- 1Postharvest and Agroprocessing Research Centre, Department of Botany and Plant Biotechnology, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 2Center of Excellence for Molecular Food Sciences, Department of Biochemistry, University of Belgrade – Faculty of Chemistry, Belgrade, Serbia
- 3Plant Science Laboratory, Cranfield University, Cranfield, United Kingdom
- 4South African Research Chairs Initiative in Sustainable Preservation and Agroprocessing Research, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Introduction: An effective and efficient drying method for preserving fresh carrots is essential in food processing. Combined drying represents a novel approach that addresses the shortcomings of conventional methods by balancing energy consumption, cost, and product quality.
Methods: This study evaluated the impact of combining oven drying (OD) with freeze-drying (FD) on drying behavior, energy requirements, costs, enzyme activity, and the physicochemical and sensory properties of dried carrots. Drying conditions included 36 hours of FD, OD, and combinations of OD and FD at 1 h of OD + 21 h of FD (OD1-FD21), 2 h of OD + 18 h of FD (OD2-FD18), 3 h of OD + 15 h of FD (OD3-FD15), and 9 h of OD.
Results and discussion: Compared to FD alone, the OD-FD combination reduced drying time by 39–50% and decreased energy consumption and costs by 40–56%. FD and OD-FD reduced polyphenol oxidase activity by 71–85% and peroxidase activity by 29–52% compared to OD alone. FD carrot slices retained significantly higher levels of β-carotene (11.67–25.96 mg/100 g DM), lycopene (9.91–21.85 mg/100 g DM), total phenolic content (7.12–10.24 mg GAE/100 g DM), and DPPH radical scavenging activity (16.44–19.38 mM AAE/100 g DM) than OD and OD-FD slices. OD-FD slices exhibited the highest levels of volatile compounds, including aldehydes, terpenes, esters, alcohols, ketones, and acids, indicating superior flavor preservation.
Conclusion: The OD2-FD18 combination emerged as the optimal method, significantly reducing energy consumption and costs while maintaining better β-carotene, total phenolic content, DPPH radical scavenging activity, and volatile compound profiles. This study highlights the potential of combined drying methods to enhance drying efficiency and product quality.
1 Introduction
Carrots are among the most widely grown and consumed vegetables globally owing to their high carotenoid, flavonoid, polyacetylene, and vitamin content, which provide diverse nutritional and health benefits (Koca Bozalan and Karadeniz, 2011; Rawson et al., 2011; Sharma et al., 2012). Carotenoids, polyphenols, and vitamins in carrots function as antioxidants, anticarcinogens, and immune system boosters (Varshney and Mishra, 2022). Moreover, carrots have been recognised for their antidiabetic, cholesterol-lowering, cardiac disease-reducing, and wound-healing properties (Singh et al., 2021). However, the high unsaturation of carotenoids, the predominant compounds in carrots, renders them highly sensitive to heat, oxygen, and lipoxygenase, resulting in colour degradation during the drying process (Cui et al., 2004; Lyu et al., 2021). Furthermore, carrots have a high moisture content, typically ranging from 80% to 90% on a wet basis, making them prone to spoilage (Sharma et al., 2012). Factors like storage temperature and microbial growth can further compromise the physical and nutritional quality of carrots (Mina et al., 2022). Hence, using an appropriate processing method is crucial to retain the physical and phytochemical properties of carrots in the dried product.
Drying is one of the earliest and most prevalent techniques for postharvest food preservation (Onwude et al., 2017). It involves the removal of moisture from a product through heat and mass transfer, significantly hindering microbial growth, enzymatic reactions, and other deteriorative processes in dried foods (Zielinska and Markowski, 2010; Doymaz, 2017). This method enhances postharvest handling and packaging, reduces food product volume and weight, and lowers transport and storage costs (Ahmed et al., 2013). Product colour and flavour qualities significantly impact customer acceptability and purchase behaviour. Volatile compounds, such as beta-ionone, alpha-ionone, and hexenal, play a vital role in defining the aromatic characteristics of carrots, contributing to their overall quality and consumer appeal. Therefore, selecting the optimal drying method is crucial to minimise any adverse effects on these volatile compounds and maintain the desired aroma and flavour profile of the final product.
Conventional methods for drying fruits and vegetables include vacuum drying, sun drying, freeze-drying, fluidised bed drying, tray drying, and oven drying (Doymaz, 2004; Kaleta et al., 2013; Antal, 2015a; Li et al., 2020). Freeze-drying (FD), which involves the removal of water through sublimation (Nowak and Jakubczyk, 2020), is highly favoured by food processors and consumers due to the excellent physical and chemical qualities of the resulting dried product. These qualities include faster rehydration, minimal shrinkage, high colour retention, low bulk density, and high nutrient and bioactive phytochemical content (Que et al., 2008; Antal, 2015a; Valadez-Carmona et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2021). The literature consistently highlights the effectiveness of FD in retaining nutrients and bioactive compounds in dried products. For instance, Jia et al. (2019) reported higher retention of β-carotene, total phenolic content, and ascorbic acid in persimmon chips dried using freeze-drying compared to oven drying and combined hot-air-microwave and vacuum-freeze-drying methods. Higher total phenolic compounds, flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity in freeze-dried cacao pod husks than microwave and hot air-dried husks have also been reported (Valadez-Carmona et al., 2017).
Nevertheless, unlike traditional drying methods such as hot air drying (HD), FD requires more energy to freeze and thaw the material, operate, and recover frozen condensers. High heat transfer resistance, especially in the final drying cycle, results in longer drying times and significantly raises operational costs (Antal et al., 2015). Moreover, the excessive energy consumption of FD has significant environmental consequences, leading to the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide (Gołasa et al., 2021). These emissions predominantly originate from the combustion of fossil fuels for energy generation. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming (Huang et al., 2009; Khampakool et al., 2019). Given the substantial investment required and the high operational expenses due to lengthy processing times and high energy consumption, the use of FD in drying horticultural produce remains limited (Huang et al., 2009). Therefore, lowering operating costs and energy usage while preserving product quality is still a major concern in FD (Khampakool et al., 2019).
Hot air drying (HD) is the most used method to dry fruits and vegetables due to its low cost and low energy consumption (Doymaz, 2017; Mina et al., 2022). Despite this, HD promotes the breakdown of key flavour components, nutrients, and colour and causes shrinkage (Gu et al., 2022; Yusuf et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2021). Given the increasing global energy costs, imperative carbon emission reductions, and consumer demand for high product quality, there is a pressing need in the food industry to develop an efficient and cost-effective drying method that leverages the advantages of both FD and HD (Cui et al., 2008; Motevali and Koloor, 2017). As explored in previous studies, combination drying techniques offer promising avenues (Cui et al., 2008; Gu et al., 2022; Yusuf et al., 2023). For instance, microwave vacuum drying combined with freeze-drying (MVD-FD) enhanced the colour, rehydration capacity, and texture of dried carrots and apple chips (Cui et al., 2008). Similarly, combining freeze-vacuum drying with hot air drying (FVD-AD) increased the ascorbic acid content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant properties in dried kiwifruit (Zhang et al., 2019). Despite the evidence in the literature regarding the quality enhancements achieved through combining drying methods for fruits and vegetables, the impact on energy consumption and production costs resulting from combining HD and FD has not been extensively studied.
Therefore, this study aimed to compare the impact of hot air drying using an oven (OD), Freeze-Drying (FD), and the combined approach of OD followed by FD (OD-FD) on energy consumption, production costs, colour, phytochemical content, enzyme activity, volatiles, and antioxidant properties of dried carrot slices.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material and sample processing
Fresh carrots were purchased from the Johannesburg Fresh Produce Market in Gauteng Province, South Africa. Only carrots of uniform size and free from any physical damage were selected for further processing. The selected carrots were washed, peeled, and manually cut into slices with a diameter of approximately 25 mm and a thickness of 5 mm. These slices were then stored in a cold room maintained at 5 ± 2°C until further use.
2.2 Pretreatment
A 3% gum Arabic (GA) solution was used as a pretreatment to minimise oxidation and degradation of antioxidants and volatiles. Carrot slices (300 g) were immersed in 250 mL of the 3% GA solution (Sigma Aldrich Co., France) and sonicated for 10 min in an ultrasonic bath (Labotec 705, Johannesburg, Gauteng, South Africa) operating at a maximum power of 600 W, a frequency of 50 Hz, and a temperature controlled at 25 ± 2°C.
2.3 Oven drying
Based on a previous study (Mina et al., 2022), carrot slices were oven-dried using an EcoTherm Economy oven (Labotec, Johannesburg, South Africa) for 9 h at 50°C, sample load density of 0.019 kg/L, with a constant airflow rate of 1.0 m/s. The hot air oven temperature was preheated to 50°C one hour before the drying process commenced to achieve steady-state conditions. Moisture content was measured using a moisture analyser (KERN DBS 60-3, Berlin, Germany) set at 105°C. The initial moisture content of the carrot slices varied between 81% and 89% (w/w), and the final moisture content was reduced to less than 6%. Following drying, the carrot slices were carefully packed in transparent polyethylene bags and stored at -20 ± 2°C until further analysis.
2.4 Freeze-drying
The carrot samples were frozen in a static air freezer at −80°C for 1 h. Subsequently, the frozen samples were freeze-dried using a Buchi Lyovapor L-200 Freeze Dryer (Postfach, CH-9230 Flawil, Switzerland) at -60°C and 0.03 mbar for 36 hours. The loss in sample weight was recorded at 3-hour intervals until constant weights were achieved.
2.5 Combined oven drying and freeze-drying
The carrot slices were first oven-dried until their moisture contents reached 50 ± 2%, 40 ± 3%, and 20 ± 2% wet basis, corresponding to oven drying durations of 1, 2, and 3 h, respectively. The samples were freeze-dried for 21, 18, and 15 h, respectively, for oven drying durations of 1, 2, and 3 h.
