879
24. Lu T-C, Wang Z-H, Feng X, Chuang PY, Fang W, Shen Y, et al. Knockdown of Stat3 activity in vivo prevents diabetic glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. (2009) 76:63–71. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.98
25. Eitner F, Westerhuis R, Burg M, Weinhold B, Gröne H-J, Ostendorf T, et al. Role of interleukin-6 in mediating mesangial cell proliferation and matrix production. vivo. Kidney Int. (1997) 51:69–78. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.9
26. Jo HA, Kim J-Y, Yang SH, Han SS, Joo KW, Kim YS, et al. The role of local IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling in high glucose–induced podocyte hypertrophy. Kidney Res Clin Pract. (2016) 35:212–8. doi: 10.1016/j.krcp.2016.09.003
27. Ortiz-Muñoz G, Lopez-Parra V, Lopez-Franco O, Fernandez-Vizarra P, Mallavia B, Flores C, et al. Suppressors of cytokine signaling abrogate diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2010) 21:763–72. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009060625
28. Sakurai T, Takai R, Bürgin H, Ishihara K, Sakamoto Y, Amano J, et al. The effects of interleukin-6 signal blockade on fertility, embryo- fetal development, and immunization In vivo. Birth Defects Res Pt B. (2012) 95:304–17. doi: 10.1002/bdrb.21019
29. Srivastava T, Joshi T, Heruth DP, Rezaiekhaligh MH, Garola RE, Zhou J, et al. A mouse model of prenatal exposure to interleukin-6 to study the developmental origin of health and disease. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:13260. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92751-6
30. Kreiner FF, Kraaijenhof JM, Von Herrath M, Hovingh GKK, Von Scholten BJ. Interleukin 6 in diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2022) 18:377–89. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2022.2045952
31. Gohda T, Makita Y, Shike T, Funabiki K, Shirato I, Tomino Y. Dilazep hydrochloride, an antiplatelet drug, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse mesangial cell IL-6 secretion and proliferation. Kidney Blood Press Res. (2001) 24:33–8. doi: 10.1159/000054203
32. Lu H, Zhou J. HBV X gene transfection upregulates IL-1β and IL-6 gene expression and induces rat glomerular mesangial cell proliferation. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci]. (2008) 28:247–50. doi: 10.1007/s11596-008-0304-5
33. Coletta I, Soldo L, Polentarutti N, Mancini F, Guglielmotti A, Pinza M, et al. Selective induction of MCP-1 in human mesangial cells by the IL-6/sIL-6R complex. Nephron Exp Nephrol. (2000) 8:37–43. doi: 10.1159/000059327
34. Schrader LI, Kinzenbaw DA, Johnson AW, Faraci FM, Didion SP. IL-6 deficiency protects against angiotensin II–induced endothelial dysfunction and hypertrophy. ATVB. (2007) 27:2576–81. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.153080
35. Su H, Lei C-T, Zhang C. Interleukin-6 signaling pathway and its role in kidney disease: An update. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:405. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00405
36. Kielar ML, John R, Bennett M, Richardson JA, Shelton JM, Chen L, et al. Maladaptive role of IL-6 in ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2005) 16:3315–25. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2003090757
37. Ranganathan P, Jayakumar C, Ramesh G. Proximal tubule-specific overexpression of netrin-1 suppresses acute kidney injury-induced interstitial fibrosis and glomerulosclerosis through suppression of IL-6/STAT3 signaling. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol. (2013) 304:F1054–65. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00650.2012
38. Zheng C, Huang L, Luo W, Yu W, Hu X, Guan X, et al. Inhibition of STAT3 in tubular epithelial cells prevents kidney fibrosis and nephropathy in STZ- induced diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:848. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2085-0
39. Nguyen T-N, Nguyen-Tran H-H, Chen C-Y, Hsu T. IL6 and CCL18 mediate cross-talk between VHL -deficient kidney cells and macrophages during development of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. (2022) 82:2716–33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-3749
40. Navar LG. Renal autoregulation: perspectives from whole kidney and single nephron studies. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol. (1978) 234:F357–70. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.5.F357
41. Brands MW, Banes-Berceli AKL, Inscho EW, Al-Azawi H, Allen AJ, Labazi H. Interleukin 6 knockout prevents angiotensin II hypertension: Role of renal vasoconstriction and janus kinase 2/Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation. Hypertension. (2010) 56:879–84. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.158071
42. Swart RM, Hoorn EJ, Betjes MG, Zietse R. Hyponatremia and inflammation: The emerging role of interleukin-6 in osmoregulation. Nephron Physiol. (2010) 118:p45–p51. doi: 10.1159/000322238
43. Ryan MJ. Does interleukin 6 contribute to renal hemodynamic changes during angiotensin II–dependent hypertension? Hypertension. (2010) 56:819–21. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.159350
44. Kovesdy CP. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease: an update 2022. Kidney Int Suppl. (2022) 12:7–11. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2021.11.003
45. Lee DL, Sturgis LC, Labazi H, Osborne JB, Fleming C, Pollock JS, et al. Angiotensin II hypertension is attenuated in interleukin-6 knockout mice. Am J Physiology-Heart Circulatory Physiol. (2006) 290:H935–H940. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00708.2005
46. Sturgis LC, Cannon JG, Schreihofer DA, Brands MW. The role of aldosterone in mediating the dependence of angiotensin hypertension on IL-6. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. (2009) 297:R1742–R1748. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.90995.2008
47. Chamarthi B, Williams GH, Ricchiuti V, Srikumar N, Hopkins PN, Luther JM, et al. Inflammation and hypertension: The interplay of interleukin-6, dietary sodium, and the renin-angiotensin system in humans. Am J Hypertension. (2011) 24:1143–8. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2011.113
