- 1The First Clinical College of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 2Laboratory Animal Science of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 3The Fourth Clinical College of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 4Department of Cardiology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Drug resistance poses a significant challenge in the treatment of breast cancer. In recent years, a variety of nanomaterials have been discovered and synthesized that can selectively target tumor cells and play a crucial role in the advancement of breast cancer therapies. As our understanding of tumor heterogeneity deepens, the emerging potential of nanomaterials in addressing drug resistance has garnered considerable attention. These materials not only selectively target tumor cells but also possess unique properties that make them promising options for cancer treatment, including low toxicity, excellent biocompatibility, ease of preparation, the ability to carry antitumor drugs, and customizable surface functions. In this review, we will comprehensively summarize two key developments in breast cancer treatment: the application of antitumor drugs and nanomaterials. We will explore the mechanisms by which nanomaterials improve drug resistance in breast cancer, targeted nanotherapy strategies to mitigate this resistance, and recent research advancements in anticancer nanomaterials. This overview aims to highlight the significant role of nanomaterials in breast cancer treatment and provide a theoretical framework for identifying optimal treatment strategies in the future.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer has the highest mortality rate among female cancers in many countries and regions, surpassing lung cancer to become the most commonly diagnosed cancer (1–3). According to the American Cancer Society (1), there will be approximately 300,590 new cases of breast cancer in 2023, resulting in an estimated 43,700 deaths.
Currently, the primary treatments for breast cancer include surgery, along with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and other methods (4). Chemotherapy is a widely used approach; however, its lack of selectivity for tumor tissues presents significant challenges (5–7). These challenges include systemic toxicity and the accumulation of chemotherapy drugs at tumor sites, which can lead to tumor resistance (8).
Breast cancer cells can develop drug resistance through a variety of complex cellular and molecular mechanisms. These mechanisms primarily include (1) drug efflux and inactivation: tumor cells may diminish drug effectiveness by increasing drug efflux and decreasing intracellular drug concentrations (9). (2) Enhanced DNA damage repair: to resist DNA damage caused by chemotherapy drugs, tumor cells may enhance their DNA repair capabilities, which results in reduced drug efficacy (10). (3) Activation of bypass signals or pro-survival pathways: tumor cells can also manipulate apoptosis pathways, allowing them to evade chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and sustain their survival. (4) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): this process can enhance tumor cell invasion and metastasis, potentially leading to increased resistance to chemotherapy drugs (11). (5) Stem-like properties: cancer stem cells may exhibit greater drug resistance, enabling them to sustain tumor growth and recurrence through their ability to self-renew and differentiate into other tumor cells (12). In summary, understanding and addressing the mechanisms of breast cancer drug resistance is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and enhancing patient survival rates.
In recent years, nanomaterials have shown significant potential in both the treatment and management of breast cancer (13). As research in nanotechnology has advanced, it has become evident that nanomaterials offer unique advantages in terms of biocompatibility, drug delivery (including drug release and localization) (14, 15), targeted therapy, antitumor effectiveness, and the ability to kill tumor cells in vivo (16). Additionally, the distinct properties of nanomaterials can influence breast cancer resistance mechanisms by controlling drug release (17, 18), thereby significantly alleviating drug resistance. Despite the variety of available nanomaterials, further study is needed to optimize their design, explore combined uses, and address toxicity concerns. Therefore, this review summarizes the latest advancements in the use of various nanomaterials for alleviating breast cancer resistance.
2 Current application status of anti-tumor drugs in breast cancer treatment
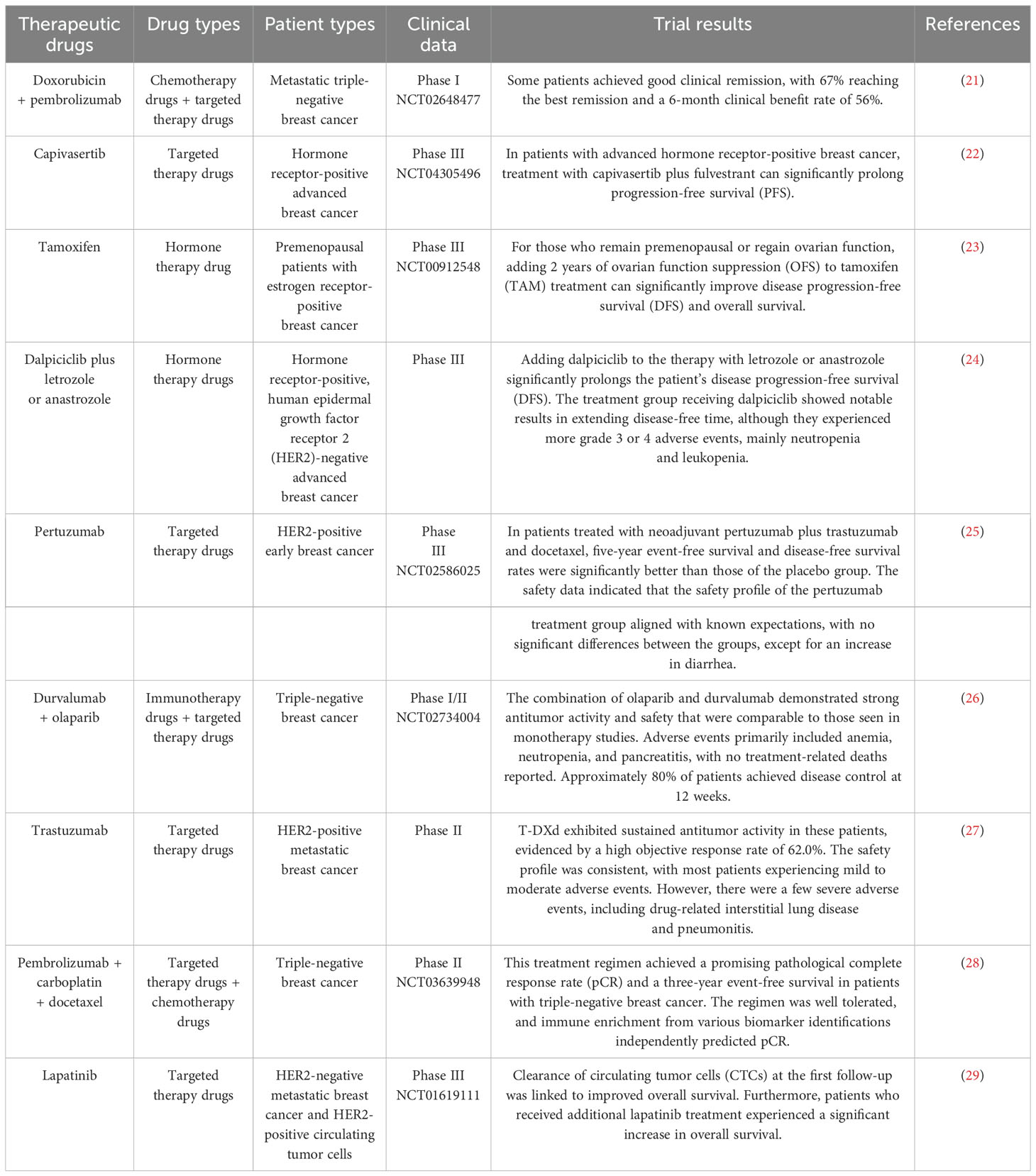
In the treatment of breast cancer, commonly used anti-tumor drugs contain chemotherapy agents such as cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, as well as immunotherapy drugs like anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies, including pembrolizumab and teslazumab. The selection of appropriate anti-tumor drugs is based on the molecular classification, clinical stage, and individual characteristics of each breast cancer case. While significant advancements have been made with these drugs, issues of drug resistance persist. To mitigate the impact of drug resistance and enhance patient survival rates, combination treatment strategies using two or three drugs are often employed to improve therapeutic effectiveness and prolong survival (19, 20) (Table 1).
3 Nanomaterials in breast cancer treatment
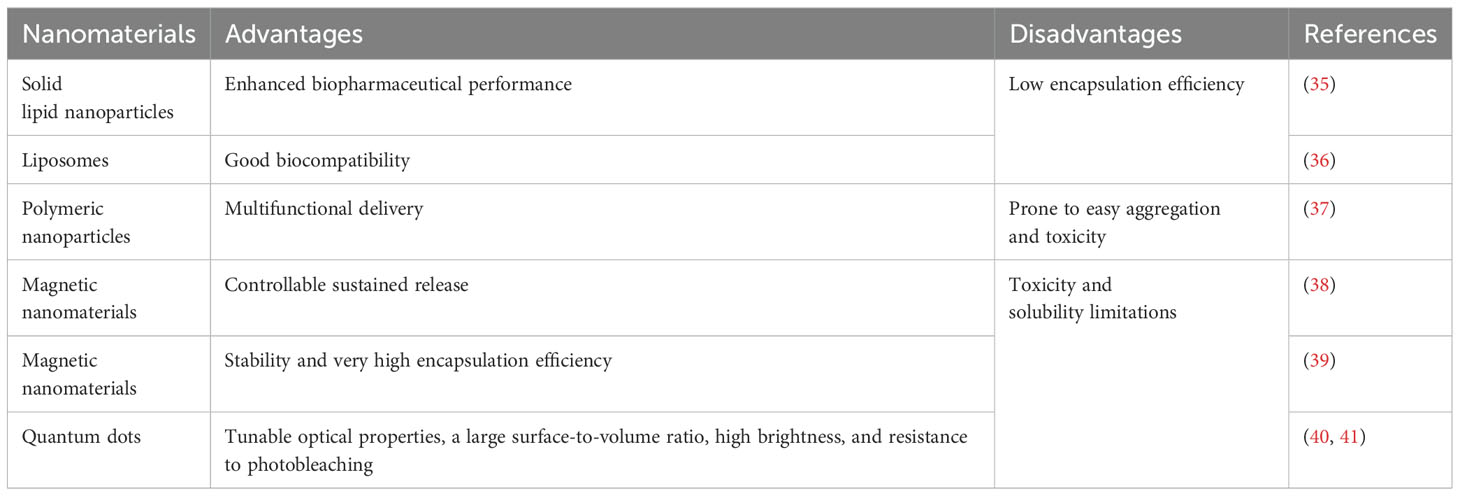
Nanomaterials can be classified based on various criteria. Common classifications include zero-dimensional (0D), one-dimensional (1D) nanomaterials, and polymers (30), as determined by their dimensions. Furthermore, when classified by chemical composition, nanomaterials can be divided into organic and inorganic categories (31). They may also be categorized according to their origin, material properties, applications, and morphology (32). Organic nanomaterials typically consist of substances found naturally in organisms or synthesized chemically. Compared to inorganic materials, they exhibit lower cytotoxicity and are biodegradable, making them a focal point of research in the field of nanomedicine (33). Inorganic nanomaterials are increasingly recognized as innovative tools for treating breast cancer due to their controlled drug release, multifunctionality, and excellent biocompatibility (18, 19, 34). The mechanisms by which nanomaterials assist in breast cancer treatment will be discussed in the following chapters. Nanomaterials used in breast cancer treatment are often categorized according to their chemical composition, as shown in Table 2.
