- 1Wonderlab Innovation Centre for Healthcare, Shenzhen Porshealth Bioengineering Co., Ltd, Shenzhen, China
- 2Department of Research and Development, Shenzhen Xbiome Biotech Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China
- 3Emergency Department, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Guangzhou, China
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, University of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences Qingdao Hospital (Qingdao Municipal Hospital), Qingdao, China
Introduction: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a widespread upper airway disorder characterized by inflammation of the nasal passages. It is immunologically mediated via the hypersensitivity type I mechanism, which is primarily elicited by the immunoglobulin E (IgE)-linking allergen-induced imbalance of the Th2/Th1 immune response. Owing to the limited efficacy of current medications, probiotics have received attention for their potential in preventing and ameliorating AR.
Methods: In this study, a Lacticaseibacillus paracasei strain, GOLDGUTLpc969 (Lpc969), isolated from the feces of healthy adults, was proven to be effective in preventing AR by LPA-induced RBL-2H3 in-vitro and OVA-induced AR mice in-vivo evaluation.
Results: The strain significantly attenuated the release of histamine and degranulation in LPS-induced RBL-2H3 cells. In the OVA-induced AR mice, L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 also exhibited a significant decrease in disease indicators such as the disease activity index (DAI score), serum IgE, and serum histamine. Treatment with L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 led to significant suppression of the Th2-related cytokines IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-13, and TNF-α in the serum of mice.
Discussion: Furthermore, a comparison of the genomes of three previously reported AR-effective L. paracasei strains (including GOLDGUTLpc969) and one non-effective L. paracasei strain revealed that the gene K03671 may play a key role in alleviating AR symptoms. In conclusion, this study highlights the efficacy of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 in AR prevention by suppressing the Th2 immune response and proposes the potential involvement of the functional gene K03671 in ameliorating AR symptoms. Therefore, L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 shows promise as a probiotic for preventing AR.
Introduction
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is an upper-airway disorder characterized by inflammation of the nasal passages, commonly caused by allergic reactions to allergens such as pollen, dust mites, or animal dander. According to the World Allergy Organization, the global prevalence rate of AR ranges from 10% to 30% in adults (1), of which approximately 3.6% of AR patients experience work absenteeism, and 36% experience reduced work productivity (2). However, the current treatments for AR patients include immunotherapy, which is expensive, leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs), and intranasal steroids, which are linked to a higher incidence of side effects and a limited therapeutic benefit (3–6). Thus, there is still a need to create safe and efficient therapeutic and preventive approaches for such public health issues.
During the pathological development of AR, the Th2-predominant response is brought on by various phases of the sensitization process. On the one hand, it leads to the hyperreactivity of the immune system to allergens, prompting the body to generate specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) and to bind to the surface of mast cells in response to the allergens (7). Upon subsequent exposure, the allergen can bind to the IgE on the mast cells, triggering their degranulation and releasing mediators, including immediately released histamine and delayed released leukotrienes (8, 9). These mediators, through multifaceted interactions, ultimately culminate in the manifestation of AR symptoms. On the other hand, the excessive activation of Th2 contributes to the persistence and chronicity of allergic inflammation (10), making targeting Th2 cells and specific IgE a promising therapeutic approach in managing allergic rhinitis.
Recently, a growing body of research in both humans and animals has linked the emergence of allergic disease to modifications in the microbiome (11). For instance, neonatal rhesus macaques with antibiotic-disrupted gut microbiota exhibited a compromised pulmonary immune system, characterized by an increased susceptibility to pneumonia, a hyperinflammatory transcriptional signature, and dysregulated homeostatic pathways within the host (12). Moreover, an analysis of bacterial DNA extracted from fecal samples of 92 asthmatic children and 88 healthy children indicated a reduction in the abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the allergic asthma group compared with the healthy group. These species have been implicated in the suppression of inflammation through the regulation of secreted metabolites, as suggested by an increase in interleukin-10 (IL-10) and a decrease in interleukin-12 (IL-12) levels (13). Similarly, clinical research suggests that with the elevation of inflammatory factors in the peripheral serum of children with asthma, their probability of intestinal flora disturbance and gastrointestinal incommensurate symptoms will be increased (14). These data support the crosstalk between gut bacteria and systemic immunity during homeostasis and allergy, suggesting that the introduction of certain probiotics may be a potential strategy to prevent allergic inflammation in the respiratory system.
Targeting the gut-lung link, numerous probiotics have been investigated for their immunoregulatory effects (15–22). Lacticaseibacillus, formerly known as Lactobacillus, is a genus from which some species have been shown to have a preventive effect on respiratory allergy. Among Lacticaseibacillus, strains of the Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus species have exhibited ameliorative and preventive effects on ovalbumin (OVA)-induced allergic mice, supported by the decreased serum IgE levels, rebalancing of Th1/Th2, and Treg/Th17 responses (23, 24). Additionally, it was uncovered that exopolysaccharides of L. rhamnosus strain LOCK900 were found to induce IgA production, which helped to explain the ability of this strain to alleviate airway inflammation (25). Moreover, species such as Lacticaseibacillus casei have been mentioned for their potential to attenuate airway disease or regulate immune responses (26, 27). Lacticaseibacillus paracasei is another species that has received considerable attention in the study of AR. L. paracasei strain MG4272 significantly suppressed the release of Th2-related cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in RAW 264.7 and RBL-2H3 cells. It also modulated the phosphorylation of STAT6 in macrophages and mast cells (22). Similarly, L. paracasei strain GM-080 (LP-33, BCRC-910220, CCTCC M 204012) was reported to have an alleviative effect on OVA-induced mice by oral administration (28). However, in the same species, L. paracasei strain BCRC 16100 demonstrated negative feedback in airway allergy (28). In conclusion, probiotics from the genus Lacticaseibacillus have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment and prevention of AR, although it is noteworthy that the effect of probiotics varies between individuals; therefore, further research is needed to identify the effective strains, dosages, and duration of treatment.
In this study, L. paracasei strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 (Lpc969), a strain isolated from the feces of healthy adults, was selected as an effective probiotic in the prevention and alleviation of AR by oral administration after a series of in vitro and in vivo experiments. The strain was first tested for its effect on histamine secretion and degranulation of the RBL-2H3 cell line. Subsequently, the effects of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 on OVA-induced allergic mice were evaluated by assessing serum immunoglobulin (Ig) levels, inflammatory cell infiltration, and serum cytokine profiles. In addition, comparative genomic analysis between GOLDGUT-Lpc969 and other AR effective/non-effective strains was investigated to mine the potential functional genes of effective strains in terms of AR prevention and alleviation.
Materials and methods
Bacteria, cells, and culture conditions
L. paracasei strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 was isolated using the serial dilution method from the fecal sample collected from a healthy adult donor in Shenzhen, China. The pure colony was picked from a De Man–Rogosa–Sharpe (MRS) agar plate and identified by colony morphologies, such as color, size, shape, transparency, and biochemical characteristics, performed using an API 20A card (BioMérieux) according to the instruction manual. The strain was inoculated and cultured overnight in the MRS medium at 37°C under anaerobic conditions. The bacterial pellet was collected by centrifugation at 4°C and 8,000 g for 10 min and washed once with PBS. The bacterial cells were then resuspended in PBS containing 15% glycerol, aliquoted into cryovials, and stored at −80°C for use in animal experiments.
The RBL-2H3 cell line was purchased from the Chinese National Infrastructure of Cell Line Resource and cultured in minimum essential medium (MEM, Gibco) supplemented with 10% v/v fetal bovine serum (FBS, Solarbio), 1% penicillin, 1% streptomycin, and 1% non-essential amino acids in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37°C. Cells were passaged when the cell density exceeded 80% and log phase cells were inoculated into a 24-well plate at 400 μl (2×105 cells) per well for further experimentation.
Whole-genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis
The whole genome of strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 was sequenced using Nanopore PromethION and Illumina NovaSeq from the Novogene Company and the generated reads were assembled using Unicycler (version 0.4.8) to combine PE150 data and Nanopore data. We used GeneMarkS (version 4.17) to retrieve the associated coding gene, RepeatMasker (version 4.0.5) to predict the interspersed repetitive sequences, tRNAscan-SE (version 1.3.1) to predict the transfer RNA, rRNAmmer (version 1.2) to predict the ribosomal RNA (rRNA), phiSpy (version 2.3) to predict the prophage, and CRISPRdigger (version 1.0) to identify the CRISPR. The whole-genome blast search was performed against the KEGG, COG, and GO databases for the prediction of gene functions (29). To access the safety of strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 in silico, the translated amino acid sequences of coding genes were aligned against the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database (ARDB) (E-value ≤ E-10, identification ≥ 40%) and the Virulence Factor Database (VFDB) (E-value ≤ E-8, with identification ≥ 40%) (30).
The phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the core genomes of strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 and the related genomes within the same genus. First, the comparative genomic analysis of the genomes was performed using Orthofinder v2.5.4 (31). Then, 3,993 homologous genes harbored by each genome were defined as the core genomes. All genes were aligned using MUSCLE (32), and columns with more than 95% gaps were trimmed using trimAL (33). Maximum likelihood trees of the genomes were constructed using IQ-TREE (34) and UFBoot (35) with a substitution model of LG+F+R10; the number of bootstraps was 100 and the evolutionary mode was LG+GAMMA. Finally, the trees were visualized on the iTOL web server (36).
