- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory, Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health and Disorders, Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Child Development and Disorders, Chongqing Key Laboratory of Child Rare Diseases in Infection and Immunity, Chongqing, China
- 2Department of Clinical Laboratory, Kunming Children’s Hospital, Kunming, China
Objective: This study assessed epidemiology characteristics, carbapenem-resistance genes, and drug resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA) and aztreonam-avibactam (AZA) in children with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae (CRKP) infections.
Methods: A total of 363 non-repetitive CRKP strains were collected from children who underwent two tertiary children’s hospital between 1 January 2021 and 30 June 2024 in Chongqing and Kunming in Southwest China. Carbapenem resistance genes and antimicrobial susceptibility were analyzed. Basic clinical characteristics of the patients were obtained from medical records.
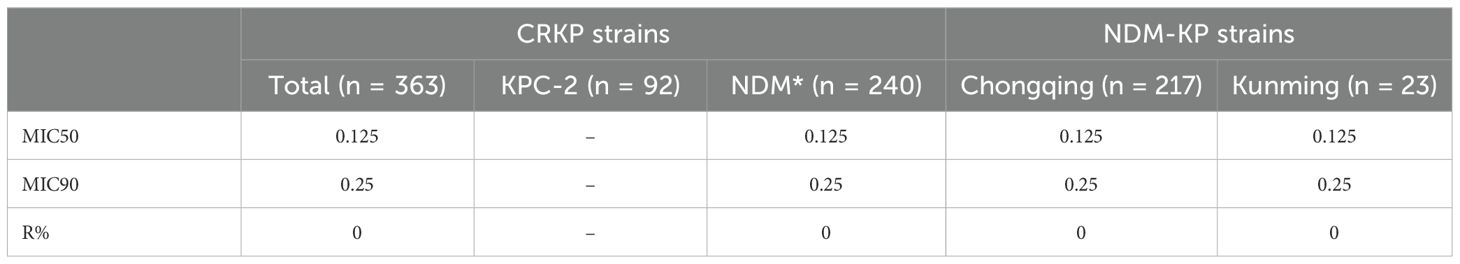
Results: blaNDM-5, blaNDM-1, and blaKPC-2 were the predominant carbapenemase genes; their detection rates were 35.8%, 30.3%, and 25.3%, respectively. Patients in the KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-KP) (median age, 90 days) were older than those producing NDM-1 and NDM-5 Klebsiella pneumoniae (NDM-KP) (median age, 37 days) (P < 0.05). The detection rate of NDM-KP in the neonatal unit was higher compared with KPC-KP (62.5% vs. 9.8%, P < 0.05), while the detection rate of NDM-KP in the intensive care unit (ICU) was decreased compared with KPC-KP (9.6% vs. 40.2%, P < 0.05). NDM-KP had lower resistance rates to aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones than KPC-KP; the resistance rate of aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones among NDM-KP and KPC-KP in Chongqing was increased compared with Kunming. The sensitivity rates of KPC-KP to CZA and NDM-KP to AZA were 100%, and the MIC50 of the CRKP to CZA and AZA were 2 μg/mL and 0.125μg/mL, respectively.
Conclusions: The epidemiological characteristics of Chinese children with CRKP infections, including the resistance genes and the antibiotic resistance of CRKP, exhibited significant variation between the two regions.KPC-KP strains had higher antimicrobial resistance in patients and thus should be given more attention in clinics and infection control.
1 Introduction
Klebsiella pneumoniae is the second leading pathogen responsible for clinical infectious diseases in China (Hu et al., 2024). It can cause infections in the respiratory system, urinary system, and various tissues, with a high morbidity and mortality rate (Hussein et al., 2013; Kontopoulou et al., 2019; Martin et al., 2018).Notably, the mortality rate among patients with K.pneumoniae-caused pneumonia is approximately 50% (Martin et al., 2018). The resistance rate of Klebsiella pneumoniae to meropenem has steadily increased from 2.9% in 2005 to 30.0% in 2023 (http://www.chinets.com/Data/GermYear) (Hu et al., 2024).Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) has become widespread globally, leading to life-threatening infections. In terms of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) per 100,000 population, the median for CRKP infections in the European Union is 11.5 (Karampatakis et al., 2023). An Australian study reported a pooled mortality rate of 37.2% due to CRKP infections (Agyeman et al., 2020). In Greece, the rate of CRKP isolates reached 66.3% in 2020, the highest among all countries (Cassini et al., 2019; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, 2019). CRKP is strongly associated with high mortality rates, particularly among critically ill and immunocompromised patients, especially young children, posing a significant threat to public health.CRKP is strongly associated with high rates of mortality, especially in critically ill and immunocompromised young patients, and poses immense threats to human health (Xu et al., 2017).In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) published a list of critical priority pathogens, including CRKP, for which there is an urgent need to develop new antibiotics (Nordmann and Poirel, 2019). Despite annual epidemiological surveillance reports on CRKP (Veeraraghavan and Walia, 2019; Yin et al., 2020), most previous studies focus on adult populations, while there is a lack of relevant literature focusing on children. Several multi-center studies conducted in different countries found differences in bacterial clones between pediatric and adult patients within the same centers (Castagnola et al., 2019). In China, the prevalence rate of CRKP is approximately 13.4% to 23% among children (Fu et al., 2021).
The production of carbapenemases, including Ambler A-class β-lactamase blaKPC, encoding metallo-β-lactamase blaNDM(B-class), and D-class β-lactamase blaOXA-48 (Lutgring, 2019), which are key mechanisms for carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae.In addition, studies have found that CRKP exhibits different molecular characteristics in children of different ages (Yin et al., 2020). For example, class A carbapenemase blaKPC-2 is mainly found in non-neonatal and adult patients, while class B carbapenemase blaNDM-1 is more prevalent in neonates (Yin et al., 2020). However, data on the clinical outcomes in children infected with CRKP are limited.
CRKP is usually resistant to the most commonly used antibiotics, and there are limited treatment options available. Since 2014, the development of new antibiotics brought new opportunities for treatments of CRKP. The novel approved antibiotics against CRKP infections include imipenem/cilastatin-relebactam, CZA, meropenem-vaborbactam, plazomicin, and eravacycline (Papp-Wallace, 2019). CZA includes a combination of a beta-lactam antibiotic and a beta-lactamase inhibitor that effectively inhibits the activity of class A, C, and some D class carbapenemases.Compared with other antibiotics, CZA can significantly improve the clinical survival rate (Theuretzbacher et al., 2021). In 2022, CZA was approved by the National Medical Products Administration for treating complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAIs) in children older than 3 months. However, none of these β-lactamase-inhibitor combinations showed activity against carbapenemase, especially for metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) (Biagi et al., 2019). Still, the recent novel antibiotic aztreonam-avibactam (AZA) represented remarkable progress in treating MBL- or other β-lactamases-producing CRKP (Zou et al., 2020).
