- 1Department of Special Education, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
- 2Department of Education and Special Education, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Supporting children’s language development, particularly oral language, is crucial as it constitutes the basis for the further development of literacy skills. This study explored patterns of primary school children’s expressive language productivity over time in relation to a professional development (PD) program designed to further teachers’ use of communication-supporting strategies to promote child talk. Framed by a Tier 2 response to intervention model, teacher-child verbal interactions were observed during structured small-group conversations. The participants were 36 children (M age 8;2 years old), with and without speech, language and communication needs (SLCN) attending three mainstream classes in two Swedish municipalities. Two teachers followed a 10-week PD program, and a third teacher participated for comparison purposes. We measured the children’s expressive language productivity in relation to the teachers’ strategy use pre-intervention, post-intervention, and at a two-month follow-up. In the results, we found a tendency that when the teachers used the strategies frequently, the children’s expressive language productivity seemed suppressed. Although the results showed a large variation in the children’s expressive language productivity, a tentative conclusion is that the children with SLCN may also be stimulated and willing to participate verbally during this type of small-group conversation. This finding suggests support for an inclusive Tier 2 approach of mixed groups with both children with and without SLCN. Based on our findings, we also suggest stressing in the PD program the need for teachers to balance their strategy use in the interactions with the children to provide ample opportunities for the children to talk and express themselves.
1 Introduction
The development of children’s oral language is an ongoing process, mostly in focus during the pre-school years but continuing through later school years as well (Snow, 2021). Oral language underpins further literacy skills and academic achievement (Hjetland et al., 2018; Snow, 2016, 2021; Snowling and Hulme, 2021; Spencer and Petersen, 2018). Therefore, alongside teaching children to acquire reading and writing skills, the practise of oral language should be continued through the compulsory school years (Snow, 2021). In previous research, language interventions targeting expressive oral language skills are delivered in both individual and group sessions, and indicate overall positive effects (Law et al., 2003; Melby-Lervåg et al., 2020; Rogde et al., 2016). Speech, language and, communication needs (SLCN) is a broad term referring to children’s variation in language skills and needs support (Dockrell et al., 2014). There can be various causes of children’s SLCN. For example, 7–10% of 4–5-year-old children are diagnosed with developmental language disorder (DLD) (Norbury et al., 2016). Although DLD affects a child’s communicative skills, identifying the presence of the disorder may not be possible by only listening to a child’s everyday language (Bawayan and Brown, 2022), and in a classroom situation these children may easily be overlooked. Children without clinical language disorders may also be at risk of developing SLCN, and an estimate is that as many as 12–13% may be affected, due to different reasons (McLeod and McKinnon, 2007). Considering SLCN as a broad term, second-language learning children may struggle with the language of instruction in school, most often provided in the majority language (Monsrud et al., 2022; Rogde et al., 2016). Although having a second language is not to be considered equal to SLCN per se, research has shown a vocabulary gap, on a group level, between second-language learning school-aged children and monolingual children (Fälth et al., 2022; Monsrud et al., 2022). Thus, second-language learning children may need support to acquire and practise the second language, not the least in encountering with the school academic language (Bengochea and Sembiante, 2024).
Schools in Sweden have a compensatory mission to support all children’s needs, and this means to compensate for differences in children’s preconditions and thus to support them achieve the educational goals of the schools (Swedish National Agency for Education, 2022). In the Swedish curriculum, expressive oral language skills are emphasised in all school subjects (Swedish National Agency for Education, 2022), and consequently, children are expected to participate in oral language-oriented classroom activities such as discussions, reasoning and presentations from an early age. However, demonstrating oral skills in the classroom can be challenging for all children, in particular for children with SLCN, and therefore many opportunities for explicit practise are needed (Dockrell et al., 2015). For instance, in a study by Ekström et al. (2023), young people, aged 13–19 years old, with DLD described what they perceived as communicative challenges in school, and participating in oral presentations, conversations, and discussions were considered particularly challenging classroom activities. Whole-class activities appeared to often entail feelings of insecurity and less willingness to participate in verbal classroom interactions among the students (Ekström et al., 2023).
Several studies in a pre-school context have examined children’s language productivity when they are exposed to teacher talk characterised by varied vocabulary, complex syntax and teachers using strategies intended to prompt child talk (Cabell et al., 2015; Girolametto et al., 2003; Girolametto and Weitzman, 2002; Justice et al., 2008; Piasta et al., 2012). Such examples of strategies that may be useful to prompt child talk can be found in the Communication-Supporting Classroom Observation Tool (CSCOT), which is a tool comprising evidence-based teacher methods to support children’s language learning, including aspects of oral language skills (Dockrell et al., 2012, 2015). One part of the CSCOT covers strategies to promote language learning interactions (Dockrell et al., 2012, 2015). As an example, in teacher-child verbal interactions, teachers may use the strategy open-ended questions instead of more closed yes/no questions to enhance child talk. Also, the strategies extending children’s utterances and encouraging children to use new words are examples of efficient strategies to support oral language (Dockrell et al., 2012, 2015). Previous research has studied the possibility of using the CSCOT in professional development (PD) programs for teachers in preschool (Nordberg, 2021), and in the early years of compulsory school with the goal of increasing teachers’ use of communication-supporting strategies in general (Andersson et al., 2022; Badar et al., 2022). In a previous study, Edlund et al. (2023) explored a small-scale PD-program targeting teachers’ use of five specific communication-supporting strategies in teacher-child interactions over time. However, to our knowledge, studies of using the CSCOT in PD programs are scarce in regard to studying child-teacher outcomes from the PD intervention in relation to language outcomes in school-aged children. One example is a study by Sandgren et al. (2023) who used the CSCOT in an 11-week continued PD program intervention in mainstream classrooms to enhance the language and communication-supporting environment, and to also study the effects on seven-year-old students. The result indicated no significant results regarding student performance due to the teachers’ participation in the PD program.
1.1 Structured small-group conversations
Although traditionally most lessons occur in larger classes, discussing the content of a text with a whole class may be a challenging task both for a teacher as well as for the students. In typical whole-class activities, there are quite limited opportunities for all children to interact with the teacher (Eadie et al., 2021; Hattie, 2008). Therefore, teachers may miss providing linguistic stimulation to children with SLCN. For students with language difficulties, whole-class verbal activities may be particularly demanding to participate in Ekström et al. (2023). An alternative to whole-class activities is to organize structured small-group conversations. Small-group conversations may be particularly suited to supporting children’s different needs in practicing oral language (King and Dockrell, 2016; Rogde et al., 2019). To read and discuss texts is a natural way to provide a meaningful context for children to verbally interact with the teacher and each other (Beck and McKeown, 2001; McKeown and Beck, 2004). In sessions involving ‘reading aloud’ followed by conversations about the text, the teacher has opportunities to take an active role in scaffolding (Vygotsky, 1962) and can support all children to engage in the conversations. Such scaffolding may be accomplished by the teacher using communication-supporting strategies such as asking open-ended questions, explaining words, extending children’s utterances, and encouraging children to use new words (Beck and McKeown, 2001; Dickinson and Porche, 2011; Dockrell et al., 2015; Wasik and Iannone-Campbell, 2012). These types of strategies may not only support language development, but also promote children’s engagement by drawing their attention to an interesting conversation (Lingwood et al., 2022).
1.2 Response to intervention
Interventions are often described within a response to intervention (RTI) tiered model, which usually has three tiers: Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3. The model stems from a framework developed to prevent school academic failure by assessing students’ specific need for support and by providing evidence-based classroom instructions (Fuchs and Fuchs, 2006). Language and communication interventions in schools can thus be provided on different RTI tiers due to a child’s specific need for support (Ebbels et al., 2019; Law et al., 2012). In regard to language and communication interventions, Tier 1 is the general teaching characterised by providing high-quality teaching to all students (Ebbels et al., 2019; Law et al., 2012). Tier 2, involves students who struggle in the mainstream classroom and hence may need additional and more intense support, which is often provided in small groups. Finally, Tier 3 involves students with persistent challenges and who are in need of continuous and individual support. Interventions provided at Tiers 2 and 3 are usually similar to the one used for Tier 1, yet with a more comprehensive intensity and duration (Fuchs and Fuchs, 2006). The present study is framed by Tier 2 with mixed small groups of children with and without SLCN to enable an inclusive approach where the children may act as language role models, and thus support a proximal development zone (Vygotsky, 1962).
1.3 The present study
The aim of the present study was to explore patterns in children’s expressive language productivity in relation to teachers’ use of communication-supporting strategies during structured small-group conversations. We explored language productivity patterns in children with two teachers following a PD program to increase the teachers’ use of five targeted communication-supporting strategies from the language learning interactions in the CSCOT: (1) use of open-ended questions, (2) extending children’s utterances, (3) labelling items and actions, (4) highlighting differences between words, and (5) encouraging the use of new words (Dockrell et al., 2012, 2015). Classroom observations with the CSCOT have, overall, shown that strategies promoting language learning interactions seem less frequently used compared to other strategies in the tool (Dockrell et al., 2015; Law et al., 2019). Hence, these types of strategies are of particular interest for teachers to increase. The targeted strategies were selected to represent verbal interactions. Non-verbal interactions such as gestures were not included in the PD program. Furthermore, in the activity of structured small-group conversations, the five chosen strategies were sought to promote children’s expressive language directly, and therefore appropriate to include. Moreover, due to the small-scale design of the present PD program, it did not seem applicable to include all language learning interaction strategies in the CSCOT. Previous research has suggested that the CSCOT can be used flexibly in observations, using the whole, or parts of the tool (Dockrell et al., 2015; Law et al., 2019). Patterns were also explored for a comparison group of children, and a teacher who did not follow the PD program. The focus of this study was to extend the analyses from the PD program (Edlund et al., 2023) to explore child outcomes.
