
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Endocrinol. , 11 October 2024
Sec. Clinical Diabetes
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2024.1399924
This article is part of the Research Topic Status, Treatment, and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers View all 3 articles
Background: Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) are a major complication associated with significant morbidity and mortality. While numerous studies have investigated risk factors for these ulcers in general, few have focused specifically on patients with Neurovascular Complications of Diabetes. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence and risk factors for DFU in this specific population.
Methods: We analyzed data from the National Institutes of Health (NIS) database for the years 2017-2019, involving a cohort of 161,834 patients aged over 18 who were diagnosed with neurovascular complications of diabetes. Demographic characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity), hospital characteristics, comorbidities, and other relevant data were included for analysis. A binary logistic regression model was generated to identify independent risk factors for DFU.
Results: The prevalence of DFU among patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes was 29.4% during the period from 2017 to 2019. Compared to patients without DFU, those with DFU had longer hospitalization times and higher costs. The multiple regression analysis revealed that Iron-deficiency anemia (OR, 1.10; 95% CI, 1.01-1.11; P=0.019), Hypertension (OR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.03-1.11; P=0.001), Obesity (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.06-1.11; P<0.001), Peripheral vascular disorders (PVD) (OR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.65-1.74; P<0.001), Osteomyelitis (OR, 7.10; 95% CI, 6.89-7.31; P<0.001), Tinea pedis (OR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.59-2.26; P<0.001), Sepsis (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 1.20-1.28; P<0.001), and onychomycosis (OR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.13-1.42; P<0.001) were independent predictors for DFU in this population.
Conclusion: The study found a high prevalence of DFU in patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes. Identifying and addressing risk factors such as deficiency anemia, hypertension, obesity, PVD, infections, and foot conditions may contribute to reducing the prevalence of DFU in this vulnerable population.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a pervasive global health challenge, with 463 million cases diagnosed globally (1). It’s characterized by multi-organ complications that expedite functional decline and mortality (2). Recent research highlights neurodegenerative and neurovascular complications as key areas of interest. Microvascular disease, a common consequence of diabetes, encompasses a range of pathological changes and symptoms, traditionally categorized as “microvascular complications.” However, there’s a shift towards classifying these as “neurovascular complications,” emphasizing the intricate interplay between microvascular and neural factors (3). In patients with diabetes, PAD in the lower extremities, often accompanied by neurological issues, is a primary contributor to DFU and tissue damage. Notably, 90% of diabetic foot ulcers are attributed to neurogenic ischemia (4). Furthermore, neuropathy impairs microvascular reactivity, exacerbating ulceration, healing impairments, and infection vulnerability (5, 6).
In pre-diabetes, microvascular dysfunction can be detected prior to macrovascular or occlusive arterial disease (6). As diabetes progresses, it disrupts the structure and function of small blood vessels, triggering microvascular diseases that ultimately cause ischemic skin tissue damage and various pathological changes and symptoms (7). The sympathetic nervous system plays a crucial role in regulating skin microcirculation during posture changes, impacting arteriovenous anastomosis and precapillary function (8). Dysfunction in endothelium-dependent microvascular regulation and sympathetic denervation-induced autonomic neuropathy, linked to sweating impairments, may contribute to diabetic foot complications. Given that dry, cracked skin is prone to infections and ulcerations, safeguarding microcirculatory function is paramount (6).
DFU, as one of the most destructive complications of DM, has been associated with numerous negative consequences, including significant impairments in quality of life, decreased mobility and independence, increased incidence and mortality rates, and a substantial burden on healthcare resources (9). Therefore, accurately identifying risk factors and implementing effective preventive measures for DFU is crucial. However, research on risk factors for DFU in patients with diabetes has yielded inconsistent results, with few studies specifically investigating these factors in patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes. To address this gap, we analyzed clinical data of patients with neurovascular disease of diabetes from the NIS database between 2017 and 2019.
By analyzing the clinical characteristics of hospitalized DFU patients with neurovascular lesions, this study aims to investigate thoroughly the potential risk factors for DFU and provide more targeted support for prevention and treatment. The findings are expected to contribute to the scientific basis for improving the rehabilitation of patients with diabetes and reducing the incidence of DFU.
