- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China
- 2Tianjin Neurological Institute, Key Laboratory of Post-Trauma Neuro-Repair and Regeneration in Central Nervous System, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Injuries, Variations and Regeneration of Nervous System, Tianjin, China
- 3Tianjin Key Laboratory of Injuries, Variations and Regeneration of Nervous System, Tianjin, China
Mitochondria are crucial organelles that play a central role in cellular metabolism and programmed cell death in eukaryotic cells. Mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy) is a selective process where damaged mitochondria are encapsulated and degraded through autophagic mechanisms, ensuring the maintenance of both mitochondrial and cellular homeostasis. Excessive programmed cell death in neurons can result in functional impairments following cerebral ischemia and trauma, as well as in chronic neurodegenerative diseases, leading to irreversible declines in motor and cognitive functions. Neuroinflammation, an inflammatory response of the central nervous system to factors disrupting homeostasis, is a common feature across various neurological events, including ischemic, infectious, traumatic, and neurodegenerative conditions. Emerging research suggests that regulating autophagy may offer a promising therapeutic avenue for treating certain neurological diseases. Furthermore, existing literature indicates that various small molecule autophagy regulators have been tested in animal models and are linked to neurological disease outcomes. This review explores the role of mitophagy in programmed neuronal death and its connection to neuroinflammation.
Introduction
Mitochondria are essential organelles responsible for cellular metabolism and function, generating the majority of the cell’s energy while also regulating cell growth and apoptosis. Damage to these structures can lead to cellular defects and is associated with various diseases (1). Often referred to as the cell’s power source, mitochondria produce most of the ATP required by cells, making them indispensable for eukaryotic life. However, during the functioning of mitochondria, a significant amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated, which can damage mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) (2). When mitochondria are damaged, they can release high levels of Ca2+ and cytochrome c into the cytoplasm, triggering cell apoptosis. Mitophagy, a vital mechanism for maintaining mitochondrial quality, ensures the clearance of damaged mitochondria, which is crucial for preserving cellular and metabolic homeostasis and, ultimately, cell survival (3). Depending on the signals that target damaged or excess mitochondria for degradation, mitophagy can be categorized into four main types: ubiquitin-dependent mitophagy, ubiquitin-independent or receptor-mediated mitophagy, lipid-based mitophagy, and micromitophagy. Of these, ubiquitin-dependent and ubiquitin-independent mitophagy are the most prevalent (4) (Figure 1).
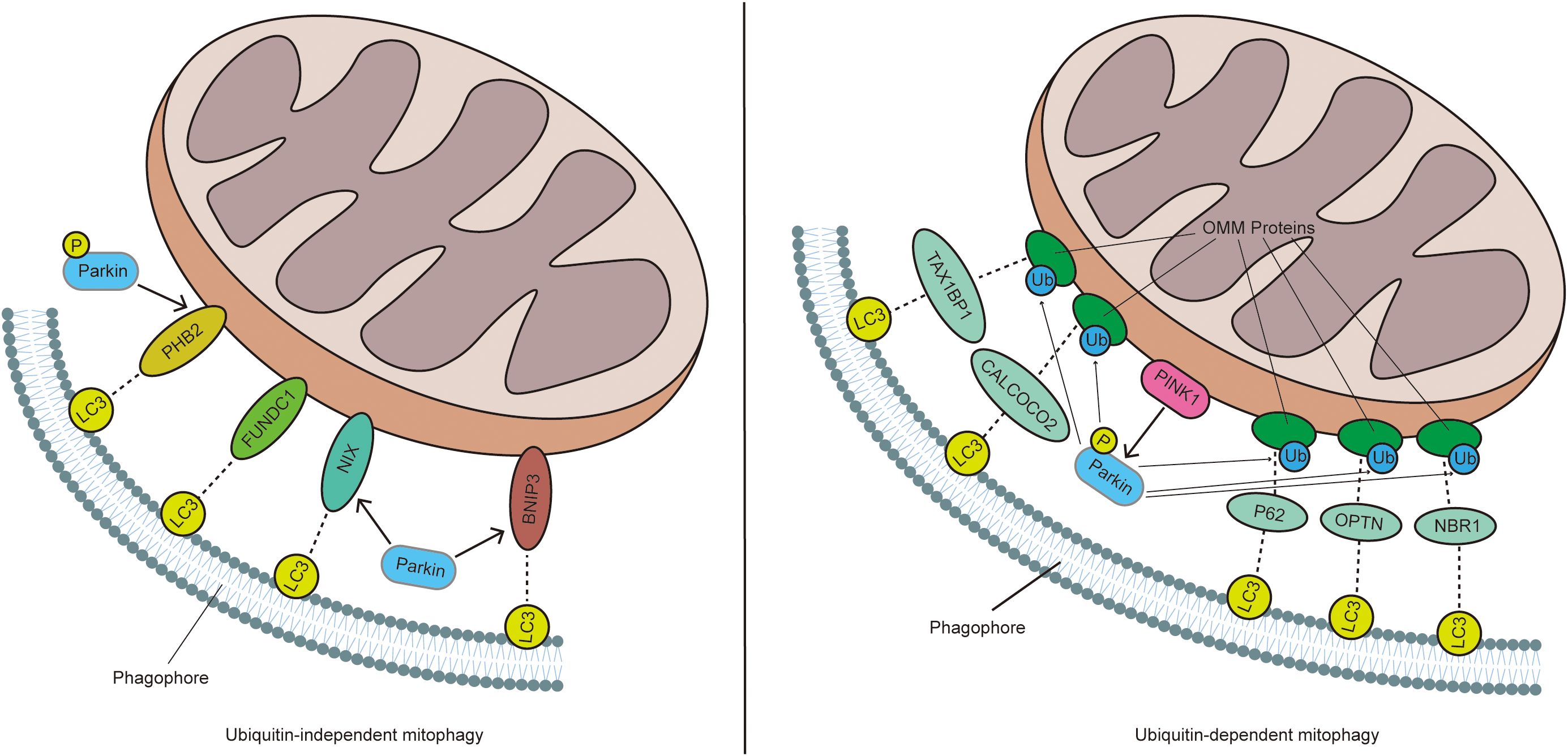
Figure 1. In ubiquitin-dependent mitophagy, a decrease in MMP leads to the accumulation of PINK1 on the OMM, which promotes the recruitment and phosphorylation of Parkin. Activated Parkin ubiquitinates mitochondrial proteins, which are then recognized by receptors such as P62, NBR1, OPTN, TAX1BP1, and CALCOCO2. These receptors interact with LC3 through their LIR domain, thereby inducing mitophagy. In contrast, in ubiquitin-independent mitophagy, mitophagy receptors like BNIP3, NIX, PHB2, and FUNDC1 are directly anchored to the OMM and mediate mitophagy by directly interacting with LC3, without the need for ubiquitination.
Ubiquitin−dependent mitophagy
As early as 2006, it was discovered that phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN)-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and Parkin operate within the same pathway, playing a crucial role in maintaining mitochondrial function (5, 6). Under normal conditions, PINK1 is imported into the mitochondria via the outer membrane translocase (TOM) complex and the inner membrane translocase (TIM23) complex, facilitated by its amino-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence. Once inside, PINK1 enters the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) complex (7). In the mitochondrial matrix, the mitochondrial processing peptidase (MPP) cleaves the N-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence of PINK1, while presenilin-associated rhomboid-like protein (PARL) further cleaves the M-segment of PINK1 (8, 9). The remaining PINK1, now with an unstable N-terminus, is released into the cytoplasm, where it is degraded by the proteasome pathway involving cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase E3 components N-recognin 1 (UBR1), UBR2, and UBR4. During this process, Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase, typically in an inactive state, remains in its natural self-inhibitory conformation within the cytoplasm (10). When mitochondria are damaged, a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) triggers the self-phosphorylation of PINK1 at Ser228 and Ser402 residues. This self-phosphorylation event recruits the E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin to the mitochondria, altering its spatial conformation and converting it into an active E3 ubiquitin ligase (11). Activated Parkin ubiquitinates several mitochondrial proteins, including mitofusin 1 (Mfn1), mitofusin 2 (Mfn2), voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein (VDAC), and dynamin-1-like protein (DRP-1) (12). These ubiquitinated proteins on the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) then recruit various autophagic receptors, such as sequestosome 1 (P62/SQSTM1) (13), neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1 (NBR1) (14), calcium binding and coiled-coil domain 2 (CALCOCO2/NDP52) (15), tax1 binding protein 1 (TAX1BP1) (16), and optineurin (OPTN) (17). Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) recognizes these receptors through the LC3-interacting region (LIR) motif and subsequently transports the dysfunctional mitochondria to autophagosomes. These autophagosomes then fuse with lysosomes, allowing the degraded mitochondria to be processed and cleared from the cell (18).
Additionally, multiple signaling pathways influence mitophagy by regulating the expression of PINK1/Parkin. Autophagy and Beclin 1 regulator 1 (AMBRA1) is essential for the effective activation of PINK1-PRKN (Parkin) signaling during mitochondrial depolarization. In the absence of AMBRA1, the autophagic response to mitochondrial damage is impaired (19). The PINK1/Parkin pathway acts as a signal transduction mechanism, labeling damaged mitochondria with ubiquitin chains and recruiting mitophagy receptors. These receptors guide the autophagosome membrane to envelop the ubiquitinated mitochondria, which are then eliminated through autophagosome-lysosome pathways (20). Several factors have been found to modulate this pathway. For instance, LncRNA H19 can inhibit the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway, thereby alleviating cardiac defects associated with obesity (21). In diabetic retinopathy, high glucose levels promote apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells and inhibit mitophagy by downregulating ROS-mediated PINK1/Parkin signaling (22). Stomatin-like protein 2 (STOML2) interacts with and stabilizes PINK1, amplifying PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy, which in turn promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (23). Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) protects granulosa cells (GCs) from hypoxic damage by activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy (24). Conversely, inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK)1/2 signaling can block docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-mediated mitophagy (25). Melatonin has also been shown to mitigate the aging of renal tubular epithelial cells induced by glyphosate and hard water by upregulating PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy (26).
Ubiquitin-independent mitophagy (receptor-dependent)
In contrast to PINK1/Parkin-mediated ubiquitination of mitophagy, several proteins located on OMM contain LC3-interacting region (LIR) motifs and act as autophagy receptors. These receptors are typically expressed on the OMM surface and can directly bind to LC3 without the need for ubiquitination, thereby initiating mitophagy (27). LC3-I is typically converted to LC3-II during mitophagy, and the LC3-II/I ratio is commonly used to reflect changes in mitophagy levels. A higher LC3-II/I ratio indicates a higher level of mitophagy (28). Key receptors that facilitate this process include Bcl2-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3), BNIP3-Like (BNIP3L)/NIP3-like protein X (NIX), prohibitin 2 (PHB2), and FUN14 domain containing 1 (FUNDC1) (29).
BNIP3, encoded by the Bnip3 gene located on human chromosome 10q26.3 and initially referred to as “NIP3”, is believed to be part of the Bcl-2 family, which regulates cell death. It contains an atypical BH3 domain, characteristic of certain Bcl-2 family proteins (30). BNIP3 is a pro-apoptotic protein that functions through the mitochondrial pathway and can induce cell death in various cell lines (31, 32). It serves as an integral node for regulating mitophagy via endosomes and proteasomes (33). In patients with EB virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, silencing of CD30 leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibits mitophagy. This inhibition, in turn, reduces the expression of BNIP3, resulting in the accumulation of damaged mitochondria and promoting tumor cell apoptosis (34). In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, the activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) under hypoxic conditions involves BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Additionally, autophagy can eliminate ROS and inhibit the HIF-1α/NLRP3 pathway, thereby reducing hypoxia-induced FLS pyroptosis (35). DHA regulates mitophagy through the PPARγ-LC3-BNIP3 pathway, inducing apoptosis in cells, reducing adipocyte numbers, and inhibiting lipid accumulation (36). Furthermore, 6-Gingerol exerts a protective effect against placental injury in preeclampsia by reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting excessive mitophagy caused by mitochondrial dysfunction (37).
