- 1Department of Islamic Education, Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogykarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
- 2Department of General Education and Character, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia
The mental health of students is a significant issue, particularly in the face of the difficulties posed by a complicated familial setting. The significance of religious education in mitigating the impact of the family environment on students' mental health is gaining prominence, particularly in major Indonesian cities like Surabaya, Jakarta, Yogyakarta, and Bandung. This study encompassed a total of 498 senior high school students residing in four major cities in Indonesia. The association between family environment, religious education, and students' mental health was assessed using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) and the bootstrapping approach for data analysis. The findings indicated that religion education had a crucial role as a moderator in the relationship between family environment and the mental health of pupils. Religious education enhanced students' ability to withstand pressure from an unsupportive familial context and had a beneficial impact on students' mental health. This study emphasizes the significance of incorporating religious education inside the family as a means of promoting students' mental health. The practical implication of this study is the creation of educational programs that prioritize enhancing religious values inside the family as a strategic measure to enhance the mental health of pupils.
1 Introduction
The issue of adolescent mental health has gained global prominence and is increasingly recognized as an area of critical concern. Adolescents face numerous challenges in contemporary life that can significantly impact their psychological wellbeing. Among the most influential factors is the home environment, which plays a central role in shaping the mental health of young people. However, as family structures and dynamics continue to evolve, it is important to explore additional variables that may help mitigate the negative effects of family environments on adolescents' mental health. One often-overlooked factor is the role of religious education.
Recent studies highlight the significant impact of the family environment on adolescent mental health. For instance, Foster et al. (2016) demonstrated that family involvement in various activities has a positive and lasting effect on the mental health of adolescents. Similarly, Pearson and Wilkinson (2013) found that strong family relationships correlate with improved mental health outcomes, including lower levels of depression, anxiety, and suicidal tendencies, as well as higher self-esteem and life satisfaction. Bevilacqua et al. (2017) further suggest that family support can protect against negative behaviors such as bullying and cyberbullying, contributing to better mental health and emotional resilience in adolescents.
However, not all families are able to provide an optimal environment for children's cognitive and emotional development. Factors such as financial stress, family conflict, and parental absence can hinder a family's ability to promote mental wellbeing in children. For example, Yap et al. (2017) found a strong association between low-quality parent-child relationships, characterized by a lack of warmth and involvement, and an increased likelihood of substance abuse, which often signals underlying mental health issues.
Religious education may serve as an important moderator in this context. Brewer et al. (2015) found that religious coping mechanisms and religion-based social support had a significant and positive impact on adolescent mental health. These findings underscore the potential role of religious education not only in providing ethical guidance but also as a source of psychological support for adolescents facing life challenges. Additionally, recent research by Counted et al. (2022) demonstrated that positive religious coping strategies are linked to higher levels of hope and overall wellbeing in adolescents. When implemented effectively, religious education can serve as a substantial protective factor for mental health.
However, the relationship between religious education and mental health is complex and not always straightforward. Hanefar et al. (2016) caution that an overly rigid approach to religious education may have adverse effects on adolescents' mental health. Therefore, it is crucial to adopt a more flexible and context-sensitive approach to incorporating religious education as a moderating factor. In line with this, Koohbanani et al. (2013) found that combining emotional intelligence development with religious education can enhance adolescents' emotional resilience, further supporting the case for a comprehensive approach to religious education that addresses both spiritual and emotional growth.
While integrating spiritual principles into adolescent mental health promotion shows promise, it is essential to consider the diversity of religious practices (King and Roeser, 2009). Estrada et al. (2019) argue that mental health interventions for adolescents should respect cultural and religious diversity to be effective. This highlights the need for a flexible and adaptable strategy when using religious education as a moderating element in mental health promotion. Brewer et al. (2015) also emphasize that the practice of religion, rather than merely its belief system, can significantly contribute to adolescent wellbeing, provided it is integrated meaningfully into daily life.
Moreover, religious education plays a critical role in shaping adolescent identity, which in turn impacts mental health. Hardy and King (2019) found that religious education significantly influences adolescent identity development, which can either protect or hinder mental health depending on how it is approached. Barton et al. (2014) further support the view that religious education within the family is essential for positive mental health outcomes. Their study suggests that the religiosity of adolescents is often linked to the religiosity of their parents, underscoring the importance of family-based religious education.
