- 1Department of Public Health, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 2Medical Library, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Statistics, Sungkyunkwan University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Introduction: In 2020, global cancer statistics reported 19.3 million new cases and 10 million deaths annually, highlighting the urgent need for effective treatments. Current therapies, such as surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, have limitations in comprehensively addressing solid tumor. Recent advances in cancer biology and immuno-oncology, including CAR-T cell therapy, show promise but face efficacy challenges against solid tumors.
Methods: This meta-analysis systematically reviewed studies from PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and ClinicalTrials.gov databases up to May 2024 to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of unmodified NK cell therapies in solid tumors. The included trials focused on reporting objective response rates (ORR).
Results: Thirty-one trials involving 600 patients across various cancers (e.g., NSCLC, HCC, breast, ovarian) were analyzed. NK cell therapies demonstrated promising ORRs, particularly 72.3% in hepatocellular carcinoma, often in combination with local therapies. Safety profiles were favorable, with fatigue being the most common adverse event.
Discussion: NK cell therapies represent a promising treatment option for solid tumors, offering a viable alternative to genetically modified cell therapies like CAR-T. Further research is needed to optimize the clinical utility of NK cell therapy and integrate it effectively into standard cancer treatment regimens.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42023438410, identifier CRD42023438410.
Introduction
According to the Global Cancer Statistics of 2020, 19.3 million new cases of cancer are diagnosed annually worldwide, with 10 million individuals succumbing to the disease. The most prevalent cancer types include breast cancer (11.7%), lung cancer (11.4%), prostate cancer (7.3%), skin cancer (6.2%), colorectal cancer (6.0%), stomach cancer (5.6%), and liver cancer (4.7%). Notably, lung cancer (18.0%), liver cancer (8.3%), and stomach cancer (7.7%) emerge as the leading causes of cancer-related mortality (1).
Traditional cancer therapies, such as surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, have been standard treatment options for decades. However, their limitations in addressing the complex nature of cancer are becoming increasingly apparent. Recent advances in cancer molecular biology and immuno-oncology have introduced precision and targeted therapeutics, which aim to selectively eliminate cancer cells while minimizing collateral toxicity and side effects.
One significant advancement is CAR-T cell therapy, where genetically engineered immune cells are designed to recognize and eliminate tumor cells with specific surface antigens. CAR-T therapy has shown remarkable success, especially in managing aggressive B-cell malignancies, offering renewed hope for patients. Nevertheless, this approach faces challenges, including limited efficacy against solid tumors, pronounced toxicities like cytokine release syndrome (CRS), complex manufacturing processes, and high costs (2).
In response, alternative strategies such as CAR-NK and CAR-M cells have been developed (2). These innovative therapies aim to leverage the potential of Natural Killer (NK) cells, key components of the human immune system known for their role in innate immunity through cell-mediated cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (3).
Furthermore, NK cells offer several advantages including non-MHC-restricted recognition, the ability to infiltrate tumor microenvironments, potent cytolytic capabilities, and a favorable safety profile with a reduced risk of complications such as CRS, graft-versus- host-disease (GvHD), and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). These attributes make NK cells promising candidates for treating solid tumors (4).
Unlike CAR-T cell therapies, NK cell-based therapies can utilize various sources, including peripheral blood (PB) from healthy donors, umbilical cord blood (UCB), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), or commercially available NK cell lines. This versatility allows for cost-effective mass production and off-the-shelf availability, providing on-demand treatment options (2, 5).
Given these promising attributes, ongoing research is exploring the potential of NK cells, particularly through the development of CAR-NK cells, marking a new frontier in cancer therapy. This meta-analysis aims to systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of unmodified NK cells as a treatment modality for solid cancer patients. This meta-analysis represents a critical step toward integrating NK cell-based therapies into clinical practice and facilitating evidence-based decision-making in cancer therapeutics.
Materials and methods
Literature search and screening
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to identify published clinical trials that utilized combination therapies involving natural killer cells, as well as trials did not, with a focus on reporting objective response rates. The PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and ClinicalTrials.gov databases were searched for papers published from database inception through May 2024, using the terms ‘neoplasms’, ‘hematologic neoplasms’ and ‘killer cells, natural’ (Appendix A). Additionally, we manually examined references from relevant reviews and articles to avoid omitting any pertinent studies.
The PRISMA guidelines were followed during the review process (6). A prospective protocol was registered in PROSPERO, CRD42023438410.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The selection criteria included: (1) articles reporting prospective clinical trials which were published before the literature review date; (2) participants were diagnosed solid cancer; (3) articles in which participants were treated with natural killer cells; and (4) clinical trials reporting the objective response rate. Studies not matching the selection criteria were excluded. Exclusion criteria were: (1) studies without full-text available; (2) non-interventional studies; (3) studies lacking efficacy assessment parameters; and (4) studies in which participants were treated with agents other than NK cells. HS Park and KR Kim independently conducted the literature search and data extraction. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion with a senior author (HW Yim). For publications reporting duplicate populations, we only included the most recent study or the study reporting the most complete efficacy data.
Data extraction
Data extraction was conducted using standardized, pre-piloted forms for study tabulation and quality assessment. Independent investigators (HS Park and KR Kim) extracted the following information: study characteristics (first author, year of publication, if applicable, country, phase, study design, patient number, age, gender, cancer type, previous treatment history, cell origin, expansion duration, infusion dose, dose schedule, adverse events, and treatment response (complete response, partial response, stable disease, progressive disease, objective response rate [ORR], disease control rate [DCR]), and survival (progression-free survival [PFS], overall survival [OS], 6-month and 1-year survival rates). ORR was defined as the sum of all patients demonstrating complete or partial response divided by the total of evaluable patients, and DCR was defined as the sum of all patients demonstrating complete or partial response or stable disease divided by the total of evaluable patients.
Outcome measurement
The primary outcome was objective response rate (ORR), defined as the sum of all patients demonstrating complete or partial response divided by the total of evaluable patients. The secondary outcome was disease control rate (DCR), defined as the sum of all patients demonstrating complete or partial response or stable disease divided by the total of evaluable patients. Safety endpoint was adverse events of any grade, as reported by the individual trials.
Subgroup analysis
Several subgroup analyses were conducted to examine the impact of various factors on the efficacy of NK cell immunotherapy in solid cancer. The subgroups included cancer type, age, study year, subject number, cell origin, expansion duration, infusion dose, IL-2 administration, lymphodepleting chemotherapy regimen, combination treatment. Subgroups were analyzed if they appeared in at least two studies.