2.6 Cost and energy requirements determination
The energy required to produce 1 kg of dried carrot slices for each drying process was measured using a watt meter (Revolt Watt Meter, Gauteng, South Africa). Energy costs were calculated based on the Eskom price per kWh in 2023, and carbon dioxide emissions were calculated according to Goggins and Adams (2021).
2.7 Physicochemical properties
2.7.1 Colour
Colour measurements were assessed using CIELAB coordinates (L*, a*, and b*) with a calibrated colourimeter (Konica Minolta Chroma Meter CR-400, Osaka, Japan). The total colour difference (ΔE) was calculated using Equation 1, as described by Adetoro et al. (2020b).
where L∗, a∗, and b∗ represent lightness/darkness, redness/greenness, and yellowness/blueness, respectively. ΔL*, Δa*, Δb* represent change in lightness/darkness, redness/greenness, and yellowness/blueness, respectively.
2.7.2 Rehydration ratio
Rehydration capacity was measured according to Adetoro et al. (2020c). In brief, dried carrot samples weighing 5 g were immersed in 100 mL of distilled water at room temperature for 1 h. Subsequently, the water from the rehydrated carrots was drained, and any excess water was blotted using a paper towel. Equation 2 was used to calculate the rehydration ratio.
where, is the weight of wet carrot slices at time t, and is the initial weight of dry carrot slices.
2.7.3 β-carotene and lycopene content
The extraction of β-carotene and lycopene, as described by Wright and Kader (1997), with slight modification. In triplicate, 2 g of carrot powder (ground under liquid nitrogen) were added to a glass pill vial, followed by the addition of 10 mL of an ethanol and hexane mixture (1:1) containing 0.02% 2,6-di-ter-butyl-p-cresol (BHT). The solution was vortexed and sonicated in an ultrasonic bath (Labotec 705, Gauteng, South Africa) at a frequency of 50 Hz, power of 500 W, and a temperature of 25°C for 10 minutes. The mixture was centrifuged (D-37520; ThermoFisher Scientific, Stratos, United Kingdom) at 8400 x g for 5 minutes. The absorbance of the samples was measured using UV spectrophotometry (SP-UV 300, Spectrum Instruments, Shanghai, China) at 470 nm under dim light conditions. Quantifications were performed using calibration curves for β-carotene (0–0.01 mg/mL; R² = 0.958) and lycopene (1.0–6.0 µg/mL; R² = 0.9937). The results were expressed as milligrams of β-carotene per 100 grams of dry matter (mg β-carotene/100 g DM) and milligrams of lycopene per 100 grams of dry matter (mg lycopene/100 g DM).
2.7.4 Total phenolic content
The total phenolic content (TPC) was determined using a modified Folin-Ciocalteu method with methanolic extracts of dried carrots (Adetoro, 2020a). Briefly, 2 g of carrot powder (ground under liquid nitrogen) were mixed with 10 mL of distilled water, vortexed, and then centrifuged (D-37520, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Stratos, United Kingdom) at 8400 x g for 5 minutes. The supernatant (50 μL) was combined with 450 μL of 50% methanol, 500 μL of Folin-Ciocalteau reagent, and 2.5 mL of 2% sodium carbonate solution. This mixture was incubated in darkness at room temperature for 40 min. The absorbance of the samples was measured using a UV spectrophotometer (SP-UV 300, Spectrum Instruments, Shanghai, China) at 725 nm under dim light. A gallic acid standard curve (0–0.1 mg/mL; R² = 0.9825) was used, and the results were reported as milligrams of gallic acid equivalent per 100 grams of dry matter (mg GAE/100 g DM).
2.7.5 DPPH radical scavenging activity
The DPPH radical scavenging activity was determined according to Mina et al. (2022). Triplicate samples of carrot powder (2 g) were mixed with 10 mL of distilled water, vortexed, and then centrifuged (D-37520, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Stratos, United Kingdom) at 10,000 x g for 5 minutes. The supernatant (30 μL) was mixed with 1470 μL of 50% methanol and 1500 μL of DPPH solution. The mixture was incubated in darkness at room temperature for 30 minutes. The absorbance of the samples was then measured using a UV spectrophotometer (SP-UV 300, Spectrum Instruments, Shanghai, China) at 517 nm under dim light. The DPPH radical scavenging activity of the samples was calculated using the ascorbic acid standard curve (0–2.0 mM, R² = 0.999), and the results were reported as ascorbic acid equivalent (mM AAE/100 g DM).
2.8 Microstructure analysis
The microstructures of FD, OD, and OD-FD carrot samples were studied using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Tescan Vega 3, Brno, Czech Republic). Briefly, the samples were placed on adhesive tape and then coated with a fine layer of gold using a sputter coater. The coated samples were then examined at 2500x magnification.
2.9 Enzyme activity analysis
2.9.1 Crude enzyme extraction
Dried carrots were finely ground into powder and mixed with 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7), 0.05 M EDTA, and 60 g/L polyvinyl polypyrrolidone (PVPP) in a 1:10 ratio. The mixture was vortexed for 1 minute and then ultrasonicated (Sonic Clean, Labotec, Johannesburg, South Africa) for 15 min at 50 Hz, power of 600 W, and temperature of 0°C. The extracts were centrifuged at 10,000 x g at 4°C for 5 minutes and kept at 4°C for 2 hours. The supernatants were used as crude enzyme extracts for further analyses.
2.9.2 Polyphenol oxidase
Polyphenol oxidase activity was determined using a modified method by Morodi et al. (2022). Crude enzyme extracts (200 µL) were added to 50 µL of 0.06 M catechol and 2.8 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7) at 25 °C. The absorbance was measured at 398 nm at 1-minute intervals for 3 minutes using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (SP-UV 300, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Shanghai, China). Sodium phosphate buffer and catechol were used as blank solutions. A change in absorbance of 0.01 per minute was defined as one unit of enzyme activity per millilitre per minute (U/min/mL).
2.9.3 Peroxidase
Peroxidase activity was determined using a modified method by Nxumalo et al. (2022). Crude enzyme extracts (200 µL) were added to 2.2 mL of 0.3% guaiacol (dissolved in sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7) at 30°C and 0.6 mL of 0.3% hydrogen peroxide. The absorbance was recorded at 470 nm at 1-minute intervals for 3 min using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (SP-UV 300, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Shanghai, China). A change in absorbance of 0.01 per minute was defined as one unit of enzyme activity per millilitre per minute (U/min/mL).
2.10 Volatile compounds analysis
Five hundred milligrams of dried carrot samples were placed in a vial, to which 5 mL of a 20% sodium chloride (NaCl) solution and 100 µL of a 10 ppm anisole-d8 solution (used as an internal standard) were added, and the mixture was vortexed. The vial was then loaded onto the sample tray, and 1 µL of the sample was injected into a gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer (GC-MS) system in the splitless mode for analysis via solid-phase microextraction (SPME)-GC-MS. Separation of the volatile compounds was carried out on a gas chromatograph (6890N, Agilent Technologies Network) equipped with an Agilent Technologies inert XL EI/CI Mass Selective Detector (MSD) (5975B, Agilent Technologies Inc., Palo Alto, CA). The system included a CTC Analytics PAL autosampler for automated sampling. The volatiles were separated on a ZB-Wax capillary column (30 m length, 0.25 mm internal diameter, 0.25 µm film thickness; Phenomenex, Torrance, California, United States). Helium was used as the carrier gas at a 1.0 mL/min flow rate. The injector temperature was set at 240°C, and splitless injection was employed. The oven temperature program started at 40°C for 17 minutes, followed by an increase to 240°C at a rate of 8°C/min, with a final hold at 240°C for 2 minutes. The MSD operated in full scan mode, with source and quadrupole temperatures maintained at 230°C and 150°C, respectively. The transfer line temperature was held at 250°C. The mass spectrometer operated in electron impact (EI) mode with an ionisation energy of 70 eV, scanning across a mass range of 30 to 700 m/z. Mass spectral data from the NIST and Wiley Libraries and retention indices were used to identify volatile compounds. The relative content (%) of each volatile compound was then calculated by dividing the peak area of each component by the total peak area of all identified compounds.
2.11 Statistical analysis
All experiments were carried out in triplicate and subjected to statistical analysis using Statistica software (Statistica 13.0, StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). Data were analysed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and Duncan's multiple range test was used to separate the differences between the treatment means (p < 0.05). All results were expressed as mean ± standard error. Microsoft Excel software version 16.0.13029.20344 (Microsoft Corporation, Washington, USA) was used to produce graphs. A heatmap was generated based on normalised data with the Euclidean distance and Ward’s method clustering algorithm to visualise the relative abundance of metabolites in carrots after different drying conditions.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Energy requirements, costs, and carbon dioxide emission
The energy consumption associated with the processing of fruits and vegetables plays a significant role in both greenhouse gas emissions and production costs (Khampakool et al., 2019). Table 1 presents the energy requirements, costs, and carbon dioxide emissions for the different methods used to dry carrot slices. The results indicate that FD consumed the most energy, resulting in the highest cost and carbon dioxide emissions. Conversely, OD had the lowest energy consumption (0.61 kWh/kg), costs (R0.89, where R stands for South African Rand), and carbon dioxide emissions (7.60 kg CO2) compared to FD. Combining OD and FD reduced the energy use, costs, and carbon dioxide emissions of FD by 40.81–55.78%, highlighting its potential to enhance sustainability in food processing by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs (Saleh et al., 2020). An oven drying of 3h followed by 15h of freeze-drying (OD3-FD15) had the lowest energy and cost requirements among OD-FD methods. This result can be attributed to the higher moisture loss during OD, resulting in a shorter FD duration. These findings align with Jiang et al. (2017), who reported that freeze-drying combined with microwave vacuum drying reduced energy consumption by approximately 71.92% compared to FD of okra. Similarly, a 70% decrease in drying costs was reported for blanched, freeze-dried, and hot air-dried apple cubes (Antal et al., 2015). Our findings suggest that implementing oven drying as a pretreatment to freeze drying can enable food loss and waste and reduce resource consumption (energy and cost).