There have been very few studies on the activity of CRKP against CAZ and AZA in children. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multicenter study that analyzed epidemiology characteristics of CRKP, genes related to CRKP, and drug resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA) and aztreonam-avibactam (AZA) in children. The present study also compared differences between genetic types and geographic regions. These data provide strong evidence for the clinical treatment, prevention, and control of CRKP in children.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bacterial strains
A total of 363 nonduplicate clinical CRKP isolates collected from patients who underwent two tertiary children’s hospital between 1 January 2021 and 30 June 2024 in Chongqing and Kunming in Southwest China were analyzed. Isolates identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) were performed using the automated BD Phoenix™ M50 Microbiology System. P. aeruginosa ATCC27853 and E. coli ATCC 25922 were used as quality controls.
CRKP was defined as a resistant strain to any carbapenem antimicrobials (i.e., minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of ≥ 2 μg/mL against ertapenem or ≥ 4 μg/mL against meropenem or imipenem. The results were interpreted by the breakpoint criteria recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) M100-S34 guidelines from 2024 (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), 2024).
2.2 Screening of carbapenemase genes
PCR was performed to screen the carbapenemase encoding genes, including blaKPC, blaNDM, blaIMP, blaVIM, and blaOXA-48-like. Positive PCR products were sequenced by Sanger sequencing (Sangon Biotech), and the sequences were blasted in GenBank (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). The primers used for detecting these carbapenemase genes have been reported previously (Zhou et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2018).
2.3 In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing
The MICs of CRKP strains were determined using the standard broth microdilution method and were interpreted according to CLSI criteria (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), 2024). All CRKP strains were tested for MICs of CZA; only the NDM-KP strain detected MICs of AZA. For CZA and AZA testing, AVI was tested at a fixed concentration of 4 mg/L, while ceftazidime and aztreonam were added at different concentrations, respectively. The testing MICs range of CZA was 0.016/4–256/4 μg/mL. The testing MICs range of AZA was 0.032/4–64/4 μg/mL. MICs breakpoints for CZA were interpreted as CLSI guidelines (2024) (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), 2024). The MICs breakpoints for AZA were interpreted using the 2024 CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), 2024) breakpoints (interpretation via 2024 EUCAST criteria (EUCAST, 2024) is provided in Supplementary Table S2). P. aeruginosa ATCC27853 and E. coli ATCC 25922 were used as quality control strains. MICs were determined in triplicate on two separate days.
2.4 Definitions
Neonatal patients were defined as those no older than 28 days, while pediatric patients were defined as those between 29 days and 14 years old (Nichols et al., 2015).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Raw data were processed using Whonet 5.6 software and then calculated using GraphPad Prism 5. The age difference was further determined using the Mann-Whitney U test, and categorical data were evaluated using the Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Statistical significance was confirmed if the two-tailed P-value was < 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Carbapenem resistance gene of CRKP strains
Of the 363 CRKP isolates, 363 (100%) strains were successfully identified with the carbapenemase genes; blaNDM-5 (35.8%, 130/363) was a predominant gene, followed by blaNDM-1 (30.3%, 110/363), blaKPC-2 (25.3%, 92/363), and blaVIM (8.5%, 31/363). The detection rates of blaKPC-2 and blaNDM (blaNDM-1 and blaNDM-5) were 18.0%, 54.1%, and 75.1%, 31.1% in Chongqing and Kunming, respectively. Compared to Kunming, the detection rate of blaNDM-5 and blaNDM-1 increased while blaKPC-2 and blaVIM decreased in Chongqing (all P < 0.05) (Figure 1A). In addition, blaNDM-5 was the most prevalent in Chongqing, while blaKPC-2 was the most prevalent in Kunming. Also, the detection rates of four carbapenem resistance genes were significantly different in Chongqing and Kunming (all P < 0.05) (Figure 1B).
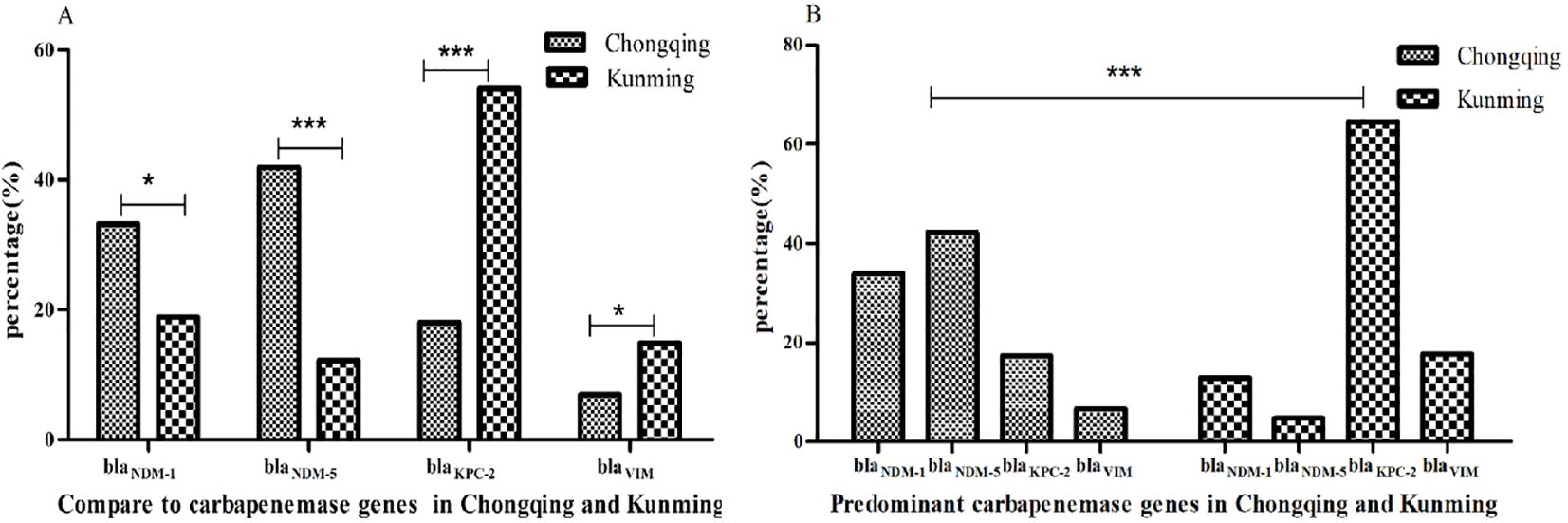
Figure 1. Resistance genes of CRKP isolates. (A) Compare to carbapenemase genes in Chongqing and Kunming. (B) Predominant carbapenemase genes in Chongqing and Kunming.**indicate statistical significance with P < 0.01, ***indicate statistical significance with P < 0.001.