Statistical analysis
We performed a meta-analysis using Comprehensive Meta-analysis 4.0. Event rate (ER) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for each outcome. Pooled ORR and DCR were calculated using fixed- and random-effects models depending on the heterogeneity across the included studies (7). The heterogeneity was assessed using I2 values. Generally, I2 values of 25% represent low heterogeneity, and I2 values of 50% and 75% are evidence of moderate and high heterogeneity, respectively. When no statistically significant heterogeneity existed, the analysis was calculated with a fixed-effect model; otherwise, a random-effect model was used. P values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant (8). We performed subgroup analysis to assess the efficacy of natural killer cells with different clinical parameters in all available studies.
The analysis of safety data, the secondary evaluative variable, was conducted using R software version 4.3.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). The “epiR” package was employed to calculate the incidence rate and its corresponding 95% confidence interval.
Begg’s and Egger’s tests were used to assess publication bias and a publication bias was indicated by p-value < 0.05 in Begg’s or Egger’s values (9, 10). Sensitivity analyses were conducted using both fixed and random effects models.
The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the ROBINS-I tool (Risk of Bias in Non-Randomized Studies of Interventions), which assesses the risk of bias across seven domains: confounding, participant selection, intervention classification, deviations from intended interventions, missing data, outcome measurement, and selection of reported results. Each study was categorized as having low, moderate, or high risk of bias. Risk of bias was independently assessed by two reviewers, with disagreements resolved by a third reviewer. To explore the impact of study bias on outcomes, we conducted a separate analysis of studies classified as having low or moderate risk of bias (11).
Results
Selection of clinical trials
A total of 3076 publications were retrieved through the initial literature search, and 1905 studies remained after duplications were excluded. After reviewing titles and abstracts, 1774 publications were excluded because the topics were irrelevant, the articles were reviews, the studies were not used NK cells as an intervention, or no usable data were reported. 131 potentially relevant articles were identified for detailed review.
After a full-text review, 100 studies were excluded for the following reasons: 52 lacked full text or relevant information, 37 involved patients with pre-existing partial response (PR) or higher responsiveness, 8 were used cells other than NK cells, 3 were non-intervention studies.
After this process, 31 clinical trials involving 600 patients were identified as eligible to be included in the meta-analysis (Figure 1) (12–42).
Characteristics of the included trials
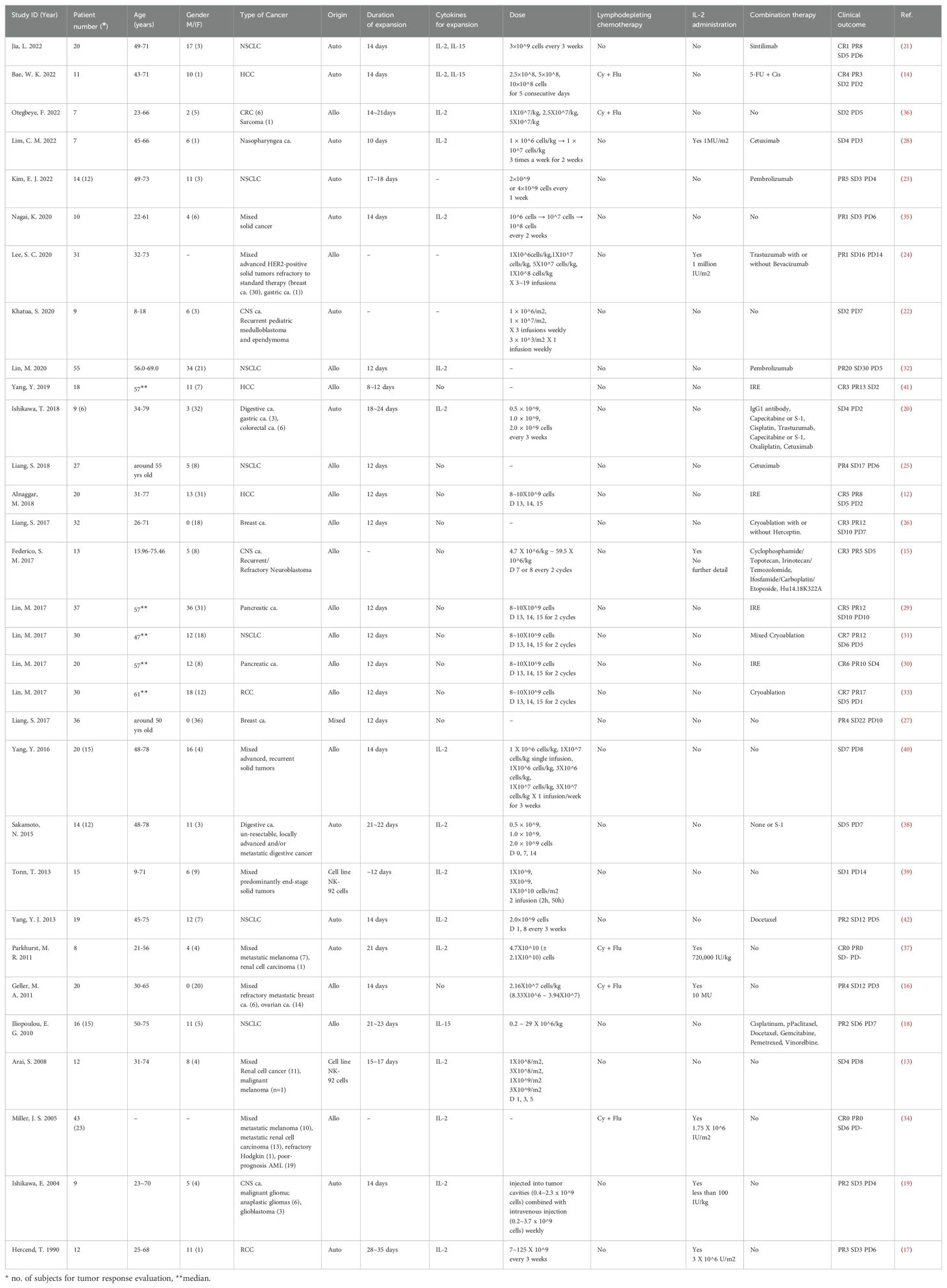
A total of 600 patients were included in this meta-analysis from 31 selected references. All the studies focused on solid tumor patients, and they were further classified by cancer type, with 7 studies involving Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC), 3 studies on Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), and 2 studies each on Breast and Ovarian Cancer, Pancreatic Cancer, Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC), Central Nervous System Tumors (CNS tumor), and Digestive System Cancers. One study was centered on Nasopharyngeal Cancer, while 9 studies encompassed all solid tumor types. Regarding the origin of cells, 15 studies used allogeneic cells, 12 used autologous cells, 2 employed cell lines, and 1 study utilized both allogeneic and autologous cells. Additionally, 8 studies incorporated lymphodepleting chemotherapy prior to NK cell infusion, 8 combined NK cell therapy with IL-2, and 19 studies combined NK cell therapy with other anticancer treatments. These characteristics reflect the diversity within the meta-analysis, covering patient demographics, cell sources, cancer types, and the incorporation of various treatment approaches.
