
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol., 16 January 2025
Sec. Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Disorders : Autoimmune Disorders
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501364
This article is part of the Research TopicGender Affirming Hormone Therapy and its Immunological ImplicationsView all articles
Biological sex is closely associated with the properties and extent of the immune response, with males and females showing different susceptibilities to diseases and variations in immunity. Androgens, predominantly in males, generally suppress immune responses, while estrogens, more abundant in females, tend to enhance immunity. It is also established that sex hormones at least partially explain sex biases in different diseases, particularly autoimmune diseases in females. These differences are influenced by hormonal, genetic, and environmental factors, and vary throughout life stages. The advent of gender-affirming hormone therapy offers a novel opportunity to study the immunological effects of sex hormones. Despite the limited studies on this topic, available research has revealed that testosterone therapy in transgender men may suppress certain immune functions, such as type I interferon responses, while increasing inflammation markers like TNF-α. Transgender women on estrogen therapy also experience alterations in coagulation-related and inflammatory characteristics. Furthermore, other possible alterations in immune regulation can be inferred from the assessment of inflammatory and autoimmune markers in transgender individuals receiving hormone therapy. Understanding the complex interactions between sex hormones and the immune system, particularly through the unique perspective offered by gender-affirming hormone therapies, may facilitate the development of targeted therapies for infections and autoimmune diseases while also improving healthcare outcomes for transgender individuals. Here we review immune dynamics throughout life in both sexes and provide a summary of novel findings drawn from studies exploring gender-affirming hormone therapy.
The immune system combats internal and external threats by employing a multitude of tools that operate in strict unison to create a formidable, near-infallible machine, which not only detects and neutralizes the ‘non-self’ but also continuously (re)assesses its foes and (re)calibrates its approaches while unleashing its force majeure (1, 2). Despite its limitations that come in various forms (eg, genetic and acquired deficiencies or evasive infections) and the well-understood fact that it is not devoid of errors in target selection (ie, autoimmunity) (3, 4), the human immune system is a dynamic biological network that is more often than not triumphant in the evolutionary arms race against ever-changing internal and external threats.
Such a comprehensive organization with a battlefield that encompasses the whole organism requires systems-wide check-and-balance mechanisms (5). These control mechanisms are enforced and maintained by numerous regulators, including the multitude of factors that are directly or indirectly associated with biological sex. Males and females differ not only in their susceptibility to certain diseases but also in how their immune systems respond to infections, vaccines, cancers, and other conditions (6). These differences are influenced by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors, with sex hormones being critical since they underlie the divergent characteristics of sex (7). Androgenic hormones are generally accepted to weaken immune response, while estrogenic hormones usually have the opposite effect (8–10). Nonetheless, it has been notoriously challenging to determine the degree to which these hormones alter immune functions, largely because it is almost impossible to account for all biases and confounders that emerge from comparing the two sexes. Age and developmental stage are other sub-characteristics that further complicate analyses since these properties alter the production and response to sex hormones.
The emergence of gender-affirming hormone therapy (GAHT) and its utilization in different age groups represents a unique opportunity to not only understand how transgender individuals respond to this treatment but to also examine the impact of sex hormones on immunity. Comprehension of the impacts of the primary sex hormones on immune functioning can yield essential knowledge that can facilitate the development of target-specific medical treatments in infections or autoimmune disease and improve healthcare strategies concerning transgender individuals.
The immune system consists of both innate and adaptive defense mechanisms. Innate immunity acts as the first line of defense by responding to structures that are consistently unique to invading microorganisms, which are recognized by the pattern recognition receptors of primarily dendritic cells and macrophages (1). The macrophages are masters of phagocytosis and cell lysis, yielding a powerful initial response to outside insults. The innate response also induces cytokine release and is the principal source of inflammation (11). Despite their strong presence and early response, macrophages and the innate response as a whole cannot recognize or deal with all threats, necessitating deployment of the otherwise-specialized elements of the immune system. Cytokine release is one of the factors that activates these specialized systems, namely the adaptive immune response, which recognizes and eliminates pathogens and infected cells through specific cytokine secretion and antibody production, while also creating an archive of previously-recognized threats (12). Lymphocytes, with their multitude of sub-specialized cells, are the cornerstone of the adaptive immune response. They produce antibodies and employ cell-mediated immune responses, which are respectively the responsibilities of B and T lymphocytes (12).
The classical categorization of sex hormones relies upon their different distributions in the sexes, with androgens dominating in males and estrogens dominating in females (Figure 1). Other categories with numerous members also exist. For instance, the progestogens include progesterone, which is a crucial hormone for females and contributes to numerous sex-related and unrelated functions (13). Irrespective of their sex-based distribution or physiological impact, all sex hormones are produced in healthy individuals and are structurally defined as steroids, which contain the 4-fused-ringed, 17-carbon steroid skeleton (“gonane”). This skeleton provides the fundamental basis for the unique physical and physiological properties of sex hormones, facilitating their transport, permeability, recognition, and functions (14, 15). Sex hormones exert their biological effects by binding to nuclear receptors, which function as ligand-activated transcription factors. Upon hormone binding, these receptors undergo conformational changes, dimerization, translocate to the nucleus, and bind to specific hormone response elements within the genome, thereby regulating the expression of target genes (16).
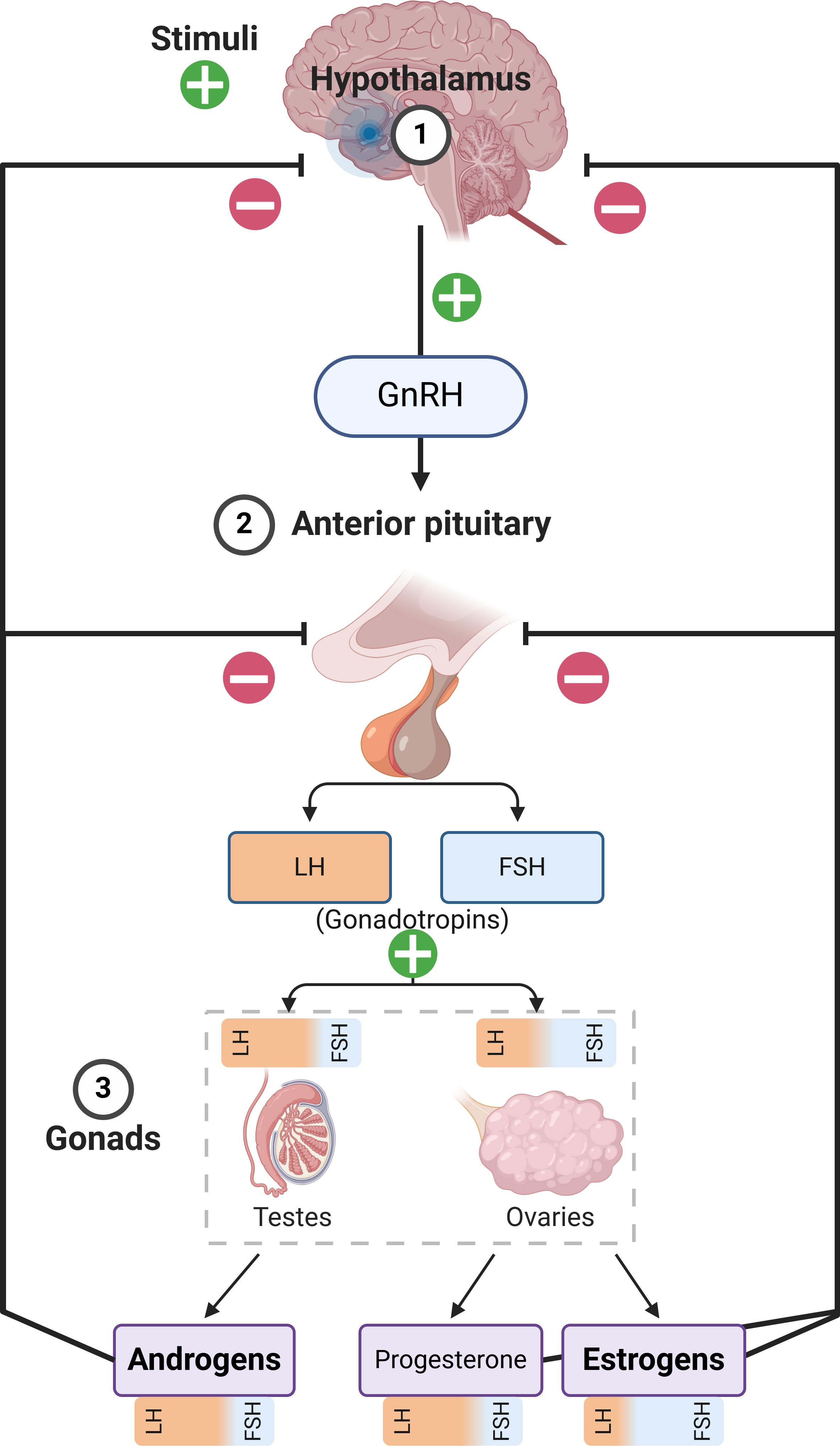
Figure 1. Summary of the Hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis. It must be noted that androgens and estrogens are produced in both males and females in different tissues, at vastly different concentrations. The figure only describes the primary production pathways in order to emphasize sex-related differences with respect to hormonal production, while also showing the influence of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) on the gonads and the production of the respective hormones. GnRH, Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone.
Sex-specific differences in susceptibility to autoimmune diseases, certain cancers, and infectious diseases have been documented widely. It is accepted that the evolutionary basis for this difference is the different requirements of the male and female immune systems –due to specific challenges unique to each sex. In particular, the female immune system needs to survive the immunosuppressive pregnancy period to create offspring while ensuring that the metabolic cost of maintaining the immune system is not too high, and also, immune response must be flexible enough to allow for pregnancy (17, 18). At baseline, females have stronger innate and adaptive immune responses compared to males, leading to faster infection clearance than males, better vaccination outcomes, and more potent serological response (19). This advantage is not solely confined to the urgency of the response either; males suffer from higher mortality rates after infection, even when adjusted for age, whereas females often mount stronger humoral immune responses, cytokine production, and T cell response after immune challenge (20), which likely explains their higher survival rates following infectious diseases (21).
A well-established method for assessing immunological states or properties is the characterization of circulating immune cells. Sex influences the composition of circulating white blood cells (leukocytes), either through sex hormone-related or independent mechanisms. Aggregated data from studies evaluating responses to different pathogens show that the number and activities of cells generating the innate immune response, including macrophages and dendritic cells, are higher in females relative to males (22, 23). Of note, the immune response is predominantly driven by type 1 helper T cells (Th1) and cellular immunity in males, while the female sex exhibits superior properties regarding B and T cell maturation and a stronger antibody response that is largely attributable to the dominance of type 2 helper T cells (Th2) (23, 24). Another subset of T helpers that has strong evidence of sex hormone-based modulation is the Th17 subset, which is downregulated by both estrogens and androgens (25) and is involved in the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases through various mechanisms including their production of pro-inflammatory cytokines that sustain/prolong inflammation (26, 27). Flow cytometric immunophenotyping of healthy volunteers reveal higher levels of CD4+ T cells in females, which may indicate enhanced thymic activity –an organ with profound effects on lymphocytes and autoimmunity (28). The elimination of autoreactive T cells in the thymus via negative T-cell selection may be less stringent in females compared to males. The autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene plays a critical role in this process by promoting the expression of tissue-specific antigens in medullary thymic epithelial cells, which are then presented to naïve T cells (29). Sex hormones drive AIRE expression in medullary thymic epithelial cells, and studies of human thymic samples and mouse models have revealed that AIRE expression is higher in males compared to females, partially explaining the divergence in developing autoimmune disease (30, 31). The sex differences also extend to CD19+ B-cells, regulatory T cells, plasma cells, and both naïve CD8+ and mucosa-associated invariant T-cells (32). On the other hand, females generally have lower absolute or relative levels of monocytes, myeloid cells, and lower absolute counts of natural killer (NK) cells than males (33). Furthermore, the adaptive immune response shows a more apparent sexual difference in antibody responses, wherein females appear to have greater antibody secretion, higher basal immunoglobulin levels, and higher B cell counts (22).
In addition to the aforementioned factors, male and female infectious responses are directly linked to genetic, biological, and behavioral differences, which include previous exposures to pathogens and sex hormones (20, 34). However, the stronger response to infections among females is also described in the earlier stages of life, before sex hormones exert their ultimate effects, indicating that sex chromosomes and other baseline differences could offer additional explanations for immunological divergence (35). Autoimmune disease susceptibility is also relatively higher among females even before puberty, although the differences between the sexes are less apparent (24). The X chromosome contains at least 50 genes with well-known immune-related functions, including some important for immune cell identity (FOXP3), cellular activation and intracellular signaling (CD40LG, TLR7, IRAK1, IL13RA1/2, NEMO, TASL, IL-9R), leukocyte trafficking (CD99, CXCR3), immune cell differentiation and proliferation (IL-2RG, BTK), and cellular metabolism (OGT, CYBB) (20). Although most alleles on one of the X chromosomes are randomly silenced during female embryogenesis, a subset of genes escape this inactivation. X-inactivation escape results in a gene dosage difference between women and men, which is likely a major factor underlying immune function differences between the sexes. Furthermore, the polymorphism of X-linked genes, cellular mosaicism for X-linked parental alleles, and X-linked miRNA upregulation of several proteins have been suggested to account for immunological sex differences and potentially to create advantages for women in terms of improved host responses to infectious challenges (36), possibly as a result of the modulation of cellular machinery during innate immune responses (37). A recent study proposed a novel mechanism for the increased risk of autoimmunity in diseases with a female bias. The authors suggested that immune responses in patients with diseases such as SLE resulted in targeting of components contributing to the X-inactivation process (38). The number of X chromosomes also impacts autoimmune susceptibility, as clearly demonstrated by the higher frequency of female-discriminant autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjögren’s syndrome) among individuals with sex chromosome aberrations such as Klinefelter Syndrome (47XXY) and trisomy X (47XXX) (20). However, women with Turner syndrome (45X) also have an elevated risk of developing female-biased autoimmune thyroid disease, which may seem paradoxical given their single X chromosome karyotype (39).
Despite well-established evidence highlighting the strong role of the X chromosome in regulating immune-related genes, the Y chromosome does have some regulatory influence in shaping immune characteristics in males, as well as being a source of male-specific genetic governance. Evidence for this impact has been gained from different approaches, including murine models of chromosome Y deficiency, detection of chromosome-specific immunoregulatory effects, and examination of manifestations in human males with loss-of-Y. For instance, a mutant mice strain was found to demonstrate Y-linked immunodeficiency involving B and NK cell depletion without an impact on T cells (40). It may be tempting to associate such attributes to hormonal alterations that could confound the analyses; however, it has been demonstrated in coxsackievirus-infected mice that the reduced survival attributed to Y chromosome polymorphism was unassociated with testosterone levels (41), indicating a non-hormonal regulatory role for the Y chromosome on immune response (41). In men with loss-of-Y, fibrotic and inflammatory changes involving macrophages have been understood to underlie cardiac injury (42). Furthermore, polymorphisms in the Y chromosome have been associated with transcriptional changes in macrophages and CD4 T cells, which may be associated with allergic encephalitis and multiple sclerosis, respectively (43).
