- 1Medical School, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
- 2Institute of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Science, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Hengyang, Hunan, China
- 3Laboratory Medicine Center, Shenzhen Luohu Hospital Group, the Third Affiliated Hospital (The Affiliated Luohu Hospital) of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
- 4First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China
- 5Department of Preventive Medicine, Medical School, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) is a member of the AKR1B subfamily. It is mainly found in cytoplasm, and it is typically expressed in the stomach and intestines. Given that its expression is low or absent in other tissues, AKR1B10 is a potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for various digestive system diseases. Here, we review recent research progress on AKR1B10 in digestive system tumors such as hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, pancreatic carcinoma, oral squamous cell carcinoma, laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma, over the last 5 years. We also discuss the current trends and future research directions for AKR1B10 in both oncological and non-oncological diseases to provide a scientific reference for further exploration of this gene.
1 Introduction
AKR1B10 is an NADPH-dependent reductase belonging to subfamily 1B of the aldo-keto reductases (AKRs). It was first discovered by Professor De-Liang Cao in 1998 (1). AKR1B10 encodes proteins that catalyze the reduction of aldehydes, ketones, and quinones. It interacts with heat- shock protein 90α and regulates lipid synthesis via acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase α (ACCα), thereby playing a central role in cancer lipid metabolism (2).
According to RNA-sequencing and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis, the enzyme is highly expressed in the stomach, small intestine, and colon, but its expression is downregulated in gastrointestinal (GI) cancers and inflammatory bowel disease (3–7). At the same time, it is increased in normal tissues such as the liver, thymus, and prostate. Its expression is upregulated in the presence of cancer, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and certain skin diseases (8–11). Further, the expression of this enzyme is elevated in cancer cells that are resistant to clinical anticancer drugs such as ethoxyquin, doxorubicin, and lipopolysaccharide (12–14), suggesting a potential association between the AKR1B10 expression and resistance to chemotherapy. This underscores the growing evidence that AKR1B10 could be a promising target for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors and other related diseases (11).
In this paper, we review the research progress on AKR1B10 in digestive system tumors in the last 5 years, and provide a reference for the subsequent research of AKR1B10 in more diseases.
2 Structure and function of AKR1B10
2.1 AKR1B10 structure
Based on sequence similarity, the AKR family is divided into 16 major classes, namely, AKR1-AKR16, with each number representing a different class, and each family is further divided into subfamilies based on >60% sequence homology with each other. There have been 15 AKR family members identified thus far, including AKR1A, AKR1B, AKR1C, AKR1E, AKR6A, and AKR7A subfamilies. Among them, AKR1B1, AKR1B10, and AKR1B15 in the AKR1B subfamily have been widely studied for their role in tumors (11–15). AKR1B10 shares more than 68% homology with AKR1B1 and up to 91.5% homology with AKR1B15 (1, 16, 17), so AKR1B10 is often compared to both in studies of enzymatic function and inhibitors.
Structurally, AKR1B10 contains beta strands, alpha helices, and turn features, as well as a macrocycle that controls substrate specificity and a conserved cofactor- binding domain. A total of 35 posttranslational modifications have been predicted for AKR1B10, including phosphorylation modifications at 16 sites, acetylation modifications at 10 sites, ubiquitination modifications at 6 sites, nitrosylation modifications at 2 sites, and glycosylation modification at 1 site (18–20) (Figure 1). However, further exploration is needed to determine the actual function of these modification sites.
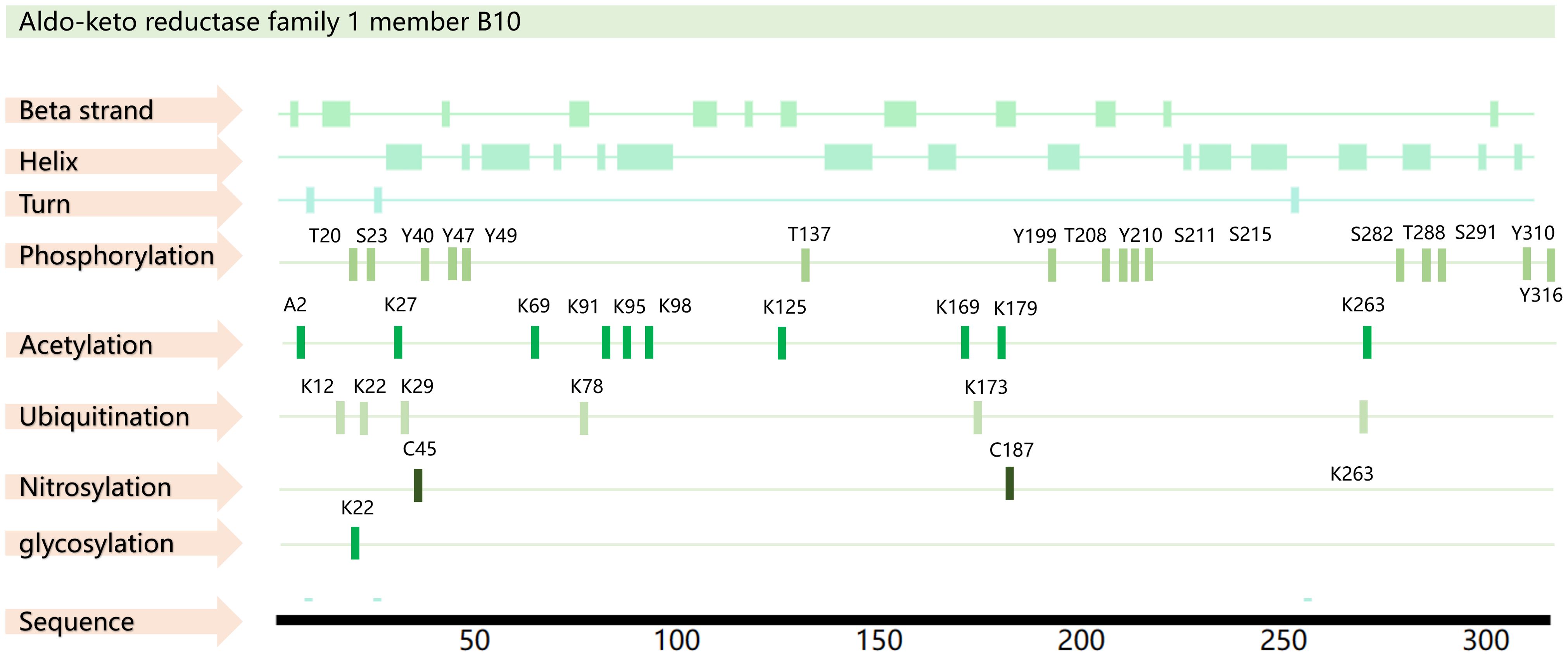
Figure 1. AKR1B10 sequence and PTM sites. The amino acid sequence of AKR1B10 was obtained from the UniProt database (https://www.uniprot.org/), and the PTM sites were obtained from the PhosphoSitePlus database(https://www.phosphosite.org/) and PTMcode 2 database(PTMcode 2: Home (embl.de)).
2.2 AKR1B10 function
AKR1B10, also known as AKR1B11, exhibits catalytic activity for all-trans retinaldehyde, H+, and NADPH (21, 22). It facilitates the reduction of aldehydes and ketones carboxylic compounds, thereby mitigating damage to proteins and DNA. This detoxification helps to maintain cellular homeostasis and thereby protects the cells. Its potent retinaldehyde reductase activity can indirectly influence cell differentiation (23). This enzyme also interacts with ACCα to inhibit apoptosis by upregulating ACCα expression to promote lipid synthesis, reduce mitochondrial membrane damage, and inhibit cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation (24, 25).
3 AKR1B10 and tumors of the digestive system
The development of tumors necessitates a restructuring of cellular metabolism, which underscores the significance of understanding the role of metabolism in tumorigenesis. Metabolic alterations are a notable hallmark of tumors and can profoundly affect various functions of both normal and cancerous cells, including cell proliferation and migration. Progression of gastrointestinal (GI) tumors is closely related to metabolism; thus, metabolomics studies offer fresh perspectives on the metabolic mechanisms of GI tumors. The principal metabolic changes associated with tumors encompass abnormal uptake of glucose and amino acids, and the generation of essential substances and NADPH through metabolic pathways (26). Functioning as an NADPH-dependent reductase, AKR1B10 assumes a critical role in metabolic activities, such as lipid synthesis, transport, oxidation, drug metabolism, and cellular signaling. Further, AKR1B10 stands as a key participant in the cellular antioxidant defense mechanism, essential for maintaining intracellular redox homeostasis via reduction reactions (11, 25).
The mRNA and protein levels of 12 known AKR family members, namely, AKR1A1, AKR1B1, AKR1B10, AKR1B15, AKR1C1, AKR1C2, AKR1C3, AKR1C4, AKR1D1, AKR1E2, AKR7A2, and AKR7A3, have been evaluated by next-generation sequencing (NGS) and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Most of the AKR isoforms were found to be highly expressed in the duodenum and jejunum regions, and the expression declined toward the rectum, with AKR1B10 having the highest expression level (27–29). Consequently, conducting thorough research into the connection between AKR1B10 and GI tumors holds significant promise (Figure 2).
