- 1Faculty of Education, University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland
- 2Faculty of Education, Southwest University, Chongqing, China
This study conducts various economic approaches implemented worldwide to augment teachers’ recruitment and retention. It commences by situating the criticality of teacher recruitment and retention within the broader ambit of educational expansion and reform worldwide. Each nation prioritizes recruiting and retaining high-caliber educators, acknowledging the critical role that remuneration and additional professional opportunities play in attracting and sustaining individuals within the teaching profession. This systematic literature review analyzes the Economic approaches to teacher recruitment and retention. Using the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols Statement), this literature review is those articles successfully published between 2017 and 2023. The study uses two well-known internet sources: Web of Science and Scopus. There are 215 publications, including 15 papers with the most citations for this thorough literature study. This study emphasizes the importance of economic incentives, such as salary and professional development opportunities, in attracting and retaining skilled teachers in educational institutions. This study finds that policymakers and educational administrators worldwide have pertinent insights and data poised to aid in formulating more efficacious economic strategies for recruiting and retaining teachers. The recommendations are based on a nuanced understanding of the interplay between financial factors and educational efficacy, seeking to inform future policy directions and academic discourse in this field.
1 Introduction
Teaching effectiveness in a school depends on several variables, including appropriate resources, instruction, and instructional leadership, but is often guided by people who work in the classroom. Staffing teachers in classrooms, in effect, is a result of both recruiting and retention activities. The rationale for this inquiry stems from the fundamental importance of education to the worldwide economy and society. According to Oyshi et al. (2021), the quality of education significantly impacts a nation’s economic growth rate. The crux lies in recruiting and retaining teachers, which is increasingly receiving attention in educational research. Shiddike (2020) noted that the education system worldwide has specific challenges in maintaining a competent and proficient teaching workforce.
These issues are exacerbated by policy and economic constraints. This study examines the dynamic relationship between economic theory and educational practice in this context, explicitly emphasizing worldwide. Manundu (2023) has identified cash incentives, career advancement opportunities, and improved working conditions as effective strategies for retaining teachers in their positions. The objective is to provide policymakers, teachers, and researchers with ideas grounded on rigorous research and applicable in practical settings (Islam and Chowdhury, 2021). However, it would assist them in formulating effective strategies for enhancing education worldwide. The supply and demand model is essential for attracting and maintaining employees. Worldwide, the pool of prospective teachers is determined by monetary compensation and non-monetary employment characteristics (World Health Organization, 2010).
Extensive studies indicate that future and present teachers respond to salary increases (Murnane et al., 1989; Borman and Dowling, 2008; Rothstein, 2015). However, the magnitude of this impact remains uncertain due to little investigation. Non-monetary variables that impact the supply of teachers include their school location, proximity to their school, and the accessibility of the teaching profession (Lentini et al., 2023). The emotional satisfaction experienced by teachers in the classroom plays a significant role in their job retention. The need for teachers and the structural limits through which such demands are articulated often impact the teacher population (Lyons and Zhang, 2023).
The number and characteristics of teachers demanded depend on many variables, including student school enrollment, teacher attrition, and the capacity and desire to compensate for teaching (Rothstein, 2015). Recruiting and retaining teachers is crucial when discussing the quality and fairness of education. Teachers are essential to educational systems since they have a central role in influencing student outcomes and determining the quality of education (Darling-Hammond et al., 2017).
Nevertheless, (García and Weiss, 2019a,b) noted that hiring and keeping skilled educators presents considerable obstacles worsened by insufficient pay, elevated work pressure, and insufficient chances for professional growth. These issues not only undermine the stability of the teaching personnel but also hinder the attainment of educational objectives. These techniques are based on the assumption that economic variables considerably impact teachers’ career choices and retention rates (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). Hence, it is crucial to evaluate the efficacy of these measures to formulate policies that might improve the rates of teacher recruitment and retention.
This study aims to thoroughly gather, combine, and evaluate the current research on economic strategies for recruiting and retaining teachers. The goal is to identify gaps in the existing research, provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of various monetary policies, and offer recommendations for policymakers, educational leaders, and stakeholders. Factors such as institutional restrictions, the expertise, and efficiency of recruiting officials, available information on training individual teachers, budgeting for expenditures, qualification and licensing policies, tenure policies, and teacher contract requirements can all influence the global ability to recruit and retain teachers summarizing the main questions, which are:
RQ1: What are the impacts of economic strategies on teacher recruitment and retention globally, and how effective are they in addressing challenges across different contexts?
2 Literature review
2.1 Defining teacher recruitment and retention
Teacher recruitment is the systematic procedure of enticing and choosing competent persons to occupy teaching posts in schools or educational organizations (Ingersoll, 2020). However, See et al. (2020) noted that this process involves diverse tasks, such as promoting job openings, reaching out to possible applicants, evaluating applications, conducting interviews, and eventually choosing people for employment. The efficacy of teacher recruitment endeavors hinges on the educational systems’ capacity to attract a substantial pool of candidates and discern and employ individuals with the requisite qualifications, skills, and dispositions to positively impact student learning and the institution’s educational objectives (Washington-Lawson, 2021).
Teacher retention refers to the strategies and practices employed by educational institutions to encourage teachers to remain in their positions for an extended period (Reitman and Karge, 2019). According to Sawaneh and Kamara (2019), retention strategies focus on creating a supportive and fulfilling work environment that addresses teachers’ professional, financial, and personal needs. These strategies include competitive salary packages, opportunities for career advancement, effective management, a positive school atmosphere, and initiatives that promote a healthy work-life balance. Furthermore, maintaining a stable and skilled teaching staff is essential for improving student performance and ensuring consistency in educational programs (Sadler, 2017). Both teacher recruitment and retention are influenced by various factors, including the supply and demand of teachers. Effective recruitment and retention methods are vital for addressing teacher shortages, enhancing the quality of education, and ensuring equitable educational opportunities for all students.
2.2 The supply of teachers
The supply of teachers refers to the availability of qualified individuals willing and able to offer educational services at various levels of the educational system (García and Weiss, 2019a,b). This concept encompasses the current pool of teachers within a given school area or educational sector and the potential inflow of new teachers through education and training programs. However, Loeb and Myung (2020) find that the supply of teachers is influenced by many factors, such as wages, working conditions, psychological benefits and costs, school location, and barriers to entry, which can adequate for maintaining educational quality, meeting student learning needs, and achieving educational equity.
Teacher supply and demand dynamics are complex and multifaceted, requiring careful monitoring and strategic planning by educational authorities and policymakers (George and Wooden, 2023). However, the efforts to enhance the supply of teachers should include initiatives to improve teacher training and professional development, increase salaries and benefits to make the profession more attractive and implement targeted recruitment strategies.
2.2.1 Wages
Wages are the monetary compensation employers pay employees in exchange for their labor (Lazear, 2018). Extensive study indicates that individuals are more likely to choose a teaching career when teachers’ starting income is comparatively high compared to other occupations (Han et al., 2018; Chiong et al., 2017; Ingersol et al., 2018). Drawing on several data points, García and Weiss (2019a, 2019b) noticed that highly trained teachers are especially vulnerable to shifts in comparable pay. Over time, higher levels of teacher remuneration have been linked to shifts in teacher productivity (Feng and Sass, 2017). Wages can also affect retention, which is strongly related to the choice to keep teachers (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). While a teacher responds to wages, a significant part of the variance in teacher compensation occurs within districts representing variations in alternative pay, not within labor markets.
