- 1Universidad César Vallejo, Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Escuela de Estomatología, Piura, Peru
- 2Manatee Oral and Facial Surgery Center, Bradenton, FL, United States
- 3Asociación Médica de Investigación y Servicios en Salud, Lima, Peru
- 4Universidad Continental, Huancayo, Peru
Introduction: The burnout syndrome affects diverse populations and among them undergraduate students, which can weigh down their academic performance and professional future.
Objective: This study aims to determine the prevalence and factors associated with burnout syndrome among dental students from seven Cuban universities.
Methods: Multicenter, observational, analytical and cross-sectional study developed in 7 Cuban universities. The validated version of the Maslach Burnout Inventory-Students Survey (MBI-SS) was used as a dependent variable. Prevalence ratios and 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
Results: A total of 738 students participated, of whom 470 (63.8%) were women. The average age was 21.7 ± 1.7 years. The prevalence of burnout was 34.8% (n = 257). In the multivariate model, it was found that having an academic advisor was associated with a high burnout score (RPa: 2.10; 95% CI: 1.18–3.74; p = 0.012). In contrast, having published a scientific article was associated with a lower score (RPa: 0.38; 95% CI: 0.23–0.64; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: One third of the students presented burnout. Having an academic tutor and having made a scientific publication were the associated factors identified.
1 Introduction
Mental illnesses represent a global challenge, with profound personal and social implications (Wainberg et al., 2017). Each diagnosis of anxiety, depression or stress not only reflects statistical data, but also human experiences that affect the quality of life and performance of those who suffer from them (Lukasik et al., 2019). In the university environment, these conditions are of particular concern, since students face academic, social and emotional pressures that place them in a situation of vulnerability. This stage of training, marked by constant demands and the need to make momentous decisions, can generate stress levels capable of triggering more complex mental health problems (Campbell et al., 2022).
In particular, dentistry students face unique demands. In addition to the pressures common in college life, they must manage hands-on activities that demand technical and emotional precision. From preclinical to patient treatment, the fear of error, academic burden and inherent responsibility increase their risk of developing burnout syndrome (BS) (Maragha et al., 2023). Understanding the impact of the BS on this group is crucial to promote their mental health and ensure a balanced academic training. This phenomenon requires comprehensive prevention and management strategies to mitigate its impact and optimize the quality of dental education (Di Mario et al., 2024).
Poor working conditions in various service sectors are closely linked to an increase in psychosocial problems, which affect both physical and mental health. Within work-related disorders, mental disorders are second only to musculoskeletal disorders (Moukarzel et al., 2019). BS is closely linked to a number of chronic stressors, especially in response to work dynamics. Those suffering from this disorder experience both mental and physical impairment (Rodrigues et al., 2018) accompanied by negative attitudes toward their interpersonal environment, which can generate feelings of despair and hopelessness in individuals (Güler et al., 2019).
Healthcare workers face significant challenges that affect both their physical and mental wellbeing and arise from the inherent demands of their work, as well as personal and social pressures. In addition, the constant need to stay up-to-date and trained to provide the best possible care to patients contributes to this burnout. A compounding factor is the lack of adequate resources to meet institutional goals, which can also compromise treatment success (Koppmann et al., 2021). These conditions, when persisting for prolonged periods and linked to both external and internal factors of professionals, can result in BS (García-Torres et al., 2021; El Dabbah and Elhadi, 2023).
It has been recognized that following the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare personnel experienced an increase in BS and workload, highlighting the importance of consistently monitoring their physical and mental health to safeguard their overall wellbeing (Fukushima et al., 2023). Among healthcare professions, nursing, medical practice—defined here as the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases in various clinical settings and dentistry, understood as the health specialty focused on the care and treatment of oral pathologies, were the most affected (Littzen-Brown et al., 2023; Crudden et al., 2023; Owen et al., 2022). Furthermore, dentists experienced a negative impact on their professional development due to the close proximity required in their work environment, which constitutes a high-risk setting for infection. This heightened their stress and concern about contracting the disease. As a result, psychological support and monitoring were essential to mitigate their burnout.
Globally, health sciences students face challenges that not only demand their maximum academic capabilities but also significantly affect their psychological wellbeing, resulting in issues such as anxiety, BS, and reduced empathy. Anxiety is characterized by excessive worry, tension, and difficulty managing stress; BS by emotional exhaustion, cynical or indifferent attitudes toward others (depersonalization), and a low sense of personal achievement; while empathy—the ability to understand and share others’ emotions—may diminish in contexts of prolonged stress. These conditions underscore the need for university policies that prioritize mental health and enhance the academic experience of this group (Sulaiman et al., 2023).
The results of a study conducted at a university in Paris revealed significant levels of depression and death-related thoughts among students of dentistry, pharmacy, and medicine. Factors associated with these issues included marital status, financial difficulties, academic workload, experiences of humiliation, and sexual harassment. These findings highlight the critical need for continuous psychological support for health sciences students throughout their undergraduate education (Frajerman et al., 2022).
In Iran, it was identified that the presence of BS was higher in students with low financial support and altruistic motivations for career choice (Mohebbi et al., 2021). A study in the United States reported that 40% of dental students presented BS associated with depression. Another study in that country found moderate correlations between emotional intelligence and levels of stress and BS (Deeb et al., 2018).
In Brazil, approximately 30% of health sciences students were found to be at risk of developing BS, with veterinary medicine and dentistry students showing a higher prevalence of symptoms (Costa et al., 2012). In Peru, a survey of students from four universities reported that nearly a quarter of them exhibited signs of BS (Ramírez-López and Asmat-Abanto, 2024).
In Cuba, evidence on BS is limited due to a lack of research on the subject. For instance, studies on dentists reported low levels of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization but high levels of personal accomplishment, which prevented the occurrence of BS (Arias et al., 2020). Regarding undergraduate students, the literature review identified only the report by Gil and Cruz (2018) on dental interns, which found high levels of emotional exhaustion and low levels of depersonalization.
It is essential to continue researching BS as academic and social conditions evolve over time. These changes may be influenced by the implementation of new teaching methodologies, technological advancements, and significant social transformations. A prominent example is the COVID-19 pandemic, which has directly impacted how students experience this syndrome. Moreover, such variations may alter the factors associated with its development, underscoring the importance of adapting research and prevention strategies to current circumstances.
