- 1Department of Biomedical and Chemical Engineering, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, United States
- 2Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Program, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, United States
- 3Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
- 4Department of Biology, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, United States
Obesity is a major modifiable risk factor leading to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Excessive fat storage in obesity promotes the progressive infiltration of immune cells into adipose tissue, resulting in the release of pro-inflammatory factors such as cytokines and adipokines. These inflammatory mediators circulate through the bloodstream, propagating inflammation both in the periphery and in the central nervous system. Gut dysbiosis, which results in a leaky intestinal barrier, exacerbates inflammation and plays a significant role in linking obesity to the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through the gut-brain/gut-brain-liver axis. Inflammatory states within the brain can lead to insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, autolysosomal dysfunction, and increased oxidative stress. These disruptions impair normal neuronal function and subsequently lead to cognitive decline and motor deficits, similar to the pathologies observed in major neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. Understanding the underlying disease mechanisms is crucial for developing therapeutic strategies to address defects in these inflammatory and metabolic pathways. In this review, we summarize and provide insights into different therapeutic strategies, including methods to alter gut dysbiosis, lifestyle changes, dietary supplementation, as well as pharmacological agents derived from natural sources, that target obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
1 Introduction
Obesity is a metabolic syndrome characterized by lipid accumulation and is commonly associated with low-grade inflammation due to increased infiltration and activation of innate and adaptive immune cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells, neutrophils, B cells, and T cells, within peripheral tissues such as adipose tissues (1, 2) and can contribute to neuroinflammation (3, 4). Under obesity conditions, excess free fatty acids (FFAs) decrease the lipid storage capability of adipose tissue, resulting in hypertrophic adipocytes and overproduction of adipokines and cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interferon-γ, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and IL-18 triggering systemic inflammation (5, 6). Circulating inflammatory factors can further propagate peripheral inflammation and activate macrophages in other organs such as the liver and pancreas, as well as trigger brain inflammation (5, 7) (Figure 1A). Obesity condition can further increase BBB permeability, making the brain more vulnerable to inflammation (8). Neuroinflammation is characterized by the activation of microglia and astrocytes (9, 10), along with the release of proinflammatory and neurotoxic mediators within the brain. Initially a protective mechanism, excess neuroinflammation can lead to neuronal dysfunctions (1, 4) and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s (AD), multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson Disease (PD) (11, 12), which currently do not have effective treatments.
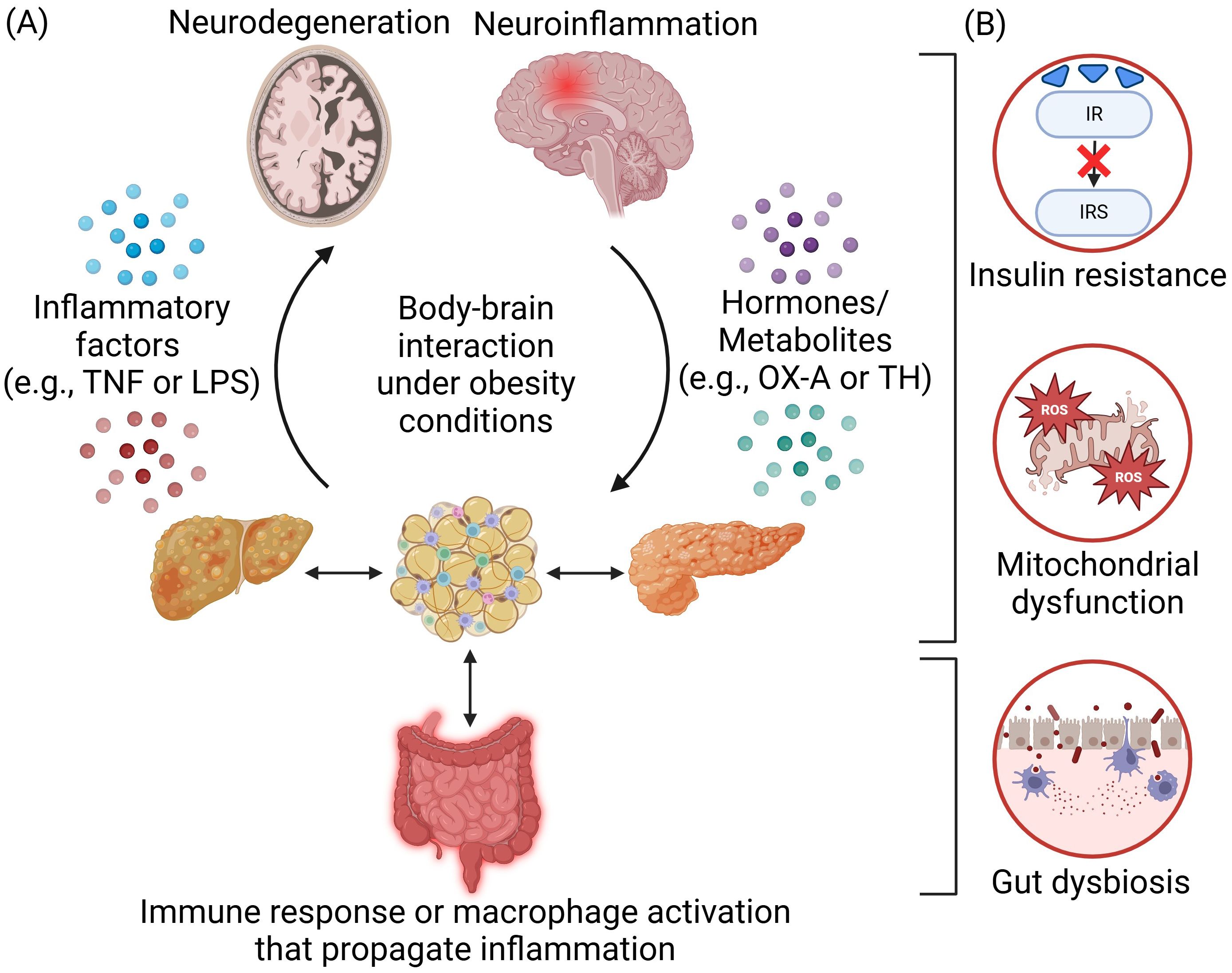
Figure 1. Body-brain interaction under obesity conditions. (A) Obesity-induced inflammation arises from the adipose tissues and is propagated across different peripheral organs in the body through immune response or macrophage activation. The communication and interaction between the body and the brain are mediated by inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and hormones or metabolites such as orexin-A (OX-A) and thyroid hormone (TH). Overnutrition will lead to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the brain, which could also, in turn, regulate appetite and satiety as well as the extent of obesity. (B) Several key disease mechanisms of obesity-induced neurological disorders include insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and gut dysbiosis. Created in https://BioRender.com.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms governing the pathogenesis of obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration holds the key to discovering novel therapeutics and providing more effective treatments. While body-brain interaction including the gut-brain/gut-liver-brain axis involves the orchestration of multiple organs and cell types (13, 14), a central disease mechanism lies in the crosstalk of inflammation (e.g., cytokines/adipokines production/circulation and gut dysbiosis) and metabolic dysregulations (e.g., insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and autolysosomal impairments) (Figure 1B). Metabolic dysfunctions are predominant in obesity and neurodegenerative diseases. Obesity can impair insulin signaling that is crucial for hepatic, pancreatic, and neuronal function (15). Inflammatory factors trigger pathways that inhibit insulin receptor (IR) and insulin receptor substrate (IRS) phosphorylation, leading to insulin resistance in the body and brain (16, 17). Under obesity conditions, there are higher levels of mitochondrial fragmentation (18, 19), overproduction of ROS (20), and higher oxidative stress that can further impair mitochondria (21). The autolysosomal pathway is crucial for clearing cellular debris and damaged organelles. Impaired function can lead to excess lipid accumulation, damaged mitochondria, increased ROS production, and inflammation, contributing to obesity in both the body and brain (22, 23). Additionally, obesity-induced gut dysbiosis can increase the intestinal permeability, leading to a “leaky gut” and increased secretion of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which can further trigger inflammation (24). These factors collectively propagate inflammation throughout the body including the brain (14) (Figure 2A).
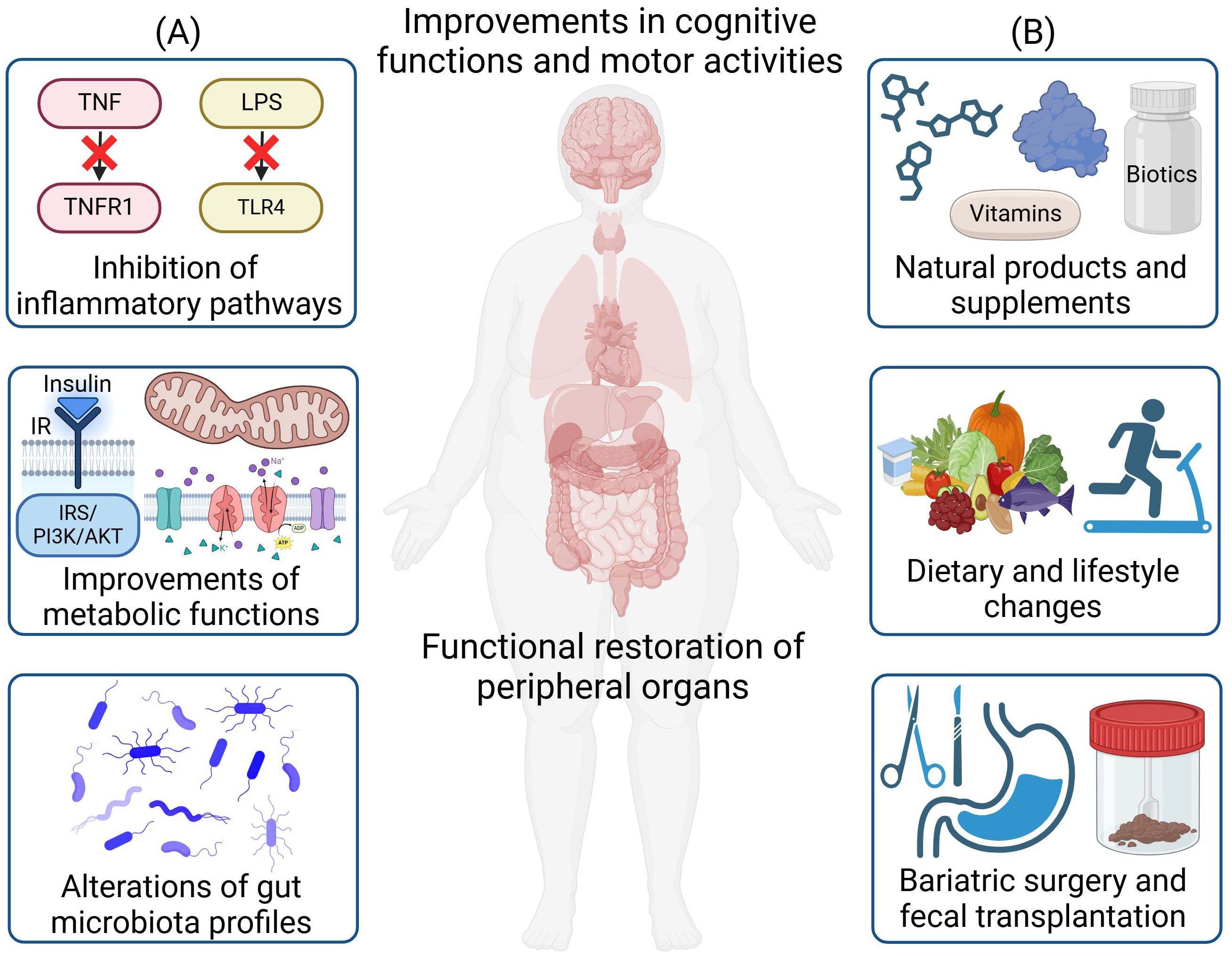
Figure 2. Therapeutic strategies for the treatment of obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. (A) Major disease mechanisms for therapeutic targeting include the inhibition of inflammatory pathways, improvements in metabolic functions, and alterations of gut microbiota profiles. (B) Therapeutic strategies include the administration of natural products and supplements, dietary and lifestyle changes, as well as bariatric surgery and fecal microbiota transplantation. These treatments will lead to functional restoration of peripheral organs and the brain, along with improvements in cognitive functions and motor activities. Created in https://BioRender.com.
