- 1Department of Science, Ministry of Education and Skills Development, Shari Higher Secondary School, Paro, Bhutan
- 2Department of Science, Ministry of Education and Skills Development, Wangbama Central School, Thimphu, Bhutan
Introduction: We developed the IATPDI questionnaire, comprising seven scales for assessing teachers’ implementation of assessment methods, content, process, and product differentiation, familiarity with and use of various differentiated instruction (DI) strategies, factors influencing DI implementation, and resources used to enhance DI efficacy. This study examined the psychometric properties of the initial four scales with 35 items.
Methods: The questionnaire was administered to a sample of 237 Bhutanese teachers (66.2% male, 33.8% female), and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was used for psychometric evaluation.
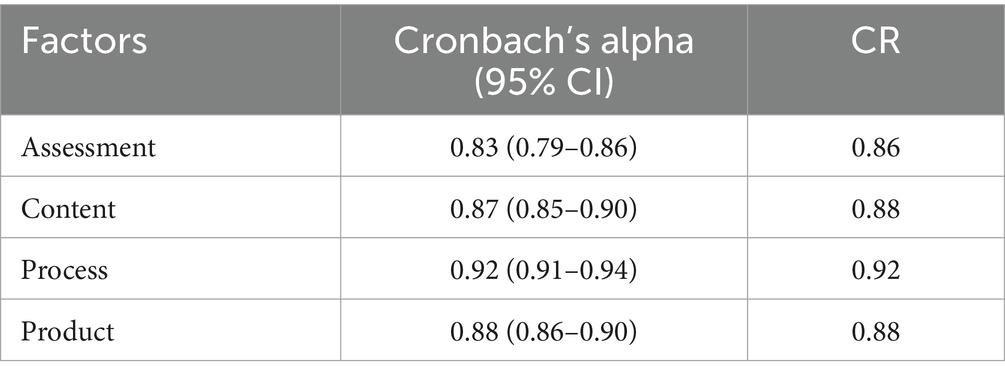
Results: CFA supported the hypothesized four scales (CFI = 0.911, TLI = 0.903, SRMR = 0.052, RMSEA = 0.059, χ2/df = 1.58). Cronbach’s alpha coefficients ranged from 0.83 to 0.92, and Composite reliability (CR) ranged from 0.86 to 0.92, indicating high internal consistency reliability. Inter-factor correlations supported discriminant validity for most factor pairs, but correlations exceeding 0.85 between some pairs suggested potential overlap, prompting further investigation. Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values for assessment, content, process, and product factors were 0.50, 0.41, 0.53, and 0.51, respectively. While AVE for process and product factors surpassed the commonly accepted threshold (0.50) for convergent validity, the assessment factor approached the threshold and the content factor fell below it, indicating the need for further refinement of its indicators. However, all standardized factor loadings were significant (p < 0.05), confirming convergent validity.
Discussion: These results indicate that the proposed four scales of the IATPDI questionnaire are reliable and valid in measuring the intended constructs. Nevertheless, they also highlight the need for further refinement in identified areas to enhance the tool.
1 Introduction
Addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by student diversity in general classrooms stands as a paramount objective for educational systems worldwide. Students are diverse in terms of learning traits such as different readiness levels, interests and learning profiles (Tomlinson et al., 2003) due to a multitude of factors, including individual abilities, disabilities, cultural background, language barriers, socioeconomic status, religion, and gender identities (Coubergs et al., 2017; Gibbs and McKay, 2021). In the face of such challenges, the traditional one-size-fits-all didactic approach, once considered a standard, is now inadequate to meet the needs of diverse students (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017; Letzel et al., 2020). Students no longer conform to a singular mold, as some excel in visual learning settings, while others thrive through auditory or kinesthetic methods (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017). As such, it is essential to provide personalized educational support and scaffolding that cater to their unique abilities, needs, backgrounds and prior experiences (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017).
Grounded in the educational theories and principles such as cognitive psychology, learning styles, and inclusive education (Gheyssens et al., 2023; Hall, 2002; Subban, 2006), differentiated instruction (DI) has emerged as a pedagogical panacea globally (Gheyssens et al., 2023; Shareefa et al., 2019; Subban, 2006). Although Jean Piaget, Lev Vygotsky, John Dewey, and Howard Gardner did not explicitly address DI in their theories, their foundational ideas serve as a theoretical backdrop for DI (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017; Kapusnick and Hauslein, 2001; Subban, 2006; Williams, 2013). Briefly, Piaget’s four main stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational, representing different periods in a child’s intellectual growth (Zhang, 2023), emphasize the importance of tailoring instruction and activities to match child’s cognitive readiness within each stage (Glenn, 2007), an idea supported by Vygotsky’s zone of proximal development (ZPD) theory. Vygotsky’s ZPD theory posited that child’s optimal learning and progression to each stage occurs with external support, known as scaffolding, within ZPD, where interaction between a novice and an expert, such as teacher or a knowledgeable peer, promotes skill acquisition by transferring information (Kapusnick and Hauslein, 2001; Sarmiento-Campos et al., 2022; Subban, 2006; Zhang, 2023; Tomlinson et al., 2003). The ZPD refers to the range of tasks that a learner can perform with the help of a teacher or a knowledgeable peer, but cannot perform independently (Zhang, 2023). Research suggests that teachers should teach within a child’s ZPD (Tomlinson et al., 2003), failing which may impede students’ ability to learn and their educational progress. This is because delivering content beyond learners’ ZPD leads to frustration and withdrawal, while presenting below their mastery level demotivates learners and impedes progress (Tomlinson et al., 2003). Moreover, DI’s emphasis on student-centered learning, experiential learning, and individualized instruction resonates with Dewey’s pragmatism and progressive education (Williams, 2017). Likewise, DI principles stem from Howard Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences (Kapusnick and Hauslein, 2001), which suggest that intelligence is not a singular, fixed, entity, but a collection of multiple intelligences, each representing different ways individuals process information and showcase mastery of learning. Additionally, DI embodies the ethos of inclusive education (Gheyssens et al., 2020a), which emphasizes the creation of learning environments that cater to the diverse needs, abilities, and backgrounds of all students (UNICEF, 2017). DI empower teachers to scaffold instruction according to both struggling and advanced students’ readiness levels, interests, and preferred learning modalities (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017; Tomlinson, 2001), leading to inclusive and responsive educational practices and greater student success (Porta et al., 2022). As such, DI has been shown to promote equity and inclusivity (Dema et al., 2022; Gheyssens et al., 2023; Porta et al., 2022; Pozas et al., 2019), enhance academic success (Onyishi and Sefotho, 2021; Reis et al., 2007), students’ engagement and motivation (Santangelo and Tomlinson, 2009), foster positive attitude towards learning (Reis et al., 2007), and lead to a drop in referral cases (Lewis and Batts, 2005).
Recently, realizing the importance of DI, Bhutan embarked on a journey to integrate DI into its mainstream educational framework to address the challenges of diverse learners in the classrooms. Specifically, the Bhutan Professional Standards for Teachers (BPST, Ministry of Education, 2020a), oblige all K-12 Bhutanese teachers to integrate DI into their teaching methodologies to cater to the needs of individual Bhutanese students. This requirement for DI practices in schools across the country was substantiated by various studies. Research conducted by Bhutan Council for School Examinations and Assessment and Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2019), Bhutan Council for School Examinations and Assessment (2016), and Royal Education Council (2009) revealed a growing gap in the quality of students’ grade-mandated learning outcomes, as highlighted in the Bhutan Education Blueprint 2014–2024 (Ministry of Education, 2020b). To support teachers in practicing DI, teachers across the nation are provided with professional development (PD) workshops adopting training of trainers (ToT) approach to enhance their skills in designing differentiated lesson plans and assessments. Notably, a recent study showed that Bhutanese teachers have a positive attitude toward DI (Dema et al., 2022), highlighting the impact of this support. However, there is a lack of research detailing the current practices of DI in Bhutanese classrooms, including the specific challenges teachers face and the resources they need to enhance their efficacy in DI implementation. To address these gaps, there is a need for a valid and reliable assessment instrument to understand teachers’ practices, perceptions and needs regarding DI.