3.1 Solid lipid nanoparticles
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) are made from safe physiological lipid components and exhibit good biocompatibility (42, 43). Granja et al. developed SLNs that encapsulate the antitumor drug mitoxantrone and functionalized them with 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[folate(polyethylene glycol) (DSPE-PEG-FA) ligands to enhance blood circulation and tumor selectivity. This reduces systemic side effects and enhances cellular uptake through processes such as macropinocytosis and clathrin-coated pits (43). CS/Lf/PTS-SLNs, prepared by Aly et al., improved drug solubility and bioavailability, achieving more effective tumor cell treatment. They enhance drug efficacy by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor, downregulating cyclin D1, and upregulating caspase-3 and BAX (44). SLN-DTX developed by da Rocha et al. enhances drug uptake in cells, promotes cell accumulation in the G2-M phase, and induces cell apoptosis, thereby increasing cytotoxicity. Figure 1 illustrates the mechanisms by which SLN-DTX treatment induced tumor cell apoptosis, reduced tumor cell proliferation and BCL-2 expression, inhibited tumor growth, and prevented lung metastasis (45). Figure 2 illustrates the four components of SLN-DIX: Pluronic, span, compritol and Docetaxel. Pindiprolu et al. demonstrated that PBA-Niclo-SLN induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, curtails STAT3, CD44/CD24 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) stem cell subsets, and markers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ultimately inducing tumor cell apoptosis and curtailing recurrence of TNBC (46). These findings indicate that solid lipid nanomaterials may serve as promising carriers for treating breast cancer and preventing its metastasis and recurrence.
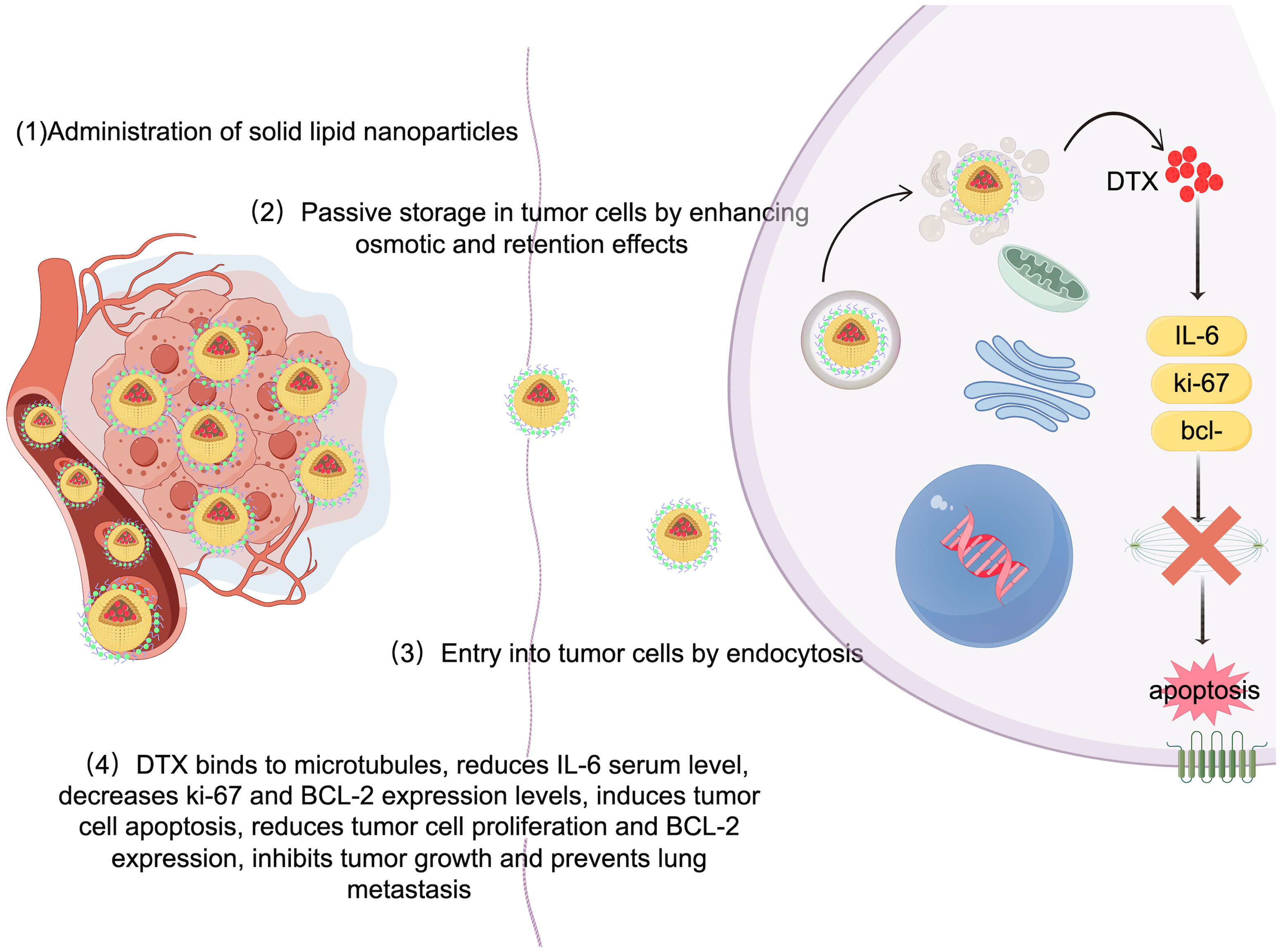
Figure 1. Mechanism of SLN-DTX in the treatment of breast cancer. Legend description: mechanism of SLN-DTX in the treatment of breast cancer (Created with Figdraw).
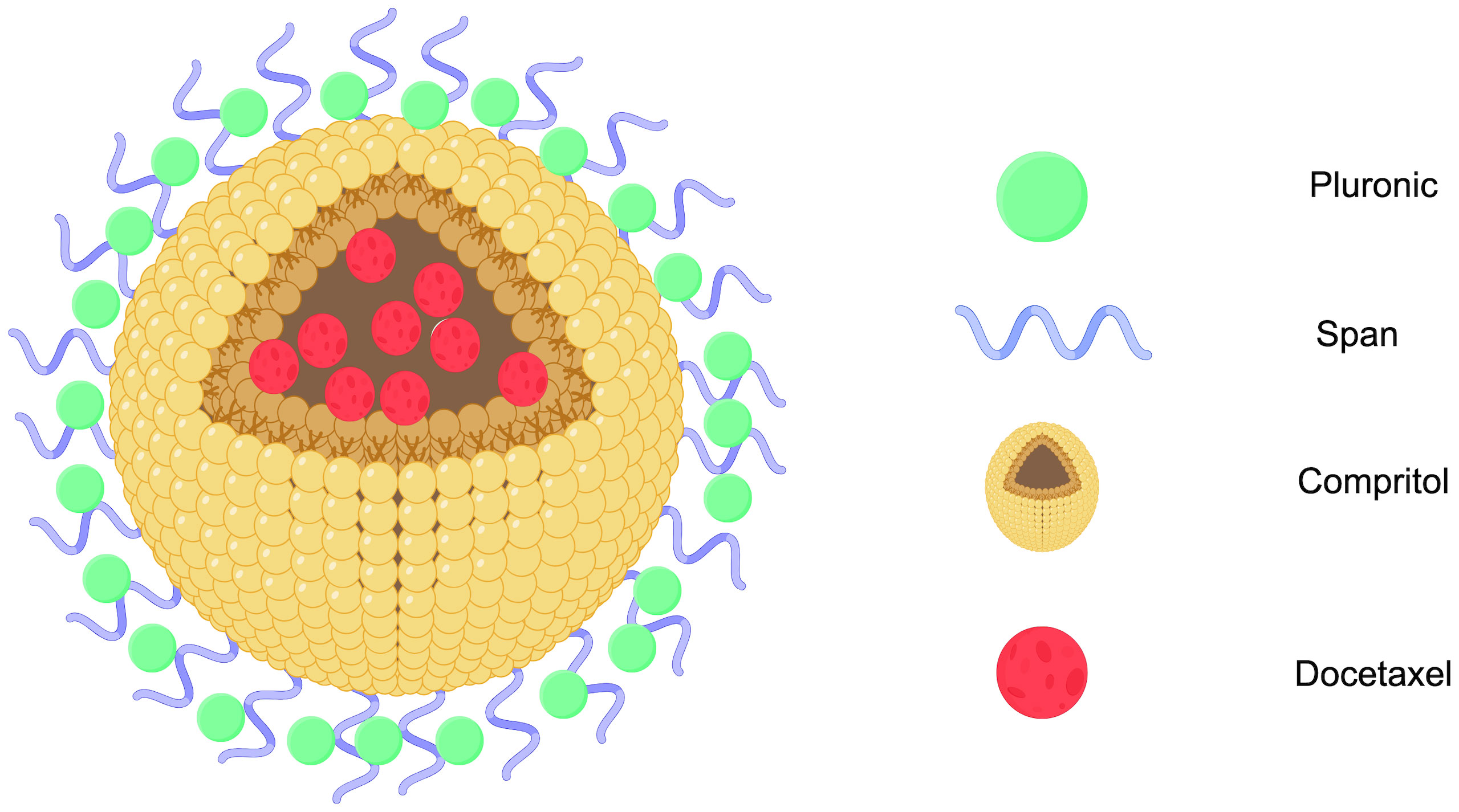
Figure 2. SLN-DTX structure diagram (Created with Figdraw). STN-DTX is assembled from four substances Pluronic, span, compritol and Docetaxel. The nanoparticles enhance drug uptake within breast cancer cells.
3.2 Liposomes
Liposomes are nanocarriers characterized by a closed spherical vesicle structure made up of a phospholipid bilayer. With a composition similar to that of biological membranes, they can fuse with cell membranes to facilitate targeted intracellular drug release. Liposomes are capable of encapsulating both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, enhancing drug loading, and providing sustained and controlled drug release (47). Boratto et al. highlighted the advantages of liposomes for intracellular delivery and release, positioning them as promising carriers for breast cancer treatment. Their pH-sensitive liposome preparation (pHSL-TS-DOX) demonstrated improved drug delivery at the intracellular level, greater accumulation in tumors, and sustained release of doxorubicin (DOX). Additionally, treatment with pHSL-TS-DOX resulted in cell cycle arrest primarily in the G1 phase, which may contribute to slowing the proliferation of tumor cells (48). Furthermore, APA-functionalized liposomes (EGA-EML-APA) developed by Badr-Eldin et al. enhance cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cells. By inducing G2/M and S phase arrest in MCF-7 cells, this process includes upregulating the expression of p53, bax, and casp3, downregulating bcl2, reducing NF-κB activity, increasing TNFα expression, and triggering significant apoptotic activity (49). Chen et al. created KLA-modified liposomes co-loaded with 5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel (KLA-5-FU/PTX Lps), which displayed enhanced cytotoxicity against MDA-MB-231 cells. The proposed anti-tumor mechanism in Figure 3 suggests that the KLA peptide facilitates liposome absorption into tumor cells and selectively targets mitochondria, leading to mitochondrial membrane disruption, the loss of membrane potential, cytochrome C release, caspase-3 upregulation, and activation of the apoptotic pathway in tumors (Figure 3). As such, KLA-5-FU/PTX Lps is a promising system for treating TNBC (50). Collectively, these studies indicate that functionalized liposomes hold significant potential in the fight against breast cancer.