In this review, our goal is to summarize and provide insights into therapeutic strategies that can mediate obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through the body-brain axis. In particular, we will focus on a variety of therapies including (1) small molecules and biologics that modulate inflammatory and metabolic pathways, (2) approaches to alter gut microbiota to remedy gut dysbiosis, (3) effect of exercise and diet interventions, (4) vitamins and supplements, and (5) natural products and derivatives (Figure 2B). We will further provide future perspectives on emerging therapies as well as the need to further dissect body-brain interaction through precision and personalized medicine such as through the use of multi-omics to resolve heterogeneity in specific cell types contributing to the disease pathogenesis of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through different axes of body-brain interactions.
2 Crosstalk between inflammation and metabolic dysfunctions
2.1 Alterations of inflammatory signaling pathways
Inflammatory cytokine receptor signaling such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) (25, 26) as well as pattern recognition receptor signaling such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) (27) play key roles in mediating inflammation in the body-brain interaction. Stimulation of both signaling pathways lead to the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) transcription factor that could increase the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and also induces activation of immune cells which propagate inflammation between the peripheral and central nervous systems (25, 26). Administration of a soluble TNF inhibitor (XPro1595) to mice fed on high-fat high sugar diet (HFHS) ameliorated liver metabolic disturbances and gut lipocalin-2 levels. In addition, it decreased insulin signaling impairment in the brain, and attenuated glial activation related neuroinflammation and cognitive deficits associated with HFHS diet (28). A TLR4 inhibitor (TAK-242) inhibited inflammation in the adipose tissue but exerted no significant effects on body weight, adiposity, and a range of metabolic measures. In the brain, obese mice treated with TAK-242 exhibited a significant reduction in microglial activation, improved levels of neurogenesis, and inhibition of soluble amyloid beta (Aβ) levels (29). Recently developed receptor-specific inhibitors for TNFR1 (30–33) and TLR4 (34, 35) may also hold promise to mediate obesity induced inflammation. The crosstalk between inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, such as the interaction between TNF-TNFR1 and LPS-TLR4 pathways with insulin signaling impairment (23, 28), mitochondrial dysregulations (36, 37), and autolysosomal defects (22, 38, 39), may provide more insights to the pathogenesis of obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through body-brain interaction.
Biological molecules such as fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), which is a stress-inducible endocrine hormone predominantly secreted by the liver (40), regulates metabolic homeostasis and possess anti-inflammatory properties (41). FGF21 activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway and suppresses NF-κB signaling, thereby reducing oxidative stress (42). Treatment of recombinant human FGF21 (rFGF21) in HFD mice reduced body weight, improved glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in the body, and resulted in reduced expression of inflammatory cytokines TNF and IL-1β. It also suppressed microglia activation in the hippocampus, thereby reducing neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction and anxiety-like behavior (43). Treatment with FGF21 in HFD rats improved peripheral insulin sensitivity, hippocampal synaptic plasticity, increased dendritic spine density, restoration of brain mitochondrial function, and reduced apoptosis in brain cells, collectively mitigating cognitive decline (44). nOrexin-A (OX-A) or hypocretin-1, a neuropeptide expressed mainly in the brain hypothalamus as well as in several peripheral tissues such as in the intestinal villi has been shown to regulate inflammatory responses (45). Loss of orexin leads to increased microglial activation, increased pro-inflammatory TNF and the mitochondria-associated enzyme immune responsive gene-1, and cognitive decline, which is worsened upon feeding with HFD (46). In microglial under palmitic acid treatment, OX-A addition reduced pro-inflammatory markers TNF, IL-6, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and reduced hypothalamic neuronal cell death (47). The neuroprotective effect of OX-A is mediated through PKC and PI3K signaling pathways, as well as upregulation of somatostatin receptors, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and endothelin-1 (48). OX-A has also been shown to attenuate peripheral inflammation in the gut and reduce the transport of inflammatory mediators such as LPS from the body to the brain, hence decreasing the propagation of neuroinflammation (49). In sum, TNF inhibitors, rFGF21 and OX-A biological molecules play important roles in attenuating both peripheral inflammation and neuroinflammation.
2.2 Restoration of metabolic functions
Obesity-induced neuroinflammation contributes to insulin resistance, and promotion of insulin signaling attenuates neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (50). Restoration of insulin signaling pathway such as through the usage of anti-diabetic drugs is a strategy to alleviate obesity-induced neurodegeneration (51). Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) targeting drugs are insulin sensitizers that have shown promise in clinical trials with AD and PD patients (52, 53). GLP-1 exhibits pleiotropic effects owing to the widespread expression of GLP-1 receptors (GLP-1R) across multiple organs, brain regions such as the hypothalamus and amygdala, and various cell types, including microglia and astrocytes. These receptors play key roles in regulating appetite, reward processing, emotional responses, and neuroprotection (52, 53). GLP-1 modulation increases IR and IRS phosphorylation thus improving brain insulin signaling and reducing long term depression. In addition, GLP-1 reduces microglial activation, reactive astrogliosis, thereby attenuating neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (52, 53). GLP-1R agonists, approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity, have demonstrated neuroprotective effects in neurodegenerative diseases through suppressing neuroinflammation (52). Vildagliptin is an inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), an enzyme that degrades glucagon-like-peptide 1 (GLP-1), and has been used to rescue insulin resistance in pancreatic β-cells with lipid overload (54). Treatment with vildagliptin on HFD rat significantly elevates neuronal GLP-1 level, increased brain insulin signaling and attenuated cognitive impairment (55). In another study comparing combined administration of vildagliptin and energy restriction to vildagliptin only, it was shown that HFD rats with combined administration showed decreased body weight, visceral fat, plasma insulin, and reduced total plasma cholesterol levels. Moreover, the brain insulin sensitivity, mitochondrial function, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and cognitive function were restored (56). Dapagliflozin is sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor that has also shown effects in restoring insulin sensitivity and neuroprotection in obesity-induced insulin resistance. In a study comparing the effects of Vildaglipti and Dapagliflozin, it was shown that single treatment of either drug resulted in improved brain mitochondrial function, insulin signaling, apoptosis and prevented cognitive decline. Dapagliflozin showed greater efficacy in enhancing peripheral insulin sensitivity, reducing weight gain, and improving hippocampal synaptic plasticity compared to vildagliptin. Notably, the combination of these drugs exhibited superior efficacy in improving brain insulin sensitivity and reducing oxidative stress than either drug alone. These findings suggest that a combination of both drugs could represent a promising therapeutic approach for neuroprotection in obese insulin-resistant conditions, although further studies are needed to fully understand their synergistic mechanisms (57). Metformin, a widely used drug for insulin resistance, has been shown to restore insulin signaling in the liver of obese mice. Additionally, it enhanced insulin signaling in the hippocampus of HFD-fed mice and improved their cognitive function (58). Obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance downregulate mitochondrial fusion and upregulate fission, thereby impairing mitochondrial function and exacerbating neurodegeneration. Hence, targeting mitochondrial dysfunction is a viable strategy. In HFD mice, a combined approach consisting of both mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 (Mdivi-1) and mitochondrial fusion promoter (M1) exerted neuroprotection through balancing mitochondrial dynamics, reducing ROS production and depolarization of mitochondrial membranes, thereby improving mitochondrial function (59). The administration of Mdivi-1 and M1 also reduced Aβ aggregation, tau hyperphosphorylation and ameliorated BBB breakdown due to obesity (59). Other studies also demonstrated the beneficial effects of Mdivi-1 in reducing expression of mitochondrial fission protein Drp-1 in palmitate treated hippocampal neural stem cells of rats (60) and HFD rats (61). Garlic extract (Allium sativum) decreased body weight, visceral fat, plasma cholesterol, and MDA levels in HFD rats, and improved brain mitochondrial function, insulin signaling and cognitive functions in HFD rats (62). More evidence is required to strengthen the notion of crosstalk between inflammation and metabolic dysfunctions (63, 64) and how this interplay leads to the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration through body-brain interaction under obesity conditions. While the interplay between inflammation and insulin signaling impairment (65, 66) or mitochondrial dysfunction (67, 68) have been established, the link between inflammation and autophagy or lysosomal defects are emerging pathogenic mechanisms that warrant more investigations (22). Several HFD mouse models have illustrated impairments in autolysosomal functions including lysosomal acidification defects (69, 70), together with indications of inflammation. There are further evidence connecting autolysosomal dysfunction and neuroinflammation (22, 71, 72) although this has not yet been established in the HFD rodent models and is an area for future investigations.
3 Modulation of gut-brain/gut-liver-brain axis
3.1 Alteration of gut microbiota
Gut microbiota is closely linked to brain function via the gut-brain/gut-liver-brain axis, and alterations in microbiota during obesity can lead to neuronal impairment (13). In addition, disruption of the gut barrier leads to more bacteria or their metabolites entering the liver, which contributes to hepatic disorders and influence neural signaling through the gut-liver-brain axis (13). Hence, balancing the microbiota plays an important role in attenuating obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Biotics, including probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and paraprobiotics, have been tested in both animal and human trials. These studies have shown a link between gut microbes and immune biomarkers, resulting in improved overall health (73). Treatment with gut commensal Akkermansia muciniphila reduced TNF, IL-1β and IL-6 expression in the hippocampus, and reduced hippocampal microgliosis in HFD mice, thereby restoring neuronal development and synapse plasticity (74). Akkermansia muciniphila subtype (A. muciniphilasub) produced short chain fatty acids and improved the spatial memory and blood glucose control in HFD mice (75). Oral supplementation with probiotic Clostridium butyricum greatly reduced inflammatory cytokines within the hippocampus of HFD and fiber deficient mice, improved neuronal and synaptic functions and reduced plasma LPS levels, which can be a key mediator in propagating inflammation along the gut-brain axis (76). Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LB1.5 supplementation on HFD mice lowered inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and glial activation in the cerebral cortex (77). Other supplementations of Lactobacillus paracasei (78) and Bifidobacterium infantis (79) into obese mice also demonstrated effects in reducing neuroinflammation (i.e., IL-6, TNF, and CD11b levels) (79) and increasing neuronal and synaptic functions through increasing the levels of synaptosomal associated protein 25 (78), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD95) (78, 79). Lactobacillus paracasei also reduced inhibitory phosphorylation of IRS to reduce insulin resistance within obese mouse brains (78).
Probiotics including Lactobacilli, Streptococci, and Bifidobacteria, has been shown to reduce the development of liver and brain-related diseases through the gut-liver-brain axis (80, 81). In a study exploring the supplementation of prebiotic (Xyloolidosaccharide), probiotic (Lactobacillus paracasei HII01), or synbiotics in HFD mice, all of the three supplementations reduced microglial activation, reduced ROS production, and attenuated brain mitochondrial dysfunction and restored cognitive function (82). Synbiotics have demonstrated efficacy in modulating the immune system and addressing neurological disorders linked to impaired liver function through the gut-liver-brain axis (83). In individuals with obesity, supplementation with probiotics containing Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium lactis, Bifidobacterium longum, and Bifidobacterium bifidum has been shown to increase the abundance of beneficial gut bacteria, such as Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, and reduce systemic inflammation (84).