The disparity in infection response has most recently been shown by the COVID-19 pandemic (44), with higher estrogen levels yielding better outcomes among patients (45). It is however crucial to note that while male bias regarding susceptibility to infectious disease is almost universally true for the great majority of infectious agents (46, 47), females may suffer from relatively greater disease burden and severity when exposed to certain infections, including influenza, Legionella pneumophila, and Toxoplasma gondii (48, 49), which might be associated with estrogen levels based on studies showing lower severity before puberty (50) and also weakened immune response in pregnancy (51). However, lower susceptibility is likely to translate into lower overall disease burden in the female population. Testosterone, on the other hand, causes a broad suppression of defensive responses and may ease the spread and impact of different types of infections, including parasitic diseases (46, 52) and uropathogenic Escherichia coli (53), among others. Of note, despite the much higher frequency of urinary tract infection in females and the higher proportion of Escherichia coli isolation in female patients compared to males, estrogen has been suggested to alter virulence and neutrophil responses which come together to improve the clearance of this pathogen in females (54). Furthermore, androgen exposure in mice has been shown to restrict the phagocytic prowess of neutrophils attracted to the site of infection, plausibly linked to their stunted maturation (55) and exemplifying a direct impact on innate immunity. This limited functionality of neutrophils in the infectious microenvironment has been replicated by other research, this time showing that a higher number of neutrophils are drawn to the site of infection in male mice (further aggravated by testosterone administration), presumably to counteract their limited capacity to clear the infection due to immaturity and limited functionality (56).
Immunological sex variations are also evident in terms of vaccine efficacy and side effects. Females have better seroconversion but also a higher likelihood of adverse events following immunization, especially local adverse events and allergic reactions (47, 57, 58). The initial response to vaccination is the innate immune system recognizing the non-self, leading to localized inflammation at the injection site and possibly activating allergic response pathways, including anaphylaxis. This is followed by adaptive immune activation which may be boosted by estrogen presence, conferring an advantage for better vaccine response. As such, the female immune system can create a stronger and possibly longer-lasting antibody repertoire after receipt of various vaccines, including smallpox, yellow fever, influenza, and hepatitis A and B (6).
Apart from the ‘mini puberty’ during infancy, sex hormone production lays dormant throughout childhood (59), with the primary exceptions being gradual increases in anti-Müllerian hormone (in females) and inhibin B (in males). In infants, a higher overall leukocyte count is observed regardless of sex, which necessitates age-specific reference intervals for clinical purposes (60). In terms of cell types and their abundance in the circulation, there are two ‘flips’ between neutrophils and lymphocytes throughout life, both within the early childhood. Data from postpartum studies and longitudinal data collection show that neutrophil count is generally higher compared to lymphocyte count in neonates until around 1-2 months, but lymphocytes prevail as the most common cell type from thereon until 3-5 years of age –when neutrophils regain the lead (61–65). This second ‘flip’ in the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is postulated to reflect immune maturation and the lifelong balance between the activities of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Moreover, the cytokine profiles also indicate an inversion around 1-3 years of age from a largely anti-inflammatory potential to a vigilant preparedness to produce and secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines (66, 67). These age-related variations during early childhood appear to lose clinical relevance quite swiftly, giving way to the dormancy period of sex hormones in which the great majority of immunological parameters are similar in boys and girls (Figure 2).
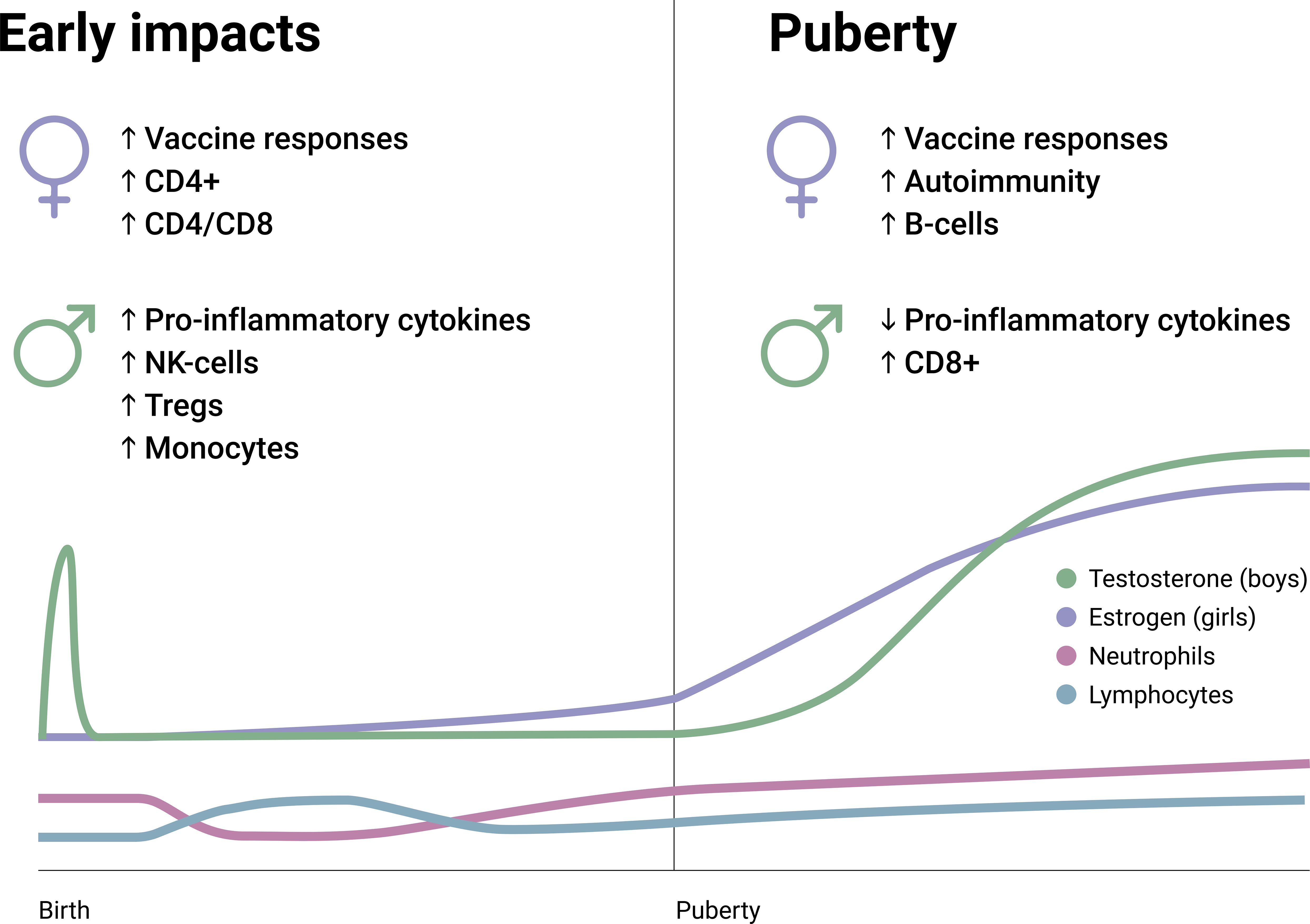
Figure 2. Early and pubertal differences regarding immune constituents and characteristics between boys and girls. Also, pubertal hormone changes (testosterone and estrogen) and the changes in neutrophil and lymphocyte frequencies are summarized on an arbitrary longitudinal scale. CD4+, Cluster of differentiation 4; CD8+, Cluster of differentiation 8; NK, Natural killer; T regs, T regulatory cells.
The early development of the immune system is greatly influenced by environmental exposure as the immune system begins recognizing threats and mounting responses of its own after birth, giving rise to multidimensional variations in relation with the bi-directional relationship between microbiome and immune development (68). The fetal immune system prefers the generation of regulatory T cells which suppress the differentiation and activities of other T cells (69). This might be an adaptive function that facilitates environmental tolerance and might also be associated with the absence of threats. The neonate has susceptibilities to infections and allergies, which are explained by the naïve adaptive immune system and the favoring of Th2 responses rather than Th1 – in correlation with the levels of corresponding cytokines that reveal an anti-inflammatory profile (70–72). Possible regulatory effects have been shown for microbial exposure (68, 73), while breastfeeding and other environmental exposures appear to salvage Th1 response to some degree (74). Furthermore, neonates have rudimentary cellular responses due to limited cytokine production and immaturity in antigen presentation. Repeat challenges to the early immune system generally result in weaker reactivity, a phenomenon recognized as ‘neonate tolerance’ that can underlie lifelong tolerance to select antigens (75), which might be beneficial in the autoimmunity and microbiome contexts but not in terms of initial infectious defense. Indeed, the young innate immune system appears to fail in mounting a sufficient response to pathogenic bacterial challenge (76, 77), creating a predisposition to sepsis (78). This outcome is partially explained by limited TLR-based activation despite the intactness of the machinery required to mount such response (76, 79). Anti-viral and vaccine responses carry a similar hindrance: type I, II, and III interferons suffer an impediment due to dysfunctional signaling that cannot be attributed to lack of response elements (72, 80, 81). These unique regulations involving different aspects of immunity add a functional dimension to the limitations posed by quantitative deficiencies in the cellular components of the immune system in neonates and infants.
Although natural development gives way to more adult-like immunoreactivity profiles in growing children, T cells still appear to have limited inflammatory activation until adulthood (82). Infants continue to manifest early immune system characteristics which may remain relatively dominant well into school age and even puberty (65), but the immune system shows considerable maturation throughout this period (83), particularly with the acceleration of baseline pro-inflammatory potential and the decay of the anti-inflammatory ‘buffer’ of cytokines (67, 84). This maturation is exemplified by the generation of lifelong immunity following vaccination or exposure to childhood infections among school-age children; whereas, antibody levels created by earlier vaccinations are known to diminish quickly (85). Nonetheless, older infants and school age children appear to possess adult-like expression of response elements, including HLA and TLR4 (67), with relatively higher levels of TLR4 –but not TLR2– in boys (86).
At the onset of puberty, a complex set of biochemical changes occur in fairly quick succession. While the exact triggering mechanisms are incompletely understood, the immediate origin of pubertal hormonal changes is the pulsatile release of gonadotropin releasing hormone from the hypothalamus, which induces downstream effects on the pituitary, and in turn, the gonads (Figure 1) (87). The systemic response differs based on sex, and males emerge with a testosterone-dominated sex hormone profile, while estradiol and progesterone are induced at far greater levels among females (88, 89). This system is called the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, which primarily contributes to reproductive development; whereas, in parallel, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis also gains increased functionality during puberty and is closely associated with the development and maturation of immune characteristics. There are very few studies that have explored the immunological impact of sex hormones in this specific period, so there is a paucity of specific data in this regard. Males and females also differ in terms of the age of puberty onset and its length, with female puberty beginning around 10-11 years of age and reaching maturity by 15-16 years, while male puberty begins later (11-12 years) and maturity may be delayed (17-18 years) –which increases the complexity of studying this period in relative terms (90). However, available evidence points to a gradual progression towards the immunological characteristics of adulthood in the pubertal period, with few exceptions (Figure 2).
Puberty can trigger the onset of autoimmunity by inducing the expression of androgen-regulated autoantigens. A study of patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I, caused by biallelic loss-of-function mutations in the AIRE gene, identified the prostate-specific enzyme transglutaminase 4 as a major autoantibody target (91). Autoantibodies to this androgen-regulated protein were unique to post-pubertal male patients and longitudinal follow-up revealed that they were triggered by the pubertal onset of transglutaminase 4 expression. Interestingly, the finding of transglutaminase 4 autoantibodies in a single female patient was attributed to receipt of androgenic treatment, which might have triggered transglutaminase 4 (91).
A study involving pubertal and post-pubertal cisgender and transgender individuals as well as post-pubertal patients with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus reported significantly higher regulatory T cell counts in post-pubertal cisgender males compared to post-pubertal cisgender females (92). In recipients of GAHT, regulatory T cells were found to experience significant shifts that resembled the transcriptomic differences between cisgender males and females, indicating that sex hormones indeed exert ambivalent effects on immune characteristics during puberty. Crucially, the sex-related differences in regulatory cell counts disappeared, but transcriptomic differences were replicated in the subset of patients with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. The authors attributed this to a possible dysregulation of sex hormone signaling in the presence of autoimmune pathologies (92).
During female puberty, the menstruation-related fluctuations in estradiol, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone begin, triggering secondary sex characteristics. In a study evaluating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) before and after puberty, estrogen was suggested to be associated with differential methylation of numerous immune-regulating DNA regions in pre- and post-pubertal PBMCs (93). Such variations are also observed during the shorter periods in menstruation. For instance, regulatory T cells with FOXP3, CD4 and CD25 positivity are increased during the estrogen-dominated period of menstruation but decreased following ovulation, indicating a direct impact of estrogens in circulatory cell composition and immunity (94). Taking into account the gradual settling of the menstrual cycle into its adult characteristics during the early stages of puberty, it is difficult to attribute the differences from males to a single factor or hormone. However, population-wide analyses of circulatory cells may shed some light into the development. For instance, adolescent females are described to have relatively higher levels of eosinophils and lower levels of monocytes compared to males of similar age (95). A relatively recent population-based study on this topic intriguingly showed higher eosinophils in males and younger individuals, and male sex retained its significance even after multivariable adjustment for many potentially-confounding factors—including age (96). The low monocyte levels in female adolescents perhaps foreshadow their relatively limited activity/cytotoxicity in adult females compared to males (64, 95, 97). Females have a considerably higher risk for the great majority of autoimmune diseases, which often show a striking increase in incidence following menarche (98–101), indicating the impact of hormones and particularly the rise of estrogen. Furthermore, premature puberty has also been associated with higher likelihoods of autoimmune thyroiditis (102) and multiple sclerosis (100).
Testosterone levels increase at three distinct time points in males: during the prenatal, neonatal, and pubertal stages. The former two peaks are accepted to facilitate the development of the male reproductive tract. During male puberty, androgens promote secondary sexual characteristics and, critically, trigger spermatogenesis (103). Observational studies focusing on pubertal changes in androgens show that boys experience a steep rise in testosterone levels at and throughout puberty, usually maintaining the upward momentum until 16–18 years of age followed by a plateau that often extends to middle age (89, 104). Despite limited data regarding direct relationships with pubertal hormones, the monocyte abundance in males appears to be consistent throughout life (64), suggesting underlying mechanisms other than sex hormones. Additionally, males appear to experience a marginal delay in reaching leukocyte compositions characteristic of adults (particularly with respect to regaining neutrophil dominance) (61–64). This may be associated with the prolonged puberty period and continuous rise in testosterone levels throughout puberty. In a longitudinal study exploring genetic features during puberty, analyses showed that males had a considerably larger number of differentially-expressed genes relative to females (105). Taken together with the divergence of DNA methylation features during puberty (93) and the varying impacts of estrogen and testosterone in this regard (106), the onset of puberty appears to have the potential to at least partially shape the underlying properties associated with immune response. In this context, studies exploring DNA methylation in males and females have revealed numerous differences that may have physiological and pathological implications, including generally higher levels of autosomal methylation in females (107), differentially-methylated regions that associate with sex hormones (108), and variabilities in immune response to cancer (109).