The research questions for the study are:
I. What are the patterns regarding the quantity and quality of children’s expressive language productivity during structured small-group conversations in relation to teachers’ use of five communication-supporting strategies following a PD program?
II. What is the expressive language productivity over time for children with SLCN and for age-matched children without SLCN?
2 Method
2.1 Design
The present study is exploratory (Hallingberg et al., 2018) using a pre-, post-, and follow-up design (Shadish et al., 2002) to describe children’s expressive language productivity over time in relation to teachers’ use of five communication-supporting strategies. The research was approved by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority (protocol number 2019–02735).
2.2 Participants
2.2.1 Selection of participants
The first author contacted the principals of a total of 30 primary schools by e-mail to recruit voluntary participants for the study. The principals then forwarded information to teachers working in second-grade. We recruited the first three teachers who were eager to participate and who met the inclusion criteria of adequate degrees for teaching in primary school but with no specialist competence in teaching children with SLCN. Two of the teachers received the PD program, and one teacher participated for comparison purposes, and did not receive the PD program. After the recruitment of the teachers, the children and the parents in each class were informed about the study’s aim in general, and the observation procedure in particular. All children in each class who agreed to participate in the structured small-group conversations were allowed to take part. Although there were no exclusion criteria for the children, only the conversation groups involving children with SLCN and their age-matched peers were in focus for the analysis in the present study. Written consent was obtained from the teachers and the legal guardians and the children themselves. The participants were informed that they could end participation at any time.
2.2.2 Identification and validation of SLCN
With reference to a broad definition of SLCN (Dockrell et al., 2014), each teacher was first asked to make an initial preliminary identification of about 25% of the children from the whole class (among those children who participated) who they considered might have SLCN for different reasons. From each class, six or seven children were initially identified as having SLCN. These could include both children with clinical language disorders for instance DLD, as well as children who the teachers assessed as at-risk children. The initial identification of children with SLCN was thereafter validated with the teachers completing the Children’s Communication Checklist (CCC-2; Bishop, 2003, 2012), a screening instrument assessing children’s skills in general communication and in social language skills (i.e., interactions with others) (Bishop, 2003). The CCC-2 is a questionnaire comprising 70 items with a four-option response scale assessing challenges and strengths in communication of children aged 4:0–16:11 years (Bishop, 2003). Different aspects of communication are measured on subscales (e.g., semantics, syntax, and use of context). For the validation of children with SLCN, the cut-off values following the Swedish version of the CCC-2 manual were used (Bishop, 2012). The researcher was not involved in the procedure of the identification of children with SLCN. However, the teachers were individually informed about how to complete the CCC-2 and could contact the researcher if questions arose. For all children but one, the CCC-2 assessment coincided with the teacher’s initial assessment and was thus valid according to the consistency check in the instrument (Bishop, 2003, 2012). From a discussion with the teacher, it was clear the child had a history of difficulties related to language skills and the child was therefore still included among the children with SLCN.
2.2.3 Participants
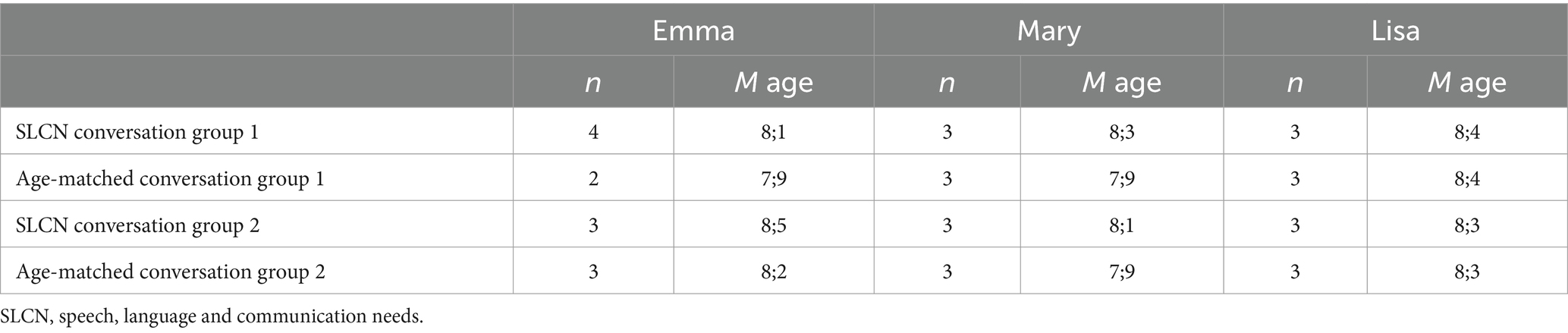
A total of 36 children aged 7–9 (M age = 8;2, SD = 0;4) from three Swedish second-grade classes in primary school participated in the current study. The schools were situated in two different Stockholm suburban municipalities with similar demographics. From each class, 12 children and their respective teachers participated. Both children with SLCN (~ 50%) and age-matched children without SLCN participated. Table 1 shows the mix of the children (i.e., SLCN and age-matched), and their ages at pre-intervention for each of the teacher’s two small conversation groups. All but one conversation group (Emma’s conversation group 1), had an even mix of children with SLCN and age-matched children. To minimise the advantage that maturity aspects could bring, the children with SLCN were in most cases slightly older or of the same age as the age-matched children without SLCN in the conversation groups. The teachers were given fictitious names in the study. Emma and Mary were the PD program teachers, and Lisa was the comparison teacher. The teachers were aged 44–47 years, and they each had 17–19 years of teaching experience in primary school.
2.3 Setting and procedure
Framed by a Tier 2 RTI model (Ebbels et al., 2019; Fuchs and Fuchs, 2006; Law et al., 2012), the setting for the teacher-child verbal interactions was structured small-group conversations (hereafter SGCs). Each of the three teachers conducted SGCs with two separate small groups of six children per group (see Table 1), performed at four time points spread evenly during the PD program, and once at the two-month follow-up. The SGCs’ duration varied ranging from 7:16 to 19:14 min (total time 390:52 min, Md = 12:44 min).The small group compositions stayed the same over time. The teachers and the children were familiar to each other since earlier. In the present study, the teachers had followed the children from grade 1 in primary school. The teachers were instructed to first read a short text of about 5 min aloud in the small group, and thereafter discuss the text content with the children for a total of about 20 min per conversation. The texts varied for each time point, yet they were the same for all conversation groups. The texts were selected by the first author with advice from a children’s book librarian and they were a variation of shorter parts of authentic and age-appropriate children’s books. The criteria were to find texts with an appealing narrative that had been published quite recently and were appropriate for about a five-minute read-aloud. The SGCs occurred in study rooms near the classrooms, with the teacher and the children sitting closely around a table. During the conversation sessions, the rest of the class remained in the ordinary classroom doing school tasks with other teachers well known to them. The procedure for the SGCs was the same for the comparison children, but without their teacher participating in the PD program. The comparison teacher received the same information as the intervention teachers about the procedure for the SGCs, but no information was given regarding the content of the PD program.
2.3.1 Intervention: the PD program
The PD program was a small-scale 10-week intervention designed to coach teachers individually to use communication-supporting strategies in their everyday classroom teaching. The strategies were selected from the CSCOT (Dockrell et al., 2012, 2015) and targeted teachers’ use of five communication-supporting strategies aiming to stimulate child talk during teacher-child interactions (see also Section 1.3 for a list of selected strategies). Two intervention teachers (i.e., Emma and Mary), received the PD program and participated in four individual coaching sessions every other or third week lasting about 1 h each time (the total time of the PD was 270 min). Each coaching session was preceded by direct observations during the teacher-child SGCs, using the CSCOT to take notes of the teachers’ strategy use in order to coach the teachers in using the targeted strategies. To provide coaching in close connection with the direct observations, the observation and coaching sessions were scheduled on the same day for each teacher. Since the first observation was a pre measurement, the intervention teachers had no detailed information about the content of the PD program. In the following first coaching session, the intervention teachers were fully introduced to the PD program and the five communication-supporting strategies. The PD program focused overall on providing the teachers with a theoretical background on the importance of using the strategies to stimulate child talk, to provide opportunities for practicing the strategies, and to reflect in feedback conversations. The teacher coaching was provided by the first author, who has a background as a special needs teacher in compulsory school. A follow-up observation was conducted 2 months after the intervention was finished. For further details on the PD program, see the previous study by Edlund et al. (2023).
2.4 Data collection
The teacher-child verbal interactions were video-recorded during the SGCs and used for the following quantified language analysis (Mercer, 2010). The equipment used was a small video camera with an external microphone, and an iPad was used as a backup camera. The cameras were placed near the teacher-child group.
2.4.1 Measures
The children’s expressive language productivity was measured over time at three time points in relation to the PD program intervention: pre-intervention, and post-intervention with 10 weeks in between, and at a two-month follow-up. The children’s language productivity was analysed in relation to the teacher’s use of the five targeted communication-supporting strategies.
2.4.1.1 Child measures
Language productivity quantity and quality were measured based on transcribed speech samples from the video-recorded data. Language productivity quantity was measured by the total number of words spoken per minute (TNW/min) (i.e., word tokens; Hoff and Naigles, 2002). Language productivity quality was measured by the number of different words spoken per minute (NDW/min) (i.e., word types; Hoff and Naigles, 2002), and mean length utterance (MLU). TNW and NDW were measured on a frequency level in rate per minute due to differences in the duration of video-recorded speech samples. MLU is the ratio between the total number of words or morphemes and the total number of utterances (Casby, 2011; Rice et al., 2010). Previous research shows a high correlation between measuring MLU with words compared to MLU measured with morphemes (Parker and Brorson, 2005), and in this study, MLU was measured on the word level.