This study is justified by the need to address an issue that significantly affects the mental and physical wellbeing of future healthcare professionals. BS, associated with chronic stressors, has negative consequences on academic performance, empathy, and the perception of personal achievement—factors critical to the quality of healthcare delivery. Cuban universities, as public and tuition-free institutions with a nationally unified curriculum, provide a unique setting for identifying specific patterns of this issue. Furthermore, the limited body of evidence on BS in this population highlights the importance of generating scientific data to design prevention and management strategies tailored to the Cuban academic and sociocultural context, particularly in a post-pandemic environment that has exacerbated risk factors associated with BS.
Thus, ongoing research allows us to adapt prevention and management strategies to current conditions. In addition, BS may manifest differently in different geographic and cultural contexts, so research in different regions allows for the identification of specific factors affecting students and the development of more effective interventions. Therefore, the present study aimed to determine the prevalence and factors associated with BS among dental students from seven Cuban universities located in different provinces across the country.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Design, sampling and participants
A multicenter, observational, analytical, and cross-sectional study was conducted. The population consisted of 1,808 dental students from the medical universities of Pinar del Río, Villa Clara, Sancti Spíritus, Ciego de Ávila, Camagüey, Granma, and Santiago de Cuba in Cuba. These provinces represent administrative divisions of the country, each with its own medical university. It is important to note that all these institutions are public and tuition-free, with a standardized academic curriculum applied uniformly across the nation, ensuring consistent training for future professionals. The survey was conducted between October 2019 and January 2020, during the pre-pandemic period of COVID-19 in Cuba. The sample (n = 738; 40.8%) was obtained by non-probabilistic and intentional sampling. To determine whether the sample had an adequate number of respondents, statistical power was calculated. Almost all variables had adequate power, except for gender (6%), having participated in extracurricular research courses (30%) and having taken a previous degree (78%). Students from all academic years who expressed interest in participating were included. In this context, “all academic years” refers to the various levels of training within the dentistry program, ranging from the first year, focused on foundational knowledge and preclinical sciences, to the final years, which encompass advanced clinical practice and specialization activities. Those who did not attend classes on the days the survey was administered were excluded. Non-response or partial response to the items of the scale used was considered as an exit criterion, a situation that did not occur.
2.2 Variables
A questionnaire was designed to request information on the following independent variables: age, sex, being a student assistant, university, academic year (first to fifth), having a supervisor, having previously studied a degree course, participation in extracurricular research courses, in research projects, in scientific events and winning award in these, as well as having published at least one scientific article.
The variables selected for the questionnaire were based on their potential relevance to BS in dental students, in line with evidence reported in the literature and the contextual characteristics of the study population (Jiménez-Ortiz et al., 2019; Campos et al., 2012; Korkmaz et al., 2023; Pepe-Nakamura et al., 2014; Ramírez-López and Asmat-Abanto, 2024). Among the variables considered were age, gender, and academic year, given their influence on the perception of academic workload and the coping strategies employed by students.
Additionally, factors such as serving as a student assistant, participation in research activities, and scientific publication were included due to their association with academic stress and levels of personal satisfaction. Other factors, such as having an academic advisor or previous experience in another degree program, were also considered, as they may influence perceptions of institutional support and external demands faced by students.
Finally, variables related to participation in scientific events and receiving award were incorporated, as they are associated with professional recognition and academic development—elements that can significantly impact students’ motivation and psychological wellbeing.
The dependent variable was the BS, assessed using the validated version of the Maslach Burnout Inventory-Students Survey (MBI-SS) in Cuban dental students (Corrales-Reyes et al., 2022). The questionnaire is anonymous and self-administered, consisting of three factors: emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and lack of personal accomplishment. It includes 11 items presented as statements, which explore aspects related to the construct under study. The questionnaire uses a 7-point Likert scale with responses ranging from “Never” to “Daily,” allowing the assessment of the frequency of these aspects. The scale demonstrated a Cronbach’s alpha coefficient of 0.81 (95% CI = 0.78–0.83), indicating good internal consistency.
2.3 Procedures, data collection and ethical issues
The questionnaire was administered during class time, with the teachers’ authorization. The objective of the study was explained to the students and they were asked to be as truthful as possible in their answers, while it was explained that participation was voluntary. Participants signed the informed consent form and were informed that they could withdraw from the study at any time. In order not to influence the results, surveyors only answered questions related to typology and form aspects of the questionnaire. On average, respondents took 10 min to answer the questionnaire.
2.4 Data analysis
An ad hoc database was created in Microsoft Excel (version 2019 for Windows). Data quality control was conducted, and responses to all items were aggregated to derive the dependent variable, ensuring consistency and reliability throughout the analysis. Students with scores in the top tercile (i.e., above the 66th percentile) were classified as having BS, and their results were compared with those in the middle and bottom terciles (i.e., scores at or below the 66th percentile).
Initially, the percentages for each response to the BS test were described, followed by the creation of a table presenting the frequencies and percentages of categorical variables. For the quantitative variables—age and year of study—medians and interquartile ranges were calculated after evaluating normality using the Shapiro–Wilk test.
Bivariate statistical results were then generated, with p-values calculated using the Wilcoxon test for the two quantitative variables and the chi-squared test (χ2) for the categorical variables. Finally, results for both crude and adjusted (multivariate) models were obtained. Prevalence ratios (PRs), 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs), and p-values were calculated using generalized linear models with a Poisson family, log-link function, and robust variance estimations, adjusted for the university attended. Variables were included in the adjusted model if they had a p-value < 0.05 in the crude model. This threshold was applied throughout the analysis to determine statistical significance.