Several instruments have been documented in the DI literature (Adlam, 2007; Coubergs et al., 2017; Gaitas and Alves Martins, 2016; Letzel et al., 2020; Pozas et al., 2019; Prast et al., 2015; Rachmawati et al., 2016; Roy et al., 2013). For instance, Adlam (2007) developed a self-report survey questionnaire to assess teachers’ familiarity with and use of various DI strategies, explore factors influencing teachers’ DI implementation, and the resources teachers need to enhance their DI efficacy. Coubergs et al. (2017) developed an instrument called DI-Quest to measure teachers’ philosophy and associated practices of DI in terms of five factors: Growth mindset, ethical compass, flexible grouping, output = input, and adaptions to interests, readiness, and learning profiles (Gheyssens et al., 2020a,b). The first two factors assess general teaching philosophies, while the subsequent two factors assess the practical application of DI strategies (Gheyssens et al., 2020a). The last factor assesses whether or not teachers adapt their instructional strategies to accommodate differences in students’ readiness, interests, and learning profiles. Specifically, the first factor delves into how teachers’ growth or fixed mindset, and their choices between curriculum-driven versus students’ need-driven approaches, influence the implementation of DI (Coubergs et al., 2017; Gheyssens et al., 2020a,b). The next two factors assess the practical application of two DI strategies. These factors underscore the significance of employing diverse grouping strategies and continuous assessments as integral component of implementing DI (Gheyssens et al., 2020b). Likewise, other researchers have developed instruments to assess teachers’ attitudes towards the practice of DI (Coubergs et al., 2017; Letzel et al., 2020), assess teachers’ use of DI strategies (Prast et al., 2015), and measure teachers’ perceived difficulty of DI strategies (Gaitas and Alves Martins, 2016). Pozas et al. (2019) developed a subject specific (i.e., Maths and German) questionnaire based on Pozas and Schneider’s (2019) taxonomy of DI practices to assess how and with which frequency German and Mathematics teachers across different schools apply DI strategies, including tiered assignments, homogenous and heterogeneous ability grouping, peer tutoring, and project-based learning in their teaching. Shareefa et al. (2019) developed a self-report questionnaire to explore elementary teachers’ perceptions regarding DI use in teaching. Rachmawati et al. (2016) developed two tools. Firstly, they developed an observation form for teachers to assess readiness level, interests, and learning profiles of students with special needs. Secondly, they developed a self-assessment tool for teachers to gauge their competency in understanding students’ readiness level, interests, and learning profiles. These tools were used for assisting teachers in planning and implementing DI effectively in inclusive school environments.
However, the abovementioned instruments lack the scales required to comprehensively assess teachers’ implementation of DI elements, including assessment methods, content, process and product differentiation (Tomlinson, 2001, 2014) based on students’ readiness level, interests, and learning profiles (Tomlinson et al., 2003). Recognizing this gap, our previous study (Dorji and Nima, 2021) addressed the limitations of questionnaire developed by Adlam (2007). We expanded this instrument by adding 35 new items, categorised into four factors: assessment methods, content, process and product differentiation (see Table 1). These additions were done to comprehensively assess teachers’ practices of DI elements in the classrooms. The revised instrument was named the Instrument to Assess Teachers’ Practice of Differentiated Instruction (IATPDI). Nevertheless, our prior study could establish only its face and content validity; refer to the instrument section for more details. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to provide psychometric evidence such as its construct, convergent and discriminant validity, and internal consistency reliability (through calculation of both Cronbach’s alpha coefficient and composite reliability) of the four scales added to Adlam’s (2007) questionnaire by conducting confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) (Coulacoglou and Saklofske, 2017; Dell’olio et al., 2018) on Bhutanese teachers’ data. Specifically, this paper examined the following question:
1. Are the four constructs added to Adlam’s (2007) questionnaire valid and reliable construct to assess teachers’ assessment methods as well as content, process, and product differentiation?
By evaluating the psychometric properties of the four constructs added, we attempt to contribute to the field of education by providing a robust and validated instrument to gain insights into prevailing practices and challenges related to DI. Specifically, the insights gained from the administration of the multifaceted IATPDI instrument to Bhutanese teachers can inform educational policy makers, teacher educators, and school administrators to get accurate and credible data to make evidence-based decisions in curriculum development, teacher training, and effective resource allocation to enhance DI practices in Bhutanese classrooms.
2 Literature
2.1 Models underpinning the IATPDI
The extant models of DI (Hall, 2002; Sousa and Tomlinson, 2018; Tomlinson, 2001, 2014) and taxonomy of DI practices (Pozas and Schneider, 2019) underpin these new scales and items. According to these models, teachers in differentiated classrooms can diversify their teaching approach by adapting four curricular elements—content, process, product, and affect or learning environment—based on individual student’s readiness level, interest, and learning profile identified through continuous formative assessments (Hall, 2002; Sousa and Tomlinson, 2018; Tomlinson et al., 2003). The procedure of DI begins with a diagnostic assessment (Hall, 2002). It is conducted before, during, and after instructions or activities, either through formal or informal way (Chapman and King, 2005; Hall, 2002) to assess student’s readiness level, interest, and learning profile (Levy, 2008; Tomlinson, 2014). Subsequently, a purposeful and meaningful differentiation of instruction and activities ensues (Chapman and King, 2005) by differentiating content, process, and product based on students’ readiness level, interest, and learning profile (Tomlinson, 2001), concluding with a post-assessment of student outcomes and an evaluation of methods used throughout the class (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017).
Content differentiation refers to making “what we teach or what we want students to learn” (Tomlinson, 2001, p. 72) such as the key concepts, principles, ideas, and skills (Corley, 2005). Some effective strategies for differentiating content includes using concept-based teaching, curriculum compacting, variety of resources and materials including web-based materials, learning contracts, conducting minilessons, giving variety of support systems in terms of time, materials, and activities; giving highlighted print materials and key ideas to make the content more accessible to all students (Kapusnick and Hauslein, 2001; Tomlinson, 2001). However, the content differentiation through these strategies should be done “without losing the sight of the prescribed curriculum to which all the students in the same grade level are entitled” (Levy, 2008, p. 165).
Process differentiation refers to using different methodologies and techniques to teach content (Levy, 2008; Puzio et al., 2020), through activities or tasks that help students “understand and assimilate facts, concepts, or skills” (Algozzine and Anderson, 2007, p. 50), and ultimately master the concepts and skills being taught (Corley, 2005). Tomlinson (2001) defines process differentiation as a “sense-making” of the teaching and learning where teachers vary the activities and strategies to teach content. Many strategies such as flexible grouping, learning contracts, tiered lesson or activity or product, independent study projects, curriculum compacting, mini-lesson, interest centers, interest groups, learning centers or stations, anchor activities, jigsaw, learning logs, literature circles, think-pair-share, varying questions, cubing, varied instructional materials (e.g., graphic organizers, manipulatives, models, etc.), peer-tutoring, choice boards or learning menus, and using eLearning tools and resources can be used to differentiate process (Algozzine and Anderson, 2007; Kapusnick and Hauslein, 2001; Strickland, 2007: Tomlinson, 2001).
Products “are culminating assessments that allow students to demonstrate how much they understand and how well they can apply their knowledge and skills after a significant segment of instruction” (Tomlinson, 2005a, 2005b, as cited in Joseph et al., 2013, p. 30). Traditionally, the assessable product of learning has taken the form of a paper, a quiz, or a presentation (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017). Product differentiation entails providing students a variety of options to demonstrate what they have learned (Puzio et al., 2020; Tomlinson, 2001). Offering students, a range of projects to exhibit their understanding at a level that aligns with their unique learning needs is one way to differentiate product (Corley, 2005). Project should include making physical models, sculptures, and dioramas. It can also be in the form of written products such as writing essays, portfolios, poems, short stories, plays, research papers, journals, and reports. Other examples include an oral and PowerPoint presentations, delivering speeches, making video documentaries and podcasts (Corley, 2005). However, teachers should give concise assessment rubrics containing clear criteria to help students understand how they will be evaluated (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017; Levy, 2008). By giving varied methods to showcase mastery of learning, teachers achieve the assessment objectives without affecting the learners who may struggle with a particular mode of showcasing mastery, due to lack of skills or abilities (Haniya and Roberts-Lieb, 2017).
Interest-based differentiation involves tailoring lessons and activities according to students’ preferences. Addressing students interest foster their motivation to learn (Santangelo and Tomlinson, 2009; Tomlinson et al., 2003) and engagement in learning (Saeed and Zyngier, 2012). Differentiating based on student’s readiness level involves teaching all students within their ZPD (Tomlinson et al., 2003) to achieve better results. Differentiating according to learning profiles entails teaching and assigning tasks that match students learning style, intelligence preferences, gender, grouping preferences, and environmental preferences (Tomlinson et al., 2003). To identify student’s areas of interest, teachers can use interest inventories. For younger children, who aren’t likely to accurately represent themselves in writing, teachers can ask students during one-on-one conference to explain what interest they have in a specific topic, and then integrate these interests into their instructional materials. Conducting tests, questioning students about their background knowledge, and using KWL charts (Know, Want, Learn charts, i.e., what students already know, what they want to know, and what they have learned about a topic) (Rahmasari et al., 2024) are some of the options to assess readiness level of each student. Learning style preferences of students, for example, can be identified by administering learning style surveys including Kolb’s Learning Style Inventory, Fleming’s VARK Learning Style Inventory and Jackson’s Learning Styles Profilers. The acronym VARK stands for Visual (V), Aural or Auditory (A), Read/Write (R), and Kinesthetic (K) learning styles. Teachers can also ask students about their preferred learning methods, observe their activities and behaviours, and use self-report multiple intelligences checklist. This approach allows teachers to tailor their instructional strategies to better meet the diverse learning needs of their students.
