- 1Department of Advanced Mechanical Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Mechanical and Biomedical Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea
Nanozymes, synthetic nanomaterials that mimic the catalytic functions of natural enzymes, have emerged as transformative technologies for biosensing, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring. Since their introduction, nanozymes have rapidly evolved with significant advancements in their design and applications, particularly through the integration of machine learning (ML). Machine learning (ML) has optimized nanozyme efficiency by predicting ideal size, shape, and surface chemistry, reducing experimental time and resources. This review explores the rapid advancements in nanozyme technology, highlighting the role of ML in improving performance across various bioapplications, including real-time monitoring and the development of chemiluminescent, electrochemical and colorimetric sensors. We discuss the evolution of different types of nanozymes, their catalytic mechanisms, and the impact of ML on their property optimization. Furthermore, this review addresses challenges related to data quality, scalability, and standardization, while highlighting future directions for ML-driven nanozyme development. By examining recent innovations, this review highlights the potential of combining nanozymes with ML to drive the development of next-generation diagnostic and detection technologies.
1 Introduction
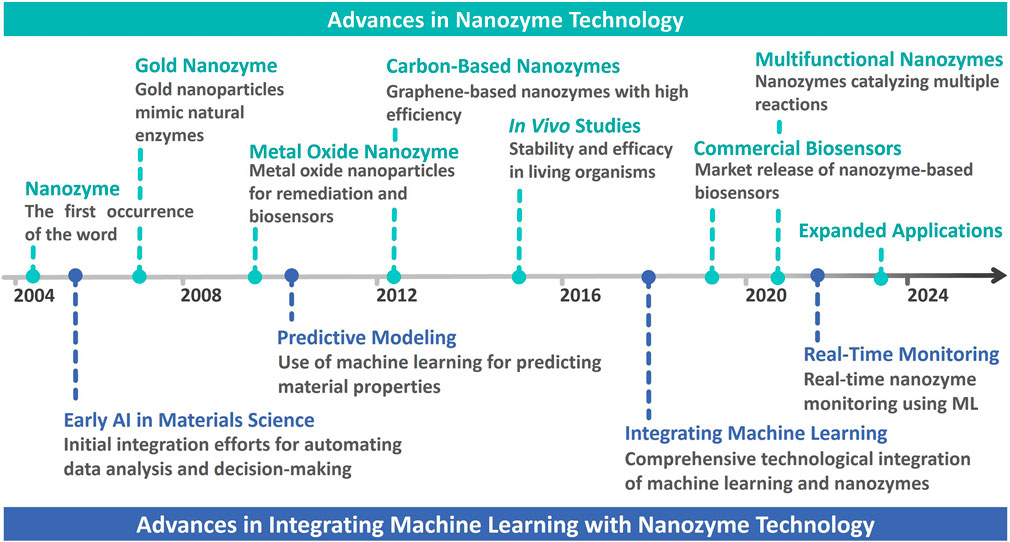
Nanozymes, a class of nanomaterials that mimic the catalytic activities of natural enzymes, have revolutionized various scientific fields since their introduction (Gao and Yan, 2016; Wu et al., 2019). The concept of nanozymes was first coined in 2004, marking the advent of a new frontier in nanotechnology (Wang et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2021a; Salvador-Morales and Grodzinski, 2022). Subsequently, the field has witnessed significant milestones such as the development of gold nanozymes in 2008, which opened new avenues for mimicking enzyme functions (Wang et al., 2020; Liang and Yan, 2019). Further, advancements in metal oxide nanozymes were recorded around 2010, demonstrating applications in remediation and biosensors. Carbon-based nanozymes emerged in 2012 owing to their high catalytic efficiency (Wu et al., 2019; Wong et al., 2021). Such developments illustrate the dynamic evolution of nanozyme technology and highlight its growing importance in various applications. Due to their diverse catalytic properties, nanozymes have become invaluable tools for developing biosensors and diagnostic applications.
Among the different types of nanozymes, electrochemical nanozymes are known for their ability to induce or enhance electrical signals, making them essential for biosensing applications requiring high sensitivity and precision, including the detection of trace amounts of biomarkers in bodily fluids. Such nanozymes enable the development of highly sensitive biosensors suitable for point-of-care diagnostics and real-time monitoring (Geng et al., 2022; Sharifi et al., 2020). Alongside other types of nanozymes, chemiluminescent nanozymes offer exceptional specificity and sensitivity, often down to a single-molecule level, making them ideal for environments where minimal background interference is crucial, such as in complex biological matrices or in vivo imaging (Wu and Qu, 2015; Roda et al., 2016).
Commercial biosensors based on nanozyme technologies possess practical potential for real-world bioapplications (Yang et al., 2015). With advancements in nanozyme technology, biosensors have increasingly leveraged the unique properties of colorimetric, electrochemical, and chemiluminescent nanozymes for detecting a wide range of biological targets, from pathogens to biomolecules, with high sensitivity, specificity, and versatility (Wang et al., 2024; Wu et al., 2021b; Chen X. et al., 2022). Such a multi-modal approach, combining visual, electrical, and luminescent signals, ensures the suitability of nanozyme-based biosensors to diverse applications, ranging from point-of-care diagnostics to environmental monitoring (Liu X. et al., 2021; Saleh and Hassan, 2023).
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various fields, and integrating machine learning (ML) into nanozyme-based bioapplications presents a significant leap forward in the field (Mujtaba et al., 2021; Yoon et al., 2024a). ML has the ability to process massive amounts of data and classify complex patterns, which has been instrumental in enhancing the functionality and applications of nanozymes in biotechnology. However, despite these advancements, nanozyme development still faces several challenges, including the need to optimize catalytic efficiency, stability, and specificity for various bioapplications. ML addresses these challenges by predicting optimal nanozyme properties, reducing experimental time and resource consumption, and enabling more precise tuning of their catalytic activities. The initial steps towards their integration began in the early 2010s, with predictive modeling used to better understand and optimize nanozyme properties (Butler et al., 2018). By 2020, ML became a key component in the real-time monitoring and analysis of nanozyme activity, allowing highly precise and dynamic bioapplications (Mou et al., 2022). The convergence of ML and nanozyme technology has led to the development of smart biosensors and diagnostic tools that can adapt and respond to changing conditions in real time, greatly enhancing their utility in medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and other bioapplications (Pramanik et al., 2020; Weerathunge et al., 2019; Xu L. et al., 2022), including the development of more sophisticated diagnostic tools that provide real-time feedback, adaption to complex biological environments, and personalized medicine applications of ML-driven nanozymes tailored to individual patient requirements (Cui et al., 2020). The synergy between the two cutting-edge technologies holds great promise for the future of biotechnology.
This article aims to review developments in nanozymes, their bioapplications, and their integration with ML, as illustrated in Figure 1. Since the inception of nanozymes in 2004, significant milestones have been achieved, including the development of gold nanozymes in 2008, pioneering the mimicry of natural enzymes, and further advancements including metal oxide and carbon-based nanozymes in 2010 and 2012, respectively (Manea et al., 2004; Li et al., 2008; Wei and Wang, 2013; Sun et al., 2018). Such developments have significantly promoted nanozyme applications, particularly in biosensing and diagnostics. This study highlights the increasing integration of ML with nanozyme-based bioapplications, a trend that began in the early 2010s with predictive modeling, and has since evolved into a critical component of real-time monitoring and dynamic applications in biotechnology (Noll and Henkel, 2020; Wagner and Rondinelli, 2016). With evolution in the synergy between nanozymes and ML, further innovations are expected, leading to more sophisticated, responsive, and personalized diagnostic tools that can adapt to complex biological environments.
2 Nanozyme development and catalytic mechanisms
2.1 Types of nanozymes
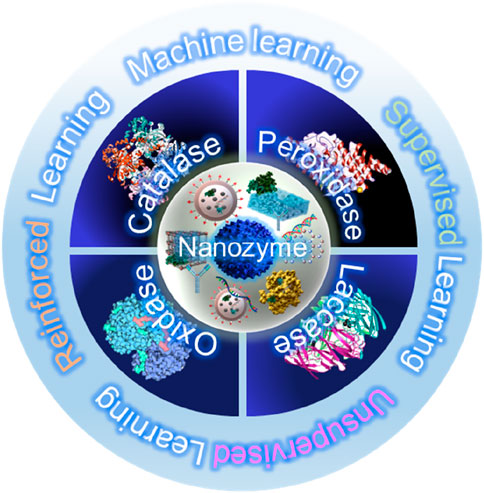
Nanozymes are engineered nanomaterials that emulate the catalytic functions of natural enzymes, as shown in Figure 2. They can be broadly classified into several types based on their material composition (Huang et al., 2019). Metallic nanozymes, including gold, silver, and platinum, are well known for their high catalytic efficiency and stability (Lou-Franco et al., 2021). Metallic nanozymes often exhibit strong enzyme-like activities owing to their ability to easily donate or accept electrons during redox reactions, which is crucial for mimicking enzymes such as oxidases, peroxidases, and catalases. Such nanozymes are widely used in biosensing and diagnostic applications because of their reliable and stable catalytic properties (Wang et al., 2018). Metal oxide nanozymes, including those based on iron, cerium, and manganese oxides, are another key category (Liu Q. et al., 2021). Particularly, such nanozymes are robust, multi-functional, and possess the ability to simultaneously perform multiple types of catalytic reactions. For example, cerium oxide nanozymes can switch between different oxidation states, enabling them to mimic both catalase and superoxide dismutase activities. Their robustness and multi-functionality make them suitable for environmental applications such as pollutant degradation and biosensor development (Meng et al., 2020). Carbon-based nanozymes, including graphene, carbon nanotubes, and carbon dots, represent a rapidly expanding category owing to their high surface area, conductivity, and tunable catalytic properties (Yang et al., 2020). Such nanozymes offer numerous active sites and are easy to chemically modify for enhancing their catalytic properties. Moreover, their excellent conductivity aids electron transfer processes, which are essential for mimicking peroxidase activity. Consequently, carbon-based nanozymes are being increasingly used in biosensors, environmental remediation, and energy-related applications (Li S. et al., 2019).
