- 1Department of Agricultural Extension and Education, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
- 2Department of Agricultural Extension and Education, Zabol University, Zabol, Iran
Today, educators experience complicated challenges in their job. The stress and burnout of educators has turned into a growing concern. In recent years, the challenges have been increased by the COVID-19 epidemic, and educators have been forced to use virtual methods for education in this situation. Under these conditions, the flexibility and resilience of educators can help people mostly in adaptability, increasing tolerance and optimal use of conditions for better learning. The present study is aimed to analyze the resilience of educators during the COVID-19 pandemic in Iran’s agricultural higher education system. The statistical population of the study were 3,640 educators of agricultural faculties of state universities (N = 3,640). Using the Krejcie and Morgan’s table and stratified random sampling with proportional assignment 347 educators were selected as the sample (n = 347). The data collection instrument was a researcher-made questionnaire whose validity was verified by calculating average variance extracted (AVE) and its reliability was confirmed by calculating Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability (CR). The collected data were analyzed using structural equation modeling and Smart PLS3.3.9 software. It was found that four investigated factors, motivational-emotional, technical skill, social, and supportive factors had positive and significant relationship with the resilience behavior of educators. Among them, motivational-emotional factors had the highest effect on the educators’ resilient behavior. Based on the findings of the research, practical recommendations have been presented to enhance the educators’ resilient behavior.
Introduction
In March 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic affected countries globally. COVID-19 is a pandemic that has severely affected human life and the global economy. This virus has spread in more than 213 countries and regions and has infected more than 695.7 million people and resulting in the death of more than 6.91 million people by October 2023 (Worldometer, 2023). This disease not only challenged the progress related to health care, but also led into disruptions in the traditional education process in educational systems, including the face-to-face higher education system, due to the need for social distancing (Mestry, 2023). Nearly 1.7 billion learners in more than 200 countries were at the risk of the COVID-19 pandemic, making it the largest disruption to education systems in human history. According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (2020), at the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, schools and universities worldwide were closed for 87% of enrolled students and for more than 60 million teachers and academics (Mestry, 2023). Also, according to the UNESCO report, the corona virus affected about 81 million students in the higher education system globally. The closure of schools and universities, as well as high social and economic costs for individuals and societies, has also brought adverse consequences for learners and educators. One of its most important outcomes is the disruption in the learning process, which has resulted into the lack of access of learners to growth and development opportunities (UNESCO, 2020). In Iran, 90% of the population of educators and students of higher education were affected by this crisis at the beginning of this disease, and it was increasing with the spread of the COVID-19 and put the lives of all people at the risk (Biriya, 2022). One of the higher education sectors that has been highly affected by the pandemic is the higher education system in agriculture field. The agricultural higher education system in Iran contains universities affiliated to the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology, Payam-e Noor University, University of Applied Science and Technology, Vocational/Polytechnic University, non-governmental higher education institutions and universities and higher education institutions affiliated to other institutions. There are 501 higher education institutes for agriculture and natural resources in Iran. Also, 220 fields of higher education in agriculture and natural resources at the associate level, 175 fields at the discrete bachelor’s, 398 fields at the bachelor level, 225 fields at the discrete master’s and 128 fields with the doctorate degree are presented in these institutes. Also, the total number of majors in Iran’s agriculture and natural resources higher education system is 4,071 (Higher Education Development Office, 2023). Based on its experimental and practical nature, this educational system is obliged to simulate the learning environment with the real world in order to provide in-depth and high-quality education to the learners in accordance with the needs of the society. With the prevalence of the coronavirus disease in Iran, educational systems showed high tendency toward virtual education in order to continue teaching and learning (Verawardina et al., 2020). As one of the important elements of educational systems, educators were required to use of digital tools that support e-learning as a part of the crisis response protocol to persist learning (Bozkurt and Sharma, 2020; Thompson and Copeland, 2020), while from the beginning, they did not like virtual education and most of them did not receive enough training in this field. Although the universities attempted to support their educators and educate them in this area, these trainings were not comprehensive and were mostly aimed at people who were interested in e-learning. Under such emergency conditions, educators face emotional and psychological confusion while teaching (Crompton et al., 2021). Feeling isolated due to being away from colleagues is another psychological impact of these conditions (Trikoilis and Papanastasiou, 2020). Several factors show that educators showed increased burnout during the pandemic (Zamarro et al., 2022; Mestry, 2023). The need for support in every aspect of the teaching world is crucial for the success and longevity of an educators (Samadi, 2020).
The review of literature shows that there is much focus on resilience as one of the factors that mitigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic (Treviño et al., 2020), because higher resilience is associated with the use of healthy coping strategies, greater subjective well-being, and fewer symptoms of mental illness (Zhang et al., 2020; Finstad et al., 2021; Gundogan, 2021; Li et al., 2021; Verdolini et al., 2021). A review of the resilience literature shows several definitions for educators’ resilience, but a definition that includes almost the main components of different definitions defines educator’s resilience as a process of the capacity of positive adaptation and continuous professional commitment and growth in challenging contexts (Beltman and Mansfield, 2018). The results of the research by Giovannini et al. (2020) showed that in a resilient society, not only people are important, but also the support of institutions, suitable formulated policies, social ties, etc. are of great importance for success. In a study done by Bartusevičienė et al. (2021), the perception of students and professors regarding the change from traditional education to online learning during the COVID-19 was examined, and it was stated that resilience depends on the availability of resources, continuous professional development, continuous communication with educators and learners, support networks, adaptation and establishment of knowledge base. Sánchez Ruiz et al. (2021) analyzed the students’ perception of the educational resilience of a university and showed that blended learning methods facilitate the resilience of the university and enhance the quality of learning. In systems in which blended learning was practiced before the start of the pandemic, resilience and adaptability were greater based on the opinion of learners. In a study, Pokhrel and Chhetri (2021) emphasized the role of e-learning tools, the view of educators and students, access challenges, affordability, and creative learning opportunities as factors influencing resilience. In previous studies, the relationship between resilience and psychological well-being, life satisfaction and positive affect has also been taken into consideration (Thajil and AL-Abrrow, 2023; Rodrigue et al., 2023; Nutini, 2023). The results of such studies are instructive, but more research is required to better understand the resilience of educators and the factors influencing it in the crisis of the COVID-19 pandemic (Zadok-Gurman et al., 2021). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the resilience of agricultural educators during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this regard, this research attempted to analyze the resilient behavior of the educators of the agricultural higher education system based on the challenges related to the COVID-19 crisis, to examine the factors affecting it, and to propose the mechanisms to improve their resilient behavior.
Theoretical framework and research hypothesis
In the higher education system, educator and learner are two important human factors. Thus, educators play a significant role in the teaching and learning process. Normally, the duties of educators are effective teaching and research (Saadvandi et al., 2018; Devlin and Samarawickrema, 2022); but in critical situations like the COVID-19 disease, which changed the total educational system of the world and increased the use of the virtual education in the higher education institutes to continue teaching and learning, the duties of the teacher include effective social services besides effective teaching and research (Purba et al., 2022; Klusman et al., 2023). Under critical situations, in addition to making efforts to achieve educational and research goals, educators are responsible for their students and should monitor their mental and emotional conditions. Resilience, which is defined as the efficient recovery of educators’ strength and morale in case of difficulties, is closely related to a strong sense of self-efficacy and motivation for teaching. Therefore, it is necessary to identify various factors that influence this process for the occurrence of resilient behavior (Gu and Day, 2007; Raghunathan et al., 2022). In the context of resilience, we can talk about risk and protective factors. In this case we are talking about risk factors. In this sense, factors affecting teachers’ resilience behavior have been investigated in different fields. In these researches, various factors such as job stress, health promotion behavior, sleep disorder, social support, knowledge, intention to prepare, macro and physical ergonomics, attitude perceived severity, self-efficacy, response effectiveness, response cost, and subjective norms in determining protective behavior during natural disasters, which play an important role in influencing educators’ resilience behavior, have been identified. In our research, we used the resilience framework developed by van Breda (2018) and Mansfield (2012) to design the educator’s resilience behavior framework. In their study van Breda (2018) and Mansfield (2012) believe that adversity evoke resilience as a process. As a process resilience is affected by some adversities. Conceptually, resilience is a process that leads to an outcome. Adapted from the mentioned framework Han (2019) suggests four dimensions of teacher resilience and those being emotional, motivational, social and profession-related. Each of these dimensions has various aspects. According to the information presented, we have formulated four research hypotheses to further explore the dimensions of educator resilience. These hypotheses are designed to investigate the relationships between various factors and the resilience behavior of educators. The following section will detail these hypotheses and the rationale behind each.