Nevertheless, there are potential risks associated with poorly executed religious education. Suh et al. (2017) warn that an emphasis on perfectionism in religious teachings may increase vulnerability to mental health issues in adolescents. This highlights the need for a balanced and holistic approach to religious education that avoids reinforcing unrealistic expectations. This study aims to examine the moderating effect of religious education on the relationship between family environment and mental health among adolescent students.
2 Literature review and theoretical framework
The family environment plays a crucial role in shaping the mental health of students (Gómez-Ortiz et al., 2018). Numerous studies have shown that the quality of familial relationships significantly influences the psychological wellbeing of children and adolescents. For example, Basu and Banerjee (2020) demonstrated that various aspects of the home environment such as parenting styles, family unity, and the quality of parent-child interactions have a substantial impact on adolescent mental health. Similarly, Pike et al. (1996) found that negative family characteristics, such as parental hostility and a lack of warmth, were strongly associated with depressive symptoms and antisocial behavior in teenagers, even when genetic factors were accounted for. These findings underscore the critical role the family environment plays in students' mental health. Adolescents raised in families marked by harmony, support, and effective communication are more likely to exhibit better mental health outcomes. In contrast, those in environments characterized by frequent conflict and a lack of emotional support are at a higher risk of developing mental health issues. Thus, the study hypothesizes that:
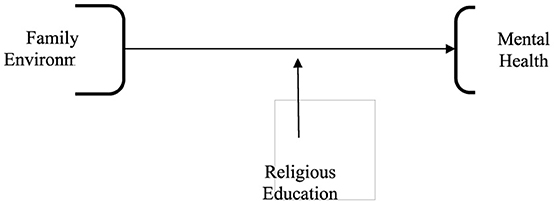
H1: The family environment significantly influences the mental health of students (X-Y).
The potential moderating effect of religious education on the relationship between family environment and adolescent mental health is an intriguing and complex topic. Several studies suggest that religious education can play a protective role in this dynamic. Van de Velde et al. (2017) found that religious participation can buffer the effects of familial stress on depressive symptoms in adolescents, with stronger protective effects observed in those with higher levels of religious devotion. Additionally, Dewi (2020) highlighted that spirituality and religiosity can serve as valuable resources for managing stress and improving mental health, especially when nurtured within a supportive family environment. These studies suggest that religious education can moderate the connection between family dynamics and student mental health, providing adolescents with a moral and spiritual foundation to better cope with life's challenges and build resilience. This understanding leads to the following hypothesis:
H2: The study examines the impact of religious education on students' mental health, specifically how it is influenced by the family environment.
Based on the theoretical foundation and several assumptions, it can be inferred that incorporating religious education into the home setting is necessary to enhance the mental health of pupils (Pires et al., 2019). The cultivation of religious education ideals and emotional stability in children relies significantly on the family's role. This study posits that there is a clear correlation between the impact of the familial environment, which is regulated by religious instruction, on the mental health of students. The study's conceptual model is depicted in Figure 1.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Participant
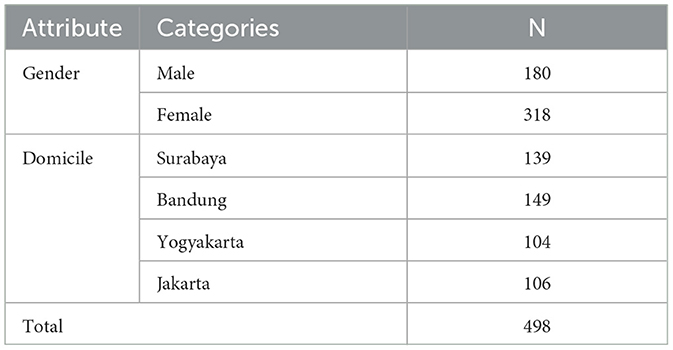
This study examines Senior High School students from four major urban areas in Indonesia: Surabaya, Jakarta, Yogyakarta, and Bandung. A sampling methodology was employed to select a representative sample of 498 students from these cities, reflecting the diversity of the urban high school population. The sampling approach, which follows established criteria for selecting a subset of individuals, ensures the generalizability of the findings (Sharma, 2017). Data on participant demographics, such as gender and place of residence, were collected to better understand the sample's composition. According to Majid (2018), using appropriate sampling techniques is crucial for ensuring the reliability and credibility of educational research in urban contexts. By focusing on these four cities, the study provides a comprehensive representation of urban high school students in Indonesia, as shown in Table 1.