2.2 Catalytic mechanisms and factors affecting catalytic activity
The catalytic mechanisms of nanozymes are influenced by several nanoscale properties crucial to their functionality (Huang et al., 2019). Size and shape are critical factors to determine the surface area available for catalytic reactions and active site distributions (An and Somorjai, 2012). Nanozymes of smaller sizes typically have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, which enhances their interaction with substrates, resulting in higher catalytic efficiency (Wang et al., 2019). The composition of nanozymes, including specific metals or metal oxides used, dictates the type of catalytic activity. Different materials offer various enzyme-mimicking functions (Das et al., 2021). For instance, platinum-based nanozymes are highly effective in hydrogenation reactions, whereas gold-based nanozymes exhibit excellent oxidase-like activity. The intrinsic properties of such materials allow effective replication of specific enzymatic functions. Additionally, surface chemistry plays a significant role in catalytic performance, as the presence of functional groups or surface modifications improve substrate binding and provide protection against degradation (Jing et al., 2013). Surface modifications can be tailored to improve the interactions between nanozymes and their target substrate, thereby enhancing specificity and catalytic turnover. For example, attaching specific ligands to the surface of a nanozyme can help in selectively binding certain biomolecules, mimicking the specificity of natural enzymes (Soares et al., 2021). The aforementioned factors influence the stability and reactivity of nanozymes. For example, a change in pH can alter the charge on the nanozyme surfaces, affecting their interaction with substrates. Similarly, temperature variation can affect the kinetic energy of a system, thereby affecting the catalytic reaction rate.
2.3 Methods of nanozyme development and limitations
Traditional nanozyme designs rely on empirical synthesis methods including chemical reduction, sol-gel processes, and hydrothermal synthesis (Chadha et al., 2022). However, conventional methods often lack the precision required to control nanoparticle size, shape, and composition. Consequently, the catalytic properties of the synthesized nanozymes vary widely, making it challenging to achieve consistent performance (Sun et al., 2018; Singh, 2019). The empirical nature of such approaches makes them time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring extensive experimentation to identify optimal synthesis conditions and functional properties. The trial-and-error approach often leads to inefficiencies, as researchers are required to test multiple variables including reaction time, temperature, and precursor concentration to fine-tune nanozyme properties. Moreover, traditional methods often struggle to achieve high specificity and stability because nanozymes typically do not match the substrate specificity of natural enzymes and can suffer from aggregation, oxidation, or loss of activity over time.
To overcome such limitations, recent advancements have focused on integrating computational approaches and ML into design processes (Gupta et al., 2021). Modern strategies enable more precise prediction of nanozyme properties by utilizing large datasets to model and predict the effects of different synthesis parameters on nanozyme performance. By leveraging data-driven models, researchers can optimize the nanozyme characteristics more efficiently, leading to the development of effective and stable nanozymes with enhanced catalytic performance for a wide range of bioapplications. New approaches not only accelerate the design process but also improve the reproducibility and scalability of nanozyme production.
3 Integration of ML in nanozyme development
3.1 Overview of ML techniques
Recently, ML is being increasingly integrated into nanozyme design, offering powerful tools for predicting and optimizing nanozyme properties (Chen et al., 2023). The integration of ML into nanozyme research has revolutionized the field, enabling more precise control of the design process and significant time reduction for experimentation. By analyzing vast datasets, ML models uncover complex relationships between nanozyme characteristics and catalytic performances, which can be difficult to discern using traditional methods. Different ML techniques such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning are applied based on specific nanozyme or sensor requirements, as shown in Figure 3. The effectiveness of these techniques is closely tied to the methods used for signal collection (Chadha et al., 2022). Signal collection plays a critical role in obtaining high-quality data, which is essential for accurate ML predictions. For example, colorimetric sensors collect optical signals based on visible color changes, electrochemical sensors measure electrical signals, and chemiluminescent sensors collect light emission signals. The nature of the signal collected directly impacts how the data is processed and the ML model applied (Gupta et al., 2021). The application of machine learning techniques in nanozyme-based sensors is highly dependent on the programming code used to implement these techniques. Each ML method—supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning—requires a distinct coding approach that impacts how sensor data is processed and how samples are detected. For example, in supervised learning, the programming code is primarily focused on training the model using labeled datasets (Chen et al., 2023). The code typically includes steps for loading data, preprocessing it (e.g., normalizing or encoding features), training the model, and making predictions. In the case of colorimetric sensors, this involves predicting the color change based on input features such as concentration levels, with code that handles both the training and evaluation phases efficiently.
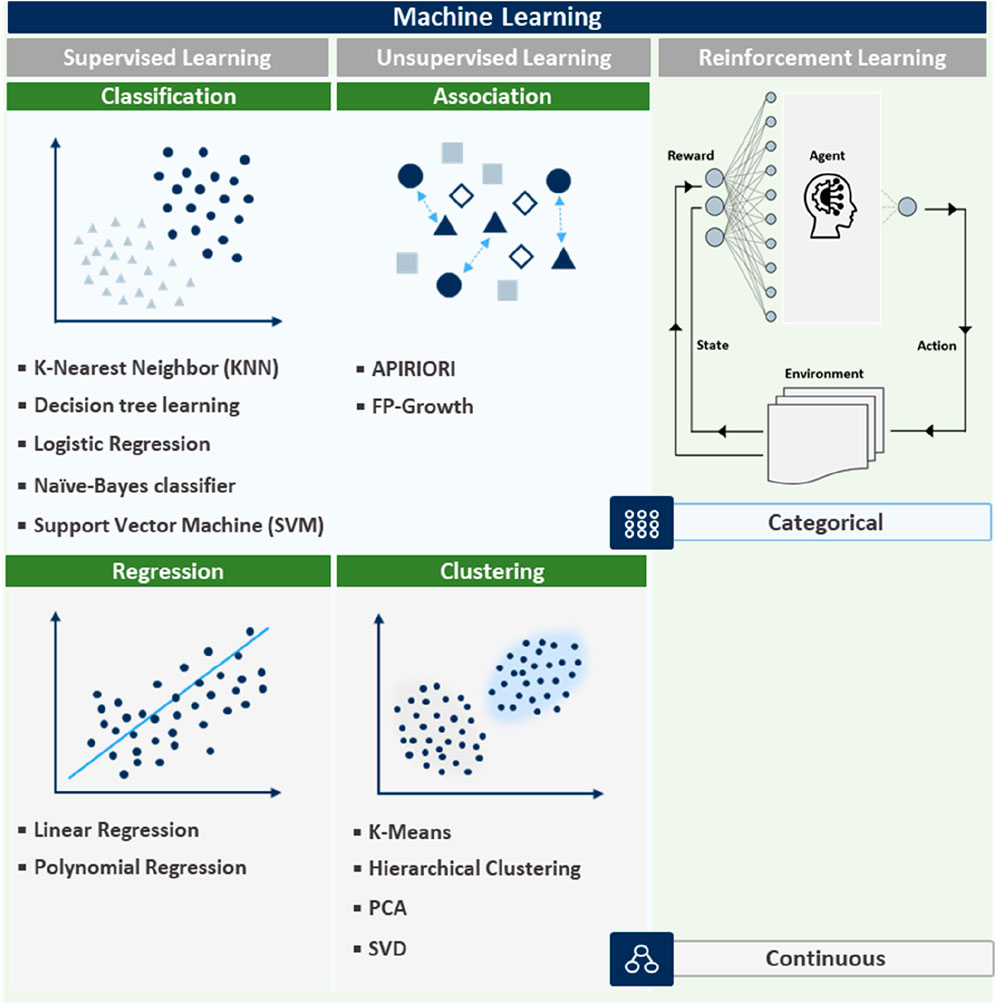
Figure 3. Overview of ML techniques: supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning with data type distinctions.
Supervised learning uses labeled data and is particularly effective for regression and classification tasks, predicting outcomes such as catalytic efficiency, stability, and specificity of nanozymes (Li Y. et al., 2023). Considering nanozyme design, supervised learning algorithms can be trained on experimental data to predict the effects of changes in synthesis conditions (including temperature, pH, and reactant concentration) on the final nanozyme properties (Li Y. et al., 2023; Zhuang et al., 2024). Such a predictive capability enables researchers to fine-tune nanozyme characteristics before physical synthesis, saving time and resources. Supervised learning is especially useful for applications such as colorimetric sensors, where precise detection and labeled data are readily available. In contrast, unsupervised learning relies on code that can discover patterns in unlabeled data, such as clustering or association rule mining. For electrochemical sensors, the code is used to analyze complex electrical signal data and group samples based on their signal characteristics (Sun et al., 2018). This involves designing algorithms that can process raw signals and cluster them into meaningful groups without prior knowledge of the data structure.
Unsupervised learning, including clustering and association techniques, identifies patterns within unlabeled data to discover new nanozyme classes and understand their properties (Arya et al., 2023; Ghahramani, 2003; Barlow, 1989). For instance, clustering algorithms group nanozymes based on their catalytic behaviors or structural features, revealing previously unrecognized relationships that can lead to the development of novel nanozyme types. However, association techniques can identify common features among high-performance nanozymes and guide the synthesis of new variants with enhanced functions. Unsupervised learning is particularly effective for electrochemical sensors, where hidden patterns in complex signal data can be uncovered and used to optimize sensor performance.
