
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Food. Sci. Technol., 14 June 2022
Sec. Food Biotechnology
Volume 2 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frfst.2022.889360
This article is part of the Research TopicImproving Protein Functionality using Conventional and Non-Conventional MethodsView all 6 articles
Plant proteins are increasingly focused upon as alternatives to animal-derived macromolecules for the encapsulation of bioactives. The rational design of encapsulation carriers should be based on a solid understanding of the interactions between the proteins and bioactives. Encapsulation technology for food applications has focused predominantly on the protection and controlled release of hydrophobic bioactives. For hydrophilic molecules, although not less important from a nutritional and health perspective, significantly fewer encapsulation systems have been explored, designed and described. As hydrophilic molecules tend to partition into the aqueous food matrix, it is even more crucial to understand and to be able to modulate the interactions between the hydrophilic bioactive and the encapsulating matrix material in food relevant conditions. Therefore, examining the nature of the interactions between anthocyanins (ACNs), a hydrophilic bioactive, and prolamin plant proteins (gliadin, hordein, secalin, and avenin) is timely. These interactions were examined using steady-state and time-resolved luminescence spectroscopy techniques. The ACN-induced quenching of the prolamins intrinsic fluorescence emission did not follow a linear Stern-Volmer relationship, but rather displayed an upward curvature for all the prolamins tested. Hence, both static and dynamic quenching likely occurred in the prolamin-ACN systems. The quenching mechanism was further explored based on the changes in fluorescence lifetime as ACN concentration increased. As the independent lifetimes of the prolamin-ACN combinations did not decrease discernibly as a function of ACN concentration, static quenching is presumably the predominant quenching mechanism. The thermodynamic parameters revealed that the interactions between secalin- and avenin-ACN are mainly driven by the hydrophobic effect, while those between gliadin- and hordein-ACN are dominated by ionic interactions. Zeta-potential measurements support the dominant ionic interactions found for gliadin and hordein. The insights gained in this research will serve as a sound basis for further studies focusing on matrix selection with regard to creating performant encapsulation systems for ACNs.
Anthocyanins (ACNs) are natural water-soluble plant pigments, which give red, blue, or purple colors to many fruits and flowers (Prior and Wu, 2006; Chung et al., 2015; Burton-Freeman et al., 2016). Besides their potential use as natural colorants in food, ACNs are also potent antioxidants (Viljanen et al., 2005; Burton-Freeman et al., 2016). The ACN structure includes a central flavylium cation (anthocyanidin core) that is glycosylated and acylated (Prior and Wu, 2006; Chung et al., 2015). While ACNs are associated with desirable functional properties and a variety of health benefits (Zhao et al., 2004; Forester and Waterhouse, 2008; Tressera-Rimbau et al., 2014; Cassidy et al., 2016; Kimble et al., 2018), they are highly susceptible to chemical degradation, leading to discoloration and loss of their bioactive properties (Chung et al., 2015; Cassidy et al., 2016; Kimble et al., 2018). Chemical degradation is hastened by exposure to high temperatures, elevated pH conditions, and the presence of certain components, such as ascorbic acid, enclosed in the food matrix (Hubbermann et al., 2006; Sui et al., 2014; Chung et al., 2015). Encapsulation is one of several strategies routinely explored to enhance the stability of labile bioactive compounds and to increase ACNs performance when used as natural food colorants (Arangoa et al., 2001; Wong et al., 2012; He et al., 2016).
Prolamin particles have shown to be promising plant-based encapsulation systems for bioactive molecules (Patel et al., 2012; Joye et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2015). In addition, particles made up of gliadin, i.e., wheat prolamin, display bioadhesive properties, which are believed to prolong their residence time in the gastrointestinal tract (Arangoa et al., 2001). Extended residence time usually increases the efficiency of a carrier for controlled release and target delivery of bioactives in the gastrointestinal tract (Arangoa et al., 2001). Gaining insights into the nature of the interactions between ACNs and prolamins is crucial for assessing ACN encapsulation, controlled release and retention efficiency of prolamin-based colloidal systems. Due to the hydrophilic nature of ACNs, the encapsulation and retention of these bioactives in the encapsulation matrix could exhibit additional challenges relative to what is experienced with hydrophobic bioactives.