3 Results
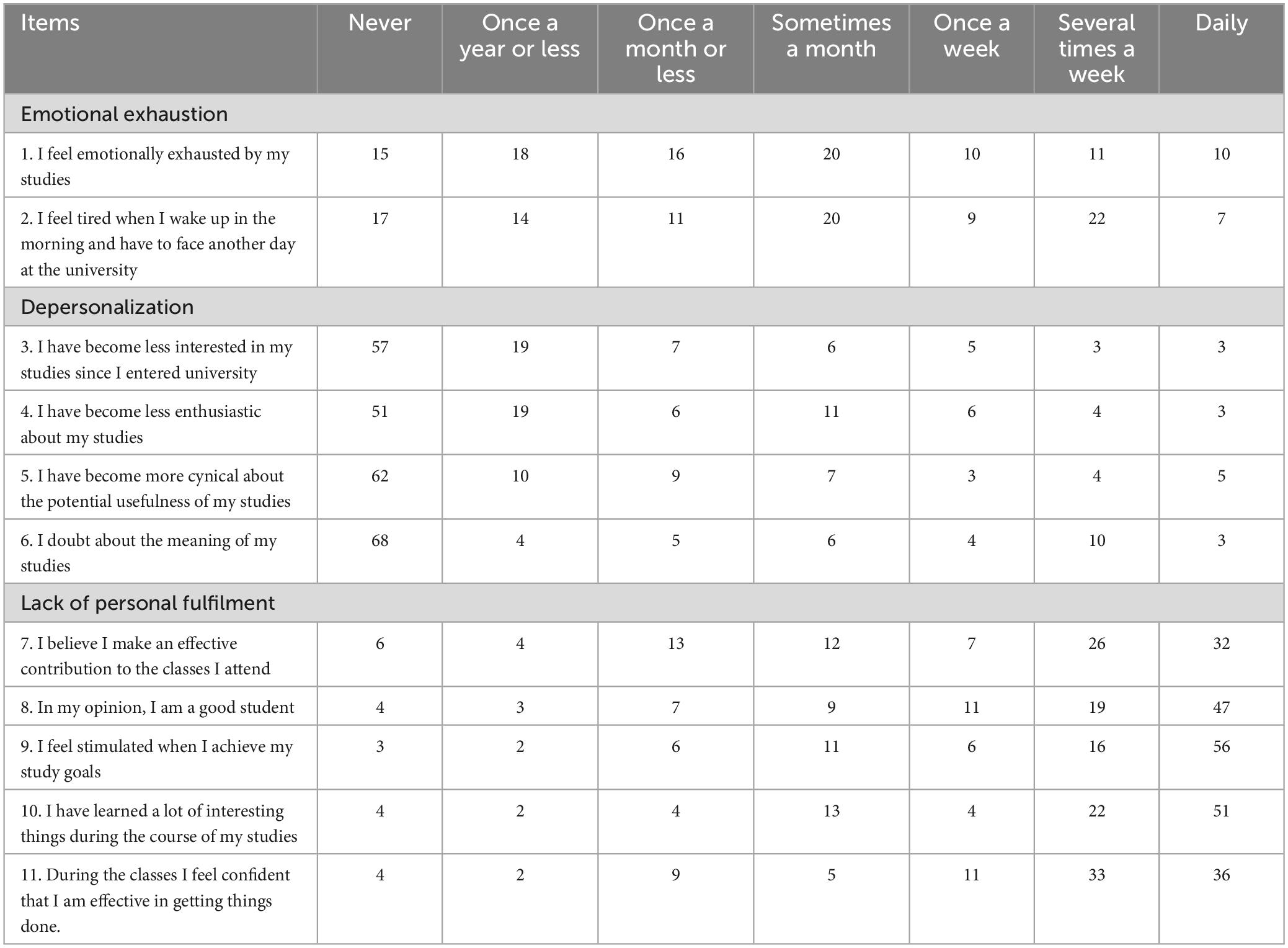
A total of 738 students participated, 63.8% (n = 470) of whom were female. The average age was 21.7 ± 1.7 years. In the dimension emotional exhaustion, respondents stated in equal measure (20%) that sometimes a month they felt emotionally exhausted (item 1), as well as tired when they woke up in the morning and had to face another day at the university (item 2). With regard to depersonalization, more than 50% of the students reported that they had never become less interested (item 3) and enthusiastic (item 4) in their studies since entering university. Furthermore, 62% reported that they never became more cynical about the potential usefulness of their studies (item 5), while 68% stated that they never doubted the meaning of their studies (item 6). In the dimension of lack of personal fulfilment, 32% of the respondents believe that they make an effective contribution to the classes they attend on a daily basis (item 7) while 47% consider that they are good students (item 8). Similarly, more than 50% of the students feel stimulated when they achieve their study goals (item 9), while they consider that they have learned many interesting things during the course of their studies (item 10). This percentage is lower when considering that 36% of respondents feel confident that they are effective in getting things done (item 11). All in all, 34.8% (n = 257) of the students suffered from BS (Table 1).