Reinforcement learning requires code that facilitates interaction between the model and its environment. In chemiluminescent sensors, the code must simulate different sensor conditions and adjust sensor parameters in real-time based on feedback from the environment. The core of the reinforcement learning code involves setting up the environment, defining a reward function, and iterating through learning episodes to optimize performance. Reinforcement learning optimizes processes by learning from interactions, which is useful for refining synthesis conditions to enhance nanozyme performance (Chen et al., 2023). During nanozyme development, reinforcement learning can be applied to iteratively improve synthesis protocols. By simulating different synthesis scenarios and learning from obtained outcomes, reinforcement learning algorithms can recommend optimal pathways for producing nanozymes with the desired properties. The approach is particularly valuable in dynamic and complex systems where the best synthesis strategy may not be apparent from initial conditions. Reinforcement learning is highly suitable for chemiluminescent sensors, which require real-time performance optimization, especially in fluctuating environments like in vivo diagnostics or environmental monitoring.
The aforementioned methods are visually categorized in Figure 3, illustrating their applications in handling both continuous and categorical data and their relevance in nanozyme research. For example, supervised learning works best for predicting quantitative outcomes (continuous data), such as catalytic rates, while unsupervised learning helps classify nanozymes into functionality-based categories (categorical data). The choice of ML technique and signal collection method are both essential for ensuring accurate predictions, optimized nanozyme performance, and reliable results across various bioapplications. By effectively utilizing ML techniques, researchers can accelerate the discovery and optimization of nanozymes, leading to more efficient and sustainable solutions in various applications, including biomedicine, environmental remediation, and industrial catalysis (Ahmed et al., 2022; Ngwabebhoh and Yildiz, 2019).
3.2 Application of ML in predicting nanozyme properties
ML is crucial for predicting key nanozyme characteristics including catalytic activity, specificity, and environmental stability. By processing large datasets, ML models can identify the most influential factors affecting nanozyme performance such as particle size, shape, and surface chemistry (Wei et al., 2022). The ability to analyze complex and large-scale data allows researchers to determine attributes that most significantly affect the efficiency and functionality of nanozymes, providing valuable insights that guide the design and optimization processes. For example, regression models can predict the optimal conditions for catalytic reactions, including ideal temperature, pH, and reactant concentration, to achieve maximum efficiency (Flynn and Chang, 2024). Such models are essential for narrowing down the vast array of potential experimental conditions to the most promising ones, thereby saving time and reducing costs associated with trial-and-error approaches. Conversely, classification models sort nanozymes based on their functional categories, such as oxidase-like, peroxidase-like, or catalase-like activities. Sorting helps to quickly identify appropriate nanozymes for specific applications such as biosensing or pollutant degradation (Li X. et al., 2019; Li X. et al., 2023).
Clustering techniques group nanozymes with similar properties, thereby facilitating the discovery of new variants with enhanced capabilities (Ai et al., 2022). For instance, clustering can reveal subgroups of nanozymes that share unique catalytic properties, which may not be immediately apparent through conventional analysis. By studying the clusters, researchers can identify common features that contribute to high performance and use the knowledge to design new nanozymes with improved functionalities. The predictive power accelerates process development, enabling efficient and better suited nanozyme designs for specific applications. Ultimately, the integration of ML into nanozyme research not only accelerates the discovery of new nanozyme variants but also enhances their performance in real-world applications, ranging from environmental remediation to advanced medical diagnostics. By leveraging the power of ML, researchers can push the boundaries of nanozymes for obtaining innovative solutions in various fields.
3.3 Case studies of ML-assisted nanozyme development
Several case studies have highlighted the effectiveness of ML in improving nanozyme designs. For instance, supervised learning has been used to enhance the catalytic activity of metal oxide nanozymes by predicting the influence of factors, such as size and surface area (Xu D. et al., 2022). In such studies, ML models have successfully identified optimal nanoparticle dimensions and surface characteristics that maximize catalytic efficiency, allowing for the fine-tuning of nanozyme properties to meet specific functional requirements. Another study has applied clustering and regression models to optimize the stability of gold nanozymes under varying pH and temperature conditions, resulting in more robust biosensors (Sun et al., 2021). Such ML-driven approaches have been particularly effective in identifying the precise environmental conditions that gold nanozymes can withstand, ensuring their stability and prolonged activity under challenging conditions including those found in biological or environmental samples. Thus, directly contributions have led to the development of reliable and durable biosensors.
Additionally, reinforcement learning has been employed to fine-tune synthesis parameters for carbon-based nanozymes to achieve optimal performance (Lewandowska et al., 2021). Particularly, reinforcement learning models have been adept at iteratively adjusting synthesis variables such as reaction time, temperature, and precursor concentrations, learning from each outcome to progressively improve nanozyme performance (Kulkarni et al., 2022). Thus, significant enhancements in the catalytic capabilities and stabilities of carbon-based nanozymes have been recorded, making them more effective for environmental remediation and energy conversion applications. The examples depicted in Figure 3 demonstrate the creation of more efficient, stable, and application-specific nanozymes using ML-based approaches. By integrating ML into the design process, researchers can precisely control nanozyme properties and tailor them to meet the specific requirements of diverse applications. The success of the aforementioned case studies underscores the transformative impact of ML on nanozyme research, offering a powerful tool for innovation in this field (Zheng et al., 2024; Cao et al., 2023).
Incorporating ML into nanozyme design represents a significant advancement, enabling the development of more targeted and effective nanozymes for use in diverse fields, such as biotechnology, medicine, and environmental science. As ML techniques continue to evolve, their applications in nanozyme research are expected to expand, driving further innovation and specialization in this rapidly growing field. The ongoing development of ML algorithms, coupled with increasing computational power, is expected to likely produce more sophisticated and efficient nanozyme designs, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements across multiple scientific and industrial domains.
4 Recent advances in nanozyme with ML application
4.1 Colorimetric sensors and ML applications
Recently, significant progresses have been made in the development of nanozyme-based colorimetric sensors, particularly through the integration of ML techniques. The innovations have expanded the capabilities of biosensing, diagnostics, and environmental monitoring, highlighting the potential of combining nanotechnology with computational approaches. The application of ML to sensors has enhanced their ability to process complex colorimetric data, such as RGB values, thereby enabling more precise detection and quantification of analytes in various environments. For instance, in studies involving the detection of cisplatin (Cis-Pt) at parts per billion (ppb) levels, as shown in Figure 4A, colorimetric changes have been accurately measured and correlated with cis-Pt concentration, demonstrating the sensitivity of the system (Yang et al., 2022). Table 1 provides an overview of various nanozyme-based colorimetric reactions, summarizing their associated colorimetric reactions, color spaces utilized, ML methods applied, and corresponding limits of detection (LOD). The concise compilation highlights the integration of ML techniques for enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of nanozyme-based diagnostic and monitoring applications in different fields.