2.2 Validity and reliability assessment
CFA is a powerful statistical technique used in psychometrics to assess the validity and reliability of measurement instruments (Coulacoglou and Saklofske, 2017; Dell’olio et al., 2018). CFA evaluates how well the collected data fit the hypothesized theoretically rooted model that specifies the relationship between the observed variables (items) and latent variables (factors) (Mueller and Hancock, 2015). Construct validity refers to the extent to which the observed variables load onto the latent variables they are intended to measure (Dell’olio et al., 2018). Convergent validity assesses the strength of the relationships between the observed variables and their corresponding latent variables (Dell’olio et al., 2018). Discriminant validity examines the extent to which factors that should not be related are, in fact, distinct from each other (Dell’olio et al., 2018). Discriminant validity is established when item that are theoretically supposed to be different are not highly correlated (Cheung et al., 2023; Dell’olio et al., 2018). Internal consistency reliability measures the degree to which different items within the same scales or factor in a survey instrument consistently measure the same underlying construct (Tavakol and Dennick, 2011). Cronbach’s alpha (coefficient ) and composite reliability (CR), also known as coefficient omega (Fu et al., 2021) or McDonald’s omega (McDonald, 1999, as cited in Cheung et al., 2023), are two common methods for estimating the internal consistency reliability. Coefficient omega is calculated using the factor loadings and error variance of the items in a CFA model (Goodboy and Martin, 2020). Higher internal consistency reliability indicates that the items within a scale or factor are measuring the same construct consistently (Cortina, 1993).
2.3 Background of Bhutanese education system
According to Gyeltshen and Zangmo (2020), modern education in Bhutan began in 1914 by sending students to India for Western education, alongside the establishment of the first modern school in country under the command of the first king of Bhutan. The core subjects included Hindi (an official language of India), English, Arithmetic, and Dzongkha (an official and national language of Bhutan). Until the 1960s, these subjects were mainly taught in Hindi, with some use of English and Dzongkha. India played a significant role in establishing Bhutan’s modern education system, allowing Bhutan to adopt the entire Indian education system, including English as the medium of instruction, along with teachers, curriculum, and teaching-learning materials (Kinley et al., 2021). Compulsory formal modern or Western education in the government system began in 1961. By 1962, English had become the main medium of classroom instruction, except for teaching Dzongkha, to help small and isolated country communicate with the world. Today, the Bhutanese education system is influenced by international practices in terms of the curricula design, delivery, and student assessment. As such, modern education in Bhutan, where English is the medium of instruction, meets global standards (Dendup, 2023). Before the advent of modern education, Bhutan primarily had traditional or monastic education focused on Buddhist philosophy, soteriology, astrology, theology, medicine, metaphysics, monastic disciplines, and religious arts such as liturgy, monastic music, dances, sculpture, and painting (Gyeltshen and Zangmo, 2020; Kinley et al., 2021). Other subjects were neglected due to the dominant role of religion, and Choekey (Classical Tibetan Language) was the medium of instruction (Dendup, 2023). Many eminent Bhutanese scholars travelled to Tibet to study Buddhist scriptures (Policy and Planning Division, 2023). Today, the education system in Bhutan comprises three main forms: general education, monastic education, and non-formal education. Among these, the general education system is the largest and is regarded as the formal education structure, consisting of seven years of primary (Pre-Primary to Class Six), two years of lower (Class Seven to Eight), middle (Class Nine to Ten), and higher secondary (Class Eleven to Twelve) schooling, followed by university education either within the country or abroad (refer to Childs et al., 2012, and Kinley et al., 2021 for more details). Education is free and mandatory for all children up to Class ten until 2018, ensuring broad access. From 2019, it is extended to Class twelve (Policy and Planning Division, 2023). The official enrolment age for the first year of primary education is 5 years old (Policy and Planning Division, 2023). Non-formal education in Bhutan, provided through an extensive network of learning centres spread across the country, has been and continues to be a crucial strategy for empowering citizens who missed formal schooling, enhancing literacy, promoting the national language, and fostering participation in local governance (Powdyel, 2016).
3 Method
3.1 Study population, sample size and sampling method
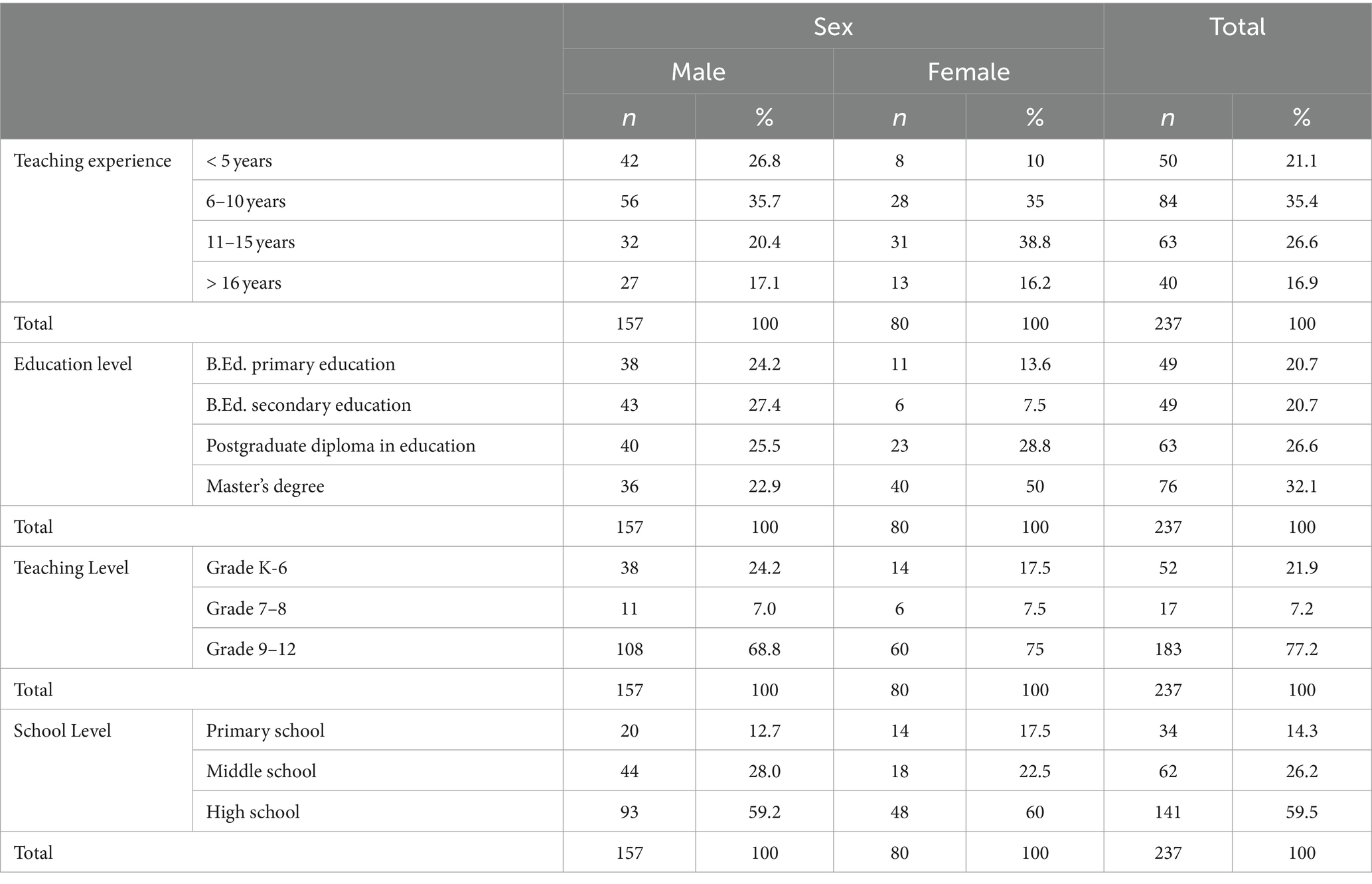
The target population was all K-12 grade public school teachers in Bhutan. There are a total of 9,670 teachers working in 500 public schools, including primary, middle, and high schools in Bhutan (Ministry of Education, 2022). To calculate the representative sample, the freely available web calculator1 was used. Using N = 9,670 as the population size at standard 95% confidence level and 5% confidence interval, a sample size of 370 teachers was initially required. To recruit study participants, a convenience sampling method was used. Survey responses were collected through popular messenger apps such as WeChat, WhatsApp, Telegram, and Facebook Messenger. Convenience sampling was deemed suitable for participant recruitment, given the practicality of reaching a diverse pool of respondents who regularly engage with these communication platforms. Participants were selected based on their accessibility and willingness to participate, making the sampling process straightforward and expeditious. Only 237 teachers completed and returned the survey form, resulting in a 64.1% return rate. Table 2 summarises the demographic characteristics of the teacher participants.
