- 1Institute of International Rivers and Eco-Security, Yunnan University, Kunming, China
- 2Erhai Watershed Ecological Environment Quality Testing Engineering Research Center of Yunnan Provincial Universities, Erhai Research Institute, West Yunnan University of Applied Sciences, Dali, China
- 3Natural Resources Bureau of Suijiang County, Zhaotong, China
- 4College of Water Conservancy, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming, China
Exploring dynamic vegetation changes and identifying the factors driving these changes are important for evaluating global ecosystem processes. Based on the pixel binary model, coefficient of variation, Theil-Sen median trend analysis, geographic detector, and Pearson correlation coefficient, this study analyzed vegetation cover variations and the factors influencing these changes in the Erhai Lake Basin, one of the most important plateau lakes in China. Vegetation cover exhibited a continuously increasing trend, with the proportion of high vegetation coverage consistently ranking first. Land cover is an effective explanatory factor for vegetation cover, and FVC shows obvious variation rules associated with elevation, land cover, population, and landform. It is important to highlight that the combination of two factors influences vegetation dynamics more significantly than one factor alone, with the interaction between land cover type and nightlight illumination being more powerful. These results enhance our understanding of the complex processes of vegetation cover variation in plateau lake catchments and offer a scientific reference for improving the spatial layout of vegetation in fragile ecosystems.
1 Introduction
Vegetation is a crucial indicator of the health of the ecological environment. It helps connect different natural components, including the atmosphere, water, living organisms, and water (Meyer and Ii, 1992; Suzuki et al., 2007; Du et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2018). Fractional vegetation coverage (FVC) indicates proportion of vertical area occupied by leaves, stems, and branches of plants on ground in relation to total area of a specific statistical region (Gitelson et al., 2002). It can characterize growth status and trend of a certain devegetation (Adams and Arkin, 1977). In the context of global climate change and an increase in extreme weather events, regional vegetation coverage has changed significantly (Bonan, 2008; Fang et al., 2018), which makes it urgent to research long-term shifts in vegetation to better understand spatio-temporal variations in regional ecological environment quality and maintain ecosystem balance (Zhong et al., 2019).
Remote sensing provides a valuable means for monitoring vegetation cover dynamics at different spatiotemporal scales with high precision and frequency (Jalonen et al., 2014; Piao et al., 2003). Many vegetation indices obtained by remote sensing inversion have become effective indicators for monitoring regional and even global vegetation activities, as well as their impacts on natural environment variety and human intervention (Huete et al., 2002; Frederic et al., 2019; Bageshree et al., 2022; Gao et al., 2022), Vegetation coverage is good at tracking the spatiotemporal variations of surface vegetation (Zhang et al., 2003). For example, Fu and Burgher (2015) discussed and analyzed the dynamic variations in vegetation coverage in the Namoi Basin and its relationship with meteorological factors and groundwater resources. Mu et al. (2012) calculated the vegetation coverage in Inner Mongolia and discovered that vegetation coverage was higher in the east and lower in the west. Meng et al. (2015) changes through meteorological factors and discovered that human activities have a significant impact on vegetation changes. MODIS NDVI has the characteristics of long-term continuity, high spatial resolution, and wide coverage, and many scholars have chosen MODIS datasets to study vegetation dynamic changes at global, regional, and watershed scales (Wylie et al., 2008; Fyllas et al., 2009; Psomas et al., 2011; Shao et al., 2016).
Owing to the large diversity of hydrothermal mechanisms and ecological environmental conditions, the causal relationship between vegetation activity and driving factors is complex and spatially heterogeneous (Piao et al., 2003; Holmgren et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2018). In previous studies, most scholars employed correlation and residual analyses to explain the causes of vegetation variation. Wang et al. (2015) and Duo et al. (2017) explored the human factors affecting vegetation in the North China Plain and southern hilly areas of China through residual analysis. He et al. (2020) used nightlight data to characterize human factors and determined that human influences were the primary factor for the decrease in vegetation in and around cities in Zhejiang Province through a correlation coefficient analysis.
However, these traditional methods are unable to elucidate the nonlinear interdependence between multiple influencing factors, especially those that are intertwined with anthropogenic influences and climate fluctuations. In other words, a single driver cannot be quantitatively determined and has certain limitations. Based on this, Wang et al. (2016) proposed a geographic detector model, which is a statistical method for determining spatial differentiation through spatial variance analysis and revealing its driving factors. It can quantitatively identify the influence of factors and their interaction intensity. Many studies have effectively applied methods at different scales to cover a variety of influencing factors, resulting in a comprehensive understanding of the driving forces controlling changes in vegetation cover (Du et al., 2016; Pei et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2019).
Ecosystems in mountainous and plateau areas are fragile and irreversible (Wang et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2019) and are particularly sensitive to climate change (Beniston et al., 1997). As the largest plateau lake in the National Nature Reserve, the Erhai Lake Basin provides various ecosystem services. Due to great differences in topography, climate, and human disturbance, there are significant differences in surface vegetation coverage and ecological conditions in the Erhai Lake Basin. Based on the NDVI dataset and 15 driving factor datasets, this study employed multiple analytical techniques to identify the spatio-temporal change characteristics of FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin and quantify the drivers affecting vegetation in the region. These results are crucial for promoting ecological restoration and guiding the local environmental protection in this area.
2 Overview of the study area
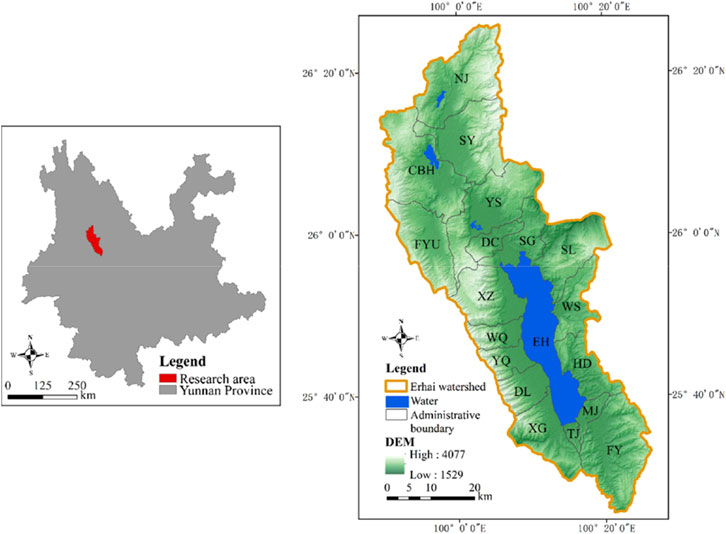
The Erhai Lake Basin is a Lancang-Mekong River system that includes the Cangshan National Nature Reserve and a typical plateau lake. It is the core area for wetland ecological functions in northwest Yunnan Province (Zhong et al., 2018). The Erhai Lake Basin is characterized by a typical low-latitude plateau subtropical monsoon climate with distinct dry seasons. The average annual temperature is about 15.2°C, and the average annual rainfall is about 1,048 mm. The vegetation distribution in the basin is vertical zonal. Diversified plant communities provide an important guarantee for the stability of the ecosystem in this region. The rock and soil types in the Erhai Lake Basin are primarily metamorphic rocks and red soil (Chen et al., 2021). Erhai Lake Basin contains 18 townships: Dali Innovation Industrial Park Manjiang Office (MJ), Shuanglang Town (SL), Xizhou Town (XZ), Dali Innovation Industrial Park Patio Office (TJ), Dali Innovation Industrial Park Fengyi Town (FY), Yinqiao Town (YQ), Wanqiao Town (WQ), Shangguan Town (SG), Xiaguan Town (XG), Dali Town (DL), Haidong Town (HD), Wase Township (WS), Cibihu Township (CBH), Fengyu Township (FYU), Sanying Township (SY), Dengchuan Township (DC), Niujie Township (NJ) and Yousuo Township (YS). The specific locations are shown (Figure 1).