All included 31 clinical trials reported the outcomes of NK cell treatment. 15 trials with 218 patients reported the number of therapeutic toxicities of NK cell. The characteristics of all included studies are summarized in Table 1.
ORR and DCR of NK cell treatment outcome
Forest plots showing the best ORR and DCR with 95% CI are presented in Figure 2.
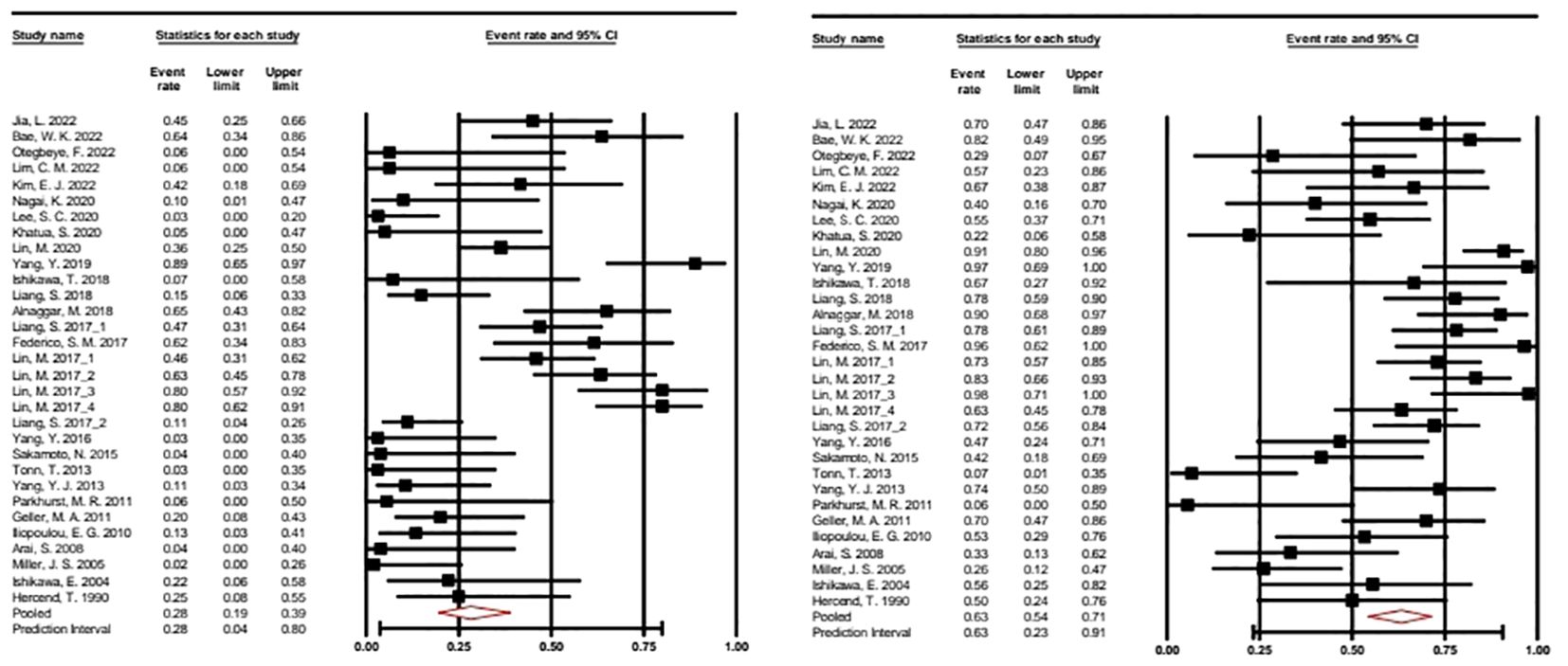
Figure 2. Forest plot of the overall response rate and disease control rate with 95% CI. A random effects model was applied. ORR: 0.282 (95% CI: 0.914–0.389). Heterogeneity: I2 = 77.192%; p = 0.000. DCR: 0.632 (95% CI: 0.543–0.713). Heterogeneity: I2 68.347%; p = 0.000. CRR, Complete response rate; ORR, Overall response rate.
In our meta-analysis of 31 selected studies, we examined both Overall Response Rate (ORR) and Disease Control Rate (DCR), using the event rate as the effect size index. To account for potential study variability, we applied a random-effects model, considering these studies as a random sample from a broader universe of similar research. For ORR, the mean effect size was calculated at 0.282 (95% CI: 0.194 - 0.389), while for DCR, it is determined as 0.632 (95% CI: 0.543 - 0.713). These values represent the response rates across the studies. Heterogeneity analysis indicated significant variability among the included studies for both ORR (I2 = 77%) and DCR (I2 = 68%), with Q-tests for heterogeneity producing highly significant results (p < 0.001) in both cases.