The data for this study was sourced from the NIS database, a 20% random sample of all hospitalized patients in the United States. This large, nationally representative sample makes the NIS ideal for conducting descriptive research, obtaining national estimates, analyzing healthcare costs, studying rare diseases, and understanding trends over time. We extracted essential patient information, including age, gender, and race, as well as basic hospital information and some related comorbidities from the database (Table 1, Figure 1).
The data was collected from the NIS database for patients hospitalized between January 1, 2017, and December 31, 2019, resulting in a dataset of 163,079 individuals. After excluding individuals with missing data (n=1,245), the final study population comprised 161,834 patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes (Figure 2). Inclusion criteria included patients diagnosed with both diabetes mellitus and neurovascular disease based on the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) codes. We excluded patients under 18 years old and those with non-pressure chronic ulcers of the thigh, calf, other lower leg regions, or unspecified lower leg locations. We compared demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with and without DFU to identify potential risk factors for developing DFU.
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS 26.0 software (IBM Corp., 2019). The study population was divided into two groups: DFU (n=47,604; 29.4%) and non-DFU (n=114,230; 70.6%). Categorical variables were compared using chi-square tests, while continuous variables were analyzed with unpaired Student’s t-tests. Descriptive analysis was conducted using frequency, constituent ratio, mean, and standard deviation. Measurement data conforming to a normal distribution are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD), while measurement data that do not conform to a normal distribution are reported as median. The count data were expressed as percentage. Logistic regression models were used to identify factors associated with DFU. Univariate analysis was first performed to identify significant variables, followed by multivariate analysis using variables with p-values < 0.05 from the univariate analysis as covariates. Statistical significance was set at P< 0.05.
Among the 161,834 patients analyzed, 37.6% were male (n=60,818) and 62.4% were female (n=101,016). The mean age was 63.15 years in the DFU group and 67.11 years in the non-DFU group (Table 2). The DFU group had a significantly higher proportion of males (70.3%) compared to the non-DFU group (Table 2).
Based on the demographic analysis, we performed multiple regression analysis on relevant variables. The results showed that age ≥ 65 years (OR: 0.67, 95% CI: 0.67-0.71, P< 0.001), female gender (OR: 0.66, 95% CI: 0.65-0.67, P< 0.001), and smoking (OR: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.76-0.79, P< 0.001) were significantly associated with DFU (Table 3).