3 Materials and methods
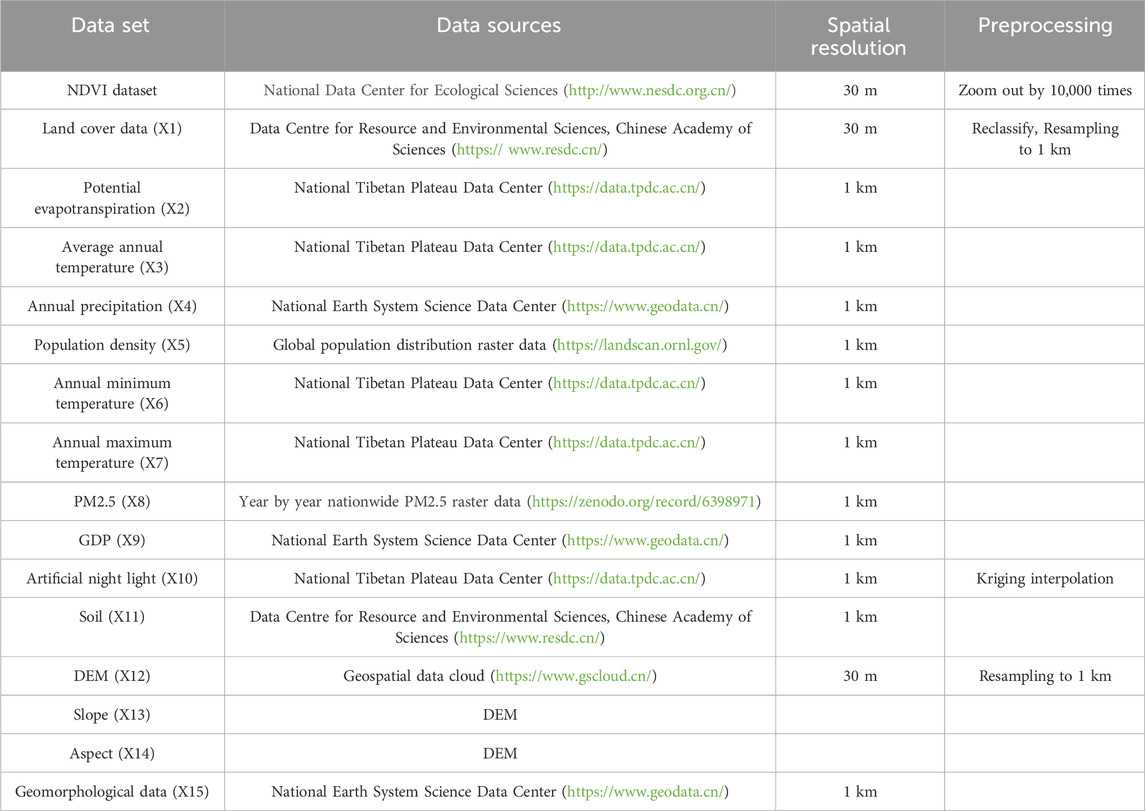
3.1 Data source and processing
The data sources and processing of the study are seen (Table 1).
3.2 Research method
3.2.1 Pixel binary model
The principle of this model is that a pixel consists of only vegetation cover and bare soil. It calculates the proportion of vegetation coverage based on NDVI. The method is widely and frequently used in detecting vegetation ecological changes (Li, 2003). The FVC was calculated using Formula 1.
where NDVImax is the pure vegetation pixel NDVI value, and NDVImin is the pixel without vegetation cover. The NDVI values with 5% and 95% confidence intervals were substituted for NDVImin and NDVImax. The FVC standard deviation characterizes the locality of the difference in FVC. By analyzing the standard deviation of the FVC in 18 townships in the Erhai Lake Basin, the spatial heterogeneity of the FVC in each region was characterized for the period 2000–2022.
3.2.2 Coefficient of variation
Coefficient of variation (CV) is the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean (Deng et al., 2017; Chaudhari and Thakkar, 2023). The variation coefficient is generally used to assess the degree of dispersion of long-term data. The variation coefficient of the average annual vegetation coverage obtained from to 2000–2022 was calculated pixel-by-pixel to determine the degree of vegetation stability. It is a dimensionless quantity that does not require the mean of the reference data (He et al., 2023). Its calculation is shown in Formulas 2, 3:
where FVCi and
3.2.3 Trend analysis
The Theil–Sen Median is a resilient non-parametric method for calculating trends. It does not depend on a specific distribution and is unaffected by outliers, making it ideal for analyzing long-term trends in FVC (Li et al., 2019; Tian et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2023). Its calculation is shown in Formula 4:
FVCi and FVCj represent the long-term datasets for years i and j, respectively. If β is positive, it suggests that there is an increase in FVC. Conversely, this indicates a decline.
The Mann-Kendall test is a distribution-free test that does not need to follow the normal distribution of measured values; the impact of outliers can be reduced to a minimum degree, making it suitable for long-term time-series data trend significance tests (Kendall, 1957; Bo-feng and Rong, 2009). The statistical test formula can be seen in Formula 5.
where, calculation of sgn can be shown in Formula 6.
Trend test is carried out with the help of Z. Z is calculated as Formula 7:
Calculation formula of Var value is shown in Formula 8:
where n denotes the number of data points. The confidence level was 95%.
3.2.4 Geographic detector
Geographical detection is a statistical technique used to reveal the driving factors behind the spatial stratification heterogeneity of objects. It is often used to identify key factors and interaction processes of spatial stratification heterogeneity. There are four main modules for geographical detection (Song et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020; Jiang et al., 2022). In this study, factors and interaction detectors were selected to examine the driving influence of vegetation in the Erhai Lake Basin.
The factor detector is primarily used to identify the spatial variability of Y(FVC) and the degree of interpretation of different factors X (each detection factor) on Y. Its explanatory power is quantified by the q value. The q value was determined using Equations 9–11:
where h = 1,2 … L is the classification of X or Y, q represents the explanatory power of the driving factors of the FVC, Nh refers to the number of units in layer h, and N indicates the total number of units in the entire region. σ2 and σh2 represent variance of FVC in class h and across region, W and T are sum of variances and total regional variances of class h respectively.
When running the geographic detector model, we need to discretize the driving factors. This study used the natural segmented point method to divide driving factors such as precipitation, temperature, altitude, GDP, and population density into 10 categories. According to the broad category criteria, soil types are divided into 16 categories, vegetation types into 10 categories, land-cover types into six categories, and geomorphic types into six categories (Zhao et al., 2015). The Erhai Lake Basin was divided into a grid of 1 km × 1 km Data from 2,188 sample points in this region were selected for analysis. The q statistics of the 15 driving factors in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020 in the Erhai Lake Basin were calculated using geographic detectors.