Sex hormones exert their most discernable impacts on immune properties and functions during the adulthood. A comprehensive summary of innate and adaptive immune characteristics in adults is presented in Table 1. Furthermore, the typical impacts of androgens and estrogens are summarized in Figures 3, 4, respectively.
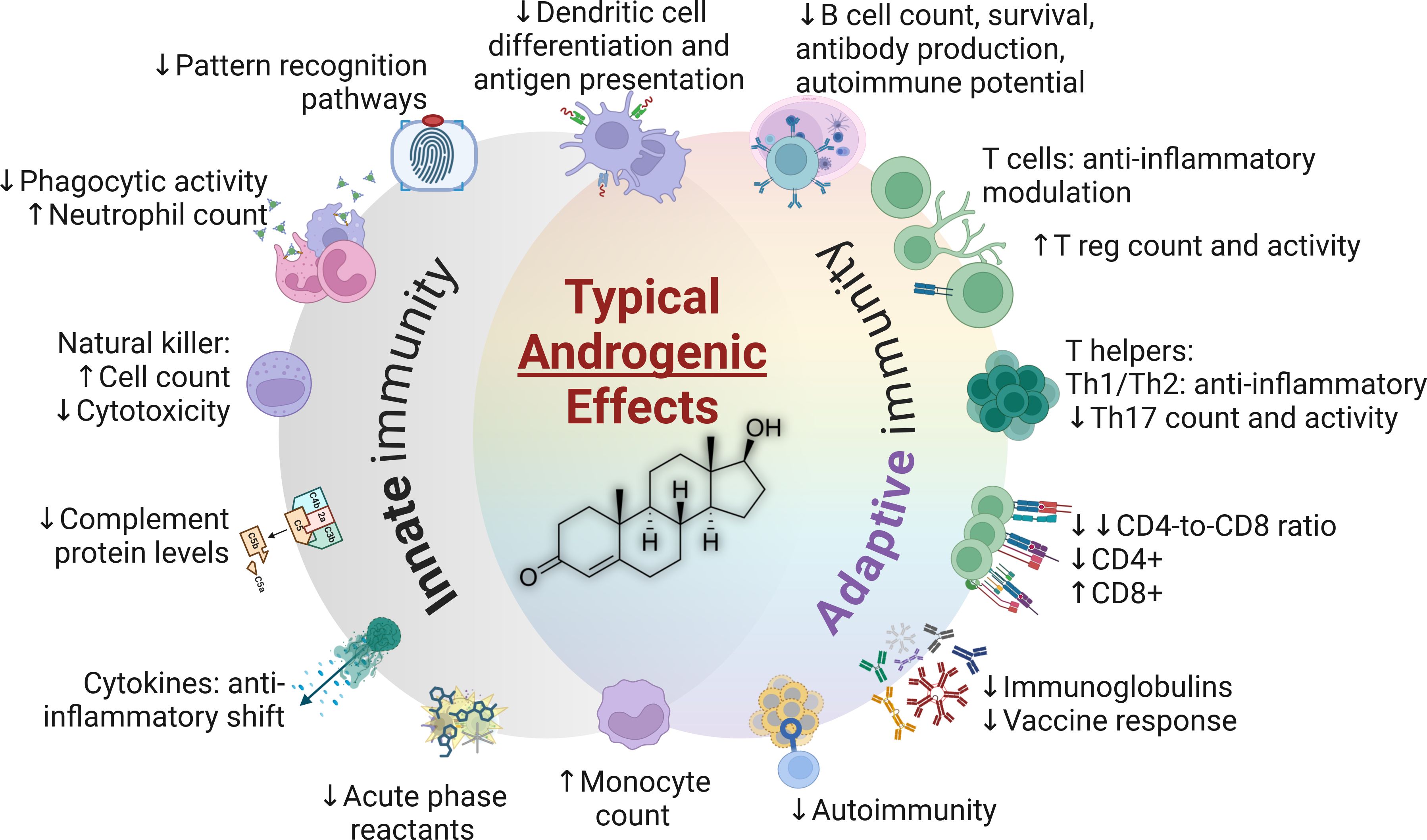
Figure 3. The typical impacts of androgens in the immune system (testosterone structure depicted in center). CD4+, Cluster of differentiation 4; CD8+, Cluster of differentiation 8; Th, T helper cells; T reg, T regulatory cells.
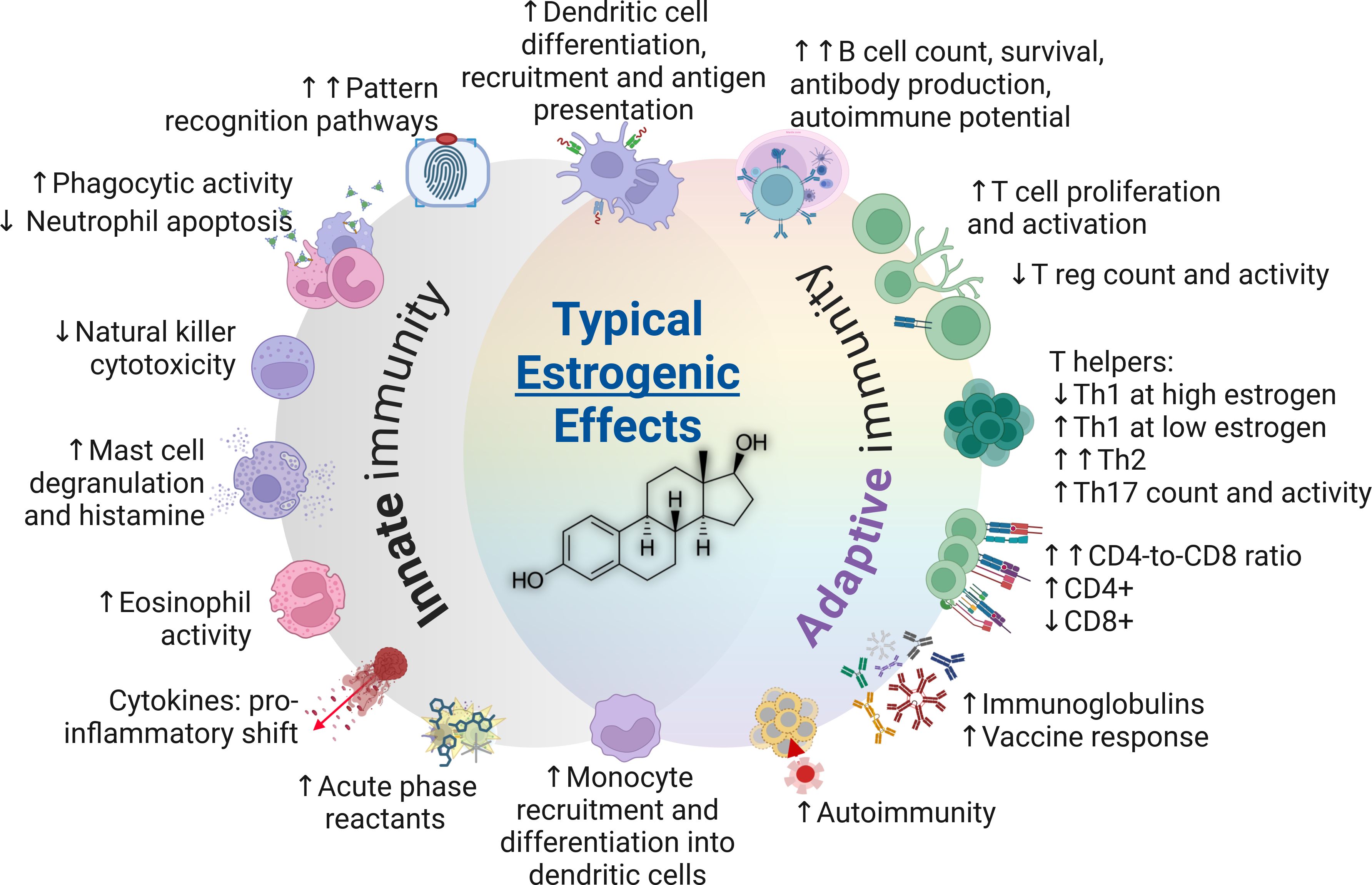
Figure 4. The typical impacts of estrogens on the immune system (estradiol structure depicted in center). CD4+, Cluster of differentiation 4; CD8+, Cluster of differentiation 8; Th, T helper cells; T reg, T regulatory cells.
Estrogens enhance immune response, with the sole exception suggested to be a mild-to-moderate decrease in cell-mediated immune responses (18). However, they also contribute to a higher vulnerability to autoimmune diseases (98–100). Estrogens promote Th2 responses and stimulate antibody production, with evidence showing an increase in regulatory T cells during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle when estrogen levels peak (94). In terms of Th1, estrogens are accepted to yield overall promoting effects at low concentrations and suppressive effects at high concentrations (7). Estrogen improves neutrophil responses and decreases their apoptotic potential (127) and activates B lymphocytes (222). Although cellular senescence is associated with weaker immune response (223), delayed apoptosis could extend the life of mature immune cells, which may improve immunoreactivity during infection but could also increase the likelihood of autoreactivity (224). Therefore, the impact of estrogen appears to be advantageous in the context of infectious response but detrimental for classical autoimmune diseases in adults (225). Estrogen receptors are present in the immune system with varying expression in different cell types, influencing both innate and adaptive immunity as demonstrated by the transcriptional and protein-level data obtained from dendritic cells, T and B cells, and monocytes (226).
It is also crucial to consider the fluctuations in estrogen levels that occur throughout life. Before menopause, females typically have about five times the circulating estrogen levels of males (227), which is accepted to be the underlying factor causing Th2 activation and Th1 suppression (6). However, levels can vary significantly with the menstrual cycle and some females experience short periods when their estrogen levels decline to male levels. These periods are typically during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle and lead to activation of Th1 responses (7), mild inflammation, and marginal elevation of specific inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein (228). Furthermore, a meta-analysis of 110 studies examining menstrual correlations with constituents of the immune system revealed that the follicular phase (higher estrogen) was associated with lower counts of circulatory immune cells, including leukocytes, neutrophils, and particularly, monocytes (125) – notably with very high heterogeneity (I^2) among results. Other studies have shown stable B cell populations during menstruation (137), higher regulatory T cells in the follicular phase relative to luteal (94), and higher NK cell count in the luteal phase relative to follicular (125, 137).
Pregnancy also influences the immune system by triggering a shift toward Th2 response and increased antibody production, while general immunoreactivity declines with higher expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines, ultimately resulting in lesser severity of many but not all forms of autoimmune conditions (213). This notion is supported by the fact that increasing estrogen and progesterone levels during pregnancy would be expected to suppress Th17 cells (25), which has been described previously (197); however, contrasting results showing increases in Th17-associated cells in pregnant women exist (132). The latter study also showed lower circulatory lymphocyte levels, lower Th1/Th2 memory cells, and progressive declines in regulatory T cells during pregnancy (both in absolute and relative terms) when compared to non-pregnant women (132). Although the great majority of immune cells rebounded to non-pregnant levels very swiftly following delivery, it was notable that the memory cells did not demonstrate this swift recovery, which is an interesting aspect that warrants further study (132). NK cells are among the immune cells that strongly deviate during pregnancy (229), both in the circulation and pregnancy decidua. While the abundance of NK cells in the decidua is recognized to facilitate placental development, the cytotoxic subset of NK cells may decline in maternal circulation (132) which facilitates implantation (230); however, available NK cells appear to mount stronger responses to viral challenge (specifically influenza) (229) in parallel with the pro-inflammatory profile of monocytes and dendritic cells in pregnant women with influenza (231). Nonetheless, suppression of the cytotoxic potential of NK cells have been shown in other types of stimulation, and it must be mentioned that NK-deficient mice appear to experience better outcomes when infected with influenza (134, 135). Taken together, pregnancy is a period when the female immune system mounts relatively weaker immune responses and less autoimmune potential that correlate with rising estrogen levels and NK cell levels. This change also appears to be responsible for elevated viral susceptibility (232) that is also partially explained by diminished type I and type III interferon responses reported by experimental studies (163, 164).
Menopause is characterized by the natural loss of estrogen synthesis (233). Coinciding with the fall in endogenous estrogen levels, the advantage conferred to females in terms of infectious diseases is largely lost (37), while the severity of autoimmune diseases lessens (234, 235). Innate immunity-related changes include declines in anti-inflammatory cytokines, neutrophils and cytotoxic potential, while pro-inflammatory mediators and effectors demonstrate a general increase (127, 172). The silencing of estrogen signaling mirrors an inversion of the CD4-to-CD8 lymphocyte ratio, weaker vaccine response, and considerable variations in T cell populations (141, 211). In systemic lupus erythematosus, the female bias is exceedingly apparent (10–15:1), similar to multiple sclerosis, Sjögren’s and other autoimmune disorders (99, 236). However, estrogens are not the only explanation to this difference, as overt autoimmunity is observed at a higher frequency among pre-pubertal females and the female bias persists after menopause (99, 236–238).
Hysterectomy and oophorectomy are procedures that result in the resection of estrogen-producing tissues. The outcomes of these procedures also appear to reduce the severity of autoimmune diseases while restricting immune response to microorganisms – as demonstrated by experimental and clinical studies (128–130).
Androgens modulate the innate immune response through a number of mechanisms, including cell proliferation, cytokine secretion, and the expression of pattern recognition receptors such as toll-like receptors (TLRs) (103). Dihydrotestosterone is far more potent that testosterone in terms of androgenic effects, but the most abundant androgen in adult men is testosterone (239). Androgens exert mainly immunosuppressive properties (240) through the induction of anti-inflammatory cytokines and suppression of nitric oxide (NO) production in neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages, acting as a limiter to their cytotoxic potential (120, 241). Testosterone also causes lower relative levels of CD4+ T cells compared to CD8+ T cells, in direct contrast to the overall impact of estrogens (37). The prohibitive impact on polymorphonuclear cells and the innate immune system, as evidenced by anti-inflammatory modulation of monocytes and macrophages (240), is one of the most prominent factors explaining the relatively weak response to infection among males (35).