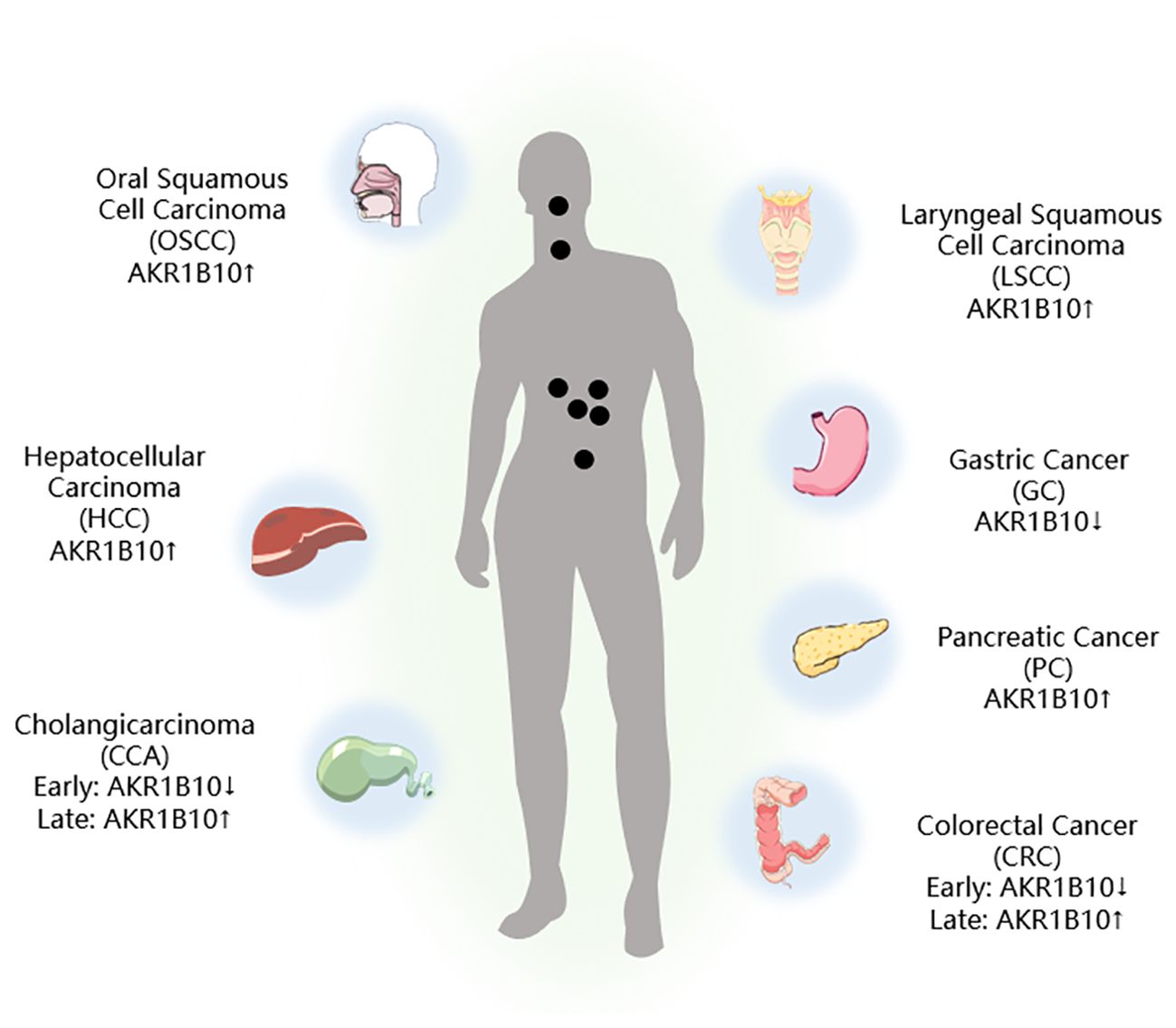
Figure 2. AKR1B10 expression in digestive tract tumors. ↑: Upregulation of AKR1B10 expression; ↓: Downregulation of AKR1B10 expression.
3.1 AKR1B10 and liver cancer
Lipids are mainly processed and metabolized in the liver. Under normal conditions, the liver can break down excess cholesterol, triacylglycerols, and glycerophospholipids, and re-release them into the blood circulation. Liver processes that act on lipids include fatty acid synthesis (FAS) and fatty acid oxidation (FAO). When the liver function is affected by the environment, drugs, genetics, and diseases and cannot synthesize and metabolize lipids properly, excess lipids accumulate in the liver, affecting its function and gradually forming fatty liver, then cirrhosis, and ultimately developing into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (30–33).
HCC is the most prevalent form of liver cancer. It is known for its aggressive nature, and ranks among the top three causes of cancer-related deaths globally (34). Despite advancements in diagnostic techniques and surgical treatments, the 5-year survival rate for patients with advanced HCC remains low, which is largely a consequence of the challenge of early detection (35).
It has been demonstrated that HCC can evolve from NAFLD, and AKR1B10 expression is upregulated in NAFLD, which is consistent with AKRB10 expression in HCC cells (9). In HCC, changes in lipid metabolic processes, such as FAS and FAO, can affect cancer cell proliferation compared with normal tissues. Specifically, upregulation of FAS may provide cancer cells with lipids required for the construction of new cell membranes, while an increase in FAO may provide additional energy to support rapid proliferation of cancer cells. Consequently, inhibiting the FAS and FAO processes may reduce the energy supply to HCC cells, and limit their growth (36). Blocking AKR1B10 expression leads to cell cycle arrest and impaired cell proliferation, indicating a potential tumorigenic role for AKR1B10 in promoting cell growth (37).
The results of a meta-analysis have shown that high expression of AKR1B10 predicts a favorable prognosis after hepatectomy (38). AKR1B10 has an overall sensitivity and specificity of 78% and 85%, respectively, for diagnosing HCC, and it appears more sensitive than alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) for detecting early-stage HCC. Further, combining AKR1B10 and AFP shows higher sensitivity and specificity for HCC diagnosis compared with using AKR1B10 or AFP alone (38). However, in the current state of research, AKR1B10 has not been widely used as a predictive test for HCC compared to AFP in clinical applications, and further comprehensive studies or large randomized controlled multicenter trials are required to delve deeper into the clinical significance of AKR1B10 in patients with HCC.
The researchers used the DepMap dataset to analyze AKR1B10 by gene effector CRISPR (DepMap Public 22Q4 + Score, Chronos) and found that upregulation of AKR1B10 expression is associated with poorer overall survival, and that HCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion are influenced by AKR1B10 activity (39). Mechanistically, AKR1B10 increases the expression of cell proliferation and the EMT-associated proteins CCND1, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, vimentin, and Twist1. AKR1B10 knockdown results in decreased levels of PI3K and AKT phosphorylation, suggesting that AKR1B10 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cell through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and this pathway has an important reference value for the assessment of HCC (39–43).
According to Liu et al., during the progression of HCC, AKR1B10 may be expressed as a compensatory mechanism to protect hepatocytes from oxidative stress (44). This upregulation could be a response to chronic liver disease and hepatocarcinogenesis, while the absence of AKR1B10 might accelerate hepatotoxin and inflammation-related hepatocarcinogenesis. Therefore, rather than being a driver of malignant transformation during HCC development, increased AKR1B10 expression in HCC may be a compensatory mechanism.
3.2 AKR1B10 and gastric cancer
Gastric cancer (GC) is a widespread malignant tumor with a grim prognosis (45). The expression of AKR1B10 in GC tissues is markedly lower than that in normal gastric tissues. In addition, clinicopathological factors suggest that increased AKR1B10 expression predicts a poor prognosis in patients with GC undergoing resection (46).
The proliferation and spread of GC cells are driven by the abnormal activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and EMT can be activated by factors such as TGF-β and mesenchymal markers (Slug, vimentin, and α-SMA), which promote cancer development. Selective inhibition of heparinase with suramin can inversely inhibit EMT activation and thereby retard the proliferation and migration of GC cells (47, 48). Notably, in early GC, all of the water-soluble compounds and volatile metabolites explored were found to be lipids, hinting at a close tie between abnormal lipid metabolism and GC development (49). Furthermore, AKR1B10 plays a role in lipid synthesis, cellular metabolism, and fatty acid oxidation. Investigating the link between AKR1B10 and GC is an intriguing area of study (25). It has been confirmed that AKR1B10 exerts a regulatory influence on EMT, which is inversely linked to with tumor volume, infiltration depth, and metastasis. Moreover, its positivity serves as a predictor of a better 5-year survival rate for patients with GC (50).
However, in contrast to the above results, Ahmed et al. verified that AKR1B10 was expressed predominantly in the cytoplasm of GC cells and that positive expression of AKR1B10 was associated with lymph node metastasis and poorer tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, which indicated a poorer prognosis for the patient (7, 46). A meta-analysis has shown that AKR1B10 expression is actually not associated with overall patient survival (51). These differences may be related to a number of factors, including the different reagent products, antibody brands, and sample sources used by investigators to validate in vivo, and in vitro experiments. Specifically, reagents from different manufacturers may vary in purity, activity, and stability, all of which may affect the consistency and reproducibility of experimental results. Similarly, antibodies from different brands may differ in specificity and affinity, which in turn may affect the accuracy of the experiment. In addition, the diversity of sample sources, such as genetic backgrounds, pathological states, and environmental exposures of different individuals, may also have a significant impact on experimental results. Therefore, to ensure the reliability and validity of experimental results, we suggest that these potential sources of variation should be fully considered in experimental design and data analysis, and appropriate measures should be taken to control and correct the effects of these variables.