48. Lee DL, Leite R, Fleming C, Pollock JS, Webb RC, Brands MW. Hypertensive response to acute stress is attenuated in interleukin-6 knockout mice. Hypertension. (2004) 44:259–63. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000139913.56461.fb
49. Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Radu S, Ouatu A, Rezus C, Ciocoiu M, et al. Arterial hypertension and interleukins: Potential therapeutic target or future diagnostic marker? Int J Hypertension. (2019) 2019:1–17. doi: 10.1155/2019/3159283
50. Sequeira-Lopez MLS, Gomez RA. Renin cells, the kidney, and hypertension. Circ Res. (2021) 128:887–907. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318064
51. Hashmat S, Rudemiller N, Lund H, Abais-Battad JM, Van Why S, Mattson DL. Interleukin-6 inhibition attenuates hypertension and associated renal damage in dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol. (2016) 311:F555–F561. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00594.2015
52. Wynne BM, Samson TK, Moyer HC, Van Elst HJ, Moseley AS, Hecht G, et al. Interleukin 6 mediated activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. Am J Physiology-Cell Physiol. (2022) 323:C1512–23. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00272.2021
53. Norlander AE, Madhur MS. Inflammatory cytokines regulate renal sodium transporters: how, where, and why? Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol. (2017) 313:F141–4. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00465.2016
54. Luther JM, Gainer JV, Murphey LJ, Yu C, Vaughan DE, Morrow JD, et al. Angiotensin II induces interleukin-6 in humans through a mineralocorticoid receptor– dependent mechanism. Hypertension. (2006) 48:1050–7. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000248135.97380.76
55. Caiazzo E, Sharma M, Rezig AOM, Morsy MI, Czesnikiewicz-Guzik M, Ialenti A, et al. Circulating cytokines and risk of developing hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res. (2024) 200:107050. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.107050
56. Meissner M, Viehmann SF, Kurts C. DAMPening sterile inflammation of the kidney. Kidney Int. (2019) 95:489–91. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.12.007
57. Speer T, Dimmeler S, Schunk SJ, Fliser D, Ridker PM. Targeting innate immunity-driven inflammation in CKD and cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 18:762–78. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00621-9
58. Han HI, Skvarca LB, Espiritu EB, Davidson AJ, Hukriede NA. The role of macrophages during acute kidney injury: destruction and repair. Pediatr Nephrol. (2019) 34:561–9. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3883-1
59. Kurts C, Ginhoux F, Panzer U. Kidney dendritic cells: fundamental biology and functional roles in health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2020) 16:391–407. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0272-y
60. Guiteras R, Flaquer M, Cruzado JM. Macrophage in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. (2016) 9:765–71. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfw096
61. Andrade-Oliveira V, Foresto-Neto O, Watanabe IKM, Zatz R, Câmara NOS. Inflammation in renal diseases: New and old players. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:1192. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01192
62. Lee S, Huen S, Nishio H, Nishio S, Lee HK, Choi B-S, et al. Distinct macrophage phenotypes contribute to kidney injury and repair. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2011) 22:317–26. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009060615
63. Rossi M, Korpak K, Doerfler A, Zouaoui Boudjeltia K. Deciphering the role of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expressing macrophages in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:306. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030306
64. Cantero-Navarro E, Rayego-Mateos S, Orejudo M, Tejedor-Santamaria L, Tejera-Muñoz A, Sanz AB, et al. Role of macrophages and related cytokines in kidney disease. Front Med. (2021) 8:688060. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.688060
65. Moeckel G, Palmer M, Cantley L, Vichot A. Quantification and localization of M2 macrophages in human kidneys with acute tubular injury. IJNRD. (2014) 415. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S66936
66. Pfenning MB, Schmitz J, Scheffner I, Schulte K, Khalifa A, Tezval H, et al. High macrophage densities in native kidney biopsies correlate with renal dysfunction and promote ESRD. Kidney Int Rep. (2023) 8:341–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.11.015
67. Islamuddin M, Qin X. Renal macrophages and NLRP3 inflammasomes in kidney diseases and therapeutics. Cell Death Discovery. (2024) 10:229. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01996-3
68. Zhu X, Li S, Zhang Q, Zhu D, Xu Y, Zhang P, et al. Correlation of increased Th17/Treg cell ratio with endoplasmic reticulum stress in chronic kidney disease. Medicine. (2018) 97:e10748. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010748
69. Turner J-E, Paust H-J, Steinmetz OM, Panzer U. The Th17 immune response in renal inflammation. Kidney Int. (2010) 77:1070–5. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.102
70. Baran P, Hansen S, Waetzig GH, Akbarzadeh M, Lamertz L, Huber HJ, et al. The balance of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-6·soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and IL-6·sIL-6R·sgp130 complexes allows simultaneous classic and trans-signaling. J Biol Chem. (2018) 293:6762–75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001163
71. Dennen P, Altmann C, Kaufman J, Klein CL, Andres-Hernando A, Ahuja NH, et al. Urine interleukin-6 is an early biomarker of acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Crit Care. (2010) 14:R181. doi: 10.1186/cc9289
72. Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders H-J. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:52. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00284-z
73. Simmons EM, Himmelfarb J, Sezer MT, Chertow GM, Mehta RL, Paganini EP, et al. Plasma cytokine levels predict mortality in patients with acute renal failure. Kidney Int. (2004) 65:1357–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00512.x