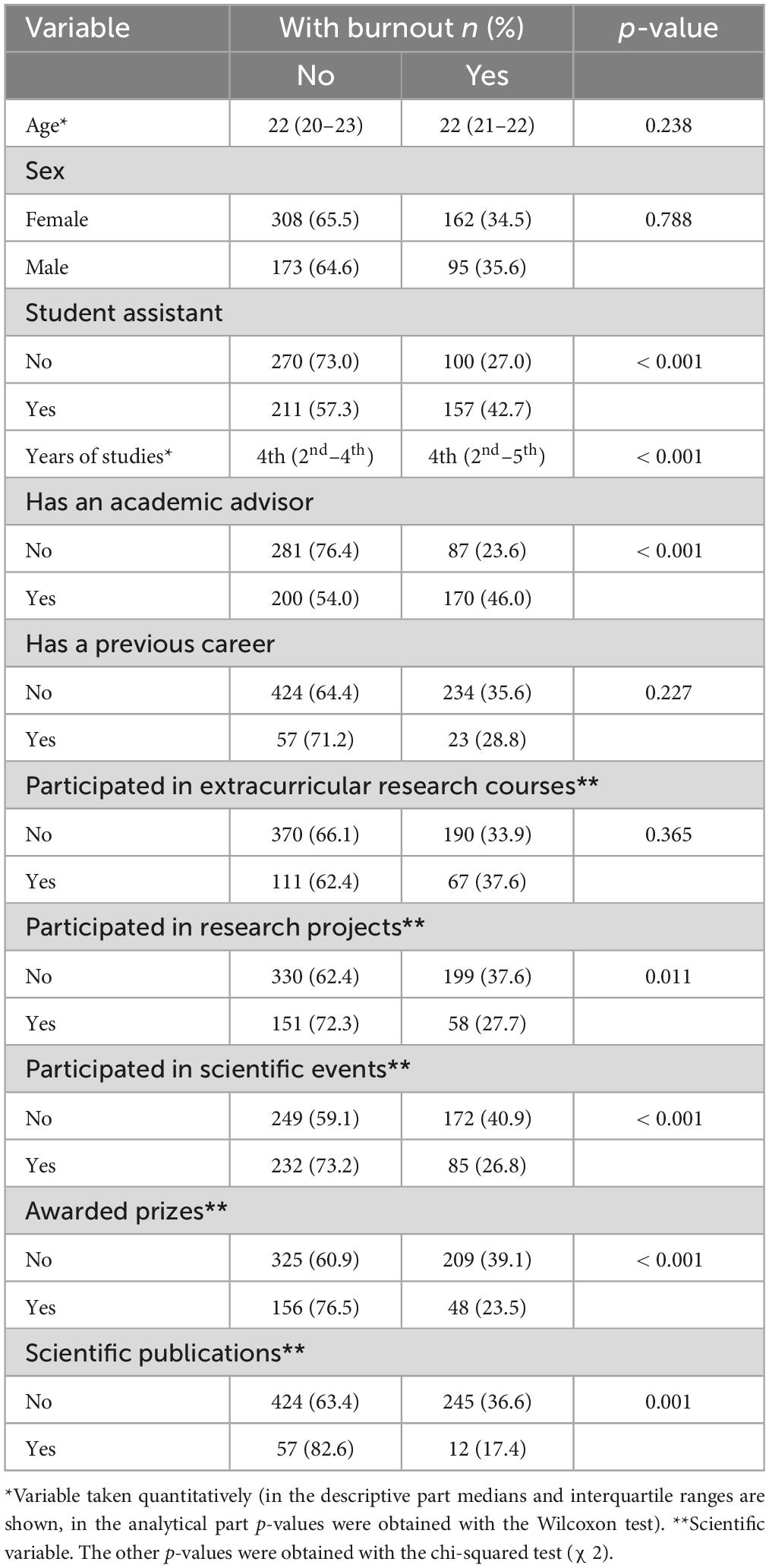
The variables that were associated with having a score in the top tercile (having BS) were being a student assistant (p < 0.001), year of study (p < 0.001), having an academic advisor (p < 0.001), having participated in research projects (p = 0.011), in scientific events (p < 0.001), having obtained award in these events (p < 0.001), as well as having published a scientific article (p = 0.001). It is important to note that regarding the association between gender and the presence of BS, no statistically significant difference was found. Men had a prevalence of 35.6%, while women had a prevalence of 34.5% (p > 0.05) (Table 2).
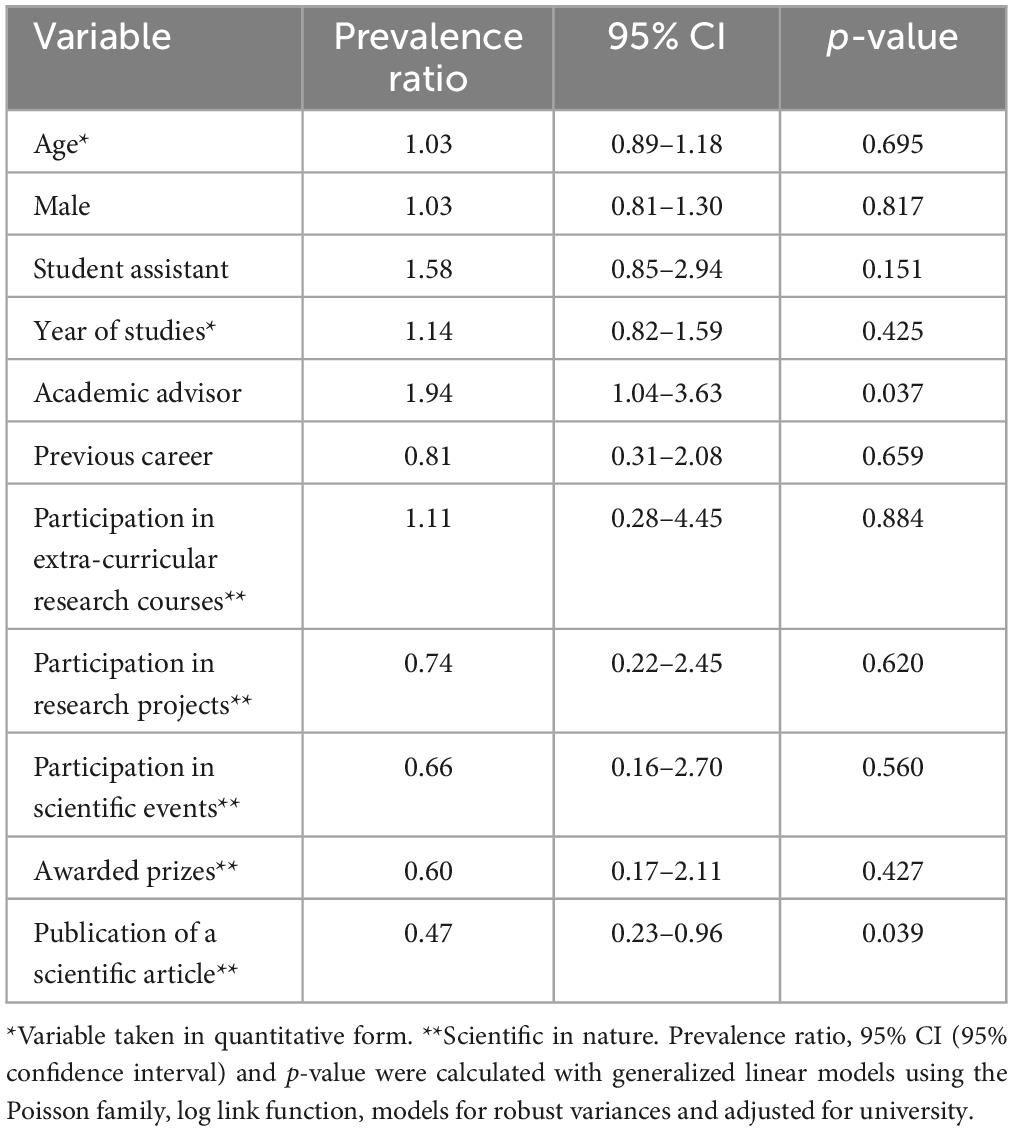
When performing the bivariate analysis, it was found that having an academic advisor was associated with having a high BS score (cPR: 1.94; 95% CI: 1.04–3.63; p = 0.037). In contrast, having published a scientific article was associated with a lower score (cPR: 0.47; 95% CI: 0.23–0.96; p = 0.039) (Table 3).
The multivariate model found that having an academic advisor was associated with a high BS score (RPa: 2.10; 95% CI: 1.18–3.74; p = 0.012). In contrast, having published a scientific article was associated with a lower score (RPa: 0.38; 95% CI: 0.23–0.64; p < 0.001), adjusted for university of studies.