Integrin subunit alpha 5 (ITGA5) is involved in cell surface adhesion and signaling. It is upregulated in GC tissues and cells. Salvage experiments have suggested that AKR1B10 may act as a potential tumor suppressor in GC, inhibiting the migration, invasion, and adhesion of GC cells by modulating ITGA5 expression (52). However, the regulatory mechanism of AKR1B10 on ITGA5, as well as how both affect the proliferation and migration of GC cells, remain unproven, and the available data are insufficient to support further studies.
The feasibility of targeting AKR1B10 is unclear due to the differences in its expression in GC and other tumors, as well as the discrepancies in findings between different investigators (35, 53). Few studies have confirmed the value of AKR1B10 in diagnosis, and prognosis prediction, and in-depth mechanistic studies are lacking. Therefore, it is important to further investigate whether AKR1B10 can be a potential target for GC treatment.
3.3 AKR1B10 and colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a prevalent and lethal form of cancer worldwide. Its intricate mechanisms hamper the effectiveness of treatments for advanced cases. Therefore, gaining insight into the mechanisms underlying CRC occurrence and progression is crucial for identifying new treatment targets. Previous studies have indicated that unusually low levels of AKR1B10 in the GI tract are closely associated with cancer development (4, 54). Yet, the role of AKR1B10 in CRC development remains poorly understood, making the exploration of its role and molecular mechanism in CRC an active area of research.
The gene AKR1B10 is typically found in intestinal epithelial cells, but its expression is low in the early stages of CRC and increases as the cancer progresses. Both in vitro and in vivo functional assays have shown that AKR1B10 expression is downregulated in CRC and is linked to the patients’ clinicopathological status (3). Deletion of AKR1B10 has been found to enhance the proliferation and migration of CRC cells in vitro, whereas overexpression of AKR1B10 has the opposite effect. In addition, patients with high AKR1B10 expression have been shown to have longer overall survival (6).
Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) plays a critical role in maintaining lipid and metabolic homeostasis, and it exhibits anti-inflammatory effects (55, 56). This suggests that FGF1 could potentially affect tumor progression through its influence on metabolic disorders. Further, AKR1B10 shows significant association with FGF1 gene and protein levels. In vivo experiments have shown that downregulation of AKR1B10 promotes tumor growth and increases FGF1 expression, suggesting that AKR1B10 may play a tumor-suppressive role in CRC by decreasing the level of FGF1 (3). In vitro studies have also demonstrated that ectopic expression of AKR1B10 significantly inhibits the proliferation, clone formation, and migration of CRC cells (54).
Liu et al. demonstrated for the first time that the expression of AKR1B10 significantly correlated with the TNM stage and clinical stage of human colon cancer. Moreover, they found that AKR1B10 promoted the production of IL-1α and IL-6 in colon cancer cells through the activation of NF-κB, and the proliferation of cancer cells was inhibited by knocking down AKR1B10, which contrasts some previous findings (57). This may be closely related to AKR1B10’s aldose reductase activity, whose protumorigenic effects are attenuated upon inhibition of the inflammatory factors IL-1α and IL-6, thereby inhibiting tumor cell growth. The latest study has shown that AKR1B10 was positive in only 12.16% of the tumor tissues of 592 patients with CRC, while AKR1B10 was not detected in 63.13% of tumor tissues, so it is speculated that AKR1B10 may be an oncogenic factor rather than a prognostic indicator for CRC (58).
In the examination of AKR1B10 in relation to autophagy, it has been discovered that when AKR1B10 interacts with GAPDH, it can trigger an NADPH-dependent reduction reaction, leading to the reduction of GAPDH. This prevents the translocation of GAPDH into the nucleus, thereby impeding autophagy progression during glucose deprivation. This study implies that not only does AKR1B10 hinders the nuclear translocation of GAPDH by interacting with it, but it also obstructs the conversion of normal cells to cancer cells by suppressing the downregulation of autophagy through AMPK phosphorylation (59). These findings offer valuable insights into the regulation of autophagy in human colon cancer.
Further, there is evidence suggesting that elevated levels of arachidonic acid (AA) can disrupt the gut microbial balance, thereby potentially contributing to the development of CRC. The drug inhibition assay revealed that AA had an inhibitory effect on AKR1B10 with an IC50 value of 1.1 μM, and was able to effectively inhibit AKR1B10-mediated 4-oxo-2-nonenal metabolism (60). In previous studies, CRC has usually been associated with inflammation and intestinal flora, which are also closely related to metabolic processes. There are no data to support whether AKR1B10 affects the development of CRC through changes in the inflammatory microenvironment or flora, suggesting that we can start from this direction in our future work to reveal the role of AKR1B10 in the inflammatory microenvironment and the intestinal flora of CRC.
3.4 AKR1B10 and pancreatic cancer
Risk factors for pancreatic cancer (PC) are closely associated with lifestyle, diet, environment, genetic factors, and genetic environmental interactions (61). Commonly recognized risk factors for PC development include smoking and chronic pancreatitis (62, 63). Excessive accumulation of nutrients and metabolites can also disrupt the body’s metabolic environment, potentially leading to direct carcinogenic effects (64, 65). Overexpression of AKR1B10 has been identified in smoking-related cancers, such as lung cancer. Since the development of PC is closely related to smoking, and AKR1B10 can be activated by tobacco-associated oncogenic transcription factors (66, 67), it has been hypothesized that AKR1B10 expression is upregulated in human PC, which was confirmed by immunohistochemical (IHC) results (68, 69).
Upon evaluating the expression and enzymatic activity of AKR1B10 in isolated human PC samples, it has been observed that AKR1B10 expression is notably increased in pancreatic precursor lesions and invasive adenocarcinomas. Knocking down AKR1B10 in PC cells results in the inhibition of the Kras and its downstream Kraf/MEK/ERK pathway, along with the upregulation of E-cadherin expression (70). This leads to the suppression of the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of PC cells. In summary, the downregulation of AKR1B10 expression is linked to heightened apoptosis, decreased protein prenylation, and inhibited Kras and its downstream effectors activation. Targeting protein prenylation, including AKR1B10 and Kras and its downstream pathways, and inducing apoptosis hold substantial promise for future research (68).
Checkpoint Suppressor 1 (CHES1) is a member of the forehead box (Fox) family of proteins that inhibit PC proliferation and invasion by regulating cellular senescence. Proteomic analyses have shown that CHES1 inhibits AKR1B10 expression, thereby suppressing PC cell activity and senescence phenotype (71). This not only suggests the feasibility of inhibiting PC progression from the CHES1/AKR1B10 signaling pathway, but also provides new ideas for cellular senescence therapies.
3.5 AKR1B10 and oral cancer
There are various histological types of oral cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma derived from epithelial cells, adenocarcinoma from salivary glands, lymphoma from tonsils, and melanoma from melanin-producing cells. Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the most prevalent tumor, accounting for approximately 90% of oral cancers (72). In Southeast Asia, OSCC is primarily linked to the use of tobacco, alcohol, and particularly betel nut (73).
There is a significant correlation between AKR1B10 and tumor size, perineural infiltration, and recurrence in OSCC (74). Elevated expression of AKR1B10 is associated with poor overall survival in OSCC, suggesting its potential as a prognostic marker (51). High levels of salivary AKR1B10 may also be linked to disease progression and poor prognosis in OSCC (75). Combining AKR1B10 immunostaining with clinicopathological features enables the categorization of patients into different risk groups, which could aid in better clinical management of OSCC and the identification of effective targeted therapies for AKR1B10-associated malignancies (74). In addition, metabolomics analysis has revealed potential disruptions in amino acid and lipid metabolism in patients with OSCC, emphasizing the link between OSCC and AKR1B10 (76). However, further research is needed to delve into the molecular mechanisms underlying the role of AKR1B10 in OSCC.
3.6 AKR1B10 and laryngeal cancer
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) originates from the epithelial tissue of the laryngeal mucosa and accounts for 90% all of laryngeal cancers (77, 78). Despite advancements in surgery and radiotherapy, the mortality rate of LSCC remains high. Consequently, there is a growing focus on exploring the molecular mechanisms involved in LSCC development and devising new therapeutic approaches.
Liu et al. observed high expression of AKR1B10 in LSCC, with its level of expression being inversely associated with differentiation and positively correlated with tumor size (79). Moreover, AKR1B10 has been found to be overexpressed in Hep-2 laryngeal carcinoma cells, and inhibiting its activity and expression in these cells with oleanolic acid resulted in inhibited proliferation, migration, and invasion (79). The microenvironment of LSCC is also influenced by glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and nitrogen metabolism (80–83). Thus, it is plausible that AKR1B10 expression is linked to LSCC development, and it stands as one of the potential prognostic indicators for the condition. However, the existing studies on AKR1B10 in LSCC are limited, and further studies with an ample number of samples are required to quantify AKR1B10 expression at the tissue level for a more comprehensive understanding of how AKR1B10 influences the phenotype of LSCC.