Postbiotics are metabolites and bioactive compounds produced by beneficial bacteria in the gut that can potentially influence brain health by mitigating neuroinflammation and slowing neurodegeneration through the gut-brain axis (85). The secondary metabolites of probiotic bacteria are short-chain fatty acids, vitamins, proteins and enzymes, organic acids like propionic acid and 3-phenyl lactic acid, and intracellular polysaccharides. Gut-derived postbiotics have been shown to restore BBB permeability (86, 87). Propionate was found to rescue LPS-induced impairment in the permeability of brain endothelial monolayers by reducing oxidative stress (88). In other studies, butyrate and propionate improved BBB integrity by regulating the organization of the actin cytoskeleton and increasing the interaction between actin and tight junction protein ZO-1, and also restored inflammation induced mitochondrial dysfunction (89). In addition, gut microbiota-derived metabolites, including SCFAs, secondary BAs, indoles, and PUFAs increase the secretion of neuroprotective GLP-1 (90, 91).
The microbiota diversity within the gut can be affected by the type of food that was consumed. Western diet enriched in high amounts of fat and sugars adversely alters gut microbiota contributing to obesity-induced neurodegenerative states (92), whereas consumption of diets rich in fruits and vegetables can reverse altered microbiota states (93). For instance, consumption of kimchi (94) and supplementation of β-glucan (95) reduced neuroinflammation and decreased gut permeability in obese mice. Kimchi further demonstrated effects in reducing BBB permeability (94). Specifically, β-glucan decreases the number of bacteria related to neurodegeneration in obese mice, increased PSD95 and synaptophysin levels, thereby improving synaptic function and memory (95). β-glucan mimics have also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties (96). The supplementation of anthocyanins increased species of gut bacteria that produces tryptophan, a precursor for kynurenic acid that can exert anti-inflammatory properties (97). Furthermore, microbiota accessible carbohydrate (98), leucine-restricted diet (99) and intermittent fasting (100) also exhibited anti-neuroinflammatory effects, improved synaptic and neuronal function (98–100), reduction in LPS levels (99), and improvement in gut permeability (98–100). In particular, leucine-restriction reshaped the structure of gut microbiota, through downregulating the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, reducing the relative abundance of inflammation-related bacteria and increasing short-chain fatty acid producing bacterial genera including Alistipes, Allobaculum, Odoribacter, and Olsenella (99).
3.2 Bariatric surgery and fecal microbiota transplantation
Surgical and other medical interventions could also reverse gut dysbiosis induced by obesity which can eventually benefit the brain. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) done on HFD rats reduced hypothalamic inflammation as seen by lowered cytokine levels and glial cells activation (101). Furthermore, BV2 microglial cells treated with plasma of HFD rats that underwent RYGB had lower inflammatory states compared to those that was treated without surgery (101). The lowered LPS levels and improvement in gut permeability after RYGB further proves the beneficial effect of bariatric surgery in attenuating obesity-induced neuronal damage via the gut-brain axis (101). Another study shows that two different types of bariatric surgery, RYGB and biliary diversion to the ileum, illustrate positive correlation in reducing neuroinflammation compared obese mice (102). Furthermore, gene encoding for protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B, which is a negative regulator of insulin signaling, was lowered after RYGB surgery (103). There is also improved glucose uptake and increased level of GLP-1, which is a positive regulator of insulin signaling, after duodenum-jejunum bypass, showing the beneficial effect on insulin signaling within the brain together with improved memory (104). A meta-analysis of existing datasets has shown improved cognition in obese patients with gastric by-pass (105), demonstrating the efficacy of this approach in human subjects.
Transplanting feces containing beneficial microbiota, or fecal microbiota transfer (FMT), from healthy donors to the intestinal tract of recipients (106) is another approach to restore gut dysbiosis (107). HFD mice that obtained fecal transplantation from mice that underwent exercise showed improved cognitive behavior, increased BDNF and tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) levels and reduced astrogliosis (108). Furthermore, the number of beneficial bacteria, L. acidophilus, L. gasseri, Christensenellaceae, Bactroidetes, and Oscillibacter was increased in mice with exercise, which may also contribute to the improvement along the gut-brain axis (108). In a study comparing the effect of FMT from RYGB donors and oral butyrate supplementation on 24 male and female subjects with metabolic syndrome, it was shown that the FMT from RYGB donors increased brain dopamine transporter and serotonin transporter binding, due to increased levels of Bacteroides uniformis compared to oral butyrate (109). However, there was no effect on body weight and insulin sensitivity. Under obesity, there is increased gut permeability and gut dysbiosis, leading to the circulation of inflammatory mediators and metabolites throughout the body, which promotes systemic inflammation and stress. Hence, greater emphasis on developing therapeutics that could ameliorate obesity-induced gut dysbiosis are needed to reduce obesity-induced inflammation.
4 Lifestyle changes
4.1 Calorie restriction
Calorie intake, meal frequency, diet quality, and gut microbiome interactions influence metabolic and molecular pathways, regulating homeostasis and inflammation in normal brain aging and CNS diseases (110). In a Brazilian longitudinal study of adult health involving 11,737 participants, it was shown that higher adherence to the planetary health diet was associated with slower memory decline (93). Calorie restriction (CR) of a reduction of 40% calories from control effectively decreased phagocytic markers such as galectin-3, dectin-1, CD16 in the white matter indicative of reduced microglial activation, leading to reduced aging-associated decline in HFD mice (111). CR also attenuated the neuroinflammatory response mediated through the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2-phosphoinositide 3-kinases-protein kinase B (TREM2-PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway, thereby reducing inflammatory cytokines iNOS, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and IL-1β in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of HFD mice (112). Additionally, CR increased proteins crucial for synaptic function in the brain such as BDNF, PSD95, and synaptophysin (112). CR in the form of intermittent fasting reduced TNF expression, decreased oxidative stress markers, and increased autophagy in the cerebellum of HFD mice (113). In mice lacking Sirt3, a mitochondrial deacetylase, the protective effects of CR on oxidative stress and damage are diminished, suggesting that the reduction in oxidative stress during CR requires Sirt3 (114). CR has been shown to increase Sirt3 activation which lead to mitochondrial protein deacetylation, as well as attenuate microglial activation and neuroinflammation (115–117). Additionally, intermittent fasting reduced HFD-induced astrocytic apoptosis and microglial activation as well as reduced memory deficits (118). Intermittent fasting has been used in elderly with obesity and shown effects in improving cognitive impairments, indicated by improved mini-mental state examination and Montreal cognitive assessment scores (119).
4.2 Exercise and other environmental stimuli
Exercise has various beneficial effects in alleviating obesity induced neurodegeneration, including increasing neurotrophic factors such as BDNF and TrkB (120–122), and improving synaptic function (123). When HFD mice are subjected to exercise (i.e., voluntary wheel running), there were reduced IL-1β in the hippocampus (124). In another study using voluntary wheel running as exercise, reduced microglial activation and cerebrovascular and white matter damage was seen in HFD mice (125). Additionally, reduction in inflammatory cytokines TNF, IL-1β, and IL-6, improved mitochondrial function and insulin signaling were seen in the hypothalamus, hippocampus and cortex of HFD mice which underwent voluntary wheel running exercise compared to sedentary mice (126). HFD rats on treadmill exercise improved aberrant brain insulin signaling, reduced hyperphosphorylation of tau protein levels (127) and beta-secretase 1 activity (128), reduced oxidative stress and inflammation, and improved mitochondrial function (129). In a study comparing between 12 weeks of aerobic exercise and 12 weeks of resistant exercise on HFD rats, both exercise regimen reduced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and improved cognitive function, with no significant difference between them (121). Interestingly, when comparing between the effects of caloric restriction and exercise on HFD rats, it was shown that long-term caloric restriction (16-weeks) has the greater systemic metabolic benefit, including improved synaptic function, neuronal insulin signaling, neurogenesis and increased mitochondrial and autophagic function (123). In addition to lifestyle changes, there are a few therapeutic strategies that leverages on environmental stimuli, such as photobiomodulation, to modulate obesity induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (130, 131). For instance, application of near infrared light therapy over HFD mice head reduced inflammatory cytokines TNF and IL-1β levels, as well as reduced microglia and astrocytes activation (130). Far infrared light has also shown effect in reducing IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF and lower the TLR4 and NF-ĸβ pathway, as well as microglial and astrocytes activation in HFD mice (131). HFD mice with environmental enrichment (i.e., equipped with nesting material, a rotating wheel, plastic tubes, and toys) improved neuronal survival and memory function in hippocampus (132, 133) and prefrontal cortex (132).
5 Dietary supplements
5.1 Vitamin and trace elements
Supplementation with vitamins and natural dietary supplements has been shown to exert neuroprotective effects by reducing neuroinflammation, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress associated with obesity. The supplementation of Vitamin D to HFD rats reduced TNF levels in hypothalamus (134) and hippocampus (135), IL-6 in hypothalamus and hippocampus (136), IL-1β in hypothalamus (136) and NF-ĸβ in hippocampus (135, 137) and hypothalamus (136). Vitamin D also reduced insulin resistance in the brains of HFD rats (134). A natural dietary supplement (NDS) containing curcuma longa, silymarin, guggul, chlorogenic acid and inulin was shown to reduce the activation of astrocytes, ROS, lipid peroxidation and NF-ĸβ, IL-6 and IL-1β levels in the cerebral cortex of HFD mice, indicative of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (138). NDS also exhibited lower levels of ROS, peroxidation, increased levels of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and increased IR expression (138). Lycopene is another dietary supplement with BBB penetrating properties that was able to decrease IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB levels within the hypothalamus of HFD rats (139). Lycopene also greatly increases activities of glutathione (GSH), SOD and catalase (CAT) and decreases malondialdehyde (MDA), a by-product of peroxidation caused by ROS, and hydrogen peroxide in the cerebrum of HFD rats (139).
Trace elements such as zinc, magnesium, iron plays an important role in regulating neuronal function (140) and obesity can lead to their dyshomeostasis thereby contributing to neurodegenerative diseases (141). It has been shown that zinc dietary supplementation can penetrate through the BBB and reduce microglial activation in the cerebral cortex as well as TLR4 expression in the hippocampus in HFD rats, although no significant effects was demonstrated in astrocytes (142). In another study, zinc supplementation downregulated phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), thereby attenuating the Janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT3) pathway and reduced inflammatory state in the hippocampus (143). Interestingly, the same study show that female HFD rats were more responsive to zinc treatment compared to male HFD rats, suggesting the need to understand more on sex differences and susceptibility to different treatments (143). Supplementation of magnesium in the forms of magnesium oxide and magnesium picolinate significantly reduced NF-ĸβ levels within the brains of HFD rats, potentially via the upregulation of Nrf2, which is an antagonist of the NF-ĸβ pathway (144). Moreover, magnesium supplementation significantly decreased brain MDA levels and increased antioxidant enzymes SOD, CAT, and GSH levels in HFD rats (144). Magnesium supplementation also increased the PI3K/Akt pathway which restored cognitive impairments in HFD rats (144).
5.2 Polyunsaturated fats
Supplementation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) as forms of omega-3 (ω3) reduced IL-1β and TNF in the hippocampus, striatum and prefrontal cortex in HFD mice (145). ω3 also reduced MDA levels in hypothalamus and hippocampus, even though reversal of antioxidant enzymes were not significant (145). ω3 also partially reversed the impairment in mitochondrial function (145). Another study also showed the anti-inflammatory effects of omega-3 through the reduction of astrocytes activation and TNF and IL-6 expression in the cerebral cortex in HFD rats (146). Similarly, other unsaturated fatty acids such as ω9, stearic acid, flax seed and olive oil also significantly reduced inflammatory states within hypothalamus of HFD rats and mice (147). α-lipoic acid reduced TNF and IL-6 in HFD ovariectomized rats (148) and abscisic acid reduced TNF and microglial numbers in hypothalamus of HFD rats (149). Palmitoylethanolamide is a naturally occurring fatty acid amide and has shown effects in reducing NF-ĸβ, IL-1β, and TNF in the hypothalamus and hippocampus while reducing activation of microglia and astrocytes in HFD mice (150). Interestingly, in a study comparing the effects between n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and n-3 PUFAs, it was shown that HFD diet enriched with n-6 PUFAs has detrimental effects on cognitive function in obese mice through upregulating toll-like receptor-myeloid differentiation factor-88-nuclear factor kappa-B (TLR-MyD88-NF-κB) inflammatory signaling pathway, while HFD enriched in n-3 PUFAs has reduced inflammatory responses (151). In another study comparing n-6 PUFAs and n-3 PUFAs, it was shown that the n-6/n-3 PUFAs ratio of 1:1 alleviated inflammatory response and insulin resistance in HFD mice (152). Supplementation of butyrate, a fatty acid produced during microbial fermentation, was able to reduce TNF, IL-1β and IL-6 levels, as well as an increase in anti-inflammatory IL-10 levels in the cerebral cortex of HFD mice (153). Butyrate also protects against oxidative as seen by increased GSH content, state 3 mitochondria respiration and decreased MDA levels (153).
