
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Educ. , 30 October 2024
Sec. Digital Learning Innovations
Volume 9 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1385205
This article is part of the Research Topic Artificial intelligence (AI) in the complexity of the present and future of education: research and applications View all 9 articles
 Nurlan Omarov1,2
Nurlan Omarov1,2 Bakhytzhan Omarov2*
Bakhytzhan Omarov2* Quwanishbay Mamutov3
Quwanishbay Mamutov3 Zhanibek Kissebayev4
Zhanibek Kissebayev4 Almas Anarbayev2
Almas Anarbayev2 Adilbay Tastanov5
Adilbay Tastanov5 Zhandos Yessirkepov1
Zhandos Yessirkepov1Introduction: In recent years, the importance of effective training methods for future physical education teacher-trainers has grown significantly, particularly in the context of online education.
Methods: This research introduces a pioneering Deep Learning Enabled Exercise Monitoring System aimed at enhancing the online education experience for these trainers. The study employs a skeleton-based approach utilizing the PoseNet model to monitor and provide real-time feedback on physical exercises such as pull-ups, push-ups, sit-ups, squats, and bicep workouts. The system achieves a remarkable accuracy rate of 99.8% by analyzing key skeletal points extracted from video frames, addressing the challenge of ensuring correct exercise execution without physical supervision–a common issue in remote learning environments.
Results: To validate the system’s effectiveness, data was collected through a series of controlled experiments involving various exercises. The system’s design focuses on low-resource requirements, making it accessible and sustainable for diverse educational contexts.
Discussion: The findings demonstrate the system’s potential to revolutionize online physical education by offering a balance of technological innovation and educational utility. This research not only elevates the quality of training for future educators but also contributes to the broader field of sustainable digital education technologies.
The advent of digital technology has revolutionized various sectors, including education and physical training. In recent years, the concept of sustainable online education has gained significant traction, particularly in the realm of training future teacher-trainers. This paradigm shift calls for innovative approaches to ensure effective training, especially in disciplines that traditionally rely on physical presence, such as physical education (PE). The importance of PE in the holistic development of individuals is well-documented (Hagenauer et al., 2023), emphasizing the need for effective training methods for teacher-trainers in this field.
The global shift toward online education, expedited by the COVID-19 pandemic, has underscored the necessity of developing remote learning tools that cater to physical training (Gómez-Núñez et al., 2023). Traditional PE training methods are challenged by the constraints of remote learning, highlighting the need for technology-driven solutions. In response, the integration of advanced technologies like deep learning and computer vision has emerged as a promising approach to facilitate remote PE training (Mennella et al., 2023). These technologies offer innovative ways to monitor and assess physical exercises, a critical aspect of PE training.
Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, has shown remarkable success in various applications, including image and pattern recognition, which are crucial for exercise monitoring (Patalas-Maliszewska et al., 2023). By leveraging deep learning techniques, it’s possible to analyze and interpret complex patterns in physical movements, enabling accurate monitoring and feedback in real-time. This capability is particularly relevant in the context of PE, where precise movement and posture are essential for effective exercise.
Moreover, the application of deep learning in exercise monitoring addresses a significant challenge in online PE training: the lack of direct supervision. In traditional settings, a trainer’s physical presence ensures correct exercise execution and immediate feedback. Deep learning technologies can replicate this oversight to an extent by providing automated, real-time analysis of exercises (Frangoudes et al., 2022). This technological intervention is not only beneficial for maintaining the quality of training but also for preventing injuries that can occur due to incorrect exercise postures (Nagy et al., 2023).
Another critical aspect of sustainable online education is accessibility. The proposed exercise monitoring system in this study utilizes a skeleton-based method, which does not require high-end processing equipment (Zheng et al., 2023). This approach democratizes access to advanced training tools, making them available to a broader range of users, including institutions with limited resources. This is particularly important for developing regions where access to advanced technology and equipment may be limited (Pham et al., 2022).
The importance of such technologies extends beyond just the realm of education. With the increasing emphasis on health and fitness, the ability to monitor and guide physical exercises accurately has wider implications. The fitness industry, rehabilitation centers, and personal training all stand to benefit from advancements in exercise monitoring technologies (Seçkin et al., 2023). This broad applicability underscores the potential of deep learning-based systems in transforming physical training across various sectors.
The effectiveness of any technological intervention, however, hinges on its accuracy and reliability. In the context of exercise monitoring, this translates to the system’s ability to correctly identify and classify different exercises and their execution. Previous studies have demonstrated varying levels of success in exercise classification using deep learning techniques (De Beukelaar and Mantini, 2023). The high accuracy rates reported in these studies provide a strong foundation for the development of more advanced and reliable systems.
Furthermore, the real-time aspect of exercise monitoring is crucial for its practical application in online education (Ren et al., 2022). The ability to provide immediate feedback not only enhances the learning experience but also ensures that exercises are performed safely and effectively. This real-time capability is a significant advancement over traditional video-based training methods, where feedback is often delayed.
In summary, the development of a Deep Learning Enabled Exercise Monitoring System represents a significant step forward in the field of sustainable online education, particularly for training future teacher-trainers in physical education. By leveraging advanced technologies like deep learning and skeleton-based analysis, this system addresses key challenges in remote PE training, including accuracy, accessibility, and real-time feedback. The potential applications of this technology extend beyond education, offering benefits to various sectors where physical training and monitoring are essential (Ray, 2023). As such, this study not only contributes to the field of online education but also opens up new avenues for research and development in technology-enabled physical.
The integration of technology in physical education (PE) has become increasingly prominent, particularly with the shift toward online and remote learning environments. This section reviews related works, focusing on the application of deep learning and other technological advancements in exercise monitoring and PE training.
Deep learning has significantly advanced physical activity recognition, a crucial component of exercise monitoring and online physical education. Over the past decade, numerous studies have demonstrated the potential of deep learning algorithms in accurately identifying and categorizing various physical activities.
One foundational study introduced the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for activity recognition, which marked a significant departure from traditional methods. This study demonstrated that CNNs could effectively process and interpret complex data from videos and sensor inputs to recognize specific physical movements with high accuracy (Thakur et al., 2022). The success of this approach has been a cornerstone in developing more sophisticated exercise monitoring systems.