There were nine missing data points spread across the three time points (pre-, post-, and follow-up) due to the children’s absence. The missing data represented children (SLCN n = 7, age-matched n = 2) from all three teacher groups. During the SGCs, there were always at least five of the six children present in each of the small groups. For language productivity quantity and quality, missing data were imputed for a current time point based on the mean of the specific absent child’s remaining values over time to stay close to the child’s actual performance over time (Engels, 2003).
2.4.1.2 Teacher measures
Each teacher’s use of the five targeted communication-supporting strategies was calculated on a frequency level as a total strategy use at each of the three time points (i.e., pre-, post-intervention, and follow-up). Total strategy use was calculated as a rate per minute due to duration differences in the video-recorded speech samples.
2.5 Data analysis
2.5.1 Transcriptions and video coding
The video-recorded SGCs were transcribed orthographically on word level using the CHILDES system (Child Language Data Exchange Systems) (MacWhinney, 2000), and the CHAT (Codes for the Human Analysis of Transcripts) guidelines (MacWhinney, 2000). The first and the fourth author conducted the transcriptions, both with previous experience of transcribing in the CHILDES system. The focus was on the teacher-child verbal interactions during the SGCs after the teacher’s read-aloud was completed. Thus, general teacher-child talk at the beginning of the conversations and the teacher’s read-aloud sessions were not included in the transcriptions. Feedback morphemes such as “mm” were transcribed but excluded from the analysis.
2.5.2 Interobserver agreement
An interobserver percentage agreement was completed for both children and teachers. Nine randomly selected six-minute video sequences from the complete data set were independently analysed by the first and the fourth authors. The procedure was blinded for the fourth author in that the teachers and the order of the time points were not revealed. For the children, agreement (%) between observers was assessed on each child’s total speech production for each of the sequences based on word and utterance level. The percentage agreement for the children on word level was M = 94.14, SD = 6.40, and the utterance level was M = 82.22, SD = 14.22. For the teachers’ transcribed speech, a point-by-point interobserver agreement (%) was completed on word and utterance level. The percentage agreement on word level was M = 93.32, SD = 1.68, and the utterance level was M = 90.46, SD = 7.43. Interobserver agreement (%) for teachers’ strategy use coding yielded M = 80.02, SD = 5.89. If there was disagreement, it was resolved through discussions.
2.5.3 Language productivity analysis
Descriptive statistics and visual inspections were used to analyse the patterns of the children’s expressive language productivity in relation to the teachers’ strategy use over time. For each teacher, total strategy use/min was analysed as an average (median) based on the two small conversation groups at each time point.
To analyse overall patterns of the children’s language quantity (TNW/min) and quality (NDW/min and MLU), each teacher’s two small conversation groups, with six children per group, were analysed as one whole group per teacher (n = 12 children). Due to the small sample and overall skewed data showing a large within-group variation, particularly for the word productivity, average values are presented in median. To further explore differences between the cases, non-parametric statistical methods were used for the analysis. We performed Kruskal–Wallis tests with post-hoc pairwise comparisons, using adjusted significance values, to explore case differences.
Given the small sample size and an overall large variation in the children’s language productivity, we used descriptive analysis based on the median value to explore differences in the children’s language productivity quantity and quality for the children with SLCN and the age-matched children. This analysis was also based on merged data from the respective teacher’s two small conversation groups. Thus, for each teacher, the analysis was based on six or seven children with SLCN and five or six age-matched children (see Table 1 for the mix of children per teacher).
3 Results
For each of the three cases of teachers and children, we present the results illustrating the children’s patterns of language productivity quantity and quality in relation to the teachers’ strategy use over time. Thereafter, we describe the language productivity in children with and without SLCN over time for each case. The results are presented visually in figures and tables. Tables 2–4 show the overall descriptive data for the children’s language productivity over time. The explored case differences between the three teachers’ children are also presented.

Table 2. Descriptive data on the children’s word productivity (TNW/min) over time for each of the teachers.
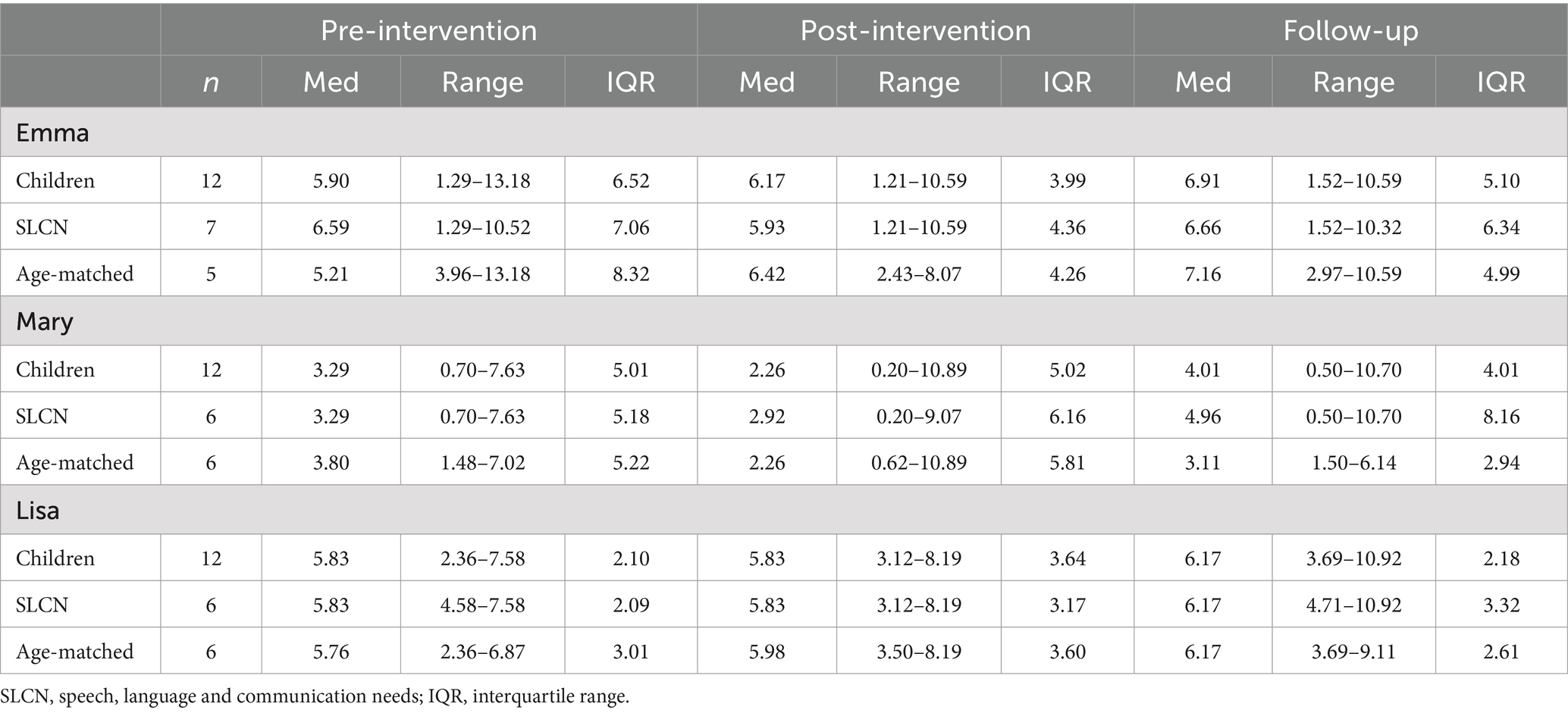
Table 3. Descriptive data on the children’s number of different words (NDW/min) over time for each of the teachers.