6 Biologically derived compounds/bioactive compounds
6.1 Compounds derived from biological/natural sources
Bioactive compounds found in naturally derived sources have been shown to have a protective effect against neurodegeneration. Anthocyanins, a class of water-soluble flavonoids widely present in fruits and vegetables, were shown to exhibit various neuroprotective mechanisms (154, 155). Administration of a natural anthocyanin pigment derived from purple sweet potato storage roots to HFD mouse was able to significantly decrease the protein expression of inflammatory cytokines, COX-2, iNOS and NF-ĸβ while increasing anti-inflammatory cytokines in their brains. It was also able to inhibit the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway which is responsible for inflammation (154). These result in improved locomotor activity and exploratory behavior (154). Blackberry anthocyanin extract decreased expression of cytokines such as TNF and IL-6 in the cortex, thymus and hippocampus of HFD rats (155). Raspberries containing anthocyanins significantly reduced cortical IL-6 levels in HFD mice (156). Peeled extract of Ananas comosus (PEAC) (157) (pineapple) reduced IL-6 in brains of HFD rats, reduced MDA levels, and lowered anxiety behaviors and acetylcholinesterase (ACHE) activity (157). Similarly, vegetables such as Momordica Charanti (bitter melon) decreased expression of inflammatory cytokines and glial activation within HFD mice brains, reduced oxidative stress, and ameliorated HFD-associated changes in BBB permeability (158). Cynara Cardunculus (Artichoke) leaves and Hericium Erinaceus Mycelium (mushroom) significantly decreased expression of TNF and IL-1β within the striatum and hippocampus of HFD (159) and HFHS fed mice (160) respectively, leading to improved neuronal survival in the dentate gyrus and spatial memory (160). Compounds like quercetin and catechin in Momordica charantia, and luteolin in Cynara cardunculus, may play a role in their protective mechanisms. However, further investigations are needed to confirm this. The administration of pomegranate seed oil, juice, fruit and leaves also reduced oxidative stress within rats that were fed a high fructose diet and led to lowered ACHE activity (161).
Green tea is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which have been studied for their potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases (162). Polyphenol compound extracted from green tea such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) lowered TNF levels through inhibition of the MAPK and NF-ĸβ pathways via oral administration in mice on a high fat high fructose diet (163). In addition, it ameliorated insulin resistance and reduced learning and memory loss (163). Another study using an oral administration of ECGC to inhibit JAK2/STAT3 pathway in microglia, reducing microglial activation and the lowering of TNF, IL-6 and IL-1β levels within the hypothalamus of HFD mice (164). Other polyphenols derived from green tea such as epicatechin (EC) and teasaponin have been shown to reduce microglial activation, TNF and IL-6 levels within the hippocampus and hypothalamus in HFD mice (165). Daidzein, a major isoflavone from soybean, have been shown to lower IL-6 levels in a model of obesity induced neurodegeneration consisting of human fetal hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons treated with palmitic acid (166). Quercetin, another flavonoid, significantly decreased the levels of TNF, IL-1β and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and microglial activation markers in the hypothalamus of HFD mice (167). This was accompanied by the upregulation of HO-1, which protected against oxidative damage and inflammation (167). Sea-buckthorn flavonoid treatment in high-fat high fructose mice activated ERK/CREB/BDNF and IRS-1/AKT pathways and inactivated the NF-κB signaling (168), thereby preventing neuronal loss and memory impairment. Another flavonoid compound isolated from sea-buckthorn, isorhamnetin, inhibited the phosphorylation levels of JNK, p38, and NF-κβ proteins in the mouse brain, thereby attenuating neuroinflammation and mitigated high fat high fructose-induced cognitive impairment (169).
6.2 Compounds derived from medicinal plants
The use of medicinal plants in traditional medicine has consistently demonstrated beneficial effects over time (170). Administration of dry leaf powder of Withania Somnifera in HFD rat brains reduced the astrocytic activation in hippocampus and piriform cortex, and microglial activation in the hypothalamus through the attenuation of inflammatory proteins such as iNOS, MCP-1, COX2, NF-ĸβ and cytokines such as TNF, IL-6 and IL-1β (171). Additionally, Withania Somnifera reduced insulin resistance through increasing mRNA expression levels of IRS1 and 2 within the hippocampus and piriform cortex (171). Similarly, Tinospora cordifolia (herbaceous vine of the family Menispermaceae, traditional ayurvedic medicine) and Astragalus membranaceus (Huang Qi, traditional Chinese medicine) also demonstrated effects in reducing glial cells activation within the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in HFD rats (172) and HFD fed-streptozotocin rats) (173) respectively. Aruncus Dioicus var. Kamtschaticus (dwarf goat’s beard) and Mori Cortex Radicis (Morus alba root cortex, traditional Chinese medicine) protected HFD mice against oxidative stress by increasing antioxidant enzymes (i.e., GSH, SOD and CAT), reducing ROS and MDA levels within their brains. Both compounds were also able to increase IRS-1/AKT insulin signaling in the brains of HFD mice (174, 175). Curcuma Amada (Mango ginger) administration attenuates the reduction of antioxidant enzymes levels together with decreasing MDA in the hippocampus of HFHS rats (176). Additionally, Mucuna pruriens (velvet bean) have been shown to reduce IL-6 levels in HFD rats and a reduction in depressive behavior (177). Vigna angularis (adzuki bean) also reduce inflammation and improve cognitive function in HFD mice (178). Thymol, a monoterpene phenol isolated from medicinal herbs, has exhibited neuroprotective effects through decreasing inflammatory cytokines level TNF and IL-1β, decreasing oxidative stress, and increasing the expression of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (179). The therapeutic effects of these compounds in mediating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress have been summarized in Figure 3.
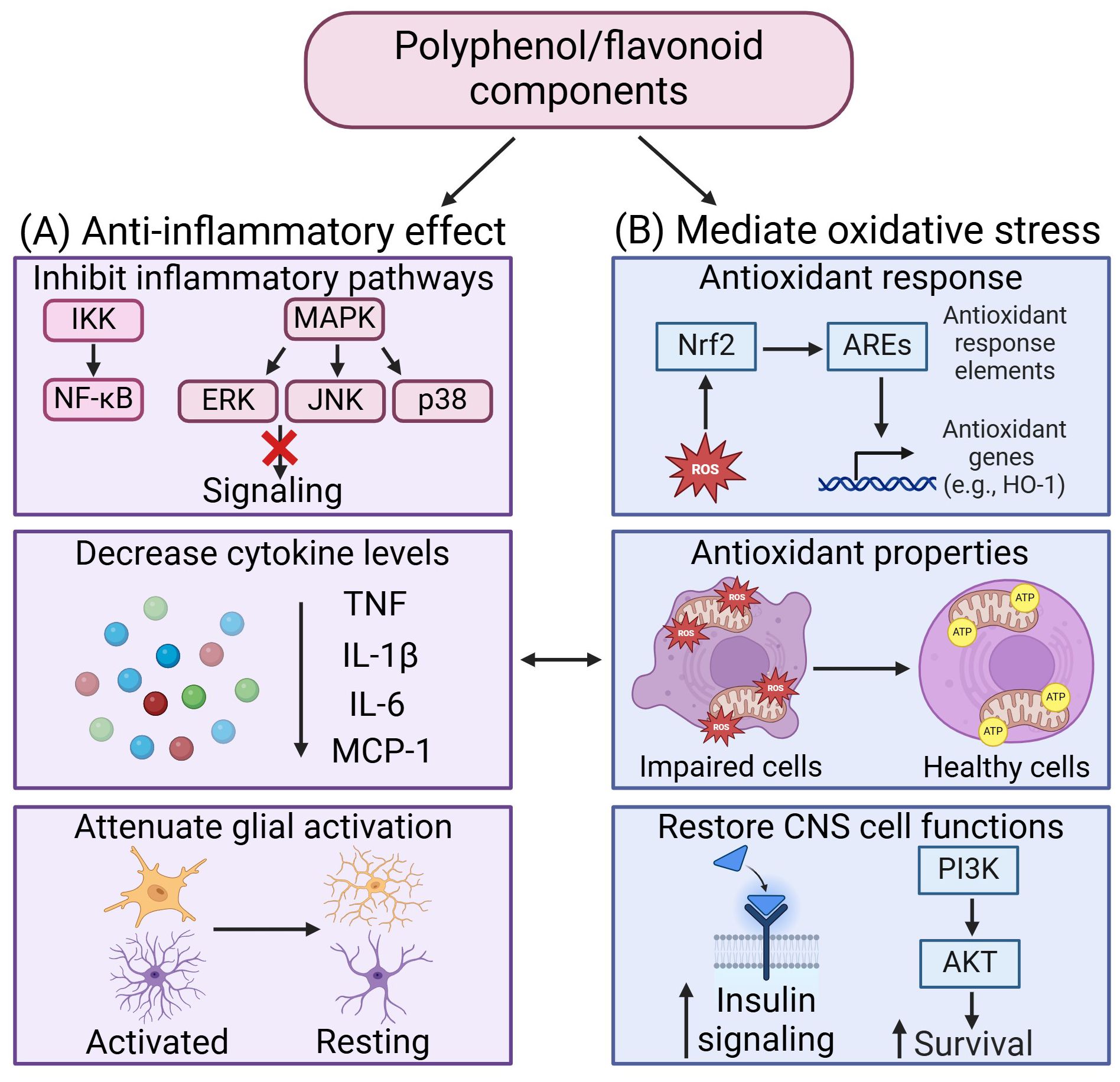
Figure 3. Therapeutic effects of polyphenol/flavonoid in mediating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. (A) The anti-inflammatory effects of polyphenol/flavonoid arise from their ability to inhibit inflammatory signaling pathways, decrease cytokine levels, and attenuate glial activation. (B) Polyphenol/flavonoid mediate oxidative stress by activating antioxidant response to enhance antioxidant properties and restore CNS cell functions. Created in https://BioRender.com.
7 Summary and future perspectives
Recent advancements in nanotherapeutics and nanomedicine have increasingly been applied to address obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. For example, garlic exosome-like nanoparticles have demonstrated the ability to inhibit both systemic and brain inflammation, enhance memory function, and improve glucose and insulin responses in mice with high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity through oral administration (180). Similarly, gold nanoparticles administered to HFD mice have been shown to reduce inflammatory markers and oxidative stress in the brain (181). Other types of nanoparticles either target gut dysbiosis (180, 182, 183) or promote autolysosomal functions in the liver and pancreas (69, 70, 184) and potentially exhibit beneficial effects to the brain via the different axes of body-brain interactions. Some of these nanoparticles are also able to partially cross the BBB to target the brain (70, 180, 183, 185) and can be further designed to include theranostic functions (186, 187) as well as improve efficacy in attenuating neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (185). It is important to note that therapies that do not cross the BBB can still be valuable for testing the effects of preventing neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in obesity by targeting the peripheral system alone (23). However, therapies that circulate through both the peripheral and central systems are likely more effective, as they can target both body-to-brain and brain-to-body pathways, offering broader therapeutic benefits. Vagus nerve stimulation can also exert neuroprotective effects (188) as well as control satiety which can be a potential therapy to modulate obesity (189).