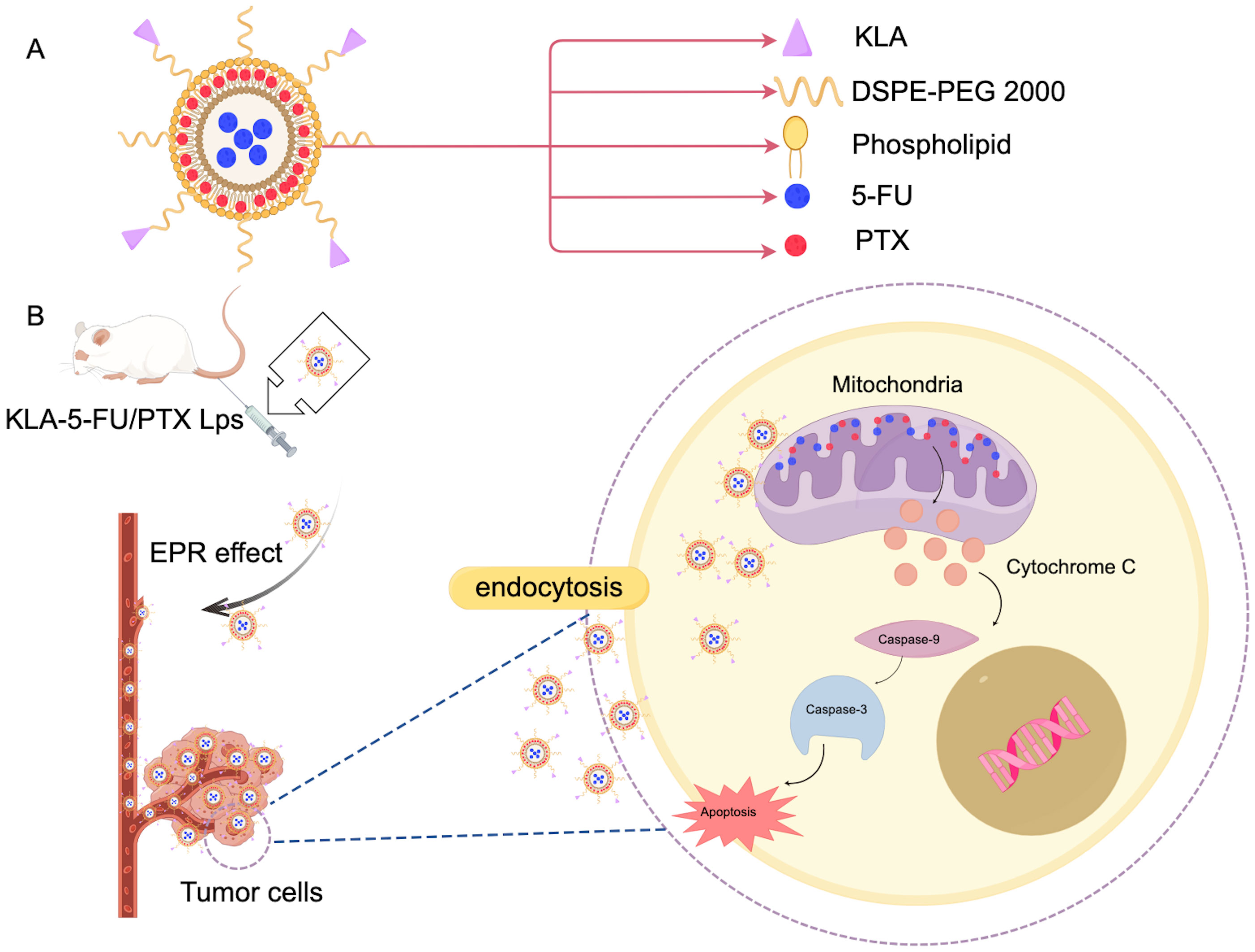
Figure 3. Mechanism of action of KLA in breast cancer treatment. (A) KLA and the main components of the administered liposomes. (B) This diagram illustrates the KLA peptide, which is delivered to the tumor cells through the EPR effect into the blood vessels. Mechanisms that promote tumor cells to endocytose liposomes, take up and selectively target mitochondria, thereby disrupting mitochondrial membranes. This process results in the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, which in turn triggers the release of cytochrome C. The release of cytochrome C upregulates caspase-3 activity, thereby activating the apoptotic pathway in tumor cells. This mechanism provides a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of breast cancer and may have potential clinical applications. (Created with Figdraw).
3.3 Polymer nanomaterials
Polymers possess a distinctive “core-shell” structure made up of micelles formed from amphiphilic molecules. In recent years, polymeric nanoparticles have emerged as significant candidate carriers in drug delivery due to their advantages, including biodegradability, improved encapsulation efficiency, biocompatibility, and controlled release (51, 52). Furthermore, by modifying the surface with ligands or targeting agents, polymers can enable multifunctional drug delivery. Bressler et al. demonstrated that by attaching AXT050 to polylactic acid-co-polylactic acid (PLGA)-PEG nanoparticles, they could accurately control the surface density of the nanoparticles. This modification allows them to serve as targeting agents for human tumor cells while exhibiting anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic properties. Such targeted modifications enhance the effectiveness of cancer nanomedicines and improve their ability to combat tumor growth (53). A study by Sharma et al. indicated that nanoparticles could effectively deliver curcumin into MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells, significantly enhancing both encapsulation efficiency and drug release capabilities. These nanoparticles have also shown the ability to diminish cell viability and suppress cell invasion and metastasis (54). Barkat et al. utilized PNP-loaded polymer nanoformulations that may aid in breast cancer treatment by restoring mitochondrial function and decreasing reactive oxygen species production and intracellular ATP levels (55). Polymer nanoparticles are characterized by their biodegradability, efficient encapsulation, controlled release, and biocompatibility, showcasing promising applications in the field of breast cancer treatment.
3.4 Magnetic nanoparticles
Magnetic nanoparticles are known for their excellent biocompatibility, controllable sustained release, and targeting capabilities, as well as their extremely high magnetocaloric effect. For example, chitosan-coated iron-manganese oxide nanoparticles (CS-MIONP) effectively conduct heat, making them an area of great interest in the field of hyperthermia for tumor cell destruction (56). Li et al. designed MUC1-C shRNA@Fe3O4MNPs, which can rapidly and stably generate heat under a constant alternating magnetic field at specific concentrations. This provides strong technical support for hyperthermia therapy in cancer. Through endocytosis, TNBC cells can effectively absorb these nanoparticles, significantly dampening their proliferation and migration. After treatment, the expression levels of key proteins in both TNBC cells and tumor tissues were significantly reduced, while the levels of apoptosis-related proteins were notably increased. This finding not only reveals the mechanism by which MUC1-C shRNA@Fe3O4MNPs impede tumor growth but also offers an important theoretical foundation for developing future cancer treatment strategies (57). As an advanced nanocarrier system, magnetic nanoparticles (TMX-AG-INP) can efficiently deliver various chemotherapy drugs, such as methotrexate and doxorubicin, to breast cancer tissues. They can also bind to gold nanoparticles and bovine albumin, producing potent anti-tumor effects. These INPs can accurately deliver miR-29a (micro-RNA) to breast cancer tissue after being coated with dextran, effectively diminishing the expression of anti-apoptotic genes. This represents a new strategy for breast cancer treatment (58). The combination of drugs with magnetic nanosystems has shown great potential for targeted drug delivery (59). This approach not only optimizes drug dosage to minimize side effects but also significantly enhances the cytotoxic effect on cancer cells, offering more effective, precise, and safer prospects for cancer treatment (60, 61).
3.5 Quantum dots
Quantum dots are semiconductor nanocrystals with sizes ranging from 2 to 10 nm and are versatile tools in biological imaging, diagnosis, and combination therapy due to their fluorescence properties (62, 63). However, one limitation of these quantum dots is their high hydrophobicity, necessitating surface coatings with polymers or multilayer ligand shells to enhance solubility. Typically, these quantum dots feature a semiconductor metal core composed of elements from groups II to VI or III to V, and their physical and chemical properties can be modified through the addition of surface ligands or polypeptides, which is particularly useful in targeted cancer treatments (64). Karami et al. developed an innovative water-in-oil-in-water double nanoemulsion method to create hydrogel nanocarriers incorporating chitosan and alumina (γ-Al2O3) along with carbon quantum dots. This method effectively addresses the challenges of low solubility and short half-life of drugs such as curcumin, significantly enhancing their effectiveness in drug release systems (65). Notably, the drug loading capacity and encapsulation efficiency of this nanocarrier surpass those of previously reported curcumin nanocarriers. Additionally, graphene quantum dots, prepared by another research team (66), exhibit low toxicity. Following exposure to cancer cells, there is a corresponding increase in the expression levels of p21 and p27. Most impressively, cells treated with these orthogonal graphene quantum dots demonstrated G2/M phase arrest and specifically induced apoptosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell lines, opening new avenues for cancer treatment and research.
4 Mechanism of action of nanomaterials in alleviating drug resistance in breast cancer
Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments for aggressive breast cancer, particularly TNBC. To tackle the challenge of drug resistance in breast cancer, various strategies can be employed, including blocking drug efflux and inactivation (8), inhibiting alternative signaling pathways, addressing DNA repair (67), suppressing the EMT process, and diminishing cancer stem cell characteristics. Nanomaterials are engaged in dampening tumor cell proliferation (68), metastasis, and invasion (69), as well as delivering chemotherapeutic drugs, promoting angiogenesis, evading immune responses, and remodeling the tumor microenvironment. Numerous studies have demonstrated that nanomaterials play a crucial role in overcoming chemotherapy resistance, the potential therapeutic mechanism of BC resistance are summarized in Figure 4, which offering promising therapeutic prospects for breast cancer treatment (70–72).