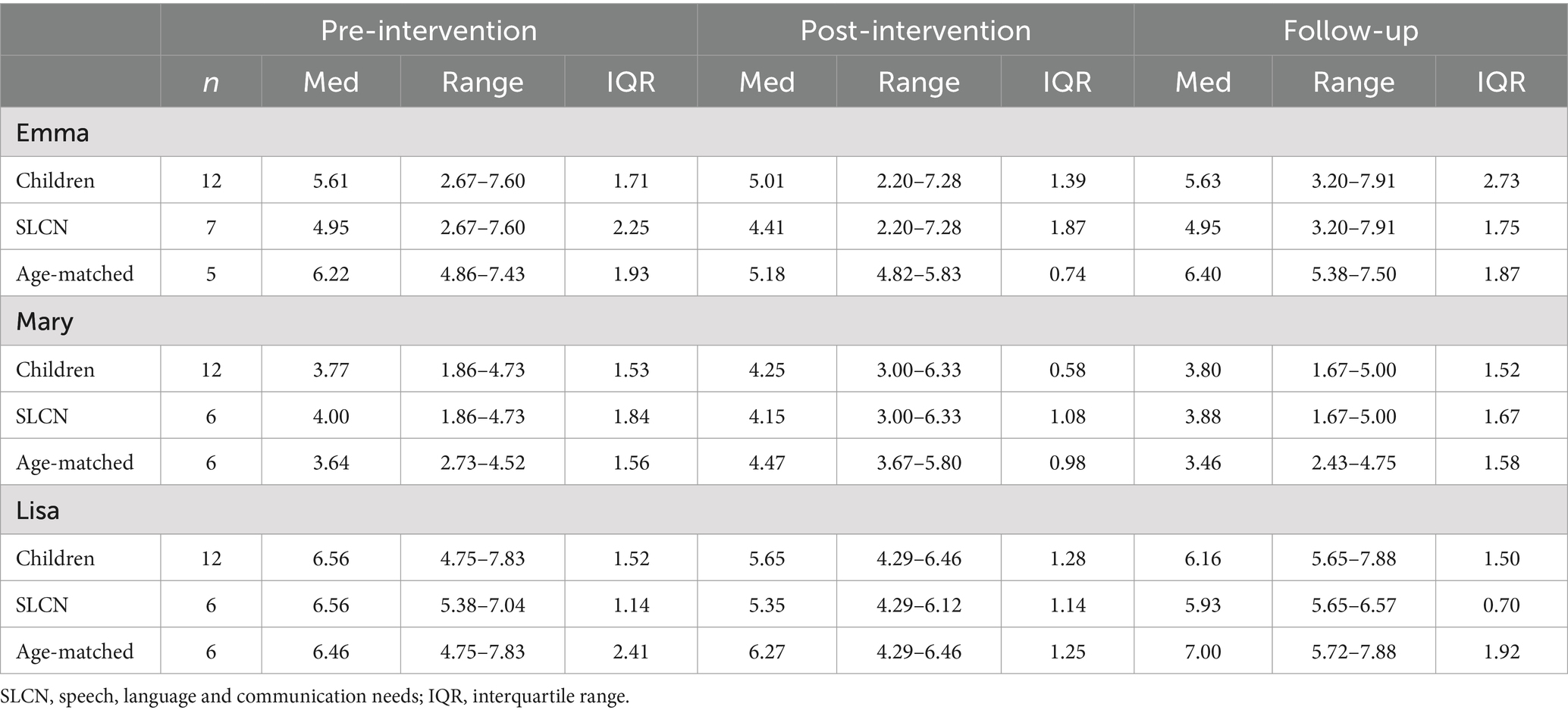
Table 4. Descriptive data on the children’s mean length utterances (MLU) over time for each of the teachers.
3.1 Case 1. Emma’s children
3.1.1 Language productivity quantity
Table 2 shows descriptive data for the children’s language productivity quantity (TNW/min). Figure 1A shows the pattern for the language productivity quantity over time for Emma’s children (i.e., SLCN and age-matched, n = 12) in relation to the teacher’s strategy use. Emma’s median strategy use/min over time was: pre- = 4.37 strategies/min, post- = 7.13 strategies/min, and follow-up = 6.55 strategies/min. A visual analysis of the children’s median word productivity (Md TNW/min = 8.53–11.56), showed that from pre- to post-intervention, the children increased their TNW/min in relation to increased teacher strategy use. Thus, the children’s pattern of word productivity followed the teacher’s strategy use. The pattern seemed to continue at follow-up, showing maintained high child word productivity in relation to the teacher’s almost maintained strategy use. Importantly, as shown in Table 2, the children showed individual differences in their word productivity demonstrated by a large variation over time (range 1.33–28.55 TNW/min).
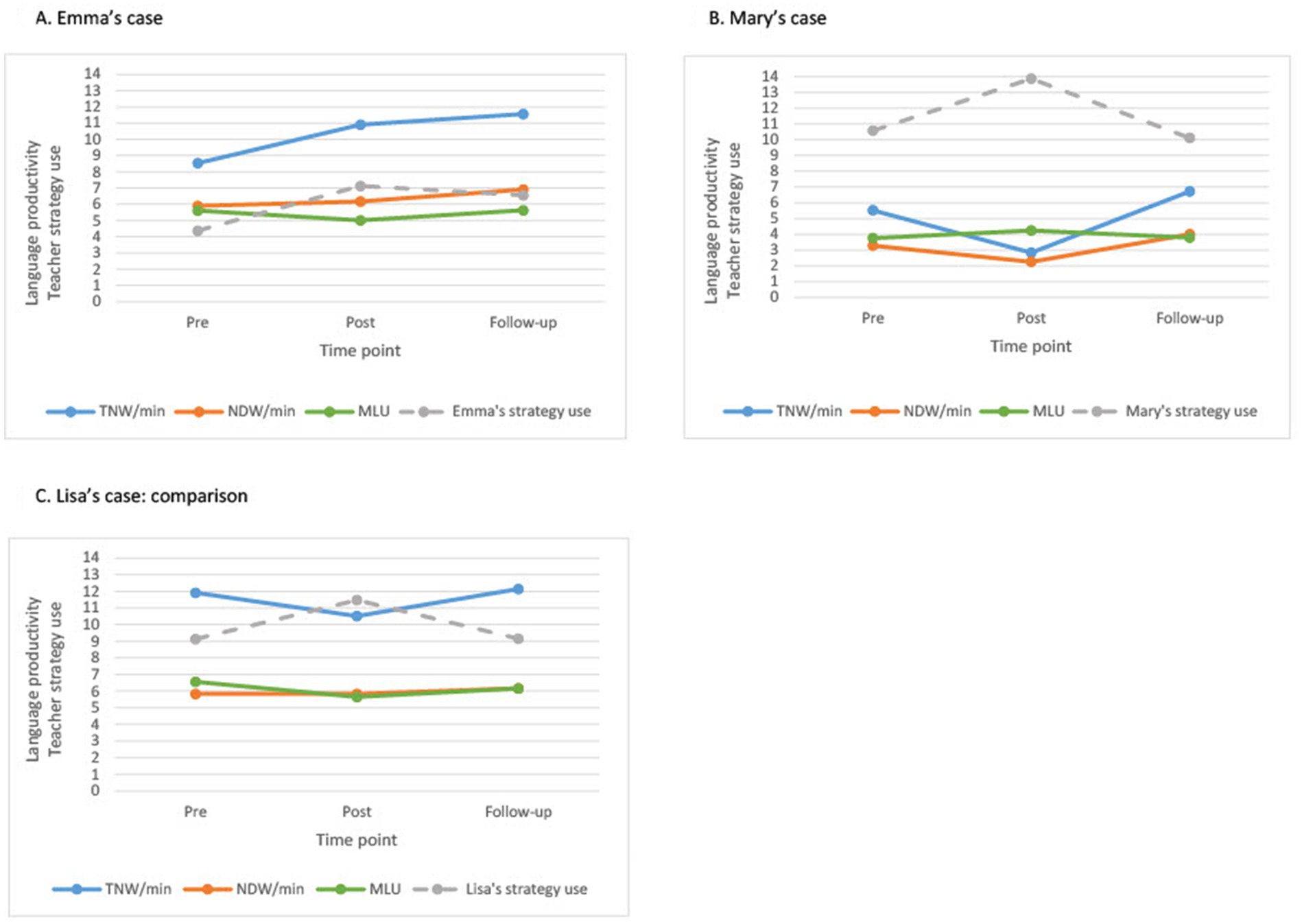
Figure 1. (A–C) The children's (n = 12 per teacher) median language productivity quantity and quality in relation to the teacher's strategy use. (A) Emma's case, (B) Mary's case, and (C) Lisa's case: comparison. TNW/min, total number of words per minute; NDW/min, number of different words per minute; MLU, mean length utterance.
3.1.2 Language productivity quality
Tables 3, 4 show descriptive data for the children’s language productivity quality (NDW/min and MLU). Figure 1A shows the pattern for the children’s language productivity quality in relation to the teacher’s strategy use over time. Overall, a visual analysis showed that the number of different words the children used (Md NDW/min = 5.90–6.91) and the utterance length (Md MLU = 5.01–5.63) indicated a pattern of small changes over time and did not follow the teacher’s increased strategy use.
3.1.3 Language productivity in children with and without SLCN
Figure 2A shows the distribution of language productivity quantity and quality in the children with SLCN and the age-matched children over time. The median word productivity seemed to be consistently slightly higher, or about the same, for the children with SLCN (Md TNW/min = 9.56–12.93) over time compared to the age-matched children (Md TNW/min = 7.50–10.77). However, as shown in Table 2, there was a large variation in the children, indicating individual differences among the children with SLCN (range 1.33–24.17 TNW/min) as well as among the age-matched peers (range 3.04–28.55 TNW/min). The distribution of NDW/min in the children with SLCN and the age-matched children was similar to that of TNW/min, also showing a variation in the children (see also Table 3). Regarding the children’s MLU over time, the children with SLCN showed consistently lower MLU (Md = 4.41–4.95) than the age-matched children (Md = 5.18–6.40). A large variation was seen for the children with SLCN. See Tables 2–4 for all numbers.