IgE-mediated RBL-2H3 degranulation assay
Rat basophilic leukemia (RBL)-2H3 cells were used to investigate the anti-allergic effects of the strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969, as previously described (37). Briefly, RBL-2H3 cells were incubated with 0.2 μg/ml anti-DNP-IgE (Sigma-Aldrich, Shanghai, China) for 16 h under 5% (v/v) CO2 at 37°C to sensitize the cells. After the stimulants were washed out, the cells were exposed to different concentrations of strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 (Lpc969, MOI = 10 or 1) for 3 h; the cells without bacterial exposure were used as a model control. The cells were then stimulated with 1 μg/ml dinitrophenyl coupled to human serum albumin (DNP-HAS, 4ADI) for 15 min. The untreated cells were used as a negative control. The culture supernatants were collected to measure the histamine content and β-hexosaminidase activity as indicators of degranulation. To assess the maximal release of β-hexosaminidase, the stimulated cell pellet was lysed with 0.1% (v/v) Triton X-100 (Sigma), and the lysis solution was collected. In some experiments, the sensitized RBL-2H3 cells were incubated with 20 μg/ml azelastine hydrochloride (AZE, Macklin) and used as a positive control for the strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969-treated groups.
Detection of histamine content and β-hexosaminidase activity
The levels of histamine and β-hexosaminidase released from RBL-2H3 cells were determined as previously reported (37). To detect histamine levels, 20 μl of 1 M NaOH solution was added to 100 μl of cell culture supernatant, and 25 μl of reaction solution (1% o-phthalaldehyde dissolved in methanol) was immediately added and thoroughly mixed. The reaction was incubated at room temperature for 4 min and then stopped by adding 10 μl of 3M HCl solution. Fluorescence intensity was then measured using a VarioskanTM LUX multimode microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with an excitation wavelength of 355 nm and an emission wavelength of 460 nm. The relative amount of histamine for each well was calculated according to the following equation:
OD460 (sample) is the fluorescence intensity at 460 nm of the sample tested, and OD460 (average of control) is the average fluorescence intensity at 460 nm of the control group.
To detect the amount of β-hexosaminidase, 25 μl of cell culture supernatant was added to an equal volume of substrate solution [5 mM 4-nitrophenyl-N-acetyl-β-glucosaminide (NP-GlcNAc) in 0.2 M sodium citrate buffer, pH 4.5, all purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China] and incubated for 1.5 h at 37°C. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 200 μl of stop solution (0.1 M Na2CO3/NaHCO3, pH 10.0). Fluorescence intensity was measured using a VarioskanTM LUX multimode microplate reader with an excitation wavelength of 355 nm and an emission wavelength of 405 nm. The relative hexosaminidase release was calculated using the following equation:
Animals
Six-week-old BALB/c mice (18 ± 2 g) were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Guangdong) and housed in the SPF animal research facility of Hongkong Polytechnic University, Shenzhen Research Institute. Food and water were provided ad libitum. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the China Council on Animal Care and Use. This study was approved by the Animal Research Ethics Board of Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Shenzhen Research Institute. Every effort was made to minimize pain and discomfort to the animals.
OVA-induced allergic rhinitis mouse model
The OVA-induced AR mouse model was established as described previously, with some modifications (38). Briefly, 36 BABL/c mice were randomly divided into a normal control group (control), model group (AR), positive control group (AZE), and strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969-treated group (GOLDGUT-Lpc969) (n=9 each group). To induce AR, mice in the AZE, AR, and GOLDGUT-Lpc969 groups were sensitized using an intraperitoneal injection of 200 μl ovalbumin (OVA) suspension (1 mg/ml OVA in saline) on days 0, 7, and 14, and then challenged daily with 500 μg OVA administered intranasally from day 21 to day 29. Mice in the control group received saline solution.
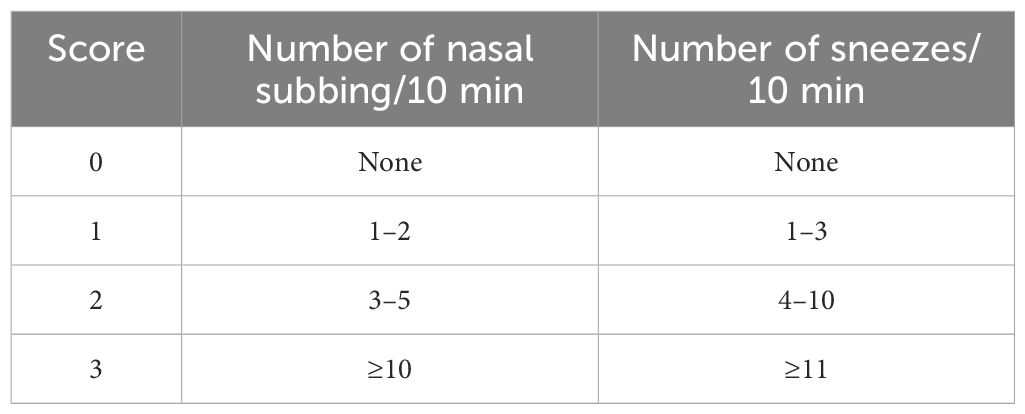
From day 14 to day 28, the probiotic intervention group received 200 μl of GOLDGUT-Lpc969 bacterial suspension at a concentration of 1×1010 CFU/ml in 0.9% saline by gavage daily, while the positive group received 15 mg/kg·BW AZE. Mice in the control and the model control groups received an equivalent volume of 0.9% saline. AR symptoms, including the frequency of nasal rubbing and sneezing within 10 min of intranasal administration, were recorded on day 28 and scored as 0, 1, 2, and 3 with increasing severity in all groups (39). The DAI score (Table 1) was calculated from the recorded scores as described previously (39). On day 29, all mice were euthanized, and samples including the blood and nasal mucosa were collected for subsequent experiments.
Evaluation of serum IgE
The serum was separated from the collected mouse blood. A mouse IgE ELISA kit (ELISA MAX™ Deluxe Set Mouse IgE, BioLegend®, CA, USA) was used to quantify the serum IgE levels of the experimental mice according to the instruction manual.
The serum was first diluted twofold with Assay Buffer A. The diluted serum was added to the wells after the 96-well plate was successfully coated with the diluted capture antibody. The plate was sealed and incubated at room temperature for 2 h with shaking at 500 rpm. After washing, the reagents were added to each well in the following order: a 1-h reaction with IgE antibody, a 30-min reaction with Avidin-HRPD solution, and a 20-min reaction with 100 μl of TBM substrate in the dark. Each addition followed the procedure of sealed cultivation with shaking and four buffer washes. Finally, the stop solution was added, and the OD450 and OD570 of each well were read after 10 min of contact. The difference between OD450 and OD570 was recorded, and the IgE concentration was calculated using the standard dose-response curve.
Serum histamine test
The level of histamine in the serum of the collected mouse blood was detected and quantified using a histamine ELISA kit (Shanghai Zhenke Biotech Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China) according to the instruction manual.
The serum was first added to a 96-well plate marked as sample wells with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled antigen, except for blank wells, and sealed for incubation at 37°C for 60 min. The plate was then washed three times with wash buffer. After the removal of residual liquid, the matrix mixture was added to all wells, and the plate was sealed for a 15-min incubation at 37°C. Finally, the stop solution was added, and the OD450 of each well was read after 10 min of contact. The difference between the OD450 of the sample wells and that of the blank group was recorded as the final absorbance value and used to calculate the histamine concentration according to the standard dose-absorbance curve generated by the histamine standard solution based on the same procedure.
Histological analysis
The nasal mucosa of euthanized mice was fixed in 4% (m/v) paraformaldehyde. After fixation, paraffin sections were prepared and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) to observe and evaluate the histopathology of the nasal mucosa.
Cytokine multiplex assay
The concentrations of the cytokines in the serum of the collected mouse blood were quantified using a LEGENDplex™ MU Th1/Th2 Panel (8-plex) assay kit (BioLegend®, CA, USA), which is a bead-based multiplex assay panel used on a flow cytometer.
The serum was first diluted twofold with assay buffer. Reagents were loaded into a V-bottom 96-well plate in the following order: assay buffer, diluted sample, and mixed beads. The plate was then sealed and incubated at 800 rpm for 2 h at room temperature. After the supernatant was discarded, the wells were washed and cleaned for antibody loading. Then, 25 µl of SA-PE was added to each well. After cultivation and cleaning, 150 μl of 1× wash buffer was added to resuspend the beads. The wells were then read by the flow cytometer, and the readings were used to calculate the cytokine concentration according to the standard dose-response curve generated by the standard solutions using the same procedure.