3.2 Measures and procedures
The research instrument consisted of 28 items, each designed with specific operational definitions for the key variables. For religious education, the instrument included 8 items that assessed three dimensions: (1) frequency of participation in religious activities (e.g., “How often do you attend prayers or study circles?”), (2) understanding and application of religious teachings (e.g., “I understand and practice the ethical principles taught in my religion”), and (3) family involvement in religious practices (e.g., “My parents actively encourage and participate in my religious activities”). All items were rated using a 5-point Likert scale, from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree” (Likert, 1932).
For family environment, 12 items measured different aspects of familial interaction and support, including: (1) emotional support (e.g., “My parents provide emotional comfort when I need it”), (2) family cohesion (e.g., “Our family spends quality time discussing problems”), and (3) parental involvement in academic and social activities (e.g., “My parents actively participate in my school events”). Additionally, participants were asked to identify their family type (nuclear, single-parent, extended, or blended) and rate their perception of the quality of family interactions (Barnes and Olson, 1985). These items were also measured on a 5-point Likert scale.
For mental health, 8 items were included to assess psychological wellbeing and stress management, covering: (1) emotional stability (e.g., “I am capable of managing my emotions during stressful situations”), (2) stress management (e.g., “I seldom engage in activities that help me relax”), and (3) self-esteem (e.g., “I have a positive view of myself”). These indicators were adapted from established scales, such as the Psychological Wellbeing Scale (Ryff, 1989) and the Perceived Stress Scale (Cohen et al., 1983).
To ensure the validity of the data, expert reviews of the questionnaire were conducted, and a pilot study involving 50 participants was carried out. Although self-reported data were the primary method, the instrument's reliability was confirmed through Cronbach's alpha (α > 0.7) (Cronbach, 1951), and findings were compared with those of previous studies. While clinical assessments such as structured interviews were not included due to resource limitations, this is acknowledged as a study limitation in the discussion.
Data collection was performed via a questionnaire distributed through Google Forms, which included statements about the three key variables. As noted by Taherdoost (2019), using a well-constructed Likert scale questionnaire is essential for ensuring data validity and reliability. The questionnaire, with five response options, was designed to facilitate respondents' engagement and provide consistent, reliable data.
3.3 Analysis
To minimize potential statistical biases, the study employed several diagnostic tests during the PLS-SEM analysis. Multicollinearity was assessed using Variance Inflation Factor (VIF), ensuring all values remained below the threshold of 5, indicating no severe multicollinearity issues issues (Hair et al., 2019). Additionally, heteroskedasticity was addressed by analyzing residual plots to verify homoscedasticity assumptions (Kline, 2016). Measurement errors were minimized by validating constructs using composite reliability (CR > 0.7) and average variance extracted (AVE > 0.5) (Fornell and Larcker, 1981).
While PLS-SEM provides robust analysis for complex models, its limitations include a sensitivity to sample size and potential overestimation of path coefficients (Hair et al., 2017). These limitations were acknowledged, and bootstrapping with 500 resamples was conducted to increase result stability (Efron and Tibshirani, 1994). Furthermore, the model's predictive accuracy was evaluated using the R-squared values for endogenous variables, which ranged from 0.6 to 0.8, indicating substantial explanatory power (Hair et al., 2017).