3.2 Clinical characteristics and epidemiology of CRKP strains
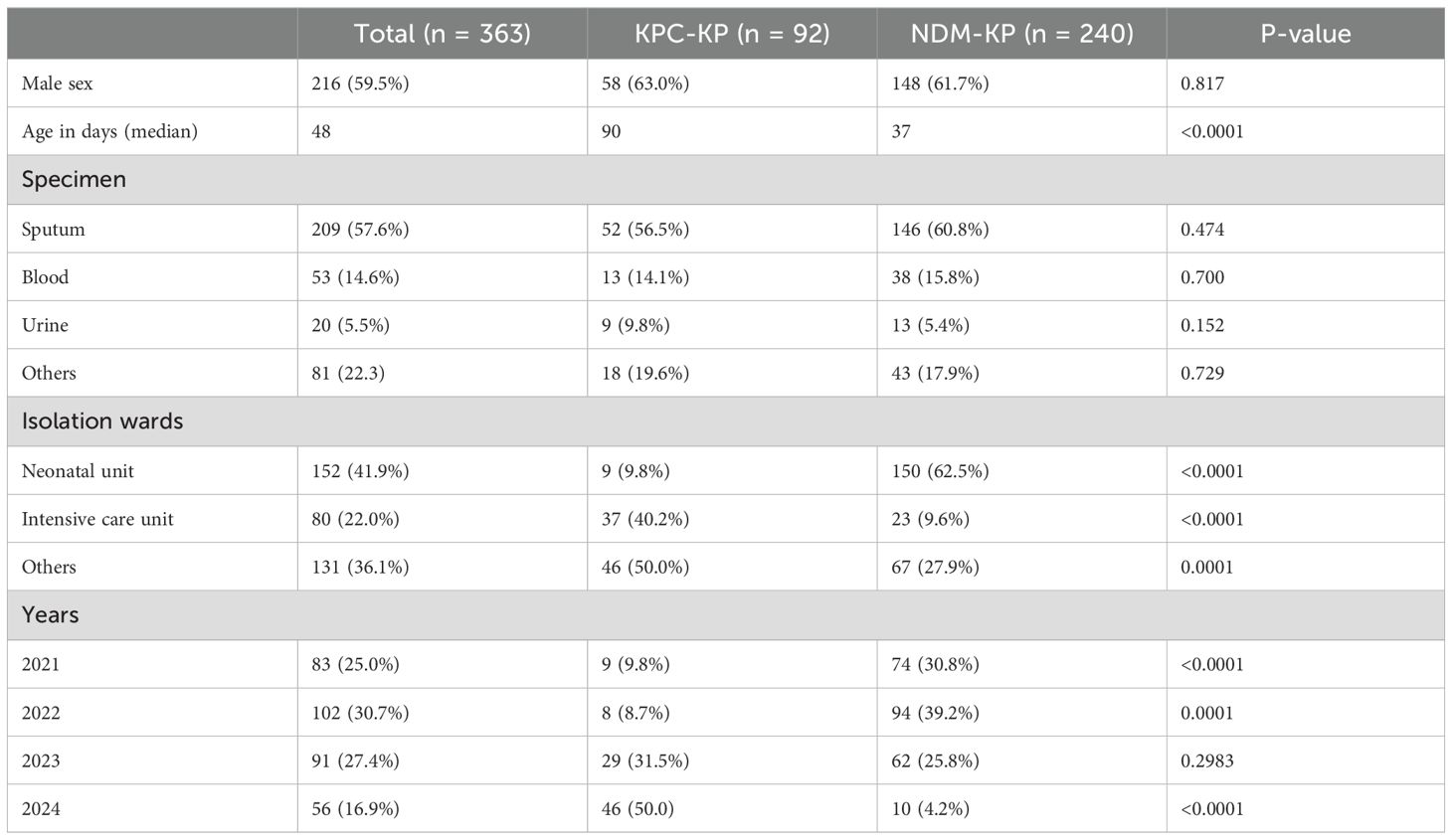
A total of 363 non-repetitive CRKP strains were collected from pediatric inpatients. The clinical characteristics of these isolates are summarized in Table 1. The female-to-male ratio was 0.7, and the proportion of males was 63.0% and 61.7% in KPC-KP and NDM-KP, respectively. Patients who were colonized or infected with CRKP had a median age of 48 days (interquartile range, 1–6120 days). Of the 363 CRKP isolates, 57.6% (n = 209) were collected from sputum, 14.6% (n = 53) from blood samples, and 5.5%% (n = 20) from urine samples. Patients in the KPC-KP (median age, 90 days) were older than the NDM-KP (median age, 37 days) (P < 0.05) (Table 1). Most CRKP strains were isolated from the neonatal unit (41.9%) and ICU (22.0%); most NDM-KP were collected from the neonatal unit (62.5%, 150/240), and isolates carrying KPC-2 were mainly detected in the ICU (40.2%, 37/92). The detection rate of NDM-KP in the neonatal unit was increased compared with KPC-KP (62.5% vs. 9.8%, P < 0.05). However, the detection rate of NDM-KP in the ICU was decreased compared with KPC-KP (9.6% vs. 40.2%, P<0.05). In addition, the detection rates of blaNDM-1 and bla NDM-5 were 57.9% (92/159) and 36.5% (58/159) in the neonatal unit, respectively. NDM-KP and KPC-KP detection rates were the highest in 2022 and 2024, respectively (Table 1).
3.3 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
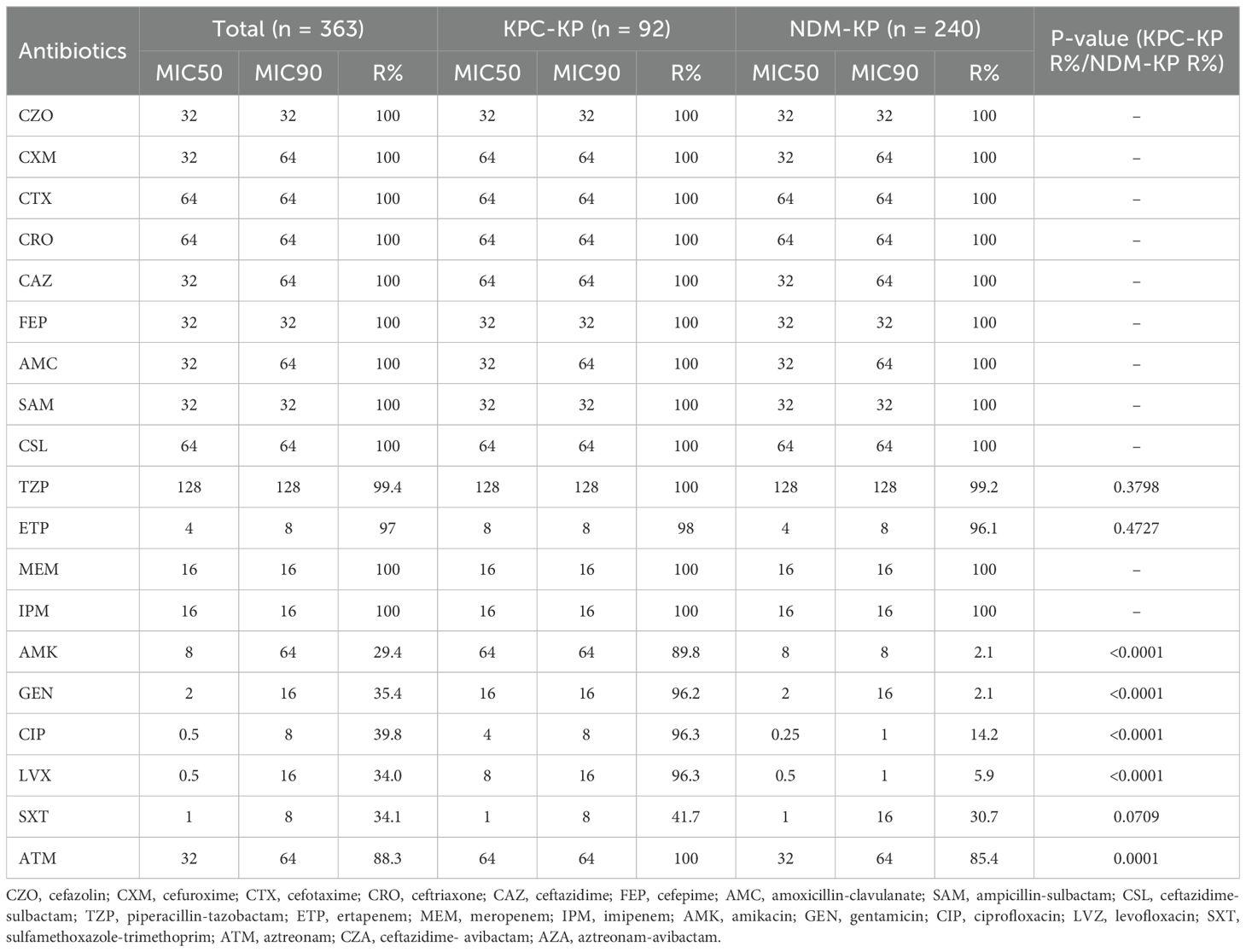
As shown in Table 2, all CRKP isolates were defined as MDR for resistance to more than three antibiotic classes. Also, all strains showed high resistance to cephalosporin antibiotics (100%). The resistance rates to aztreonam (88.3%) were higher than 70.0%. The resistance rates to amikacin, gentamicin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were 29.4%, 35.4%, and 34.1%, respectively. The percentage of