- 1Institute for the Future of Education, Tecnologico de Monterrey, Monterrey, Mexico
- 2School of Engineering, Universidad Andres Bello, Santiago, Chile
- 3Facultad de Psicología, Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey, Mexico
Educational innovation is a defining feature within educational institutions, necessitating a heightened emphasis on its promotion. However, exposure to these processes and participation tend to be highly demanding and exhausting for the teachers. Consequently, it becomes imperative for educational authorities to proactively monitor teachers’ involvement in innovation, utilizing appropriate instruments to identify and assess the associated risk factors. This study proposes a rigorously validated and reliable model for measuring the risk factors associated with emotional exhaustion among teachers in innovative educational environments. Employing a cross-sectional design, the study scrutinized the psychometric properties of a sample comprising 535 university teachers from the same higher education institution actively engaged in educational innovation. The results from the investigation revealed that the measurement model demonstrated robust evidence of construct validity, as ascertained through both exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Predictive validity was evaluated utilizing Path Analysis, while convergence validity was assessed via Average Variance Extracted. Discriminant validity was established through the Homotrait-Heterotrait ratio, and gender invariance was validated through nested-model sequencing methods. Additionally, reliability assessments were conducted using both Cronbach’s alpha and McDonald’s omega coefficients. The resultant measurement model, characterized by its parsimony, offers educational institutions a valuable instrument for safeguarding faculty wellbeing amidst the demands of educational innovation.
1 Introduction
Education stands as a cornerstone in the holistic development of individuals and societies, playing a pivotal role in poverty alleviation, inequality reduction, empowerment, and promoting peaceful values. Its significance is underscored by its inclusion as one of the sustainable development goals for 2030 by the United Nations (2015). However, the pursuit and maintenance of educational quality face numerous challenges, ranging from economic downturns and financial constraints to the emergence of new educational paradigms and shifts in the roles and responsibilities of educators (Romero and Laborín, 2016).
Teaching, as a profession, occupies a central position in societal advancement, characterized by its inherent complexity and challenges. Teachers bear a myriad of responsibilities, including the mastery, creation, organization, and dissemination of knowledge, as well as providing academic guidance and addressing the emotional needs of students (Vicente Coronado et al., 2019). To fulfill these multifaceted roles, teachers are expected to exhibit qualities such as enthusiasm, empathy, tolerance, and optimism, while also striving for continuous personal and professional development (Fernández et al., 2016; Klusmann et al., 2023).
Despite the intrinsic rewards of the teaching profession, research by Ilisko et al. (2020) and Zhao and You (2021) indicates that educators commonly experience heightened levels of stress, workload, and pressure to ensure student academic success. This amalgamation of professional and personal demands can evoke mixed emotions among teachers. While they derive satisfaction from the meaningful impact of their work on students’ lives, they also grapple with persistent challenges, such as student disengagement, resource limitations, and constraints on professional autonomy (Corbett et al., 2021, Passey, 2021; Vicente Coronado et al., 2019). When the equilibrium between positive and negative experiences is disrupted, and negative emotions accrue due to prolonged exposure to stressors, teachers may suffer emotional exhaustion (Cuadrado et al., 2022; Evers et al., 2002).
Emotional exhaustion is characterized by a sense of being overwhelmed and depleted of emotional resources and manifests as loss of energy, weakened resilience, and fatigue (Evers et al., 2002; Gil-Monte et al., 2009; Portoghese et al., 2018; Živanović et al., 2021). This set of symptoms is often considered a major component of burnout syndrome (Maslach and Leiter, 2017; Virtanen et al., 2019). The term “burnout syndrome” dates back to the 70s. Initially associated with professions involving caregiving, such as healthcare, social services, law, and education, burnout syndrome has since been observed across various occupational domains (Rocha et al., 2020; Sestili et al., 2018). It has subsequently been extended to all types of work activity (Appel-Meulenbroek et al., 2020). This syndrome represents a psychological condition comprising emotional fatigue or exhaustion, depersonalization, or cynicism, and reduced personal efficacy (Maslach et al., 1997; World Health Organization, 2019).
In the field of education, burnout has highly negative implications for the personal and professional lives of teacher (Martínez-Líbano and Yeomans, 2023; Smetackova et al., 2019), correlating with decreased job satisfaction, diminished self-efficacy, heightened stress levels, increased workloads, and diminished wellbeing (Fernández et al., 2016; Klusmann et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2023; McInerney et al., 2018; Smetackova et al., 2019). Moreover, the phenomenon exacerbates teacher turnover rates, resulting in workforce shortages, diminished social support networks, and a decline in overall educational quality (Burić et al., 2019; Cuadrado et al., 2022).
An often-overlooked factor exacerbating teacher emotional exhaustion is the implementation of educational innovation. According to Kassymova et al. (2019), implementing educational innovation engenders stress, manifesting in crises and tensions at personal, interpersonal, and organizational levels throughout the innovation process. Despite these challenges, the notion of higher education institutions abandoning innovation efforts is untenable. Hence, there arises a pressing need for mechanisms and instruments capable of identifying environments conducive to emotional exhaustion to preempt teacher burnout within innovative educational contexts.
The current study was conducted within a non-profit private higher education institution in Mexico, which prioritizes teaching quality and innovation as core objectives. Participating teachers in this study were engaged in implementing an educational innovation framework rooted in Challenge-Based Learning. Within this approach, teachers assumed multifaceted roles as facilitators, evaluators, and liaisons with external entities presenting challenges to student groups, comprising communities, companies, institutions, or organizations. This innovation aims to provide students with engaging, motivating, and meaningful learning experiences, wherein they apply acquired knowledge and develop competencies (Tecnologico de Monterrey, 2017). However, for teachers, this innovation represents both a source of reward and a significant challenge, as they must invest additional effort in assigning student groups, guiding them through challenge resolution, and facilitating presentations to external stakeholders, effectively doubling their workload.
The recognition of burnout as an occupational phenomenon by the World Health Organization, 2019, included in the 11th revision of the International Classification of Diseases, underscores the gravity of the issue. Although not classified as a medical condition, burnout is conceptualized as a syndrome stemming from chronic work-related stress that remains unaddressed (World Health Organization, 2022a,b). Additionally, the organization reported in 2019 that approximately 15% of working-age adults worldwide experienced a mental disorder, contributing to a staggering loss of twelve billion days of work annually, amounting to an economic cost of one trillion dollars (World Health Organization, 2022a,b). These findings underscore the urgent need for proactive measures to address burnout and its associated impacts on individuals and organizations.
In Mexico, the prevalence of mental health disorders is a pressing concern, with 15.4% of the adult population reporting symptoms of depression, 19.3% experiencing severe anxiety, and 31.3% exhibiting varying degrees of anxiety symptoms (INEGI, 2021). Furthermore, the Pan American Health Organization’s (2019) report in positioned Mexico within the third quintile for depressive disorders among its member countries. In response to these challenges, Mexico introduced and published the official standard NOM-035-STPS-2018, “Psychosocial Risk Factors at Work, Identification, Analysis, and Prevention,” by the Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare in 2018. This standard seeks to mitigate psychosocial risk factors and promote healthy work environments conducive to professional performance. It delineates definitions, obligations, procedures, and recommendations while incorporating a scale for measuring psychosocial risk factors. However, the validity and reliability of this scale have been subject to limited assessment, with existing studies yielding questionable results (Cano-Gutierrez et al., 2023; Gutiérrez et al., 2022; Santoyo et al., 2022). In this scenario, the regulation mentions that institutions can have their own instruments if they comply with set criteria or adjustment indices established therein.
Considering the scarcity of validated measurement instruments, a crucial need exists to develop tools for assessing risk factors for emotional exhaustion in educational innovation settings (Evers et al., 2002; Guerrero-Barona et al., 2018; Kassymova et al., 2019). Consequently, a comprehensive examination of teachers’ risk factors is warranted (Monroy-Castillo and Juárez-García, 2019; Olivares et al., 2020). The primary objective of this research is to propose a model with robust evidence of validity and reliability for measuring risk factors associated with teachers’ emotional exhaustion within innovative educational environments.
The proposed model encompasses two correlated factors, personal risks (F1) and psychosocial risks (F2), along with gender invariance. Additionally, the model assesses the predictive capacity of these factors on emotional exhaustion within innovative educational environments. Specifically, the predictive relationship model delineates a directional pathway from psychosocial to personal factors, wherein emotional exhaustion is directly influenced by personal factors and indirectly mediated by psychosocial factors. The resulting model is characterized by its parsimony and unsaturation, with the individual’s assessment of their mental wellbeing in the innovative educational environment serving as its focal point. This assessment is influenced by peer and managerial evaluations, as well as interactions that bolster self-esteem and autonomy in the teacher’s role.
