- College of Fishery, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, Guangdong, China
Introduction: The Hong Kong oyster (Crassostrea hongkongensis), as the main marine aquaculture shellfish in the South China Sea, not only has high economic and ecological value, but also is an ideal model for conducting research on pathogen-host interactions. In the cultivation process of C. hongkongensis, there is a challenge posed by vibrios. To improve the antibacterial strains of C. hongkongensis, we have studied the gene associated with immunity, PDIA3.
Methods and findings: In this study, we cloned the PDIA3 sequence of the C. hongkongensis, using the RACE technique. It has a total of 2081 bp and contains a 5'-UTR of 55 bp and a 3'-UTR of 547 bp. The ChPDIA3 gene sequence has an ORF frame that is 1479 bp in length and encodes 492 amino acids. Analysis of the phylogenetic tree constructed by Neighbor Joining method showed that ChPDIA3 clustered with other shellfishes into a single unit, which was consistent with the law of species evolution.
Discussion: The highest expression of ChPDIA3 was detected in gill tissues of the C. hongkongensis using RT-qPCR, and significantly higher expression in V. harveyi and LPS infection than Poly(I:C) (P<0.05). This may indicate that ChPDIA3 is primarily involved in the immune response against bacterial infections in the C. hongkongensis. The binding sites of miR-126-x, miR-21-y and ChPDIA3 were detected using dual luciferase experiments, respectively. The results showed that both miR-126-x and miR-21-y inhibited the 3'-UTR region of ChPDIA3. This suggested that both miR-126-x and miR-21-y inhibited ChPDIA3 expression. This study will help to further understand the function of ChPDIA3 in response to pathogen infection, thus providing new ideas for understanding the resistance and adaptation of the C. hongkongensis to Vibrio infection.
1 Introduction
The Crassostrea hongkongensis is mainly distributed in the coastal areas of the South China Sea, including the coastal areas of South China and Vietnam (Peng et al., 2021). It is worth noting that C. hongkongensis have been cultivated in the coastal areas of southern China for nearly a thousand years. The C. hongkongensis is a typical intertidal species whose living environment switches between being exposed to air and being inundated by seawater on a daily basis, thus it has a strong ability to adapt to the environment (Zhang et al., 2012). In addition, C. hongkongensis not only has a positive impact on the ecosystem, but also has high commercial value. For example, it is a high protein, low-fat aquatic product, rich in various vitamins, glycogen, fatty acids, essential amino acids, and micronutrients such as calcium, zinc, copper, selenium, etc., so it is highly popular in the market (Grabowski et al., 2012; Loaiza, 2023). However, the rapid development of the aquaculture industry has been accompanied by a gradual deterioration of the aquaculture environment, and shellfish aquaculture has been challenged by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses (Fehrenbach et al., 2024; Li et al., 2023; Shingai, 2024). Due to environmental influences, violent deaths occur frequently, causing huge economic losses to the entire farming industry. The sustained development of oyster farming has brought pressure to the marine environment, especially the spread of Vibrio disease in oysters has had a negative impact on the development of oyster farming (Dégremont, 2021; Oyanedel, 2023; Yu et al., 2023).
Vibrio harveyi, a Gram-negative bacterium, was first isolated from Carcharhinus plumbeus and Negaprion brevirostris, which was very widely distributed in the oceans (Colwell and Grimes, 1984; Grimes et al., 1984; Muthukrishnan et al., 2019). V. harveyi is a common conditional pathogen in aquaculture and has been widely recognized as a common pathogen of many commercially farmed fish (Angthong et al., 2023; Dong et al., 2017; Firmino et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2022), mollusks (Liu et al., 2014; Morot et al., 2021) and crustaceans (De Souza Valente and Wan, 2021; Rungrassamee et al., 2016) in warm waters. Some studies have shown that V. harveyi spreads mostly during the hot summer months, mainly attacking damaged body surfaces or the digestive tract of animals. V. harveyi infection causes ulcers, tissue necrosis and massive epithelial cell death in animals (Yuan et al., 2023). In addition, it triggers the generation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses in the body (Angthong et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2023; Hao et al., 2023). In summary, V. harveyi kills large numbers of marine vertebrates and invertebrates (Austin and Zhang, 2006; Travers et al., 2008).
Protein Disulfide Isomerase Family A Member 3 (PDIA3), also known as ERp57, is one of the members of the PDI family and is located mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum (Luo et al., 2008). PDIA3 is thought to be a protein disulfide isomerase involved in the proper folding and processing of proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum. It can maintain protein structure and function by catalyzing the formation and rearrangement of disulfide bonds (Hetz et al., 2006; Yoneda et al., 2001). PDIA3 may be involved in intracellular redox homeostasis. It can interact with other oxidoreductases to regulate intracellular oxidative stress and protect cells from oxidative damage (Chamberlain et al., 2019). Alternatively, PDIA3 may play a role in endoplasmic reticulum stress response, helping cells to cope with endoplasmic reticulum stress and maintain their homeostasis (Mahmood et al., 2021). Abnormal expression or function of PDIA3 has been found to be associated with certain diseases, such as inflammatory response (Wang, 2019), neurodegenerative diseases (Zhu et al., 2024), and cancer (Wang et al., 2023). In aquatic animals, the PDIA1 and PDIA3 of Dicentrarchus labrax, L. have been cloned entirety (Pinto et al., 2013). Moreover, ERp57 of Oncorhynchus mykiss was cloned and expressed in various tissues (Sever et al., 2013). Furthermore, it has been shown that PDIA3 is differentially expressed in O. mykiss in the presence of Vibrio anguillarum infection (Yang, 2023). In our previous study, we sequenced the transcriptome and miRNAome of the C. hongkongensis under V. harveyi infection, and the results showed that miR-126-x with miR-21-y had a regulatory effect on PDIA3 (Hou et al., 2023, 2024). To verify the regulatory relationship between miR-126-x and miR-21-y on PDIA3 in more depth, in this study, it is proposed to clone the full length of PDIA3 from the C. hongkongensis, using RACE technology, and their sequences were analyzed by bioinformatics. The expression pattern of PDIA3 was analyzed using RT-qPCR technology and RNA interference. Validation of miR-126-x and miR-21-y as having regulatory effects on PDIA3 using a dual luciferase reporter. This will provide new ideas for understanding the improvement of the resistance and adaptability of the C. hongkongensis to Vibrio infections, as well as for realizing the scientific culture and industrial development of the C. hongkongensis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Collection of C. hongkongensis samples
The C. hongkongensis used in the experiment were all of 2 years old, purchased from the seafood market in Xiashan District, Zhanjiang City, and temporarily reared for one week in the Shellfish Genetics and Enrichment Laboratory of Guangdong Ocean University. Chlorella was fed during the temporary incubation period, the water temperature was 28°C, the salinity was 20 ppt, continuous aeration was maintained. 108 C. hongkongensis were randomly selected, with a mean weight of 201.65 ± 22.20 g and a mean shell height of 117.03 ± 11.16 mm. They were divided into 4 groups, i.e., PBS group, Vibrio group, LPS group, and Poly(I:C) group, and each group was set up in 3 parallels, with 15 C. hongkongensis placed in each parallel group. C. hongkongensis in the Vibrio group were injected with 200 μL of V. harveyi solution at a concentration of 1×108 CFU·mL-1. The LPS group was injected with 200 μL of LPS (Solarbio, purity≥98%) solution at a concentration of 10 μg·mL-1. The Poly(I:C) group was injected with 200 μL of Poly(I:C) solution at a concentration of 5 mg·mL-1. The control group was injected with an equal amount of PBS. At 0, 12, 24, 48 and 72 h after injection, 2 C. hongkongensis were randomly selected from each parallel group and their hemolymph, gill, mantle, digestive diverticulum, adductor muscle, and gonad were sampled. All tissue samples were collected under strict sterile conditions. After collection, the samples were rapidly immersed in liquid nitrogen for snap-frozen to preserve their biological activity. They were then transferred to a -80°C low-temperature environment for storage in preparation for subsequent experiments.
2.2 Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
At each time point within each group, three C. hongkongensis individuals were randomly selected, and RNA was extracted from the hemolymph, gill, mantle, digestive diverticulum, adductor muscle, and gonad. The extraction was performed using the TransZol Up Plus RNA Kit (TransGen Biotech), following the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentration and purity were assessed using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer. RNA integrity was determined by agarose gel electrophoresis. All RNA samples were reverse transcribed using the EasyScript® One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix kit (TransGen Biotech), following the instructions.
2.3 Cloning of ChPDIA3
We screened the intermediate sequence of the ChPDIA3 gene based on the available transcriptome data (GenBank project accession PRJNA999463), and then used this sequence to design 5’RACE and 3’RACE specific primers for this gene using Primer Premier 5 (Table 1). Full-length amplification was performed using the SMARTer® RACE 5’/3’ Kit Protocol-At-A-Glance (TaKaRa), following the instructions. PCR products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis, then cut and recovered using the NucleoSpin® Gel and PCR Clean-Up kit (TaKaRa), and the recovered products were ligated into pEASY-Blunt (TransGen Biotech) vector. Trans1-T1 competent cell (TransGen Biotech) were used for transformation, and the products were placed in solid medium and incubated for 12 h in a 37°C incubator. Single colonies were screened and placed in liquid culture at 37°C, 200 rpm for 12 h. Positive cloning was performed, and the positive cloning products matching the target bands were sent to Sangon Biotech Ltd. for sequencing.