2.2.2 Working conditions
Working conditions significantly impact the complexities of the labor market for teachers. While salaries can help compensate for challenging working conditions, implementing a consistent compensation scheme comparable to that of other countries at the national level could enhance the attractiveness of the teaching profession (Stromquist, 2018). Teachers’ working conditions encompass various factors that influence their job performance, including the physical environment, classroom size, availability of resources and technology, level of administrative support, student-to-teacher ratios, and safety measures (Loeb and Myung, 2020). These elements are crucial in teachers’ ability to provide high-quality education, job satisfaction, and overall well-being. According to De Jong et al. (2017), approximately 37% of teachers in the USA leave their positions due to frustration with their administrators.
Furthermore, Averill and Major (2020) found that the perception of school leadership is closely linked to first-year teachers’ belief in the importance of maximizing their efforts, their commitment to their career choices, and their motivation to continue teaching. Effective administrators can create a positive work environment, as poor school conditions often contribute to high employee turnover (Bayer, 2017). The assessment systematically evaluates the factors that influence teacher retention and satisfaction, focusing on leadership support, resource availability, professional development, and facilities. Typically distributed online, this assessment ensures anonymity and voluntary participation, encouraging honest responses. The results can help districts identify areas for improvement, such as enhancing instructional support or optimizing workloads (Averill and Major, 2020). The insights gained can ultimately inform policies to create a supportive work environment that enhances teacher commitment and retention. Additionally, factors such as physical infrastructure, the availability of textbooks and equipment, opportunities for career development, parental involvement, and the consistency and adequacy of teacher training can influence student attrition and shape teachers’ perceptions of classroom environments.
2.2.3 Organizational support
Tangible aspects of the workplace play a role in attracting teachers, but many educators are influenced by less tangible factors related to their roles. Rumschlag (2017) found that novice teachers who feel a lack of accomplishment in their interactions with students are less likely to view teaching as a fulfilling profession and are more inclined to leave the classroom. Teachers who see themselves as effective with their students and who work in schools that provide support such as teaching resources, professional development opportunities, adequate facilities, and comprehensive frameworks for student learning are less likely to leave their schools compared to those who do not receive such organizational support. Similarly, Palmer (2017) observed that new teachers who decided to continue in their roles found their primary source of happiness in believing they were positively impacting their students’ lives. When deciding to stay, resign, or transfer to another school after their first year, teachers prioritize their sense of potential success with their students (Henry and Redding, 2020).
2.2.4 School location
The school location significantly influences teacher retention for many crucial reasons. The school’s location greatly influences teachers’ daily commute, affecting their work-life balance and job satisfaction; furthermore, the socioeconomic attributes of the region might impact the extent of community backing and resources accessible to educators, thus influencing their professional growth and inclination to remain (Rahman, 2019). Moreover, the safety and general ambiance of the place might affect a teacher’s feeling of contentment and dedication to their profession. However, Chatrakul Na Ayudhya et al. (2019) noted that the expenses associated with living in the surrounding area might affect a teacher’s economic security, affecting their choice to either stay in their current role or pursue work elsewhere. Ultimately, a school placement of a school is a complex element that significantly impacts teachers’ ability to remain in their positions by influencing several parts of their personal and professional circumstances.
2.2.5 Barriers to entry
Historically, the standard requirement for teaching in public schools worldwide has been a minimum of a bachelor’s degree, followed by obtaining a government teaching certificate (Nasser, 2017). This qualification often involves completing coursework that includes student teaching experience and successfully passing a standardized assessment test. The implementation of lower admission requirements, along with a substantial commitment to qualifications, has greatly augmented the number of persons engaged in the role of teachers who also have a better academic history than teachers who are joining more conventional routes (Jackson and Meek, 2021).
2.3 The demand for teachers
A particular educational system’s demand for teachers represents the demand for teachers within the framework of that system (Caena and Redecker, 2019). The supply of teachers determines the number of individuals willing to enter the profession and teach in a given school. Still, the number of teachers hired, and the characteristics of those teachers also depend on the demand. Among demand factors are student enrolments, teacher retirement rates, class sizes, district hiring practices, and institutional constraints described below.
2.3.1 Student enrolment and teacher retirement
Student enrolment trends and teacher retirement rates are critical factors affecting the educational sector, each influencing the capacity of schools to deliver quality education effectively (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). As student enrolment increases, the demand for qualified teachers escalates, necessitating adequate staffing to preserve optimal student-to-teacher ratios. However, this requirement is challenged by the rising trend of teacher retirements, particularly as a significant proportion of the teaching workforce reaches retirement age. The retirement of experienced teachers not only diminishes the pool of educators but also results in the loss of valuable pedagogical expertise and mentorship for newer teachers (Paula and Grīnfelde, 2018). However, The interrelation between student enrolment and teacher retirement presents a significant challenge to the sustainability of educational quality; increasing student numbers demand a corresponding increase in teaching staff, yet this need is undermined by a concurrent rise in teacher retirements, particularly among an aging workforce (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b).
2.3.2 Institutional constraints
Structural pressures beyond the direct reach of schools and the district human resources department often inform the problem of sub-optimal employment. The analysis of recruitment techniques revealed district-level initiatives about irregularities that result in suboptimal staffing trends, leniency requirements for vacancy notification, and circumstances for teaching union changeover to delayed spending plans (Ouziel, 2020).
Teachers who have resigned or retired must inform their employer during the latter part of the summer before the next academic year following the flexible employment notification requirements (Markowski et al., 2020). Under union agreements, experienced teachers can pursue last-minute promotions over their less skilled counterparts (Henry and Redding, 2020). The reluctance to employ a transfer teacher whom they have a negative opinion of or the presence of ambiguity might potentially cause a delay in the announcement of job openings (Sutcher et al., 2019). According to Jackson and Meek (2021), they found no compelling proof that the laws of seniority privilege correlated with union contracts individually influence the allocation of teachers around the school or worsen the adverse association between higher minority schools and non-credited and low-level teachers.
2.3.3 Monetary incentives
In recent years, policymakers have experimented with various ways to offer higher compensation to prospective teachers to aid recruitment and retention. Signing bonuses or crediting teachers for years of experience teaching in other districts are examples of monetary incentive bonuses for recruitment (Feng and Sass, 2018). Some bonuses are paid in increments over time to promote retention. Monetary incentives are used to recruit, retain, and inspire teachers, especially in regions with severe shortages or topics with high demand.
These incentives may manifest in several ways, such as offering signing bonuses to newly hired teachers, providing performance-based awards for attaining specific educational goals, and granting extra remuneration for teaching in schools or disciplines that are difficult to staff (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). Through financial incentives, educational institutions strive to acknowledge the worth and significance of teachers’ labor, fostering increased dedication and contentment in their profession. Studies demonstrate that while financial incentives may successfully enhance teacher recruitment and retention, their influence on teacher performance and student achievement is more complex, indicating the need for a holistic approach to teacher support and development (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b).
