- 1Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
- 2Academician Workstation, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
Despite improvements in clinical outcomes of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), mortality rates remain high, indicating the need for further understanding of the pathogenesis and developing more effective cardiac protection strategies. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) carry proteins and noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) derived from different cardiac cell populations, mainly including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, endothelial progenitor cells, cardiac progenitor cells, cardiosphere-derived cells, immune cells, fibroblasts and cardiac telocytes have vital roles under both physiological and pathological process such as myocardial infarction (MI). The content of EVs can also indicate the status of their parental cells and serve as a biomarker for monitoring the risk of cardiac injury. Examining these vesicles can offer fresh perspectives on the development of MI and assist in creating innovative treatments. Additionally, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (MSC-EVs) derived EVs have been shown to have significant potential in cardiac regeneration. In this review, we will discuss the current understanding of the role of EVs in cardiac communication, with a focus on the perspectives of EVs from various cardiac cells and MSCs for their potential uses as cardiac therapies after MI.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) continues to be a top cause of mortality globally, with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) representing one of its most critical forms (1). AMI is caused by sudden interruption of myocardial blood supply, leading to hypoxia and death of myocardial tissue, ultimately resulting in left ventricular remodeling and heart failure. The outlook for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI) (STEMI) is poorer than for those with non-STEMI within 28 days following an acute coronary syndrome (ACS). However, over a decade of monitoring, the long-term mortality rates for patients with STEMI and non-STEMI were high (19.6% and 22.8%, respectively) and similar (2). Timely reperfusion treatment through percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been shown to enhance the clinical outcomes for individuals suffering from AMI (3). Nevertheless, it is unable to promote regeneration and functional recovery of the damaged myocardium, and there is still ample scope to further improve the mortality rates among patients with MI. Heart transplantation is the only treatment for the latest stage of heart failure. Consequently, there is an immediate need to further enhance existing strategies or develop novel approaches to promote cardiac protection and repair.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), containing several molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, have the ability to act as intercellular messengers and have the disease diagnosis and therapeutic potential. The cardiovascular system consists of various cell types, mainly including cardiomyocytes (CMs), endothelial cells (ECs), endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs), cardiosphere-derived cells (CDCs), immune cells, cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) and cardiac telocytes (CTCs) (4) that communicate via paracrine (such as EVs) or cell-cell interaction and participate in numerous cardiac physiological and pathological activities, which can be either advantageous or harmful (5). In addition, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have received considerable interest owing to their potential for multilineage differentiation and ease of isolation and acquisition (6, 7). Transplantation of MSCs reportedly alleviates myocardial injury and improves cardiac function post-MI. However, it is unlikely that these benefits are solely due to the direct replacement or differentiation of MSCs into cardiac tissue, given that most transplanted cells are rapidly lost from the heart (8). Moreover, cell transplantation carries the risk of inducing rejection (9), embolism (10), calcification or ossification of the infarct area (11), and arrhythmia (12). The therapeutic benefits of MSCs are mainly due to the EVs (13), and multiple studies have shown that MSC-derived EVs (MSC-EVs) can alleviate MI through various mechanisms (14, 15).
This review aims to provide insight into EVs biogenesis, composition and uptake. Furthermore, a comprehensive review of the current knowledge about the roles of EVs released by different cardiac cell types in MI and the advancements in utilizing MSC-EVs for MI therapy. Furthermore, we highlight the major challenges that must be overcome before clinical translation and the strategies for enhancing the potency of EVs as biotherapeutics. Aiming to provide effective information for developing treatment strategies based on EVs to improve endogenous repair.
2 Biogenesis, composition and uptake of EVs
2.1 Biogenesis of EVs
EVs are small vesicles released into the extracellular space and serve as essential messengers for intercellular communication. EVs comprise proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, and their lipid bilayer membranes protect their contents from enzymatic degradation (16). EVs are primarily classified according to their origin and biogenesis. Currently, researchers have recognized at least three primary categories of EVs: exosomes, ectosomes, and apoptotic bodies (17) (Figure 1). Exosomes, ranging from 30 to 120 nm, are formed through the inward budding of endosomal compartments (18). Ectosomes form through the outward budding of the cell membrane and primarily consist of microvesicles (150–1,000 nm), large oncosomes (1–10 μm), small ectosomes (30–150 nm), and ARRDC1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) (30–150 nm), which are not depicted in the illustration. Apoptotic bodies (100–5,000 nm) are generated by fragmentation of cells undergoing apoptosis. Furthermore, there are several other specialized EVs, mainly including migrasomes (500–3,000 nm) and exophers (3.5–4 μm) (19, 20). Migrasomes are emitted from the retracting fibers of cells in motion and might serve to eliminate impaired mitochondria from cells (21). Furthermore, cells are capable of releasing nonvesicular extracellular particles (NVEPs), such as exomeres (28–50 nm) and supermeres (22–32 nm) (22, 23) (Figure 1). It is believed that they transport a range of molecules including RNA, DNA, and proteins, yet the process of how supermeres and exomeres are formed remains a mystery.