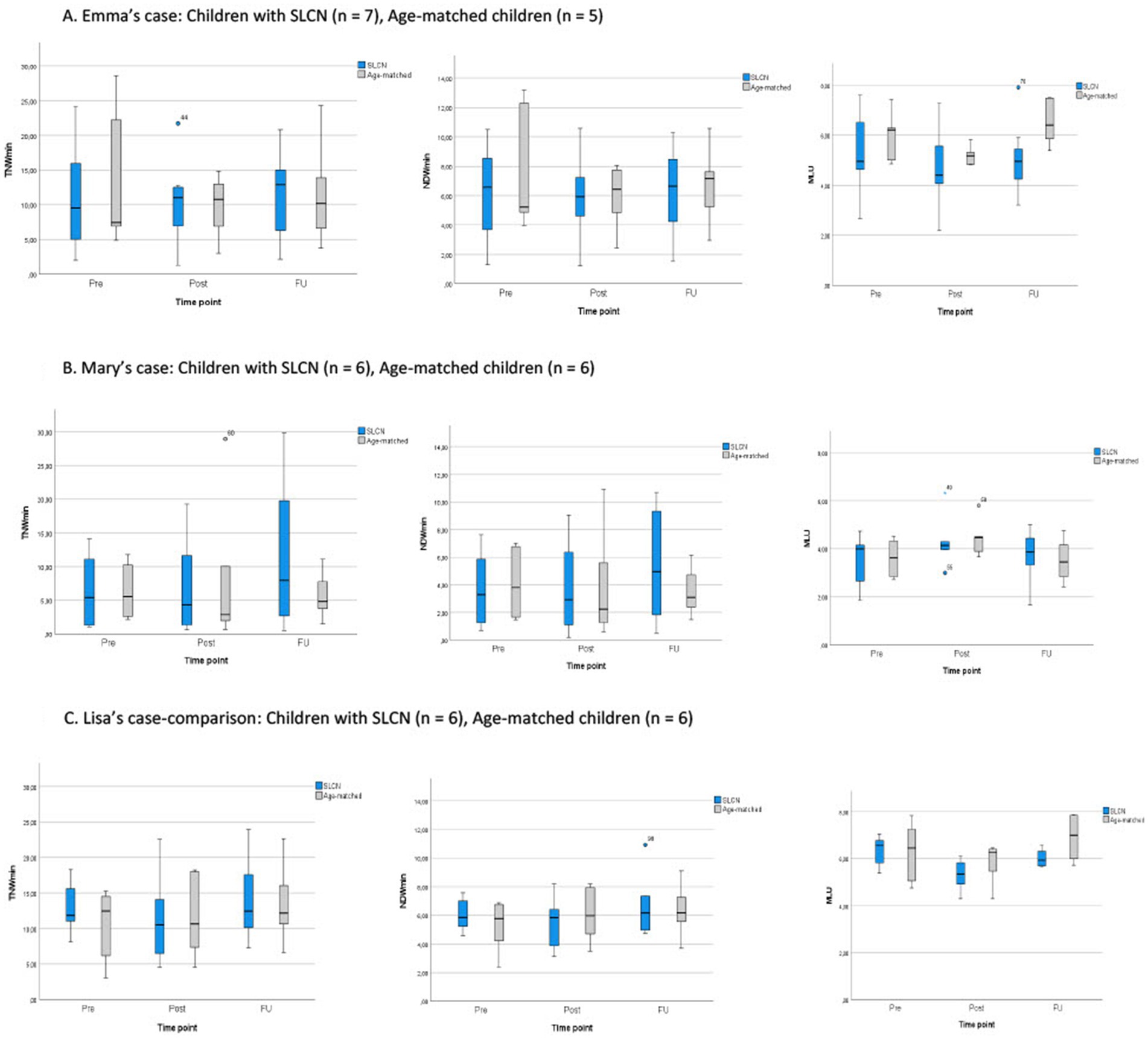
Figure 2. (A–C) Clustered boxplots showing the distribution of the language productivity quantity and quality in the children with SLCN and the age-matched children for each teacher over time. (A) Emma's case: Children with SLCN (n = 7), Age-matched children (n = 5), (B) Mary's case: Children with SLCN (n = 6), Age-matched children (n = 6), (C) Lisa's case-comparison: Children with SLCN (n = 6), Age-matched children (n = 6). SLCN, speech, language and communication needs; Pre, Pre-intervention; Post, Post-intervention; FU, follow-up. The boxplots are clustered by time point and children (i.e. SLCN and age-matched) and show minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, maximum values, and any outliers.
3.2 Case 2. Mary’s children
3.2.1 Language productivity quantity
Table 2 shows descriptive data for the children’s language productivity quantity (TNW/min). Figure 1B shows the pattern for the language productivity quantity over time for Mary’s children (i.e., SLCN and age-matched, n = 12) in relation to the teacher’s strategy use. Mary’s median strategy use/min over time was pre = 10.58 strategies/min, post = 13.88 strategies/min, and follow-up = 10.12 strategies/min. A visual analysis of the children’s median word productivity (Md TNW/min 2.84–6.73) showed that from pre to post-intervention, the children decreased their TNW/min when the teacher increased her strategy use. Thus, the pattern of the children’s word productivity did not follow the teacher’s strategy use. At follow-up, the pattern returned to about the same as at pre-intervention, showing increased child word productivity when the teacher decreased her strategy use. Also, in Mary’s case, the children showed individual differences in their word productivity, demonstrated by a large variation over time (range 0.50–29.83 TNW/min) (see Table 2).
3.2.2 Language productivity quality
Tables 3, 4 show descriptive data for the children’s language productivity quality (NDW/min and MLU). Figure 1B shows the pattern for the children’s language productivity quality in relation to the teacher’s strategy use over time. A visual analysis of the number of different words the children used (Md NDW/min = 2.26–4.01) and the utterance length (Md MLU = 3.77–4.25) showed overall small changes over time and these did not follow the teacher’s strategy use.
3.2.3 Language productivity in children with and without SLCN
Figure 2B shows that the median word productivity was about the same at pre-intervention for the children with SLCN (Md TNW/min = 5.39) and the age-matched children (Md TNW/min = 5.53). At follow-up, the children with SLCN showed increased word productivity (Md TNW/min = 7.96) compared to the age-matched children (Md TNW/min = 4.85). However, it should be noted that there was a large variation in the children with SLCN (range 0.61–29.83 TNW/min), also found in the age-matched peers (range 0.62–28.96 TNW/min). Regarding NDW/min the distribution was similar to that of TNW/min for the children with SLCN and the age-matched children, also showing a variation in the children (see also Table 3). However, even with increased word productivity for the children with SLCN, they did not tend to use longer utterances and thus their MLU was consistently short (Md = 3.88–4.15). Overall, short MLU was shown for the age-matched children as well (Md = 3.46–4.47). Regarding MLU, there seemed to be no apparent differences over time between children with and without SLCN. Also in this case, there were individual differences in the children to consider. See Tables 2–4 for all numbers.
3.3 Case 3. Lisa’s children: comparison
3.3.1 Language productivity quantity
Table 2 shows descriptive data for the children’s language productivity quantity (TNW/min). Figure 1C shows the pattern for language productivity quantity over time for the comparison children (i.e., SLCN and age-matched, n = 12) in relation to the teacher’s strategy use. Lisa’s median strategy use over time was pre = 9.13 strategies/min, post = 11.47 strategies/min, and follow-up = 9.15 strategies/min. A visual analysis of the comparison children’s pattern showed that their word productivity (Md TNW/min = 10.51–12.14) decreased slightly from pre- to post-intervention in relation to the teacher’s spontaneously increased strategy use. Thus, the pattern of the children’s word productivity did not follow the teacher’s strategy use. At follow-up, the comparison children showed about the same word productivity as at pre-intervention in relation to the teacher’s strategy use. Table 2 shows that there were individual differences in the comparison children’s word productivity over time as well (range 3.00–23.96 TNW/min).
3.3.2 Language productivity quality
Tables 3, 4 show descriptive data for the children’s language productivity quality (NDW/min and MLU). Figure 1C shows the pattern for the children’s language productivity quality in relation to the teacher’s strategy use over time. A visual analysis of the number of different words the children used (Md NDW/min = 5.83–6.17) and utterance length (Md MLU = 5.65–6.56) showed overall small changes over time and these did not follow the teacher’s strategy use.
3.3.3 Language productivity in children with and without SLCN
Figure 2C shows that the median TNW/min is about the same for the children with SLCN (Md = 10.51–12.40) and the age-matched children (Md = 10.64–12.42) over time. For NDW/min the distribution was similar to that of TNW/min for the children with and without SLCN (see also Table 3). Overall, for TNW/min and NDW/min, the children showed small changes over time and there seemed to be no apparent differences between the children with SLCN and the age-matched children. Regarding MLU, the children with SLCN showed slightly lower, or about the same MLU (Md = 5.35–6.56) compared to the age-matched children (Md = 6.27–7.00). See Tables 2–4 for all numbers.
3.4 Case differences in language productivity
Each case showed different patterns developing for the children’s expressive language productivity in relation to the teacher’s strategy use over time. Moreover, the visual analysis showed that Mary’s children stood out from the other two teachers’ children. Overall, Mary’s children seemed to produce fewer words per minute and shorter utterances compared to, especially, the comparison teacher Lisa’s children. Hence, to further understand the patterns from the visual analysis of the children’s language productivity in relation to the teachers’ strategy use, we explored the differences between the three cases. A Kruskal-Wallis test was performed for each language variable to explore whether there were any differences between the three teachers’ children (n = 12 children per teacher) over time.
With regard to language productivity quantity, the Kruskal-Wallis test yielded a statistically significant difference in word productivity (TNW/min) between the children at pre-intervention (Emma n = 12; Mary n = 12; Lisa n = 12), p = 0.045. Mary’s children produced significantly fewer words (Md = 5.53, p = 0.049) than Lisa’s children (Md = 11.91). However, there were no significant differences in word productivity between Mary and Emma’s children, nor between Emma and Lisa’s children over time. Regarding language productivity quality, no statistically significant differences were found for the number of different words used (NDW/min) between any of the teacher’s children over time. In contrast, there were statistically significant differences in MLU between the children over time (Emma, n = 12; Mary, n = 12; Lisa, n = 12), p pre = <0.001, p post =0.011, p follow-up = <0.001. Pairwise comparisons showed that Mary’s children showed significantly lower MLU at pre-intervention (Md = 3.77, p =< 0.001) and at follow-up (Md = 3.80, p = 0.008) than Emma’s children (Md pre = 5.61; Md follow-up = 5.63). Also, Mary’s children showed significantly lower MLU at pre-intervention (Md = 3.77, p =< 0.001), post-intervention (Md = 4.25, p = 0.008), and at follow-up (Md = 3.80, p =< 0.001) than Lisa’s children (Md pre = 4.98; Md post = 4.88; Md follow-up = 5.52). There were no significant differences in MLU between Emma and Lisa’s children over time.