Hypothesis 1: There is a positive relationship between motivational-emotional factors and educator’s resilience behavior.
One of the most important factors in learning is educators’ motivation to teach (Han, 2019). This motivation becomes crucial in unusual conditions, such as during the COVID-19 pandemic, when the teaching process is disrupted by stress, tension, and lack of self-confidence. In such scenarios, motivation can help educators overcome these challenges. A lack of motivation and excitement among educators disrupts the teaching process in virtual environments. Therefore, higher motivation in teachers leads to better teaching and learning quality.
To further explore this relationship, our study examines motivational-emotional factors, which refer to the psychological resilience and emotional intelligence that educators need to effectively navigate and thrive in virtual learning environments. These factors include adaptability, self-confidence, motivation, conflict resolution, and the ability to address the emotional and attitudinal needs of learners. Such competencies are essential for fostering a supportive and effective educational experience, particularly during the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Hypothesis 2: There is a positive relationship between technical-skill factors and educator’s resilience behavior.
Educators are key elements in the development of inclusive education processes (Carew et al., 2019; Sharma et al., 2021). In addition to soft skills, hard skills are also crucial in the educational actions of educators. The COVID-19 pandemic has rapidly changed the education system, making Online Distance Learning (ODL) and Emergency Distance Learning (EDL) the norm, while traditional classroom teaching has become less common. Consequently, educators had to adapt to these technological changes and their impact on the teaching process.
To effectively adapt to the technological changes brought about by the pandemic, educators need to have positive attitudes toward technology, a willingness to learn, and the necessary skills to become qualified educators. Technical-skill competence has been highlighted in several studies even before the pandemic (Kiers et al., 2022). During the COVID-19 era, having such skills significantly impacts educators’ resilience.
Furthermore, to expand the range of educational opportunities available to learners, educators must achieve and maintain a certain degree of technological competence. This competence enables them to perform daily tasks such as communicating effectively with learners and colleagues via software and applications, recording and uploading course files and projects, preparing multimedia and self-learning content, using simulated environments for teaching practical courses (e.g., videos and virtual laboratories), managing the virtual classroom space, and efficiently defending student theses and dissertations.
Research has consistently demonstrated a strong correlation between teachers’ technological proficiency and student outcomes. For instance, studies by Zadok-Gurman et al. (2021) and Ang et al. (2022) have shown that teachers with higher levels of technical skills are better equipped to deliver high-quality instruction in virtual environments, leading to improved student achievement. Additionally, previous studies have also considered the relationship between technical-skill factors and resilience (Fernandes et al., 2021; Li, 2023).
In this study, technical factors refer to the comprehensive set of skills and competencies that enable educators to effectively integrate and utilize technology in their teaching practices. This includes the ability to adapt to digital tools and platforms, create and share educational content, and facilitate interactive and engaging virtual learning environments. These competencies are crucial for maintaining resilience and delivering high-quality education, especially in the context of the rapid technological changes brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Hypothesis 3: There is a positive relationship between social factors and educator’s resilience behavior.
Besides having skills, educators should also have social competence so that they can overcome the job stress caused by e-learning. Research findings indicate that the more educators’ subjectivity is based on having support and interacting with others, the more successful responses they show to psychological pressures and difficult situations (Ellis et al., 2020; Bernasco et al., 2021). In various studies, the relationship between social support and resilience has been mentioned (Permatasari et al., 2021; Koskela et al., 2020; Raghunathan et al., 2022).
Social factors in our study focus on the interactions and relationships that facilitate effective online learning environments. These factors emphasize the importance of meaningful interactions between educators and their colleagues, as well as between educators and learners. Social support within the educational community plays a crucial role in enhancing the virtual educational experience and fostering a collaborative and supportive learning environment.
Hypothesis 4: There is a positive relationship between supportive factors and educator’s resilience behavior.
Supporting educators includes all types of educational, psychological, emotional, supportive, and technical support. The educational support aims to help educators effectively teach e-learning courses in an educational environment. Educators need training and support to teach effectively by technology. They need more knowledge than the technical and operational aspects of using technology. The training and support of educators should definitely address how to use technology to improve learning and overall performance (Hepp et al., 2015). In addition to achieving basic skills and facilitating the easy use of technologies in the educational programs, it is required for educators to be aware of all available resources and policies set forth by the institution. Some of these resources include: library (especially databases and electronic document delivery services), technical support (education design, video/graphics production, help desk and software tools access), and providing extrinsic rewards such as salary, merit pay, and promotion of educators under the difficult conditions of electronic education. Furthermore, in online learning that occurs during crises similar to the COVID-19 pandemic, educators need more support facilities to promote the teaching process (Hikam, 2020). In previous studies, the relationship between supportive factors and resilience behavior has been examined (Priolo Filho et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021).
Family support plays a crucial role in enhancing resilience by providing a stable and supportive environment. Research has shown that caring and supportive relationships within the family can significantly bolster an individual’s resilience by creating a sense of love, trust, and encouragement (Theiss, 2018). Maintaining a peaceful home environment is particularly important for educators, as it helps them stay concentrated on their work and manage the stresses associated with online teaching.
Supporting factors in our study refer to the institutional and familial resources and assistance that enhance educators’ capabilities in online teaching. These include technical and hardware support, training, and resources provided by the university and family. Familial support, such as maintaining a peaceful home environment, is crucial for helping educators stay concentrated on their work. Such support mechanisms are essential for improving the quality of virtual education, ensuring effective assessments, and fostering a resilient educational environment.
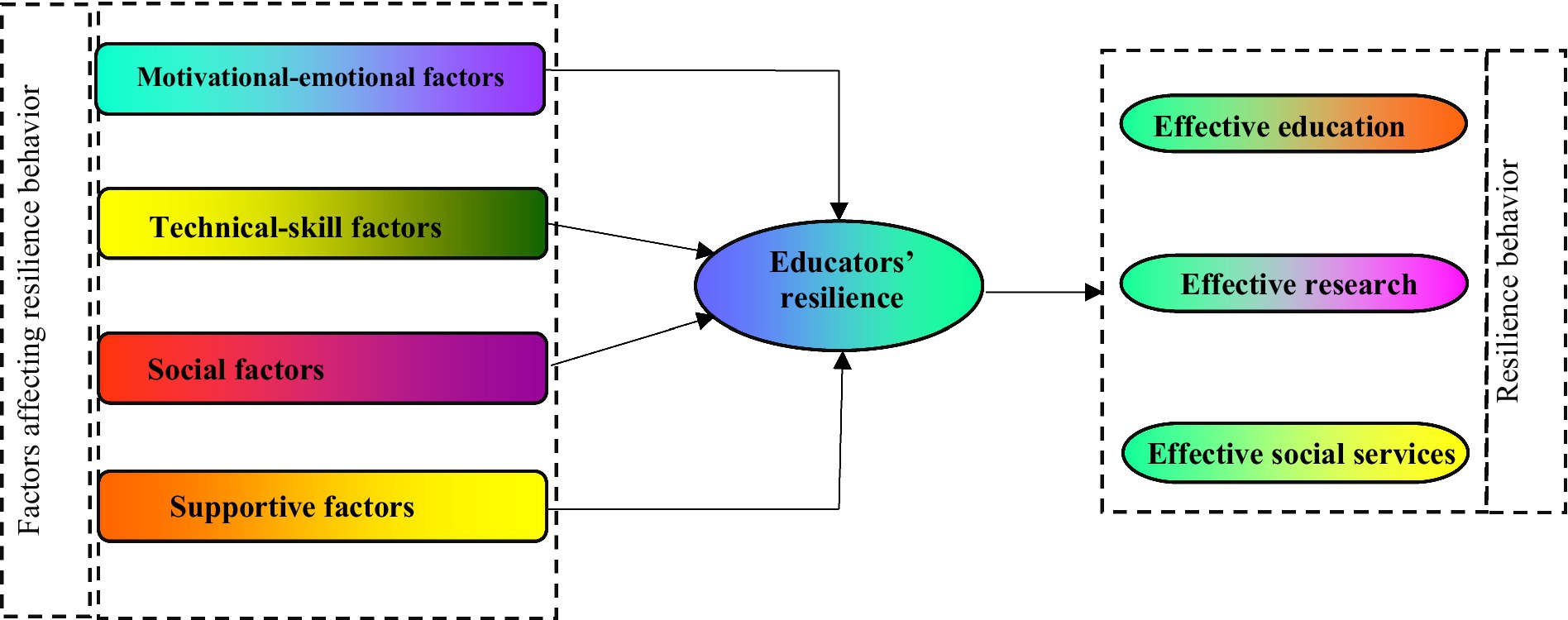
As illustrated in Figure 1, the conceptual framework of the research shows that motivational-emotional, technical-skill, social, and supportive factors significantly influence the resilient behavior of educators. The resilient behavior of educators is further characterized by three key indicators: effective education, research, and social services.