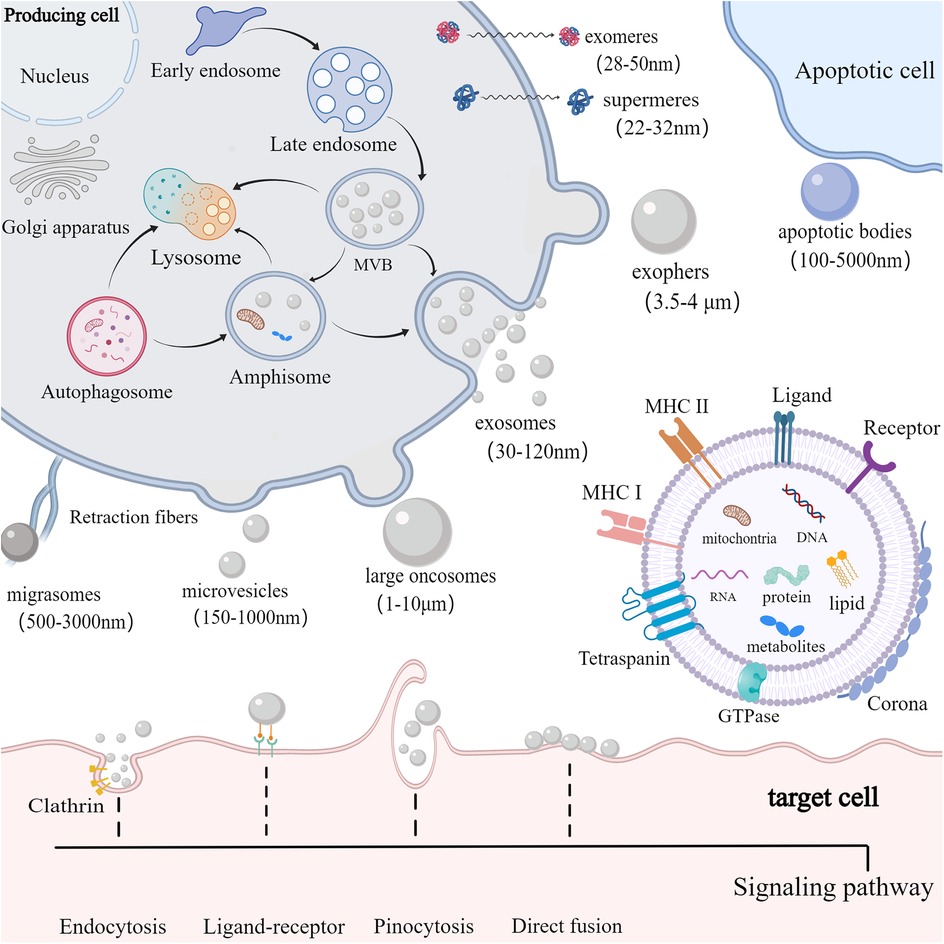
Figure 1. Biogenesis, composition and uptake of EVs. cells secrete EVs (including exosomes, ectosomes, and apoptotic bodies) and NVEPs (such as supermeres and exomeres) into the extracellular environment. Exosomes are produced via exocytosis, while ectosomes (such as microvesicles and large oncosomes) are formed through budding. Apoptotic bodies are vesicles formed during apoptosis. EVs contain proteins, DNA, RNA, lipids, metabolites, and mitochondria. EVs can also form a corona on their surface. The membrane of EVs predominantly includes GTPase, MHC class I and II molecules, tetraspanins like CD9, CD63, and CD81, as well as various receptors and ligands. EVs are primarily internalized by target cells via receptor-ligand interactions, clathrin-mediated and clathrin-independent endocytosis, pinocytosis, and direct membrane fusion.
Among those EVs, exosomes are mostly studied for therapy development. Exosomes are produced via a complex endocytic process, where the cell membrane invaginates to create early endosomes, which then mature into late endosomes or multivesicular bodies (MVBs) containing intraluminal vesicles (ILVs). When MVBs merge with the cell membrane, ILVs are discharged into the extracellular environment as exosomes (18). Certain MVBs may be directed to lysosomes for breakdown or merge with autophagosomes to form amphisomes. Amphisomes may be moved to lysosomes for breakdown, or directed to the plasma membrane to discharge their contents outside the cell. The intricate processes governing cargo sorting and the creation of ILVs involve both ESCRT-dependent and ESCRT-independent pathways (24). The ESCRT system, comprising four soluble protein complexes and auxiliary proteins like ALIX, VPS4, and TSG101 (25), plays a crucial role in directing proteins to ILVs and generating exosomes. In addition, the formation of MVBs can be promoted by the ESCRT-independent pathway (26). Studies have shown that the formation of MVBs could still occur in ESCRT-depleted cells (27).