74. Vaidya VS, Shankar K, Lock EA, Dixon D, Mehendale HM. Molecular mechanisms of renal tissue repair in survival from acute renal tubule necrosis: Role of ERK1/2 pathway. Toxicol Pathol. (2003) 31:604–18. doi: 10.1080/01926230390241945
75. Lemay S, Rabb H, Postler G, Singh AK. PROMINENT AND SUSTAINED UP-REGULATION OF GP130-SIGNALING CYTOKINES AND OF THE CHEMOKINE MIP-2 IN MURINE RENAL ISCHEMIA-REPERFUSION INJURY1. Transplantation. (2000), 959–63. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200003150-00049
76. McWilliam SJ, Wright RD, Welsh GI, Tuffin J, Budge KL, Swan L, et al. The complex interplay between kidney injury and inflammation. Clin Kidney J. (2021) 14:780–8. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa164
77. Nechemia-Arbely Y, Barkan D, Pizov G, Shriki A, Rose-John S, Galun E, et al. IL- 6/IL-6R axis plays a critical role in acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2008) 19:1106–15. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007070744
78. Shimazui T, Nakada T, Tateishi Y, Oshima T, Aizimu T, Oda S. Association between serum levels of interleukin-6 on ICU admission and subsequent outcomes in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. (2019) 20:74. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1265-6
79. for the TRIBE-AKI Consortium, Greenberg JH, Whitlock R, Zhang WR, Thiessen-Philbrook HR, Zappitelli M, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 as acute kidney injury biomarkers in pediatric cardiac surgery. Pediatr Nephrol. (2015) 30:1519–27. doi: 10.1007/s00467-015-3088-4
80. Leininger SB, Staudner ST, Vogel MJ, Mustroph J, Hubauer U, Wallner S, et al. Bioactive adrenomedullin and interleukin-6 in COVID-19: potential biomarkers of acute kidney injury and critical illness. BMC Nephrol. (2024) 25:52. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03486-1
81. Mikłaszewska M, Korohoda P, Zachwieja K, Mroczek T, Drożdż D, Sztefko K, et al. Serum interleukin 6 levels as an early marker of acute kidney injury on children after cardiac surgery. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2013) 22:377–86.
82. Liu KD, Altmann C, Smits G, Krawczeski CD, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P, et al. Serum interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 are early biomarkers of acute kidney injury and predict prolonged mechanical ventilation in children undergoing cardiac surgery: a case- control study. Crit Care. (2009) 13:R104. doi: 10.1186/cc7940
83. Reinhold SW, Straub RH, Krüger B, Kaess B, Bergler T, Weingart C, et al. Elevated urinary sVCAM-1, IL6, sIL6R and TNFR1 concentrations indicate acute kidney transplant rejection in the first 2weeks after transplantation. Cytokine. (2012) 57:379–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2011.12.006
84. Zuaiter M, Axelrod JH, Pizov G, Gofrit ON. Hyper-Interleukin-6 protects against renal ischemic-reperfusion injury–a mouse model. Front Surg. (2021) 8:605675. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.605675
85. Rops ALWMM, Jansen E, van der Schaaf A, Pieterse E, Rother N, Hofstra J, et al. Interleukin-6 is essential for glomerular immunoglobulin a deposition and the development of renal pathology in Cd37-deficient mice. Kidney Int. (2018) 93:1356–66. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.01.005
86. Fattori E, Della Rocca C, Costa P, Giorgio M, Dente B, Pozzi L, et al. Development of progressive kidney damage and myeloma kidney in interleukin-6 transgenic mice. Blood. (1994) 83:2570–9.
87. Mehrotra P, Sturek M, Neyra JA, Basile DP. Calcium channel Orai1 promotes lymphocyte IL-17 expression and progressive kidney injury. J Clin Invest. (2019) 129:4951–61. doi: 10.1172/JCI126108
88. Liu X, Hu J, Liao G, Liu D, Zhou S, Zhang J, et al. The role of regulatory T cells in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Medi. (2023) 27:3202–12. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17771
89. Stevens PE, Ahmed SB, Carrero JJ, Foster B, Francis A, Hall RK, et al. KDIGO 2024 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2024) 105:S117–S314. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.10.018
90. Francis A, Harhay MN, Ong ACM, Tummalapalli SL, Ortiz A, Fogo AB, et al. Chronic kidney disease and the global public health agenda: an international consensus. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2024) 20:473–85. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00820-6
91. Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, Sharma K, Jandeleit-Dahm KAM, Zoungas S, et al. Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2015) 1:15018. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.18
92. on behalf of the European Renal and Cardiovascular Medicine (EURECA-m) Working Group of the European Renal Association – European Dialysis Transplantation Association (ERA-EDTA), Zoccali C, Vanholder R, Massy ZA, Ortiz A, Sarafidis P, et al. The systemic nature of CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2017) 13:344–58. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.52
93. Wu D, Huang L-F, Chen X-C, Huang X-R, Li H-Y, An N, et al. Research progress on endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis in kidney diseases. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:473. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05905-x
94. Zhao W, Feng S, Wang Y, Wang C, Ren P, Zhang J, et al. Elevated urinary IL-6 predicts the progression of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int Rep. (2023) 8:519–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.12.023
95. Peterson E, Robertson A, Emlen W. Serum and urinary interleukin-6 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (1996) 5:571–5. doi: 10.1177/096120339600500603
96. Wolkow PP, Niewczas MA, Perkins B, Ficociello LH, Lipinski B, Warram JH, et al. Association of urinary inflammatory markers and renal decline in microalbuminuric type 1 diabetics. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2008) 19:789–97. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007050556