2.4 Bioinformatics analysis
We used ORFfinder (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/orffinder/) to identify open reading frame as well as sequence translations. The physicochemical properties of the amino acids were queried by the online software ProtParam (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/). The conserved domains were analyzed according to the protein information resource InterPro (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro). The full-length protein sequences of the PDIA3 homologues were downloaded at NCBI, and multiple sequence comparisons were performed using DNAMAN 5.0 with default parameters. Phylogenetic tree was constructed using Neighbor Joining in MEGA (v11.0.13).
2.5 Detection of ChPDIA3 expression by RT-qPCR
Based on the sequences obtained from RACE cloning, primers were designed for RT-qPCR using Premier 5.0 (Table 1). Reactions were performed in Light Cycler 96, as described in the instructions for the PerfectStart® Green qPCR SuperMix kit (TransGen Biotech). Each sample was processed in triplicate in Light Cycler 96. The 2-ΔΔCt method was used to calculate the relative expression of the ChPDIA3 gene in tissues of the C. hongkongensis such as hemolymph, gill, mantle, digestive diverticulum, adductor muscle, and gonad, with β-actin as the reference gene. The cDNAs of Vibrio group, LPS group, Poly(I:C) group and PBS group were taken as templates, and the rest of the conditions were the same as those mentioned above, to verify the expression of ChPDIA3 at different time points in each group.
2.6 dsRNA synthesis
Based on the sequences obtained by RACE cloning, primers were designed using Premier 5.0 (Table 1) and PCR amplification was performed using Seq Amp DNA Polymerase (TaKaRa). Cutting gel recovery, ligation, transformation, positive cloning, and bacteriophage sequencing were performed as in Section 2.3. After the bacterial fluids were sequenced, a pair of forward and reverse sequences were selected for amplification. Plasmids obtained from amplification were extracted using the GeneJET Plasmid Miniprep Kit (Thermo). The plasmids were digested using Past I-HF enzyme and the digested products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. Products from single bands were purified using the GeneJET PCR Purification Kit (Thermo). The purified products were transcribed in vitro using the T7 RNAi Transcription Kit (Vazyme Biotech) as described in its instructions. The products of in vitro transcription were extracted by phenol-chloroform-ethanol absolute, then precipitated by ethanol absolute and finally dissolved in DEPC water.
2.7 RNA interference experiments and sample collection
The C. hongkongensis used in the experiment were temporarily reared for one week. Chlorella was fed during the temporary incubation period, the water temperature was 28°C, the salinity was 20 ppt, continuous aeration was maintained. 90 C. hongkongensis of similar growth condition and free from disease and injury were randomly selected. They were divided into three groups, i.e., RNA interference group, Vibrio group and control group, and three parallels were set in each group. From the pre-experiment, dsRNA acted 24 h after injection, so the experimental group was first injected with 100 μL of dsRNA (at a concentration of 1 μg·μL-1). After 24 h, 100 μL of V. harveyi was injected. The Vibrio group was injected with an equal amount of V. harveyi solution at a concentration of 1×108 CFU·mL-1, and the control group was injected with an equal amount of 5 × PBS. 2 C. hongkongensis were randomly selected from each parallel group for sampling 12, 24 48 and 72 h after the completion of injection, respectively. The samples were first snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and later stored at -80°C for later RNA extraction.
2.8 ChPDIA3 expression pattern after RNA interference
At each time point in each group, three samples were randomly selected for RNA extraction and reverse transcription, which was performed in the same way as in Section 2.2. The cDNA at each time point was used as a template for RT-qPCR to detect the expression of ChPDIA3 in V. harveyi infection after RNA interference.
2.9 Dual luciferase experiments
The relationship between ChPDIA3 and miR-126-x and miR-21-y binding sites were selected for vector construction, respectively. The vector was prepared by Wuhan Zhibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd. and its sequence accuracy was verified. HEK293T cells were inoculated in 96-well plates at 2×104 cells/well, with 3 replicate wells per group. The medium was 100 μl of DMEM-High Sugar medium containing 10% FBS, which was incubated overnight in a 5% CO2, 37°C incubator. The transfection system was configured according to Table 2. Solution A and solution B were mixed and left to stand for 20 min at common temperature. 20 μL of transfection complex was added to each well and then placed in 5% CO2, 37°C incubator. After 48 h of transfection, the old medium was aspirated and 100 μL of PLB (Passive Lysis Buffer) was added to each well of cells. Lysis was performed on a shaker at common temperature for 15 min. After adding 20 μL of cell lysate to the luminescent plate, background values were read for 2 s using Promega’s GloMax®-Multi multifunctional enzyme marker. Add 20 μL of LAR II working solution to each well, mix quickly, and read values for 2 s. After the reading is complete, add another 20 μL of Stop & Glo® Reagent to each sample and mix quickly. Place in a luminescence detector, run the program and read the fluorescence value for 2 s. After completing the reading, save the data.
2.10 Statistical analysis
All data analyses were performed using Origin 2024 and IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0. Samples from different groups at the same time were analyzed for statistical significance using Duncan’s Multiple Range Test, the significance level was set at 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Bioinformatics of ChPDIA3
The cDNA sequence of the PDIA3 gene of the C. hongkongensis, named ChPDIA3, has been cloned using the RACE technique. ChPDIA3 has a total of 2081 bp, containing 55 bp of 5’-untranslated region (UTR) and 547 bp of 3’-UTR. The sequence of ChPDIA3 has an ORF with a length of 1,479 bp, encoding 492 amino acids (Figure 1A). The molecular weight is 55530.92 Da, the theoretical pI is 5.48, and the grand average of hydropathicity is -0.551<0, which makes it a hydrophilic protein. The results of the phylogenetic tree showed that the C. hongkongensis was clustered with other shellfish and was genetically distant from crustaceans and vertebrates. The predicted conserved structural domains of the ChPDIA3 sequence showed that the PDI_thioredoxin-like_dom are located at 23-123 aa and 368-470 aa (Figure 1B). Thioredoxin_CS in the ChPDIA3 protein has the closest homology to the C.gigas and the Ostrea edulis compared to homologs from other species (Figure 1C).The cDNA sequence of ChPDIA3 has been submitted to NCBI (GenBank: PP530092).
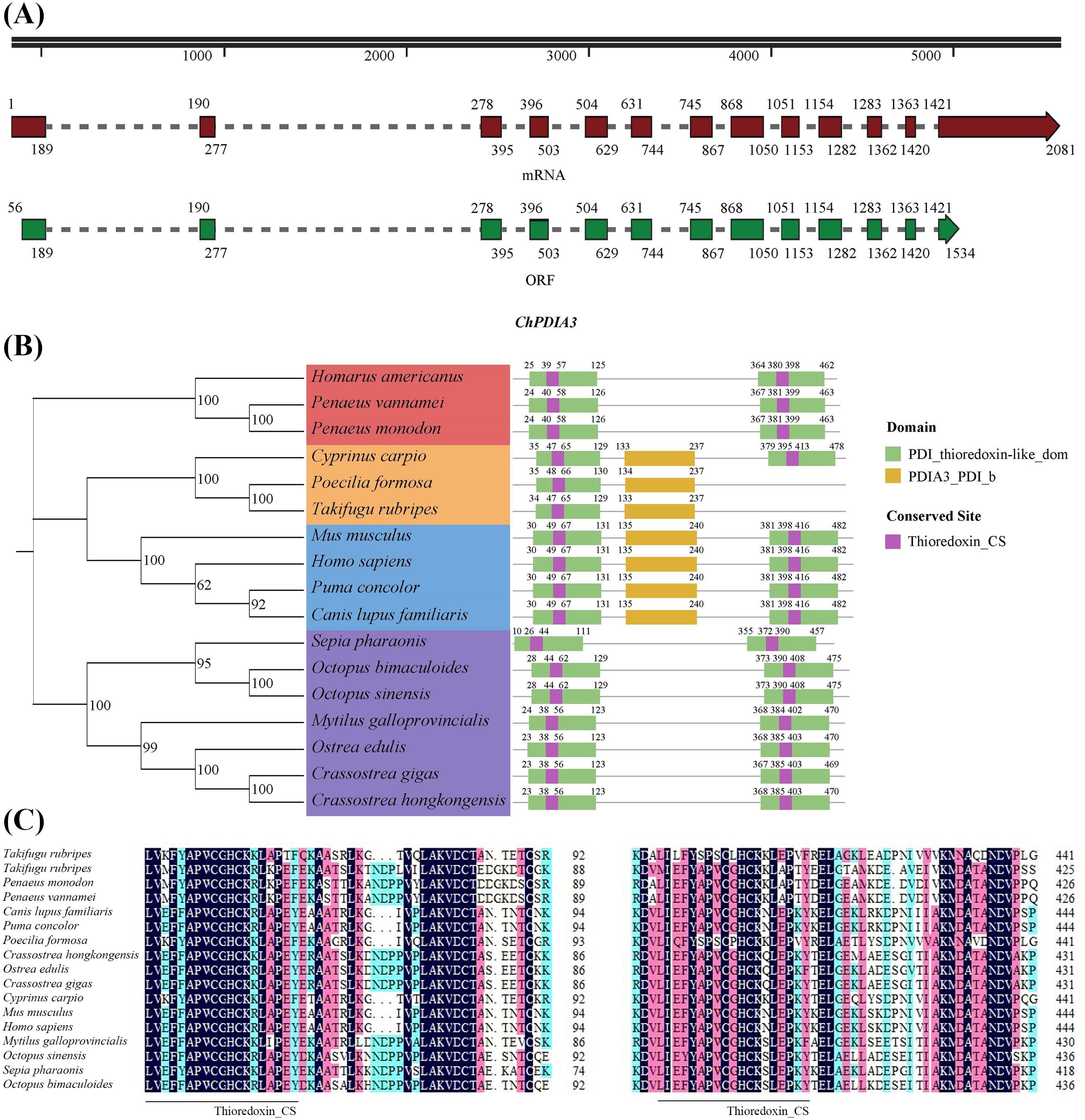
Figure 1. A PDIA3 gene in C. hongkongensis and phylogenetic tree of the ChPDIA3 protein. (A) Schematic presentation of ChPDIA3. Black line, structure of the gene in the genome. Dark red and dark green boxes, ChPDIA3 transcript and its coding region. (B) Phylogenetic tree and structural information of selected PDIA3 protein. GenBank accession number (NCBI): Homarus americanus (XP_042223300.1), Penaeus vannamei (XP_027212336.1), Penaeus monodon (XP_037788996.1), Cyprinus carpio (XP_018979324.2), Poecilia formosa (XP_007566541.1), Takifugu rubripes (XP_029700442.1), Mus musculus (NP_031978.2), Homo sapiens (NP_005304.3), Puma concolor (XP_025774328.1), Canis lupus familiaris (XP_535453.3), Sepia pharaonic(CAE1328800.1), Octopus bimaculoides (XP_014785522.1), Octopus sinensis (XP_029643538.1), Mytilus galloprovincialis (VDI57500.1), Ostrea edulis (XP_048735080.2), Crassostrea gigas (XP_011453191.2). (C) Alignment of partial PDIA3 domain containing active conserved site Thioredoxin_CS.