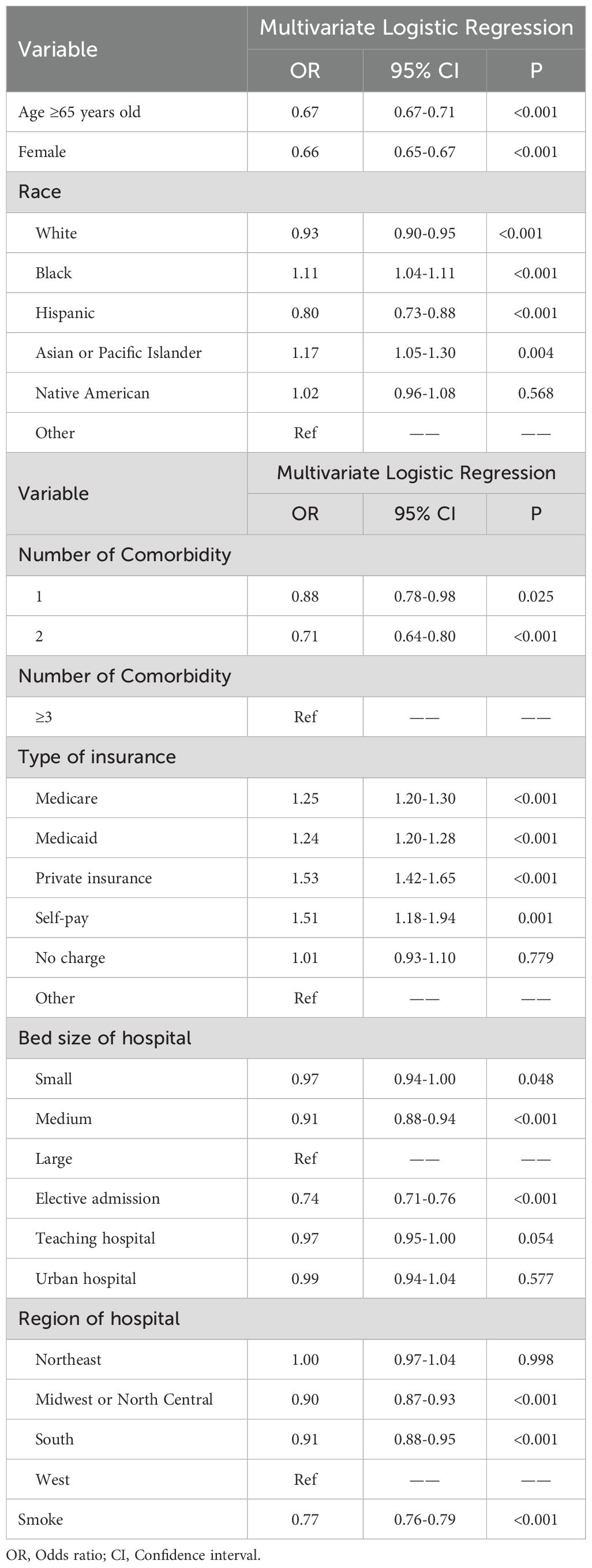
Table 3. Related risk factors of diabetes patients with neurovascular disease and diabetic foot ulcers.
Univariate analysis identified statistically significant associations (P< 0.05) between DFU and all the investigated comorbidities and complications, suggesting a correlation between DFU and these factors. Multiple regression analysis revealed several independent risk factors for DFU, including Iron-deficiency anemia (OR: 1.10, 95% CI: 1.01-1.11, P= 0.019), hypertension (OR: 1.07, 95% CI: 1.03-1.11, P= 0.001), obesity (OR: 1.08, 95% CI: 1.06-1.11, P< 0.001), PVD (OR: 1.69, 95% CI: 1.65-1.74, P< 0.001), osteomyelitis (OR: 7.10, 95% CI: 6.89-7.31, P< 0.001), tinea pedis (OR: 1.89, 95% CI: 1.59-2.26, P< 0.001), sepsis (OR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.20-1.28, P< 0.001), and onychomycosis (OR: 1.26, 95% CI: 1.13-1.42, P< 0.001).
An analysis of patient outcomes revealed that, among patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes, the length of hospitalization and total cost were significantly higher in the DFU group compared to the non-DFU group (Table 4).
This study found a 29.4% prevalence of DFU among patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes between 2017 and 2019 (Figure 3). This prevalence is lower than reported rates in Ethiopia (31.1%) and Nigeria (41.1%) (10, 11). These disparities may stem from differences in sample size, geographic location, and sociocultural factors among study populations. Additionally, our study focused specifically on patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes, a population underrepresented in previous research. Multiple regression analysis identified Iron-deficiency anemia, hypertension, obesity, PVD, osteomyelitis, tinea pedis, sepsis, and onychomycosis as independent risk factors for DFU in this study (Table 5).

Figure 3. Incidence rate of foot ulcers in diabetes patients with neurovascular disease and diabetes.
We investigated potential risk factors for DFU in the study population. The observed male predominance aligns with findings from earlier studies, such as the work by Edgar et al. (12). This may suggest a higher susceptibility to foot trauma among males, potentially contributing to a greater prevalence of DFU in this population (13). Moreover, the mean age in our study was higher compared to that reported by Hokkam et al. (14). This difference could be attributed to factors, including increased life expectancy in Europe and the United States. Besides, the prevalence of DFU among patients residing in rural areas was slightly lower than that observed in urban areas, which contradicts previous findings reported by Chowdhury et al. (11), which might be due to the relatively small sample sizes in both urban and rural groups, potentially affecting the accuracy of DFU prevalence estimates in these subgroups.