EVs of different types overlap in size, and consensus has not yet emerged on specific markers of EVs subtypes, complicating their separation with existing isolation techniques like ultrafiltration, ultracentrifugation, precipitation, immunoaffinity capture, and size exclusion chromatography (28, 29). The complexity of heterogeneous mixtures of EVs and NVEPs makes their separation even more difficult. In response to the numerous types of EVs and the uncertainty of their biogenesis, the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) recommends adopting the general term “EV” with specific operational extensions, instead of using inconsistent and potentially confusing labels like “exosomes” and “ectosomes,” which are linked to intricate and hard-to-define biogenesis processes (30). In this review, the EVs types will not be differentiated and will be collectively called EVs. Further research is required to develop optimal techniques for segregating and characterizing distinct EVs subpopulations and improving separation of distinct EVs and NVEPs, enabling the establishment of a more accurate and specific nomenclature.
2.2 Composition of EVs
A single cell is capable of generating various kinds of EVs with distinct structure and biochemical properties. A conserved range of proteins are enriched in EVs, including tetraspanins (TSPANs) (CD9, CD63, and CD81), TSG101, ALIX, and some specific lipids (17). Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are enriched on EVs compared to parent cells (31). Nonetheless, the composition of EVs cargo, including proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and organelles, as well as their membrane and corona, can differ significantly depending on their biogenesis, the source cell, cell vitality, and the culture environment (32). Microvesicles are characterized by expression of Annexin A1, Annexin A2 and α-Actinin 4 (17). ARMMs characteristically express ARRDC1 and TSG101 (33, 34). Large oncosomes feature enrichment of Annexin A1, ARF6, V-ATPase G1, and CK18 (16). Small ectosomes are characterized by expression of CD9 and CD147. Moreover, apoptotic EVs characteristically express Annexin V (35). Additionally, migrasomes are enriched with TSPAN4, cholesterol and integrins (36). Exophers contain protein aggregates and damaged mitochondria (20). It should be noted that CD9, CD63 and CD81 have long been used as exosome markers. However, there is growing acknowledgment that TSPAN-containing EVs can bud directly from the plasma membrane (37). According to their biogenesis, these EVs can be classified as ectosomes/microvessels (37). Interestingly, MSC-EVs also express CD29, CD44, and CD73, molecules that are surface markers of MSCs (38). Upon release into biological fluids, EVs interact with extracellular components to form a protein corona (PC) on their surface via electrostatic interactions and protein aggregation (39, 40). The route of EVs administration and the proteomic characteristics of different pathological conditions can impact the composition of the PC surrounding the EVs, which affects their physicochemical properties, biodistribution, and targeting ability (41, 42).
2.3 Uptake of EVs
EVs serve as a means of intercellular communication, capable of delivering diverse molecules to nearby cells or across greater distances, either through uptake or by the binding of EVs surface proteins to cell receptors. After exiting the cell, EVs are primarily internalized by target cells through interactions between receptors and ligands, clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis pathways, pinocytosis, and direct fusion, resulting in alterations in the physiological state of target cells (43). EVs possess features like minimal toxicity, reduced immune response, the ability to traverse biological barriers including the blood-brain barrier, and the capability to deliver cargo to target cells (44). In this context, a substantial body of evidence has recently emerged to demonstrate the therapeutic effects of MSC-EVs in a range of pathological conditions (45).
3 EVs derived from cardiac cells
MI causes cardiac cell death, triggers angiogenesis and inflammatory response, induces cardiac fibrosis, and ultimately leads to myocardial remodeling and heart failure. After MI, various cardiac cells, mainly including CMs, ECs, EPCs, CPCs, CDCs, macrophages (M ϕ), CFs, CTCs and epicardium-derived cells (EPDCs), can communicate with each other through EVs to promote improvement or impairment of cardiac function (Figure 2). Considering the possible importance of EVs in the mechanisms of injury, healing and tissue remodeling post-MI, understanding EVs derived from cardiac cells holds promise for improving endogenous repair opportunities through the use of intervention strategies.