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a unique intermediate steroid (prohormone) in that it is recognized by both androgen and estrogen receptors, appears to have divergent impacts on immune functions, and that it can be enzymatically transformed to these steroids through different pathways, depending on tissue exposure. DHEA has weak binding properties to androgen and estrogen receptors, which indicates that its receptor-mediated effects might be overridden or diminished by the presence of androgens or estrogens with higher receptor affinities, and also, that it could exert its effects through other signaling pathways (242, 243). It has been shown to regulate some immune responses, by suppressing the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-2 and IL-6, and stimulating anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-10 (244). These properties appear to yield physiologically-relevant impacts as evidenced by milder disease manifestations when administered to females with systemic lupus erythematosus (245–247). Based on studies in humans, DHEA is understood to increase monocyte and NK cell counts (248), restrict IL-5, IL-10 and IFN-γ secretion in patients with asthma (249), negatively correlate with the parasitic burden of malaria (DHEA-S) (250), and demonstrate diminished levels in patients with tuberculosis – similar to decreased testosterone levels (239, 251). Alluding to the contrasting effects of DHEA on immune function in the context of immunopathology, oral supplementation in patients with Addison’s disease was found to decrease NK cells while restoring regulatory T cells (252). Adding to this complexity, under experimental infectious challenges, DHEA appears to stimulate IFN-γ in parasitic infections, thereby promoting response (253) in a striking similarity to estrogen’s impact on IFN-γ (254), and also, it improves macrophage phagocytosis via NO upregulation in bacterial challenge through favoring of Th1 responses in contrast to Th2 (increased IL-2 and IFN-α; decreased IL-4 and IL-10) (255). In a study examining stress responses among males, post-stress DHEA levels were found to correlate positively with the anti-bacterial activity of saliva (256). Some of these ambivalent effects may be associated with the sensitivity of estrogen receptors to DHEA (257) and its stimulation of the NF-kB pathway (244), as well as its multiple effects on other pathways (243). Therefore, although DHEA indeed has similar immunomodulatory effects with other androgens, such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, its contrasting effects must be appreciated when interpreting the influences of this unique prohormone on immune functions, which remain limitedly understood (239).
While menopause is a clear threshold with which it is possible to explore the impact of a sudden decline in estrogen levels on female immunity, males do not have such a period with an abrupt loss of testosterone levels, but they experience a very gradual and plateau-like testosterone decrease after middle age (258), which can result in andropause in elderly men. Supportive evidence regarding the impact of testosterone on autoimmunity development (259) can be drawn from studies showing elevated autoimmunity risks among patients with hypofunctional testes (260). Data obtained from orchiectomy studies provide some more context to the matter of immune functions orchestrated by androgens. Loss of testosterone production due to orchiectomy has been associated with an increase in TNFα production in an experimental study (170), while another murine study revealed that orchiectomy yields macrophages with increased expression of TLR4 and that androgen-naïve macrophages exhibit decreased TLR4 levels in response to testosterone stimulation (118). Furthermore, in a clinical follow-up of patients who had undergone orchiectomy, a significant increase in NK cell count was identified at 3 months after surgery. Notably, the same study revealed an increase in B lymphocytes, but statistical analysis was marginally non-significant (139). Other impacts of testosterone loss include lowered IFNG expression (138), increased naïve T cell counts (191), fewer memory and regulatory T cells (138, 202), a greater propensity towards Th1 responses (191), and inversion of the CD4-to-CD8 ratio (211).
The immunosuppressive impact of testosterone is not limited to males. Females with elevated testosterone levels due to polycystic ovary syndrome have been shown to suffer from more severe COVID-19 relative to those without polycystic ovary syndrome (261) and this relationship appears to be mediated by inflammatory modulation and the facilitation of viral entry to cells (262, 263). One study specifically examining women with and without hyperandrogenism described considerable differences in the frequencies of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 symptoms. Hyperandrogenic women manifested with significantly higher frequencies of anosmia, ageusia, cough, fatigue, anorexia, and pain (264).
In addition to natural fluctuations in endogenous hormones, individuals may also experience changes due to receiving exogenous hormones, such as hormonal contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, and GAHT (233). These treatments are known to impact the homeostasis of various hormonal and metabolic pathways, including the pituitary-adrenal axis (265–267). The impact on this pathway, more so than the alterations of sex hormones, could explain many changes in immune regulation (268). For instance, testosterone and estrogen + antiandrogen therapies respectively administered to transmen and transwomen exerted effects that resembled the typical differences between cisgender males and females in terms of the pituitary-adrenal axis. Transmen experienced a decrease in cortisol production while transwomen had elevated levels (267). Based on decades of research, oral contraceptives have been established to influence a multitude of processes and systems in the body, including coagulation, hormonal homeostasis, energy metabolism, leukocyte counts, and other immunity-related parameters (269, 270). In fact, pubertal use of combined contraceptives has been associated with a decrease in Th17 lymphocytes, albeit the functionality of these cells and the levels of related cytokines were elevated – possibly balancing the overall deleterious effect (271). That being said, the effects of exogenous estrogens are varied. Estrogens alone appear to facilitate an elevation of regulatory T cells in both absolute and relative measures and promote differentiation of several cell populations, such as dendritic cells (272), with some studies reporting reduced inflammation during hormonal contraceptive use (273) while others have reported an increase in inflammatory markers and disease (274, 275). An in-depth review and contextual examination of the primary effects of exogenous sex hormones and GAHT on different diseases has described available evidence and the significant gaps and conflicts in current knowledge (276).
These conflicts may be a result of numerous treatment- and patient-related characteristics; however, the alteration of the underlying physiological ‘norm’ could be a reliable explanation. For instance, estrogen levels exceeding physiological levels have been associated with a dose-dependent effect on immune response in a meta-analysis involving multiple species. The authors revealed that supraphysiological estrogen levels had a moderate enhancing effect on immune response, while physiological levels did not (18). The same study also showed a weak relationship between higher testosterone and immunosuppression (18). Notably, an early study examining the results of anti-androgen treatment administered to transmen revealed that circulatory NOx levels (nitrite + nitrate, emerging from NO decomposition) were increased after 30 days of treatment, and correlated positively with estradiol while DHEA-S declined (120). As such, the expected results of exogenous testosterone and estrogen administration in GAHT may be feasibly aligned with their established immunoregulatory effects. In agreement with this hypothesis, GAHT was found to cause transcriptomic changes in regulatory T cells that mirrored the differences between cisgender males and females (92).
Although research concerning the impact of GAHT is yet in its infancy, exogeneous hormone treatments have long been used in patients with sex chromosome aberrations. For instance, testosterone replacement therapy in patients with Klinefelter’s Syndrome has been described to lower antibody and cytokine levels and lymphocyte counts (both T and B cells) [5]. The approaches to GAHT differ based on individual requirements and also from center to center, which may include the suppression of endogenous sex hormones as well as estrogen or testosterone administration to transgender women or transgender men, respectively. A recent study examining immune adaptations in 23 transgender men undergoing testosterone-based masculinizing treatment revealed various changes in immune cell populations when comparing data from up to 1 year of follow-up to baseline characteristics. The rise in testosterone and subsequent suppression of estradiol was found to downregulate the type I interferon system and upregulate TNF at multiple levels (277). A similar suppressive effect of GAHT on the type I interferon system was observed in an independent study of transgender men (278). Type I interferon suppression could reasonably explain poor viral outcomes in males, while the presence of lower testosterone and higher estrogen may possibly overactivate type I interferons in women, which may add another dimension to the relationship of these hormones with autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus – as evidenced by the aforementioned positive impact of DHEA on disease manifestations (245, 247, 279).
Another study assessing the impact of testosterone-based GAHT treatment on metabolic and inflammatory markers found that testosterone therapy increases leukocyte-endothelium interactions (280). This is attributed to an increase in polymorphonuclear leukocyte rolling and adhesion, along with a reduction in rolling velocity. The treatment also increased the levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, E-selectin, IL-6, and TNFα (280). However, the expected impact of cross-sex hormones may not be as clear for other immune features. This can be exemplified by a study showing that transgender women using transdermal estradiol experienced increased platelet activation and coagulation marker levels, whereas transgender men using testosterone did not show any contrasting alterations in this respect. The authors also reported that inflammatory markers appeared to be diminished among transgender women, while high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels increased in transgender men (281). Another study in transgender men and women revealed changes in gut microbiome composition following the initiation of GAHT (282). Given the important role of the microbiome in shaping immune function, these shifts may contribute to explaining immunological sex differences and related disease susceptibilities, as previously shown for autoimmune disease manifestations in mice (283).
A few case reports have documented the onset of autoimmune diseases, primarily systemic lupus erythematosus, but also systemic sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other rheumatic conditions, in transgender individuals undergoing GAHT (284). Anti-nuclear antibodies, which can precede the development of autoimmune conditions, were examined in a recent study where 36% of transmen and 31% of transwomen tested positive, compared to just 13% in the cisgender male and female population (285). This is a remarkable situation particularly for transgender men who would be expected to lose the impact of estrogen dominance on autoimmune disease susceptibility. Nonetheless, the consistently higher positivity for anti-nuclear antibodies in both transgender groups solidifies our understanding that estrogen and testosterone influence endogenous immune control mechanisms in infectious or autoimmune conditions, which is a conclusion supported by other studies revealing elevated anti-nuclear antibody levels among transgender individuals compared to the general population (286). However, it must be noted that the conflicts in the literature also extend to this relationship, as data from another study that prospectively evaluated the presence of autoantibodies among recipients of GAHT for 3 years revealed that the treatment did not yield an increased risk of developing overt autoimmune diseases (287), which could suggest that elevated immunoreactivity might not translate into an appreciable risk of clinical disease. It is also tempting to postulate that these risks might be ameliorated by the governing genetic characteristics underlying the immune functions of transgender individuals. One particular aspect is that transmen lack the Y chromosome, which, as described previously, has regulatory impact on immune function.
While available studies present conflicting results, what remains undisputed is the significance of this research area, which holds the potential to illuminate the existing knowledge gaps in GAHT and the impact of sex hormones on immune functioning. Many screening recommendations exist for transgender individuals undergoing GAHT –including assessments for cardiovascular risk, osteoporosis, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and prostate cancer (288). However, there is a need for more information to determine whether the immunological effects of GAHT and potential impacts on immune-related disease risks also need consideration. Studies evaluating this topic also offer crucial data regarding sex differences in immune function, which may in turn support development of new treatments for immune-related diseases that are better tailored to each sex.
AY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RY: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FS: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (SEXimmune, GA 949607) and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (Dnr KAW 2022.0146).
This work has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (SEXimmune, GA 949607) and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (Dnr KAW 2022.0146). Figures 1, 3, and 4 were generated in BioRender.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Marshall JS, Warrington R, Watson W, Kim HL. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. (2018) 14:49. doi: 10.1186/s13223-018-0278-1
2. Liston A, Humblet-Baron S, Duffy D, Goris A. Human immune diversity: from evolution to modernity. Nat Immunol. (2021) 22:1479–89. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01058-1
3. Raje N, Dinakar C. Overview of immunodeficiency disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. (2015) 35:599–623. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2015.07.001
4. Jung S, Gies V, Korganow A-S, Guffroy A. Primary immunodeficiencies with defects in innate immunity: focus on orofacial manifestations. Front Immunol. (2020) 11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01065
6. Klein SL, Marriott I, Fish EN. Sex-based differences in immune function and responses to vaccination. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. (2015) 109:9–15. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/tru167
7. Klein SL, Flanagan KL. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:626–38. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.90
8. Shabbir S, Khurram E, Moorthi VS, Eissa YTH, Kamal MA, Butler AE. The interplay between androgens and the immune response in polycystic ovary syndrome. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:259. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04116-4
9. Roved J, Westerdahl H, Hasselquist D. Sex differences in immune responses: Hormonal effects, antagonistic selection, and evolutionary consequences. Hormones Behavior. (2017) 88:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.11.017
10. Sciarra F, Campolo F, Franceschini E, Carlomagno F, Venneri MA. Gender-specific impact of sex hormones on the immune system. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:6302. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076302
11. Arango Duque G, Descoteaux A. Macrophage cytokines: involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Front Immunol. (2014) 5:491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00491
12. Chi H, Pepper M, Thomas PG. Principles and therapeutic applications of adaptive immunity. Cell. (2024) 187:2052–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.037
13. Pillerová M, Borbélyová V, Hodosy J, Riljak V, Renczés E, Frick KM, et al. On the role of sex steroids in biological functions by classical and non-classical pathways. update. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2021) 62:100926. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2021.100926
14. Lednicer D. Steroid chemistry at a glance. West Sussex, United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons (2011).
15. Yalcinkaya A, Öztaş YE, Sabuncuoğlu S. Sterols in inflammatory diseases: implications and clinical utility. In: Lizard G, editor. Implication of oxysterols and phytosterols in aging and human diseases. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2024). p. 261–75.