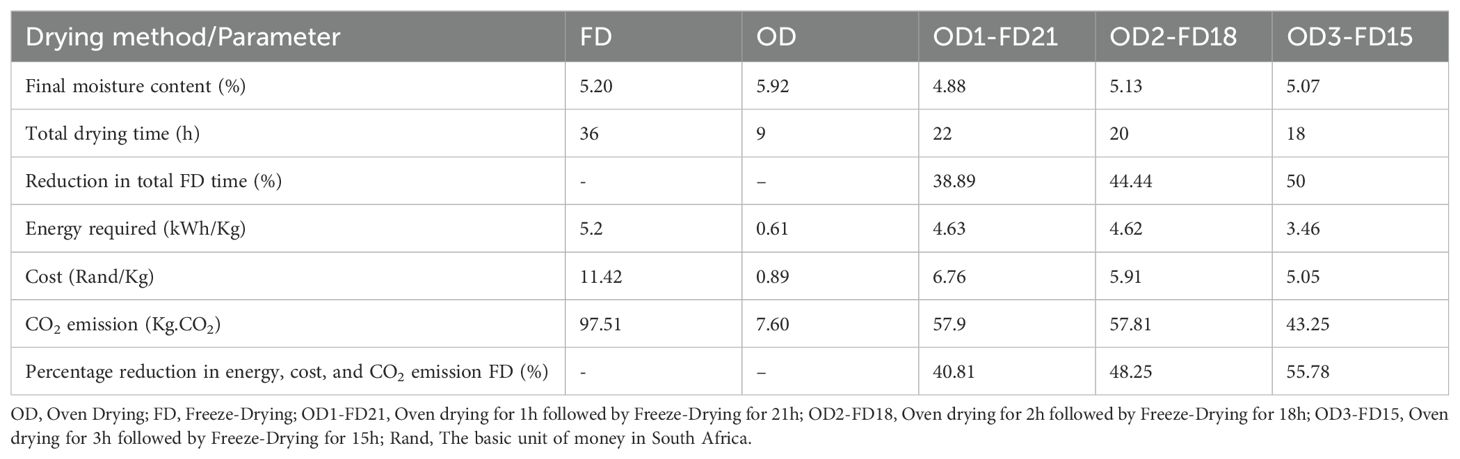
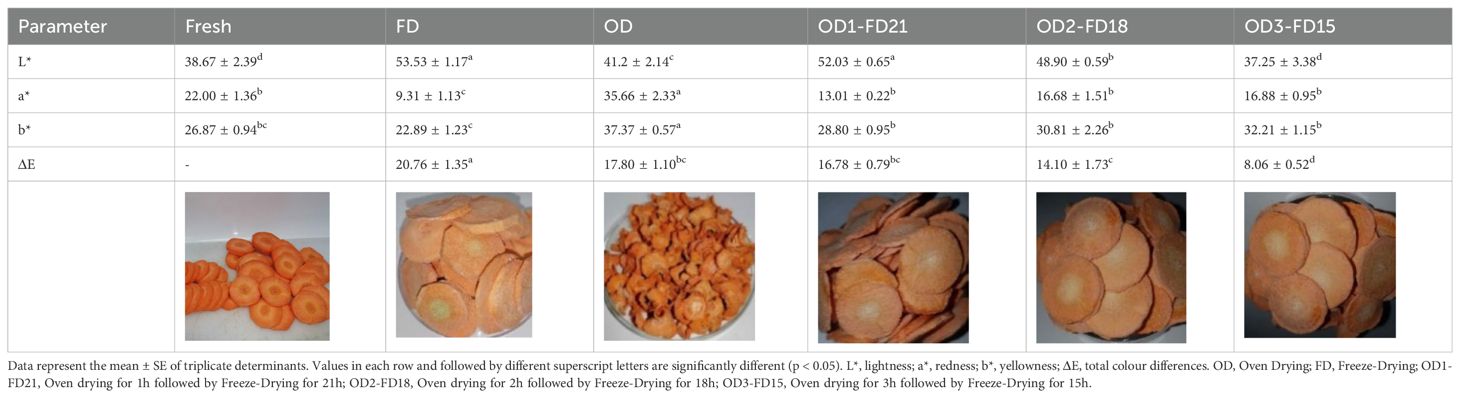
Table 1. Energy requirements, costs, carbon dioxide emission, total drying time, and moisture content of OD, FD, and OD-FD carrot slices.
3.2 Drying time and moisture content
Carrot slices dried using FD required significantly more time (36 h) compared to those dried using OD (9 h). The sublimation process in FD involves heat conduction in a vacuum, resulting in a slow heat transfer rate (Antal et al., 2015; Khampakool et al., 2019). Combining OD and FD reduced the FD time of the carrot slices by 38.89–50%, with the OD3-FD15 combination cutting the total drying time by half (Table 1). Pre-drying the carrot slices using OD before FD facilitated rapid mass transfer due to the large vapour pressure created by air on the surface of the carrot slices. This observation suggests that OD-FD has a synergistic effect in reducing the drying time of carrot slices. Zhang et al. (2019) reported a similar trend, where freeze-vacuum drying combined with hot air drying (FVD-AD) significantly reduced the drying time of kiwi fruit by 38.22%.
The moisture content of dried foods is crucial for determining their stability and susceptibility to microbial growth during storage. The final moisture content of all treated carrot samples (FD, OD, and OD-FD) ranged from 4.88% to 5.92%. The low moisture content indicates a higher concentration of nutritional compounds, enhancing the nutritional quality of the carrot samples as the moisture content decreases during drying (Iombor et al., 2014). Additionally, this results in good storage qualities and resistance to microbial growth (Vera Zambrano et al., 2019).
3.3 Colour
The preservation of colour in dried food products is of utmost importance as it directly affects consumer appeal and can indicate nutrient retention and process effectiveness. Previous literature has highlighted that enzymatic and non-enzymatic browning and caramelisation can influence the colour of dried products (Rajkumar et al., 2017). As shown in Table 2, the colour parameters indicate that freeze-dried (FD) and combined oven and freeze-dried (OD-FD) carrot slices had significantly higher L* values than fresh and oven-dried (OD) slices. Samples dried for 3 h with OD followed by 15 h with FD (OD3-FD15) showed the lowest L* (37.25), closest to fresh carrot slices (38.67). This suggests that the combined method can retain the colour of the dried carrots to a certain extent. The a* value, representing redness, was significantly higher in OD carrot slices, indicating a greater degree of colour change, likely due to the thermal effects of OD on the carotenoid pigment in carrots (Doymaz, 2017).
The OD carrot slices exhibited a higher b* value (37.37) than the FD ones (22.89). Combining the two methods significantly reduced the b* value (28.80 – 32.21) as represented in Table 2. Although this reduction in b* could be related to variations in particle size and density of the dried carrots, it did not result in a significant overall change in colour. The ΔE parameter, which measures the total colour difference based on changes in L*, b*, and a* relative to fresh carrot slices, was 20.76 for FD and 17.80 for OD. When combining both drying methods, ΔE significantly decreased, ranging from 8.06 to 16.78, with the lowest ΔE observed in the OD3-FD15 samples (Table 2).
Our findings suggest that combining OD and FD methods (OD-FD) offers superior colour retention, likely due to the reduced pigment deposition, specifically the preservation of β-carotene (Yildiz, 2022). The ΔE values support the b* findings, indicating a synergistic advantage in the OD-FD method for preserving colour. The shorter OD time may have limited non-enzymatic browning reactions, thereby preserving the natural colour of the carrots. This contrasts with the findings by Jiang et al. (2017), who reported a higher ΔE for combined freeze-drying and microwave vacuum drying compared to freeze-drying alone for okra. Therefore, the combined approach enhances the dried product's appearance by maintaining its natural colour, ensuring its competitiveness in the market.
3.4 Rehydration ratio
A dried food product's ability to absorb water depends on the extent to which its structural integrity has been compromised during the drying process. Figure 1 shows the results of dried carrot samples rehydrated for 1 h. Rehydration was more prominent in FD (4.46) than OD carrot samples (2.30). OD-FD samples had a significantly high rehydration ratio, ranging from 4.16 to 4.31. A high rehydration ratio indicates a high-quality dried product, as water can easily re-enter the cells. The high rehydration ability of FD and OD-FD samples could be attributed to increased water vapour diffusion due to enhanced porosity (Rawson et al., 2011). Additionally, the FD samples exhibited minimal disturbance of cells and tissue structures (Gu et al., 2022). In contrast, the significant textural alterations in OD samples explain their longer rehydration time. OD causes rapid water evaporation and the migration of inorganic salts to the surface of carrot slices, leading to surface hardening and, consequently, longer rehydration times (Valadez-Carmona et al., 2017). Comparable results were observed in catalytic infrared and freeze-dried chives (Gu et al., 2022).