BNIP3L/NIX is an OMM protein that belongs to the Bcl2 family of BH3-only proteins. BNIP3L acts as a mitophagy receptor by binding to LC3 through its N-terminal LIR motif (38). This interaction with ATG8 family proteins in LC3 initiates mitophagy (39). In a study involving mice, pretreatment with a NIX enhancer before corticosterone exposure increased mitophagy and synaptic density in the hippocampus, leading to improved performance in spatial memory tasks (40). Direct phosphorylation of NIX by PRKA/PKA can reverse NIX-induced mitophagy, causing BNIP3L to translocate from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm (41). FBXL4 interacts with BNIP3 and NIX, controlling their stability; a deficiency in FBXL4 ubiquitin ligase increases NIX levels, promoting mitosis (42). The interaction between mitochondrial-bound NIX and autophagosome-localized LC3 forms a mitochondria-NIX-LC3-autophagosome complex, which has been implicated in excessive mitophagy following spinal cord injury (SCI). Inhibiting NIX may serve as a neuroprotective strategy in such cases (43). In NIX-/- platelets, MMP decreases, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) levels rise, oxygen consumption declines, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production is impaired, leading to platelet dysfunction and increased risk of thrombosis (44). In patients with ulcerative colitis, the absence of NIX impairs the clearance of damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria in the intestinal epithelium, exacerbating the disease through dysregulated mtROS production (45).
FUNDC1 is a complete OMM protein with an N-terminal LC3-interacting region (LIR) motif, serving as a receptor for hypoxia-induced mitophagy (46). Under normal physiological conditions, FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy is regulated by phosphorylation at Tyr18 by SRC kinase and at Ser13 by casein kinase 2 (CK2), as well as by the inhibition of phosphatase activity through the interaction of Bcl2-like 1 (BCL2L1) with phosphoglycerate mutase 5 (PGAM5). Hypoxia stimulation leads to the degradation of BCL2L1, activating PGAM5, which catalyzes the dephosphorylation of FUNDC1 at Ser13, thereby increasing the interaction between FUNDC1 and LC3 (47). Mutations or deletions in the LIR motif of FUNDC1 impair its ability to mediate mitophagy. In cells lacking ATG5, FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy, particularly in response to hypoxia, is significantly inhibited, indicating that this process is dependent on ATG5 (48). Under hypoxic conditions, FUNDC1-mediated upregulation of mitophagy activates the ROS-HIF1α pathway, promoting the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, which ultimately leads to pulmonary vascular remodeling and hypoxic pulmonary arterial hypertension (49). The mitochondrial E3 ligase MARCH5 degrades FUNDC1, reducing mitochondrial sensitivity to hypoxia-induced mitophagy (50). Dysfunction in mitochondrial quality control caused by FUNDC1 deficiency in adipose tissue exacerbates diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome through MAPK activation, white adipose tissue remodeling, and subsequent inflammatory responses (51). Exercise increases FUNDC1 expression, which helps prevent coronary endothelial cell aging and protects elderly mice from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Additionally, FUNDC1 plays a protective role in neurons following SCI by inducing mitophagy, inhibiting mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis, and enhancing mitochondrial function (52).
Prohibitin 2 (PHB2) and PHB1 together form the mitochondrial inhibitory protein complex, where PHB2 directly binds to LC3-II, and PHB1 interacts with LC3-II through PHB2. A significant downregulation of PHB2 leads to a reduced rate of mitochondrial clearance (53). In patients with cholestatic liver injury, hepatocellular mitophagy induced by bile acids requires the interaction of PHB2 with LC3 and SQSTM1 (54). An increase in MicroRNA-24-3p levels can downregulate PHB2, which helps inhibit autophagy in myocardial fibroblasts and alleviates myocardial fibrosis (55). Under high glucose conditions, TIPE1 destabilizes PHB2 in renal tubular epithelial cells, promoting mitophagy and exacerbating tubular injury (56). Conversely, overexpression of PHB2 promotes mitophagy and delays aging in mouse myocardial cells (57).
In addition, the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) s pathway plays a critical role in shifting cells from synthetic metabolism to catabolic metabolism and serves as a key regulatory pathway for autophagy. ULK1, a conserved substrate of AMPK, is involved in this process. Activation of AMPK promotes mitophagy by enhancing mitochondrial division (58).
Lipid based mitophagy
Mitochondrial lipids, such as cardiolipin (CL), ceramide, and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), serve as mitophagic signals that facilitate the clearance of damaged mitochondria by interacting with the mitophagic machinery (59).
In healthy mitochondria, CL plays a crucial role in lipid–protein interactions necessary for mitochondrial function (60). LC3 possesses a putative CL binding site at its N-terminal α-helices, which is crucial for the direct interaction between the OMM and the mitophagosome, ultimately facilitating mitophagy (61). Ceramide selectively targets mitochondria to LC3B-II-containing autophagolysosomes. LC3B-phosphatidylethanolamine is lipidated to form LC3B-II, which then binds to ceramide on the OMM, indicating that the ceramide–LC3B-II interaction is a key factor in triggering lethal mitophagy (62). S1P is directly involved in LC3 lipidation and interacts with PHB2, playing a significant role in the regulation of mitophagy (63).
Micromitophagy
Micromitophagy is a mechanism for the targeted removal of damaged mitochondrial components through the formation of mitochondria-derived vesicles (MDVs) that bud off and are subsequently transported to lysosomes (64). MDVs are cargo-selective vesicles released from mitochondria independently of the mitochondrial fission machinery. Oxidative stress stimulates MDVs formation, and these vesicles are enriched with oxidized mitochondrial proteins (65). Although MDVs formation and transit to lysosomes occur independently of the autophagic proteins ATG5 and LC3, this process requires the involvement of PINK1 and Parkin (66). Ultimately, MDVs fuse with lysosomes to complete the hydrolysis and degradation of their contents.
Transmitophagy
Transmitophagy is a specialized mode of mitochondrial degradation in neurons with long axons. Under normal physiological conditions, axonal mitochondria of long-projection neurons are enclosed in axoplasmic membranes, which are then shed and degraded by neighboring cells (67). This process, where neuronal mitochondria are internalized and degraded by astrocytes, is known as transmitophagy (68). Mitochondria can traverse cell boundaries (69), and in neurons with long axons, they may be transferred to adjacent astrocytes for degradation (67). A significantly greater proportion of retinal ganglion cell mitochondria are degraded in the optic nerve head (ONH) than in the cell soma. Some axonal mitochondria are not degraded cell-autonomously within retinal ganglion cell axons via traditional mitophagy but are instead processed by resident astrocytes through a process termed transcellular degradation of mitochondria, or transmitophagy (70). The internalization of neuronal mitochondria is notably increased in astrocytes isolated from Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mouse brains, indicating the presence of neuron-astrocyte transmitophagy in AD (68). It has also been shown that the mitophagy of degenerating dopaminergic terminals begins in dopaminergic spheroids and concludes in the surrounding astrocytes. Neuron-astrocyte transmitophagy is critical for preventing the release of damaged mitochondria into the extracellular space and for mitigating the neuroinflammatory activity characteristic of Parkinson’s disease (PD) (71).
Mitophagy in neurons
The human brain, despite accounting for only 2% of the body’s volume, is responsible for 25% of its oxygen consumption. These high energy demands make the brain particularly vulnerable to damage during acute or chronic hypoxia or ischemia. Bioenergy depletion is also a known contributor to neuronal death in a range of neurodegenerative diseases. Beyond ATP production, neuronal mitochondria play a crucial role in Ca2+ buffering (3). The high demand for mitochondria in neurons is evident from the elevated mitochondrial density at presynaptic endings, postsynaptic densities, nodes of Ranvier, and growth cones, all of which rely on mitochondrial function to sustain neuronal activity (72). As neurons are non-proliferating cells that do not undergo mitosis, their mitochondria are especially susceptible to accumulating oxidative damage over time. Additionally, high levels of Ca2+ influx into neurons may exacerbate this stress. Unsurprisingly, mitochondrial damage and mitophagy dysfunction are linked to several age-related neurodegenerative diseases, including PD, AD, and Huntington’s disease (HD) (73).
Role of mitophagy in programmed neuronal death
While limited neuronal death is a highly regulated and necessary homeostatic mechanism for maintaining the functional development of the central nervous system, pathological neuronal loss in mature central nervous systems can lead to irreversible declines in motor and cognitive functions (74). Programmed neuronal death, including apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis, is closely associated with central nervous system (CNS) diseases, including acute CNS injuries such as intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative diseases like AD and PD. Mitochondria play a pivotal role in CNS diseases by mediating various cell death pathways (75). The regulation of mitophagy is critical in controlling ROS levels, mtDNA release, OMM rupture, MMP loss, and Ca2+ imbalance in neurons (Figure 2). Moderate mitophagy is essential for maintaining mitochondrial function and cellular homeostasis. Therefore, understanding the relationship between mitophagy and programmed neuronal death is crucial.
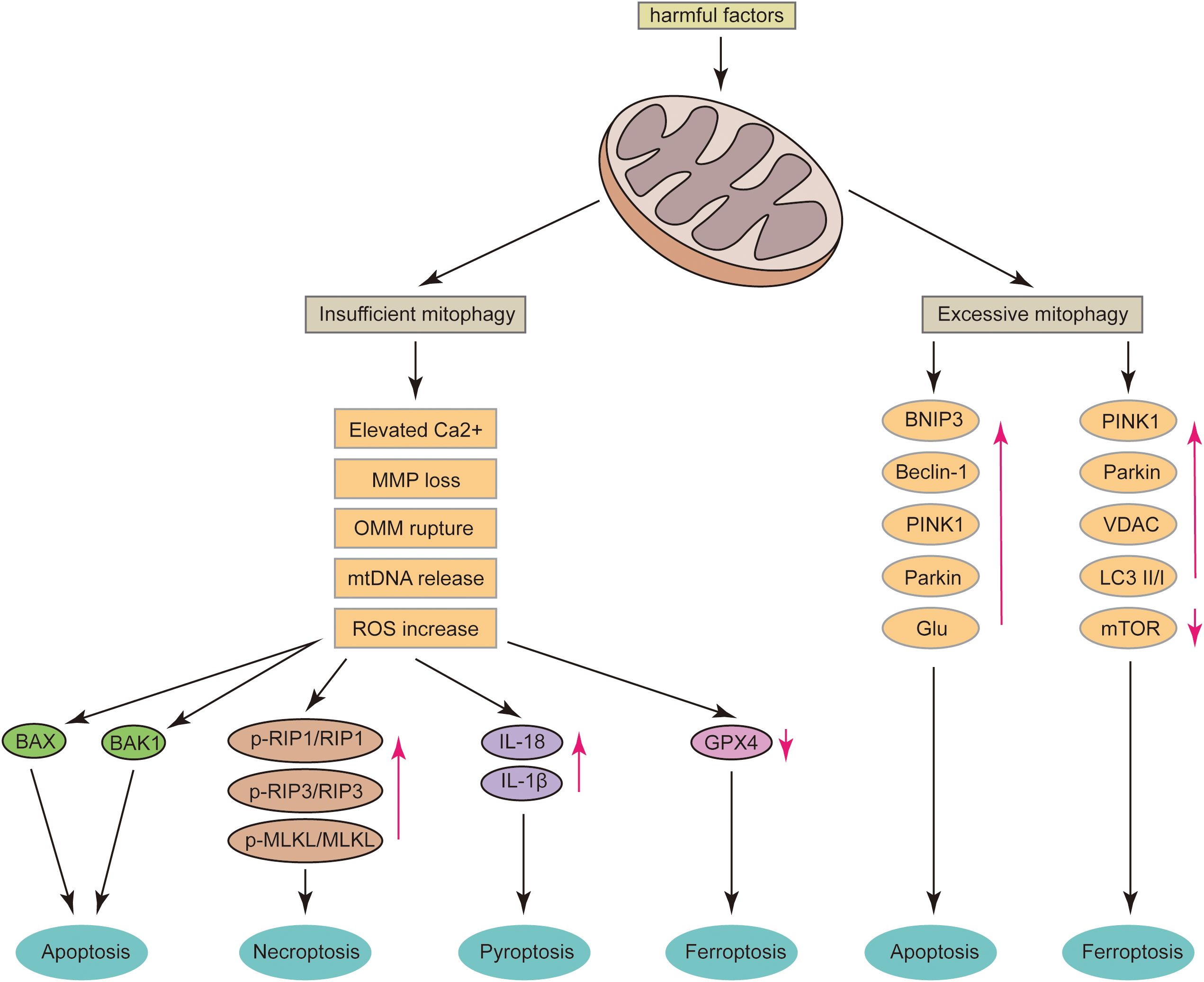
Figure 2. After mitochondrial damage, several critical events can occur, including the release of mtDNA, rupture of the OMM, loss of MMP, and an increase in Ca2+ levels. If mitophagy is insufficient, these conditions can lead to neuronal apoptosis via the BAX and BAK1 pathways; increase the ratios of p-RIP1/RIP1, p-RIP3/RIP3, and p-MLKL/MLKL, thereby promoting neuronal necroptosis; elevate neuronal IL-18 and IL-1β levels, inducing pyroptosis; and significantly reduce GPX4 levels, leading to ferroptosis. Conversely, excessive mitophagy can result in the overexpression of BNIP3, Beclin-1, PINK1, Parkin, and Glu, which may induce neuronal apoptosis. It can also cause the overexpression of PINK1, Parkin, and VDAC, increase the LC3 II/I ratio, decrease mTOR levels, and ultimately induce neuronal ferroptosis.
