- 1State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute, Jinan, China
- 2State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company, Jinan, China
- 3Shandong Smart Grid Technology Innovation Center, Jinan, China
- 4Shandong University of Technology, Zibo, China
The uncoordinated integration of numerous distributed resources poses significant challenges to the safe and stable operation of distribution networks. To address the uncertainties associated with the intermittent output of distributed power sources, we propose a multi-objective planning strategy for distribution networks based on distributionally robust model predictive control (MPC). Initially, an error fuzzy set is established on a Wasserstein sphere using historical data to enhance out-of-sample performance. Next, a multi-objective optimization framework is constructed, balancing returns and risks, and is subsequently converted into a single-objective solution using value-at-risk conditions. This is followed by the implementation of multi-step rolling optimization within the model predictive control framework. We have linearized the proposed model using the linearized power flow method and conducted a thorough validation on an enhanced IEEE 37-node test system. Distributionally robust optimization (DRO) has been shown to reduce costs by a significant 29.16% when compared to an RO method. Moreover, the energy storage capacity required has been notably reduced by 33.33% on the 29-node system and by 20% on the 35-node system. These quantified results not only demonstrate the substantial economic efficiency gains but also the enhanced robustness of our proposed planning under the uncertainties associated with renewable energy integration.
1 Introduction
With the advancement of new power system construction, distribution networks are evolving toward source-network-load-storage integration and collaborative interaction (Castro et al., 2024). The integration of large-scale distributed photovoltaic (PV) systems with uncertain output transforms distribution networks from radial passive structures into multi-power structures. This shift complicates power flow management and significantly impacts operational characteristics, leading to increased planning challenges (Zhang et al., 2023a; Esfahani et al., 2024). Addressing the capacity and scientific management of distributed power supplies and energy storage devices has thus become a research hotspot.
Many scholars have explored distribution network planning (Wang et al., 2024a; de Lima et al., 2024). For example, Pan et al. (2023) propose a collaborative planning method for distribution network and multi-energy systems, balancing multi-agent interests and improving analysis and calculation efficiency. Chen et al. (2017) introduce a multi-objective programming model based on game theory, considering the interests of source-grid-load multi-agents in a power market environment and using a particle swarm optimization algorithm for iterative optimization. Wang et al. (2022) propose a framework that considers energy storage allocation and bi-level planning of the distribution network, and the results show that this framework achieves low carbon emissions and improved economics. Subbaramaiah and Sujatha (2023) propose a multi-objective distribution network planning scheme that reduces power losses and identifies optimal wind power locations. However, these studies do not account for the impact of intermittent distributed PV output, potentially overestimating the system’s risk resilience.
Scholars have increasingly recognized the pivotal role of energy storage in addressing the challenges of integrating high levels of renewable energy sources (Liu et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024). For instance, Zheng et al. (2023) introduce an optimization framework for energy storage allocation in distribution networks with a significant penetration of photovoltaic (PV) systems. This approach addresses the source-load imbalance and voltage regulation issues, thereby reducing power losses and operational costs. Another notable contribution is made by Zhang et al. (2024), who present a method for the concurrent optimization of battery storage configuration and distribution network operations. The study demonstrates that energy storage can effectively smooth power fluctuations and enhance the network’s resilience to fault disturbances. Through planning, the capacity of energy storage in the distribution network can increase the local consumption rate of renewable energy, reduce the system operating costs, and reduce the impact of PV uncertainty on the distribution network (Ba-swaimi et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024a). However, the above literature does not consider the risk assessment component in the energy storage configuration process.