Research has since expanded to include recurrent neural networks (RNNs) for activity recognition. RNNs, known for handling sequential data, proved particularly adept at interpreting time-series data generated during physical activities, crucial for understanding and predicting patterns in human movement (Mekruksavanich and Jitpattanakul, 2022). This enhancement in accuracy was pivotal in real-time feedback applications in online PE sessions.
Additionally, integrating deep learning with real-time data processing has enabled immediate interpretation of physical movements. This is essential for real-time feedback, making deep learning algorithms suitable for live exercise monitoring without compromising accuracy (Challa et al., 2022).
Advancements in transfer learning have also played a significant role. Transfer learning, which involves applying knowledge gained from one task to related tasks, has enabled rapid deployment of deep learning models in physical activity recognition, even with limited training data specific to certain exercises (Qiu et al., 2022).
In summary, deep learning has revolutionized physical activity recognition. Its ability to process complex, multidimensional data and learn from patterns makes it an ideal tool for accurately monitoring and classifying a wide range of physical activities. These advancements enhance the efficacy of online physical training and pave the way for more personalized and adaptive PE programs.
Real-time monitoring and feedback systems represent a transformative step in sustainable education, particularly in physical training. These systems bridge the gap between traditional face-to-face instruction and online education environments, leveraging advanced technology to enhance interactivity and efficacy.
A study emphasized the importance of real-time feedback in online education, illustrating how immediate corrections and guidance can significantly improve learning experiences and outcomes in physical education. This is particularly relevant in exercises where the risk of injury due to incorrect posture is high (Whelan et al., 2021). Real-time monitoring systems ensure that learners receive timely and accurate feedback, akin to having a physical instructor present.
Further research explored sensor-based technologies in real-time exercise monitoring, allowing precise tracking of movements and providing instant feedback to the user. This approach has proven beneficial in maintaining engagement and motivation among learners, as they receive immediate responses to their actions (Hussain et al., 2022).
Another significant contribution involved developing a framework for real-time feedback systems tailored for sustainable online education. This framework emphasized the adaptability of these systems to various educational contexts, ensuring broad applicability across different learning environments and disciplines (Bennani et al., 2022).
The efficacy of such systems in real-world educational settings was demonstrated in a study where a sensor-based real-time feedback system was implemented in a remote learning course. The findings showed notable improvements in student engagement and learning outcomes, validating the system’s potential in online education (Li et al., 2022).
Studies have also highlighted these systems’ potential to reduce the digital divide in education. By enabling effective remote learning experiences, real-time feedback systems make quality education more accessible to students in diverse geographical locations and with varying resource levels (Setiawan et al., 2022).
Lastly, key research addressed the challenges and solutions in implementing these systems, such as ensuring data privacy and managing bandwidth requirements for seamless real-time communication. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the widespread adoption and success of real-time monitoring and feedback systems in sustainable education (Zalostiba et al., 2019; Chen, 2022).
In essence, real-time monitoring and feedback systems significantly advance online education. Their ability to provide immediate, personalized feedback enhances the learning experience, especially in disciplines requiring physical interaction, and paves the way for a more inclusive and effective digital learning environment.
Despite significant strides in exercise monitoring technology, several challenges persist. Addressing these is essential for future advancements, particularly in sustainable education and physical training.
A primary challenge is the variability in human movements and individual physical attributes, leading to discrepancies in exercise recognition systems’ accuracy. Customizing these systems to account for a diverse range of body types, movement patterns, and skill levels remains a significant undertaking. Adaptive algorithms that can learn and adjust to individual differences are essential for overcoming this challenge (Morrison et al., 2022).
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in the effectiveness of exercise monitoring technologies. Studies have shown that varying lighting conditions, backgrounds, and space constraints can significantly impact these systems’ performance. Developing robust algorithms capable of functioning accurately in diverse environmental settings is a key area of focus for researchers (Weakley et al., 2021; Debnath et al., 2022).
Integrating exercise monitoring technology with wearable devices presents another set of challenges, particularly concerning data accuracy and privacy concerns. Ensuring the security and confidentiality of sensitive health data collected through these devices is paramount. Additionally, improving the accuracy and reliability of data from wearable devices is crucial for their effective use in exercise monitoring (Suchomel et al., 2021).
A pivotal study pointed out the need for cross-disciplinary collaboration in this field. Combining expertise from computer science, sports science, and healthcare can lead to more holistic and effective exercise monitoring solutions. This interdisciplinary approach is vital for addressing the complex challenges inherent in this field (Zabasta et al., 2017).
Future research directions include exploring the use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in exercise monitoring. These technologies have the potential to enhance user engagement and provide more immersive and interactive training experiences. Additionally, the application of machine learning techniques for predictive analytics in physical training could lead to personalized and more effective training regimens (Doskarayev et al., 2023).
In summary, while exercise monitoring technology has made significant advancements, addressing its current challenges and exploring new interdisciplinary and innovative approaches are crucial for its future development. These efforts will enhance the effectiveness of physical training and contribute to the broader field of sustainable education.
Future teacher-trainers in sports and physical education must meet several conditions and adhere to specific standards to ensure they are well-prepared to educate and train the next generation of physical education professionals. These standards encompass educational qualifications, practical skills, and technological proficiency, which are essential for effective teaching and training in modern educational environments.
A fundamental requirement for future teacher-trainers in sports is possessing the appropriate educational background. This typically includes:
1. Bachelor’s Degree in Physical Education or Related Field: An undergraduate degree provides the foundational knowledge in sports science, exercise physiology, biomechanics, and pedagogy.
2. Advanced Degrees (Master’s or Doctorate): Many institutions require or prefer teacher-trainers to hold advanced degrees, which offer deeper expertise and specialized knowledge in areas such as sports psychology, curriculum development, and advanced training techniques.
In addition to academic qualifications, practical skills and hands-on experience are critical:
1. Coaching and Training Experience: Practical experience in coaching or training athletes at various levels is essential. This experience helps future teacher-trainers understand the practical aspects of physical training and athlete management.
2. Certifications: Obtaining certifications from recognized bodies (e.g., NSCA, ACSM, or national sports federations) in specific sports or training methodologies is often required. These certifications validate the trainer’s expertise and commitment to professional development.