Research method
From the paradigmatic aspect the research is quantitative. It is non-experimental in terms of variables control and is applied in terms of purpose. In terms of the data analysis, it is descriptive, correlational and causal-relational which has done through survey method.
Statistical population, sample size and sampling method
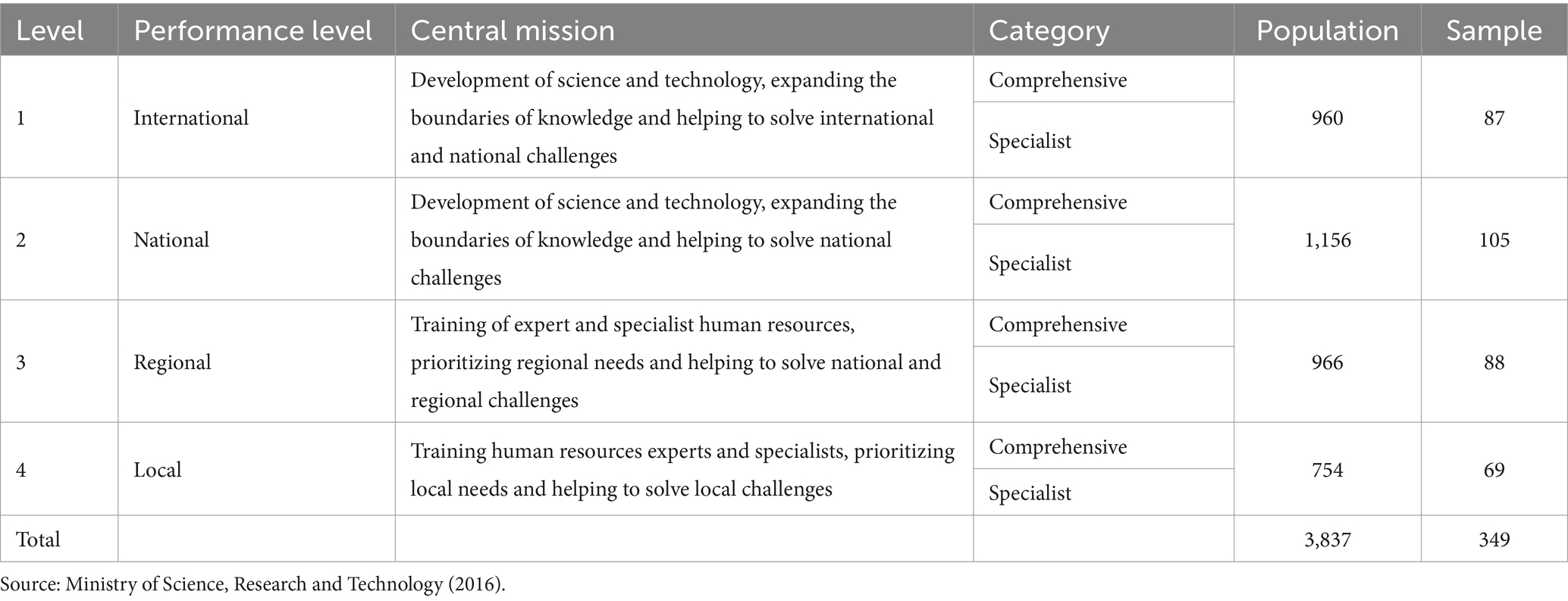
The statistical population of the research includes 3,837 full-time faculty members in the agricultural faculties of Iran’s state universities. The sample size was estimated as 349 using Krejcie and Morgan’s table (Krejcie and Morgan, 1970), and finally 288 people completed the research questionnaires (return rate: 82.5%). To select research samples, the ranking of universities and state higher education institutions was used. Iran’s Ministry of Science, Research and Technology has ranked state universities and institutions of higher education in four levels of performance (international, national, regional and local) and in two comprehensive and specialized categories according to their main missions (Iran’s Ministry of Science Research and Technology, 2016). In order to select the samples, a stratified random method with proportional assignment was applied. Thus, the universities located in each of the international, national, regional and local levels were considered as the constituent classes of the statistical population, and from each class, a few universities (having faculty of agriculture) were randomly selected from each category of comprehensive and specialized for sample selection (Table 1).
Research instrument and data collection methods
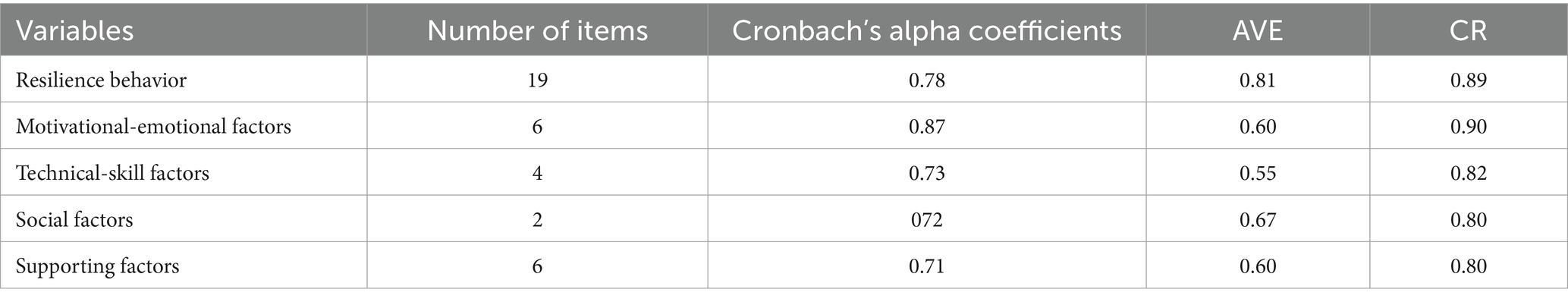
Questionnaire was the main instrument of data collection. Research variables were measured using a five-point Likert scale from “very little = 1” to “very much = 5.” The various sections of the questionnaire include personal and professional factors, the resilient behavior of educators including effective education, effective research and effective social services, and the factors affecting the educators’ resilient behavior at the risk of the COVID-19 pandemic included motivational-emotional factors, technical-skill factors, social and supportive factors. In order to determine the validity of the research questionnaire, besides seeking opinions from experts (face validity), the average variance extracted (AVE) was applied to determine the degree of convergent validity. The reliability of the questionnaire was verified by calculating Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability (CR). Table 2 shows the different sections of the questionnaire, the number of items in each section, and the values related to validity and reliability.
As shown in Table 2, the values of Cronbach’s alpha coefficients and composite reliability of all studied variables are higher than 0.7 and acceptable. Convergent validity also exists when AVE is greater than 0.5. As shown in the table, all the variables have good convergence.
Data analysis
In this study, percentage, mean and standard deviation statistics were applied to describe the variables using SPSS26 software and confirmatory factor analysis method with the partial least squares approach was used for hypothesis testing with Smart PLS3.3.9 software.