Methods such as stochastic optimization, robust optimization, and distributionally robust optimization (DRO) are commonly used to address the uncertainty in high-proportion renewable energy predictions. Stochastic optimization assumes prediction errors follow specific probability distributions and uses manageable probability constraints (Wang et al., 2024b; Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024b). Robust optimization finds optimal solutions under worst-case scenarios, often resulting in overly conservative outcomes. DRO, on the other hand, uses real data to generate fuzzy sets and estimate distribution parameters, making it more suitable for complex, high-dimensional, multi-constraint problems (Skalyga et al., 2023). However, these constraints can turn the problem into a non-convex, nonlinear stochastic optimization challenge. Thus, a comprehensive approach that considers both economic benefits and operational safety is required. DRO focuses on establishing fuzzy sets with a flexible and diverse optimization framework. The Wasserstein distance, a measure of the difference between probability distributions, accurately describes similarities and differences by considering shape and weight information (Lu and Zhou, 2024).
Based on this analysis, the main contributions of this study are: (1) We consider energy storage capacity configuration and use a radius-controllable Wasserstein ball to construct a fuzzy set that achieves good out-of-sample performance, mitigating data overfitting and use distributed robust methods to balance robustness and economy. (2) Utilizing conditional value at risk (CVaR), we define optimization objectives for operation cost and constraint violation risk, transforming the multi-objective problem into a single-objective solution. (3) In order to reduce the error in PV forecasting, we implement rolling optimization within the model predictive control (MPC) framework.
2 Distributionally robust multi-objective model based on a Wasserstein sphere
2.1 Fuzzy set model based on a Wasserstein ball
Currently, there are two primary methods to model constraint distribution in distributionally robust optimization (DRO). One method involves moment-based fuzzy sets, such as unimodality (Zhang et al., 2021), symmetry (Wang et al., 2024c), and directional derivatives (Jiao et al., 2021), where fuzzy sets are defined as confidence intervals based on goodness-of-fit tests. The other method treats the fuzzy set as a ball in probability space, with the radius determined by metrics such as the Wasserstein metric, Kullback–Leibler divergence, and Prohorov metric.
Among these, the Wasserstein distance is particularly effective in measuring differences between two probability distributions. By considering both the shape and weight information of the distributions, it accurately captures the similarities and differences between them. In this paper, we construct fuzzy sets using the Wasserstein metric to achieve better out-of-sample performance and enhanced flexibility with radius control. Esfahani et al. (2024) demonstrated the effectiveness of data-driven Wasserstein metrics in solving distributed robust optimization re-representation problems. Inspired by this, our study employs the Wasserstein ball to construct fuzzy sets derived from limited prediction error data, thus achieving controllable data sets. Assuming the uncertainty set is a polyhedron, the prediction error
where
The Wasserstein metric quantifies the minimum “distance” required to morph one probability distribution into another. The fuzzy set is delineated by encompassing all distributions within a controllable Wasserstein radius centered on the uniform empirical distribution derived from the training dataset, like Equation 3.
where
2.2 System optimization objective
The optimization goal of the system is to seek the balance between the operation cost and risk of the distribution network. Therefore, the objective function includes the sum of the operating cost function
1) The operating cost function
where
where
where
where
where
2) The violation constraint risk function
The risk function
where
2.3 System constraints
2.3.1 PV output constraint
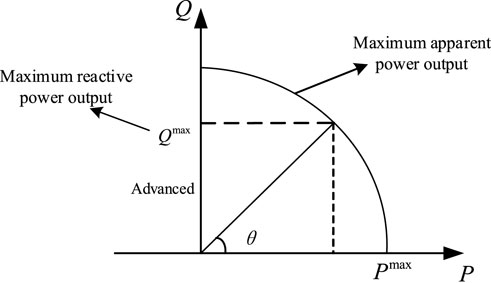
The distributed PV is connected to the distribution network through the inverter, and the relationship curve of the active and reactive power output characteristics is shown in Figure 1.
The relationship between the adjustable reactive power of the PV inverter on bus
The reactive power output is limited by the power factor angle
where the power factor angle
2.3.2 Energy storage constraints
where Equation 13 demonstrates the state-of-charge constraints for energy storage.
where
2.3.3 Distribution network model
Suppose that the distribution network with
where
where the superscript “*” represents the conjugate operation, and the complex power
3 Multi-objective planning based on DROMPC
3.1 Dynamic characteristics with MPC
Consider
where the state variable
Let the control domain be
where
3.2 Linearized approximate power flow
In this paper, the linearization method of literature (Alizadeh and Capitanescu, 2022) is used to linearize the power flow model shown in Equation 16. In a balanced, symmetrical distribution network, the common coupling point connected to the power grid is denoted as node 0, serving as the bus set that connects the load and the distributed generator.
