- 1Central China branch of State Grid Co., Ltd. Central China Power Dispatching and Control Center of State Grid, Beijing, China
- 2Beijing Kedong Electric Power Control System Co., Ltd., Beijing, China
A matching method based on a hybrid neural network is proposed to improve the accuracy of online matching for a power grid fault handling plan. First, the ERNIE 3.0 encoding and double-pointer decoding module are used to replace the generative model in the universal information extraction (UIE) framework, and the mapping relationship between entities and entity labels of the fault handling plan is trained by adjusting the hyperparameters of the UIE framework. Then, the semantic distance between the fault equipment, fault type, fault phenomenon, and the entity of the fault handling plan is calculated based on the residual vector-embedding vector-encoded vector (RE2). The hybrid neural network model for power grid fault handling plan matching is established. Finally, by verifying the fault-related data of a regional power grid, the proposed fault handling plan matching method shows higher matching accuracy and stronger generalization ability than other algorithms. The average precision rate, recall rate, and F1 value of the built fault handling plan matching model are 97.61%, 98.24%, and 97.91%, respectively, which can support auxiliary decisions for timely and rapid treatment of power grid faults.
1 Introduction
The operation characteristics and control mode of new power systems are highly complex, the number of monitoring objects is growing geometrically, and the high discreteness and uncertainty put forward higher requirements for fault handling (Guo et al., 2021; Mingjie et al., 2020; Junbo et al., 2023). A power grid fault handling plan is needed to deal with emergencies and abnormal faults. Such a plan can provide workers with an emergency fault handling and recovery strategy. At present, the fault handling plan of the power grid exists in the form of unstructured text, which mainly relies on manual searching and matching when applying the fault handling plan. Because the power grid fault handling plan has not been computerized and objectified, it is difficult to correlate and map with the real-time model and operation information of the power grid, meaning that current plans cannot be directly used to assist decision-making in fault handling (Jianming et al., 2020; Huaiwei et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2021a). Therefore, it is urgent to study the electronic and online matching methods of power grid fault handling plans to improve the online application and response capabilities of power grid fault handling plans.
Named entity recognition and text similarity calculation are keys to matching (Kai et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2021). Traditional named entity recognition and text similarity calculations mostly adopt rules, statistics, machine learning, and other modeling methods. Wei et al. (2023) use the bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT)-whitening linear transformation method to optimize the sentence vector of the BERT and use the multi-view recurrent neural network to perform two-way interactive calculation of the BERT dynamic word vector at different positions of the two sentences. Zheng et al. (2021) improve the model structure of a lexical semantic feature-based skip convolutional neural network, apply it to matching dispatching texts and knowledge graph entities, and reach a high level of overall accuracy of entity linking. Shao et al. (2020) implement the dependency-syntax-tree construction of actual defect texts and standard defect classification texts from power equipment and propose a method of pruning, segmentation, and reconstruction of the power equipment dependency syntax tree using the characteristics of the defect text. Their proposed method has improved efficiency and accuracy.
Rule-based recognition methods must manually define many recognition dictionaries and extract templates. When the text changes, any rules that require time to compile will also fail, resulting in high labor costs, low flexibility, poor generalization ability, and other problems. The entity recognition and text similarity matching methods based on statistics and machine learning make it difficult to identify the complex and changeable semantic features of the fault handling plans due to the simple structure of the algorithm and the limited samples. Huang et al. (2024) propose a fast and effective lightweight method based on a text clustering topic model, which does not rely on external background knowledge and can match the similarity of general texts. Although it avoids the limitations of specific fields in general application scenarios, it is limited to a single English text, which does not prove the feasibility of complex and changeable multi-language scenarios. Wang et al. (2021b) solve certain statistical inference problems and study pre-given domain knowledge to improve the accuracy of entity relation extraction in unstructured text. However, a high-performance and scalable learning inference engine has not been introduced, and the method cannot support the fast operation of more machine learning and even deep learning algorithms.
Compared with rules and machine learning methods, deep learning can understand the interdependence between language sequences at a deeper level and better represent the relationship between key features and various event elements. Dong et al. (2023) propose a knowledge graph construction method for the intelligent retrieval of power grid dispatching and control information and verify that the proposed method has high recognition accuracy and can support intelligent retrieval of regulatory information in different scenarios. Jun et al. (2023) propose a semantic analysis model of power equipment text based on a super large-scale pre-training method (Power BERT), adopt the multi-head attention mechanism and multi-layer embedded semantic expression structure, and implement understanding and analysis of the information contained in the power text. Tian et al. (2020) propose a method for analyzing power grid equipment defects based on a BERT pre-trained language model and classify the fault locations of power grid equipment. Zhang and Degen (2021) propose an event trigger word extraction model based on the fusion of the event argument attention and encoder layers that can effectively use the event element information and improve the performance of trigger extraction.
With the development of deep learning and high-performance computing technology, natural language processing (NLP) technology has made a qualitative leap, and gratifying progress has been made in named entity recognition and text similarity matching. On named entity recognition, Yu et al. (2020) use a word2vec model to transform scheduling procedures into word vectors and use attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory and conditional random field (BiLSTM-CRF) to identify operating rules and entity knowledge of fault handling process, supporting the construction of a power grid fault handling knowledge base. Tong et al. (2020) use a Skip-gram model to achieve vector-quantization of power scheduling text, realize pattern clustering and semantic understanding of power statements based on a hierarchical clustering algorithm, and use regular expressions to identify important information in power outage plan text. Chen et al. (2021) propose a Power BERT pre-training model based on a training power corpus that converted transformer defect text into a word vector and established an entity recognition model based on BiLSTM-CRF to improve the entity recognition accuracy of transformer defect text. In text similarity matching, Yang et al. (2022) construct a text-matching algorithm based on convolutional neural network (CNN) and LSTM models by using the improved BERT pre-training language model to match similar fault cases, and the matching accuracy is higher. Bao et al. (2022) compare the application of the term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) algorithm and best matching 25 (BM25) algorithm in the recommendation system, verify the superiority of the BM25 algorithm, and propose an improvement plan for semantic generalization that has certain guiding significance for matching. Jianming et al. (2022) propose a power grid scheduling intent recognition method based on the fusion model of ALBERT and RE2 and realized scheduling intent classification through RE2 text similarity calculation. Bo et al. (2020) combine the characteristics of a power system, build a fault processing knowledge graph based on NLP technology, and carry out power grid fault disposal through online retrieval and matching. Based on the visual feature-enhanced long short-term memory model, Wenxuan et al. (2022) realize the automatic matching of fault phenomenon and power dispatching fault handling plan, which improves the fault handling response to a certain extent.