Given the involvement of multiple organs and cell types in mediating interactions, it is crucial to dissect gene or protein level changes in specific cell types to target the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration under obesity conditions. Inflammatory cells such as macrophages and brain glial cells are key targets for modulating inflammation and its spread across organs and cell types, which can lead to neuronal death. To advance precision and personalized medicine, utilizing multi-omics technologies like metabolomics and microbiome sequencing (190, 191), as well as data mining of existing datasets (192, 193), is essential for elucidating disease mechanisms and developing more effective targeting strategies.
Author contributions
JZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. CL is supported by a start-up grant from the Department of Biology at Syracuse University and JZ is supported by a start-up grant from the Department of Biomedical and Chemical Engineering at Syracuse University.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the funding sources for supporting this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. O’Brien PD, Hinder LM, Callaghan BC, Feldman EL. Neurological consequences of obesity. Lancet Neurol. (2017) 16:465–77. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30084-4
2. Zatterale F, Longo M, Naderi J, Raciti GA, Desiderio A, Miele C, et al. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Front Physiol. (2020) 10:1607. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01607
3. Cai D. Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in overnutrition-induced diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 24:40–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2012.11.003
4. Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Natteru PA, Selvakumar GP, Saeed D, Zahoor H, et al. Neuroinflammation induces neurodegeneration. J Neurol Neurosurg Spine. (2016) 1(1):1003.
5. Neto A, Fernandes A, Barateiro A. The complex relationship between obesity and neurodegenerative diseases: an updated review. Front Cell Neurosci. (2023) 17:1294420. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1294420
6. Wen X, Zhang B, Wu B, Xiao H, Li Z, Li R, et al. Signaling pathways in obesity: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2022) 7:298. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01149-x
7. Hong Y, Yu J, Su Y, Mei F, Li M, Zhao K, et al. High-fat diet aggravates acute pancreatitis via TLR4-mediated necroptosis and inflammation in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:8172714. doi: 10.1155/2020/8172714
8. Feng Z, Fang C, Ma Y, Chang J. Obesity-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction: phenotypes and mechanisms. J Neuroinflamm. (2024) 21:110. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03104-9
9. Hasel P, Aisenberg WH, Bennett FC, Liddelow SA. Molecular and metabolic heterogeneity of astrocytes and microglia. Cell Metab. (2023) 35:555–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.006
10. Lo CH, Skarica M, Mansoor M, Bhandarkar S, Toro S, Pitt D. Astrocyte heterogeneity in multiple sclerosis: current understanding and technical challenges. Front Cell Neurosci. (2021) 15:726479. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.726479
11. Mazon JN, de Mello AH, Ferreira GK, Rezin GT. The impact of obesity on neurodegenerative diseases. Life Sci. (2017) 182:22–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.06.002
12. Pitt D, Lo CH, Gauthier SA, Hickman RA, Longbrake E, Airas LM, et al. Toward precision phenotyping of multiple sclerosis. Neurol - Neuroimmunology Neuroinflamm. (2022) 9:e200025. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200025
13. Yan M, Man S, Sun B, Ma L, Guo L, Huang L, et al. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: the implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2023) 8:443. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01673-4
14. Loh JS, Mak WQ, Tan LKS, Ng CX, Chan HH, Yeow SH, et al. Microbiota–gut–brain axis and its therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:37. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01743-1
15. de la Monte SM, Longato L, Tong M, Wands JR. Insulin resistance and neurodegeneration: roles of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. (2009) 10:1049–60.
16. Sripetchwandee J, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. Links between obesity-induced brain insulin resistance, brain mitochondrial dysfunction, and dementia. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2018) 9:496. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00496
17. Cheke LG, Bonnici HM, Clayton NS, Simons JS. Obesity and insulin resistance are associated with reduced activity in core memory regions of the brain. Neuropsychologia. (2017) 96:137–49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.01.013
18. Galizzi G, Palumbo L, Amato A, Conigliaro A, Nuzzo D, Terzo S, et al. Altered insulin pathway compromises mitochondrial function and quality control both in in vitro and in vivo model systems. Mitochondrion. (2021) 60:178–88. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.08.014
19. Xia W, Veeragandham P, Cao Y, Xu Y, Rhyne TE, Qian J, et al. Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation. Nat Metab. (2024) 6:273–89. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-00978-0
20. Bruce-Keller AJ, White CL, Gupta S, Knight AG, Pistell PJ, Ingram DK, et al. NOX activity in brain aging: Exacerbation by high fat diet. Free Radic Biol Med. (2010) 49:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.03.006
21. de Mello AH, Costa AB, Engel JDG, Rezin GT. Mitochondrial dysfunction in obesity. Life Sci. (2018) 192:26–32. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.019
22. Asimakidou E, Reynolds R, Barron AM, Lo CH. Autolysosomal acidification impairment as a mediator for TNFR1 induced neuronal necroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regener Res. (2024) 19:1869–70. Available at: https://journals.lww.com/nrronline/fulltext/2024/09000/autolysosomal_acidification_impairment_as_a.5.aspx.
23. Asimakidou E, Saipuljumri EN, Lo CH, Zeng J. Role of metabolic dysfunction and inflammation along the liver–brain axis in animal models with obesity induced neurodegeneration. Neural Regener Res. (2024) 20:1069–76. Available at: https://journals.lww.com/nrronline/abstract/9900/role_of_metabolic_dysfunction_and_inflammation.355.aspx.
24. An L, Wirth U, Koch D, Schirren M, Drefs M, Koliogiannis D, et al. The role of gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and the intestinal barrier in fatty liver diseases. J Gastrointest Surg. (2022) 26:671–83. doi: 10.1007/s11605-021-05188-7
25. Yang J, Ran M, Li H, Lin Y, Ma K, Yang Y, et al. New insight into neurological degeneration: Inflammatory cytokines and blood–brain barrier. Front Mol Neurosci. (2022) 15:1013933. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/molecular-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnmol.2022.1013933.
26. Huang X, Hussain B, Chang J. Peripheral inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2021) 27:36–47. doi: 10.1111/cns.13569
27. Batista CRA, Gomes GF, Candelario-Jalil E, Fiebich BL, de Oliveira ACP. Lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation as a bridge to understand neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(9):2293. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092293
28. De Sousa Rodrigues ME, Houser MC, Walker DI, Jones DP, Chang J, Barnum CJ, et al. Targeting soluble tumor necrosis factor as a potential intervention to lower risk for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2020) 12:1. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0546-4
29. Moser VA, Uchoa MF, Pike CJ. TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242 attenuates the adverse neural effects of diet-induced obesity. J Neuroinflamm. (2018) 15:306. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1340-0
30. Vunnam N, Yang M, Lo CH, Paulson C, Fiers WD, Huber E, et al. Zafirlukast is a promising scaffold for selectively inhibiting TNFR1 signaling. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. (2023) 3:270–82. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.2c00048
31. Zeng J, Loi GWZ, Saipuljumri EN, Romero Durán MA, Silva-García O, Perez-Aguilar JM, et al. Peptide-based allosteric inhibitor targets TNFR1 conformationally active region and disables receptor–ligand signaling complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2024) 121:e2308132121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308132121
32. Lo CH, Schaaf TM, Thomas DD, Sachs JN. Fluorescence-Based TNFR1 Biosensor for Monitoring Receptor Structural and Conformational Dynamics and Discovery of Small Molecule Modulators BT - The TNF Superfamily: Methods and Protocols. Bayry J, editor. New York, NY: Springer US (2021) p. 121–37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1130-2_9
33. Lo CH. TNF receptors: Structure-function relationships and therapeutic targeting strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. (2025) 1867:184394. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2024.184394
34. Romerio A, Peri F. Increasing the chemical variety of small-molecule-based TLR4 modulators: an overview. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1210. Available at: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01210.
35. Zhang Y, Liang X, Bao X, Xiao W, Chen G. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) inhibitors: Current research and prospective. Eur J Med Chem. (2022) 235:114291. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114291
36. Cavaliere G, Cimmino F, Trinchese G, Catapano A, Petrella L, D’Angelo M, et al. From obesity-induced low-grade inflammation to lipotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction: altered multi-crosstalk between adipose tissue and metabolically active organs. Antioxidants. (2023) 12(6):1172. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061172
37. Balan AI, Halaţiu VB, Scridon A. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction: A link between obesity and atrial fibrillation. Antioxidants. (2024) 13(1):117. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010117
38. Lo CH, Zeng J, Loi GWZ, Saipuljumri EN, O’Connor LM, Indajang J, et al. Defective lysosomal acidification contributes to TNFR1 mediated neuronal necroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. bioRxiv. (2023), 2023.10.12.562041. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.12.562041
39. Lee JW, Nam H, Kim LE, Jeon Y, Min H, Ha S, et al. TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) activation suppresses autophagy through inhibition of FOXO3 and impairs phagocytic capacity of microglia. Autophagy. (2019) 15:753–70. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1556946
40. Fisher FM, Maratos-Flier E. Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol. (2016) 78:223–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105339
41. Hua L, Li J, Yang Y, Jiang D, Jiang X, Han X, et al. Liver-derived FGF21 is required for the effect of time-restricted feeding on high-fat diet-induced fatty liver in mice. FASEB J. (2023) 37:e22898. doi: 10.1096/fj.202202031R
42. Yu Y, He J, Li S, Song L, Guo X, Yao W, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation by activating Nrf2 and suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2016) 38:144–52. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.05.026
43. Wang Q, Yuan J, Yu Z, Lin L, Jiang Y, Cao Z, et al. FGF21 attenuates high-fat diet-induced cognitive impairment via metabolic regulation and anti-inflammation of obese mice. Mol Neurobiol. (2018) 55:4702–17. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0663-7
44. Sa-Nguanmoo P, Tanajak P, Kerdphoo S, Satjaritanun P, Wang X, Liang G, et al. FGF21 improves cognition by restored synaptic plasticity, dendritic spine density, brain mitochondrial function and cell apoptosis in obese-insulin resistant male rats. Horm Behav. (2016) 85:86–95. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2016.08.006
45. Vraka K, Mytilinaios D, Katsenos AP, Serbis A, Baloyiannis S, Bellos S, et al. Cellular localization of orexin 1 receptor in human hypothalamus and morphological analysis of neurons expressing the receptor. Biomolecules. (2023) 13(4):592. doi: 10.3390/biom13040592
46. Duffy CM, Hofmeister JJ, Nixon JP, Butterick TA. High fat diet increases cognitive decline and neuroinflammation in a model of orexin loss. Neurobiol Learn Mem. (2019) 157:41–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.11.008
47. Duffy CM, Yuan C, Wisdorf LE, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, Nixon JP, et al. Role of orexin A signaling in dietary palmitic acid-activated microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. (2015) 606:140–4. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.08.033
48. Pasban-Aliabadi H, Esmaeili-Mahani S, Abbasnejad M. Orexin-A protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity: involvement of PKC and PI3K signaling pathways. Rejuvenation Res. (2016) 20:125–33. doi: 10.1089/rej.2016.1836
49. Tunisi L, Forte N, Fernández-Rilo AC, Mavaro I, Capasso R, D’Angelo L, et al. Orexin-A prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation at the level of the intestinal barrier. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2019) 10:219. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00219