3.2 Expression of ChPDIA3 in different tissues
The expression of ChPDIA3 in different tissues was examined using RT-qPCR, and the results are shown in Figure 2. ChPDIA3 was expressed in tissues such as hemolymph, gill, mantle, digestive diverticulum, adductor muscle and gonad. And the highest expression was found in gill (P<0.05). Therefore, gills were targeted for subsequent studies.
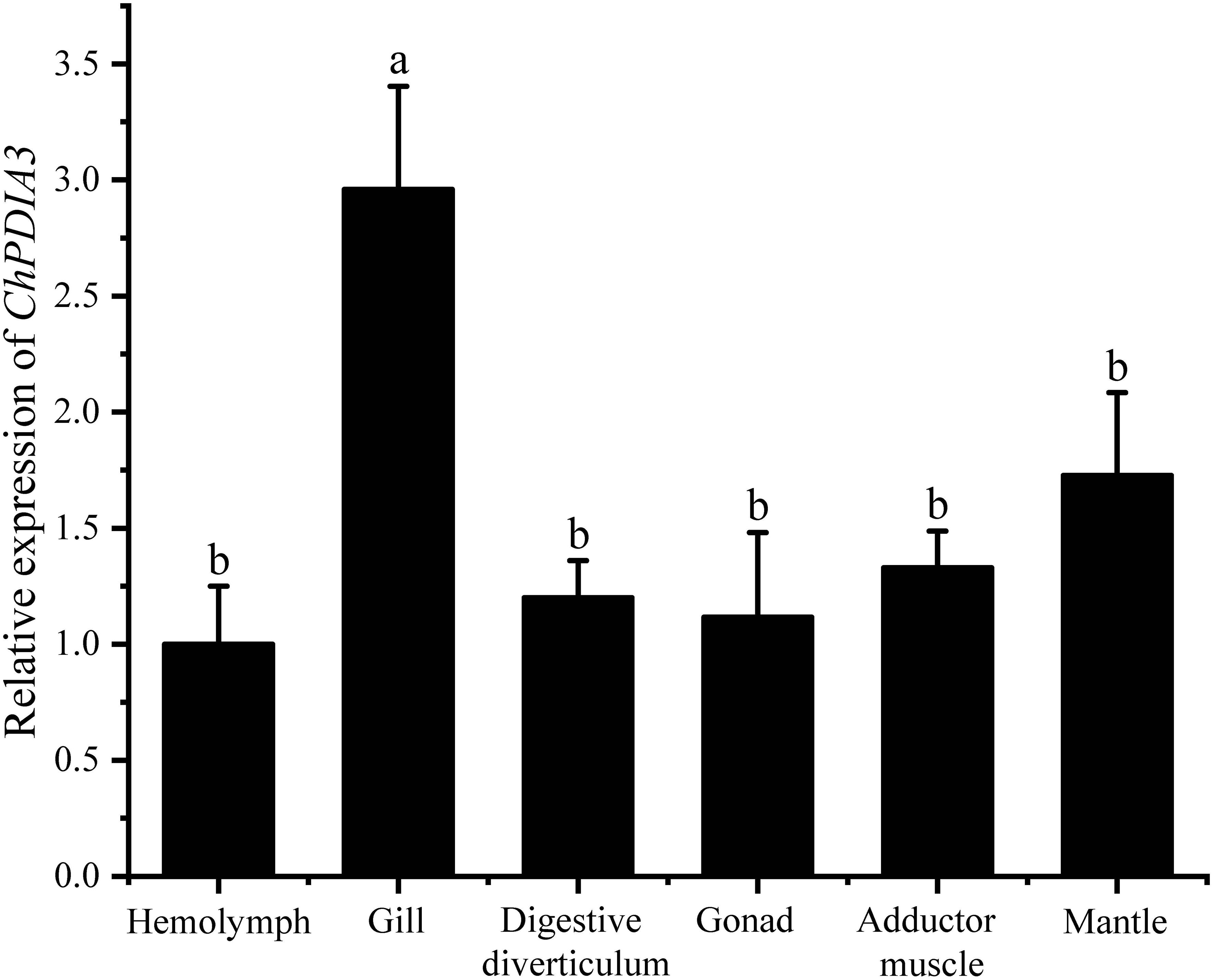
Figure 2. Expression of ChPDIA3 in different tissues of the C. hongkongensis. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatment groups (P<0.05).
3.3 Expression pattern of ChPDIA3 in gill
The relative expression of ChPDIA3 in the gill tissues of the C. hongkongensis under PBS, V. harveyi, LPS and Poly (I:C) treatments, at different time points, was examined using RT-qPCR. The results are shown in Figure 3, under V. harveyi and LPS treatments, the expression of ChPDIA3 was significantly higher that of the other groups (P<0.05). And the highest expression at 12h after treatment, after which the expression of ChPDIA3 gradually decreased. The expression of ChPDIA3 in the gills of C. hongkongensis treated with Poly(I:C) was significantly lower than that of the PBS group (P<0.05), but showed a gradually increasing trend.
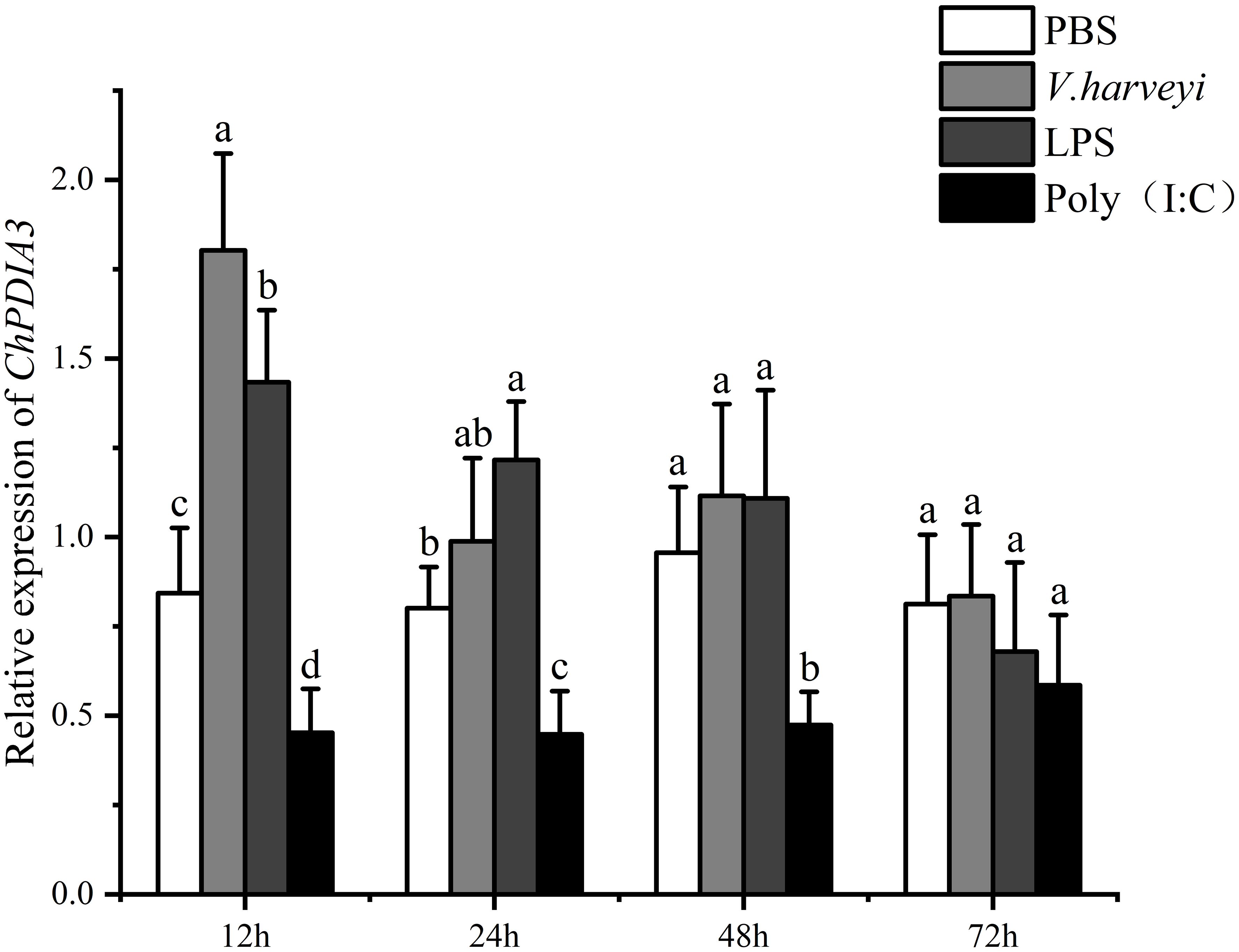
Figure 3. Expression pattern of ChPDIA3 in different treatment groups. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatment groups (P<0.05).