Research on power grid fault handling plan matching is scant. Due to the large differences in the text of fault handling plans in various fields and the large number of characters, the current studies do not extract key features in advance but directly use the text for matching, which greatly affects the matching time and accuracy between power grid fault events and a large number of plans. Therefore, this article first extracts the key features of the power grid fault handling plan, calculates the semantic similarity between the key features of the plan and the fault events, and improves the matching accuracy.
To realize the objectification and online intelligent matching of the fault handling plan, a matching method based on a hybrid neural network is proposed. First, based on a universal information extraction (UIE) framework, the entity recognition model of a power grid fault handling plan is constructed, and the plan is digitized and objectified. The semantic distance between fault event features and plan entities is then calculated based on the residual vector-embedding vector-encoded vector (RE2), leading to the construction of a hybrid neural network model for matching. Finally, it is verified using the fault-related data of a regional power grid.
2 Basic theory
2.1 Universal information extraction framework
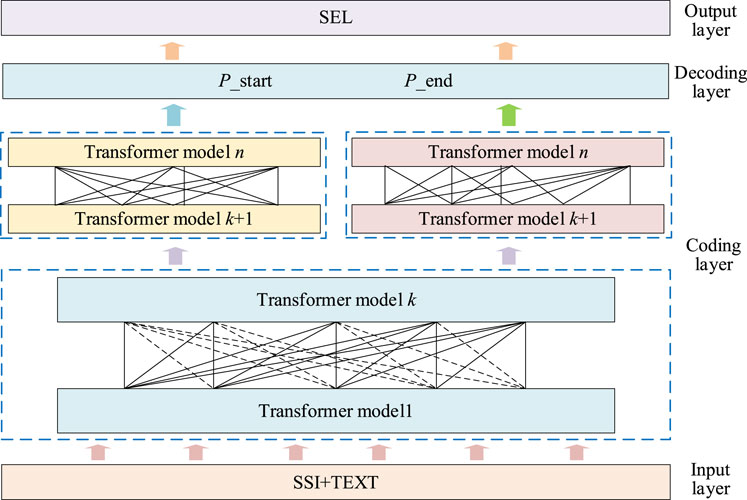
The UIE framework models the information extraction task as a text-to-structure transformation (Lu et al., 2022). It can identify and structure specific information from unstructured text. The UIE framework uses structural extraction language (SEL) and encodes the extraction structure of different tasks into a unified representation, identifying the extraction target adaptively through structural schema instructor (SSI) based on the prompt mechanism. Based on the domain knowledge and terminology characteristics of power grid dispatching, the structural schema instructor captures the structural characteristics of specific fault entities. It determines the boundaries and categories of entities by analyzing their context information. It can automatically identify the entity of the dispatching object in the power grid fault disposal plan and assign the corresponding category label to the entity. Then, it aligns the input and output of the prediction model and obtains text features through a large-scale pre-training model that is combined with a double-pointer decoding module for information extraction. The overall architecture of the UIE framework is shown in Figure 1.
The structural schema instructor is designed as follows: First, the entity types in the fault disposal plan are determined, such as fault type, equipment name, processing principles, etc., and the patterns for different types of entities are designed, such as common description words and patterns for fault types. Then, the context in which the entity appears is considered, the context window is built, and the associated vocabulary of the entity is analyzed. Finally, the domain knowledge base (such as the processing manual) is integrated with the pattern guide to provide additional background information, and the designed pattern is iteratively optimized to adjust the design and improve the accuracy.
The double-pointer decoding module initializes two pointers. The starting pointer moves backward from the first word of the text and evaluates the possibility of each position as the starting position of the entity. The termination pointer moves forward from the last word of the text, evaluating the likelihood of each position as an entity termination position. The joint score is calculated by combining the context information, and the start and end positions with the highest scores are selected as the prediction results of the entity boundary.
UIE takes the defined structure extraction pattern and text sequence as input to generate a linearized output, as shown in Equation 1.
In the formula, s represents the defined structure extraction mode, x represents the input text, y represents the extracted and generated structured result, and ⊕ represents the connection symbol (Tong et al., 2020).
The overall input of UIE is shown in Equation 2.
where
After expanding the above content, the final input result of the model is shown in Equation 3.
where [spot] is the entity identifier of different categories and [text] indicates the text content to be added.
The UIE framework adopts a discriminative extraction model and takes the ERNIE 3.0 pre-training model as an encoder. The model learns the lexical, syntactic, and semantic information of the language by setting various pre-training tasks. Figure 1 shows the ERNIE 3.0 encoding layer, which consists of two layers of network structure. The lower layer is a general representation module that can capture the underlying basic features of natural language, and the upper layer is a task-specific representation module that can encode the features according to the adapted tasks. When the model is fine-tuned, the lower general representation module is fixed, and only the task-specific representation module is fine-tuned to improve the training efficiency.