Comparative genomic analysis
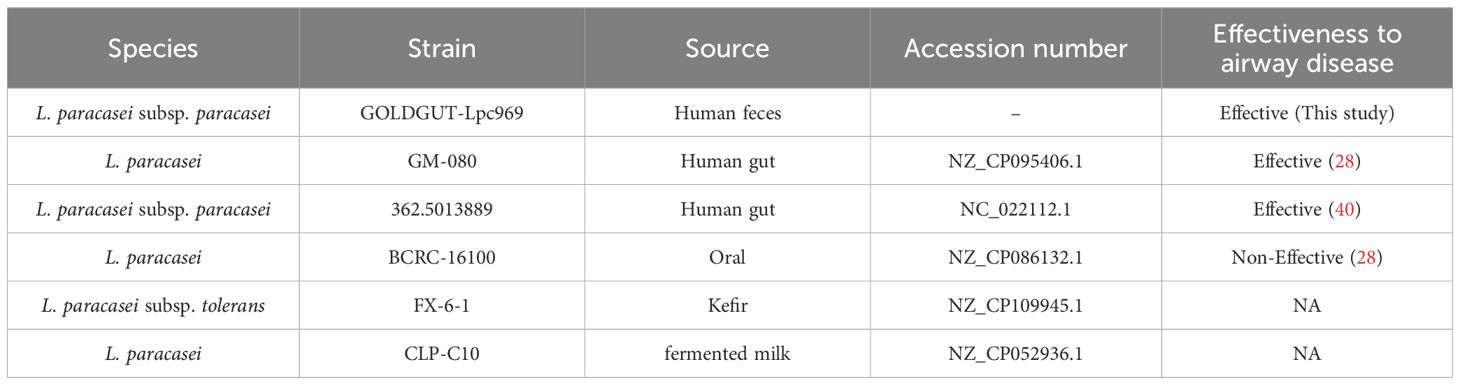
To further understand the mechanism underlying the efficacy of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 in AR prevention, the comparative genomic analysis was performed based on the whole-genome sequences of GOLDGUT-Lpc969 and three other L. paracasei strains that have been shown to be effective in alleviating respiratory disease (Table 2). Among them, L. paracasei GM-080 (28) and L. paracasei 362.5013889 (40) have been reported to alleviate airway disease, and L. paracasei strain BCRC_16100 has been reported to be ineffective in alleviating respiratory disease (28). All homologous genes within the pangenome were annotated using EggNOG v5.0.2 (41).
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Differences between means were tested for statistical significance using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukeys multiple comparison test, and the homogeneity of the variance of the data was assessed using the Brown–Forsythe test and Bartletts test. Differences between groups were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05.
Results
Taxonomy and genomic analysis of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969
Strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 was first identified as L. paracasei by sequence analysis of the 16S rRNA gene using the BLAST algorithm, and the biochemical reaction detected using the API 20A strip demonstrated that strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 can produce acid from D-glucose, D-mannitol, D-sucrose, D-mannose, D-trehalose, and D-melezitose, the unique biochemical characteristics that distinguish L. paracasei subsp. paracasei from L. paracasei subsp. tolerans (42). Genomic phylogenetic analysis with different Lacticaseibacillus species revealed that strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 forms a distinct clade with other strains of L. paracasei (Figure 1C, Table 2). These results demonstrated that strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 belongs to the species of L. paracasei subsp. Paracasei.
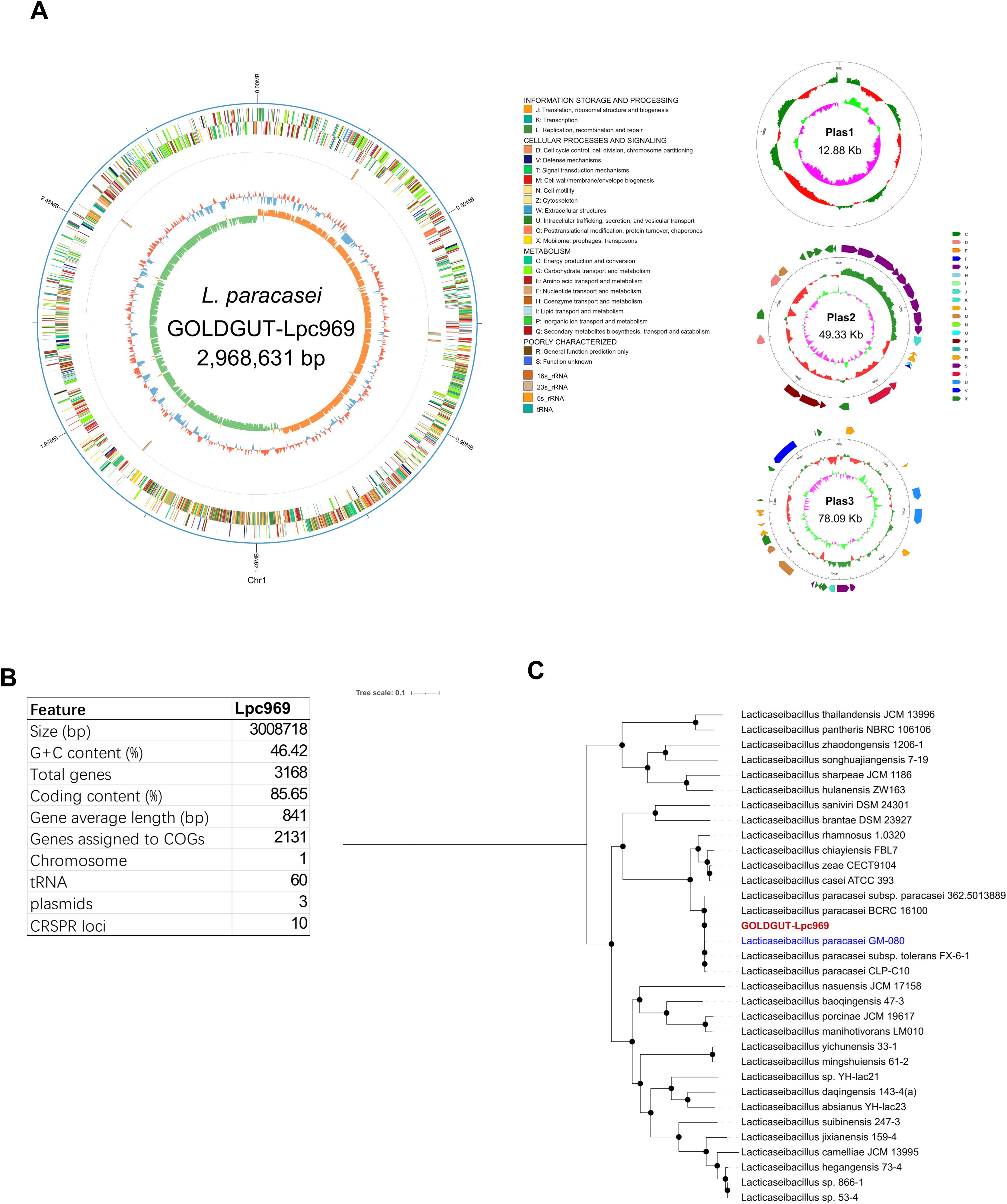
Figure 1. Whole-genome sequencing analysis of GOLDGUT-Lpc969.(A) Circular genome graph of GOLDGUT-Lpc969. (B) Summary of the general features of the GOLDGUT-Lpc969 genome. (C) Maximum likelihood tree of GOLDGUT-Lpc969 with other known Lacticaseibacillus strains.
L. paracasei subsp. paracasei strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 possesses a circular genome with a size of 2,968,631 base pairs (bp) and three additional circular plasmids of 12.88 kbp (kbp), 49.33 kbp, and 78.09 kbp (Figure 1A). A total of 3,168 protein-coding sequences assigned to 2,131 COGs were identified, and 60 tRNAs, 5 23S rRNAs, 5 16S rRNAs, 5 5S rRNAs, and 10 CRISPR sequences were predicted in the genome (Figure 1B).
We assessed the safety of strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 using the whole-genome sequencing analysis standards for probiotic safety provided by the European Food Safety Authority (43). Diamond software was used to search the Virulence Factor Database to identify putative virulence factors. The sequence homologies of all these factors were less than 80%, and most of them lacked definitive functions. Subsequent analysis of the amino acid sequences encoded by the strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 genome against the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Database revealed putative resistance genes with sequence homologies all below 55%. Taken together, these results suggest a high safety profile for strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969.
L. paracasei prevents anti-DNP-IgE-induced histamine secretion and the degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells
RBL-2H3 is a basophilic leukemia cell line and is commonly used for allergy-related studies. Azelastine (AZE) is an anti-allergic reagent that inhibits the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators. In this experiment, AZE was adopted as a positive medicine to better understand the efficacy of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-lpc969.
As shown in Figure 2A, the levels of histamine secretion by the treated RBL-2H3 cells were significantly higher than the control group (increased by approximately 63%). Although significant decreases were observed in the groups treated with L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 at MOIs of 10 and 1, the significance was higher than that of AZE. These results indicate that L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 can reduce histamine levels released by anti-DNP-IgE-induced RBL-2H3 cells.