The complex form of the node voltage is
where
The injection power presented in Equation 20 can be formulated as follows:
Assuming that
Ignoring the influence of the higher-order term
where
Given
Let
The voltage amplitude is approximately equal to
The voltage constraint is shown in Equation 27:
where
3.3 DROMPC for distribution network planning
In this paper, the device constraints and voltage constraints under different times and nodes can be summarized as follows:
where
Define an affine constraint set
where
where
Because the result is the maximum of two affine functions, the expression is convex in
The above multi-objective DRO is equivalently restated as a single-objective quadratic programming using the method of Lin et al. (2023). The objective is to minimize the total worst-case CVaR of the function and affine constraints. The specific form of the subproblem of MPC is as follows Equation 33:
where
4 Simulation and discussion
4.1 System description and parameter settings
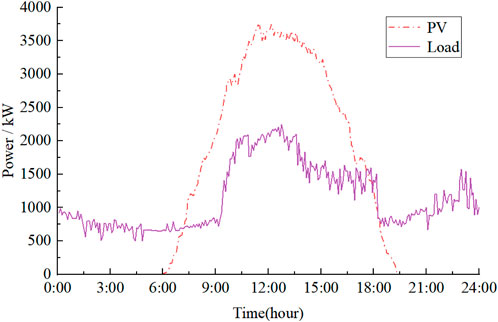
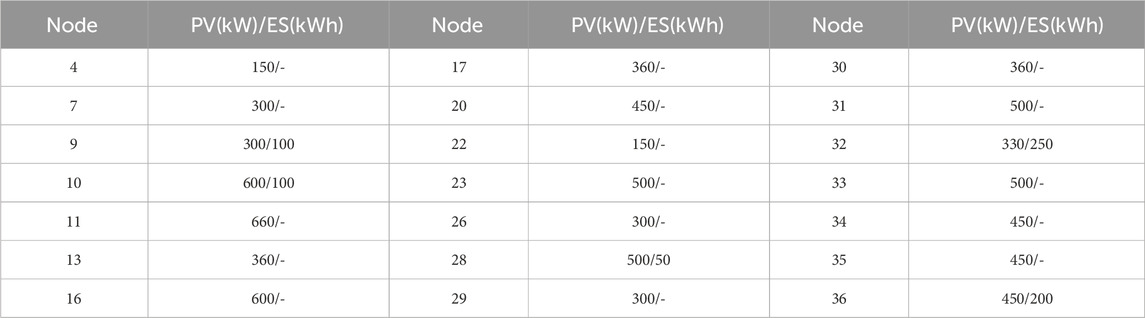
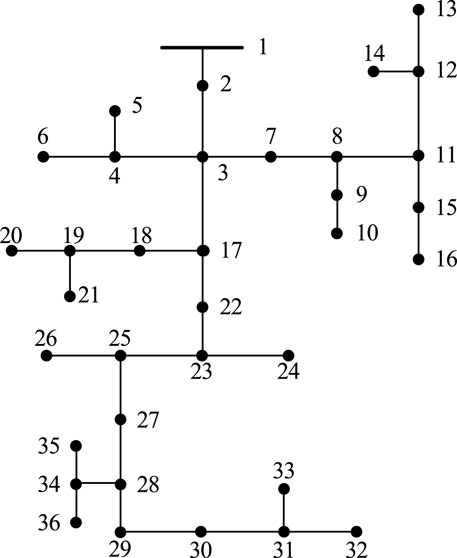
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed optimization framework, we conducted simulations using the improved IEEE 37-bus system, with network parameters derived from Reference Chen et al. (2023). The modified network is a single-phase equivalent network, as shown in Figure 2, and includes 21 PV inverters. Table 1 lists their positions and capacities. Figure 3 displays the total available PV power and total load demand throughout the day. The energy storage charge and discharge efficiency are set at 90%.