Fluorescence quenching studies are often used to assess the nature and extent of the interactions between proteins and bioactive compounds, including polyphenols (Lakowicz, 2006; Skrt et al., 2012; Keppler et al., 2014; Joye et al., 2015). Fluorescence quenching, i.e., decrease of fluorescence intensity, in these studies is driven by a variety of processes such as energy transfer due to molecular interactions among protein segments or between the protein and the quencher or formation of ground-state complexes between the fluorophore and quencher molecules, or collisional quenching (Lakowicz, 2006). Static quenching often involves the formation of non-fluorescent complexes between the quencher and fluorophore, while dynamic quenching refers to non-radiative decay triggered by the collision between the two molecules (Lakowicz, 2006; Joye et al., 2015). Fluorescence quenching studies on interactions between prolamin proteins and polyphenols generally focus on the Trp fluorescence of prolamin proteins. Skrt et al. (2012) explored the interactions between various catechins, flavones and hydroxycinnamic acids, and bovine serum albumin through fluorescence quenching. They found that the binding affinity between esterified catechins and the protein is higher, while it is the lowest for epigallocatechin, compared with the other polyphenols included in their study. Similarly, Joye et al. (2015) investigated the complexation of resveratrol to zein and gliadin through fluorescence quenching. Based on the thermodynamic data, these researchers concluded that while the interaction between (the more hydrophobic) zein and resveratrol is dominated by the hydrophobic effect, the interactions between gliadin and resveratrol are mainly stabilized by hydrogen bonds. However, no in-depth study of the interaction between ACN and different prolamins has been published. The focus on ACN and prolamins is justifiable due to their economic potential and scientific value as natural (but unstable) colorants (ACN) and as protective encapsulation vehicles for bioactives (prolamins) for food applications. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to explore the nature of the interaction between ACNs from bilberry extract (BE) (mainly delphinidin-derivatives) and several prolamin proteins (i.e., gliadin, hordein, secalin and avenin) using steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopic techniques. The gained insights should build a sound basis for further studies focusing on prolamin matrix selection with regard to creating highly performant and tunable encapsulation systems for ACNs.
Commercial wheat gluten was purchased from Bulk Barn (Bulk Barn Foods, Aurora, ON, Canada). Barley and oats were from Wintermar Farms (West Montrose, ON, Canada), while rye was donated by the Department of Plant Sciences of the University of Guelph (Guelph, ON, Canada). Barley, rye, and oats wholemeal samples were prepared by grinding barley, rye, and oats using a UDY mill (UDY Corporations, Fort Collins, CO, United States) with a 0.50 mm screen. BE was purchased from Evergreen Biotech Inc. (Xian, China). All chemicals, reagents, and solvents were of analytical grade and purchased from Fisher Scientific (Mississauga, ON, Canada).
Prolamin proteins were extracted from commercial wheat gluten, barley, rye, and oats wholemeal by suspending 100 g of these powders in 400 ml 70% (v/v) aqueous ethanol. The suspensions were stirred for 2 h at room temperature prior to being centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 g using an Allegra X-15R centrifuge (Beckman Coulter Inc., Indianapolis, IN, United States). The supernatants were vacuum filtered using Q5 Fisherbrand filter paper (ThermoFisher Scientific, Mississauga, ON, Canada) and then left overnight at 4°C to allow insoluble material to sediment, prior to being centrifuged (10,000 g for 10 min) and vacuum filtered (using Q5 Fisherbrand filter paper) for a second time. The final gliadin, hordein, secalin, and avenin extracts contained about 9.3, 1.0, 0.9, and 0.6% (w/v) protein as determined by DUMAS analysis (Leco FP-528, Leco Inc., St. Joseph, MI, United States).
Ethanol/acetate buffer mixtures were prepared by combining ethanol with sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.5, 0.100 M) at a 7:3 volume ratio. A protein concentration study was conducted for each prolamin prior to the quenching experiments. The protein concentration was optimized to ensure enough fluorescence emission while preventing the inner filter effect, i.e., re-absorbance of the emission due to excessive concentration of the fluorophore. Based on the results of the protein concentration study, for subsequent measurements, the prolamin extracts were diluted with the ethanol/acetate buffer mixture to reach the optimized protein concentration of 0.017, 0.018, 0.010, and 0.005 (w/v) for gliadin, hordein, secalin, and avenin, respectively. A 0.030% (w/v) BE solution was prepared by dissolving the BE powder in the ethanol/acetate buffer mixture. The BE solutions were then filtered using a 0.45 um syringe filter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Mississauga, ON, Canada). Solutions with different BE concentrations (i.e., quencher) were mixed with the protein solutions, while keeping the protein concentration constant (i.e., optimized protein concentration). The BE concentration in the quenching experiments varied between 0 and 4.86 × 10–2 mM.