16. Sever R, Glass CK. Signaling by nuclear receptors. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2013) 5:a016709. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016709
17. Rainville JR, Tsyglakova M, Hodes GE. Deciphering sex differences in the immune system and depression. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2018) 50:67–90. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2017.12.004
18. Foo YZ, Nakagawa S, Rhodes G, Simmons LW. The effects of sex hormones on immune function: a meta-analysis. Biol Rev. (2017) 92:551–71. doi: 10.1111/brv.12243
19. Migliore L, Nicolì V, Stoccoro A. Gender specific differences in disease susceptibility: the role of epigenetics. Biomedicines. (2021) 9:652. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060652
20. Forsyth KS, Jiwrajka N, Lovell CD, Toothacre NE, Anguera MC. The conneXion between sex and immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. (2024) 24:487–502. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-00996-9
21. Fink AL, Klein SL. The evolution of greater humoral immunity in females than males: implications for vaccine efficacy. Curr Opin Physiol. (2018) 6:16–20. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2018.03.010
22. Ghosh S, Klein RS. Sex drives dimorphic immune responses to viral infections. J Immunol. (2017) 198:1782–90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601166
23. Sender R, Weiss Y, Navon Y, Milo I, Azulay N, Keren L, et al. The total mass, number, and distribution of immune cells in the human body. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2023) 120:e2308511120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308511120
24. Billi AC, Kahlenberg JM, Gudjonsson JE. Sex bias in autoimmunity. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2019) 31:53–61. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000564
25. Alanazi H, Zhang Y, Fatunbi J, Luu T, Kwak-Kim J. The impact of reproductive hormones on T cell immunity; normal and assisted reproductive cycles. J Reprod Immunol. (2024) 165:104295. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2024.104295
26. Qian Y, Kang Z, Liu C, Li X. IL-17 signaling in host defense and inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2010) 7:328–33. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2010.27
27. Maione F, Paschalidis N, Mascolo N, Dufton N, Perretti M, D’Acquisto F. Interleukin 17 sustains rather than induces inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. (2009) 77:878–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.11.011
28. Stankiewicz LN, Salim K, Flaschner EA, Wang YX, Edgar JM, Lin BZ, et al. Sex biased human thymic architecture guides T cell development through spatially defined niches. Developmental Cell. (2025) 60:152–169.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.09.011
29. Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen Z, Berzins SP, Turley SJ, et al. Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science. (2002) 298:1395–401. doi: 10.1126/science.1075958
30. Dragin N, Bismuth J, Cizeron-Clairac G, Biferi MG, Berthault C, Serraf A, et al. Estrogen-mediated downregulation of AIRE influences sexual dimorphism in autoimmune diseases. J Clin Invest. (2016) 126:1525–37. doi: 10.1172/JCI81894
31. Zhu ML, Bakhru P, Conley B, Nelson JS, Free M, Martin A, et al. Sex bias in CNS autoimmune disease mediated by androgen control of autoimmune regulator. Nat Commun. (2016) 7:11350. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11350
32. Patin E, Hasan M, Bergstedt J, Rouilly V, Libri V, Urrutia A, et al. Natural variation in the parameters of innate immune cells is preferentially driven by genetic factors. Nat Immunol. (2018) 19:302–14. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0049-7
33. Abdullah M, Chai PS, Chong MY, Tohit ER, Ramasamy R, Pei CP, et al. Gender effect on in vitro lymphocyte subset levels of healthy individuals. Cell Immunol. (2012) 272:214–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.10.009
34. Vázquez-Martínez ER, García-Gómez E, Camacho-Arroyo I, González-Pedrajo B. Sexual dimorphism in bacterial infections. Biol Sex Differ. (2018) 9:27. doi: 10.1186/s13293-018-0187-5
35. Jaillon S, Berthenet K, Garlanda C. Sexual dimorphism in innate immunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2019) 56:308–21. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8648-x
36. Libert C, Dejager L, Pinheiro I. The X chromosome in immune functions: when a chromosome makes the difference. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:594–604. doi: 10.1038/nri2815
37. Giefing-Kröll C, Berger P, Lepperdinger G, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. How sex and age affect immune responses, susceptibility to infections, and response to vaccination. Aging Cell. (2015) 14:309–21. doi: 10.1111/acel.2015.14.issue-3
38. Dou DR, Zhao Y, Belk JA, Zhao Y, Casey KM, Chen DC, et al. Xist ribonucleoproteins promote female sex-biased autoimmunity. Cell. (2024) 187:733–49.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.12.037
39. De Sanctis V, Khater D. Autoimmune diseases in Turner syndrome: an overview. Acta Biomed. (2019) 90:341–4. doi: 10.23750/abm.v90i3.8737
40. Sun S-L, Horino S, Itoh-Nakadai A, Kawabe T, Asao A, Takahashi T, et al. Y chromosome–linked B and NK cell deficiency in mice. J Immunol. (2013) 190:6209–20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300303
41. Case LK, Toussaint L, Moussawi M, Roberts B, Saligrama N, Brossay L, et al. Chromosome Y regulates survival following murine coxsackievirus B3 infection. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics. (2012) 2:115–21. doi: 10.1534/g3.111.001610
42. Sano S, Horitani K, Ogawa H, Halvardson J, Chavkin NW, Wang Y, et al. Hematopoietic loss of Y chromosome leads to cardiac fibrosis and heart failure mortality. Science. (2022) 377:292–7. doi: 10.1126/science.abn3100
43. Case LK, Wall EH, Dragon JA, Saligrama N, Krementsov DN, Moussawi M, et al. The Y chromosome as a regulatory element shaping immune cell transcriptomes and susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Genome Res. (2013) 23:1474–85. doi: 10.1101/gr.156703.113
44. Jin JM, Bai P, He W, Wu F, Liu XF, Han DM, et al. Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: focus on severity and mortality. Front Public Health. (2020) 8:152. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00152
45. Mauvais-Jarvis F, Klein SL, Levin ER. Estradiol, progesterone, immunomodulation, and COVID-19 outcomes. Endocrinology. (2020) 161:1–8. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa127
46. Bernin H, Lotter H. Sex bias in the outcome of human tropical infectious diseases: influence of steroid hormones. J Infect Dis. (2014) 209 Suppl 3:S107–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit610
47. Klein SL. Sex influences immune responses to viruses, and efficacy of prophylaxis and treatments for viral diseases. Bioessays. (2012) 34:1050–9. doi: 10.1002/bies.201200099
48. Daher D, Shaghlil A, Sobh E, Hamie M, Hassan ME, Moumneh MB, et al. Comprehensive overview of toxoplasma gondii-induced and associated diseases. Pathogens. (2021) 10:1351. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10111351
49. vom Steeg LG, Klein SL. SeXX matters in infectious disease pathogenesis. PloS Pathog. (2016) 12:e1005374. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005374
50. Suber F, Kobzik L. Childhood tolerance of severe influenza: a mortality analysis in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2017) 313:L1087–l95. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00364.2017
51. Kim HM, Kang YM, Song BM, Kim HS, Seo SH. The 2009 pandemic H1N1 influenza virus is more pathogenic in pregnant mice than seasonal H1N1 influenza virus. Viral Immunol. (2012) 25:402–10. doi: 10.1089/vim.2012.0007
52. Silva JL, Pinzan CF, Duarte A, Goulart A, Sampaio PA, Bulhões GP, et al. Testosterone leads to Trypanosoma cruzi glycoprotein synthesis and increased of inflammatory mediators in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Exp Parasitol. (2024), 263–264:108798. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2024.108798
53. Wu R, Pettersson C, Demirel I. Testosterone increases the virulence traits of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1422747. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1422747
54. Pettersson C, Wu R, Demirel I. Estrogen-stimulated uropathogenic E. coli mediate enhanced neutrophil responses. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:23030. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74863-x
55. Hreha TN, Collins CA, Cole EB, Jin RJ, Hunstad DA. Androgen exposure impairs neutrophil maturation and function within the infected kidney. mBio. (2024) 15:e0317023. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03170-23
56. Er-Lukowiak M, Hänzelmann S, Rothe M, Moamenpour DT, Hausmann F, Khatri R, et al. Testosterone affects type I/type II interferon response of neutrophils during hepatic amebiasis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1279245. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279245
57. Yalcinkaya A, Cavalli M, Cederholm A, Aranda-Guillén M, Behere A, Mildner H, et al. No link between type I interferon autoantibody positivity and adverse reactions to COVID-19 vaccines. NPJ Vaccines. (2024) 9:42. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00829-9
58. Kiely M, Tadount F, Lo E, Sadarangani M, Wei SQ, Rafferty E, et al. Sex differences in adverse events following seasonal influenza vaccines: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Epidemiol Community Health. (2023) 77:791–801. doi: 10.1136/jech-2023-220781
59. Renault CH, Aksglaede L, Wøjdemann D, Hansen AB, Jensen RB, Juul A. Minipuberty of human infancy - A window of opportunity to evaluate hypogonadism and differences of sex development? Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2020) 25:84–91. doi: 10.6065/apem.2040094.047
60. Fish JD, Lipton JM, Lanzkowsky P eds. Appendix 1 - Hematological reference values. In: Lanzkowsky's manual of pediatric hematology and oncology, Seventh, vol. p . London, United Kingdom: Academic Press. p. 767–80.
61. Li K, Peng YG, Yan RH, Song WQ, Peng XX, Ni X, et al. Age-dependent changes of total and differential white blood cell counts in children. (Engl). (2020) 133:1900–7. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000854
62. Shiga S, Koyanagi I, Ohsaga J, Ichiyama S, Kannagi R. Clinical reference values for laboratory hematology tests calculated using the iterative truncation method with correction: Part 2, Reference values for white blood cell (WBC) count, WBC differential including segmented neutrophil, band neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte, eosinophil, basophil, platelet count and mean platelet volume. Rinsho Byori. (1999) 47:281–8.
63. Song M, Dai S, Li J, Liu W, Zhang M, Ma L. Establishment of pediatric reference intervals for complete blood count parameters in capillary blood in Beijing. Int J Lab Hematology. (2021) 43:1363–72. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13631
64. Nah EH, Kim S, Cho S, Cho HI. Complete blood count reference intervals and patterns of changes across pediatric, adult, and geriatric ages in korea. Ann Lab Med. (2018) 38:503–11. doi: 10.3343/alm.2018.38.6.503
65. Shearer WT, Rosenblatt HM, Gelman RS, Oyomopito R, Plaeger S, Stiehm ER, et al. Lymphocyte subsets in healthy children from birth through 18 years of age: The pediatric AIDS clinical trials group P1009 study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2003) 112:973–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.07.003
66. Kollmann Tobias R, Levy O, Montgomery Ruth R, Goriely S. Innate immune function by toll-like receptors: distinct responses in newborns and the elderly. Immunity. (2012) 37:771–83. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.10.014
67. Nguyen M, Leuridan E, Zhang T, De Wit D, Willems F, Van Damme P, et al. Acquisition of adult-like TLR4 and TLR9 responses during the first year of life. PloS One. (2010) 5:e10407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010407
68. Olin A, Henckel E, Chen Y, Lakshmikanth T, Pou C, Mikes J, et al. Stereotypic immune system development in newborn children. Cell. (2018) 174:1277–92.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.06.045
69. Mold JE, Michaëlsson J, Burt TD, Muench MO, Beckerman KP, Busch MP, et al. Maternal alloantigens promote the development of tolerogenic fetal regulatory T cells in utero. Science. (2008) 322:1562–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1164511
70. Abrahamsson TR, Sandberg Abelius M, Forsberg A, Björkstén B, Jenmalm MC. A Th1/Th2-associated chemokine imbalance during infancy in children developing eczema, wheeze and sensitization. Clin Exp Allergy. (2011) 41:1729–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03827.x
71. Gasparoni A, Ciardelli L, Avanzini A, Castellazzi AM, Carini R, Rondini G, et al. Age-related changes in intracellular th1/th2 cytokine production, immunoproliferative T lymphocyte response and natural killer cell activity in newborns, children and adults. Biol Neonate. (2003) 84:297–303. doi: 10.1159/000073638
72. Basha S, Surendran N, Pichichero M. Immune responses in neonates. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. (2014) 10:1171–84. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2014.942288
73. Li J, Shen N, He W, Pan Y, Wu J, Zhao R, et al. Gut microbiome impact on childhood allergic rhinitis and house dust mite IgE responses. Pediatr Res. (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41390-024-03645-y
74. Duramad P, Harley K, Lipsett M, Bradman A, Eskenazi B, Holland NT, et al. Early environmental exposures and intracellular th1/th2 cytokine profiles in 24-month-old children living in an agricultural area. Environ Health Perspectives. (2006) 114:1916–22. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9306
75. Zaghouani H, Hoeman CM, Adkins B. Neonatal immunity: faulty T-helpers and the shortcomings of dendritic cells. Trends Immunol. (2009) 30:585–91. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2009.09.002
76. Levy O, Zarember KA, Roy RM, Cywes C, Godowski PJ, Wessels MR. Selective impairment of TLR-mediated innate immunity in human newborns: neonatal blood plasma reduces monocyte TNF-alpha induction by bacterial lipopeptides, lipopolysaccharide, and imiquimod, but preserves the response to R-848. J Immunol. (2004) 173:4627–34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.7.4627
77. Al-Hertani W, Yan SR, Byers DM, Bortolussi R. Human newborn polymorphonuclear neutrophils exhibit decreased levels of MyD88 and attenuated p38 phosphorylation in response to lipopolysaccharide. Clin Invest Med. (2007) 30:E44–53. doi: 10.25011/cim.v30i2.979
78. Dai W, Zhou W. A narrative review of precision medicine in neonatal sepsis: genetic and epigenetic factors associated with disease susceptibility. Transl Pediatr. (2023) 12:749–67. doi: 10.21037/tp-22-369
79. Anderson J, Bender G, Minh Thang C, Quang Thanh L, Thi Trang Dai V, Van Thanh P, et al. TLR responses in preterm and term infant cord blood mononuclear cells. Pathogens. (2023) 12:596. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12040596
80. Goenka A, Halliday A, Gregorova M, Milodowski E, Thomas A, Williamson MK, et al. Young infants exhibit robust functional antibody responses and restrained IFN-γ production to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep Med. (2021) 2:100327. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100327
81. Schüller SS, Sadeghi K, Wisgrill L, Dangl A, Diesner SC, Prusa AR, et al. Preterm neonates display altered plasmacytoid dendritic cell function and morphology. J Leukoc Biol. (2013) 93:781–8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1011525
82. Rudolph ME, McArthur MA, Barnes RS, Magder LS, Chen WH, Sztein MB. Differences between pediatric and adult T cell responses to in vitro staphylococcal enterotoxin B stimulation. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:498. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00498
83. Hayward AC, Fragaszy EB, Bermingham A, Wang L, Copas A, Edmunds WJ, et al. Comparative community burden and severity of seasonal and pandemic influenza: results of the Flu Watch cohort study. Lancet Respir Med. (2014) 2:445–54. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70034-7
84. Burl S, Townend J, Njie-Jobe J, Cox M, Adetifa UJ, Touray E, et al. Age-dependent maturation of toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine responses in Gambian infants. PloS One. (2011) 6:e18185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018185
85. van der Staak M, Ten Hulscher HI, Nicolaie AM, Smits GP, de Swart RL, de Wit J, et al. Long-term dynamics of measles virus-specific neutralizing antibodies in children vaccinated before 12 months of age. Clin Infect Dis. (2024). doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae537
86. Bannister EG, Smith C, Visvanathan K, Thompson A, Hardikar W. TLR2 and TLR4 in healthy children: Age and gender differences. J Paediatrics Child Health. (2013) 49:1082–3. doi: 10.1111/jpc.2013.49.issue-12
87. Bangalore Krishna K, Witchel SF. Normal puberty. Endocrinol Metab Clinics North America. (2024) 53:183–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2024.01.001
88. Howard SR. Interpretation of reproductive hormones before, during and after the pubertal transition-Identifying health and disordered puberty. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2021) 95:702–15. doi: 10.1111/cen.14578
89. Senefeld JW, Lambelet Coleman D, Johnson PW, Carter RE, Clayburn AJ, Joyner MJ. Divergence in timing and magnitude of testosterone levels between male and female youths. JAMA. (2020) 324:99–101. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5655
90. Brix N, Ernst A, Lauridsen LLB, Parner E, Støvring H, Olsen J, et al. Timing of puberty in boys and girls: A population-based study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. (2019) 33:70–8. doi: 10.1111/ppe.2019.33.issue-1
91. Landegren N, Sharon D, Shum AK, Khan IS, Fasano KJ, Hallgren Å, et al. Transglutaminase 4 as a prostate autoantigen in male subfertility. Sci Transl Med. (2015) 7:292ra101. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa9186
92. Robinson GA, Peng J, Peckham H, Butler G, Pineda-Torra I, Ciurtin C, et al. Investigating sex differences in T regulatory cells from cisgender and transgender healthy individuals and patients with autoimmune inflammatory disease: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Rheumatol. (2022) 4:e710–e24. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00198-9
93. Thompson EE, Nicodemus-Johnson J, Kim KW, Gern JE, Jackson DJ, Lemanske RF, et al. Global DNA methylation changes spanning puberty are near predicted estrogen-responsive genes and enriched for genes involved in endocrine and immune processes. Clin Epigenetics. (2018) 10:62. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0491-2
94. Arruvito L, Sanz M, Banham AH, Fainboim L. Expansion of CD4+CD25+and FOXP3+ regulatory T cells during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle: implications for human reproduction. J Immunol. (2007) 178:2572–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2572
95. Valiathan R, Ashman M, Asthana D. Effects of ageing on the immune system: infants to elderly. Scandinavian J Immunol. (2016) 83:255–66. doi: 10.1111/sji.2016.83.issue-4
96. Hartl S, Breyer MK, Burghuber OC, Ofenheimer A, Schrott A, Urban MH, et al. Blood eosinophil count in the general population: typical values and potential confounders. Eur Respir J. (2020) 55:1901874. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01874-2019
97. Varghese M, Clemente J, Lerner A, Abrishami S, Islam M, Subbaiah P, et al. Monocyte trafficking and polarization contribute to sex differences in meta-inflammation. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.826320
98. Reich DS, Lucchinetti CF, Calabresi PA. Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:169–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1401483
99. Yang Q, Kennicott K, Zhu R, Kim J, Wakefield H, Studener K, et al. Sex hormone influence on female-biased autoimmune diseases hints at puberty as an important factor in pathogenesis. Front Pediatr. (2023) 11:1051624. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1051624
100. Jacobs BM, Noyce AJ, Bestwick J, Belete D, Giovannoni G, Dobson R. Gene-environment interactions in multiple sclerosis: A UK biobank study. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2021) 8:e1007. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000001007
101. Hoeve M, Kalinina Ayuso V, Schalij-Delfos NE, Los LI, Rothova A, de Boer JH. The clinical course of juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis in childhood and puberty. Br J Ophthalmol. (2012) 96:852–6. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2011-301023