3.4 ChPDIA3 expression in V. harveyi infection after RNA interference
The expression of ChPDIA3 after silencing by dsRNA was detected by RT-qPCR. The results showed that the expression of ChPDIA3 was significantly lower than that of C. hongkongensis injected with PBS and V. harveyi at all four time points (P<0.05). The inhibitory effect was most significant at 12 h of V. harveyi injection (P<0.05), and the inhibitory effect gradually failed after 72 h of injection, when the expression started to increase (Figure 4A). In the protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum pathway, the expression of its downstream genes was also downregulated when ChPDIA3 was silenced by dsRNA. Except for LMAN2, the expression levels of the other two genes did not show significant differences at 12 hours (P>0.05). It was not until 48 hours that the expression level of CALR exhibited significant differences (P<0.05). Furthermore, the expression levels of LMAN1 and LMAN2 became progressively less significant compared to the control group (P>0.05) (Figures 4B–D).
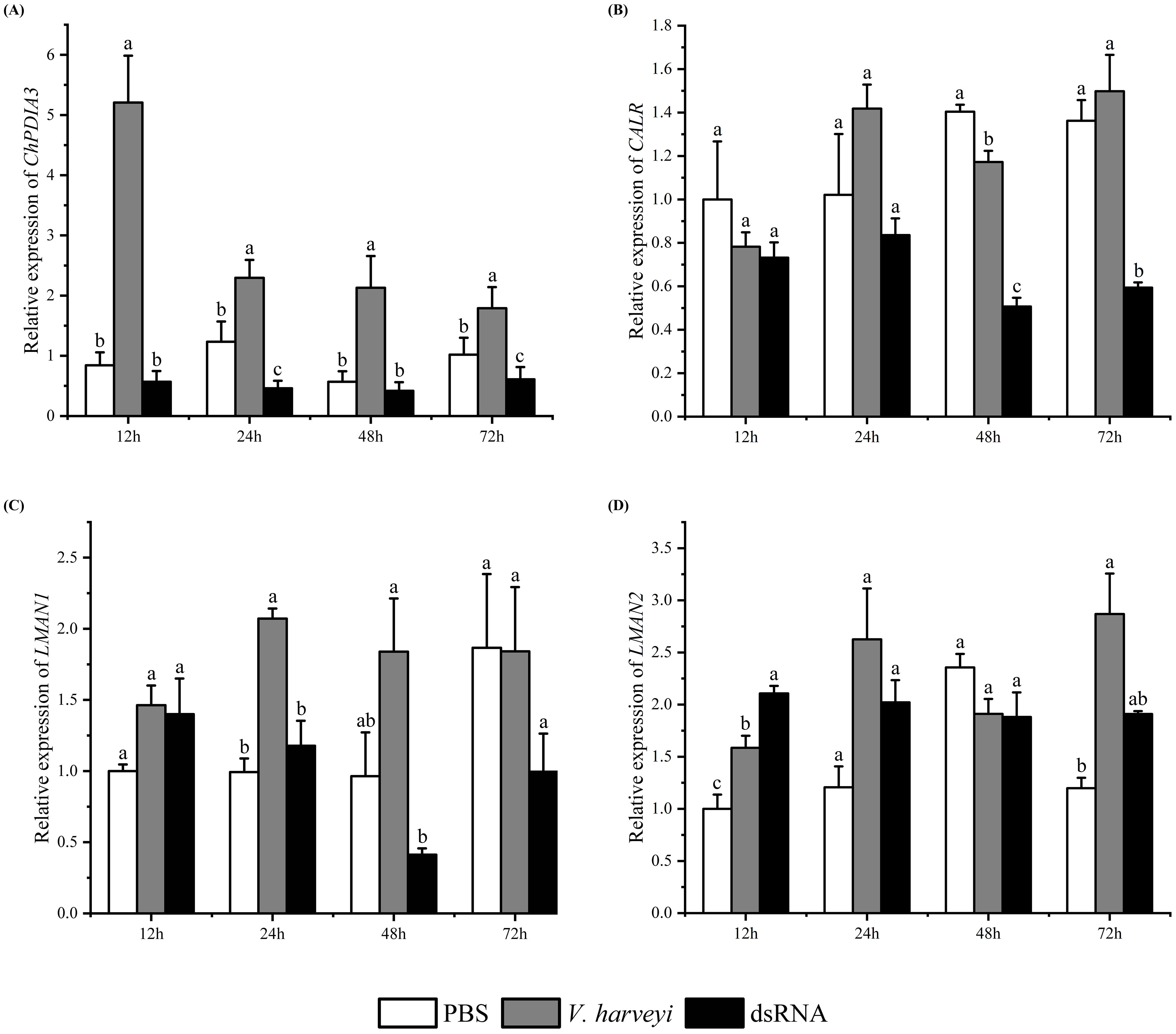
Figure 4. Expression patterns of genes after RNA interference. (A) shows the expression of the ChPDIA3 gene at different time points (12h, 24h, 48h, 72h) in the RNA interference group, the Vibrio group (injected with Vibrio harveyi), and the control group (injected with PBS) after RNA interference. (B–D) display the expression trends of downstream genes of ChPDIA3 (such as CALR, LMAN1, and LMAN2) in the endoplasmic reticulum protein processing pathway at different time points when ChPDIA3 is silenced by dsRNA. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between treatment groups (P<0.05).
3.5 Dual luciferase report
The luciferase activities of miR-126-x mimics, miR-21-y mimics and their pmirGLO-PDIA3-3’-UTR co-transfected HEK293T cell lines were assayed by dual luciferase experiments to validate the targeting relationship between miR-126-x, miR-21-y and ChPDIA3, respectively. The results showed that both miR-126-x and miR-21-y inhibited ChPDIA3. In the miR-126-x group, compared with mimics NC (control group), luciferase activity extremely significantly decreased (P<0.01), being 74.93% of the mimics NC (control) group’s level. Mutating the predicted site, the luciferase activity was restored to 99.13% of the control (P>0.05) (Figure 5A). In the miR-21-y mimics group, dual luciferase activity extremely significantly (P<0.01), dropping by 76.94% compared to the control group. Mutating the predicted site restored the luciferase activity to 100.68% of the control (P>0.05) (Figure 5B).