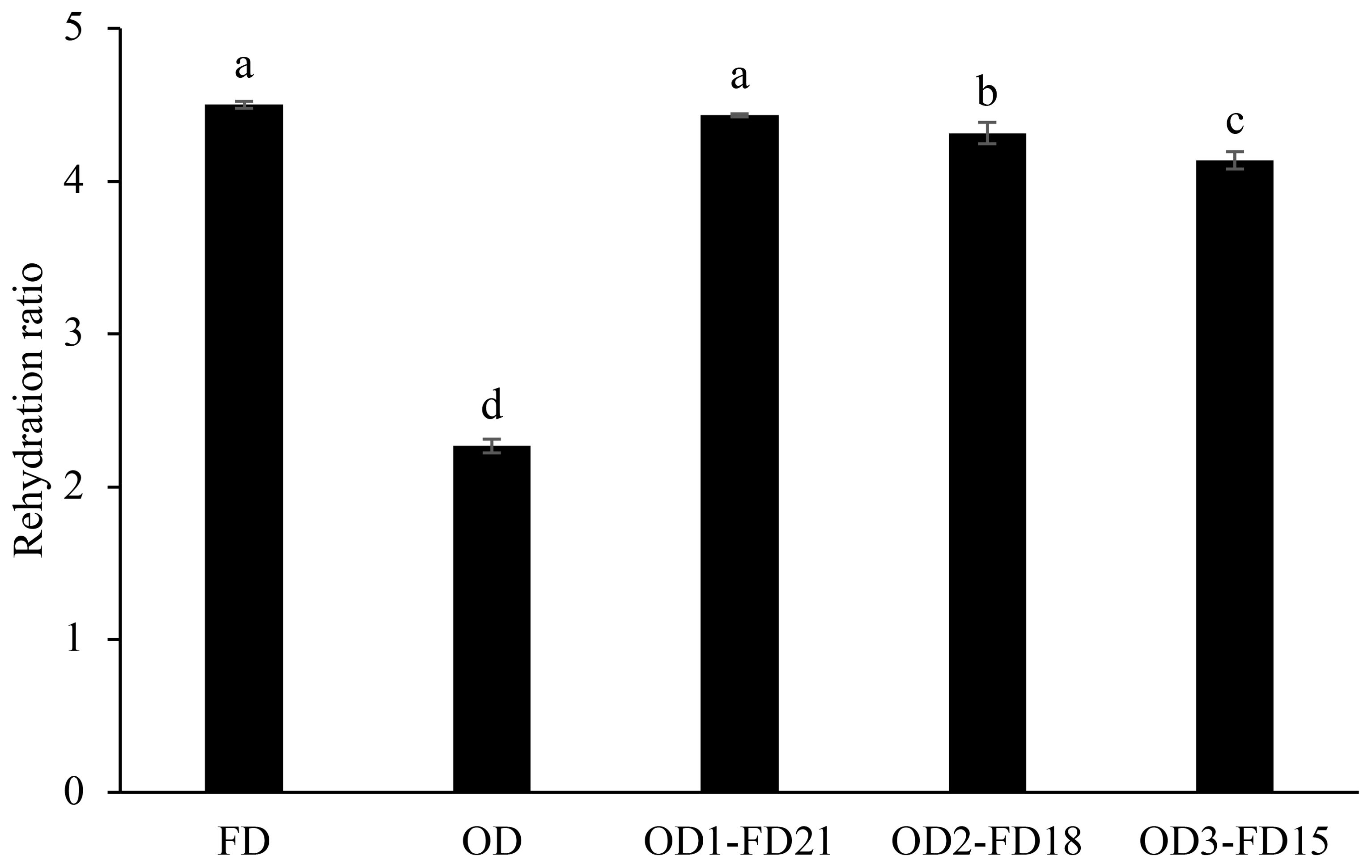
Figure 1. Rehydration ratio of dried carrot slices. OD, Oven Drying; FD, Freeze-Drying; OD1-FD21, Oven drying for 1h followed by Freeze-Drying for 21h; OD2-FD18, Oven drying for 2h followed by Freeze-Drying for 18h; OD3-FD15, Oven drying for 3h followed by Freeze-Drying for 15h. Different letters on each bar indicate significant differences among drying types at p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test. Vertical error bars indicate the standard error.
3.5 β-carotene content, lycopene content, total phenolic content, and radical scavenging activity
The β-carotene content results of FD, OD, and OD-FD samples are presented in Figure 2. FD and OD-FD samples showed a significantly higher β-carotene content (23.43-25.96 mg/100 g) than OD (11.67 mg/100 g). The absence of oxygen and low temperature could have prevented oxidative or temperature-related degradation of these colour pigments during FD. Similar results were reported by Rawson et al. (2011), who reported that freeze-dried carrot discs showed 28.4% higher total carotenoids than hot air-dried samples. Similarly, FD and OD-FD (16.44-19.50mg/100g) samples showed a significantly higher (p < 0.05) lycopene content than OD (10.29). Like in β-carotene, limited exposure to OD, low temperature, and limited oxygen during FD could be contributing factors (Rojas et al., 2020; Saleh et al., 2020). Among the OD-FD samples, Figure 3 presents the total phenolic content of OD, FD, and OD-FD carrot slices. FD carrot slices showed a 1.4-fold higher TPC than OD carrot slices. OD-FD considerably (p < 0.05) increased the TPC when compared with the carrot slices dried by OD alone. The lower TPC in OD carrot samples could be attributed to the enzymatic (polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase) and non-enzymatic oxidation of phenolic compounds during drying (Papoutsis et al., 2017). This is supported by the POD and PPO activity results (Table 3). Overall, FD and OD- FD retained the most TPC, implying improved retention of polyphenols during the drying processes. The observations agree with those reported by Papoutsis et al. (2017), in which FD lemon pomace had the highest TPC compared to hot air and vacuum-dried lemon pomace. However, the TPC results from the present study contradict those reported by Ferenczi et al. (2014).
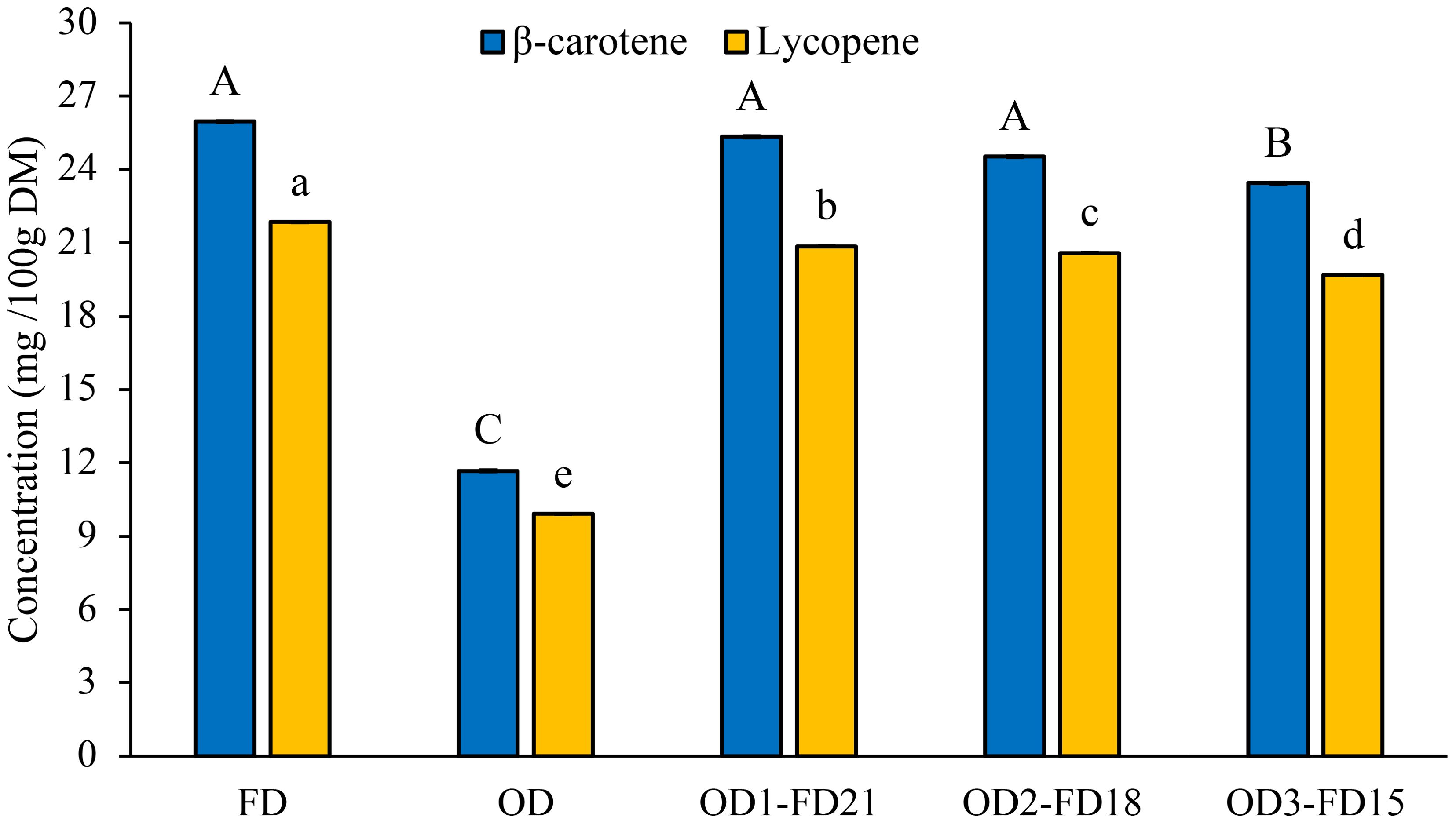
Figure 2. β-carotene content and lycopene content of dried carrot slices. OD, Oven Drying; FD, Freeze- Drying; OD1-FD21, Oven drying for 1h followed by Freeze-Drying for 21h; OD2-FD18, Oven drying for 2h followed by Freeze-Drying for 18h; OD3-FD15, Oven drying for 3h followed by Freeze-Drying for 15h. Different letters (upper for β-carotene and lower for lycopene) on each bar indicate significant differences among drying types at p<0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test. Vertical error bars indicate the standard error.