Steady-state fluorescence measurements were performed using a Shimadzu RF-5301PC spectrofluorimeter (Shimadzu Scientific Instruments Inc., Kyoto, Japan). Measurements were performed at five different temperatures (15, 20, 25, 30 and 35°C). In all experiments, the slit width (excitation and emission) was set at 3 nm. The excitation wavelength was set at 280 nm, and the prolamins emission signal was collected from 290 to 450 nm.
Fluorescence lifetimes measurements were carried out using a Time-Correlated Single-Photon Counting (TCSPC) accessory on a Fluoromax Plus C spectrophotometer (Horiba Jobin Yvon, Kyoto, Japan) using a 283 nm nanoLED as the light source. The sample preparation was the same as described previously for the steady-state fluorescence measurements. 0.04% (w/v) LUDOX was used as a scatterer to measure the instrument response function (IRF). The decays were analyzed using DAS-6 decay analysis software. The lifetimes were calculated using a multi exponential approach and the non-extensive distribution (NED) method as programmed within the DAS software (Horiba Scientific, Edison, NJ, United States). The goodness of fit of the decay data was assessed using the
Zeta-potential values were measured using laser Doppler electrophoresis (Zetasizer Nano ZS, Malvern Instruments Ltd., Worcestershire, United Kingdom). Samples were transferred to a disposable capillary-cell (Malvern Instruments Ltd., Worcestershire, United Kingdom) prior to the measurement. All proteins were solubilized in 70% aqueous ethanol. Gliadin and hordein were analyzed at a concentration of 1.0% (w/v), while secalin and avenin were analyzed at 0.9 and 0.6% (w/v), respectively. All measurements were conducted at 25°C.
Gliadin extract was diluted to 1.0% (w/v) using 70% (v/v) aqueous ethanol, while the other prolamin extracts were kept at their final extracted concentrations [i.e., 1.0, 0.9, and 0.6% (w/v) for hordein, secalin and avenin, respectively]. The separation of the proteins in the prolamin extracts was performed using a Gemini-NX-C18 column (Gemini 5 um C18 110 A, 250 × 4.6 mm) on a modular LC-10 HPLC system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The detector wavelength was set at 214 nm and the injection volume for the extracts was 20 uL. A binary gradient profile was used for sample elution. Eluent A was MilliQ-water, to which trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) [0.1% (v/v)] was added. Eluent B was acetonitrile (ACN), to which also TFA [0.1% (v/v)] was added. A linear gradient from 20 to 56% (v/v) eluent B over 60 min was used to separate the proteins based on their polarity. The gradient elution program was run at a constant flow rate of 0.8 mL/min, and the column oven was set at 50°C.
All samples were prepared in triplicate unless stated otherwise. The results are reported as mean values with accompanying standard deviations represented by error bars in all figures. To assess the significance of results obtained, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed on the data sets, followed by Tukeys post-hoc test, both at a significance level of p < 0.05. The fluorescence spectra collected for the fluorescence quenching study were normalized based on each prolamin’s maximum Trp fluorescence intensity in the absence of ACNs.
The fluorescence spectra of gliadin and secalin displayed two peaks (
Fluorescence emission spectra, measured at an excitation wavelength of 280 nm, were recorded for all prolamins (i.e., gliadin, hordein, secalin, and avenin) as a function of increasing BE concentration (Figure 1A, Supplementary Figure S2). Trp fluorescence quenching increased with increasing concentration of ACNs. As outlined above, fluorescence quenching can either be dynamic, resulting from the collision between fluorophore and quencher, or static, originating from the formation of ground state complexes between the fluorophore and quencher (Lakowicz, 2006; Joye et al., 2015).