2 Materials and methods
This quantitative study uses a cross-sectional survey design (Creswell, 2012). All participants were informed that their involvement was voluntary and that their personal data would be handled in accordance with prevailing regulations.
2.1 Participants
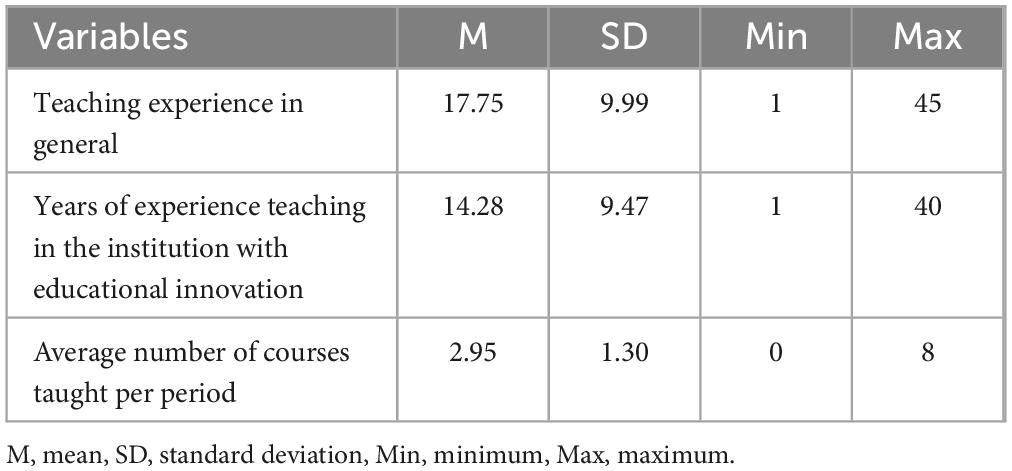
A non-probabilistic method was used to select the sample. A total of 535 university teachers participated, which is a statistically representative sample of the subpopulation that used the educational innovation. The teachers come from the six faculties that make up the higher education institution. These educators were engaged in a semester-long educational innovation initiative centered on challenge-based learning in collaboration with an external partner (Tecnologico de Monterrey, 2017). Of the participants, 314 (58.70%) identified themselves as male, 214 (40%) as female, and 7 (1.30%) opted not to disclose their gender. The mean age of the participants was 46.08 years (SD = 8.96 years). Regarding employment status, 300 participants were full-time (56.07%), while the remaining 235 were part-time faculty members. Most teachers (89%) reported exclusive employment within the institution. Regarding academic qualifications, 222 (41.50%) teachers indicated that they had a doctoral degree, 295 (55.14%) had a master’s degree, and 18 (3.36%) possessed a professional degree. To complement the characterization of the participants, Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics about overall teaching experience, specific teaching experience, and the average number of courses historically taught.
2.2 Instruments
This section presents the two scales implemented, their description, and their characteristics.
2.2.1 Scale of risk factors associated with emotional exhaustion in innovative educational environments (FRADI in Spanish acronym)
This proposal was designed based on the contributions of Bitran et al. (2019), Guerrero-Barona et al. (2018), Monroy-Castillo and Juárez-García (2019), and Unda Rojas et al. (2020). Initially, it comprised 23 Likert-type items with options ranging from 0 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree). The scale underwent a rigorous content validation process. Through a content validation process, the experts recommended the exclusion of 8 items and the inclusion of 2 new items, resulting in a refined scale consisting of 17 items.
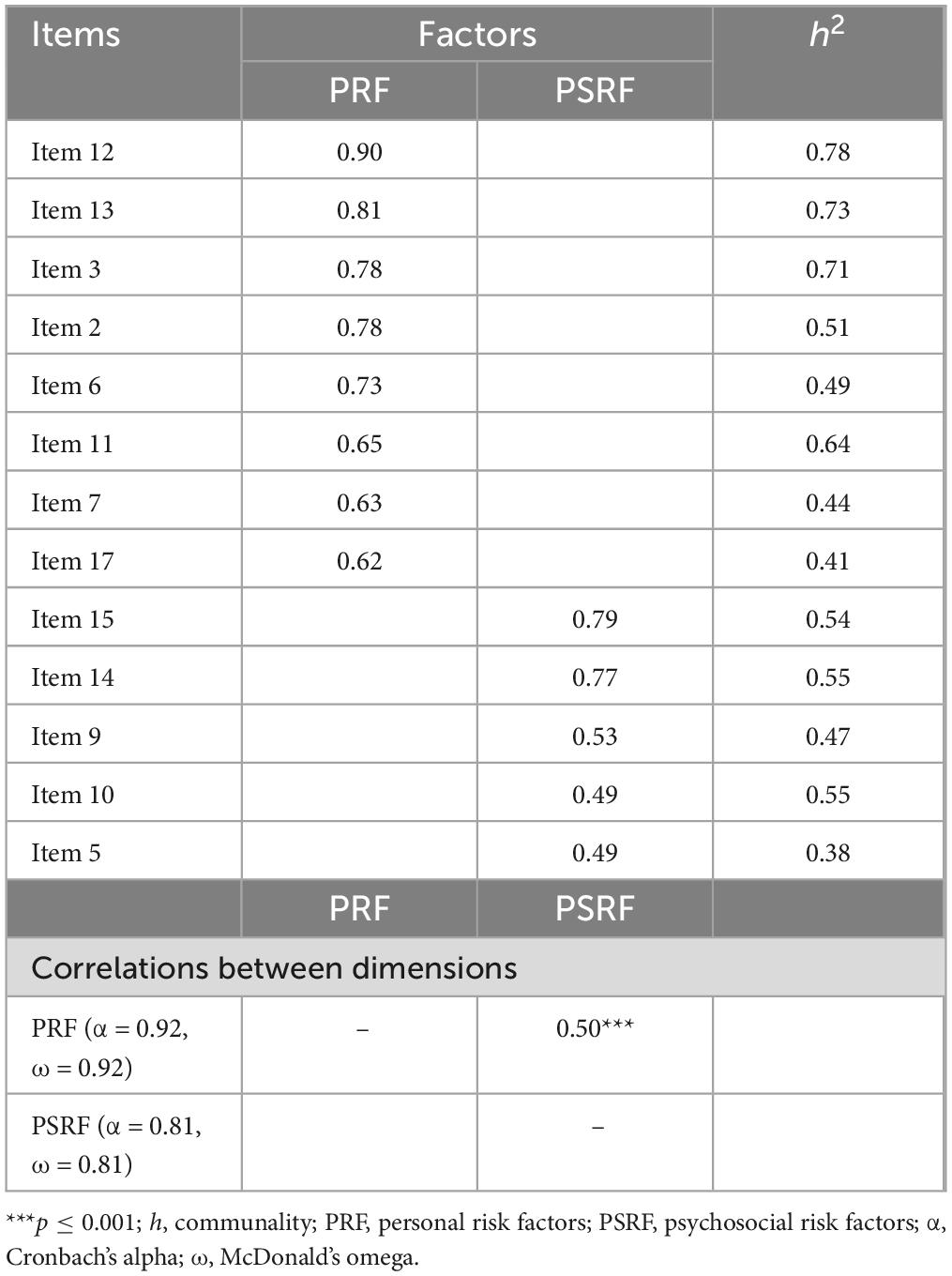
Table 2 provides a comprehensive overview of the scale items and their corresponding dimensions. These dimensions include:
1. Personal risk factors (PRF). These factors directly impact an individual’s physical, emotional, and cognitive wellbeing, thereby impeding the fulfillment of basic needs.
2. Psychosocial risk factors (PSRF). Derived from the nature of the role, these factors encompass interactions and perceptions of a peer or leader.
This segmentation enables a nuanced exploration of the various facets contributing to emotional exhaustion within innovative educational environments.