Subgroup analysis based on various clinical factors
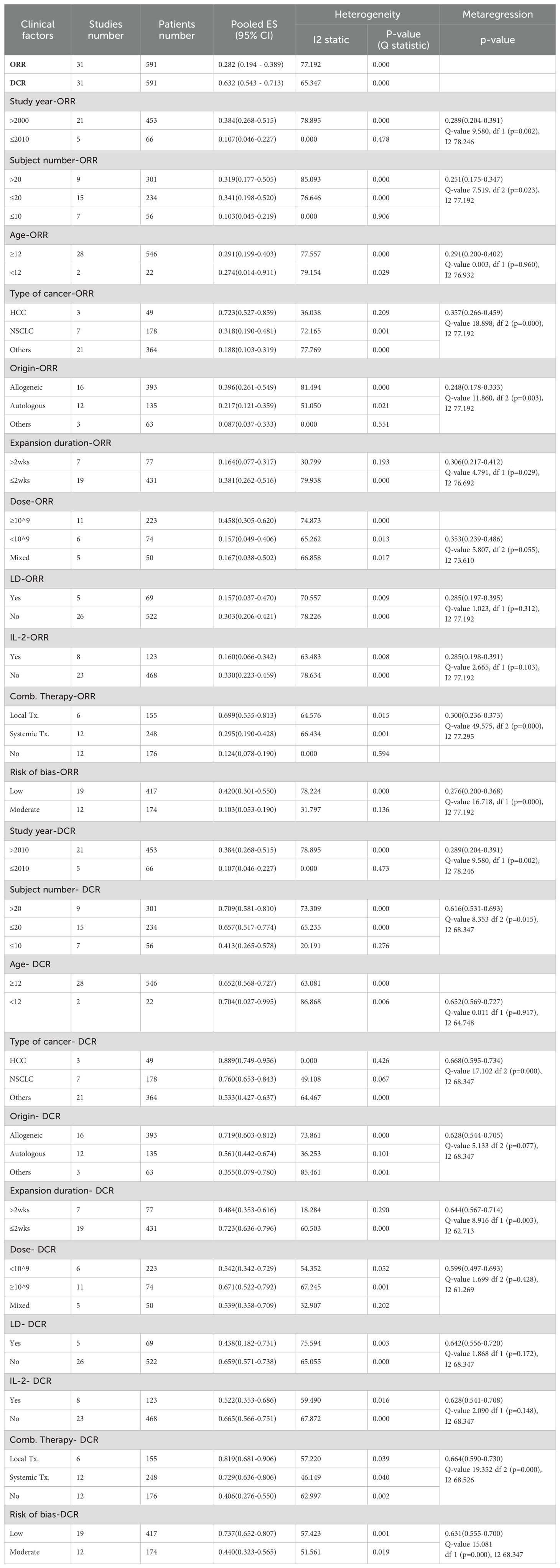
Due to a considerable heterogeneity detected in ORR and DCR, we conducted several comprehensive subgroup analyses and metaregressions according to the protocol designed at the beginning of the study. The results of subgroup analyses and metaregressions based on different factors are presented in Table 2, including the number of studies, the number of patients, pooled ORR and DCR with 95% CI, heterogeneity and p-value for metaregression. The random effects model was applied due to significant heterogeneity as shown in Table 2.
Sub-analysis for ORR showed statistically significant results, with a 72.3% (0.527-0.859) ORR in hepatocellular carcinoma patients and 69.9% (0.555-0.813) in patients receiving combination with local treatment, and allogenic NK cells showed better ORR at 39.6% (0.261-0.549) than autologous NK cells. In addition, 38.1% (0.262-0.516) showed a better response rate when the culture period was within 2 weeks, and 45.8% (0.305-0.620) when the number of cells administered was ≥10^9. Contrary to expectations, the use of lymphodepletion or IL-2 administration demonstrated significantly lower ORR, with values of 30.3% (95% CI: 0.206-0.421) and 33.0% (95% CI: 0.223-0.459), respectively.
These results showed a similar trend in the sub-analysis of DCR.
Overall incidence of AEs
The meta-analysis included 15 out of the 31 studies, comprising a total of 218 participants, where adverse events with specified Grades were reported. Among Grade 1-2 adverse events, fatigue was the most common, at 44% (95% CI: 0.34-0.56), followed by nausea at 37% (95% CI: 0.25-0.53) and anemia at 33% (95% CI: 0.22-0.47). Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions included Headache occurred in 25% (95% CI: 0.16-0.37), Anorexia in 8% (95% CI: 0.02-0.20), and neutropenia at 7% (95% CI: 0.03-0.16). Notably, no cases of Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) or Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD), common side effects of cell therapies like CAR-T, were reported (Figure 3).
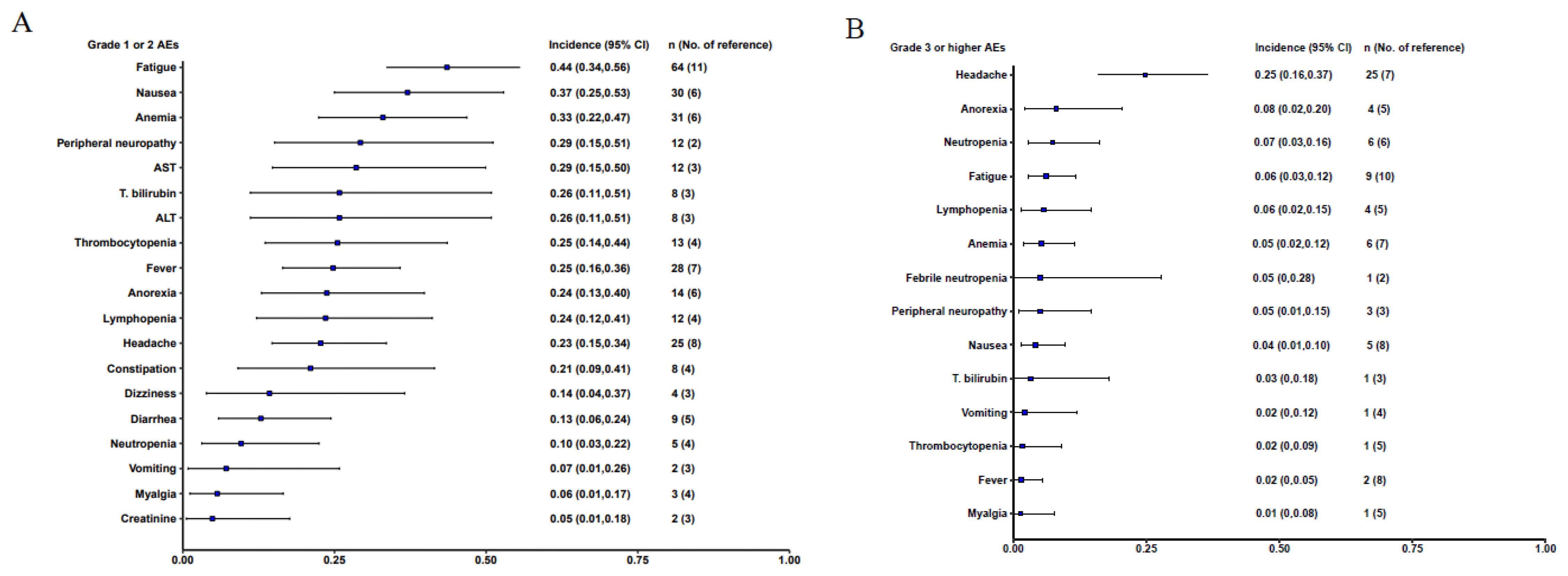
Figure 3. Forest plot of the overall incidence AEs with 95% CI. (A). Grade 1 or 2 adverse events; (B) Grade 3 or higher adverse event.