3.2 Instrument
As stated above, the analysed instrument is IATPDI, a self-report questionnaire consisting of four sections: A, B, C, and D, with a total of 40 items (see Supplementary material). The development of this questionnaire has been previously reported in detail (see Dorji and Nima, 2021). Briefly, Section A, consisting of 7 items, explores the demographic information of the teachers. Section B, the present study’s main focus, examines how teachers practice the DI elements—different assessment techniques, content, process, and product differentiation—and has 35 items (see Table 1). Each item has a four-option rating scale: “never” = 1, “seldom (infrequently)” = 2, “sometimes (on certain occasions or in certain circumstances)” = 3 and “often (frequently or many times)” = 4. Under Section C, items 36 and 37 explores teachers’ familiarity with and use of various DI strategies. Each item has a dichotomous rating scale: “yes” = 1, “no” = 2. Under Section D, items 38 and 39 explore factors influencing teachers’ DI implementation, and item 40 explores the resources teachers would use to enhance their DI efficacy. Each item has a check all that apply option. Sections C and D were adapted from Adlam (2007). Permission to adapt and use her survey questionnaire was obtained in our prior study (Dorji and Nima, 2021).
Our prior study (Dorji and Nima, 2021) could only establish its face and content validity. Two rounds of Delphi method were executed to confirm the face and content validity of the IATPDI questionnaire. Two DI experts from Australian universities (see Supplementary material) were requested to rate individual items in terms of clarity and relevancy to the construct being measured using a 4-point ordinal rating scale adapted from Davis’s (1992). The rigorous expert judgement and review of each item confirmed IATPDI’s face validity. Content validity was quantified by calculating the content validity index (CVI) for individual items (I-CVI). Additionally, to assess the content validity of the overall scale, both S-CVI/Universal Agreement (S-CVI/UA) and S-CVI/Average (S-CVI/Ave) were calculated. Furthermore, to remove random chance agreement, modified kappa coefficients was also calculated (Shrotryia and Dhanda, 2019). Except for item 2, the I-CVI for each item was 1, yielding an average S-CVI score of 0.98. The S-CVI/UA and S-CVI/Ave were also 0.98. Similarly, except for item 2, Kappa statistics for each item were 1, reflecting a substantial level of agreement among raters regarding the relevance or appropriateness of individual items in the IATPDI questionnaire. The I-CVI value and kappa statistic coefficient for item 2 were 0 and − 0.33, respectively. This particular item under the assessment construct was rated by the two experts as “the item is somewhat relevant to the measured domain,” leading to such issues. Nevertheless, the item was revised and retained in the questionnaire.
3.3 Data collection
The link to the Google Form was sent to teachers via email and messaging platforms (Facebook Messenger, Telegram, WhatsApp, and WeChat), with measures in place to allow only one response per teachers. Teachers completed the survey form in English. The survey was carried out from September 1 to 30, 2023.
3.4 Ethical clearance
Permission to collect data was sought from the Teacher Professional Support Division (TPSD) under Ministry of Education and Skills Development (MOESD), erstwhile known as Ministry of Education (MOE), the district education office, and the principals of selected schools. Moreover, teacher participants were explicitly notified on the first page of the online survey created using Google Form that their participation is entirely voluntary. By responding to the survey, participants were considered to have provided informed consent, acknowledging their voluntary participation in the study. Furthermore, participants were informed that the study’s findings would not identify specific informants and that the collected data would be used exclusively for the stated research purpose.
3.5 Data analysis
Data from a Google spreadsheet was imported, cleaned, and analysed using the statistical software R version 4.3.2. Statistical analyses were considered significant at the p < 0.05 level.
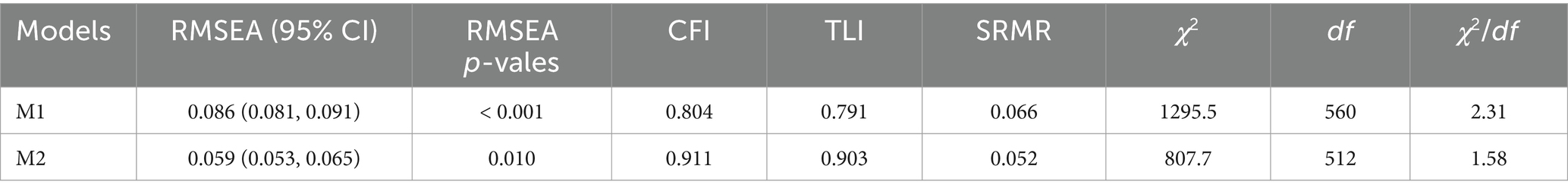
Prior to performing CFA analysis, the multivariate normality assumption of the data was checked using Mardia’s test using the mardia () function from the mvnormalTest package (). No missing data was recorded because the data was collected through a Google Form, where each question was made mandatory. Teachers could not proceed to the next question or submit the form without answering all questions, ensuring complete responses throughout the dataset. To confirm the construct validity of the IATPDI instrument, CFA was computed using the cfa () function in the lavaan package (Rosseel, 2012). Since Mardia’s test revealed the absence of multivariate normality in the data, we used robust maximum likelihood (MLR) as the model estimator (Roos and Bauldry, 2022), as it is robust to non-normality data. We started with a uni-factor model, positing a single factor for all observed variables. Since it was rejected due to poor fit, we proceeded with a four-factor model, assigning the observed variables to their hypothesised factors accordingly. To assess how well the proposed model fits the observed data, widely used goodness-of-fit indices, such as chi-square (χ2) test goodness-of-fit, χ2/df, Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) with 95% confidence interval (CI), Comparative Fit Index (CFI), Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI), and Standardised Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR) were used. For a detailed understanding of each fit index, please refer to Goretzko et al. (2024). The CFA model was deemed to be a good fit for the data when the χ2 test result was non-significant (p > 0.05) (Roos and Bauldry, 2022) and the χ2/df < 2.0 (Hu and Bentler, 1999). However, it is crucial to note that, due to the χ2 test’s sensitivity to the sample size and deviations from multivariate normality in the data, more importance was placed on other fit indices (Roos and Bauldry, 2022). The χ2 test tends to yield significant results in samples exceeding 100 (Roos and Bauldry, 2022). The adequacy of the other fit indices was assessed by comparing them to established threshold values recommended in prior studies (Hu and Bentler, 1999; Roos and Bauldry, 2022). Specifically, fit of the model to the data was indicated by RMSEA ≤0.05, CFI ≥ 0.95, and SRMR <0.08. Furthermore, a value of 0.40 or larger was used as a criterion for acceptable standardised factor loadings (Tabachnick and Fidell, 2013).
Finally, after establishing an acceptable model fit, Cronbach’s alpha coefficients were calculated for each of the four proposed constructs to assess their internal consistency reliability. The benchmarks: “>0.9—Excellent, >0.8—Good, >0.7—Acceptable, >0.6—Questionable, >0.5—Poor, and < 0.5—Unacceptable” were followed to interpret it (George and Mallery, 2019, p. 243). In addition, CR using the formula given in Cheung et al.’s (2023) paper was also calculated to measure internal consistency reliability. The value of 0.70 or higher was used as a cut-off for CR (Hair et al., 2009). While Cronbach’s alpha coefficient is the most frequently reported estimate of internal consistency reliability, research indicates that CR calculated using factor loadings derived from CFA yields more accurate reliability coefficients compared to alpha (Kalkbrenner, 2021). Furthermore, a correlation coefficient of less than or equal to 0.85 among the factor in the final measurement model was used as a cut-off for the discriminant validity of the measurement model (Brown, 2015; Cheung et al., 2023). Dell’olio et al. (2018) asserted that discriminant validity can be confirmed if the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) of all the possible pairs of constructs is greater than the square of the correlation between them. Additionally, an AVE value greater than or equal to 0.50 was used as a cut-off for the convergent validity of the measurement model (Cheung et al., 2023; Dell’olio et al., 2018). AVE was calculated by summing the squared standardised factor loadings (R2) of all the indicators for a construct and dividing by the number of indicators (Cheung et al., 2023; Henseler et al., 2015). Convergent validity was also confirmed if the standardised factor loadings were statistically significant (p < 0.05) (Dell’olio et al., 2018) and if the CR was equal to or more than 0.70 (Hair et al., 2009).