50. Vinuesa A, Pomilio C, Gregosa A, Bentivegna M, Presa J, Bellotto M, et al. Inflammation and insulin resistance as risk factors and potential therapeutic targets for alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci. (2021) 15:653651. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.653651
51. Spinelli M, Fusco S, Grassi C. Brain insulin resistance and hippocampal plasticity: mechanisms and biomarkers of cognitive decline. Front Neurosci. (2019) 13:788. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00788
52. Kopp KO, Glotfelty EJ, Li Y, Greig NH. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and neuroinflammation: Implications for neurodegenerative disease treatment. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 186:106550. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106550
53. Wong CK, McLean BA, Baggio LL, Koehler JA, Hammoud R, Rittig N, et al. Central glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor activation inhibits Toll-like receptor agonist-induced inflammation. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:130–143.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.11.009
54. Nag S, Mandal S, Mukherjee O, Majumdar T, Mukhopadhyay S, Kundu R. Vildagliptin inhibits high fat and fetuin-A mediated DPP-4 expression, intracellular lipid accumulation and improves insulin secretory defects in pancreatic beta cells. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167047. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167047
55. Pipatpiboon N, Pintana H, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. DPP 4-inhibitor improves neuronal insulin receptor function, brain mitochondrial function and cognitive function in rats with insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet consumption. Eur J Neurosci. (2013) 37:839–49. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12088
56. Pintana H, Tanajak P, Pratchayasakul W, Sa-nguanmoo P, Chunchai T, Satjaritanun P, et al. Energy restriction combined with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor exerts neuroprotection in obese male rats. Br J Nutr. (2016) 116:1700–8. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516003871
57. Sa-nguanmoo P, Tanajak P, Kerdphoo S, Jaiwongkam T, Pratchayasakul W, Chattipakorn N, et al. SGLT2-inhibitor and DPP-4 inhibitor improve brain function via attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance, inflammation, and apoptosis in HFD-induced obese rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2017) 333:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.08.005
58. Tanokashira D, Kurata E, Fukuokaya W, Kawabe K, Kashiwada M, Takeuchi H, et al. Metformin treatment ameliorates diabetes-associated decline in hippocampal neurogenesis and memory via phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1. FEBS Open Bio. (2018) 8:1104–18. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12436
59. Maneechote C, Chunchai T, Apaijai N, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. Pharmacological targeting of mitochondrial fission and fusion alleviates cognitive impairment and brain pathologies in pre-diabetic rats. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:3690–702. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02813-7
60. Kim S, Kim C, Park S. Mdivi-1 protects adult rat hippocampal neural stem cells against palmitate-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:1947. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091947
61. Maneechote C, Pintana H, Kerdphoo S, Janjek S, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. Differential temporal therapies with pharmacologically targeted mitochondrial fission/fusion protect the brain against acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in prediabetic rats: The crosstalk between mitochondrial apoptosis and inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. (2023) 956:175939. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175939
62. Pintana H, Sripetchwandee J, Supakul L, Apaijai N, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn S. Garlic extract attenuates brain mitochondrial dysfunction and cognitive deficit in obese-insulin resistant rats. Appl Physiology Nutrition Metab. (2014) 39:1373–9. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2014-0255
63. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. (2017) 542:177–85. doi: 10.1038/nature21363
64. Xourafa G, Korbmacher M, Roden M. Inter-organ crosstalk during development and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2024) 20:27–49. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00898-1
65. Szukiewicz D. Molecular mechanisms for the vicious cycle between insulin resistance and the inflammatory response in obesity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(12):9818. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129818
66. Suren Garg S, Kushwaha K, Dubey R, Gupta J. Association between obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance: Insights into signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2023) 200:110691. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110691
67. Vringer E, Tait SWG. Mitochondria and cell death-associated inflammation. Cell Death Differ. (2023) 30:304–12. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01094-w
68. Marchi S, Guilbaud E, Tait SWG, Yamazaki T, Galluzzi L. Mitochondrial control of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:159–73. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00760-x
69. Lo CH, O’Connor LM, Loi GWZ, Saipuljumri EN, Indajang J, Lopes KM, et al. Acidic nanoparticles restore lysosomal acidification and rescue metabolic dysfunction in pancreatic β-cells under lipotoxic conditions. ACS Nano. (2024) 18:15452–67. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c09206
70. Zeng J, Acin-Perez R, Assali EA, Martin A, Brownstein AJ, Petcherski A, et al. Restoration of lysosomal acidification rescues autophagy and metabolic dysfunction in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2573. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38165-6
71. Quick JD, Silva C, Wong JH, Lim KL, Reynolds R, Barron AM, et al. Lysosomal acidification dysfunction in microglia: an emerging pathogenic mechanism of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflamm. (2023) 20:185. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02866-y
72. Lo CH. Towards clinical translation of biomarkers and therapies targeting autolysosomal acidification dysfunction in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration—an interview with Prof. David Rubinsztein Aging Pathobiol Ther. (2024) 6:138–40. doi: 10.31491/APT.2024.09.153
73. Revankar NA, Negi PS. Biotics: An emerging food supplement for health improvement in the era of immune modulation. Nutr Clin Pract. (2023) 39(2):311–29. doi: 10.1002/ncp.11036
74. Yang Y, Zhong Z, Wang B, Xia X, Yao W, Huang L, et al. Early-life high-fat diet-induced obesity programs hippocampal development and cognitive functions via regulation of gut commensal Akkermansia muciniphila. Neuropsychopharmacology. (2019) 44:2054–64. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0437-1
75. Wu F, Guo X, Zhang M, Ou Z, Wu D, Deng L, et al. An Akkermansia muciniphila subtype alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders and inhibits the neurodegenerative process in mice. Anaerobe. (2020) 61:102138. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.102138
76. Zheng M, Ye H, Yang X, Shen L, Dang X, Liu X, et al. Probiotic Clostridium butyricum ameliorates cognitive impairment in obesity via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 115:565–87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.11.016
77. Schmidt NP, Molz P, Fraga BS, Bondarczuk NH, Silveira PD, Ferri MH, et al. Effect of probiotic lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LB1.5 on anxiety-like behavior, neuroprotection and neuroinflammation markers of male mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients. (2024) 16:879. doi: 10.3390/nu16060879
78. Ji Y, Lang X, Wang W, Li S, Zhao C, Shen X, et al. Lactobacillus paracasei ameliorates cognitive impairment in high-fat induced obese mice via insulin signaling and neuroinflammation pathways. Food Funct. (2021) 12:8728–37. doi: 10.1039/D1FO01320C
79. Jena PK, Setayesh T, Sheng L, Di Lucente J, Jin LW, Wan Y-JY. Intestinal microbiota remodeling protects mice from western diet-induced brain inflammation and cognitive decline. Cells. (2022) 11:504. doi: 10.3390/cells11030504
80. Chen J, Vitetta L. Gut microbiota metabolites in NAFLD pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(15):5214. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155214
81. Snigdha S, Ha K, Tsai P, Dinan TG, Bartos JD, Shahid M. Probiotics: Potential novel therapeutics for microbiota-gut-brain axis dysfunction across gender and lifespan. Pharmacol Ther. (2022) 231:107978. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107978
82. Chunchai T, Thunapong W, Yasom S, Wanchai K, Eaimworawuthikul S, Metzler G, et al. Decreased microglial activation through gut-brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese-insulin resistant rats. J Neuroinflamm. (2018) 15:11. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1055-2
83. Hijová E. Synbiotic supplements in the prevention of obesity and obesity-related diseases. Metabolites. (2022) 12(4):313. doi: 10.3390/metabo12040313
84. Sergeev IN, Aljutaily T, Walton G, Huarte E. Effects of synbiotic supplement on human gut microbiota, body composition and weight loss in obesity. Nutrients. (2020) 12(1):222. doi: 10.3390/nu12010222
85. González-Lozano E, García-García J, Gálvez J, Hidalgo-García L, Rodríguez-Nogales A, Rodríguez-Cabezas ME, et al. Novel horizons in postbiotics: lactobacillaceae extracellular vesicles and their applications in health and disease. Nutrients. (2022) 14(24):5296. doi: 10.3390/nu14245296
86. Hoyles L, Pontifex MG, Rodriguez-Ramiro I, Anis-Alavi MA, Jelane KS, Snelling T, et al. Regulation of blood-brain barrier integrity by microbiome-associated methylamines and cognition by trimethylamine N-oxide. Microbiome. (2021) 9:235. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01181-z
87. Stachulski AV, Knausenberger TB-A, Shah SN, Hoyles L, McArthur S. A host-gut microbial amino acid co-metabolite, p-cresol glucuronide, promotes blood-brain barrier integrity in vivo. Tissue Barriers. (2023) 11:2073175. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2022.2073175
88. Hoyles L, Snelling T, Umlai U-K, Nicholson JK, Carding SR, Glen RC, et al. Microbiome-host systems interactions: protective effects of propionate upon the blood-brain barrier. Microbiome. (2018) 6:55. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0439-y
89. Knox EG, Aburto MR, Tessier C, Nagpal J, Clarke G, O’Driscoll CM, et al. Microbial-derived metabolites induce actin cytoskeletal rearrangement and protect blood-brain barrier function. iScience. (2022) 25:105648. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105648
90. Miyamoto J, Igarashi M, Watanabe K, Karaki S-I, Mukouyama H, Kishino S, et al. Gut microbiota confers host resistance to obesity by metabolizing dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids. Nat Commun. (2019) 10:4007. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11978-0
91. Masse KE, Lu VB. Short-chain fatty acids, secondary bile acids and indoles: gut microbial metabolites with effects on enteroendocrine cell function and their potential as therapies for metabolic disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1169624. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1169624
92. Noble EE, Hsu TM, Kanoski SE. Gut to brain dysbiosis: mechanisms linking western diet consumption, the microbiome, and cognitive impairment. Front Behav Neurosci. (2017) 11:9. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00009
93. Gomes Gonçalves N, Cacau LT, Ferreira NV, Lotufo PA, Goulart AC, Viana MC, et al. Adherence to the planetary health diet and cognitive decline: findings from the ELSA-Brasil study. Nat Aging. (2024) 4:1465–76. doi: 10.1038/s43587-024-00666-4
94. Kim N, Lee J, Song HS, Oh YJ, Kwon M-S, Yun M, et al. Kimchi intake alleviates obesity-induced neuroinflammation by modulating the gut-brain axis. Food Res Int. (2022) 158:111533. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111533
95. Shi H, Yu Y, Lin D, Zheng P, Zhang P, Hu M, et al. [amp]]beta;-glucan attenuates cognitive impairment via the gut-brain axis in diet-induced obese mice. Microbiome. (2020) 8:143. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00920-y
96. Xiao R, Zeng J, Bressler EM, Lu W, Grinstaff MW. Synthesis of bioactive (1→6)-β-glucose branched poly-amido-saccharides that stimulate and induce M1 polarization in macrophages. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4661. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32346-5
97. Marques C, Fernandes I, Meireles M, Faria A, Spencer JPE, Mateus N, et al. Gut microbiota modulation accounts for the neuroprotective properties of anthocyanins. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:11341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29744-5
98. Shi H, Wang Q, Zheng M, Hao S, Lum JS, Chen X, et al. Supplement of microbiota-accessible carbohydrates prevents neuroinflammation and cognitive decline by improving the gut microbiota-brain axis in diet-induced obese mice. J Neuroinflamm. (2020) 17:77. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01760-1