3. Continuous Professional Development: Engaging in ongoing education and training to stay updated with the latest advancements in sports science, training techniques, and educational methods.
With the increasing integration of technology in education and training, future teacher-trainers must be proficient in using various technological tools:
1. Familiarity with Exercise Monitoring Systems: Understanding and effectively utilizing exercise monitoring systems, such as those employing deep learning and computer vision, to enhance training and feedback.
2. Online Teaching Platforms: Proficiency in using online education platforms (e.g., Moodle, Blackboard) to deliver courses, manage student progress, and provide virtual coaching.
3. Data Analysis and Interpretation: Skills in analyzing performance data and interpreting the results to make informed decisions about training regimens and educational strategies.
Future teacher-trainers must adhere to established pedagogical standards to ensure they can deliver high-quality education:
1. Evidence-Based Teaching Methods: Employing teaching methods and practices that are supported by scientific research and evidence to ensure effective learning outcomes.
2. Student-Centered Approach: Focusing on the needs and progress of individual students, providing personalized guidance, and fostering an inclusive learning environment.
3. Assessment and Feedback: Utilizing various assessment methods to evaluate student performance accurately and providing constructive feedback to facilitate continuous improvement.
Ethical conduct and professionalism are paramount in the field of sports education:
1. Adherence to Ethical Guidelines: Following ethical guidelines set by professional bodies, including respect for student confidentiality, fairness, and integrity in all educational and training activities.
2. Role Modeling: Serving as positive role models for students, demonstrating the values of dedication, discipline, and a commitment to lifelong learning.
As the field of sports education evolves, future teacher-trainers should be prepared to adapt to emerging trends and innovations:
1. Integration of New Technologies: Embracing new technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), to create immersive learning experiences.
2. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Collaborating with experts in fields such as nutrition, psychology, and data science to provide a holistic approach to sports education and training.
3. Global Standards and Practices: Understanding and incorporating global standards and best practices to ensure their training methods are on par with international benchmarks.
In summary, the preparation of future teacher-trainers in sports and physical education involves a comprehensive approach that includes educational qualifications, practical skills, technological proficiency, adherence to pedagogical and ethical standards, and a readiness to embrace future trends and innovations. These conditions and standards ensure that teacher-trainers are equipped to provide high-quality education and training, fostering the development of competent and well-rounded physical education professionals.
The Materials and Methods section of this research paper provides a detailed exposition of the methodologies, tools, and procedures employed in the development and evaluation of the Deep Learning Enabled Exercise Monitoring System. This section is structured to offer clarity and reproducibility of the research process, ensuring that the study can be critically assessed and, if necessary, replicated by other researchers in the field. It encompasses a comprehensive description of the hardware and software components, the dataset used for training and testing the system, the algorithmic approach, and the statistical methods applied for data analysis. This section is fundamental in outlining the systematic approach taken to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
Figure 1 presents a detailed flowchart of the proposed exercise monitoring system, illustrating the sequential processes involved. The system begins with the initialization of the PoseNet model, followed by capturing a real-time video feed from the camera. The next step involves obtaining keypoint coordinates and skeleton angles from the video feed. This data is then bifurcated; one path involves applying deep learning techniques for action classification, while the other path focuses on validating the accuracy of exercise execution through the analysis of coordinates and angles. Subsequently, skeleton graphs are created to display the exercise angles and keypoints for each frame. Based on this analysis, the system makes a decision on whether the exercise is performed correctly or not, concluding the monitoring process. This comprehensive approach ensures precise monitoring and real-time feedback, thereby enhancing the quality and effectiveness of remote physical education.
Figure 2 illustrates the process of skeletal detection during a physical exercise session. Initially, the individual engaging in the exercise must establish an internet connection for their device to access the web-based monitoring system. As the person commences their physical activity, a live video of their movements is captured via a webcam and fed into the PoseNet model as input. Upon identifying a human pose within a video frame, the PoseNet model proceeds to extract key points, utilizing 2D coordinates (x, y) to pin-point each body joint in the frame. These key points are critical for calculating the distances and angles within the skeletal structure. This data is then transmitted to a deep learning model, which classifies the type of exercise being performed. Additionally, the coordinates and angles derived are employed to verify the correctness of the exercise execution, ensuring that the movements align with the prescribed exercise standards.
The concept underlying three-point coordinate determination involves the calculation of the joint angle between two vectors utilizing the principles of the law of cosines, as illustrated in Figure 3.
Subsequently, we can ascertain the cosine value of the angle denoted as “B” (Equation 1):
The representation of the human body can be conceptualized as in Equation 2:
Here, θ denotes the parameters of the neural network, while xi represents the training samples from the dataset. To classify the human body’s representation, denoted as rb(xi; θ), a fully connected neural network layer is utilized. This layer functions prior to the standardization process facilitated by the “Softmax” layer.
denotes the weights matrix of the neural network. represents the training samples from the dataset. is the bias term. encompasses the parameters of the neural network, including and . Softmax function transforms the network outputs into a probability distribution.
Additionally, an extra neural network is employed, which undergoes training through the minimization of category cross-entropy loss. The process begins with the transmission of human action frames to PoseNET, which is responsible for the extraction of key points. Subsequently, these skeleton points are mapped in the feature space through their coordinates. The neural network is then trained utilizing these key points of the human skeleton.
Figure 4 illustrates the comprehensive structure of the system we propose. This sys-tem is divided into three distinct subtasks. Initially, the PoseNET model is applied to the input video frames to ascertain the human pose in each frame. Following this, the second subtask involves the extraction of key points from each frame as vectors, with PoseNET yielding 17 key points for every frame, resulting in vectors comprising 34 elements. Subsequently, these vectors are merged into a singular vector which is then forwarded for feature learning and activity recognition. The final subtask involves training a convolutional neural network specifically for detecting instances of violence. There are two primary methodologies for detecting human body positions in RGB images: top-down and bottom-up algorithms. The top-down approach begins with activating a human detector and then evaluating bodily joints within the identified bounding boxes. Examples of this approach include PoseNET (Kendall et al., 2015), HourglassNet (Li et al., 2021), and Hornet (Li et al., 2021). Conversely, bot-tom-up algorithms, such as Open Space (Chen et al., 2015) and PifPaf (Kreiss et al., 2019), function differently, aggregating information from individual image points to identify human poses.