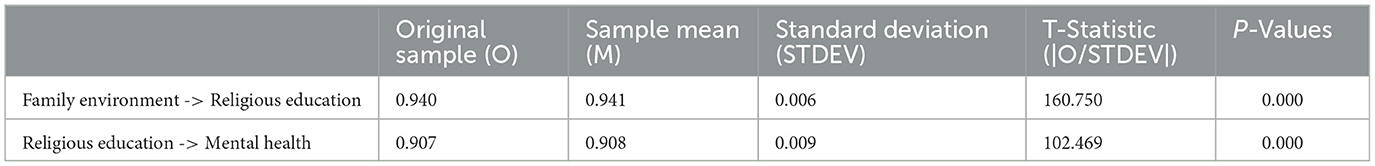
The significance of path coefficients was determined using T-statistics (|O/STDEV| > 1.96) and p-values (< 0.05), which were complemented by an assessment of effect size (f-squared) (Cohen et al., 1983). This combination of metrics ensured a comprehensive understanding of the strength and relevance of each relationship. Additionally, the interpretation of results considered the potential influence of measurement error and addressed it by cross-referencing findings with existing literature to ensure consistency.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Results
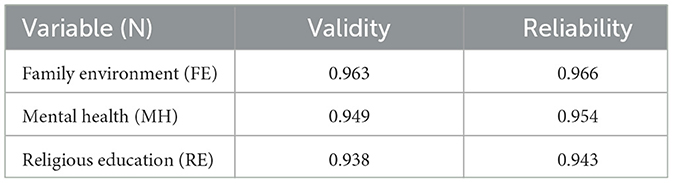
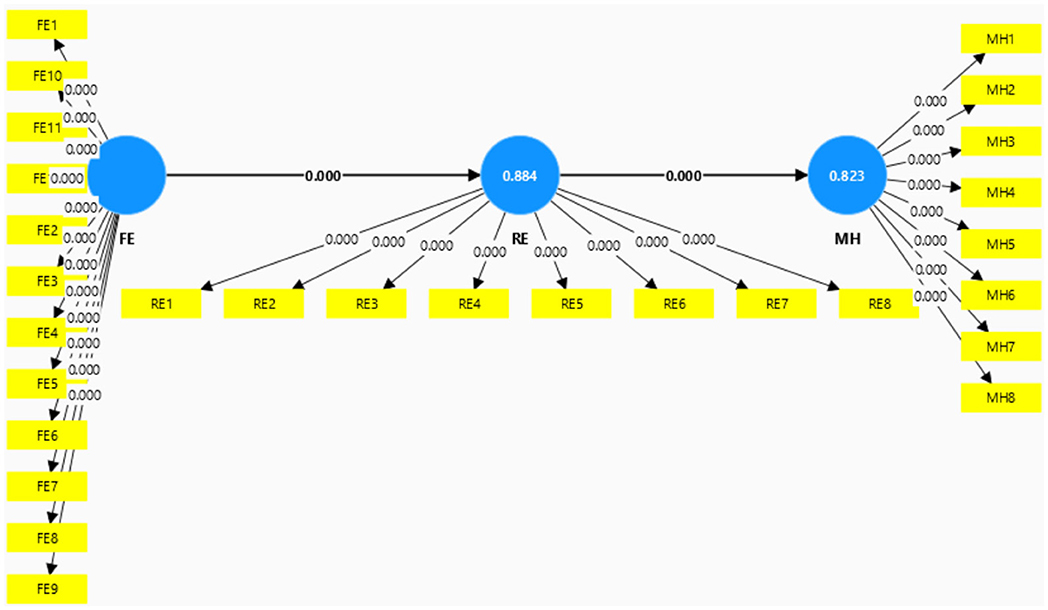
The Smart-PLS program was utilized to assess the validity and dependability of the data. The findings of this examination are displayed in Table 2. Out of the 498 data points that were examined, the researcher employed a standard criterion of 0.7 to assess the validity and reliability.
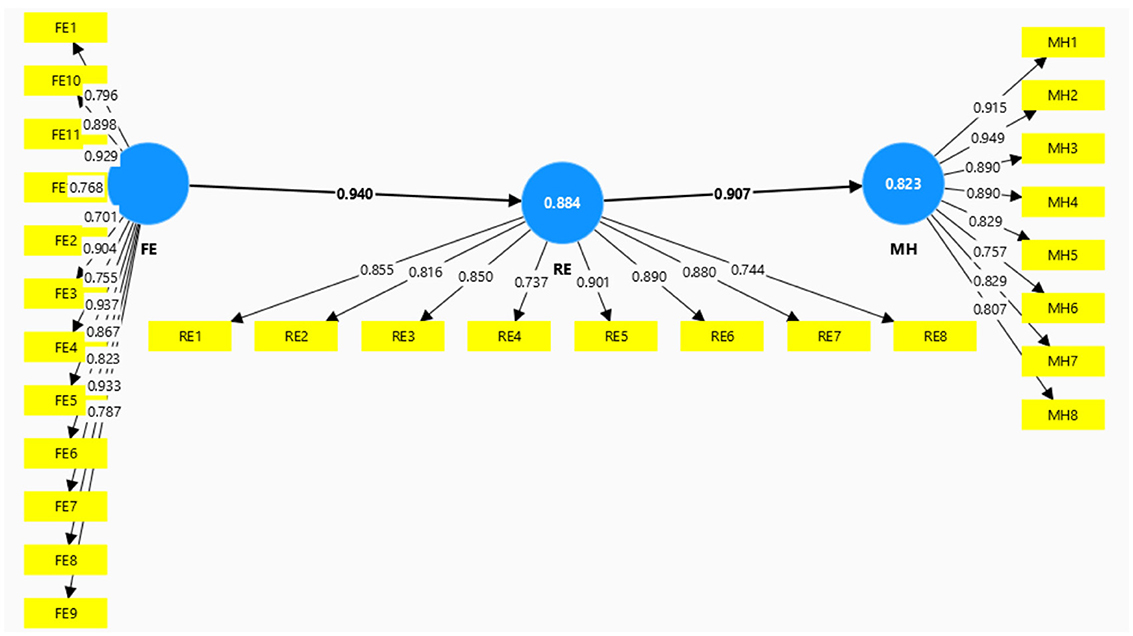
The study results presented in Figure 2 demonstrate that all items possess a validity value beyond the 0.70 threshold. The analysis of these outcomes indicates that all questionnaire items can be deemed legitimate. The validated research instrument encompasses multiple components, each with a different amount of items. The Family Environment component comprises a total of 12 inquiries. Religious Education and Mental Health are both allocated 8 questions each. Consequently, the questionnaire employed in this study has undergone a thorough validation process to guarantee the dependability of the data collection tool.