99. Wang D, Wang L, Han L, Wang B, Shi R, Ye J, et al. Leucine-restricted diet ameliorates obesity-linked cognitive deficits: involvement of the microbiota–gut–brain axis. J Agric Food Chem. (2023) 71:9404–18. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01524
100. Liu Z, Dai X, Zhang H, Shi R, Hui Y, Jin X, et al. Gut microbiota mediates intermittent-fasting alleviation of diabetes-induced cognitive impairment. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:855. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14676-4
101. Chen J, Haase N, Haange S-B, Sucher R, Münzker J, Jäger E, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass contributes to weight loss-independent improvement in hypothalamic inflammation and leptin sensitivity through gut-microglia-neuron-crosstalk. Mol Metab. (2021) 48:101214. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101214
102. Herrick MK, Favela KM, Simerly RB, Abumrad NN, Bingham NC. Attenuation of diet-induced hypothalamic inflammation following bariatric surgery in female mice. Mol Med. (2018) 24:56. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0057-y
103. Liu J-Y, Mu S, Zhang S-P, Guo W, Li Q-F, Xiao X-Q, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery suppresses hypothalamic PTP1B protein level and alleviates leptin resistance in obese rats. Exp Ther Med. (2017) 14:2536–42. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4801
104. Ruze R, Xu Q, Liu G, Li Y, Chen W, Cheng Z, et al. Central GLP-1 contributes to improved cognitive function and brain glucose uptake after duodenum-jejunum bypass on obese and diabetic rats. Am J Physiology-Endocrinology Metab. (2021) 321:E392–409. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00126.2021
105. Li C, Song J, Zhao J, Wang C, Zhang C, Wang H, et al. The effects of bariatric surgery on cognition in patients with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Obes Related Dis. (2022) 18:1323–38. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2022.07.007
106. Ser H-L, Letchumanan V, Goh B-H, Wong SH, Lee L-H. The use of fecal microbiome transplant in treating human diseases: too early for poop? Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:519836. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.519836
107. Zhang Z, Mocanu V, Cai C, Dang J, Slater L, Deehan EC, et al. Impact of fecal microbiota transplantation on obesity and metabolic syndrome—A systematic review. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2291. doi: 10.3390/nu11102291
108. Park S-S, Kim S-H, Kim C-J, Shin M-S, Park Y-J, Kim T-W. Effects of exercise and microbiota transplant on the memory of obesity-induced mice. J Exerc Rehabil. (2022) 18:162–70. doi: 10.12965/jer.2244272.136
109. Hartstra AV, Schüppel V, Imangaliyev S, Schrantee A, Prodan A, Collard D, et al. Infusion of donor feces affects the gut–brain axis in humans with metabolic syndrome. Mol Metab. (2020) 42:101076. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101076
110. Fontana L, Ghezzi L, Cross AH, Piccio L. Effects of dietary restriction on neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. J Exp Med. (2021) 218(2):e20190086. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190086
111. Yin Z, Raj DD, Schaafsma W, van der Heijden RA, Kooistra SM, Reijne AC, et al. Low-fat diet with caloric restriction reduces white matter microglia activation during aging. Front Mol Neurosci. (2018) 11:65. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00065
112. Wang R, Zhou Z, Wang D, Zhao Q, Zhang C, Liu C, et al. Caloric restriction ameliorates high-fat diet induced cognitive deficits through attenuating neuroinflammation via the TREM2-PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Food Funct. (2021) 12:6464–78. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02946G
113. Ebrahim HA, El-Gamal R, Sherif RN. Intermittent fasting attenuates high-fat diet-induced cerebellar changes in rats: involvement of TNF-α, autophagy, and oxidative stress. Cells Tissues Organs. (2021) 210:351–67. doi: 10.1159/000519088
114. Qiu X, Brown K, Hirschey MD, Verdin E, Chen D. Calorie restriction reduces oxidative stress by SIRT3-mediated SOD2 activation. Cell Metab. (2010) 12:662–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2010.11.015
115. Tyagi A, Nguyen CU, Chong T, Michel CR, Fritz KS, Reisdorph N, et al. SIRT3 deficiency-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammasome formation in the brain. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:17547. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35890-7
116. Tyagi A, Musa M, Labeikovsky W, Pugazhenthi S. Sirt3 deficiency induced down regulation of insulin degrading enzyme in comorbid Alzheimer’s disease with metabolic syndrome. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:19808. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23652-5
117. Tyagi A, Pugazhenthi S. A promising strategy to treat neurodegenerative diseases by SIRT3 activation. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24(2):1615. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021615
118. Lee J, An HS, Shin HJ, Jang HM, Im CO, Jeong Y, et al. Intermittent fasting reduces neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in high-fat diet-fed mice by downregulating lipocalin-2 and galectin-3. Nutrients. (2024) 16:159. doi: 10.3390/nu16010159
119. Ooi TC, Meramat A, Rajab NF, Shahar S, Ismail IS, Azam AA, et al. Intermittent fasting enhanced the cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment by inducing biochemical and metabolic changes: A 3-year progressive study. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2644. doi: 10.3390/nu12092644
120. Kim T-W, Baek K-W, Yu HS, Ko I-G, Hwang L, Park J-J. High-intensity exercise improves cognitive function and hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in obese mice maintained on high-fat diet. J Exerc Rehabil. (2020) 16:124–31. doi: 10.12965/jer.2040050.025
121. Maryam K, Ali H. Aerobic and resistance exercises affect the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway, and hippocampal neuron density of high-fat diet-induced obese elderly rats. Physiol Behav. (2023) 264:114140. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2023.114140
122. Kim T-W, Choi H-H, Chung Y-R. Treadmill exercise alleviates impairment of cognitive function by enhancing hippocampal neuroplasticity in the high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Exerc Rehabil. (2016) 12:156–62. doi: 10.12965/jer.1632644.322
123. Pantiya P, Thonusin C, Chunchai T, Ongnok B, Nawara W, Arunsak B, et al. Higher untrained fitness exerts a neuroprotection in Independence to caloric restriction or exercise in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Exp Neurol. (2023) 365:114416. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114416
124. Spencer SJ, D’Angelo H, Soch A, Watkins LR, Maier SF, Barrientos RM. High-fat diet and aging interact to produce neuroinflammation and impair hippocampal- and amygdalar-dependent memory. Neurobiol Aging. (2017) 58:88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.06.014
125. Graham LC, Grabowska WA, Chun Y, Risacher SL, Philip VM, Saykin AJ, et al. Exercise prevents obesity-induced cognitive decline and white matter damage in mice. Neurobiol Aging. (2019) 80:154–72. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.03.018
126. Ruegsegger GN, Vanderboom PM, Dasari S, Klaus KA, Kabiraj P, McCarthy CB, et al. Exercise and metformin counteract altered mitochondrial function in the insulin-resistant brain. JCI Insight. (2019) 4(18):e130681. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.130681
127. Li R, Ding X, Geetha T, Fadamiro M, St Aubin CR, Shim M, et al. Effects of genistein and exercise training on brain damage induced by a high-fat high-sucrose diet in female C57BL/6 mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2022/1560435
128. Cheng J, Chen L, Han S, Qin L, Chen N, Wan Z. Treadmill running and rutin reverse high fat diet induced cognitive impairment in diet induced obese mice. J Nutr Health Aging. (2016) 20:503–8. doi: 10.1007/s12603-015-0616-7
129. Koo J-H, Kang E-B. Effects of treadmill exercise on the regulatory mechanisms of mitochondrial dynamics and oxidative stress in the brains of high-fat diet fed rats. J Exerc Nutr Biochem. (2019) 23:28–35. doi: 10.20463/jenb.2019.0005
130. Saieva S, Taglialatela G. Near-infrared light reduces glia activation and modulates neuroinflammation in the brains of diet-induced obese mice. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:10848. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14812-8
131. Zhang J, Li S, Cheng X, Tan X, Huang Y, Dong H, et al. Far-infrared therapy based on graphene ameliorates high-fat diet-induced anxiety-like behavior in obese mice via alleviating intestinal barrier damage and neuroinflammation. Neurochem Res. (2024) 49:1735–50. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04133-9
132. de Souza RM, de Souza L, MaChado AE, de Bem Alves AC, Rodrigues FS, Aguiar AS, et al. Behavioural, metabolic and neurochemical effects of environmental enrichment in high-fat cholesterol-enriched diet-fed mice. Behav Brain Res. (2019) 359:648–56. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.09.022
133. Ismail TR, Yap CG, Naidu R, Pamidi N. Environmental enrichment and metformin improve metabolic functions, hippocampal neuron survival, and hippocampal-dependent memory in high-fat/high-sucrose diet-induced type 2 diabetic rats. Biol (Basel). (2023) 12:480. doi: 10.3390/biology12030480
134. Nameni G, Hajiluian G, Shahabi P, Farhangi MA, Mesgari-Abbasi M, Hemmati M-R, et al. The impact of vitamin D supplementation on neurodegeneration, TNF-α Concentration in hypothalamus, and CSF-to-plasma ratio of insulin in high-fat-diet-induced obese rats. J Mol Neurosci. (2017) 61:247–55. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0864-y
135. Hajiluian G, Abbasalizad Farhangi M, Nameni G, Shahabi P, Megari-Abbasi M. Oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairment in obesity can be reversed by vitamin D administration in rats. Nutr Neurosci. (2018) 21:744–52. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1348436
136. Farhangi MA, Mesgari-Abbasi M, Nameni G, Hajiluian G, Shahabi P. The effects of vitamin D administration on brain inflammatory markers in high fat diet induced obese rats. BMC Neurosci. (2017) 18:81. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0400-1
137. Hajiluian G, Nameni G, Shahabi P, Mesgari-Abbasi M, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Farhangi MA. Vitamin D administration, cognitive function, BBB permeability and neuroinflammatory factors in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Int J Obes. (2017) 41:639–44. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2017.10
138. Nuzzo D, Amato A, Picone P, Terzo S, Galizzi G, Bonina F, et al. A natural dietary supplement with a combination of nutrients prevents neurodegeneration induced by a high fat diet in mice. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1130. doi: 10.3390/nu10091130
139. Ugbaja RN, Ugwor EI, Dosumu OA, James AS, Thomas FC, Ezenandu EO, et al. Lycopene abrogates obesity-provoked hyperactivity of neurosignalling enzymes, oxidative stress and hypothalamic inflammation in female Wistar rats. Neurochem Int. (2021) 149:105125. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105125
140. Wandt VK, Winkelbeiner N, Bornhorst J, Witt B, Raschke S, Simon L, et al. A matter of concern – Trace element dyshomeostasis and genomic stability in neurons. Redox Biol. (2021) 41:101877. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101877
141. Totten MS, Pierce DM, Erikson KM. Diet-induced obesity disrupts trace element homeostasis and gene expression in the olfactory bulb. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3909. doi: 10.3390/nu12123909
142. de Oliveira S, Feijó G dos S, Neto J, Jantsch J, Braga MF, Castro LF dos S, et al. Zinc supplementation decreases obesity-related neuroinflammation and improves metabolic function and memory in rats. Obesity. (2021) 29:116–24. doi: 10.1002/oby.23024
143. Hafez LM, Aboudeya HM, Matar NA, El-Sebeay AS, Nomair AM, El-hamshary SA, et al. Ameliorative effects of zinc supplementation on cognitive function and hippocampal leptin signaling pathway in obese male and female rats. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:5072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31781-8
144. Orhan C, Tuzcu M, Deeh Defo PB, Sahin N, Ojalvo SP, Sylla S, et al. Effects of a novel magnesium complex on metabolic and cognitive functions and the expression of synapse-associated proteins in rats fed a high-fat diet. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2022) 200:247–60. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02619-z
145. de Mello AH, Schraiber R de B, Goldim MP de S, Garcez ML, Gomes ML, de Bem Silveira G, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids attenuate brain alterations in high-fat diet-induced obesity model. Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 56:513–24. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1097-6
146. de Andrade AM, Fernandes M da C, de Fraga LS, Porawski M, Giovenardi M, Guedes RP. Omega-3 fatty acids revert high-fat diet-induced neuroinflammation but not recognition memory impairment in rats. Metab Brain Dis. (2017) 32:1871–81. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0080-7