In the domain of machine learning and particularly in systems involving classification tasks, the accuracy evaluation parameter stands as a pivotal metric. It quantifies the degree to which a model correctly identifies or classifies cases within a dataset. Fundamentally, accuracy is the proportion of true results (both true positives and true negatives) among the total number of cases examined. Mathematically, it is expressed as the ratio of the number of correct predictions to the total number of predictions made.
Accuracy serves as a primary measure for assessing the performance of a model, especially in scenarios where the classes are well-balanced (Tursynova and Omarov, 2021). In the context of a physical exercise monitoring system, for instance, accuracy would indicate how often the system correctly identifies the type of exercise being performed or recognizes the correctness of the exercise posture.
For each class c, the matrix shows the true positives (TP), false positives (FP), false negatives (FN), and true negatives (TN) values.
Precision is a crucial metric in statistics and machine learning, representing the accuracy of positive predictions among all predicted positives (Omarov et al., 2023). It quantifies the model’s ability to avoid false positives, ensuring that when it identifies something as positive, it is indeed accurate. A high precision value indicates a low rate of false alarms, signifying a reliable and trustworthy model. In applications such as healthcare, finance, and information retrieval, precision is paramount, as misclassifying positives can have severe con-sequences. Achieving a balance between precision and recall is essential, as they are often inversely related, and optimizing precision requires careful tuning of classification thresholds and model design.
Recall, also known as sensitivity or true positive rate, is a crucial performance metric in the fields of statistics and machine learning (Omarov et al., 2022). It measures the ability of a model to correctly identify all actual positive instances within a dataset. In essence, it quantifies the model’s completeness in capturing relevant information. A high recall indicates that the model effectively finds most of the positive cases, minimizing false negatives. This metric is particularly important in applications like medical diagnosis and information retrieval, where missing positive instances can lead to critical errors. Balancing recall with precision is a common challenge, as increasing one often comes at the expense of the other, highlighting the trade-off between thoroughness and accuracy.
The F-score, commonly referred to as the F1-score, is a fundamental metric within the realms of statistics and machine learning, primarily employed to evaluate classification models (Mitova et al., 2022). This metric serves as a robust measure of a model’s performance by effectively harmonizing the precision and recall metrics. By taking their harmonic mean, the F-score strikes a balance between precision, which gages the accuracy of positive predictions, and recall, which assesses the model’s capacity to capture actual positive instances. This harmonic mean formulation is particularly advantageous when dealing with imbalanced datasets or situations where the consequences of false positives and false negatives differ. In summary, the F-score provides a comprehensive and balanced assessment of a model’s capability to maintain a trade-off between the precision and recall dimensions of classification performance.
In the field of machine learning and statistical modeling, the loss evaluation parameter, often referred to as “loss function” or “cost function,” is a critical component in the development and assessment of models. It quantifies the difference between the predicted outputs of a model and the actual values, serving as a measure of the model’s error. The primary purpose of a loss function is to guide the optimization process during training, where the model’s parameters are adjusted to minimize this error.
Figure 5 presents the accuracy outcome of the testing phase for the model in question. In Figure 5, the validation and test accuracies of the neural networks are depicted, specifically in the context of physical bullying detection over a span of eight learning epochs. These results reveal that the model’s accuracy nears 99% following a training duration of eight epochs.
Figure 6 illustrates the trajectory of the neural network’s loss function values across the same eight epochs of training. Notably, these results highlight that the validation loss remains remarkably low even in the early stages of the training process.
Table 1 offers a comparative analysis of the results achieved by the proposed exercise monitoring system against those of leading-edge research in the field. The evaluation of the proposed system’s efficacy is conducted through three primary metrics: precision, re-call, and F-score. It is noteworthy, however, that several studies in the domain do not employ recall and F-score as evaluative parameters. In such scenarios, accuracy emerges as the principal metric for comparing the effectiveness of the proposed methodologies. Moreover, the table also reflects on the processing times of various approaches, a factor of-ten not reported in many studies. This omission is frequently attributed to the variability in datasets and the disparate performance capabilities of computing equipment used in different research projects, making direct comparisons less straightforward.
Figure 7 illustrates the application of the proposed framework in the context of real-time monitoring of bicep exercises. This framework is specifically designed to compute the angle (no more than 35 degrees) formed at the elbow joint in relation to a reference line. The reference line in question is established by drawing a parallel to the horizontal plane from the line connecting the two hands. This methodical approach enables precise evaluation of the exercise form, focusing on the critical aspect of elbow alignment during biceps exercises.
Figure 8 showcases the implementation of the proposed framework, specifically tailored for the real-time monitoring of squat exercises. This framework functions by deter-mining whether the exercise being performed is a squat, achieved through the calculation of the angle (no more than 35 degrees) at the knee joint. The precise measurement of this angle is crucial for assessing the correctness of the squatting motion, thus enabling the framework to accurately identify and evaluate the execution of the squat by the athlete.
Figure 9 depicts the utilization of the proposed framework in the real-time monitoring of sit-up exercises. The framework operates by calculating a specific angle to deter-mine whether the athlete is correctly performing a sit-up. This angle (no more than 35 degrees), crucial in the assessment of the sit-up execution, allows the system to accurately discern and evaluate the movement, ensuring that the exercise is being carried out as intended. This methodical approach to angle measurement is central to the framework’s ability to provide precise and reliable real-time feedback on sit-up exercises.
Figure 10 illustrates the application of the proposed framework for the real-time monitoring of pull-up exercises. This framework functions by assessing the angle formed at the elbow joint to determine the correct execution of a push-up by the athlete. A key feature of this system is the implementation of a counter mechanism, which increments by 1 each time the elbow angle is reduced to less than 30 degrees. This precise measurement of the elbow angle is critical for ensuring the accuracy of the push-up count and for confirming the proper form and execution of the exercise. This methodological approach enables the framework to provide reliable and real-time feedback on the athlete’s push-up performance.
Figure 11 presents the operational dynamics of the proposed framework, specifically designed for the real-time monitoring of push-up exercises. This framework determines the execution of a push-up by calculating two critical angles: one at the elbow and the other formed by a line between the two hands and elbows, in relation to a horizontal reference.