Table 3 indicates that, statistically, a coefficient value >0.7 is typically seen as a robust indication, signifying a substantial positive correlation or impact between variables. The coefficient can encompass a range of statistical metrics, such as correlation, which is used to assess the strength and direction of the association between two variables (Kock and Hadaya, 2018). The assessment of validity and reliability using the Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) approach demonstrates that the entire dataset is of high quality and accurately depicts the connections between variables. The questionnaire instrument employed demonstrated high levels of consistency and reliability in assessing the impact of family environmental factors on the mental health of kids, with religious education serving as a moderating variable. Validity and reliability are distinct yet interconnected properties of measurement. Both factors are crucial in guaranteeing the precision and uniformity of research instruments. Mohajan (2017) asserts that validity and reliability are essential factors when assessing a measurement instrument. Validity refers to the degree to which a tool accurately assesses the specific concept it is designed to evaluate. Reliability pertains to the instrument's capacity to consistently measure. In this study, data analysis also includes the use of bootstrapping techniques to test hypotheses and determine the importance of direct, total, and indirect effects. The table presents the bootstrapping findings, which comprise the Original Sample (O), Sample Mean (M), Standard Deviation (STDEV), T-Statistic (|O/STDEV|), and P-Values.
Figure 3 illustrates that the application of the bootstrapping method yielded intriguing findings regarding the interplay of factors in this investigation. The variable X, which represents the family environment, had a significant impact on the moderator variable, with a coefficient of 0.940. The T-statistic value obtained was 160.750, with a standard deviation (STDEV) of 0.006, leading to a p-value of 0.000. This p-value is significantly lower than the significance threshold of 0.05. This discovery suggests that the first hypothesis (H1) can be affirmed, showing a statistically substantial impact. Moreover, the variable of religious education demonstrated a noteworthy and beneficial influence on the mental health of students. This is supported by the p-value, which is < 0.05, indicating the beneficial impact of religious instruction on students' mental health. The analysis of these results indicates that high-quality religious education significantly enhances mental health. In summary, our analysis highlights the significance of family environment elements and religious education in shaping and sustaining favorable mental health among students.
4.2 Discussion
This study acknowledges the diversity of family structures in Indonesia, including nuclear, extended, and single-parent families, and how these structures influence the moderating effect of religious education on mental health. Different family types shape how religious values are transmitted and how adolescents internalize these teachings. The findings suggest that religious education, when combined with a supportive family environment, is a critical factor in promoting mental wellbeing. However, it is important to recognize that while the family environment is a primary factor, its influence on mental health may vary across different family types, including those with less religious involvement. Acknowledging these variations helps avoid interpretation bias and ensures a broader understanding of the factors that influence mental health outcomes.
While the study supports the hypothesis that a supportive family environment positively impacts mental health, it is essential to highlight the complexity of this relationship. Although previous studies indicate that a positive family environment contributes significantly to adolescent wellbeing (Fosco et al., 2019), the impact of religious education is likely moderated by family dynamics. This means that while a nurturing family environment fosters mental resilience, the benefits of religious education may not be as pronounced in families with weak or inconsistent religious involvement. Interpretation bias can occur if we overlook these nuances and present overly optimistic conclusions about the universality of religious education's benefits. By addressing this complexity, the study avoids narrowing its interpretations and allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how religious education interacts with family support.