3.2.5 Correlation analysis
Correlation coefficients (CC) were used to analyze the relationship between two or more variables (Liu et al., 2020). In this study, we examined the relationships among FVC, annual maximum temperature, and annual rainfall.
where Rxy is the CC between two variables, x is the annual maximum temperature and annual rainfall, and y is the FVC, n is duration of time;
4 Results and analysis
4.1 Spatio-temporal dynamic characteristics of FVC
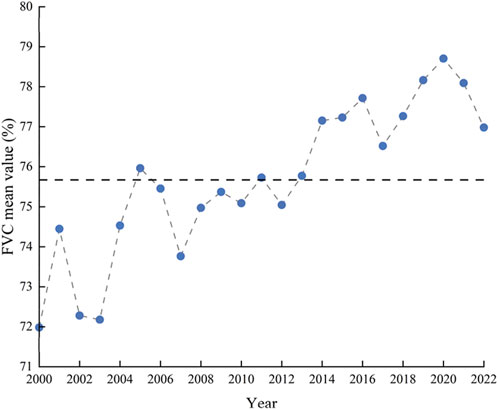
From 2000 to 2022, the FVC in the Erhai Basin was low in the middle and south and high in the surrounding areas (Figure 2). The high area accounts for 70.36% of the whole basin and is concentrated in the eastern and western parts of Erhai Lake, especially Cangshan Mountain in the western part of the Erhai Lake Basin. Overall, FVC presents a fluctuating upward trend, and the peak value appears in 2001, 2005, 2009, 2011, 2016, and 2020. The historical high point (78.71%) was reached in 2020, which shows the time changes of different levels of FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2022 (Figure 3). The coverage area gradually increased from 59.20% to 73.12%, which was higher than the annual average (70.36%). Middle and high coverage decreased from 19.72% in 2000 to 9.96% in 2022, lower than the multi-year average (13.45%), while the latter decreased from 7.86% in 2000 to 3.60% in 2022, lower than the multi-year average (4.11%).
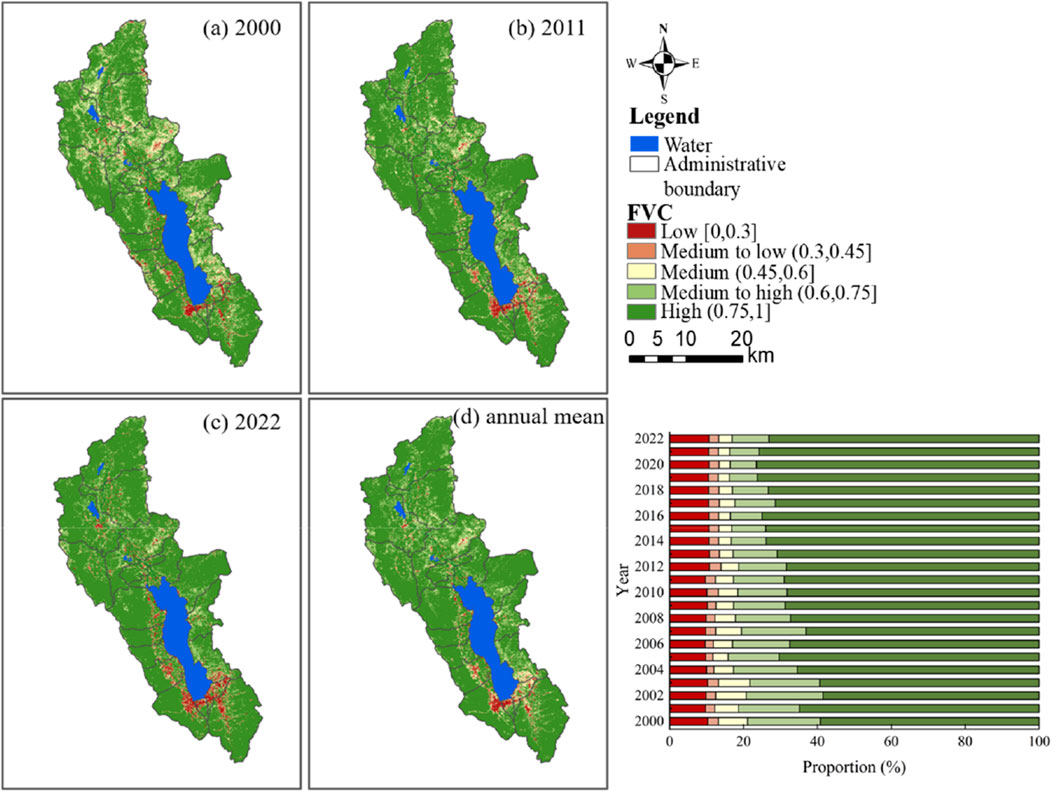
Figure 2. Temporal and spatial changes of vegetation coverage (A–D) and the proportion of each type in each year.
4.2 Change trend of FVC
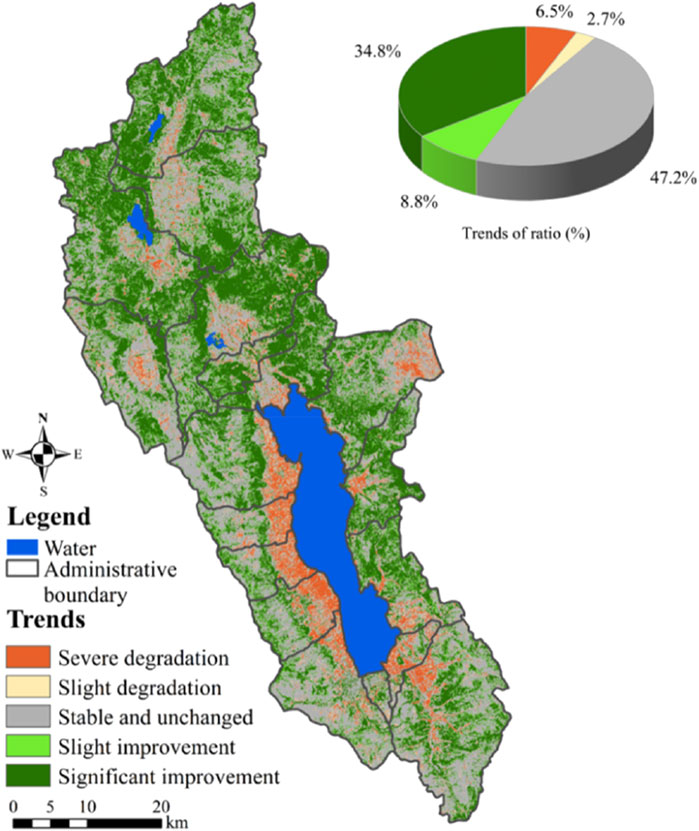
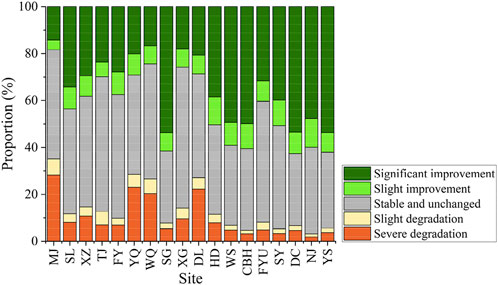
The results showed that FVC increased significantly, accounting for 34.8% (Figure 4). A significant increase of 8.8%, a significant decrease of 2.7%, and a very significant decrease of 6.5% were observed; overall, the increased area was higher than the decreased area, with a difference of 34.4%. In addition, 47.2% of the regions exhibited no notable changes in FVC. Spatially, an extremely significant increase in FVC over the past 23 years was observed, mainly in the north. It is worth noting that SG, DC, and CBH significantly increased by more than 50%, and significantly decreased areas were mainly distributed in MJ and sites (YQ, DL, WQ, and XZ) in the western Erhai Lake Basin.