Mitophagy and neuronal apoptosis
Mechanisms of mitophagy and neuronal apoptosis
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a self-destructive cellular mechanism involving multiple biological events. Mitochondria play a crucial role in regulating apoptosis pathways. Apoptosis depends on the Bcl-2 protein family, with two key pro-apoptotic proteins, Bcl-2 associated X protein (BAX) and Bcl-2 antagonist killer 1 (BAK1), which induce cell apoptosis through OMM (76). BAX and BAK1 are essential for neuronal apoptosis (77, 78), and they interact with VDAC2 to ensure their ability to penetrate the OMM and exert their effects (79, 80). In healthy cells, cytochrome c functions as a component of the electron transport chain within the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Upon mitochondrial damage, the permeability of the OMM increases, leading to the release of apoptotic factors such as cytochrome c. The depletion of cytochrome c in mitochondria increases ROS production, exacerbating mitochondrial dysfunction and promoting cell apoptosis. Mitophagy plays a protective role by transporting defective mitochondria to lysosomes for degradation, eliminating ROS, and inhibiting apoptosis (81, 82). Excessive accumulation of Ca2+ in the mitochondrial matrix can cause matrix expansion, leading to the rupture of the OMM and the subsequent release of cytochrome c (83). Additionally, the release of mtDNA can act as a trigger for inflammation. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy prevents the release of mtDNA into the cytoplasm by removing damaged mitochondria, thereby alleviating cGAS/STING-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (84).
Targeted treatment to mitophagy-mediated neuronal apoptosis
Activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy can mitigate neuronal apoptosis induced by prion PrP106-126 (20) and cadmium (85). Compounds such as salidroside (Sal) (86), DHA (87), and triiodothyronine (T3) (88) have been shown to enhance the PINK1/Parkin pathway. Additionally, DJ-1 can activate the ERK1/2 pathway and improve mTOR signaling in dopaminergic neurons (89); Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) increases AMPK phosphorylation and boosts FUNDC1 expression (90), while the LncRNA MEG3 promotes FUNDC1 expression through the Rac1-ROS axis (91). Furthermore, dexmedetomidine enhances the PINK1/Parkin pathway by activating AMPK (92). These pathways collectively promote mitophagy, reduce ROS production, prevent mitochondrial-dependent neuronal apoptosis, and exert neuroprotective effects. 2,2’,4,4’-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether (PBDE-47) induces mitochondrial abnormalities by impairing PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy, leading to excessive apoptosis and, consequently, promoting neuronal loss and subsequent neurobehavioral defects. Melatonin counteracts PBDE-47-induced damage by activating the AMPK/ULK1 signaling pathway, thereby restoring mitophagy and preventing neuronal apoptosis (93).
Mitophagy and neuronal necroptosis
Mechanisms of mitophagy and neuronal necroptosis
Necroptosis is a form of regulated programmed cell necrosis. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is the most widely studied inducer of necroptosis. Upon binding to its receptor, TNF-α induces a conformational change in the TNF receptor, which recruits several proteins to the cytoplasmic portion of the receptor. These proteins include Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain protein (TRADD), receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), cellular inhibitor of apoptosis-1 (cIAP1), cIAP2, and TNFα receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). In the absence of caspase 8, these proteins form membrane complexes that induce the formation of RIPK1-RIPK3 necrosomes. This leads to mitochondrial hyperpolarization, lysosomal membrane permeabilization, and ROS production, ultimately activating Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like protein (MLKL), which disrupts the plasma membrane and results in cell death (94). Necroptosis is closely associated with ATP depletion, ROS accumulation, calcium overload, and the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores (MPTP) (95). For example, increased expression of RIPK3 can suppress the AMPK pathway and inhibit Parkin-mediated mitophagy. The loss of mitophagy enhances the opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores (MPTP), ultimately leading to cellular necroptosis (96). Tricalcium phosphate (TCP) has been shown to enhance the kinase activity of RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL, thereby promoting cell necroptosis. ROS scavengers can inhibit the increase in the p-RIP1/RIP1, p-RIP3/RIP3, and p-MLKL/MLKL ratios caused by TCP particles (97). Mitochondria, as the primary organelles responsible for ATP production and a major source of ROS, play a crucial role in necroptosis. Mitophagy, regulated by PINK1, influences the expression of MLKL and, consequently, necroptosis (98).
Targeted treatment to mitophagy-mediated neuronal necroptosis
RIPK3 can reduce Parkin phosphorylation levels, thereby decreasing the interaction between Parkin and LC3, which is typically induced by hypoxic injury. This inhibition of mitophagy by RIPK3 plays a critical role in cell death mechanisms. During ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury, RIPK1 is phosphorylated, leading to the subsequent phosphorylation of RIPK3, which promotes the activation of MLKL. Once activated, MLKL executes the cell death program. PGAM5, a mitochondrial membrane protein, acts as an important protective gene against ischemic injury. It serves as an anchor for the RIP1-RIP3-MLKL complex within mitochondria, promoting mitophagy and protecting cells from necroptosis (99). Sterile alpha and toll/interleukin 1 receptor motif-containing protein 1 (SARM1) is a central determinant of axonal degeneration. Its upregulation enhances the RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signaling axis, thereby promoting neuronal necroptosis. Rapamycin has been shown to enhance mitophagy and alleviate neuronal necroptosis, particularly in conditions involving SARM1 aggregation, such as acrylamide-induced dying-back neuropathy (100). In patients with PD, ROS generation and mitochondrial depolarization can trigger neuronal necroptosis. This process can be inhibited by inactivating RIP1. Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), a known inhibitor of RIP1 kinase activity, increases the levels of TOMM20 and PHB1 proteins, which are involved in mitochondrial function. This increase is accompanied by the upregulation of LONP1, a mitochondrial protease that plays a role in the PINK1-dependent mitophagy pathway. By enhancing mitophagy, Nec-1 prevents MLKL phosphorylation and the subsequent plasma membrane rupture associated with p-MLKL, thereby mitigating neuronal necroptosis (101).
Mitophagy and neuronal pyroptosis
Mechanisms of mitophagy and neuronal pyroptosis
Pyroptosis is a recently identified pro-inflammatory mode of cell death, triggered by various inflammation-related caspases. The assembly and activation of inflammasome complexes in response to intracellular and extracellular pathological signals lead to the activation of inflammatory caspases 1, 4, 5, and 11, ultimately causing mitochondrial outer membrane permeability (MOMP) and subsequent cell death (102). The hallmark event of pyroptosis involves the processing of IL-18 and IL-1β, and the activation of the pore-forming protein gasdermin-D (GSDMD), which culminates in cell membrane rupture and the release of IL-18 and IL-1β (103). While canonical GSDMD is cleaved by caspases 1, 4, 5, and 11, another variant, gasdermin-E (GSDME), is cleaved by caspase-3, linking non-inflammatory apoptosis to pyroptosis. GSDME-dependent pyroptosis also results in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 (104). Current research suggests a negative feedback loop between mitophagy and pyroptosis (105). Inflammasome-mediated activation of caspase-1 inhibits mitophagy, aggravating mitochondrial damage. Conversely, the absence of the key mitophagy regulator Parkin exacerbates mitochondrial damage, promoting pyroptosis (106). This mechanism may be associated with pyroptosis-induced mitochondrial ROS release and disruption of membrane integrity. Additionally, potassium efflux and cytochrome c are crucial in the regulation of mitophagy and pyroptosis (107).
Targeted treatment to mitophagy-mediated neuronal pyroptosis
Anesthesia and surgery can lead to insufficient PINK1-mediated mitophagy, which in turn activates the caspase-3/GSDME pyroptosis signaling axis, ultimately resulting in postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Overexpression of PINK1 has been shown to alleviate cognitive impairment and reduce caspase-3/GSDME-dependent pyroptosis (108). SNAP25 plays a key role in promoting PINK1-dependent mitophagy, rescuing defects in the PINK1/Parkin pathway, facilitating the conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II, preventing abnormal accumulation of P62, and suppressing the activation of the caspase-3/GSDME axis. These actions collectively hinder neuronal pyroptosis and offer neuroprotection against POCD (109). Tumor necrosis factor α-induced protein 1 (TNFAIP1) impairs mitophagy and triggers excessive neuronal pyroptosis by inhibiting SNAP25 expression. A deficiency in TNFAIP1 function enhances PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy in HT22 cells, thereby preventing caspase-3/GSDME-dependent pyroptosis. Conversely, increased TNFAIP1 function inhibits mitophagy and promotes pyroptosis (110). PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy may act as an endogenous neuroprotective mechanism during the pathological progression of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (CI/R) by modulating NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Glycosides have been shown to activate key mitophagy markers, such as LC3-II/LC3-I and P62, and the PINK1/Parkin mitophagy pathway, which alleviates neuronal pyroptosis following middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) induced oxygen-glucose depletion/reoxidation (OGD/R) in rats (111). Following traumatic brain injury (TBI), levels of IL-1β, IL-18, cleaved caspase-1, GSDMD, and TNF-α increase. The expression of the PINK1/Parkin pathway is enhanced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes, significantly inhibiting the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and improving secondary neuronal pyroptosis after TBI (112). Dexmedetomidine has been shown to reduce postoperative cognitive impairment in aged rats by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and suppressing caspase-1/GSDMD-induced pyroptosis in hippocampal neurons (113).
Mitophagy and neuronal ferroptosis
Mechanisms of mitophagy and neuronal ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of cell death characterized by the toxic accumulation of lipid peroxides on the cell membrane (114). This process is marked by the loss of activity of the lipid repair enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), accompanied by the buildup of lipid ROS (115). The production of mitochondrial ROS can promote lipid peroxidation, leading to ferroptosis; however, treatment with mitochondria-targeted lipophilic antioxidants can significantly rescue cells from GPX4 inactivation-induced ferroptosis (116). ATP consumption activates AMPK, which effectively inhibits ferroptosis by phosphorylating and inactivating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) (117). Additionally, mitochondrial biosynthetic products involved in cellular metabolism influence the ferroptosis pathway (118). Mitophagy reduces ferroptosis through the ROS/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)/GPX4 axis. Inhibition of BNIP3/Parkin or PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy exacerbates ROS release, lipid peroxidation, and cellular ferroptosis (119). Moreover, the phosphorylation of FUNDC1 can disrupt mitophagy and mitochondrial quality control, ultimately leading to cellular ferroptosis (120). Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH), a mitochondrial enzyme located on the outer surface of the mitochondrial inner membrane, plays a crucial role in this process. Coenzyme Q (CoQ) is primarily synthesized in mitochondria, and DHODH is well-positioned to reduce CoQ to CoQH2, thereby exerting its anti-ferroptosis function within mitochondria. When GPX4 is inactivated, DHODH can detoxify lipid peroxides and prevent mitochondrial ferroptosis (118).