2.3.4 Teacher induction and mentoring
The practice of employing novice teachers in recruiting and mentoring roles to promote the integration of new teachers into the profession and enhance staff involvement has become widespread in school systems (Loeb and Myung, 2020). Induction services often include seminars, initial training for inexperienced instructors, and establishing pre-existing peer support networks for teachers (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). The duration, intricacy, and quality of the mentoring experiences will vary considerably among programs. However, mentoring programs often pair inexperienced and experienced teachers (Rahman, 2019). According to Ronfeldt and McQueen (2017), studies indicate that current mentorship programs can potentially enhance novice instructors’ performance effectively. Reviewing 10 empirical research studies, Loeb and Myung (2020) found empirical evidence for the argument that mentoring services significantly affect and retain teachers. Rumschlag (2017) found that the attrition rates of new teachers decreased as the number of induction components increased, including mentoring, preparation time with colleagues in the same subject, regular collaboration with other teachers, and integration into an established network of educators. In addition, schools that provide teachers with more autonomy and administrative support had lower teacher attrition and migrations.
2.3.5 Performance-based pay
Several policymakers contend that the traditional method of compensating teachers based on their years of training and the number of university units does not allow teachers to enhance students’ academic achievement (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). Consequently, this system dissuades highly effective teachers from entering the classroom. Performance-related pay is a variable compensation where a percentage of instructors’ pay is contingent upon evaluating their effectiveness in improving student academic performance (Loeb and Myung, 2020). However, the appraisal unit might consist of absolute students, student groups, or educational institutions, and the prize may be contingent upon student evaluation outcomes, criteria, or peer assessment (Lentini et al., 2023).
Advocates of performance-based pay systems argue that compensating instructors according to a predetermined set of objectives would enhance their motivation and aid in attracting and retaining top-notch personnel (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). Detractors of performance-based remuneration systems contend that evaluating the output of teachers is too diverse and arduous. Furthermore, Loeb and Myung's (2020) studies showed there is concern that implementing performance-based compensation may lead to manipulating incentives, perhaps promoting less effective methods of long-term learning, such as focusing only on test preparation.
Moreover, merit-based prizes may lead to rivalry among faculty members within the same institution, thereby diminishing the teaching profession’s attractiveness, especially for risk-averse ones (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). Kelley (1999) analyzed how school-based achievement award systems inspired teachers to change or enhance teaching methods in Kentucky, North Carolina, Colorado, and Maryland and found that these systems encouraged teachers to a large degree by establishing environments that improved intrinsic incentives and concentrated teacher efforts. Ballou and Podgursky (1993) observed that teachers in schools utilizing compensation dependent on results did not feel demoralized by the program or hostile toward it, and those teachers of disadvantaged and low-achieving students were generally supportive of the system.
2.4 Improving hiring practices
Improving hiring practices for school teachers is crucial for ensuring educational institutions attract and retain high-quality teachers, directly impacting student learning outcomes (Badrul et al., 2018). A comprehensive approach involves streamlining the recruitment process to make it more efficient and less biased. It includes using standardized evaluation criteria and diverse hiring panels to assess candidates’ competencies and fit for the school culture (Borman and Dowling, 2008). However, investing in robust professional development and mentorship programs from the outset can also enhance teacher retention by providing clear pathways for career progression and job satisfaction (Loeb and Myung, 2020). Moreover, adopting flexible hiring strategies that recognize non-traditional qualifications and experiences can broaden the pool of potential candidates, particularly in subject areas experiencing teacher shortages (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b).
Regarding the contractual restrictions imposed on the principals during the recruitment process, it is sometimes necessary for the principals to hire instructors at a later stage. More competent instructors may have already assumed positions (Castro, 2022). Consequently, there is a higher rate of late recruitment of teachers. Removing institutional constraints on administrators and district staff might enhance the efficiency of the recruitment process. Jackson and Meek (2021) suggest that urban districts simplify the hiring process to expedite employment opportunities and to improve their capacity to discern competent instructors from the applicant pool. The objective of the due process reform for school teachers is to provide an equitable and open system for handling disciplinary and performance-related matters while striking a balance between holding teachers accountable and safeguarding their rights (Darling-Hammond et al., 2017). Dos Santos (2019) noted that the changes usually simplify the processes for controlling complaints and enforcing corrective measures, promoting a fairer and more effective resolution process in educational institutions. Teacher retention laws were first implemented to protect teachers who have completed their probationary period from being dismissed prematurely (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). Opportunities for job security may attract potential teachers to the teaching profession and retain instructors in the classroom. Although little research has been conducted on the influence of teaching tenure on the recruitment and retention of educators, a study by Loeb and Myung (2020) examined variations in probationary periods by suggesting the implementation of increased pay.
Salaries for novice and experienced educators are generally higher in school districts located in states with more extended probationary periods (Feng and Sass, 2018). Additionally, Feng and Sass (2018) found that receiving tenure can be a significant factor in attracting new teachers, as many consider the possibility of early tenure when choosing where to work. A teacher’s lack of knowledge about tenure and its benefits can influence their decision to remain in the profession. Once the probationary period is over, tenure provides considerable career security and stability in the teaching field. However, it also complicates terminating underperforming teachers (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). This serves as a warning that not all instances of teacher turnover will lead to positive outcomes.
3 Methodology
This study was conducted through a systematic literature review using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) criteria. A systematic literature review is “the analysis of analysis” (Glass, 1976). A thorough study could help put together several studies with straightforward research questions. The systematic literature review constantly evolves and includes several analyses (Zamore et al., 2018). The systematic literature review is a rapidly increasing approach that provides for various investigations (Zamore et al., 2018). These guidelines are intended to inform review authors on what data must be provided to assess the review’s quality appropriately.
This systematic literature review analyzes the economic approaches to teacher recruitment and retention. Using the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Protocols Statement), this literature review is those articles successfully published between 2017 and 2023. Three well-known internet sources are used in the study: Web of Science, Scopus, and ProQuest. There are 215 publications, including 15 papers with the most citations for this thorough literature study. Three primary stages comprise a systematic search strategy.
3.1 Identification
A subset of publications pertinent to the current study was chosen as a representative sample. The selection procedure consists of three steps. The first step was identifying the term and formulating a search phrase for the widely used Web of Science and Scopus database. Its multidisciplinary approach and quality-control technique make it suitable for performing systematic literature reviews. A papers database was created using the Web of Science and Scopus search string, focusing on the most relevant phrase. The details may be seen in Table 1. The first phase of the systematic literature review (SLR) process entails. In the first stage of the systematic literature review (SLR) technique, the authors obtained 215 articles from the Web of Science database.
3.2 Screening
The primary objective of the preliminary screening step was to eliminate redundant data. The first screening criteria pertained to the nature of the investigation. The writers focused on scholarly articles that included empirical research, including both primary and secondary data. Therefore, the analysis did not have documents such as conference papers, book chapters, reviews, comments, editorials, retraction notices, erratum letters, data articles, and books. In addition, only papers produced in the English language were assessed for this investigation. The current investigation also concentrated on 6 years to get relevant information from the Web of Science and Scopus databases (2017–2023). Based on these criteria (Table 2), 115 articles were deemed inappropriate for inclusion.