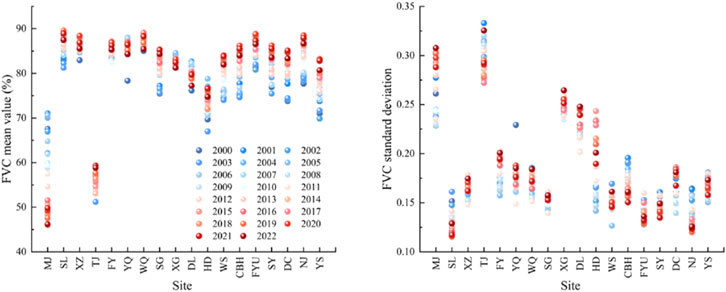
Among the different administrative regions, TJ and MJ had the lowest FVC, but TJ showed a change from low to high FVC (Figure 5). MJ indicating a continuous decline. In addition to TJ and MJ, the average FVC in the other 16 towns was greater than 73.70%. The multiyear mean for WQ was 87.47%, followed by SL (86.29%), XZ (85.85%), YQ (85.74), FYU (85.48%), and FY (85.07%). The FVC standard deviation analysis results showed that in 2000–2022, the minimum standard deviation of SL, followed by NJ, XZ, FY, WQ, SG, XG, DL, WS, CBH, FYU, SY, DC, and YS FVC, was relatively smooth; MJ, TJ, and HD varied greatly (Figure 6).
4.3 Stability analysis of FVC
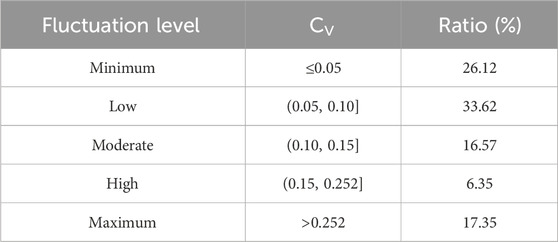
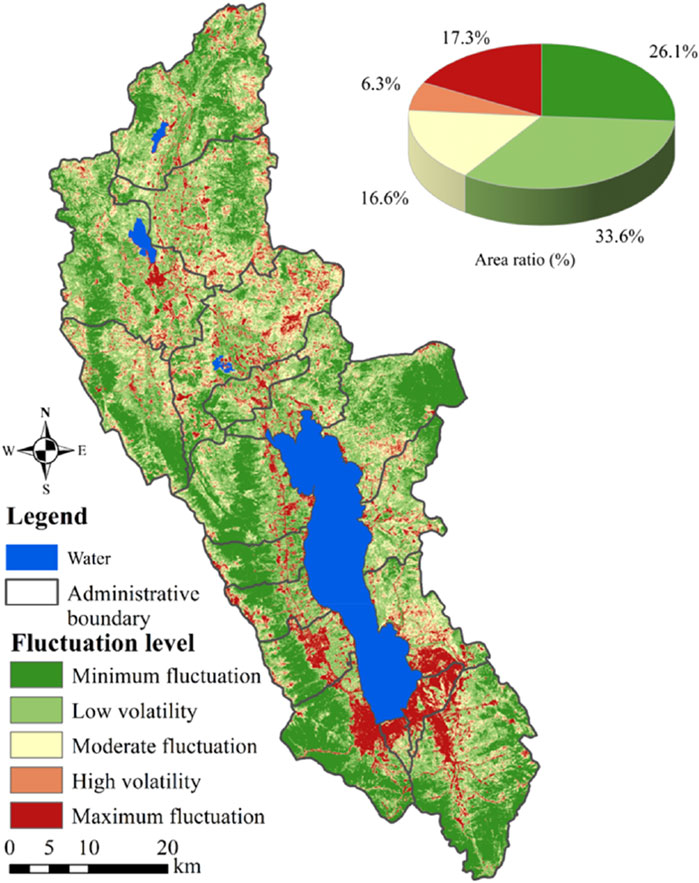
The Cv values represent the extent of variability within a dataset. The stability distribution of vegetation coverage in the Erhai Lake Basin was obtained by calculating the variation coefficient of the vegetation coverage image pixel-by-pixel. The stability of FVC from 2000 to 2022 shows minimal and slight fluctuations in most regions as a whole (Table 2; Figure 7). According to the classification results of Cv, 59.74% of the regions with minimum and slight fluctuations were mainly distributed in the Cangshan region, with high forest cover and little influence of human activities. The largest floating area accounted for 17.35% and was mainly concentrated in the south of the Erhai Lake Basin. The main reason for this is that under the influence of regional development (development zone) and urban expansion (Xiaguan Town), the surface of this area has changed greatly, resulting in the maximum floating phenomenon of regional vegetation. The proportion of the moderately floating area was 16.57%, which was mainly concentrated in the north of the Erhai Lake Basin. Its area was intertwined with the highly floating area. Although the area is affected by urbanization, its impact is small.