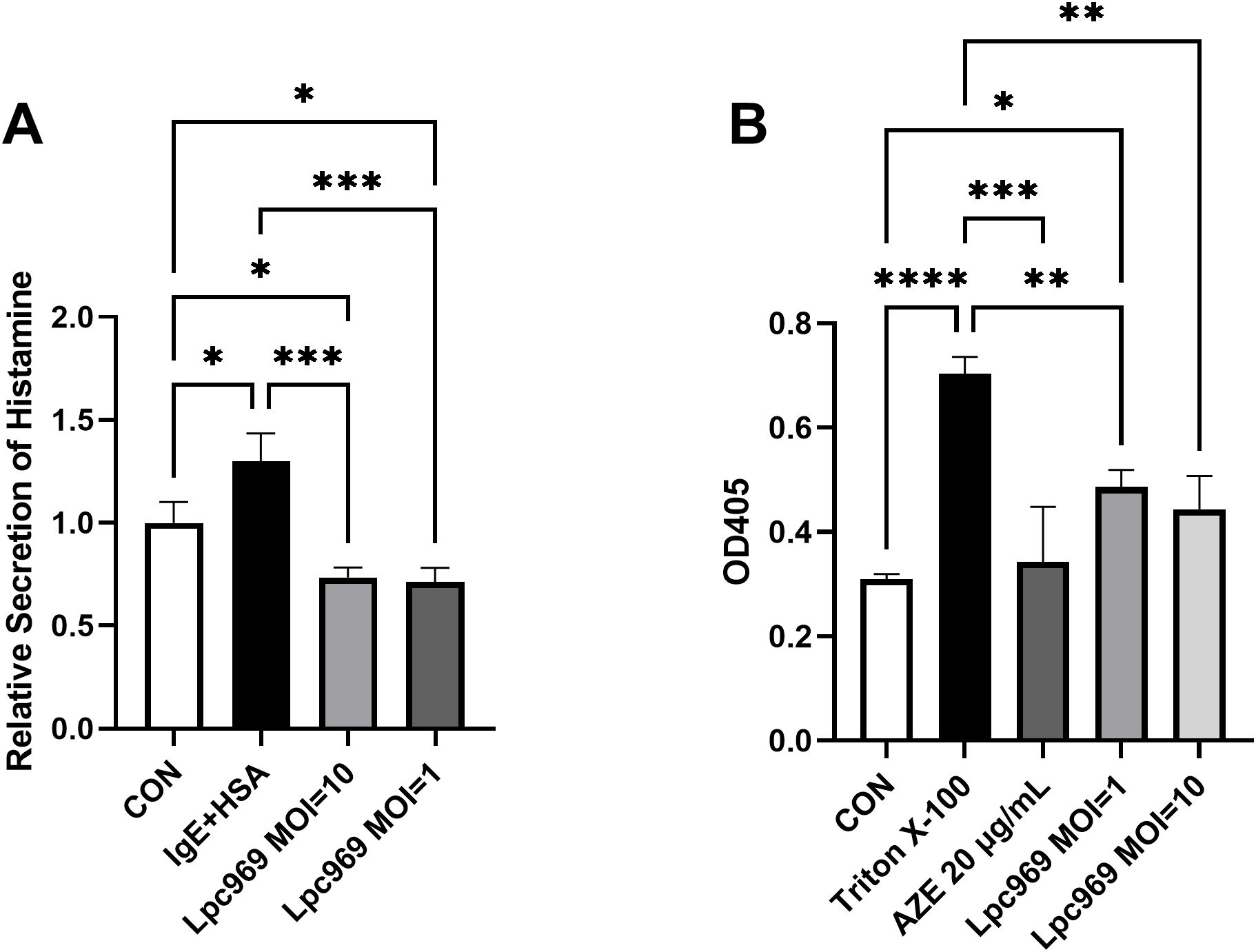
Figure 2. L. paracasei prevents anti-DNP-IgE-induced histamine secretion and the degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells. Relative secretion of histamine (A) and the OD405 (B) of the IgE+HAS treated/untreated groups. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
The enzyme β-hexosaminidase, a marker of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells, has been widely employed to track mast cell degranulation, as it occurs simultaneously with histamine release. The higher degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells shown in Figure 2B was represented by the higher OD405 value in a colorimetric assay. Triton X-100 is a surfactant that can cause cell rupture, resulting in cell degranulation. The stimulated RBL-2H3 cells treated with Triton X-100 showed significantly higher levels of degranulation than the control group. In contrast, significant decreases were observed in the AZE-treated groups. Although not as drastic as AZE, the intervention of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 at MOIs of 10 and 1 also significantly suppressed the degranulation level of the anti-DNP-IgE-induced RBL-2H3 model in a dose-dependent manner. These results indicate that L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 can attenuate the extent of RBL-2H3 cell degranulation induced by anti-DNP-IgE.
Oral administration of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 prevents the OVA-induced AR symptoms in mice
The evaluation of the effect of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 was assessed from four aspects: average DAI, serum IgE, serum histamine, and a histological assessment. AZE is a commonly used medicine for the topical treatment of the symptoms of AR. It acts as an immunomodulator in the anti-allergic process, serving to stabilize the mast cell membrane, thereby inhibiting the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from mast cells. In this experiment, AZE was adopted as a positive medicine to better understand the efficacy of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969.
The DAI score is an important indicator used to assess the symptoms of AR in mice, including scoring the frequency of sneezing, nasal rubbing, and nasal discharge. A higher score indicates more severe AR symptoms in mice, as shown in Figure 3A. The DAI score of mice in the AR group increased significantly compared with the control group. The score decreased significantly after the treatment with L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 and AZE compared with the AR group; L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 was even slower than AZE. These results demonstrated that L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 can alleviate the increased DAI score caused by OVA and significantly reduce the severity of AR symptoms.
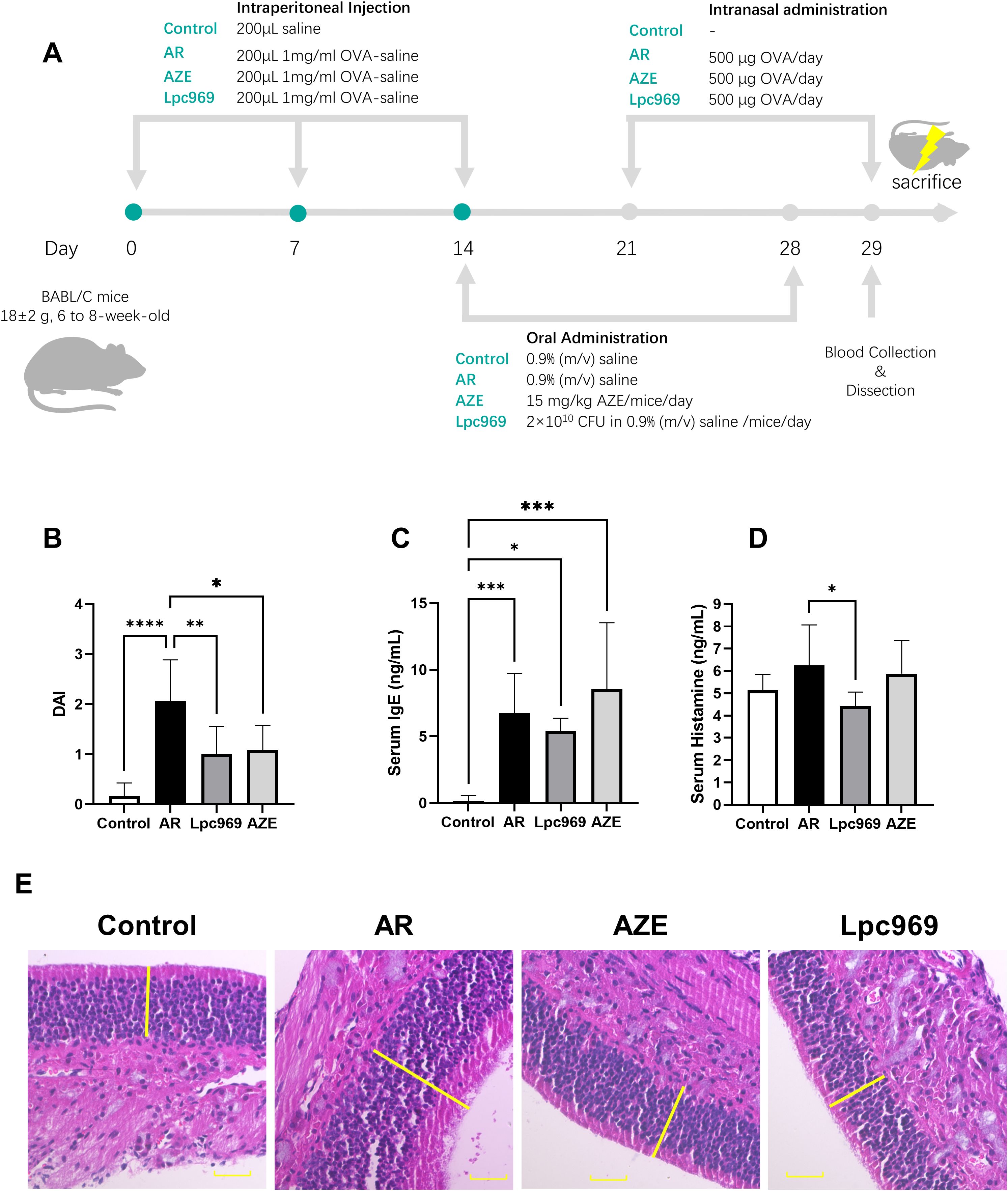
Figure 3. Evaluation of the protective effect of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 in OVA-induced AR mice. (A) Illustration of the experimental procedure used for the induction of the OVA-induced AR mouse model. (B) Average DAI. (C) Concentration of serum IgE. (D) Concentration of serum histamine. (F) Representative photomicrographs of pathological sections of the nasal mucosa of mice. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
Oral administration of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 prevents the OVA-induced elevation of serum IgE in mice
The excessive production of IgE supports the immune systems overreaction during the course of AR. Elevated blood levels of IgE are observed in most AR patients and have also been reported as a common symptom in OVA-induced AR mice. As shown in Figure 3B, the AR mouse group exhibited a significant increase in serum IgE after OVA sensitization compared with the control group. This phenomenon was also observed in the AZE group, which had even higher serum IgE levels than the AR group. Treatment with L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 showed a decrease in serum IgE levels, indicating the potential function of the strain in preventing AR.