Our study revealed that patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes and Iron-deficiency anemia have a 1.10-fold greater risk of DFU compared to patients with diabetes without anemia, echoing previous research on anemia’s link to heightened foot complications (15–18). Anemia in diabetics exacerbates DFU risk via mechanisms like tissue hypoxia, metabolic dysfunction, and reduced glucose uptake, leading to hyperglycemia. Chronic hyperglycemia causes vascular damage, potentially resulting in foot complications and even mortality (19). Charcot arthropathy, a severe diabetic-specific arthropathic condition, arises from neurological and orthopedic factors, causing neuropathy and bone/joint deformities. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy drives foot complications, especially Charcot arthropathy, emphasizing its pivotal role. A study by Madeline Lyons. et al. found anemia increases the risk of Charcot arthropathy in diabetics by 1.798-fold, with complication risks escalating as the deformity progresses (20). However, the precise mechanisms underlying anemia’s impact on Charcot arthropathy are unclear, necessitating further research to unravel this complex relationship and develop targeted therapies for diabetics.
Our study found a higher prevalence of DFU among patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes and hypertension. This association aligns with previous research demonstrating the link between hypertension and both microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetes (21). Hypertension, or high blood pressure, can damage the blood vessels, including those in the feet, leading to reduced blood flow and impaired perfusion. This can result in ischemia, a condition where the tissues do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients due to inadequate blood supply. Ischemia is a crucial factor in the development and worsening of DFU, as it impairs wound healing and increases the risk of infection (22). Additionally, the combined effects of hypertension and hyperglycemia can lead to inadequate blood supply and decreased local oxygen saturation in the lower limbs, ultimately weakening tissue resistance and immunity.
Our study further found that patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes and obesity experience a 1.08-fold increased risk of developing DFU compared to non-obese patients. These findings are consistent with previous research conducted in Ethiopia, Kenya, and Malaysia, highlighting regional concordance in this association (23). Obesity is associated with several metabolic derangements that can contribute to the development of DFU. Firstly, obesity often leads to insulin resistance, a key feature of type 2 diabetes (24). Secondly, obesity can exacerbate inflammation, which can impair wound healing and promote the development of infections. Additionally, excess weight can put pressure on the feet, leading to increased shear forces and the formation of DFU, particularly in patients with neuropathy (10).
Moreover, patients with PVD were found to have a 1.69-fold higher risk of DFU compared to those without PVD. PVD encompasses arterial and venous system diseases, and its complex nature often leads to asymptomatic DFU in the early stages, progressing to chronic non-healing ulcers with prominent tissue loss in later stages. PVD, such as atherosclerosis and peripheral artery disease (PAD), can cause narrowing or blockage of blood vessels in the legs and feet. This results in reduced blood flow and ischemia, which can impair wound healing and increase the risk of infection. The impact of PAD, which involves the narrowing or blockage of arteries in the lower limbs leading to reduced blood flow (25), is well-documented. It has been reported that PAD contributes to 50-70% of DFU cases and is a significant risk factor for delayed wound healing, infection, amputation, and mortality in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes (26).
Furthermore, our study revealed a 7.01-fold increased risk of DFU in patients with osteomyelitis compared to those without. This association is supported by evidence demonstrating a strong link between diabetes and the increased risk of both acute and chronic osteomyelitis (27). Osteomyelitis is a bone infection that can occur in the feet of patients with diabetes. This infection can destroy bone tissue, causing structural instability and increasing the risk of ulceration. Osteomyelitis can also impair wound healing and promote the development of sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by widespread infection in the body (28). Several studies support the bidirectional relationship between DFU and osteomyelitis. Lavery et al. (29) found that the presence of osteomyelitis negatively impacts diabetic foot infection outcomes, potentially promoting DFU development. Similarly, Zhang et al. (30) identified diabetes foot osteomyelitis (DFO) as a complex complication arising after DFU and requiring surgical intervention, further establishing its role as an independent risk factor for DFU recurrence. Furthermore, Yesil et al. (28) emphasize the significance of osteomyelitis as a risk factor for major amputation among DFU patients, extending its impact beyond DFU occurrence.