To summarise, although the children’s word productivity did not differ significantly more than between Mary and Lisa’s children at the pre-intervention, the result implies that there was less ongoing child talk for Mary’s children at that time point. The result also implies that the number of different words used (NDW/min) was similar in all of the three teacher’s children over time. Regarding MLU, the analysis supports the results from the visual inspection. Mary’s children produced shorter utterances over time compared to Emma and Lisa’s children. The differences in MLU between Mary and Lisa’s children were maintained over time.
4 Discussion
The first research question explored the children’s expressive language productivity quantity and quality in relation to the teacher’s use of five communication-supporting strategies following our PD program. Overall, as shown also in the comparison case, there was a tendency that when the teachers used the strategies frequently, the children’s expressive language productivity seemed suppressed. Also, in general, there was a large variation in the children’s expressive language productivity, meaning that there were individual differences in the children’s verbal participation during the SGCs. The visual analysis for the children with the two teachers following the PD program showed different patterns developing over time. In Emma’s case, the overall pattern showed that the children’s word productivity (TNW/min) seemed to be affected positively in relation to Emma’s increased strategy use during the SGCs. Although there were individual differences in the children, the children’s word productivity followed the teacher’s strategy use during the intervention (pre- to post-intervention). That is, the children produced more words when the teacher increased her strategy use. The children’s word productivity also seemed to be maintained at the follow-up 2 months after the PD program. Emma seemed skilled in bringing forward the children’s talk in the interactions. In Mary’s case, however, the opposite pattern was seen, in which the children’s word productivity did not follow the teacher’s strategy use. Despite a large variation in the children, and Mary’s efforts in applying the targeted strategies, her frequent use of the strategies during the intervention seemed to reduce the children’s opportunities to participate in the conversations. At the follow-up, the children showed a more positive pattern of increased word productivity, possibly an effect of the teacher’s decreased strategy use. Yet Mary’s children also showed individual differences in their language productivity during the SGCs. For the comparison children, a pattern similar to that of Mary’s children was seen, in which the children’s word productivity did not follow the teacher Lisa’s strategy use, yet the pattern was not as apparent as in Mary’s case. Overall, the comparison children decreased their word productivity when the teacher spontaneously increased her strategy use. Lisa seemed skilled in actively and spontaneously using the strategies, and at the same time providing the children with many opportunities to talk.
The visual analysis of the children’s language productivity quality showed overall patterns of small changes over time in relation to the teachers’ strategy use. Regardless of the teacher’s strategy use, for each teacher the children showed about the same number of different words used (NDW/min) over time, and a similar pattern was shown for utterance length (MLU). Although there were individual differences in the children, the outcomes for these language variables seemed to be consistent over time.
In order to gain further understanding of the patterns, we also conducted an explorative case difference analysis, which showed a significantly lower word productivity in Mary’s children compared to the comparison children at the pre-intervention, indicating there had been a difference in the two groups of children from the beginning. This difference should be carefully interpreted since observations were not independent (i.e., the same sample of children was measured over time). However, a possible interpretation might be that since Mary and the comparison teacher Lisa used about the same number of the five targeted communication-supporting strategies at pre-intervention, other strategies or teaching techniques not included in the PD program could possibly explain the difference in child outcome. For example, the amount of teacher talk could be an explanatory factor. In our previous study, we found that Mary talked more than Emma and the comparison teacher Lisa over time (Edlund et al., 2023). Moreover, the case difference analysis also showed that Emma and Lisa’s children produced significantly longer MLU compared to Mary’s children over time. This finding of consistently lower levels of MLU shown by Mary’s children, and the lower word productivity at pre-intervention may indicate that overall, Mary’s children experienced less opportunity to interact and talk during the conversations. In contrast, Emma and Lisa’s children showed other patterns where overall, there seemed to be more opportunities to talk during the SGCs. We can only speculate from what was observed during the SGC’s in our study, but teacher differences beyond the targeted strategies such as pace, pausing, and ensuring opportunities for all children to talk may indeed have affected the teacher-child interactions, also discussed in our previous study (Edlund et al., 2023). Although it was not part of the PD program, the teachers themselves raised these issues in the feedback conversations during the coaching sessions. Furthermore, the finding also raises the question of whether there might also have been some misjudgments in the children’s communicative skills from the beginning in Mary’s group, meaning that there may have been children among the age-matched children with SLCN. According to Rice et al. (2010), children with language impairment have lower average levels of MLU on word level than children without language impairment measured over time.
The second research question explored patterns of expressive language productivity quantity and quality in children with, and without SLCN. Our results showed that both the children with SLCN and the age-matched children had opportunities to talk during the SGCs. Regardless of whether they had SLCN or not, the children seemed to express themselves on about an equal level. Overall, it did not appear as if the children with SLCN as a group were less talkative compared to their age-matched peers. At times, the children with SLCN demonstrated a higher language productivity level (i.e., TNW/min and NDW/min) than their age-matched peers. However, and as mentioned above, the children showed large individual differences, and some children almost did not talk at all during the SGCs. Still, it was noticeable that some of the most talkative were children with SLCN. However, regarding utterance length, the age-matched children seemed to overall show higher levels of MLU compared to the children with SLCN, which was expected (Rice et al., 2010). The exception was Mary’s children, who regardless of whether they had SLCN or not, showed low MLU in relation to their age (Rice et al., 2010).
For all three teachers, the children showed a large variation, most likely due to individual differences, regardless of whether they had SLCN or not. The large variation indicates that some children were particularly verbally active during the SGCs while some were less active, or not active at all. A possible explanation is that some children may have been more withdrawn and not so keen on participating in the conversations, while other children were more willing to engage and thus might have tended to get more opportunities to talk. Furthermore, the teachers’ pre-understanding of which of the children were identified with SLCN, may have influenced them to make an extra effort to engage the children with SLCN in the SGCs. The preparation phase of the teachers identifying and validating the children with SLCN, may by itself have had an impact on the teachers’ communicative behaviours during the SGCs. By performing the assessment in the CCC-2 (Bishop, 2003, 2012), the teachers, including the comparison teacher who performed the same assessment procedure, may have “tuned in” to children’s language and communication skills from the beginning. Also, the teachers and the children in this study had an established relationship with each other, meaning that behavioural patterns may have developed between the teachers and the children that might have affected the children’s outcomes (İnan-Kaya and Rubie-Davies, 2022). There is a risk that the teachers, with their knowledge of the children’s individual preconditions of communicative skills, were unaware that they directed their attention and interactions to specific children based on their previous experience of the abilities and behaviour of those children. On the other hand, considering the naturalistic design of the intervention, also involving SGCs between teachers and children in each class, it is inevitable the teachers would not know the children’s abilities. The naturalistic design may be considered a strength of the ecological validity in the study, hence feasible for teachers to implement in their classroom teaching. An alternative could have been to have another teacher, without knowledge and earlier experience of the children’s abilities and behaviour, conduct the SGCs to reach a clearer effect of the intervention. However, one also needs to consider that a teacher with no previous relationship with the children might affect the children’s willingness to engage and participate in the conversations. Indeed, there could also be other possible explanations to the children’s outcomes. For example, various approaches could have been taken by the teachers in organising which children were given opportunities to talk during the SGCs, potentially influencing the outcomes for the children.
Based on a broad definition of SLCN (Dockrell et al., 2014), the teachers in the present study were asked to first identify about 25% of the children in their respective classes with SLCN due to different reasons. The teachers had been informed that the identification of SLCN could include not only children with a formal diagnosis (e.g., DLD) but also children considered as having SLCN due to other reasons. Although the subsequent validation overall was according to the CCC-2 instrument (Bishop, 2003, 2012), there is a risk in relying on classroom performance to determine what are perceived as language difficulties and what are not (Bawayan and Brown, 2022). It may be a challenging task for teachers who by profession are not trained to assess children with communicative difficulties in their profession. Hence, in this study, on a whole-class level, there is a risk that we both over- and under-identified children with SLCN. An alternative to assessing only a few children could be to perform the CCC-2 (Bishop, 2003, 2012) on the whole-class. However, the CCC-2 assessment may be time-consuming to perform for the teachers. In our study we choose not to conduct the CCC-2 assessment on a whole-class level, taking into consideration the teachers’ daily work schedule. Thus, only the children who were initially identified by the teacher based on their previous experiences were validated by the CCC-2 instrument (Bishop, 2003, 2012).
The present study was designed to be framed by a Tier 2 RTI model with the intervention provided in small-group constellations (Ebbels et al., 2019; Fuchs and Fuchs, 2006; Law et al., 2012). Based on the results of this study, showing small differences overall between the children with SLCN and the age-matched children regarding word productivity (TNW/min) and number of different words used (NDW/min), using carefully designed mixed groups of children with and without SLCN may be a feasible approach to a Tier 2 intervention with SGCs for children with SLCN. Several studies have shown that small-group constellations may be beneficial for providing opportunities for children to practise their oral language (Beck and McKeown, 2001; King and Dockrell, 2016; McKeown and Beck, 2004; Rogde et al., 2019; Wasik and Iannone-Campbell, 2012). Involving not only children with SLCN at Tier 2, but also children without SLCN could be a way of avoiding segregating solutions in the mainstream classroom. In thus creating a proximal development zone (Vygotsky, 1962), not only could the teachers scaffold the children with SLCN in their practise of oral language during SGCs, but there may also be opportunities for the children to scaffold each other. Also, having opportunities to practise oral language in small-group constellations with peers from an early age at school, might prevent future challenges in whole-class verbal activities (Ekström et al., 2023). Importantly, it may not be feasible for all children to participate to the same extent in each small-group conversation session, yet the teacher has a crucial task of ensuring all children have an equal opportunity to talk and engage in the conversations (McKeown and Beck, 2004).