Targeted treatment to mitophagy-mediated neuronal ferroptosis
Following TBI, the expression of PINK1 and Parkin significantly increases. Exosome treatment further enhances the expression of PINK1 and Parkin in neurons, while decreasing ACSL4 expression and increasing GPX4 levels in the treatment group (112). This suggests that human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce neuronal ferroptosis through PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy, providing neuroprotection in TBI (112). Caveolin-1 (Cav-1) regulates the mitochondrial fission-mitophagy axis to maintain mitochondrial quality, thereby alleviating neuronal ferroptosis and significantly improving diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction (DACD) (121). Acteoside (ACT) activates the Nrf2-mitophagy axis, upregulates GPX4 and XCT, reduces lipid peroxidation, and mitigates ferroptosis. ACT treatment has been shown to preserve dopaminergic neurons, curb ferroptosis in these cells, and alleviate cognitive and behavioral deficits in PD (122). DR-Ab, an antibody targeting the DR-region of the Na+/K+-ATPase (NKA)α subunit, disrupts the cytosolic interaction between NKAα1 and Parkin, facilitating Parkin’s translocation to mitochondria and enhancing mitophagy. DR-Ab also promotes the formation of the surface NKAα1/XCT complex, thereby inhibiting XCT-dependent ferroptosis. Given NKAα1’s role as a key regulator of ferroptosis and mitophagy, its DR-region presents a promising therapeutic target for PD (123).
Excessive mitophagy induces neuronal death
In neurological diseases, most secondary neuronal apoptosis is attributed to insufficient mitophagy, while in some cases, the pathogenesis is linked to excessive mitophagy (Table 1). Excessive mitophagy can exacerbate mitochondrial damage, leading to subsequent neuronal apoptosis and ferroptosis (124). NIX primarily regulates basal levels of mitophagy under physiological conditions, whereas BNIP3 exclusively triggers excessive mitophagy, resulting in cell death (125). Inhibiting BNIP3 may protect hippocampal neural cells from OGD/R, reduce excessive mitophagy caused by CI/R injury, maintain mitochondrial integrity, reduce neuronal apoptosis, and improve neurological function (126). Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), a NAD+-dependent deacetylase, induces mitophagy by deacetylating downstream targets such as Mfn2. Inhibiting SIRT1 expression can alleviate mitophagy and suppress neuronal apoptosis following CI/R (127). FBXL4 mutations lead to excessive mitophagy through the accumulation of BNIP3/BNIP3L, resulting in mitochondrial DNA depletion and dysfunction in cortical neurons (128). Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) significantly decreases the expression of proteins such as P62, CTSD, and LAMP1, while increasing the expression of beclin-1, Parkin, and BNIP3, as well as the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio, and the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria to the cytoplasm. These changes induce lysosomal dysfunction, promote autophagic volume accumulation, and lead to excessive autophagy in neurons, ultimately triggering neuronal apoptosis (129). Melatonin can reduce the levels of mitophagy proteins PINK1 and Parkin, decrease the colocalization of Tom20 and LC3, alleviate neuronal hypoxia after stroke, and improve post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) (130). The basolateral amygdala (BLA), a key structure in encoding emotional valence and responding to stress and threats, can experience excessive elimination of mitochondria due to overexpression of PINK1 and Parkin, resulting in anxiety in stressed mice (131). Excess glutamate (Glu) can induce excessive mitophagy by activating the glutamate receptor 2 (GluR2)-Parkin pathway, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, a deficiency in monoamine neurotransmitters, and the development of diabetes-related depression (DD) in rats (132). Tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP) enhances iron ion influx into mitochondria and mitochondrial depolarization via activation of VDAC channels, triggering excessive mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway, leading to mitophagy-related ferroptosis and TDCPP-induced neurotoxicity (133). Exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) significantly upregulates HO-1, which mediates PM2.5-induced mitophagy-dependent ferroptosis in hippocampal neurons. The upregulation of HO-1 increases the LC3-II/I ratio, decreases mTOR expression, and leads to excessive autophagy, exacerbating ferroptosis in PM2.5-exposed hippocampal neurons. Inhibiting mitophagy or ferroptosis may be key therapeutic targets to mitigate neurotoxicity following PM2.5 exposure (134).
Mitophagy in neurodegeneration
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) are a spectrum of complex, heterogeneous disorders characterized by the progressive degeneration of neurons, affecting both the central and peripheral nervous systems (135). Two regions of the brain particularly vulnerable to oxidative damage are the hippocampus and the substantia nigra (SN). Hippocampal degeneration is a hallmark of diabetic encephalopathy and AD, while SN degeneration is characteristic of PD (136). Selective neurodegeneration in AD and PD is associated with increased oxidative stress markers in these brain regions (137). At the organellar level, mitochondrial dysfunction is a prominent phenotype in neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, the accumulation of damaged mitochondria in most NDDs suggests dysregulation of the mitophagy pathway (135). Biologically, AD is defined by two principal neuropathological hallmarks: the abnormal accumulation of extracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and intracellular tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles (138). Insufficient mitochondrial function and bioenergy output in AD patients may lead to reduced cellular energy levels, while the concomitant leakage of electrons promotes the formation of ROS. These ROS can damage proteins, membrane lipids, and nucleic acids. By initiating membrane lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial ROS may also promote the accumulation of pathological extracellular Aβ peptides and intraneuronal hyperphosphorylated tau protein, leading to the formation of AD-defining Aβ plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, which further exacerbate mitochondrial defects (139, 140). Mitophagy reduces AD-related tau hyperphosphorylation and prevents cognitive impairment, indicating that impaired clearance of defective mitochondria is a key event in AD pathogenesis and that mitophagy could be a potential therapeutic target (141). Impairment of mitophagy was initially associated with PD based on observations that brain samples from PD patients showed accumulation of autophagosomes containing damaged mitochondria (142). Additionally, mutations in PINK1 and Parkin, which are critical proteins involved in mitophagy, have been linked to the early onset of autosomal recessive PD (143). Neuronal mitochondrial dysfunction and disruptions in the mitophagy pathway are significant contributors to the onset of PD. Huntington’s disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding the huntingtin protein. The mutant huntingtin protein does not affect the PINK1/Parkin pathway but disrupts the interaction of mitophagy adaptors OPTN, CALCOCO2, SQSTM1/P62, and NBR1 with LC3, leading to impaired fusion of mitochondria and autophagosomes and a compromised mitophagy mechanism (144). This damage is partially recovered by overexpressing PINK1, which improves mitochondrial integrity and protects neural function (145).
Role of mitophagy in neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation refers to the inflammatory response in the CNS triggered by brain or spinal cord injury, infection, ischemia, diabetes, intraocular pressure, or as a consequence of autoimmunity and aging. This inflammation is primarily driven by the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, second messengers such as nitric oxide and prostaglandins, and ROS (146). The core basis of neuroinflammation are likely consistent across various conditions, including aging, metabolic diseases like hypertension and diabetes, and cerebral insults such as stroke and injury. The inflammatory mediator TNF-α has been identified as a key player and biomarker of neuroinflammation (147). Inflammatory signals are typically responses to pathogens or foreign substances. However, new evidence suggests that mitochondria or mitochondrial components—including mtDNA, mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM), cardiolipin, cytochrome c, formyl peptides, high mobility group B protein 1 (HMGB1), and ATP—can mimic pathogens and trigger injury responses (148). Therefore, the role of mitophagy in neuroinflammation warrants further discussion.
Microglial mitophagy in neuroinflammation
Microglia are ubiquitously distributed in the brain and serve as the principal innate immune cells, acting as the first responders to pathological insults (149). These cells express a variety of receptors, including the CD200 receptor, colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor, chemokine receptor (CX3CL1), neurotrophic factors, and neurotransmitters, all of which play significant roles in neuroinflammation (150). Upon activation by endogenous stimuli generated after injury or infection, inhibitor of NF-κB (i-κB), which is bound to nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in the cytoplasm of microglia, is phosphorylated and degraded by i-κB kinase. This process causes NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus, where it promotes the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokine genes (151). Damaged neurons also release fractalkine (CX3CL1) ligands, which are recognized by the CX3CL1 receptor on microglia (152). Activated microglia can exhibit different gene expression patterns, with the M1 phenotype associated with pro-inflammatory effects and the M2 phenotype with anti-inflammatory effects (153). The surface of microglia contains Aβ receptors, such as NOD-like receptors (NLRs), Toll-like receptors (TLRs), and receptors for advanced glycation end products (RAGE). Aβ can penetrate the cell membrane of microglia, bind to the intracellular domain of NLRs, and activate inflammasomes containing NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3). Aβ can also bind to RAGE, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α (154). Mitochondria play a critical role in neuroinflammation. When microglia are treated with mitochondrial lysates, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) expression decreases, while TNF-α expression increases, along with elevated levels of MMP-8 and IL-8, redistribution of NF-κB towards the nucleus, and increased phosphorylation of p38 MAPK. mtDNA directly obtained from mitochondria has been shown to increase TNF-α mRNA levels in microglia. These findings suggest that at least one mitochondrial-derived damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule, mtDNA, can induce inflammatory changes in microglia and neuronal cell lines, thereby triggering neuroinflammation (148). The ability of mitophagy induction to reduce neuroinflammation may be explained by several mechanisms and benefits in microglia. First, the accumulation of damaged mitochondria releases DAMPs, including increased ROS production, decreased ATP levels, and elevated oxidative stress (155). Second, blockage of mitophagy has been shown to increase ROS levels, which in turn activates the NLRP3 inflammasome (156). Additionally, the mitophagy inducer mitochonic acid 5 (MA-5) has been reported to reduce neuroinflammation. Treatment of microglia with MA-5 leads to improved mitochondrial quality, dependent on the mitophagy activator Bcl2/BNIP3 (157). Collectively, mitophagy may inhibit neuroinflammation through multiple pathways.
Recent studies have increasingly shown that mitophagy in microglia can alleviate neuroinflammation, which is believed to be a contributing factor to AD. Inadequate mitophagy is partly implicated in the pathogenesis of AD. As a receptor involved in mitophagy, OPTN can mitigate neuroinflammation through the AIM2 and RIPK1 pathways, and a deficiency in OPTN may be a potential factor leading to the development of AD (154). Treatment with T3 enhances mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway, facilitating the degradation of damaged mitochondria, reducing ROS release, and subsequently decreasing microglial cell aggregation and activation. This process helps alleviate neuroinflammation following subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) (88). Copper exposure has been shown to activate microglia, leading to the secretion of inflammatory products, early activation of the ROS/NF-κB pathway, and subsequent mitophagy disorders in microglial cells, ultimately resulting in microglia-mediated neuroinflammation (158). Mitophagy disorders are characterized by excessive mtROS production, which has been observed in overactivated primary microglia and BV-2 cells, driving microglial polarization toward the M1 pro-inflammatory state. Mitophagy deficiency in microglia not only exacerbates neuroinflammation but also impairs their phagocytic function, leading to further neuronal damage (159). Compounds such as Nrf2 (160), divanillyl sulfone (DS) (161), quercetin (Qu) (162), and polygala saponins (PSS) (163) have been shown to promote mitophagy in microglia, improve the accumulation of ROS from dysfunctional mitochondria, inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and alleviate neuroinflammation. In a sleep apnea mouse model, NLRP3 deficiency was found to protect against intermittent hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation by promoting the PINK1/Parkin mitophagy pathway in microglia (164). Additionally, inhibiting the activation of the HMGB1/RAGE axis increases stress-induced mitophagy flux, thereby reducing microglia-mediated neuroinflammation (165).