Religious education plays a key role in shaping individual character, fostering positive attitudes and resilience, and contributing to improved mental health (Shodiq et al., 2024). Previous studies confirm that religious education helps adolescents develop coping mechanisms, social support, and a sense of purpose (Brewer et al., 2015). However, it is also important to recognize that the moderating effect of religious education depends on how it is integrated into the family environment. This study shows that while religious education enhances mental health outcomes in supportive family settings, it may have less impact in families where religious involvement is minimal. Confirmation bias can arise if the findings are interpreted only through the lens of the hypothesis that religious education always improves mental health, without considering the broader socio-cultural and familial factors that mediate its effect.
Recent trends indicate a rise in mental health issues among students, often linked to limited family involvement and a decline in strong religious values (Riekie et al., 2017). In Islamic culture, the family is viewed as central to fostering a high-quality generation, and religious practices within the home significantly influence family relationships and overall wellbeing. The family plays a crucial role in imparting and reinforcing religious beliefs, which form the foundation for strong mental health. However, the study also acknowledges the potential adverse effects of rigid or doctrinaire religious practices, which can lead to psychological strain or identity conflict in adolescents. These findings are in line with research by Hill and Pargament (2003), which suggests that when religious education is enforced without consideration for personal autonomy, it may induce stress, guilt, or other negative outcomes in adolescents struggling with their beliefs.
Wen et al. (2019) found that adolescents who engage in religious activities and maintain open communication with their parents experience lower levels of depressive symptoms. This study confirms that the integration of religious values and the active role of the family are essential for maintaining and improving students' mental health. However, this conclusion must be viewed with caution. As noted in the data, religious education's effect is moderated by family involvement, meaning that religious education alone may not be sufficient to foster mental wellbeing without adequate familial support. The study also revealed that the relationship between religious education and mental health is not always linear, suggesting that other moderating factors such as cultural practices, socioeconomic status, and peer influences may shape these outcomes.
This study further reveals that all the variables examined have a significant impact, supporting each of the proposed hypotheses. However, it is important to emphasize that while the family environment is the primary factor, its effect on mental health is complex and influenced by additional moderating factors. The proactive role of religious beliefs in enhancing students' mental wellbeing is notable, but it is essential to recognize that its influence is contingent upon a supportive family environment. Acknowledging the potential limitations and variability in these relationships is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the research and avoiding the pitfalls of confirmation bias.
4.3 Limitation
The study has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, while it includes a sample of 498 senior high school students from four major cities in Indonesia, this may not fully represent the diverse socio-economic and cultural contexts of all regions, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the reliance on self-reported data could introduce biases, affecting the reliability of the reported family environment, religious education, and mental health status. The cross-sectional design captures data at a single point in time, which restricts causal inferences, while the focus on religious education as a moderator does not account for other potential influencing factors, such as peer relationships or community support. Moreover, the cultural specificity of the findings may not apply to other settings with different family dynamics and educational practices, and the study may not adequately address the variability in religious education content. There is also a risk of unmeasured confounding variables, such as socioeconomic status and external stressors, which could impact mental health outcomes. Lastly, the positive aspects of religious education are emphasized, without considering potential negative consequences, such as pressure associated with religious expectations, which might adversely affect mental health. These limitations highlight the need for future research to adopt a more comprehensive approach to understanding the relationships between family environment, religious education, and mental health.
5 Conclusion
This study's results underscore the significance of cooperation between the familial context and religious instruction in preserving children's mental health. Religious education serves as a moderating variable that enhances the beneficial influence of the home environment on children's psychological wellbeing. In essence, good religious education may enhance familial support, so fostering a more favorable environment for pupils' mental wellbeing. Achieving this necessitates tight coordination between family and religious education, which will fortify their connection and amplify mutually supportive beneficial components. This research demonstrates that religious education significantly aids teenagers in managing obstacles encountered in a less supportive familial context, while concurrently exerting a beneficial impact on their mental health. Consequently, it is imperative to develop educational programs that emphasize religious concepts within the familial environment as a technique to enhance children's psychological wellbeing. Consequently, the incorporation of religious beliefs inside the family is not just a distinct facet of schooling, but also a fundamental component in fostering an atmosphere conducive to children's mental health.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. AM: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. AD: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. NV: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. FN: Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. LG: Data curation, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We acknowledge this work has been funded by the Directorate of Research, Technology and Community Service - Directorate General of Higher Education, Research and Technology - Ministry of Education, Culture, Research and Technology of the Republic of Indonesia (Direktorat Riset, Teknologi, dan Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat- Direktorat Jenderal Pendidikan Tinggi, Riset, dan Teknologi - Kementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Riset, Dan Teknologi Republik Indonesia), Contract Number 48/KP/LRI/VI/2024 under the programme of DRTPM 2024.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Author disclaimer
The opinions expresses here in are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of funding agency.