The current study used quantitative language measures (i.e., TNW/min, NDW/min, and MLU), to explore verbal participation and the effect on children’s expressive language productivity. These variables can be described as proximal outcome measures to study child talk and have been used in previous studies of teachers’ use of communicative strategies in teacher-child interactions, similar to the targeted communication-supporting strategies in the present study (Girolametto and Weitzman, 2002; Justice et al., 2008; Piasta et al., 2012). However, these quantitative variables may not be sensitive enough to capture positive changes because of the short duration of the PD program in this study. Verbal participation may also be approached in other ways. For instance, collecting other child outcomes with a focus on a more qualitative approach to child engagement in conversations, considering, for example, level of engagement and motivation (Lingwood et al., 2022) could be a complement to the quantitative language measures in this study. Studying when the children show high and low engagement in conversation activities through other behaviours than verbal expression (Lingwood et al., 2022), may inform the teacher-child interactions further. Although analysis of quantified classroom talk may have its limitations in exploring teacher-child interactions, excluding more qualitative aspects of language analysis (Mercer, 2010), it is a useful tool in the assessment of children’s oral language skills (Bawayan and Brown, 2022). Observations using recording, transcribing, and analysing may be applied to inform about children’s oral language skills and their needs for support (Bawayan and Brown, 2022). Analysing quantitative language measures such as those used in this study may provide details on children’s oral language, which may support the planning of classroom-based interventions.
5 Limitations and future research
There are several limitations to address in the present study. In the design, we used a small sample to explore and gain insights in regard to the children’s expressive language productivity in relation to the teachers’ PD intervention before proceeding with any larger implementation (Hallingberg et al., 2018). In future research, a larger sample of children and teachers is needed to disentangle what impact the teachers’ PD program may have on the children’s expressive language productivity. A larger sample would allow statistical analysis of the main effect and the interaction effect of the research questions explored descriptively in the present study.
A possible confounding variable often mentioned with video data is subject reactivity (Kazdin, 1982), and this may have affected both the children and the teachers during the video-recorded observations in this study. Subject reactivity occurs when the participants act differently due to the situation of being observed (Kazdin, 1982). The video observations conducted in this study might have contributed to the patterns of changes in the children’s expressive language productivity in relation to the teachers’ strategy use. This was also seen for the comparison between children and teacher. However, Blikstad-Balas (2017) argues that reactivity during video observations may not be more severe compared to other forms of observational research and that participants seldom notice the cameras after a while. In the present study, video rather than audio recordings were necessary to be able to keep track of the individual children’s speech production. To reduce any reactivity effects, the observer (i.e., the first author) visited the children and the teachers to inform them about the procedure of the filming and to answer any questions. In all three groups, the teachers and the children were used to using iPads (or a similar device) in different school activities, which were among the items of filming equipment used in this study.
Another limitation to note is that the teachers themselves conducted the assessment of the children with SLCN, which may have affected the child outcomes in this study. If the teachers had been blinded to the children’s linguistic preconditions, the outcomes may have been different. However, according to the CCC-2 instrument, the assessment needs to be conducted by someone familiar with the child since earlier to rate the child’s communicative abilities, which was the case for the teachers in the present study. Besides the teacher assessment with CCC-2 (Bishop, 2003, 2012), we had no further insight into the background causes of the children’s SLCN, meaning that the causes could have varied greatly among the children in the present study. Still, this reflects mainstream classrooms and the natural variation that teachers meet and relate to in their everyday teaching.
Future research might design a similar extended study to cover a longer period to evaluate the impact on children’s expressive language productivity. Also, extending the duration of each of the SGCs to explore whether the children will have more opportunities to talk in relation to the teacher’s strategy use is warranted. In the present study, the teachers were instructed to plan for conversations of about 20 min (including 5 min of read-aloud). The reason for this was that this type of classroom activity, involving only a few children may be quite a concentrated and intensive situation compared to regular whole-class activities. Moreover, there were also practical reasons for the design, related to the school schedule. Importantly, previous research shows that teachers tend to use the majority (70–80%) of the talking time of class time on average (Hattie, 2008). A similar distribution of teacher-student talk was found in a study by Eadie et al. (2021). Longer conversation time may not automatically lead to increased opportunities for children to talk; it could also result in more time for teachers to expand their utterances. Therefore, in future studies, we suggest highlighting in the PD program the importance of teachers balancing their strategy use in the interactions with the children, ensuring ample opportunities for the children to talk, and moreover arranging the conversations to enable for all children to participate. Finally, it would be interesting to study peer effects in future studies exploring children’s expressive language productivity during SGCs. In the present study, there were not only ongoing teacher-child interactions during the conversations but also verbal interaction between the children that might encourage the children among themselves to participate in the conversations.
6 Conclusion
When teacher talk is characterised by communicative techniques similar to the present study’s communication-supporting strategies (Dockrell et al., 2012, 2015) to stimulate child talk, it has been shown to be beneficial for children’s language development eventually (Dickinson and Porche, 2011). The results from this study indicate that in terms of child opportunities to talk, teachers’ frequent use of targeted communication-supporting strategies may be less beneficial. Perhaps the construct of some of the strategies might develop children’s language over a longer period but an effect may be more difficult to see in the immediate situation. Some of the strategies naturally involve the extended language of the teacher, which may leave fewer opportunities for the children to talk. Although there was a small sample in the present study and a large variation in the children’s expressive language productivity, a tentative conclusion might be that the children’s opportunities to talk seem suppressed when teachers use the targeted communication-supporting strategies frequently during SGCs. Yet when the teachers are balancing their strategy use in the interactions with the children, this may benefit the verbal participation of the children with SLCN.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because of the confidential nature of the primary data. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to a2FyaW4uZWRsdW5kQHNwZWNwZWQuc3Uuc2U=.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority (protocol number 2019–02735). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
KE: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. LK: Writing – review & editing. HH: Writing – review & editing. EB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The Research School in Special Education Directed toward Early Interventions in Early Childhood Education (Swedish Research Council 2017–03683).
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the teachers and the children who participated in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Andersson, K., Sandgren, O., Rosqvist, I., Lyberg Åhlander, V., Hansson, K., and Sahlén, B. (2022). Enhancing teachers’ classroom communication skills – measuring the effect of a continued professional development programme for mainstream school teachers. Child Lang. Teach. Therapy 38, 166–179. doi: 10.1177/02656590211070997
Badar, S. R., Clegg, J., and Spencer, S. (2022). Increasing teachers’ use of communication-supporting strategies: findings from an exploratory study using the communication supporting classroom observation tool (CSCOT) in primary schools in Brunei. Support Learn. 37, 180–208. doi: 10.1111/1467-9604.12404
Bawayan, R., and Brown, J. A. (2022). Diagnostic decisions of language complexity using informal language assessment measures. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools. 53, 466–478. doi: 10.1044/2021_LSHSS-21-00065
Beck, I. L., and McKeown, M. G. (2001). Text talk: capturing the benefits of read-aloud experiences for young children. Read. Teach. 55, 10–20.
Bengochea, A., and Sembiante, S. F. (2024). Effective vocabulary interventions for young emergent bilinguals: a best-evidence synthesis. Rev. Educ. 12:e3458. doi: 10.1002/rev3.3458
Bishop, D. V. M. (2003). The children’s communication checklist. 2nd Edn. UK: Pearson Clinical Assessment.
Bishop, D. V. M. (2012). The children’s communication checklist. 2nd Edn. Sweden: Swedish version. Pearson Clinical Assessment.