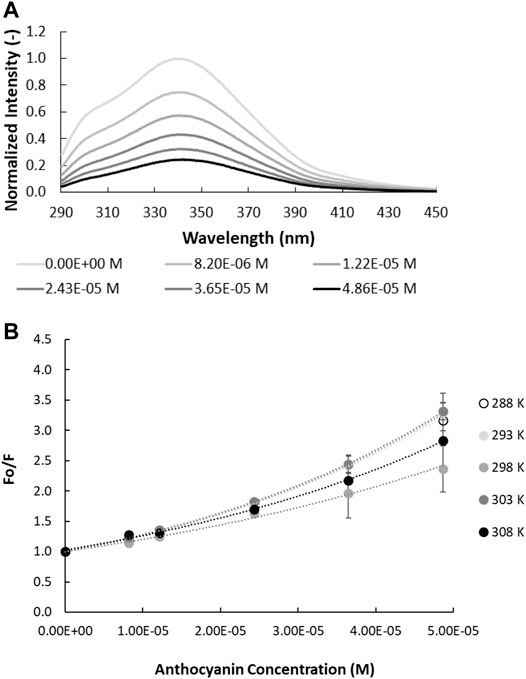
FIGURE 1. Quenching of intrinsic gliadin fluorescence by anthocyanins. (A) Fluorescence spectra of gliadin (0.017% w/v; λex = 280 nm; pH = 4.50 in ethanol/acetate buffer, 298 K as function of anthocyanin concentration. (B) Relative intrinsic fluorescence of gliadin fluorescence as a function of anthocyanin concentration. The temperature at which the experiment is carried out is specified in the legend.
Fluorescence quenching can be described by the Stern-Volmer equation:
where
Nanosecond resolved fluorescence decay profiles of all prolamins
where
The independent lifetimes of all prolamins-ACN combinations did not decrease as ACN concentration increases (Table 1, Supplementary Table S1). This suggests that the quenching mechanism for the various prolamin-ACN solutions is predominantly static, although dynamic quenching may still occur concurrently but contributes less to the quenching process (Lakowicz, 1999; Paul et al., 2013). It should be noted, however, that the amplitude-weighted lifetime

TABLE 1. Time-resolved fluorescence decay parameters of gliadin in the presence of increasing anthocyanin concentration (
Non-covalent interactions between proteins and small molecules can take several forms: ionic interaction, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals interaction, as well as the hydrophobic effect (Acharya et al., 2013; Paul et al., 2013; Joye et al., 2015). The ACN-prolamin interactions can be quantitatively assessed in terms of the binding constant (
in which
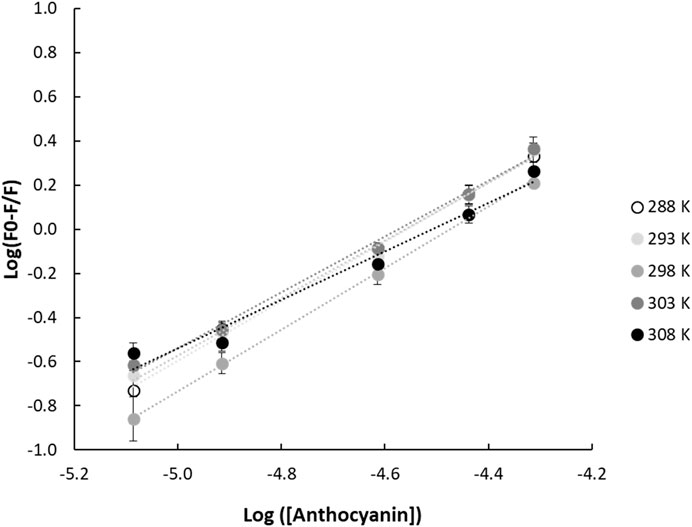
FIGURE 2. Double logarithmic linear regression plots of (F0-F/F) and anthocyanin concentration for gliadin-anthocyanin samples measured at different temperatures. F0 and F are the fluorescence emission intensities of the protein in the absence and presence of quencher, respectively.