Publication bias, sensitivity analysis, and risk of bias
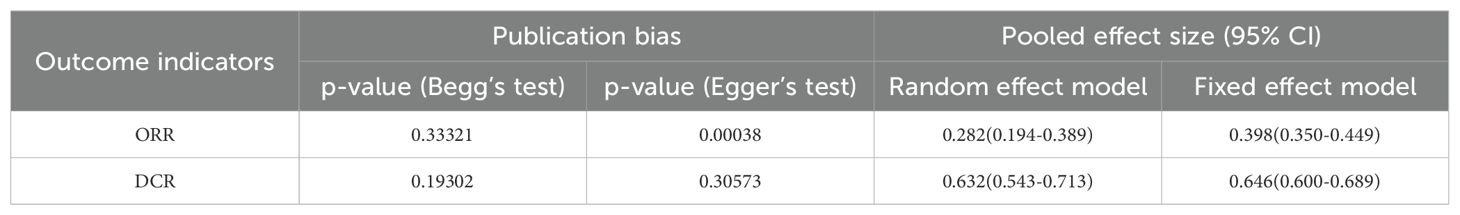
Begg’s rank correlation and Egger’s regression analyses were performed to evaluate publication bias. A publication bias was indicated by p-value < 0.05 in Begg’s or Egger’s tests. Publication bias was detected for ORR. In the sensitivity analysis, a significant difference was observed in the pooled ES for the best ORR and DCR based on the fixed and random effects models (Table 3).
Sensitivity analyses were performed to assess the stability of the results by sequentially removing each study. The removal of any single study did not change the overall statistical results, indicating that the results of this study were statistically robust (Figure 4).
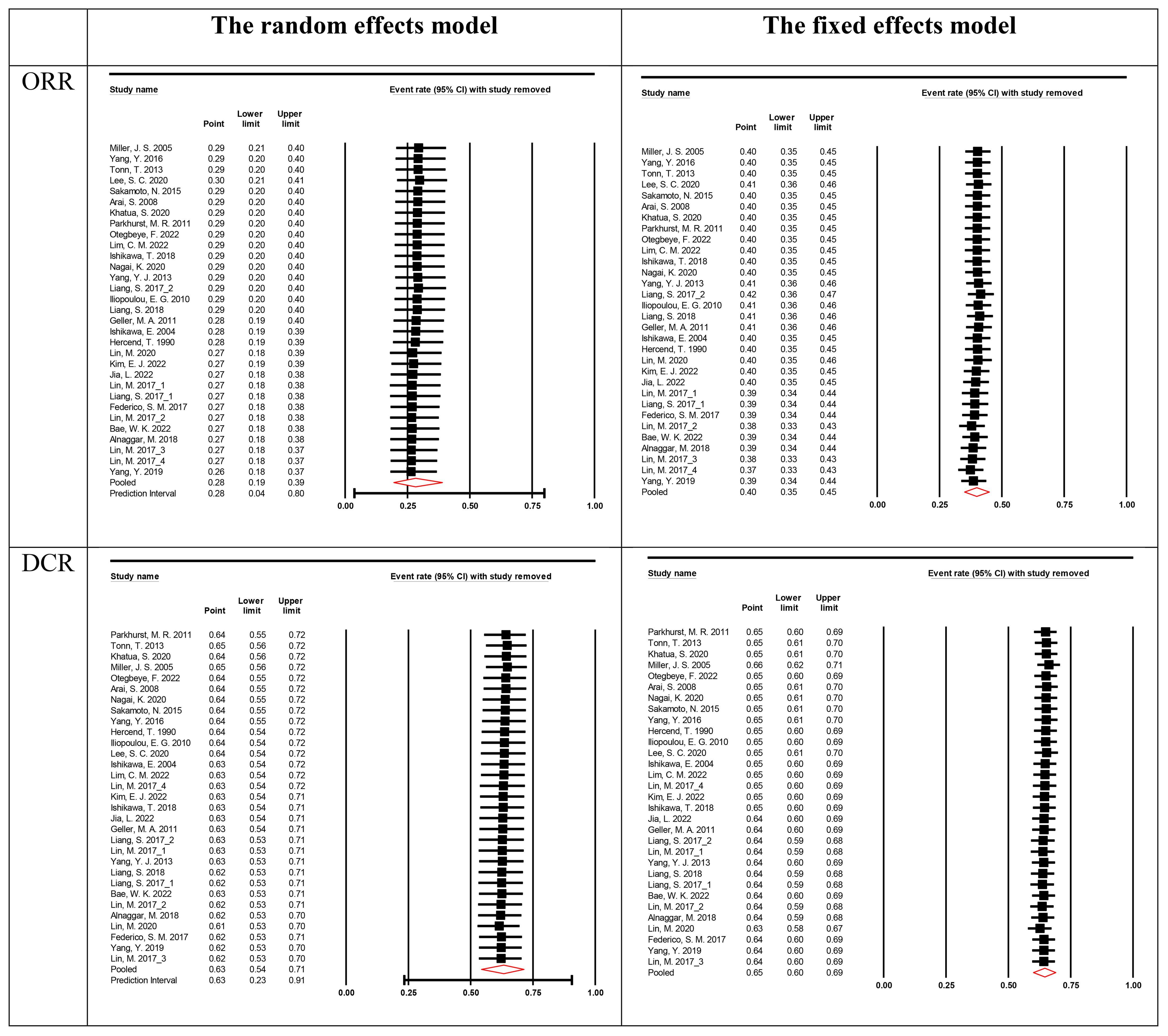
Figure 4. Sensitivity analysis for the best overall response rate. The vertical line on the left indicated the total lower CI, the vertical line in the middle indicated the total pooled effect size and the vertical line on the right indicated the total higher CI. The circle indicated the pooled effect size after deleting the study.
Using the ROBINS-I tool, we assessed the risk of bias in 19 studies as low and in 12 studies as moderate (Appendix B). This thorough evaluation enabled us to explore the relationship between study quality and reported outcomes, specifically Overall Response Rate (ORR) and Disease Control Rate (DCR). Our analysis revealed a clear pattern: studies with low risk of bias consistently demonstrated more favorable outcomes (Tables 2, 3).
Discussion
In our study, we conducted a meta-analysis and systematic review of 31 studies involving the administration of non-genetically modified natural killer (NK) cells to patients with solid tumors. The objective response rate (ORR), defined as a response of partial response or better, was 28.2% (95% CI: 0.194 - 0.389), and the disease control rate (DCR), defined as stable disease or better, was 63.2% (95% CI: 0.543 - 0.713).
The meta-analysis included studies ranging from the early stages of NK cell research starting in 1999 to advancements in technology up to 2020, without limiting the timeframe. Consequently, the more recent studies from 2011 to 2020 showcased an ORR of 38.4% (95% CI: 0.268-0.515) and a DCR of 72.7% (95% CI: 0.648-0.794), suggesting the possibility that advancements in NK cell manufacturing technology and related developments may contribute to the enhanced efficacy of cell therapy, indicating the potential of NK cells as a new option for solid tumor patients without effective treatments.