For the general presentation module, Transformer-XL (Transformer with extra-long context) is used as the backbone network (Bonetta et al., 2021), and a memory loop mechanism is used to model the dependency of longer text sequences and enhance the learning of the relationship between the previous and subsequent text contents in long text sequences. The ability to capture the desired lexical and syntactic underlying language features is strengthened by setting the number of layers and parameters. The adjustable parameters during model training are set as follows: the number of hidden layers is 12, the dictionary size is 40,000, the number of attention heads is 12, the maximum sequence length is 2048, the number of neurons in the middle layer is 3,072, the number of neurons in the hidden layer is 768, the training period is 250 epochs, the maximum learning rate is 1 × 10−5, and the batch size is 32.
The presentation module also uses Transformer-XL as the backbone network for specific tasks but learns high-level semantic features based on different modes of tasks. An improved Transformer, Transformer-XL, solves the problems of context fragmentation and slow reasoning speed and improves the ability to capture long-term dependencies based on the fragment recursion mechanism. Transformer-XL provides input in the form of fixed-length fragments during training, which is characterized by the ability to cache the state of the previous fragment and then reuse the hidden layer state of the previous fragment when calculating the current segment. This gives Transformer-XL the ability to model longer-term dependencies.
Two consecutive fragments of length L are represented as
where SG (·) is a stop-gradient, indicating that this part does not participate in the backpropagation calculation;
In the decoding layer, double pointers P_start and P_end are connected to decode, and then the start and end positions of the entity are predicted. The entity prediction loss function is calculated shown in Equations 7–9.
In the above formula, cross-entropy represents the cross-entropy loss function, Lstart represents the loss value of the starting position, Pstart represents the predicted entity starting position, and Ystart represents the entity starting position. Lend represents the loss value of the end position, Pend represents the predicted entity end position, and Yend represents the end position of the entity. Lspan represents the entity loss value, pi,j represents the probability of predicting the entity, and yi,j represents the position of predicting the entity xi,j.
Finally, the decoded entity is generated in a structured format according to structural extraction language encoding, and the entity recognition result of the UIE framework is obtained.
2.2 RE2 model
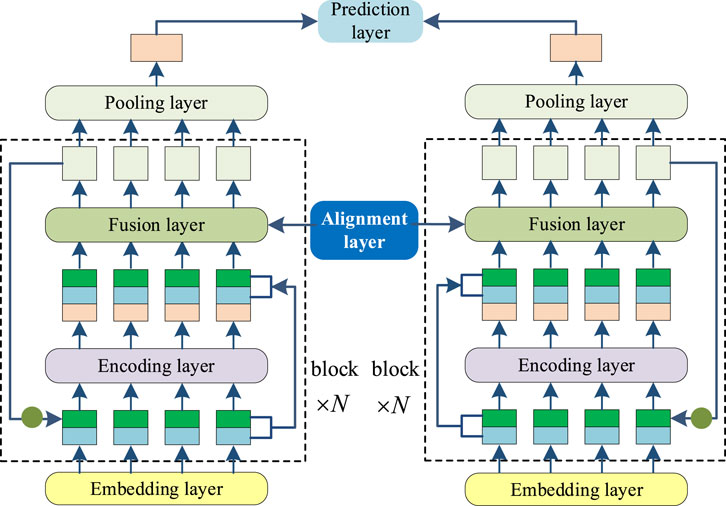
The RE2 model uses a fast and powerful neural network to match common text similarity. Compared with other text-matching models, the RE2 model considers three inter-sequence alignment features named the original point alignment feature, the previous alignment feature, and the context feature. In terms of data structure, the model fully integrates the residual vector, embedding vector, and encoded vector, which can significantly reduce the number of parameters and simplify reasoning and calculation. The model structure is shown in Figure 2.
The model consists of six parts, including an embedding layer, an encoding layer, an alignment layer, a fusion layer, a pooling layer, and a prediction layer, and is generally divided into an input layer, an intermediate processing layer, and an output layer. The part surrounded by the dotted lines in the figure is the intermediate processing layer, called the block, which is independently cycled N times. Three kinds of intermediate vectors are calculated by the RE2 model: embedding vectors (on behalf of original pointwise features, denoted by blue rectangles), residual vectors (on behalf of previous aligned features, denoted by green rectangles), and encoded vectors (on behalf of contextual features, denoted by orange color rectangles). The fault text is treated symmetrically in all layers except the prediction layer, and all parameters are shared between two sequences. The RE2 model has a left and right symmetrical structure.
In the RE2 model, N blocks are connected by enhanced residuals to input richer inter-sequence features into the alignment layer. First, the input of each block is spliced by the sum of the input of the initial embedding layer and the output of the first two blocks. Its mathematical definition is shown in Equations 10–12. Second, in each block, the alignment fusion layer is enhanced by the residual module; that is, the outputs of the first two layers, the embedding layer and the encoding layer, are spliced as inputs.
where o(n) is the output of the nth block, x(n) is the input of the nth block, xi(1) is the input of the first block, and oi(n−1) and oi(n−2) are the output of the (n-1)th and (n-2)th blocks, respectively.
The alignment layer aligns the location or token of the two faulty text sequences. That is, through a layer of feedforward neural network and then dot product operation, the similarity matrix of two sequences and output vectors
where a and b are input representations of the two sequences, respectively; eij is the similarity matrix of two vectors. F represents a single-layer feedforward network, the dot product operation function.
The fusion layer fuses the input and output vectors of the alignment layer through three strategies: direct concatenation, combined subtraction concatenation, and combined matrix dot multiplication concatenation and aggregates the information of the two text sequences at the same time. The mathematical definition is shown in Equation 18.
In the formula, G1, G2, G3, and G represent the single-layer feedforward network with independent parameters corresponding to the four operations of direct splicing, combined subtraction, combined matrix dot multiplication, and fusion splicing, respectively.