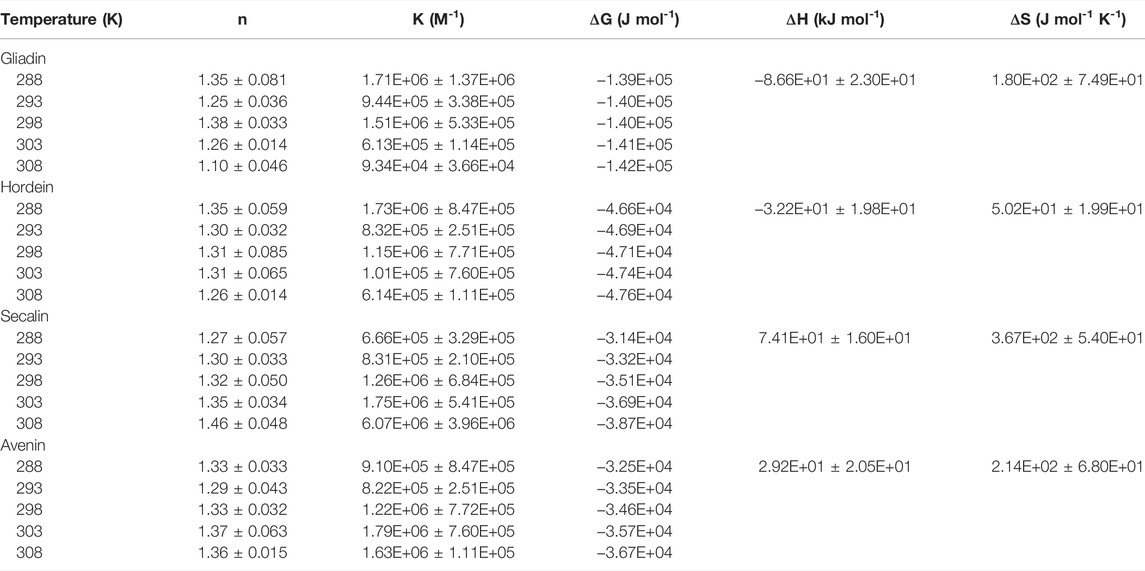
TABLE 2. Binding and thermodynamic parameters of the quenching of intrinsic prolamin fluorescence by anthocyanins as function of temperature.
The Stern-Volmer plots of gliadin, avenin, hordein and secalin in the presence of increasing concentration of ACN (Figure 1B, Supplementary Figure S3) show a non-monotonic effect of temperature. A progressive reduction or increase in quenching as temperature increases would indicate static or dynamic quenching, respectively (Lakowicz, 1999). This non-monotonic effect of temperature on the fluorescence quenching suggests that the different prolamins undergo conformational changes in the presence of ACNs as temperature increases (Chang and Lee, 1984).
Assuming that the mechanism of ACN-induced quenching of the intrinsic fluorescence of prolamins is caused predominantly by static quenching, the thermodynamic parameters (
where
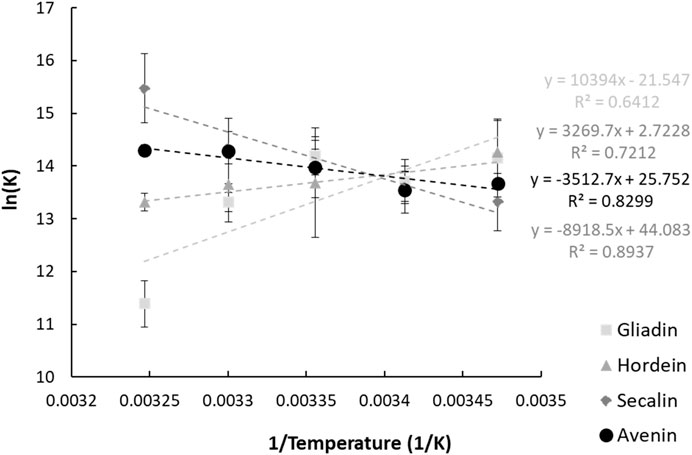
FIGURE 3. Vant Hoff plots of the interaction between anthocyanins and the four prolamin proteins. The parameters and goodness of fit measures will be better presented in a table.
The obtained thermodynamic parameters for ACN-prolamin interactions are shown in Table 2. The Gibbs free energy is negative for all four prolamins, which indicates that the interactions between the four prolamins and ACNs are spontaneous. The negative
As Ross and Subramanian (1981) described the thermodynamic parameters per non-covalent interaction and based on their findings, we assume that the negative change in enthalpy and positive change in entropy indicate that ionic interactions drive the gliadin-ACN and hordein-ACN interaction. In contrast, the positive enthalpy and entropy change suggest that the predominant interaction processes of secalin-ACN and avenin-ACN are through the hydrophobic effect. The flavylium core of anthocyanins would accommodate interactions driven by the hydrophobic effect. The hydrophobic effect was also found to be the main interaction type for ACN-whey protein systems (Ren and Giusti, 2021) and ACN-black soybean protein isolate systems (Wang and Xie, 2019). Very recently, Guo et al. (2022) studied the interactions between gliadin and grape skin ACN extracts and also reported the hydrophobic effect to be the dominant type of interaction.