Astrocyte mitophagy in neuroinflammation
Although initially considered to have only passive functions, recent studies have revealed that astrocytes play active and essential roles in maintaining brain homeostasis (166). Pro-inflammatory reactive astrocytes upregulate several genes, such as those involved in the complement cascade, and induce the production of pro-inflammatory factors like IL-1β, TNF-α, and NO (167). Inflammatory mediators secreted by microglia, including IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, and C1q, can activate pro-inflammatory astrocytes (168). When primary astrocytes and microglia are activated by cytokines, there is an upregulation of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) activation. NFAT is positively regulated by IL-1β, and in a positive feedback loop, IL-1β expression is dependent on NFAT and L-type Ca2+ channels (169). Mitophagy helps reduce cellular Ca2+ and NFAT levels by clearing damaged mitochondria (3, 170). Additionally, the activation of astrocytes can mediate a neuroinflammatory response in dopaminergic neurons through the generation of ROS and lipid peroxidation (171). Mitophagy can alleviate mitochondrial injury caused by ROS accumulation and lipid peroxidation (172).
There are currently limited studies on the role of astrocyte mitophagy in neuroinflammation. Manganese treatment significantly reduces Mfn2 mRNA levels in astrocytes and induces neuroinflammation by impairing mitochondrial dynamics, further supporting the role of mitophagy dysfunction in mediating astrocyte-induced neuroinflammation (173). ATP-sensitive potassium (K-ATP) channels, which couple cell metabolism to membrane potential, are crucial in this context. Kir6.1, a pore-forming subunit of the K-ATP channel, is prominently expressed in astrocytes and plays a role in regulating their function. The astrocytic Kir6.1/K-ATP channel has been shown to promote mitophagy. In the substantia nigra compacta of Kir6.1 knockout mice, the expression of p65, activation of caspase-1, and levels of IL-1β, NLRP3, and TNF-α in response to MPP+ stimulation were significantly higher in astrocytes from Kir6.1 KO mice compared to those from wild-type mice (174). Resolvin D1 has been found to enhance mitophagy by activating ALX4/FPR2 receptors on astrocytes, thereby protecting mitochondria in primary astrocytes and ultimately guarding against neuroinflammation after TBI (175). Benzopyrene (BaP), associated with cognitive decline and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases, may contribute to these conditions by inhibiting PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy, leading to neuroinflammation in the brain (176).
Neuronal mitophagy in neuroinflammation
Neuronal cell death is a significant driver of neuroinflammation. Traditionally, the relationship between neurons and inflammation is viewed with inflammation acting upon neurons. However, neurons can also actively contribute to inflammation, creating a bi-directional relationship where neurons are both recipients and instigators of inflammation (177). Evidence suggests that neuronal apoptosis can disrupt the homeostatic microglial phenotype, further influencing inflammatory responses (178). Other forms of cell death, such as necroptosis and pyroptosis, have more direct consequences for neuroinflammation. Lytic cell death, as seen in necroptosis and pyroptosis, leads to the release of intracellular components that act as DAMPs, which incite further inflammation (179). Neurons undergoing pyroptotic cell death also release potent inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β (180). Similarly, activation of necroptosis has been linked to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and the release of IL-1β (181). When neuronal cells are treated with mitochondrial lysate, levels of TNF-α and NF-κB protein increase, while I-κB protein levels decrease, indicating a heightened inflammatory response (148). Treatment with the mitophagy inducer urolithin A has been shown to improve synaptic connectivity and reduce neuroinflammation in neurons, highlighting the importance of mitophagy in resolving cytosolic mtDNA-triggered inflammation (182). Considering that mitophagy can inhibit neuronal necroptosis and pyroptosis, mitophagy plays a protective role against neuron-induced neuroinflammation.
Conclusion and future perspective
In this article, we explored the relationship between mitophagy and both programmed neuronal death and neuroinflammation. We also examined the potential interplay between mitophagy, programmed neuronal death, and neuroinflammation. Additionally, we briefly discussed the role of mitophagy in neurodegeneration. Furthermore, we highlighted potential targets for future clinical treatments aimed at addressing neuronal death and neuroinflammation.
Programmed neuronal death and neuroinflammation play crucial roles in both acute central nervous system injuries and chronic degenerative diseases. Numerous studies have shown that mitochondrial damage and dysfunction are closely linked to these processes. Mitophagy regulates the quality and quantity of mitochondria in neurons, making its dysfunction or overactivation significantly related to neuronal death and neuroinflammation. In most cases, the activation of mitophagy has a protective effect on damaged neurons and supports cell survival. However, in instances where cell death is mediated by excessive mitophagy, therapeutic interventions that further enhance mitophagy may not rescue the phenotype. Therefore, it is essential to study the relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction and disease progression across various disease states and to explore how mitochondrial homeostasis can be achieved through mitophagy, thereby potentially delaying or treating neurological diseases. Moreover, there is currently no literature indicating whether excessive mitophagy leads to neuronal necroptosis and pyroptosis, warranting further research in this area. Additionally, no experiments have yet investigated whether neuronal apoptosis and ferroptosis contribute to neuroinflammation, nor has the relationship between mitophagy, programmed neuronal death, and neuroinflammation been fully established. Further research is needed to explore these critical aspects.
Although studies have shown that autophagy benefits neurons by reducing damage and death, and have explored its potential mechanisms at the cellular level, no research has yet determined the optimal extent to which autophagy should be controlled to achieve the best outcomes. Further investigation in this area is necessary. Specifically, more research at the cellular level is needed to understand the mechanisms and physiology of mitophagy in mitigating programmed neuronal death and neuroinflammation. While numerous animal and cell experiments have demonstrated the potential therapeutic role of mitophagy in neurological disease models, there are currently no relevant agonists that have been applied to humans. It remains unclear whether these agents would have similar effects in human subjects. Additionally, the pharmacology and genetics of mitophagy as a treatment for neurological diseases are still being explored in animal and cellular studies, with no clinical evidence available yet. Furthermore, no animal research has determined whether enhancing neuronal function could potentially harm other organs or systems. Therefore, future experiments should investigate whether treating neurological diseases with mitophagy agonists might lead to secondary damage to other organs or systems. Continued efforts are required to translate these findings into clinical research and to elucidate the potential mechanisms involved.
Author contributions
YZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82271399), the Project of Tianjin Applied Basic and Multiple Support Research (No. 21JCZDJC00910), the Tianjin Health Care Elite Prominent Young Doctor Development Program, the Young and Middle-aged Backbone Innovative Talent Program, and Clinical Talent Training “123” Climbing Plan of Tianjin Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Palikaras K, Lionaki E, Tavernarakis N. Mechanisms of mitophagy in cellular homeostasis, physiology and pathology. Nat Cell Biol. (2018) 20:1013–22. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0176-2
2. Annesley SJ, Fisher PR. Mitochondria in health and disease. Cells. (2019) 8(7). doi: 10.3390/cells8070680
3. Ashrafi G, Schwarz TL. The pathways of mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. (2013) 20:31–42. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.81
4. Choubey V, Zeb A, Kaasik A. Molecular mechanisms and regulation of mammalian mitophagy. Cells. (2021) 11(1). doi: 10.3390/cells11010038
5. Park J, Lee SB, Lee S, Kim Y, Song S, Kim S, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Drosophila PINK1 mutants is complemented by parkin. Nature. (2006) 441:1157–61. doi: 10.1038/nature04788
6. Clark IE, Dodson MW, Jiang C, Cao JH, Huh JR, Seol JH, et al. Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature. (2006) 441:1162–6. doi: 10.1038/nature04779
7. Pickles S, Vigie P, Youle RJ. Mitophagy and quality control mechanisms in mitochondrial maintenance. Curr Biol. (2018) 28:R170–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.004
8. Greene AW, Grenier K, Aguileta MA, Muise S, Farazifard R, Haque ME, et al. Mitochondrial processing peptidase regulates PINK1 processing, import and Parkin recruitment. EMBO Rep. (2012) 13:378–85. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.14
9. Jin SM, Lazarou M, Wang C, Kane LA, Narendra DP, Youle RJ. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates PINK1 import and proteolytic destabilization by PARL. J Cell Biol. (2010) 191:933–42. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201008084
10. Yamano K, Youle RJ. PINK1 is degraded through the N-end rule pathway. Autophagy. (2013) 9:1758–69. doi: 10.4161/auto.24633
11. Fiesel FC, Fričová D, Hayes CS, Coban MA, Hudec R, Bredenberg JM, et al. Substitution of PINK1 Gly411 modulates substrate receptivity and turnover. Autophagy. (2022) 19:1711–32. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2151294
12. Sarraf SA, Raman M, Guarani-Pereira V, Sowa ME, Huttlin EL, Gygi SP, et al. Landscape of the PARKIN-dependent ubiquitylome in response to mitochondrial depolarization. Nature. (2013) 496:372–6. doi: 10.1038/nature12043
13. Kumar AV, Mills J, Lapierre LR. Selective autophagy receptor p62/SQSTM1, a pivotal player in stress and aging. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:793328. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.793328
14. Noda NN, Ohsumi Y, Inagaki F. Atg8-family interacting motif crucial for selective autophagy. FEBS Lett. (2010) 584:1379–85. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.018
15. Chen W, Ouyang X, Chen L, Li L. Multiple functions of CALCOCO family proteins in selective autophagy. J Cell Physiol. (2022) 237:3505–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30836
16. Yao RQ, Ren C, Xia ZF, Yao YM. Organelle-specific autophagy in inflammatory diseases: a potential therapeutic target underlying the quality control of multiple organelles. Autophagy. (2021) 17:385–401. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1725377
17. Evans CS, Holzbaur ELF. Lysosomal degradation of depolarized mitochondria is rate-limiting in OPTN-dependent neuronal mitophagy. Autophagy. (2020) 16:962–4. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1734330
18. Uoselis L, Nguyen TN, Lazarou M. Mitochondrial degradation: Mitophagy and beyond. Mol Cell. (2023) 83:3404–20. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.08.021
19. Di Rienzo M, Romagnoli A, Ciccosanti F, Refolo G, Consalvi V, Arena G, et al. AMBRA1 regulates mitophagy by interacting with ATAD3A and promoting PINK1 stability. Autophagy. (2022) 18:1752–62. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1997052
20. Jie L, Mengyu L, Xixi Z, Zhiping L, Dongming Y, Mengyang Z, et al. PINK1-parkin-mediated neuronal mitophagy deficiency in prion disease. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13(2). doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04613-2
21. Wang SH, Zhu XL, Wang F, Chen SX, Chen ZT, Qiu Q, et al. LncRNA H19 governs mitophagy and restores mitochondrial respiration in the heart through Pink1/Parkin signaling during obesity. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:557. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03821-6
22. Zhang Y, Xi X, Mei Y, Zhao X, Zhou L, Ma M, et al. High-glucose induces retinal pigment epithelium mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and inhibits mitophagy by regulating ROS/PINK1/Parkin signal pathway. BioMed Pharmacother. (2019) 111:1315–25. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.01.034
23. Zheng Y, Huang C, Lu L, Yu K, Zhao J, Chen M, et al. STOML2 potentiates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and regulates sensitivity to lenvatinib. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:16. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01029-3
24. Li C, Zhou J, Liu Z, Zhou J, Yao W, Tao J, et al. FSH prevents porcine granulosa cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis via activating mitophagy through the HIF-1alpha-PINK1-Parkin pathway. FASEB J. (2020) 34:3631–45. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901808RRR