The output of the last block in the fusion layer is taken as the input of the pooling layer. After dimensionality reduction, two sequence vectors v1 and v2 are outputted and then input into the prediction layer. The results of text matching are predicted after multi-layer feedforward network H. A detailed and simplified representation of the prediction layer is shown in the Equations 19–20.
where
3 The matching method of a power grid fault handling plan based on a hybrid neural network
3.1 The structure and implementation process of a hybrid neural network
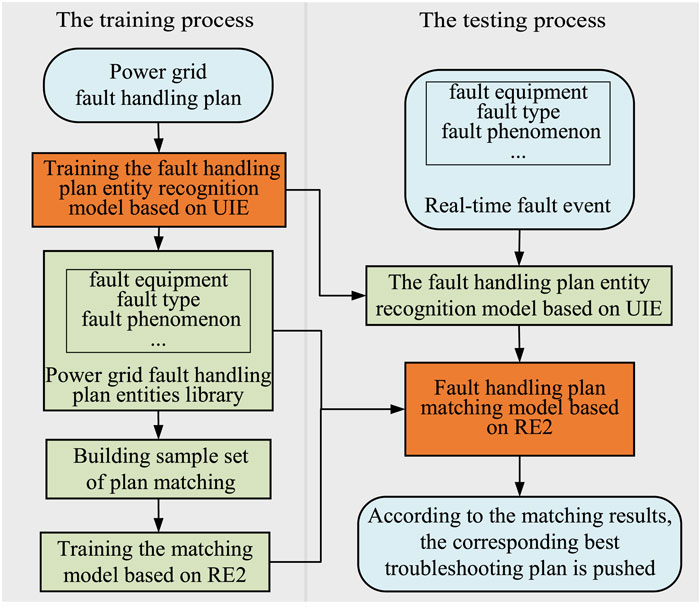
Modeling the entire text of the power grid fault handling plan would consume much computing time during the match processes, and any invalid information in the plan will also affect the matching effect. Therefore, when establishing the matching model, it is necessary to first identify the entity of the fault handling plan and extract the key features of each plan. The similarity calculation between the key features and the power grid fault events can both reduce the matching time and improve the matching accuracy. In order to solve the above problems, a matching model of the fault handling plan based on the UIE-RE2 hybrid neural network is built; each type of entity key feature of the fault handling plan is extracted through the UIE entity recognition model, which sifts out the useless interference information. The RE2 text similarity meter model is used to calculate the semantic similarity distance between the fault event and each type of entity key features of the fault handling plan. Based on the above principle, the effective information semantics can be calculated in a maximized manner. The model training time can be reduced by extracting and calculating the optimal features, and the matching accuracy of the troubleshooting plan can be improved. The matching process is shown in the following figure.
In the training stage, the marked power grid fault handling plan is first used as the input of the UIE framework. The entity recognition model is established by fine-tuning the model parameters, and entities such as fault equipment, fault type, and fault phenomenon are extracted. Then, the plan matching sample set is built based on the plan’s entities library, and the sample set is trained based on the RE2 network to establish the text similarity calculation model between the fault handling plan and the fault event.
In the test stage of the model, the occurrence of power grid fault events and the key feature entities of the power grid fault handling plan are simultaneously input into the trained RE2 model, and the similarity value between the text of each plan and the text of the real-time fault event is calculated and ranked according to the high and low scores. This ranking allows the best troubleshooting plan to be matched and sent to the requester. The basic principle of the UIE-RE2 model and the specific implementation of the proposed method are described below. The process of matching model of power grid fault handling plan is shown in the Figure 3.
3.2 Entity recognition of fault handling plan based on UIE
Aiming at the problem of low accuracy of structured extraction caused by the differentiation of fault disposal plans in different regions, this article proposes an entity and event recognition method for fault disposal plans based on the UIE framework and improves the internal structure of the UIE framework. The original UIE framework uses the text-to-text transfer transformer (T5) generative model, which is more suitable for wide-area general entity extraction tasks. ERNIE 3.0 coding and the double-pointer decoding module replace the T5 model in the original framework, and the problem of entity nested recognition difficulty in the power grid fault plan data is specifically improved.
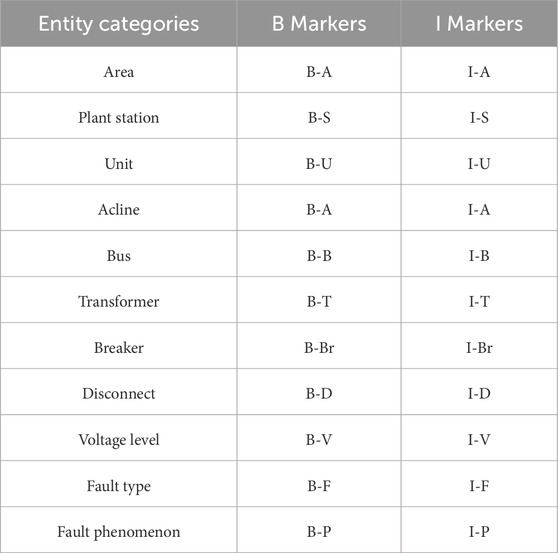
The event logic of a power grid fault handling plan is complex, the forms of expression are diverse, and there are many types of entities. It is difficult to effectively identify the entity elements of the event based on rules. An entity recognition model based on deep learning is an effective method of extracting the entity of the power grid fault handling plan. In this article, the key features of each plan are defined as fault equipment, fault type, and fault phenomenon, and the entity types include area, station, unit, acline, bus, transformer, breaker, disconnect, voltage, fault type, and fault phenomenon. The BIO labeling specification is used to tag the 11 types of entities of the power grid fault handling plan, and the entity labeling labels are generated, as shown in Table 1.