4 Results
4.1 Sample description
Table 2 summarises the demographic characteristics of the teacher participants who responded to the IATPDI questionnaire.
4.2 Psychometric properties
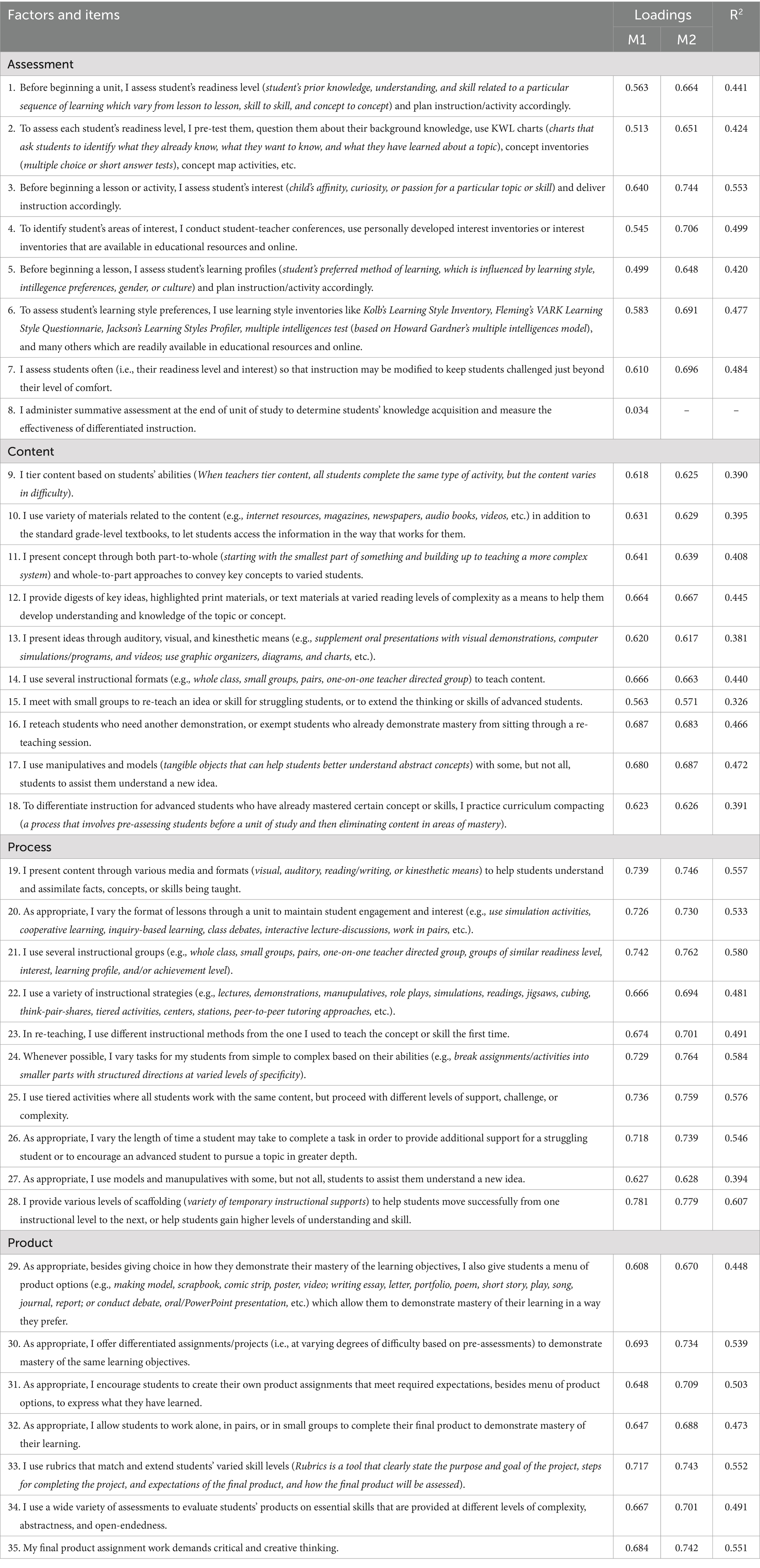
As seen in Table 3, the initial uni-factor model (M1) yielded an inadequate fit with the data. However, in the CFA model (M2), after assigning the observed variables to their hypothesised factors, removing item 8 under the assessment factor with factor loading below 0.40, and adjusting the model following the modification indices, the model fit improved. Item 8 was problematic due to its notably low variance in the survey response. Except χ2 (p < 0.001), all the goodness-of-fit indices, including the χ2/df passed the threshold recommended in prior papers (Hu and Bentler, 1999; Roos and Bauldry, 2022). Additionally, factor loadings were inspected to assess the strength and significance of the relationships between each observed variable and its corresponding latent factors. All the standardised factor loadings of 34 items depicted in Table 3 were statistically significant (p < 0.05) ranging from 0.57 to 0.78, further confirming convergent validity (Dell’olio et al., 2018). The results support the construct validity of the proposed construct for the IATPDI instrument within the studied sample. Tables 1, 3 display the results of the tested measurement models (M1 and M2). The standardised factor loadings of the tested model and the R2 of the ultimate model (M2) are shown in Table 1.
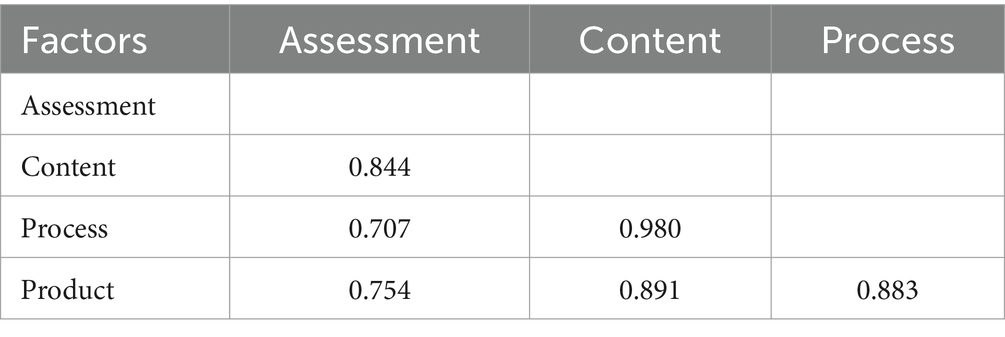
Table 4 presents the correlations between the factors. The inter-factor correlations support discriminant validity for most factor pairs, except between content and process, content and product, and process and product, where correlations exceed the specified threshold of 0.85. This suggests a potential overlap or shared variance between content and process as well as content and product factors, prompting further investigation or model refinement to ensure the distinctiveness of the constructs. However, since the AVE of all the possible pairs of factors was not greater than the square of the correlation between them, discriminant validity, according to Dell’olio et al.’s (2018) criteria, was not confirmed for all the proposed factors.
The AVE values for assessment, content, process, and product factors are 0.50, 0.41, 0.53, and 0.51, respectively. The AVE of process and product factors surpassed the commonly accepted 0.50 threshold, indicating satisfactory convergent validity (Dell’olio et al., 2018). However, the assessment factor is at the limit of 0.5, and the content factor is below the threshold value. The entire scale’s AVE is at the limit of 0.50, suggesting substantial shared variance among indicators, supporting the convergent validity of the entire measurement model. The marginal AVE value for the content factor suggests the need for further examination or refinement of its indicators. Additionally, since all the standardised factor loadings of 34 items depicted in Table 3 are statistically significant (p < 0.05), convergent validity is further confirmed (Dell’olio et al., 2018).
4.3 Reliability
The Cronbach’s alpha of the entire scale is 0.96 (95% CI: 0.95–0.97), indicating excellent internal consistency reliability (George and Mallery, 2019). The Cronbach’s alpha of the four factors (Table 5) indicates good to excellent internal consistency reliability. Additionally, CR range from 0.86 to 0.92, reinforcing the reliability of the proposed latent factors.