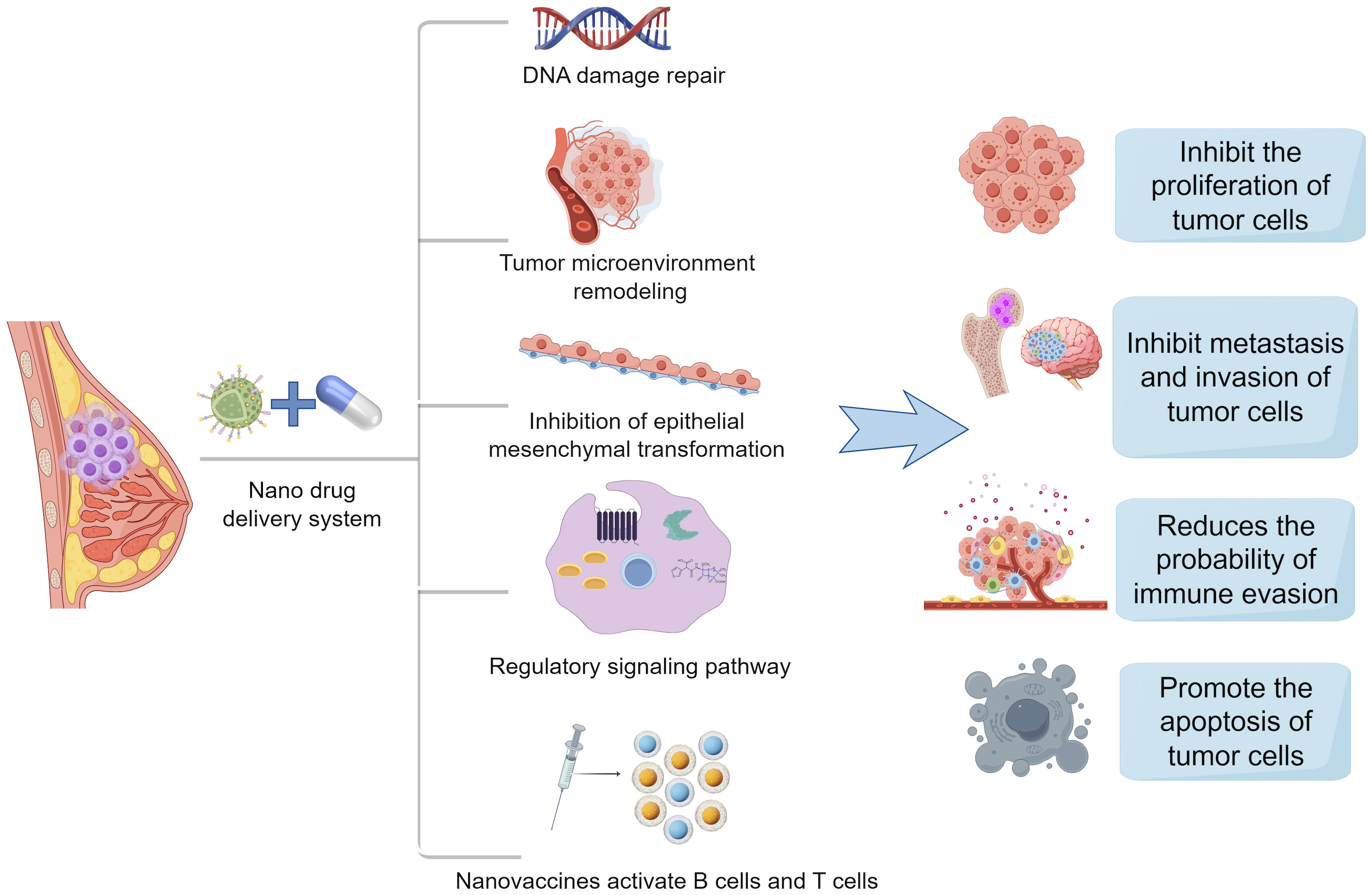
Figure 4. Mechanisms of action of nanodrug delivery systems in breast cancer therapy. Nanodrug delivery systems in the treatment of breast cancer often inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells, inhibit the metastasis and invasion of tumor cells, reduce immune escape, and promote the apoptosis of tumor cells by DNA damage repair, remodeling of tumor microenvironment, inhibition of epithelial mesenchymal transition, regulation of signaling pathways, and activation of B cells and T cells by nanovaccines.(Created with Figdraw).
4.1 Inhibition of drug efflux
Cytotoxic drugs need to be fully taken up by cancer cells to effectively treat cancer. Increasing drug uptake may help reduce chemotherapy resistance (73, 74). One of the most common mechanisms behind chemotherapy resistance is the drug efflux mediated by transmembrane pumps. To combat this issue, researchers have utilized acid-grafted poly(β-amino ester) nanoparticles to encapsulate cleavage protein B, aiming to overcome multidrug resistance to chemotherapy drugs. These nanoparticles have a pH-sensitive release function, which enhances drug release as the pH decreases. Importantly, they can also reverse multidrug resistance by halting the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and affecting the energy supply for drug efflux, thereby providing a new strategy for breast cancer treatment (75). Guo’s team successfully developed folic acid-modified nanoparticles ((DOX + CUR)-FA-NPs) based on star-shaped polyester (FA-TRI-CL), which are particularly effective in curbing P-gp to counteract resistance. P-gp is a transmembrane transporter that expels drugs from cells, leading to chemotherapy resistance. By impeding P-gp, (DOX + CUR)-FA-NPs significantly prevent resistant cells from excreting the drugs, thus enhancing their accumulation in tumor cells and alleviating chemotherapy resistance (76). Researchers also prepared D-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-resveratrol solid lipid nanoparticles (TPGS-Res-SLNs), which successfully reduced the expression of multidrug resistance-related proteins such as P-gp and BCRP. This reduction diminishes the excretion and inactivation of chemotherapy drugs in cells, increasing both the concentration and duration of drug action. Furthermore, TPGS-Res-SLNs curtailed the EMT of cancer cells, decreasing their ability to invade and metastasize, while enhancing the effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs. In summary, TPGS-Res-SLNs represent a promising approach to alleviate drug resistance in breast cancer (77). Figure 5 shows the composition and mechanism of tpgs-res-sln (Figure 5). Cancer cells develop drug resistance partly by using efflux pumps (such as P-gp and BCRP) to expel anticancer drugs, which lowers drug concentrations in cells and weakens treatment effects. Ptx-SLN bypasses these efflux pumps in breast cancer cells, facilitating better drug entry and improving anticancer effects, especially in multidrug-resistant cells, offering new hope for treating drug-resistant breast cancer (78). Recent studies have introduced an intelligent and multifunctional MoS2 nano-theranostic platform (MoS2-PEI-HA) that targets CD44-overexpressing cancer cells and decomposes in the tumor microenvironment due to hyaluronidase, which accelerates the release of the chemotherapeutic drug DOX. The MoS2 also enhances near-infrared photothermal conversion, promoting DOX release in the acidic environment of tumors through mild laser irradiation (74). Most notably, this technology can downregulate the expression of P-gp, which is associated with drug resistance, thereby reducing drug efflux, increasing intracellular drug accumulation, and effectively reversing drug resistance. Guney et al. developed a new type of talazoparib SLN and found that the efflux of talazoparib in TNBC cells was mediated by BCRP and MRP1 pumps. Talazoparib-SLNs significantly improved the therapeutic effects of talazoparib and suppressed the expression of MDR1, BCRP, and MRP1 genes and proteins. In summary, targeting the expression of genes related to drug efflux pumps is an effective strategy for alleviating drug resistance in breast cancer (79).
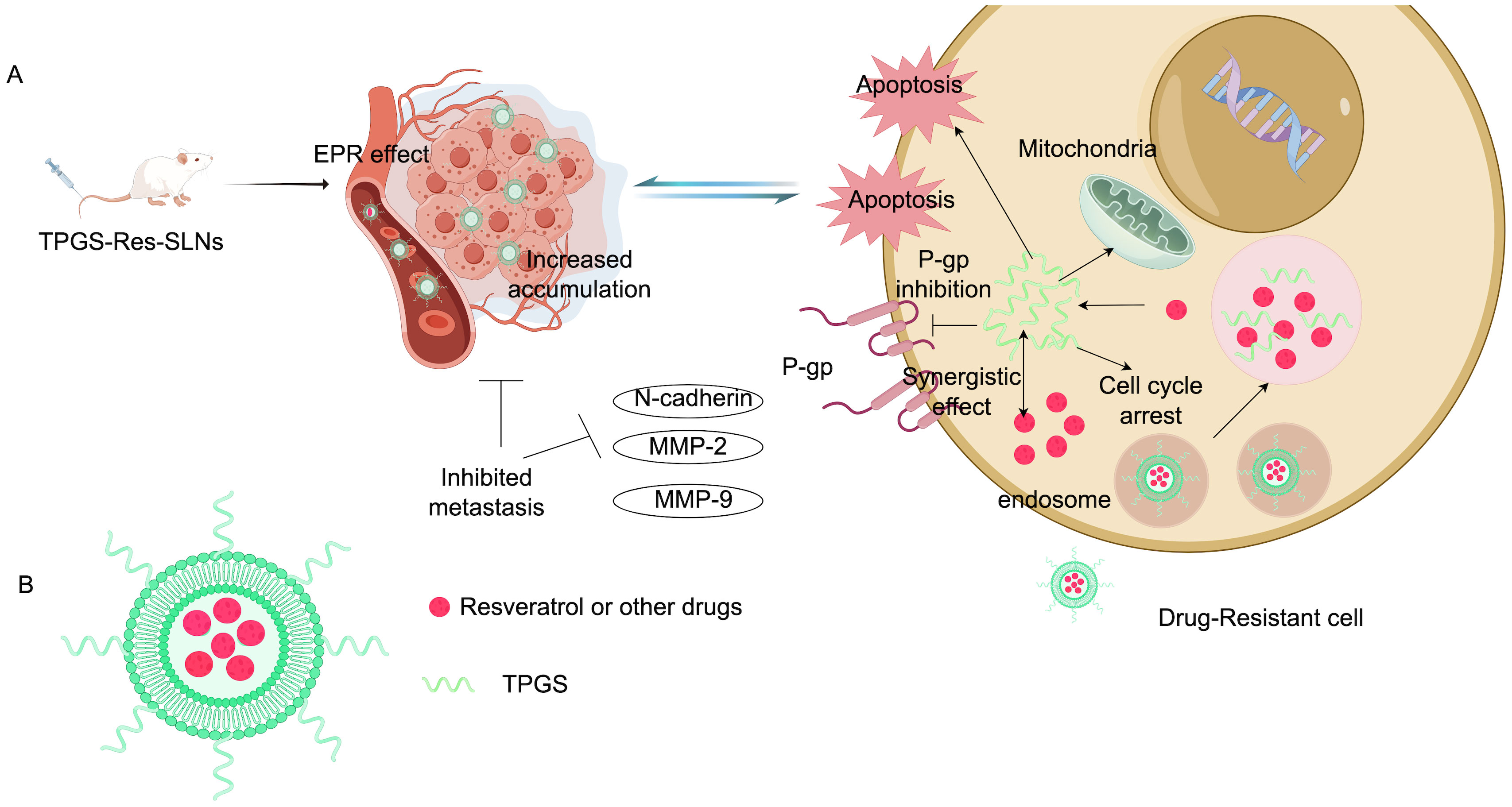
Figure 5. Composition and mechanism of TPGS-Res-SLNs. (A) Illustration: TPGS-Res-SLNs reduce the expression of P-gp and BCRP-related proteins. TPGS-Res-SLNs also refrain from the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells and attenuate the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. (B) Characterization diagram of TPGS-Res-SLNs (Created with Figdraw).