3.3 Eligibility
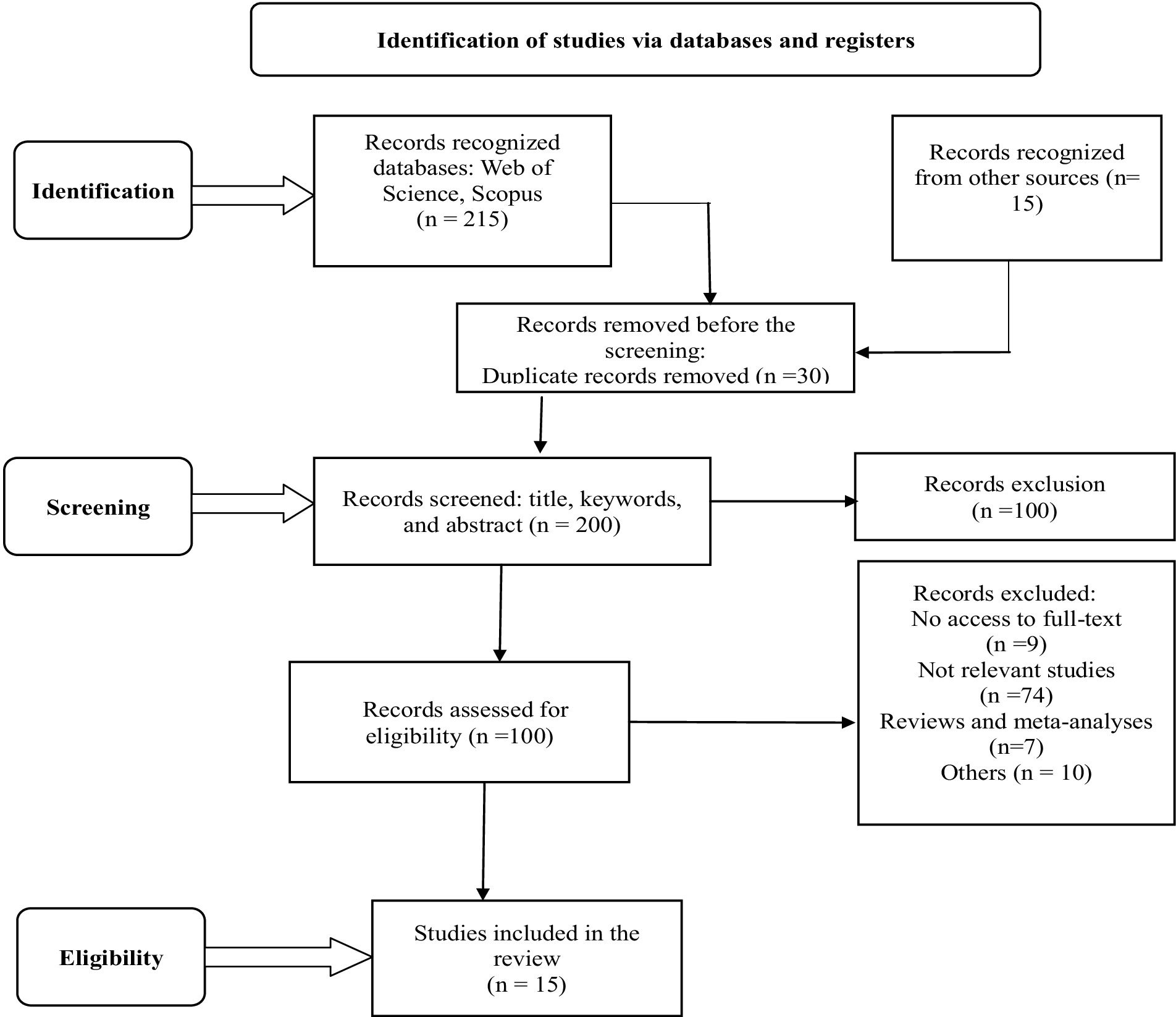
In the third stage of the selection process, the remaining 100 studies underwent additional refinement. The titles, abstracts, and content were examined to verify their compliance with the research criteria and alignment with the study’s objective. One hundred publications were excluded, resulting in a selection of just the 15 most cited articles for the qualitative assessment. The screening method was concluded by analyzing those 100 publications. After conducting the first eligibility screening, we selected 15 papers that had received many citations (Table 3). These articles were then subjected to additional evaluation (see Figure 1).
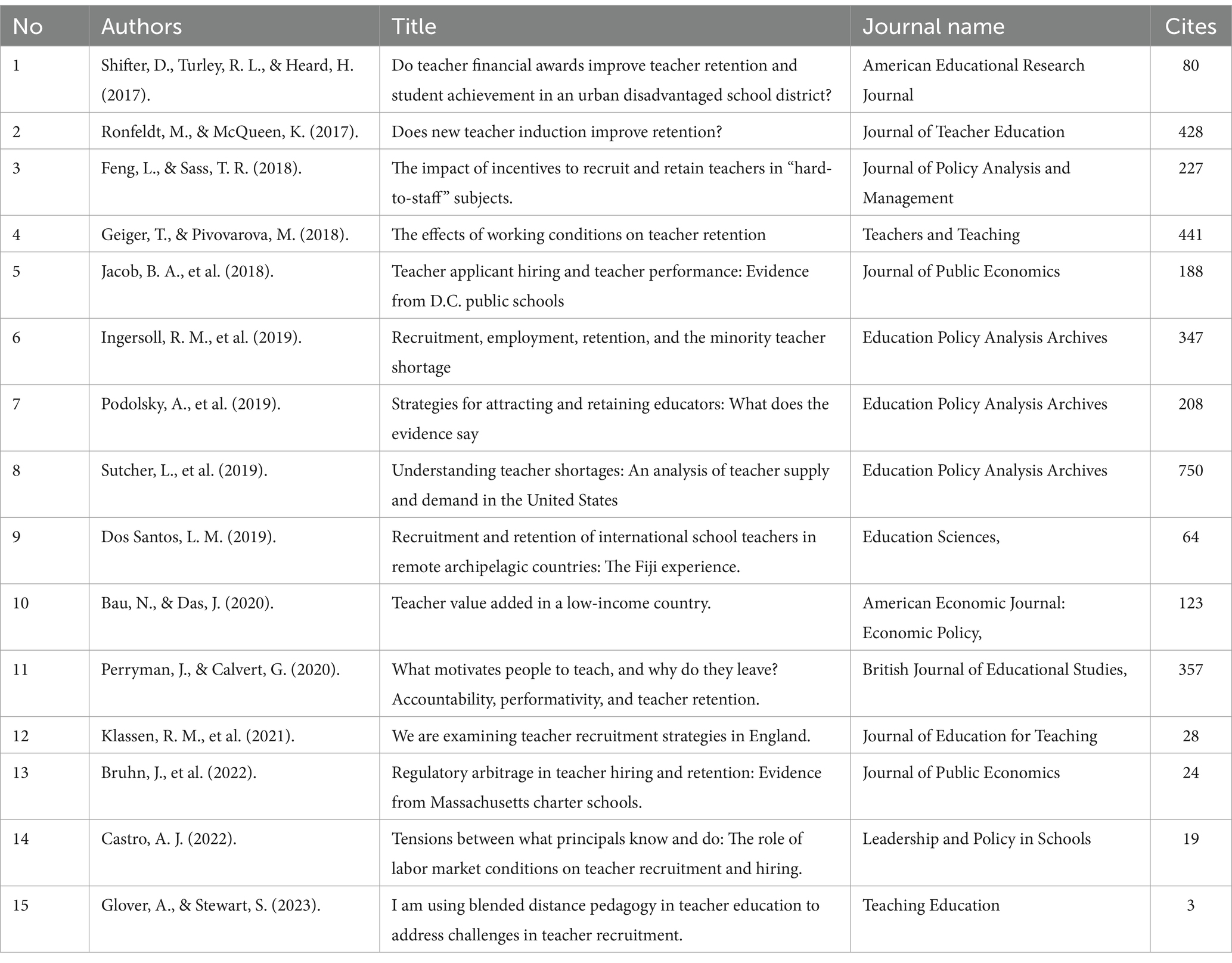
Table 3. Significant publications and citations in economic aspects of teacher recruitment and retention.