5 Discussion
As mentioned earlier, our prior study (Dorji and Nima, 2021) established both the face and content validity of the IATPDI questionnaire. This process involved evaluating the clarity and relevance of each item to the proposed construct. To ensure rigour, two content experts from two Australian universities participated in this evaluation process through two rounds of the Delphi method. Using a 4-point ordinal rating scale adapted from Davis (1992), these experts critically analysed the suitability of each questionnaire item. This meticulous scrutiny affirmed the questionnaire’s face and content validity. Content validity was further quantified by calculating the CVI for individual items (I-CVI) and both S-CVI/UA and S-CVI/Ave for the overall scale (S-CVI). To remove random chance agreement, modified kappa coefficients were also calculated. The results indicated a high level of agreement among the raters, demonstrating that majority of the items were appropriate for measuring the intended constructs. However, one notable exception was item 2 under the assessment construct, which presented issues in terms of I-CVI value and kappa statistic coefficient. Both the experts rated item 2 as “the item is somewhat relevant to the measured domain,” leading to such issues. Nevertheless, we revised it based on the two experts’ feedback and retained it in the questionnaire.
The present study conducted CFA to assess how well the observed variables align with the proposed latent constructs (Mueller and Hancock, 2015) and to provide evidence of the questionnaire’s construct validity. Since the questionnaire’s development process was rooted in an extensive review of existing literature on DI, CFA was preferred over exploratory factor analysis (EFA). EFA can limit researchers’ control when they have a priori model in mind (Fu et al., 2021). Following CFA, various psychometric analyses were conducted. This includes construct, convergent, and discriminant validity, as well as internal consistency reliability (measured through both Cronbach’s alpha and CR) of the four constructs integrated into Adlam’s (2007) questionnaire. Research suggests that solely reporting CFA results is not sufficient to demonstrate the quality of measurement scales (Fornell and Larcker, 1981, as cited in Cheung et al., 2023). Initially, the uni-factor model, that is, all items crammed under one factor, showed inadequate fit with the data, indicating the need for refinement. After making adjustments—such as assigning observed variables to their hypothesised factors, removing the underperforming item (i.e., item 8), and modifying the model based on modification indices—a significant improvement in the model was observed. All the fit indices, such as CFI, TLI, RMSEA, and SRMR, indicated an acceptable fit to the data, endorsing the validity of the proposed four-factor structure of the questionnaire. Given the χ2 test of goodness-of-fit’s sensitivity to sample size and departures from multivariate normality, greater emphasis was placed on the aforementioned fit indices to assess model adequacy. The correlation analysis revealed strong support for discriminant validity among most factor pairs, although correlations between content and process and content and product factors exceeded the specified threshold, suggesting potential overlap. Further refinement may be needed to ensure the distinctiveness of these constructs. Convergent validity is supported by satisfactory AVE values for all factors except content, indicating the need for refinement of its indicators (Cheung et al., 2023). Moreover, statistically significant (p < 0.05) standardised factor loadings of all 34 items, further supported the convergent validity (Cheung et al., 2023; Dell’olio et al., 2018). Cronbach’s alpha is excellent for the entire scale, with a value at 0.96, and good to excellent (0.83 to 0.92) for individual factors (George and Mallery, 2019). CR, ranging from 0.86 to 0.92, further reinforce the internal consistency reliability of the latent factors (Cheung et al., 2023) and convergent validity (Hair et al., 2009). Although, item 8 (I administer summative assessment at the end of the unit of study to determine students’ knowledge acquisition and measure the effectiveness of differentiated instruction) yielded factor loading from CFA below threshold (i.e., 0.40), possibly due to its low variance in survey responses, it remains integral. It evaluates whether teachers are implementing summative assessment practices to gauge students’ achievement and to make instructional adjustments to meet the diverse needs of all students. Therefore, we recommend retaining it within the IATPDI instrument. Collectively, the foregoing psychometric properties and the findings from our previous study affirm the IATPDI’s validity and reliability. The whole approach discussed above aligns with the established practices in questionnaire development (Cheung et al., 2023; Davis, 1992; Lynn, 1986; Polit and Beck, 2006; Polit et al., 2007; Rubio et al., 2003).
With IATPDI’s comprehensive structure, including demographic information, exploration of DI elements, familiarity with DI strategies, factors influencing DI implementation, and preferred resources for enhancing DI efficacy, this instrument offers researchers and educators a means to evaluate and understand the multifaceted aspects of DI practice. Recently, Dema et al. (2022) developed a self-report questionnaire consisting of 15 items to explore Bhutanese teachers’ perceptions regarding DI. Dema and her colleagues adapted these 15 items from the scholarly works of Shareefa et al. (2019) and Richards-Usher (2013) to suit the local context of Bhutan. The practical implications of Dema and her team’s instrument, as well as ours, are substantial. Together, they can serve as a foundational tool for further DI research endeavours aimed at gaining nuanced analysis of teachers’ practices, perceptions, and needs regarding DI. For instance, our questionnaire can serve as a valuable tool for evaluating how teachers’ demographic variables (i.e., gender, school level, teaching experience, teaching level, teaching subject, teaching period, class size, and qualification) influence the implementation of DI. Furthermore, researchers can explore questions such as: What is the extent of implementation of DI elements among Bhutanese teachers? How familiar are they with the DI strategies? How frequently are DI strategies used in the classrooms? What factors help or deter the use of DI elements in their classrooms? The answers to these questions, in turn, can inform targeted interventions and PD initiatives to improve DI practices of both novice and expert teachers, aligning with the focus areas highlighted in the first and second standards of BPST, ultimately enhancing students’ learning outcomes (Coubergs et al., 2017; Porta et al., 2022). The first and second standards of BPST mandate all Bhutanese teachers to integrate DI into their teaching processes to cater to the needs of students and establish a supportive, interactive, and safe classroom atmosphere that inspires all students to achieve high levels of knowledge and skills (Ministry of Education, 2020a,b).
As our initially developed IATPDI questionnaire was structured in a Likert-type responses and check-all that apply format, we supplemented it with one open-ended question (Can you describe a specific instance or example from your teaching experience where you successfully implemented differentiated instruction? Please elaborate on the strategies you used, challenges you faced, and the outcomes for your students) to capture additional qualitative insights. Research suggests that measures requiring respondents to select one option from a predefined set leave less room for interpretation (Kupffer et al., 2024). The inclusion of open-ended questions allows teachers to provide detailed explanations, examples, and insights into the nuances and complexities of how DI is implemented, that closed-ended questions alone may not capture. Specifically, open-ended questions offer several advantages: (a) they allow teachers to clarify their responses or ratings; (b) analysing open-ended responses helps identify patterns, themes, and trends across teachers’ practices of DI; (c) they provide a platform for teachers to express any challenges, barriers, or limitations they encounter when implementing DI; and (d) they enable teachers to share innovative or effective strategies they have developed for implementing DI. Such foregoing insights can be valuable for targeted interventions and support strategies to address obstacles to effective implementation, share best practices, and inform PD initiatives. The final version of the IATPDI questionnaire is available as Supplementary material.
In conclusion, the IATPDI instrument stands as a valid and reliable tool for research and practical application in educational contexts. However, the validation process is not without limitations. Firstly, the data was based on self-reporting by teachers rather than objective observations and interviews, potentially introducing bias. It is possible that actual practices do not entirely align with reported practices. Secondly, the convenience sampling method employed in this study may limit the generalizability of the findings beyond the sample group, as the sample obtained through Messenger apps (i.e., by sending the links of Google Form) may not be fully representative of the broader population. Thirdly, the study’s result could be influenced by subject variables. The participants were predominately high school teachers. Therefore, replication of this study with a larger, more diverse, and random sample and integrating classroom observations and interviews is warranted. Additionally, the examination of the psychometric properties of IATPDI beyond the Bhutanese context is necessary to check its cross-cultural validity and generalizability.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Ministry of Education and Skills Development, district education office, and school principals. Moreover, teachers were informed on the first page of the Google Form survey that their participants was voluntary, and responding implied informed consent. Furthermore, it was made clear that their identities would remain confidential, and the data would be used solely for the research.
Author contributions
TD: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization. PN: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Supervision, Software, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Dr. Carol Le Lant from Flinders University, Australia and Rebecca Saunders from Murdoch University, Australia, for their participation in face and content validation of the survey questionnaire via Delphi method.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2024.1445865/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^https://www.calculator.net/sample-size-calculator.html?type=1&cl=95&ci=5&pp=50&ps=9670&x=Calculate
References
Adlam, E. (2007). Differentiated instruction in the elementary school: investigating the knowledge elementary teachers possess when implementing differentiated instruction in their classrooms [Dissertations/master’s thesis]. University of Windsor. Available at: https://scholar.uwindsor.ca/etd/4643 (Accessed April, 10, 2024).