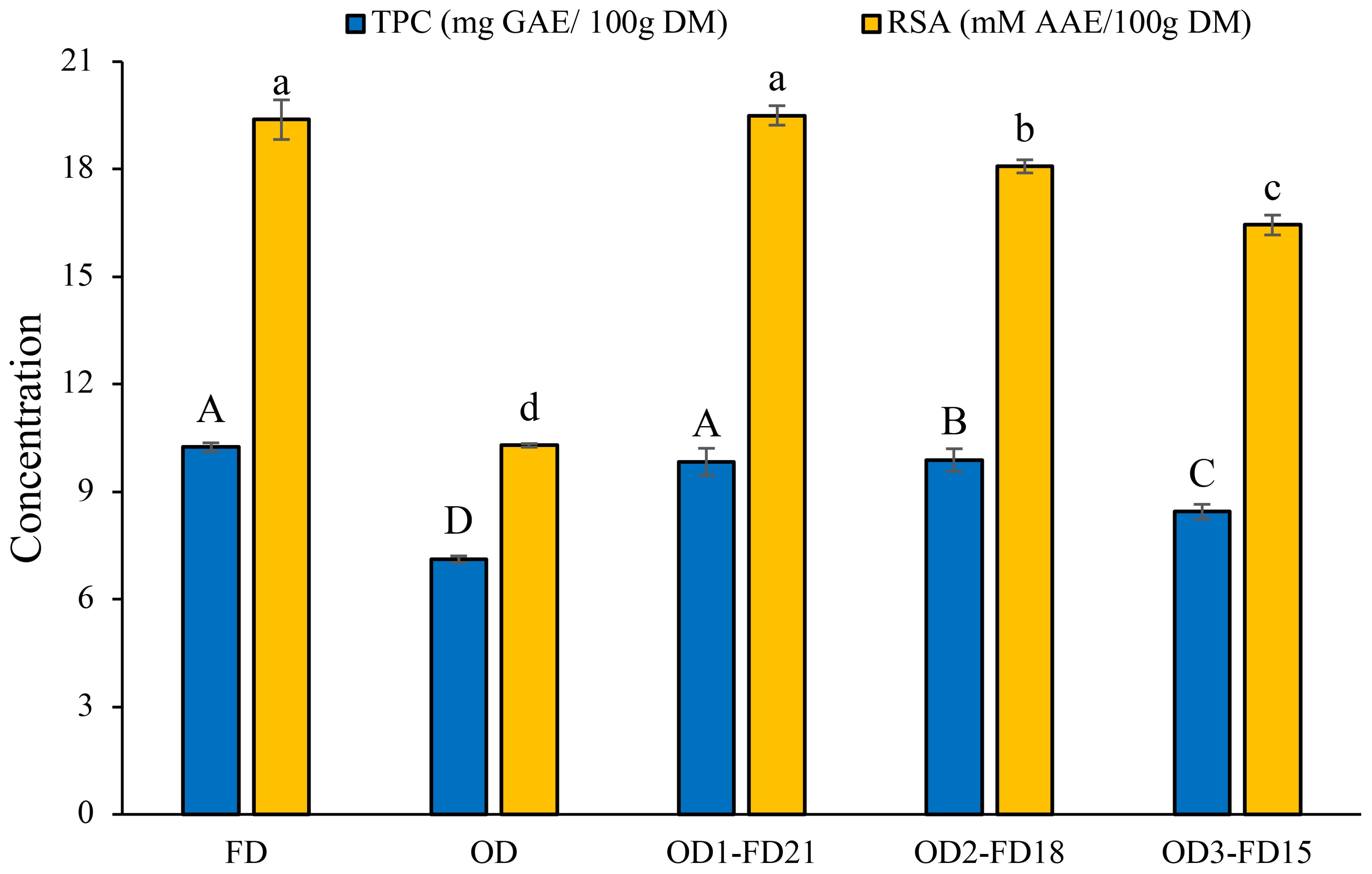
Figure 3. Total phenolic content (TPC) and Radical scavenging activity (RSA using DPPH assay) of dried carrot slices. OD, Oven Drying; FD, Freeze-Drying; OD1-FD21, Oven drying for 1h followed by Freeze-Drying for 21h; OD2-FD18, Oven drying for 2h followed by Freeze-Drying for 18h; OD3-FD15, Oven drying for 3h followed by Freeze-Drying for 15h. Different letters (upper for TPC and lower for RSA) on each bar indicate significant differences among drying types at p < 0.05 by Duncan's multiple range test. Vertical error bars indicate the standard error.
TPC was lower in FD apple slices than in hot-air and combined microwave and hot air-dried apple slices. The difference in the conditions of operation could explain the variation.
The DPPH radical scavenging activity was evaluated to assess the antioxidant activity of the dried carrot slices. Antioxidants scavenge free radicals from body cells and prevent or reduce cell oxidation damage, contributing to improved health (Que et al., 2008). The antioxidant activity of dried carrot slices was significantly affected by the different drying methods (p < 0.05), as seen in Figure 3. FD (19.38 AAE/100 g DM) and OD-FD samples (16.44–19.31 AAE/100 g DM) exhibited higher radical scavenging activity than OD samples (10.29 AAE/100 g DM). The higher DPPH radical scavenging activity of FD and OD-FD samples than in OD could be due to the significantly higher antioxidant compounds, including the β-carotenes, lycopene, and total polyphenols, observed in the respective treatments. Papoutsis et al. (2017) and Que et al. (2008) reported a higher antioxidant capacity in lemon pomace and pumpkin flour dried by hot air than those dried by freeze-drying. These results can guide the development of functional and health-oriented foods for wellness.
3.6 Enzyme activities (PPO and POD)
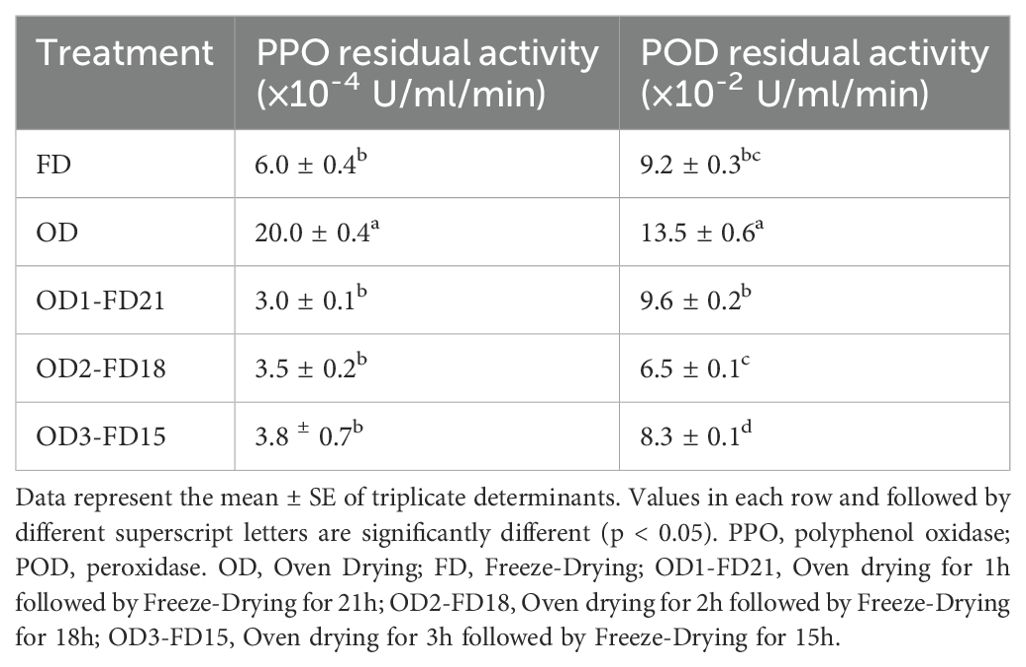
The enzymatic browning reactions mediated by polyphenol oxidase (PPO) and peroxidase (POD) in phenolic compounds during processing result in the discolouration of fruits and vegetables, impairing sensory quality and perceived nutritional value, thus rendering them undesirable to consumers (Morsy and Rayan, 2019). The residual activity of PPO and POD, which is inactivated by thermal processing, is commonly used as a quality indicator to assess the effectiveness of drying methods on fruits and vegetables. It is crucial to emphasise that none of the pretreatments resulted in the total inactivation of the POD and PPO enzymes. As exhibited in Table 3, PPO residual activity was highest in OD carrots (20 ×10-4 U/ ml/ min), which was significantly (p < 0.05) higher than in FD (6.0 ×10-4 U/ ml/ min) and OD-FD samples (3.0-3.8 ×10-4 U/ ml/ min). Regarding POD activity, the highest and lowest residual activity was observed in oven dried (OD) (13.5 ×10-2 U/ ml/ min) and 2 hours oved dried and 21 hours freeze dried (OD2-FD18) carrot samples (6.5 ×10-2 U/ ml/ min), respectively. The lower PPO and POD residual activities in FD and OD-FD suggest that these methods were more effective in inactivating the PPO and PDO enzymes. This is a positive outcome, considering the role of these enzymes in the development of undesirable qualities in dried fruits and vegetables (Sagar and Suresh Kumar, 2010).
3.7 Microstructure analysis
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed to evaluate the effects of different drying methods on the macrostructure and surface morphology of the dried carrot slices (Figure 4). The SEM image of OD samples showed collapsed cell walls and excessive shrinkage (Figure 4A). This can be explained by the loss of cell turgor pressure and internal stress that resulted in tissue collapse and crust formation during drying (Yao et al., 2020). Similarly, Monteiro et al. (2018) found that the cellular collapse of pumpkin slices was caused by hot air drying because of crust formation that resulted from internal stress, causing most of the capillaries to collapse and resulting in irreversible structural changes. The microstructures of FD, OD1-FD21, and OD2-FD18 samples showed similar surface morphology with less structural damage. During the FD process, ice crystals inside the drying fruit were sublimated, and the structures of the spaces that initially contained the sublimed ice were preserved. This could have facilitated the formation of a spongy structure (Huang et al., 2021; An et al., 2022). The SEM images of OD and OD3-FD15 slices showed collapsed cell walls.