3.7 AKR1B10 and biliary cancer
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a relatively rare type of cancer within the digestive system, but it is the most common aggressive malignant tumor of the biliary tract. It is closely associated with metabolism and is the second most prevalent primary malignant tumor of the liver, following HCC. CCA mainly originates from the epithelium of the bile ducts and can affect the entire biliary tract (84, 85). Changes in amino acid and lipid metabolism during the development of CCA provide ample nutrients for the growth and spread of cancer cells (86). This underscores the close relationship between CCA and metabolism. Diagnosis of CCA is often delayed due to the lack of obvious clinical symptoms, resulting in many patients having reached advanced stages at the time of diagnosis. Limited understanding of the molecular mechanisms of CCA further restricts early diagnosis and treatment.
According to the IHC analysis, AKR1B10 expression is upregulated during the middle and early stages of high differentiation, and downregulated in the later stage of low differentiation in CCA (87). This indicates that AKR1B10 could serve as a valuable marker for CCA proliferation and differentiation. Cai et al. revealed an upregulation pattern of AKR1B10 expression and its oncogenic effects in CCA. Their investigation of genes associated with AKR1B10 led to the discovery that the tumor-promoting function of methyltransferase 3 (METTL3) relied on the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification of AKR1B10. Further, they found that the knockdown of AKR1B10 reversed the tumor-promoting effects induced by METTL3 overexpression (88). These findings open up new avenues for future studies on the role of AKR1B10 in tumors.
4 AKR1B10 inhibitors
The differential expression of AKR1B10 in tumor and normal tissues has prompted the exploration of its role in tumor therapy. The quest for effective AKR1B10 inhibitors has the potential to enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy and open up new prospects for clinical cancer treatment. These inhibitors can be broadly categorized into four groups, namely, aldose reductase inhibitors (ARIs), endogenous substances, and natural and chemically synthesized sources (89). Among natural inhibitors, frangula emodin, aloe emodin, frangulin A, and frangulin B have demonstrated superior inhibition of AKR1B10 compared with AKR1B1, with IC50 values falling within the low micromolar range (3.5-16.6 μM) (90). Oleanolic acid, a triterpenoid, stands as an earlier and widely used natural inhibitor, exhibiting higher selectivity for AKR1B10 compared with AKR1B1, potentially attributed to the nonconserved residues Val301 and Gln303 in AKR1B10 (91). In addition, the aldose reductase inhibitor epalrestat, despite its potential for causing DNA damage, when combined with drugs such as sorafenib and doxorubicin, enhances the sensitivity of cancer cells to the drug (92, 93). 7-Hydroxy-2-oxo-2H-chromene-3-carboxylic Acid [3 (4-Fluorophenyl) propyl] amide (HCCFA) demonstrates more stable inhibition among chemosynthetic inhibitors (94–96). Moreover, in Ejaz’s computer simulation study, two quinolones, namely, quinine and quinidine, have been anticipated to be potential AKR1B10 inhibitors (97). Overall, the prediction of small molecule drugs targeting AKR1B10 through network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation stands as a promising approach for screening potential inhibitors. Experimental validation in tandem with the screening results will provide a reliable scientific reference for new drug development (Table 1).
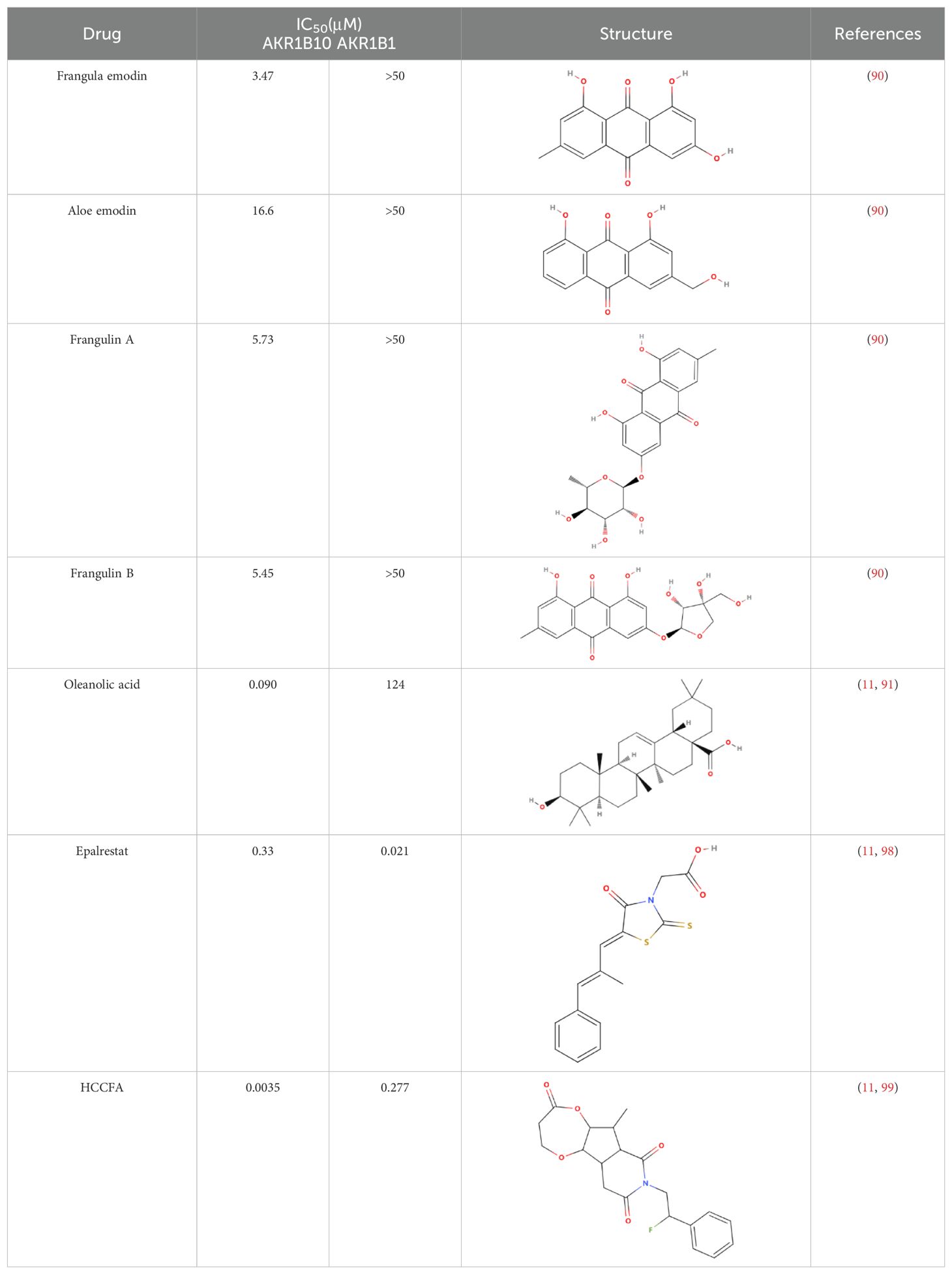
Table 1. Some AKR1B10 inhibitors, and their drug half-inhibitory concentrations (IC50), and chemical structural formulas.
5 Conclusions
AKR1B10, one of the major members of the aldo-keto reductase family, has its gene located on chromosome 7q33 and consists of 316 amino acids, including a total of 13846 bases (100). AKR1B10 is involved in a variety of physiological activities, such as detoxification, and retinoic acid/retinol metabolism, and influences cell survival through the regulation of lipid synthesis, mitochondrial function and oxidative status, and carbonyl levels (101–103) (Figure 3). Since its discovery in 1998, AKR1B10 has been investigated as a potential biomarker in a number of oncological diseases, including breast, lung, endometrial, bladder, and renal cell carcinomas, as well as in a number of chronic diseases, such as alcoholic hepatitis, NAFLD, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (40, 104–110). This paper reviews the research progress on AKR1B10 in liver, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, oral, laryngeal, and bile duct cancers, which are digestive tumor diseases, and emphasizes that, except for the downregulation of AKR1B10 expression in GC and CRC, AKR1B10 is overexpressed in the rest of the solid tumors, and it thus has potential as a diagnostic and prognostic indicator in all of these solid tumors.