Algozzine, B., and Anderson, K. M. (2007). Tips for teaching: differentiating instruction to include all students. Prev. Sch. Fail. Altern. Educ. Child. Youth 51, 49–54. doi: 10.3200/psfl.51.3.49-54
Bhutan Council for School Examinations and Assessment (2016). National education assessment 2016. Thimphu: Bhutan Council for School Examinations and Assessment.
Bhutan Council for School Examinations and Assessment and Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2019). Education in Bhutan: Findings from Bhutan’s experience in PISA for development. Thimphu: Bhutan Council for School Examinations and Assessment.
Chapman, C., and King, R. (2005). 11 Practical ways to guide teachers toward differentiation (and an evaluation tool). Learn. Prof. 26, 20–25.
Cheung, G. W., Cooper-Thomas, H. D., Lau, R. S., and Wang, L. C. (2023). Reporting reliability, convergent and discriminant validity with structural equation modeling: a review and best-practice recommendations. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 41, 745–783. doi: 10.1007/s10490-023-09871-y
Childs, A., Tenzin, W., Johnson, D., and Ramachandran, K. (2012). Science education in Bhutan: issues and challenges. Int. J. Sci. Educ. 34, 375–400. doi: 10.1080/09500693.2011.626461
Corley, M. A. (2005). Differentiated instruction: adjusting to the needs of all learners. Focus Basics 7, 13–16.
Cortina, J. M. (1993). What is coefficient alpha? An examination of theory and applications. J. Appl. Psychol. 78, 98–104. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.78.1.98
Coubergs, C., Struyven, K., Vanthournout, G., and Engels, N. (2017). Measuring teachers’ perceptions about differentiated instruction: the DI-quest instrument and model. Stud. Educ. Eval. 53, 41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.stueduc.2017.02.004
Coulacoglou, C., and Saklofske, D. H. (2017). Psychometrics and psychological assessment: Principles and applications. London: Academic Press, An Imprint of Elsevier.
Davis, L. L. (1992). Instrument review: getting the most from a panel of experts. Appl. Nurs. Res. 5, 194–197. doi: 10.1016/s0897-1897(05)80008-4
Dell’olio, L., Ibeas, A., de Oña, J., and de Oña, R. (2018). “Structural Equation Models,” in Public transportation quality of service: Factors, models, and applications, eds. Dell’olio, L., Ibeas, A., De Oña, J., and De Oña, R. (Netherlands: Elsevier), 141–154.
Dema, D., Klibthong, S., and Srisurakul, T. (2022). Exploring Bhutanese teachers’ perceptions of differentiated instruction in inclusive schools in Bhutan. Australas. J. Spec. Inclusive Educ. 46, 88–100. doi: 10.1017/jsi.2022.4
Dendup, P. (2023). “English medium instruction in the Bhutanese education system: a historical journey” in English as a medium of instruction in South Asia. eds. R. A. Giri, A. Padwad, and M. M. N. Kabir (London: Routledge), 145–155.
Dorji, T., and Nima, P. (2021). Evaluating content validity of an instrument to assess teachers’ practice of differentiated instruction (IATPDI). Bhutan J. Res. Dev. 10, 75–96. doi: 10.17102/bjrd.rub.10.2.006
Fu, Y., Wen, Z., and Wang, Y. (2021). A comparison of reliability estimation based on confirmatory factor analysis and exploratory structural equation models. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 82, 205–224. doi: 10.1177/00131644211008953
Gaitas, S., and Alves Martins, M. (2016). Teacher perceived difficulty in implementing differentiated instructional strategies in primary school. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 21, 544–556. doi: 10.1080/13603116.2016.1223180
George, D., and Mallery, P. (2019). IBM SPSS statistics 26 step by step: A simple guide and reference. New York: Routledge.
Gheyssens, E., Consuegra, E., Engels, N., and Struyven, K. (2020a). Good things come to those who wait: the importance of professional development for the implementation of differentiated instruction. Front. Educ. 5, 1–14. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.00096
Gheyssens, E., Coubergs, C., Griful-Freixenet, J., Engels, N., and Struyven, K. (2020b). Differentiated instruction: the diversity of teachers’ philosophy and praxis to adapt teaching to students’ interests, readiness and learning profiles. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 26, 1383–1400. doi: 10.1080/13603116.2020.1812739
Gheyssens, E., Griful-Freixenet, J., and Struyven, K. (2023). “Differentiated instruction as an approach to establish effective teaching in inclusive classrooms” in Effective teaching around the world: Theoretical, empirical, methodological and practical insights. eds. R. Maulana, M. Helms-Lorenz, and R. M. Klassen (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 677–689.
Gibbs, K., and McKay, L. (2021). Differentiated teaching practices of Australian mainstream classroom teachers: a systematic review and thematic analysis. Int. J. Educ. Res. 109:101799. doi: 10.1016/j.ijer.2021.101799
Glenn, C. B. (2007). “Critical consciousness and pedagogy: Reconceptualizing student-centered dialogue as educational practice” in The Praeger handbook of education and psychology, vol. 4. eds. J. L. Kincheloe and R. A. Horn (Steinberg, USA: Praeger Publishers), 755–767.
Goodboy, A. K., and Martin, M. M. (2020). Omega over alpha for reliability estimation of unidimensional communication measures. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 44, 422–439. doi: 10.1080/23808985.2020.1846135
Goretzko, D., Siemund, K., and Sterner, P. (2024). Evaluating model fit of measurement models in confirmatory factor analysis. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 84, 123–144. doi: 10.1177/00131644231163813
Gyeltshen, K., and Zangmo, S. (2020). “School education in Bhutan” in Handbook of education Systems in South Asia. eds. P. M. Sarangapani and R. Pappu (Singapore: Springer), 479–508.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., and Anderson, R. E. (2009). Multivariate data analysis. 7th Edn. United States: Prentice-Hall.
Hall, T. (2002). Differentiated instruction: effective classroom practices report. National Center on Accessing the General Curriculum, (US Department of Education), 1–9.
Haniya, S., and Roberts-Lieb, S. (2017). “Differentiated learning: diversity dimensions of e-learning” in E-learning ecologies. eds. B. Cope and M. Kalantzis (New York: Routledge), 183–206.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 43, 115–135. doi: 10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Hu, L., and Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 6, 1–55. doi: 10.1080/10705519909540118
Joseph, S., Thomas, M., Simonette, G., and Ramsook, L. (2013). The impact of differentiated instruction in a teacher education setting: successes and challenges. Int. J. High. Educ. 2, 28–40. doi: 10.5430/ijhe.v2n3p28
Kalkbrenner, M. T. (2021). Alpha, omega, and H internal consistency reliability estimates: reviewing these options and when to use them. Couns. Outcome Res. Eval. 14, 77–88. doi: 10.1080/21501378.2021.1940118
Kapusnick, R. A., and Hauslein, C. M. (2001). The ‘silver cup’ of differentiated instruction. Kappa Delta Pi Rec. 37, 156–159. doi: 10.1080/00228958.2001.10518493
Kinley,, Reeta, R., and Chophel, S. (2021). “A journey towards STEM education in Bhutan: an educational review” in STEM education from Asia: Trends and perspectives. eds. T. W. Teo, A. Tan, and P. Teng (London: Routledge), 49–62.
Kupffer, R., Frick, S., and Wetzel, E. (2024). Detecting careless responding in multidimensional forced-choice questionnaires. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 84, 887–926. doi: 10.1177/00131644231222420
Letzel, V., Pozas, M., and Schneider, C. (2020). ‘It’s all about the attitudes!’–introducing a scale to assess teachers’ attitudes towards the practice of differentiated instruction. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 6, 1–15. doi: 10.1080/13603116.2020.1862402
Levy, H. M. (2008). Meeting the needs of all students through differentiated instruction: helping every child reach and exceed standards. The Clearing House: J. Educ. Strateg. Issues Ideas 81, 161–164. doi: 10.3200/tchs.81.4.161-164
Lewis, S. G., and Batts, K. (2005). How to implement differentiated instruction? Adjust, adjust, adjust: North Carolina project begins with encouragement from administrators. J. Staff. Dev. 26, 26–31.
Lynn, M. R. (1986). Determination and quantification of content validity. Nurs. Res. 35, 382–386. doi: 10.1097/00006199-198611000-00017
Ministry of Education (2020a). Bhutan professional standards for teacher. Thimphu: Ministry of Education.
Ministry of Education (2020b). Bhutan education blue print 2014–2024: Rethinking education. Thimphu: Ministry of Education.