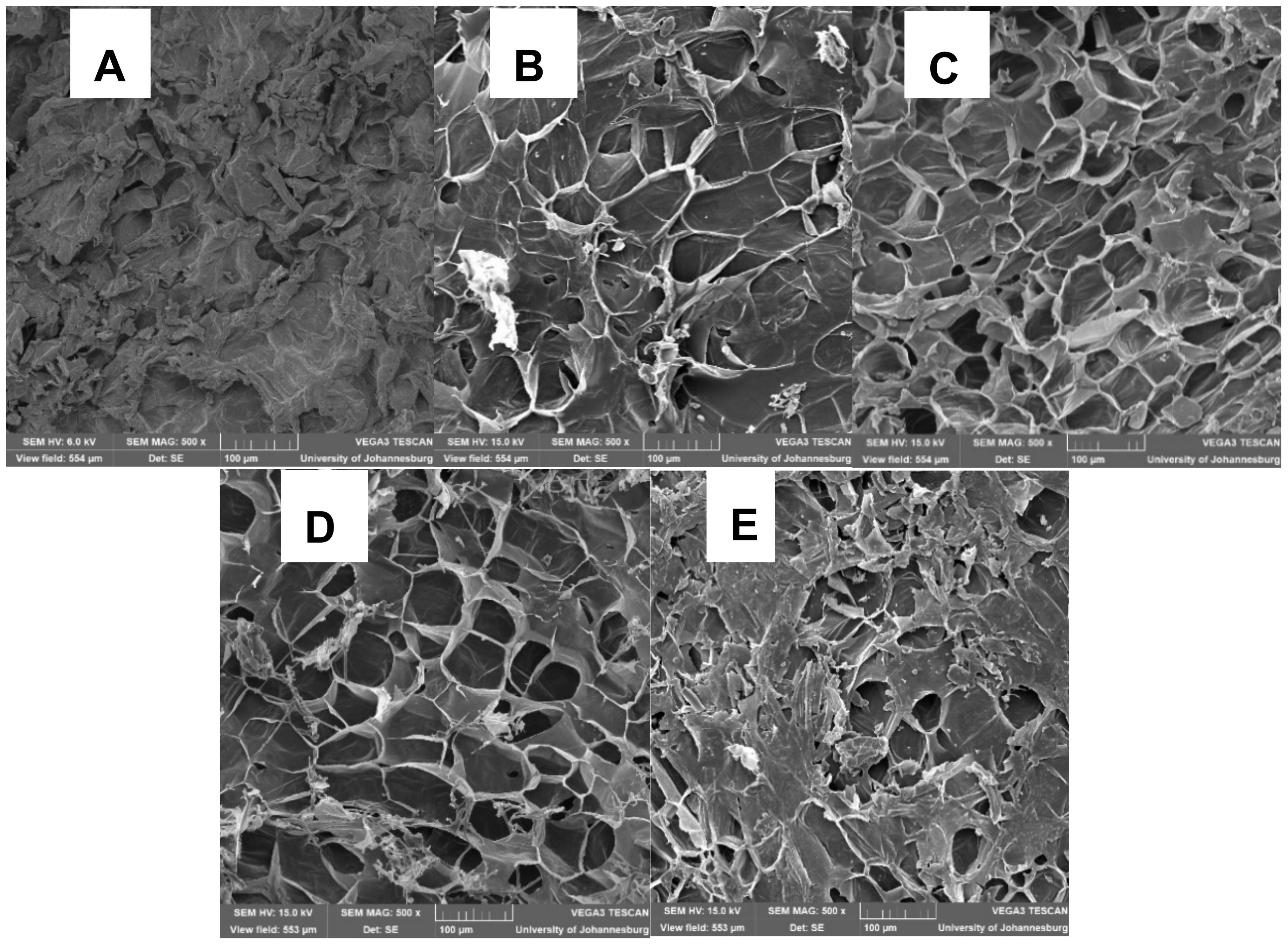
Figure 4. Scanning electron micrographs (SEM at 2500X) of the dried carrot slices (A) Oven-dried, (B) freeze-dried, (C) OD1-FD21: Oven drying for 1h followed by Freeze-Drying for 21h; (D) Oven drying for 2h followed by Freeze-Drying for 18h; and (E) OD3-FD15: Oven drying for 3h followed by Freeze- Drying for 15h.
Increasing the OD time from OD1-FD21 to OD3-FD15 impacted the cell structures of the carrot slices due to the increased dehydration rate in OD (Huang et al., 2012). The SEM results are consistent with the rehydration ratio results in which OD and OD3-FD15 exhibited the lowest rehydration ratios among the samples.
3.8 Volatile compounds
In the present study, a total of 45 volatiles for OD and 49 volatiles for FD and OD-FD were observed (Supplementary Table S1). The dried carrots were mainly comprised of various groups of volatiles, including aldehydes, terpenes, alcohols, ketones, acids, and esters, as determined from the GC–MS analysis (Supplementary Table S1). While previous studies have explored the volatiles of carrots (Rajkumar et al., 2017; Keser et al., 2020; Keskin et al., 2021), this study is the first to investigate the effects of various drying methods and their combinations (OD, FD, OD1-FD21, OD2-FD18, OD3-FD15) on the retention of aroma compounds in dried carrots samples. The results reveal that the drying process influences the concentration of the metabolites in dried carrots. Hence, the dried carrots obtained by application of combined drying (OD followed by FD) present a relative abundance of many metabolites (Figure 5). Figure 5 shows that the combinations OD2-FD18 and OD3-FD15 tend to handle dried carrots with the highest content of metabolites regardless of the class of volatiles. This confirms that these samples, besides their health benefits and resource effectiveness, provide high-quality sensory profiles (flavour), highlighting their strategic market potential that can be leveraged for premium dried products.
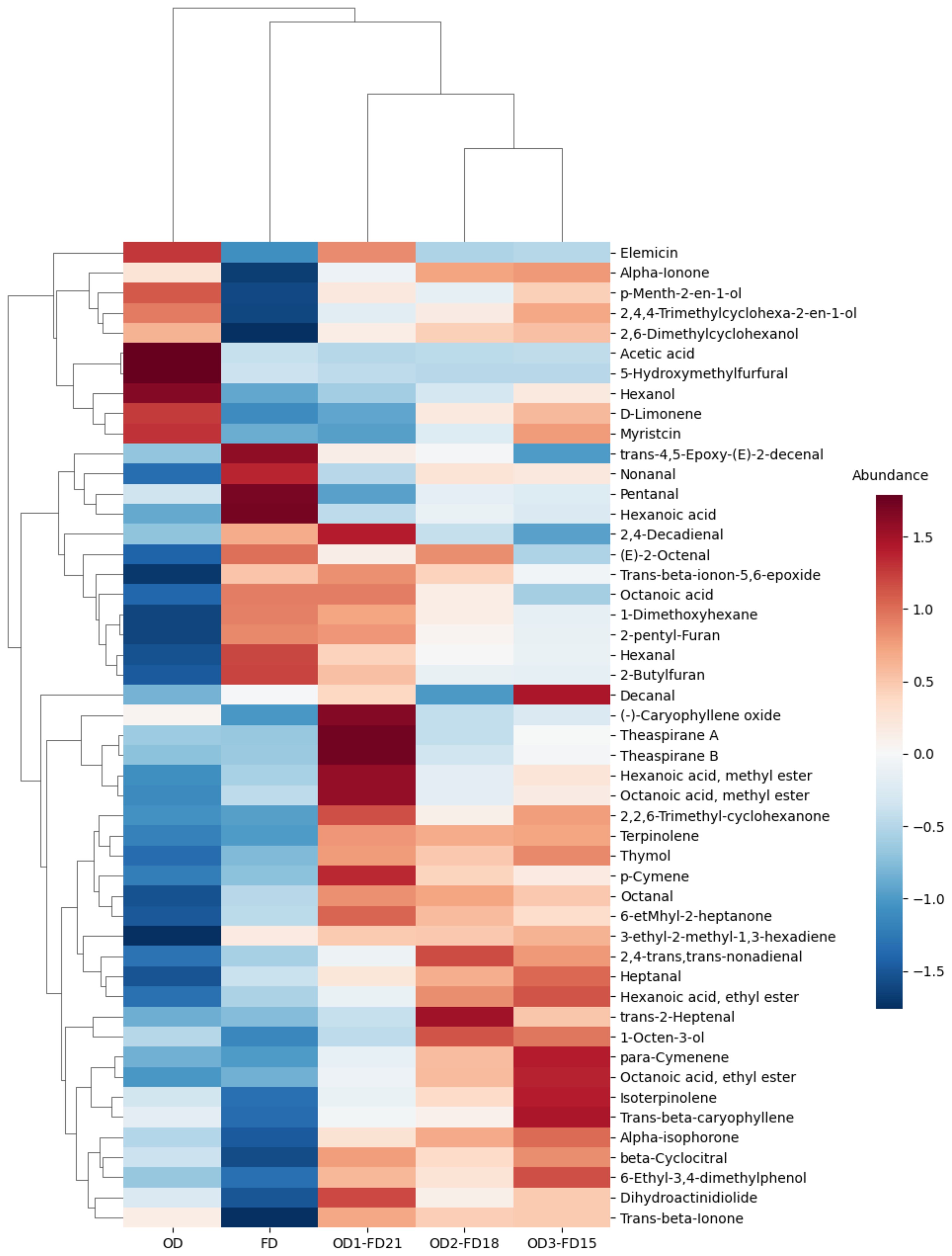
Figure 5. Heat map showing the relative abundance of the identified compounds from the freeze-dried (FD), oven-dried (OD) and combined Oven-Freeze-dried carrot slices. OD, Oven Drying, FD, Freeze- Drying; OD1-FD21, Oven drying for 1h followed by Freeze-Drying for 21h; OD2-FD18, Oven drying for 2h followed by Freeze-Drying for 18h; OD3-FD15, Oven drying for 3h followed by Freeze-Drying for 15h. Metabolites highly expressed are coloured in red while metabolites with low expression are shown in blue colour (colour scale).
Aldehydes emerged as the most dominant flavour group in carrot slices (Supplementary Table S1). Among the aldehydes identified, hexanal and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural were the predominant compounds contributing to the aroma of carrots. Generally, aldehydes are particularly abundant in FD and OD-FD compared to OD carrots, suggesting minimal oxidation of aldehyde compounds. However, 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural showed a high level of OD (12 %) compared to FD and OD-FD (0.12 – 0.74 %). The compound can be formed from the degradation of sugars through caramelisation, which can occur during oven drying (Kowalski et al., 2013).