97. Suzuki D, Miyazaki M, Naka R, Koji T, Yagame M, Jinde K, et al. In situ hybridization of interleukin 6 in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. (1995) 44:1233–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.44.10.1233
98. Donate-Correa J, Ferri CM, Sánchez-Quintana F, Pérez-Castro A, González-Luis A, Martín-Núñez E, et al. Inflammatory cytokines in diabetic kidney disease: Pathophysiologic and therapeutic implications. Front Med (Lausanne). (2020) 7:628289. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.628289
99. Huang SU-S, Kulatunge O, O’Sullivan KM. Deciphering the genetic code of autoimmune kidney diseases. Genes. (2023) 14:1028. doi: 10.3390/genes14051028
100. Idasiak-Piechocka I, Miedziaszczyk M, Woźniak A, Pawliczak E, Kaczmarek E, Oko A. Interleukin-6 and epidermal growth factor as noninvasive biomarkers of progression in chronic glomerulonephritis. Am J Physiology-Cell Physiol. (2023) 325:C1267–75. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00058.2023
101. Smolen JS, Feist E, Fatenejad S, Grishin SA, Korneva EV, Nasonov EL, et al. Olokizumab versus placebo or adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. (2022) 387:715–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2201302
102. Pandolfi F, Franza L, Carusi V, Altamura S, Andriollo G, Nucera E. Interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. IJMS. (2020) 21:5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155238
103. Kapoor T, Bathon J. Renal manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatic Dis Clinics North America. (2018) 44:571–84. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2018.06.008
104. Mori S, Yoshitama T, Hidaka T, Hirakata N, Ueki Y. Effectiveness and safety of tocilizumab therapy for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and renal insufficiency: a real-life registry study in japan (the ACTRA-RI study). Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:627–630. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206695
105. Fukuda M, Sawa N, Hoshino J, Ohashi K, Motoaki M, Ubara Y. Tocilizumab preserves renal function in rheumatoid arthritis with AA amyloidosis and end-stage kidney disease: Two case reports. CN. (2021) 95:54–61. doi: 10.5414/CN109971
106. Yamada S, Tsuchimoto A, Kaizu Y, Taniguchi M, Masutani K, Tsukamoto H, et al. Tocilizumab-induced remission of nephrotic syndrome accompanied by secondary amyloidosis and glomerulonephritis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. CEN Case Rep. (2014) 3:237–43. doi: 10.1007/s13730-014-0127-0
107. Iijima T, Suwabe T, Sumida K, Hayami N, Hiramatsu R, Hasegawa E, et al. Tocilizumab improves systemic rheumatoid vasculitis with necrotizing crescentic glomerulonephritis. Modern Rheumatol. (2015) 25:138–42. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2013.874748
108. Yoshimura Y, Watanabe S, Yamanouchi M, Ikuma D, Mizuno H, Sekine A, et al. Tocilizumab attenuates anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated nephritis occurring during abatacept and adalimumab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med. (2023) 62:2099–102. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0858-22
109. Sakai R, Ito M, Yoshimoto K, Chikuma S, Kurasawa T, Kondo T, et al. Tocilizumab monotherapy uncovered the role of the CCL22/17- CCR4 + treg axis during remission of crescentic glomerulonephritis. Clin Trans Imm. (2020) 9:e1203. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1203
110. Berti A, Cavalli G, Campochiaro C, Guglielmi B, Baldissera E, Cappio S, et al. Interleukin-6 in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Rationale for successful treatment with tocilizumab. Semin Arthritis Rheumatism. (2015) 45:48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.02.002
111. Rovin BH, Van Vollenhoven RF, Aranow C, Wagner C, Gordon R, Zhuang Y, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of treatment with sirukumab (CNTO 136) in patients with active lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:2174–83. doi: 10.1002/art.39722
112. Groza Y, Jemelkova J, Kafkova LR, Maly P, Raska M. IL-6 and its role in IgA nephropathy development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2022) 66:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2022.04.001
113. Gross JL, De Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, Canani LH, Caramori ML, Zelmanovitz T. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. (2005) 28:164–76. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.1.164
114. Timper K, Denson JL, Steculorum SM, Heilinger C, Engström-Ruud L, Wunderlich CM, et al. IL-6 improves energy and glucose homeostasis in obesity via enhanced central IL-6 trans-signaling. Cell Rep. (2017) 19:267–80. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.043
115. Perello M, Raingo J. Leptin activates oxytocin neurons of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in both control and diet-induced obese rodents. PloS One. (2013) 8:e59625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059625
116. Caba M, Meza E, Escobar C, Jiménez A, Caba-Flores MD, Moreno-Cortés ML, et al. Oxytocinergic cells of the posterior hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus participate in the food entrained clock. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:19957. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99266-0
117. Ellingsgaard H, Hauselmann I, Schuler B, Habib AM, Baggio LL, Meier DT, et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat Med. (2011) 17:1481–9. doi: 10.1038/nm.2513
118. Saini A, Faulkner SH, Moir H, Warwick P, King JA, Nimmo MA. Interleukin-6 in combination with the interleukin-6 receptor stimulates glucose uptake in resting human skeletal muscle independently of insulin action. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2014) 16:931–6. doi: 10.1111/dom.12299
119. Carey AL, Steinberg GR, Macaulay SL, Thomas WG, Holmes AG, Ramm G, et al. Interleukin-6 increases insulin- stimulated glucose disposal in humans and glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation In vitro via AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes. (2006) 55:2688–97. doi: 10.2337/db05-1404