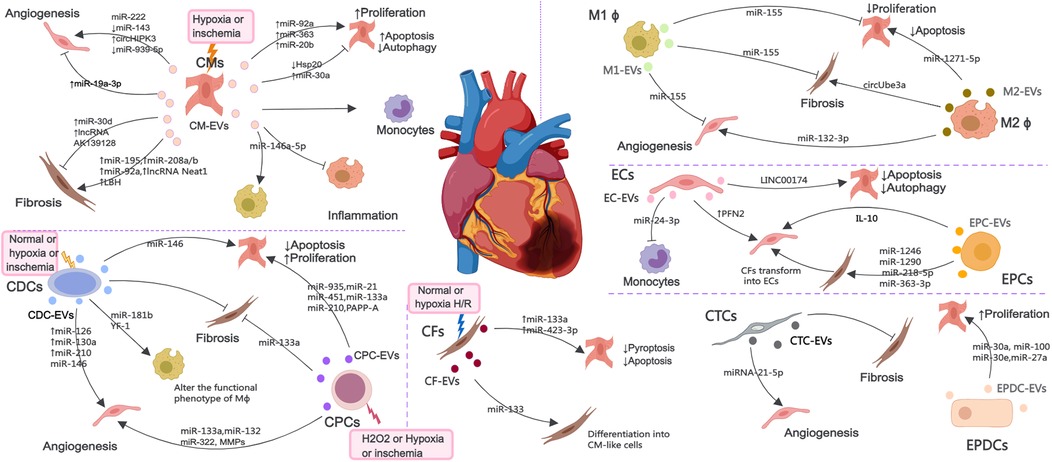
Figure 2. The EV-mediated cross-talk among various cardiac cells such as CMs, ECs, EPCs, CPCs, CDCs, Mϕ, CFs, CTCs and EPDCs under normal, H2O2, hypoxia or ischemia condition, which are involved in the regulation of angiogenesis, inflammatory response, cell death and myocardial fibrosis.
3.1 CM-derived EVs
EVs secreted by CMs (CM-EVs) mediate communication between cardiac cells under healthy and ischemic conditions. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) that control gene expression at the post-transcriptional level (46). EVs secreted by CMs cultured under hypoxic or ischemic conditions can protect cardiac microvascular ECs (CMECs) from oxidative damage and promote angiogenesis, which are attributable to miR-222, miR-143 and circHIPK3 (47–49). Interestingly, the EVs derived from CMs treated with hyperbaric oxygen can induce upregulation of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 (lncRNA MALAT) in CM-EVs to suppress miR-92a expression, thereby promoting neovascularization (50). Nonetheless, inhibition of miR-19a-3p in CM-EVs can downregulate the protein level of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and promotes ECs proliferation and angiogenesis after MI (51). MiR-939-5p (52) levels were notably reduced in EVs from the coronary serum of myocardial ischemia patients, enhancing angiogenesis via the miR-939-inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-NO pathways, with CMs potentially being the origin of these bioactive EVs.
AMI increases the production of cardiac EVs, originating mainly from CMs and ECs. EVs accumulating in the ischemic myocardium are rapidly taken up by infiltrating monocytes and regulate local inflammation (53). MiR-146a-5p derived from CM-EVs can induce inflammation and exert anti-inflammatory effects by regulating macrophages polarization (54). EVs derived from ferroptotic CMs induce M1 macrophages (M1 ϕ) polarization and exacerbate cardiac inflammation during MI (55). The effect of CM-EVs on CFs under hypoxic or ischemic conditions seems to be inconsistent in different studies, and can promote fibrosis reversal through miR-195 (56), miR-208a/b (57), miR-92a (58), lncRNA Neat1 (59) and limb-bud and heart (LBH) (60), or inhibit fibrosis response through lncRNA AK139128 (61) and miR-30d (62).
CM-EVs can also act on CMs and regulate their survival. EVs from hypoxic CMs regulate autophagy by transferring miR-30a between CMs (63). After MI, the expression of HSP20 in CM-EVs decreases, leading to CMs apoptosis and inflammatory response (64). MiR-92a, miR-363, and miR-20b (belonging to the miR-106a-363 cluster) secreted from EVs derived from human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived CMs (iCMs) promote CMs re-entry into the cell cycle, induce cell proliferation and improve ischemic myocardial injury (65). In addition, circulating EVs from infarcted hearts can mediate the transfer of myocardiac miRNAs to bone marrow (BM) mononuclear cells, downregulate CXCR4 expression, and increase the number of circulating progenitor cells. Therefore, infarcted hearts released EVs can induce systemic responses for cardiac repair (66).