4 Discussion
A career in medical sciences is a stressful environment as students take on responsibilities for learning a huge amount of information, clinical practice with patients, among other tasks that are assigned to them and demand great efforts of time and energy that can affect their mental health (Hadid et al., 2020).
BS is prevalent among dental students (Jiménez-Ortiz et al., 2019; Campos et al., 2012; Korkmaz et al., 2023), potentially due to the demanding nature of their training, which requires the acquisition of diverse competencies along with practical and clinical skills (Khanal and Shrestha, 2021). Several studies identify dentistry as one of the most stressful professions within the health sector (Chen-Yi et al., 2019; Awlaczyk et al., 2020; Shao et al., 2020).
In the present study, one third of the students were found to have BS, which coincides with Pepe-Nakamura et al. (2014) in their research with Brazilian students. In a study developed in Peruvian dental students, a quarter of them presented BS (Ramírez-López and Asmat-Abanto, 2024). This prevalence of BS may be due to a combination of different factors specific to their training as well as to the academic environment in which the students find themselves. Students often feel under pressure to achieve good academic results, which may contribute to the development of the syndrome. In addition, clinical placements can be emotionally exhausting, as students have to deal with real patients, which can lead to anxiety and worry about making mistakes. In addition, students may feel that they are in constant competition with their peers, which can lead to excessive self-demand and thus to the development of BS.
With regard to emotional exhaustion, most students reported occasionally feeling emotionally drained by their studies and feeling tired upon waking in the morning. Although the characteristics of exhaustion are similar regardless of occupation, culture, or ethnicity, no significant differences were found between genders (Khammissa et al., 2022). It is noteworthy that fatigue or the feeling of physical and mental exhaustion limits students’ ability to complete assigned tasks (Alvares et al., 2020; Caldwell et al., 2019).
Chauca et al. (2023) found that 48.3% of participants experienced emotional exhaustion, which could be attributed to factors such as engaging in clinical practice with patients, a heavy academic workload, the challenges of certain treatments, and limited experience in interacting with patients (Mohebbi et al., 2021).
The emotional exhaustion experienced by many students, manifested as fatigue and difficulty in fulfilling academic responsibilities, is a clear indicator of BS. This exhaustion is not only physical but also mental and emotional, significantly affecting those facing high levels of demand, particularly in clinical practice. The academic workload and lack of experience in patient care make this situation even more challenging.
One-fifth of the respondents reported feeling tired upon waking and facing another day at university. Insufficient sleep negatively impacts attention (Engle-Friedman et al., 2018) and memory (Lo et al., 2016). Therefore, students should prioritize adequate sleep to maintain energy and motivation for university activities, as quality sleep has been shown to improve the likelihood of achieving good academic performance (Kassarnig et al., 2017; Hershner and Chervin, 2014).
Depersonalization is characterized by a negative or distant emotional response toward others, marked by cold, indifferent, or even cynical attitudes (Bang and Reio, 2017). In this study, more than half of the respondents reported never experiencing a decrease in their interest or enthusiasm since starting university. Nikolovska et al. (2020) found that 33.9% of dental students at a university in Macedonia were willing to change their career, and 64.5% had lost their motivation to study. The authors attributed this to factors such as low income for dentists in private practices, an oversaturation of professionals, and limited job opportunities after graduation. Motivation is essential for pursuing a university degree as it influences how individuals allocate their time, the level of dedication to a given task, and the time they persist in it (Kavousipour et al., 2015). Interest and motivation increase the likelihood of students engaging in learning and problem-solving (Renninger and Bachrach, 2015). Identifying depersonalization is crucial, as it can lead to disconnection from patients or peers, negatively affecting interpersonal relationships and reducing empathy, especially in high-stress educational or professional settings (De Clercq et al., 2019).
In this study, students reported not developing significant cynicism toward the value of their studies. This can be explained by contextual and cultural factors. Similar to findings by Al-Hallak et al. (2018) in Saudi Arabia, dental students often associate their education with positive aspects such as social prestige, economic opportunities, and the ability to directly impact people’s wellbeing. This sense of purpose and social recognition may buffer against the development of cynicism, a core characteristic of BS. Moreover, as Karagir et al. (2021) pointed out, the perceived long-term benefits, such as professional respect and status, reinforce the belief that the sacrifices made during their education are worthwhile. These factors contribute to students maintaining a positive and resilient outlook on academic challenges, limiting the development of cynical attitudes.
In this study, one-third of the students believed they contributed effectively to their classes daily. Students’ positive perceptions of their class contributions and confidence in their effectiveness are directly linked to their sense of personal accomplishment, which can mitigate emotional exhaustion, a hallmark of burnout. This sense of achievement and competence can be further enhanced through methodologies like active learning, which has been shown to foster the development of essential competencies in undergraduate education (Perez et al., 2023). In this context, active learning approaches, such as direct patient care, enable students to apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios, fostering growth as competitive future dentists (Palatta et al., 2017). This active participation not only boosts self-confidence but also encourages self-directed learning, leading to more robust and effective training (Lim et al., 2022). Thus, the relationship between personal accomplishment and active learning enriches students’ overall education, counteracting the negative effects of BS.
In this study, more than half of the respondents reported feeling motivated daily to achieve their academic goals and confident in their ability to complete their tasks effectively. This finding aligns with previous studies, such as Al-Ansari et al. (2015), which suggest that a positive perception of learning enhances student performance. However, some students, despite their confidence in theoretical knowledge, expressed concerns about their clinical skills and practical application. Motivation, faculty support (Alqarni, 2021), and a positive learning environment (Gil et al., 2023) are critical factors in helping students achieve their objectives. Although motivation is key, it is also influenced by variables such as gender, socioeconomic context, and family support (Almalki, 2019). Regarding clinical confidence, combining theory with practical instruction has been shown to improve self-perception (Sjöström and Brundin, 2021), particularly when simulated patients are used (Marsden et al., 2022; Gilmour et al., 2016). This study confirms that students tend to feel more confident in performing simple dental treatments than in more complex ones, as suggested by Elmanaseer et al. (2023).
One of the keys to teaching students lies in having responsive teachers, as it increases the likelihood of better grades, skills and encourages leadership, attendance and interaction in class (Rajadurai et al., 2023). In the present research it was found that students who had an academic advisor had higher BS scores. Although studies with methodological designs that allow causality to be established are needed, some hypotheses can be put forward to try to explain these results. For example, advisors may have certain expectations and, on that basis, exert some kind of pressure on students to achieve in the academic sphere, which may contribute to an increase in the level of BS.