25. Chen J, Wang D, Zong Y, Yang X. DHA protects hepatocytes from oxidative injury through GPR120/ERK-mediated mitophagy. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(11). doi: 10.3390/ijms22115675
26. Zhang L, Ding F, Wu X, Wang R, Wan Y, Hu J, et al. Melatonin ameliorates glyphosate- and hard water-induced renal tubular epithelial cell senescence via PINK1-Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2023) 255:114719. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114719
27. Villa E, Marchetti S, Ricci J-E. No parkin zone: mitophagy without parkin. Trends Cell Biol. (2018) 28:882–95. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.07.004
28. Xiaolian Y, Jie X, Yuzhu X, Chengxing W, Fangmei L, Jie Y. Regulatory mechanism of perinatal nonylphenol exposure on cardiac mitochondrial autophagy and the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in male offspring rats. Phytomedicine. (2024) 126(0). doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155434
29. Fu C, Cao N, Liu W, Zhang Z, Yang Z, Zhu W, et al. Crosstalk between mitophagy and innate immunity in viral infection. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1064045. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1064045
30. Gao A, Jiang J, Xie F, Chen L. Bnip3 in mitophagy: Novel insights and potential therapeutic target for diseases of secondary mitochondrial dysfunction. Clin Chim Acta. (2020) 506:72–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.02.024
31. Zhang J, Ney PA. Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. (2009) 16:939–46. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.16
32. Ray R, Chen G, Vande Velde C, Cizeau J, Park JH, Reed JC, et al. BNIP3 heterodimerizes with Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L) and induces cell death independent of a Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3) domain at both mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial sites. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275(2). doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.2.1439
33. Delgado JM, Shepard LW, Lamson SW, Liu SL, Shoemaker CJ. The ER membrane protein complex restricts mitophagy by controlling BNIP3 turnover. EMBO J. (2024) 43:32–60. doi: 10.1038/s44318-023-00006-z
34. Wang WT, Xing TY, Du KX, Hua W, Guo JR, Duan ZW, et al. CD30 protects EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells against mitochondrial dysfunction through BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Cancer Lett. (2024) 583:216616. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216616
35. Hong Z, Wang H, Zhang T, Xu L, Zhai Y, Zhang X, et al. The HIF-1/ BNIP3 pathway mediates mitophagy to inhibit the pyroptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 127:111378. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111378
36. Bian C, Yuan X, Zeng C, Sun J, Kaneko G, Ji H. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibits abdominal fat accumulation by promoting adipocyte apoptosis through PPARgamma-LC3-BNIP3 pathway-mediated mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. (2024) 1869:159425. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2023.159425
37. Li A, Zhao M, Yang Z, Fang Z, Qi W, Zhang C, et al. et al: 6-Gingerol alleviates placental injury in preeclampsia by inhibiting oxidative stress via BNIP3/LC3 signaling-mediated trophoblast mitophagy. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1243734. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1243734
38. Zhang Y, Weng J, Huan L, Sheng S, Xu F. Mitophagy in atherosclerosis: from mechanism to therapy. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1165507. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165507
39. Novak I, Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Zhang J, Wild P, Rozenknop A, et al. Nix is a selective autophagy receptor for mitochondrial clearance. EMBO Rep. (2010) 11:45–51. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.256
40. Choi GE, Lee HJ, Chae CW, Cho JH, Jung YH, Kim JS, et al. BNIP3L/NIX-mediated mitophagy protects against glucocorticoid-induced synapse defects. Nat Commun. (2021) 12(1). doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20679-y
41. da Silva Rosa SC, Martens MD, Field JT, Nguyen L, Kereliuk SM, Hai Y, et al. BNIP3L/Nix-induced mitochondrial fission, mitophagy, and impaired myocyte glucose uptake are abrogated by PRKA/PKA phosphorylation. Autophagy. (2020) 17:2257–72. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1821548
42. Elcocks H, Brazel AJ, McCarron KR, Kaulich M, Husnjak K, Mortiboys H, et al. FBXL4 ubiquitin ligase deficiency promotes mitophagy by elevating NIX levels. EMBO J. (2023) 42:e112799. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112799
43. Nie P, Wang H, Yu D, Wu H, Ni B, Kong J, et al. NIX mediates mitophagy in spinal cord injury in rats by interacting with LC3. Cell Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 42:1983–94. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01082-7
44. Zhang W, Ma Q, Siraj S, Ney PA, Liu J, Liao X, et al. Nix-mediated mitophagy regulates platelet activation and life span. Blood Adv. (2019) 3:2342–54. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019032334
45. Vincent G, Novak EA, Siow VS, Cunningham KE, Griffith BD, Comerford TE, et al. Nix-mediated mitophagy modulates mitochondrial damage during intestinal inflammation. Antioxidants Redox Signaling. (2020) 33:1–19. doi: 10.1089/ars.2018.7702
46. Titus AS, Sung EA, Zablocki D, Sadoshima J. Mitophagy for cardioprotection. Basic Res Cardiol. (2023) 118:42. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01009-x
47. Liu H, Zang C, Yuan F, Ju C, Shang M, Ning J, et al. The role of FUNDC1 in mitophagy, mitochondrial dynamics and human diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. (2022) 197:114891. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114891
48. Wang S, Long H, Hou L, Feng B, Ma Z, Wu Y, et al. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2023) 8(1). doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01503-7
49. Liu R, Xu C, Zhang W, Cao Y, Ye J, Li B, et al. FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy and HIF1α activation drives pulmonary hypertension during hypoxia. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13(7). doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05091-2
50. Chen Z, Liu L, Cheng Q, Li Y, Wu H, Zhang W, et al. Mitochondrial E3 ligase MARCH5 regulates FUNDC1 to fine-tune hypoxic mitophagy. EMBO Rep. (2017) 18:495–509. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643309
51. Wu H, Wang Y, Li W, Chen H, Du L, Liu D, et al. Deficiency of mitophagy receptor FUNDC1 impairs mitochondrial quality and aggravates dietary-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome. Autophagy. (2019) 15:1882–98. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1596482
52. Chen D, Zhou L, Chen G, Lin T, Lin J, Zhao X, et al. FUNDC1-induced mitophagy protects spinal cord neurons against ischemic injury. Cell Death Discovery. (2024) 10(1). doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01780-9
53. Lahiri V, Klionsky DJ. PHB2/prohibitin 2: An inner membrane mitophagy receptor. Cell Res. (2017) 27:311–2. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.23
54. Xiao Y, Zhou Y, Lu Y, Zhou K, Cai W. PHB2 interacts with LC3 and SQSTM1 is required for bile acids-induced mitophagy in cholestatic liver. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:160. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0228-8
55. Zhang Y, Wang Z, Lan D, Zhao J, Wang L, Shao X, et al. MicroRNA-24-3p alleviates cardiac fibrosis by suppressing cardiac fibroblasts mitophagy via downregulating PHB2. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 177:106124. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106124
56. Liu L, Bai F, Song H, Xiao R, Wang Y, Yang H, et al. Upregulation of TIPE1 in tubular epithelial cell aggravates diabetic nephropathy by disrupting PHB2 mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol. (2022) 50:102260. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102260
57. Wang L, Tang XQ, Shi Y, Li HM, Meng ZY, Chen H, et al. Tetrahydroberberrubine retards heart aging in mice by promoting PHB2-mediated mitophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2023) 44:332–44. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00956-w
58. Ning P, Jiang X, Yang J, Zhang J, Yang F, Cao H. Mitophagy: A potential therapeutic target for insulin resistance. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:957968. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.957968
59. Praharaj PP, Naik PP, Panigrahi DP, Bhol CS, Mahapatra KK, Patra S, et al. Intricate role of mitochondrial lipid in mitophagy and mitochondrial apoptosis: its implication in cancer therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2019) 76:1641–52. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2990-x
60. Mark SS, Richard JS, Federica D, Judy H. Interactions between phospholipids and NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) from bovine mitochondria. Biochemistry. (2006) 45(1). doi: 10.1021/bi051809x
61. Charleen TC, Hülya B, Valerian E K. LC3 binds externalized cardiolipin on injured mitochondria to signal mitophagy in neurons: implications for Parkinson disease. Autophagy. (2013) 10(2). doi: 10.4161/auto.27191
62. David S R, Can ES, Wenhui J, Suriyan P, Salih G, Shanmugam Panneer S, et al. Ceramide targets autophagosomes to mitochondria and induces lethal mitophagy. Nat Chem Biol. (2012) 8(10). doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1059
63. Graham MS, Melanie P, Jie L, Ludovic G, Jeremy CA, Nitai CH, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate produced by sphingosine kinase 2 in mitochondria interacts with prohibitin 2 to regulate complex IV assembly and respiration. FASEB J. (2010) 25(2). doi: 10.1096/fj.10-167502
64. Soubannier V, McLelland G, Zunino R, Braschi E, Rippstein P, Fon E, et al. A vesicular transport pathway shuttles cargo from mitochondria to lysosomes. Curr Biol CB. (2012) 22:135–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.11.057
65. Soubannier V, Rippstein P, Kaufman B, Shoubridge E, McBride H. Reconstitution of mitochondria derived vesicle formation demonstrates selective enrichment of oxidized cargo. PloS One. (2012) 7:e52830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052830
66. McLelland G, Soubannier V, Chen C, McBride H, Fon E. Parkin and PINK1 function in a vesicular trafficking pathway regulating mitochondrial quality control. EMBO J. (2014) 33:282–95. doi: 10.1002/embj.201385902
67. Davis CH, Marsh-Armstrong N. Discovery and implications of transcellular mitophagy. Autophagy. (2014) 10:2383–4. doi: 10.4161/15548627.2014.981920
68. Lampinen R, Belaya I, Saveleva L, Liddell JR, Rait D, Huuskonen MT, et al. Neuron-astrocyte transmitophagy is altered in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis. (2022) 170:105753. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105753
69. Shih EK, Robinson MB. Role of astrocytic mitochondria in limiting ischemic brain injury? Physiol (Bethesda). (2018) 33:99–112. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00038.2017
70. Davis CH, Kim KY, Bushong EA, Mills EA, Boassa D, Shih T, et al. Transcellular degradation of axonal mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2014) 111:9633–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404651111
71. Morales I, Sanchez A, Puertas-Avendano R, Rodriguez-Sabate C, Perez-Barreto A, Rodriguez M. Neuroglial transmitophagy and Parkinson’s disease. Glia. (2020) 68:2277–99. doi: 10.1002/glia.23839
72. Morris RL, Hollenbeck PJ. The regulation of bidirectional mitochondrial transport is coordinated with axonal outgrowth. J Cell Sci. (1993) 104:917–27. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.3.917
73. Zhang L, Dai L, Li D. Mitophagy in neurological disorders. J Neuroinflamm. (2021) 18:297. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02334-5
74. Shi M, Chai Y, Zhang J, Chen X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated neuronal death and innate immune response in neurological diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:794580. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.794580
75. Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Mitochondrial mechanisms of neuronal cell death: potential therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2017) 57:437–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-105001
76. Adams JM, Cory S. Life-or-death decisions by the Bcl-2 protein family. Trends Biochem Sci. (2001) 26(1). doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01740-0
77. Lin L, Min Z, Peter S, Liang C, Sika Z. Developmental attenuation of neuronal apoptosis by neural-specific splicing of bak1 microexon. Neuron. (2020) 107(6). doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.036
78. Steckley D, Karajgikar M, Dale LB, Fuerth B, Swan P, Drummond-Main C, et al. Puma is a dominant regulator of oxidative stress induced bax activation and neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci. (2007) 27:12989–99. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3400-07.2007
79. Lauterwasser J, Todt F, Zerbes RM, Nguyen TN, Craigen W, Lazarou M, et al. The porin VDAC2 is the mitochondrial platform for Bax retrotranslocation. Sci Rep. (2016) 6(0). doi: 10.1038/srep32994