Results
Based on the results, the average age of the respondents was 45.70 with a standard deviation of 9.497. More than 3/4 of the respondents in this study (75.7%) were men. The majority of respondents were married (251 individuals, equivalent to 86.8 percent). The highest frequency is related to educators with experience less than or equal to 10 years (53.0%). Based on academic rank, nearly half of the educators were assistant professor (42.8%). Based on being infected with COVID-19, the results showed that a little more than half of the respondents were infected with COVID-19 (51.4%). More than half of the respondents (53.5%) have experienced the death of friends and relatives due to the COVID-19 disease.
According to another section of the results of the research, PowerPoint presentation has been used by educators more than other methods (63.2%). “Using simulation and model software” was also the least used method of online education. Based on the use of technology tools for online education, the results showed that creating groups in WhatsApp software was the highly applied task among different online education tools (45.5%). The results related to the existence of educational facilities in the place of residence of the educators indicated that the majority of them did not have access to the appropriate bandwidth to provide education and only 30.9% admitted that they had this facility. Examining the opinions of the respondents about the benefits of electronic education indicated that most of them believe that “management of teaching time and place” and mitigating commuting costs are among the important benefits of e-learning. The results of examining the views of the respondents regarding the disadvantages of electronic education demonstrated that most of them selected “lack of in-person communication with learners and other educators” as one of the disadvantages of e-learning. Regarding the continuation of e-learning after the quarantine period, it was found that the majority of respondents agreed with the use of electronic education after this period as “a substitute for the classroom in special conditions [air pollution, snowfall, etc. (68 percent) and 49 percent of the educators considered the use of electronic training as “a complement to in-person training” suitable]. However, most of the respondents did not agree with the