In this verification case, the upper and lower limits of voltage optimization are set to
4.2 Simulation results
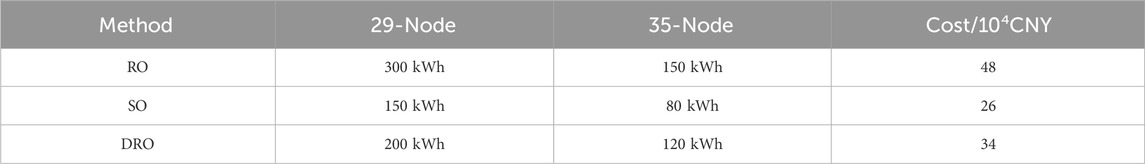
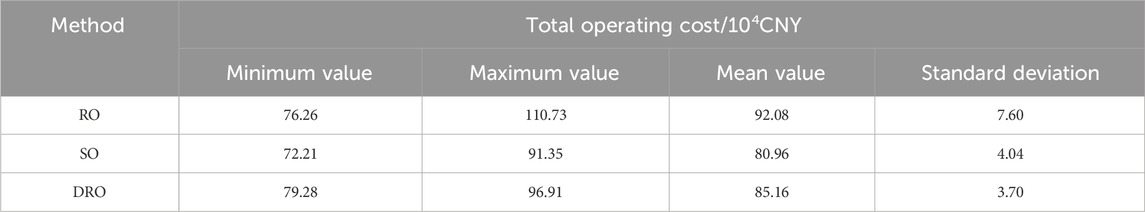
Table 3 now includes a comprehensive comparison of energy storage planning results using the DRO-based MPC method proposed in this paper, along with the RO and SO methods for the 29th and 35th nodes. The table provides specific numerical values for the energy storage configurations obtained through each method. Table 4 presents a detailed comparison of operating costs under various strategic planning methods. The table now includes exact figures for the maximum, mean, and standard deviation of total operating costs for each method.
The quantified results, as shown in Table 3, indicate that the use of the DRO method leads to a 29.16% reduction in cost compared to the RO method, with energy storage capacities reduced by 33.33% and 20% on the 29- and 35-node systems, respectively. Furthermore, Table 4 reveals that the DRO method achieves maximum, mean, and standard deviation values of total operating costs that are 12.5%, 0.75%, and 51.3% lower than those obtained using the RO method, respectively.
These improvements are attributed to the DRO method’s ability to utilize real data, offering more flexible and reliable planning support. This approach avoids the excessive conservatism and economic sacrifices associated with the RO method, which adopts a worst-case distribution strategy, and the SO method, which, despite using a preset probability distribution for energy storage capacity configuration, lacks adaptability in actual scheduling.
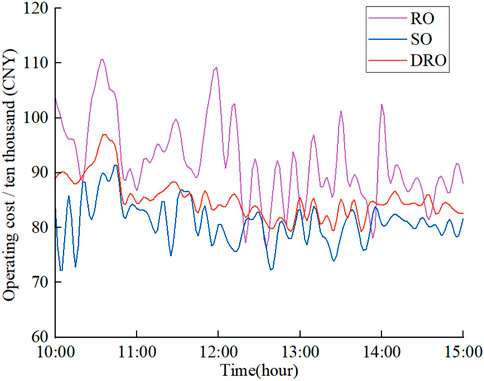
The SO, RO, and DRO methods are used for optimization under the same planning scheme. Figure 4 shows the system operation cost from 10:00 to 15:00 for each method. Table 3 presents the maximum, minimum, average, and standard deviation of the system operation costs under these different methods. The results indicate that the proposed method outperforms the traditional RO method in terms of operation cost and demonstrates better economic efficiency. Although the proposed method is less economical than the SO method, it has a smaller skewness, leading to smoother system operation under uncertainty.