80. Emily HYC, Tatiana VS, Jill KF, William JC, Stanley J K. VDAC2 inhibits BAK activation and mitochondrial apoptosis. Science. (2003) 301(5632). doi: 10.1126/science.1083995
81. Li Y, Wu K, Zeng S, Zou L, Li X, Xu C, et al. The role of mitophagy in viral infection. Cells. (2022) 11(4). doi: 10.3390/cells11040711
82. Jiang X, Wang X. Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. (2004) 73:87–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073706
83. Zamzami N, Kroemer G. The mitochondrion in apoptosis: how Pandora’s box opens. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2001) 2(1):67–71. doi: 10.1038/35048073
84. Sliter DA, Martinez J, Hao L, Chen X, Sun N, Fischer TD, et al. Parkin and PINK1 mitigate STING-induced inflammation. Nature. (2018) 561:258–62. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0448-9
85. Wen S, Wang L, Zhang C, Song R, Zou H, Gu J, et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy modulates cadmium-induced apoptosis in rat cerebral cortical neurons. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 244:114052. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114052
86. Gu C, Li L, Huang Y, Qian D, Liu W, Zhang C, et al. Salidroside Ameliorates Mitochondria-Dependent Neuronal Apoptosis after Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Partially through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Promoting Mitophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longevity. (2020) 2020:1–22. doi: 10.1155/2020/3549704
87. Sun E, Zhang J, Deng Y, Wang J, Wu Q, Chen W, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates brain damage by promoting mitophagy in mice with ischaemic stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:3119649. doi: 10.1155/2022/3119649
88. Chang H, Lin C, Li Z, Shen Y, Zhang G, Mao L, et al. T3 alleviates neuroinflammation and reduces early brain injury after subarachnoid haemorrhage by promoting mitophagy via PINK 1-parkin pathway. Exp Neurol. (2022) 357:114175. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.114175
89. Gao H, Yang W, Qi Z, Lu L, Duan C, Zhao C, et al. DJ-1 protects dopaminergic neurons against rotenone-induced apoptosis by enhancing ERK-dependent mitophagy. J Mol Biol. (2012) 423:232–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.06.034
90. Cai Y, Yang E, Yao X, Zhang X, Wang Q, Wang Y, et al. FUNDC1-dependent mitophagy induced by tPA protects neurons against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Redox Biol. (2021) 38:101792. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101792
91. Wang Z, Xia P, Hu J, Huang Y, Zhang F, Li L, et al. LncRNA MEG3 Alleviates Diabetic Cognitive Impairments by Reducing Mitochondrial-Derived Apoptosis through Promotion of FUNDC1-Related Mitophagy via Rac1-ROS Axis. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2021) 12:2280–307. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00682
92. Chen C, Chen Y, Liu T, Song D, Ma D, Cheng O. Dexmedetomidine can enhance PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy in MPTP-induced PD mice model by activating AMPK. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:7511393. doi: 10.1155/2022/7511393
93. Dong L, Sun Q, Qiu H, Yang K, Xiao B, Xia T, et al. Melatonin protects against developmental PBDE-47 neurotoxicity by targeting the AMPK/mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res. (2023) 75:e12871. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12871
94. Xinfang Y, Qipan D, Ann MB, Zigang D, Ya C. The role of necroptosis, an alternative form of cell death, in cancer therapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. (2013) 13(7):883–893. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2013.811180
95. Nele V, Tom VB, Dmitri VK, Nele F, Peter V. Molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology of necrotic cell death. Curr Mol Med. (2008) 8(3):207–220. doi: 10.2174/156652408784221306
96. Zhu P, Wan K, Yin M, Hu P, Que Y, Zhou X, et al. RIPK3 Induces Cardiomyocyte Necroptosis via Inhibition of AMPK-Parkin-Mitophagy in Cardiac Remodelling after Myocardial Infarction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:6635955. doi: 10.1155/2021/6635955
97. Yang P, Xu B, Zhu R, Zhang T, Wang Z, Lin Q, et al. ROS-mediated mitophagy and necroptosis regulate osteocytes death caused by TCP particles in MLO-Y4 cells. Toxicology. (2023) 496:153627. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2023.153627
98. Mizumura K, Cloonan SM, Nakahira K, Bhashyam AR, Cervo M, Kitada T, et al. Mitophagy-dependent necroptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of COPD. J Clin Invest. (2014) 124:3987–4003. doi: 10.1172/JCI74985
99. Yang YD, Li ZX, Hu XM, Wan H, Zhang Q, Xiao R, et al. Insight into crosstalk between mitophagy and apoptosis/necroptosis: mechanisms and clinical applications in ischemic stroke. Curr Med Sci. (2022) 42:237–48. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2579-3
100. Shuai W, Yiyu Y, Zhigang Y, Mingxue S, Zhidan L, Shulin S, et al. Mitophagy suppresses motor neuron necroptotic mitochondrial damage and alleviates necroptosis that converges to SARM1 in acrylamide-induced dying-back neuropathy. J Neurochem. (2023) 166(3). doi: 10.1111/jnc.15889
101. Alegre-Cortes E, Muriel-Gonzalez A, Canales-Cortes S, Uribe-Carretero E, Martinez-Chacon G, Aiastui A, et al. Toxicity of necrostatin-1 in parkinson’s disease models. Antioxidants (Basel). (2020) 9(6). doi: 10.3390/antiox9060524
102. Petr B, Vishva M D. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16(7). doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.58
103. Kovacs SB, Miao EA. Gasdermins: effectors of pyroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. (2017) 27:673–84. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.05.005
104. Zhu JH, Ouyang SX, Zhang GY, Cao Q, Xin R, Yin H, et al. GSDME promotes MASLD by regulating pyroptosis, Drp1 citrullination-dependent mitochondrial dynamic, and energy balance in intestine and liver. Cell Death Differ. (2024). doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01343-0
105. Hong-Guang D, Ya L, Xu-Sheng L, Xin-Qiang L, Kang-Rong W, Miao-Yun W, et al. Hypercapnia promotes microglial pyroptosis via inhibiting mitophagy in hypoxemic adult rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2020) 26(11). doi: 10.1111/cns.13435
106. Jiujiu Y, Hajime N, Tomohiko M, Hai H, Lori B, Hal MH, et al. Inflammasome activation leads to Caspase-1-dependent mitochondrial damage and block of mitophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2014) 111(43). doi: 10.1073/pnas.1414859111
107. Li Q, Shi N, Cai C, Zhang M, He J, Tan Y, et al. The role of mitochondria in pyroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:630771. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.630771
108. Wei W, Bo Z, Wenwei G, Wenqin S, Jiabao H, Lei Z, et al. Inhibition of PINK1-mediated mitophagy contributes to postoperative cognitive dysfunction through activation of caspase-3/GSDME-dependent pyroptosis. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2023) 14(7). doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00691
109. Wang W, Gao W, Zhang L, Xia Z, Zhao B. SNAP25 ameliorates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by facilitating PINK1-dependent mitophagy and impeding caspase-3/GSDME-dependent pyroptosis. Exp Neurol. (2023) 367:114463. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114463
110. Wang W, Gao W, Gong P, Song W, Bu X, Hou J, et al. Neuronal-specific TNFAIP1 ablation attenuates postoperative cognitive dysfunction via targeting SNAP25 for K48-linked ubiquitination. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:356. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01390-z
111. Jiao K, Lai Z, Cheng Q, Yang Z, Liao W, Liao Y, et al. Glycosides of Buyang Huanwu decoction inhibits inflammation associated with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via the PINK1/Parkin mitophagy pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 325:117766. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117766
112. Zhang L, Lin Y, Bai W, Sun L, Tian M. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome suppresses programmed cell death in traumatic brain injury via PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29:2236–58. doi: 10.1111/cns.14159
113. Chen Y, Wei G, Feng X, Lei E, Zhang L. Dexmedetomidine enhances Mitophagy via PINK1 to alleviate hippocampal neuronal Pyroptosis and improve postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly rat. Exp Neurol. (2024) 379:114842. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114842
114. Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2021) 22:266–82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
115. Stockwell BR, Jiang X, Gu W. Emerging mechanisms and disease relevance of ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. (2020) 30:478–90. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.02.009
116. Anja J, Lukas H, Michael D, Matthias P, Sylvia K, Robert G, et al. Mitochondrial rescue prevents glutathione peroxidase-dependent ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2018) 117(0). doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.01.019
117. Hyemin L, Fereshteh Z, Yilei Z, Jitendra Kumar M, Jongchan K, Li Z, et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. (2020) 22(2). doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0461-8
118. Gan B. Mitochondrial regulation of ferroptosis. J Cell Biol. (2021) 220(9). doi: 10.1083/jcb.202105043
119. Lin Q, Li S, Jin H, Cai H, Zhu X, Yang Y, et al. Mitophagy alleviates cisplatin-induced renal tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis through ROS/HO-1/GPX4 axis. Int J Biol Sci. (2023) 19:1192–210. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.80775
120. Chu C, Wang X, Yang C, Chen F, Shi L, Xu W, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps drive intestinal microvascular endothelial ferroptosis by impairing Fundc1-dependent mitophagy. Redox Biol. (2023) 67:102906. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102906
121. Tang W, Yan C, He S, Du M, Cheng B, Deng B, et al. Neuron-targeted overexpression of caveolin-1 alleviates diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction via regulating mitochondrial fission-mitophagy axis. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21:357. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01328-5
122. Han Z, Wang B, Wen YQ, Li YN, Feng CX, Ding XS, et al. Acteoside alleviates lipid peroxidation by enhancing Nrf2-mediated mitophagy to inhibit ferroptosis for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 223(0). doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.07.018
123. Zhang X, Li G, Chen H, Nie XW, Bian JS. Targeting NKAalpha1 to treat Parkinson’s disease through inhibition of mitophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. (2024) 218:190–204. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.04.002
124. Huang Y, Liang B, Li Z, Zhong Y, Wang B, Zhang B, et al. Polystyrene nanoplastic exposure induces excessive mitophagy by activating AMPK/ULK1 pathway in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells and dopaminergic neurons. vivo. Particle Fibre Toxicol. (2023) 20(1). doi: 10.1186/s12989-023-00556-4
125. Shi RY, Zhu SH, Li V, Gibson SB, Xu XS, Kong JM. BNIP3 interacting with LC3 triggers excessive mitophagy in delayed neuronal death in stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2014) 20:1045–55. doi: 10.1111/cns.12325
126. Deng Z, Ou H, Ren F, Guan Y, Huan Y, Cai H, et al. LncRNA SNHG14 promotes OGD/R-induced neuron injury by inducing excessive mitophagy via miR-182-5p/BINP3 axis in HT22 mouse hippocampal neuronal cells. Biol Res. (2020) 53(1). doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00304-4
127. Xue LX, Chen SF, Xue SX, Liu PD, Liu HB. LncRNA TUG1 compromised neuronal mitophagy in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting sirtuin 1. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2022) 38:1121–36. doi: 10.1007/s10565-022-09700-w
128. Chen Y, Jiao D, Liu Y, Xu X, Wang Y, Luo X, et al. FBXL4 mutations cause excessive mitophagy via BNIP3/BNIP3L accumulation leading to mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome. Cell Death Differ. (2023) 30:2351–63. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01205-1
129. Su SH, Wu YF, Wang DP, Hai J. Inhibition of excessive autophagy and mitophagy mediates neuroprotective effects of URB597 against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:733. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0755-y
130. Shi Y, Fang Q, Hu Y, Mi Z, Luo S, Gan Y, et al. Melatonin ameliorates post-stroke cognitive impairment in mice by inhibiting excessive mitophagy. Cells. (2024) 13(10). doi: 10.3390/cells13100872
131. Wang H, Xiong WC, Mei L. Excessive mitophagy for anxiety. Neuron. (2021) 109:3715–6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.11.007
132. Liu J, Liu L, Han YS, Yi J, Guo C, Zhao HQ, et al. The molecular mechanism underlying mitophagy-mediated hippocampal neuron apoptosis in diabetes-related depression. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:7342–53. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16763
133. Qian B, Jiang RJ, Song JL, Wang CQ. Organophosphorus flame retardant TDCPP induces neurotoxicity via mitophagy-related ferroptosis. Vivo vitro. Chemosphere. (2022) 308:136345. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136345