102. Kyritsi EM, Vasilakis IA, Kosteria I, Mantzou A, Gryparis A, Kassi E, et al. High frequency of autoimmune thyroiditis in euthyroid girls with premature adrenarche. Front Pediatr. (2023) 11:1064177. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1064177
103. Vancolen S, Sébire G, Robaire B. Influence of androgens on the innate immune system. Andrology. (2023) 11:1237–44. doi: 10.1111/andr.13416
104. Khairullah A, Klein LC, Ingle SM, May MT, Whetzel CA, Susman EJ, et al. Testosterone trajectories and reference ranges in a large longitudinal sample of male adolescents. PloS One. (2014) 9:e108838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108838
105. Resztak JA, Choe J, Nirmalan S, Wei J, Bruinsma J, Houpt R, et al. Analysis of transcriptional changes in the immune system associated with pubertal development in a longitudinal cohort of children with asthma. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:230. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35742-z
106. Moore SR, Humphreys KL, Colich NL, Davis EG, Lin DTS, MacIsaac JL, et al. Distinctions between sex and time in patterns of DNA methylation across puberty. BMC Genomics. (2020) 21:389. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06789-3
107. Grant OA, Wang Y, Kumari M, Zabet NR, Schalkwyk L. Characterising sex differences of autosomal DNA methylation in whole blood using the Illumina EPIC array. Clin Epigenetics. (2022) 14:62. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01279-7
108. Harbs J, Rinaldi S, Keski-Rahkonen P, Liu X, Palmqvist R, Van Guelpen B, et al. An epigenome-wide analysis of sex hormone levels and DNA methylation in male blood samples. Epigenetics. (2023) 18:2196759. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2196759
109. Patel D, McElroy JP, Weng DY, Sahar K, Reisinger SA, Freudenheim JL, et al. Sex-related DNA methylation is associated with inflammation and gene expression in the lungs of healthy individuals. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:14280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65027-y
110. Aomatsu M, Kato T, Kasahara E, Kitagawa S. Gender difference in tumor necrosis factor-α production in human neutrophils stimulated by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2013) 441:220–5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.042
111. Lefèvre N, Corazza F, Valsamis J, Delbaere A, De Maertelaer V, Duchateau J, et al. The number of X chromosomes influences inflammatory cytokine production following toll-like receptor stimulation. Front Immunol. (2019) 10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01052
112. Young NA, Wu LC, Burd CJ, Friedman AK, Kaffenberger BH, Rajaram MV, et al. Estrogen modulation of endosome-associated toll-like receptor 8: an IFNα-independent mechanism of sex-bias in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. (2014) 151:66–77. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2014.01.006
113. Berghöfer B, Frommer T, Haley G, Fink L, Bein G, Hackstein H. TLR7 ligands induce higher IFN-alpha production in females. J Immunol. (2006) 177:2088–96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.4.2088
114. Regis E, Fontanella S, Lin L, Howard R, Haider S, Curtin JA, et al. Sex differences in innate anti-viral immune responses to respiratory viruses and in their clinical outcomes in a birth cohort study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:23741. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03044-x
115. Ono S, Tsujimoto H, S-i H, Takahata R, Kinoshita M, Mochizuki H. Sex differences in cytokine production and surface antigen expression of peripheral blood mononuclear cells after surgery. Am J surgery. (2005) 190:439–44. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.03.031
116. Buschow SI, Biesta PJ, Groothuismink ZMA, Erler NS, Vanwolleghem T, Ho E, et al. TLR7 polymorphism, sex and chronic HBV infection influence plasmacytoid DC maturation by TLR7 ligands. Antiviral Res. (2018) 157:27–37. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.06.015
117. Gryaznova MV, Kozarenko ON, Ivannikova VM, Smirnova YD, Burakova IY, Altukhova OB, et al. Pattern-recognition receptors and cervical microbiome in patients with early miscarriages. Int J Inflammation. (2024) 2024:5320926. doi: 10.1155/2024/5320926
118. Rettew JA, Huet-Hudson YM, Marriott I. Testosterone reduces macrophage expression in the mouse of toll-like receptor 4, a trigger for inflammation and innate immunity. Biol Reproduction. (2008) 78:432–7. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.063545
119. Di Zazzo A, De Piano M, Coassin M, Mori T, Balzamino BO, Micera A. Ocular surface toll like receptors in ageing. BMC Ophthalmol. (2022) 22:185. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02398-8
120. Valenti S, Fazzuoli L, Giusti M. Circulating nitric oxide levels increase after anti-androgen treatment in male-to-female transsexuals. J Endocrinol Invest. (2003) 26:522–6. doi: 10.1007/BF03345214
121. Spitzer JA. Gender differences in some host defense mechanisms. Lupus. (1999) 8:380–3. doi: 10.1177/096120339900800510
122. Weinstein Y, Ran S, Segal S. Sex-associated differences in the regulation of immune responses controlled by the MHC of the mouse. J Immunol. (1984) 132:656–61. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.132.2.656
123. Yang F, Zheng Q, Jin L. Dynamic function and composition changes of immune cells during normal and pathological pregnancy at the maternal-fetal interface. Front Immunol. (2019) 10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02317
124. Mohammad I, Starskaia I, Nagy T, Guo J, Yatkin E, Väänänen K, et al. Estrogen receptor α contributes to T cell–mediated autoimmune inflammation by promoting T cell activation and proliferation. Sci Signaling. (2018) 11:eaap9415. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aap9415
125. Notbohm HL, Moser F, Goh J, Feuerbacher JF, Bloch W, Schumann M. The effects of menstrual cycle phases on immune function and inflammation at rest and after acute exercise: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Physiologica. (2023) 238:e14013. doi: 10.1111/apha.v238.4
126. Çalışkan S, Kaba S, Özsoy E, Koca O, Akyüz M, Öztürk Mİ. The hematological parameters in testicular cancer. J Oncological Sci. (2017) 3:117–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jons.2017.10.002
127. Molloy EJ, O’Neill AJ, Grantham JJ, Sheridan-Pereira M, Fitzpatrick JM, Webb DW, et al. Sex-specific alterations in neutrophil apoptosis: the role of estradiol and progesterone. Blood. (2003) 102:2653–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-02-0649
128. Souza C, Oliveira HBM, Santos Júnior MN, Silva MO, Coqueiro IL, Silva Í BSD, et al. Ovarian hormones influence immune response to Staphylococcus aureus infection. Braz J Infect Dis. (2020) 24:534–44. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2020.10.004
129. Namjou B, Scofield RH, Kelly JA, Goodmon E, Aberle T, Bruner GR, et al. The effects of previous hysterectomy on lupus. Lupus. (2009) 18:1000–5. doi: 10.1177/0961203309104315
130. Rocca WA, Gazzuola-Rocca L, Smith CY, Grossardt BR, Faubion SS, Shuster LT, et al. Accelerated accumulation of multimorbidity after bilateral oophorectomy: A population-based cohort study. Mayo Clin Proc. (2016) 91:1577–89. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.08.002
131. Pujantell M, Skenteris NT, Claussen JM, Grünhagel B, Thiele RJ, Altfeld M. Sex-dependent differences in type I IFN-induced natural killer cell activation. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1277967. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1277967
132. Forsberg A, Abrahamsson TR, Nilsson L, Ernerudh J, Duchén K, Jenmalm MC. Changes in peripheral immune populations during pregnancy and modulation by probiotics and ω-3 fatty acids. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:18723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75312-1
133. Kolanska K, Suner L, Cohen J, Ben Kraiem Y, Placais L, Fain O, et al. Proportion of cytotoxic peripheral blood natural killer cells and T-cell large granular lymphocytes in recurrent miscarriage and repeated implantation failure: case-control study and meta-analysis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). (2019) 67:225–36. doi: 10.1007/s00005-019-00546-5
134. Abdul-Careem MF, Mian MF, Yue G, Gillgrass A, Chenoweth MJ, Barra NG, et al. Critical role of natural killer cells in lung immunopathology during influenza infection in mice. J Infect Diseases. (2012) 206:167–77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis340
135. Zhou G, Juang SWW, Kane KP. NK cells exacerbate the pathology of influenza virus infection in mice. Eur J Immunol. (2013) 43:929–38. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242620
136. Hao S, Zhao J, Zhou J, Zhao S, Hu Y, Hou Y. Modulation of 17beta-estradiol on the number and cytotoxicity of NK cells in vivo related to MCM and activating receptors. Int Immunopharmacol. (2007) 7:1765–75. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2007.09.017
137. Lee S, Kim J, Jang B, Hur S, Jung U, Kil K, et al. Fluctuation of peripheral blood T, B, and NK cells during a menstrual cycle of normal healthy women. J Immunol. (2010) 185:756–62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904192
138. Page ST, Plymate SR, Bremner WJ, Matsumoto AM, Hess DL, Lin DW, et al. Effect of medical castration on CD4+ CD25+ T cells, CD8+ T cell IFN-gamma expression, and NK cells: a physiological role for testosterone and/or its metabolites. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2006) 290:E856–63. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00484.2005
139. Yang N, Xiao H, Wang W, Li S, Yan H, Wang Y. Effects of doctors' empathy abilities on the cellular immunity of patients with advanced prostate cancer treated by orchiectomy: the mediating role of patients' stigma, self-efficacy, and anxiety. Patient Prefer Adherence. (2018) 12:1305–14. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S166460
140. Hirokawa K, Utsuyama M, Hayashi Y, Kitagawa M, Makinodan T, Fulop T. Slower immune system aging in women versus men in the Japanese population. Immun Ageing. (2013) 10:19. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-10-19
141. Han A, Kim JY, Kwak-Kim J, Lee SK. Menopause is an inflection point of age-related immune changes in women. J Reprod Immunol. (2021) 146:103346. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2021.103346
142. Giglio T, Imro MA, Filaci G, Scudeletti M, Puppo F, De Cecco L, et al. Immune cell circulating subsets are affected by gonadal function. Life Sci. (1994) 54:1305–12. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00508-7
143. Al-Attar A, Presnell SR, Peterson CA, Thomas DT, Lutz CT. The effect of sex on immune cells in healthy aging: Elderly women have more robust natural killer lymphocytes than do elderly men. Mech Ageing Dev. (2016) 156:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2016.04.001
144. Benson VS, Hartl S, Barnes N, Galwey N, Van Dyke MK, Kwon N. Blood eosinophil counts in the general population and airways disease: a comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. (2022) 59:2004590. doi: 10.1183/13993003.04590-2020
145. Zierau O, Zenclussen AC, Jensen F. Role of female sex hormones, estradiol and progesterone, in mast cell behavior. Front Immunol. (2012) 3:169. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00169
146. Siroux V, Curt F, Oryszczyn MP, Maccario J, Kauffmann F. Role of gender and hormone-related events on IgE, atopy, and eosinophils in the Epidemiological Study on the Genetics and Environment of Asthma, bronchial hyperresponsiveness and atopy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2004) 114:491–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.05.027
147. Edelstam G, Lowbeer C, Kral G, Gustafsson SA, Venge P. New reference values for routine blood samples and human neutrophilic lipocalin during third-trimester pregnancy. Scandinavian J Clin Lab Invest. (2001) 61:583–91. doi: 10.1080/003655101753267937
148. Gaya da Costa M, Poppelaars F, van Kooten C, Mollnes TE, Tedesco F, Würzner R, et al. Age and sex-associated changes of complement activity and complement levels in a healthy caucasian population. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2664. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02664
149. Sodhi EU, Philpott HT, Carter MM, Birmingham TB, Appleton CT. Sex-differences and associations between complement activation and synovial vascularization in patients with late-stage knee osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:890094. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.890094
150. He YD, Xu BN, Song D, Wang YQ, Yu F, Chen Q, et al. Normal range of complement components during pregnancy: A prospective study. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2020) 83:e13202. doi: 10.1111/aji.13202
151. Sayegh RA, Tao XJ, Awwad JT, Isaacson KB. Localization of the expression of complement component 3 in the human endometrium by in situ hybridization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1996) 81:1641–9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.4.8636381
152. El Khoudary SR, Shields KJ, Chen HY, Matthews KA. Menopause, complement, and hemostatic markers in women at midlife: the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation. Atherosclerosis. (2013) 231:54–8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.08.039
153. Yilmazer M, Fenkci V, Fenkci S, Aktepe O, Sonmezer M, Kurtay G. Association of serum complement (C3, C4) and immunoglobulin (IgG, IgM) levels with hormone replacement therapy in healthy post-menopausal women. Hum Reproduction. (2003) 18:1531–5. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deg292
154. Torcia MG, Nencioni L, Clemente AM, Civitelli L, Celestino I, Limongi D, et al. Sex differences in the response to viral infections: TLR8 and TLR9 ligand stimulation induce higher IL10 production in males. PloS One. (2012) 7:e39853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039853
155. Marriott I, Bost KL, Huet-Hudson YM. Sexual dimorphism in expression of receptors for bacterial lipopolysaccharides in murine macrophages: a possible mechanism for gender-based differences in endotoxic shock susceptibility. J Reprod Immunol. (2006) 71:12–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2006.01.004
156. Asai K, Hiki N, Mimura Y, Ogawa T, Unou K, Kaminishi M. Gender differences in cytokine secretion by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: role of estrogen in modulating LPS-induced cytokine secretion in an ex vivo septic model. Shock. (2001) 16:340–3. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200116050-00003
157. Rodas L, Martínez S, Riera-Sampol A, Moir HJ, Tauler P. Blood cell in vitro cytokine production in response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation in a healthy population: effects of age, sex, and smoking. Cells. (2021) 11:103. doi: 10.3390/cells11010103
158. Zhai H, Zhang N, Mo D, Qin T. CCL20 is a potential therapeutic target associated with immune infiltration in breast cancer. J Int Med Res. (2023) 51:3000605231171762. doi: 10.1177/03000605231171762
159. Mateen S, Saeed H, Moin S, Khan AQ, Owais M. T helper cell subpopulations repertoire in peripheral blood and its correlation with sex of newly diagnosed arthritis patients: A gender based study. Int Immunopharmacology. (2019) 74:105675. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105675
160. Gracey E, Yao Y, Green B, Qaiyum Z, Baglaenko Y, Lin A, et al. Sexual dimorphism in the th17 signature of ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2016) 68:679–89. doi: 10.1002/art.39464
161. Yu C, Liu C, Jiang J, Li H, Chen J, Chen T, et al. Gender differences in rheumatoid arthritis: interleukin-4 plays an important role. J Immunol Res. (2020) 2020:4121524. doi: 10.1155/2020/4121524
162. Piccinni MP, Giudizi MG, Biagiotti R, Beloni L, Giannarini L, Sampognaro S, et al. Progesterone favors the development of human T helper cells producing Th2-type cytokines and promotes both IL-4 production and membrane CD30 expression in established Th1 cell clones. J Immunol. (1995) 155:128–33. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.155.1.128
163. Engels G, Hierweger AM, Hoffmann J, Thieme R, Thiele S, Bertram S, et al. Pregnancy-related immune adaptation promotes the emergence of highly virulent H1N1 influenza virus strains in allogenically pregnant mice. Cell Host Microbe. (2017) 21:321–33. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.02.020
164. Littauer EQ, Esser ES, Antao OQ, Vassilieva EV, Compans RW, Skountzou I. H1N1 influenza virus infection results in adverse pregnancy outcomes by disrupting tissue-specific hormonal regulation. PloS Pathog. (2017) 13:e1006757. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006757
165. Eagan LE, Chesney CA, Mascone SE, Shenouda N, Ranadive SM. Interleukin-6 is higher in naturally menstruating women compared with oral contraceptive pill users during the low-hormone phase. J Appl Physiol (1985). (2021) 131:544–52. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00921.2020
166. Leppänen J, Randell K, Schwab U, Pihlajamäki J, Romppanen J, Keski-Nisula L, et al. Endothelial function and concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha during a long agonist IVF protocol. J Reprod Immunol. (2021) 148:103434. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2021.103434
167. Brundin PMA, Landgren BM, Fjällström P, Shamekh MM, Gustafsson J, Johansson AF, et al. Expression of sex hormone receptor and immune response genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells during the menstrual cycle. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:721813. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.721813
168. Malkin CJ, Pugh PJ, Jones RD, Kapoor D, Channer KS, Jones TH. The effect of testosterone replacement on endogenous inflammatory cytokines and lipid profiles in hypogonadal men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2004) 89:3313–8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031069
169. Maggio M, Basaria S, Ble A, Lauretani F, Bandinelli S, Ceda GP, et al. Correlation between testosterone and the inflammatory marker soluble interleukin-6 receptor in older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2006) 91:345–7. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-1097
170. Santello FH, Caetano LC, Filipin MDV, Brazão V, Caetano LN, Toldo MPA, et al. Does orchiectomy enhance the immune-stimulatory effects of melatonin during experimental Chagas’ disease? Res Veterinary Sci. (2012) 93:819–25. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2011.09.019
171. Ng MK, Liu PY, Williams AJ, Nakhla S, Ly LP, Handelsman DJ, et al. Prospective study of effect of androgens on serum inflammatory markers in men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2002) 22:1136–41. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000022167.80130.A6
172. Kumru S, Godekmerdan A, Yilmaz B. Immune effects of surgical menopause and estrogen replacement therapy in peri-menopausal women. J Reprod Immunol. (2004) 63:31–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2004.02.001
173. Papaporfyriou A, Bartziokas K, Papachatzopoulou E, Grapatsas K, Kallieri M, Spathis A, et al. Effects of menopause and fat mass in asthmatic inflammation. J Asthma. (2024) 61:1488–96. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2024.2362859
174. Grandys M, Majerczak J, Zapart-Bukowska J, Duda K, Kulpa JK, Zoladz JA. Lowered serum testosterone concentration is associated with enhanced inflammation and worsened lipid profile in men. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:735638. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.735638
175. Ritchie RF, Palomaki GE, Neveux LM, Navolotskaia O, Ledue TB, Craig WY. Reference distributions for the negative acute-phase serum proteins, albumin, transferrin and transthyretin: A practical, simple and clinically relevant approach in a large cohort. J Clin Lab Analysis. (1999) 13:273–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2825(1999)13:6<273::AID-JCLA4>3.0.CO;2-X
176. Popotas A, Casimir GJ, Corazza F, Lefèvre N. Sex-related immunity: could Toll-like receptors be the answer in acute inflammatory response? Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1379754. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1379754
177. van den Broe NR, Letsky EA. Pregnancy and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Bjog. (2001) 108:1164–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2003.00267.x
178. Friis H, Gomo E, Mashange W, Nyazema N, Kaestel P, Wieringa F, et al. The acute phase response to parturition: A cross- sectional study in Zimbabwe. Afr J Reprod Health (ISSN: 1118-4841). (2009) 13:61–8.