resistance to ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin was 39.8% and 34.0%, respectively. Of note, the KPC-KP group showed a different antibiotic resistance spectrum to the non-β-lactams than the NDM-KP group. The MIC50 of gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin in the KPC-KP group (16, 4, 8, respectively) was higher than in the NDM-KP group (2, 0.25, 0.5, respectively). Compared with the KPC-KP group, the NDM-KP group had lower resistance rates to amikacin (2.1% vs. 89.8%), gentamicin (2.1% vs. 96.2%), ciprofloxacin (14.2% vs. 96.3%), levofloxacin (5.9% vs. 96.3%) and aztreonam (85.4% vs. 100%) (all P < 0.05, Table 2).
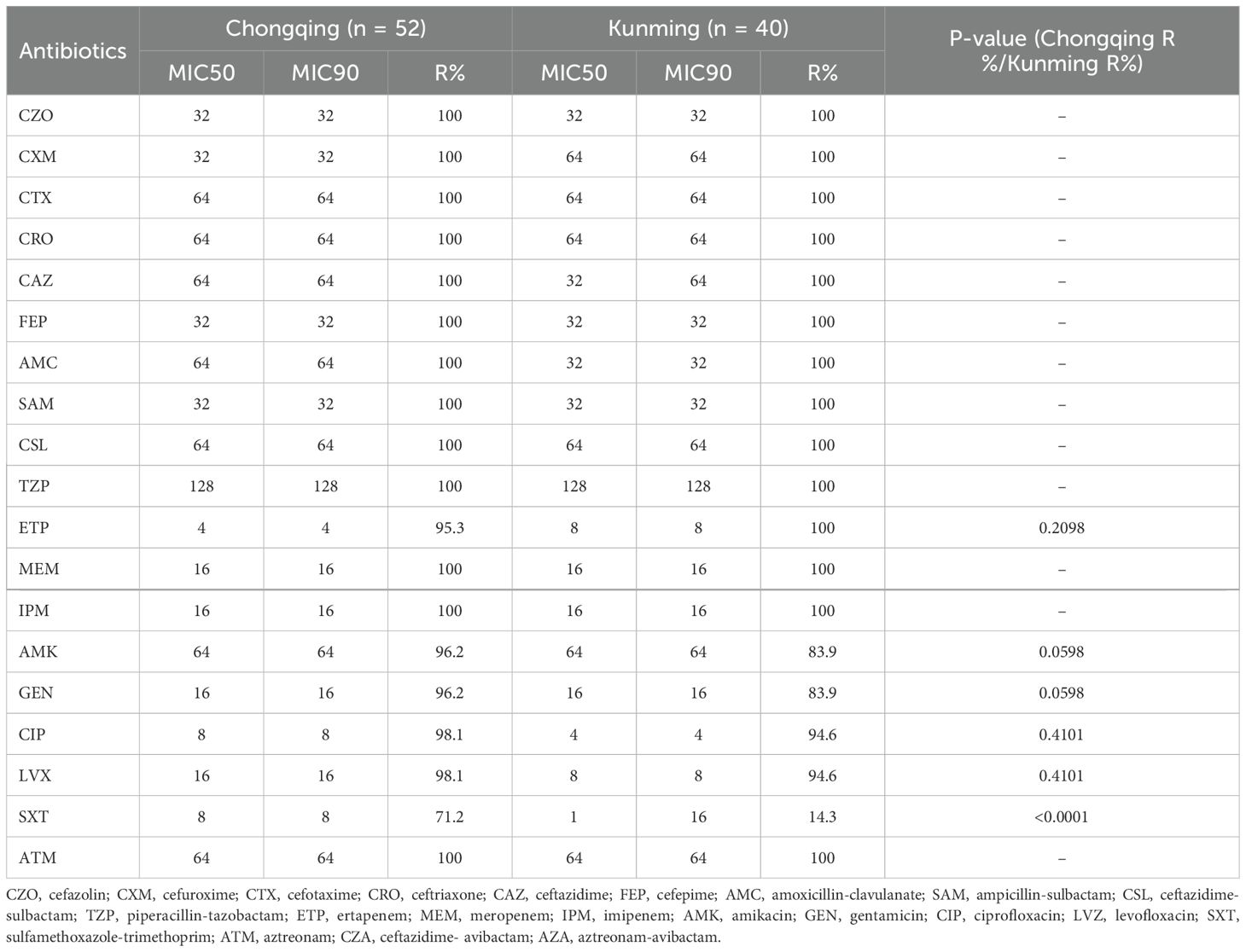
As shown in Table 3, the KPC-KP strains showed differences in antibiotic resistance rates between Chongqing and Kunming; the resistance rate of ertapenem in Chongqing was lower than that in Kunming, while the resistance rates to amikacin, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin in Chongqing were higher than those in Kunming. The MIC50 of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim in Chongqing (8) was higher than in Kunming (1), Chongqing also showed greater resistance to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim than Kunming (P < 0.05, Table 3).
As shown in Table 4, the NDM-KP strains showed differences in antibiotic resistance rates between Chongqing and Kunming.Compared with Kunming, the lower resistance rates to piperacillin-tazobactam, ertapenem and aztreonam were found in Chongqing, while the resistance rates to amikacin, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin in Kunming were lower than those in Chongqing. The MIC50 of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim in Chongqing (1) was lower than in Kunming (16), while the resistance rates to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim in Chongqing was lower than those in Kunming(P<0.05, Table 4).