The entity recognition model is trained by taking the plan label dataset as input and the structured entity of the plan as output. The ERNIE3.0 model is used as the encoding network of the UIE framework. During training, the model’s parameters are fine-tuned by adding a professional corpus of fault handling plans, iteratively learning the text data and label representation in the standard fault handling plan dataset, optimizing the parameters of the hidden layer in the ERNIE3.0 network, and realizing the encoding representation of professional power terms in the text of contingency plan. The double-pointer decoding module is connected to predict the start position and the end position of the entity. The entity recognition, fault type, and fault phenomenon are realized through Softmax and argmax functions.
During model training, the adjustable parameters are set as follows: a training period of 250, a maximum learning rate of 1e−5, a batch size of 32, an increment random inactivation ratio of the attention network of 0.1, the activation function of the hidden Gaussian error limit unit (GELU) layer, the inactivation ratio of hidden layer network of 0.1, the number of hidden layer neurons of 768, the standard deviation of 0.02, the number of intermediate layer neurons is 3,072, the number of attention heads is 12, the number of Transformer layers is 12, the activation function of pool layer is tanh, and the size of dictionary is 4,000. The initial parameters of the pre-trained ERNIE 3.0 model are fine-tuned. It inherits the deep learning of the ERNIE 3.0 model on the massive corpus and, at the same time, deepens the understanding of the model of the professional language of the power grid fault handling plan, which reduces the time-consuming searching for optimization of the initial parameters of the training model and improves the entity recognition accuracy of the model.
3.3 Power grid fault handling plan matching based on RE2
The key characteristic information of the power grid fault handling plan, such as fault equipment, fault type, and fault phenomena, is extracted from the entity recognition results and stored as an entity library. The original plans are parsed into the corresponding entity’s semantic information. At the same time, combined with manual local corrections, the plan matching sample set is constructed. The sample set is trained based on the RE2 algorithm, and the matching model is established. The matching and pushing of the power grid fault handling plan are realized based on the trained model. The training process of the RE2 model is as follows:
First, the fault events and the fault handling plans are simultaneously input into the RE2 model, denoted as Text1 and Text2, respectively, and transformed into an embedding vector, a residual vector after vector encoding in the embedding layer, with both vectors having a dimension of 300. Then, the N blocks connected in an augmented residual manner are semantically computed, the similarity between the two sequences is computed using the dot product method, and the output of the last block is used as input to the pooling layer. Finally, the dimensionality-reduced sequence vectors are input to the prediction layer, and the similarity score Ck of the fault handling plan is output after computation by the multi-layer feedforward network.
The parameters of the model are as follows: the number of hidden layer neurons is 150, the size of the convolution kernel is 3, the number of intermediate processing layers is 2, the number of encoding layers is 2, the alignment between sequences is linear, the mode of vector fusion is full, the interlayer connection is aug, the optimizer is Adam, and the number of output categories is 2. The hyperparameters of the training process are: the batch size is 32, the number of training rounds is 200, the initial learning rate is
4 Example analysis
4.1 Research target
Using the relevant data from a regional power grid in China as the research target, a large number of power grid fault handling plans and historical fault cases were obtained. The BIO labeling specification was used to mark the plans, and 5,348 entities were generated. The entities were divided into 3,744 training samples, 1,070 validation samples, and 534 test samples in an 8:1:1 ratio. At the same time, the plan sample set is constructed according to the entities and the historical fault cases. Considering that there are few actual faults in the power grid, this article enhances the fault events to create many usable samples. When constructing the matching sample set, the identified plan entities and power grid fault events must be rewritten into phrases with the same syntax structure, such as fault device-fault type-cause-fault phenomenon. Using the above methods, 6,448 matching text pairs of power grid fault handling plans are constructed. With a ratio of 8:1:1, all matching text pairs were divided into 3,224 training samples, 2,257 validation samples, and 967 test samples.
4.2 Evaluation index of the model
The precision rate (P), recall rate (R), and comprehensive evaluation index (F1 value) were used to evaluate the accuracy of entity recognition and text matching. Entity recognition of a fault handling plan is a multi-classification task, so the macro average method is used to calculate the values of each evaluation index. The time taken to match a single plan (T) was used to measure the speed of text matching. The calculation expressions of each index are shown in Equations 21–23.
where P is the precision rate; R is the recall rate; F1 is the comprehensive evaluation index; TP is the number of correct samples predicted; FP indicates the number of samples that were incorrectly predicted to the class; FN indicates the number of samples in which the text of that class was incorrectly predicted to other categories.
4.3 Analysis of model effect
The training set and validation set samples were trained based on the UIE framework, and 534 test set samples were used to verify the recognition effect of the entity recognition model. The average precision rate, recall rate, and F1 value of the entity recognition model were 96.57%, 97.12%, and 96.84%, respectively. For the test samples, the recognition effect of the model on 11 types of entities in the plan was higher than 95%, and the model shows strong generation ability. The precision rate can reach 100% for some entities with obvious characteristics that are not easily confused with other types of entities. The average precision rate, recall rate, and F1 value of the entity recognition model were 96.15%, 96.44%, and 96.29%, respectively. The overall effect is significant, indicating that the framework proposed in this article is suitable for entity information extraction of fault handling plans.
The entity recognition effect of the power grid fault handling plan based on the UIE framework is further analyzed. This method extracts entities based on the prompt mechanism, which is more conducive to acquiring effective features in the text content of the plan. In addition, the UIE framework in this article takes entity recognition as a discriminative extraction task to predict the starting and ending positions of entities. The model decodes the number of entity categories contained in the input content several times, extracting one category of entities each time. Although this operation increases the times of entity recognition to a certain extent, it can avoid the phenomenon that the general sequence annotation model cannot represent the entity nesting problem well. Second, the internal improvement of the text UIE framework uses the ERNIE3.0 large model, and its nested multi-layer Transformer-XL also enables it to capture text features well. For the above reasons, the UIE framework proposed in the article has achieved excellent results in entity recognition.