2.2.2 Emotional distress scale
Traditional burnout measurement scales face criticism regarding their theoretical structure, empirical fit, and consistency in reporting psychometric properties (Kristensen et al., 2005; Shoman et al., 2021). Notably, various models have been proposed for measuring burnout, such as the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI; Maslach et al., 1997), Copenhagen Burnout Inventory (CBI; Kristensen et al., 2005), and Oldenburg Burnout Inventory (Demerouti et al., 2003). Among these inventories, the MBI stands out for the number of burnout research that applies it (Bravo et al., 2021). However, critiques of its structural composition suggest that the depersonalization dimension may be viewed as a coping mechanism, while personal fulfillment is perceived as a consequence (Kristensen et al., 2005; Shoman et al., 2021). Moreover, interpreting MBI results necessitates analyzing and interpreting scores independently for each dimension (Maslach and Leiter, 2021), with inconclusive data regarding interdimensional correlations (Živanović et al., 2021).
In contrast, the CBI seeks to rectify certain aspects of the MBI by focusing on investigating exhaustion across various life domains. However, recent studies have indicated challenges in maintaining the scale’s structural integrity, necessitating adjustments to item formulations and resulting in solutions comprising 2 to 4 highly correlated factors (Bolatova et al., 2021; Jeon et al., 2019; Piperac et al., 2021; Wongtrakul et al., 2021).
In this study, we elected to utilize the Emotional Exhaustion subscale from the model proposed by Gil-Monte et al. (2009) for assessing Work-Burnout Syndrome, which has demonstrated validity and reliability in Mexican higher education teaching populations. Within this model, Emotional Exhaustion is defined as the experience of emotional and physical depletion resulting from daily encounters with problematic individuals or situations in the workplace. The subscale comprises four items rated on a Likert-type scale ranging from 0 (never) to 4 (always).
2.3 Ethical considerations
The study was reviewed and approved by the Experimentation and Measurement Impact Office of the participating educational institution. In addition, the guidelines established by the American Psychological Association (2017) for the development of research with respect to data confidentiality and obtaining informed consent were followed. Participants were informed of the purpose of the research, the estimated duration, and the different stages of the study. They were also given the possibility of refusing to participate and a contact address for questions about the project. Moreover, a complete privacy notice1 used by Tecnologico de Monterrey was also added. Finally, it is worth mentioning that none of the data collected is considered sensitive personal data in Mexico (Cámara de Diputados del H. Congreso de la Unión, 2010).
2.4 Data analysis
Six expert judges participated in the content validity analysis, including two psychometric experts, a psychology professional, a professor in educational innovation (Beltran-Sanchez and Dominguez, 2021), and two project-lead researchers with experience in education and research.
Construct validation was performed with exploratory factor analysis (EFA, n = 278) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA, n = 257). The following parameters were considered to carry out the EFA:
• Data normality. Measured by symmetry and kurtosis scores (± 3; George and Mallery, 2019).
• Data adequacy. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin test (KMO > 0.80) and Bartlett’s sphericity test with p = 0.050 verified the presence of multicollinearity (Cea, 2004).
• Communalities with values equal to or greater than 0.30 (DeVellis, 2012).
• Factor loads greater than 0.35 (Hair et al., 2019).
• Explained variance greater than 50% (Cea, 2004; Hair et al., 1999; Merenda, 1997).
• Extraction method: maximum likelihood
• Rotation method: Oblimin
Similarly, for the execution of the CFA, the maximum likelihood (ML) method was used for the estimation of parameters and compliance with the adjustment indices proposed by Hair et al. (2019), Cea (2004), and Byrne (2016) was ensured, which are:
• Absolute Fit Indices
○ Likelihood ratio (X2). The p-value is expected to be ≥ 0.05.
○ Goodness-of-fit index (GFI): The accepted value ≥ 0.90.
○ Adjusted goodness-of-fit ratio (AGFI): The accepted value ≥ 0.90.
○ Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR): Values ≤ 0.05.
• Incremental adjustment indices:
○ Comparative Adjustment Index (CFI): The accepted value ≥ 0.90.
○ Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI): The accepted value ≥ 0.90.
○ Incremental Fit Index (IFI): The accepted value ≥ 0.90.
• Discrepancy-Based Adjustment Indices:
○ Root Mean Square Area of Approximation (RMSEA). Values ≤ 0.08 are expected.
○ Standardized chi-square (X2/df): Indicates the fit of the model; values between 1 and 3 are desired.
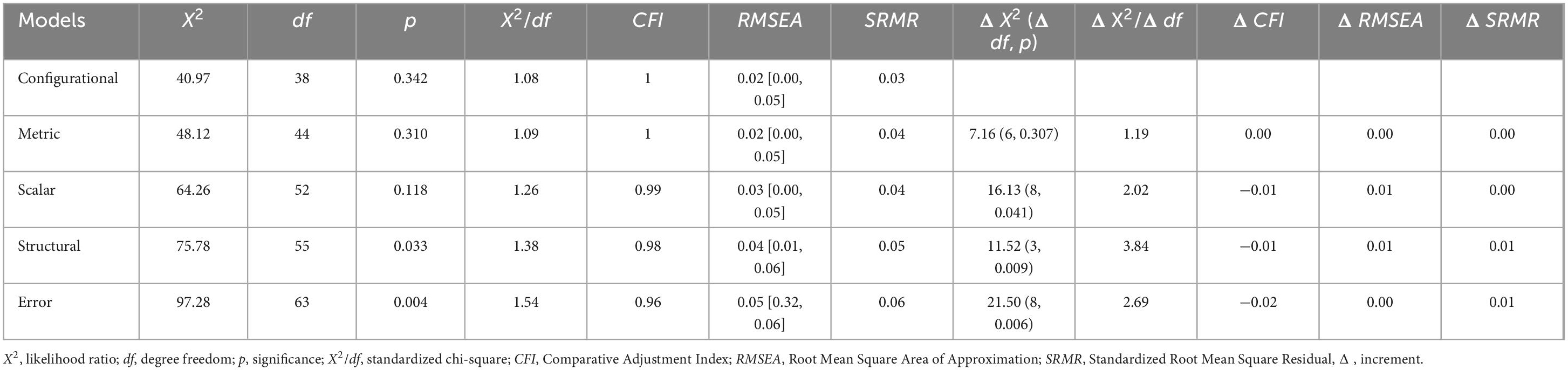
Additionally, a multigroup analysis was performed to determine the invariance between men (n = 257) and women (n = 257) using nested models: configurational (without constraints), metric (with constraints on structural weights), scalar (constraints on intercepts), structural (constraints on covariances) and error (with restrictions on residuals). This approach also used ML, and confidence intervals were calculated using the bias-corrected percentile method and accelerated from 1,000 Bootstrap samples. The confidence level was set at 90%. Following Chen (2007), the following five goodness-of-fit difference indices (among nested models) and cut-off points were used: ΔX2 (p > 0.050), Δ X2/df (< 3), ΔCFI (< 0.01), ΔRMSEA (< 0.015) y ΔSRMR (< 0.03, constraints on structural weights; < 0.01 when comparing intercepts and errors).
Convergent validity was determined using the Average Variance Extracted (AVE), which, according to Hair et al. (2019), must be greater than 0.50. This value is the average of the squared loads of all the items associated with the construct. The Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio (HTMT), equal to or less than 0.90 (Henseler et al., 2015), was used to evaluate discriminant validity. Similarly, predictive validity was performed using structural equation modeling (SEM) with the same cut-off points in goodness-of-fit indices as in CFA. Additionally, the invariance for gender was tested with the goodness-of-fit difference indices mentioned for this process using the same method of estimation of parameters and confidence intervals.
Finally, reliability was assessed using the internal consistency of the scale using Cronbach’s alpha (α ≥ 0.70, Nunnally and Bernstein, 1994; DeVellis, 2012) and McDonald’s omega (ω ≥ 0.80, McDonald, 1999; Feißt et al., 2019; Hayes and Coutts, 2020).
3 Results
3.1 Construct validity
3.1.1 Exploratory factor analysis
In the first execution of the exploratory factor analysis (EFA), two of the items (8 and 16) were excluded because they did not meet the commonality criterion since they had a score lower than 0.30. Subsequently, in a second iteration of the EFA, although the commonality criterion was satisfied, two items (1 and 4) exhibited ambiguous loadings and were consequently removed.
The final EFA was conducted utilizing the maximum likelihood extraction method with oblique rotation. The dataset demonstrated high multicollinearity, with Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy yielding 0.91, and Bartlett’s test of sphericity indicating significance (χ2 = 2,063.26, p < 0.001). The resulting model consisted of 13 items distributed across two dimensions, collectively accounting for 55.45% of the variance. The first dimension, comprising personal risk factors, encompassed eight items, explaining 46.16%, and the second dimension, representing psychosocial risk factors, comprised five items, explaining 9.29% of the variance. The overall reliability of the 13 items was acceptable, with Cronbach’s alpha (α) and McDonald’s omega (ω) coefficients both calculated at 0.91. Refer to Table 3 for further details.