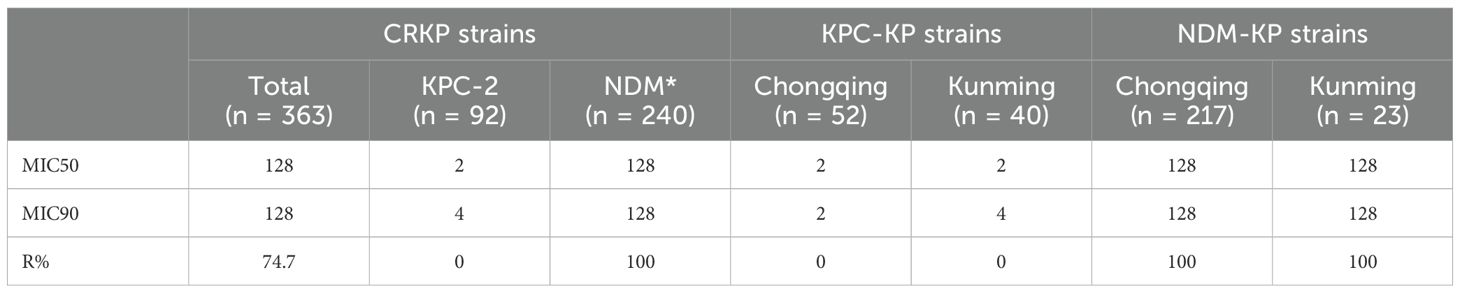
The resistance rates to CZA (74.7%) were higher than 70.0%. Moreover, a much lower level of resistance to AZA (0%) was observed in this study. Additionally, The MIC50 of CZA in the KPC-KP group (2) was lower than that in the NDM-KP group (128). In addition, NDM-KP strains had greater resistance to CZA than the KPC-KP group (P<0.05). MICs for CZA isolates ranged from 0.5 to 4 µg/mL; MIC50 and MIC90 of KPC-KP strains were 2 and 4 µg/mL, and MICs for AZA isolates ranged from ≤ 0.032 to 2 µg/mL. MIC50 and MIC90 of NDM-KP strains were 0.125 and 0.25 µg/mL, respectively (Tables 5, 6, Figure 2).
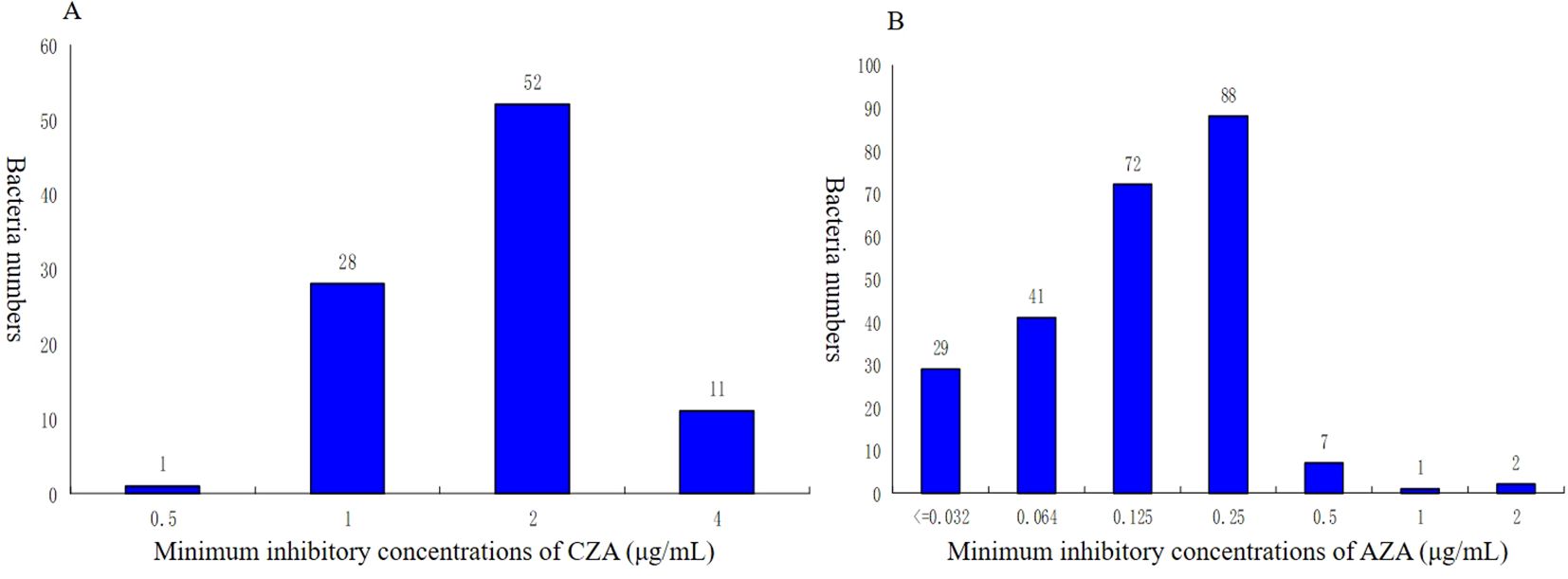
Figure 2. Distribution of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) for CZA and AZA of CRKP. (A) Minimum inhibitory concentrations of CZA (µg/ml). (B)Minimum inhibitory concentrations of AZA (µg/ml). CZA, ceftazidime-avibactam; AZA, aztreonam-avibactam.
Discussion
The epidemiological study of CRKP infection is vital for developing clinical treatment strategies and evaluating the effectiveness of different treatment approaches. Regional differences in the distribution of bacteria exist due to variations in climate, economy, and medical conditions. Regional variations in CRKP prevalence have been reported (Wyres and Holt, 2022). Children, as a special population, have underdeveloped organs, relatively lower immune function, and are therefore more susceptible to bacterial infections. Furthermore, the composition and resistance profiles of pathogenic bacteria differ between children and adults. Understanding the resistance patterns and regional variations of antibiotics is thus of great importance.Currently, data on the clinical and epidemiology of CRKP infection with different resistant gene types are limited in children. This is the first multicenter study on the epidemiological characteristics of CRKP in children, its associated genes, and resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA) and aztreonam-avibactam (AZA), comparing differences across genetic types and geographic regions. Some studies (Castagnola et al., 2019) detected differences in bacterial clones among pediatric and adult patients within the same centers. The prevalent carbapenem-resistant gene in Chinese adults was blaKPC,while the prevalent carbapenem-resistant genes widely vary in pediatric patients (Wang et al., 2018; Li et al., 2022). Domestic and international studies have shown that blaNDM is the most common carbapenemase gene in the pediatric population (Zhou et al., 2022; Ilham et al., 2023). Early studies (Wang et al., 2018) reported that blaNDM-5 is rarely found in Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. In the present study, the most frequently detected carbapenemase was blaNDM-5 (35.8%), and the primary carbapenem resistance gene was blaNDM-5 and blaKPC-2 in the Chongqing and Kunming, respectively, which may be due to regional variations of CRKP (Wyres and Holt, 2022). We inferred that the frequent switch of predominant carbapenemase genotype might result from the introduction of those strains from different sources (like regions, age, or specimen) with different prevalent carbapenemase genes or transformation of some mobile elements carrying carbapenemase genes that underwent transfers between species (Marques et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2018). Although the underlying mechanism remains unclear, this further emphasizes the importance of active resistance monitoring for CRKP in pediatric patients.