4 Results and finding
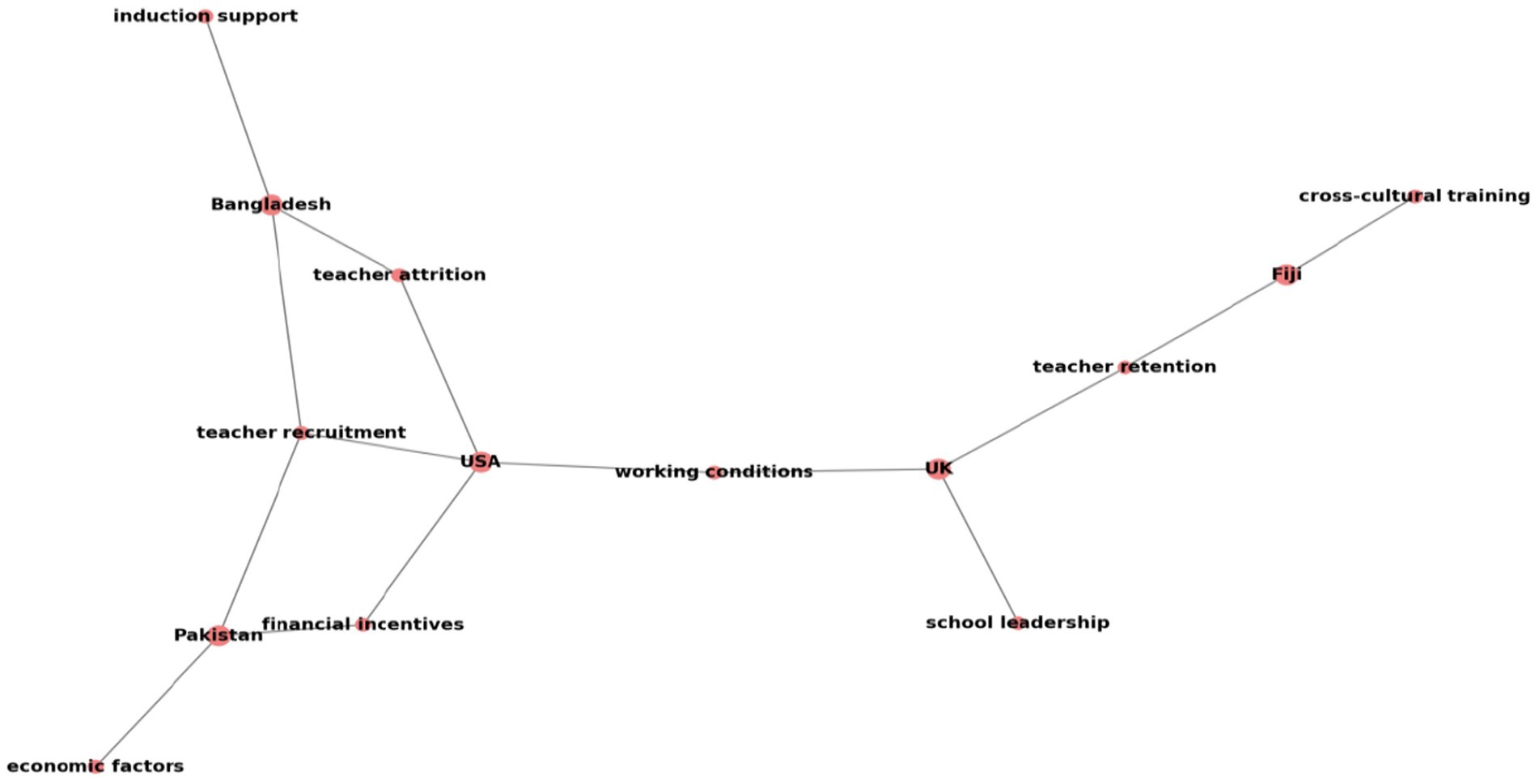
A comprehensive search was conducted on the Web of Science and Scopus databases to research the relevant literature. “Economic Approaches to Teacher Recruitment and Retention” was used as a keyword in the search for suitable material. Only English-language articles were assessed for this search, explicitly focusing on articles as a document type. This literature review covers publications published from 2017 to 2023. After doing the first search, a total of 215 articles were found. After eliminating 100 papers that were outdated and irrelevant to the study’s aims, this literature review’s final extent and comprehensiveness were determined to be 100 articles. In conclusion, this systematic review selected 15 highly cited papers from the U.K., the USA, Fiji, and Pakistan. Table 4 presents a concise overview of the main characteristics common throughout the 15 studies analyzed in this literature assessment.
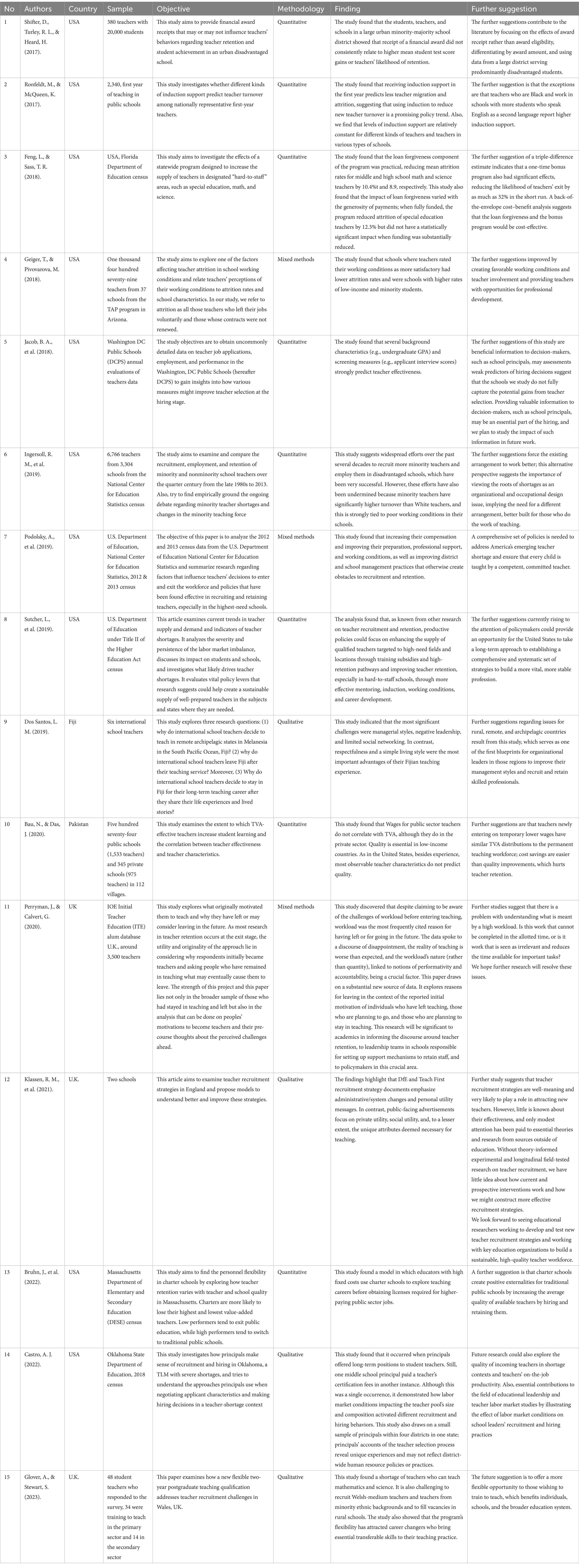
Table 4. Reviewing of highly cited articles on economic aspects of teacher recruitment and retention.