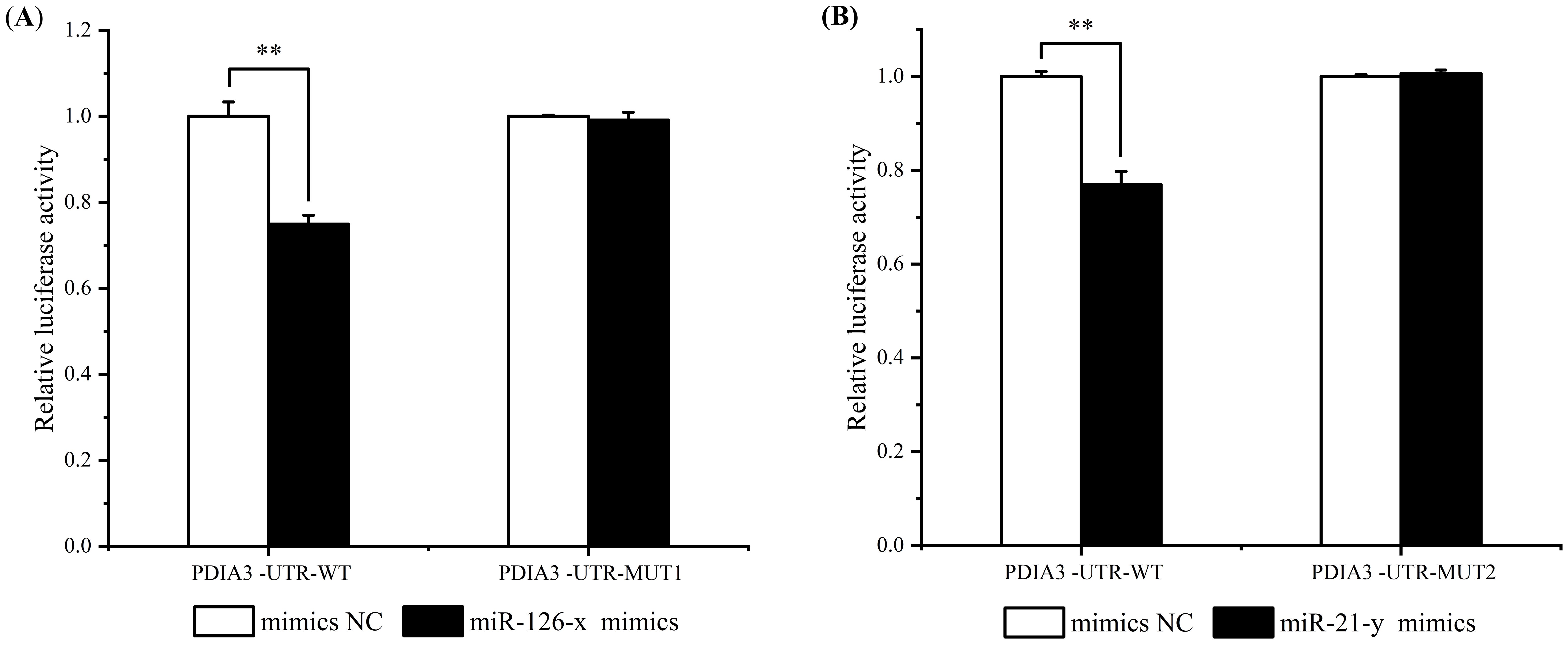
Figure 5. Dual luciferase detection of miR-126-x and miR-21-y regulation of ChPDIA3. (A) represents the miR - 126 - x mimics group, showing the luciferase activity of HEK293T cell lines co - transfected with miR - 126 - x mimics and pmirGLO - PDIA3 - 3’ - UTR. (B) represents the miR - 21 - y mimics group, indicating the luciferase activity of HEK293T cell lines co - transfected with miR - 21 - y mimics and pmirGLO - PDIA3 - 3’ - UTR. “*” indicates an extremely significant difference between groups (P < 0.01).
4 Discussion
4.1 Bioinformatics analysis of ChPDIA3
PDIA3, also known as 1,25D3-MARRS or ERp57, is a member of the PDI family, which functions as an endoplasmic reticulum-based redox chaperone protein that interacts with various fibrosis-related proteins. In the endoplasmic reticulum, PDIA3 acts as a molecular chaperone and redox catalyst to regulate glycoprotein folding (Oliver et al., 1999). In our previous study, PDIA3 was significantly enriched in the protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum pathway (Hou et al., 2023). In this study, the cDNA sequence of PDIA3 from the C. hongkongensis, was obtained by RACE cloning technology. The homogeneous analysis demonstrated that the nucleic acid sequence and amino acid sequence of this gene are relatively conserved, especially conserved site Thioredoxin_CS (Fritz-Wolf et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2024). It was hypothesized that ChPDIA3 was identified as a homologous gene of PDIA3 in the C. hongkongensis. Therefore, the mechanism of ChPDIA3 might be similar to that of other species that have been studied. In addition, in shellfish and crustaceans, the ChPDIA3 sequence contains the PDI_thioredoxin-like_dom conserved domain, whereas the PDIA3_PDI_b conserved domain is also present in fish and mammals. This difference may indicate some evolution and differentiation in the structure and function of the PDI_thioredoxin-like_dom conserved domain in the PDIA3 sequences of different species. The PDI_thioredoxin-like_dom conserved domain is usually associated with the function of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), which plays an important role in the endoplasmic reticulum, helping proteins to fold correctly and form disulfide bonds (Mahmood et al., 2021). However, differences in the conserved domains in the PDIA3 sequences of different species may reflect differences in their functional requirements or adaptive strategies for this conserved domain during evolution. Differences in the conserved domains in the PDIA3 sequences of different species may imply that they have diverged in functions such as protein folding and endoplasmic reticulum stress response. These species may have evolved specific PDIA3 structures and functions during adaptation to different environments and lifestyles (Liu et al., 2022; Trnková et al., 2013). When they are exposed to specific endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions or protein folding requirements, which contribute to the alteration of the PDIA3 sequence and the evolution of the conserved domains (Huang et al., 2009; Pinto et al., 2013).
Hydrophilicity plays an important role in the immune response (Boquet et al., 1995). It was found that there was a significant hydrophilic complementation between the complementary determining regions (CDR) of anti-neuropeptide substance monoclonal antibody (mAb SP31) and the C-terminal pentapeptide epitope of SP. Peptides that retained the hydrophilicity feature were recognized by mAb SP31 with reduced affinity even though the sequence differed from that of SP, whereas peptides with altered hydrophilicity feature showed a significant decrease in antibody binding affinity or even failed to bind. In addition, the degree of hydrophilic complementarity was closely related to the binding affinity, with peptides with similar ydrophilic profiles having a higher binding affinity to mAb SP31, while peptides with large differences in hydrophilicity showed significantly lower affinity (Hanin et al., 1997). Kinetic studies also suggest that hydrophilic complementarity is important in maintaining the stability of antigen-antibody complexes and may regulate binding affinity by affecting conformational changes and interaction stability after complex formation (Bhat et al., 1994; Van Oss, 1995). hydrophilicity also plays an important role in the immunomodulation of viral infections. The β-convex trigger loop region (QGEESND) of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) is hydrophilic and complementary to specific peptides (e.g., LITVLNI) in the interleukin-1 type I receptor (IL-1R1), and this complementarity influences viral binding to the receptor as well as the subsequent immune response (Heal et al., 1999). In the present study, ChPDIA3 is a hydrophilic protein, and we speculated that ChPDIA3 may play important roles in immune responses through various mechanisms, such as participating in antigen processing and presentation, regulating immune cell activity, influencing cytokine production and secretion, and interacting with other immune-related molecules, thus positively affecting the body’s immune defenses and maintenance of immune homeostasis. However, these roles still need further experimental validation and in-depth studies.
4.2 Expression patterns of ChPDIA3
Due to its function as a molecular chaperone, PDIA3 expression rises when cells are stressed. It has been reported that PDIA3 can trigger Bak-dependent apoptosis by affecting mitochondrial outer membrane permeability (Zhao et al., 2015). Moreover, PDIA3 has functions such as regulating inflammation and oxidative stress (Wang, 2019) and inhibiting cancer cells (Yang et al., 2024). PDIA3 also plays an important role in immune activity in aquatic animals. Immunity-related proteins such as PDIA3 were significantly up-regulated in the intestine of Cynoglossus semilaevis in response to Shewanella algae infection (Han et al., 2020). The expression level of ERp57 protein in O. mykiss was elevated in peripheral blood leukocytes and RTS11 macrophage-like cell lines in response to stimulation with double-stranded RNA and phytohaemagglutinin, which also suggests a possible conserved function of ERp57 in the endoplasmic reticulum and activation of immune responses in O. mykiss (Sever et al., 2013). This may be due to the respiratory, filter feeding and immunological effects of the gills of the C. hongkongensis (Xie et al., 2023; Yue et al., 2024). This makes it possible for C. hongkongensis to be frequently exposed to externally supported disease-causing microorganisms such as bacteria and viruses. The gills of the C. hongkongensis, as respiratory organs, are the first to come into contact with the outside world, which also makes the gills of the C. hongkongensis play an irreplaceable role in its immune defense activities. The expression of ChPDIA3 was significantly higher in V. harveyi and LPS infections relative to controls.