147. Cintra DE, Ropelle ER, Moraes JC, Pauli JR, Morari J, de Souza CT, et al. Unsaturated fatty acids revert diet-induced hypothalamic inflammation in obesity. PloS One. (2012) 7:e30571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030571
148. Miao Y, Ren J, Jiang L, Liu J, Jiang B, Zhang X. [amp]]alpha;-lipoic acid attenuates obesity-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation and increases the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in ovariectomized rats fed a high-fat diet. Int J Mol Med. (2013) 32:1179–86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1482
149. Sánchez-Sarasúa S, Moustafa S, García-Avilés Á, López-Climent MF, Gómez-Cadenas A, Olucha-Bordonau FE, et al. The effect of abscisic acid chronic treatment on neuroinflammatory markers and memory in a rat model of high-fat diet induced neuroinflammation. Nutr Metab (Lond). (2016) 13:73. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0137-3
150. Lama A, Pirozzi C, Severi I, Morgese MG, Senzacqua M, Annunziata C, et al. Palmitoylethanolamide dampens neuroinflammation and anxiety-like behavior in obese mice. Brain Behav Immun. (2022) 102:110–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.02.008
151. Fan R, Hua Y, Shen J, Xiao R, Ma W. Dietary fatty acids affect learning and memory ability via regulating inflammatory factors in obese mice. J Nutr Biochem. (2022) 103:108959. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.108959
152. Ma X, Guo Y, Xu J, Wang X, Dong S, Gao Y, et al. Effects of distinct n-6 to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid ratios on insulin resistant and AD-like phenotypes in high-fat diets-fed APP/PS1 mice. Food Res Int. (2022) 162:112207. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112207
153. Cavaliere G, Catapano A, Trinchese G, Cimmino F, Penna E, Pizzella A, et al. Butyrate improves neuroinflammation and mitochondrial impairment in cerebral cortex and synaptic fraction in an animal model of diet-induced obesity. Antioxidants. (2022) 12:4. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010004
154. Li J, Shi Z, Mi Y. Purple sweet potato color attenuates high fat-induced neuroinflammation in mouse brain by inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB activation. Mol Med Rep. (2018) 17(3):4823–31. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8440
155. Meireles M, Marques C, Norberto S, Fernandes I, Mateus N, Rendeiro C, et al. The impact of chronic blackberry intake on the neuroinflammatory status of rats fed a standard or high-fat diet. J Nutr Biochem. (2015) 26:1166–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.05.008
156. Carey AN, Pintea GI, Van Leuven S, Gildawie KR, Squiccimara L, Fine E, et al. Red raspberry ( Rubus ideaus ) supplementation mitigates the effects of a high-fat diet on brain and behavior in mice. Nutr Neurosci. (2021) 24:406–16. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1641284
157. Ajayi AM, John KA, Emmanuel IB, Chidebe EO, Adedapo ADA. High-fat diet-induced memory impairment and anxiety-like behavior in rats attenuated by peel extract of Ananas comosus fruit via atheroprotective, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Metabol Open. (2021) 9:100077. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100077
158. Nerurkar PV, Johns LM, Buesa LM, Kipyakwai G, Volper E, Sato R, et al. Momordica charantia (bitter melon) attenuates high-fat diet-associated oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm. (2011) 8:64. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-64
159. Piccinini A, Oliveira MP, Silva MR, Bett GS, Becker IB, Mendes TF, et al. Effects of ethanolic extract of cynara cardunculus (Artichoke) leaves on neuroinflammatory and neurochemical parameters in a diet-induced mice obesity model. Neurochem Res. (2022) 47:1888–903. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03572-6
160. Tsai Y-C, Lin Y-C, Huang C-C, Villaflores OB, Wu T-Y, Huang S-M, et al. Hericium erinaceus mycelium and its isolated compound, erinacine A, ameliorate high-fat high-sucrose diet-induced metabolic dysfunction and spatial learning deficits in aging mice. J Med Food. (2019) 22:469–78. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4288
161. Amri Z, Ghorbel A, Turki M, Akrout FM, Ayadi F, Elfeki A, et al. Effect of pomegranate extracts on brain antioxidant markers and cholinesterase activity in high fat-high fructose diet induced obesity in rat model. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2017) 17:339. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1842-9
162. Afzal O, Dalhat MH, Altamimi ASA, Rasool R, Alzarea SI, Almalki WH, et al. Green tea catechins attenuate neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive deficits. Molecules. (2022) 27:7604. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217604
163. Mi Y, Qi G, Fan R, Qiao Q, Sun Y, Gao Y, et al. EGCG ameliorates high-fat– and high-fructose-induced cognitive defects by regulating the IRS/AKT and ERK/CREB/BDNF signaling pathways in the CNS. FASEB J. (2017) 31:4998–5011. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700400RR
164. Mao L, Hochstetter D, Yao L, Zhao Y, Zhou J, Wang Y, et al. Green tea polyphenol (–)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) attenuates neuroinflammation in palmitic acid-stimulated BV-2 microglia and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5081. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205081
165. Kang J, Wang Z, Oteiza PI. (–)-Epicatechin mitigates high fat diet-induced neuroinflammation and altered behavior in mice. Food Funct. (2020) 11:5065–76. doi: 10.1039/D0FO00486C
166. Morelli S, Piscioneri A, Guarnieri G, Morelli A, Drioli E, De Bartolo L. Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of daidzein in human hypothalamic GnRH neurons in an in vitro membrane-based model. BioFactors. (2021) 47:93–111. doi: 10.1002/biof.1701
167. Yang J, Kim C-S, Tu T, Kim M-S, Goto T, Kawada T, et al. Quercetin protects obesity-induced hypothalamic inflammation by reducing microglia-mediated inflammatory responses via HO-1 induction. Nutrients. (2017) 9:650. doi: 10.3390/nu9070650
168. Mulati A, Ma S, Zhang H, Ren B, Zhao B, Wang L, et al. Sea-buckthorn flavonoids alleviate high-fat and high-fructose diet-induced cognitive impairment by inhibiting insulin resistance and neuroinflammation. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:5835–46. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00876
169. Mulati A, Zhang X, Zhao T, Ren B, Wang L, Liu X, et al. Isorhamnetin attenuates high-fat and high-fructose diet induced cognitive impairments and neuroinflammation by mediating MAPK and NFκB signaling pathways. Food Funct. (2021) 12:9261–72. doi: 10.1039/D0FO03165H
170. Panickar KS. Beneficial effects of herbs, spices and medicinal plants on the metabolic syndrome, brain and cognitive function. Ingenta Connect. (2013) 13:13–29. doi: 10.2174/1871524911313010004
171. Kaur T, Kaur G. Withania somnifera as a potential candidate to ameliorate high fat diet-induced anxiety and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm. (2017) 14:201. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0975-6
172. Singh H, Bajaj P, Kalotra S, Bhandari A, Kaur T, Singh AP, et al. Tinospora cordifolia ameliorates brain functions impairments associated with high fat diet induced obesity. Neurochem Int. (2021) 143:104937. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104937
173. Huang Y-C, Tsay H-J, Lu M-K, Lin C-H, Yeh C-W, Liu H-K, et al. Astragalus membranaceus-Polysaccharides Ameliorates Obesity, Hepatic Steatosis, Neuroinflammation and Cognition Impairment without Affecting Amyloid Deposition in Metabolically Stressed APPswe/PS1dE9 Mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:2746. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122746
174. Park SB, Kang JY, Kim JM, Park SK, Yoo SK, Lee U, et al. Effect of Aruncus dioicus var. kamtschaticus Extract on Neurodegeneration Improvement: Ameliorating Role in Cognitive Disorder Caused by High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity. Nutrients. (2019) 11:1319. doi: 10.3390/nu11061319
175. You S, Jang M, Kim G-H. Mori cortex radicis attenuates high fat diet-induced cognitive impairment via an IRS/akt signaling pathway. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1851. doi: 10.3390/nu12061851
176. Nissankara Rao LS, Kilari EK, Kola PK. Protective effect of Curcuma amada acetone extract against high-fat and high-sugar diet-induced obesity and memory impairment. Nutr Neurosci. (2021) 24:212–25. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1616436
177. Tavares Rl, Vasconcelos MHAd, Dutra MLdV, D’Oliveira AB, Lima MdS, Salvadori MGdSS, et al. Mucuna pruriens administration minimizes neuroinflammation and shows anxiolytic, antidepressant and slimming effects in obese rats. Molecules. (2020) 25:5559. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235559
178. Choi JM, Lee SI, Cho EJ. Effect of vigna angularis on high-fat diet-induced memory and cognitive impairments. J Med Food. (2020) 23:1155–62. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2019.4644
179. Fang F, Li H, Qin T, Li M, Ma S. Thymol improves high-fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in mice via ameliorating brain insulin resistance and upregulating NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Metab Brain Dis. (2017) 32:385–93. doi: 10.1007/s11011-016-9921-z
180. Sundaram K, Mu J, Kumar A, Behera J, Lei C, Sriwastva MK, et al. Garlic exosome-like nanoparticles reverse high-fat diet induced obesity via the gut/brain axis. Theranostics. (2022) 12:1220–46. doi: 10.7150/thno.65427
181. Prá M, Ferreira GK, de Mello AH, Uberti MF, Engel NA, Costa AB, et al. Treatment with isolated gold nanoparticles reverses brain damage caused by obesity. Materials Sci Engineering: C. (2021) 120:111392. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111392
182. Sundaram K, Mu J, Kumar A, Behera J, Lei C, Sriwastva MK, et al. Oral Administration of Plant Exosome-Like Nanoparticles Inhibits Brain Inflammation by Targeting Microglial Cells and Gut Akkermansia Muciniphila in Obese Mice (2021). Available online at: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3789261 (Accessed December 20, 2024).
183. Yang L, Wang Y, Li Z, Wu X, Mei J, Zheng G. Brain targeted peptide-functionalized chitosan nanoparticles for resveratrol delivery: Impact on insulin resistance and gut microbiota in obesity-related Alzheimer’s disease. Carbohydr Polym. (2023) 310:120714. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120714
184. Zeng J, Shirihai OS, Grinstaff MW. Modulating lysosomal pH: a molecular and nanoscale materials design perspective. JoLS J Life Sci. (2020) 2:25–37. doi: 10.36069/jols/20201204
185. Asimakidou E, Tan JKS, Zeng J, Lo CH. Blood-brain barrier-targeting nanoparticles: biomaterial properties and biomedical applications in translational neuroscience. Pharm (Basel). (2024) 17(5):612. doi: 10.3390/ph17050612
186. Lo CH, Zeng J. Application of polymersomes in membrane protein study and drug discovery: Progress, strategies, and perspectives. Bioeng Transl Med. (2023) 8:e10350. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10350
187. Mendes M, Sousa JJ, Pais A, Vitorino C. Targeted theranostic nanoparticles for brain tumor treatment. Pharmaceutics. (2018) 10(4):181. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040181
188. Chunchai T, Samniang B, Sripetchwandee J, Pintana H, Pongkan W, Kumfu S, et al. Vagus nerve stimulation exerts the neuroprotective effects in obese-insulin resistant rats, leading to the improvement of cognitive function. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:26866. doi: 10.1038/srep26866
189. de Lartigue G. Role of the vagus nerve in the development and treatment of diet-induced obesity. J Physiol. (2016) 594:5791–815. doi: 10.1113/JP271538
190. Zhang X, Li L, Butcher J, Stintzi A, Figeys D. Advancing functional and translational microbiome research using meta-omics approaches. Microbiome. (2019) 7:154. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0767-6
191. Chen C, Wang J, Pan D, Wang X, Xu Y, Yan J, et al. Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases. MedComm (Beijing). (2023) 4:e315. doi: 10.1002/mco2.315
192. O’Connor LM, O’Connor BA, Lim SB, Zeng J, Lo CH. Integrative multi-omics and systems bioinformatics in translational neuroscience: A data mining perspective. J Pharm Anal. (2023) 13:836–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.011
Keywords: obesity, metabolic dysfunction, neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, body-brain interactions, therapeutic targeting
Citation: Zeng J, Cheong LYT and Lo CH (2025) Therapeutic targeting of obesity-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1456948. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1456948
Received: 29 June 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 17 January 2025.
Edited by:
Hendrik Lehnert, University of Salzburg, AustriaReviewed by:
Alpna Tyagi, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesPanida Sittipo, Burapha University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Zeng, Cheong and Lo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chih Hung Lo, Y2xvMTAxQHN5ci5lZHU=; Jialiu Zeng, anplbmcyMkBzeXIuZWR1
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jialiu Zeng
Jialiu Zeng Lenny Yi Tong Cheong
Lenny Yi Tong Cheong Chih Hung Lo
Chih Hung Lo