3.2 EC and EPC-derived EVs
ECs and EPCs are another important source of EVs during MI and play a important role in maintaining and establishing the integrity of blood vessels. The levels of profilin 2 (PFN2) in serum and EC-EVs of patients, mice, and pigs with MI are elevated. PFN2 and EVs from PFN2-overexpressing ECs can enhance ECs proliferation, migration, and tube formation, and increase vessel numbers in infarcted myocardium (67). Khan et al. have demonstrated that EVs secreted by EPCs (EPC-EVs) can inhibit cell apoptosis, reduce scar size, and promote neovascularization after MI (68). Inflammation can impair the repair of the heart by EPC-EVs, and interleukin-10 (IL-10) deficiency weakens the repair effect of EPC-EVs on infarcted myocardium by upregulating integrin-linked kinase (68). CFs have innate plasticity and can acquire CMs or endothelial phenotype upon exposure to transcription factors and other molecules (69, 70). EPC-EVs facilitate the transformation of CFs into ECs, enhance angiogenesis post-MI, and prevent myocardial fibrosis by delivering miR-1246, miR-1290, miR-218-5p, and miR-363-3p to CFs (71, 72). Recently, zhao et al. have found that coculture with EPC-EVs improved human umbilical venous ECs (HUVECs) proliferation, angiogenic and migration ability, while alleviated hypoxia-induced apoptosis in vitro.
Krüppel-Like Factor 2 is highly expressed in ECs under laminar flow and has anti-inflammatory effects. EVs secreted by ECs overexpressing krüppel-Like Factor 2 inhibit Ly6CHigh monocytes recruitment by shuttle miR-24-3p, improve ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury, and alleviate cardiac inflammation (73). LncRNA 174 (LINC00174) in EC-EVs mitigate I/R-induced myocardial damage by inhibiting p53-mediated autophagy and apoptosis of CMs (74).
3.3 CDC and CPC-derived EVs
CDCs and CPCs have shown significant potential in promoting the regeneration and repair of damaged myocardium (75, 76). The anti-apoptosis effect of CPCs derived EVs (CPC-EVs) can be mediated by pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) (77) and various RNAs, mainly including miR-21, miR-451, miR-935, miR-133a, and miR-210 (78–82). In addition, miR-133a in CPC-EVs can improve cardiac function in a rat MI model by reducing fibrosis and hypertrophy and increasing CMs proliferation and vascularization (81). CPC-EVs can also promote ECs immigration via the degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) (83). MiR-132 in CPC-EVs has the potential to boost angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo by suppressing RasGAP-p120 (82). Bioengineered CPC-EVs carrying a pro-angiogenic miR-322 can increase ECs migration and capillary tube formation via increased NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2)-derived ROS, and enhance angiogenesis in the border zones of infarcted hearts (84). EVs derived from hypoxic CPCs (H-CPC-EVs) can enhance tube formation of ECs and reduce the expression of profibrotic gene in transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-stimulated fibroblasts and cardiac fibrosis after I/R injury (85). The angiogenesis ability of H-CPC-EVs is highly correlated with oxygen concentration, with the angiogenesis effect being most effective at 5% O2 concentration and the angiogenesis signaling pathway at 1% O2 concentration (86). In addition, Emmert et al. have evaluated the safety, feasibility and efficacy of human derived CPC-EVs in a pig model of AMI. Intracoronary (IC) delivery of EVs reduced infarct size, improved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), significantly alleviated myocardial fibrosis, and increased vascular density (87).
CDCs derived EVs (CDC-EVs) can exert cardioprotective effects by transferring miR-146 (partially beneficial), thereby reducing CMs apoptosis and promoting angiogenesis (88). EVs released by hypoxic CDCs can induce angiogenesis via enrichment of miR-126, miR-130a, and miR-210 (89). In addition, CDC-EVs also act on macrophages by transferring Y RNA fragments (YF1), enhancing the secretion of IL-10, reducing CMs apoptosis, and promoting ischemic heart repair (90). CDC-EVs can polarize M1 ϕ to a proangiogenic phenotype dependent on arginase 1 upregulation and independent of VEGF-A, which promote angiogenesis (91). CDC-EVs can modify the polarization state of macrophages by transfer of miR-181b into macrophages that inhibits proinflammatory signaling and enhances phagocytosis to promote a cardioprotective response in vivo (92). This helps to understand the immune regulatory mechanism of CDC-EVs in macrophages polarization after AMI. Study has revealed a mechanism for amplifying the biological activity of EVs, in which CDC-EVs promote SDF1 and VEGF secretion of fibroblasts, promote angiogenesis, and reduce scar quality after MI by promoting phenotypic transformation from inert fibroblasts to therapeutic active cells (93). In a large animal study, intramyocardial (IM) delivery of CDC-EVs was found to reduce scar formation, prevent adverse remodeling, and increase vascular density in pigs with AMI and chronic MI (CMI), but it appears to have the disadvantage of requiring IM delivery (94). In addition, CDC-EVs can inhibit ventricular arrhythmias in chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy by reducing fibrosis, eliminating slow conduction electrical pathways, and suppressing ventricular arrhythmias (95).