Oral administration of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 prevents the OVA-induced elevation of serum histamine in mice
Histamine is a pivotal mast-cell-producing mediator involved in local immune and inflammatory responses and is a major contributor to itching. Serum histamine levels positively correlate with the severity of allergic symptoms. As shown in Figure 4C, OVA-induced AR resulted in increased serum histamine levels in the AR group compared with those in the control group. This increase was slightly restored by AZE treatment, but significantly decreased by preventive treatment with L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969, suggesting the alleviation of histamine release and related phenomena in AR.
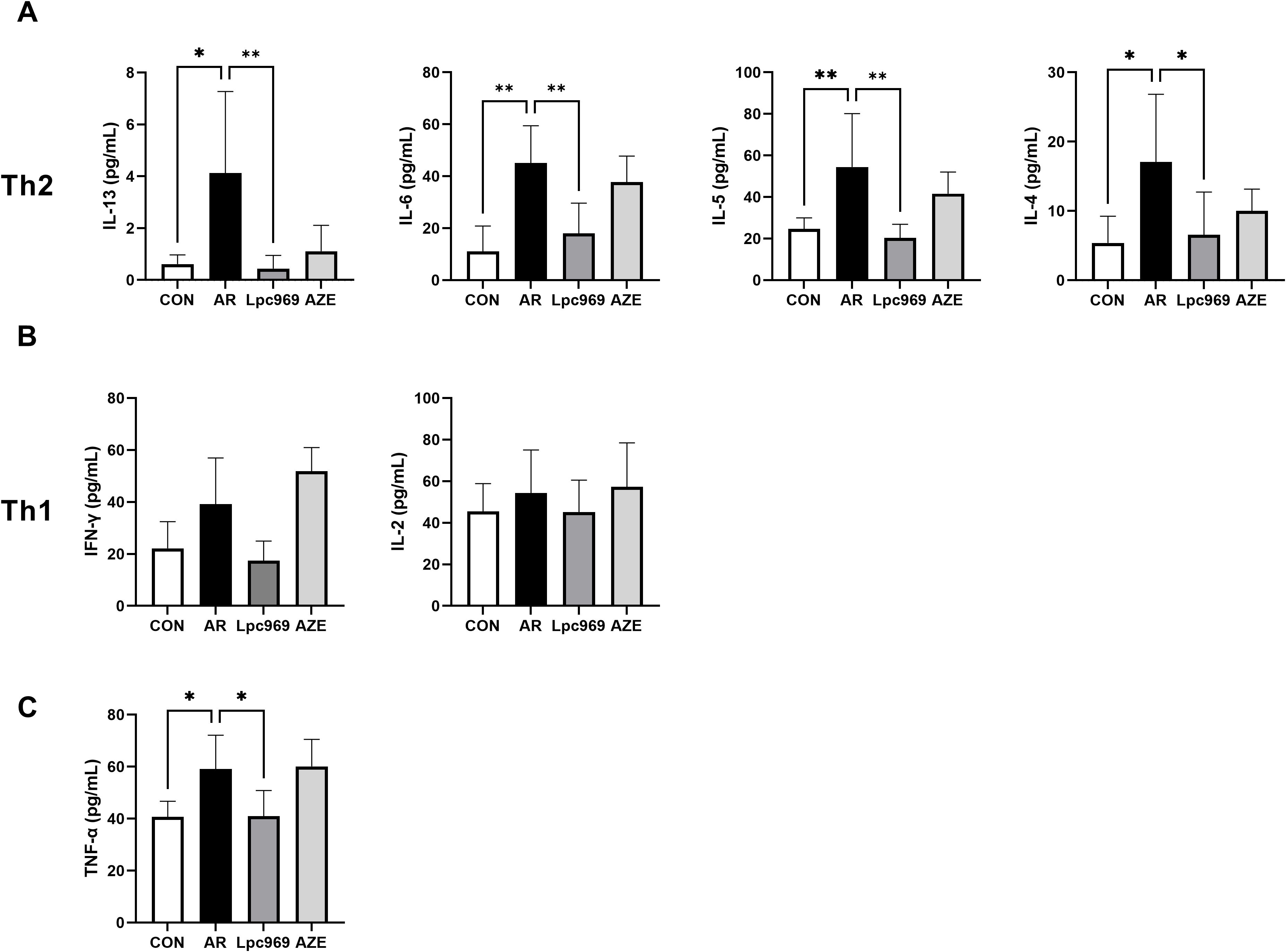
Figure 4. Serum cytokine levels of OVA-induced AR and treated mice. (A) Serum level of Th2-secreted cytokines. (B) Serum level of Th1-secreted cytokines. (C) Serum level of TNF-α. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Oral administration of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 prevents the OVA-induced histopathological change of nasal mucosa in mice
Compared with healthy mice, histopathologic sections of nasal mucosa from AR mice show features such as cilia loss, vascular congestion, vascular proliferation, mucosal thickening, and inflammatory cell infiltration. As shown in Figure 3E, mice in the control group had an intact and ordered nasal mucosal surface without mucosal enlargement. In contrast, the AR group exhibited obvious mucosal thickening, and the mucosal surface was unevenly arranged. Mice treated with L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 and AZE showed obvious recovery, with intact and ordered epithelial structures and mucosal thickness restored to levels similar to those of the control group.
In conclusion, these studies demonstrated that oral administration of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 reduced the DAI in mice, along with decreased levels of IgE and histamine, and restored the nasal mucosal structure and thickness. The results support the efficacy of GOLDGUT-Lpc969 in the prevention of AR symptoms.
Oral administration of L. paracasei regulates the serum cytokine level of OVA-induced murine AR
IL-13, IL-6, IL-5, and IL-4 are Th2 cytokines, whereas IFN-γ and IL-2 are Th1 cytokines. In this study, the levels of all these cytokines in mouse serum tended to increase after OVA stimulation, indicating an active Th2 and Th1 inflammatory response. AZE treatment conferred some inhibition of the secretion of Th2 cytokines, e.g., approximately 50% for IL-5 and IL4, 20% for IL-6, and 80% for IL-13, with a slight increase in the secretion of the Th1 cytokines IFN-γ and IL-2 in comparison with the AR group. L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 treatment also lowered the levels of all the above cytokines close to those of the control group, showing significant suppression on the secretion of Th2 cytokines (Figure 4A), especially IL-13, with over a 90% reduction compared with the AR group, and a moderate inhibition on that of the Th1 cytokines (Figure 4B). These results suggest that L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 can suppress the Th1 and Th2 inflammatory responses while alleviating AR symptoms by significantly reducing Th2 cytokines and reversing the bias of the Th2 response.
Apart from the Th1 and Th2 cytokines, the mast-cell-secreted TNF-α also significantly decreased in the probiotic group compared with the model group, recovering to a level close to that of the control group (Figure 4C). This result suggested a lower activity of mast cells.
Screening of unique gene by comparison of effective/non-effective L. paracasei strains in treating airway disease
In a further comparative genomic analysis, we aimed to identify unique genes that were specific to the strains effective in the treatment or prevention of AR. The probiotic strain L. paracasei 362.5013889 was validated in a rigorous randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, which highlighted the protective effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HEAL9, when co-administered with L. paracasei 8700:2 (L. paracasei 362.5013889), against a range of rhinitis symptoms in adults, including nasal discharge, congestion, and sneezing (40). L. paracasei GM-080 has received support from studies highlighting its potential to alleviate OVA-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and reduce airway inflammation in a mouse experiment and its association with increased levels of IFN-γ in a well-controlled double-blind clinical trial. In contrast, the group treated with L. paracasei BCRC_16100 in the same experiment exhibited no significant increase in IFN-γ levels and no significant improvement in the other parameters assessed (28) (Table 2). Therefore, three effective L. paracasei strains, including 362.501889, GM-080, and GOLDGUT-Lpc969, in this study, and one non-effective L. paracasei strain, BCRC 16100, were selected for comparative genomic analysis.
As a result, 20 effective strain-only genes (Figure 5) were screened, encoding CRISPR-associated proteins, transposases, transcriptional regulators, and transport systems. Of note is the presence of K03671 (thioredoxin), a secretory protein that functions as an anti-inflammatory, an anti-allergen, a redox regulator, and an antioxidant in all effective strains. In addition, thioredoxin has been considered a promising future target for the treatment of digestive tract irritation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and some allergic diseases such as allergic asthma, AR, food allergy, and contact dermatitis (44). This implies a possible correlation between the thioredoxin gene K03671 and the alleviating effect of L. paracasei on AR. However, empirical substantiation is required to firmly establish this association.