Our study findings also suggest that both onychomycosis and tinea pedis are independent risk factors for DFU. Onychomycosis can affect the feet of patients with diabetes. This infection can cause thickening and distortion of the nails, which can lead to pressure points and ulceration. Additionally, onychomycosis can disrupt the normal anatomy of the foot, making it more susceptible to injury and infection (31). Tinea pedis can disrupt the skin’s barrier function, making it more susceptible to injury and infection. In patients with diabetes, tinea pedis can lead to the development of DFU, particularly in areas of the feet that are already compromised by neuropathy or ischemia (32). This aligns with research by Akkus et al., who reported a significantly higher prevalence of fungal infections between the toes, soles, and toenails in patients with DFU compared to those without (31). They further highlight that poor blood glucose control and PVD in patients with diabetes increase susceptibility to fungal infections, potentially contributing to DFU development.
Sepsis poses a severe complication in vulnerable DFU patients, elevating the risk of non-traumatic amputation, multi-organ failure, and even death. Sepsis is characterized by a systemic inflammatory response that can lead to organ dysfunction and, in some cases, death. Sepsis can exacerbate the underlying neurovascular complications of diabetes, further impairing wound healing and increasing the risk of amputation (33).
While this study did not find an association between diabetes type and DFU, research by Mariam et al. suggests that diabetes type is a strong predictor of DFU. Their findings indicate a 2.58-fold increased risk of developing DFU in patients with type 2 diabetes compared to type 1 (34). Additionally, studies conducted in Nigeria, Egypt, and Asia have reported a significant association between type 2 diabetes and DFU occurrence (10, 35, 36). These discrepancies might stem from differences in the utilized databases and study populations.
The strengths of this study lie in its substantial sample size and utilization of the NIS database, which enables precise identification of patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes. However, it is important to acknowledge several limitations, including retrospective biases and data constraints. To address these, rigorous data cleaning, statistical adjustments, and discussions on generalizability were employed. Nevertheless, the ICD coding system’s evolution and inherent limitations pose challenges, affecting diagnosis specificity and ulcer severity scores’ accuracy. This may lead to undercoding of complications and misleading conclusions. Moreover, the underutilization of low-cost diagnostic measures further compromises assessments. To mitigate these issues, validation using multiple data sources is essential. Additionally, the HCUP-NIS database’s lack of clinical fine-grained data and focus on hospitalization data hinder in-depth analysis and risk adjustment, impacting medical quality and outcome assessments. Consequently, comprehensive analysis of the medical system is limited, posing challenges to fully understanding patient diagnosis and treatment. Our findings have significant clinical and public health implications for patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes. By identifying DFU risk factors, we can inform targeted screening and prioritize high-risk patients for foot exams and education. Modifiable risk factors can guide preventive interventions and lifestyle modifications. Furthermore, novel biomarkers may pave the way for personalized medicine. A multidisciplinary approach, focusing on both neurological and vascular components, is crucial for comprehensive care, emphasizing collaboration among healthcare providers. Ultimately, our findings underscore the importance of early DFU detection and management to reduce morbidity, disability, and healthcare costs. Prevention efforts and timely interventions can improve patient outcomes and alleviate financial burdens.
This study found a high prevalence of DFU among patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes between 2017 and 2019. Several factors, including iron-deficiency anemia, hypertension, obesity, PVD, osteomyelitis, tinea pedis, sepsis, and onychomycosis, were associated with DFU. Our findings on DFU risk factors align with prior studies, emphasizing the crucial role of glycemic control. While age, gender, and comorbidities may exert varying impacts due to study differences, our work underscores the significance of neuropathy-focused paradigm. We advocate a holistic approach that integrates neural and vascular factors in DFU prevention and treatment. Future research should strive for large-scale, standardized studies to clarify DFU risks and identify universal predictors. To this point in the field of health care, to ensure that patients with accessibility and improve the diagnosis, treatment and the result is very important. Given Singh AV et al. Research, future research should give priority to meet strict regulatory standards of safety and efficacy evaluation (37). Our research contributes to refining DFU guidelines and evidence-based medicine, aiming to alleviate the global DFU burden and elevate patient quality of life. Moreover, our findings deepen the understanding of DFU risks and challenge existing paradigms. This knowledge can empower preventative strategies and ultimately reduce the prevalence of DFU.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because All data used in this study were anonymized and no patient privacy was involved.