3.4 Macrophage-derived EVs
After MI, immune cells like monocytes and macrophages move to the injured site to remove dead cells. Macrophages are versatile cells within the innate immune system, essential for initiating inflammation and aiding in tissue repair following MI. In addition, it also participates in interactions with other cardiac cells to coordinate the post MI process within the heart tissue. Following MI, EVs derived from M1 ϕ (M1-EVs) deliver miR-155 to ECs, diminishing their angiogenic capacity by concurrently targeting Rac family small GTPase 1, p21 (RAC1)-activated kinase 2, sirtuin 1 (Sirt1), and protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 2 (96), to CFs to decrease the expression of son of sevenless 1, thereby inhibiting CFs proliferation and promoting inflammation by lowering the levels of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (97), and to CMs to inhibit CMs proliferation by inhibiting the IL-6R/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway (98).
EVs derived from M2 ϕ (M2-EVs) promote angiogenesis after MI by delivering miR-132-3p to ECs and downregulating the expression of THBS1 (99). M2-EVs can also deliver miR-1271-5p to CMs, alleviating hypoxia induced apoptosis via down-regulating SOX6 (100) and release circUbe3a into CFs, promoting proliferation, migration, and phenotype transformation of CFs by repressing RhoC, exacerbating myocardial fibrosis after AMI (101).
3.5 CF-derived EVs
During cardiac stress, CFs proliferate and differentiate into myofibroblasts, secreting ECM proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to cardiac fibrosis and remodeling. CFs are both a source of cardiac protection and a carrier of disease fibrosis. EVs secreted by CFs under hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) can mimic the beneficial effects of ischemic post-treatment through miR-423-3p, reducing apoptosis of CMs (102) and deliver miR-133a to CMs, targeting ELAVL1 and preventing pyroptosis caused by I/R (103). Moreover, EVs secreted by CFs (CF-EVs) can also regulate their own differentiation. MiRNA-133 in CF-EVs can promote the differentiation of CFs into CM-like cells (104). Under hypoxic conditions, multiple ECM proteins in CFs are upregulated, and CF-EVs have different effects on the viability of CMs at different stages of hypoxia and reoxygenation (105). Treatment of fibroblasts with long-term, low-dose sulforaphane can enhance the release of their anti-remodeling CM-targeted EVs, effectively reducing cardiac hypertrophy and scar size and improving cardiac function post-MI (106).
3.6 Other cardiac cell-derived EVs
CTCs are a type of stromal cell with elongated extensions. MiRNA-21-5p in EVs released by CTCs (CTC-EVs) can target the cell death inducing p53 target 1 gene, which suppresses apoptosis of ECs under ischemic and hypoxic conditions, facilitating angiogenesis and regeneration following MI (107). In addition, CTC-EVs can also decrease cardiac fibrosis following MI (108). The outermost layer of the heart, known as the epicardium, can be reactivated following an injury to an adult heart. EPDCs can release EVs (EPDC-EVs) carrying miR-30a, miR-100, miR-30e, and miR-27a, promoting the proliferation of CMs after myocardial injury (109). In addition, clusterins of EVs in pericardial fluid from AMI patients improve MI by activating the epicardium, increasing arterial generation, and reducing CMs apoptosis (110).
Although some EVs are generated under normoxic conditions and cannot reflect the state of the infarcted tissue, their beneficial effects can provide us with ideas for developing new treatment strategies. The majority of research relies on EVs extracted from cells grown in vitro, potentially failing to represent the properties of EVs released by different cells in ischemic heart tissue in vivo. The seemingly opposite therapeutic effects may reflect different levels of stress on cardiac cells, and it is necessary to further elucidate the interactions between EVs from different sources in the development of MI. In addition, it is necessary to explore the components of EVs and their interactions with specific cardiac targets. This will deepen our understanding of the function of EVs and pave the way for new treatment strategies to alleviate MI and promote cardiac repair.
4 Biological functions of MSC-EVs in MI
4.1 Promotion of angiogenesis
MSC-EVs contain various ncRNAs and paracrine effector molecules that promote angiogenesis (Figure 3). CMECs are derived from coronary microvessels exhibiting rapid expansion, tube formation, and proangiogenic abilities. CMECs are susceptible to damage under ischemic and hypoxic conditions. MSC-EVs containing miR-543 can enter CMECs and downregulate collagen type IV alpha 1 (COL4A1), promotes CMECs angiogenesis after MI (111). Adipose-derived MSC-EVs (ADMSC-EVs) containing miR-205 which enhance the proliferation and migration of MECs, inhibit apoptosis, reduce cardiac fibrosis, and increase angiogenesis in mice with MI (112). The role of miRNA-21 in promoting angiogenesis has been well-researched, with evidence showing that EVs from human endometrial MSCs (EnMSCs) containing miR-21 enhance microvascular density via the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway, offering better cardioprotection than those from BMMSCs or ADMSCs (113). Additionally, miRNA-132 in MSC-EVs was discovered to promote tube formation in HUVECs by suppressing the target gene p120RasGap, thereby boosting neovascularization in the peri-infarct region (114). Similarly, miR-210 downregulated the Efna3 gene to enhance angiogenesis and provide therapeutic benefits for MI (115). Xu et al. (116) have revealed that neonatal rat CMs (NRCMs) cultured under hypoxic conditions treated with EVs derived from BMMSCs, ADMSCs, and umbilical cord MSCs (UCMSCs) reduced apoptosis and promoted angiogenesis by increasing levels of VEGF, basic fibroblast growth factor, and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Notably, ADMSC-EVs exhibited the most pronounced effects. In mice with MI, IM injection of cardiac MSC-EVs was shown to promote capillary angiogenesis in the infarcted area, stimulate CMs proliferation, and improve cardiac function (117). In addition, Takov et al. have demenstrated for the first time that EVs secreted from human foetal amniotic fluid MSCs can protect hearts from I/R injury in vivo and markedly stimulated ECs migration in vitro, but did not protect isolated primary CMs in models of simulated I/R injury and were not proangiogenic in vitro (118). The combined effects of multiple active substances in MSC-EVs collectively regulate post-MI angiogenesis.