Table 4 offers a clear summary of the critical characteristics of the published articles. These articles evaluate the economic factors related to teacher recruitment and retention. This systematic review explores several aspects, including the supply and demand for teachers, the hiring process, working conditions, psychological benefits and costs, school location, barriers to entry, monetary incentives, mentoring, and performance-based pay. Each article emphasizes the economic dimensions of teacher recruitment and retention (Figure 2).
5 Discussion
Studies conducted across various articles in the USA indicate that a crucial factor significantly impacts teacher recruitment and retention, particularly in today’s economic landscape. Providing financial awards, although it is not always working to improve teacher recruitment and retention, could be a good concept, especially for lower-income countries (Shifter et al., 2017), but (Feng and Sass, 2018) found that the impact of loan forgiveness varied with the generosity of payments; when fully funded, the program reduced attrition of unique. However, Ronfeldt and McQueen (2017) observed that various forms of induction assistance indicate teacher turnover rates among a sample of first-year instructors representing the whole country. If new teachers get induction help in their first year, it will likely result in lower teacher migration and attrition rates. It also suggests that employing induction programs to decrease turnover among new teachers is a desirable policy approach worldwide. In their study, Feng and Sass (2018) examined the impact of a statewide program to address teacher shortages in certain “hard-to-staff” regions around the globe.
On the other hand, several variables influence the departure of teachers from their jobs, particularly the working circumstances at schools. These conditions are closely linked to teachers’ opinions of their work environment and may impact attrition rates and school characteristics. Our analysis defines attrition as the combined group of instructors who left their employment willingly and those whose contracts were not extended (Geiger and Pivovarova, 2018). Additionally, it has been shown that schools with a higher proportion of low-income and minority children, where teachers viewed their working circumstances as more favorable, saw lower turnover rates. Jacob et al. (2018) discussed the importance of decision-makers, such as school principals, using quick predictors to inform hiring decisions. School principals should be an essential part of the hiring process because they have firsthand knowledge of the actual situation in their schools. School principals can efficiently assess background characteristics, such as undergraduate GPA, and screening measures, such as applicant interview scores, which can strongly predict teacher effectiveness. Alternatively, suppose a high-quality teacher cannot be found. In that case, Ingersoll et al. (2017) suggest recruiting more minority instructors and placing them in underprivileged schools, which might be a viable solution.
Nevertheless, these efforts have been compromised due to the much greater attrition rate among minority teachers compared to their White counterparts. This phenomenon is closely associated with unfavorable working conditions inside their schools, hindering their ability to meet the need for instructors. Another potential solution to address the worldwide lack of teachers might be considered. Podolsky et al. (2019a,b) and Sutcher et al. (2019) discovered that their work increased compensation and improved preparation, professional support, and working conditions. They also found that district and school management practices, which often hinder recruitment and retention, were enhanced. It is recommended that policymakers in each country implement policies that focus on two main areas: enhancing the supply of qualified teachers in high-need fields and locations through training subsidies and high-retention pathways and improving teacher retention, particularly in schools that are difficult to staff, through more effective mentoring, induction, working conditions, and career development. Bruhn et al. (2022) state that educators with significant fixed expenses use charter schools to test out teaching professions before acquiring the necessary licenses for more lucrative roles in the public sector. Principals at these schools provide long-term work opportunities to student teachers.
Additionally, the administration of a middle school covered a teacher’s certification expenses separately. Although this was an isolated incident, it highlighted how changes in labor market conditions influenced the size and composition of the teaching pool, resulting in different recruiting and hiring practices (Castro, 2022). This research also relies on a limited sample of principals from four districts in a single state. The stories provided by principals on the teacher selection process highlight distinct experiences that may not necessarily represent the whole district’s human resource policies or practices. This study examines the impact of labor market circumstances on school leaders’ recruiting and hiring practices, focusing on educational leadership and teacher labor market research. In conclusion, the facts presented in the USA studies highlight the importance of investing in teacher recruitment and retention worldwide.
In the context of Fiji (Dos Santos, 2019), the article has received 39 citations. From a society’s position for cross-cultural training, this research study contributes to our comprehension of the career decisions and professional development of educators working in foreign schools in Fiji. Teachers, school administrators, and other educators at foreign schools may use the data from Dos Santos’s (2019) research to establish a beneficial framework worldwide. Attendees discussed prominent issues, potential results, leadership ideologies, and reasons for staying or leaving educational institutions in Fiji and abroad. This study is among the first to examine international school teachers’ career choices and professional growth in distant areas such as the Pacific. Hence, the results will guide those seeking to improve and enrich their educational working environment to retain teachers by fulfilling the supply and demand strategy for teachers.
On the other hand, in lower-income countries like Pakistan, newly hired teachers who receive temporary lower wages have similar distributions of Teacher Value-Added (TVA) as the permanent teaching workforce. In this situation, achieving cost savings rather than quality improvements is more straightforward, negatively impacting teacher retention. A study conducted by Bau and Das (2020) revealed that wages for public sector teachers in Pakistan do not correlate with TVA, although they do in the private sector. High quality is crucial in low-income nations. Like the United States, most teacher traits that may be seen, other than from experience, do not accurately predict quality.
Research in the U.K. suggests that the motivation to retain individuals might be included as an additional part of economic approaches. In their 2020 study, Perryman and Calvert found that teacher retention is influenced by motivation and respect, particularly during the departure stage. These factors contribute to a positive notion of teacher retention. Nevertheless, the discussion surrounding disappointment in teaching reveals that the experience is more damaging than anticipated. The nature of the workload, rather than its quantity, is particularly significant concerning performance and responsibility. This issue is crucial in the discourse on teacher retention. In this scenario, the school leadership must establish support systems that motivate and encourage staff members. While policy-making can offer specific incentives, the primary source of motivation is often derived from the psychological benefits.
Glover and Stewart (2023) provide a flexible option for those motivated to train as teachers, which may be beneficial in addressing the lack of instructors capable of teaching mathematics and science. Recruiting Welsh-medium teachers and instructors from minority ethnic origins and filling openings in remote schools pose additional challenges. Additionally, it demonstrated that the program’s adaptability appealed to those transitioning careers who had crucial transferable abilities to use in their teaching methods. Hence, the results will guide those seeking to improve and enrich their educational and economic aspects to help retain teachers globally.