ZF: Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Visualization. JH: Investigation, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YLiu: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HX: Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YLia: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Software, Supervision. HD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Nursing Research Program, Southern Medical University (2021) (grant numbers Y2021012) and Overseas Famous Teacher Project of Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2022) (grant numbers 2022GXJK152).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Wu B, Niu Z, Hu F. Study on risk factors of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus and establishment of prediction model. Diabetes Metab J. (2021) 45:526–38. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0100
2. Gasecka A, Siwik D, Gajewska M, Jaguszewski MJ, Mazurek T, Filipiak KJ, et al. Early biomarkers of neurodegenerative and neurovascular disorders in diabetes. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:2807. doi: 10.3390/jcm9092807
3. Araszkiewicz A, Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz D. Retinal neurodegeneration in the course of diabetes-pathogenesis and clinical perspective. Curr Neuropharmacology. (2016) 14:805–9. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666160225154536
4. Mariadoss AVA, Sivakumar AS, Lee CH, Kim SJ. Diabetes mellitus and diabetic foot ulcer: Etiology, biochemical and molecular based treatment strategies via gene and nanotherapy. BioMed Pharmacother. (2022) 151:113134. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113134
5. Barwick AL, Tessier JW, Janse de Jonge X, Ivers JR, Chuter VH. Peripheral sensory neuropathy is associated with altered postocclusive reactive hyperemia in the diabetic foot. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2016) 4:e000235. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000235
6. Balasubramanian G, Vas P, Chockalingam N, Naemi R. A synoptic overview of neurovascular interactions in the foot. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2020) 11:308IF: 5.2 Q1. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00308IF:5.2Q1
8. Stirban A. Microvascular dysfunction in the context of diabetic neuropathy. Curr Diabetes Rep. (2014) 14:541.
9. Alexiadou K, Doupis J. Management of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Ther. (2012) 3:4. doi: 10.1007/s13300-012-0004-9IF:3.8Q2
10. Ogbera AO, Adedokun A, Fasanmade OA, Ohwovoriole AE, Ajani M. The foot at risk in Nigerians with diabetes mellitus-the Nigerian scenario. Int J Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 4:165–73.
11. Edgar J, Peters G, Lavery LA, Armstrong DG, Diabetic lowerextremity infection. Influence of physical, psychological, and social factors. J Diabetes Complications. (2005) 19:107–12.
12. Norris FH. Epidemiology of trauma: frequency and impactof different potentially traumatic events on different demographic groups. J Consult. Clin Psychol. (1992) 60:409–18.
13. Hokkam EN. Assessment of risk factors in diabetic foot ulceration and their impact on the outcome of the disease. Prim Care Diabetes. (2009) 3:219–24. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2009.08.009
14. Chowdhury HK, Khan MH, Wadud JR. Risk factors for thedevelopment of diabetic foot ulcer in Bangladesh. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2000) 50:282.
15. Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Stensel V, Forsberg RC, Davignon DR, Smith DG, et al. A prospective study of risk factors for diabetic foot ulcer. The seattle diabetic foot study. Diabetes Care. (1999) 22:1036–42.
16. El-Shazly M, Zaki A, Nicolucci A. Care-related risk factors for chronic diabetic complications in developing countries: a case from Egypt. Public Health. (2002) 116:289–96.
17. Bresäter LE, Welin L, Romanus B. Foot pathology and risk factors for diabetic foot disease in elderly men. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (1996) 32:103–9.
18. Xiong J, Hu H, Guo R, Wang H, Jiang H. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a new strategy for the treatment of diabetes complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:646233. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.646233
19. Wright JA, Oddy MJ, Richards T. Presence and characterisation of anaemia in diabetic foot ulceration. Anemia. (2014) 2014:104214. doi: 10.1155/2014/104214IF:2.9
20. Lyons M, McGregor PC, Pinzur MS, Adams W, Wilkos-Prostran L. Risk reduction and perioperative complications in patients with diabetes and multiple medical comorbidities undergoing charcot foot reconstruction. Foot ankle Int. (2021) 42:902–9. doi: 10.1177/1071100721995422
21. American Diabetes Association. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care. (2020) 43:S111–s134. doi: 10.2337/dc20-S010
22. Sowers JR, Epstein M, Frohlich ED. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: an update. Hypertension (Dallas Tex: 1979). (2001) 37:1053–9.