120. Lin W, Song H, Shen J, Wang J, Yang Y, Yang Y, et al. Functional role of skeletal muscle-derived interleukin-6 and its effects on lipid metabolism. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1110926. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1110926
121. Biazi GR, Uemura IGF, Miksza DR, Ferraz LS, Diaz BF, Bertolini GL, et al. Interleukin 6 acutely increases gluconeogenesis and decreases the suppressive effect of insulin on cAMP-stimulated glycogenolysis in rat liver. Cell Biochem Funct. (2023) 41:609–18. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3817
122. Carey AL, Febbraio MA. Interleukin-6 and insulin sensitivity: friend or foe? Diabetologia. (2004) 47:1135–42. doi: 10.1007/s00125-004-1447-y
123. Kado S, Nagase T, Nagata N. Circulating levels of interleukin-6, its soluble receptor and interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor complexes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetologica. (1999) 36:67–72. doi: 10.1007/s005920050147
124. Vozarova B, Weyer C, Hanson K, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE. Circulating interleukin-6 in relation to adiposity, insulin action, and insulin secretion. Obes Res. (2001) 9:414–7. doi: 10.1038/oby.2001.54
125. Pickup JC, Chusney GD, Thomas SM, Burt D. Plasma interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor α and blood cytokine production in type 2 diabetes. Life Sci. (2000) 67:291–300. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00622-6
126. Carey AL, Bruce CR, Sacchetti M, Anderson MJ, Olsen DB, Saltin B, et al. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-? are not increased in patients with type 2 diabetes: evidence that plasma interleukin-6 is related to fat mass and not insulin responsiveness. Diabetologia. (2004) 47:1029–37. doi: 10.1007/s00125-004-1403-x
127. Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, Katz DR, Miles JM, Yudkin JS, et al. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-α, in vivo 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1997) 82:4196–200. doi: 10.1210/jcem.82.12.4450
128. Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiology-Endocrinology Metab. (2001) 280:E745–51. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2001.280.5.E745
129. Koshino A, Schechter M, Sen T, Vart P, Neuen BL, Neal B, et al. Interleukin-6 and cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: New insights from CANVAS. Diabetes Care. (2022) 45:2644–2652. doi: 10.2337/dc22-0866
130. Sanchez-Alamo B, Shabaka A, Cachofeiro V, Cases-Corona C, Fernandez-Juarez G. Serum interleukin-6 levels predict kidney disease progression in diabetic nephropathy. CN. (2022) 97:1–9. doi: 10.5414/CN110223
131. Lee H-M, Kim J-J, Kim HJ, Shong M, Ku BJ, Jo E-K. Upregulated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. (2013) 62:194–204. doi: 10.2337/db12-0420
132. Shahzad K, Bock F, Dong W, Wang H, Kopf S, Kohli S, et al. Nlrp3-inflammasome activation in non-myeloid-derived cells aggravates diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. (2015) 87:74–84. doi: 10.1038/ki.2014.271
133. Cahill CM, Rogers JT. Interleukin (IL) 1β induction of IL-6 is mediated by a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent AKT/IκB kinase α pathway targeting activator protein-1. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:25900–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707692200
134. Ridker PM, Howard CP, Walter V, Everett B, Libby P, Hensen J, et al. Effects of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on hemoglobin A1c, lipids, c-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and fibrinogen: A phase IIb randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Circulation. (2012) 126:2739–48. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.122556
135. Wu R, Liu X, Yin J, Wu H, Cai X, Wang N, et al. IL-6 receptor blockade ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting inflammasome in mice. Metabolism. (2018) 83:18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.01.002
136. Harcourt BE, Forbes JM, Matthews VB. Obesity-induced renal impairment is exacerbated in interleukin-6-knockout mice. Nephrology. (2012) 17:257–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2011.01547.x
137. Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Ahrén B, Rudling M, Carlsten H, Dickson SL, et al. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat Med. (2002) 8:75–9. doi: 10.1038/nm0102-75
138. Patsalos O, Dalton B, Himmerich H. Effects of IL-6 signaling pathway inhibition on weight and BMI: A systematic review and meta-analysis. IJMS. (2020) 21:6290. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176290
139. Schultz O, Oberhauser F, Saech J, Rubbert-Roth A, Hahn M, Krone W, et al. Effects of inhibition of interleukin-6 signalling on insulin sensitivity and lipoprotein (A) levels in human subjects with rheumatoid diseases. PloS One. (2010) 5:e14328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014328
140. Feigerlová E, Battaglia-Hsu S-F. IL-6 signaling in diabetic nephropathy: From pathophysiology to therapeutic perspectives. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2017) 37:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.03.003
141. Toriu N, Yamanouchi M, Hiramatsu R, Hayami N, Hoshino J, Sekine A, et al. Tocilizumab prevents renal function of a patient with diabetic kidney disease: case report. Modern Rheumatol Case Rep. (2019) 3:53–6. doi: 10.1080/24725625.2018.1477489
142. Brosius FC, Tuttle KR, Kretzler M. JAK inhibition in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia. (2016) 59:1624–7. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4021-5
143. Tuttle KR, Brosius FC, Adler SG, Kretzler M, Mehta RL, Tumlin JA, et al. JAK1/JAK2 inhibition by baricitinib in diabetic kidney disease: results from a phase 2 randomized controlled clinical trial. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant. (2018) 33:1950–9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx377
144. Hashmi MF, Benjamin O, Lappin SL. End-stage renal disease, in: StatPearls. (2024). Treasure Island (FL: StatPearls Publishing. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499861/ (Accessed July 5, 2024).