replacement of this type of education as the main method of academic education and only 3.8% agreed with this method. Considering the strengths and weaknesses of virtual education, a total of 46.5% of the respondents chose the resumption of face-to-face education as a method of academic education in the post-corona era, and only 2% of educators selected e-learning.
Evaluation of measurement part of the model
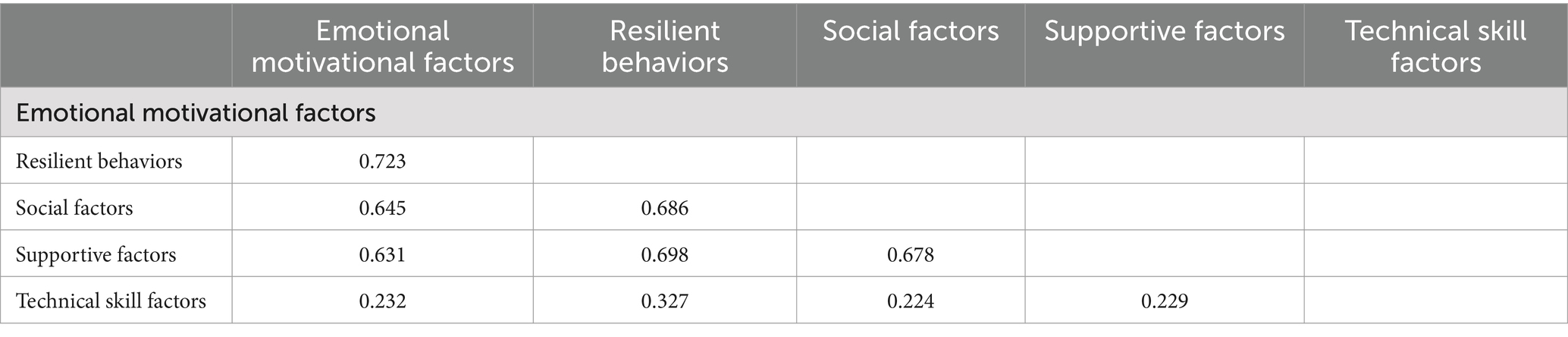
This section of the findings is presented in order to evaluate the relationship between indicators and latent variables of the model. For this purpose, convergent and divergent validity was calculated and confirmatory factor analysis was used to verify the components and items proposed to measure each variable. Convergent validity was verified by calculating the average variance extracted (AVE), which was mentioned in the research methodology section. In order to evaluate the divergent validity, the HTMT criterion was used. Coefficients below 0.9 show acceptable divergence between variables (Table 3).
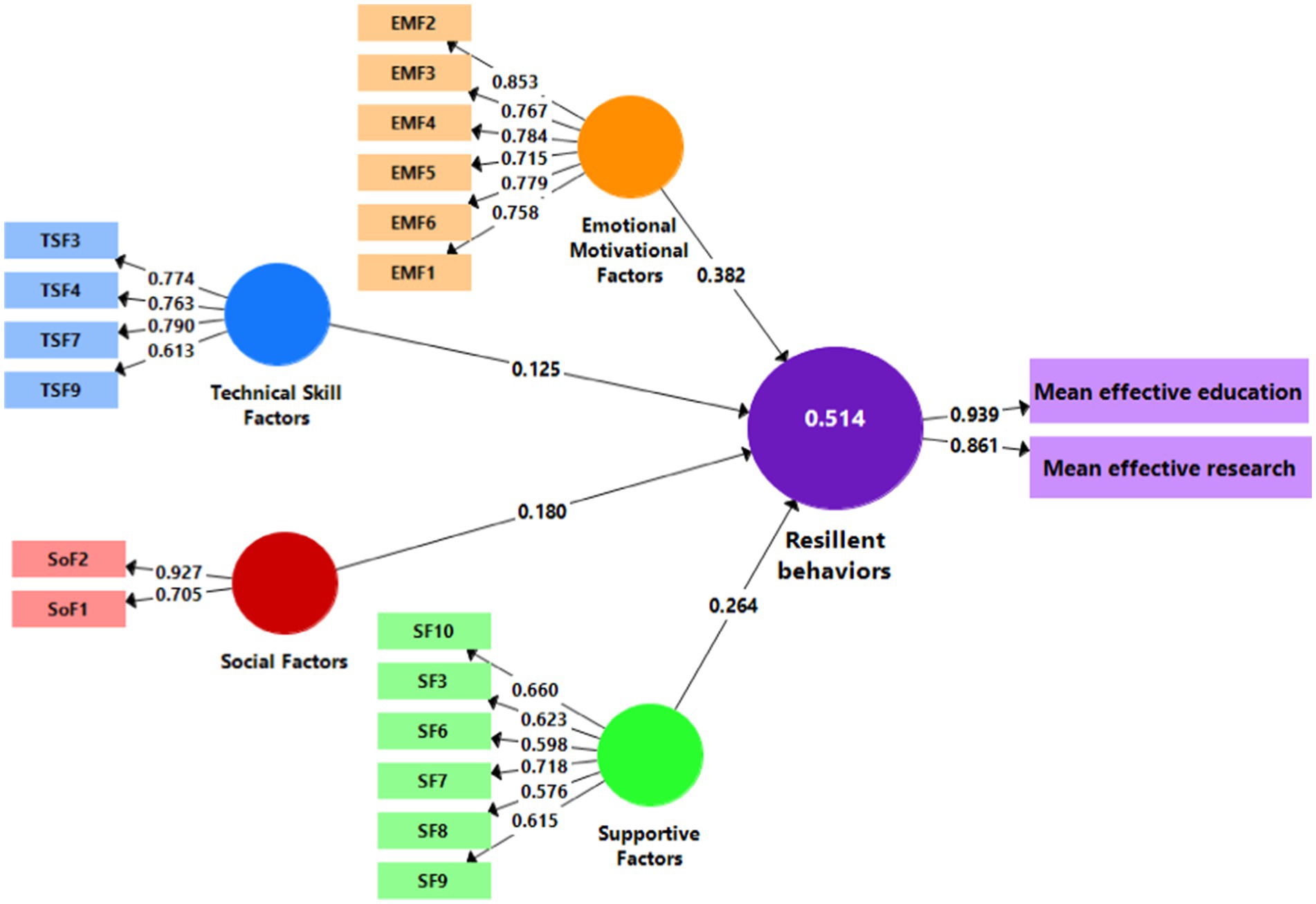
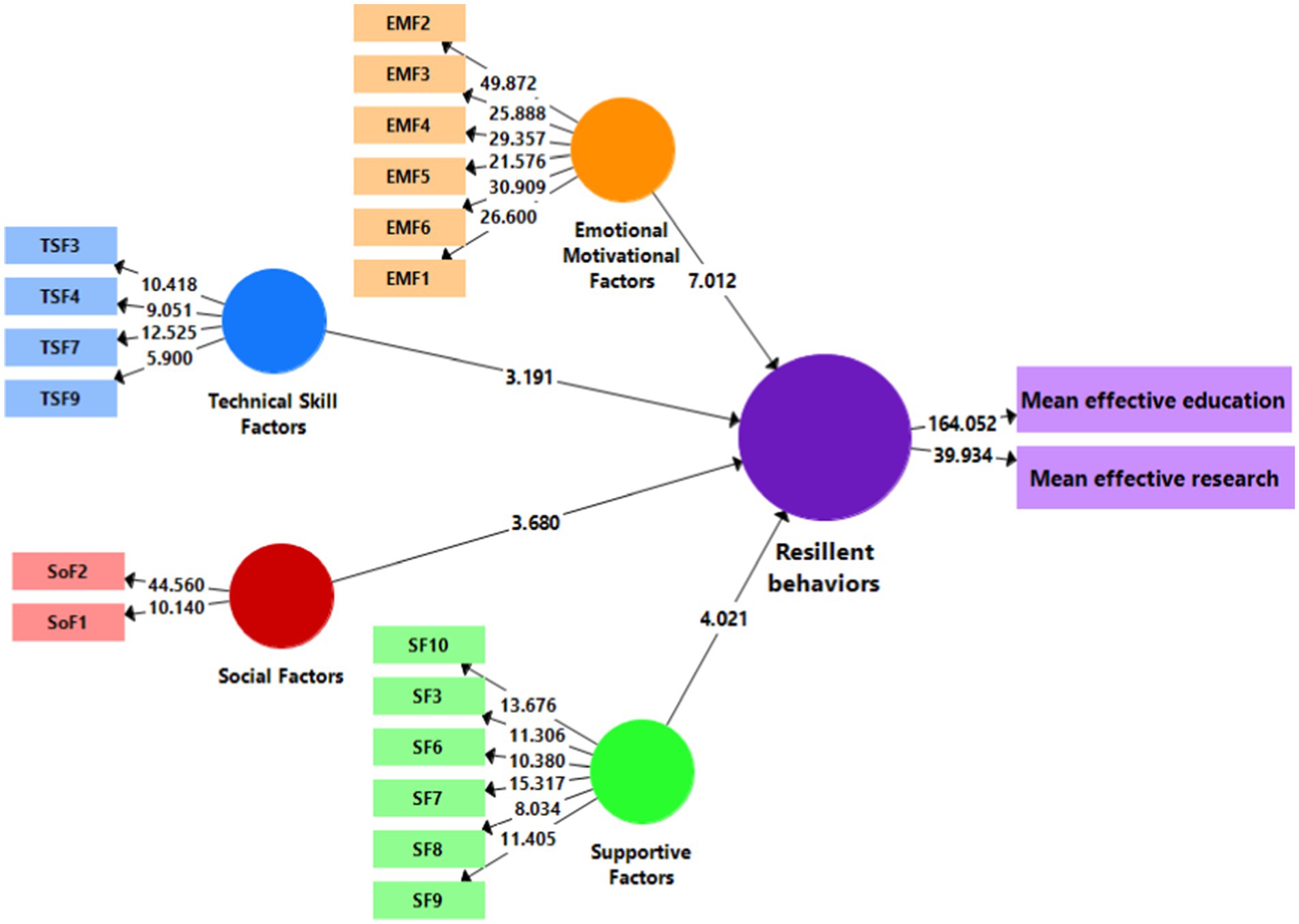
In the following, in order to confirm the components and items proposed to measure different concepts and variables, the confirmatory factor analysis was used with the partial least squares approach using Smart PLS software. Therefore, the accuracy of the indicators or measures selected for each category was evaluated to see if the measures have adequate accuracy to measure their structure or not? Figure 2 shows the significant values of the analysis model of the educators’ resilience in the agricultural higher education system during the COVID-19 pandemic in the standard estimation mode. Figure 3 indicates the t-values for the factors of each structure and Table 4 shows both of the obtained values for this model. As shown, all the factors have factor loading values higher than 0.5 and significant. According to these interpretations, it can be stated that the measurement model is homogeneous and the reliability of the indicator or measures is supported. It should be noted that a significant level of 1% was obtained for all factors.
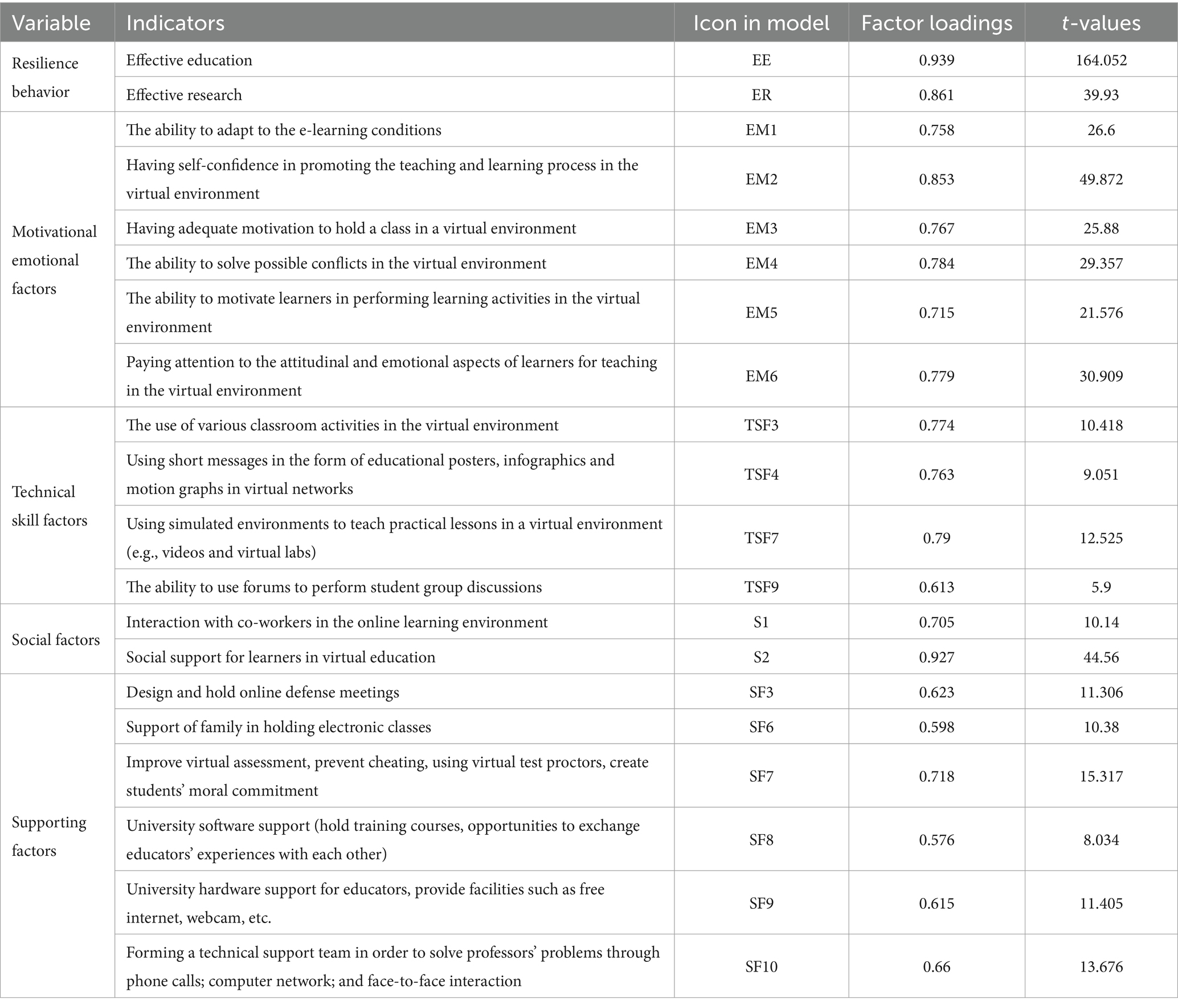
Table 4. Factor loadings and t-values for the indicators of each variable in the educators’ resilience model in the agricultural higher education system.