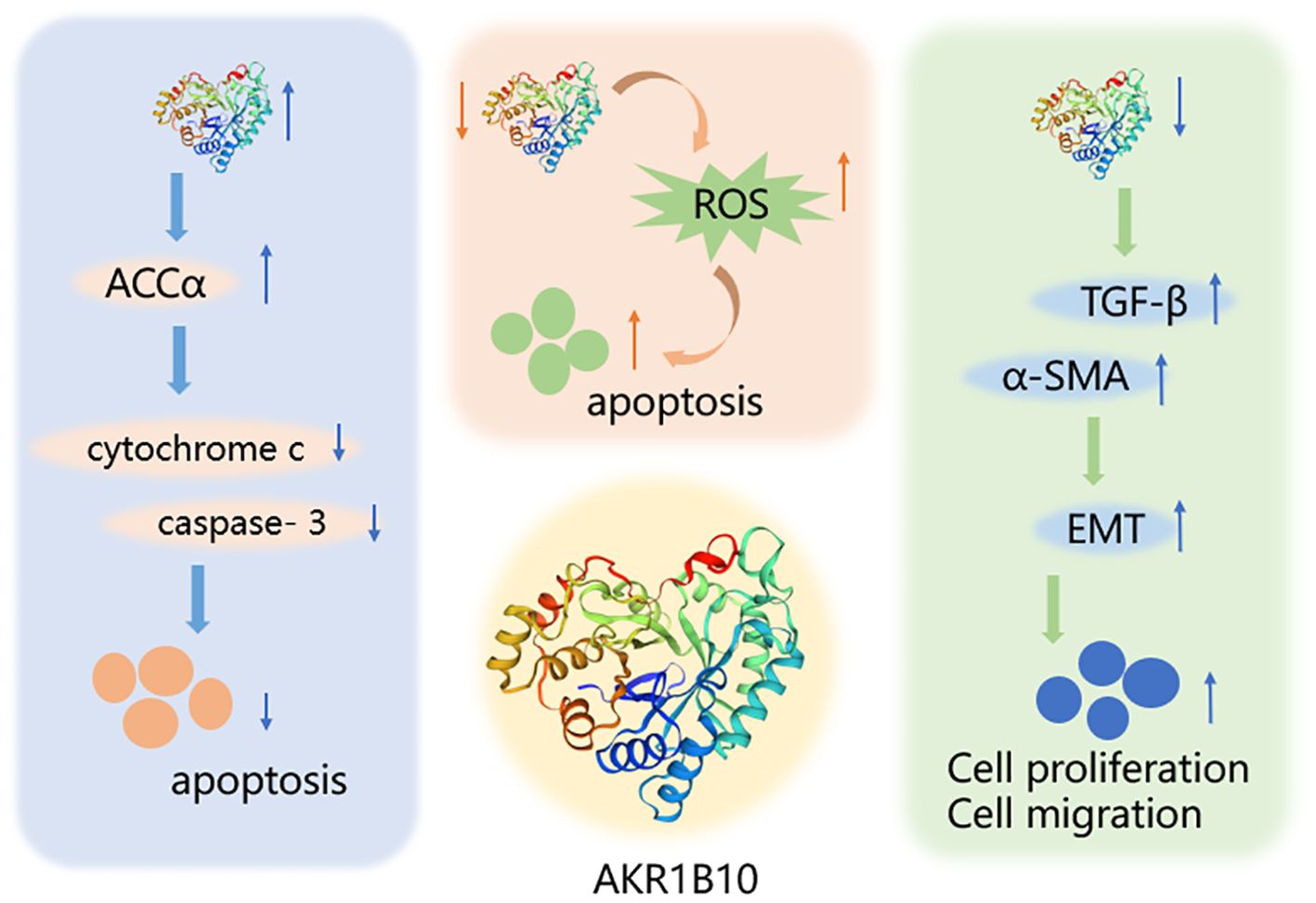
Figure 3. Mechanism of AKR1B10 in digestive system tumors. AKR1B10 can play a role in digestive system tumors by participating in lipid synthesis, oxidative stress, and epithelial mesenchymal transition. An upward arrow indicates an increase in content and a downward arrow indicates a decrease in content.
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) studies have confirmed that HCC cells are significantly more dependent on AKR1B10, an enzyme that plays a crucial role in regulating the proliferation and migration of HCC cells. Importantly, AKR1B10 exhibits a high degree of specificity in HCC, which provides a theoretical basis for the development of specific inhibitors targeting AKR1B10, which are expected to improve patients’ quality of life by producing only minor toxicities in the treatment of HCC (111). In addition, data from large cohort studies further support the diagnostic value of AKR1B10 as a potential HCC serum marker superior to conventional AFP, which may contribute to the early diagnosis and prognostic assessment of HCC (112). Despite the remarkable progress of AKR1B10 in HCC, AKR1B10 and related GWAS studies in other GI tumors are still lacking. Given the multifunctionality of AKR1B10 in metabolism and tumor biology, exploring its expression pattern and function in more GI tumors will be a promising research direction.
The study of AKR1B10 and its relationship with digestive system tumors has revealed its potential role in regulating the proliferation and migration of tumor cells through involvement in the PI3K/AKT and Kras signaling pathways. The development of highly selective AKR1B10 inhibitors offers promising prospects for improving tumor treatment and survival rates for patients with cancer (Figure 4).
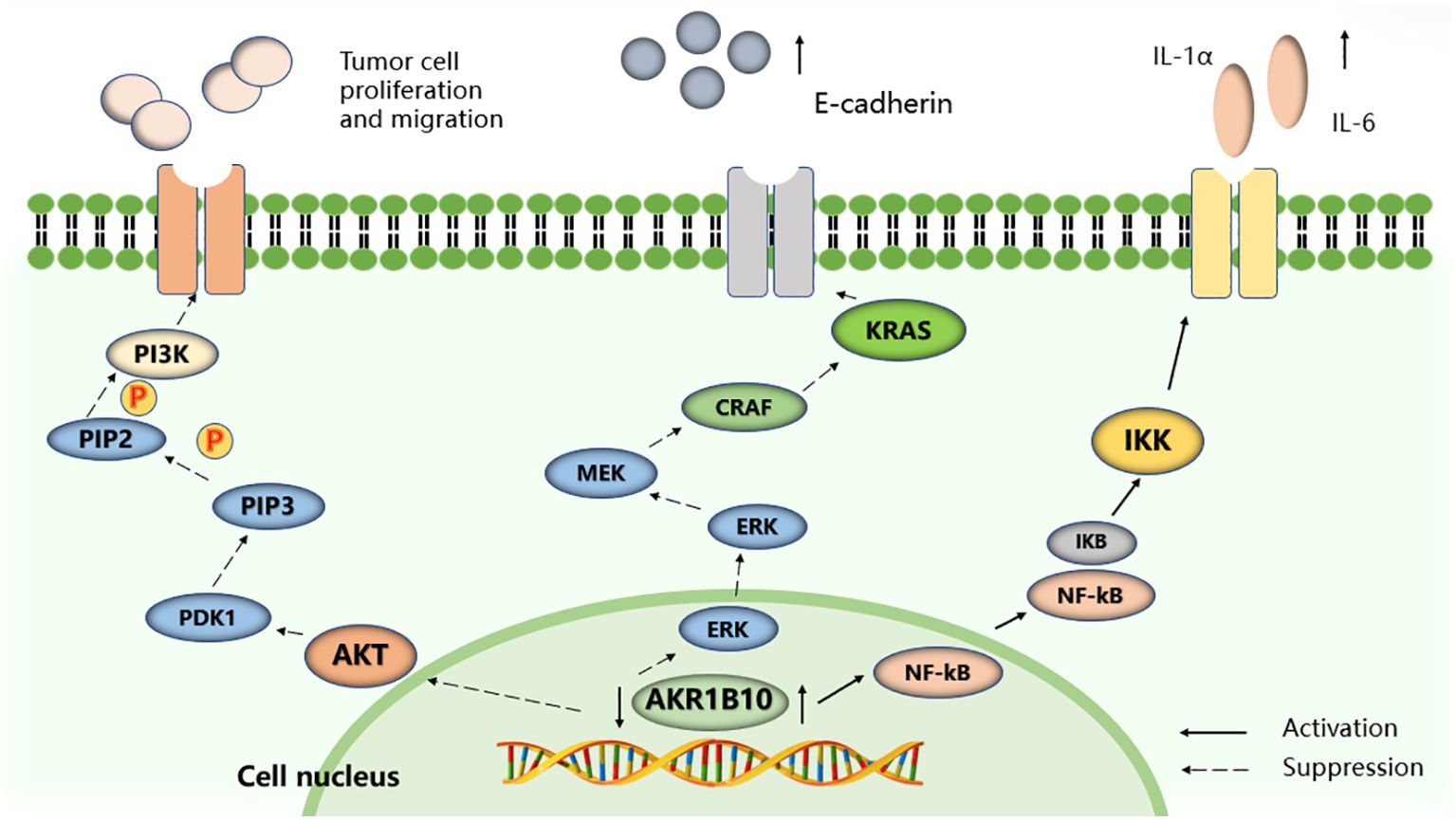
Figure 4. Selected signaling pathways regulated by AKR1B10. AKR1B10 promotes IL-1α and IL-6 production in colon cancer cells by activating the NF-KB signaling pathway. Silencing the expression of AKR1B10 can regulate the Kras-E-cadherin pathway and inhibit the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells, and reduce the phosphorylation level of PI3K and AKT to promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of HCC cells.
It is important to note that tumors are heterogeneous (113), and the pathogenic and metabolic mechanisms of AKR1B10 can differ between different tumor types. The expression of AKR1B10 may also vary across different sites and stages of the same tumor. For example, its expression is high in early to mid-stage HCC, but decreases in advanced stages (114). In addition, AKR1B10 expression is downregulated in pre- CCA, but increases after progression (54). In GC, high expression of AKR1B10 tends to predict a poor prognosis for patients undergoing surgical treatment (7). In addition to the tumor itself affecting AKR1B10, external factors such as therapeutic means and therapeutic drugs, and the nutritional status of the patient may also have an effect on the differential expression of AKR1B10 between different tumors.
Meanwhile, AKR1B10 may play different roles at different stages of tumor development. In the early and proliferative stages of tumors, AKR1B10 may play a tumorigenic role by promoting cell growth and proliferation, which is consistent with our observation that inhibition of AKR1B10 expression resulted in cell cycle arrest and impaired cell proliferation (37). However, in the post hepatectomy setting, high expression of AKR1B10 may be associated with liver repair and regenerative capacity, which may explain the association with favorable prognosis observed in the meta-analysis (38). The complexity of the tumor microenvironment may also contribute to this apparent contradiction. AKR1B10 may play different roles within tumor cells and in the tumor microenvironment, and these roles may affect both tumor growth and patient prognosis. Moreover, patient populations differ in terms of tumor stage, treatment modality, and genetic background, and these factors may collectively influence the relationship between AKR1B10 expression and prognosis.