Blikstad-Balas, M. (2017). Key challenges of using video when investigating social practices in education: contextualization, magnification, and representation. Int. J. Res. Method Educ. 40, 511–523. doi: 10.1080/1743727X.2016.1181162
Cabell, S. Q., Justice, L. M., McGinty, A. S., DeCoster, J., and Forston, L. D. (2015). Teacher–child conversations in preschool classrooms: contributions to children’s vocabulary development. Early Child. Res. Q. 30, 80–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2014.09.004
Casby, M. W. (2011). An examination of the relationship of sample size and mean length of utterance for children with developmental language impairment. Child Lang. Teach. Therapy 27, 286–293. doi: 10.1177/0265659010394387
Dickinson, D. K., and Porche, M. V. (2011). Relation between language experiences in preschool classrooms and Children’s kindergarten and fourth-grade language and Reading abilities. Child Dev. 82, 870–886. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2011.01576.x
Dockrell, J. E., Bakopoulou, I., Law, J., Spencer, S., and Lindsay, G. (2012). Developing a communication supporting classroom observation tool. Depart. Educ. 1–83. doi: 10.1037/t50370-000
Dockrell, J. E., Bakopoulou, I., Law, J., Spencer, S., and Lindsay, G. (2015). Capturing communication supporting classrooms: the development of a tool and feasibility study. Child Lang. Teach. Ther. 31, 271–286. doi: 10.1177/0265659015572165
Dockrell, J., Lindsay, G., Roulstone, S., and Law, J. (2014). Supporting children with speech, language and communication needs: an overview of the results of the better communication research Programme: supporting children with speech-language and communication needs. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 49, 543–557. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12089
Eadie, P., Stark, H., Snow, P., Gold, L., Watts, A., Shingles, B., et al. (2021). Teacher talk in early years classrooms following an Oral language and literacy professional learning program. J. Res. Educ. Effect. 15, 302–329. doi: 10.1080/19345747.2021.1998938
Ebbels, S. H., McCartney, E., Slonims, V., Dockrell, J. E., and Norbury, C. F. (2019). Evidence-based pathways to intervention for children with language disorders. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 54, 3–19. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12387
Edlund, K., Kjellmer, L., Hemmingsson, H., and Berglund, E. (2023). Primary school teachers’ patterns in using communication-supporting strategies following a professional development program: lessons learned from an exploratory study with three teachers. Front. Educ. 8:1036050, 1–12. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2023.1036050
Ekström, A., Sandgren, O., Sahlén, B., and Samuelsson, C. (2023). ‘It depends on who I’m with’: how young people with developmental language disorder describe their experiences of language and communication in school. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 58, 1168–1181. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12850
Engels, J. (2003). Imputation of missing longitudinal data: a comparison of methods. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 56, 968–976. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(03)00170-7
Fälth, L., Selenius, H., and Egerhag, H. (2022). A cross-sectional study on reading among young L1 and L2 students in Sweden. Eur. J. Spec. Needs Educ. 38, 233–244. doi: 10.1080/08856257.2022.2050973
Fuchs, D., and Fuchs, L. S. (2006). Introduction to response to intervention: what, why, and how valid is it? Read. Res. Q. 41, 93–99. doi: 10.1598/RRQ.41.1.4
Girolametto, L., and Weitzman, E. (2002). Responsiveness of child care providers in interactions with toddlers and preschoolers. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Schools 33, 268–281. doi: 10.1044/0161-1461(2002/022)
Girolametto, L., Weitzman, E., and Greenberg, J. (2003). Training day care staff to facilitate Children’s language. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 12, 299–311. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2003/076)
Hallingberg, B., Turley, R., Segrott, J., Wight, D., Craig, P., Moore, L., et al. (2018). Exploratory studies to decide whether and how to proceed with full-scale evaluations of public health interventions: a systematic review of guidance. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 4:104. doi: 10.1186/s40814-018-0290-8
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: a synthesis of over 800 Meta-analyses relating to achievement. London: Routledge.
Hjetland, H. N., Lervåg, A., Lyster, S.-A. H., Hagtvet, B. E., Hulme, C., and Melby-Lervåg, M. (2018). Pathways to reading comprehension: a longitudinal study from 4 to 9 years of age. J. Educ. Psychol. 111, 751–763. doi: 10.1037/edu0000321
Hoff, E., and Naigles, L. (2002). How children use input to acquire a lexicon. Child Dev. 73, 418–433. doi: 10.1111/1467-8624.00415
İnan-Kaya, G., and Rubie-Davies, C. M. (2022). Teacher classroom interactions and behaviours: indications of bias. Learn. Instr. 78:101516. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2021.101516
Justice, L. M., Mashburn, A., Pence, K. L., and Wiggins, A. (2008). Experimental evaluation of a preschool language curriculum: influence on Children’s expressive language skills. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 51, 983–1001. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2008/072)
Kazdin, A. E. (1982). Observer effects: reactivity of direct observation. New Direct. Methodol. Soc. Behav. Sci. 14, 5–19.
King, S. E., and Dockrell, J. E. (2016). Investigating affordance of opportunity for young children’s language interactions in a nursery setting: how can small group talk act as a forum for language learning? J. Early Child. Res. 14, 351–369. doi: 10.1177/1476718X14552877
Law, J., Garrett, Z., and Nye, C. (2003). Speech and language therapy interventions for children with primary speech and language delay or disorder. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 1–77. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004110
Law, J., Lee, W., Lindsay, G., Roulstone, S., Wren, Y., and Zeng, B. (2012). “What works”: interventions for children and young people with speech, language and communication needs. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/collection/better-communication-research-programme (Accessed November 18, 2021).
Law, J., Tulip, J., Stringer, H., Cockerill, M., and Dockrell, J. (2019). Teachers observing classroom communication: an application of the communicating supporting classroom observation tool for children aged 4–7 years. Child Lang. Teach. Therapy 35, 203–220. doi: 10.1177/0265659019869792
Lingwood, J., Lampropoulou, S., Bezenac, C. D., Billington, J., and Rowland, C. (2022). Children’s engagement and caregivers’ use of language-boosting strategies during shared book reading: a mixed methods approach. J. Child Lang. 50, 1436–1458. doi: 10.1017/S0305000922000290
MacWhinney, B. (2000). The Childes project: Tools for analyzing talk. Transcription format and programs. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
McKeown, M. G., and Beck, I. L. (2004). Transforming knowledge into professional development resources: six teachers implement a model of teaching for understanding text. Elem. Sch. J. 104, 391–408. doi: 10.1086/499759
McLeod, S., and McKinnon, D. H. (2007). Prevalence of communication disorders compared with other learning needs in 14 500 primary and secondary school students. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 42, 37–59. doi: 10.1080/13682820601173262
Melby-Lervåg, M., Hagen, Å. M., and Lervåg, A. (2020). Disentangling the far transfer of language comprehension gains using latent mediation models. Dev. Sci. 23, e12929–e12914. doi: 10.1111/desc.12929
Mercer, N. (2010). The analysis of classroom talk: methods and methodologies. Br. J. Educ. Psychol. 80, 1–14. doi: 10.1348/000709909X479853
Monsrud, M.-B., Rydland, V., Geva, E., Thurmann-Moe, A. C., and Halaas Lyster, S.-A. (2022). The advantages of jointly considering first and second language vocabulary skills among emergent bilingual children. Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 25, 42–58. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2019.1624685
Norbury, C. F., Gooch, D., Wray, C., Baird, G., Charman, T., Simonoff, E., et al. (2016). The impact of nonverbal ability on prevalence and clinical presentation of language disorder: evidence from a population study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 57, 1247–1257. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12573
Nordberg, A. (2021). Support of language and communication in the ‘tambour situation’ in Swedish preschools. Early Child Dev. Care 191, 699–712. doi: 10.1080/03004430.2019.1645134
Parker, M. D., and Brorson, K. (2005). A comparative study between mean length of utterance in morphemes (MLUm) and mean length of utterance in words (MLUw). First Lang. 25, 365–376. doi: 10.1177/0142723705059114
Piasta, S. B., Justice, L. M., Cabell, S. Q., Wiggins, A. K., Turnbull, K. P., and Curenton, S. M. (2012). Impact of professional development on preschool teachers’ conversational responsivity and children’s linguistic productivity and complexity. Early Child. Res. Q. 27, 387–400. doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2012.01.001
Rice, M. L., Smolik, F., Perpich, D., Thompson, T., Rytting, N., and Blossom, M. (2010). Mean length of utterance levels in 6-month intervals for children 3 to 9 years with and without language impairments. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 53, 333–349. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2009/08-0183)
Rogde, K., Hagen, Å. M., Melby-Lervåg, M., and Lervåg, A. (2019). The effect of linguistic comprehension instruction on generalized language and reading comprehension skills: a systematic review. Campbell Syst. Rev. 15:e1059. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1059
Rogde, K., Melby-Lervåg, M., and Lervåg, A. (2016). Improving the general language skills of second-language learners in kindergarten: a randomized controlled trial. J. Res. Educ. Effect. 9, 150–170. doi: 10.1080/19345747.2016.1171935
Sandgren, O., Andersson, K., Lyberg Åhlander, V., Rosqvist, I., Hansson, K., and Sahlén, B. (2023). A randomized controlled trial of the effectiveness of teacher continued professional development on student language outcomes. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 58, 879–891. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12829
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., and Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Snow, P. C. (2016). Elizabeth usher memorial lecture: language is literacy is language - positioning speech-language pathology in education policy, practice, paradigms and polemics. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 18, 216–228. doi: 10.3109/17549507.2015.1112837
Snow, P. C. (2021). SOLAR: the science of language and reading. Child Lang. Teach. Therapy 37, 222–233. doi: 10.1177/0265659020947817
Snowling, M. J., and Hulme, C. (2021). Annual research review: Reading disorders revisited – the critical importance of oral language. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 62, 635–653. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13324
Spencer, T. D., and Petersen, D. B. (2018). Bridging Oral and written language: an Oral narrative language intervention study with writing outcomes. Lang. Speech Hear. Serv. Schools 49, 569–581. doi: 10.1044/2018_LSHSS-17-0030
Swedish National Agency for Education. (2022). Curriculum for the compulsory school, preschool class and school-age educare 2022. Available at: www.skolverket.se (Accessed October 1, 2023).
Keywords: expressive language productivity, communication-supporting strategies, structured small-group conversations, response to intervention, primary school
Citation: Edlund K, Kjellmer L, Hemmingsson H and Berglund E (2024) An exploratory study of children’s expressive language productivity in relation to teachers’ use of communication-supporting strategies. Front. Educ. 9:1308388. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2024.1308388
Edited by:
Joseph Mintz, University College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Viveka Lyberg Åhlander, Åbo Akademi University, FinlandWeifeng Han, Flinders University, Australia
Copyright © 2024 Edlund, Kjellmer, Hemmingsson and Berglund. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Karin Edlund, a2FyaW4uZWRsdW5kQHNwZWNwZWQuc3Uuc2U=
†ORCID: Karin Edlund, orcid.org/0000-0002-1849-2619
 Karin Edlund
Karin Edlund Liselotte Kjellmer
Liselotte Kjellmer Helena Hemmingsson
Helena Hemmingsson Eva Berglund1
Eva Berglund1