145. Gusev E, Solomatina L, Zhuravleva Y, Sarapultsev A. The pathogenesis of end-stage renal disease from the standpoint of the theory of general pathological processes of inflammation. IJMS. (2021) 22:11453. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111453
146. Herbelin A, Ureña P, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J, Descamps-Latscha B. Elevated circulating levels of interleukin-6 in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. (1991) 39:954–60. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.120
147. Barreto DV, Barreto FC, Liabeuf S, Temmar M, Lemke H-D, Tribouilloy C, et al. Plasma interleukin-6 is independently associated with mortality in both hemodialysis and pre-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. (2010) 77:550–6. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.503
148. Chertow GM, Chang AM, Felker GM, Heise M, Velkoska E, Fellström B, et al. IL-6 inhibition with clazakizumab in patients receiving maintenance dialysis: a randomized phase 2b trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:2328–36. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03043-1
149. Hattori Y, Ubara Y, Sumida K, Hiramatsu R, Hasegawa E, Yamanouchi M, et al. Tocilizumab improves cardiac disease in a hemodialysis patient with AA amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Amyloid. (2012) 19:37–40. doi: 10.3109/13506129.2011.636460
150. Uda H, Saiki O. Tocilizumab postpones the start of hemodialysis compared to conventional oral treatment in amyloid a amyloidosis patients with advanced renal insufficiency by suppressing serum SAA levels. Amyloid. (2017) 24:62–3. doi: 10.1080/13506129.2017.1301420
151. Seneschall C, Law S, Roufosse C, Woodham S, Kousios A. Tocilizumab (anti-IL-6) treatment for AA renal amyloidosis in a patient with advanced chronic kidney disease, a case report. J Nephrol. (2024) 37(4):1147–52. doi: 10.1007/s40620-023-01845-z
152. Kilić P, Ikić L, Mayer M, Artuković M, Maštrović Radončić K, Ikić Matijašević M. Safe and efficient use of tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis patient on maintenance hemodialysis: A case report. Medicina. (2023) 59:1517. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091517
153. Krishnaswami S, Chow V, Boy M, Wang C, Chan G. Pharmacokinetics of tofacitinib, a janus kinase inhibitor, in patients with impaired renal function and end-stage renal disease. J Clin Pharmacol. (2014) 54:46–52. doi: 10.1002/jcph.178
154. Chen L, Ahmed E, Wang T, Wang Y, Ochando J, Chong AS, et al. TLR signals promote IL-6/IL-17-Dependent transplant rejection. J Immunol. (2009) 182:6217–25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803842
155. Casiraghi F, Ruggenenti P, Noris M, Locatelli G, Perico N, Perna A, et al. SEQUENTIAL MONITORING OF URINE-SOLUBLE INTERLEUKIN 2 RECEPTOR AND INTERLEUKIN 6 PREDICTS ACUTE REJECTION OF HUMAN RENAL ALLOGRAFTS BEFORE CLINICAL OR LABORATORY SIGNS OF RENAL DYSFUNCTION. Transplantation. (1997) 63:1508–14. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199705270-00023
156. Di Paolo S, Gesualdo L, Stallone G, Ranieri E, Schena F. Renal expression and urinary concentration of EGF and IL-6 in acutely dysfunctioning kidney transplanted patients. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant. (1997) 12:2687–93. doi: 10.1093/ndt/12.12.2687
157. Sadeghi M, Daniel V, Wiesel M, Hergesell O, Opelz G. High urine sIL-6R as a predictor of late graft failure in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. (2003) 76:1190–1194. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000090345.19569.F3
158. Kaden J, Priesterjahn R. Increasing urinary IL-6 levels announce kidney graft rejection. Transplant Int. (2000) 13:S34–41. doi: 10.1007/s001470050271
159. Van Oers MH, van der Heyden AA, Aarden LA. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) in serum and urine of renal transplant recipients. Clin Exp Immunol. (1988) 71:314–9.