Metabolic studies in tumors have gained increasing attention from researchers, particularly in addressing key issues such as detection, traceability, and the impact of metabolites on tumor development. Further, there is a growing focus on identifying effective targets involved in metabolic pathways (115, 116).
In summary, the exploration of AKR1B10 expression in tumors, investigation of its interactions, and research of the molecular mechanisms of AKR1B10 are important research directions. Combining in vivo and in vitro studies with clinical samples will likely yield valuable results, which can significantly contribute to early tumor diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of novel therapeutic approaches in the future.
Author contributions
YS: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AQ: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. XW: Writing – review & editing. SS: Writing – review & editing. YH: Resources, Writing – original draft. QH: Resources, Writing – original draft. JZ: Writing – review & editing. DL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SY: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Shenzhen University Medical-Engineering Interdisciplinary Research Fund Project (2023YG022); the 2023 International Science and Technology Independent Cooperation Project (GJHZ20220913144213025); Shenzhen Natural Science Foundation Project (JCYJ20240813114502004); Open Fund for Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Integrative Pathogen Biology in Chinese and Western Medicine (2022KFJJ08); and Hunan Province Chinese Medicine Research Program Project (2021031).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (China) and the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Union Shenzhen Hospital (China)for supporting our study. We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com.cn) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cao D, Fan ST, Chung SS. Identification and characterization of a novel human aldose reductase-like gene. J Biol Chem. (1998) 273:11429–35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.19.11429
2. Huang C, Cao Z, Ma J, Shen Y, Bu Y, Khoshaba R, et al. AKR1B10 activates diacylglycerol (DAG) second messenger in breast cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. (2018) 57:1300–10. doi: 10.1002/mc.22844
3. Yao Y, Wang X, Zhou D, Li H, Qian H, Zhang J, et al. Loss of AKR1B10 promotes colorectal cancer cells proliferation and migration via regulating FGF1-dependent pathway. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:13059–75. doi: 10.18632/aging.103393
4. Dai GP, Wang LP, Wen YQ, Ren XQ, Zuo SG. Identification of key genes for predicting colorectal cancer prognosis by integrated bioinformatics analysis. Oncol Lett. (2020) 19:388–98. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11068
5. Shen Y, Ma J, Yan R, Ling H, Li X, Yang W, et al. Impaired self-renewal and increased colitis and dysplastic lesions in colonic mucosa of AKR1B8-deficient mice. Clin Cancer Res. (2015) 21:1466–76. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2072
6. Zu X, Yan R, Pan J, Zhong L, Cao Y, Ma J, et al. Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 protects human colon cells from DNA damage induced by electrophilic carbonyl compounds. Mol Carcinog. (2017) 56:118–29. doi: 10.1002/mc.22477
7. Ahmed S, Jiang ZN, Zheng ZH, Li Y, Wang XJ, Tang X. AKR1B10 expression predicts response of gastric cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Lett. (2019) 17:773–80. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9705
8. Gao Y, Yi X, Ding Y. Combined transcriptomic analysis revealed AKR1B10 played an important role in psoriasis through the dysregulated lipid pathway and overproliferation of keratinocyte. BioMed Res Int. (2017) 2017:8717369. doi: 10.1155/2017/8717369
9. Zeng F, Zhang Y, Han X, Zeng M, Gao Y, Weng J. Predicting non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression and immune deregulations by specific gene expression patterns. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:609900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.609900
10. Feng G, Li XP, Niu CY, Liu ML, Yan QQ, Fan LP, et al. Bioinformatics analysis reveals novel core genes associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gene. (2020) 742:144549. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144549
11. Endo S, Matsunaga T, Nishinaka T. The role of AKR1B10 in physiology and pathophysiology. Metabolites. (2021) 11:332. doi: 10.3390/metabo11060332
12. Nishinaka T, Miura T, Okumura M, Nakao F, Nakamura H, Terada T. Regulation of aldo-keto reductase AKR1B10 gene expression: involvement of transcription factor Nrf2. Chem Biol Interact. (2011) 191:185–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2011.01.026
13. Morikawa Y, Kezuka C, Endo S, Ikari A, Soda M, Yamamura K, et al. Acquisition of doxorubicin resistance facilitates migrating and invasive potentials of gastric cancer MKN45 cells through up-regulating aldo-keto reductase 1B10. Chem Biol Interact. (2015) 230:30–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.02.005
14. Shaw N, Yang B, Millward A, Demaine A, Hodgkinson A. AKR1B10 is induced by hyperglycemia and lipopolysaccharide in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Cell Stress Chaperones. (2014) 19:281–7. doi: 10.1007/s12192-013-0455-6
15. Singh M, Kapoor A, Bhatnagar A. Oxidative and reductive metabolism of lipid-peroxidation derived carbonyls. Chem Biol Interact. (2015) 234:261–73. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.12.028
16. Gimenez-Dejoz J, Kolar MH, Ruiz FX, Crespo I, Cousido-Siah A, Podjarny A, et al. Substrate specificity, inhibitor selectivity and structure-function relationships of Aldo-Keto Reductase 1B15: A novel human retinaldehyde reductase. PloS One. (2015) 10:e134506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134506
17. Weber S, Salabei JK, Moller G, Kremmer E, Bhatnagar A, Adamski J, et al. Aldo-keto Reductase 1B15 (AKR1B15): a mitochondrial human aldo-keto reductase with activity toward steroids and 3-keto-acyl-CoA conjugates. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290:6531–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.610121
18. Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P. SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. (2021) 49:D458–60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa937
19. Zahn-Zabal M, Michel PA, Gateau A, Nikitin F, Schaeffer M, Audot E, et al. The neXtProt knowledgebase in 2020: data, tools and usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res. (2020) 48:D328–34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz995
20. Barshir R, Fishilevich S, Iny-Stein T, Zelig O, Mazor Y, Guan-Golan Y, et al. GeneCaRNA: A comprehensive gene-centric database of human non-coding RNAs in the geneCards suite. J Mol Biol. (2021) 433:166913. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166913
21. Crosas B, Hyndman DJ, Gallego O, Martras S, Pares X, Flynn TG, et al. Human aldose reductase and human small intestine aldose reductase are efficient retinal reductases: consequences for retinoid metabolism. Biochem J. (2003) 373:973–9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021818
22. Gallego O, Ruiz FX, Ardevol A, Dominguez M, Alvarez R, de Lera AR, et al. Structural basis for the high all-trans-retinaldehyde reductase activity of the tumor marker AKR1B10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2007) 104:20764–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705659105
23. Belyaeva OV, Adams MK, Popov KM, Kedishvili NY. Generation of retinaldehyde for retinoic acid biosynthesis. Biomolecules. (2019) 10:5. doi: 10.3390/biom10010005
24. Guo M, Wang T, Ge W, Ren C, Ko BC, Zeng X, et al. Role of AKR1B10 in inflammatory diseases. Scand J Immunol. (2024) 100:e13390. doi: 10.1111/sji.13390
25. van Weverwijk A, Koundouros N, Iravani M, Ashenden M, Gao Q, Poulogiannis G, et al. Metabolic adaptability in metastatic breast cancer by AKR1B10-dependent balancing of glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:2698. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10592-4
26. Pavlova NN, Zhu J, Thompson CB. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. (2022) 34:355–77. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.01.007
27. Penning TM. The aldo-keto reductases (AKRs): Overview. Chem Biol Interact. (2015) 234:236–46. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.09.024
28. Penning TM, Wangtrakuldee P, Auchus RJ. Structural and functional biology of Aldo-Keto reductase steroid-transforming enzymes. Endocr Rev. (2019) 40:447–75. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00089
29. Hirosawa K, Fujioka H, Morinaga G, Fukami T, Ishiguro N, Kishimoto W, et al. Quantitative analysis of mRNA and protein expression levels of aldo-keto reductase and short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase isoforms in the human intestine. Drug Metab Dispos. (2023) 51:1569–77. doi: 10.1124/dmd.123.001402
30. Badmus OO, Hillhouse SA, Anderson CD, Hinds TD, Stec DE. Molecular mechanisms of metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): functional analysis of lipid metabolism pathways. Clin Sci (Lond). (2022) 136:1347–66. doi: 10.1042/CS20220572
31. Alves-Bezerra M, Cohen DE. Triglyceride metabolism in the liver. Compr Physiol. (2017) 8:1–8. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c170012
32. Alannan M, Fayyad-Kazan H, Trezeguet V, Merched A. Targeting lipid metabolism in liver cancer. Biochemistry-Us. (2020) 59:3951–64. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00477
33. Geng Y, Faber KN, de Meijer VE, Blokzijl H, Moshage H. How does hepatic lipid accumulation lead to lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? Hepatol Int. (2021) 15:21–35. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10121-2
34. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73:17–48. doi: 10.3322/caac.21763
35. DiStefano JK, Davis B. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of AKR1B10 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). (2019) 11:486. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040486
36. Xu Z, Yuan KF. Lipid metabolic reprogramming and metabolic stress in liver cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. (2021) 52:561–5. doi: 10.12182/20210760506
37. Wang J, Zhou Y, Fei X, Chen X, Chen Y. Biostatistics mining associated method identifies AKR1B10 enhancing hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and degenerated by miR-383-5p. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:11094. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29271-3
38. Wang Z, Pei Y, Li W, Zhang J, Liu J. Clinical value of AKR1B10 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e279591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279591
39. Tian K, Deng Y, Li Z, Zhou H, Yao H. AKR1B10 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Lett. (2024) 27:18. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.14151
40. Qu J, Li J, Zhang Y, He R, Liu X, Gong K, et al. AKR1B10 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via the PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. (2021) 11:163. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00677-3
41. Wang C, Yang Z, Xu E, Shen X, Wang X, Li Z, et al. Apolipoprotein C-II induces EMT to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Clin Transl Med. (2021) 11:e522. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.522
42. Wang Y, Li Y, Wang L, Chen B, Zhu M, Ma C, et al. Cinnamaldehyde suppressed EGF-induced EMT process and inhibits ovarian cancer progression through PI3K/AKT pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:779608. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.779608
43. Dian MJ, Li J, Zhang XL, Li ZJ, Zhou Y, Zhou W, et al. MST4 negatively regulates the EMT, invasion and metastasis of HCC cells by inactivating PI3K/AKT/Snail1 axis. J Cancer. (2021) 12:4463–77. doi: 10.7150/jca.60008
44. Liu Y, Zhang J, Liu H, Guan G, Zhang T, Wang L, et al. Compensatory upregulation of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 to protect hepatocytes against oxidative stress during hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Cancer Res. (2019) 9:2730–48.