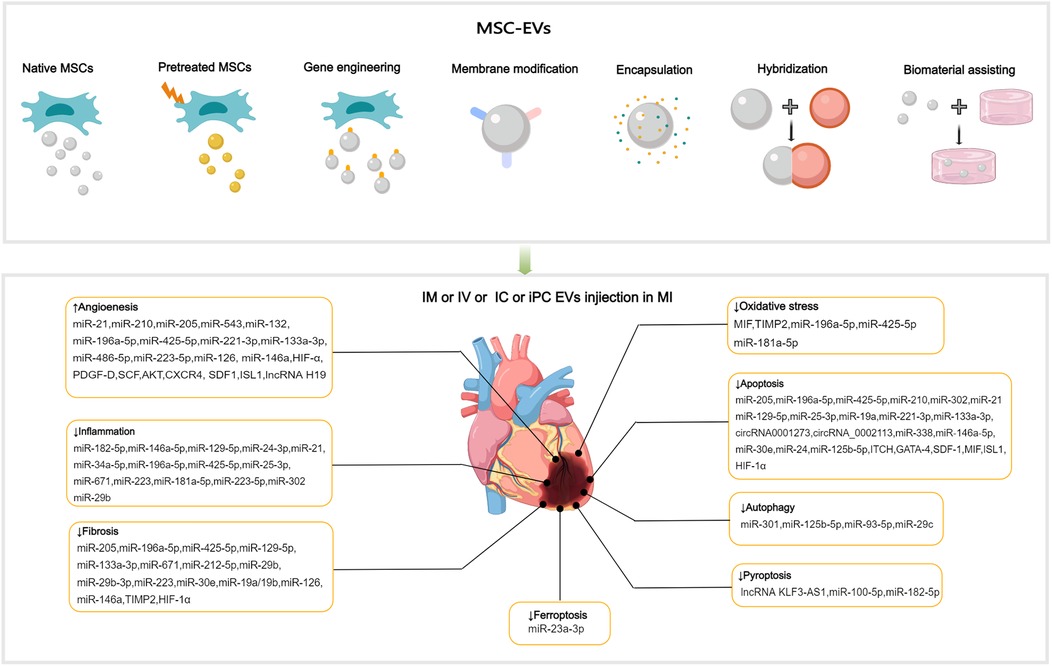
Figure 3. Applications of MSC-EVs in MI. MSC-EVs can be utilized in their original state and enhanced autophagy through preconditioning, gene engineering,membrane modification, encapsulation, hybridization and biomaterial-assisting. EVs can be applied via IM, IV, IC and iPC injection in MI or I/R animal models. MSC-EVs can improve angiogenesis, inflammation, cell death (such as apoptosis, autophgy, pyroptosis, ferroptosis), oxidatve stress and cardiac fibrosis after MI.
4.2 Anti-inflammation
MI can cause a strong inflammatory response, and the duration and intensity of this inflammation are closely related to the prognosis. MiR-182-5p within BMMSC-EVs can reduce inflammation and enhance heart function after MI by suppressing the TLR4/nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway (119) (Figure 3). High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) acts as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP), triggering cytokine release and attracting inflammatory cells (120). The transfer of miR-129-5p through BMMSC-EVs has been shown to inhibit CMs apoptosis, cardiac fibrosis, and inflammatory response in mice with MI by targeting HMGB1 (121). Shi et al. have reported that UCMSC-EVs promote the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts within an inflammatory setting, reducing the inflammatory reaction and CMs apoptosis post-MI, while not exacerbating cardiac fibrosis (122). The transcription factor forehead box o3 (Foxo3) plays a critical role in T cells activation (123). Recent studies have revealed that intrapericardial (iPC) injection of MSC-EVs accumulate in the mediastinal lymph nodes and induce regulatory T cells (Tregs) differentiation, promoting cardiac repair. The absorption of MSC-EVs by MHC-II + APCs triggers Foxo3 activation through the PP-2A/Foxo3 signaling route. Foxo3 promotes the production of IL-10, IL-33, and IL-34, establishing a Treg-inducing niche in mediastinal lymph nodes. Ultimately, this coordination results in the resolution of inflammation and the promotion of cardiac repair post-MI (124). The observed immunomodulatory effects post-MI indicate the potential of EVs to coordinate the transition from the inflammatory to the resolution phase following ischemic injury.