Mollusks typically possess a relatively unsophisticated adaptive immune system, thus relying predominantly on their innate immunity to counteract against foreign pathogens (Chakroun et al., 2021; Tincu and Taylor, 2004; Yang et al., 2021). The innate immune response is characterized by its swift activation, commencing promptly during the initial phase of acute infections(L. Li et al., 2024; Olasard et al., 2024). V. harveyi, a Gram-negative bacterium, and LPS, a component of the Gram-negative bacterial cell wall, are both potent activators of the innate immune response (Shi et al., 2024; Yao et al., 2024). They can stimulate pattern recognition receptors (PRR), such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) (Kawai and Akira, 2010). This recognition mechanism can trigger a rapid inflammatory response, which may include the upregulation of ChPDIA3 as part of the cellular stress response to invading pathogens (Mahmood et al., 2021).In our study, focusing on the C. hongkongensis, we had observed the highest expression levels of ChPDIA3 at 12 hours post-infection with V. harveyi and LPS. This had suggested that during the incipient stages of infection, C. hongkongensis may have bolstered its defense mechanisms by enhancing the proper folding and maturation of proteins critical for immune function, such as antimicrobial peptides (Yoo et al., 2019). Additionally, the early phase of bacterial invasion was likely to have provoked oxidative stress, which in turn, may have activated the unfolded protein response (UPR). Given that ChPDIA3 had played a role in modulating oxidative stress through its interactions with other oxidoreductases (Chamberlain et al., 2019), its heightened expression during the early infection stages may have served as a cellular protective response to oxidative challenges. However, our sampling regimen, initiated at 12 hours post-infection, precluded a more precise determination of the peak expression timing of ChPDIA3. In future related studies, we will consider collecting samples at earlier time points after infection. This will help us more accurately depict the changing trend of the expression level of ChPDIA3, so as to evaluate the importance of ChPDIA3 in the early immune response. Furthermore, we observed a significant downregulation of ChPDIA3 expression in C. hongkongensis that had been treated with Poly(I:C). This phenomenon may have been associated with the immune pathways activated by viral infections, which might not have relied on the function of ChPDIA3. For instance, RNA sensing pathways played a primary role in response to viral infections (Kourko et al., 2023; Yue et al., 2023), while ChPDIA3 may have been more involved in the immune response to bacterial infections. These findings suggested that ChPDIA3 may have played distinct roles in response to different immune challenges, and its expression regulation could have been closely linked to signaling pathways specific to certain pathogens.
The endoplasmic reticulum protein processing pathway is of crucial significance in the folding, modification, and transport of proteins within cells. PDIA3, being a vital member of this pathway, interacts with downstream genes that are indispensable for maintaining the normal physiological functions of cells. In this study, when the ChPDIA3 was silenced, the expression of the downstream genes of the ChPDIA3 in the endoplasmic reticulum protein processing pathway was successively down-regulated. We hypothesized that in response to V. harveyi infection, ChPDIA3 might have adjusted the protein processing and folding process by regulating the expression of downstream genes to enhance cellular defenses or adapt to infection-induced stress responses. For example, CALR (calreticulin), which was involved in protein folding and quality control, and changes in its expression might have affected the correct folding and stability of intracellular proteins, thereby influencing the cellular immune response and stress resistance (Galluzzi and Kroemer, 2022; Ziffels et al., 2019). LMAN1 (mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 1) and LMAN2 (mannose-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2), which played a role in innate immunity, and the down-regulation of their expression might have affected the ability of oysters to recognize and clear pathogens (Kwon et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2010). This further emphasized the importance of ChPDIA3 in the immune defense system of the C. hongkongensis and its critical position in the complex regulatory network in response to V. harveyi infection.
4.3 Regulation of ChPDIA3 by miR-126-x and miR-21-y
As a unique endothelial cell-associated miRNA, as well as a novel tumour suppressor gene, miR-126 plays a key role in the onset, progression and metastasis of various types of cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, melanoma and lung cancer. For example, cellular processing of MPM-derived spheroids by exosomal delivery of miR-126 leads to massive cell death and prevents tumour growth in vivo (Monaco et al., 2022). Overexpression of miR-126-3p in ovarian cancer cells inhibited cell proliferation and invasion as well as phosphorylation of AKT and ERK1/2 (Xiang and Cheng, 2018). The miR-21 family includes members such as miR-21-5p and miR-21-3p. These miRNAs play important regulatory roles in cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis and other processes, and play an important role in the treatment of cancer. The exosome miR-21-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma cells can affect hepatocellular carcinoma cell development and patient prognosis by regulating SP1/XBP1 and promoting M2 polarization in TAMs (Hu et al., 2024). miR-21 is elevated in canine mammary tumors and positively correlates with gene expression of IL-6 and TNF-α and also with the proliferation index (Ki67 index) of tumour cells (Abbate et al., 2023). In this study, the binding sites of miR-126-x, miR-21-y and ChPDIA3 were detected using dual luciferase experiments, respectively. The results showed that both miR-126-x and miR-21-y inhibited the 3’-UTR region of ChPDIA3. This suggested that they might be involved in the regulation of ChPDIA3 gene expression. And the expression of ChPDIA3 may be related to the response of C. hongkongensis to V. harveyi infection. When faced with V. harveyi infection, the organism may affect the expression of ChPDIA3 by regulating the expression levels of miR-126-x and miR-21-y, thereby modulating the immune response or other relevant physiological processes of the organism in response to the infection. This regulatory mechanism helps the C. hongkongensis to better resist V. harveyi infection and maintain the health and homeostasis of the organism.
4.4 Potential applications in aquaculture
Our findings on the role of ChPDIA3 in C. hongkongensis and its regulation by miR-126-x and miR-21-y offer potential applications for the aquaculture industry, particularly in enhancing disease resistance in oysters. One promising application is through selective breeding programs. By identifying and selecting oysters with higher levels of ChPDIA3 expression or those with genetic variants that enhance the gene’s function, breeders can develop lines with greater resistance to bacterial infections, such as those caused by V. harveyi. This approach will enable the breeding of oyster strains that are more resilient to disease outbreaks and reduce reliance on antibiotics, thereby promoting more sustainable and environmentally friendly aquaculture practices (Chamberlain et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023). Additionally, the manipulation of miRNA expression levels, such as miR-126-x and miR-21-y, can be explored as a genetic engineering strategy. By regulating these miRNA levels, it is possible to increase the expression of ChPDIA3 and other immune-related genes, thereby enhancing the overall immune response in oysters (Chu et al., 2021; Pan, 2024; Qin et al., 2024). This could be particularly useful in hatcheries and nurseries, where oysters are most susceptible to infections. In conclusion, our study may contribute to the selection of disease-resistant oyster strains and disease control. However, the results of the current study are still some distance from direct application in production and require further in-depth research.
4.5 Limitations of this study
While our study provides new insights into the role of ChPDIA3 and its regulation by miR-126-x and miR-21-y in the immune response of C. hongkongensis against V. harveyi infection, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the experimental design primarily focused on laboratory conditions, which may not fully replicate the complex environmental factors encountered in natural aquaculture settings. Factors such as water temperature, salinity, and the presence of other pathogens can significantly influence the expression and function of immune-related genes. Second, the study utilized a limited number of time points for sampling, which may not capture the complete dynamics of the immune response over the entire course of infection. Future studies would likely necessitate more frequent sampling to better understand the temporal changes in gene expression and the potential involvement of other immune pathways. Additionally, while the dual luciferase experiments provided evidence of miRNA regulation, the study did not explore the downstream effects of ChPDIA3 on other components of the immune system in detail, such as signaling pathways. Further research is needed to elucidate the broader network of interactions and pathways involved in the immune response mediated by ChPDIA3.