References
Barnes, H. L., and Olson, D. H. (1985). Parent-adolescent communication and the circumplex model. Child Dev. 56:438. doi: 10.2307/1129732
Barton, A. L., Snider, J. B., Vazsonyi, A. T., and Cox, J. L. (2014). Adolescent religiosity as a mediator of the relationship between parental religiosity and adolescent health outcomes. J. Relig. Health 53, 86–94. doi: 10.1007/s10943-012-9596-7
Basu, S., and Banerjee, B. (2020). Impact of environmental factors on mental health of children and adolescents: a systematic review. Children Youth Serv. Rev. 119:105515. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105515
Bevilacqua, L., Shackleton, N., Hale, D., Allen, E., Bond, L., Christie, D., et al. (2017). The role of family and school-level factors in bullying and cyberbullying: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 17, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0907-8
Brewer, G., Robinson, S., Sumra, A., Tatsi, E., and Gire, N. (2015). The influence of religious coping and religious social support on health behaviour, health status and health attitudes in a british christian sample. J. Relig. Health 54, 2225–2234. doi: 10.1007/s10943-014-9966-4
Cohen, S., Kamarck, T., and Mermelstein, R. (1983). A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 24:385. doi: 10.2307/2136404
Counted, V., Pargament, K. I., Bechara, A. O., Joynt, S., and Cowden, R. G. (2022). Hope and well-being in vulnerable contexts during the COVID-19 pandemic: does religious coping matter? J. Posit. Psychol. 17, 70–81. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2020.1832247
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 16, 297–334. doi: 10.1007/BF02310555
Dewi, K. T. S. (2020). The influence of spiritual intelligence and emotional intelligence on job satisfaction and nursing performance. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Bus. 4, 66–73. doi: 10.23887/ijssb.v4i1.24339
Efron, B., and Tibshirani, R. J. (1994). An Introduction to the Bootstrap. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC. doi: 10.1201/9780429246593
Estrada, C. A. M., Lomboy, M. F. T. C., Gregorio, E. R., Amalia, E., Leynes, C. R., Quizon, R. R., et al. (2019). Religious education can contribute to adolescent mental health in school settings. Int. J. Ment. Health Syst. 13, 1–6. doi: 10.1186/s13033-019-0286-7
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 18:39. doi: 10.2307/3151312
Fosco, G. M., Mak, H. W., Ramos, A., LoBraico, E., and Lippold, M. (2019). Exploring the promise of assessing dynamic characteristics of the family for predicting adolescent risk outcomes. J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. Allied Disc. 60, 848–856. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13052
Foster, K., Maybery, D., Reupert, A., Gladstone, B., Grant, A., Ruud, T., et al. (2016). Family-focused practice in mental health care: an integrative review. Child Youth Serv. 37, 129–155. doi: 10.1080/0145935X.2016.1104048
Gómez-Ortiz, O., Romera, E. M., Ortega-Ruiz, R., and Del Rey, R. (2018). Parenting practices as risk or preventive factors for adolescent involvement in cyberbullying: contribution of children and parent gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:2664. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15122664
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2017). PLS-SEM: indeed a silver bullet. J. Market. Theory Pract. 19, 139–152. doi: 10.2753/MTP1069-6679190202
Hair, J. F., Risher, J. J., Sarstedt, M., and Ringle, C. M. (2019). When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 31, 2–24. doi: 10.1108/EBR-11-2018-0203
Hanefar, S. B., Sa'ari, C. Z., and Siraj, S. (2016). A synthesis of spiritual intelligence themes from islamic and western philosophical perspectives. J. Relig. Health 55, 2069–2085. doi: 10.1007/s10943-016-0226-7
Hardy, S. A., and King, P. E. (2019). Processes of religious and spiritual influence in adolescence: introduction to a special section. J. Res. Adolesc. 29, 244–253. doi: 10.1111/jora.12509
Hill, P. C., and Pargament, K. I. (2003). Advances in the conceptualization and measurement of religion and spirituality: implications for physical and mental health research. Am. Psychol. 58, 64–74. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.58.1.64
King, P. E., and Roeser, R. W. (2009). “Religion and spirituality in adolescent development,” in Handbook of Adolescent Psychology, 435–478. doi: 10.1002/9780470479193.adlpsy001014
Kline, R. B. (2016). “Principles and practice of structural equation modeling,” in Canadian Graduate Journal of Sociology and Criminology, eds. N. Tabri and C. M. Elliott (New York: The Guilford Press).