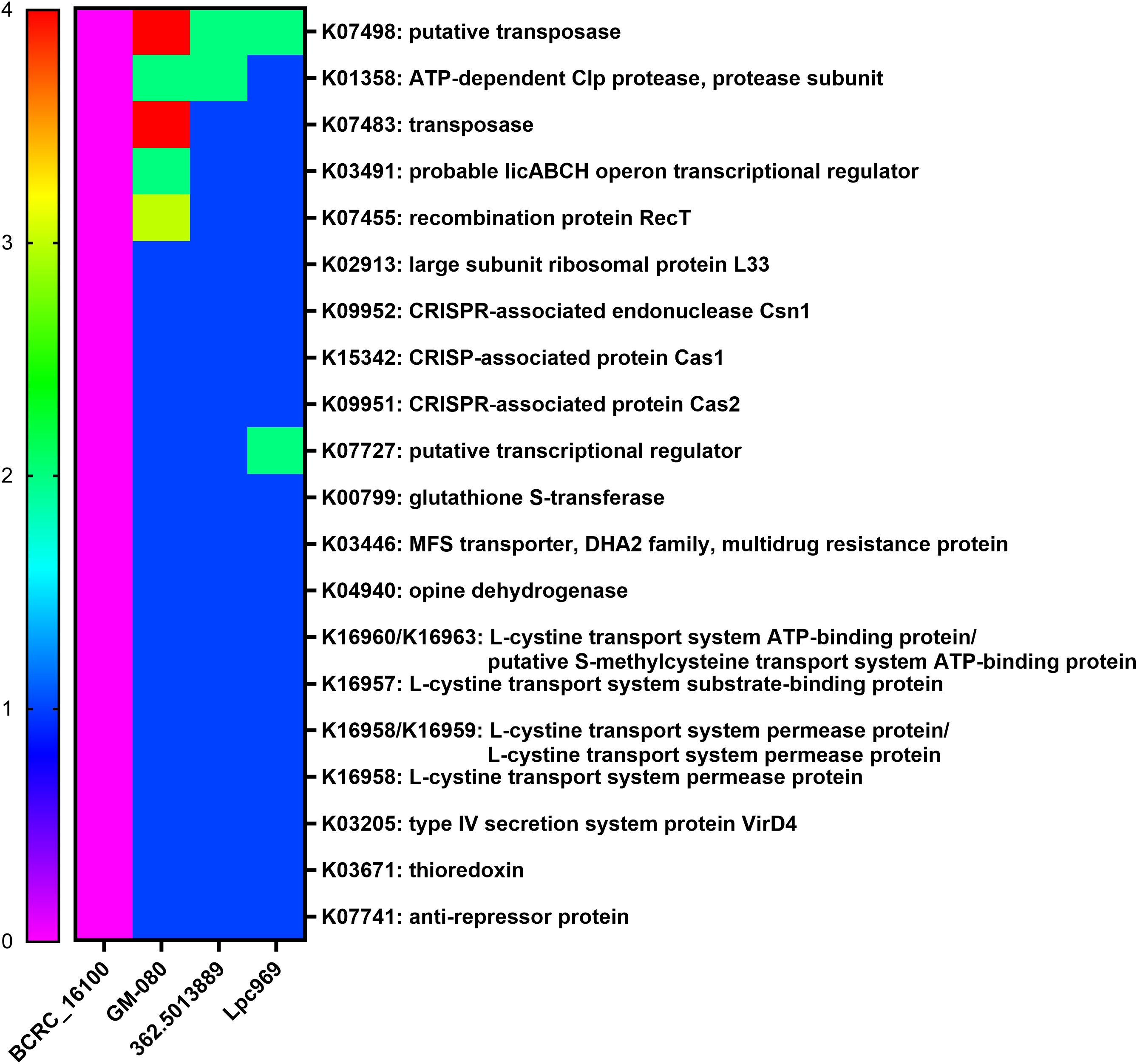
Figure 5. Distribution of the core genes and their copy numbers in airway-disease-effective/non-effective L. paracasei strains. The heatmap shows the copy number of genes solely expressed in the airway-disease-effective L. paracasei strains, including GOLDGUT-Lpc969, but not in the non-effective strains. Green represents the allergy-related protein.
Discussion
This study provides a novel strain L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 with a well-characterized safety profile, determines its significant suppression on the Th2 immune response, and suggests a functional gene K03671 as a potential key gene in the prevention and alleviation of AR symptoms.
An imbalance in favor of humoral immune responses mediated by Th2 cells over cell-mediated responses led by Th1 cells has been implicated as a major cause of allergy (45). During the development of AR, the overactivation of Th2 immune responses leads to IgE-mediated type I hypersensitivity, which subsequently stimulates mast cell degranulation and histamine release (46). In turn, the histamine increases the secretion of Th2 cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and inhibits the production of the Th1 cytokines IL-2 and IFN-γ through the upregulation of prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide (7), thereby exacerbating the allergy. The results of the present study showing a significant reduction in Th2 cytokines, serum histamine, IgE, and other disease indicators in probiotic-treated mice are consistent with the decreased histamine and degranulation rate in the L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 group (Figures 2, 3), indicating suppressed Th2 immune activity. Moreover, the decreased level of TNF-α suggests a reduction in mast cell activity, which contributes to the alleviation of AR symptoms (Figure 4C).
Based on the above mechanism, several strains have been reported and demonstrated to have protective or therapeutic effects on AR. Oral administration of L. plantarum NR16 isolated from kimchi was reported to ameliorate murine AR by rebalancing the Th1:Th2 ratio by decreasing Th2 cytokine production, thus inhibiting the production of allergen-specific antibodies in specific mucosal lesions (47). Similarly, 109 CFU freeze-dried powder of L. plantarum HEAL9 and L. paracasei 8700:2 was clinically proven to be effective in protecting cold-prone adults from multiple colds (40). These findings justify the efficacy of specific strains in rebalancing Th1/Th2 inflammatory responses.
Subsequently, the investigation of the screened 20 effective strain-only genes revealed the potential function of the gene K03671 in alleviating respiratory allergy. The gene K03671 putatively encodes thioredoxin (TRX1), a reductase of oxidized cysteine residues and cleaver of disulfide bonds (48). In the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, the reaction of thioredoxin and thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) is known to stimulate the expression of the NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome (49). Assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome eventually leads to the caspase 1 (CASP1)-dependent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), which can activate T cells and promote the production of Th2 cytokines, such as IL-13, IL-6, and IL-5, to stimulate pro-inflammatory effects (44, 50) (Figure 6). In general, the pathway determining the remarkable role of the thioredoxin encoded by K03671 in the inflammatory effects is plausibly inferred from the existing experimental and comparative genomic results, and may find further validation through additional studies.
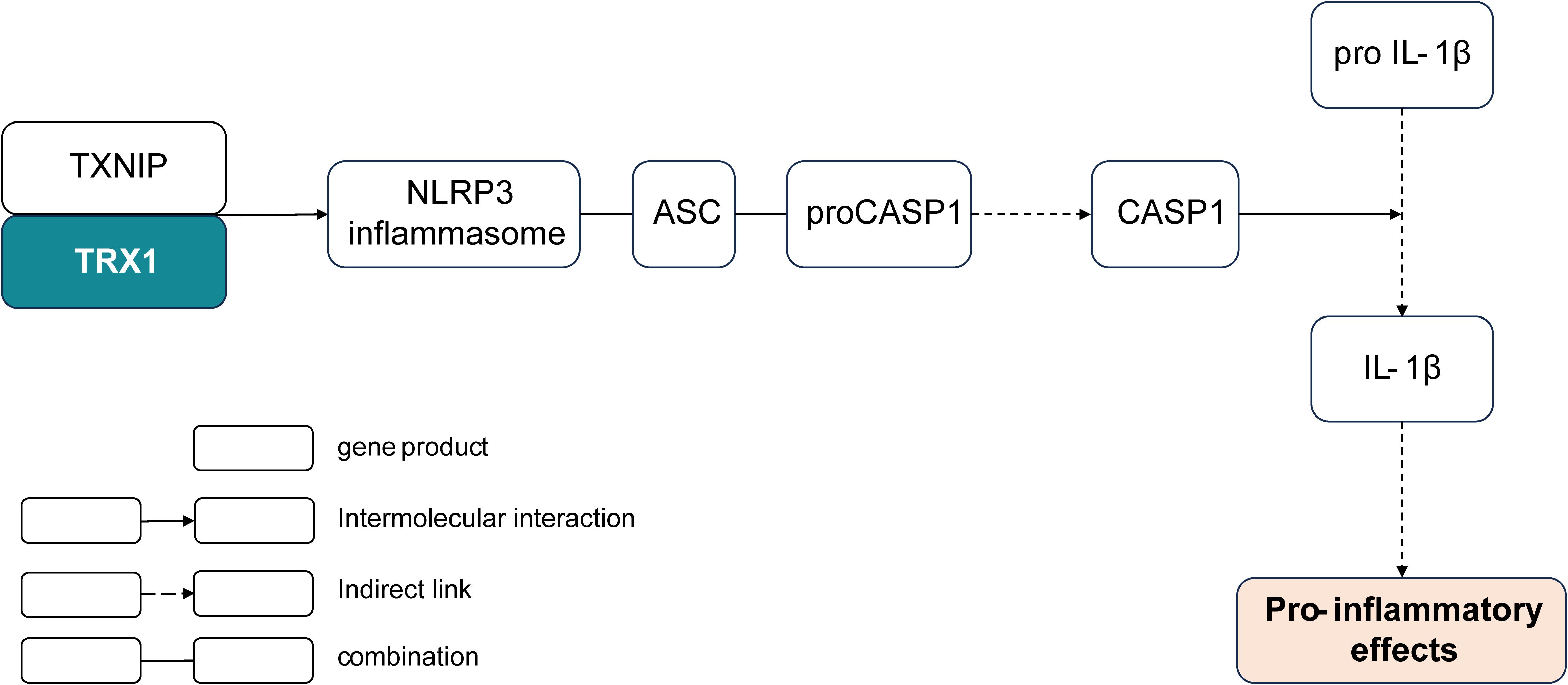
Figure 6. Shortcut of the K03671-encoded thioredoxin involved in the pro-inflammatory pathway. TRX, thioredoxin; TXNIP, thioredoxin-interacting protein; NLRP3, NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; ACS, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; CASP1, caspase 1.