4.4 Quantitative the drivers of FVC
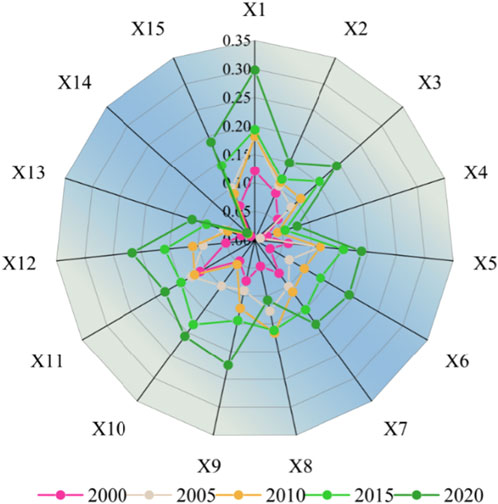
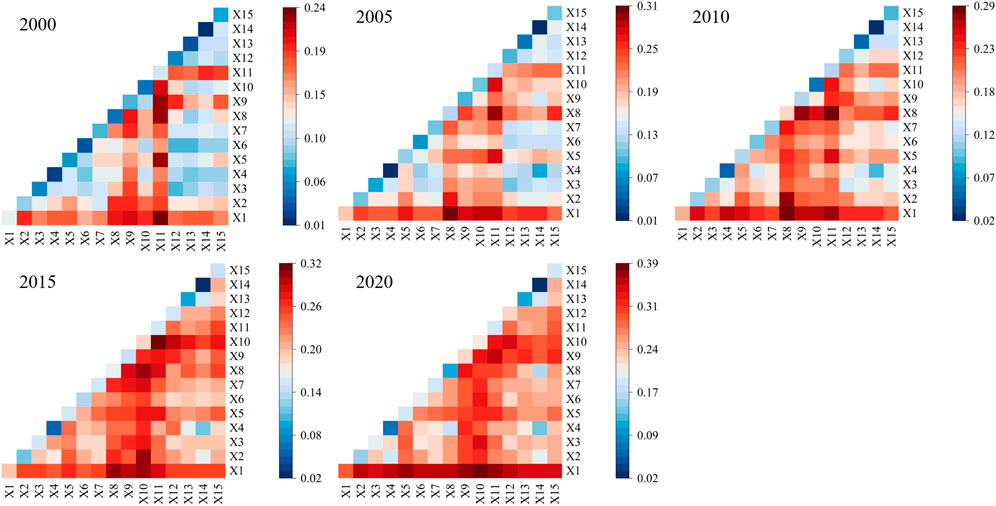
To examine how different geographical factors affect changes in the FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin, 15 relevant variables were detected using a geographical detector and 2,188 sampling points were investigated. Land cover (X1) and soil type (X11) had the highest explanatory powers, with average mean q-values of 0.196 and 0.138, respectively (Figure 8). The lowest q values were for the slope direction (X14) and annual rainfall (X4), with values of 0.016 and 0.042, respectively. Based on the mean q value, driving factors in order from high to low is: land cover (0.196) > soil type (0.138) > GDP (0.131)> population density (0.127) > elevation (0.125) > highest temperature (0.124) in > PM2.5 (0.122) > annual average temperature (0.119) > artificial light (0.118)> landform (0.117) > potential evapotranspiration (0.114)> annual minimum temperature (0.105) > slope (0.067) >annual rainfall (0.042) >aspect of slope (0.016). Therefore, land cover and soil type were the main explanatory variables of the FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin and were identified as the main factors. The explanatory abilities of the land cover and soil type were relatively stable. At the same time, other geographical factors such as GDP, population density, elevation, annual maximum temperature and potential evapotranspiration are considered as secondary driving factors. Annual rainfall, slope direction, and slope had the lowest explanatory powers, and the mean q values were all less than 0.1, indicating that they had the least impact on vegetation cover in the Erhai Lake Basin (Figure 8). In general, human activity factors, represented by land cover, had a primary influence on the spatial distribution of the FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin. The influence of land cover type on anthropogenic factors gradually increased over time, especially during 2015–2020, when the q value increased from 0.194 in 2015 to 0.298 in 2020. The impact of social factors such as population growth and human activities will be more closely related to FVC changes and ecological environment evolution in the future.
Detecting the spatial variations in vegetation associated with different drivers provides insight into the changes in the explanatory power of individual drivers. The Geodetector tool effectively revealed the interactions between drivers that lead to changes in vegetation cover. The results showed that the influence of any two of the 15 driving factors on the FVC was more significant than the effect of each factor alone. Additionally, the effects of the two-factor and nonlinear enhancements are shown. Land cover type ∩ night light (q = 0.385), land cover type ∩ GDP (q = 0.372), land cover type ∩ soil type (q = 0.365) and land cover type ∩ population density (q = 0.363) are main factors influencing geographical distribution of vegetation cover in Erhai Lake Basin. Land cover type, as the most important driving factor, can better explain the geographical distribution of the FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin by interacting with other driving factors (Figure 9). After the interaction between human factors, the explanatory power was significantly improved.
4.5 Effects of natural factors on FVC in Erhai Lake basin
4.5.1 Geomorphic factor
The mean and standard deviation of the vegetation coverage of each geomorphic type showed that the average vegetation coverage of the large rolling mountains was 0.934 and reached its highest value (0.950) in 2020. The average vegetation coverage of the middle elevation plain was 0.630 and reached its lowest value (0.591) in 2012 (Figure 10). In addition, the large undulating mountains had the lowest standard deviation and the most stable change, followed by the large undulating mountains, medium undulating mountains, small undulating mountains, medium-altitude hills, and medium-altitude plains, among which the latter had the greatest change.
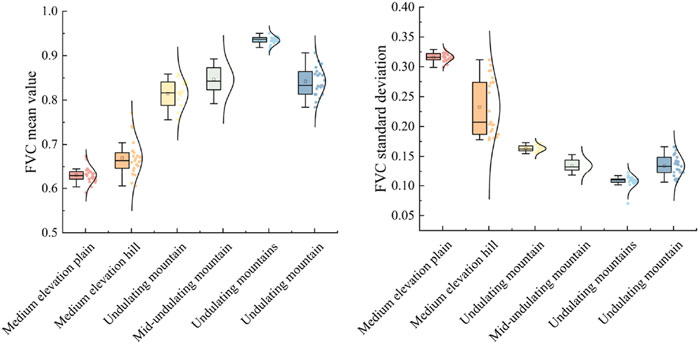
Figure 10. Relationship between mean and standard deviation of vegetation coverage and geomorphic types in Erhai Lake Basin.
4.5.2 Topographic factor
The change trend of the average vegetation coverage and its 50 m interval in the elevation area were analyzed and calculated (Figure 11). The results show that the FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin exhibited a wavy evolutionary trend. In the initial stage, from 1,550 to 2,150 m, the trend showed a large fluctuation and then increased with increasing altitude. The average FVC peak at 3,000 m (0.898). Above this height, the trend experienced a slight slowdown and gradually stabilized regionally. In addition, at 1,650 m and 2000 m, the standard deviation of the average FVC was the largest at 0.264 and 0.347, respectively, with a large range of changes.
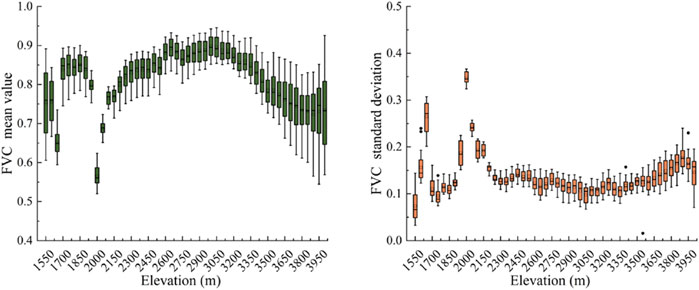
Figure 11. Relationship between mean and standard deviation of vegetation coverage and altitude in Erhai Lake Basin.
4.5.3 Climatic factor
Through the creation of 2,833 sampling points in the entire Erhai Lake Basin, the mean FVC, annual maximum temperature, and annual precipitation during 2000–2022 were extracted for Pearson bivariate correlation analysis (Figure 12), which showed that in the past 23 years, FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin had a significant negative correlation with the annual maximum temperature, with CC ranging from −0.283 to −0.380, and CC reaching its highest value in 2020, while the correlation coefficient had a significant positive relationship with annual precipitation, with values ranging from 0.239 to 0.423, and CC reaching a higher value in 2013.
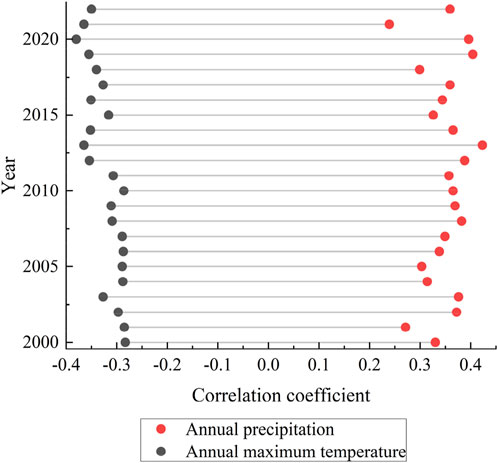
Figure 12. Relationship between FVC and annual maximum temperature and annual precipitation in Erhai Lake Basin (p < 0.01).