Another hypothesis could be related to the nature of the supervisor-student interaction. If this relationship lacks understanding and cooperation, it may become difficult to manage, potentially disrupting the learner’s educational environment and contributing to elevated levels of BS. Additionally, supervisors may overload students with assignments or tasks, leading to increased stress and exacerbating BS. These challenges, when combined with the intrinsic demands of the dentistry program—widely recognized as highly rigorous—may create an environment conducive to the development of BS among students with an academic advisor.
On the contrary, having published a scientific article was associated with a lower BS score. Several hypotheses can be put forward to explain this result. For example, publishing a scientific article provides a sense of achievement and recognition for the work done. This sense of achievement may increase personal motivation and satisfaction, thus reducing the risk of BS. In addition, the process of research and publication develops important skills, such as analytical skills, problem solving, and time management. These skills can help students better manage academic and clinical demands, so that they may be less likely to develop the syndrome (Pham Thi and Duong, 2024).
In the same vein, it is important to highlight that research often involves collaboration with teachers and peers, fostering a supportive environment and teamwork that can provide a sense of community and belonging—key factors for promoting mental health. Additionally, publishing an article can create opportunities for future prospects, such as scholarships, residencies, or academic positions. A positive and hopeful outlook on one’s future career can significantly reduce stress and BS. These combined factors may explain the lower prevalence of BS observed among dentistry students who have published scientific articles (Javed et al., 2024).
Based on the findings, we suggest that educational decision-makers implement targeted strategies to mitigate BS among dental students and promote their academic development. First, we recommend offering practical workshops on scientific publishing to motivate and support students interested in research, which could help alleviate BS associated with academic overload. Additionally, it is crucial to provide professional development and training sessions for academic advisors, focusing on effective mentoring techniques and stress management. These sessions should emphasize the importance of fostering a supportive environment and open communication, enabling advisors to help students navigate academic challenges without exerting additional pressure.
It is important to acknowledge certain limitations of the study, including selection bias, as the sample was obtained using non-probability sampling methods. Three variables—gender, participation in extracurricular research courses, and previous enrollment in another degree program—exhibited insufficient statistical power. This lack of power reduces the ability to detect significant associations and limits the interpretation of results related to these variables. Consequently, the analyses should be considered exploratory and interpreted with caution. Future studies should be designed with appropriate sample sizes to ensure sufficient statistical power, enabling more robust and generalizable conclusions regarding these factors. The data obtained for both sexes/genders might suggest an imbalance in participant enrollment. However, this perception is not accurate. It is important to note that this variable is essential for accurately characterizing the study population. Nevertheless, based on the statistical power calculations in our research, the results should be interpreted as preliminary reference points for the proportion of the dependent variable observed in each sex/gender. These findings may serve as a foundation for future studies to investigate whether this variable can be used as a reliable indicator for making more robust inferences. Given that optimal statistical power was not achieved, these results should be considered baseline or referential data rather than definitive conclusions. Finally, the BS was assessed with a self-report measure, where responses could be influenced by social desirability biases. Additional methods such as in-depth interviews are recommended. Similarly, it is necessary to develop studies with methodological designs that allow causality to be established.
Despite these limitations, the study is important for its contribution to scientific knowledge of the factors related to BS in Cuban dental students. Continued research on BS allows for the identification of new associated factors that may not have been previously considered.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the participants or participants legal guardian/next of kin was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
BC-A: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. IC-R: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. PH-P: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. CM: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Ansari, A., El Tantawi, M., AbdelSalam, M., and Al-Harbi, F. (2015). Academic advising and student support: help-seeking behaviors among Saudi dental undergraduate students. Saudi Dent. J. 27, 57–62. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2014.11.011
Al-Hallak, K. R., Nassani, M. Z., Heskul, M. M., Doumani, M. D., and Darwish, M. (2018). Reasons for choosing dentistry as a career among dental students in Saudi Arabia. Eur. J. Dent. 2, 275–280. doi: 10.4103/ejd.ejd_335_17
Almalki, S. A. (2019). Influence of motivation on academic performance among dental college students. Open Access Macedonian J. Med. Sci. 7, 1374–1381. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.319
Alqarni, M. A. (2021). Assessing dental students’ professional satisfaction with operative dentistry teaching and curriculum: a study in Saudi Arabia. Medicine 100:e26459. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026459
Alvares, M., Thomaz, E., Lamy, Z., Nina, R., Pereira, M., and Garcia, J. (2020). Burnout syndrome among healthcare professionals in intensive care units: a cross-sectional population-based study. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intens. 32, 251–260. doi: 10.5935/0103-507x.20200036
Arias, Y., Herrero, Y., Cabrera, Y., Chibás, D., and García, Y. (2020). Manifestaciones psicológicas frente a la situación epidemiológica causada por la COVID-19. Rev. Haban Cienc. Méd. 19 (Supl.):e3350.
Awlaczyk, M., Siembida, J., Balaj, K., and Rajewska-Rager, A. (2020). The assessment of stress level, anxiety, depressive symptoms, and defense mechanisms among Polish and English medical students. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 19:29. doi: 10.1186/s12991-020-00274-7
Bang, H., and Reio, T. G. (2017). Examining the role of cynicism in the relationships between burnout and employee behavior. Rev. Psicol. Trabajo Organ. 83, 217–227. doi: 10.1016/j.rpto.2017.07.002
Caldwell, J., Caldwell, L., Thompson, L., and Lieberman, H. (2019). Fatigue and its management in the workplace. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 96, 272–289. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.10.024
Campbell, F., Blank, L., Cantrell, A., Baxter, S., Blackmore, C., Dixon, J., et al. (2022). Factors that influence mental health of university and college students in the UK: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 22:1778. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13943-x
Campos, J. A., Jordani, P. C., Zucoloto, M. L., Bonafé, F. S., and Maroco, J. (2012). Burnout syndrome among dental students. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 215, 155–165. doi: 10.1590/s1415-790x2012000100014
Chauca, L., Lascano, L., Jaramillo, L., Cevallos, C., Cevallos-Pozo, G., Velasquez, B., et al. (2023). The prevalence of the burnout syndrome and factors associated in the students of dentistry in integral clinic: a cross-sectional study. Int. J. Dent. 2023, 1–6. doi: 10.1155/2023/5576835
Chen-Yi, L., Ju-Hui, W., and Je-Kang, D. (2019). Work stress and occupational burnout among dental staff in a medical center. J. Dent. Sci. 14, 295–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2019.01.006
Corrales-Reyes, I. E., Villegas-Maestre, J. D., Berenguer-Gouarnaluses, J. A., Torres-Fernández, L. S., Mamani-Benito, O. J., and Carranza-Esteban, R. F. (2022). Evidencias de validez y confiabilidad de una escala de burnout en estudiantes cubanos de Estomatología. Rev. Cubana Med. Militar. 51:e02201847.