160. Waiser J, Budde K, Katalinic A, Kuerzdorfer M, Riess R, Neumayer HH. Interleukin-6 expression after renal transplantation. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant. (1997) 12:753–9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/12.4.753
161. Muczynski KA, Leca N, Anderson AE, Kieran N, Anderson SK. Multicolor flow cytometry and cytokine analysis provides enhanced information on kidney transplant biopsies. Kidney Int Rep. (2018) 3:956–69. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2018.02.012
162. Raasveld MHM, Weening JJ, Kerst JM, Surachno S, Ten Berge RJM. Local production of interleukin-6 during acute rejection in human renal allografts. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant. (1993) 8:75–8. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.ndt.a092278
163. Wang H, Guan Q, Lan Z, Li S, Ge W, Chen H, et al. Prolonged renal allograft survival by donor interleukin-6 deficiency: association with decreased alloantibodies and increased intragraft T regulatory cells. Am J Physiology-Renal Physiol. (2012) 302:F276–83. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00258.2011
164. Riella LV, Yang J, Chock S, Safa K, Magee CN, Vanguri V, et al. Jagged2-signaling promotes IL -6-dependent transplant rejection. Eur J Immunol. (2013) 43:1449–58. doi: 10.1002/eji.201243151
165. Shen H, Goldstein DR. IL-6 and TNF-α synergistically inhibit allograft acceptance. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:1032–40. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008070778
166. Kawai T, Sachs DH, Sykes M, Cosimi AB. HLA-mismatched renal transplantation without maintenance immunosuppression. N Engl J Med. (2013) 368:1850–2. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1213779
167. Korn T, Bettelli E, Gao W, Awasthi A, Jäger A, Strom TB, et al. IL-21 initiates an alternative pathway to induce proinflammatory TH17 cells. Nature. (2007) 448:484–7. doi: 10.1038/nature05970
168. Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang Y-H, et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:1133–41. doi: 10.1038/ni1261
169. Yang L, Anderson DE, Baecher-Allan C, Hastings WD, Bettelli E, Oukka M, et al. IL-21 and TGF-β are required for differentiation of human TH17 cells. Nature. (2008) 454:350–2. doi: 10.1038/nature07021
170. McGeachy MJ, Bak-Jensen KS, Chen Y, Tato CM, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, et al. TGF-β and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain TH-17 cell–mediated pathology. Nat Immunol. (2007) 8:1390–7. doi: 10.1038/ni1539
171. Volpe E, Servant N, Zollinger R, Bogiatzi SI, Hupé P, Barillot E, et al. A critical function for transforming growth factor-β, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human TH-17 responses. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:650–7. doi: 10.1038/ni.1613
172. Harbour SN, DiToro DF, Witte SJ, Zindl CL, Gao M, Schoeb TR, et al. T h 17 cells require ongoing classic IL-6 receptor signaling to retain transcriptional and functional identity. Sci Immunol. (2020) 5:eaaw2262. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaw2262
173. Samson M, Audia S, Janikashvili N, Ciudad M, Trad M, Fraszczak J, et al. Brief report: Inhibition of interleukin-6 function corrects Th17/Treg cell imbalance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatism. (2012) 64:2499–503. doi: 10.1002/art.34477
174. Thiolat A, Semerano L, Pers YM, Biton J, Lemeiter D, Portales P, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor blockade enhances CD39+ regulatory T cell development in rheumatoid arthritis and in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:273–83. doi: 10.1002/art.38246
175. Pesce B, Soto L, Sabugo F, Wurmann P, Cuchacovich M, López MN, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor blockade on the balance between regulatory T cells and T helper type 17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Immunol. (2013) 171:237–42. doi: 10.1111/cei.12017
176. Aqel SI, Kraus EE, Jena N, Kumari V, Granitto MC, Mao L, et al. Novel small molecule IL-6 inhibitor suppresses autoreactive Th17 development and promotes treg development. Clin Exp Immunol. (2019) 196:215–25. doi: 10.1111/cei.13258
177. Jordan SC, Ammerman N, Choi J, Huang E, Najjar R, Peng A, et al. Evaluation of clazakizumab (Anti–Interleukin-6) in patients with treatment-resistant chronic active antibody-mediated rejection of kidney allografts. Kidney Int Rep. (2022) 7:720–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.01.1074
178. Chandran S, Leung J, Hu C, Laszik ZG, Tang Q, Vincenti FG. Interleukin-6 blockade with tocilizumab increases tregs and reduces T effector cytokines in renal graft inflammation: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Transplant. (2021) 21:2543–54. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16459
179. Zhao X, Boenisch O, Yeung M, Mfarrej B, Yang S, Turka LA, et al. Critical role of proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 in allograft rejection and tolerance. Am J Transplant. (2012) 12:90–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03770.x
180. Vo AA, Choi J, Kim I, Louie S, Cisneros K, Kahwaji J, et al. A phase I/II trial of the interleukin-6 receptor–specific humanized monoclonal (Tocilizumab) + intravenous immunoglobulin in difficult to desensitize patients. Transplantation. (2015) 99:2356–63. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000741
181. Jouve T, Laheurte C, Noble J, Weinhard J, Daligault M, Renaudin A, et al. Immune responses following tocilizumab therapy to desensitize HLA-sensitized kidney transplant candidates. Am J Transplant. (2022) 22:71–84. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16709
182. Vo AA, Huang E, Ammerman N, Toyoda M, Ge S, Haas M, et al. Clazakizumab for desensitization in highly sensitized patients awaiting transplantation. Am J Transplant. (2022) 22:1133–44. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16926
183. Doberer K, Duerr M, Halloran PF, Eskandary F, Budde K, Regele H, et al. A randomized clinical trial of anti–IL-6 antibody clazakizumab in late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection. JASN. (2021) 32:708–22. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020071106
184. Choi J, Aubert O, Vo A, Loupy A, Haas M, Puliyanda D, et al. Assessment of tocilizumab (Anti–Interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal) as a potential treatment for chronic antibody-mediated rejection and transplant glomerulopathy in HLA-sensitized renal allograft recipients. Am J Transplant. (2017) 17:2381–9. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14228