The text-matching set is trained based on the RE2 algorithm, and 967 test samples are used to verify the effect of the text-matching model. The average precision rate, recall rate, and F1 value of the RE2 algorithm for the training samples are 97.61%, 98.24%, and 97.91%, respectively. For the test samples, the average precision rate, recall rate, and F1 value of this model are 97.55%, 98.07%, and 97.81%, respectively. On the one hand, the plan matching model based on the targeted plan can reduce the long segment plan calculation time and improve the training speed of the model. On the other hand, the targeted fault handling plan has filtered out most of the interference information, which helps to improve the accuracy of plan matching.
4.4 Comparative analysis of models
To verify the effect of the proposed entity recognition model based on UIE on the subsequent plan matching, the UIE-RE2 model is compared with the RE2 model. The content of this part mainly compares the different matching effects of plan matching after plan parsing and the direct plan matching method. Furthermore, this section focuses on measuring the impact of plan parsing on the matching performance improvement of the UIE-RE2 model. The UIE-RE2 and RE2 models are trained on the plan matching sample set in this section. Then, two models are tested using 967 test samples. The test results are shown in Table 2.
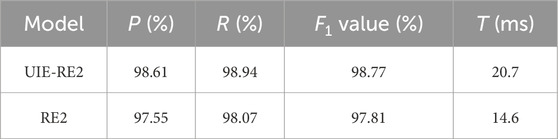
As shown in Table 2, the F1 value of the comprehensive evaluation index of plan matching of the UIE-RE2 model proposed in this article reaches 98.27%, which is 0.46% higher than the F1 value of the RE2 model that directly matches without plan parsing. It shows that the UIE model learns the lexical, syntactic, and semantic information of the language by setting various pre-training tasks, and it can generate entities in structured format according to structural extraction language encoding. The invalid information in plans can be removed through the above methods. The object-oriented plans are obtained, which is equivalent to the semantic enhancement of the plan text. A higher-quality plan matching sample set is constructed on this basis so that the UIE-RE2 model can achieve more accurate plan matching. The average time for matching a single plan of the UIE-RE2 model is 20.7 ms, which is slower than that of the RE2 model, and T is 6.1 ms higher. It shows that the UIE model takes the ERNIE 3.0 pre-training model as the encoder. During training, fine-tuning of model parameters is computationally intensive and requires more time and computing resources. After the model is trained, when using the trained model for entity recognition of fault handling plan, the speed is very fast, on the ms level, and has little impact on the efficiency of the overall model for plan matching.
In order to verify the matching effect of the proposed matching model based on RE2, it was compared with the matching model based on TF-IDF and BM25. This section mainly compares the performance of different text similarity calculation models. The above models are built on the entity recognition model based on the UIE framework to match the plan with real-time power grid fault events. The results of running 967 test samples to test the above three models are shown in Table 3.
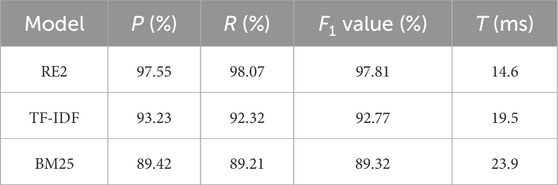
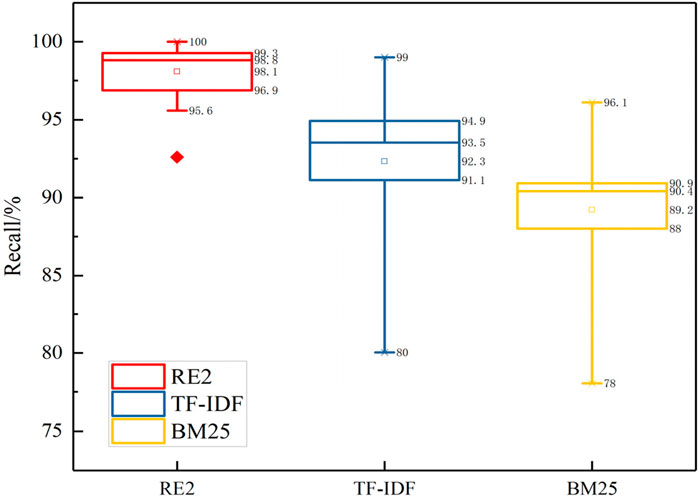
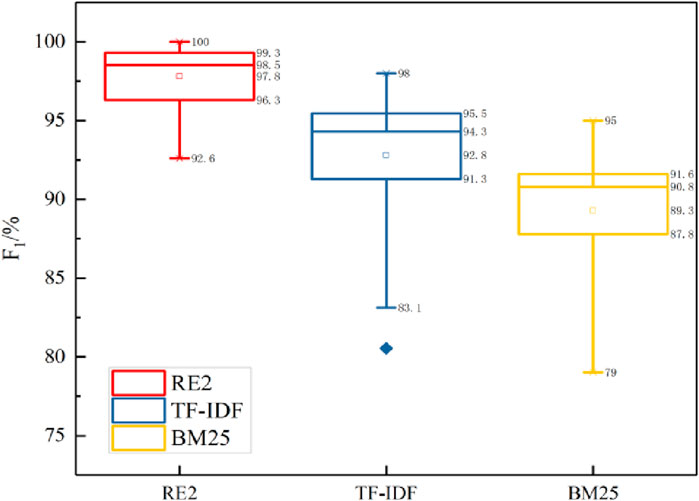
According to the data in Table 3, the F1 value of the comprehensive evaluation index of the RE2 model is 97.81%, which is significantly better than that of the TF-IDF and BM25 models, and the F1 value is 5.04% and 8.49% higher, respectively. It shows that the RE2 model can extract semantic features of power grid fault handling plans more effectively by using a deep neural network, learning the differences among different plans, and is more suitable for dealing with complex syntax nested plans. The average time for matching a single plan of the RE2 model is 14.6 ms, which is significantly faster than that of the TF-IDF and BM25 models, and T is 4.9 ms and 9.3 ms lower, respectively. It shows that the RE2 model fully integrates the original point alignment features, previous alignment features, and contextual features embedded in the scheduling object entities, which naturally removes the invalid information in the plans and thus can improve the overall computational efficiency of the matching model. Results from the test sample matching process of the three models in Table 3 are drawn as the box diagrams shown in Figures 4–7.