Costa, E. F., Santos, S. A., Santos, A. T., Melo, E. V., and Andrade, T. M. (2012). Burnout syndrome and associated factors among medical students: a cross-sectional study. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67, 573–580. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2012(06)05
Crudden, G., Margiotta, F., and Doherty, A. M. (2023). Physician burnout and symptom of anxiety and depression: burnout in Consultant Doctors in Ireland Study (BICDIS). PLoS One 18:e0276027. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276027
De Clercq, D., Ul Haq, I., and Azeem, M. (2019). The relationship between workplace incivility and depersonalization towards co-workers: roles of job-related anxiety, gender, and education. J. Manag. Organ. 26, 1–22. doi: 10.1017/jmo.2019.76
Deeb, G. R., Braun, S., Carrico, C., Kinser, P., Laskin, D., and Golob Deeb, J. (2018). Burnout, depression, and suicidal ideation in dental and dental hygiene students. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 22, e70–e74. doi: 10.1111/eje.12259
Di Mario, S., Rollo, E., Gabellini, S., and Filomeno, L. (2024). How stress and burnout impact the quality of life amongst healthcare students: an integrative review of the literature. Teach. Learn. Nurs. 19, 315–323. doi: 10.1016/j.teln.2024.04.009
El Dabbah, N. A., and Elhadi, Y. A. M. (2023). High levels of burnout among health professionals treating COVID-19 patients in two Nile basin countries with limited resources. Sci. Rep. 13:6455. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33399-2
Elmanaseer, W. R., Al-Omoush, S. A., Alamoush, R. A., Abu Zaghlan, R., and Alsoleihat, F. (2023). Dental students’ perception and self-perceived confidence level in key dental procedures for general practice and the impact of competency implementation on their confidence level, Part I (Prosthodontics and Conservative Dentistry). Int. J. Dent. 2023:2015331. doi: 10.1155/2023/2015331
Engle-Friedman, M., Mathew, G. M., Martinova, A., Armstrong, F., and Konstantinov, V. (2018). The role of sleep deprivation and fatigue in the perception of task difficulty and use of heuristics. Sleep Sci. 11, 74–84. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20180016
Frajerman, A., Chaumette, B., Krebs, M. O., and Morvan, Y. (2022). Mental health in medical, dental, and pharmacy students: a cross-sectional study. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 10:100404. doi: 10.1016/j.jadr.2022.100404
Fukushima, H., Imai, H., Miyakoshi, C., Naito, A., Otani, K., Matsuishi, K., et al. (2023). The sustained psychological impact of coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on hospital workers 2 years after the outbreak: a repeated cross-sectional study in Kobe. BMC Psychiatry 23:313. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-04788-8
García-Torres, M., Aguilar-Castro, J., and García-Méndez, M. (2021). Bienestar psicológico y burnout en personal de salud durante la pandemia de COVID-19. Escritos Psicol. 14, 96–106.
Gil, J., and Cruz, D. (2018). El burnout académico y el engagement en estudiantes de quinto año de Estomatología. Edumecentro 10, 37–53.
Gil, Y., Hong, J., Ban, J., Kwon, J., and Lee, J. (2023). Dental students’ perception of their educational environment in relation to their satisfaction with dentistry major: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med. Educ. 23:508. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04485-w
Gilmour, A., Welply, A., Cowpe, J., Bullock, A., and Jones, R. (2016). The undergraduate preparation of dentists: confidence levels of final year dental students at the School of Dentistry in Cardiff. BDJ 221, 349–354. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2016.686
Güler, Y., Şengül, S., Çaliş, H., and Karabulut, Z. (2019). Burnout syndrome should not be underestimated. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992) 65, 1356–1360. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.65.11.1356
Hadid, A., Shadid, A., Shadid, A., Almutairi, F., Almotairi, K., Aldarwish, T., et al. (2020). Stress, burnout, and associated risk factors in medical students. Cureus 12:e6633. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6633
Hershner, S., and Chervin, R. (2014). Causes and consequences of sleepiness among college students. Nat. Sci. Sleep 6, 73–84. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S62907
Javed, M. Q., Ahmad, Z., Muhammad, M., Binrayes, A., Niazi, I., Nawabi, S., et al. (2024). Burnout level evaluation of undergraduate dental college students at Middle Eastern University. BMC Med. Educ. 24:1155. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06149-9
Jiménez-Ortiz, J., Islas-Valle, R., Jiménez-Ortiz, J., Pérez-Lizárraga, E., Hernández-García, M., and González-Salazar, F. (2019). Emotional exhaustion, burnout, and perceived stress in dental students. J. Int. Med. Res. 47, 4251–4259. doi: 10.1177/0300060519859145
Karagir, A., Khairnar, M., Adaki, D., Dhole, R., Patil, D., and Sale, M. (2021). Assessment of the factors influencing dental students to choose dentistry as a career: a cross-sectional study. J. Dent. Res. 32, 153–157. doi: 10.4103/ijdr.IJDR_407_19
Kassarnig, V., Bjerre-Nielsen, A., Mones, E., Lehmann, S., and Lassen, D. D. (2017). Class attendance, peer similarity, and academic performance in a large field study. PLoS One 12:e0187078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187078
Kavousipour, S., Noorafshan, A., Pourahmad, S., and Dehghani-Nazhvani, A. (2015). Achievement motivation level in students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences and its influential factors. J. Adv. Med. Educ. Prof. 3, 26–32.