134. Li X, Ran Q, He X, Peng D, Xiong A, Jiang M, et al. HO-1 upregulation promotes mitophagy-dependent ferroptosis in PM2.5-exposed hippocampal neurons. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2024) 277:116314. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116314
135. Jetto CT, Nambiar A, Manjithaya R. Mitophagy and neurodegeneration: between the knowns and the unknowns. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:837337. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.837337
136. Michael AK, Stephen J K. The effect of exercise on hippocampal integrity: review of recent research. Int J Psychiatry Med. (2005) 35(1). doi: 10.2190/hx7l-4b40-pqny-2a4p
137. Grillo CA, Piroli GG, Rosell DR, Hoskin EK, Mcewen BS, Reagan LP. Region specific increases in oxidative stress and superoxide dismutase in the hippocampus of diabetic rats subjected to stress. Neuroscience. (2003) 121(1). doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(03)00343-9
138. Meichen Y, Olaf S, Andrew J S. The human connectome in Alzheimer disease - relationship to biomarkers and genetics. Nat Rev Neurol. (2021) 17(9). doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00529-1
139. Hong X, Jisong G, Laura AB, Jing X, Alberto S-P, Brian J B. Mitochondrial alterations near amyloid plaques in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. J Neurosci. (2013) 33(43). doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.1836-13.2013
140. Maria M, P Hemachandra R. Abnormal interaction of VDAC1 with amyloid beta and phosphorylated tau causes mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet. (2012) 21(23). doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds360
141. Evandro FF, Yujun H, Konstantinos P, Bryan AA, Jesse SK, Beimeng Y, et al. Mitophagy inhibits amyloid-β and tau pathology and reverses cognitive deficits in models of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci. (2019) 22(3). doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0332-9
142. Zhu J, Guo F, Shelburne J, Watkins S, Chu C. Localization of phosphorylated ERK/MAP kinases to mitochondria and autophagosomes in Lewy body diseases. Brain Pathol (Zurich Switzerland). (2003) 13:473–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2003.tb00478.x
143. Valente E, Abou-Sleiman P, Caputo V, Muqit M, Harvey K, Gispert S, et al. Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Sci (New York NY). (2004) 304:1158–60. doi: 10.1126/science.1096284
144. Franco-Iborra S, Plaza-Zabala A, Montpeyo M, Sebastian D, Vila M, Martinez-Vicente M. Mutant HTT (huntingtin) impairs mitophagy in a cellular model of Huntington disease. Autophagy. (2021) 17:672–89. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1728096
145. Khalil B, El Fissi N, Aouane A, Cabirol-Pol M, Rival T, Liévens J. PINK1-induced mitophagy promotes neuroprotection in Huntington's disease. Cell Death Dis. (2015) 6:e1617. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.581
146. Charmpilas N, Fang EF, Palikaras K. Mitophagy and neuroinflammation: A compelling interplay. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2023) 21:1477–81. doi: 10.2174/1570159X20666220628153632
147. Zhang L, Song H, Ding J, Wang DJ, Zhu SP, Liu C, et al. The mechanism of TNF-alpha-mediated accumulation of phosphorylated tau protein and its modulation by propofol in primary mouse hippocampal neurons: role of mitophagy, NLRP3, and p62/keap1/nrf2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:8661200. doi: 10.1155/2022/8661200
148. Wilkins HM, Carl SM, Weber SG, Ramanujan SA, Festoff BW, Linseman DA, et al. Mitochondrial lysates induce inflammation and Alzheimer's disease-relevant changes in microglial and neuronal cells. J Alzheimers Dis. (2015) 45:305–18. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142334
149. Baufeld C, O'Loughlin E, Calcagno N, Madore C, Butovsky O. Differential contribution of microglia and monocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neural Transm (Vienna Austria 1996). (2018) 125:809–26. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1795-7
150. Pocock JM, Kettenmann H. Neurotransmitter receptors on microglia. Trends Neurosci. (2007) 30:527–35. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.07.007
151. Xu H, Qin W, Hu X, Mu S, Zhu J, Lu W, et al. Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of OTULIN ameliorates microglia activation and neuroinflammation by depressing the activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. J Neuroinflamm. (2018) 15:83. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1117-5
152. Cardona AE, Pioro EP, Sasse ME, Kostenko V, Cardona SM, Dijkstra IM, et al. et al: Control of microglial neurotoxicity by the fractalkine receptor. Nat Neurosci. (2006) 9:917–24. doi: 10.1038/nn1715
153. Prinz M, Priller J. Microglia and brain macrophages in the molecular age: from origin to neuropsychiatric disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2014) 15:300–12. doi: 10.1038/nrn3722
154. Cao LL, Guan PP, Zhang SQ, Yang Y, Huang XS, Wang P. Downregulating expression of OPTN elevates neuroinflammation via AIM2 inflammasome- and RIPK1-activating mechanisms in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Neuroinflamm. (2021) 18:281. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02327-4
155. Green D, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G. Mitochondria and the autophagy-inflammation-cell death axis in organismal aging. Sci (New York NY). (2011) 333:1109–12. doi: 10.1126/science.1201940
156. Zhou R, Yazdi A, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. (2011) 469:221–5. doi: 10.1038/nature09663
157. Lei Q, Tan J, Yi S, Wu N, Wang Y, Wu H. Mitochonic acid 5 activates the MAPK-ERK-yap signaling pathways to protect mouse microglial BV-2 cells against TNFα-induced apoptosis via increased Bnip3-related mitophagy. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2018) 23:14. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0081-5
158. Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Lu L, Zhang H, Zhao C, Pu Y, et al. Copper induces microglia-mediated neuroinflammation through ROS/NF-kappaB pathway and mitophagy disorder. Food Chem Toxicol. (2022) 168:113369. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113369
159. Liu Y, Wang M, Hou X-O, Hu L-F. Roles of microglial mitophagy in neurological disorders. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:979869. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.979869
160. Cheng Y, Liu M, Tang H, Chen B, Yang G, Zhao W, et al. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics indicated nrf2/OPTN-mediated mitophagy inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:6630281. doi: 10.1155/2021/6630281
161. Shao S, Xu CB, Chen CJ, Shi GN, Guo QL, Zhou Y, et al. Divanillyl sulfone suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation via inducing mitophagy to ameliorate chronic neuropathic pain in mice. J Neuroinflamm. (2021) 18:142. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02178-z
162. Han X, Xu T, Fang Q, Zhang H, Yue L, Hu G, et al. Quercetin hinders microglial activation to alleviate neurotoxicity via the interplay between NLRP3 inflammasome and mitophagy. Redox Biol. (2021) 44:102010. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102010
163. Qiu WQ, Ai W, Zhu FD, Zhang Y, Guo MS, Law BY, et al. et al: Polygala saponins inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation via SHP-2-Mediated mitophagy. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 179:76–94. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.263
164. Wu X, Gong L, Xie L, Gu W, Wang X, Liu Z, et al. NLRP3 deficiency protects against intermittent hypoxia-induced neuroinflammation and mitochondrial ROS by promoting the PINK1-parkin pathway of mitophagy in a murine model of sleep apnea. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:628168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.628168
165. Zhang S, Hu L, Jiang J, Li H, Wu Q, Ooi K, et al. HMGB1/RAGE axis mediates stress-induced RVLM neuroinflammation in mice via impairing mitophagy flux in microglia. J Neuroinflamm. (2020) 17:15. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1673-3
166. Oksanen M, Lehtonen S, Jaronen M, Goldsteins G, Hämäläinen R, Koistinaho J. Astrocyte alterations in neurodegenerative pathologies and their modeling in human induced pluripotent stem cell platforms. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS. (2019) 76:2739–60. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03111-7
167. Liddelow S, Barres B. Reactive astrocytes: production, function, and therapeutic potential. Immunity. (2017) 46:957–67. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.06.006
168. Liddelow S, Guttenplan K, Clarke L, Bennett F, Bohlen C, Schirmer L, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature. (2017) 541:481–7. doi: 10.1038/nature21029
169. Sama M, Mathis D, Furman J, Abdul H, Artiushin I, Kraner S, et al. Interleukin-1beta-dependent signaling between astrocytes and neurons depends critically on astrocytic calcineurin/NFAT activity. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:21953–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800148200
170. Sun J, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Hu L, Zhao L, Wang H, et al. Metabolic regulator LKB1 controls adipose tissue ILC2 PD-1 expression and mitochondrial homeostasis to prevent insulin resistance. Immunity. (2024) 57:1289–1305.e1289. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.04.024
171. Trudler D, Nash Y, Frenkel D. New insights on Parkinson’s disease genes: the link between mitochondria impairment and neuroinflammation. J Neural Transm (Vienna). (2015) 122:1409–19. doi: 10.1007/s00702-015-1399-z
172. Rademaker G, Boumahd Y, Peiffer R, Anania S, Wissocq T, Liégeois M, et al. Myoferlin targeting triggers mitophagy and primes ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Redox Biol. (2022) 53:102324. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102324
173. Sarkar S, Malovic E, Harischandra DS, Ngwa HA, Ghosh A, Hogan C, et al. Manganese exposure induces neuroinflammation by impairing mitochondrial dynamics in astrocytes. Neurotoxicology. (2018) 64:204–18. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2017.05.009
174. Hu Z-L, Sun T, Lu M, Ding J-H, Du R-H, Hu G. Kir6.1/K-ATP channel on astrocytes protects against dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease via promoting mitophagy. Brain Behavior Immun. (2019) 81:509–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.07.009
175. Ren YZ, Zhang BZ, Zhao XJ, Zhang ZY. Resolvin D1 ameliorates cognitive impairment following traumatic brain injury via protecting astrocytic mitochondria. J Neurochem. (2020) 154:530–46. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14962
176. Paing YMM, Eom Y, Lee SH. Benzopyrene represses mitochondrial fission factors and PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in primary astrocytes. Toxicology. (2024) 508:153926. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153926
177. Mangalmurti A, Lukens JR. How neurons die in Alzheimer's disease: Implications for neuroinflammation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. (2022) 75:102575. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102575
178. Krasemann S, Madore C, Cialic R, Baufeld C, Calcagno N, El Fatimy R, et al. The TREM2-APOE pathway drives the transcriptional phenotype of dysfunctional microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunity. (2017) 47:566–581.e569. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.08.008
179. Sarhan M, Land W, Tonnus W, Hugo C, Linkermann A. Origin and consequences of necroinflammation. Physiol Rev. (2018) 98:727–80. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2016
180. Adamczak S, de Rivero Vaccari J, Dale G, Brand F, Nonner D, Bullock M, et al. Pyroptotic neuronal cell death mediated by the AIM2 inflammasome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2014) 34:621–9. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.236
181. Conos S, Chen K, De Nardo D, Hara H, Whitehead L, Núñez G, et al. Active MLKL triggers the NLRP3 inflammasome in a cell-intrinsic manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2017) 114:E961–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613305114
Keywords: mitophagy, apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, neuroinflammation
Citation: Zhu Y, Zhang J, Deng Q and Chen X (2024) Mitophagy-associated programmed neuronal death and neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 15:1460286. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1460286
Received: 05 July 2024; Accepted: 10 September 2024;
Published: 02 October 2024.
Edited by:
Yong Cao, Capital Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ravi Manjithaya, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, IndiaHeather M. Wilkins, University of Kansas Medical Center Research Institute, United States
Bowen Sun, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Zhang, Deng and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin Chen, eGluY2hlbnRpYW5qaW5AMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Yanlin Zhu
Yanlin Zhu Jianning Zhang
Jianning Zhang Quanjun Deng1,2,3
Quanjun Deng1,2,3 Xin Chen
Xin Chen