Evaluation of the whole model
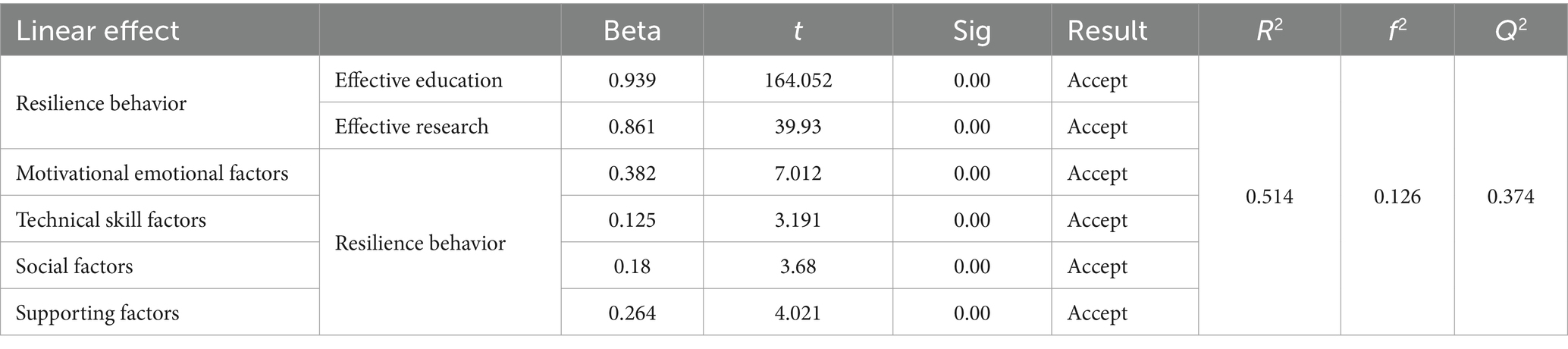
In this section, to analyze the resilient behavior of educators in the higher education system, the quality of the selected structural model was evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R2), effect size fit index (F2), Steven-Geisser index (Q2) and goodness of fit index (GOF) (Table 5). The R2 value is about the endogenous variables of the model, which shows the influence of an exogenous variable on an endogenous variable as a criterion for weak, medium and strong values. Effective education and effective research are three endogenous variables that have been confirmed as the resilient behavior of educators. The coefficient of determination R2 for this variable is estimated as 0.514, which is moderately strong and indicates a good fit of the model. The F2 effect size fit index, which is used for exogenous variables, was calculated as 0.126 for four motivational-emotional, technical-skill, social and support variables and has a moderate predictive power. The fit index of the structural model Q2 determines the predictive power of the model in endogenous structures. If this value is positive, it shows that the fit of the model is good and the model has good predictive power. Q2 for this model is estimated at 0.374, which indicates the good fit of the model and the appropriate predictive power (Table 5).
To estimate the total fit of the model, the indicators in Table 6 were used. The values of the squared Euclidean distance (d-ULS) and geodesic distance (d-G) indices were significant at the 0.05 level, which indicates that the model estimation was performed efficiently. The SRMR value is equal to 0.010, which indicates the measurement error in the good fit correlation matrix.
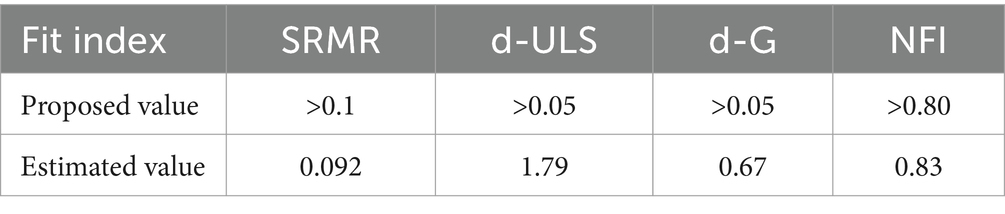
Table 6. Fit indices of the resilient behavior model of educators in the higher agricultural education system.
The goodness of fit index (GOF) is another index that is used to measure the fit of the model and its generalizability to society. This index indicates the overall fit of the model and is calculated from the following equation:
As shown in Table 7, the value of this index for the variable of educators’ resilient behavior is 0.32. Compared to the 0.01, 0.15 and 0.36 values recommended by Kline (2016) as a criterion for weak, medium and strong values, it can be concluded that the goodness model has an appropriate and suitable fit and can be generalized to the research population.
Discussion
With the outbreak of the COVID-19 disease in Iran, the higher education system of this country changed from a traditional system to a virtual education environment. This environment was unknown to many educational authorities and learners. Under this condition, the higher education system was required to promote teaching and learning in the virtual space. According to the results, 51.4% of agricultural educators in Iran were infected with the COVID-19. In addition, the rate of infection of family, relatives and friends, and death due to this disease in the family of educators, and the death of friends and relatives of educators were 45.1, 41.1, 30.9 and 53.5%, respectively, so this showed that to what extent agricultural educators were affected by the COVID-19 disease in Iran. Educators play an important role in the learning process of learners and act as one of the most important components of attaining the goal of education during crisis. In order to realize education in crisis conditions, educators consider new roles such as enhancing self-efficacy and self-confidence, identifying and selecting virtual education policies, and the ability to adapt in different environments. In order to fulfill such roles, educators should be resilient in case of crisis (Newman and Dale, 2005; Edmeade and Buzinde, 2021; Edmeade and Buzinde, 2021).
In this study, the level of resilience of educators in facing the conditions caused by the outbreak of the COVID-19 disease was investigated in the three dimensions of education, research and effective social services and the related effective factors. Effective education and research during the Coronavirus pandemic in the context of electronic teaching is an education during which the teacher can create interaction between self-understanding, comprehensive understanding and perceiving the conditions caused by the epidemic in the online education environment. The factors affecting the resilient behavior of educators during the COVID-19 disease crisis were investigated and measured in the form of four motivational-emotional, technical-skill, social, and supportive factors. There is a positive and significant relationship between motivational-emotional factors and educators’ resilience behavior. In other words, the more motivated the educators, the higher their resiliency. This result is consistent with previous findings (Ang et al., 2022; Naidu, 2021; Bozkurt, 2022). Resilient people have mental health, sense of self-improvement, high motivation, emotional control and higher self-confidence, and are less exposed to risky and uncontrolled behaviors. Under the conditions caused by the COVID-19, even people who were completely healthy could not use their abilities due to the dominance of impacts related to health and mental health.
The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated a rapid shift to remote learning, demanding a new set of skills from educators. To effectively facilitate online learning, teachers required a robust skill set that extended beyond traditional pedagogical methods. Adequate ability and skill to improve the learning process in the virtual platform, in addition to teaching skills, is referred to the ability to work in the online environment and with software, which educators should have this capability. The results of this research showed that there is positive and significant relationship between technical-skill factors and educators’ resilient behavior. This result is consistent with the results of previous studies (Zadok-Gurman et al., 2021; Ang et al., 2022). Due to the rapid spread of the Corona virus, educators that have more skills for working in virtual environment had more resilience behavior. Technology competency enable educators to be more efficient in performing their daily tasks such as communicating effectively with learners and co-workers through software and applications, recording and uploading lesson files and projects, correct management of the virtual classroom space, and learners’ defending thesis sessions. Technical-skill factors are one of the factors that their strengthening can bring better results in the future in the resilient behavior of educators in accordance with their competencies.
According to another part of the research results, there is a positive and significant relationship between social factors and educators’ resilient behavior. This finding is in line with previous findings (Permatasari et al., 2021; Dändliker et al., 2022). Research findings (Mengistie, 2021) indicate that the more educators know that they are supported and interacting with others, the more successful responses they show to psychological pressures and difficult situations. It can also be stated that the perceived social support (peers, co-workers, family and educators) plays an important role in improving their resilience (Beltman et al., 2011; Liu and Chu, 2022; Li, 2023). Based on the results, there is a positive and significant relationship between supportive factors and educators’ resilient behavior. The results of previous findings (Priolo Filho et al., 2020; Keener et al., 2021) confirm this research finding. A part of the created values is related to promoting the adaptation of the educational system to electronic education, reducing errors, enhancing the effectiveness of education, increasing synergy and finally, the formation of a culture that supports the effective application of new technologies in education. Due to the sudden emergence of e-learning, the presence of an efficient and effective support team is useful and reduces the stress and anxiety of educators to a great extent. Providing equipment and technical training to improve ICT in universities, educators and learners, for better performing virtual and online education during widespread crises, is one of the supports presented by the universities. According to Vrasidas (2015), just having the resources does not imply that ICT can be easily implemented but there needs to be the presence of other supportive factors such as staff readiness (Vrasidas, 2015). The required strategies in universities and research centers to conduct related researches are to present suitable solutions in dealing with such difficult Corona conditions.