Terpenes are important constituents that highly influence the carrot aroma's quality and quantity (Polat et al., 2022). In this study, the combined drying method of OD3-FD15 retained the highest percentage of terpenes (27.20 %). The major terpenes identified were D-limonene and terpinolene. Oven drying exhibited a significantly higher D-Limonene (19,04 %). Similar findings have been reported in previous studies on carrots (Çavdar and Eda, 2023). D-Limonene, known for its various health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antinociceptive, anticancer, antidiabetic, antihyperalgesic, antiviral, and gastroprotective properties, is abundant in carrots (Vieira et al., 2018). Terpinolene has been associated with cooked carrot aroma in processed products. Its non-detection in oven-dried carrots and its presence in FD and combinations (OD-FD) could indicate a thermo-sensitivity of the compound under long exposure at high temperatures (Supplementary Table S1). Terpinolene is less dense than water and almost insoluble in water. As a result, this compound likely evaporates easily during OD due to the carrot's structure and size allowing for gradual evaporation, even at 50°C. Conversely, during freeze-drying, the compound is kept at a much lower temperature (-60°C) protecting it against evaporation (Rajkumar et al., 2017). The presence of terpinolene in the combined OD-FD method may be attributed to the shorter duration that these samples spent in the oven dryer compared to those subjected exclusively to OD.
The combined drying of OD3-FD15 showed the highest percentage of alcohols (3.91 %). The identified compounds were Hexanol, 6-Ethyl-3,4-dimethylphenol, 1-Octen-3-ol, p-Menth-2-en-1-ol, 2,4,4, Trimethylcyclohexa-2-en-1-ol, 2,6-Dimethylcyclohexanol.
Acetic acid was distinctly the most prevalent organic acid in the oven-dried carrots. Previous studies have suggested that acetic acid, a byproduct of carbohydrate metabolism, increases concentration during drying (Guclu et al., 2021). High acetic acid (could be responsible for the presence of off-flavours, notably OD samples, which showed a percentage of 19.23 %. Four ester compounds, including Hexanoic acid methyl ester, Hexanoic acid ethyl ester, Octanoic acid methyl ester and Octanoic acid ethyl ester, were identified in dried carrot samples (Supplementary Table S1). However, Hexanoic acid ethyl ester was not detected in the oven-dried sample. Therefore, oven drying affects the amount of Hexanoic acid ethyl ester. This volatile class was found to be the most dominant in carrot samples obtained from combined drying (OD-FD).
Phenolic compounds are known for their bioactive properties, including free radical elimination, metal chelation, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, and antioxidant activities (Takó et al., 2020). Thymol, an important phenolic compound, was absent in the oven-dried samples but detected in the FD and OD-FD samples. Thymol is known for its antifungal activity, as demonstrated in previous studies (Nagoor Meeran et al., 2017; Karakus et al., 2023).
Overall, the combined drying method (OD-FD) proved more effective in retaining the most important volatile groups of aldehydes, terpenes, alcohols and ketones.
4 Conclusion
This study assessed the efficacy of oven-drying (OD), freeze-drying (FD) and a combined oven-freeze-drying (OD-FD) method for drying carrot slices, considering quality, energy demands, financial costs, and environmental impacts. Our findings indicate that the combined OD-FD approach significantly enhances various aspects of the drying process, including energy efficiency, economic viability, and environmental sustainability. Among the methods evaluated, OD2-FD18 (oven drying for 2 hours followed by freeze-drying for 18 hours) demonstrated superior retention of key phytonutrients like β-carotene and lycopene, and preserving antioxidant properties, including total phenolic content (TPC) and DPPH radical scavenging activity. Additionally, OD2-FD18 minimised alterations to surface morphology and microstructure while maintaining essential volatile compounds, enhancing the usability and sensory qualities of the dried product. This combined drying method also resulted in lower energy consumption, costs, and CO2 emissions compared to FD alone, while preserving residual enzyme activities of POD and PPO. Therefore, OD2-FD18 emerges as a highly effective approach for producing dried carrot slices with desirable quality, sustainability, and commercial viability.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZM: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. TK: Data curation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. TF: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YS: Data curation, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. OF: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is based on the research supported wholly/in part by the National Research Foundation of South Africa (Grant Number: SPAR231013155231), the Gauteng Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (GDARD) and the University Research Committee at the University of Johannesburg. The opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed are those of the author(s) alone.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fhort.2024.1447957/full#supplementary-material
References
Adetoro A. O. (2020a). Development of value-added dried pomegranate arils and juice powder: Effects of cultivar, harvest maturity and storage duration of whole fruit (Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch University) (Accessed 11 May 2023). Doctoral dissertation.
Adetoro A. O., Opara U. L., Fawole O. A. (2020b). Effect of blanching on enzyme inactivation, physicochemical attributes and antioxidant capacity of hot-air dried pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) arils (cv. Wonderful). Processes 9, 25. doi: 10.3390/pr9010025
Adetoro A. O., Opara U. L., Fawole O. A. (2020c). Effect of hot-air and freeze-drying on the quality attributes of dried pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) arils during long-term cold storage of whole fruit. Agriculture 10, 493. doi: 10.3390/agriculture10110493
Ahmed N., Singh J., Chauhan H., Anjum P. G. A., Kour H. (2013). Different drying methods: their applications and recent advances. Int. J. Food Nutr. Saf. 4, 34–42.
Antal T. (2015a). Comparative study of three drying methods: freeze, hot air-assisted freeze and infrared-assisted freeze modes. Agron. Res. 13, 863–878.
Antal T., Kerekes B., Sikolya L., Tarek M. (2015). Quality and drying characteristics of apple cubes subjected to combined drying (FD pre-drying and HAD finish-drying). J. Food Process. Preservation 39, 994–1005. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.12313
Çavdar H. K., Eda A. D. A. L. (2023). Effect of freeze-drying and oven-drying on volatiles, bioactive and structural properties of hawthorn (Crataegus tanacetifolia) fruit. Akademik Gıda 21, 202–210. doi: 10.24323/akademik-gida.1382905
Cui Z. W., Li C. Y., Song C. F., Song Y. (2008). Combined microwave-vacuum and freeze-drying of carrot and apple chips. Drying Technol. 26, 1517–1523. doi: 10.1080/07373930802463960
Cui Z. W., Xu S. Y., Sun D. W. (2004). Effect of microwave-vacuum drying on the carotenoids retention of carrot slices and chlorophyll retention of Chinese chive leaves. Drying Technol. 22, 563–575. doi: 10.1081/DRT-120030001
Doymaz İ. (2004). Pretreatment effect on sun drying of mulberry fruits (Morus alba L.). J. Food Eng. 65, 205–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.01.016
Doymaz İ. (2017). Drying kinetics, rehydration and colour characteristics of convective hot-air drying of carrot slices. Heat Mass Transfer 53, 25–35. doi: 10.1007/s00231-016-1791-8
Ferenczi S., Czukor B., Cserhalmi Z. (2014). Evaluation of microwave vacuum drying combined with hot-air drying and compared with freeze-and hot-air drying by the quality of the dried apple product. Periodica Polytechnica Chem. Eng. 58, 111–116. doi: 10.3311/PPch.7082
Gołasa P., Wysokiński M., Bieńkowska-Gołasa W., Gradziuk P., Golonko M., Gradziuk B., et al. (2021). Sources of greenhouse gas emissions in agriculture, with particular emphasis on emissions from energy used. Energies 14, 3784. doi: 10.3390/en14133784
Gu C., Ma H., Tuly J. A., Guo L., Zhang X., Liu D., et al. (2022). Effects of catalytic infrared drying in combination with hot air drying and freeze-drying on the drying characteristics and product quality of chives. Food Sci. Technol. 161, 113363. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113363
Guclu G., Keser D., Kelebek H., Keskin M., Sekerli Y. E., Soysal Y., et al. (2021). Impact of production and drying methods on the volatile and phenolic characteristics of fresh and powdered sweet red peppers. Food Chem. 338, 128129. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128129
Huang L. L., Lian M. M., Duan X., Li B., Yang S. Z. (2021). Studies on the quality and moisture distribution of kiwifruit dried by freeze-drying combined with microwave vacuum drying. J. Food Process Eng. 44, 13581. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.13581
Huang L. L., Zhang M., Mujumdar A. S., Sun D. F., Tan G. W., Tang S. (2009). Studies on decreasing energy consumption for a freeze-drying process of apple slices. Drying Technol. 27, 938–946. doi: 10.1080/07373930902901844
Huang L. L., Zhang M., Wang L. P., Mujumdar A. S., Sun D. F. (2012). Influence of combination drying methods on composition, texture, aroma and microstructure of apple slices. Food Sci. Technol. 47, 183–188. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.12.009
Iombor T. T., Olaitan I. N., Ede R. A. (2014). Proximate composition, antinutrient content and functional properties of soursop flour as influenced by oven and freeze drying methods. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2, 106–110. doi: 10.12944/CRNFSJ
Jia Y., Khalifa I., Hu L., Zhu W., Li J., Li K., et al. (2019). Influence of three different drying techniques on persimmon chips’ characteristics: A comparison study among hot-air, combined hot-air-microwave, and vacuum-freeze-drying techniques. Food Bioproducts Process. 118, 67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2019.08.018
Jiang N., Liu C., Li D., Zhang Z., Liu C., Wang D., et al. (2017). Evaluation of freeze-drying combined with microwave vacuum drying for functional okra snacks: Antioxidant properties, sensory quality, and energy consumption. Food Sci. Technol. 82, 216–226. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.04.015
Kaleta A., Górnicki K., Winiczenko R., Chojnacka A. (2013). Evaluation of drying models of apple (var. Ligol) dried in a fluidized bed dryer. Energy Conversion Manage. 67, 179–185. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2012.11.011
Karakus S., Atıcı O., Turan M., Azizi S., Hajizadeh H. S., Kaya O. (2023). Volatile organic compounds produced by some synthetic essential oils as biological fumigants against Botrytis cinerea on apples. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 10, 136. doi: 10.1186/s40538-023-00505-5