4.6 Effects of human activities
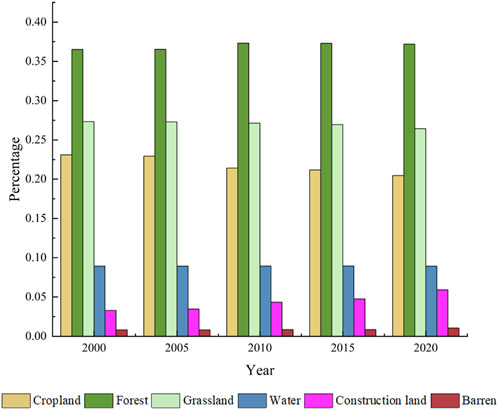
From 2000 to 2020, the proportion of construction land area increased from 3.29% to 5.93% (Figure 13). This may make the FVC of the construction land increase area fluctuate greatly, and may even be the main reason for the degradation of this area. The area of cropland has decreased significantly. Forests and grassland accounted for the highest proportion of all land cover in each year. The sum of the two accounted for more than half of the total area in 5 years, which further explained the high vegetation coverage in Erhai Lake Basin.
Population density of the Erhai Lake Basin was classified according to global population levels. It is an extremely rare area (<1 people/km2), rare area (1–25 people/km2), medium zone (25–100 people/km2), and dense area (>100 people/km 2). As shown in Figure 14, the sparse population density area had the highest mean FVC (0.841) and lowest standard deviation (0.166), followed by the very sparse population density area (0.836), and the medium population area (0.782). It is worth noting that the sparse population density area had the lowest mean FVC (0.689) but the highest standard deviation (0.268).
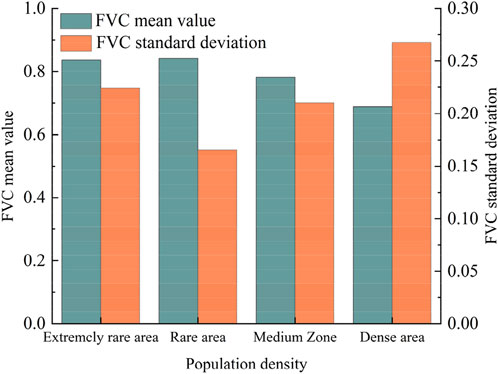
Figure 14. Relationship between mean and standard deviation of vegetation coverage and population density in Erhai Lake Basin.
5 Discussion
5.1 Spatio-temporal variations of FVC
Vegetation plays an important role in carbon sequestration, energy exchange and biodiversity support, and vegetation coverage has become an important index to evaluate ecological quality. Understanding the dynamic changes of vegetation on the scale of plateau watershed is of great significance for resource managers to manage ecological environment systems. In this study, the spatiotemporal characteristics of the FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin, a typical plateau basin in Yunnan Province, and a quantitative analysis of the factors in the last 23 years were investigated. The topography of the Erhai Lake Basin is complex, and meteorology, topography, and human factors have a significant influence on FVC in the region. From the perspective of spatiotemporal variations, from 2000 to 2022, FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin exhibited an upward trend, with a notable increase covered by medium vegetation. Vegetation degradation in the western and southeastern parts of the Erhai Lake Basin was evident. In 2020, the FVC of Erhai Lake Basin reached the highest value (78.71%), and the high coverage area was mainly distributed in Cangshan Mountain in the west of Erhai Basin, and the vegetation change in this area was very small, which was not only related to the regional climate of Cangshan Mountain, but also closely related to the long-term support of the government for Cangshan Nature Reserve. The FVC mainly increased significantly (34.8%), and mainly distributed in SG and DC. On the whole, the FVC of Erhai Lake Basin maintained a good trend and showed an increasing trend.
5.2 Analysis of driving factors of FVC
The factors influencing the FVC are cross-complex, and the geographical detector model is helpful for analyzing the specific driving mechanism in detail. From 2000 to 2022, land-cover type was the dominant factor, and the explanatory power of land-cover type was high. Land cover type was the main factor influencing the spatial variation in vegetation cover in the Erhai Lake Basin, but the q value of each driving factor underwent significant changes over time. The q values for the 15 driving factors selected showed an increasing trend, particularly the influence of land cover type, annual minimum temperature, potential evapotranspiration, and night lights on the spatial differentiation of FVC showed an increasing trend. According to the results of the interactive detection and analysis, it is evident that the FVC of the Erhai Lake Basin is greatly affected by human activities, and the interaction between land cover type and night light or GDP factors has the strongest effect, with a q value of more than 0.372.
In the context of global warming, the dynamic change of vegetation has spatial heterogeneity (Shahid et al., 2018), and is closely related to climate factors. The analysis results of geographic detectors showed that the annual maximum temperature and annual rainfall had a large q value. Therefore, the correlation between FVC and annual maximum temperature and annual rainfall in each year from 2000 to 2022 was evaluated by means of pearson correlation analysis, and the impact of these two climate factors on FVC was evaluated. The results showed that FVC was negatively correlated with annual maximum temperature and positively correlated with annual rainfall, and both showed significant correlation (p < 0.01). By averaging the correlation coefficients over 23 years, the effect of annual rainfall (0.35) is greater than that of annual maximum temperature (−0.32). Because of the low latitude of Erhai Lake Basin, high temperature may promote the evaporation of soil water and the closure of plant stomata, thus affecting the photosynthesis of vegetation (Gu et al., 2018). Regions with high FVC were mainly concentrated on the large rolling mountains with an altitude of 2,700–3,200 m, while the areas above 3,800 m may have a decrease in FVC caused by a large amount of snow. At high altitudes, higher-temperature environments are suitable for plant growth. However, the positive benefits of rising temperatures on vegetation growth may be offset by the susceptibility of vegetation to the limiting effect of water availability (Liu et al., 2019; Qiao et al., 2021). In this study, the annual maximum temperature was negatively correlated with FVC, which also proved this point. The area of forest and grassland were in the forefront, which also explained the reason for the highest proportion of high FVC in the Erhai Lake Basin. In addition, the FVC of MJ showed a relatively obvious trend of extremely significant reduction, with a large standard deviation. MJ is a part of the National Dali Economic and Technological Development Zone. Some cropland was transferred to construction land in MJ. The fluctuation was obvious, which may be related to the economic development of this region. In general, the FVC of Erhai Lake Basin is a complicated process influenced by the interaction of human and natural factors.
5.3 Limitations
The changing nature of vegetation is a complex process influenced by various factors. The study of the coupling effect of natural and human factors is helpful to further deepen our understanding of the dynamic forces of the FVC in plateau lake watersheds, but the study still has some limitations. The potential driving factors considered in this study were not comprehensive. The implementation of the farmland conversion project, the delayed effect of climate change on vegetation growth, and more meteorological, socioeconomic, and policy factors need to be determined to reduce the uncertainty of the research on vegetation changes (Feng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). In addition, in this study, a pixel binary model was utilized to assess the FVC in the Earhai Lake Basin using remote sensing. However, in some arid areas, such as Haidong Town, the pixel binary model may not solve the uncertainty caused by it, and the pixel third model can compensate for it well. Future studies combining the two models may yield better results (Ning et al., 2023). Thus, vegetation cover trends can be analyzed more accurately.