Kock, N., and Hadaya, P. (2018). Minimum sample size estimation in PLS-SEM: The inverse square root and gamma-exponential methods. Inf. Syst. J. 28, 227–261. doi: 10.1111/isj.12131
Koohbanani, S. E., Dastjerdi, R., Vahidi, T., and Far, M.-H. G. (2013). The relationship between spiritual intelligence and emotional intelligence with life satisfaction among Birjand gifted female high school students. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 84, 314–320. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.06.558
Majid, U. (2018). Research fundamentals: study design, population, and sample size. Undergr. Res. Nat. Clin. Sci. Technol. J. 2, 1–7. doi: 10.26685/urncst.16
Mohajan, H. K. (2017). Two criteria for good measurements in research: validity and reliability. Ann. Spiru Haret Univ. Econ. Series 17, 59–82. doi: 10.26458/1746
Pearson, J., and Wilkinson, L. (2013). Family relationships and adolescent well-being: are families equally protective for same-sex attracted youth? J. Youth Adolesc. 42, 376–393. doi: 10.1007/s10964-012-9865-5
Pike, A., Reiss, D., Hetherington, E. M., and Plomin, R. (1996). Using MZ differences in the search for nonshared environmental effects. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 37, 695–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1996.tb01461.x
Pires, M., Wright, B., Kaye, P. M., da Conceição, V., and Churchill, R. C. (2019). The impact of leishmaniasis on mental health and psychosocial well-being: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 14:e0223313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223313
Riekie, H., Aldridge, J. M., and Afari, E. (2017). The role of the school climate in high school students' mental health and identity formation: a South Australian study. Br. Educ. Res. J. 43, 95–123. doi: 10.1002/berj.3254
Ryff, C. D. (1989). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. J. Person. Soc. Psychol. 57, 1069–1081. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.57.6.1069
Shodiq, S. F., Syamsudin, S., Dahliyana, A., Kurniawaty, I., and Faiz, A. (2024). Social media use and online prosocial behaviour among high school students: The role of moral identity, empathy, and social self-efficacy. Integr. Educ. 28, 454–468. doi: 10.15507/1991-9468.116.028.202403.454-468
Suh, H., Gnilka, P. B., and Rice, K. G. (2017). Perfectionism and well-being: A positive psychology framework. Pers. Individ. Dif. 111, 25–30. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.01.041
Taherdoost, H. (2019). What is the best response scale for survey and questionnaire design; review of different lengths of rating scale/attitude scale/likert scale. Int. J. Acad. Res. Manage. 8, 2296–1747.
Van de Velde, S., Van der Bracht, K., and Buffel, V. (2017). The relation between religion and depression in Europe: the moderating role of the religious context. Int. J. Comp. Sociol. 58, 515–532. doi: 10.1177/0020715217736361
Wen, M., Ren, Q., Korinek, K., and Trinh, H. N. (2019). Living in skipped generation households and happiness among middle-aged and older grandparents in China. Soc. Sci. Res. 80, 145–155. doi: 10.1016/j.ssresearch.2019.01.004
Keywords: religious education, family environment, psychological wellbeing, social assistance, mental health
Citation: Shodiq SF, Makrufi AD, Dahliyana A, Valencia NP, Nurunisa FA and Goselfa L (2025) The impact of religious education in mitigating the effects of family environment on students' mental health. Front. Educ. 10:1523461. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2025.1523461
Received: 06 November 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Irwan Abdullah, Gadjah Mada University, IndonesiaReviewed by:
Esa Nur Wahyuni, Universitas Islam Negeri Maulana Malik Ibrahim, IndonesiaNadiatus Salama, Walisongo State Islamic University, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Shodiq, Makrufi, Dahliyana, Valencia, Nurunisa and Goselfa. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sadam Fajar Shodiq, c2FkYW1mYWphcnNob2RpcUBmYWkudW15LmFjLmlk
 Sadam Fajar Shodiq
Sadam Fajar Shodiq Anisa Dwi Makrufi1
Anisa Dwi Makrufi1