3.1.2 Confirmatory factor analysis
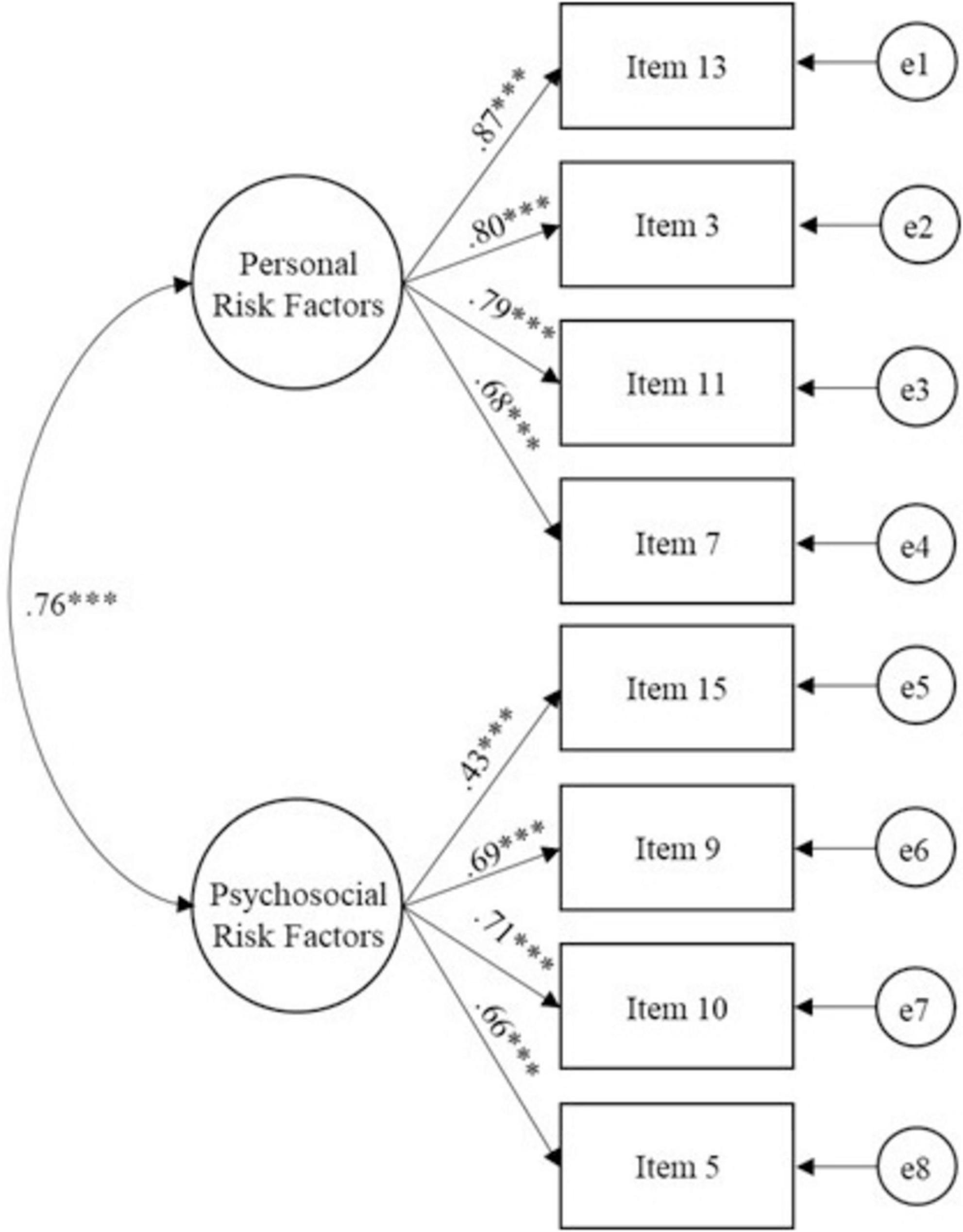
Building upon the structure obtained in the EFA, the measurement model was confirmed. The maximum likelihood method was used to estimate parameters and determine the fit between the theoretical and empirical models in the CFA. The results obtained in the indices indicate that the fit of the model to the observed data was confirmed: X2 = 25.89, p = 0.133, df = 19; X2/df = 1.36; SRMR = 0.03; RMSEA = 0.04, CI [0.00, 0.07]; CFI = 0.99; NFI = 0.97; GFI = 0.98; AGFI = 0.96; TLI = 0.99 e IFI = 0.99. Furthermore, significant factor loadings were observed for all items, ranging from 0.43 to 0.87 (see Figure 1). Following the recommendation of modification indices, five items (2, 6, 12, 14, and 17) were subsequently removed from the analysis. These findings collectively underscore the robustness of the measurement model, affirming its validity in capturing the underlying constructs of interest.
3.1.3 Convergence and discriminant validity
Evidence of convergent validity was found, as a score equal to 0.51 was obtained in the extracted average variance, along with standardized measure weights greater than 0.50 and reliability scores greater than 0.80 for McDonald’s omega and Cronbach’s alpha. Regarding divergent validity, a value equal to 0.91 was obtained when calculating the Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio (HTMT), which can be considered moderate discrimination.
3.1.4 Measurement invariance
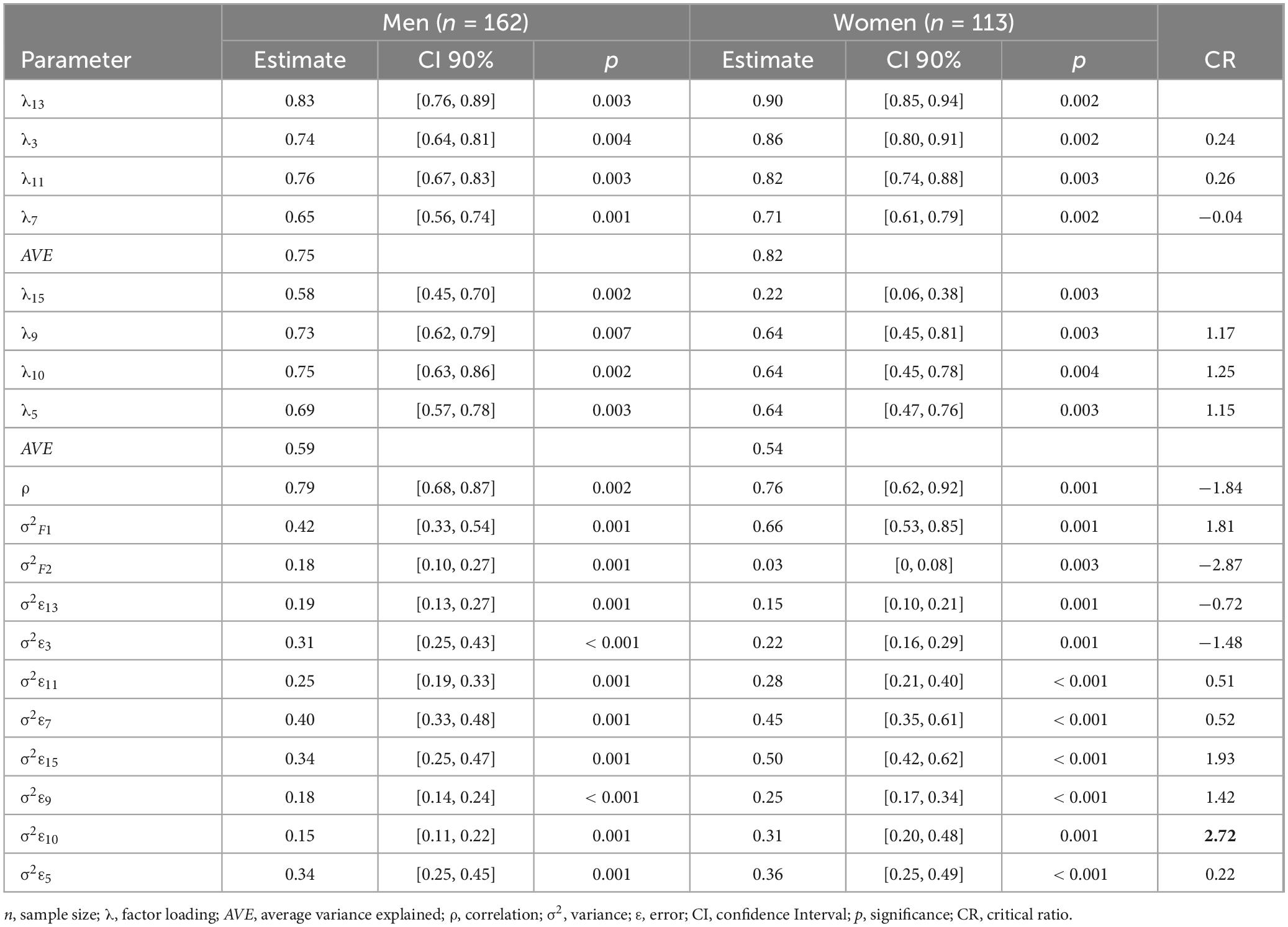
An analysis of the statistical significance of the parameters for evaluating invariance between men and women was performed. In the five nested models of both samples by gender, all parameters were statistically significant (p < 0.05). It was found that the confidence intervals of the parameters overlap in their estimation in each of the two samples by gender, except for the variance of the psychosocial factors dimension (σ2F2), which was higher (σ2F2 = 0.18, 90% CI [0.10, 0.27]) in men than women (σ2F2 = 0.03, 95% CI [0, 0.08]). Also, the likelihood ratio (critical ratio CR) statistics that compare both samples in each parameter were in the range (−2, 2), except the CR corresponding to the variance mentioned above, CR(σF2) = −2.87 < −2 (see Table 4).