Differences were also observed in the distribution of NDM-KP and KPC-KP among different departments and patients of different ages. A total of 363 CRKPs were concentrated in the neonatal unit and ICU (63.9%). The average age of CRKP detection was 48 days, which is consistent with previous literature reports (Flannery et al., 2022; Yin et al., 2021). Our results showed that patients in the KPC-KP were older than those NDM-KP (90 days vs. 37 days, P < 0.05). In this study, the detection rate of blaNDM-1 was 57.9% in the neonatal unit, which is consistent with the molecular epidemiological studies of CRKP(blaNDM-1 is the main resistance mechanism of CRKP strains of neonatal) (Qin et al., 2014; Yin et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2021). CRKP-producing NDM was mainly distributed in younger neonates while CRKP-producing KPC-2 was mainly found in older non-neonates. Noteworthy, we observed a trend of the emergence of carbapenem resistance gene with CRKP from carrying NDM to KPC-2 in Chinese children. BlaKPC-2 is the most common A-class β-lactamase, with stronger transmission ability and higher toxicity than other carbapenemase genes (Deshpande et al., 2006; Nordmann et al., 2009). It is more commonly found in older children and adult patients. In fact, there have been many hospital outbreak reports at home and abroad (Gaspar et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022; Maltezou et al., 2009).
Our results showed that CRKP was a multi-drug-resistant bacterium, with resistance rates of > 95% to first, second, and third-generation cephalosporins, enzyme inhibitors, and carbapenems, indicating a dire situation of drug resistance, which is consistent with previous studies (Cienfuegos-Gallet et al., 2022; Lei et al., 2022). However, the sensitivity to aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones was higher, which may be due to the limited use of these antibiotics in pediatric patients due to renal, ear, and cartilage toxicity. When facing the problem of multi-drug resistance can still be treated with those antibiotics. Currently, it is believed that the treatment of CRKP infections is better with combined drug therapy than when using single drugs. Although there is a lack of research on the treatment of children, the treatment for adult patients can be used as a helpful reference; however, adjustments should be made in terms of drug dosage and variety. Our findings also suggested that alternating the use of antibiotics and strengthening the rational use of antibiotics can partially restore the sensitivity of antibiotics. We observed different resistance patterns in KPC-KP and NDM-KP, which is similar to the results of other pediatric studies (Liao et al., 2020). Compared to NDM-KP, KPC-KP showed more severe resistance to antibiotics such as amikacin, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, which should be taken seriously by clinicians and infection control professionals.
The antibiotic susceptibility results revealed significant differences in KPC-KP and NDM-KP across different regions. In Kunming, the resistance rates of CRKP to amikacin, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin were lower than those in Chongqing. This finding suggests that antimicrobial resistance exhibits regional variation, which is consistent with other studies reporting significant regional variations in bacterial characteristics, clinical outcomes, and antimicrobial resistance in global CRKP epidemics (Wang et al., 2022).Interestingly, for the KPC-KP, the resistance rate to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim was significantly higher in the Chongqing than in the Kunming, while for the NDM-KP, it was significantly lower. Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim has a high sensitivity, probably due to potential adverse reactions such as allergic reactions and liver and kidney function damage in children, which may limit its use. When facing the problem of multi-drug resistance and economic pressure, tuberculosis can still be treated with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim in combination with other drugs.
CRKP can be caused by different mechanisms, among which the production of carbapenemases is the most common. The Ambler class A (e.g., KPC), Ambler class B (e.g., NDM), and Ambler class D (e.g., OXA-48-like) carbapenemases are the three major classes of carbapenemases. Class A carbapenemases have serine-based hydrolytic activity (Bush, 2018; Lee et al., 2016).These enzymes are primarily KPC carbapenemases, whose activity can be inhibited by avibactam. The enzyme-producing strains are typically sensitive to CZA. Metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) enzymes (which encompass the Ambler class B enzymes) require the presence of metal for their activity (Bush, 2018; Lee et al., 2016).These enzymes are primarily NDM carbapenemases, and their activity cannot be inhibited by avibactam. Few of the enzyme-producing strains are sensitive to aztreonam. Therefore, distinguishing between KPC- and NDM-producing strains is crucial for the development of effective therapeutic strategies. In recent years, the availability of several novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations has given hope for the clinical treatment of CRKP. In this study, drug susceptibility tests were performed for CZA and AZA. CZA is an intravenously administered combination of the third-generation cephalosporin Ceftazidime and the novel, non-β-lactam β lactamase inhibitor avibactam. It exhibits excellent in vitro activity against various significant gram-negative pathogens, including numerous enterobacteriaceae producing OXA-48, AmpC, and extended-spectrum β-lactamases. However, some reports have documented CZA resistance to KPC-KP in China (Zhou et al., 2024; Zou et al., 2019). The present study found the resistance rates of CRKP to CZA of 74.7%, which is higher than the 36.0% reported by Dan Li (Li et al., 2023). The difference in susceptibility rates of CRKP to CZA may be attributed to the different types of carbapenemase produced. This study found that all KPC-KP strains were sensitive to CZA due to the ability of avibactam to inhibit KPC enzyme activity. We tested CZA resistance in MBL-producing strains to verify its efficacy in treating pediatric CRKP infections. The results showed that all MBL-producing strains (NDM-KP) were resistant to CZA, as CZA is ineffective against MBL-producing strains due to the inability of avibactam to inhibit the activity of metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) enzymes. The MIC50 of CZA in KPC-KP strains (2) was higher than the value of 1 reported in adult patients by Chunhong Zou (Zou et al., 2020). Therefore, it is crucial to consider age and regional variations to establish baseline data for future treatments, and to strengthen monitoring of CZA drug resistance.As AZA may simultaneously target different types of carbapenemases, it could theoretically be used to treat CRKP infections that produce variable carbapenemases. This study showed that all the studied NDM-KP were 100% sensitive to AZA (MIC50 = 0.125 mg/L, MIC90 = 0.25 mg/L) in vitro, which is lower than the MIC50 = 1 mg/L and MIC90 = 4 mg/L reported by Dan Li (Li et al., 2023).Aztreonam is the only clinically used β-lactam antibiotic stable to MBL hydrolysis. As Enterobacteriaceae carrying MBLs may frequently harbor additional aztreonam-inactivating β-lactamases, the activity of aztreonam against these isolates is often compromised. However, the addition of avibactam to aztreonam makes this combination effective against MBL producers (Das et al., 2019; Li et al., 2015). Therefore, AZA has been proposed as a treatment for infections caused by MBL producers. A study reported that blaNDM is the most common carbapenemase gene in the pediatric population (Ilham et al., 2023; Zou et al., 2022). Consequently, the use of AZA for treating CRKP infections in the pediatric population is crucial.