Particularly noteworthy were the high ORR of 72.3% (95% CI: 0.527-0.859) and DCR of 88.9% (95% CI: 0.749-0.956) observed in hepatocellular carcinoma. Among the three clinical trials involving liver cancer patients, two included irreversible electroporation (IRE) and one involved a combination with intrahepatic arterial chemotherapy. When NK cells were combined with local therapies, such as IRE, the observed ORR was 69.9% (95% CI: 0.555-0.813), and the DCR was 81.9% (95% CI: 0.681-0.906). Notably, these outcomes exhibited superior efficacy compared to the concomitant use of systemic treatments (ORR 0.295, 95% CI: 0.190-0.428; DCR 0.729, 95% CI: 0.636-0.806) or administration of NK cells alone (ORR 0.124, 95% CI: 0.078-0.190; DCR 0.406, 95% CI: 0.276-0.550). This underscores the heightened effectiveness achieved through the strategic selection of combination therapies, emphasizing their potential in maximizing the therapeutic impact of NK cells. Hence, choosing appropriate combination therapies tailored to each cancer type is crucial to optimizing the therapeutic efficacy of NK cells.
Cytokines such as IL-2 and IL-15 play a role in the development of NK cell cytotoxic function and stimulation of NK cell proliferation when administered during cell culture or in combination with cells (43–46). Among the 31 studies included in the meta-analysis, 16 studies used IL-2, two studies used both IL-2 and IL-15, and one study used IL-15 for NK cell expansion. Additionally, eight studies administered IL-2 to patients. Despite IL-2 being recognized for its critical role in immune system activation and induction of tumor cell death through Fc γ receptor binding, our meta-analysis revealed lower ORR and DCR when combined with IL-2, with respective values of 0.160 (95% CI: 0.066-0.342) and 0.522 (95% CI: 0.353-0.686), compared to non-combined scenarios (ORR 0.330, 95% CI: 0.223-0.459; DCR 0.665, 95% CI: 0.566-0.751) (47).
One of the known function of IL-2 is to promote T cell proliferation. However, at low doses, IL-2 selectively stimulates the expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs). This increase in Tregs can suppress the overall immune response against tumors by inhibiting the activity of cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. Although the exact doses of IL-2 used in the studies were not specified, it is plausible that low-dose IL-2 contributed to reduced NK cell efficacy by promoting Treg expansion. Elevated Treg levels may have suppressed NK cell activity, thereby diminishing the effectiveness of NK cell therapy (48).
Similar trends were observed regarding the use of lymphodepleting chemotherapy (LD). Although LD is commonly used in CAR-T cell therapy to enhance therapeutic efficacy, it was performed in five clinical cases in our meta-analysis (49). Surprisingly, our meta-analysis found that cases without LD showed higher ORR 30.3% (95% CI: 0.206-0.421) and DCR 66.5% (95% CI: 0.566-0.751) compared to those with LD (ORR 15.7%, 95% CI: 0.037-0.470; DCR 43.8%, 95% CI: 0.182-0.731) (50).
Despite potential biases due to limited sample sizes and study numbers, the observed results raise questions about the application of IL-2 and LD in solid tumors, indicating the need for further investigation.
Regarding NK cell sourcing, allogeneic cells demonstrated superior efficacy compared to autologous cells (ORR 39.6%, 95% CI: 0.261-0.549; DCR 71.9%, 95% CI: 0.603-0.812 vs. ORR 21.7%, 95% CI: 0.121-0.359; DCR 56.1%, 95% CI: 0.442-0.674). This enhanced efficacy of allogeneic NK cells can be attributed to the donor-recipient incompatibility in killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I. In allogeneic settings, the mismatch between the KIRs on donor NK cells and the MHC class I molecules on recipient cells disrupts the inhibitory signaling that would normally suppress NK cell activity. This mismatch leads to greater NK cell activation, allowing the allogeneic NK cells to target and destroy tumor cells more effectively. Furthermore, autologous NK cells are often derived from patients who have received extensive prior cancer treatments, like chemotherapy or radiation. These treatments can impair NK cell function by causing exhaustion, altering their phenotype, and reducing their cytotoxic potential. As a result, NK cells from pre-treated patients may be less effective compared to those from healthy donors, further limiting the efficacy of autologous NK cell therapy (51, 52).
The advantages of allogeneic NK cells, particularly their off-the-shelf potential, were highlighted, considering the lengthy and costly production process of CAR-T cells. Although recent developments aim to simplify the manufacturing process and explore allogeneic CAR-T cells, challenges such as graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) persist. Notably, NK cell characteristics demonstrated higher efficacy without reports of GvHD or cytokine release syndrome (CRS) (53).
The most commonly reported adverse event was fatigue, highlighting the safety advantages of NK cells. Through this meta-analysis, we have demonstrated that non-genetically modified NK cells can be an effective and safe option for solid tumors. The diverse results from subgroup analyses provide insights into various considerations for the future development of NK cell therapies.
Our Robins-I analysis revealed a consistent trend of improved ORR and DCR in studies with low risk of bias, emphasizing the importance of reducing bias for reliable outcomes. Both ORR and DCR analyses revealed a significant improvement in studies with low bias, highlighting a stronger treatment effect. This emphasizes the importance of reducing bias for reliable outcomes and underscores the need for rigorous study design and execution when evaluating treatment efficacy.
Strengths and weaknesses
Strengths
Pioneering Exploration in Solid Tumor Patients: This study represents the first meta-analysis to explore the efficacy of NK cells specifically in solid tumor patients. While there have been meta-analyses on NK cell administration in hematologic cancers, this study breaks new ground by focusing on solid tumor patients. Considering the expanding scope of cell therapies, including NK cells, beyond hematologic malignancies, this research is poised to contribute significantly.
Conducting Diverse Subgroup Analyses: To address potential heterogeneity from studies spanning an extended period, this research conducted diverse subgroup analyses. By exploring factors such as study timelines, cell origins, cell culture durations, and cancer types, the study aimed to identify sources of heterogeneity and investigate efficacy outcomes based on various characteristics.
Robustness in Pre-defined Sensitivity Analyses: The key findings demonstrated robustness through pre-defined sensitivity analyses.
No Restriction on Publication Years: By including all research on NK cell therapy up to the present without restricting publication years, the study provides a comprehensive overview of the field.
Weaknesses
Inherent Challenges in Cross-Trial Comparisons: Ensuring comparability across clinical trials conducted over several decades is challenging. Given the diverse solid tumor types included and changes in standard therapies for these cancers over the 20-year period, the study may not be directly applicable to contemporary clinical decision-making.