5 Conclusion
The PDIA3 gene has been identified to play an important role in the infection of C. hongkongensis infected under V. harveyi. In this paper, the PDIA3 sequence of the C. hongkongensis was cloned. The homogeneous analysis demonstrated that the nucleic acid sequence and amino acid sequence of this gene are relatively conserved. It is proved that ChPDIA3 has a similar mechanism to other homologous genes. ChPDIA3 was most highly expressed in gill tissues of the C. hongkongensis as detected by qPCR, and its expression was higher than that of Poly (I:C) in the presence of V. harveyi and LPS infections. This may indicate that ChPDIA3 is primarily involved in the immune response against bacterial infections in the C. hongkongensis. Dual luciferase reported that both miR-126-x and miR-21-y inhibited the expression of ChPDIA3. In practical application, the expression level or gene sequence polymorphism of ChPDIA3 gene can be used as an important molecular marker for disease resistance selection, and it is expected to breed oyster varieties with stronger disease resistance by selecting individuals with specific ChPDIA3 expression characteristics for breeding.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: GenBank: PP530092.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
YH: Data curation, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FZ: Investigation, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft. XL: Investigation, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft. DH: Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft. ZL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Special Fund of Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. KTP20210288, No. KTP20240564).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbate, J. M., Arfuso, F., Riolo, K., Giudice, E., Brunetti, B., Lanteri, G. (2023). Upregulation of miR-21 and pro-inflammatory cytokine genes IL-6 and TNF- α in promoting a pro-tumorigenic microenvironment in canine mammary carcinomas. Res. Veterinary Sci. 164, 105014. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2023.105014
Angthong, P., Uengwetwanit, T., Uawisetwathana, U., Koehorst, J. J., Arayamethakorn, S., Schaap, P. J., et al. (2023). Investigating host-gut microbial relationship in Penaeus monodon upon exposure to Vibrio harveyi. Aquaculture 567, 739252. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739252
Austin, B., Zhang, X.-H. (2006). Vibrio harveyi: A significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 43, 119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.01989.x
Bhat, T. N., Bentley, G. A., Boulot, G., Greene, M. I., Tello, D., Dall’Acqua, W., et al. (1994). Bound water molecules and conformational stabilization help mediate an antigen-antibody association. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91, 1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1089
Boquet, D., Déry, O., Frobert, Y., Grassi, J., Couraud, J. Y. (1995). Is hydropathic complementarity involved in antigen-antibody binding? Mol. Immunol. 32, 303–308. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(95)00012-4
Chakroun, I., Fedhila, K., Mahdhi, A., Mzoughi, R., Saidane, D., Esteban, M.Á., et al. (2021). Atypical Salmonella Typhimurium persistence in the pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas, and its effect on the variation of gene expression involved in the oyster’s immune system. Microbial Pathogenesis 160, 105185. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105185
Chamberlain, N., Korwin-Mihavics, B. R., Nakada, E. M., Bruno, S. R., Heppner, D. E., Chapman, D. G., et al. (2019). Lung epithelial protein disulfide isomerase A3 (PDIA3) plays an important role in influenza infection, inflammation, and airway mechanics. Redox Biol. 22, 101129. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101129
Chen, Y., Cao, B., Zheng, W., Xu, T. (2023). ACKR4a induces autophagy to block NF-κB signaling and apoptosis to facilitate Vibrio harveyi infection. iScience 26, 106105. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106105
Chu, X., Gu, Y., Sheng, W., Sun, J., Morgan, J. A., Lewis, D. F., et al. (2021). Downregulation of miR-126-3p expression contributes to increased inflammatory response in placental trophoblasts in preeclampsia. J. Reprod. Immunol. 144, 103281. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2021.103281
Colwell, R. R., Grimes, D. J. (1984). Vibrio diseases of marine fish populations. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 37, 265–287. doi: 10.1007/BF01989311
Dégremont, L. (2021). Susceptibility variation to the main pathogens of Crassostrea gigas at the larval, spat and juvenile stages using unselected and selected oysters to OsHV-1 and/or V. aestuarianus. J. Invertebrate Pathology. 183, 107601. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2021.107601
De Souza Valente, C., Wan, A. H. L. (2021). Vibrio and major commercially important vibriosis diseases in decapod crustaceans. J. Invertebrate Pathol. 181, 107527. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2020.107527
Dong, H. T., Taengphu, S., Sangsuriya, P., Charoensapsri, W., Phiwsaiya, K., Sornwatana, T., et al. (2017). Recovery of Vibrio harveyi from scale drop and muscle necrosis disease in farmed barramundi, Lates calcarifer in Vietnam. Aquaculture 473, 89–96. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.02.005
Fehrenbach, G. W., Murphy, E., Pogue, R., Carter, F., Clifford, E., Major, I. (2024). Comprehensive analysis and assessment of exposure to enteric viruses and bacteria in shellfish. Mar. Environ. Res. 196, 106404. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2024.106404
Firmino, J., Furones, M. D., Andree, K. B., Sarasquete, C., Ortiz-Delgado, J. B., Asencio-Alcudia, G., et al. (2019). Contrasting outcomes of Vibrio harveyi pathogenicity in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata and European seabass, Dicentrachus labrax. Aquaculture 511, 734210. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734210
Fritz-Wolf, K., Kehr, S., Stumpf, M., Rahlfs, S., Becker, K. (2011). Crystal structure of the human thioredoxin reductase–thioredoxin complex. Nat. Commun. 2, 383. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1382
Galluzzi, L., Kroemer, G. (2022). Calreticulin surface presentation can promote quality control of hematopoietic stem cells. Trends Immunol. 43, 950–952. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.10.008
Grabowski, J. H., Brumbaugh, R. D., Conrad, R. F., Keeler, A. G., Opaluch, J. J., Peterson, C. H., et al. (2012). Economic valuation of ecosystem services provided by oyster reefs. BioScience 62, 900–909. doi: 10.1525/bio.2012.62.10.10
Grimes, D. J., Stemmler, J., Hada, H., May, E. B., Maneval, D., Hetrick, F. M., et al. (1984). Vibrio species associated with mortality of sharks held in captivity. Microbial Ecol. 10, 271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF02010940
Han, Z., Sun, J., Wang, A., Lv, A., Hu, X., Chen, L., et al. (2020). Differentially expressed proteins in the intestine of Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther following a Shewanella algae challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 104, 111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.06.013
Hanin, V., Déry, O., Boquet, D., Sagot, M.-A., Christophe, C., Couraud, J.-Y., et al. (1997). Importance of hydropathic complementarity for the binding of the neuropeptide substance P to a monoclonal antibody: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mol. Immunol. 34, 829–838. doi: 10.1016/S0161-5890(97)00119-3
Hao, P., Han, L., Quan, Z., Jin, X., Li, Y., Wu, Y., et al. (2023). Integrative mRNA-miRNA interaction analysis associated with the immune response of Strongylocentrotus intermedius to Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 134, 108577. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108577
Heal, J. R., Bino, S., Ray, K. P., Christie, G., Miller, A. D., Raynes, J. G. (1999). A search within the IL-1 type I receptor reveals a peptide with hydropathic complementarity to the IL-1β trigger loop which binds to IL-1 and inhibits in vitro responses. Mol. Immunol. 36, 1141–1148. doi: 10.1016/S0161-5890(99)00129-7
Hetz, C., Bernasconi, P., Fisher, J., Lee, A.-H., Bassik, M. C., Antonsson, B., et al. (2006). Proapoptotic BAX and BAK modulate the unfolded protein response by a direct interaction with IRE1a. Science 312, 572–576. doi: 10.1126/science.1123480
Hou, Y., Liao, T., Zhang, F., Zhang, T., Wang, L., Lv, W., et al. (2024). MicroRNA transcriptome analysis reveals the immune regulatory mechanism of Crassostrea hongkongesis against Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 145, 109354. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1050464823008409. (Accessed January 1, 2024).
Hou, Y., Zhang, T., Zhang, F., Liao, T., Li, Z. (2023). Transcriptome analysis of digestive diverticula of Hong Kong oyster (Crassostrea hongkongesis) infected with Vibrio harveyi. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 142, 109120. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.109120
Hu, Z., You, L., Hu, S., Yu, L., Gao, Y., Li, L., et al. (2024). Hepatocellular carcinoma cell-derived exosomal miR-21-5p promotes the polarization of tumor-related macrophages (TAMs) through SP1/XBP1 and affects the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 126, 111149. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111149
Huang, T., Olsvik, P. A., Krøvel, A., Tung, H., Torstensen, B. E. (2009). Stress-induced expression of protein disulfide isomerase associated 3 (PDIA3) in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 154, 435–442. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2009.08.009
Kawai, T., Akira, S. (2010). The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 11, 373–384. doi: 10.1038/ni.1863
Kourko, O., Hawke, L. G., Ormiston, M. L., Gee, K. (2023). IFN-β activates cytotoxic function of human natural killer cells toward IL-27 and poly(I:C) stimulated PC3 and DU145 cells. Cell. Immunol. 387, 104718. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2023.104718
Kwon, S.-H., Oh, S., Nacke, M., Mostov, K. E., Lipschutz, J. H. (2016). Adaptor protein CD2AP and L-type lectin LMAN2 regulate exosome cargo protein trafficking through the Golgi complex. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 25462–25475. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.729202
Li, L., Cui, J., Qu, Y., Ma, J., Chen, J., Zhao, Y., et al. (2024). IKK2 modulates the innate immune response of Zhikong scallop (Chlamys farreri) to bacterial and viral stimuli through the MyD88-dependent Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Aquaculture 591, 741148. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.741148
Li, X., Shi, C., Yang, B., Li, Q., Liu, S. (2023). High temperature aggravates mortalities of the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) infected with Vibrio: A perspective from homeostasis of digestive microbiota and immune response. Aquaculture 568, 739309. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739309
Liu, S., Deng, T., Hua, L., Zhao, X., Wu, H., Sun, P., et al. (2022). Novel functional mutation of the PDIA3 gene affects milk composition traits in Chinese Holstein cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 105, 5153–5166. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-21035
Liu, X., Ji, C., Zhao, J., Wang, Q., Li, F., Wu, H. (2014). Metabolic profiling of the tissue-specific responses in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis towards Vibrio harveyi challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 39, 372–377. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.05.033
Loaiza, I. (2023). Comparative analysis of nutritional quality of edible oysters cultivated in Hong Kong. J. Food Composition Analysis. 118, 105159. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2023.105159
Luo, D., He, Y., Zhang, H., Yu, L., Chen, H., Xu, Z., et al. (2008). AIP1 is critical in transducing IRE1-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 11905–11912. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710557200