Mueller, R. O., and Hancock, G. R. (2015). “Factor analysis and latent structure analysis: confirmatory factor analysis” in International encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences: Second Edition. ed. J. D. Wrigth (Netherlands: Elsevier), 686–690.
Onyishi, C. N., and Sefotho, M. M. (2021). Differentiating instruction for learners’ mathematics self-efficacy in inclusive classrooms: can learners with dyscalculia also benefit? S. Afr. J. Educ. 41, 1–15. doi: 10.15700/saje.v41n4a1938
Policy and Planning Division (2023). Annual education statistics: 2023. Thimphu: Ministry of Education and Skills Development.
Polit, D. F., and Beck, C. T. (2006). The content validity index: are you sure you know what’s being reported? Critique and recommendations. Res. Nurs. Health 29, 489–497. doi: 10.1002/nur.20147
Polit, D. F., Beck, C. T., and Owen, S. V. (2007). Is the CVI an acceptable indicator of content validity? Appraisal and recommendations. Res. Nurs. Health 30, 459–467. doi: 10.1002/nur.20199
Porta, T., Todd, N., and Gaunt, L. (2022). ‘I do not think I actually do it well’: a discourse analysis of Australian senior secondary teachers’ self-efficacy and attitudes towards implementation of differentiated instruction. J. Res. Spec. Educ. Needs 22, 297–305. doi: 10.1111/1471-3802.12568
Powdyel, T. S. (2016). “Non-formal education in Bhutan: origin, evolution, and impact” in Education in Bhutan: Culture, schooling, and gross national happiness, vol. 36. eds. M. Schuelka and T. Maxwell (Singapore: Springer), 169–180.
Pozas, M., Letzel, V., and Schneider, C. (2019). Teachers and differentiated instruction: exploring differentiation practices to address student diversity. J. Res. Spec. Educ. Needs 20, 217–230. doi: 10.1111/1471-3802.12481
Pozas, M., and Schneider, C. (2019). Shedding light on the convoluted terrain of differentiated instruction (DI): proposal of a DI taxonomy for the heterogeneous classroom. Open Educ. Stud. 1, 73–90. doi: 10.1515/edu-2019-0005
Prast, E. J., Van de Weijer-Bergsma, E., Kroesbergen, E. H., and Van Luit, J. E. H. (2015). Readiness-based differentiation in primary school mathematics: expert recommendations and teacher self-assessment. Frontline Learn. Res. 3, 90–116. doi: 10.14786/flr.v3i2.163
Puzio, K., Colby, G. T., and Algeo-Nichols, D. (2020). Differentiated literacy instruction: boondoggle or best practice? Rev. Educ. Res. 90, 459–498. doi: 10.3102/0034654320933536
Rachmawati, M. A., Nu’man, T. M., Widiasmara, N., and Wibisono, S. (2016). Differentiated instruction for special needs in inclusive schools: a preliminary study. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 217, 585–593. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2016.02.053
Rahmasari, B. S., Munir, A., and Adi Nugroho, H. M. (2024). The role of peer tutoring integrated with KWL charts in the development of students’ inferential skills. Cogent Educ. 11:2335810. doi: 10.1080/2331186X.2024.2335810
Reis, S. M., McCoach, D. B., Coyne, M., Schreiber, F. J., Eckert, R. D., and Gubbins, E. J. (2007). Using planned enrichment strategies with direct instruction to improve reading fluency, comprehension, and attitude toward reading: an evidence-based study. Elem. Sch. J. 108, 3–23. doi: 10.1086/522383
Richards-Usher, L. (2013). Teachers perception and implementation of differentiated instruction in the private elementary and middle schools [Doctoral dissertation]. Capella University.
Roos, J. M., and Bauldry, S. (2022). Confirmatory factor analysis: quantitative applications in the social sciences, 189 (SAGE publications). Available at: https://us.sagepub.com/en-us/nam/confirmatory-factor-analysis/book269092#preview (Accessed May 12, 2024).
Rosseel, Y. (2012). Lavaan: an R package for structural equation modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 48, 1–36. doi: 10.18637/jss.v048.i02
Roy, A., Guay, F., and Valois, P. (2013). Teaching to address diverse learning needs: development and validation of a differentiated instruction scale. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 17, 1186–1204. doi: 10.1080/13603116.2012.743604
Royal Education Council (2009). The quality of school education in Bhutan – Reality and opportunities. Bhutan: Thimphu.
Rubio, D. M., Berg-Weger, M., Tebb, S. S., Lee, E. S., and Rauch, S. (2003). Objectifying content validity: conducting a content validity study in social work research. Soc. Work. Res. 27, 94–104. doi: 10.1093/swr/27.2.94
Saeed, S., and Zyngier, D. (2012). How motivation influences student engagement: a qualitative case study. J. Educ. Learn. 1, 252–267. doi: 10.5539/jel.v1n2p252
Santangelo, T., and Tomlinson, C. A. (2009). The application of differentiated instruction in postsecondary environments: benefits, challenges, and future directions. Int. J. Teach. Learn. High. Educ. 20, 307–323. Available at: https://www.isetl.org/Ijtlhe/ijtlhe-article-view.php?mid=366
Sarmiento-Campos, N. V., Lázaro-Guillermo, J. C., Silvera-Alarcón, E. N., Cuellar-Quispe, S., Huamán-Romaní, Y. L., Apaza, O. A., et al. (2022). A look at Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory (SCT): the effectiveness of scaffolding method on EFL learners’ speaking achievement. Educ. Res. Int. 2022, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2022/3514892
Shareefa, M., Moosa, V., Zin, R. M., Abdullah, N. Z. M., and Jawawi, R. (2019). Teachers’ perceptions on differentiated instruction: do experience, qualification and challenges matter? Int. J. Learn. Teach. Educ. Res. 18, 214–226. doi: 10.26803/ijlter.18.8.13
Shrotryia, V. K., and Dhanda, U. (2019). Content validity of assessment instrument for employee engagement. SAGE Open 9, 1–7. doi: 10.1177/2158244018821751
Sousa, D. A., and Tomlinson, C. A. (2018). Differentiation and the brain: How neuroscience supports the learner-friendly classroom. 2nd Edn. Bloomington, IN: Solution Tree Press.
Tabachnick, B. G., and Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using multivariate statistics: Pearson new international edition. (6th ed) Edn. United States: Pearson Education.
Tavakol, M., and Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2, 53–55. doi: 10.5116/ijme.4dfb.8dfd
Tomlinson, C. A. (2001). How to differentiate instruction in mixed-ability classrooms. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Tomlinson, C. A. (2014). The differentiated classroom: Responding to the needs of all learners. 2nd Edn. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
Tomlinson, C. A., Brighton, C., Hertberg, H., Callahan, C. M., Moon, T. R., Brimijoin, K., et al. (2003). Differentiating instruction in response to student readiness, interest, and learning profile in academically diverse classrooms: a review of literature. J. Educ. Gift. 27, 119–145. doi: 10.1177/016235320302700203
UNICEF. (2017). Inclusive education: including children with disabilities in quality learning: what needs to be done. Inclusive Education, 4. Available at: https://www.unicef.org/eca/sites/unicef.org.eca/files/IE_summary_accessible_220917_brief.pdf (Accessed May, 18, 2024).
Williams, R. C. (2013). “Differentiated instruction and inquiry-based learning in middle school and high school social studies” in Differentiated instruction: Content area applications and other consideration for teaching grades 5–12 in the twenty-first century. ed. E. F. Sparapani (United States: University Press of America), 127–140.
Williams, M. K. (2017). John Dewey in the 21st century. J. Inq. Action Educ. 9, 91–102. Available at: https://digitalcommons.buffalostate.edu/jiae/vol9/iss1/7
Keywords: differentiated instruction, confirmatory factor analysis, content validity index, Bhutanese teachers, DI instrument, education, Delphi method, psychometric properties
Citation: Dorji T and Nima P (2024) Psychometric properties of an instrument to assess teachers’ practice of differentiated instruction (IATPDI): a confirmatory factor analysis on Bhutanese teachers’ data. Front. Educ. 9:1445865. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1445865
Edited by:
Janet Clinton, The University of Melbourne, AustraliaReviewed by:
Andra Diaconescu, Politehnica University of Timișoara, RomaniaRuth Aston, The University of Melbourne, Australia
Katina Tan, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia, in collaboration with reviewer RA
Copyright © 2024 Dorji and Nima. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tshering Dorji, dHNoZXJpbmdkb3JqaTg2QGVkdWNhdGlvbi5nb3YuYnQ=
 Tshering Dorji
Tshering Dorji Pelden Nima
Pelden Nima