Keser D., Guclu G., Kelebek H., Keskin M., Soysal Y., Sekerli Y. E., et al. (2020). Characterization of aroma and phenolic composition of carrot (Daucus carota ‘Nantes’) powders obtained from intermittent microwave drying using GC–MS and LC–MS/MS. Food Bioproducts Process. 119, 350–359. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2019.11.016
Keskin M., Guclu G., Sekerli Y. E., Soysal Y., Selli S., Kelebek H. (2021). Comparative assessment of volatile and phenolic profiles of fresh black carrot (Daucus carota L.) and powders prepared by three drying methods. Scientia Hortic. 287, 110256. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110256
Khampakool A., Soisungwan S., Park S. H. (2019). Potential application of infrared assisted freeze-drying (IRAFD) for banana snacks: Drying kinetics, energy consumption, and texture. Food Sci. Technol. 99, 355–363. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.09.081
Koca Bozalan N., Karadeniz F. (2011). Carotenoid profile, total phenolic content, and antioxidant activity of carrots. Int. J. Food Properties 14, 1060–1068. doi: 10.1080/10942910903580918
Kowalski S. J., Łechtańska J. M., Duda-Chodak A., Zięć G. (2013). 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furfural (HMF)-heat-induced formation, occurrence in food and biotransformation-a review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 63 (4), 207-225. doi: 10.2478/v10222-012-0082-4
Li Y., Wang X., Wu Z., Wan N., Yang M. (2020). Dehydration of hawthorn fruit juices using ultrasound-assisted vacuum drying. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 68, 105219. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105219
Lyu Y., Bi J., Chen Q., Li X., Wu X., Hou H., et al. (2021). Discoloration investigations of freeze-dried carrot cylinders from physical structure and color-related chemical compositions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 101, 5172–5181. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.v101.12
Mina Z. P., Kaseke T., Fadiji T., Fawole O. A. (2022). Effect of gum Arabic and ethanol pretreatments on drying kinetics and quality attributes of dried carrot slices. Heliyon. 8, e12037. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12037
Monteiro R. L., Link J. V., Tribuzi G., Carciofi B. A., Laurindo J. B. (2018). Effect of multi-flash drying and microwave vacuum drying on the microstructure and texture of pumpkin slices. Food Sci. Technol. 96, 612–619. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.06.023
Morodi V., Kaseke T., Fawole O. A. (2022). Impact of gum Arabic coating pretreatment on quality attributes of oven-dried red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) Fruit. Processes 10, 1629. doi: 10.3390/pr10081629
Morsy N. E., Rayan A. M. (2019). Effect of different edible coatings on biochemical quality and shelf life of apricots (Prunus armenica L. cv Canino). J. Food Measurement Characterization 13, 3173–3182. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00240-2
Motevali A., Koloor R. T. (2017). A comparison between pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions from operation of different dryers based on energy consumption of power plants. J. Cleaner Production 154, 445–461. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.219
Nagoor Meeran M. F., Javed H., Al Taee H., Azimullah S., Ojha S. K. (2017). Pharmacological properties and molecular mechanisms of thymol: prospects for its therapeutic potential and pharmaceutical development. Front. Pharmacol. 8, 260734. doi: doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00380
Nowak D., Jakubczyk E. (2020). The freeze-drying of foods—The characteristic of the process course and the effect of its parameters on the physical properties of food materials. Foods 9, 1488. doi: 10.3390/foods9101488
Nxumalo K. A., Fawole O. A., Oluwafemi O. S. (2022). Evaluating the efficacy of gum arabic-zinc oxide nanoparticles composite coating on shelf-life extension of mandarins (cv. Kinnow). Front. Plant Sci. 13, 953861. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.953861
Onwude D. I., Hashim N., Janius R., Abdan K., Chen G., Oladejo A. O. (2017). Non-thermal hybrid drying of fruits and vegetables: A review of current technologies. Innovative Food Sci. Emerging Technol. 43, 223–238. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2017.08.010
Papoutsis K., Pristijono P., Golding J. B., Stathopoulos C. E., Bowyer M. C., Scarlett C. J., et al. (2017). Effect of vacuum-drying, hot air-drying and freeze-drying on polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of lemon (Citrus limon) pomace aqueous extracts. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52, 880–887. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.2017.52.issue-4
Polat S., Guclu G., Kelebek H., Keskin M., Selli S. (2022). Comparative elucidation of colour, volatile and phenolic profiles of black carrot (Daucus carota L.) pomace and powders prepared by five different drying methods. Food Chem. 369, 130941.
Que F., Mao L., Fang X., Wu T. (2008). Comparison of hot air-drying and freeze-drying on the physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) flours. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 43, 1195–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2007.01590.x
Rajkumar G., Shanmugam S., Galvao M. D. S., Leite Neta M. T. S., Dutra Sandes R. D., Mujumdar A. S., et al. (2017). Comparative evaluation of physical properties and aroma profile of carrot slices subjected to hot air and freeze-drying. Drying Technol. 35, 699–708. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2016.1206925
Rawson A., Tiwari B. K., Tuohy M. G., O’donnell C. P., Brunton N. (2011). Effect of ultrasound and blanching pretreatments on polyacetylene and carotenoid content of hot air and freeze-dried carrot discs. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 18, 1172–1179. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2011.03.009
Rojas M. L., Silveira I., Augusto P. E. D. (2020). Ultrasound and ethanol pre-treatments to improve convective drying: Drying, rehydration and carotenoid content of pumpkin. Food Bioproducts Process. 119, 20–30. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2019.10.008
Sagar V. R., Suresh Kumar P. (2010). Recent advances in drying and dehydration of fruits and vegetables: a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 47, 15–26. doi: 10.1007/s13197-010-0010-8
Saleh R. M., Kulig B., Emiliozzi A., Hensel O., Sturm B. (2020). Impact of critical control-point based intermittent drying on drying kinetics and quality of carrot (Daucus carota var. laguna). Thermal Sci. Eng. Prog. 20, 100682. doi: 10.1016/j.tsep.2020.100682
Sharma K. D., Karki S., Thakur N. S., Attri S. (2012). Chemical composition, functional properties and processing of carrot—a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 49, 22–32. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0310-7
Singh M. N., Srivastava R., Yadav I. (2021). Study of different varieties of carrot and its benefits for human health: a review. J. Pharmacognosy Phytochem. 10, 1293–1299. doi: 10.22271/phyto.2021.v10.i1r.13529
Takó M., Kerekes E. B., Zambrano C., Kotogán A., Papp T., Krisch J., et al. (2020). Plant phenolics and phenolic-enriched extracts as antimicrobial agents against food-contaminating microorganisms. Antioxidants 9, 165. doi: 10.3390/antiox9020165
Valadez-Carmona L., Plazola-Jacinto C. P., Hernández-Ortega M., Hernández-Navarro MaríaD., Villarreal F., Necoechea-Mondragón H., et al. (2017). Effects of microwaves, hot air and freeze-drying on the phenolic compounds, antioxidant capacity, enzyme activity and microstructure of cacao pod husks (Theobroma cacao L.). Innovative Food Sci. Emerging Technol. 41, 378–386. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2017.04.012
Varshney K., Mishra K. (2022). An analysis of health benefits of carrot. Int. J. Innovative Res. Eng. Manage. 9, 211–214. doi: 10.55524/ijirem.2022.9.1.40
Vieira A. J., Beserra F. P., Souza M. C., Totti B. M., Rozza A. L. (2018). Limonene: Aroma of innovation in health and disease. Chemico-Biological Interact. 283, 97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.007
Wright K. P., Kader A. A. (1997). Effect of controlled-atmosphere storage on the quality and carotenoid content of sliced persimmons and peaches. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 10, 89–97. doi: 10.1016/S0925-5214(96)00062-2
Yao L., Fan L., Duan Z. (2020). Effect o f different pretreatments followed by hot-air and far-infrared drying on the bioactive compounds, physicochemical property and microstructure of mango slices. Food Chem. 305, 125477. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125477
Yildiz G. (2022). Color, microstructure, physicochemical, textural and sensory properties with the retention of secondary metabolites in convective-, microwave-and freeze-dried carrot (Daucus carota) slices. Br. Food J. 124, 3922–3935. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-03-2021-0308
Yusuf E. H., Wojdyło A., Lech K., Masztalerz K., Nowicka P. (2023). The effect of combined drying process (OD-CD-VMD) on nutritional, phytochemical, and sensory profiles, and biological activities of colored dried carrot. Food Sci. Technol. 173, 114231. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.114231
Zambrano M. V., Dutta B., Mercer D. G., MacLean H. L., Touchie M. F. (2019). Assessment of moisture content measurement methods of dried food products in small-scale operations in developing countries: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 88, 484–496. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.006
Zhang L., Qiao Y., Wang C., Liao L., Liu L., Shi D., et al. (2019). Effects of freeze vacuum drying combined with hot air drying on the sensory quality, active components, moisture mobility, odors, and microstructure of kiwifruits. J. Food Qual 2019, 1-11. doi: 10.1155/2019/8709343
Zhou C., Feng Y., Zhang L., Yagoub A. E. A., Wahia H., Ma H., et al. (2021). Rehydration characteristics of vacuum freeze-and hot air-dried garlic slices. Food Sci. Technol. 143, 111158. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111158
Keywords: bioactive compounds, energy consumption, carrot slices, freeze-drying, oven drying, quality attributes
Citation: Mina ZP, Kaseke T, Fadiji T, Silue Y and Fawole OA (2025) Combined oven/freeze drying as a cost and energy-efficient drying method for preserving quality attributes and volatile compounds of carrot slices. Front. Hortic. 3:1447957. doi: 10.3389/fhort.2024.1447957
Received: 12 June 2024; Accepted: 16 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Vijay Yadav Tokala, The Postharvest Education Foundation, United StatesReviewed by:
Karina Di Scala, Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata, ArgentinaGulcin Yildiz, Iğdır Üniversitesi, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Mina, Kaseke, Fadiji, Silue and Fawole. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Olaniyi Amos Fawole, T2xhbml5aWZAdWouYWMuemE=
 Zobabalo Progress Mina1
Zobabalo Progress Mina1 Tafadzwa Kaseke
Tafadzwa Kaseke Tobi Fadiji
Tobi Fadiji Olaniyi Amos Fawole
Olaniyi Amos Fawole