Conclusion
Since educators play a crucial role in the learning process of learners, they are considered as one of the most fundamental factors of the realization of education during crisis. Resilience is referred to the ability to absorb shocks combined with positive adaptation and transforming structures into facilities for facing changes in the long term, and people with such characteristics have resilient behavior. Based on the results obtained from research in the academic field, education and research are important indicators of resilient behavior among educators, and many factors affect these indicators, but motivational-emotional, technical-skill, social and supportive factors are effective factors on these indicators that were investigated and measured in this study. Among the influencing factors on educators’ resilient behavior, motivational-emotional factors were significant in structural equations and had the highest effect. Mental and physical health increases the potential of the educator and protects the teacher in stressful and challenging situations, but technical-skill factors had lowest effect than other factors.
Limitations
Despite the important results obtained in this study, the generalization of the results of this research has some limitations. First, this research was conducted among some of agricultural educators, and generalization of the data should be done cautiously. On the other hand, the statistical population of this research were educators in the agricultural sector, which can have useful results for other researchers in other disciplines, but the results of this study can be similar or contrary to the results of similar research among educators in other fields. In addition, it should be mentioned that the factors contributing to educators’ resilience are thematic, as they relate to the specific adversities and do not affect educators’ resilience to another type of adversities. Also, the authors believe that considering that this research was conducted during Coronavirus disease and the respondents completed the electronic questionnaire, this may not have real answers in some cases.
Future directions
In this study, it was attempted to identify some of the most important factors that affect the educators’ resilience in the agricultural higher education system during the Corona outbreak. According to the data gaps in this research, one of the topics that can be examined in the future is the identification of other factors affecting resilience. Also, other researchers can investigate the impact of the factors identified in this research among the educators of other educational institutes. In addition, identifying mechanisms for the greater impact of the factors identified in this research on the resilience of educators is another important issue that can be studied by researchers in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the participants was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
MG: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ang, W. H. D., Shorey, S., Lopez, V., Chew, H. S. J., and Lau, Y. (2022). Generation Z undergraduate students’ resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative study. Curr. Psychol. 41, 8132–8146. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-01830-4
Bartusevičienė, I., Pazaver, A., and Kitada, M. (2021). Building a resilient university: ensuring academic continuity-transition from face-to-face to online in the COVID-19 pandemic. WMU J. Marit. Aff. 20, 151–172. doi: 10.1007/s13437-021-00239-x
Beltman, S., and Mansfield, C. F. (2018). “Resilience in education: an introduction” in Resilience in education: concepts, contexts, and connections. eds. M. Wosnitza, F. Peixoto, S. Beltman, and C. F. Mansfield (Cham: Springer), 3–9.
Beltman, S., Mansfield, C., and Price, A. (2011). Thriving not just surviving: a review of research on teacher resilience. Educ. Res. Rev. 6, 185–207. doi: 10.1016/j.edurev.2011.09.001
Bernasco, E. L., Nelemans, S. A., van der Graaff, J., and Branje, S. (2021). Friend support and internalizing symptoms in early adolescence during COVID-19. J. Res. Adolesc. 31, 692–702. doi: 10.1111/jora.12662
Biriya, (2022). Higher education in the era of Corona in Iran and the world. Marine Sci. Educ. 9, 241–252. doi: 10.22034/rmt.2022.543798.2057
Bozkurt, A. (2022). Resilience, adaptability, and sustainability of higher education: a systematic mapping study on the impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and the transition to the new normal. J. Learn. Dev. 9, 1–16. doi: 10.56059/jl4d.v9i1.590
Bozkurt, H., and Sharma, R. C. (2020). Emergency remote teaching in a time of global crisis due to CoronaVirus pandemic. Asian J Dist Edu. 15, 1–16.
Carew, M. T., Deluca, M., Groce, N., and Kett, M. (2019). The impact of an inclusive education intervention on teacher preparedness to educate children with disabilities within the lakes region of Kenya. Int. J. Incl. Educ. 23, 229–244. doi: 10.1080/13603116.2018.1430181
Crompton, H., Burke, D., Jordan, K., and Wilson, S. (2021). Learning with technology during emergencies: a systematic review of K-12 education. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 52, 1554–1575. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13114
Dändliker, L., Brünecke, I., Citterio, P., Lochmatter, F., Buchmann, M., and Grütter, J. (2022). Educational concerns, health concerns and mental health during early COVID-19 school closures: the role of perceived support by teachers, family, and friends. Front. Psychol. 12:6569. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.733683
Devlin, M., and Samarawickrema, G. (2022). A commentary on the criteria of effective teaching in post-COVID higher education. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 41, 21–32. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2021.2002828
Edmeade, J., and Buzinde, C. N. (2021). Educators’ personal resilience in the context of disasters triggered by natural hazards: the case of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI). Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 66:102571. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102571
Ellis, W. E., Dumas, T. M., and Forbes, L. M. (2020). Physically isolated but socially connected: psychological adjustment and stress among adolescents during the initial COVID-19 crisis. Can. J. Behav. Sci. 52, 177–187. doi: 10.1037/cbs0000215
Fernandes, P. R. D. S., Jardim, J., and Lopes, M. C. D. S. (2021). The soft skills of special education teachers: evidence from the literature. Educ. Sci. 11:125. doi: 10.3390/educsci11030125
Finstad, G. L., Giorgi, G., Lulli, L. G., Pandolfi, C., Foti, G., León-Perez, J. M., et al. (2021). Resilience, coping strategies and posttraumatic growth in the workplace following COVID-19: a narrative review on the positive aspects of trauma. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:9453. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189453
Giovannini, E., Benczur, P., Campolongo, F., Cariboni, J., and Manca, A. R. (2020). Time for transformative resilience: the COVID-19 emergency. JRC working papers, no. JRC120489. Joint Research Centre-Seville site.
Gu, Q., and Day, C. (2007). Teachers resilience: a necessary condition for effectiveness. Teach. Teach. Educ. 23, 1302–1316. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2006.06.006
Gundogan, S. (2021). The mediator role of the fear of COVID-19 in the relationship between psychological resilience and life satisfaction. Curr. Psychol. 40, 6291–6299. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-01525-w
Han, J. (2019). Teacher motivation: definition, research development and implications for teachers. Cogent Educ. 3:1217819. doi: 10.1080/2331186X.2016.1217819
Hepp, P., Fernández, M. À. P., and García, J. H. (2015). Teacher training: technology helping to develop an innovative and reflective professional profile. RUSC. Univ. Know. Soc. J. 12, 30–43. doi: 10.7238/rusc.v12i2.2458
Hikam, F. F. (2020). Peran Keluarga Dalam Pembelajaran Berbasis E-Learning Pada Masa Wabah COVID-19. Pandawa 2, 194–203. doi: 10.36088/pandawa.v2i2.695
Keener, T. A., Hall, K., Wang, K., Hulsey, T., and Piamjariyakul, U. (2021). Quality of life, resilience, and related factors of nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nurse Educ. 46, 143–148. doi: 10.1097/NNE.0000000000000969
Kiers, J., Seinhorst, J., Zwanenburg, M., and Stek, K. (2022). Which strategies and corresponding competences are needed to improve supply chain resilience: a COVID-19 based review. Logistics 6:12. doi: 10.3390/logistics6010012
Kline, R. B. (2016). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
Klusman, U., Aldrup, K., Roloff-Bruchmann, J., Carstensen, B., Wartenberg, G., Hansen, J., et al. (2023). Teachers’ emotional exhaustion during the COVID-19 pandemic: levels, changes, and relations to pandemic-specific demands. Teach. Teach. Educ. 121:103908. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2022.103908
Koskela, T., Pihlainen, K., Piispa-Hakala, S., Vornanen, R., and Hämäläinen, J. (2020). Parents’ views on family resiliency in sustainable remote schooling during the COVID-19 outbreak in Finland. Sustain. For. 12:8844. doi: 10.3390/su12218844
Krejcie, R. V., and Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 30, 607–610. doi: 10.1177/001316447003000308
Li, S. (2023). The effect of teacher self-efficacy, teacher resilience, and emotion regulation on teacher burnout: a mediation model. Front. Psychol. 14:1185079. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1185079
Li, F., Luo, S., Mu, W., Li, Y., Ye, L., Zheng, X., et al. (2021). Effects of sources of social support and resilience on the mental health of different age groups during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Psychiatry 21:16. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-03012-1
Liu, H., and Chu, W. (2022). Exploring EFL teacher resilience in the Chinese context. System 105:102752. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2022.102752
Mansfield, C. (2012). Promoting resilience for teachers and their students: a four-dimensional view. The Children’s hospital education research institute conference. Sydney: Murdoch University.