Confirmed Heterogeneity and Potential Bias in Analyses: Despite using random-effect models to account for heterogeneity, the diversity in concomitant treatment and patient populations may introduce potential biases. Despite conducting various subgroup analyses, differences in study designs might still impact the results.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis confirms the efficacy of NK cell administration in patients with solid tumors, demonstrating a significant increase in Overall Response Rate (ORR) and Disease Control Rate (DCR). Additionally, the safety profile of NK cell therapy is reinforced by the absence of significant adverse events, such as Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
It is crucial to consider variations in efficacy based on cancer types and combination therapies for informed treatment decisions. Looking ahead, cell-based therapies, particularly those involving advanced genetic manipulation of NK cells, represent a pivotal frontier in drug development. Refining NK cells, especially through the use of allogeneic cells, promises not only enhanced efficacy but also a favorable toxicity profile. This progress is expected to lead to the development of optimized NK cells as off-the-shelf products, ushering in a transformative new era in cell-based therapies. Continued exploration and integration of these advancements are essential for improving patient outcomes and revolutionizing therapeutic strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GK: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. NK: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SH: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. HY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454427/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Maalej KM, Merhi M, Inchakalody VP, Mestiri S, Alam M, Maccalli C, et al. CAR-cell therapy in the era of solid tumor treatment: current challenges and emerging therapeutic advances. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01723-z
3. Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:503–10. doi: 10.1038/ni1582
4. Laskowski TJ, Biederstadt A, Rezvani K. Natural killer cells in antitumour adoptive cell immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2022) 22:557–75. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00491-0
5. Liu S, Galat V, Galat Y, Lee YKA, Wainwright D, Wu L. NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: from basic biology to clinical development. J Hematol Oncol. (2021) 14:7. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01014-w
6. Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and metaanalysis protocols (PRISMA-p) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. (2015) 350:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647
7. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. (1986) 7:177–88. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
8. Turner RM, Davey J, Clarke MJ, Thompson SG, Higgins JP. Predicting the extent of heterogeneity in meta-analysis, using empirical data from the cochrane database of systematic reviews. Int J Epidemiol. (2012) 41:818–27. doi: 10.1093/ije/dys041
9. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. (1994) 50:1088–101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
10. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
11. Sterne JA, Hernan MA, Reeves BC, Savovic J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-i: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. (2016) 355:i4919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4919
12. Alnaggar M, Lin M, Mesmar A, Liang S, Qaid A, Xu K, et al. Allogenic natural killer cell immunotherapy combined with irreversible electroporation for stage IV hepatocellular carcinoma: survival outcome. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 48:1882–93. doi: 10.1159/000492509
13. Arai S, Meagher R, Swearingen M, Myint H, Rich E, Martinson J, et al. Infusion of the allogeneic cell line NK-92 in patients with advanced renal cell cancer or melanoma: a phase I trial. Cytotherapy. (2008) 10:625–32. doi: 10.1080/14653240802301872
14. Bae WK, Lee BC, Kim HJ, Lee JJ, Chung IJ, Cho SB, et al. A phase I study of locoregional high-dose autologous natural killer cell therapy with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:879452. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.879452
15. Federico SM, McCarville MB, Shulkin BL, Sondel PM, Hank JA, Hutson P, et al. A pilot trial of humanized anti-GD2 monoclonal antibody (hu14.18K322A) with chemotherapy and natural killer cells in children with recurrent/refractory neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:6441–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0379
16. Geller MA, Cooley S, Judson PL, Ghebre R, Carson LF, Argenta PA, et al. A phase II study of allogeneic natural killer cell therapy to treat patients with recurrent ovarian and breast cancer. Cytotherapy. (2011) 13:98–107. doi: 10.3109/14653249.2010.515582
17. Hercend T, Farace F, Baume D, Charpentier F, Droz JP, Triebel F, et al. Immunotherapy with lymphokine-activated natural killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2: a feasibility trial in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Biol Response Mod. (1990) 9:546–55.
18. Iliopoulou EG, Kountourakis P, Karamouzis MV, Doufexis D, Ardavanis A, Baxevanis CN, et al. A phase I trial of adoptive transfer of allogeneic natural killer cells in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2010) 59:1781–9. doi: 10.1007/s00262-010-0904-3
19. Ishikawa E, Tsuboi K, Saijo K, Harada H, Takano S, Nose T, et al. Autologous natural killer cell therapy for human recurrent malignant glioma. Anticancer Res. (2004) 24:1861–71.
20. Ishikawa T, Okayama T, Sakamoto N, Ideno M, Oka K, Enoki T, et al. phase I clinical trial of adoptive transfer of expanded natural killer cells in combination with IgG1 antibody in patients with gastric or colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. (2018) 142:2599–609. doi: 10.1002/ijc.v142.12
21. Jia L, Chen N, Chen X, Niu C, Liu Z, Ma K, et al. Sintilimab plus autologous NK cells as second-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer previous treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1074906. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1074906
22. Khatua S, Cooper LJN, Sandberg DI, Ketonen L, Johnson JM, Rytting ME, et al. phase I study of intraventricular infusions of autologous ex vivo expanded NK cells in children with recurrent medulloblastoma and ependymoma. Neuro Oncol. (2020) 22:1214–25. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa047
23. Kim EJ, Cho YH, Kim DH, Ko DH, Do EJ, Kim SY, et al. A phase I/IIa randomized trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of SNK01 plus pembrolizumab in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 54:1005–16. doi: 10.4143/crt.2021.986
24. Lee SC, Shimasaki N, Lim JSJ, Wong A, Yadav K, Yong WP, et al. phase I trial of expanded, activated autologous NK-cell infusions with trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive cancers. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26:4494–502. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-0768
25. Liang S, Lin M, Niu L, Xu K, Wang X, Liang Y, et al. Cetuximab combined with natural killer cells therapy: An alternative to chemoradiotherapy for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Am J Cancer Res. (2018) 8:879–91.