Further research on thioredoxin revealed the mechanism of the therapeutic effect of thioredoxin on airway allergy through the downregulation of interleukin-13 (IL-13) expression and eosinophil activity. A study of the suppressive effect of thioredoxin on airway inflammation using a mouse model of asthma showed that IL-13 and exotoxin production were significantly reduced in TRX-transgenic (TRX-Tg) mice, which reduced eosinophil recruitment and decreased mucus metaplasia. This phenomenon was explained by the inhibition of the production of migration inhibitory factor, an upstream modulator of airway inflammation, in TRX-Tg mice (51). Moreover, IL-13 response status has been clinically shown to correlate with clinical responses and Th2 responses in the late phase after allergen challenge (52). These results are consistent with the significant decrease in IL-13 in L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969-treated AR mice compared with the model group in our study, explaining the protective effect of strain GOLDGUT-Lpc969 against AR symptoms.
In addition to the well-documented IL-13 and eosinophil activity (53, 54), research has also indicated the regulation of thioredoxin, including the reduction of goblet cell proliferation (55), eosinophil infiltration (56), the viscosity of cystic fibrosis sputum (57), and leukocyte infiltration into sites of inflammation (58), which contributes to the allergic symptoms. However, there is a study that suggests that intra-thioredoxin treatment exerts no obvious influence on systemic Th1/Th2 immune modulation (51), which is inconsistent with the experimental results obtained from the significant suppression of the Th2 immune response of L. paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969 presented in this study. Furthermore, a study suggests that the downregulation of SHP-1 leads to a shift toward a Th2-type immunity (59). On the one hand, TRX can reactivate SHP-2 to a catalytic structure by reduction (60), whereas thioredoxin reductase (TRR) can maintain the reduction in the oxidized TRX. SHP-1, which shares structural similarities with SHP-2, acts as a negative regulator of cell proliferation, migration, and survival through dephosphorylation, whereas SHP-2 acts as a positive factor through phosphorylation (60–63). Functionally, they exhibit antagonistic effects, potentially neutralizing or balancing each others activities. Therefore, it is plausible to infer that thioredoxin expressed by K03671 influences the activity of SHP-2 through the TRX/TRR system, thereby downregulating the expression or activity of SHP-1 to some certain extent and indirectly promoting the upregulation of Th2 cytokines, which is opposite to the experimental results. As a result, it is inferred that there is an uncovered relationship between SHP-1 and the TRX/TRR/TRXIP system. Conversely, thioredoxin (TRX) can inhibit the formation of hydrogen peroxide and free radicals (64) and prevent the increased Th2 immune response induced by H2O2 (65). Accordingly, it provides insight into the preference for further exploration focusing on the gut-lung axis to determine the function of effective genes in probiotics, especially L. paracasei, in the oxidative microenvironment of respiratory health.
Our investigation of the therapeutic strain effective against AR has revealed the potential key gene K03671 in the amelioration of AR symptoms, contributing to our understanding of the underlying mechanism of AR-effective L. paracasei in ways that were previously unexplored. However, several intriguing issues remain unanswered, such as the verification of the thioredoxin production of the AR-effective strains and the significantly reduced Th2 activity. Addressing these gaps will undoubtedly deepen our understanding of the screening strategy for AR-effective strains. Subsequent research efforts could focus on the development of other effective genes in AR-effective strains and the determination of K03671 expression.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) repository, accession number SRX24771855.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Shenzhen Research Institute. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. XS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TS: Resources, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. CH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JP: Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. XD: Writing – review & editing. HH: Writing – review & editing. GX: Writing – review & editing. PW: Writing – review & editing. KL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Shenzhen Research Institute, for providing animal facilities for maintain the mice. Additionally, we would like to express our deepest gratitude to Yulong Zhang, Xinyu Guo, Bingfang Wei, and Lijun Wang for their invaluable support in the experimental design and execution of our research. Their expertise and dedication were instrumental in the successful completion of this study.
Conflict of interest
Authors XS, CH, JP, XD, and HH were employed by Shenzhen Xbiome Biotech Co., Ltd. Authors XZ, TS, SZ, ZZ, and GX were employed by Shenzhen Porshealth Bioengineering Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Pawankar R, Canonica GW, Holgate ST, Lockey RF, Blaiss MS. WAO white book on allergy. Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States of America: World Allergy Organization (2011). pp. 156–7.
2. Vandenplas O, Vinnikov D, Blanc PD, Agache I, Bachert C, Bewick M, et al. Impact of rhinitis on work productivity: a systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunology: In Pract. (2018) 6:1274–1286.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.09.002
3. Donaldson AM, Choby G, Kim DH, Marks LA, Lal D. Intranasal corticosteroid therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis of reported safety and adverse effects in adults. Otolaryngology–Head Neck Surg. (2020) 163:1097–108. doi: 10.1177/0194599820931455
4. Ince M, Ruether P. Histamine and antihistamines. Anaesthesia Intensive Care Med. (2021) 22:749–55. doi: 10.1016/j.mpaic.2021.07.025
5. Li L, Liu R, Peng C, Chen X, Li J. Pharmacogenomics for the efficacy and side effects of antihistamines. Exp Dermatol. (2022) 31:993–1004. doi: 10.1111/exd.14602
6. Siddiqui Z, Walker A, Pirwani MM, Tahiri M, Syed I. Allergic rhinitis: diagnosis and management. Br J Hosp Med. (2022) 83:1–9. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2021.0570
7. Packard KA, Khan MM. Effects of histamine on Th1/Th2 cytokine balance. Int Immunopharmacol. (2003) 3:909–20. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5769(02)00235-7
8. Amin K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir Med. (2012) 106:9–14. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2011.09.007
9. Galli SJ, Tsai M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat Med. (2012) 18:693–704. doi: 10.1038/nm.2755
10. Lei F, Zhu D, Sun J, Dong Z. Effects of minimal persistent inflammation on nasal mucosa of experimental allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinology Allergy. (2010) 24:e23–8. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2010.24.3414
11. Zhang D, Li S, Wang N, Tan HY, Zhang Z, Feng Y. The cross-talk between gut microbiota and lungs in common lung diseases. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:301. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00301
12. Stevens J, Steinmeyer S, Bonfield M, Peterson L, Wang T, Gray J, et al. The balance between protective and pathogenic immune responses to pneumonia in the neonatal lung is enforced by gut microbiota. Sci Trans Med. (2022) 14:eabl3981. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl3981
13. Demirci M, Tokman HB, Uysal HK, Demiryas S, Karakullukcu A, Saribas S, et al. Reduced Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii levels in the gut microbiota of children with allergic asthma. Allergologia Immunopathologia. (2019) 47:365–71. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.009
14. Zhang Y, Li T, Yuan H, Pan W, Dai Q. Correlations of inflammatory factors with intestinal flora and gastrointestinal incommensurate symptoms in children with asthma. Med Sci Monitor: Int Med J Expirem Clin Res. (2018) 24:7975–9. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910854
15. Peng G-C, Hsu C-H. The efficacy and safety of heat-killed Lactobacillus paracasei for treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis induced by house-dust mite. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2005) 16:433–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2005.00284.x
16. Konieczna P, Groeger D, Ziegler M, Frei R, Ferstl R, Shanahan F, et al. Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 administration induces Foxp3 T regulatory cells in human peripheral blood: potential role for myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Gut. (2012) 61:354–66. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-300936
17. Konieczna P, Akdis CA, Quigley EM, Shanahan F, O'Mahony L. Portrait of an immunoregulatory bifidobacterium. Gut Microbes. (2012) 3:261–6. doi: 10.4161/gmic.20358
18. Hiippala K, Barreto G, Burrello C, Diaz-Basabe A, Suutarinen M, Kainulainen V, et al. Novel odoribacter splanchnicus strain and its outer membrane vesicles exert immunoregulatory effects in vitro. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:575455. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.575455
19. Zhao W, Pan W, Xu Y, Zhang J, Wan J, Jiang H. The immune regulatory role of Lactobacillus acidophilus: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Bioscience. (2020) 36:100656. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100656
20. Varsha KK, Maheshwari AP, Nampoothiri KM. Accomplishment of probiotics in human health pertaining to immunoregulation and disease control. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2021) 44:26–37. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.06.020
21. Cavalcanti RFP, Gadelha FAAF, Paiva Ferreira LKD, Paiva Ferreira LAM, Chaves Júnior JV, de Araújo Batista RS, et al. Limosilactobacillus fermentum modulates the gut-airway axis by improving the immune response through FOXP3 activation on combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS). Immunobiology. (2023) 228:152721. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2023.152721
22. Lee JY, Kang JH, Jung YR, Kang CH. Lactobacillus gasseri MG4247 and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MG4272 and MG4577 Modulate Allergic Inflammatory Response in RAW 264.7 and RBL-2H3 cells. Probiotics Antimicrobial Proteins. (2023) 15:1092–101. doi: 10.1007/s12602-022-09950-4
23. Song J, Li Y, Li J, Wang H, Zhang Y, Suo H. Lactobacillus rhamnosus 2016SWU.05.0601 regulates immune balance in ovalbumin-sensitized mice by modulating expression of the immune-related transcription factors and gut microbiota. J Sci Food Agric. (2020) 100:4930–9. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10554