4.2 Interference with signaling pathways
Cell signaling plays a crucial role in the key stages of hormone-independent breast cancer tumorigenesis, including cell proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, and metastasis (80). Understanding the abnormalities in the signaling pathways that contribute to resistant breast cancer cells can help identify specific peptides and modify their properties to selectively target these pathways. This section provides a brief overview of the role these signaling pathways play in breast cancer chemotherapy resistance. Defects in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways are known to cause multidrug resistance and promote cancer metastasis. Yin et al. developed a pH-sensitive nanocomplex that co-delivers paclitaxel (PTX) and siRNA to metastatic breast cancer. The siRNA targets and silences Akt expression in 4T1 metastatic breast cancer cells. In these cells, PTX-loaded micelle/siAkt nanocomplexes (PMA) successfully downregulated P-gp, upregulated Caspase-3 expression, and resulted in Akt gene knockdown. Beyond promising in vitro results, PMA demonstrated both efficacy and safety in vivo. In 4T1 tumor-bearing mice, PMA achieved 94.1% tumor inhibition and 96.8% reduction in breast cancer lung metastasis. Furthermore, the PMA nanocomplex is characterized by very low toxicity and does not cause lesions in normal tissues (81). Guney et al. discovered that TNBC cells often overexpress Notch1 receptors while underexpressing miR-34a microRNA. To tackle this issue, they encapsulated miR-34a mimics within poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles (NPs), creating N1-34a-NPs. These nanoparticles were functionalized to bind to the overexpressed Notch1 receptors on the surface of TNBC cells, thereby interfering with Notch signaling through the associated signaling cascade. Their experiments showed that N1-34a-NPs could effectively regulate Notch signaling and its downstream targets in TNBC cells, leading to cell senescence and reduced proliferation and migration. This study suggests that nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery of miR-34a and Notch1 antibodies may serve as a promising alternative treatment strategy for TNBC, warranting further optimization and in vivo investigation (79). Additionally, studies have indicated that Dox-HBDL nanoparticles significantly enhance therapeutic effects on drug-resistant breast cancer cells. This nanoparticle activates the intracellular JNK pathway, promoting apoptosis and inducing the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential while increasing reactive oxygen species levels in the cytoplasm. This mechanism further activates the pro-apoptotic JNK signaling in drug-resistant cells, hindering drug degradation and increasing apoptosis and cell death (82). Cheng et al. reported similar findings in nanoparticles that co-deliver DOX and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, where pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate served as a chemosensitizer, enhancing intracellular drug levels by halting the NF-κB pathway (83). The researchers designed pH-sensitive nanoparticles from poly(orthoester carbamate) copolymers, which are stable in neutral pH environments but degrade rapidly in slightly acidic conditions (84, 85). Liang et al. identified novel functional roles for heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1) in regulating chemoresistance and ferroptotic cell death in breast cancer. HSPB1 could bind with Ikβ-α and promote its ubiquitination-mediated degradation, leading to increased nuclear translocation and activation of NF-κB signaling. Thus, targeting HSPB1 and combinational induction of ferroptosis with anticancer drugs would be a potential therapeutic strategy to overcome chemoresistance in breast cancer (86).
4.3 Inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
A recent study demonstrates that present a novel approach of combinatorial treatment of DOX with dietary indole 3,3’-diindolylmethane (DIM). They combined DIM with DOX and delivered to the CSCs concomitantly by loading them in mesoporous silica nanoparticles encapsulated in exosomes (e-DDMSNP), which improved the specificity, stability and better homing ability of DIM and DOX in the in vitro and in vivo CSC niche. Therefore, this novel exosome nanopreparation has great potential to target CSC and EMT (87).SKN@FPD NM is a novel type of nanodrug delivery system. By leveraging the inhibitory effects of SKN, this nanomaterial can effectively disrupt the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, thereby reducing the metastatic potential of breast cancer cells. Furthermore, this combination therapy enhances tumor cell toxicity while reducing the risk of drug resistance and treatment failure (88). In summary, nanodrug delivery systems offer a promising strategy for overcoming drug resistance in breast cancer.
Nanodrug-carrying systems have also demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in addressing drug resistance across various malignant cancers. For instance, some researchers have developed a nanosystem based on programmed DNA self-assembly of Rab26 siRNA-loaded nanoparticles for treating drug resistance in lung cancer (66). Additionally, miRNA and PTX can be delivered through RAW-PANP, presenting a new method for tackling PTX-resistant TNBC. Simultaneously, RAW-PANP can serve as an effective drug delivery system for targeted therapy in TNBC (89).
5 Application of targeted nano-drug delivery in breast cancer drug resistance
5.1 Passive drug targeting
In normal tissues, the vascular structure is compact, whereas in tumor sites, it is abnormal with wider pores. This difference allows nanomaterials to penetrate tumor tissue more easily, a phenomenon known as the enhanced permeability retention effect (90). Passive targeting is a drug delivery approach that leverages these anatomical and physiological differences in tissue. Specifically, it utilizes the enhanced permeability retention effect, which is influenced by certain changes in tumor tissues, such as large gaps in the blood vessel endothelium, limited lymphatic drainage, and disrupted tissue architecture. These factors increase the likelihood of macromolecular particles gathering in tumor sites (91). Nanomaterials can further enhance the enhanced permeability retention effect by adjusting their particle size at the tumor area, thereby increasing their effectiveness against breast cancer (35, 92). These nanomaterials can be categorized into various delivery methods, including liposomes, micelles, nanogels, and nanoparticles (93). Addressing common challenges in treating TNBC, such as chemotherapy resistance and off-target damage, researchers led by Chen et al. developed a novel type of nanoparticle. This formulation combines polylactic acid-co-polylactic acid with a lipid shell, enabling it to carry drugs such as paclitaxel and anti-miR-221, along with perfluoropropane for ultrasound-triggered release. These nanoparticles are delivered to the tumor site by macrophages, utilizing the innate targeting ability of these cells to enhance treatment precision. Experimental results demonstrate that this system significantly increases the sensitivity of TNBC cells to chemotherapeutic agents while minimizing harm to normal tissues (94). Additionally, Xiong et al. created DOX-TA-ICG particles (DTIG) with a diameter of (74 ± 2) nm. Upon arrival at the tumor site, DTIG experiences increased proton concentration, causing them to further condense through electrostatic interactions, which enhances their uptake by tumor cells. As proton concentration rises in the lysosome (pH = 4.5), DTIG aggregation becomes more pronounced, ultimately forming larger particles with a diameter of 1.5 μm that escape the lysosome. Once in the cytoplasm, the near-neutral environment prompts DTIG to quickly transform into larger hydrophilic particles measuring 120-200 nm (95). In summary, at the tumor site, the high permeability and retention characteristics of nanomaterials may improve the accumulation of chemotherapeutic drugs, thereby mitigating breast cancer resistance and reducing off-target damage (93).
5.2 Active drug targeting
Targeted molecular therapy enhances the precision of cancer treatments and is one of the most effective methods in targeted therapy. Active targeting relies on the interaction between a targeting agent and its corresponding receptor, allowing nanoparticles to specifically bind to antigens expressed by tumor cells. This method improves drug delivery efficiency and specificity (96). In breast cancer treatment, several key molecular targets have been identified, including human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, vascular endothelial growth factor, folate receptors, somatostatin receptors, vascular endothelial cell adhesion molecules, estrogen receptors, and cyclooxygenase-2 (97). A study by Mamnoon et al. developed hypoxia-responsive polymer nanoparticles (HRPs) functionalized with 17β-estradiol (E2) for the targeted delivery of DOX in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. They prepared estradiol-coupled polymer-DOX complexes (E2-DOX-HRPs), which demonstrated a higher DOX loading efficiency compared to non-targeted preparations. Under hypoxic conditions, E2-DOX-HRPs exhibited enhanced antiproliferative effects, significantly reducing cell viability and causing spheroid shrinkage in three-dimensional cultures of MCF-7 cells. These findings indicate that the targeted HRP formulation successfully recognized estrogen receptors on breast cancer cells and released more DOX under tumor hypoxia, enhancing the anticancer effect of DOX and effectively alleviating chemotherapy resistance (98).
5.3 The physical and chemical targeting effect of nanocarriers enhances the targeting of breast cancer cells
Physical and chemical targeting is a method to enhance the targeted therapeutic effects on cancers such as breast cancer by precisely delivering drugs to specific transport sites through external forces such as temperature, magnetic fields, and pH. Temperature-sensitive carriers can be made into thermosensitive agents, allowing them to release drugs in thermotherapy target areas (99); or magnetic materials can be applied to form magnetic guidance agents with drugs, which, guided by external magnetic fields in vitro, reach and localize in specific target areas through the bloodstream (100); pH-sensitive carriers can also be utilized to prepare pH-sensitive agents, enabling drug release in specific target areas (101). Embolic agents can block blood supply and nutrition in target areas, serving a dual role in embolization and targeted chemotherapy. Puluhulawa et al. used Chemical grafting of chitosan nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid as a targeted ligand to control drug release through ph-responsive stimulation, and the high selectivity of hyaluronic acid for CD44 receptors allowed these nanoparticles to accumulate more in cells that overexpress these receptors (102). Zhang et al. developed the “cell targeting destructive” multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles (HA-Olb-PPMNPs). Under rotating magnetic field (RMF), HA-Olb-PPMNPs can produce physical transfer of mechanical force through incomplete rotation, which can cause a “two-strike” effect on cells, in which the “first strike” is to destroy the membrane structure, and the other “second strike” is to activate the lysosomal-mitochondrial pathway to induce apoptosis by damaging the lysosome (103). Nasri et al. developed a new monoclonal antibody conjugated dual stimuli lipid-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles (L-MSNs) platform, first synthesizing MSN and then using prepared pH and heat-sensitive niosome coated to produce L-MSN. Use a key-lock interaction between trastuzumab and HER-2 receptors on the cancer cell membrane to deliver specifically targeted drugs to the cancer cell, stimulating the endocytosis of particles into the cell, which then disrupts the lipid layer at acidic pH and lysosome temperature, leading to enhanced release of PTX and GEM (104).
6 Research progress in anticancer nanomaterials
Chemotherapy, surgery, hormone therapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapy form the core strategies for breast cancer treatment. Despite these methods, researchers continue to explore new treatments and drugs. Patients participating in clinical trials not only have the opportunity to try potentially advanced therapies but also contribute to cancer research, fostering collaboration among breast cancer patients. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has officially approved the use of palbociclib, ribociclib, and everolimus in combination with hormone therapy for the treatment of advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Clinical studies have shown that ribociclib can effectively extend the survival of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Additionally, Abemaciclib is approved for use alongside or following hormone therapy, specifically for patients with hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. Table 3 provides a list of drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration from 2021 to 2023.