179. Jorgensen JM, Yang Z, Lönnerdal B, Chantry CJ, Dewey KG. Plasma Ferritin and Hepcidin Are Lower at 4 Months Postpartum among Women with Elevated C-Reactive Protein or α1-Acid Glycoprotein1. J Nutr. (2017) 147:1194–9. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.245803
180. Kaplan SA, Johnson-Levonas AO, Lin J, Shah AK, Meehan AG. Elevated high sensitivity C-reactive protein levels in aging men with low testosterone. Aging Male. (2010) 13:108–12. doi: 10.3109/13685530903440424
181. Dougherty RH, Rohrer JL, Hayden D, Rubin SD, Leder BZ. Effect of aromatase inhibition on lipids and inflammatory markers of cardiovascular disease in elderly men with low testosterone levels. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). (2005) 62:228–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02205.x
182. Wilhelmson AS, Lantero Rodriguez M, Stubelius A, Fogelstrand P, Johansson I, Buechler MB, et al. Testosterone is an endogenous regulator of BAFF and splenic B cell number. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:2067. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04408-0
183. Thurmond TS, Murante FG, Staples JE, Silverstone AE, Korach KS, Gasiewicz TA. Role of estrogen receptor alpha in hematopoietic stem cell development and B lymphocyte maturation in the male mouse. Endocrinology. (2000) 141:2309–18. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.7.7560
184. Lü FX, Abel K, Ma Z, Rourke T, Lu D, Torten J, et al. The strength of B cell immunity in female rhesus macaques is controlled by CD8+ T cells under the influence of ovarian steroid hormones. Clin Exp Immunol. (2002) 128:10–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01780.x
185. Teilmann SC, Clement CA, Thorup J, Byskov AG, Christensen ST. Expression and localization of the progesterone receptor in mouse and human reproductive organs. J Endocrinol. (2006) 191:525–35. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06565
186. Erlandsson MC, Jonsson CA, Islander U, Ohlsson C, Carlsten H. Oestrogen receptor specificity in oestradiol-mediated effects on B lymphopoiesis and immunoglobulin production in male mice. Immunology. (2003) 108:346–51. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01599.x
187. Martins C, Lima J, Nunes G, Borrego LM. Regulatory T and B cells in asthmatic women: variations from pregnancy to postpartum. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2017) 27:46–57. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0086
188. Lima J, Martins C, Leandro MJ, Nunes G, Sousa MJ, Branco JC, et al. Characterization of B cells in healthy pregnant women from late pregnancy to post-partum: a prospective observational study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. (2016) 16:139. doi: 10.1186/s12884-016-0927-7
189. Kamada M, Irahara M, Maegawa M, Yasui T, Yamano S, Yamada M, et al. B cell subsets in postmenopausal women and the effect of hormone replacement therapy. Maturitas. (2001) 37:173–9. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5122(00)00180-8
190. Yan J, Greer JM, Hull R, O'Sullivan JD, Henderson RD, Read SJ, et al. The effect of ageing on human lymphocyte subsets: comparison of males and females. Immun Ageing. (2010) 7:4. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-7-4
191. Morse MD, McNeel DG. Prostate cancer patients on androgen deprivation therapy develop persistent changes in adaptive immune responses. Hum Immunol. (2010) 71:496–504. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2010.02.007
192. Afshan G, Afzal N, Qureshi S. CD4+CD25(hi) regulatory T cells in healthy males and females mediate gender difference in the prevalence of autoimmune diseases. Clin Lab. (2012) 58:567–71.
193. Vasanthakumar A, Chisanga D, Blume J, Gloury R, Britt K, Henstridge DC, et al. Sex-specific adipose tissue imprinting of regulatory T cells. Nature. (2020) 579:581–5. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2040-3
194. Singh RP, Bischoff DS. Sex hormones and gender influence the expression of markers of regulatory T cells in SLE patients. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:619268. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.619268
195. Groneberg M, Hoenow S, Marggraff C, Fehling H, Metwally NG, Hansen C, et al. HIF-1α modulates sex-specific Th17/Treg responses during hepatic amoebiasis. J Hepatology. (2022) 76:160–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.09.020
196. Gomez-Lopez N, Vega-Sanchez R, Castillo-Castrejon M, Romero R, Cubeiro-Arreola K, Vadillo-Ortega F. Evidence for a role for the adaptive immune response in human term parturition. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2013) 69:212–30. doi: 10.1111/aji.2013.69.issue-3
197. Santner-Nanan B, Peek MJ, Khanam R, Richarts L, Zhu E, Fazekas de St Groth B, et al. Systemic increase in the ratio between foxp3+ and IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells in healthy pregnancy but not in preeclampsia1. J Immunol. (2009) 183:7023–30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901154
198. Wang W, Zhao Y, Zhou X, Sung N, Chen L, Zhang X, et al. Dynamic changes in regulatory T cells during normal pregnancy, recurrent pregnancy loss, and gestational diabetes. J Reprod Immunol. (2022) 150:103492. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2022.103492
199. Somerset DA, Zheng Y, Kilby MD, Sansom DM, Drayson MT. Normal human pregnancy is associated with an elevation in the immune suppressive CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T-cell subset. Immunology. (2004) 112:38–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01869.x
200. Lu L, Lu Y, Zhang L. Regulatory T cell and T helper 17 cell imbalance in patients with unexplained infertility. Int J Womens Health. (2024) 16:1033–40. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S455733
201. Xia Y, Liu A, Li W, Liu Y, Zhang G, Ye S, et al. Reference range of naïve T and T memory lymphocyte subsets in peripheral blood of healthy adult. Clin Exp Immunol. (2022) 207:208–17. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxab038
202. Pearce H, Hutton P, Chaudhri S, Porfiri E, Patel P, Viney R, et al. Spontaneous CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses directed against cancer testis antigens are present in the peripheral blood of testicular cancer patients. Eur J Immunol. (2017) 47:1232–42. doi: 10.1002/eji.201646898
203. Maret A, Coudert JD, Garidou L, Foucras G, Gourdy P, Krust A, et al. Estradiol enhances primary antigen-specific CD4 T cell responses and Th1 development in vivo. Essential role estrogen receptor α Expression hematopoietic Cells Eur J Immunol. (2003) 33:512–21. doi: 10.1002/immu.200310027
204. Mohamad N-V, Wong SK, Wan Hasan WN, Jolly JJ, Nur-Farhana MF, Ima-Nirwana S, et al. The relationship between circulating testosterone and inflammatory cytokines in men. Aging Male. (2019) 22:129–40. doi: 10.1080/13685538.2018.1482487
205. Javadian A, Salehi E, Bidad K, Sahraian MA, Izad M. Effect of estrogen on Th1, Th2 and Th17 cytokines production by proteolipid protein and PHA activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from multiple sclerosis patients. Arch Med Res. (2014) 45:177–82. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2014.01.002
206. Jansson L, Olsson T, Holmdahl R. Estrogen induces a potent suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Neuroimmunol. (1994) 53:203–7. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(94)90030-2
207. Hughes GC, Choubey D. Modulation of autoimmune rheumatic diseases by oestrogen and progesterone. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2014) 10:740–51. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.144
208. Shen Z, Vom Steeg LG, Patel MV, Rodriguez-Garcia M, Wira CR. Impact of aging on the frequency, phenotype, and function of CD4+ T cells in the human female reproductive tract. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1465124. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1465124
209. Hewagama A, Patel D, Yarlagadda S, Strickland FM, Richardson BC. Stronger inflammatory/cytotoxic T-cell response in women identified by microarray analysis. Genes Immun. (2009) 10:509–16. doi: 10.1038/gene.2009.12
210. Lissauer D, Piper K, Goodyear O, Kilby MD, Moss PAH. Fetal-specific CD8+ Cytotoxic T cell responses develop during normal human pregnancy and exhibit broad functional capacity. J Immunol. (2012) 189:1072–80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200544
211. Strindhall J, Skog M, Ernerudh J, Bengner M, Löfgren S, Matussek A, et al. The inverted CD4/CD8 ratio and associated parameters in 66-year-old individuals: the Swedish HEXA immune study. Age (Dordr). (2013) 35:985–91. doi: 10.1007/s11357-012-9400-3
212. Khan SR, van der Burgh AC, Peeters RP, van Hagen PM, Dalm V, Chaker L. Determinants of serum immunoglobulin levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:664526. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.664526
213. Bränn E, Edvinsson Å, Rostedt Punga A, Sundström-Poromaa I, Skalkidou A. Inflammatory and anti-inflammatory markers in plasma: from late pregnancy to early postpartum. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:1863. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38304-w
214. Wang CS, Wang ST, Chou P. Efficacy and cost-effectiveness of influenza vaccination of the elderly in a densely populated and unvaccinated community. . Vaccine. (2002) 20:2494–9. doi: 10.1016/S0264-410X(02)00181-0
215. Engler RJ, Nelson MR, Klote MM, VanRaden MJ, Huang CY, Cox NJ, et al. Half- vs full-dose trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (2004-2005): age, dose, and sex effects on immune responses. Arch Intern Med. (2008) 168:2405–14. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.513
216. Kay AW, Blish CA. Immunogenicity and clinical efficacy of influenza vaccination in pregnancy. Front Immunol. (2015) 6. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00289
217. Wu S, Wang L, Dong J, Bao Y, Liu X, Li Y, et al. The dose- and time-dependent effectiveness and safety associated with COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Diseases. (2023) 128:335–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.01.018
218. Lang PO, Mendes A, Socquet J, Assir N, Govind S, Aspinall R. Effectiveness of influenza vaccine in aging and older adults: comprehensive analysis of the evidence. Clin Interv Aging. (2012) 7:55–64. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S25215
219. Manzoli L, Ioannidis JP, Flacco ME, De Vito C, Villari P. Effectiveness and harms of seasonal and pandemic influenza vaccines in children, adults and elderly: a critical review and re-analysis of 15 meta-analyses. Hum Vaccin Immunother. (2012) 8:851–62. doi: 10.4161/hv.19917
220. Gubbels Bupp MR, Potluri T, Fink AL, Klein SL. The confluence of sex hormones and aging on immunity. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1269. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01269
221. Su JR, Moro PL, Ng CS, Lewis PW, Said MA, Cano MV. Anaphylaxis after vaccination reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, 1990-2016. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2019) 143:1465–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.12.1003
222. Taneja V. Sex hormones determine immune response. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1931. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01931
223. Vaena S, Chakraborty P, Lee HG, Janneh AH, Kassir MF, Beeson G, et al. Aging-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by ceramide signaling inhibits antitumor T cell response. Cell Rep. (2021) 35:109076. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109076
224. Grimaldi CM, Cleary J, Dagtas AS, Moussai D, Diamond B. Estrogen alters thresholds for B cell apoptosis and activation. J Clin Invest. (2002) 109:1625–33. doi: 10.1172/JCI0214873
225. Pilling D, Consalvo KM, Kirolos SA, Gomer RH. Differences between human male and female neutrophils in mRNA, translation efficiency, protein, and phosphoprotein profiles. Res Sq. (2024). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4284171/v1
226. Hill L, Jeganathan V, Chinnasamy P, Grimaldi C, Diamond B. Differential roles of estrogen receptors α and β in control of B-cell maturation and selection. Mol Med. (2011) 17:211–20. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00172
227. Zittermann A, Schwarz I, Scheld K, Sudhop T, Berthold HK, von Bergmann K, et al. Physiologic fluctuations of serum estradiol levels influence biochemical markers of bone resorption in young women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2000) 85:95–101. doi: 10.1210/jcem.85.1.6250
228. Gold EB, Wells C, Rasor MO. The association of inflammation with premenstrual symptoms. J Womens Health (Larchmt). (2016) 25:865–74. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2015.5529
229. Le Gars M, Seiler C, Kay AW, Bayless NL, Starosvetsky E, Moore L, et al. Pregnancy-induced alterations in NK cell phenotype and function. Front Immunol. (2019) 10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02469
230. Kwak-Kim J, Gilman-Sachs A. Clinical implication of natural killer cells and reproduction. Am J Reprod Immunol. (2008) 59:388–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2008.00596.x
231. Le Gars M, Kay AW, Bayless NL, Aziz N, Dekker CL, Swan GE, et al. Increased proinflammatory responses of monocytes and plasmacytoid dendritic cells to influenza A virus infection during pregnancy. J Infect Diseases. (2016) 214:1666–71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw448
232. Memoli MJ, Harvey H, Morens DM, Taubenberger JK. Influenza in pregnancy. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. (2013) 7:1033–9. doi: 10.1111/irv.2013.7.issue-6
233. Harding AT, Heaton NS. The impact of estrogens and their receptors on immunity and inflammation during infection. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:909. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040909
234. Shah L, Elshaikh AO, Lee R, Joy Mathew C, Jose MT, Cancarevic I. Do menopause and aging affect the onset and progression of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus? Cureus. (2020) 12:e10944. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10944
235. Bove R. Autoimmune diseases and reproductive aging. Clin Immunol. (2013) 149:251–64. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2013.02.010
236. Ucciferri CC, Dunn SE. Effect of puberty on the immune system: Relevance to multiple sclerosis. Front Pediatr. (2022) 10:1059083. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.1059083
237. Moulton VR. Sex hormones in acquired immunity and autoimmune disease. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2279. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02279
238. Angum F, Khan T, Kaler J, Siddiqui L, Hussain A. The prevalence of autoimmune disorders in women: A narrative review. Cureus. (2020) 12:e8094. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8094
239. Buendía-González FO, Legorreta-Herrera M. The similarities and differences between the effects of testosterone and DHEA on the innate and adaptive immune response. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:1768. doi: 10.3390/biom12121768
240. Ainslie RJ, Simitsidellis I, Kirkwood PM, Gibson DA. RISING STARS: Androgens and immune cell function. J Endocrinol. (2024) 261:e230398. doi: 10.1530/JOE-23-0398
241. Friedl R, Brunner M, Moeslinger T, Spieckermann PG. Testosterone inhibits expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in murine macrophages. Life Sci. (2000) 68:417–29. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00953-X
242. Williams MR, Ling S, Dawood T, Hashimura K, Dai A, Li H, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone inhibits human vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation independent of ARs and ERs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2002) 87:176–81. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.1.8161
243. Huang K, Cheng L, Jiang C, Zheng C, Cai H. Dehydroepiandrosterone inhibits ADAMTS expression via an ERK-dependent mechanism in chondrocytes. PloS One. (2024) 19:e0313560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313560
244. Prall SP, Muehlenbein MP. Chapter four - DHEA modulates immune function: A review of evidence. In: Litwack G, editor. Vitamins and hormones, vol. 108 . London, United Kingdom: Academic Press (2018). p. 125–44.