This figure distinctively illustrates both correct and incorrect instances of push-up execution. It delineates cases where the line formed between the elbows is either parallel or not parallel to the horizontal plane. Such a detailed analysis aids in accurately assessing the proper form and technique of the pull-up, thereby ensuring the effectiveness of the exercise and the reliability of the monitoring system.
In this study’s experimental setup, two distinct groups were formed for pedagogical assessment: the experimental group, which interacted with the elective course using the newly proposed system, and the control group, which engaged with the same course content but through conventional teaching methods. This division was implemented to critically assess the effectiveness of the proposed educational approach. Evaluations after each lesson were systematically carried out to measure students’ comprehension of the material and their levels of motivation. The scoring system was based on the precise recognition and selection of course elements, awarding one point for each correctly identified item.
Additionally, the study aimed to explore the impact of these different teaching methods on student performance more thoroughly. To this end, a research hypothesis was developed, concentrating on the relationship between the instructional strategy and student outcomes. In conjunction with this, an anonymous survey was distributed to the students. The decision to maintain the anonymity of the questionnaire was deliberate, in-tended to elicit frank and honest feedback. This confidentiality, coupled with the students’ knowledge of their exam results, was expected to encourage more genuine and introspective responses. Such an approach was anticipated to enhance the quality and depth of the data gathered for the analysis of the study’s findings.
Hypothesis I.
H0: Application of an exercise monitoring system will reduce muscle injury between athletes.
H1: Application of an exercise monitoring system will not reduce muscle injury between athletes.
Hypothesis II.
H0: Application of an exercise monitoring system will increase motivation rate between athletes.
H1: Application of an exercise monitoring system will not increase motivation rate between athletes.
The collected questionnaire data were subjected to statistical analysis using SPSS software (Version 26). A diverse range of statistical methods, including Pearson correlation, Independent samples T-test, and ANOVA (Janczyk et al., 2023; Rouder et al., 2023), was employed for the analysis of the data derived from the questionnaires and tests. The selection of these statistical tools was strategic, aiming to conduct a thorough examination of the relationship between different teaching strategies and their respective learning outcomes. Additionally, these methods facilitated a comparative analysis of the proposed exercise monitoring system versus traditional teaching methodologies.
Subsequent sections of this paper are devoted to a detailed exposition of each aspect of the methodology employed in this study. This includes a comprehensive description of the game used in the experimental group and an in-depth analysis of the pedagogical experiment’s outcomes. The objective of adopting this detailed approach is to provide a holistic insight into the effectiveness of the proposed strategy in mitigating muscle traumas. This extensive analysis is intended to contribute to a deeper understanding of the impact and efficacy of innovative teaching methodologies in educational settings.
In the context of this research paper, the hypothesis was formulated to assess the impact of an exercise monitoring system on athletes, specifically concerning muscle injury rates. The null hypothesis (H0) posited that the application of an exercise monitoring system will reduce muscle injury between athletes.
To investigate this hypothesis, an independent samples t-test was conducted to compare the muscle injury rates between two distinct groups: the Experimental Group (utilizing the exercise monitoring system) and the Control Group (employing traditional methods). Results are demonstrated in Table 2.
The Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances indicated that there was no statistically significant difference in variances between the two groups (F = 2.263, p = 0.137), suggesting that equal variances could be assumed. The results of the t-test under both equal variances assumed and equal variances not assumed conditions showed a highly statistically significant difference in mean injury rates between the two groups [t (78) = −12.929, p < 0.001].
The mean difference in injury rates between the Experimental Group and the Control Group was approximately −4.975, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from −5.741 to −4.209. These findings suggest that the application of the exercise monitoring system led to a substantial and statistically significant reduction in muscle injury rates among athletes. These results support the alternative hypothesis (Ha) and indicate the effectiveness of the exercise monitoring system in mitigating muscle injuries. Further analysis and discussion are necessary to validate and interpret these findings comprehensively within the context of the research hypothesis.
In this research study, the hypothesis posited that the implementation of an exercise monitoring system would lead to an increase in the motivation rate among athletes. To investigate this hypothesis, an independent samples t-test was conducted to compare the final exam results between two distinct groups: the Experimental Group (utilizing the exercise monitoring system) and the Control Group (employing traditional methods). The results is illustrated in Table 3.
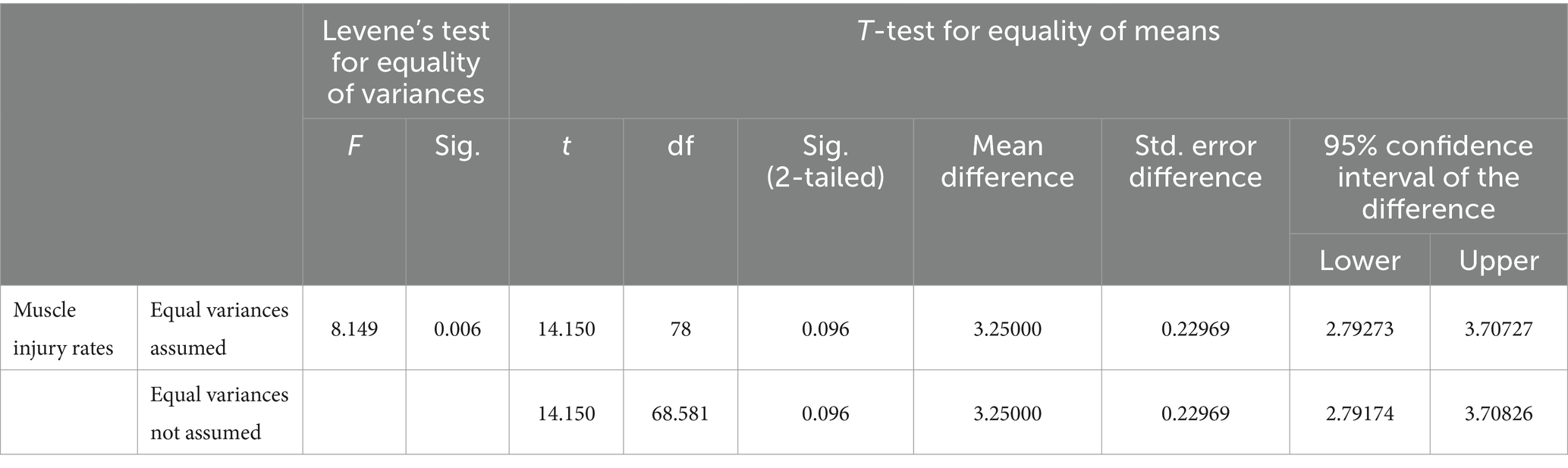
Table 3. Independent samples test between final exams results of experimental group and control group.