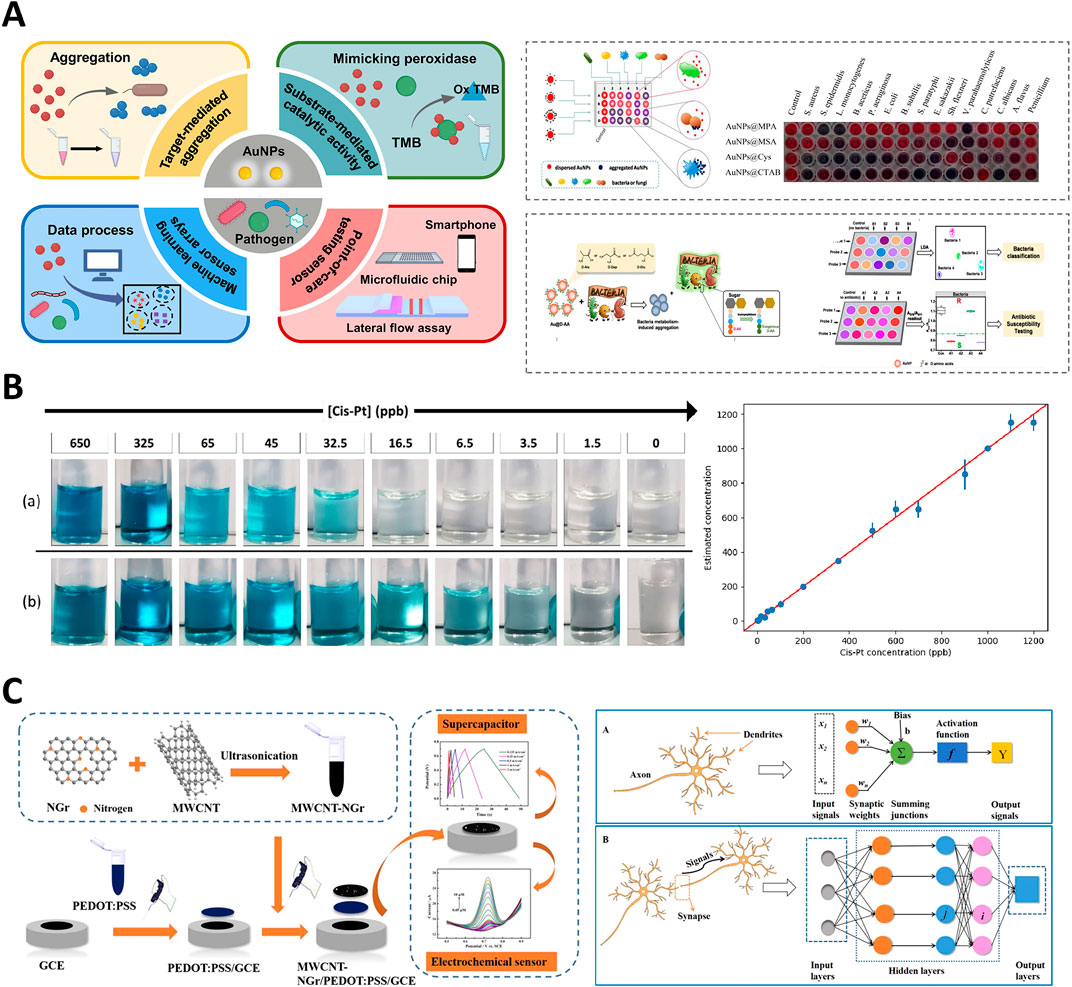
Figure 4. Integration of gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotube-based nanozymes in colorimetric and electrochemical sensors. (A) Schematic of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric pathogen detection systems. Adapted with permission (Yang et al., 2022) copyright 2022, MDPI. (B) Colorimetric detection of cisplatin at ppb levels using nanocatalyst-enhanced assays. Adapted with permission (Mastronardi et al., 2022), copyright 2022, MDPI. (C) Multi-walled carbon nanotube-N-doped graphene nanohybrid for electrochemical sensing and energy storage applications. Adapted with permission (Xue et al., 2020), copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
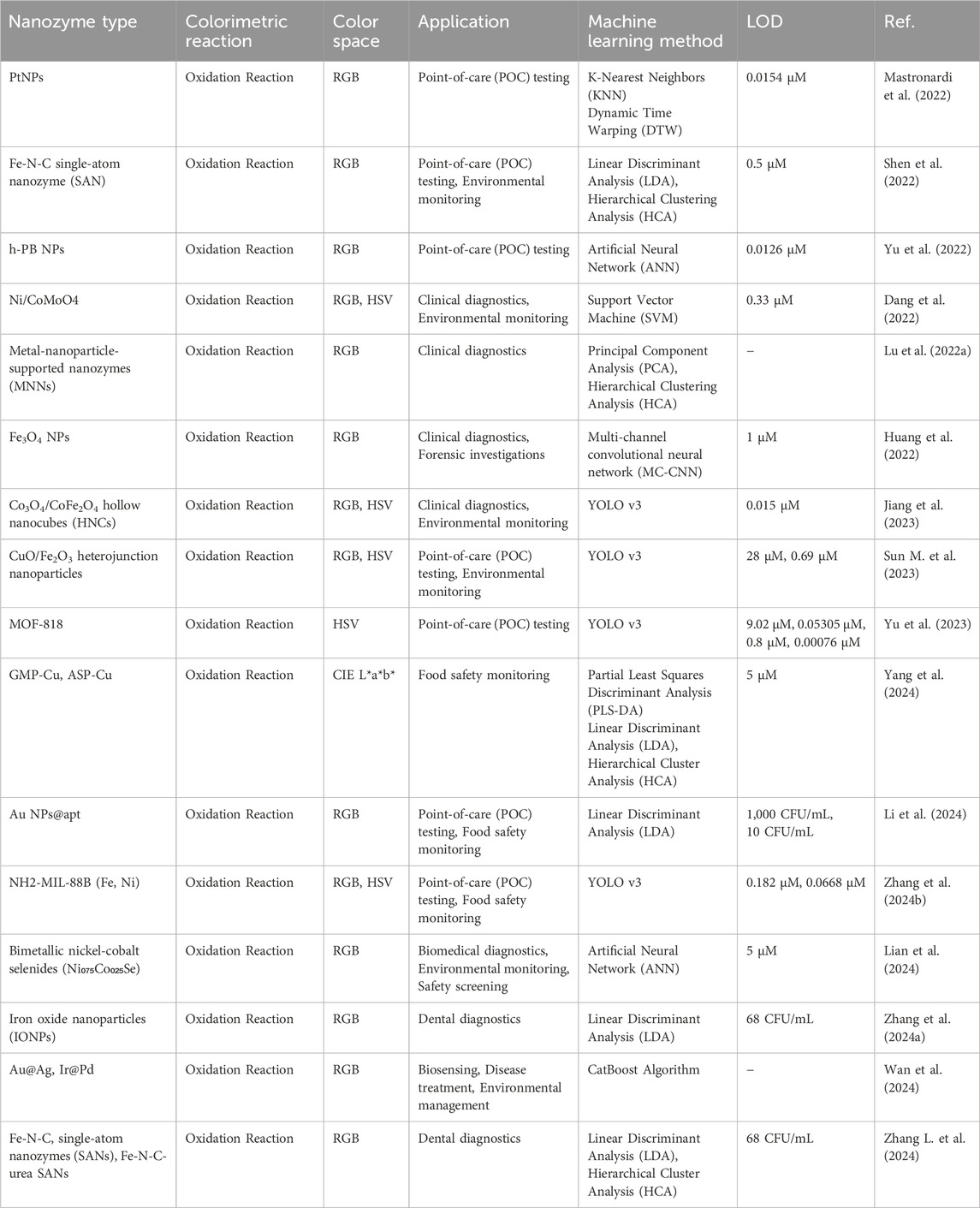
Table 1. Overview of nanozyme-based colorimetric reactions integrated with machine learning for advanced diagnostic and monitoring applications.
In 2022, (Huang et al., 2022) introduced a deep learning-assisted method employing Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles for real-time visualization and recognition of complex information within latent fingerprints (Huang et al., 2022). The method significantly enhanced the accuracy and depth of fingerprint analysis, demonstrating the powerful impact of combining ML with nanozyme technology in forensic science. The ability to analyze complex patterns with high precision underscores the potential of ML-driven nanozymes for improving forensic diagnostics. Such advancements were mirrored by Mastronardi et al. (2022), who developed a fast colorimetric test to detect cisplatin in biological samples (Mastronardi et al., 2022). Their study demonstrated the capability of ML models to process colorimetric data obtained from a series of reactions, where changes in the intensity of the blue color were directly related to the cisplatin concentration, enabling the precise monitoring of drug levels, as shown in Figure 4B. In another notable advancement, Lu et al., in (2022) developed a metal-nanoparticle-supported nanozyme-based colorimetric sensor array aimed at the precise identification of oral bacteria and proteins (Lu et al., 2022a). Their innovation provided a robust platform for oral health diagnostics, allowing accurate detection of bacterial species and protein markers associated with dental diseases. They highlighted the growing role of nanozyme-based sensors in clinical diagnostics, particularly under conditions requiring rapid and precise detection.
In 2024, (Wan et al., 2024) leveraged ML-accelerated high-throughput computational screening to identify bimetallic nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity (Wan et al., 2024). Using ML, They significantly streamlined the discovery process, reducing the time and resources required to identify highly active nanozymes. Their study exemplified the synergy between computational techniques and nanotechnology, offering a model for more efficient discovery and development of functional nanozymes. Building on these advancements, (Dang et al., 2022) constructed a Ni-CoMoO4 heterostructure with strong Ni–O–Co bonds to enhance multi-functional nanozyme activity (Dang et al., 2022). The heterostructure demonstrated improved catalytic performance, particularly in environmental applications such as pollutant degradation. They highlighted the potential of tailored nanostructures to boost the efficiency and applicability of nanozymes in diverse bioapplications.
To further expand the scope of nanozyme applications, Sun Q. et al. (2023) developed a Mo single-atom nanozyme anchored on a 2D N-doped carbon film (Sun Q. et al., 2023). The system was designed to visually monitor choline levels and evaluate intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, thereby providing new insights into the catalytic mechanisms of nanozymes and their roles in cellular processes. They illustrated the dual diagnostic and therapeutic potential of nanozymes, particularly in monitoring and influencing cellular activity. Similarly, Zhang L. et al. (2024) introduced an enhanced “electronic tongue” based on a DNA-encoded nanozyme sensor array for the discrimination and elimination of dental bacteria (Zhang L. et al., 2024). The innovation represented a significant advancement in dental diagnostics, and offered a powerful tool for identifying and targeting pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity. The integration of DNA technology with nanozyme sensors underscored the interdisciplinary nature of modern biosensing approaches by blending molecular biology with nanotechnology. Yang et al. (2022) provided a comprehensive summary of recent progress in colorimetric sensors based on gold nanoparticles for pathogen detection (Yang et al., 2022).
4.2 Integration of nanozymes with ML for advanced bioapplications
The integration of nanozymes with ML represents a transformative approach in advanced bioapplications that combines the unique catalytic properties of nanozymes with the predictive and analytical power of ML algorithms. The synergy has the potential to significantly enhance sensitivity, specificity, and overall performance of biosensing and therapeutic platforms. By leveraging the strengths of both technologies, researchers are focusing on developing innovative solutions that not only improve the detection of critical biomarkers, but also enable more effective treatment and environmental remediation. This section explores recent advancements in the field, highlighting key studies that have demonstrated the potential of combining nanozymes with ML for cutting-edge bioapplications. Table 2 provides a concise overview of various nanozyme-based electrochemical reactions, summarizing their associated electrochemical reactions, detection technologies, applications, ML methods, and limits of detection (LOD). The table highlights the integration of ML techniques for enhancing the performance and specificity of nanozyme-based detection systems across various fields.