26. Liang S, Niu L, Xu K, Wang X, Liang Y, Zhan M, et al. Tumor cryoablation in combination with natural killer cells therapy and herceptin in patients with HER2-overexpressing recurrent breast cancer. Mol Immunol. (2017) 92:45–53. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.10.003
27. Liang S, Xu K, Niu L, Wang X, Liang Y, Zhang M, et al. Comparison of autogeneic and allogeneic natural killer cells immunotherapy on the clinical outcome of recurrent breast cancer. OncoTargets Ther. (2017) 10:4273–81. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S139986
28. Lim CM, Liou A, Poon M, Koh LP, Tan LK, Loh KS, et al. phase I study of expanded natural killer cells in combination with cetuximab for recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:2277–86. doi: 10.1007/s00262-022-03158-9
29. Lin M, Liang S, Wang X, Liang Y, Zhang M, Chen J, et al. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation combined with allogeneic natural killer cell immunotherapy for patients with unresectable (stage III/IV) pancreatic cancer: a promising treatment. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2017) 143:2607–18. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2513-4
30. Lin M, Liang S, Wang X, Liang Y, Zhang M, Chen J, et al. Short-term clinical efficacy of percutaneous irreversible electroporation combined with allogeneic natural killer cell for treating metastatic pancreatic cancer. Immunol Lett. (2017) 186:20–7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.03.018
31. Lin M, Liang SZ, Wang XH, Liang YQ, Zhang MJ, Niu LZ, et al. Clinical efficacy of percutaneous cryoablation combined with allogenic NK cell immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Immunol Res. (2017) 65:880–7. doi: 10.1007/s12026-017-8927-x
32. Lin M, Luo H, Liang S, Chen J, Liu A, Niu L, et al. Pembrolizumab plus allogeneic NK cells in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:2560–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI132712
33. Lin M, Xu K, Liang S, Wang X, Liang Y, Zhang M, et al. Prospective study of percutaneous cryoablation combined with allogenic NK cell immunotherapy for advanced renal cell cancer. Immunol Lett. (2017) 184:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.03.004
34. Miller JS, Soignier Y, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, McNearney SA, Yun GH, Fautsch SK, et al. Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood. (2005) 105:3051–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2974
35. Nagai K, Harada Y, Harada H, Yanagihara K, Yonemitsu Y, Miyazaki Y. Highly activated ex vivo-expanded natural killer cells in patients with solid tumors in a phase I/IIa clinical study. Anticancer Res. (2020) 40:5687–700. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14583
36. Otegbeye F, Cooper B, Caimi P, Zamborsky K, Reese-Koc J, Hillian A, et al. A phase I study to determine the maximum tolerated dose of ex vivo expanded natural killer cells derived from unrelated, HLA-disparate adult donors. Transplant Cell Ther. (2022) 28:250. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.02.008
37. Parkhurst MR, Riley JP, Dudley ME, Rosenberg SA. Adoptive transfer of autologous natural killer cells leads to high levels of circulating natural killer cells but does not mediate tumor regression. Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 17:6287–97. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1347
38. Sakamoto N, Ishikawa T, Kokura S, Okayama T, Oka K, Iden M, et al. phase I clinical trial of autologous NK cell therapy using novel expansion method in patients with advanced digestive cancer. J Transl Med. (2015) 13:277. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0632-8
39. Tonn T, Schwabe D, Klingemann HG, Becker S, Esser R, Koehl U, et al. Treatment of patients with advanced cancer with the natural killer cell line NK-92. Cytotherapy. (2013) 15:1563–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.06.017
40. Yang Y, Lim O, Kim TM, Ahn YO, Choi H, Chung H, et al. phase I study of random healthy donor-derived allogeneic natural killer cell therapy in patients with malignant lymphoma or advanced solid tumors. Cancer Immunol Res. (2016) 4:215–24. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0118
41. Yang Y, Qin Z, Du D, Wu Y, Qiu S, Mu F, et al. Safety and short-term efficacy of irreversible electroporation and allogenic natural killer cell immunotherapy combination in the treatment of patients with unresectable primary liver cancer. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. (2019) 42:48–59. doi: 10.1007/s00270-018-2069-y
42. Yang YJ, Park JC, Kim HK, Kang JH, Park SY. A trial of autologous ex vivo-expanded NK cell-enriched lymphocytes with docetaxel in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer as second- or third-line treatment: phase IIa study. Anticancer Res. (2013) 33:2115–22.
43. Wu Y, Tian Z, Wei H. Developmental and functional control of natural killer cells by cytokines. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00930
44. Wang N, Meng Y, Wu Y, He J, Liu F. Efficacy and safety of chimeric antigen receptor T cell immunotherapy in b-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Immunotherapy. (2021) 13:345–57. doi: 10.2217/imt-2020-0221
45. Paul S, Lal G. The molecular mechanism of natural killer cells function and its importance in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1124. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01124
46. Geller MA, Miller JS. Use of allogeneic NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. (2011) 3:1445–59. doi: 10.2217/imt.11.131
47. Mortara L, Balza E, Bruno A, Poggi A, Orecchia P, Carnemolla B. Anti-cancer therapies employing IL-2 cytokine tumor targeting: contribution of innate, adaptive and immunosuppressive cells in the anti-tumor efficacy. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02905
48. Sprent J, Boyman O. Optimising IL-2 for cancer immunotherapy. Immune Netw. (2024) 24:e5. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e5
49. Mohty M, Minnema MC. Lymphodepleting conditioning regimens. In: Kroger N editors. The EBMT/EHA CAR-T cell handbook. (Cham CH: Springer Nature). (2022). 131–3.
50. Bechman N, Maher J. Lymphodepletion strategies to potentiate adoptive t-cell immunotherapy - what are we doing; where are we going? Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2021) 21:627–37. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1857361
51. Lim O, Jung MY, Hwang YK, Shin EC. Present and future of allogeneic natural killer cell therapy. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:286. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00286
52. Terme M, Ullrich E, Delahaye NF, Chaput N, Zitvogel L. Natural killer cell-directed therapies: moving from unexpected results to successful strategies. Nat Immunol. (2008) 9:486–94. doi: 10.1038/ni1580
53. Balfour H. Could CAR T therapies be manufactured in one day. Eur Pharm Rev. (2022). Available at: https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/169838/could-car-t-therapies-be-manufactured-in-one-day/.
Keywords: killer cells, natural, NK cells, neoplasms, review, systematic, meta-analysis
Citation: Park H, Kim G, Kim N, Ha S and Yim H (2024) Efficacy and safety of natural killer cell therapy in patients with solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 15:1454427. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1454427
Received: 25 June 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 16 October 2024.
Edited by:
Massimiliano Petrini, Scientific Institute of Romagna for the Study and Treatment of Tumors (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Yuan Tian, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, ChinaHiroshi Terunuma, Biotherapy Institute of Japan, Inc., Japan
Yanlin Yu, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United States
Copyright © 2024 Park, Kim, Kim, Ha and Yim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hyeonwoo Yim, eTE2OTNAY2F0aG9saWMuYWMua3I=
 Heesook Park
Heesook Park Gyurin Kim1
Gyurin Kim1 Hyeonwoo Yim
Hyeonwoo Yim