The predominant nature of the interaction between the prolamins and ACNs is further substantiated by studying the zeta-potential and hydrophobicity of the prolamins. Gliadin, hordein, and secalin show a positive zeta-potential, with secalin having the smallest magnitude of zeta-potential (Table 3). In contrast, under the test conditions, 0.1% w/v avenin, and the bilberry extract have a negative zeta-potential below -9 mV. Therefore, gliadin and hordein (zeta-potential of 11.93 and 8.18 mV) are able to interact with bilberry ACN extract (zeta-potential of -9.46 mV) through attractive electrostatic forces. However, the small magnitude of the zeta-potential of secalin may minimize the electrostatic attraction between secalin and ACNs in BE.
RP-HPLC chromatograms for gliadin, hordein, secalin, and avenin were divided into sections differing in hydrophobicity and in accordance with the groups identified by Wieser and Belitz (Wieser and Belitz, 1989) (Figure 4). Since the prolamin extracts have different protein concentrations, the elution times, rather than the peak intensities, were compared among the different prolamins. The RP-HPLC chromatograms show that the gliadin extract had more polar proteins (classified in the chromatogram as
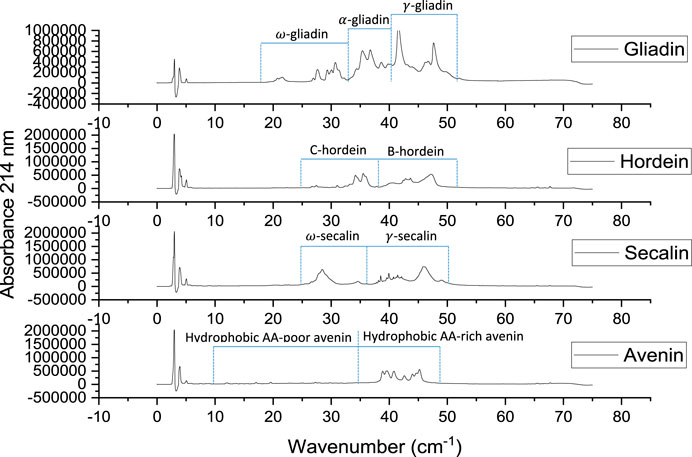
FIGURE 4. Reverse-phase HPLC chromatograms of gliadin (1.00% w/v), hordein (1.01% w/v), secalin (0.87% w/v), and avenin (0.59% w/v) extracts.
This study was able to identify a dominant interaction type between ACNs in BE and each of the prolamins. A molecular docking study would be needed to confirm these findings and gain further insight into the (other) interaction types and molecular arrangement of anthocyanins and prolamins. Furthermore, a commercial extract of bilberries was used here as the anthocyanin source. However, not all components present in this extract are anthocyanins and other components (such as proteins or small sugar molecules) may have contributed to the observed results.
In conclusion, this study relied on fluorescence quenching results to explore the interaction of ACNs with different prolamins. Although prolamins as hydrophobic plant proteins have gained a lot of attention as a matrix material for encapsulation systems for bioactives, to consolidate their potential, more understanding is needed regarding the dominant interaction type driving encapsulation. The four studied prolamins, surprisingly, interact differently with ACNs. While gliadin and hordein interact through ionic interactions, secalin and avenins interaction with ACN seems to be predominantly driven by the hydrophobic effect. The gathered insights illustrate the versatility of these proteins and the need of this understanding as a sound basis for the rational design of encapsulation systems that perform well in terms of encapsulation, controlled release and/or retention of bioactives in a specific food context. The significance of this study lies in 1) the unique combination of minimally invasive steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence analyses to unravel the interactions between ACN and prolamins, and 2) the fundamental insights in the dominant interaction types between ACN, an unstable but economically important natural colorant and bioactive, and prolamins, a group of proteins with unique properties making them highly suitable to conveniently produce encapsulation vehicles for a range of bioactives. These insights will be crucial for future development of powerful protective encapsulation systems for ACN for a range of food applications.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
JS: Conceptualization; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Validation; Visualization; Writing original draft. AC: Resources; Writing Review and Editing. MC: Formal analysis; Methodology; Validation; Supervision; Visualization; Writing—review and editing. IJ: Conceptualization; Formal analysis; Funding acquisition; Resources; Supervision; Visualization; Writing—review and editing.