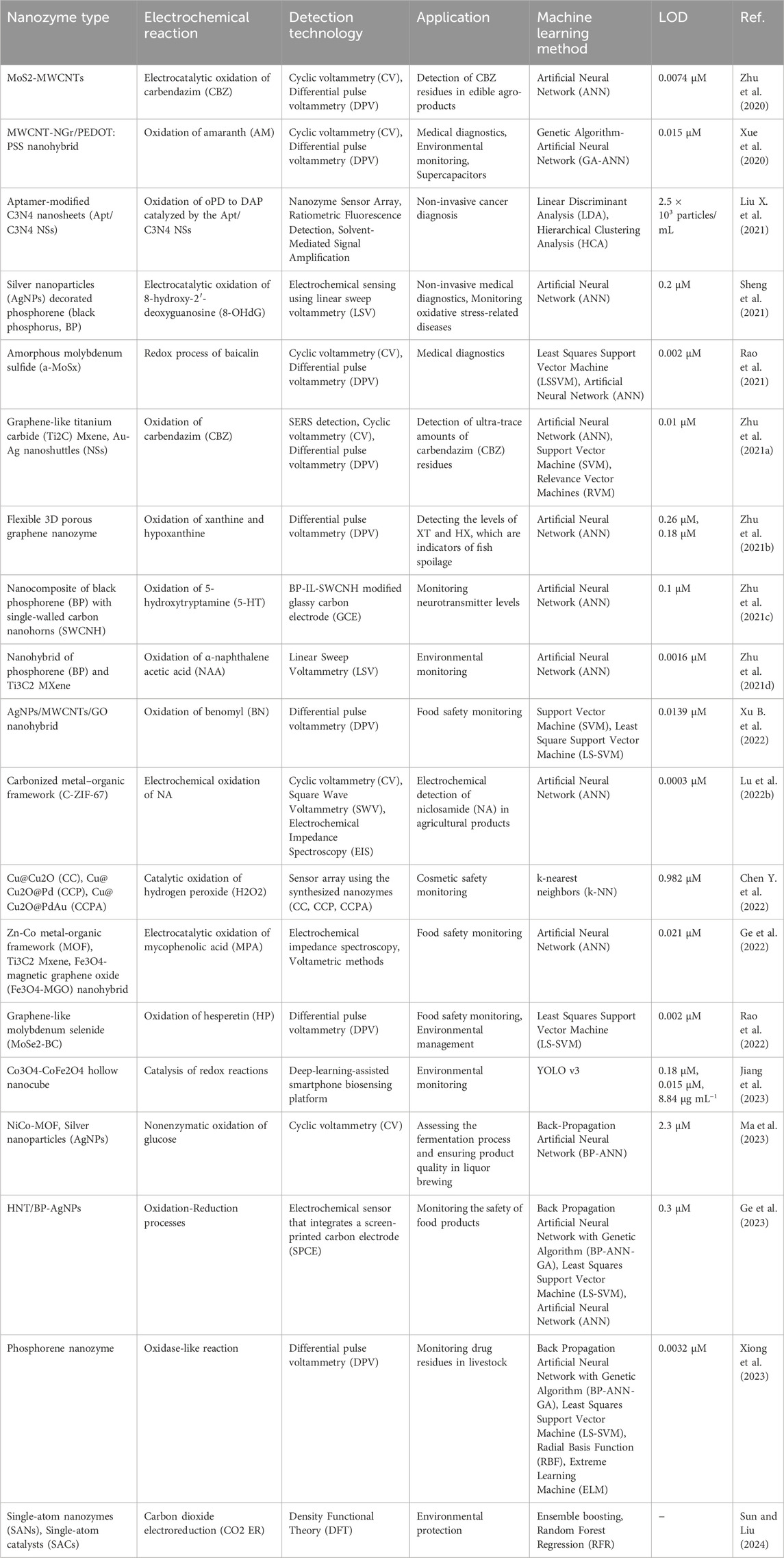
Table 2. Overview of nanozyme-based electrochemical reactions integrated with machine learning for advanced detection technologies and bioapplications.
In 2021, (Liu M.-X. et al.,) developed a nanozyme sensor array that utilized a sovent-driven approach for enhanced signal amplification in the ultrasensitive detection of exosomal protein, which are crucial biomarkers for cancer identification (Liu M.-X. et al., 2021). Their innovative approach demonstrated exceptional sensitivity and specificity, making it a promising tool for early cancer diagnosis. They underscored the potential of nanozymes for improving the detection of low-abundance biomarkers, which is essential for timely and accurate disease diagnosis. As shown in Figure 4C, Xue et al. (2020) introduced a multi-walled carbon nanotube-N-doped graphene (MWCNT-NGr) nanohybrid integrated with poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT) for electrochemical applications (Xue et al., 2020). The nanohybrid was specifically designed for intelligent sensors and supercapacitors, and exhibited enhanced electrochemical performance owing to the synergistic effects of the materials. Xue et al. highlighted the potential of combining carbon-based nanomaterials with conducting polymers to improve the efficiency and functionality of electrochemical biosensors and energy storage devices. Similarly, Sheng et al. (2021) introduced a stable nanosilver-decorated phosphorene nanozyme combined with phosphorus-doped porous carbon microspheres (Sheng et al., 2021). Their system was specifically designed for the intelligent sensing of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, a biomarker associated with oxidative DNA damage often linked to cancer. The integration of nanosilver and phosphorene provided enhanced catalytic activity and stability, marking a significant advancement in cancer detection technology. They illustrated improvements to the performance of biosensors by combining different nanomaterials, particularly in challenging biological environments.
Further, Rao et al. (2021) focused on the green synthesis of an amorphous molybdenum sulfide nanocomposite with biochar microspheres (Rao et al., 2021). The composite was used in a voltammetric sensing platform that exhibited high sensitivity and selectivity for baicalin, a compound with important pharmacological effects. Wang highlighted the potential of using eco-friendly materials to develop advanced biosensors, which are increasingly important for sustainable technology development. Liu Q. et al. (2021) explored the therapeutic applications of nanozymes by developing Au-ZnO-based Trojan nanogenerators activated by ultrasound for targeted electrostimulation and enhanced catalytic therapy for tumors (Ma et al., 2021). Their study presented a novel integration of nanozyme technology with therapeutic applications, offering new avenues for cancer treatment by improving the efficacy of catalytic therapies. They demonstrated the versatility of nanozymes not only as diagnostic tools, but also as active agents in therapeutic interventions.
In 2022, (Xu B. et al., 2022) developed a Ni-CoMoO4 heterostructure featuring robust Ni–O–Co bonds to enhance multi-functional nanozyme activity (Xu B. et al., 2022). The heterostructure exhibited enhanced catalytic performance, particularly in environmental applications such as pollutant degradation. Chen et al. showcased the potential of nanozymes in addressing environmental challenges and highlighted their role in environmental remediation. Finally, (Lu X. et al., 2022) explored the synergy between ML and nanozyme technology by developing a ML strategy to optimize the performance of electrochemical sensors and supercapacitors using carbonized metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) (Lu X. et al., 2022). The application of ML algorithms significantly improved the sensitivity and accuracy of the sensors, demonstrating the powerful role that ML could play in refining and enhancing nanozyme-based systems. They indicated the growing trend toward integrating computational approaches with nanotechnology to achieve better performance and more precise control over sensor characteristics.
5 Challenges and future perspectives
Recent advancements in nanozyme-based detection technologies, particularly the integration of ML, have shown great promise for clinical and environmental applications. However, several challenges must be addressed to fully realize their potential. One of the primary challenges is to ensure the quality and robustness of the data used in ML models. The success of ML-driven diagnostic tools depends heavily on the diversity, accuracy, and relevance of training data (Park et al., 2023; Leem et al., 2022). Comprehensive datasets that accurately represent real-world conditions are crucial for effective generalization of ML models across different scenarios. Without high-quality data, these models may produce inconsistent or inaccurate predictions, limiting their reliability in clinical diagnostics or environmental monitoring (Yoon et al., 2024a; Jeon et al., 2022a). Therefore, the development of extensive, high-quality datasets is essential for the advancement of ML-integrated nanozyme technology.
Another significant challenge involves scaling up the production of nanozyme-based technologies, while maintaining consistent quality and performance (Ai et al., 2022; Singh et al., 2023). Transitioning from laboratory-scale synthesis to commercial production presents difficulties in ensuring that each nanozyme system meets the stringent quality standards. Additionally, incorporating sophisticated ML algorithms into these technologies in a cost-effective manner is crucial for their widespread adoption (Lowe et al., 2022; Zeebaree, 2024). Overcoming the challenges related to scalability and cost-effectiveness is critical for the successful commercialization of nanozyme-based technologies. Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols for the synthesis, testing, and validation of nanozyme-based detection methods poses a challenge to their broader adoption. Establishing standardized methods is vital to ensure reproducibility across studies and applications (Jeon H.-J. et al., 2022; Jeon et al., 2021; Park et al., 2021). Standardization would also facilitate comparisons between research groups and streamline the regulatory approval process, which is necessary for the commercial deployment of these technologies.
Looking towards the future, specific areas of research should focus on improving data quality, scalability, and standardization in nanozyme technologies. The integration of ML with nanozyme technology offers immense potential to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and applicability of both colorimetric and electrochemical detection systems across various bioapplications (Qian et al., 2022). In the context of colorimetric detection, advanced image-processing techniques, such as color correction, normalization, and transformation are necessary to standardize and improve the accuracy of detection across different devices. ML, with its ability to analyze complex datasets, can significantly enhance the precision and reliability of these systems by learning from data and adapting to various conditions.
Similarly, in the field of electrochemical detection, ML can optimize the interpretation of complex electrochemical signals, thereby improving the sensitivity and specificity of these methods. Techniques such as cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry, when integrated with ML algorithms like artificial neural networks (ANNs) and support vector machines (SVMs), can be fine-tuned to detect trace amounts of analytes with higher accuracy (Kurani et al., 2023; Ragab et al., 2019). The approach can be particularly useful in applications such as environmental monitoring and non-invasive medical diagnostics, where detecting low concentrations of substances is critical. Furthermore, the potential of optical hyperspectral imaging (HSI) to obtain more detailed spectral information beyond the primary RGB colors represents a promising avenue for improving both colorimetric detection methods (Jeon et al., 2022b; Yoon et al., 2024b). Recent advancements have made it possible to implement low-cost hyperspectral imaging techniques on smartphones, thereby enhancing the accuracy of glucose detection and other bioapplication analyses.