Khammissa, R. A. G., Nemutandani, S., Feller, G., Lemmer, J., and Feller, L. (2022). Burnout phenomenon: neurophysiological factors, clinical features, and aspects of management. J. Int. Med. Res. 50:3000605221106428. doi: 10.1177/03000605221106428
Khanal, S., and Shrestha, S. (2021). Perceived stress among undergraduate students in a dental college: a descriptive cross-sectional study. J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 59, 892–896. doi: 10.31729/jnma.6446
Koppmann, A., Cantillano, V., and Alessandri, C. (2021). Distrés moral y burnout en el personal de salud durante la crisis por COVID-19. Rev. Med. Clin. Condes 32, 75–80. doi: 10.1016/j.rmclc.2020.12.009
Korkmaz, C., Dikicier, S., and Atay, A. (2023). Assessment of burnout level among clinical dental students during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Med. Educ. 23:767. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04729-9
Lim, J., Ko, H., Park, J., and Ihm, J. (2022). Effect of active learning and online discussions on the academic performances of dental students. BMC Med. Educ. 22:312. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03377-9
Littzen-Brown, C., Dolan, H., Norton, A., Bethel, C., May, J., and Rainbow, J. (2023). Unbearable suffering while working as a nurse during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative descriptive study. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. Adv. 5:100127. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2023.100127
Lo, J. C., Chong, P. L., Ganesan, S., Leong, R. L., and Chee, M. W. (2016). Sleep deprivation increases formation of false memory. J. Sleep Res. 25, 673–682. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12436
Lukasik, M., Waris, O., Soveri, A., Lehtonen, M., and Laine, M. (2019). The relationship of anxiety and stress with working memory performance in a large non-depressed sample. Front. Psychol. 10:4. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00004
Maragha, T., Perez-Garcia, A., Shuler, C., Walker, J., and Von Bergmann, H. (2023). Preclinical dental students and their learning environment: a wellbeing perspective. J. Dent. Educ. 87, 572–583. doi: 10.1002/jdd.13778
Marsden, J. E., Deboo, S. P., Cripps, M., Longridge, N. N., Aspden, M., and Fox, K. (2022). Improving dental student confidence through the use of simulated patient cases. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. doi: 10.1111/eje.12867 [Epub ahead of print]
Mohebbi, S. Z., Gholami, M., Chegini, M., Ghoreyshi, Y., Gorter, R. C., and Bahramian, H. (2021). Impact of career choice motivation on academic burnout in senior dental students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Med. Educ. 21:52. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02475-w
Moukarzel, A., Michelet, P., Durand, A. C., Sebbane, M., Bourgeois, S., Markarian, T., et al. (2019). Burnout syndrome among emergency department staff: prevalence and associated factors. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019:6462472. doi: 10.1155/2019/6462472
Nikolovska, J., Eaton, K. A., Kenig, N., and Hysi, D. (2020). Motivation to follow a career in dentistry of students in three South-East European countries. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 54, 175–185. doi: 10.15644/asc54/2/8
Owen, C., Seddon, C., Clarke, K., Bysouth, T., and Johnson, D. (2022). The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the mental health of dentists in Wales. Br. Dent. J. 232, 44–54. doi: 10.1038/s41415-021-3756-7
Palatta, A. M., Kassebaum, D. K., Gadbury-Amyot, C. C., Karimbux, N. Y., Licari, F. W., Nadershahi, N. A., et al. (2017). Change is here: ADEA CCI 2.0-A learning community for the advancement of dental education. J. Dent. Educ. 81, 640–648. doi: 10.21815/JDE.016.040
Pepe-Nakamura, A., Míguez, C., and Arce, R. (2014). Equilibrio psicológico y burnout académico. Rev. Inv. Educ. 2, 32–39.
Perez, A., Green, J., Moharrami, M., Gianoni-Capenakas, S., Kebbe, M., Ganatra, S., et al. (2023). Active learning in undergraduate classroom dental education- a scoping review. PLoS One 18:e0293206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0293206
Pham Thi, T. D., and Duong, N. T. (2024). Investigating learning burnout and academic performance among management students: a longitudinal study in English courses. BMC Psychol. 12:219. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01725-6
Rajadurai, S., Sandhu, R., Hockaday, M., and Park, S. (2023). The role of peer teachers in dental skills education - A phenomenological study. J. Curr. Teach. 12:135. doi: 10.5430/jct.v12n4p135
Ramírez-López, A. E., and Asmat-Abanto, A. S. (2024). Burnout syndrome in peruvian dental students: a prevalence study. Braz. J. Oral Sci. 23:e241300. doi: 10.20396/bjos.v23i00.8671300
Renninger, K., and Bachrach, J. (2015). Studying triggers for interest and engagement using observational methods. Educ. Psychol. 50, 58–69. doi: 10.1080/00461520.2014.999920
Rodrigues, H., Cobucci, R., Oliveira, A., Cabral, J. V., Medeiros, L., Gurgel, K., et al. (2018). Burnout syndrome among medical residents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 13:e0206840. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206840
Shao, R., He, P., Ling, B., Tan, L., Xu, L., Hou, Y., et al. (2020). Prevalence of depression and anxiety and correlations between depression, anxiety, family functioning, social support, and coping styles among Chinese medical students. BMC Psychol. 8:38. doi: 10.1186/s40359-020-00402-8
Sjöström, M., and Brundin, M. (2021). The effect of extra educational elements on the confidence of undergraduate dental students learning to administer local anaesthesia. Dent. J. 9:77. doi: 10.3390/dj9070077
Sulaiman, R., Ismail, S., Shraim, M., El Hajj, M. S., Kane, T., and El-Awaisi, A. (2023). Experiences of burnout, anxiety, and empathy among health profession students in Qatar University during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychol. 11:111. doi: 10.1186/s40359-023-01132-3
Keywords: prevalence, burnout, dental students, Cuba, dentistry
Citation: Cossio-Alva BA, Corrales-Reyes IE, Herrera-Plasencia PM and Mejia CR (2025) Prevalence and factors associated with burnout in dental students of seven Cuban universities. Front. Educ. 9:1488937. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1488937
Received: 30 August 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 22 January 2025.
Edited by:
Maura Pilotti, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Saudi ArabiaReviewed by:
Arifi N. Waked, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Saudi ArabiaMaryam Bojulaia, Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2025 Cossio-Alva, Corrales-Reyes, Herrera-Plasencia and Mejia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bryan Alexis Cossio-Alva, YmNvc3Npb0B1Y3YuZWR1LnBl
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Bryan Alexis Cossio-Alva
Bryan Alexis Cossio-Alva Ibraín Enrique Corrales-Reyes
Ibraín Enrique Corrales-Reyes Paul Martín Herrera-Plasencia
Paul Martín Herrera-Plasencia Christian R. Mejia
Christian R. Mejia