The authors acknowledge the Ontario Ministry of Research and Innovation Early Researcher Awards Program and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Discovery Program for funding this research.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frfst.2022.889360/full#supplementary-material
Acharya, D. P., Sanguansri, L., and Augustin, M. A. (2013). Binding of Resveratrol with Sodium Caseinate in Aqueous Solutions. Food Chem. 141 (2), 1050–1054. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.03.037
Arangoa, M. A., Campanero, M. A., Renedo, M. J., Ponchel, G., and Irache, J. M. (2001). Gliadin Nanoparticles as Carriers for the Oral Administration of Lipophilic Drugs. Relationships Between Bioadhesion and Pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Res. 18 (11), 1521–1527. doi:10.1023/a:1013018111829
Burton-Freeman, B., Sandhu, A., and Edirisinghe, I. (2016). “Anthocyanins,” in Nutraceuticals: Efficacy, Safety and Toxicity. Editor R. C. Gupta (London, UK: Academic Press), 489–500. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-802147-7.00035-8
Cassidy, A., Bertoia, M., Chiuve, S., Flint, A., Forman, J., and Rimm, E. B. (2016). Habitual Intake of Anthocyanins and Flavanones and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 104, 587–594. doi:10.3945/ajcn.116.133132.587
Chang, G.-G., and Lee, H.-J. (1984). Monitoring Protein Conformational Changes by Quenching of Intrinsic Fluorescence. J. Biochem. Biophysical Methods 9, 351–355. doi:10.1016/0165-022X(84)90019-8
Chung, C., Rojanasasithara, T., Mutilangi, W., and McClements, D. J. (2015). Enhanced Stability of Anthocyanin-Based Color in Model Beverage Systems Through Whey Protein Isolate Complexation. Food Res. Int. 76, 761–768. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2015.07.003
Forester, S. C., and Waterhouse, A. L. (2008). Identification of Cabernet Sauvignon Anthocyanin Gut Microflora Metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 9299–9304. doi:10.1021/jf801309n
Ghisaidoobe, A., and Chung, S. (2014). Intrinsic Tryptophan Fluorescence in the Detection and Analysis of Proteins: A Focus on Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Techniques. Ijms 15 (12), 22518–22538. doi:10.3390/ijms151222518
Guo, Z., Huang, Y., Huang, J., Li, S., Zhu, Z., Deng, Q., et al. (2022). Formation of Protein-Anthocyanin Complex Induced by Grape Skin Extracts Interacting with Wheat Gliadins: Multi-Spectroscopy and Molecular Docking Analysis. Food Chem. 385, 132702. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132702
He, Z., Zhu, H., Xu, M., Zeng, M., Qin, F., and Chen, J. (2016). Complexation of Bovine β-Lactoglobulin with Malvidin-3-O-Glucoside and its Effect on the Stability of Grape Skin Anthocyanin Extracts. Food Chem. 209, 234–240. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.04.048
Hubbermann, E. M., Heins, A., Stöckmann, H., and Schwarz, K. (2006). Influence of Acids, Salt, Sugars and Hydrocolloids on the Colour Stability of Anthocyanin Rich Black Currant and Elderberry Concentrates. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 223, 83–90. doi:10.1007/s00217-005-0139-2
Joye, I. J., Davidov-Pardo, G., Ludescher, R. D., and McClements, D. J. (2015). Fluorescence Quenching Study of Resveratrol Binding to Zein and Gliadin: Towards a More Rational Approach to Resveratrol Encapsulation Using Water-Insoluble Proteins. Food Chem. 185, 261–267. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.128
Keppler, J. K., Stuhldreier, M. C., Temps, F., and Schwarz, K. (2014). Influence of Mathematical Models and Correction Factors on Binding Results of Polyphenols and Retinol with β-Lactoglobulin Measured with Fluorescence Quenching. Food Biophys. 9, 158–168. doi:10.1007/s11483-013-9328-x
Kimble, R., Keane, K. M., Lodge, J. K., Howatson, G., Kimble, R., Keane, K. M., et al. (2018). Dietary Intake of Anthocyanins and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 59 (0), 3032–3043. doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1509835
Lakowicz, J. R. (1999). “Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy,” in Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy (New York, NY: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-3061-6
Lakowicz, J. R. (2006). Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy. New York: Springer Science+Business Media.