Mengistie, T. A. (2021). Higher education students’ learning in COVID-19 pandemic period: the Ethiopian context. Res. Globalizat. 3:100059. doi: 10.1016/j.resglo.2021.100059
Mestry, R. (2023). The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on higher education institutions in South Africa: resilience of academics. S. Afr. J. Educ. 43, S1–S10. doi: 10.15700/saje.v43ns1a2414
Naidu, S. (2021). Building resilience in education systems post-COVID-19. Distance Educ. 42, 1–4. doi: 10.1080/01587919.2021.1885092
Newman, L., and Dale, A. (2005). Network structure, diversity, and proactive resilience. Building: a response to Tompkins and Adger. Ecol. Soc. 10:1001r02. doi: 10.5751/ES-01396-1001r02
Nutini, A. E. (2023). The impact of self-compassion on emotional and biological markers of stress in youth (Doctoral dissertation: University of British Columbia.
Permatasari, N., Ashari, F. R., and Ismail, N. (2021). Contribution of perceived social support (peer, family, and teacher) to academic resilience during COVID-19. Golden Ratio Soc. Sci. Educ. 1, 01–12. doi: 10.52970/grsse.v1i1.94
Pokhrel, S., and Chhetri, R. (2021). A literature review on impact of COVID-19 pandemic on teaching and learning. Higher Edu. Future 8, 133–141. doi: 10.1177/2347631120983481
Priolo Filho, S. R., Goldfarb, D., Zibetti, M. R., and Aznar-Blefari, C. (2020). Brazilian child protection professionals’ resilient behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic. Child Abuse Negl. 110:104701. doi: 10.1016/j.chiabu.2020.104701
Purba, R., Herman, H., Purba, A., Hutauruk, A. F., Silalahi, D. E., Julyanthry, J., et al. (2022). Improving teachers’ competence through the implementation of the 21st century competencies in a post-COVID-19 pandemic. Jurnal Masyarakat Mandiri 6, 1486–1497. doi: 10.31764/jmm.v6i2.7340
Raghunathan, S., Darshan Singh, A., and Sharma, B. (2022). Study of resilience in learning environments during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Educ. 6:552. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.677625
Rodrigue, C., Rodgers, R., Carbonneau, N., Bégin, C., and Dion, J. (2023). COVID-19-related distress, body image, and eating behaviors: a cross-sectional explanatory model. BMC Psychol. 12:117. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3015512/v1
Saadvandi, M., Abbasi, E., and Farhadian, H. (2018). Learning environment characteristics in competence-based agricultural higher education. J. Agric. Educ. Administ. Res. 10, 109–122.
Samadi, A. (2020). How can support and stability prevent teacher burnout and support teacher retention? School of education and leadership student capstone projects. Summer. 526. Available at: https://digitalcommons.hamline.edu/hse_cp/526.
Sánchez Ruiz, L. M., Moll-López, S., Moraño-Fernández, J. A., Llobregat-Gómez, N., and Llobregat-Gómez, J. A. (2021). B-learning and technology: enablers for university education resilience. An experience case under COVID-19 in Spain. Sustain. For. 13:3532. doi: 10.3390/su13063532
Sharma, K., Dhungana, G., Adhikari, S., Bista Pandey, A., and Sharma, M. (2021). Depression and anxiety among patients with type ii diabetes mellitus in Chitwan medical college teaching hospital, Nepal. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2021, 1–8. doi: 10.1155/2021/8846915
Thajil, K. M., and AL-Abrrow, H. (2023). The effect of the bright triad on positive innovation in healthcare sector: the mediating role of emotional intelligence. Int. J. Healthc. Manag. 17, 285–296. doi: 10.1080/20479700.2023.2177608
Theiss, J. A. (2018). Family communication and resilience. J. Appl. Commun. Res. 46, 10–13. doi: 10.1080/00909882.2018.1426706
Thompson, K. M., and Copeland, C. (2020). Inclusive considerations for optimal online learning in times of disasters and crises. Informat. Learn. Sci. 121, 481–486. doi: 10.1108/ILS-04-2020-0083
Treviño, M. E. M. V., Campillo, L. M. G., Macías-Valadez, M. Z., and Quevedo, F. R. (2020). Depression and anxiety among patients with type ii diabetes mellitus in Chitwan medical college teaching hospital, Nepal. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2021, 1–8.
Trikoilis, D., and Papanastasiou, E. C. (2020). Una mirada a la historia para la resiliencia ante el COVID-19. Kuxulkab’. 26, 79–92.
UNESCO (2020). COVID-19 educational disruption and response, UNESCO. Available at: https://www.unesco.org/en/articles/covid-19-educational-disruption-and-response
van Breda, A. D. (2018). A critical review of resilience theory and its relevance for social work. Soc. Work 54, 1–18. doi: 10.15270/54-1-611
Verawardina, U., Asnur, L., Luthfini Lubis, A., Hendriyani, Y., Ramadhani, D., Parma Dewi, I., et al. (2020). Reviewing online learning facing the COVID-19 outbreak. Talent Dev. Excellence 12, 385–392.
Verdolini, N., Amoretti, S., Montejo, L., García-Rizo, C., Hogg, B., Mezquida, G., et al. (2021). Resilience and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Affect. Disord. 283, 156–164. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.01.055
Vrasidas, C. (2015). The rhetoric of reform and teachers’ use of ICT. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 46, 370–380. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12149
Worldometer, (2023). Spain coronavirus. WWW.Document. Available at: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/Spain/ (Accessed October 30, 2023).
Zadok-Gurman, T., Jakobovich, R., Dvash, E., Zafrani, K., Rolnik, B., Ganz, A. B., et al. (2021). Effect of inquiry-based stress reduction (IBSR) intervention on well-being, resilience and burnout of teachers during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:3689. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073689
Zamarro, G., Camp, A., Fuchsman, D., and McGee, J. B. (2022). Understanding how COVID-19 has changed teachers’ chances of remaining in the classroom (march 1, 2022). Sinquefield Center for Applied Economic Research Working Paper no. 22–01. Fayetteville, AR: University of Arkansas.
Keywords: agricultural higher education system, COVID-19 pandemic crisis, educators’ resilient behavior, motivational emotional factors, structural equation modeling
Citation: Ghiasvand M, Abbasi E, Saadvandi M and Pariab J (2024) Educator’s resilience in agricultural higher education system during COVID-19 pandemic: empirical evidence from Iran. Front. Educ. 9:1413657. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1413657
Edited by:
Arumugam Raman, University of Northern Malaysia, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Elena Mirela Samfira, University of Life Sciences “King Mihai I” from Timisoara, RomaniaYasir Hayat Mughal, Qassim University, Saudi Arabia
Karmen Drljic, University of Primorska, Slovenia
Copyright © 2024 Ghiasvand, Abbasi, Saadvandi and Pariab. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Enayat Abbasi, ZW5heWF0LmFiYmFzaUBtb2RhcmVzLmFjLmly
†ORCID: Enayat Abbasi, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5238-7185
Jaber Pariab, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7799-4176
 Maryam Ghiasvand1
Maryam Ghiasvand1 Enayat Abbasi
Enayat Abbasi Mahsa Saadvandi
Mahsa Saadvandi