The goodness of fit of the configural (unconstrained), metric (constrained structural weights), and scalar (with additional constraints on intercepts) model was good for the indices-based data: p for X2 > 0.05, X2/df < 2, CFI > 0.95 and RMSEA < 0.05. The structural model (with additional constraints on the covariance between the two factors) and the error model (with constraints on the variances of the measurement errors) presented an acceptable fit. The chi-square test did not maintain the null goodness-of-fit hypothesis, but it was for the indices X2/df < 2, CFI > 0.95, and the value of RMSEA was less than 0.075.
Imposing constraints on structural weights and intercepts (scalar invariance) maintained the null hypothesis of invariance. Models with constraints on structural variances-covariances and structural residuals have a loss in goodness-of-fit considering X2 but not X2/df, CFI, RMSEA, and SRMR (see Table 5).
3.2 Validity predictive
The predictive validity of the FRADI two-factor model was tested using structural equations. A predictive Emotional Exhaustion (EE) model was specified (see Figure 2). This model proposed that psychosocial factors (F2) do not directly affect emotional exhaustion but are indirectly mediated by personal factors (F1). Consequently, only personal factors (F1) directly affect emotional exhaustion. It was found that the two factors of the FRADI scale explained 56% of the variance of this variable. The two direct effects were significant (F2 → F1 and F1 → EE), as well as the indirect effect (F1| F2 → EE), with large effect sizes being greater than 0.30 (Cohen, 1988; see Table 6). There is no suggestion when reviewing the goodness-of-fit improvement indices, such as specifying the direct prediction of emotional exhaustion by psychosocial risk factors. Even if this pathway is added, it is not significant.
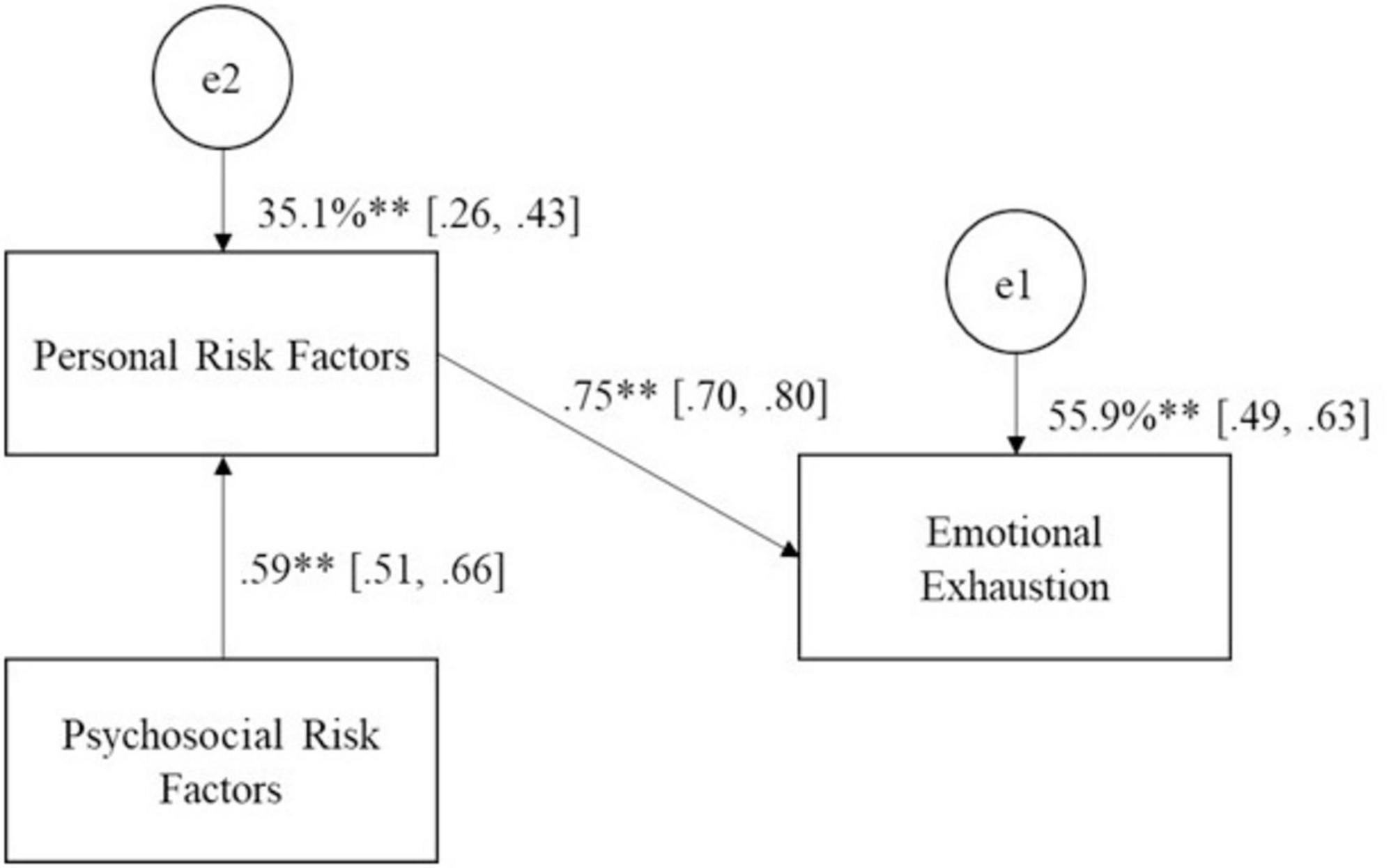
Figure 2. Estimates for the last nested model with structural residuals additionally constrained (M6). e = error, **p < 0.010, 90% confidence interval [lower limit, upper limit].
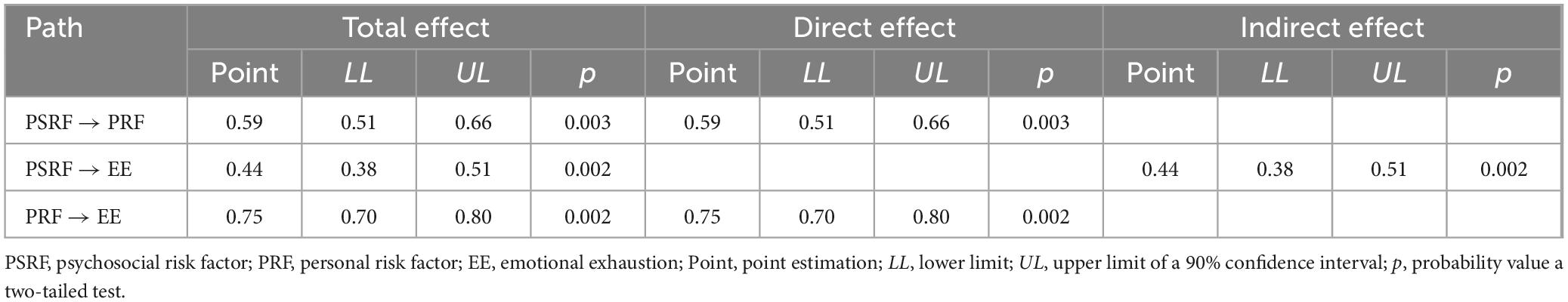
Table 6. Standardized indirect, direct, and total effects in the nested model with structural residual constraints, whose estimates are expected of women and men.