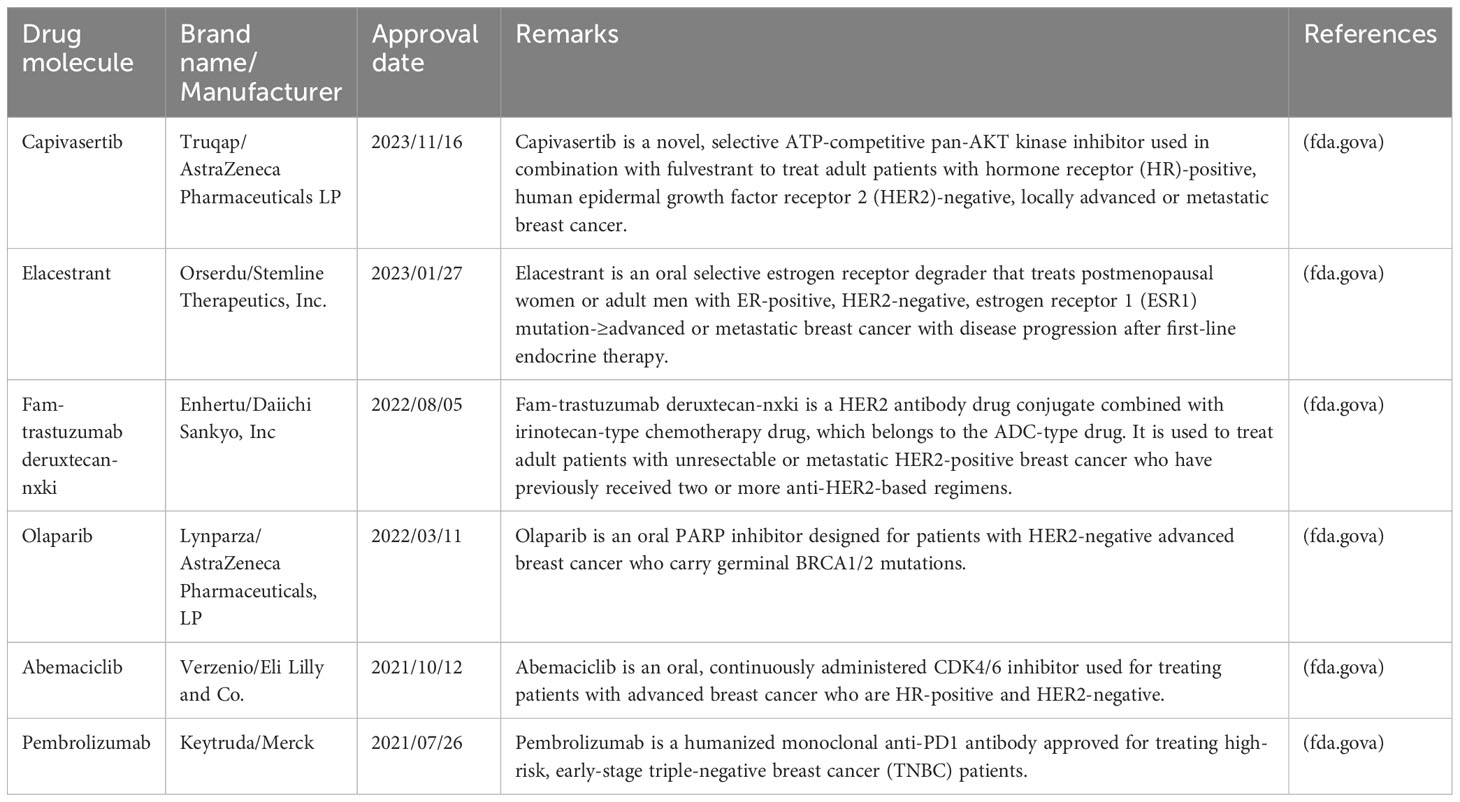
Table 3. List of the drugs approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration from 2021–2023 for advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
7 Challenges and hopes
Cancer drug resistance remains a significant challenge in current cancer treatments and is responsible for the majority of cancer-related fatalities. However, the versatility of nanomaterials offers a revolutionary approach to combat this issue and provides new hope. These materials can serve both diagnostic and therapeutic functions, allowing for precise tumor localization and drug delivery while enhancing treatment efficacy and minimizing harm to healthy tissues. Advancements in this technology are expected to lead to breakthroughs in cancer therapy and offer patients more personalized and effective treatment options. This review begins by classifying different nanomaterials and explaining their mechanisms of action, particularly in breast cancer research. Nonetheless, the design, optimization, and potential biomedical applications of these nanomaterials require further investigation.
Firstly, nanomaterials’ capability to deliver functional substances to diseased cells makes them promising therapeutic carriers and potential targets for overcoming drug resistance. However, preparing nanomaterials to target specific sites demands significant time, effort, and financial resources, complicating their clinical application. Furthermore, identifying the optimal target carriers to develop the most effective combined strategies while minimizing adverse effects in treatment should be a key focus for future research in this area. Secondly, while nanomaterials have demonstrated good tolerance and minimal side effects, their toxicity remains a critical concern in medical and environmental applications. Additionally, nanomaterials can facilitate dynamic measurement of various biological components associated with tumor resistance, holding unique potential for monitoring cancer’s complex dynamics and potentially serving as candidate biomarkers for predicting and assessing treatment outcomes in breast cancer patients. However, optimizing detection methods and maximizing the advantages of nanomaterials in breast cancer treatment to achieve synergistic effects of “1 + 1>2” still requires extensive research and exploration. Despite their many beneficial properties, nanomaterials can also present toxic effects due to their unique physical and chemical characteristics. For instance, their small size and high surface area may increase the likelihood of interactions with biological systems, leading to adverse effects such as cytotoxicity, immunotoxicity, and genotoxicity, which can result in inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and cellular damage, potentially disrupting physiological functions. Thus, careful attention to toxicity issues, along with implementing safety measures during the design, synthesis, and application of nanomaterials, is essential to ensure their safety and reliability.
Despite the substantial challenges, with ongoing advancements in science and technology and the progress of clinical research, we believe that nanomaterials have the potential to become vital tools in treating breast cancer resistance and bring renewed hope to patients.
Author contributions
CG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XM: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. BZ: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. KC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WD: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program Project, China Medical University and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2022-MS-180).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca: A Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Amato O, Guarneri V, Girardi F. Epidemiology trends and progress in breast cancer survival: earlier diagnosis, new therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol. (2023) 35:612–19. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000991
3. Ibrahim A, El Baldi M, Mohammed S, El Rhazi K, Benazzouz B. Cancer statistics in Yemen: incidence and mortality, in 2020. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:962. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18207-4
4. Fisusi FA, Akala EO. Drug combinations in breast cancer therapy. Pharm Nanotechnology. (2019) 7:3–23. doi: 10.2174/2211738507666190122111224
5. Baxter DE, Kim B, Hanby AM, Verghese ET, Sims AH, Hughes TA. Neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer upregulates the cytotoxic drug pump abcg2/bcrp, and may lead to resistance to subsequent chemotherapy. Clin Breast Cancer. (2018) 18:481–88. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2018.07.002
6. Sharma A, Jasrotia S, Kumar A. Effects of chemotherapy on the immune system: implications for cancer treatment and patient outcomes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. (2024) 397:2551–66. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02781-2
7. Lohiya DV, Mehendale AM, Lohiya DV, Lahoti HS, Agrawal VN. Novel chemotherapy modalities for different cancers. Cureus. (2023) 15:e45474. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45474
8. An J, Peng C, Tang H, Liu X, Peng F. New advances in the research of resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:9644. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179644
9. Dallavalle S, Dobricic V, Lazzarato L, Gazzano E, Machuqueiro M, Pajeva I, et al. Improvement of conventional anti-cancer drugs as new tools against multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist Update. (2020) 50:100682. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100682
10. Battista T, Fiorillo A, Chiarini V, Genovese I, Ilari A, Colotti G. Roles of sorcin in drug resistance in cancer: one protein, many mechanisms, for a novel potential anticancer drug target. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:887. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040887
11. Navas T, Kinders RJ, Lawrence SM, Ferry-Galow KV, Borgel S, Hollingshead MG, et al. Clinical evolution of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human carcinomas. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:304–18. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3539
12. Garcia-Mayea Y, Mir C, Masson F, Paciucci R, LLeonart ME. Insights into new mechanisms and models of cancer stem cell multidrug resistance. Semin Cancer Biol. (2020) 60:166–80. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.022
13. Orrantia-Borunda E, Acuna-Aguilar LE, Ramirez-Valdespino CA. Nanomaterials for breast cancer. (2022) 149–162. doi: 10.36255/exon-publications-breast-cancer-nanomaterials
14. Matiyani M, Rana A, Pal M, Dokwal S, Sahoo NG. Polyamidoamine dendrimer decorated graphene oxide as a ph-sensitive nanocarrier for the delivery of hydrophobic anticancer drug quercetin: a remedy for breast cancer. J Pharm Pharmacol. (2023) 75:859–72. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgad036
15. Borah A, Pillai SC, Rochani AK, Palaninathan V, Nakajima Y, Maekawa T, et al. Gant61 and curcumin-loaded plga nanoparticles for gli1 and pi3k/akt-mediated inhibition in breast adenocarcinoma. Nanotechnology. (2020) 31:185102. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab6d20
16. Li D, Hu X, Zhang S. Biodegradation of graphene-based nanomaterials in blood plasma affects their biocompatibility, drug delivery, targeted organs and antitumor ability. Biomaterials. (2019) 202:12–25. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.02.020
17. Zhang P, Ye G, Xie G, Lv J, Zeng X, Jiang W. Research progress of nanomaterial drug delivery in tumor targeted therapy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2023) 11:1240529. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1240529
18. Mohebian Z, Babazadeh M, Zarghami N. In vitro efficacy of curcumin-loaded amine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles against mcf-7 breast cancer cells. Adv Pharm Bull. (2023) 13:317–27. doi: 10.34172/apb.2023.035
19. Leung JH, Tai YS, Wang SY, Yip FH, Tsung-Chin H, Chan AL. Cost-effectiveness of trastuzumab biosimilar combination therapy and drug wastage as first-line treatment for her2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast. (2022) 65:91–7. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2022.07.007
20. Tang L, Yang X, Yin Q, Cai K, Wang H, Chaudhury I, et al. Investigating the optimal size of anticancer nanomedicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2014) 111:15344–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411499111
21. Egelston CA, Guo W, Yost SE, Ge X, Lee JS, Frankel PH, et al. Immunogenicity and efficacy of pembrolizumab and doxorubicin in a phase i trial for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy. (2023) 72:3013–27. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03470-y
22. Turner NC, Oliveira M, Howell SJ, Dalenc F, Cortes J, Gomez Moreno HL, et al. Capivasertib in hormone receptor–positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:2058–70. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2214131
23. Kim H, Lee JW, Nam SJ, Park B, Im S, Lee ES, et al. Adding ovarian suppression to tamoxifen for premenopausal breast cancer: a randomized phase iii trial. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:434–43. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00126
24. Zhang P, Zhang Q, Tong Z, Sun T, Li W, Ouyang Q, et al. Dalpiciclib plus letrozole or anastrozole versus placebo plus letrozole or anastrozole as first-line treatment in patients with hormone receptor-positive, her2-negative advanced breast cancer (dawna-2): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2023) 24:646–57. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00172-9
25. Jiang Z, Ouyang Q, Sun T, Zhang Q, Teng Y, Cui J, et al. Toripalimab plus nab-paclitaxel in metastatic or recurrent triple-negative breast cancer: a randomized phase 3 trial. Nat Med. (2024) 30:249–56. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02677-x
26. Domchek SM, Postel-Vinay S, Im S, Park YH, Delord J, Italiano A, et al. Olaparib and durvalumab in patients with germline brca-mutated metastatic breast cancer (mediola): an open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2, basket study. Lancet Oncol. (2020) 21:1155–64. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30324-7
27. Saura C, Modi S, Krop I, Park YH, Kim SB, Tamura K, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated patients with her2-positive metastatic breast cancer: updated survival results from a phase ii trial (destiny-breast01). Ann Oncol. (2024) 35:302–07. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2023.12.001
28. Sharma P, Stecklein SR, Yoder R, Staley JM, Schwensen K, O’Dea A, et al. Clinical and biomarker findings of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab and carboplatin plus docetaxel in triple-negative breast cancer: neopact phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2024) 10:227–35. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.5033