6 Conclusion
Erhai Lake, the largest plateau lake in the National Nature Reserve, has important ecological functions. This research examined the spatiotemporal dynamic features and driving mechanisms of FVC in this area during 2000–2022 by using NDVI datasets and 15 driving factor data sources. The results show that:
(1) The FVC of the Erhai Lake Basin was low in the middle and south but high around the basin. Regions with high FVC were primarily concentrated in the Cangshan region west of the Erhai Lake Basin. The changes in XG, TJ, MJ, and HD in the south of the Erhai Lake Basin fluctuated greatly, and the FVC in the northern Erhai Lake Basin was more evident.
(2) The q values for land cover and soil type were the highest. Various factors showed significant interactions, and the q value indicated that the interaction exceeded the interaction related to individual factors. The interaction between land cover and night light had a stronger impact.
(3) There was a correlation between each factor and vegetation cover. The trends and average vegetation cover changes were related to elevation, land cover, population, and terrain. The correlation coefficients between the annual maximum temperature and FVC indicated a negative relationship, which significantly impacted ecosystem dynamics.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
ZL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WH: Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. XH: Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Yunnan Agricultural Joint Fund Key Project (202301BD070001-133) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060304).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adams, J., and Arkin, G. (1977). A light interception method for measuring row crop ground cover. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. - SSSAJ 41, 789–792. doi:10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100040037x
Bageshree, K., Abhishek, S., and Kinouchi, T. (2022). Unraveling the multiple drivers of greening-browning and leaf area variability in a socioeconomically sensitive drought-prone region. Climate 10, 70. doi:10.3390/cli10050070
Beniston, M., Diaz, H. F., and Bradley, R. S. (1997). Climatic change at high elevation sites: an overview. Clim. Change. 36, 233–251. doi:10.1023/A:1005380714349
Bo-feng, C., and Rong, Y. (2009). Advance and evaluation in the Long Time series vegetation trends research based on remote sensing. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 13, 1170–1186. doi:10.11834/jrs.20090614
Bonan, G. (2008). Forests and climate change: forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 320, 1444–1449. doi:10.1126/science.1155121
Chaudhari, K., and Thakkar, A. (2023). Neural network systems with an integrated coefficient of variation-based feature selection for stock price and trend prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 219, 119527. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2023.119527
Chen, H., Guo, Z. C., and He, P. (2021). Spatial and temporal changes of vegetation coverage in Erhai Lake Basin from 1988 to 2018. Remote Sens. Land and Resour. doi:10.6046/gtzyyg.2020283
Deng, X. Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Z. H., and Yao, J. Q. (2017). Spatiotemporal dynamics of evapotranspiration in arid area of northwest China. Acta Ecol. sin. doi:10.5846/stxb201601270190
Du, J., Shu, J., Yin, J., Yuan, X., Jiaerheng, A., Xiong, S., et al. (2015). Analysis on spatio-temporal trends and drivers in vegetation growth during recent decades in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observation Geoinformation 38, 216–228. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2015.01.006
Du, Z., Xu, X., Zhang, H., Wu, Z., and Liu, Y. (2016). Geographical detector-based identification of the impact of major determinants on aeolian desertification risk. PloS one 11, e0151331. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0151331
Duo, A., Zhao, W. J., Gong, Z. N., Zhang, M., and Fan, Y. B. (2017). Temporal and spatial changes of climate and their effects on vegetation coverage in the North China Plain from 1981 to 2013. Acta Ecol. sin. 37, 576–592. doi:10.5846/stxb201507301600
Fang, W., Huang, S., Huang, Q., Huang, G., Meng, E., and Luan, J. (2018). Reference evapotranspiration forecasting based on local meteorological and global climate information screened by partial mutual information. J. Hydrology 561, 764–779. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.038
Feng, D., Yang, C., Fu, M., Wang, J., Zhang, M., Sun, Y., et al. (2020). Do anthropogenic factors affect the improvement of vegetation cover in resource-based region? J. Clean. Prod. 271, 122705. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122705
Frederic, B., Plummer, S., and Schaepman-Strub, G. (2019). An overview of global leaf area index (LAI): methods, products, validation, and applications. Rev. Geophys. 57, 739–799. doi:10.1029/2018RG000608
Fu, B., and Burgher, I. (2015). Riparian vegetation NDVI dynamics and its relationship with climate, surface water and groundwater. J. Arid. Environ. 113, 59–68. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2014.09.010
Fyllas, N. M., Patiño, S., Baker, T. R., Bielefeld Nardoto, G., Martinelli, L. A., Quesada, C. A., et al. (2009). Basin-wide variations in foliar properties of Amazonian forest: phylogeny, soils and climate. Biogeosciences 6, 2677–2708. doi:10.5194/bg-6-2677-2009
Gao, W., Zheng, C., Liu, X., Lu, Y., Chen, Y., Wei, Y., et al. (2022). NDVI-based vegetation dynamics and their responses to climate change and human activities from 1982 to 2020: a case study in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Ecol. Indic. 137, 108745. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108745
Gitelson, A. A., Kaufman, Y. J., Stark, R., and Rundquist, D. (2002). Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 80, 76–87. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00289-9
Gu, Z., Xingwu, D., Shi, Y., Li, Y., and Pan, X. (2018). Spatiotemporal variation in vegetation coverage and its response to climatic factors in the Red River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 93, 54–64. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.04.033
He, X., Zhang, F., Cai, Y., Tan, M. L., and Chen, N. W. (2023). Spatio-temporal changes in fractional vegetation cover and the driving forces during 2001–2020 in the northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (30), 75511–75531. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-27702-x
He, Z. H., Zhang, Y. H., He, Y., Zhang, X. W., Cai, J. Z., and Lei, L. P. (2020). Analysis of vegetation change trend and driving factors in Zhejiang Province in recent 20 years. J. Ecol. Environ. 29, 1530–1539. doi:10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.08.004
Holmgren, M., Hirota, M., Nes, E., and Scheffer, M. (2013). Effects of interannual climate variability on tropical tree cover. Nat. Clim. Change 3, 755–758. doi:10.1038/nclimate1906
Huete, A., Didan, K., Miura, T., Rodriguez, E. P., Gao, X., and Ferreira, L. G. (2002). Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 83, 195–213. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00096-2
Jalonen, J., Järvelä, J., Koivusalo, H., and Hyyppä, H. (2014). Deriving floodplain topography and vegetation characteristics for hydraulic engineering applications by means of terrestrial laser scanning. J. Hydraulic Eng. 140, 04014056. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000928
Jiang, W., Niu, Z., Wang, L., Yao, R., Gui, X., Xiang, F., et al. (2022). Impacts of drought and climatic factors on vegetation dynamics in the yellow River Basin and yangtze River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 14, 930. doi:10.3390/rs14040930
Li, M. (2003). Study on estimation method of vegetation coverage by remote sensing. Master, Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences. (Institute of Remote Sensing Application).