Mahmood, F., Xu, R., Awan, M. U. N., Song, Y., Han, Q., Xia, X., et al. (2021). PDIA3: Structure, functions and its potential role in viral infections. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy 143, 112110. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112110
Monaco, F., De Conti, L., Vodret, S., Zanotta, N., Comar, M., Manzotti, S., et al. (2022). Force-feeding Malignant mesothelioma stem-cell like with exosome-delivered miR-126 induces tumour cell killing. Trans. Oncol. 20, 101400. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101400
Morot, A., El Fekih, S., Bidault, A., Le Ferrand, A., Jouault, A., Kavousi, J., et al. (2021). Virulence of Vibrio harveyiORM4 towards the European abalone Haliotis tuberculata involves both quorum sensing and a type III secretion system. Environ. Microbiol. 23, 5273–5288. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15592
Muthukrishnan, S., Defoirdt, T., Ina-Salwany, M. Y., Yusoff, F. M., Shariff, M., Ismail, S. I., et al. (2019). Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio harveyi causing Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) in Penaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) isolated from Malaysian shrimp ponds. Aquaculture 511, 734227. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734227
Olasard, P., Suksri, P., Taneerat, C., Rungrassamee, W., Sathapondecha, P. (2024). In silico identification and functional study of long non-coding RNA involved in acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 152, 109768. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109768
Oliver, J. D., Roderick, H. L., Llewellyn, D. H., High, S. (1999). ERp57 functions as a subunit of specific complexes formed with the ER lectins calreticulin and calnexin. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 2573–2582. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.8.2573
Oyanedel, D. (2023). Crassostrea gigas oysters from a non-intensive farming area naturally harbor potentially pathogenic vibrio strains. J. Invertebrate Pathology. 196, 107856. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2022.107856
Pan, H. (2024). MiR-192 and miR-731 synergically inhibit RGNNV infection by targeting ULK1-mediated autophagy in sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus). Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules. 282, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136748
Peng, D., Zhang, S., Zhang, H., Pang, D., Yang, Q., Jiang, R., et al. (2021). The oyster fishery in China: Trend, concerns and solutions. Mar. Policy 129, 104524. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104524
Pinto, R. D., Moreira, A. R., Pereira, P. J. B., Dos Santos, N. M. S. (2013). Two thioredoxin-superfamily members from sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.): Characterization of PDI (PDIA1) and ERp57 (PDIA3). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 35, 1163–1175. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2013.07.024
Qin, X., Huo, X., Dong, J., Liu, X., Wei, X., Chen, S., et al. (2024). METTL14 depletion induces trophoblast cell dysfunction by inhibiting miR–21-5p processing in an m6A-dependent manner. Int. Immunopharmacol. 142, 113200. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113200
Rungrassamee, W., Klanchui, A., Maibunkaew, S., Karoonuthaisiri, N. (2016). Bacterial dynamics in intestines of the black tiger shrimp and the Pacific white shrimp during Vibrio harveyi exposure. J. Invertebrate Pathol. 133, 12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2015.11.004
Sever, L., Bols, N. C., Dixon, B. (2013). The cloning and inducible expression of the rainbow trout ERp57 gene. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 34, 410–419. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2012.11.001
Shi, C., Lin, T.-H., Qu, C. (2024). The role of pattern recognition receptors in the innate immune system of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 154, 109946. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109946
Shingai, T. (2024). Temporal variation in the concentrations and profiles of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxin in scallop (Mizuhopecten yessoensis) and bloody clam (Anadara broughtonii) collected from the coast of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. Toxicon 243, 107710. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2024.107710
Tincu, J. A., Taylor, S. W. (2004). Antimicrobial peptides from marine invertebrates. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 48, 3645–3654. doi: 10.1128/aac.48.10.3645-3654.2004
Travers, M.-A., Le Goïc, N., Huchette, S., Koken, M., Paillard, C. (2008). Summer immune depression associated with increased susceptibility of the European abalone, Haliotis tuberculata to Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 25, 800–808. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2008.08.003
Trnková, L., Ricci, D., Grillo, C., Colotti, G., Altieri, F. (2013). Green tea catechins can bind and modify ERp57/PDIA3 activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gen. Subj. 1830, 2671–2682. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.11.011
Van Oss, C. J. (1995). Hydrophobic, hydrophilic and other interactions in epitope-paratope binding. Mol. Immunol. 32, 199–211. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)00124-J
Wang, W.-T. (2019). PDIA3-regulted inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to the traumatic brain injury (TBI) in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 518, 657–663. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.100
Wang, R., Lin, X., Zha, G., Wang, J., Huang, W., Wang, J., et al. (2022). Mechanism of enrofloxacin-induced multidrug resistance in the pathogenic Vibrio harveyi from diseased abalones. Sci. Total Environ. 830, 154738. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154738
Wang, L., Wang, X., Zhang, J., Duan, J., Tang, C., Zhang, L., et al. (2023). The role of PDIA3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its value as A diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. Heliyon 9, e22596. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22596
Xiang, G., Cheng, Y. (2018). MiR-126-3p inhibits ovarian cancer proliferation and invasion via targeting PLXNB2. Reprod. Biol. 18, 218–224. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2018.07.005
Xie, Z., Shi, J., Shi, Y., Tu, Z., Hu, M., Yang, C., et al. (2023). Physiological responses to salinity change and diel-cycling hypoxia in gills of Hong Kong oyster Crassostrea hongkongensis. Aquaculture 570, 739443. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739443
Yang, Q. (2023). Transcriptome analysis of liver, gill and intestine in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) symptomatically or asymptomatically infected with Vibrio Anguillarum Fish Shellfish Immunol. 135, 108643. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108643
Yang, M., Li, Q., Yang, H., Li, Y., Lu, L., Wu, X., et al. (2024). Downregulation of PDIA3 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth through cell cycle regulation. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy 173, 116336. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116336
Yang, B., Lin, Y., Huang, Y., Shen, Y.-Q., Chen, Q. (2024). Thioredoxin (Trx): A redox target and modulator of cellular senescence and aging-related diseases. Redox Biol. 70, 103032. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103032
Yang, W., Tran, N. T., Zhu, C.-H., Yao, D.-F., Aweya, J. J., Gong, Y., et al. (2021). Immune priming in shellfish: A review and an updating mechanistic insight focused on cellular and humoral responses. Aquaculture 530, 735831. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735831
Yao, T., Tong, Z., Lu, J., Fu, S., Cheng, C., Ye, L. (2024). A novel C-type lectin, perlucin, from the small abalone, Haliotis diversicolor involved in the innate immune defense against Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 155, 110029. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.110029
Yoneda, T., Imaizumi, K., Oono, K., Yui, D., Gomi, F., Katayama, T., et al. (2001). Activation of caspase-12, an endoplastic reticulum (ER) resident caspase, through tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2-dependent mechanism in response to the ER stress. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 13935–13940. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010677200
Yoo, D. Y., Cho, S. B., Jung, H. Y., Kim, W., Lee, K. Y., Kim, J. W., et al. (2019). Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 significantly reduces ischemia-induced damage by reducing oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurochemistry Int. 122, 19–30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.11.002
Yu, F., Chen, J., Lin, J., Zhong, Z., Lu, Y., Zeng, X., et al. (2023). TLR4 involved in immune response against Vibrio Parahaemolyticus by MyD88-dependent pathway in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 134, 108591. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108591
Yuan, Y., Guan, H., Huang, Y., Luo, J., Jian, J., Cai, S., et al. (2023). Involvement of Nrf2 in the immune regulation of Litopenaeus vannamei against Vibrio harveyi infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 133, 108547. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108547
Yue, Y.-X., Jia, B.-B., Wang, J.-R., Weng, Y.-Z., Mao, G.-X., Lu, Y., et al. (2023). 4-Octyl itaconate inhibits poly(I:C)-induced interferon-β secretion in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages partially by activating Nrf2. Heliyon 9, e23001. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23001
Yue, C., Ran, Y., Yang, C., Ibrahim, S., Song, X., Lü, W., et al. (2024). The effects of salinity stress on Crassostrea hongkongensis gill morphology, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Aquaculture 583, 740621. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.740621
Zhang, G., Fang, X., Guo, X., Li, L., Luo, R., Xu, F., et al. (2012). The oyster genome reveals stress adaptation and complexity of shell formation. Nature 490, 49–54. doi: 10.1038/nature11413
Zhang, Y., Liu, Z., Zhang, B. (2023). Separate roles of LMAN1 and MCFD2 in ER-to-Golgi trafficking of FV and FVIII. Blood Adv. 7, 1286–1296. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008788
Zhao, G., Lu, Li (2015). Proapoptotic activities of protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) and PDIA3 protein, a role of the Bcl-2 protein Bak*. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 8949–8963. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.619353
Zheng, C., Liu, H., Zhou, J., Zhang, B. (2010). EF-hand domains of MCFD2 mediate interactions with both LMAN1 and coagulation factor V or VIII. Blood 115, 1081–1087. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241877
Zhu, C., Yao, X., Liu, D., Zhang, G., Zhu, Y., Chi, H., et al. (2024). Neuroinflammation attenuation effects by celastrol and PDIA3 in the amygdala, hippocampus and dorsal raphe nucleus of obese mice. J. Pharm. Anal. 14, 287–290. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.10.002
Keywords: Crassostrea hongkongensis, Vibrio harveyi, PDIA3, miRNA regulation, immune response
Citation: Hou Y, Zhang F, Liu X, Huang D and Li Z (2025) ChPDIA3 targeted by miR-126-x and miR-21-y responds to Vibrio harveyi infection in Crassostrea hongkongensis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 15:1533154. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1533154
Received: 27 November 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 14 February 2025.
Edited by:
Natarajaseenivasan Kalimuthusamy, Regional Medical Research Centre (ICMR), IndiaReviewed by:
Changhong Cheng, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute (CAFS), ChinaSumaiya Krishnamoorthi, Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer (ACTREC), India
Copyright © 2025 Hou, Zhang, Liu, Huang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhimin Li, bGl6aGltaW44MTFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Yongkang Hou
Yongkang Hou Fangqi Zhang
Fangqi Zhang Xiaokun Liu
Xiaokun Liu Dongming Huang
Dongming Huang Zhimin Li
Zhimin Li