Additionally, this prediction model’s invariance between men and women was verified. The unrestricted model (M1) got an excellent fit (X2 = 0.34, p = 0.845; CFI = 1, RMSEA ≤ 0.01[0.00, 0.07], SRMR = 0.01). The nested model with structural weight constraints (M2) also had an excellent fit and when compared with M1, no statistically significant differences were found (ΔX2 = 1.75, p = 0.418; ΔCFI = 0.00, ΔRMSEA = 0.00, ΔSRMR = 0.00). The nested model with additional constraints on the intercepts (M3) had an excellent fit and when compared with M2, differences were found by the likelihood ratio difference test (p = 0.044), but not in the goodness-of-fit indices that are less sensitive to sample size (ΔCFI = −0.01, ΔRMSEA = 0.01, ΔSRMR = 0.00). The nested model with additional constraints on the means (M4) similarly had an excellent fit, and when compared to M3, no differences were found (ΔX2 = 0.25, p = 0.616; ΔCFI = 0.00, ΔRMSEA = 0.01, ΔSRMR = 0.00). The nested model with additional constraint on the variance of the exogenous factor (M5) also had an excellent fit, and when contrasted with the M4, no differences were found either (ΔX2 = 0.78, p = 0.376; ΔCFI = 0.00, ΔRMSEA = 0.00, ΔSRMR = 0.00). Finally, the nested model with additional constraints on the variances of the structural errors (M6) obtained a good fit, and when contrasted with the M5, differences were found between them (ΔX2 = 10.94, p = 0.004; ΔCFI = −0.03, ΔRMSEA = 0.00, ΔSRMR = 0.01). Model 6 can be seen in Figure 2. By having all the parameters constrained between the two samples, the estimates of their parameters were the same in the samples of women and men.
4 Discussion
The objective of this study was to propose a model with evidence of validity and reliability to measure the risk factors for emotional exhaustion of teachers in innovative educational environments, which was fulfilled per the results obtained in each of the statistical analyses.
According to Rojas-Mata et al. (2022) and Santoyo et al. (2022), both in Latin America and in Mexico, the development of instruments to assess risk factors at work is still incipient, and this is reflected in the scale of production of measurement instruments. With the advent of NOM-035 in Mexico, some first drafts and studies related to the instrument proposed in the standard have been carried out. Studies conducted to determine the psychometric properties of this scale have been questioned.
Cano-Gutierrez et al. (2023) conducted a first analysis with a large sample of Mexican education and industry workers (n = 2,149). Their results indicated an inadequate fit and the exclusion of a considerable number of items from the original model, which comprised 62 items distributed into eight factors. The final solution had three dimensions measured with 42 items (X2 = 11,683.4, df = 1,762, p < 0.01; CFI = 0.95, NNFI = 0.95, GFI = 0.96, SRMR = 0.07, RMSEA = 0.06; F1: k = 20, α = 0.94, ω = 0.95, F2: k = 19, α = 0.95, ω = 0.96 y F3: k = 3, α = 0.63, ω = 0.64). On the other hand, Gutiérrez et al. (2022) presented evidence of validity and reliability of the subscale corresponding to the domain of Labor Relations in the industry environment with 250 company supervisors. Their results indicated good reliability with scores above 0.88 in Cronbach’s alpha coefficient and an adequate fit in exploratory factor analysis (X2 = 2,140.77, df = 26, p ≤ 0.001, KMO = 84). The factor loads were greater than 0.50 and explained 79.43% of the variance; however, the theoretical structure of the domain was not maintained. In addition to the above, Santoyo et al. (2022) reported their validity and reliability results from research with 403 company workers. Their findings provided evidence of reliability (α = 0.92, ω = 0.93). The fit values in confirmatory factor analysis were inappropriate (X2/df = 2.68, GFI = 0.65, CFI = 0.72, RMSEA = 0.06). In addition, it was necessary to eliminate items and rely on the original theoretical structure, obtaining a five-dimensional solution with more than 60 items. Finally, Unda et al. (2016) tested a model with 500 higher education professors; the result was a five-dimensional model comprising 31 items. Their proposal provided satisfactory validity evidence (X2 = 5,656.65, df = 1,128, p ≤ 0.001; KMO = 0.90) and attained 60.1% of explained variance. Regarding the reliability of the subscales, the Cronbach’s alpha coefficient scores ranged from 0.92 to 0.75.
Compared to the previous scales, the model proposed here is parsimonious, comprising eight items distributed in two dimensions. The personal risk factor for emotional exhaustion in innovative educational environments, reduced to four items, indicates decreased time for self-care and eating, feelings of imbalance between personal and academic life, and greater emotional demands to participate in educational innovation. Excluded were reduced hours of sleep, academic overload, perception of decreased self-efficacy, greater physical demand, greater cognitive demand, less time to rest, and a more stressful environment. Consequently, this simplified factor accentuates an imbalance toward the work to the person’s detriment. The psychosocial risk element factor, reduced to four items, indicates a feeling that one’s participation in educational innovation is not valued by peers, less tolerance, greater social isolation, and decreased autonomy to face responsibilities. Left out were lack of appreciation by the bosses and feeling deficient support when participating in educational innovation. Consequently, this simplified factor accentuates the loss of quality in social interaction with less peer appreciation, less tolerance, more feelings of isolation, and more dependence.
In addition, the scale proposed here is invariant between men and women at a scalar level. The adjustment indices are high, and the results obtained in terms of reliability are excellent (McDonald, 1999) The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was used for its measurement, which assumes that the items are tau-equivalent, and the omega coefficient does not require this assumption (Hayes and Coutts, 2020); the assumption of tau-equivalence was sustained (Chechi and Chakraborty, 2020). On the other hand, it should be noted that the sample size was adequate for the execution of exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses (Byrne, 2016).
The Average Variance Extracted score was higher than recommended (Moral-de-la Rubia, 2019), confirming the scale’s convergent validity, which means the items are closely related to their latent factor. Regarding discriminant validity, the HTMT score was outside the cut-off point recommended by Henseler et al. (2015), so its result can be considered moderate. This may be due to the high and complex correlation between the personal and psychosocial factors that comprise the FRADI scale.
Furthermore, this study shows evidence of external validity through a predictive analysis of emotional exhaustion, explaining 56% of the variance of this construct, thus providing greater certainty to the model for measuring risk factors. In addition, a high level of invariance between genders was confirmed, which provides certainty when comparing the results of women and men. Likewise, it was found that psychosocial risk factors indirectly influence emotional exhaustion in an innovative educational environment through personal factors and not directly. The core of burnout is the perception of internal balance and wellbeing concerning the teaching activity. However, this perception is influenced by psychosocial factors about the loss of quality in social interaction in the innovative educational environment, with less peer appreciation, less tolerance, more feelings of isolation, and more dependence.
5 Conclusion
This study successfully developed and validated the FRADI scale, a psychometric instrument designed to measure risk factors associated with emotional exhaustion in innovative educational environments. The scale demonstrates strong psychometric properties, including reliability and validity, making it a valuable tool for educational institutions aiming to monitor and support teacher wellbeing. The study’s findings highlight the critical importance of addressing both personal and psychosocial risk factors that contribute to emotional exhaustion, especially in contexts where educational innovation is emphasized. These goals are achieved, and all the criteria established by NOM-035-STPS-2018 (Secretaría del Trabajo y Previsión Social, 2018) are satisfactorily met.
Notably, the results emphasize that personal factors, such as reduced time for self-care and increased emotional demands, directly predict emotional exhaustion. Meanwhile, psychosocial factors, such as feelings of social isolation and diminished autonomy, indirectly influence this outcome through their impact on personal wellbeing. This underscores the need for comprehensive support systems that address both individual and social aspects of teachers’ professional lives.
Although the study provides a robust model to assess risk factors for emotional exhaustion, some limitations must be recognized, which should be addressed as future lines of research, such as: (a) the participants belong to a single institution of higher education, so it is advisable to explore the psychometric properties and test invariance considering contracts, grades, ages, public and private institutions, different educational levels and other innovative environments different from the educational one, since some of these factors have been observed as determinants (Ribeiro et al., 2020); (b) the cross-sectional design limits the ability to draw conclusions about changes over time, so it is recommended to consider longitudinal approaches to better understand these dynamics and determine temporal reliability; (c) studies with samples that transcend and allow cross-cultural comparisons, starting with Spanish-speaking countries and transferring their application to countries of other languages through translation; (d) conduct interventions derived from the results of the measurement model with the aim of preventing emotional exhaustion; (e) conduct studies with samples that transcend and allow cross-cultural comparisons, starting with Spanish-speaking countries and transferring their application to countries of other languages through translation; (f) carry out interventions derived from the results of the measurement model with the aim of preventing emotional exhaustion.