23. Nyamu PN, Otieno CF, Amayo EO, McLigeyo SO. Risk factors and prevalence of diabetic foot ulcers at Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi. East Afr Med J. (2003) 80:36–43.
24. Amogne W, Reja A, Amare A. Diabetic foot disease in Ethiopian patients: a hospital based study. Ethiopian J Health Dev. (2011) 25:17–21.
25. Conte MS, Bradbury AW, Kolh P, White JV, Dick F, Fitridge R, et al. Global vascular guidelines on the management of chronic limb-threatening ischemia. J Vasc Surg. (2019) 69:3S–125S.e40.
26. McDermott K, Fang M, Boulton AJM, Selvin E, Hicks CW. Etiology, epidemiology, and disparities in the burden of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. (2023) 46:209–21. doi: 10.2337/dci22-0043
27. Bury DC, Rogers TS, Dickman MM. Osteomyelitis: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. (2021) 104:395–402.
28. Yesil S, Akinci B, Yener S, Bayraktar F, Karabay O, Havitcioglu H, et al. Predictors of amputation in diabetics with foot ulcer: single center experience in a large Turkish cohort. Hormones (Athens). (2009) 8:286–95. doi: 10.14310/horm.2002.1245
29. Lavery LA, Ryan EC, Ahn J, Crisologo PA, Oz OK, La Fontaine J, et al. The infected diabetic foot: re-evaluating the IDSA diabetic foot infection classification. Clin Infect Dis. (2019) 70:1573–9.
30. Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, Shi Y, He X, Zhou Z, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:905–6.
31. Akkus G, Evran M, Gungor D, Karakas M, Sert M, Tetiker T. Tinea pedis and onychomycosis frequency in diabetes mellitus patients and diabetic foot ulcers. A cross sectional - observational study. Pak J Med Sci. (2016) 32:891–5. doi: 10.12669/pjms.324.10027IF:2.2Q3
32. Zhong A, Li G, Wang D, Sun Y, Zou X, Li B. The risks and external effects of diabetic foot ulcer on diabetic patients: A hospital-based survey in Wuhan area, China. Wound Repair regeneration: Off Publ Wound Healing Soc [and] Eur Tissue Repair Soc. (2017) 25:858–63.
33. Sun B, Chen Y, Man Y, Fu Y, Lin J, Chen Z. Clinical value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and prognostic nutritional index on prediction of occurrence and development of diabetic foot-induced sepsis. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1181880. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1181880
34. Mariam TG, Alemayehu A, Tesfaye E, Mequannt W, Temesgen K, Yetwale F, et al. Prevalence of Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Associated Factors among Adult Diabetic Patients Who Attend the Diabetic Follow-Up Clinic at the University of Gondar Referral Hospital, North West Ethiopia, 2016: Institutional-Based Cross-Sectional Study. J Diabetes Res. (2017) 2017:2879249. doi: 10.1155/2017/2879249
35. Saad N, Elhadedy K, Ramadan N, Mohmady O, Farid M. The prevalence and risk categorization of diabetic foot complications in cohort group in, Beni Suif, Egypt. Life Sci J. (2013) 3:10.
36. Yadav R, Tiwari P, Dhanaraj E. Risk factors and complications of type 2 diabetes. Rev Article. (2008) 9:8–12.
Keywords: neurovascular disease, diabetes, diabetic foot ulcer, risk factors, health management
Citation: Fan Z, Huang J, Liu Y, Xie H, Yang Q, Liang Y and Ding H (2024) Multifactorial analysis of risk factors for foot ulcers in patients with neurovascular complications of diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 15:1399924. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1399924
Received: 16 March 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 11 October 2024.
Edited by:
Christina Parker, Queensland University of Technology, AustraliaReviewed by:
Leila Yazdanpanah, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, IranCopyright © 2024 Fan, Huang, Liu, Xie, Yang, Liang and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yue Liang, Y2F0aGllbHk5OEAxNjMuY29t; Hong Ding, MTA3ODM1MzAxQHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.