The group statistics indicate that the Experimental Group had a notably higher mean final exam result (M = 9.5500, SD = 0.81492) compared to the Control Group (M = 6.3000, SD = 1.20256).
The Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances showed a statistically significant difference in variances between the two groups (F = 8.149, p = 0.006), suggesting unequal variances. However, both equal variances assumed and equal variances not assumed t-tests were conducted. The results revealed a statistically significant difference in mean final exam results between the two groups [t (78) = 14.150, p < 0.006] under both assumptions.
The mean difference between the Experimental Group and the Control Group was approximately 3.25, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 2.793 to 3.707. These findings indicate a substantial and statistically significant difference in final exam results, suggesting that the application of the exercise monitoring system had a positive impact on motivation and academic performance among athletes. Further analyses and interpretations may be necessary to delve deeper into the implications of these results for the study’s hypothesis.
The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to examine the relation-ship between students’ motivation rates and their final exam results in two distinct groups: the experimental group, which utilized the proposed exercise monitoring system for learning, and the control group, which employed traditional teaching methods. The results are demonstrated in Table 4.
The results revealed a statistically significant difference in final exam results between the two groups [F (8, 65) = 4.103; Sig. = 0.001]. The between-groups variance (Sum of Squares = 9548.624) significantly outweighed the with-in-groups variance (Sum of Squares = 18906.781), indicating that the proposed exercise monitoring system had a notable impact on students’ performance. Further post-hoc analyses may be conducted to identify specific group differences and gain deeper insights into the observed effects. These findings suggest the potential pedagogical value of integrating the exercise monitoring system into educational practices.
The Discussion section of this research paper critically examines the findings of the study on the proposed Deep Learning Enabled Exercise Monitoring System and its implications in the context of sustainable online education for future teacher-trainers.
The empirical findings from the conducted experiments underscore an exceptional degree of precision, with the system achieving a 99.8% accuracy rate in the recognition and monitoring of physical exercises. This remarkable accuracy underscores the system’s efficacy in discerning among various exercise types, a fundamental criterion for any instructional apparatus within the realm of physical training. The incorporation of the PoseNet model, alongside the meticulous extraction and analytical processing of key positional points, has been pivotal in attaining such a high level of accuracy. In the domain of physical education, where the erroneous performance of exercises could precipitate injuries, the importance of such precision cannot be overstated. This system, through its deployment of advanced computational models and algorithms, not only enhances the safety and effectiveness of physical training but also represents a significant advancement in the application of technology to educational methodologies, ensuring that learners engage in physical activities with the utmost accuracy and safety.
A paramount advantage of the envisaged system lies in its capability to facilitate real-time monitoring and feedback, an attribute of considerable value within the paradigm of online learning. The absence of a physical instructor in such settings often hinders the instantaneous provision of corrective guidance and feedback. However, the system’s real-time feedback mechanism effectively bridges this gap, ensuring that learners receive immediate information regarding the accuracy of their exercise execution, thereby closely emulating the experience of in-person training sessions. This instantaneous feedback loop plays a critical role not only in ensuring the proper performance of exercises but also in significantly bolstering learner engagement and motivation. Through this mechanism, the system provides a dynamic and interactive learning environment, enabling learners to adjust their techniques in real-time, which is instrumental in enhancing the overall effectiveness and satisfaction of the training experience.
The incorporation of the envisaged system within the framework of online physical education curricula possesses the potential to substantially ameliorate the caliber and effectiveness of instructional methodologies employed. Characterized by its inherent flexibility and minimal requisites for resources, this system emerges as an exemplary instrument across a diverse spectrum of educational entities, especially those encumbered by constrained access to sophisticated technological infrastructures. This attribute assumes pronounced significance within the ambit of sustainable educational practices, fostering an equitable distribution of high-quality instructional resources. Consequently, it underpins the broader objective of democratizing access to superior training mechanisms, thereby facilitating an inclusive educational environment that transcends traditional barriers to resource availability.
The juxtaposition of the proposed technological system against conventional physical training methodologies elucidates numerous benefits inherent to the former. Notably, the system’s provision of precision and consistency represents a qualitative leap unattainable through traditional pedagogical strategies, particularly within the confines of remote education paradigms. Nonetheless, it is imperative to acknowledge that technology-facilitated systems are designed to augment rather than supplant traditional training modalities. The integration of technological advancements with conventional techniques engenders a synergistic educational milieu, thereby enhancing the overall efficacy and comprehensiveness of the training experience. This fusion not only leverages the strengths of both paradigms but also addresses their individual limitations, paving the way for a more holistic approach to physical education.
Despite the encouraging outcomes demonstrated, the study identified a spectrum of challenges and limitations inherent to the system’s deployment. Notably, the inherent variability in human kinematics and the plethora of individual physiological differences present substantial hurdles to achieving unerring accuracy within the system’s operational parameters. Although exemplary performance metrics were recorded within controlled environmental conditions, the system’s adaptability and efficacy in heterogeneous settings–characterized by fluctuating lighting conditions and spatial limitations–warrant additional investigative scrutiny. Moreover, the system’s dependency on robust internet connectivity to facilitate real-time feedback mechanisms introduces a potential constraint, particularly within geographical locales where digital infrastructure is either underdeveloped or non-existent. This dependency underscores a critical area for further development, aiming to enhance the system’s resilience and operational viability across a broader array of environmental and infrastructural contexts.
Future research endeavors should pivot toward amplifying the system’s adaptability to encompass a more extensive array of physical environments and account for the vast spectrum of individual physiological variances. The exploration into integrating cutting-edge technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) harbors the potential to significantly elevate the interactivity and overall efficacy of the training modules. Such technological incorporations could usher in a new era of immersive and engaging physical education experiences. Furthermore, broadening the system’s repertoire to include a diverse assortment of exercises, coupled with the integration of sophisticated adaptive learning algorithms, promises to refine the personalization of training programs. This advancement would not only cater to the unique fitness levels and preferences of each individual but also enhance the motivational aspects of physical training, thereby fostering a more tailored and effective learning environment.