6 Conclusion
The economic aspects of teacher recruitment and retention have revealed several crucial conclusions. The research emphasizes that teacher recruitment and retention are affected by a multifaceted interaction of financial variables, such as compensation levels, benefit packages, and incentives for professional growth (Podolsky et al., 2019a,b). The following studies showed that offering competitive salaries and benefits is essential for recruiting and keeping highly skilled teachers, especially in regions and disciplines with the most severe shortages. Furthermore, the study highlights the significance of non-monetary factors, such as job satisfaction, working conditions, and support within the school environment (Castro, 2022). The following variables impact teacher recruitment and retention in conjunction with economic incentives. Bruhn et al. (2022) research indicates that while competitive pay is vital, it may not be enough to guarantee long-term retention without considering the broader professional context. After analyzing those articles, we can get some suggestions that teacher recruitment and retention interventions should take a comprehensive approach, including all relevant factors and aspects. This strategy should address explicit economic incentives and consider structural improvements to enhance the appeal of the teaching profession. Possible changes may include avenues for upward mobility, enhancement of professional growth, and enhancements in school working conditions. This study also highlights notable deficiencies in the existing research, such as the need for further longitudinal studies to comprehend the enduring consequences of economic incentives on teacher retention and the distinct effects of these incentives in different settings and among varied teacher demographics.
Furthermore, there is a need for more thorough assessments of policy initiatives to determine their efficacy and cost-effectiveness. Future studies should thoroughly explore how economic and non-economic variables combine to impact teacher career choices. The objective of such a study should be to provide empirical information that may assist policymakers in formulating successful ways to recruit and retain teachers of exceptional caliber, eventually enhancing educational results.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TN: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MF: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Averill, R. M., and Major, J. (2020). What motivates higher education educators to innovate? Exploring competence, autonomy, and relatedness–and connections with wellbeing. Educ. Res. 62, 146–161. doi: 10.1080/00131881.2020.1755877
Badrul, A. K. M., Shaidullah,, and Raj, R. (2018). How teaching conditions predict teacher turnover in Bangladesh schools. Peabody J. Educ. 80, 44–70.
Ballou, D., and Podgursky, M. (1993). Teachers' attitudes toward merit pay: examining conventional wisdom. ILR Rev. 47, 50–61. doi: 10.1177/001979399304700104
Bau, N., and Das, J. (2020). Teacher value added in a low-income country. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Pol. 12, 62–96. doi: 10.1257/pol.20170243
Bayer, A. (2017). School principals' views on administration work, their "frequent turnover," and its effects on their work. Qual. Rep. 22, 1471–1487. doi: 10.46743/2160-3715/2017.2719
Borman, G. D., and Dowling, N. M. (2008). Teacher attrition and retention: a meta-analytic and narrative review of the research. Rev. Educ. Res. 78, 367–409. doi: 10.3102/0034654308321455
Bruhn, J., Imberman, S., and Winters, M. (2022). Regulatory arbitrage in teacher hiring and retention: evidence from Massachusetts charter schools. J. Public Econ. 215:104750. doi: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2022.104750
Caena, F., and Redecker, C. (2019). Aligning teacher competence frameworks to 21st-century challenges: the case for the European digital competence framework for educators (Digcompedu). Eur. J. Educ. 54, 356–369. doi: 10.1111/ejed.12345
Castro, A. J. (2022). Tensions between what principals know and do: the role of labor market conditions on teacher recruitment and hiring. Leadersh. Policy Sch. 21, 756–779. doi: 10.1080/15700763.2020.1833352
Chatrakul Na Ayudhya, U., Prouska, R., and Beauregard, T. A. (2019). The impact of global economic crisis and austerity on quality of working life and work-life balance: a capabilities perspective. Eur. Manag. Rev. 16, 847–862. doi: 10.1111/emre.12128
Chiong, C., Menzies, L., and Parameshwaran, M. (2017). Why do long‐serving teachers stay in the teaching profession? Analysing the motivations of teachers with 10 or more years’ experience in England. Br. Educ. Res. J. 43, 1083–1110. doi: 10.1002/berj.3302
Darling-Hammond, L., Burns, D., Campbell, C., Goodwin, A. L., Hammerness, K., Low, E. L., et al. (2017). Empowered educators: how high-performing systems shape teaching quality around the world. USA: John Wiley & Sons.
De Jong, D., Grundmeyer, T., and Yankey, J. (2017). Identifying and addressing themes of job dissatisfaction for secondary principals. School Leadersh. Manag. 37, 354–371. doi: 10.1080/13632434.2017.1338253
Dos Santos, L. M. (2019). Recruitment and retention of international school teachers in remote archipelagic countries: the Fiji experience. Edu. Sci. 9:132. doi: 10.3390/educsci9020132
Feng, L., and Sass, T. R. (2017). Teacher quality and teacher mobility. Educ. Finance Policy 12, 396–418. doi: 10.1162/EDFP_a_00214
Feng, L., and Sass, T. R. (2018). The impact of incentives to recruit and retain teachers in “hard-to-staff” subjects. J. Policy Anal. Manage. 37, 112–135. doi: 10.1002/pam.22037
García, E., and Weiss, E. (2019a). “The teacher shortage is real, large and growing, and worse than we thought” in The first report in" the perfect storm in the teacher labor market" series (USA: Economic Policy Institute).
García, E., and Weiss, E. (2019b). “U.S. schools struggle to hire and retain teachers” in The second report in" the perfect storm in the teacher labor market" series (USA: Economic Policy Institute).
Geiger, T., and Pivovarova, M. (2018). The effects of working conditions on teacher retention. Teachers Teach. 24, 604–625. doi: 10.1080/13540602.2018.1457524
George, B., and Wooden, O. (2023). Managing the strategic transformation of higher education through artificial intelligence. Admin. Sci. 13:196. doi: 10.3390/admsci13090196
Glass, G. V. (1976). Primary, secondary, and meta-analysis of research. Educ. Res. 5, 3–8. doi: 10.3102/0013189X005010003
Glover, A., and Stewart, S. (2023). Using a blended distance pedagogy in teacher education to address challenges in teacher recruitment. Teach. Educ. 35, 1–23. doi: 10.1080/10476210.2023.2223526
Han, S. W., Borgonovi, F., and Guerriero, S. (2018). What motivates high school students to want to be teachers? The role of salary, working conditions, and societal evaluations about occupations in a comparative perspective. Am. Educ. Res. J. 55, 3–39. doi: 10.3102/0002831217729875
Henry, G. T., and Redding, C. (2020). The consequences of leaving school early: the effects of within-year and end-of-year teacher turnover. Educ. Finance Policy 15, 332–356. doi: 10.1162/edfp_a_00274
Ingersol, R. M., Merrill, E., Stuckey, D., and Collins, G. (2018). “Seven trends: the transformation of the teaching force” in Updated October 2018. CPRE research report# R.R. 2018–2 (University of Pennsylvania: Consortium for Policy Research in Education).
Ingersoll, R. M. (2020). “Misdiagnosing the teacher quality problem” in The state of education policy research (University of Pennsylvania: Routledge), 291–306.
Ingersoll, R. M., May, H., and Collins, G. (2017). Minority teacher recruitment, employment, and retention. CPRE Research Reports: 1987 to 2013.