In summary, future research should focus on addressing key challenges, including data quality, scalability, and standardization, while exploring new ML-driven advancements in detection technologies. By overcoming these challenges, the field can move towards the development of powerful, precise, and accessible diagnostic tools that have wide-ranging clinical and environmental applications. The continued integration of nanozymes with machine learning will likely drive further innovations, leading to more precise, reliable, and widely available detection technologies that can be applied across a range of clinical and environmental settings.
Author contributions
Y-SP: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. BP: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. H-JJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by 2023 Research Grant from Kangwon National University and the “Innovative Human Resource Development for Local Intellectualization” support program (IITP-2023-RS-2023-00260267) supervised by the IITP and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Korea, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant under the auspices of the Korea government (MEST) (RS-2023-00213379) and Korea and Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS)” through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) (2022RIS-005).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmed, S. F., Mofijur, M., Rafa, N., Chowdhury, A. T., Chowdhury, S., Nahrin, M., et al. (2022). Green approaches in synthesising nanomaterials for environmental nanobioremediation: technological advancements, applications, benefits and challenges. Environ. Res. 204, 111967. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111967
Ai, Y., Hu, Z. N., Liang, X., Sun, H. b., Xin, H., and Liang, Q. (2022). Recent advances in nanozymes: from matters to bioapplications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2110432. doi:10.1002/adfm.202110432
An, K., and Somorjai, G. A. (2012). Size and shape control of metal nanoparticles for reaction selectivity in catalysis. ChemCatChem 4, 1512–1524. doi:10.1002/cctc.201200229
Arya, S. S., Dias, S. B., Jelinek, H. F., Hadjileontiadis, L. J., and Pappa, A.-M. (2023). The convergence of traditional and digital biomarkers through AI-assisted biosensing: a new era in translational diagnostics? Biosens. Bioelectron. 235, 115387. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2023.115387
Barlow, H. B. (1989). Unsupervised learning. Neural Comput. 1, 295–311. doi:10.1162/neco.1989.1.3.295
Butler, K. T., Davies, D. W., Cartwright, H., Isayev, O., and Walsh, A. (2018). Machine learning for molecular and materials science. Nature 559, 547–555. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0337-2
Cao, C., Yang, N., Wang, X., Shao, J., Song, X., Liang, C., et al. (2023). Biomedicine meets nanozyme catalytic chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 491, 215245. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215245
Chadha, U., Selvaraj, S. K., Ashokan, H., Hariharan, S. P., Mathew Paul, V., Venkatarangan, V., et al. (2022). Complex nanomaterials in catalysis for chemically significant applications: from synthesis and hydrocarbon processing to renewable energy applications. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–72. doi:10.1155/2022/1552334
Chen, X., Ding, L., Huang, X., and Xiong, Y. (2022). Tailoring noble metal nanoparticle designs to enable sensitive lateral flow immunoassay. Theranostics 12, 574–602. doi:10.7150/thno.67184
Chen, Y., Lin, P., Zou, X., Liu, L., Ouyang, S., Chen, H., et al. (2022). Machine-learning-aided identification of steroid hormones based on the anisotropic galvanic replacement generated sensor array. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 370, 132470. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2022.132470
Chen, Z., Yu, Y., Gao, Y., and Zhu, Z. (2023). Rational design strategies for nanozymes. ACS Nano 17, 13062–13080. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c04378
Cui, F., Yue, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., and Zhou, H. S. (2020). Advancing biosensors with machine learning. ACS Sensors 5, 3346–3364. doi:10.1021/acssensors.0c01424
Dang, Y., Wang, G., Su, G., Lu, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, T., et al. (2022). Rational construction of a Ni/CoMoO4 heterostructure with strong Ni–O–Co bonds for improving multifunctional nanozyme activity. ACS Nano 16, 4536–4550. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c11012
Das, B., Franco, J. L., Logan, N., Balasubramanian, P., Kim, M. I., and Cao, C. (2021). Nanozymes in point-of-care diagnosis: an emerging futuristic approach for biosensing. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 193–251. doi:10.1007/s40820-021-00717-0
Flynn, C. D., and Chang, D. (2024). Artificial intelligence in point-of-care biosensing: challenges and opportunities. Diagnostics 14, 1100. doi:10.3390/diagnostics14111100
Gao, L., and Yan, X. (2016). Nanozymes: an emerging field bridging nanotechnology and biology. Sci. China Life Sci. 59, 400–402. doi:10.1007/s11427-016-5044-3
Ge, Y., Camarada, M. B., Liu, P., Qu, M., Wen, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2022). A portable smart detection and electrocatalytic mechanism of mycophenolic acid: a machine learning-based electrochemical nanosensor to adapt variable-pH silage microenvironment. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 372, 132627. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2022.132627
Ge, Y., Li, M., Zhong, Y., Xu, L., Lu, X., Hu, J., et al. (2023). Halloysite nanotube/black phosphorene nanohybrid modified screen-printed carbon electrode as an ultra-portable electrochemical sensing platform for smartphone-capable detection of maleic hydrazide with machine learning assistance. Food Chem. 406, 134967. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134967
Geng, H., Vilms Pedersen, S., Ma, Y., Haghighi, T., Dai, H., Howes, P. D., et al. (2022). Noble metal nanoparticle biosensors: from fundamental studies toward point-of-care diagnostics. Accounts Chem. Res. 55, 593–604. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00598
Gupta, R., Srivastava, D., Sahu, M., Tiwari, S., Ambasta, R. K., and Kumar, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence to deep learning: machine intelligence approach for drug discovery. Mol. Divers. 25, 1315–1360. doi:10.1007/s11030-021-10217-3
Huang, R., Zhou, Y., and Hu, J. (2022). Deep learning-assisted Fe3O4 NPs for in-situ visual recognition of multi-dimensional information on latent fingerprints. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 366, 132020. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2022.132020
Huang, Y., Ren, J., and Qu, X. (2019). Nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 119, 4357–4412. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00672
Jeon, H. J., Kim, H. S., Chung, E., and Lee, D. Y. (2022b). Nanozyme-based colorimetric biosensor with a systemic quantification algorithm for noninvasive glucose monitoring. Theranostics 12, 6308–6338. doi:10.7150/thno.72152
Jeon, H.-J., Kim, S., Park, S., Jeong, I.-K., Kang, J., Kim, Y. R., et al. (2021). Optical assessment of tear glucose by smart biosensor based on nanoparticle embedded contact lens. Nano Lett. 21, 8933–8940. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01880
Jeon, H. J., Leem, J. W., Ji, Y., Park, S. M., Park, J., Kim, K. Y., et al. (2022a). Cyber-physical watermarking with inkjet edible bioprinting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2112479. doi:10.1002/adfm.202112479
Jiang, S., Su, G., Wu, J., Song, C., Lu, Z., Wu, C., et al. (2023). Co3O4/CoFe2O4 hollow nanocube multifunctional nanozyme with oxygen vacancies for deep-learning-assisted smartphone biosensing and organic pollutant degradation. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 15, 11787–11801. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c22136
Jing, L., Zhou, W., Tian, G., and Fu, H. (2013). Surface tuning for oxide-based nanomaterials as efficient photocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 9509–9549. doi:10.1039/c3cs60176e
Kulkarni, M. B., Ayachit, N. H., and Aminabhavi, T. M. (2022). Recent advancements in nanobiosensors: current trends, challenges, applications, and future scope. Biosensors 12, 892. doi:10.3390/bios12100892
Kurani, A., Doshi, P., Vakharia, A., and Shah, M. (2023). A comprehensive comparative study of artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector machines (SVM) on stock forecasting. Ann. Data Sci. 10, 183–208. doi:10.1007/s40745-021-00344-x
Leem, J. W., Jeon, H.-J., Ji, Y., Park, S. M., Kwak, Y., Park, J., et al. (2022). Edible matrix code with photogenic silk proteins. ACS Central Sci. 8, 513–526. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.1c01233
Lewandowska, H., Wojciuk, K., and Karczmarczyk, U. (2021). Metal nanozymes: new horizons in cellular homeostasis regulation. Appl. Sci. 11, 9019. doi:10.3390/app11199019
Li, H., Xu, H., Yao, S., Wei, S., Shi, X., Zhao, C., et al. (2024). Colorimetry/fluorescence dual-mode detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on self-assembly of MCOF with Au NPs nanozyme coupled AIEgen. Talanta 270, 125505. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2023.125505
Li, S., Hou, Y., Chen, Q., Zhang, X., Cao, H., and Huang, Y. (2019). Promoting active sites in MOF-derived homobimetallic hollow nanocages as a high-performance multifunctional nanozyme catalyst for biosensing and organic pollutant degradation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 2581–2590. doi:10.1021/acsami.9b20275
Li, X., Liu, J., Chen, J., Qiu, H., and Niu, X. (2023). Recent progress in nanozyme-based sensors for ion detection: strategies, trends, and challenges. Sensors Diagnostics 2, 307–319. doi:10.1039/d2sd00233g
Li, X., Qi, Z., Liang, K., Bai, X., Xu, J., Liu, J., et al. (2008). An artificial supramolecular nanozyme based on β-cyclodextrin-modified gold nanoparticles. Catal. Lett. 124, 413–417. doi:10.1007/s10562-008-9494-5