24. Dehghani S, Edalatian Dovom MR, Yavarmanesh M, Sankian M. Effect of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum isolated from food and human origin on reduction of IgE-dependent hypersensitivity in Balb/c mice. Immunobiology. (2022) 227:152292. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152292
25. Srutkova D, Kozakova H, Novotna T, Gorska S, Hermanova PP, Hudcovic T, et al. Exopolysaccharide from Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus induces IgA production in airways and alleviates allergic airway inflammation in mouse model. Eur J Immunol. (2023) 53:2250135. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250135
26. Martens K, De Boeck I, Jokicevic K, Kiekens F, Farré R, Vanderveken OM, et al. Lacticaseibacillus casei AMBR2 restores airway epithelial integrity in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. (2021) 13:560–75. doi: 10.4168/aair.2021.13.4.560
27. Zhang N, Zeng W, Du T, Wei H, Tian W, Meng Y, et al. Lacticaseibacillus casei CNRZ1874 supplementation promotes M1 alveolar macrophage activation and attenuates Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Appl Microbiol. (2023) 134:lxad022. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxad022
28. Lin E-K, Chang WW, Jhong JH, Tsai WH, Chou CH, Wang IJ. Lacticaseibacillus paracasei GM-080 ameliorates allergic airway inflammation in children with allergic rhinitis: from an animal model to a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Cells. (2023) 12:768. doi: 10.3390/cells12050768
29. Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Ishiguro-Watanabe M, Tanabe M. KEGG: integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. (2021) 49:D545–51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa970
30. Luo G, Li B, Yang C, Wang Y, Bian X, Li W, et al. Major traditional probiotics: comparative genomic analyses and roles in gut microbiome of eight cohorts. Front Microbiol. (2019) 10:712. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00712
31. Emms DM, Kelly S. OrthoFinder: phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. (2019) 20:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1832-y
32. Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. (2004) 32:1792–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340
33. Capella-Gutiérrez S, Silla-Martínez JM, Gabaldón T. trimAl: a tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics. (2009) 25:1972–3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348
34. Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, von Haeseler A, et al. IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol. (2020) 37:1530–4. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa015
35. Hoang DT, Chernomor O, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ, Vinh LS. UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol Biol Evol. (2018) 35:518–22. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx281
36. Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. (2016) 44:W242–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw290
37. Lian Q, Cheng Y, Zhong C, Wang. Inhibition of the IgE-mediated activation of RBL-2H3 cells by TIPP, a novel thymic immunosuppressive pentapeptide. Int J Mol Sci. (2015) 16:2252–68. doi: 10.3390/ijms16012252
38. Ko M-T, Huang S-C, Kang H-Y. Establishment and characterization of an experimental mouse model of allergic rhinitis. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. (2015) 272:1149–55. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3176-2
39. Zhu Y, Yu J, Zhu X, Yuan J, Dai M, Bao Y, et al. Experimental observation of the effect of immunotherapy on CD4+ T cells and Th1/Th2 cytokines in mice with allergic rhinitis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:5273. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32507-6
40. Ahrén IL, Hillman M, Nordström EA, Larsson N, Niskanen TM. Fewer community-acquired colds with daily consumption of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum HEAL9 and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei 8700: 2. A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Nutr. (2021) 151:214–22. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa353
41. Huerta-Cepas J, Szklarczyk D, Heller D, Hernández-Plaza A, Forslund SK, Cook H, et al. eggNOG 5.0: a hierarchical, functionally and phylogenetically annotated orthology resource based on 5090 organisms and 2502 viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. (2019) 47:D309–14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1085
42. Collins MD, Phillips BA, Zanoni P. Deoxyribonucleic Acid Homology Studies of Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus paracasei sp. nov., subsp. paracasei and subsp. tolerans, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus sp. nov., comb. nov. Int J Systematic Evolutionary Microbiol. (1989) 39:105–8. doi: 10.1099/00207713-39-2-105
43. Rychen G, Aquilina G, Azimonti G, Bampidis V, Bastos ML, Bories G, et al. Guidance on the characterisation of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms. EFSA J. (2018) 16:e05206. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5206
44. Wang J, Zhou J, Wang C, Fukunaga A, Li S, Yodoi J, et al. Thioredoxin-1: A promising target for the treatment of allergic diseases. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:883116. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.883116
45. van Oosterhout AJ, Motta AC. Th1/Th2 paradigm: not seeing the forest for the trees. Eur Respir J. (2005) 25:591–3. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00014105
46. Zhu J, Paul WE. CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults. Blood. (2008) 112:1557–69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-078154
47. Yang J, Bae J, Choi CY, Choi SP, Yun HS, Chun T. Oral administration of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NR16 isolated from Kimchi ameliorates murine allergic rhinitis. Lett Appl Microbiol. (2022) 75:152–60. doi: 10.1111/lam.13716
48. Nakamura H, Nakamura K, Yodoi J. Redox regulation of cellular activation. Annu Rev Immunol. (1997) 15:351–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.351
49. Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. (2010) 11:136–40. doi: 10.1038/ni.1831
50. Swanson KV, Deng M, Ting JP-Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat Rev Immunol. (2019) 19:477–89. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0165-0
51. Torii M, Wang L, Ma N, Saito K, Hori T, Sato-Ueshima M, et al. Thioredoxin suppresses airway inflammation independently of systemic Th1/Th2 immune modulation. Eur J Immunol. (2010) 40:787–96. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939724
52. Campion NJ, Villazala-Merino S, Thwaites RS, Stanek V, Killick H, Pertsinidou E, et al. Nasal IL-13 production identifies patients with late-phase allergic responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2023) 152:1167–1178.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.06.026
53. Ichiki H, Hoshino T, Kinoshita T, Imaoka H, Kato S, Inoue H, et al. Thioredoxin suppresses airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation in asthma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2005) 334:1141–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.007
54. Nakamura T, Nakamura H, Hoshino T, Ueda S, Wada H, Yodoi J. Redox regulation of lung inflammation by thioredoxin. Antioxidants Redox Signaling. (2005) 7:60–71. doi: 10.1089/ars.2005.7.60
55. Imaoka H, Hoshino T, Okamoto M, Sakazaki Y, Sawada M, Takei S, et al. Endogenous and exogenous thioredoxin 1 prevents goblet cell hyperplasia in a chronic antigen exposure asthma model. Allergology Int. (2009) 58:403–10. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.09-OA-0086
56. Zhou J, Wang C, Wu J, Fukunaga A, Cheng Z, Wang J, et al. Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects and molecular mechanisms of thioredoxin on respiratory system diseases. Antioxidants Redox Signaling. (2020) 32:785–801. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7807
57. Rancourt RC, Lee RL, O'Neill H, Accurso FJ, White CW. Reduced thioredoxin increases proinflammatory cytokines and neutrophil influx in rat airways: Modulation by airway mucus. Free Radical Biol Med. (2007) 42:1441–53. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.02.007
58. Hoshino T, Nakamura H, Okamoto M, Kato S, Araya S, Nomiyama K, et al. Redox-active protein thioredoxin prevents proinflammatory cytokine- or bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2012) 168:1075–83. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200209-982OC
59. Cho SH, Oh SY, Lane AP, Lee J, Oh MH, Lee S, et al. Regulation of nasal airway homeostasis and inflammation in mice by SHP-1 and th2/th1 signaling pathways. PloS One. (2014) 9:e103685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103685
60. Chen C-Y, Willard D, Rudolph J. Redox regulation of SH2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatases by two backdoor cysteines. Biochemistry. (2009) 48:1399–409. doi: 10.1021/bi801973z
61. Poole AW, Jones ML. A SHPing tale: Perspectives on the regulation of SHP-1 and SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases by the C-terminal tail. Cell Signalling. (2005) 17:1323–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.05.016
62. Lopez-Ruiz P, Rodriguez-Ubreva J, Cariaga AE, Cortes MA, Colás B. SHP-1 in cell-cycle regulation. Anti-Cancer Agents Medicinal Chem. (2011) 11:89–98. doi: 10.2174/187152011794941154
63. Marasco M, Berteotti A, Weyershaeuser J, Thorausch N, Sikorska J, Krausze J, et al. Molecular mechanism of SHP2 activation by PD-1 stimulation. Sci Adv. (2020) 6:eaay4458. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay4458
64. Pannala VR, Dash RK. Mechanistic characterization of the thioredoxin system in the removal of hydrogen peroxide. Biophys J. (2015) 108:610a–1a. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3323
Keywords: allergic rhinitis, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Th2 immune response, probiotic, immunomodulation, gene K03671
Citation: Zhou X, Song X, Shu T, Zhang S, Zhang Z, Hu C, Pan J, Dai X, Hao H, Xiao G, Wang P and Liu K (2024) Prevention and alleviation of allergic rhinitis by oral administration of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei GOLDGUT-Lpc969. Front. Immunol. 15:1444778. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444778
Received: 12 June 2024; Accepted: 05 September 2024;
Published: 30 September 2024.
Edited by:
Maryam Dadar, Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute, IranReviewed by:
Marcos Edgar Herkenhoff, University of São Paulo, BrazilEdith Ponce-Alquicira, Autonomous Metropolitan University, Mexico
Valerie Diane Valeriano, Karolinska Institutet (KI), Sweden
Copyright © 2024 Zhou, Song, Shu, Zhang, Zhang, Hu, Pan, Dai, Hao, Xiao, Wang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoxun Xiao, c2hhd25Ad29uZGVybGFiLnRvcA==; Pengfei Wang, d2FuZ3BmOUBtYWlsLnN5c3UuZWR1LmNu; Kai Liu, S2FpbGl1QHVvci5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiaoli Zhou
Xiaoli Zhou Xizi Song
Xizi Song Ting Shu
Ting Shu Silu Zhang1
Silu Zhang1 Huaijie Hao
Huaijie Hao Guoxun Xiao
Guoxun Xiao Pengfei Wang
Pengfei Wang Kai Liu
Kai Liu