Islam, T., and Chowdhury, R. (2021). Policy reforms and teacher recruitment in worldwide: a policy analysis. J. Educ. Policy Rev. 22, 175–190.
Jackson, D., and Meek, S. (2021). Embedding work-integrated learning into accounting education: the state of play and pathways to future implementation. Acc. Educ. 30, 63–85. doi: 10.1080/09639284.2020.1794917
Jacob, B. A., Rockoff, J. E., Taylor, E. S., Lindy, B., and Rosen, R. (2018). Teacher applicant hiring and teacher performance: evidence from D.C. public schools. J. Public Econ. 166, 81–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2018.08.011
Kelley, C. (1999). The motivational impact of school-based performance awards. J. Pers. Eval. Educ. 12, 309–326. doi: 10.1023/A:1008011810852
Klassen, R. M., Rushby, J. V., Durksen, T. L., and Bardach, L. (2021). Examining teacher recruitment strategies in England. J. Educ. Teach. 47, 163–185. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2021.1876501
Lazear, E. P. (2018). Compensation and incentives in the workplace. J. Econ. Perspect. 32, 195–214. doi: 10.1257/jep.32.3.195
Lentini, V., Gimenez, G., and Valbuena, J. (2023). Educational inequality and the poverty trap in teacher recruitment. J. Dev. Stud. 59, 716–738. doi: 10.1080/00220388.2023.2172330
Loeb, S., and Myung, J. (2020). “Economic approaches to teacher recruitment and retention” in The economics of education (Stanford, CA, USA: Stanford University, Elsevier), 403–414.
Lyons, E., and Zhang, L. (2023). Salary transparency and gender pay inequality: evidence from Canadian universities. Strateg. Manag. J. 44, 2005–2034. doi: 10.1002/smj.3483
Manundu, P. K. (2023). Institutional motivational practices influencing teacher retention in public secondary schools in Kamukunji sub-county, Nairobi County, Kenya (South Eastern Kenya University: Doctoral dissertation).
Markowski, M., Cleaver, K., and Weldon, S. M. (2020). An integrative review of the factors influencing older nurses’ timing of retirement. J. Adv. Nurs. 76, 2266–2285. doi: 10.1111/jan.14442
Murnane, R., Singer, J., and Willett, J. (1989). The influences of salaries and" opportunity costs" on teachers' career choices: evidence from North Carolina. Harv. Educ. Rev. 59, 325–347. doi: 10.17763/haer.59.3.040r1583036775um
Nasser, R. (2017). Qatar’s educational reform past and future: challenges in teacher development. Open Rev. Educ. Res. 4, 1–19. doi: 10.1080/23265507.2016.1266693
Oyshi, F. J., Suhi, S. S., Sultana, A., Jahan, N., and Hossain, M. T. (2021). The academic achievement of secondary students in Bangladesh: assessing the role of socioeconomic status, school attributes, and academic activities. Educ. Res. Int. 2021, 1–10. doi: 10.1155/2021/5360672
Palmer, P. J. (2017). The courage to teach: exploring the inner landscape of a teacher's life. Singapore: John Wiley & Sons.
Paula, L., and Grīnfelde, A. (2018). The role of mentoring in the professional socialization of novice teachers. Probl. Educ. 21st Cent. 76, 364–379. doi: 10.33225/pec/18.76.364
Perryman, J., and Calvert, G. (2020). What motivates people to teach, and why do they leave? Accountability, performativity, and teacher retention. Br. J. Educ. Stud. 68, 3–23. doi: 10.1080/00071005.2019.1589417
Podolsky, A., Kini, T., and Darling-Hammond, L. (2019a). Does teaching experience increase teacher effectiveness? A review of US research. JPCC 4, 286–308. doi: 10.1108/JPCC-12-2018-0032
Podolsky, A., Kini, T., Darling-Hammond, L., and Bishop, J. (2019b). Strategies for attracting and retaining educators: what does the evidence say? Educ. Policy Anal. Arch. 27:38. doi: 10.14507/epaa.27.3722
Rahman, M. F. (2019). Impact of flexible work arrangements on job satisfaction among the female teachers in the higher education sector. Work 11, 97–107. doi: 10.7176/EJBM/11-18-11
Reitman, G. C., and Karge, B. D. (2019). Investing in teacher support leads to teacher retention: six supports administrators should consider for new teachers. Multicult. Educ. 27, 7–18.
Ronfeldt, M., and McQueen, K. (2017). Does new teacher induction really improve retention? J. Teach. Educ. 68, 394–410. doi: 10.1177/0022487117702583
Rothstein, J. (2015). Teacher quality policy when supply matters. Am. Econ. Rev. 105, 100–130. doi: 10.1257/aer.20121242
Rumschlag, K. E. (2017). Teacher burnout: a quantitative analysis of emotional exhaustion, personal accomplishment, and depersonalization. Int. Manag. Rev. 13:22.
Sadler, D. R. (2017). “Assuring academic achievement standards: from moderation to calibration” in International teacher judgement practices (London: Routledge), 15–29.
Sawaneh, I. A., and Kamara, F. K. (2019). An effective employee retention policies as a way to boost organizational performance. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 7, 41–48. doi: 10.11648/j.jhrm.20190702.12
See, B. H., Morris, R., Gorard, S., Kokotsaki, D., and Abdi, S. (2020). Teacher recruitment and retention: a critical review of international evidence of most promising interventions. Educ. Sci. 10:262. doi: 10.3390/educsci10100262
Shiddike, M. O. (2020). Faculty engagement in professional development: a worldwide case study. Canada: The University of Regina.
Shifter, D., Turley, R. L., and Heard, H. (2017). Do teacher financial awards improve teacher retention and student achievement in an urban disadvantaged school district? Am. Educ. Res. J. 54, 1117–1153. doi: 10.3102/0002831217716540
Sutcher, L., Darling-Hammond, L., and Carver-Thomas, D. (2019). Understanding teacher shortages: an analysis of teacher supply and demand in the United States. Educ. Policy Anal. Arch. 27, 1–35. doi: 10.14507/epaa.27.3696
Washington-Lawson, K. T. (2021). Teacher hiring in public school districts: decision-making competencies, person-environment fit, evaluation and assessment measures (Doctoral dissertation): Southeastern Louisiana University.
World Health Organization (2010). Increasing access to health workers in remote and rural areas through improved retention: global policy recommendations : World Health Organization.
Keywords: teacher recruitment and retention, economic approaches, supply of teachers, demand for teachers, hiring process
Citation: Shaoan MMR, Namanyane T, Feng M and Arif M (2025) A systematic literature review on the importance of teacher recruitment and retention in global educational reform. Front. Educ. 9:1447752. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1447752
Edited by:
Cheryl J. Craig, Texas A and M University, United StatesReviewed by:
Nashwa Ismail, University of Liverpool, United KingdomWilliam L. Sterrett, Baylor University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Shaoan, Namanyane, Feng and Arif. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Md Mirajur Rhaman Shaoan, bS5zaGFvYW5AdXcuZWR1LnBs; c2Fvbm1pcmFqQGVtYWlsLnN3dS5lZHUuY24=
 Md Mirajur Rhaman Shaoan
Md Mirajur Rhaman Shaoan Tebatso Namanyane2
Tebatso Namanyane2