In conclusion, promoting teacher wellbeing is essential for maintaining high-quality education, particularly in environments prioritizing innovation. The FRADI scale offers educational leaders a practical tool for identifying and mitigating the risk factors associated with emotional exhaustion, ultimately contributing to healthier, more sustainable educational practices.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because confidentiality issues. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to AD, YW5nZWxlcy5kb21pbmd1ZXpAdGVjLm14.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Instituto Tecnologico y de Estudios Superiores de Monterrey. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contribuions
JB-S: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JM: Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by project ID # I035–IFE005–C1-T3–E of the Challenge-Based Research Funding Program 2022 by Tecnologico de Monterrey, Mexico.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the technical support of Writing Lab, Institute for the Future of Education, Tecnologico de Monterrey, Mexico, in producing this work. We also acknowledge the support of the Impact Measurement Office and the coordination team of the educational innovation for facilitating the implementation of this study and all the participants. Finally, we offer a special mention to the team of experts for their support in the validation process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
American Psychological Association (2017). Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct. Washington, DC: APA.
Appel-Meulenbroek, R., Voordt, T., van der, Aussems, R., Arentze, T., and Le Blanc, P. (2020). Impact of activity-based workplaces on burnout and engagement dimensions. J. Corporate Real Estate 22, 279–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2022.101920
Beltran-Sanchez, J. A., and Dominguez, A. (2021). Scale to measure stressful characteristics in educational environments: A case of a Mexican university. Proc. Int. Conf. Educ. 7, 604–613. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14030051
Bitran, M., Zúñiga, D., Pedrals, N., Echeverría, G., Vergara, C., Rigotti, A., et al. (2019). Burnout in students of health-care professions. Risk and protection factors. Rev. Med. Chile 147, 510–517. doi: 10.4067/S0034-98872019000400510
Bolatova, A. K., Seisembekova, T. Z., Askarovaa, A. Z., Igenbayevaa, B., Smailovab, D. S., and Hosseinic, H. (2021). Psychometric properties of the copenhagen burnout inventory in a sample of medical students in Kazakhstan. Psychol. Russia State Art 14, 13–22. doi: 10.11621/pir.2021.0202
Bravo, D. M., Suárez-Falcón, J. C., Bianchi, J. M., Segura-Vargas, M. A., and Ruiz, F. J. (2021). Psychometric properties and measurement invariance of the maslach burnout inventory–general survey in Colombia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:5118. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105118
Burić, I., Slišković, A., and Penezić, Z. (2019). Understanding teacher well-being: A cross-lagged analysis of burnout, negative student-related emotions, psychopathological symptoms, and resilience. Educ. Psychol. 39, 1136–1155. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21040511
Byrne, B. M. (2016). Structural Equation Modelling with AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming, 3rd Edn. Milton Park: Routledge.
Cámara de Diputados del H. Congreso de la Unión (2010). Ley Federal de Protección de Datos Personales en Posesión de los Particulares. Available online at: https://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/ref/lfpdppp.htm
Cano-Gutierrez, J. C., Pérez-Morán, J. C., Bernal-Baldenebro, B., Arenas-Meneses, D., Vazquez-Lira, R., and Olguín-Tiznado, J. E. (2023). Factor structure and measurement invariance of the psychosocial risk factors inventory of NOM-035-STPS-2018. Front. Psychol. 13:1022707. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1022707
Cea, M. (2004). Análisis Multivariable. Teoría y Práctica en la Investigación Social, 2nd Edn. Síntesis: Madrid, Spain.
Chechi, V. K., and Chakraborty, R. (2020). Testing the assumptions of tau- equivalence and reliability analysis in the academic emotion regulation questionnaire (AERQ) subscales. J. Crit. Rev. 7, 1830–1838.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Struc. Equ. Modeling 14, 464–504.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd Edn. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Corbett, L., Phongsavan, P., Peralta, L. R., and Bauman, A. (2021). Understanding the characteristics of professional development programs for teachers’ health and wellbeing: Implications for research and practice. Aust. J. Educ. 65, 139–152. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.848322
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational Research: Planning, Conducting and Qualitative Research, 4th Edn. London: Pearson.
Cuadrado, E., Jiménez-Rosa, M., and Tabernero, C. (2022). Risk and protective factors of emotional exhaustion in teachers. A moderating mediation on emotional exhaustion. Rev. Psicol. Trabajo Las Organ. 38, 111–120. doi: 10.5093/jwop2022a10
Demerouti, E., Bakker, A. B., Vardakou, I., and Kantas, A. (2003). The convergent validity of two burnout instruments: A multitrait-multimethod analysis. Eur. J. Psychol. Assess. 19, 12–23. doi: 10.1027/1015-5759.19.1.12
DeVellis, R. (2012). Scale Development. Theory and Applications, 4th Edn. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.
Evers, W., Brouwers, A., and Tomic, W. (2002). Burnout and self-efficacy: A study on teachers’ beliefs when implementing an innovative educational system in the Netherlands. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 72, 227–243. doi: 10.1348/000709902158865
Feißt, M., Hennigs, A., Heil, J., Moosbrugger, H., Kelava, A., Stolpner, I., et al. (2019). Refining scores based on patient reported outcomes – statistical and medical perspectives. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 19:167. doi: 10.1186/s12874-019-0806-9
Fernández, V., Chamarro, A., Longás, J., and Segura, J. (2016). Evaluación del bienestar y la salud de los docentes en centros concertados. Rev. Complutense Educ. 28, 897–912. doi: 10.1016/j.rpto.2015.07.001
George, D., and Mallery, P. (2019). IBM SPSS Statistics 25 Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference, 14th Edn. Milton Park: Routledge.
Gil-Monte, P., Unda, S., and Sandoval, J. (2009). Validez factorial del “cuestionario para la evaluación del síndrome de quemarse por el trabajo” (CESQT) en una muestra de maestros mexicanos. Salud Mental 32, 205–214.
Guerrero-Barona, E., Gómez, del Amo, R., Moreno-Manso, J. M., and Guerrero-Molina, M. (2018). Factores de riesgo psicosocial, estrés percibido y salud mental en el profesorado. Clín. Contemporánea 9(1), E2, 1–12.
Gutié,rrez, M. G., Reyes, R. M., De La Riva, J., Maldonado, A. A., and García, H. (2022). Norma oficial Mexicana 035, Factores de riesgo psicosocial en el trabajo: Validación del dominio relaciones en el trabajo. RIDE Revista Iberoamericana para la Investigación y el Desarrollo Educativo 12:e363. doi: 10.23913/ride.v12i24.1223
Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R., and Black, W. (1999). Análisis Multivariante, 5th Edn. Hoboken, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Hair, J., Black, W., Babin, B., and Anderson, R. (2019). Multivariate Data Analysis, 8th Edn. Andover, MA: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Hayes, A. F., and Coutts, J. J. (2020). Use omega rather than Cronbach’s alpha for estimating reliability. But. Commun. Methods Meas. 14, 1–24.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 43, 115–135. doi: 10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Ilisko, D., Badjanova, J., and Ignatjeva, S. (2020). Teachers’ engagement with work and their psychological well-being. Soc. Integr. Educ. Proc. Int. Sci. Conf. 5:102.
INEGI (2021). Resultados de la Primera Encuesta Nacional de Bienestar Autorreportado (ENBIARE), Comunicado de Prensa Núm. 772/21. Aguascalientes: INEGI.
Jeon, G. S., You, S. J., Kim, M. G., Kim, Y. M., and Cho, S. (2019). Psychometric properties of the Korean version of the Copenhagen Burnout Inventory in Korean homecare workers for older adults. PLoS One 14:e0221323. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221323
Kassymova, G. K., Valeeva, G. V., Stepanova, O. P., Goroshchenova, O. A., Gasanova, R. R., and Kulakova, A. A. (2019). Stress of the innovation and innovations in education. Bull. Natl. Acad. Sci. Republic Kazakhstan 6, 288–300. doi: 10.32014/2019.2518-1467.173
Klusmann, U., Aldrup, K., Roloff-Bruchmann, J., Carstensen, B., Wartenberg, G., Hansen, J., et al. (2023). Teachers’ emotional exhaustion during the COVID-19 pandemic: Levels, changes, and relations to pandemic-specific demands. Teach. Teach. Educ. 121:103908. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2022.103908
Kristensen, T. S., Borritz, M., Villadsen, E., and Christensen, K. B. (2005). The Copenhagen burnout inventory: A new tool for the assessment of burnout. Work Stress 19, 192–207.