29. Fehm T, Mueller V, Banys-Paluchowski M, Fasching PA, Friedl TWP, Hartkopf A, et al. Efficacy of lapatinib in patients with her2-negative metastatic breast cancer and her2-positive circulating tumor cells—the detect iii clinical trial. Clin Chem. (2024) 70:307–18. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvad144
30. Huang H, Wang Y, Wu X, Zhang J, Huang X. Nanomaterials for modified asphalt and their effects on viscosity characteristics: a comprehensive review. Nanomaterials (Basel). (2024) 14:1503. doi: 10.3390/nano14181503
31. Li J, Lu W, Yang Y, Xiang R, Ling Y, Yu C, et al. Hybrid nanomaterials for cancer immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2204932. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204932
32. Martin-Pardillos A, Martin-Duque P. Cellular alterations in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism due to interactions with nanomaterials. J Funct Biomater. (2023) 14: 274. doi: 10.3390/jfb14050274
33. Alves A, Bruinsmann FA, Guterres SS, Pohlmann AR. Organic nanocarriers for bevacizumab delivery: an overview of development, characterization and applications. Molecules. (2021) 26:4127. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144127
34. Zhang L, Zhu C, Huang R, Ding Y, Ruan C, Shen XC. Mechanisms of reactive oxygen species generated by inorganic nanomaterials for cancer therapeutics. Front Chem. (2021) 9:630969. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.630969
35. Jain A, Sharma G, Kushwah V, Garg NK, Kesharwani P, Ghoshal G, et al. Methotrexate and beta-carotene loaded-lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles: a preclinical study for breast cancer. Nanomedicine (Lond). (2017) 12:1851–72. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0011
36. Sandal P, Patel P, Singh D, Gupta GD, Kurmi BD. Alpha-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-based cationic liposome for the intracellular delivery of doxorubicin in mda-mb-231 triple-negative breast cancer cell line. Assay Drug Dev Technol. (2023) 21:345–56. doi: 10.1089/adt.2023.067
37. DeVeaux S, Gomillion CT. Assessing the potential of chitosan/polylactide nanoparticlesfor delivery of therapeutics for triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Regenerative Eng Trans Med. (2019) 5:61–73. doi: 10.1007/s40883-018-0089-4
38. Soltany P, Miralinaghi M, Shariati FP. Folic acid conjugated poly (amidoamine) dendrimer grafted magnetic chitosan as a smart drug delivery platform for doxorubicin: in-vitro drug release and cytotoxicity studies. Int J Biol Macromolecules: Structure Funct Interact. (2024) 257:127564. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127564
39. Bhattacharya S, Prajapati BG, Ali N, Mohany M, Aboul-Soud M, Khan R. Therapeutic potential of methotrexate-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and polyethylene glycol against breast cancer: development, characterization, and comprehensive in vitro investigation. ACS Omega. (2023) 8:27634–49. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03430
40. Zoghi M, Pourmadadi M, Yazdian F, Nigjeh MN, Rashedi H, Sahraeian R. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/carbon quantum dots/fe(2)o(3) nanocomposite comprising curcumin for targeted drug delivery in breast cancer therapy. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 249:125788. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125788
41. Ghanbari N, Salehi Z, Khodadadi AA, Shokrgozar MA, Saboury AA. Glucosamine-conjugated graphene quantum dots as versatile and ph-sensitive nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of curcumin targeting to breast cancer. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2021) 121:111809. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111809
42. Ozgenc E, Karpuz M, Arzuk E, Gonzalez-Alvarez M, Sanz MB, Gundogdu E, et al. Radiolabeled trastuzumab solid lipid nanoparticles for breast cancer cell: in vitro and in vivo studies. ACS Omega. (2022) 7:30015–27. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03023
43. Granja A, Nunes C, Sousa CT, Reis S. Folate receptor-mediated delivery of mitoxantrone-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles to breast cancer cells. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 154:113525. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113525
44. Aly S, El-Kamel AH, Sheta E, El-Habashy SE. Chondroitin/lactoferrin-dual functionalized pterostilbene-solid lipid nanoparticles as targeted breast cancer therapy. Int J Pharm. (2023) 642:123163. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123163
45. Da RM, Da SP, Radicchi MA, Andrade B, de Oliveira JV, Venus T, et al. Docetaxel-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prevent tumor growth and lung metastasis of 4t1 murine mammary carcinoma cells. J Nanobiotechnology. (2020) 18:43. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-00604-7
46. Ss PS, Krishnamurthy PT, Ghanta VR, Chintamaneni PK. Phenyl boronic acid-modified lipid nanocarriers of niclosamide for targeting triple-negative breast cancer. Nanomedicine (Lond). (2020) 15:1551–65. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2020-0003
47. Tran P, Nguyen TN, Lee Y, Tran PN, Park JS. Docetaxel-loaded plga nanoparticles to increase pharmacological sensitivity in mda-mb-231 and mcf-7 breast cancer cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. (2021) 25:479–88. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.5.479
48. Boratto FA, Lages EB, Loures CMC, Sabino AP, Malachias A, Townsend DM, et al. Alpha-tocopheryl succinate and doxorubicin-loaded liposomes improve drug uptake and tumor accumulation in a murine breast tumor model. BioMed Pharmacother. (2023) 165:115034. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115034
49. Badr-Eldin SM, Aldawsari HM, Fahmy UA, Ahmed O, Alhakamy NA, Al-Hejaili OD, et al. Optimized apamin-mediated nano-lipidic carrier potentially enhances the cytotoxicity of ellagic acid against human breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23: 9440. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169440
50. Chen T, Chen H, Jiang Y, Yan Q, Zheng S, Wu M. Co-delivery of 5-fluorouracil and paclitaxel in mitochondria-targeted kla-modified liposomes to improve triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Pharm (Basel). (2022) 15:881. doi: 10.3390/ph15070881
51. Geszke-Moritz M, Moritz M. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems: comprehensive overview, perspectives and challenges. Polymers (Basel). (2024) 16:2536. doi: 10.3390/polym16172536
52. Verma R, Singh V, Koch B, Kumar M. Evaluation of methotrexate encapsulated polymeric nanocarrier for breast cancer treatment. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. (2023) 226:113308. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113308
53. Bressler EM, Kim J, Shmueli RB, Mirando AC, Bazzazi H, Lee E, et al. Biomimetic peptide display from a polymeric nanoparticle surface for targeting and antitumor activity to human triple-negative breast cancer cells. J BioMed Mater Res A. (2018) 106:1753–64. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36360
54. Sharma A, Hawthorne S, Jha SK, Jha NK, Kumar D, Girgis S, et al. Effects of curcumin-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles in mda-mb231 human breast cancer cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). (2021) 16:1763–73. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2021-0066
55. Barkat A, Rahman M, Alharbi KS, Altowayan WM, Alrobaian M, Afzal O, et al. Biocompatible polymeric nanoparticles for effective codelivery of tamoxifen with ganoderic acid a: systematic approach for improved breast cancer therapeutics. J Clust Sci. (2023) 34:1483–97. doi: 10.1007/s10876-022-02332-4
56. Phalake SS, Somvanshi SB, Tofail SAM. Functionalized manganese iron oxide nanoparticles: a dual potential magneto-chemotherapeutic cargo in a 3d breast cancer model. Nanoscale. (2023) 15:15686–99. doi: 10.1039/d3nr02816j
57. Li Z, Guo T, Zhao S, Lin M. The therapeutic effects of muc1-c shrna@fe(3)o(4) magnetic nanoparticles in alternating magnetic fields on triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:5651–70. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S426849
58. Khan Z, Sattar S, Abubakar M, Arshed MJ, Aslam R, Shah STA, et al. Preparation andin vitro evaluation of tamoxifen-conjugated, eco-friendly, agar-based hybrid magnetic nanoparticles for their potential use in breast cancer treatment. ACS Omega. (2023) 8:25808–16. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00844
59. Bulatao BP, Nalinratana N, Jantaratana P, Vajragupta O, Rojsitthisak P, Rojsitthisak P. Lutein-loaded chitosan/alginate-coated fe(3)o(4) nanoparticles as effective targeted carriers for breast cancer treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 242:124673. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124673
60. Markhulia J, Kekutia S, Mikelashvili V, Saneblidze L, Tsertsvadze T, Maisuradze N, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of doxorubicin-loaded magnetite nanoparticles on triple-negative breast cancer cell lines. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15:1758. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061758
61. Fekri KS, Zamani H, Salehzadeh A. Antibacterial potential and cytotoxic activity of iron oxide nanoparticles conjugated with thymol (fe(3)o(4)@glu-thymol) on breast cancer cells and investigating the expression of bax, casp8, and bcl-2 genes. Biometals. (2023) 36:1273–84. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00516-7
62. Nene LC, Nyokong T. Photo-sonodynamic combination activity of cationic morpholino-phthalocyanines conjugated to nitrogen and nitrogen-sulfur doped graphene quantum dots against mcf-7 breast cancer cell line. vitro. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. (2021) 36:102573. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102573
63. Tao J, Feng S, Liu B, Pan J, Li C, Zheng Y. Hyaluronic acid conjugated nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for identification of human breast cancer cells. BioMed Mater. (2021) 16:055001. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac0d93
64. Tiwari P, Shukla RP, Yadav K, Singh N, Marwaha D, Gautam S, et al. Dacarbazine-primed carbon quantum dots coated with breast cancer cell-derived exosomes for improved breast cancer therapy. J Control Release. (2024) 365:43–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.11.005
65. Karami MH, Pourmadadi M, Abdouss M, Kalaee MR, Moradi O, Rahdar A, et al. Novel chitosan/gamma-alumina/carbon quantum dot hydrogel nanocarrier for targeted drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 251:126280. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126280
66. Ku TH, Shen WT, Hsieh CT, Chen GS, Shia WC. Specific forms of graphene quantum dots induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4046. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044046
67. Liu M, Fu M, Yang X, Jia G, Shi X, Ji J, et al. Paclitaxel and quercetin co-loaded functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles overcoming multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2020) 196:111284. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111284