Li, Y., Wang, X., Chen, Y., and Wang, M. (2019). Land surface temperature variations and their relationship to fractional vegetation coverage in subtropical regions: a case study in Fujian Province, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 41, 2081–2097. doi:10.1080/01431161.2019.1685714
Liu, H., Jiao, F., Yin, J., Li, T., Gong, H., Wang, Z., et al. (2020). Nonlinear relationship of vegetation greening with nature and human factors and its forecast – a case study of Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 111, 106009. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106009
Liu, L., Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Li, D., Zhang, Y., Qin, D., et al. (2019). Elevation-dependent decline in vegetation greening rate driven by increasing dryness based on three satellite NDVI datasets on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 107, 105569. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105569
Meng, D., Li, X., Gong, H., and Qu, Y. (2015). Analysis of spatial-temporal change of NDVI and its climatic driving factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolis circle from 2001 to 2013. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 17, 1001–1007. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1047.2015.01001
Meyer, W. B., and Ii, B. L. T. (1992). Human population growth and global land-cover/cover change. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 23, 39–61. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.23.110192.000351
Mu, S. J., Li, J. L., Chen, Y. Z., Gang, C. C., Zhou, W., and Ju, W. M. (2012). Spatial-temporal changes of vegetation coverage in Inner Mongolia from 2001 to 2010. Acta Geogr. sin. 67, 1255–1268. doi:10.11821/xb201209010
Ning, L., Peng, W., Yu, Y., Xiang, J., and Wang, Y. (2023). Quantifying vegetation change and driving mechanism analysis in Sichuan from 2000 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 11. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2023.1261295
Pei, Z. L., Yang, Q. K., Wang, C. M., Pang, G. W., and Yang, L. H. (2019). Spatial distribution of vegetation coverage in the upper reaches of the Yellow River and its influencing factors. Arid zone Res. 36, 546–555. doi:10.13866/j.azr.2019.03.03
Piao, S., Fang, J., Zhou, L., Guo, Q., Henderson, M., Ji, W., et al. (2003). Interannual variations of monthly and seasonal normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in China from 1982 to 1999. J. Geophys. Res. 108. doi:10.1029/2002JD002848
Psomas, A., Kneubühler, M., Huber, S., Itten, K., and Zimmermann, N. E. (2011). Hyperspectral remote sensing for estimating aboveground biomass and for exploring species richness patterns of grassland habitats. Int. J. Remote Sens. 32, 9007–9031. doi:10.1080/01431161.2010.532172
Qiao, Y., Jiang, Y., and Zhang, C. (2021). Contribution of karst ecological restoration engineering to vegetation greening in southwest China during recent decade. Ecol. Indic. 121, 107081. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107081
Shahid, M., Cong, Z., and Zhang, D. (2018). Understanding the impacts of climate change and human activities on streamflow: a case study of the Soan River basin, Pakistan. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 134, 205–219. doi:10.1007/s00704-017-2269-4
Shao, Y., Lunetta, R. S., Wheeler, B., Iiames, J. S., and Campbell, J. B. (2016). An evaluation of time-series smoothing algorithms for land-cover classifications using MODIS-NDVI multi-temporal data. Remote Sens. Environ. 174, 258–265. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.023
Song, Y., Wang, J., Ge, Y., and Xu, C. (2020). An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: cases with different types of spatial data. GIScience and Remote Sens. 57, 593–610. doi:10.1080/15481603.2020.1760434
Sun, M., Ji, Z., Jiao, N., Lun, F., Sun, Q., and Sun, D. (2023). Mapping grassland based on bio-climate probability and intra-annual time-series abundance data of vegetation habitats. Remote Sens. 15, 4723. doi:10.3390/rs15194723
Suzuki, R., Masuda, K., and Dye, D. (2007). Interannual covariability between actual evapotranspiration and PAL and GIMMS NDVI of northern Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 106, 387–398. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2006.10.016
Tian, Z. H., Ren, Z. G., and Wei, H. T. (2022). The driving mechanism of spatio-temporal vegetation evolution in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. 43, 743–751. doi:10.13227/j.hjkx.202105213
Wang, J., Wang, K., Zhang, M., and Zhang, C. (2015). Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation cover in hilly Southern China. Ecol. Eng. 81, 451–461. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.04.022
Wang, J., Zhang, T., and Fu, B.-J. (2016). A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 67, 250–256. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.052
Wang, X., Wang, B., Xu, X., Liu, T., Duan, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2018). Spatial and temporal variations in surface soil moisture and vegetation cover in the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 95, 320–330. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.07.058
Wylie, B. K., Zhang, L., Bliss, N., Ji, L., Tieszen, L. L., and Jolly, W. M. (2008). Integrating modelling and remote sensing to identify ecosystem performance anomalies in the boreal forest, Yukon River Basin, Alaska. Int. J. Digital Earth 1, 196–220. doi:10.1080/17538940802038366
Yan, S. J., Wang, H., and Jiao, K. W. (2019). Spatiotemporal dynamics and quantitative attribution of vegetation in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Geo-Information Sci. 21, 767–780. doi:10.12082/dqxxkx.2019.180578
Zhang, K., Lü, Y., Yihe, F. B., et al. (2018). The effects of restoration on vegetation trends: spatiotemporal variability and influencing factors. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb., 1–9. doi:10.1017/S1755691018000518
Zhang, K., Lv, Y. H., Fu, B. J., Yin, L. C., and Yu, D. D. (2020). Impact of vegetation cover change on ecosystem services in the Loess Plateau and its threshold value. Acta Geogr. sin. 75, 949–960. doi:10.11821/dlxb202005005
Zhang, X., Yue, Y., Tong, X., Wang, K., Qi, X., Deng, C., et al. (2021). Eco-engineering controls vegetation trends in southwest China karst. Sci. Total Environ. 770, 145160. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145160
Zhang, Y. X., Li, X. B., and Chen, Y. H. (2003). A review of multi-scale remote sensing and field measurement methods for grassland vegetation coverage. Prog. Earth Sci., 85–93. doi:10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2003.01.0085
Zhao, L., Dai, A., and Dong, B. (2018). Changes in global vegetation activity and its driving factors during 1982–2013. Agric. For. Meteorology 249, 198–209. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.11.013
Zhao, S. Y., Gong, Z. N., and Liu, X. Y. (2015). Correlation analysis of vegetation coverage and drought conditions in North China from 2001 to 2013. Acta Geogr. Sin. 70, 717–729. doi:10.11821/dlxb201505004
Zhong, C., Peng, W. F., Zhang, L. F., Luo, Y., Dong, Y. B., and Wang, M. F. (2019). Spatial-temporal changes and driving forces of vegetation coverage in the upper reaches of the Minjiang River from 2006 to 2016. Acta Ecol. sin. 39, 1583–1594. doi:10.5846/stxb201805040993
Keywords: fractional vegetation cover, spatio-temporal variations, trend analysis, driving factors, erhai lake basin
Citation: Liu Z, Hu W, Ma L and Huang X (2024) Spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover and its influencing factors in highland lake basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1502208. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1502208
Received: 26 September 2024; Accepted: 06 November 2024;
Published: 28 November 2024.
Edited by:
Xulin Guo, University of Saskatchewan, CanadaReviewed by:
Muhammad Shahid, Brunel University London, United KingdomXiaoyan Song, Northwest A and F University, China
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Hu, Ma and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenxian Hu, eXVpZXJjb2ZlYkAxNjMuY29t; Xiaoxia Huang, aHh4X214eUAxMjYuY29t
 Zhoujiang Liu1
Zhoujiang Liu1 Wenxian Hu
Wenxian Hu