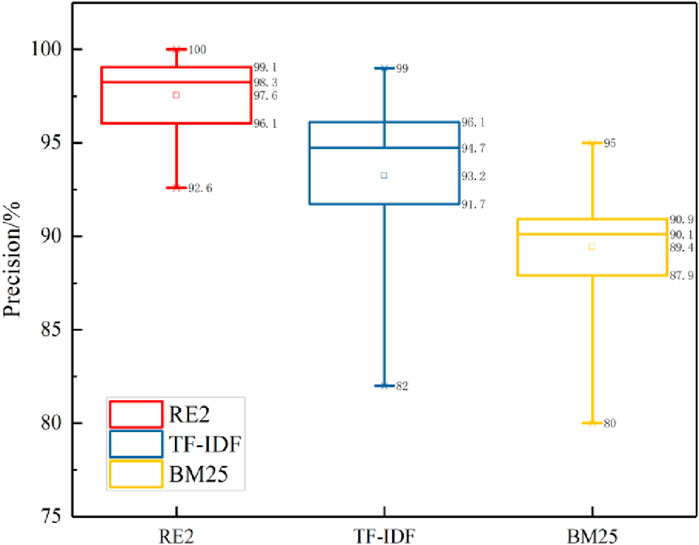
As shown in the Figure 4, it can be concluded that the matching effect of the RE2 model is significant for a text semantic matching task, such as the power grid fault handling plan, which has relatively complex syntax components. The F1 value of the RE2 model is maintained at 92%–100%, and there is no obvious deviation for different plans. Compared with the TF-IDF and BM25 models, the F1 value of some plans is only about 80%, and the matching effect of the method proposed in this article is significant. Through analysis, it is found that the power grid fault handling plan matching model based on RE2 fully integrates the original point alignment features of target words, previous alignment features, and plan context features. Using the matching results to modify the classification weight of the model can greatly improve the accuracy and practicability of text matching. The matching model based on BM25 does not consider the semantic correlation between the terms of the plan, so the score is often inaccurate or low, and the text length of the plan is different, so the parameters need to be adjusted according to the actual situation, which directly affects the overall performance of the model. The matching model based on TF-IDF ignores the order of entities and calculates TF-IDF scores only on the basis of word frequency and inverse document frequency, which cannot capture the semantic information of context in plans. Meanwhile, the algorithm is greatly affected by the document length; certain errors in the feature weights of longer texts lead to the failure of the model to accurately measure the similarity of texts. Overall performance is limited. In summary, the matching model of the power grid fault handling plan based on RE2 has higher accuracy and faster matching speed than the UIE model, and the overall convergence and stability of the model are superior; the effect of plan matching is better.
A comprehensive intelligent alarm will introduce the fault information in the case of a power grid failure. The proposed model will analyze the information, make similarity calculations with many fault handling plans, recommend the plan with the best match to the current fault, and provide auxiliary troubleshooting decisions for the dispatching and operation of the power grid. Through artificial intelligence and networked implementation methods, the model establishes an intelligent fault disposal process engine, provides the most accurate reference to dispatchers in a timely manner, and realizes the closed-loop management of the process of power grid fault handling.
5 Conclusion
This article proposes a matching method for a power grid fault handling plan based on a UIE-RE2 hybrid neural network. First, the plan is digitized using the UIE framework, and the characteristics of fault equipment, fault type, and fault phenomena are identified, effectively extracting the key elements. The interference of other information with the matching model of the plan is overcome. Then, the matching sample set of the fault handling plan is constructed, and the semantic similarity calculation model between the fault handling plan and the fault event is trained based on RE2, which can best match the plan to the characteristics of the fault event. Finally, the plans are verified using regional power grid fault-related data. When the UIE-RE2 hybrid neural network is compared with an RE2 model, it is found that the UIE-RE2 network can achieve more accurate plan matching by first carrying out plan parsing. When the RE2 method is compared with BM25 and TF-IDF algorithms, it is found to have higher matching accuracy, faster matching speed, and stronger generalization ability. The proposed algorithm can provide auxiliary decision-making for timely and rapid response to faults. Because the fault handling plan is prepared in advance, the fault disposal strategy cannot deal with all faults, and studying the fault handling plan generation technology based on artificial intelligence is the focus of the next research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
DX: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, and writing–original draft. XX: conceptualization, data curation, project administration, and writing–original draft. YZ: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing–original draft. LS: formal analysis, methodology, resources, software, and writing–original draft. TL: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, and writing–review and editing. XL: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, and writing–original draft. YQ: formal analysis, investigation, methodology, project administration, and writing–original draft. TJ: data curation, investigation, project administration, visualization, and writing–original draft. YW: data curation, formal analysis, writing–review and editing, and project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the Science and Technology Project of the Central China branch of the State Grid Corporation of China (52140023000P).