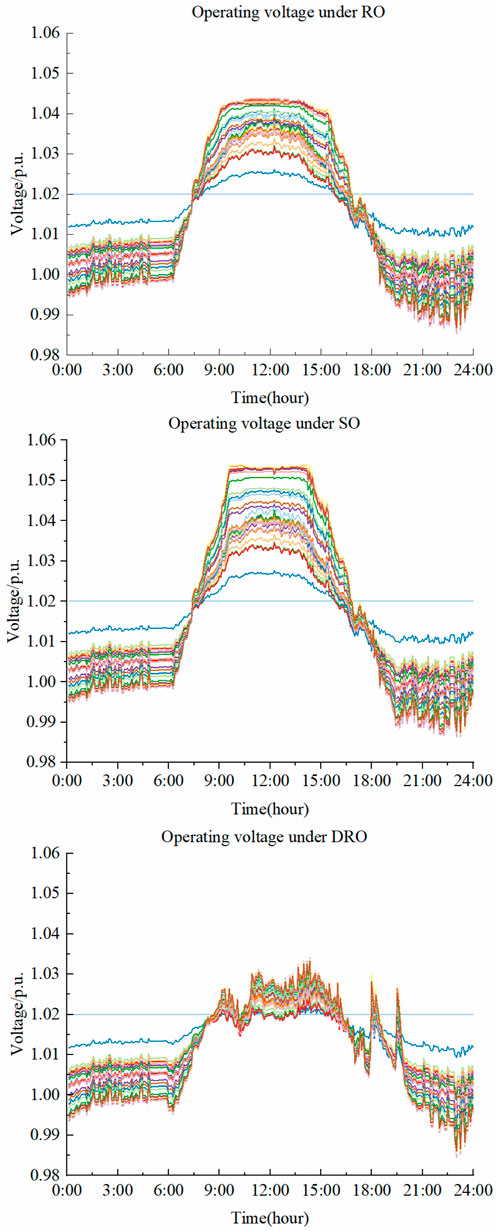
Figure 5 shows the operating voltages under the three planning strategies. It is evident that under the SO method, high uncertainty impacts lead to voltage limit violations due to excessive emphasis on economic factors, significantly reducing system robustness. The proposed method considers worst-case planning results by solving the distribution cluster containing the empirical distribution, aligning better with the modeling of uncertain outputs from different renewable energy sources, and thus offers stronger robustness than traditional stochastic optimization.
In summary, the DRO-based MPC method proposed in this paper effectively balances the relationship between economic efficiency and robustness. The proposed planning comprehensively addresses the probability of prediction errors. The average reduction in PV power achieved with this strategy is 645.510 kW, providing an effective control approach for managing significant deviations in PV predictions. Although ensuring voltage security and stability, the proposed strategy increases the average power reduction by 36.851%, thereby enhancing the distribution network’s robustness in handling the uncertainties associated with renewable energy predictions.
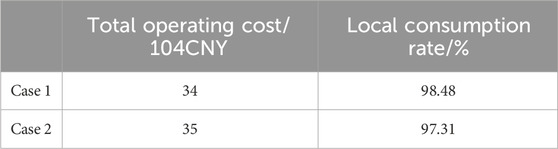
Table 5 presents a comparative analysis of system costs and PV consumption rates under two scenarios for the IEEE 37-node system. “Case 1” includes energy storage configuration, while “Case 2” does not. The data clearly show that including energy storage leads to a 2.85% reduction in system cost and a 1.2% increase in the PV in-situ consumption rate.