This study has two limitations. Firstly, ceftazidime-avibactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, and imipenem-relebactam are three novel antimicrobial agents used for the treatment of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cefiderocol is a novel siderophore cephalosporin targeting Gram-negative bacteria, including strains with NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. However, meropenem-vaborbactam, imipenem-relebactam, and cefiderocol are not available in China, and thus, we did not test them. Secondly, phylogenetic analysis was not performed on all carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains.
In conclusion, we analyzed the clinical characteristics, carbapenem resistance gene, and resistance to CZA and AZA of 363 CRKP in Chinese children, as well as the differences between different regions and carbapenem gene, identifying blaNDM-5, blaNDM-1, and blaKPC-2 as the primary resistance genes. There were differences in carbapenem resistance gene and antibiotic resistance rates among different regions. KPC-KP and NDM-KP showed different clinical and molecular epidemiological characteristics, with KPC-KP showing more severe resistance, thus posing a more serious challenge to hospital infection control.AZA is preferentially used in regions with a high prevalence of NDM-KP, particularly in the pediatric population. Therefore, it is essential to tailor treatments based on resistance profiles and to strengthen the monitoring of drug resistance in CRKP infections in children, enabling clinicians to effectively treat CRKP infections and curb the global spread of drug-resistant bacteria.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Children’s Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
CJ: Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CW: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. XR: Software, Writing – review & editing. XC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HW: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WX: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agyeman, A., Bergen, P., Rao, G., Nation, R., Landersdorfer, C. (2020). A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment outcomes following antibiotic therapy among patients with carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Int. J. Antimicrobial Agents 55, 105833. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.10.014
Biagi, M., Wu, T., Lee, M., Patel, S., Butler, D., Wenzler, E. (2019). ). searching for the optimal treatment for metallo- and serine-β-Lactamase producing enterobacteriaceae: Aztreonam in combination with ceftazidime-avibactam or meropenem-vaborbactam. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 63, e01426–19. doi: 10.1128/aac.01426-19
Bush, K. (2018). Past and present perspectives on β-lactamases. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 62. doi: 10.1128/aac.01076-18
Cassini, A., Högberg, L., Plachouras, D., Quattrocchi, A., Hoxha, A., Simonsen, G., et al. (2019). Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the european economic area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19, 56–66. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(18)30605-4
Castagnola, E., Tatarelli, P., Mesini, A., Baldelli, I., La Masa, D., Biassoni, R., et al. (2019). Epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing enterobacteriaceae in a pediatric hospital in a country with high endemicity. J. Infection Public Health 12, 270–274. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.11.003
Cienfuegos-Gallet, A., Zhou, Y., Ai, W., Kreiswirth, B., Yu, F., Chen, L. (2022). Multicenter genomic analysis of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae from bacteremia in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0229021. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02290-21
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2024). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 34th (Wayne, PA: CLSI). CLSI supplement M100.
Das, S., Li, J., Riccobene, T., Carrothers, T. J., Newell, P., Melnick, D., et al. (2019). Dose selection and validation for ceftazidime-avibactam in adults with complicated intra-abdominal infections, complicated urinary tract infections, and nosocomial pneumonia. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 63, e02187-18. doi: 10.1128/aac.02187-18
Deshpande, L., Rhomberg, P., Sader, H., Jones, R. (2006). Emergence of serine carbapenemases (KPC and SME) among clinical strains of enterobacteriaceae isolated in the united states medical centers: report from the MYSTIC progra-2005). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 56, 367–372. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2006.07.004
EUCAST (2024). v14.0. breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters (Växjö, Sweden: European Committee on Antimicrobial SusceptibilityTesting).
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (2019) Surveillance atlas of infectious diseases. Available at: https://atlas.ecdc.europa.eu/public/index.aspx?Dataset=27&HealthTopic=4 (Accessed 30 June 2022).
Flannery, D., Chiotos, K., Gerber, J., Puopolo, K. (2022). Neonatal multidrug-resistant gram-negative infection: epidemiology, mechanisms of resistance, and management. Pediatr. Res. 91, 380–391. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01745-7
Fu, P., Xu, H., Jing, C., Deng, J., Wang, H., Hua, C., et al. (2021). Bacterial epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance profiles in children reported by the ISPED program in China, 2016 to 2020. Microbiol. Spectr. 9, e0028321. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00283-21
Gaspar, G., Tamasco, G., Abichabki, N., Scaranello, A., Auxiliadora-Martins, M., Pocente, R., et al. (2022). Klebsiella pneumoniaeNosocomial outbreak of extensively drug-resistant (Polymyxin b and carbapenem) in a collapsed university hospital due to COVID-19 pandemic. Antibiotics (Basel Switzerland) 11. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060814
Hu, F., Pan, Y., Li, H., Han, R., Liu, X., Ma, R., et al. (2024). Carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae capsular types, antibiotic resistance and virulence factors in China: a longitudinal, multi-centre study. Nat. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01612-1
Huang, J., Chen, X., Yang, J., Zhao, Y., Shi, Y., Ding, H., et al. (2022). Klebsiella pneumoniae Outbreak of KPC-producing ST15 strains in a chinese tertiary hospital: resistance and virulence analyses. J. Med. Microbiol. 71 (2). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001494
Hussein, K., Raz-Pasteur, A., Finkelstein, R., Neuberger, A., Shachor-Meyouhas, Y., Oren, I., et al. (2013). Impact of carbapenem resistance on the outcome of patients' hospital-acquired bacteraemia caused by klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Hosp. Infection 83, 307–313. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2012.10.012
Ilham, D., Souad, L., Asmae, L., Kawtar, N., Mohammed, T., Nabila, S. (2023). Prevalence, antibiotic resistance profile, MBLs encoding genes, and biofilm formation among clinical carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales isolated from patients in Mohammed VI University Hospital Centre, Morocco. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 76, ovad107. doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovad107
Karampatakis, T., Tsergouli, K., Behzadi, P. (2023). Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenem-resistant : Virulence factors, molecular epidemiology and latest updates in treatment options. Antibiotics (Basel Switzerland) 12, 234. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020234
Konstantina, K., Elias, I., Eleni, A., Polychronis, T., Efthymia, P., Ergina, M., et al. (2019). The clinical significance of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae rectal colonization in critically ill patients: from colonization to bloodstream infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 68, 326–335. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000921
Lee, C., Lee, J., Park, K., Kim, Y., Jeong, B., Lee, S. (2016). Global dissemination of carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, genetic context, treatment options, and detection methods. Front. Microbiol. 7, 895. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00895
Lei, J., Zhou, W. X., Lei, K., Chen, D., Zhang, P. Q., Xue, L., et al. (2022). [Analysis of molecular and clinical characteristics of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent klebsiella pneumoniae in the intensive care unit]. Zhonghua yu fang yi xue za zhi [Chinese J. Prev. Medicine] 56, 63–68. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20210812-00781