In summary, this research paper has presented a comprehensive analysis of a novel Deep Learning Enabled Exercise Monitoring System, tailored for sustainable online education, particularly in training future teacher-trainers. The study successfully demonstrated the system’s efficacy in accurately monitoring and providing real-time feedback on various physical exercises. With an impressive accuracy rate of 98%, the system marks a significant advancement in the field of remote physical education. The incorporation of the PoseNet model for key point extraction and the subsequent analysis of skeletal structures has proven effective in ensuring precise exercise monitoring. This technological in-novation not only enhances the quality of physical education in an online setup but also addresses the challenges posed by traditional training methods, especially in terms of consistent feedback and assessment. However, the study also acknowledges the limitations, including variability in human movements and environmental factors, suggesting areas for future enhancements. The potential integration with AR and VR technologies, along with the adaptation to a wider array of physical environments, represents promising future research directions. Overall, this study contributes significantly to the domain of digital education technologies, offering a viable and effective solution for the challenges faced in online physical training and setting a precedent for future innovations in sustainable education.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the [patients/ participants OR patients/participants legal guardian/next of kin] was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
NO: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. BO: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. QM: Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZK: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AA: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AT: Investigation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Akhil, S. (2023). Computer vision-based hand exercise monitoring. Adv. Emerg. Comput. Technol. 65:28.
Al Shloul, T., Javeed, M., Gochoo, M., Alsuhibany, S. A., Yasin Ghadi, Y., Jalal, A., et al. (2023). Student’s health exercise recognition tool for E-learning education. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 35, 149–161. doi: 10.32604/iasc.2023.026051
Balkhi, P., and Moallem, M. (2022). A multipurpose wearable sensor-based system for weight training. Automation 3, 132–152. doi: 10.3390/automation3010007
Bennani, S., Maalel, A., and Ben Ghezala, H. (2022). Adaptive gamification in E-learning: A literature review and future challenges. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 30, 628–642. doi: 10.1002/cae.22477
Challa, S. K., Kumar, A., and Semwal, V. B. (2022). A multibranch CNN-BiLSTM model for human activity recognition using wearable sensor data. Vis. Comput. 38, 4095–4109. doi: 10.1007/s00371-021-02283-3
Chen, W. (2022). [Retracted] Application of sensor-based intelligent wearable devices in information physical education. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022:5075425. doi: 10.1155/2022/5075425
Chen, C., Asoni, D. E., Barrera, D., Danezis, G., and Perrig, A. (2015). HORNET: high-speed onion routing at the network layer. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSAC conference on computer and communications security, pp. 1441-1454.
De Beukelaar, T. T., and Mantini, D. (2023). Monitoring resistance training in real time with wearable technology: current applications and future directions. Bioengineering 10:1085. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10091085
Debnath, B., O’Brien, M., Yamaguchi, M., and Behera, A. (2022). A review of computer vision-based approaches for physical rehabilitation and assessment. Multimedia Systems 28, 209–239. doi: 10.1007/s00530-021-00815-4
Doskarayev, B., Omarov, N., Omarov, B., Ismagulova, Z., Kozhamkulova, Z., Nurlybaeva, E., et al. (2023). Development of computer vision-enabled augmented reality games to increase motivation for sports. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 14. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2023.0140428
Frangoudes, F., Matsangidou, M., Schiza, E. C., Neokleous, K., and Pattichis, C. S. (2022). Assessing human motion during exercise using machine learning: A literature review. IEEE Access 10, 86874–86903. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3198935
Gómez-Núñez, M. I., Cano-Muñoz, M. Á., and Gómez-Núñez, J. A. (2023). “Research competence development in higher education through a virtual educational escape room” in Learning with escape rooms in higher education online environments. ed. M. I. Gómez-Núñez (Hershey: IGI Global), 114–133.
Hagenauer, G., Lazarides, R., and Järvenoja, H. (2023). Motivation and emotion in learning and teaching across educational contexts: Theoretical and methodological perspectives and empirical insights. Milton Park: Taylor and Francis.
Hussain, A., Zafar, K., Baig, A. R., Almakki, R., AlSuwaidan, L., and Khan, S. (2022). Sensor-based gym physical exercise recognition: data acquisition and experiments. Sensors 22:2489. doi: 10.3390/s22072489
Janczyk, M., Pfister, R., Janczyk, M., and Pfister, R. (2023). “One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)” in Understanding inferential statistics: From A for significance test to Z for confidence interval (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 97–125.
Kendall, A., Grimes, M., and Cipolla, R. (2015). Posenet: A convolutional network for real-time 6-dof camera relocalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 2938–2946.
Kreiss, S., Bertoni, L., and Alahi, A. (2019) Pifpaf: composite fields for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 11977–11986.
Li, W. T., Li, L. W., Li, S. Y., Mou, J. C., and Hei, Y. Q. (2021). Efficient vertex coordinate prediction-based CSP-hourglass net for object OBB detection in remote sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3133662
Li, Y., Yang, L., He, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, W., et al. (2022). Low-cost data glove based on deep-learning-enhanced flexible multiwalled carbon nanotube sensors for real-time gesture recognition. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4:2200128. doi: 10.1002/aisy.202200128
Mekruksavanich, S., and Jitpattanakul, A. (2022). Rnn-based deep learning for physical activity recognition using smartwatch sensors: A case study of simple and complex activity recognition. Math. Biosci. Eng. 19, 5671–5698. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022265
Mennella, C., Maniscalco, U., De Pietro, G., and Esposito, M. (2023). A deep learning system to monitor and assess rehabilitation exercises in home-based remote and unsupervised conditions. Comput. Biol. Med. 166:107485. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107485
Mitova, M., Tomov, P., Kunicina, N., Patlins, A., Mansurova, M., Namsrai, O. E., et al. (2022). Towards to sustainability of education: the mutual cooperation with partners in smart city project. In: 2022 IEEE 7th international energy conference (ENERGYCON), Riga, Latvia, pp. 1–6.