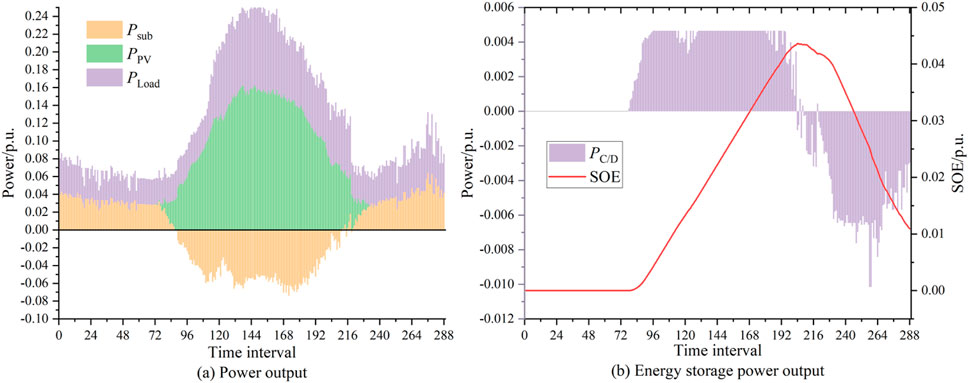
Figure 6A illustrates the purchased and sold power from the substation for the IEEE 37-node system. Figure 6B depicts the charging and discharging patterns of the energy storage system. These figures demonstrate how excess PV output is stored during periods of low demand and utilized during high demand, effectively performing peak-shaving and load-balancing functions that enhance the economic efficiency and reliability of the distribution network.
4.3 The influence of different Wasserstein spheres
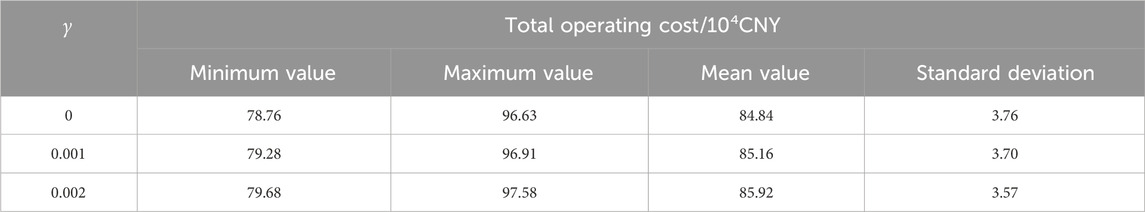
To illustrate the impact of the Wasserstein sphere radius on planning results, various radius values are used to compare the total operational costs. As shown in Table 6, increasing the radius of the Wasserstein sphere results in a broader coverage of uncertainties by the fuzzy set. This broader coverage leads to more conservative decision-making, which in turn raises operating costs but results in a smoother operational mode. Consequently, the proposed method allows for more flexible control of robustness and economic efficiency by adjusting the radius of the Wasserstein sphere.
5 Conclusion
This paper introduces a multi-objective planning approach for DRO power systems utilizing MPC to tackle the uncertainty challenges posed by high levels of renewable energy integration in distribution networks. The proposed method offers a flexible balance between economic efficiency and operational robustness. The key quantitative conclusions drawn from our analysis are:
(1) The DRO-MPC approach significantly mitigates the impact of uncertainty from large-scale distributed PV output on distribution network planning. It enhances economic efficiency and maintains system robustness, reducing costs by 29.16% compared to the RO method. Additionally, the energy storage capacity is optimized, resulting in a 33.33% reduction on the 29-node system and a 20% reduction on the 35-node system.
(2) By transforming the computationally intensive multi-objective problem into a streamlined single-objective solution, our method overcomes the limitations inherent in traditional multi-objective optimization approaches.