185. Pottebaum AA, Venkatachalam K, Liu C, Brennan DC, Murad H, Malone AF, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in the treatment of acute active antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Direct. (2020) 6:e543. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000000988
186. Lavacca A, Presta R, Gai C, Mella A, Gallo E, Camussi G, et al. Early effects of first-line treatment with anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab for chronic active antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. Clin Transplant. (2020) 34:e13908. doi: 10.1111/ctr.13908
187. Pearl M, Weng PL, Chen L, Dokras A, Pizzo H, Garrison J, et al. Long term tolerability and clinical outcomes associated with tocilizumab in the treatment of refractory antibody mediated rejection (AMR) in pediatric renal transplant recipients. Clin Transplant. (2022) 36:e14734. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14734
188. Noble J, Giovannini D, Laamech R, Imerzoukene F, Janbon B, Marchesi L, et al. Tocilizumab in the treatment of chronic antibody-mediated rejection post kidney transplantation: Clinical and histological monitoring. Front Med. (2021) 8:790547. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.790547
189. Daligault M, Bardy B, Noble J, Bourdin A, Masson D, Naciri Bennani H, et al. Marginal impact of tocilizumab monotherapy on anti- HLA alloantibodies in highly sensitized kidney transplant candidates. Transplant Direct. (2021) 7:e690. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001139
190. Kumar D, Yakubu I, Safavi F, Levy M, Moinuddin I, Kimball P, et al. Lack of histological and molecular signature response to tocilizumabin kidney transplants with chronic active antibody mediated rejection: A case series. Kidney360. (2020) 1:663–70. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000182019
191. Massat M, Congy-Jolivet N, Hebral A-L, Esposito L, Marion O, Delas A, et al. Do anti-IL-6R blockers have a beneficial effect in the treatment of antibody-mediated rejection resistant to standard therapy after kidney transplantation? Am J Transplant. (2021) 21:1641–9. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16391
192. Busque S, Leventhal J, Brennan DC, Steinberg S, Klintmalm G, Shah T, et al. Calcineurin-Inhibitor-Free immunosuppression based on the JAK inhibitor CP-690,550: A pilot study in De novo kidney allograft recipients. Am J Transplant. (2009) 9:1936–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02720.x
193. Busque S, Vincenti FG, Tedesco Silva H, O’Connell PJ, Yoshida A, Friedewald JJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of a tofacitinib- based immunosuppressive regimen after kidney transplantation: Results from a long-term extension trial. Transplant Direct. (2018) 4:e380. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000000819
194. Naesens M, Kuypers DRJ, Sarwal M. Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 4:481–508. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04800908
195. Miller CL, Madsen JC. Targeting IL-6 to prevent cardiac allograft rejection. Am J Transplant. (2022) 22:12–7. doi: 10.1111/ajt.17206
196. Sommer W, Avsar M, Aburahma K, Salman J, Kaufeld KT, Rojas SV, et al. Heart transplantation across preformed donor-specific antibody barriers using a perioperative desensitization protocol. Am J Transplant. (2022) 22:2064–76. doi: 10.1111/ajt.17060
197. Betz UAK, Bloch W, Van Den Broek M, Yoshida K, Taga T, Kishimoto T, et al. Postnatally induced inactivation of gp130 in mice results in neurological, cardiac, hematopoietic, immunological, hepatic, and pulmonary defects. J Exp Med. (1998) 188:1955–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1955
198. Schreiber S, Aden K, Bernardes JP, Conrad C, Tran F, Höper H, et al. Therapeutic interleukin-6 trans-signaling inhibition by olamkicept (sgp130Fc) in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:2354–2366.e11. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.062
199. Wagner F, Schreiber S, Bagger Y, Bruzelius K, Falahati A, Sternebring O, et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of single- and multiple-ascending doses of olamkicept: Results from randomized, placebo-controlled, first-in-human phase i trials. Clin Trans Sci. (2024) 17:e13832. doi: 10.1111/cts.13832
200. Berg AF, Ettich J, Weitz HT, Krusche M, Floss DM, Scheller J, et al. Exclusive inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling by soluble gp130FlyRFc. Cytokine: X. (2021) 3:100058. doi: 10.1016/j.cytox.2021.100058
201. Cha DR. Interleukin-6 signaling in podocyte hypertrophy. Kidney Res Clin Pract. (2016) 35:195–6. doi: 10.1016/j.krcp.2016.10.001
202. Kang S, Kishimoto T. Interplay between interleukin-6 signaling and the vascular endothelium in cytokine storms. Exp Mol Med. (2021) 53:1116–23. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00649-0
203. Wassmann S, Stumpf M, Strehlow K, Schmid A, Schieffer B, Böhm M, et al. Interleukin-6 induces oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction by overexpression of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circ Res. (2004) 94:534–41. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000115557.25127.8D
204. Li Y, Zhao J, Yin Y, Li K, Zhang C, Zheng Y. The role of IL-6 in fibrotic diseases: Molecular and cellular mechanisms. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:5405–14. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75876
Keywords: acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, inflammation, anti-cytokine therapy, kidney transplantation, trans-signaling, IL-6
Citation: Gubernatorova EO, Samsonov MY, Drutskaya MS, Lebedeva S, Bukhanova D, Materenchuk M and Mutig K (2024) Targeting inerleukin-6 for renoprotection. Front. Immunol. 15:1502299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1502299
Received: 26 September 2024; Accepted: 08 November 2024;
Published: 11 December 2024.
Edited by:
Lili Zhou, Southern Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Edmund Chung, Children’s Hospital at Westmead, AustraliaXianliang Rui, Harvard Medical School, United States
Copyright © 2024 Gubernatorova, Samsonov, Drutskaya, Lebedeva, Bukhanova, Materenchuk and Mutig. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ekaterina O. Gubernatorova, ZWthdGVyaW5hLmd1YmVybmF0b3JvdmE0MTJAZ21haWwuY29t; Kerim Mutig, a211dGlnQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Ekaterina O. Gubernatorova
Ekaterina O. Gubernatorova Mikhail Y. Samsonov3
Mikhail Y. Samsonov3 Marina S. Drutskaya
Marina S. Drutskaya Svetlana Lebedeva
Svetlana Lebedeva Maria Materenchuk
Maria Materenchuk Kerim Mutig
Kerim Mutig