Morrison, M., Martin, D. T., Talpey, S., Scanlan, A. T., Delaney, J., Halson, S. L., et al. (2022). A systematic review on fitness testing in adult male basketball players: tests adopted, characteristics reported and recommendations for practice. Sports Med. 52, 1491–1532. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01626-3
Nagarkoti, A., Teotia, R., Mahale, A. K., and Das, P. K. (2019). Realtime indoor workout analysis using machine learning, computer vision. In: 2019 41st annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC), IEEE, pp. 1440–1443.
Nagy, M., Lăzăroiu, G., and Valaskova, K. (2023). Machine intelligence and autonomous robotic Technologies in the Corporate Context of SMEs: deep learning and virtual simulation algorithms, cyber-physical production networks, and industry 4.0-based manufacturing systems. Appl. Sci. 13:1681. doi: 10.3390/app13031681
Omarov, B., Narynov, S., Zhumanov, Z., Gumar, A., and Khassanova, M. (2022). A skeleton-based approach for campus violence detection. Comput. Mater. Contin. 72, 315–331. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2022.024566
Omarov, B., Nurmash, N., Doskarayev, B., Zhilisbaev, N., Dairabayev, M., Orazov, S., et al. (2023). A novel deep neural network to analyze and monitoring the physical training relation to sports activities. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 14:977. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2023.0140977
Patalas-Maliszewska, J., Pajak, I., Krutz, P., Pajak, G., Rehm, M., Schlegel, H., et al. (2023). Inertial sensor-based sport activity advisory system using machine learning algorithms. Sensors 23:1137. doi: 10.3390/s23031137
Pham, Q. T., Nguyen, D. A., Nguyen, T. T., Nguyen, T. N., Nguyen, D. T., Pham, D. T., et al. (2022). A study on skeleton-based action recognition and its application to physical exercise recognition. In: Proceedings of the 11th international symposium on information and communication technology, pp. 239–246.
Qiu, S., Zhao, H., Jiang, N., Wang, Z., Liu, L., An, Y., et al. (2022). Multi-sensor information fusion based on machine learning for real applications in human activity recognition: state-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 80, 241–265. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.11.006
Ray, P. P. (2023). ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet of things and cyber-physical systems.
Ren, Q., Li, M., Kong, T., and Ma, J. (2022). Multi-sensor real-time monitoring of dam behavior using self-adaptive online sequential learning. Autom. Constr. 140:104365. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104365
Rouder, J. N., Schnuerch, M., Haaf, J. M., and Morey, R. D. (2023). Principles of model specification in ANOVA designs. Comput. Brain Behav. 6, 50–63. doi: 10.1007/s42113-022-00132-7
Seçkin, A. Ç., Ateş, B., and Seçkin, M. (2023). Review on wearable Technology in Sports: concepts, challenges and opportunities. Appl. Sci. 13:10399. doi: 10.3390/app131810399
Setiawan, R., Devadass, M. M. V., Rajan, R., Sharma, D. K., Singh, N. P., Amarendra, K., et al. (2022). IoT based virtual E-learning system for sustainable development of smart cities. J Grid Comput 20:24. doi: 10.1007/s10723-022-09616-z
Suchomel, T. J., Nimphius, S., Bellon, C. R., Hornsby, W. G., and Stone, M. H. (2021). Training for muscular strength: methods for monitoring and adjusting training intensity. Sports Med. 51, 2051–2066. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01488-9
Thakur, D., Biswas, S., Ho, E. S., and Chattopadhyay, S. (2022). Convae-lstm: convolutional autoencoder long short-term memory network for smartphone-based human activity recognition. IEEE Access 10, 4137–4156. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3140373
Tursynova, A., and Omarov, B. (2021). 3D U-net for brain stroke lesion segmentation on ISLES 2018 dataset. In: 2021 16th international conference on electronics computer and computation (ICECCO), IEEE, pp. 1–4.
Weakley, J., Morrison, M., García-Ramos, A., Johnston, R., James, L., and Cole, M. H. (2021). The validity and reliability of commercially available resistance training monitoring devices: a systematic review. Sports Med. 51, 443–502. doi: 10.1007/s40279-020-01382-w
Whelan, M. E., Denton, F., Bourne, C. L. A., Kingsnorth, A. P., Sherar, L. B., Orme, M. W., et al. (2021). A digital lifestyle behaviour change intervention for the prevention of type 2 diabetes: a qualitative study exploring intuitive engagement with real-time glucose and physical activity feedback. BMC Public Health 21, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09740-z
Zabasta, A., Carreira, P., Nikiforova, O., Amaral, V., Kunicina, N., Goulão, M., et al. (2017). Developing a mutually-recognized cross-domain study program in cyber-physical systems. In: 2017 IEEE global engineering education conference (EDUCON), Athens, Greece, pp. 791–799.
Zalostiba, D., Caiko, J., Ziravecka, A., Patlins, A., Kunicina, N., and Ribickis, L. (2019). Quality assurance in developing of international electrical engineering study programs. In: 2019 IEEE 60th international scientific conference on power and electrical engineering of Riga Technical University (RTUCON), Riga, Latvia, pp. 1–6.
Zheng, K., Wu, J., Zhang, J., and Guo, C. (2023). A skeleton-based rehabilitation exercise assessment system with rotation invariance. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 31, 2612–2621. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3282675
Keywords: online education, distance learning, exercise monitoring, physical eductaion, deep learning, computer vision, artificial intelligence
Citation: Omarov N, Omarov B, Mamutov Q, Kissebayev Z, Anarbayev A, Tastanov A and Yessirkepov Z (2024) Deep learning enabled exercise monitoring system for sustainable online education of future teacher-trainers. Front. Educ. 9:1385205. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1385205
Received: 12 February 2024; Accepted: 18 July 2024;
Published: 30 October 2024.
Edited by:
Carina Soledad González González, University of La Laguna, SpainReviewed by:
Su-Kit Tang, Macao Polytechnic University, Macao SAR, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Omarov, Omarov, Mamutov, Kissebayev, Anarbayev, Tastanov and Yessirkepov. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bakhytzhan Omarov, YmFraHl0emhhbm9tYXJvdkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.