45. Erratum: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2020) 70:313. doi: 10.3322/caac.21609
46. Liu YY, Liu YW, Huang GK, Hung KC, Lin YH, Yeh CH, et al. Overexpression of AKR1B10 predicts poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients undergoing surgical resection. Curr Oncol. (2022) 30:85–99. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30010007
47. Ramesh V, Brabletz T, Ceppi P. Targeting EMT in cancer with repurposed metabolic inhibitors. Trends Cancer. (2020) 6:942–50. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.06.005
48. Shao X, Wu J, Yu S, Zhou Y, Zhou C. AKR1B10 inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Aging (Albany NY). (2021) 13:22298–314. doi: 10.18632/aging.203538
49. Liu ZC, Wu WH, Huang S, Li ZW, Li X, Shui GH, et al. Plasma lipids signify the progression of precancerous gastric lesions to gastric cancer: a prospective targeted lipidomics study. Theranostics. (2022) 12:4671–83. doi: 10.7150/thno.74770
50. Yao HB, Xu Y, Chen LG, Guan TP, Ma YY, He XJ, et al. AKR1B10, a good prognostic indicator in gastric cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2014) 40:318–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.12.014
51. Liu R, Zheng S, Yang CY, Yu Y, Peng S, Ge Q, et al. Prognostic value of aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) in digestive system cancers: A meta-analysis. Med (Baltimore). (2021) 100:e25454. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025454
52. Yao H, Hu J, Shao Y, Shah Q, Zheng S. Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 restrains cell migration, invasion, and adhesion of gastric cancer via regulating integrin subunit alpha 5. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2023) 34:1197–205. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2023.22555
53. Liu W, Song J, Du X, Zhou Y, Li Y, Li R, et al. AKR1B10 (Aldo-keto reductase family 1 B10) promotes brain metastasis of lung cancer cells in a multi-organ microfluidic chip model. Acta Biomater. (2019) 91:195–208. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.04.053
54. Taskoparan B, Seza EG, Demirkol S, Tuncer S, Stefek M, Gure AO, et al. Opposing roles of the aldo-keto reductases AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 in colorectal cancer. Cell Oncol (Dordr). (2017) 40:563–78. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0351-7
55. Gasser E, Moutos CP, Downes M, Evans RM. FGF1 - a new weapon to control type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2017) 13:599–609. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.78
56. Liang G, Song L, Chen Z, Qian Y, Xie J, Zhao L, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 1 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by an anti-inflammatory mechanism. Kidney Int. (2018) 93:95–109. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.05.013
57. Liu C, Shi L, Li W, Huang Z, Wang S, Xu P, et al. AKR1B10 accelerates the production of proinflammatory cytokines via the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in colon cancer. J Mol Histol. (2022) 53:781–91. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10093-7
58. Ye X, Wang T, Zhong L, Farres J, Xia J, Zeng X, et al. Aldo-keto reductase 1B10 as a Carcinogenic but Not a Prognostic Factor in Colorectal Cancer. J Cancer. (2024) 15:1657–67. doi: 10.7150/jca.91064
59. Li W, Liu C, Huang Z, Shi L, Zhong C, Zhou W, et al. AKR1B10 negatively regulates autophagy through reducing GAPDH upon glucose starvation in colon cancer. J Cell Sci. (2021) 134:jcs255273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.255273
60. Hara A, Endo S, Matsunaga T, Soda M, El-Kabbani O, Yashiro K. Inhibition of aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 by unsaturated fatty acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. (2016) 609:69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2016.09.010
61. Chang KJ, Parasher G, Christie C, Largent J, Anton-Culver H. Risk of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: disparity between African Americans and other race/ethnic groups. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. (2005) 103:349–57. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20771
62. Ru N, Xu XN, Cao Y, Zhu JH, Hu LH, Wu SY, et al. The impacts of genetic and environmental factors on the progression of chronic pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 20:e1378–87. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.08.033
63. Klein AP. Pancreatic cancer epidemiology: understanding the role of lifestyle and inherited risk factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:493–502. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00457-x
64. Ruze R, Song J, Yin X, Chen Y, Xu R, Wang C, et al. Mechanisms of obesity- and diabetes mellitus-related pancreatic carcinogenesis: a comprehensive and systematic review. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:139. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01376-w
65. Zhong H, Liu S, Zhu J, Wu L. Associations between genetically predicted levels of blood metabolites and pancreatic cancer risk. Int J Cancer. (2023) 153:103–10. doi: 10.1002/ijc.34466
66. Cubillos-Angulo JM, Fukutani ER, Cruz L, Arriaga MB, Lima JV, Andrade BB, et al. Systems biology analysis of publicly available transcriptomic data reveals a critical link between AKR1B10 gene expression, smoking and occurrence of lung cancer. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e222552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222552
67. Kang MW, Lee ES, Yoon SY, Jo J, Lee J, Kim HK, et al. AKR1B10 is associated with smoking and smoking-related non-small-cell lung cancer. J Int Med Res. (2011) 39:78–85. doi: 10.1177/147323001103900110
68. Chung YT, Matkowskyj KA, Li H, Bai H, Zhang W, Tsao MS, et al. Overexpression and oncogenic function of aldo-keto reductase family 1B10 (AKR1B10) in pancreatic carcinoma. Mod Pathol. (2012) 25:758–66. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2011.191
69. Connor JP, Esbona K, Matkowskyj KA. AKR1B10 expression by immunohistochemistry in surgical resections and fine needle aspiration cytology material in patients with cystic pancreatic lesions; potential for improved nonoperative diagnosis. Hum Pathol. (2017) 70:77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.10.006
70. Zhang W, Li H, Yang Y, Liao J, Yang GY. Knockdown or inhibition of aldo-keto reductase 1B10 inhibits pancreatic carcinoma growth via modulating Kras-E-cadherin pathway. Cancer Lett. (2014) 355:273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.031
71. Kong D, Wu Y, Tong B, Liang Y, Xu F, Chi X, et al. CHES1 modulated tumorigenesis and senescence of pancreas cancer cells through repressing AKR1B10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167214. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167214
72. Tan Y, Wang Z, Xu M, Li B, Huang Z, Qin S, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinomas: state of the field and emerging directions. Int J Oral Sci. (2023) 15:44. doi: 10.1038/s41368-023-00249-w
73. Lin WJ, Jiang RS, Wu SH, Chen FJ, Liu SA. Smoking, alcohol, and betel quid and oral cancer: a prospective cohort study. J Oncol. (2011) 2011:525976. doi: 10.1155/2011/525976
74. Fang CY, Lin YH, Chen CL. Overexpression of AKR1B10 predicts tumor recurrence and short survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Oral Pathol Med. (2019) 48:712–9. doi: 10.1111/jop.12891
75. Ko HH, Peng HH, Cheng SJ, Kuo MY. Increased salivary AKR1B10 level: Association with progression and poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. (2018) 40:2642–7. doi: 10.1002/hed.25370
76. Li XB, Liu LW, Li N, Jia QQ, Wang XS, Long JL, et al. Identification of serum biomarkers and evaluation of metabolism disorders in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2021) 56:926–32. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20200908-00495
77. Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. (2024) 74:12–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21820
78. Broseghini E, Filippini DM, Fabbri L, Leonardi R, Abeshi A, Dal Molin D, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNAs in patients with laryngeal cancer: A systematic review. Noncoding RNA. (2023) 9:9. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9010009
79. Liu J, Ban H, Liu Y, Ni J. The expression and significance of AKR1B10 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:18228. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97648-y
80. Li JD, Chen Y, Jing SW, Wang LT, Zhou YH, Liu ZS, et al. Triosephosphate isomerase 1 may be a risk predictor in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: a multi-centered study integrating bulk RNA, single-cell RNA, and protein immunohistochemistry. Eur J Med Res. (2023) 28:591. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01568-8
81. Meng X, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Liu P, Liu Z, He Y. Single-cell analyses reveal the metabolic heterogeneity and plasticity of the tumor microenvironment during head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Cancer Res. (2024) 84:2468–83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-1344
82. Liu Y, Liu N, Zhou X, Zhao L, Wei W, Hu J, et al. Constructing a prognostic model for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on glucose metabolism related genes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1245629. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1245629
83. Xiong Y, Si Y, Feng Y, Zhuo S, Cui B, Zhang Z. Prognostic value of lipid metabolism-related genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Immun Inflammation Dis. (2021) 9:196–209. doi: 10.1002/iid3.379