245. Chang DM, Lan JL, Lin HY, Luo SF. Dehydroepiandrosterone treatment of women with mild-to-moderate systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2002) 46:2924–7. doi: 10.1002/art.v46:11
246. Wierman ME, Kiseljak-Vassiliades K. Should dehydroepiandrosterone be administered to women? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 107:1679–85. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac130
247. Nordmark G, Bengtsson C, Larsson A, Karlsson FA, Sturfelt G, Rönnblom L. Effects of dehydroepiandrosterone supplement on health-related quality of life in glucocorticoid treated female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. (2005) 38:531–40. doi: 10.1080/08916930500285550
248. Yen SS, Morales AJ, Khorram O. Replacement of DHEA in aging men and women. Potential remedial effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (1995) 774:128–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb17377.x
249. Choi IS, Cui Y, Koh YA, Lee HC, Cho YB, Won YH. Effects of dehydroepiandrosterone on Th2 cytokine production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from asthmatics. Korean J Intern Med. (2008) 23:176–81. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2008.23.4.176
250. Leenstra T, ter Kuile FO, Kariuki SK, Nixon CP, Oloo AJ, Kager PA, et al. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels associated with decreased malaria parasite density and increased hemoglobin concentration in pubertal girls from western Kenya. J Infect Diseases. (2003) 188:297–304. doi: 10.1086/jid.2003.188.issue-2
251. . Rey AD, Mahuad CV, Bozza VV, Bogue C, Farroni MA, Bay LM, et al. Endocrine and cytokine responses in humans with pulmonary tuberculosis. Brain Behavior Immunity. (2007) 21:171–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2006.06.005
252. Coles AJ, Thompson S, Cox AL, Curran S, Gurnell EM, Chatterjee VK. Dehydroepiandrosterone replacement in patients with Addison's disease has a bimodal effect on regulatory (CD4+CD25hi and CD4+FoxP3+) T cells. Eur J Immunol. (2005) 35:3694–703. doi: 10.1002/eji.200526128
253. Santos CD, Toldo MPA, Santello FH, Filipin MDV, Brazão V, do Prado Júnior JC. Dehydroepiandrosterone increases resistance to experimental infection by Trypanosoma cruzi. Veterinary Parasitology. (2008) 153:238–43. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.01.039
254. Cernetich A, Garver LS, Jedlicka AE, Klein PW, Kumar N, Scott AL, et al. Involvement of gonadal steroids and gamma interferon in sex differences in response to blood-stage malaria infection. Infect Immun. (2006) 74:3190–203. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00008-06
255. Cao J, Yu L, Zhao J, Ma H. Effect of dehydroepiandrosterone on the immune function of mice in vivo and in vitro. Mol Immunol. (2019) 112:283–90. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.06.004
256. Prall SP, Larson EE, Muehlenbein MP. The role of dehydroepiandrosterone on functional innate immune responses to acute stress. Stress Health. (2017) 33:656–64. doi: 10.1002/smi.v33.5
257. Webb SJ, Geoghegan TE, Prough RA, Michael Miller KK. The biological actions of dehydroepiandrosterone involves multiple receptors. Drug Metab Rev. (2006) 38:89–116. doi: 10.1080/03602530600569877
258. Davey RA, Grossmann M. Androgen receptor structure, function and biology: from bench to bedside. Clin Biochem Rev. (2016) 37:3–15.
259. Trigunaite A, Dimo J, Jørgensen TN. Suppressive effects of androgens on the immune system. Cell Immunol. (2015) 294:87–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.02.004
260. Lahita RG. Sex and gender influence on immunity and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1142723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142723
261. de Medeiros SF, Yamamoto MMW, de Medeiros MAS, Yamamoto A, Barbosa BB. Polycystic ovary syndrome and risks for COVID-19 infection: A comprehensive review: PCOS and COVID-19 relationship. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2022) 23:251–64. doi: 10.1007/s11154-022-09715-y
262. Birtolo MF, Vena W, Pizzocaro A, Lavezzi E, Brunetti A, Jaafar S, et al. Serum testosterone mirrors inflammation parameters in females hospitalized with COVID-19. J Endocrinological Invest. (2023) 46:939–45. doi: 10.1007/s40618-022-01957-6
263. Di Stasi V, Rastrelli G, Inglese F, Beccaria M, Garuti M, Di Costanzo D, et al. Higher testosterone is associated with increased inflammatory markers in women with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: preliminary results from an observational study. J Endocrinol Invest. (2022) 45:639–48. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01682-6
264. Cadegiani FA, Lim RK, Goren A, McCoy J, Situm M, Kovacevic M, et al. Clinical symptoms of hyperandrogenic women diagnosed with COVID-19. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereology. (2021) 35:e101–e4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.17004
265. Stephens MA, Mahon PB, McCaul ME, Wand GS. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response to acute psychosocial stress: Effects of biological sex and circulating sex hormones. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2016) 66:47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.12.021
266. Juster R-P, Raymond C, Desrochers AB, Bourdon O, Durand N, Wan N, et al. Sex hormones adjust “sex-specific” reactive and diurnal cortisol profiles. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2016) 63:282–90. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.10.012
267. Fuss J, Claro L, Ising M, Biedermann SV, Wiedemann K, Stalla GK, et al. Does sex hormone treatment reverse the sex-dependent stress regulation? A longitudinal study on hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis activity in transgender individuals. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2019) 104:228–37. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.02.023
268. D’Onofrio V, Sékaly RP. The immune-endocrine interplay in sex differential responses to viral infection and COVID-19. Trends Immunol. (2024) 45:943–58. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2024.10.004
269. Fisch IR, Freedman SH. Smoking, oral contraceptives, and obesity. Effects white Blood Cell count. Jama. (1975) 234:500–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.1975.03260180040020
270. Özcan Ö, Elzen WPJD, Hillebrand JJ, Heijer MD, Loendersloot LLV, Fischer J, et al. The effect of hormonal contraceptive therapy on clinical laboratory parameters: a literature review. Clin Chem Lab Med (CCLM). (2024) 62:18–40. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2023-0384
271. Konstantinus IN, Balle C, Jaumdally SZ, Galmieldien H, Pidwell T, Masson L, et al. Impact of hormonal contraceptives on cervical T-helper 17 phenotype and function in adolescents: results from a randomized, crossover study comparing long-acting injectable norethisterone oenanthate (NET-EN), combined oral contraceptive pills, and combined contraceptive vaginal rings. Clin Infect Diseases. (2019) 71:e76–87. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1063
272. Laffont S, Seillet C, Guéry JC. Estrogen receptor-dependent regulation of dendritic cell development and function. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00108
273. Doran MF, Crowson CS, O'Fallon WM, Gabriel SE. The effect of oral contraceptives and estrogen replacement therapy on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a population based study. J Rheumatol. (2004) 31:207–13.
274. Divani AA, Luo X, Datta YH, Flaherty JD, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A. Effect of oral and vaginal hormonal contraceptives on inflammatory blood biomarkers. Mediators Inflamm. (2015) 2015:379501. doi: 10.1155/2015/379501
275. Quinn KM, Cox AJ, Roberts L, Pennell EN, McKeating DR, Fisher JJ, et al. Temporal changes in blood oxidative stress biomarkers across the menstrual cycle and with oral contraceptive use in active women. Eur J Appl Physiol. (2021) 121:2607–20. doi: 10.1007/s00421-021-04734-0
276. White AA, Lin A, Bickendorf X, Cavve BS, Moore JK, Siafarikas A, et al. Potential immunological effects of gender-affirming hormone therapy in transgender people - an unexplored area of research. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. (2022) 13:20420188221139612. doi: 10.1177/20420188221139612
277. Lakshmikanth T, Consiglio C, Sardh F, Forlin R, Wang J, Tan Z, et al. Immune system adaptation during gender-affirming testosterone treatment. Nature. (2024) 633:155–64. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07789-z
278. Grünhagel B, Borggrewe M, Hagen SH, Ziegler SM, Henseling F, Glau L, et al. Reduction of IFN-I responses by plasmacytoid dendritic cells in a longitudinal trans men cohort. iScience. (2023) 26:108209. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108209
279. Chang DM, Chu SJ, Chen HC, Kuo SY, Lai JH. Dehydroepiandrosterone suppresses interleukin 10 synthesis in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheumatic Diseases. (2004) 63:1623–6. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.016576
280. Iannantuoni F, Salazar JD, Martinez de Marañon A, Bañuls C, López-Domènech S, Rocha M, et al. Testosterone administration increases leukocyte-endothelium interactions and inflammation in transgender men. Fertil Steril. (2021) 115:483–9. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.08.002
281. Schutte MH, Kleemann R, Nota NM, Wiepjes CM, Snabel JM, T'Sjoen G, et al. The effect of transdermal gender-affirming hormone therapy on markers of inflammation and hemostasis. PloS One. (2022) 17:e0261312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261312
282. Liwinski T, Auer MK, Schröder J, Pieknik I, Casar C, Schwinge D, et al. Gender-affirming hormonal therapy induces a gender-concordant fecal metagenome transition in transgender individuals. BMC Med. (2024) 22:346. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03548-z
283. Markle JG, Frank DN, Mortin-Toth S, Robertson CE, Feazel LM, Rolle-Kampczyk U, et al. Sex differences in the gut microbiome drive hormone-dependent regulation of autoimmunity. Science. (2013) 339:1084–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1233521
284. Mathias K, Mathias L, Amarnani A, Samko T, Lahita RG, Panush RS. Challenges of caring for transgender and gender diverse patients with rheumatic disease: presentation of seven patients and review of the literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. (2023) 35:117–27. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000894
285. Ramos SG, Ingenito F, Mormandi EA, Nagelberg AJ, Otero PM, Lessa CF, et al. High prevalence of altered immunological biomarkers in a transgender population. Autoimmune Infect Diseases: Open Access. (2020) 3:125. doi: 10.16966/2470-1025.125
286. Selmi C, Ceribelli A, Generali E, Scirè CA, Alborghetti F, Colloredo G, et al. Serum antinuclear and extractable nuclear antigen antibody prevalence and associated morbidity and mortality in the general population over 15 years. Autoimmun Rev. (2016) 15:162–6. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.10.007
287. Marconi M, Riitano G, Fisher AD, Cocchetti C, Pagano MT, Capozzi A, et al. Gender-affirming hormone therapy and autoimmunity: new insights from a three-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Immunol. (2023). doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad122
Keywords: immune system, sex difference, gender-affirming hormone therapy, androgens, estrogens, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases
Citation: Yalcinkaya A, Yalcinkaya R, Sardh F and Landegren N (2025) Immune dynamics throughout life in relation to sex hormones and perspectives gained from gender-affirming hormone therapy. Front. Immunol. 15:1501364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501364
Received: 24 September 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 16 January 2025.
Edited by:
Boris Novakovic, Royal Children’s Hospital, AustraliaReviewed by:
Marisa Benagiano, University of Florence, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Yalcinkaya, Yalcinkaya, Sardh and Landegren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ahmet Yalcinkaya, YWhtZXQueWFsY2lua2F5YUBpbWJpbS51dS5zZQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.