Conflict of interest
Authors DX, XX, TL, and XL were employed by Central China branch of State Grid Co. Ltd. and Authors BZ, YZ, LS, YQ, TJ, and YW were employed by Beijing Kedong Electric Power Control System Co., Ltd.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bao, Z., Wang, H., and Shiwei, H. U. (2022). Comparative analysis of correlation scoring algorithms based on content similarity. Electron. Test. (19), 52–55.
Bonetta, G., Cancelliere, R., Liu, D., and Vozila, P. (2021). Retrieval-augmented transformer-XL for close-domain dialog generation. 34. doi:10.32473/flairs.v34i1.128369
Bo, W., Jian, N., and Yong, Z. (2020). Auxiliary decision technology and application of power grid fault disposal based on knowledge understanding of fault preplan[C]//2020 5th international conference on power and renewable Energy (ICPRE). IEEE, 246–251.
Chen, J., Wang, Y., and Hu, J. (2021). Power entity information recognition based on deep learning. Power Syst. Technol. 45 (6), 2141–2149.
Dong, L., Zhang, Y., and Junbo, P. (2023). Construction and application of knowledge graph for intelligent retrieval of power grid dispatching and control information. Electr. Power 56 (07), 78–84.
Guo, R., Yang, Q., and Liu, S. (2021). Construction and application of power grid fault handing knowledge graph. Power Syst. Technol. 45 (6), 2092–2100.
Huaiwei, H., Ying, F., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Research and application of semantic modeling of fault handling plan based on natural language understanding. Electr. POWER ICT 20 (5), 68–73.
Huang, Z., Ganqing, M. O., and Keman, Y. U. (2024). General text matching based on topic model. Comput. Appl. Softw. 41 (05), 310–318+349.
Jiang, Y., Sun, S., and Qiu, C. (2021). Named entity recognition in power fault disposal preplan text. Electr. Power Eng. Technol. 40 (5), 177–183.
Jianming, Y., He, L., and Lianfei, S. (2022). Method of power grid dispatch intention recognition based on ALBERT and RE2 fusion model. Power Syst. Prot. Control 50 (12), 144–151.
Jianming, Y. U., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Construction and application of knowledge graph for intelligent dispatching and control. Power Syst. Prot. Control 48 (3), 29–35.
Jun, J., Qiang, Y., and Fu, H. (2023). Research on pre-training language model construction and text semantic analysis based on power equipment big data. Proc. CSEE 43 (03), 1027–1037.
Junbo, P. I., Qi, S., and Sun, W. (2023). An entity and event recognition method of power grid fault handling plan based on UIE framework. Electr. Power 56 (12), 138–146.
Kai, W., Gang, Z., and Xiaocheng, G. (2023). Semi-supervised entity recognition for power dispatching knowledge modeling. Power Syst. Technol. 47 (09), 3855–3864.
Lu, Y., Liu, Q., and Dai, D. (2022). Unified structure generation for universal information extraction. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2203.12277
Mingjie, L., Hongzhu, T., and Hongqiang, X. (2020). The technical framework and application prospect of artificial intelligence application in the field of power grid dispatching and control. Power Syst. Technol. 44 (2), 393–400.
Shao, G., Wang, H., and Wu, X. (2020). Precise information identification method of power equipment defect text based on dependency parsing. Automation Electr. Power Syst. 44 (12), 178–185.
Tian, Y., Yuan, Y., and Liu, H. (2020). BERT pre-trained language model for defective text classification of power grid equipment. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 44 (4), 446–453.
Tong, J., Wu, Z., and Lin, G. (2020). Power dispatching text analysis and application based on natural language understanding. Power Syst. Technol. 44 (11), 4148–4155.
Wang, F., Wei, H., and Zhang, Y. (2021a). Research and application on intelligent dispatching robot for grid line fault handling. Electr. Autom. 43 (3), 1–3.
Wang, S., Liu, W., and Yang, H. (2021b). Entity relation extraction based on natural language processing and machine learning. Res. Libr. Sci. (18), 39–48.
Wei, Z., Wang, W., and Yufang, G. (2023). Electric power text matching model based on pre-training model and multi-view recurrent neural network. J. Chongqing Univ. Posts Telecommun. Nat. Sci. Ed. 35 (03), 545–553.
Wenxuan, J., Cui, J., and Bin, F. (2022). Power dispatching fault plan matching based on visual character enhancement. Proc. CSEE 42 (15), 5439–5448.
Yang, W., Cui, Q., and Jiafeng, Q. (2022). Intelligent matching method for fault cases based on improve BERT. Shandong Electr. Power 49 (02), 47–53.
Yu, D., Shang, X., and Weimin, M. I. (2020). Deep learning based knowledge extraction method for text of power grid dispatch and control. Automation Electr. Power Syst. 44 (24), 161–168.
Zhang, P., and Degen, H. (2021). Research on trigger word extraction based on the fusion of event argument attention and encoder layer. J. Chin. Comput. Syst. 42 (4), 673–677.
Keywords: power grid fault handling plan, universal information extraction framework, residual vector-embedding vector-encoded vector, hybrid neural network model, entity recognition, text matching
Citation: Xiao D, Xu X, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Shan L, Liu T, Li X, Qiao Y, Jiang T and Wang Y (2024) Power grid fault handling plan matching method based on a hybrid neural network. Front. Energy Res. 12:1468651. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2024.1468651
Received: 22 July 2024; Accepted: 13 November 2024;
Published: 24 December 2024.
Edited by:
Yunqi Wang, Monash University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Song Zhang, Northeast Electric Power University, ChinaGuangda Wang, State Grid Energy Research Institute (SGCC), China
Hui Li, University of Macau, China
Hong Tan, China Three Gorges University, China
Copyright © 2024 Xiao, Xu, Zhang, Zhang, Shan, Liu, Li, Qiao, Jiang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu Wang, MTg4MDAxMDk3NTZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Dajun Xiao1
Dajun Xiao1 Yu Wang
Yu Wang