(3) The planning scheme’s adaptability is further enhanced by the variable radius of the Wasserstein sphere, allowing for greater flexibility and tailored responses to different operational scenarios.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YL: conceptualization, funding acquisition, and writing–original draft. KL: investigation, methodology, and writing–original draft. RF: investigation, methodology, and writing–original draft. JC: conceptualization, supervision, and writing–review and editing. YZ: supervision and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors YL and KL, were employed by State Grid Shandong Electric Power Research Institute and State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that this study received funding from the State Grid Shandong Electric Power Company Technology Project on Renewable Energy Dominated Regional Power Grid Islanding Mechanism and High Reliability Control and Protection Technology (No. 52062623S034). The funder had the following involvement in the study: design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, and the writing of this article.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alizadeh, M. I., and Capitanescu, F. (2022). A tractable linearization-based approximated solution methodology to stochastic multi-period AC security-constrained optimal power flow. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 38 (6), 5896–5908. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2022.3220283
Ba-swaimi, S., Verayiah, R., Ramachandaramurthy, V. K., and Alahmad, A. K. (2024). Long-term optimal planning of distributed generations and battery energy storage systems towards high integration of green energy considering uncertainty and demand response program. J. Energy Storage 100, 113562. doi:10.1016/j.est.2024.113562
Castro, F., Canizes, B., Soares, J., Almeida, J., and Vale, Z. (2024). Comprehensive framework for distribution network multi-investment expansion planning: emissions, uncertainty, and resource remuneration integration. Energy Convers. Manag. 316, 118734. doi:10.1016/j.enconman.2024.118734
Chen, H., Gao, P., Liu, K., Chen, L., and Huang, W. (2024). Joint expansion planning for data centers and distribution networks based on conditional value-at-risk theory considering low carbon characteristics. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 229, 110162. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2024.110162
Chen, J., Zheng, J., Wu, P., Zhang, L., and Wu, Q. (2017). Dynamic particle swarm optimizer with escaping prey for solving constrained non-convex and piecewise optimization problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 86, 208–223. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2017.05.047
Chen, Y., Jacob, R. A., Gel, Y. R., Zhang, J., and Poor, H. V. (2023). Learning power grid outages with higher-order topological neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 39 (1), 720–732. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2023.3266956
de Lima, T. D., Lezama, F., Soares, J., Franco, J. F., and Vale, Z. (2024). Modern distribution system expansion planning considering new market designs: review and future directions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 202, 114709. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2024.114709
Dong, G., Zhu, Z., Lou, Y., Yu, J., Wu, L., and Wei, J. (2024). Optimal charging of lithium-ion battery using distributionally robust model predictive control with Wasserstein metric. IEEE Trans. Industrial Inf. 20 (5), 7630–7640. doi:10.1109/tii.2024.3363079
Esfahani, M., Alizadeh, A., Amjady, N., and Kamwa, I. (2024). A distributed VPP-integrated co-optimization framework for energy scheduling, frequency regulation, and voltage support using data-driven distributionally robust optimization with Wasserstein metric. Appl. Energy 361, 122883. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.122883
Fan, W., Tan, Z., Li, F., Zhang, A., Ju, L., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). A two-stage optimal scheduling model of integrated energy system based on CVaR theory implementing integrated demand response. Energy 263, 125783. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.125783
Jiao, P. H., Chen, J. J., Cai, X., Wang, L., Zhao, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). Joint active and reactive for allocation of renewable energy and energy storage under uncertain coupling. Appl. Energy 302, 117582. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117582
Li, J. Y., Chen, J. J., Wang, Y. X., and Chen, W. (2024b). Combining multi-step reconfiguration with many-objective reduction as iterative bi-level scheduling for stochastic distribution network. Energy 290, 130198. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.130198
Li, Z., Pu, H., and Li, T. (2024a). Knowledge mapping and evolutionary analysis of energy storage resource management under renewable energy uncertainty: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Energy Res. 12, 1394318. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2024.1394318