Ma, P., Zhang, L., Dong, H., and Yu, J. (2023). The relationships between teachers’ emotional labor and display rules, trait emotions, exhaustion, and classroom emotional climate. Front. Psychol. 14:957856. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.957856
Martínez-Líbano, J., and Yeomans, M.-M. (2023). Emotional exhaustion variables in trainee teachers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. J. Investigation Health Psychol. Educ. 13, 271–283. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe13020021
Maslach, C., and Leiter, M. P. (2017). New insights into burnout and health care: Strategies for improving civility and alleviating burnout. Med. Teach. 39, 160–163. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2016.1248918
Maslach, C., and Leiter, M. P. (2021). How to Measure Burnout Accurately and Ethically. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Business Review.
Maslach, C., Jackson, S. E., and Leiter, M. P. (1997). “The Maslach burnout inventory manual,” in Evaluating stress: A Book of Resources, 3rd Edn, eds C. P. Zalaquett and R. J. Wood (Lanham, MA: Scarecrow Education), 191–218.
McInerney, D. M., Korpershoek, H., Wang, H., and Morin, A. J. S. (2018). Teachers’ occupational attributes and their psychological wellbeing, job satisfaction, occupational self-concept and quitting intentions. Teach. Teach. Educ. 71, 145–158.
Merenda, P. F. (1997). A guide to the proper use of factor analysis in the conduct and reporting of research: Pitfalls to avoid. Meas. Eval. Counseling Dev. 30, 156–164.
Monroy-Castillo, A., and Juárez-García, A. (2019). Factores de riesgo psicosocial laboral en académicos de instituciones de educación superior en Latinoamérica: Una revisión sistemática. Propósitos y Representaciones 7, 248–272.
Moral-de-la Rubia, J. (2019). Revisión de los criterios para validez convergente estimada a través de la varianza media extraída. Psychologia 13, 25–41.
Olivares, L., Nieto, G., Velázquez, K. I., and López, A. (2020). Factores asociados al síndrome de burnout en profesores de universidades públicas en el noroeste de México. Apuntes de Psicología 38, 59–66.
Pan American Health Organization (2019). The Burden of Mental Disorders. Washington, DC: Pan American Health Organization.
Piperac, P., Todorovic, J., Terzic-Supic, Z., Maksimovic, A., Karic, S., Pilipovic, F., et al. (2021). The validity and reliability of the copenhagen burnout inventory for examination of burnout among preschool teachers in Serbia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:6805. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18136805
Portoghese, I., Leiter, M. P., Maslach, C., Galletta, M., Porru, F., D’Aloja, E., et al. (2018). Measuring burnout among university students: Factorial validity, invariance, and latent profiles of the italian version of the maslach burnout inventory student survey (MBI-SS). Front. Psychol. 9:2105. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02105
Ribeiro, B. M., Martins, J. T., and Dalri, R. (2020). Burnout syndrome in primary and secondary school teachers in southern Brazil. Rev. Brasileira Med. Trabalho 18, 337–342.
Rocha, F. L. R., de Jesus, L. C., Marziale, M. H. P., Henriques, S. H., Marôco, J., and Campos, J. A. D. B. (2020). Burnout syndrome in university professors and academic staff members: Psychometric properties of the Copenhagen Burnout Inventory–Brazilian version. Psicologia Reflexão e Crítica 33:11. doi: 10.1186/s41155-020-00151-y
Rojas-Mata, I., Suárez-Escalona, R., and Cavazos-Salazar, R. L. (2022). Factores de riesgo psicosocial en trabajadores universitarios: Un estudio comparativo antes y durante el COVID-19. CienciaUAT 17, 61–72.
Romero, M., and Laborín, J. F. (2016). Calidad de vida en docentes de educación pública superior. Educ. Humanismo 18, 205–224.
Santoyo, F., Echerri, D., and Figueroa, J. A. (2022). Evaluación de la validez del cuestionario de los factores de riesgo psicosocial y evaluación del entorno organizacional propuesto por la NOM-035-STPS-2018. Contaduría Adm. 67:339.
Secretaría del Trabajo y Previsión Social (2018). Factores de Riesgo Psicosocial en el Trabajo-Identificación, Análisis y Prevención (NOM-035-STPS-2018). Diario Oficial de la Federación. Juarez: Secretariat of the Interior.
Sestili, C., Scalingi, S., Cianfanelli, S., Mannocci, A., Del Cimmuto, A., De Sio, S., et al. (2018). Reliability and use of copenhagen burnout inventory in italian sample of university professors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:1708. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15081708
Shoman, Y., Marca, S. C., Bianchi, R., Godderis, L., van der Molen, H. F., and Guseva Canu, I. (2021). Psychometric properties of burnout measures: A systematic review. Epidemiol. Psychiatric Sci. 30:e8. doi: 10.1017/S2045796020001134
Smetackova, I., Viktorova, I., Pavlas Martanova, V., Pachova, A., Francova, V., and Stech, S. (2019). Teachers between job satisfaction and burnout syndrome: What makes difference in czech elementary schools. Front. Psychol. 10:2287. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02287
Unda Rojas, S., Hernández-Toledano, R. A., García-Arreola, O., and Esquivel Lozada, C. (2020). Factores de riesgo psicosocial predictores del Síndrome de quemarse por el trabajo (SQT) (Burnout) en docentes de bachillerato. Informacio Psicol. 119, 91–107.
Unda, S., Uribe, F., Jurado, S., García, M., Tovalín, H., and Juárez, A. (2016). Elaboración de una escala para valorar los factores de riesgo psicosocial en el trabajo de profesores universitarios. Rev. Psicol. Trabajo Las Organ. 32, 67–74.
Vicente Coronado, M. S., López Arroyo, P., Trejo Martín, C., and González Ballester, S. (2019). Satisfacción docente y su influencia en la satisfacción del alumnado. Int. J. Dev. Educ. Psychol. Rev. INFAD Psicol. 3, 37–56.
Virtanen, T. E., Vaaland, G. S., and Ertesvåg, S. K. (2019). Associations between observed patterns of classroom interactions and teacher wellbeing in lower secondary school. Teach. Teach. Educ. 77, 240–252. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2018.10.013
Wongtrakul, W., Dangprapai, Y., Saisavoey, N., and Sa-nguanpanich, N. (2021). Reliability and validity study of the Thai adaptation of the Copenhagen burnout inventory-student survey (CBI-SS) among preclinical medical students at the Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand. PLoS One 16:e0261887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261887
World Health Organization (2019). Burn-out an “Occupational Phenomenon”: International Classification of Diseases. Geneva: WHO.
World Health Organization (2022a). Mental Health at Work: Policy Brief. Geneva: World Health Organization and International Labour Organization.
Zhao, X., and You, X. (2021). The impact of psychological capital on vocational well-being: The mediation effect of emotional labor and its invariance across ethnicities. Curr. Psychol. 40, 102–112. doi: 10.1007/s12144-019-00287-w
Keywords: risk assessment, emotional exhaustion, psychometrics, university teachers, faculty, educational innovation, higher education
Citation: Beltran-Sanchez JA, Dominguez A and Moral de la Rubia J (2024) Scale of risk factors associated with emotional exhaustion in innovative educational environments: psychometric study of teachers. Front. Educ. 9:1481515. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1481515
Received: 16 August 2024; Accepted: 14 October 2024;
Published: 06 November 2024.
Edited by:
Sarfraz Aslam, UNITAR International University, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Lada Kaliska, Matej Bel University, SlovakiaIvette Margarita Espinoza Díaz, University of Rovira i Virgili, Spain
Copyright © 2024 Beltran-Sanchez, Dominguez and Moral de la Rubia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Angeles Dominguez, YW5nZWxlcy5kb21pbmd1ZXpAdGVjLm14
 Jesus Alfonso Beltran-Sanchez
Jesus Alfonso Beltran-Sanchez Angeles Dominguez
Angeles Dominguez Jose Moral de la Rubia
Jose Moral de la Rubia