Patel, A. R., Heussen, P. C. M., Hazekamp, J., Drost, E., and Velikov, K. P. (2012). Quercetin Loaded Biopolymeric Colloidal Particles Prepared by Simultaneous Precipitation of Quercetin With Hydrophobic Protein in Aqueous Medium. Food Chem. 133, 423–429. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.054
Paul, B. K., Ray, D., and Guchhait, N. (2013). Unraveling the Binding Interaction and Kinetics of a Prospective Anti-HIV Drug With a Model Transport Protein: Results and Challenges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15 (4), 1275–1287. doi:10.1039/c2cp42539d
Prior, R. L., and Wu, X. (2006). Anthocyanins: Structural Characteristics that Result in Unique Metabolic Patterns and Biological Activities. Free Radic. Res. 40 (10), 1014–1028. doi:10.1080/10715760600758522
Ren, S., and Giusti, M. M. (2021). Monitoring the Interaction Between Thermally Induced Whey Protein and Anthocyanin by Fluorescence Quenching Spectroscopy. Foods 10 (2), 310. doi:10.3390/foods10020310
Ross, P. D., and Subramanian, S. (1981). Thermodynamics of Protein Association Reactions: Forces Contributing to Stability. Biochemistry 20 (11), 3096–3102. doi:10.1021/bi00514a017
Skrt, M., Benedik, E., Podlipnik, Č., and Ulrih, N. P. (2012). Interactions of Different Polyphenols With Bovine Serum Albumin Using Fluorescence Quenching and Molecular Docking. Food Chem. 135, 2418–2424. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.114
Sui, X., Dong, X., and Zhou, W. (2014). Combined Effect of pH and High Temperature on the Stability and Antioxidant Capacity of Two Anthocyanins in Aqueous Solution. Food Chem. 163, 163–170. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.04.075
Tresserra-Rimbau, A., Rimm, E. B., Medina-Remón, A., Martínez-González, M. A., de la Torre, R., Corella, D., et al. (2014). Inverse Association Between Habitual Polyphenol Intake and Incidence of Cardiovascular Events in the PREDIMED Study. Nutr. Metabolism Cardiovasc. Dis. 24, 639–647. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2013.12.014
Viljanen, K., Kylli, P., Hubbermann, E.-M., Schwarz, K., and Heinonen, M. (2005). Anthocyanin Antioxidant Activity and Partition Behavior in Whey Protein Emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 53, 2022–2027. doi:10.1021/jf047975d
Wang, C., and Xie, Y. (2019). Interaction of Protein Isolate with Anthocyanin Extracted from Black Soybean and its Effect on the Anthocyanin Stability. J. Food Sci. 84 (11), 3140–3146. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.14816
Wieser, H., and Belitz, H.-D. (1989). Amino Acid Compositions of Avenins Separated by Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Cereal Sci. 9 (3), 221–229. doi:10.1016/S0733-5210(89)80004-9
Wong, B. T., Zhai, J., Hoffmann, S. V., Aguilar, M.-I., Augustin, M., Wooster, T. J., et al. (2012). Conformational Changes to Deamidated Wheat Gliadins and β-Casein Upon Adsorption to Oil-Water Emulsion Interfaces. Food Hydrocoll. 27, 91–101. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.08.012
Xiao, J., Nian, S., and Huang, Q. (2015). Assembly of Kafirin/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles to Enhance the Cellular Uptake of Curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 51, 166–175. doi:10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.05.012
Keywords: protein, encapsulation, anthocyanin, fluorescence, food, prolamin
Citation: Salamun JW, Chen A, Corradini MG and Joye IJ (2022) Probing Prolamin-Anthocyanin Interactions for the Rational Design of Plant-Based Encapsulation Systems. Front. Food. Sci. Technol. 2:889360. doi: 10.3389/frfst.2022.889360
Received: 04 March 2022; Accepted: 05 May 2022;
Published: 14 June 2022.
Edited by:
Viridiana Tejada-Ortigoza, Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education (ITESM), MexicoReviewed by:
Ninganagouda R. Patil, B V B College of Engineering and Technology, IndiaCopyright © 2022 Salamun, Chen, Corradini and Joye. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Maria G. Corradini, bWNvcnJhZGlAdW9ndWVscGguY2E=; Iris J. Joye, aWpveWVAdW9ndWVscGguY2E=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.