Lin, Z., Wu, Q., Chen, H., Ji, T., Xu, Y., and Sun, H. (2023). Scenarios-oriented distributionally robust optimization for energy and reserve scheduling. Ieee Trans. Power Syst. 38 (3), 2943–2946. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2023.3244018
Liu, J., Chen, J., Yan, G., Chen, W., and Xu, B. (2023). Clustering and dynamic recognition based auto-reservoir neural network: a wait-and-see approach for short-term park power load forecasting. Iscience 26 (8), 107456. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.107456
Lu, X., and Zhou, K. (2024). A distributionally robust optimization approach for optimal load dispatch of energy hub considering multiple energy storage units and demand response programs. J. Energy Storage 78, 110085. doi:10.1016/j.est.2023.110085
Ma, S., Liu, L., and Cheng, H. (2024). Power generation–network–load–energy storage co-planning under uncertainty. Front. Energy Res. 12, 1355047. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2024.1355047
Pan, Y., Zhu, M., Lv, Y., Yang, Y., Liang, Y., Yin, R., et al. (2023). Building energy simulation and its application for building performance optimization: a review of methods, tools, and case studies. Adv. Appl. Energy 10, 100135. doi:10.1016/j.adapen.2023.100135
Ren, C., Wei, Z., Zhou, Y., Chen, S., Han, H., Sun, G., et al. (2024). Distributionally robust CVaR optimization for resilient distribution system planning with consideration for long-term and short-term uncertainties. Reliab. Eng. & Syst. Saf. 251, 110378. doi:10.1016/j.ress.2024.110378
Skalyga, M., Amelin, M., Wu, Q., and Söder, L. (2023). Distributionally robust day-ahead combined heat and power plants scheduling with Wasserstein Metric. Energy 269, 126793. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2023.126793
Subbaramaiah, K., and Sujatha, P. (2023). Optimal DG unit placement in distribution networks by multi-objective whale optimization algorithm & its techno-economic analysis. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 214, 108869. doi:10.1016/j.epsr.2022.108869
Wang, C., Liu, C., Chen, J., and Zhang, G. (2024a). Cooperative planning of renewable energy generation and multi-timescale flexible resources in active distribution networks. Appl. Energy 356, 122429. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122429
Wang, D., Zhang, C., Li, J., Zhu, L., Zhou, B., Zhou, Q., et al. (2024b). A novel interval power flow method based on hybrid box-ellipsoid uncertain sets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 39 (4), 6111–6114. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2024.3391921
Wang, H., Shen, X., and Liu, J. (2022). Planning of new distribution network considering green power certificate trading and carbon emissions trading. Energies 15 (7), 2435. doi:10.3390/en15072435
Wang, Y. X., Chen, J. J., Zhao, Y. L., and Xu, B. (2024c). Incorporate robust optimization and demand defense for optimal planning of shared rental energy storage in multi-user industrial park. Energy 301, 131721. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.131721
Zhang, C., Liu, Q., Zhou, B., Chung, C. Y., Li, J., Zhu, L., et al. (2022). A central limit theorem-based method for DC and AC power flow analysis under interval uncertainty of renewable power generation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 14 (1), 563–575. doi:10.1109/tste.2022.3220567
Zhang, H., Wang, J., Zhao, X., and Yang, J. (2023b). Risk-assessment of carbon-dioxide recycling in a gas-fired power plant using CVaR-based convex optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 416, 137898. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137898
Zhang, Q., Guo, Y., Wang, Z., and Bu, F. (2021). Distributed optimal conservation voltage reduction in integrated primary-secondary distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 12 (5), 3889–3900. doi:10.1109/tsg.2021.3088010
Zhang, Q., Yan, J., Gao, H. O., and You, F. (2023a). A systematic review on power systems planning and operations management with grid integration of transportation electrification at scale. Adv. Appl. Energy 11, 100147. doi:10.1016/j.adapen.2023.100147
Zhang, Y. Q., Chen, J. J., Wang, Y. X., and Feng, L. (2024). Enhancing resilience of agricultural microgrid through electricity–heat–water based multi-energy hub considering irradiation intensity uncertainty. Renew. Energy 220, 119739. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2023.119739
Keywords: distributionally robust optimization, model predictive control, uncertainty, distribution network planning, distributed resources
Citation: Li Y, Li K, Fan R, Chen J and Zhao Y (2024) Multi-objective planning of distribution network based on distributionally robust model predictive control. Front. Energy Res. 12:1478040. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1478040
Received: 09 August 2024; Accepted: 01 October 2024;
Published: 06 November 2024.
Edited by:
Cong Zhang, Hunan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yang Liu, South China University of Technology, ChinaZhenjia Lin, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Fan, Chen and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiajia Chen, ampjaGVuQHNkdXQuZWR1LmNu
 Yudun Li1,2
Yudun Li1,2 Jiajia Chen
Jiajia Chen