Li, C., Jiang, X., Yang, T., Ju, Y., Yin, Z., Yue, L., et al. (2022). Genomic epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 20, 1154–1167. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.02.005
Li, D., Yu, H., Huang, X., Long, S., Zhang, J. (2023). ). in vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam, imipenem-relebactam, aztreonam-avibactam, and comparators toward carbapenem-resistant and hypervirulent isolates. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e0280623. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02806-23
Li, H., Estabrook, M., Jacoby, G., Nichols, W., Testa, R., Bush, K. (2015). In vitro susceptibility of characterized β-lactamase-producing strains tested with avibactam combinations. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 59, 1789–1793. doi: 10.1128/aac.04191-14
Liao, W., Liu, Y., Zhang, W. (2020). Virulence evolution, molecular mechanisms of resistance and prevalence of ST11 carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae in China: A review over the last 10 years. J. Global Antimicrobial Resistance 23, 174–180. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.09.004
Lutgring, J. (2019). Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: An emerging bacterial threat. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 36, 182–186. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2019.04.011
Maltezou, H., Giakkoupi, P., Maragos, A., Bolikas, M., Raftopoulos, V., Papahatzaki, H., et al. (2009). Outbreak of infections due to KPC-2-producing klebsiella pneumoniae in a hospital in crete (Greece). J. Infection 58, 213–219. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2009.01.010
Marques, C., Belas, A., Aboim, C., Cavaco-Silva, P., Trigueiro, G., Gama, L., et al. (2019). Evidence of sharing of klebsiella pneumoniae strains between healthy companion animals and cohabiting humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 57. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01537-18
Martin, R., Cao, J., Wu, W., Zhao, L., Manthei, D., Pirani, A., et al. (2018). Identification of pathogenicity-associated loci in klebsiella pneumoniae from hospitalized patients. mSystems 3. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00015-18
Nichols, C., Cruz Espinoza, L., von Kalckreuth, V., Aaby, P., Ahmed El Tayeb, M., Ali, M., et al. (2015). Bloodstream infections and frequency of pretreatment associated with age and hospitalization status in sub-saharan africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. America 61 Suppl 4, S372–S379. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ730
Nordmann, P., Cuzon, G., Naas, T. (2009). The real threat of klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase-producing bacteria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 9, 228–236. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(09)70054-4
Nordmann, P., Poirel, L. (2019). Epidemiology and diagnostics of carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. America 69, S521–S528. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz824
Papp-Wallace, K. (2019). The latest advances in β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations for the treatment of gram-negative bacterial infections. Expert Opin. Pharmacotherapy 20, 2169–2184. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1660772
Qin, S., Fu, Y., Zhang, Q., Qi, H., Wen, J., Xu, H., et al. (2014). High incidence and endemic spread of NDM-1-positive enterobacteriaceae in henan province, China. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 58, 4275–4282. doi: 10.1128/aac.02813-13
Theuretzbacher, U., Carrara, E., Conti, M., Tacconelli, E. (2021). Role of new antibiotics for KPC-producing klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 76, i47–i54. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa497
Veeraraghavan, B., Walia, K. (2019). Antimicrobial susceptibility profile & resistance mechanisms of global antimicrobial resistance surveillance system (GLASS) priority pathogens from india. Indian J. Med. Res. 149, 87–96. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR21418
Wang, M., Earley, M., Chen, L., Hanson, B. M., Yu, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2022). Clinical outcomes and bacterial characteristics of carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae complex among patients from different global regions (CRACKLE-2): a prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, 401–412. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(21)00399-6
Wang, Q., Wang, X., Wang, J., Ouyang, P., Jin, C., Wang, R., et al. (2018). Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae: Data from a longitudinal large-scale CRE study in chin-2016). Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. America 67, S196–S205. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy660
Wyres, K., Holt, K. (2022). Regional differences in carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, 301–390. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(21)00425-4
Xu, L., Sun, X., Ma, X. (2017). Systematic review and meta-analysis of mortality of patients infected with carbapenem-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrobials 16, 18. doi: 10.1186/s12941-017-0191-3
Yin, L., He, L., Miao, J., Yang, W., Wang, X., Ma, J., et al. (2020). Actively surveillance and appropriate patients placements' contact isolation dramatically decreased Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae infection and colonization in pediatric patients in China. J. Hosp. Infection 31, S0195-6701(20)30130-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2020.03.031
Yin, L., He, L., Miao, J., Yang, W., Wang, X., Ma, J., et al. (2021). Carbapenem-resistant enterobacterales colonization and subsequent infection in a neonatal intensive care unit in Shanghai, China. Infection Prev. Pract. 3, 100147. doi: 10.1016/j.infpip.2021.100147
Zhang, F., Xie, L., Wang, X., Han, L., Guo, X., Ni, Y., et al. (2016). Further Spread of bla NDM-5 in Enterobacteriaceae via IncX3 Plasmids in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 7, 424. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00424
Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., Yin, Y., Chen, H., Jin, L., Gu, B., et al. (2018). Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections: Report from the China CRE network. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 62, e01882-17. doi: 10.1128/aac.01882-17
Zhou, J., Yan, G., Tang, C., Liu, J., Fu, P., Ding, L., et al. (2024). Emergence of ceftazidime-avibactam resistance in bla KPC-33 -harbouring ST11 Klebsiella pneumoniae in a paediatric patient. Int. J. Antimicrobial Agents 63, 107163. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107163
Zhou, T., Zhang, X., Guo, M., Ye, J., Lu, Y., Bao, Q., et al. (2013). Phenotypic and molecular characteristics of carbapenem-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae from a teaching hospital in Wenzhou, southern China. Japanese J. Infect. Dis. 66, 96–102. doi: 10.7883/yoken.66.96
Zhou, Y., Zhao, Z., Zeng, L., Peng, J., Zhou, S., Min, L., et al. (2022). Surveillance of carbapenem-resistant in a paediatric hospital in China revealed the dynamics of carbapenemase and the prevalence of ST2735 K. pneumoniae. J. Med. Microbiol. 71 (1). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001482
Zou, C., Wei, J., Shan, B., Chen, X., Wang, D., Niu, S. (2020). EnterobacteriaceaeIn vitro activity of ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam-avibactam against carbapenem-resistant isolates collected from three secondary hospitals in southwest China between 2018 and 2019. Infection Drug Resistance 13, 3563–3568. doi: 10.2147/idr.S273989
Keywords: carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, ceftazidime-avibactam, aztreonam-avibactam, KPC-2, NDM-1 and NDM-5, epidemiology characteristics, pediatric patient
Citation: Ran X, Chen X, Wang C, Wang H, Xie W and Jing C (2025) Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in Chinese children: in vitro activities of ceftazidime-avibactam and aztreonam-avibactam against carbapenemase-producing strains in a two-center study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1545999. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1545999
Received: 16 December 2024; Accepted: 17 February 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Costas C. Papagiannitsis, University of Thessaly, GreeceReviewed by:
Alberto Antonelli, University of Florence, ItalyPandora Jim Tsolakidou, General Hospital of Volos, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Ran, Chen, Wang, Wang, Xie and Jing. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chunmei Jing, amNtNzkxMjAzQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xia Ran1†
Xia Ran1† Chunmei Jing
Chunmei Jing