Li, X., Wang, L., Du, D., Ni, L., Pan, J., and Niu, X. (2019). Emerging applications of nanozymes in environmental analysis: opportunities and trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 120, 115653. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2019.115653
Li, Y., Zhang, R., Yan, X., and Fan, K. (2023). Machine learning facilitating the rational design of nanozymes. J. Mater. Chem. B 11, 6466–6477. doi:10.1039/d3tb00842h
Lian, M., Shi, F., Cao, Q., Wang, C., Li, N., Li, X., et al. (2024). Based colorimetric sensor using bimetallic Nickel-Cobalt selenides nanozyme with artificial neural network-assisted for detection of H2O2 on smartphone. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 311, 124038. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2024.124038
Liang, M., and Yan, X. (2019). Nanozymes: from new concepts, mechanisms, and standards to applications. Accounts Chem. Res. 52, 2190–2200. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00140
Liu, M.-X., Zhang, H., Zhang, X.-W., Chen, S., Yu, Y.-L., and Wang, J.-H. (2021). Nanozyme sensor array plus solvent-mediated signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive ratiometric fluorescence detection of exosomal proteins and cancer identification. Anal. Chem. 93, 9002–9010. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.1c02010
Liu, Q., Zhang, A., Wang, R., Zhang, Q., and Cui, D. (2021). A review on metal-and metal oxide-based nanozymes: properties, mechanisms, and applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 154–253. doi:10.1007/s40820-021-00674-8
Liu, X., Wu, W., Cui, D., Chen, X., and Li, W. (2021). Functional micro-/nanomaterials for multiplexed biodetection. Adv. Mater. 33, 2004734. doi:10.1002/adma.202004734
Lou-Franco, J., Das, B., Elliott, C., and Cao, C. (2021). Gold nanozymes: from concept to biomedical applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 13, 10–36. doi:10.1007/s40820-020-00532-z
Lowe, M., Qin, R., and Mao, X. (2022). A review on machine learning, artificial intelligence, and smart technology in water treatment and monitoring. Water 14, 1384. doi:10.3390/w14091384
Lu, X., Liu, P., Bisetty, K., Cai, Y., Duan, X., Wen, Y., et al. (2022b). An emerging machine learning strategy for electrochemical sensor and supercapacitor using carbonized metal–organic framework. J. Electroanal. Chem. 920, 116634. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116634
Lu, Z., Lu, N., Xiao, Y., Zhang, Y., Tang, Z., and Zhang, M. (2022a). Metal-nanoparticle-supported nanozyme-based colorimetric sensor array for precise identification of proteins and oral bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 11156–11166. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c25036
Ma, K., Qi, G., Wang, B., Yu, T., Zhang, Y., Li, H., et al. (2021). Ultrasound-activated Au/ZnO-based Trojan nanogenerators for combined targeted electro-stimulation and enhanced catalytic therapy of tumor. Nano Energy 87, 106208. doi:10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106208
Ma, Y., Leng, Y., Huo, D., Zhao, D., Zheng, J., Zhao, P., et al. (2023). A portable sensor for glucose detection in Huangshui based on blossom-shaped bimetallic organic framework loaded with silver nanoparticles combined with machine learning. Food Chem. 429, 136850. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136850
Manea, F., Houillon, F., Pasquato, L., and Scrimin, P. (2004). Nanozymes: gold-nanoparticle-based transphosphorylation catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 6165–6169. doi:10.1002/anie.200460649
Mastronardi, V., Moglianetti, M., Ragusa, E., Zunino, R., and Pompa, P. P. (2022). From a chemotherapeutic drug to a high-performance nanocatalyst: a fast colorimetric test for cisplatin detection at ppb level. Biosensors 12, 375. doi:10.3390/bios12060375
Meng, Y., Li, W., Pan, X., and Gadd, G. M. (2020). Applications of nanozymes in the environment. Environ. Sci. Nano 7, 1305–1318. doi:10.1039/c9en01089k
Mou, X., Wu, Q., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, C., et al. (2022). Nanozymes for regenerative medicine. Small methods 6, 2200997. doi:10.1002/smtd.202200997
Mujtaba, J., Liu, J., Dey, K. K., Li, T., Chakraborty, R., Xu, K., et al. (2021). Micro-bio-chemo-mechanical-systems: micromotors, microfluidics, and nanozymes for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 33, 2007465. doi:10.1002/adma.202007465
Ngwabebhoh, F. A., and Yildiz, U. (2019). Nature-derived fibrous nanomaterial toward biomedicine and environmental remediation: today's state and future prospects. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136, 47878. doi:10.1002/app.47878
Noll, P., and Henkel, M. (2020). History and evolution of modeling in biotechnology: modeling and simulation, application and hardware performance. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 18, 3309–3323. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2020.10.018
Park, S., Hwang, J., Jeon, H.-J., Bae, W. R., Jeong, I.-K., Kim, T. G., et al. (2021). Cerium oxide nanoparticle-containing colorimetric contact lenses for noninvasively monitoring human tear glucose. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 5198–5210. doi:10.1021/acsanm.1c00603
Park, S., Nam, D. Y., Jeon, H.-J., Han, J. H., Jang, D., Hwang, J., et al. (2023). Chromophoric cerium oxide nanoparticle-loaded sucking disk-type strip sensor for optical measurement of glucose in tear fluid. Biomaterials Res. 27, 135. doi:10.1186/s40824-023-00469-5
Pramanik, P. K. D., Solanki, A., Debnath, A., Nayyar, A., El-Sappagh, S., and Kwak, K.-S. (2020). Advancing modern healthcare with nanotechnology, nanobiosensors, and internet of nano things: taxonomies, applications, architecture, and challenges. IEEE Access 8, 65230–65266. doi:10.1109/access.2020.2984269
Qian, S., Cui, Y., Cai, Z., and Li, L. (2022). Applications of smartphone-based colorimetric biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 11, 100173. doi:10.1016/j.biosx.2022.100173
Ragab, D. A., Sharkas, M., Marshall, S., and Ren, J. (2019). Breast cancer detection using deep convolutional neural networks and support vector machines. PeerJ 7, e6201. doi:10.7717/peerj.6201
Rao, L., Lu, X., Xu, L., Zhu, Y., Xue, T., Ge, Y., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of kudzu vine biochar decorated graphene-like MoSe2 with the oxidase-like activity as intelligent nanozyme sensing platform for hesperetin. Chemosphere 289, 133116. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133116
Rao, L., Zhou, P., Liu, P., Lu, X., Duan, X., Wen, Y., et al. (2021). Green preparation of amorphous molybdenum sulfide nanocomposite with biochar microsphere and its voltametric sensing platform for smart analysis of baicalin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 898, 115591. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115591
Roda, A., Mirasoli, M., Michelini, E., Di Fusco, M., Zangheri, M., Cevenini, L., et al. (2016). Progress in chemical luminescence-based biosensors: a critical review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 76, 164–179. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.017
Saleh, H. M., and Hassan, A. I. (2023). Synthesis and characterization of nanomaterials for application in cost-effective electrochemical devices. Sustainability 15, 10891. doi:10.3390/su151410891
Salvador-Morales, C., and Grodzinski, P. (2022). Nanotechnology tools enabling biological discovery. ACS Nano 16, 5062–5084. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c10635
Sharifi, M., Hasan, A., Attar, F., Taghizadeh, A., and Falahati, M. (2020). Development of point-of-care nanobiosensors for breast cancers diagnosis. Talanta 217, 121091. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121091
Shen, L., Khan, M. A., Wu, X., Cai, J., Lu, T., Ning, T., et al. (2022). Fe–N–C single-atom nanozymes based sensor array for dual signal selective determination of antioxidants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 205, 114097. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2022.114097
Sheng, Y., Zhu, Y., Cerón, M. L., Yi, Y., Liu, P., Wang, P., et al. (2021). A stable nanosilver decorated phosphorene nanozyme with phosphorus-doped porous carbon microsphere for intelligent sensing of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 895, 115522. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115522
Singh, R., Umapathi, A., Patel, G., Patra, C., Malik, U., Bhargava, S. K., et al. (2023). Nanozyme-based pollutant sensing and environmental treatment: trends, challenges, and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 854, 158771. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158771
Singh, S. (2019). Nanomaterials exhibiting enzyme-like properties (nanozymes): current advances and future perspectives. Front. Chem. 7, 46. doi:10.3389/fchem.2019.00046
Soares, P. I., Romao, J., Matos, R., Silva, J. C., and Borges, J. P. (2021). Design and engineering of magneto-responsive devices for cancer theranostics: nano to macro perspective. Prog. Mater. Sci. 116, 100742. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100742
Sun, F., Liang, Y., Jin, L., Shi, J., and Shang, L. (2021). Weak interaction-tailored catalytic interface of ultrasmall gold nanoclusters as enzyme mimics for enhanced colorimetric biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 58209–58219. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c18523
Sun, H., and Liu, J.-y. (2024). A feasible strategy for designing cytochrome P450-mimic sandwich-like single-atom nanozymes toward electrochemical CO2 conversion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 661, 482–492. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2024.01.171
Sun, H., Zhou, Y., Ren, J., and Qu, X. (2018). Carbon nanozymes: enzymatic properties, catalytic mechanism, and applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 9224–9237. doi:10.1002/anie.201712469
Sun, M., Zhao, L., Liu, T., Lu, Z., Su, G., Wu, C., et al. (2023). Construction of CuO/Fe2O3 nanozymes for intelligent detection of glufosinate and chlortetracycline hydrochloride. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 54466–54477. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c12157