84. Brindley PJ, Bachini M, Ilyas SI, Khan SA, Loukas A, Sirica AE, et al. Cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2021) 7:65. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00300-2
85. Yang PC, Chen YJ, Li XY, Hsiao CY, Cheng BB, Gao Y, et al. Irreversible electroporation treatment with intraoperative biliary stenting for unresectable perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: A pilot study. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:710536. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.710536
86. Raggi C, Taddei ML, Rae C, Braconi C, Marra F. Metabolic reprogramming in cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. (2022) 77:849–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.04.038
87. Heringlake S, Hofdmann M, Fiebeler A, Manns MP, Schmiegel W, Tannapfel A. Identification and expression analysis of the aldo-ketoreductase1-B10 gene in primary Malignant liver tumors. J Hepatol. (2010) 52:220–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.11.005
88. Cai J, Cui Z, Zhou J, Zhang B, Lu R, Ding Y, et al. METTL3 promotes glycolysis and cholangiocarcinoma progression by mediating the m6A modification of AKR1B10. Cancer Cell Int. (2022) 22:385. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02809-2
89. Huang L, He R, Luo W, Zhu YS, Li J, Tan T, et al. Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 inhibitors: potential drugs for cancer treatment. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discovery. (2016) 11:184–96. doi: 10.2174/1574892811888160304113346
90. Westermann M, Adomako-Bonsu AG, Thiele S, Cicek SS, Martin HJ, Maser E. Inhibition of human carbonyl reducing enzymes by plant anthrone and anthraquinone derivatives. Chem Biol Interact. (2022) 354:109823. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109823
91. Takemura M, Endo S, Matsunaga T, Soda M, Zhao HT, El-Kabbani O, et al. Selective inhibition of the tumor marker aldo-keto reductase family member 1B10 by oleanolic acid. J Nat Prod. (2011) 74:1201–6. doi: 10.1021/np200118q
92. Geng N, Jin YY, Zhu SX, Li YR, Zheng LY, Zhu WJ, et al. Aldo-keto reductase family 1 B10 participates in the regulation of hepatoma cell cycle through p27/p-Rb signaling pathway. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2020) 28:861–7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20191113-00418
93. Bailly C. Moving toward a new horizon for the aldose reductase inhibitor epalrestat to treat drug-resistant cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. (2022) 931:175191. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175191
94. Hara A, Endo S, Matsunaga T, Soda M, Yashiro K, El-Kabbani O. Long-chain fatty acids inhibit human members of the aldo-keto reductase 1C subfamily. J Biochem. (2017) 162:371–9. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvx041
95. Endo S, Xia S, Suyama M, Morikawa Y, Oguri H, Hu D, et al. Correction to synthesis of potent and selective inhibitors of Aldo-Keto reductase 1B10 and their efficacy against proliferation, metastasis, and cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells. J Med Chem. (2018) 61:1380. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01911
96. Cousido-Siah A, FX R, Fanfrlik J, Gimenez-Dejoz J, Mitschler A, Kamlar M, et al. IDD388 polyhalogenated derivatives as probes for an improved structure-based selectivity of AKR1B10 inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol. (2016) 11:2693–705. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00382
97. Ejaz SA, Saeed A, Birmani PR, Katubi KM, Elqahtani ZM, Al-Buriahi MS, et al. In-silico Investigations of quinine and quinidine as potential Inhibitors of AKR1B1 and AKR1B10: Functional and structural characterization. PloS One. (2022) 17:e271602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271602
98. Zhang L, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Li Z, Chen S, Zhai J, et al. Inhibitor selectivity between aldo-keto reductase superfamily members AKR1B10 and AKR1B1: role of Trp112 (Trp111). FEBS Lett. (2013) 587:3681–6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.09.031
99. Endo S, Xia S, Suyama M, Morikawa Y, Oguri H, Hu D, et al. Synthesis of potent and selective inhibitors of Aldo-Keto reductase 1B10 and their efficacy against proliferation, metastasis, and cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells. J Med Chem. (2017) 60:8441–55. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00830
100. Gimenez-Dejoz J, Weber S, Fernandez-Pardo A, Moller G, Adamski J, Porte S, et al. Engineering aldo-keto reductase 1B10 to mimic the distinct 1B15 topology and specificity towards inhibitors and substrates, including retinoids and steroids. Chem Biol Interact. (2019) 307:186–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.04.030
101. Wang C, Yan R, Luo D, Watabe K, Liao DF, Cao D. Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 promotes cell survival by regulating lipid synthesis and eliminating carbonyls. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:26742–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.022897
102. Jung YJ, Lee EH, Lee CG, Rhee KJ, Jung WS, Choi Y, et al. AKR1B10-inhibitory Selaginella tamariscina extract and amentoflavone decrease the growth of A549 human lung cancer cells. Vitro vivo J Ethnopharmacol. (2017) 202:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.010
103. Shi L, Guo S, Zhang S, Gao X, Liu A, Wang Q, et al. Glycyrrhetinic acid attenuates disturbed vitamin a metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through AKR1B10. Eur J Pharmacol. (2020) 883:173167. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173167
104. Duan W, Liu W, Xia S, Zhou Y, Tang M, Xu M, et al. Warburg effect enhanced by AKR1B10 promotes acquired resistance to pemetrexed in lung cancer-derived brain metastasis. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:547. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04403-0
105. Hojnik M, Frkovic GS, Verdenik I, Rizner TL. AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 as prognostic biomarkers of endometrioid endometrial carcinomas. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:3398. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143398
106. Huang Z, Yan Y, Zhu Z, Liu J, He X, Dalangood S, et al. CBX7 suppresses urinary bladder cancer progression via modulating AKR1B10-ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:537. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03819-0
107. Zheng L, Zhang X, Pan X, Huang Z, Zhang M, Xian J, et al. AKR1B10 is a new sensitive and specific marker for fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. (2023) 36:100303. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2023.100303
108. Wu Y, Qi Y, Bai Y, Zhang H, Zhu W, Zhou S, et al. LncRNA 1700020I14Rik promotes AKR1B10 expression and activates Erk pathway to induce hepatocyte damage in alcoholic hepatitis. Cell Death Discovery. (2022) 8:374. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01135-w
109. Govaere O, Hasoon M, Alexander L, Cockell S, Tiniakos D, Ekstedt M, et al. A proteo-transcriptomic map of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease signatures. Nat Metab. (2023) 5:572–8. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00775-1
110. Xu W, Gao Y, Zhang J, Zhang R, Chen Q. AKR1B10 expression in benign prostatic hyperplasia and its related mechanism. Oncol Lett. (2021) 22:683. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12944
111. Satow R, Shitashige M, Kanai Y, Takeshita F, Ojima H, Jigami T, et al. Combined functional genome survey of therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2010) 16:2518–28. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2214
112. Du Z, Liu X, Wei X, Luo H, Li P, Shi M, et al. Quantitative proteomics identifies a plasma multi-protein model for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:15552. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72510-9
113. Ma L, Hernandez MO, Zhao Y, Mehta M, Tran B, Kelly M, et al. Tumor cell biodiversity drives microenvironmental reprogramming in liver cancer. Cancer Cell. (2019) 36:418–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.08.007
114. Xie C, Ye X, Zeng L, Zeng X, Cao D. Serum AKR1B10 as an indicator of unfavorable survival of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. (2023) 58:1030–42. doi: 10.1007/s00535-023-02011-9
115. Martinez-Reyes I, Chandel NS. Cancer metabolism: looking forward. Nat Rev Cancer. (2021) 21:669–80. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00378-6
Keywords: AKR1B10, metabolism, mechanisms, review, digestive system tumors
Citation: Shen Y, Qiu A, Huang X, Wen X, Shehzadi S, He Y, Hu Q, Zhang J, Luo D and Yang S (2024) AKR1B10 and digestive tumors development: a review. Front. Immunol. 15:1462174. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462174
Received: 09 July 2024; Accepted: 26 November 2024;
Published: 16 December 2024.
Edited by:
Ze-Kun Liu, Fourth Military Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Dongdong Yan, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesLi Li, University of California, San Francisco, United States
Copyright © 2024 Shen, Qiu, Huang, Wen, Shehzadi, He, Hu, Zhang, Luo and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dixian Luo, bHVvZGl4aWFuXzJAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Shenghui Yang, c2hlbmdodWl5YW5nQDEyNi5jb20=
 Yao Shen
Yao Shen Ailin Qiu2
Ailin Qiu2 Jian Zhang
Jian Zhang Dixian Luo
Dixian Luo Shenghui Yang
Shenghui Yang