68. Singhai NJ, Maheshwari R, Ramteke S. Cd44 receptor targeted ‘smart’ multi-walled carbon nanotubes for synergistic therapy of triple-negative breast cancer. Colloid Interface Sci Commun. (2020) 35:100235. doi: 10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100235
69. Hu M, Cheng N, Wang S, Li R, Liu Y, Wang L, et al. Salvianolic acid b-loaded polydopamine-modified hollow mesoporous organic silica nanoparticles for treatment of breast cancer metastasis via suppressing cancer-associated fibroblasts. Eur J Pharm Sci. (2024) 192:106641. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2023.106641
70. Zhang X, Li N, Zhang G, Li J, Liu Y, Wang M, et al. Nano strategies for artemisinin derivatives to enhance reverse efficiency of multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Curr Pharm Des. (2023) 29:3458–66. doi: 10.2174/0113816128282248231205105408
71. Samson A, Park S, Kim SY, Min DH, Jeon NL, Song JM. Liposomal co-delivery-based quantitative evaluation of chemosensitivity enhancement in breast cancer stem cells by knockdown of grp78/clu. J Liposome Res. (2019) 29:44–52. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2017.1420081
72. Nosrati H, Adibtabar M, Sharafi A, Danafar H, Hamidreza KM. Pamam-modified citric acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles as ph sensitive biocompatible carrier against human breast cancer cells. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. (2018) 44:1377–84. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2018.1451881
73. Li J, Zhang W, Gao Y, Tong H, Chen Z, Shi J, et al. Near-infrared light and magnetic field dual-responsive porous silicon-based nanocarriers to overcome multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells with enhanced efficiency. J Mater Chem B. (2020) 8:546–57. doi: 10.1039/c9tb02340b
74. Dong X, Yin W, Zhang X, Zhu S, He X, Yu J, et al. Intelligent mos(2) nanotheranostic for targeted and enzyme-/ph-/nir-responsive drug delivery to overcome cancer chemotherapy resistance guided by pet imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2018) 10:4271–84. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b17506
75. Li W, Fu Y, Sun J, Gong H, Yan R, Wang Y. Construction and in vitro evaluation of ph-sensitive nanoparticles to reverse drug resistance of breast cancer stem cells. Discovery Oncol. (2024) 15:21. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-00873-w
76. Guo F, Yu N, Jiao Y, Hong W, Zhou K, Ji X, et al. Star polyester-based folate acid-targeting nanoparticles for doxorubicin and curcumin co-delivery to combat multidrug-resistant breast cancer. Drug Delivery. (2021) 28:1709–21. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1960926
77. Wang W, Zhou M, Xu Y, Peng W, Zhang S, Li R, et al. Resveratrol-loaded tpgs-resveratrol-solid lipid nanoparticles for multidrug-resistant therapy of breast cancer: in vivo and in vitro study. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2021) 9:762489. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.762489
78. Xu W, Bae EJ, Lee MK. Enhanced anticancer activity and intracellular uptake of paclitaxel-containing solid lipid nanoparticles in multidrug-resistant breast cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine. (2018) 13:7549–63. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S182621
79. Guney EG, Cecener G, Egeli U, Tunca B. Talazoparib nanoparticles for overcoming multidrug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:6230–45. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29552
80. Marra A, Trapani D, Viale G, Criscitiello C, Curigliano G. Practical classification of triple-negative breast cancer: intratumoral heterogeneity, mechanisms of drug resistance, and novel therapies. NPJ Breast Cancer. (2020) 6:54. doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00197-2
81. Yin J, Lang T, Cun D, Zheng Z, Huang Y, Yin Q, et al. Erratum: ph-sensitive nano-complexes overcome drug resistance and inhibit metastasis of breast cancer by silencing akt expression: erratum. Theranostics. (2020) 10:2399–400. doi: 10.7150/thno.42847
82. Zhong W, Shen Z, Wang M, Wang H, Sun Y, Tao X, et al. Tumor microenvironment responsive nanomicelle with folic acid modification co-delivery of doxorubicin/shikonin for triple negative breast cancer treatment. Pharm (Basel). (2023) 16:374. doi: 10.3390/ph16030374
83. Cheng X, Li D, Sun M, He L, Zheng Y, Wang X, et al. Co-delivery of dox and pdtc by ph-sensitive nanoparticles to overcome multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. (2019) 181:185–97. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.042
84. Cheng X, Li H, Ge X, Chen L, Liu Y, Mao W, et al. Tumor-microenvironment- responsive size-shrinkable drug-delivery nanosystems for deepened penetration into tumors. Front Mol Biosci. (2020) 7:576420. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.576420
85. Al-Jubori AA, Sulaiman GM, Tawfeeq AT, Mohammed HA, Khan RA, Mohammed S. Layer-by-layer nanoparticles of tamoxifen and resveratrol for dual drug delivery system and potential triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics. (2021) 13:1098. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13071098
86. Liang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ye F, Luo D, Li Y, et al. Hspb1 facilitates chemoresistance through inhibiting ferroptotic cancer cell death and regulating nf-κb signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:434. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05972-0
87. Sarkar R, Biswas S, Ghosh R, Samanta P, Pakhira S, Mondal M, et al. Exosome-sheathed porous silica nanoparticle-mediated co-delivery of 3,3’-diindolylmethane and doxorubicin attenuates cancer stem cell-driven emt in triple negative breast cancer. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:285. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02518-0
88. Wang B, Zhang R, Wang Y, Qian H, Wu D, He B, et al. Targeting rab26 to conquer cisplatin-resistant lung cancer with self-assembled dna nanomaterials. Biomacromolecules. (2023) 24:2063–74. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c01493
89. Zhang L, Ren Z, Lu J, Mo X, Lin J, Li Y, et al. Nanoparticles carrying paclitaxel and anti-mir-221 for breast cancer therapy triggered by ultrasound. Cell Death Discovery. (2023) 9:298. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01594-9
90. Aloss K, Hamar P. Augmentation of the epr effect by mild hyperthermia to improve nanoparticle delivery to the tumor. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2024) 1879:189109. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189109
91. Du M, Ouyang Y, Meng F, Ma Q, Liu H, Zhuang Y, et al. Nanotargeted agents: an emerging therapeutic strategy for breast cancer. Nanomedicine (Lond). (2019) 14:1771–86. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2018-0481
92. Jain A, Sharma T, Kumar R, Katare OP, Singh B. Raloxifene-loaded slns with enhanced biopharmaceutical potential: qbd-steered development, in vitro evaluation, in vivo pharmacokinetics, and ivivc. Drug Delivery Transl Res. (2022) 12:1136–60. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00990-x
93. Huang M, Zhai BT, Fan Y, Sun J, Shi YJ, Zhang XF, et al. Targeted drug delivery systems for curcumin in breast cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. (2023) 18:4275–311. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S410688
94. Chen X, He H, Guo X, Hou M, Zhang X, Li S, et al. Calcium orthophosphate in liposomes for co-delivery of doxorubicin hydrochloride/paclitaxel in breast cancer. Mol Pharm. (2023) 20:3914–24. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00015
95. Xiong H, Wang Z, Wang C, Yao J. Transforming complexity to simplicity: protein-like nanotransformer for improving tumor drug delivery programmatically. Nano Lett. (2020) 20:1781–90. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05008
96. Tang L, Li J, Zhao Q, Pan T, Zhong H, Wang W. Advanced and innovative nano-systems for anticancer targeted drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. (2021) 13:1151. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13081151
97. Abdellatif A, Aldalaen SM, Faisal W, Tawfeek HM. Somatostatin receptors as a new active targeting sites for nanoparticles. Saudi Pharm J. (2018) 26:1051–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.05.014
98. Mamnoon B, Feng L, Froberg J, Choi Y, Sathish V, Mallik S. Hypoxia-responsive, polymeric nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery to estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell spheroids. Mol Pharm. (2020) 17:4312–22. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00754
99. Yasothamani V, Karthikeyan L, Shyamsivappan S, Haldorai Y, Seetha D, Vivek R. Synergistic effect of photothermally targeted nir-responsive nanomedicine-induced immunogenic cell death for effective triple negative breast cancer therapy. Biomacromolecules. (2021) 22:2472–90. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00244
100. Eluu SC, Obayemi JD, Yiporo D, Salifu AA, Oko AO, Onwudiwe K, et al. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (lhrh)-conjugated cancer drug delivery from magnetite nanoparticle-modified microporous poly-di-methyl-siloxane (pdms) systems for the targeted treatment of triple negative breast cancer cells. J Funct Biomater. (2024) 15:209. doi: 10.3390/jfb15080209
101. Zeng X, Wang H, Zhang Y, Xu X, Yuan X, Li J. Ph-responsive hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for enhanced triple negative breast cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. (2022) 17:1437–57. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S360500
102. Puluhulawa LE, Joni IM, Elamin KM, Mohammed A, Muchtaridi M, Wathoni N. Chitosan-hyaluronic acid nanoparticles for active targeting in cancer therapy. Polymers (Basel). (2022) 14:3410. doi: 10.3390/polym14163410
103. Zhang Y, Hu H, Tang W, Zhang Q, Li M, Jin H, et al. A multifunctional magnetic nanosystem based on “two strikes” effect for synergistic anticancer therapy in triple-negative breast cancer. J Control Release. (2020) 322:401–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.03.036
Keywords: breast cancer, nanomaterials, anticancer drugs, drug resistance, targeted therapy
Citation: Guan C, Han Y, Ling Z, Meng X, Zhang B, Dong W, Zhang D and Chen K (2024) Nanomaterials: breaking the bottleneck of breast cancer drug resistance. Front. Immunol. 15:1492546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1492546
Received: 07 September 2024; Accepted: 28 October 2024;
Published: 13 November 2024.
Edited by:
Teruyoshi Sasayama, Kyushu University, JapanReviewed by:
Nian-Qiu Shi, Jilin Medical University, ChinaWentao Liu, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2024 Guan, Han, Ling, Meng, Zhang, Dong, Zhang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Keyan Chen, a3ljaGVuQGNtdS5lZHUuY24=; Wanwei Dong, d3dkb25nQGNtdS5lZHUuY24=; Di Zhang, ZHpoYW5nODdAY211LmVkdS5jbg==
 Chao Guan
Chao Guan Yahao Han2
Yahao Han2 Keyan Chen
Keyan Chen