Sun, Q., Xu, X., Liu, S., Wu, X., Yin, C., Wu, M., et al. (2023). Mo single-atom nanozyme anchored to the 2D N-doped carbon film: catalytic mechanism, visual monitoring of choline, and evaluation of intracellular ROS generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 36124–36134. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c04761
Wagner, N., and Rondinelli, J. M. (2016). Theory-guided machine learning in materials science. Front. Mater. 3, 28. doi:10.3389/fmats.2016.00028
Wan, K., Wang, H., and Shi, X. (2024). Machine learning-accelerated high-throughput computational screening: unveiling bimetallic nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity. ACS Nano 18, 12367–12376. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c01473
Wang, D., Jana, D., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Metal–organic framework derived nanozymes in biomedicine. Accounts Chem. Res. 53, 1389–1400. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00268
Wang, H., Wan, K., and Shi, X. (2019). Recent advances in nanozyme research. Adv. Mater. 31, 1805368. doi:10.1002/adma.201805368
Wang, K., Meng, X., Yan, X., and Fan, K. (2024). Nanozyme-based point-of-care testing: revolutionizing environmental pollutant detection with high efficiency and low cost. Nano Today 54, 102145. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2023.102145
Wang, Q., Wei, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, E., and Dong, S. (2018). Nanozyme: an emerging alternative to natural enzyme for biosensing and immunoassay. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 105, 218–224. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2018.05.012
Weerathunge, P., Behera, B. K., Zihara, S., Singh, M., Prasad, S. N., Hashmi, S., et al. (2019). Dynamic interactions between peroxidase-mimic silver NanoZymes and chlorpyrifos-specific aptamers enable highly-specific pesticide sensing in river water. Anal. Chim. Acta 1083, 157–165. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2019.07.066
Wei, H., and Wang, E. (2013). Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 6060–6093. doi:10.1039/c3cs35486e
Wei, Y., Wu, J., Wu, Y., Liu, H., Meng, F., Liu, Q., et al. (2022). Prediction and design of nanozymes using explainable machine learning. Adv. Mater. 34, 2201736. doi:10.1002/adma.202201736
Wong, E. L., Vuong, K. Q., and Chow, E. (2021). Nanozymes for environmental pollutant monitoring and remediation. Sensors 21, 408. doi:10.3390/s21020408
Wu, J., Wang, X., Wang, Q., Lou, Z., Li, S., Zhu, Y., et al. (2019). Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 1004–1076. doi:10.1039/c8cs00457a
Wu, L., and Qu, X. (2015). Cancer biomarker detection: recent achievements and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 2963–2997. doi:10.1039/c4cs00370e
Wu, L., Wang, Y., Xu, X., Liu, Y., Lin, B., Zhang, M., et al. (2021b). Aptamer-based detection of circulating targets for precision medicine. Chem. Rev. 121, 12035–12105. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01140
Wu, L., Zhou, S., Wang, G., Yun, Y., Liu, G., and Zhang, W. (2021a). Nanozyme applications: a glimpse of insight in food safety. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 727886. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.727886
Xiong, Y., Wu, R., Xu, L., Zhong, Y., Ge, Y., Wen, Y., et al. (2023). Machine learning for design of phosphorene nanozyme sensor and its intelligent analysis of clenbuterol in animal-derived agro-products. J. Electrochem. Soc. 170, 047505. doi:10.1149/1945-7111/acc9e1
Xu, B., Li, S., and Liu, H. (2022). Photoresponsive nanozymes, nanozymes: design, synthesis, and applications. ACS Publ., 163–187. doi:10.1021/bk-2022-1422.ch007
Xu, D., Wu, L., Yao, H., and Zhao, L. (2022). Catalase-like nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, and their applications. Small 18, 2203400. doi:10.1002/smll.202203400
Xu, L., Xiong, Y., Wu, R., Geng, X., Li, M., Yao, H., et al. (2022). An emerging machine learning strategy for the fabrication of nanozyme sensor and voltametric determination of benomyl in agro-products. J. Electrochem. Soc. 169, 047506. doi:10.1149/1945-7111/ac6143
Xue, T., Liu, P., Zhang, J., Xu, J., Zhang, G., Zhou, P., et al. (2020). Multiwalled carbon nanotube-N-doped graphene/poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrenesulfonate) nanohybrid for electrochemical application in intelligent sensors and supercapacitors. ACS Omega 5, 28452–28462. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c02224
Yang, D., Chen, Z., Gao, Z., Tammina, S. K., and Yang, Y. (2020). Nanozymes used for antimicrobials and their applications. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 195, 111252. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111252
Yang, G., Zhu, C., Du, D., Zhu, J., and Lin, Y. (2015). Graphene-like two-dimensional layered nanomaterials: applications in biosensors and nanomedicine. Nanoscale 7, 14217–14231. doi:10.1039/c5nr03398e
Yang, J., Wang, X., Sun, Y., Chen, B., Hu, F., Guo, C., et al. (2022). Recent advances in colorimetric sensors based on gold nanoparticles for pathogen detection. Biosensors 13, 29. doi:10.3390/bios13010029
Yang, X., Bi, Z., Yin, C., Huang, H., and Li, Y. (2024). A novel hybrid sensor array based on the polyphenol oxidase and its nanozymes combined with the machine learning based dual output model to identify tea polyphenols and Chinese teas. Talanta 272, 125842. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2024.125842
Yoon, I., Han, J. H., and Jeon, H.-J. (2024b). Advances in platelet-dysfunction diagnostic technologies. Biomolecules 14, 714. doi:10.3390/biom14060714
Yoon, I., Han, J. H., Park, B. U., and Jeon, H.-J. (2024a). Blood-inspired random bit generation using microfluidics system. Sci. Rep. 14, 7474. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-58088-6
Yu, K., Li, M., Chai, H., Liu, Q., Hai, X., Tian, M., et al. (2023). MOF-818 nanozyme-based colorimetric and electrochemical dual-mode smartphone sensing platform for in situ detection of H2O2 and H2S released from living cells. Chem. Eng. J. 451, 138321. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.138321
Yu, Z., Gong, H., Li, M., and Tang, D. (2022). Hollow prussian blue nanozyme-richened liposome for artificial neural network-assisted multimodal colorimetric-photothermal immunoassay on smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 218, 114751. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2022.114751
Zeebaree, I. (2024). The distributed machine learning in cloud computing and web technology: a review of scalability and efficiency. J. Inf. Technol. Inf. 3.
Zhang, L., Qi, Z., Yang, Y., Lu, N., and Tang, Z. (2024). Enhanced “electronic tongue” for dental bacterial discrimination and elimination based on a DNA-encoded nanozyme sensor array. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16, 11228–11238. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c17134
Zhang, Y., Khan, M. A., Yu, Z., Yang, W., Zhao, H., Ye, D., et al. (2024a). The identification of oral cariogenic bacteria through colorimetric sensor array based on single-atom nanozymes. Small, 2403878. doi:10.1002/smll.202403878
Zhang, Y., Wang, M., Shao, C., Liu, T., Sun, M., Wu, C., et al. (2024b). Nanozyme-induced deep learning-assisted smartphone integrated colorimetric and fluorometric dual-mode for detection of tetracycline analogs. Anal. Chim. Acta 1297, 342373. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2024.342373
Zheng, L., Cao, M., Du, Y., Liu, Q., Emran, M. Y., Kotb, A., et al. (2024). Artificial enzyme innovations in electrochemical devices: advancing wearable and portable sensing technologies. Nanoscale 16, 44–60. doi:10.1039/d3nr05728c
Zhu, X., Lin, L., Wu, R., Zhu, Y., Sheng, Y., Nie, P., et al. (2021d). Portable wireless intelligent sensing of ultra-trace phytoregulator α-naphthalene acetic acid using self-assembled phosphorene/Ti3C2-MXene nanohybrid with high ambient stability on laser induced porous graphene as nanozyme flexible electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 179, 113062. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2021.113062
Zhu, X., Liu, P., Ge, Y., Wu, R., Xue, T., Sheng, Y., et al. (2020). MoS2/MWCNTs porous nanohybrid network with oxidase-like characteristic as electrochemical nanozyme sensor coupled with machine learning for intelligent analysis of carbendazim. J. Electroanal. Chem. 862, 113940. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.113940
Zhu, X., Liu, P., Xue, T., Ge, Y., Ai, S., Sheng, Y., et al. (2021a). A novel graphene-like titanium carbide MXene/Au–Ag nanoshuttles bifunctional nanosensor for electrochemical and SERS intelligent analysis of ultra-trace carbendazim coupled with machine learning. Ceram. Int. 47, 173–184. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.121
Zhu, Y., Liu, P., Xue, T., Xu, J., Qiu, D., Sheng, Y., et al. (2021b). Facile and rapid one-step mass production of flexible 3D porous graphene nanozyme electrode via direct laser-writing for intelligent evaluation of fish freshness. Microchem. J. 162, 105855. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2020.105855
Zhu, Y., Xue, T., Sheng, Y., Xu, J., Zhu, X., Li, W., et al. (2021c). Ionic liquid-assisted ultrasonic exfoliation of phosphorene nanocomposite with single walled carbon nanohorn as nanozyme sensor for derivative voltammetric smart analysis of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Microchem. J. 170, 106697. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2021.106697
Keywords: nanozyme, machine learning, bioapplication, colorimetric, biosensing
Citation: Park Y-S, Park BU and Jeon H-J (2024) Advances in machine learning-enhanced nanozymes. Front. Chem. 12:1483986. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1483986
Received: 21 August 2024; Accepted: 30 September 2024;
Published: 17 October 2024.
Edited by:
Chuanhui Huang, Technical University Dresden, GermanyReviewed by:
Zhengxing Li, University of California, San Diego, United StatesTianran Lin, Guangxi Normal University, China
Copyright © 2024 Park, Park and Jeon. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hee-Jae Jeon, amVvbjIyQGthbmd3b24uYWMua3I=
 Yeong-Seo Park1
Yeong-Seo Park1 Hee-Jae Jeon
Hee-Jae Jeon