Following MI, cardiac macrophages undergo a transition from proinflammatory M1 ϕ in the early stage (1–3 days) to reparative M2 ϕ, which predominate in the late stage (after 5 days) (125). This transition is crucial in limiting inflammation and facilitating cardiac repair. Through gene sequencing and bioinformatics, it was discovered that miR-24-3p within UCMSC-EVs can suppress the expression of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C beta 3 and activate the NF-κB pathway, resulting in the promotion of M2 ϕ polarization and alleviation of inflammatory responses post-MI (126). Furthermore, ADMSC-EVs are capable of triggering the sphingosine 1-phosphate/sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine phosphate receptor 1 signaling pathway, resulting in the polarization of M2 ϕ. This results in a reduction in local inflammation and cardiac injury following MI (127). Compared with BMMSC-EVs, EVs derived from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-pretreated BMMSCs exhibited superior therapeutic effects in terms of promoting M2 ϕ polarization in vitro and alleviating post-MI inflammation and CMs apoptosis in vivo by mediating macrophage polarization in an MI mouse model (128). The immunomodulatory properties of ADMSC-EVs may not be constitutive but are instead induced by the inflammatory microenvironment. The immunosuppressive effect was apparent only when ADMSCs were pre-activated by proinflammatory stimuli. Pre-activated ADMSCs release EVs with higher levels of miRNAs (such as miR-34a-5p, miR-21, and miR-146a-5p) that regulate the M2 phenotype untreated EVs (129).
4.3 Anti-oxidative stress
Elevated oxidative stress and overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) following MI intensify mitochondrial DNA damage, leading to greater myocyte injury and a subsequent rise in fibrosis and tissue remodeling (130, 131). Mitochondrial transplantation is a promising novel therapy for CVD. Mitochondrial transfer between cells can be achieved through several methods, mainly including tunneling nanotubes, EVs, and cell fusion (132). EVs facilitate the transfer of functional mitochondria to recipient cells, rescuing damaged cells through multiple pathways (133, 134). MSC-EVs were discovered to restore mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) levels in recipient cells through the delivery of TFAM mRNA and mitochondrial DNA. This process prevents mtDNA damage and cytoplasmic mtDNA leakage, effectively alleviating mitochondrial damage and inflammation in acute kidney injury cells and animal models (135). MSC-EVs represent a promising avenue for the development of nanotherapies for diseases characterized by mitochondrial damage. Currently, no direct evidence demonstrates the independent functionality of mitochondria in EVs (136). It is noteworthy that damaged cells release mitochondrial DAMPs into circulation, which may have notable immune consequences. Interestingly, selective packaging of mitochondrial proteins into EVs appears to prevent this process (137, 138). The macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is essential for regulating cell homeostasis (139). Compared with BMMSC-EVs, injection of EVs derived from BMMSCs overexpressing MIF elicited superior cardioprotective effects in attenuation of CMs injury post-MI by inhibiting mitochondrial fragmentation, apoptosis, and ROS overexpression via activation of the AMPK signaling pathway (140) (Figure 3). BMMSC-EVs, which contain miR-214, can target Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) to inhibit oxidative stress-related injuries in cardiac stem cells (CSCs), including apoptosis, calcium imbalance, and excessive ROS accumulation (141). In ADMSC-EVs, miR-196a-5p and miR-425-5p were found to mitigate CMs ischemia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and excessive ROS production, increase angiogenesis, and promote M2 ϕ polarization. Furthermore, miR-196a-5p can reduce and reverse myofibroblast activation and decrease collagen production (142).
4.4 Cell death reduction
4.4.1 Reducing cellular apoptosis and autophagy
Following MI, myocardial cells undergo apoptosis and severe autophagy, causing cardiac injury and deterioration of cardiac function. Moderate autophagy during myocardial ischemia is essential for maintaining tissue viability. The relationship between cellular autophagy and apoptosis is complex, and maintaining a balance between the two is critical for cell survival (143, 144). The process of cell apoptosis is mainly initiated by mitochondrial, death receptor, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) pathways (145–147). BMMSC-EVs preconditioned with hypoxia reduced CMs apoptosis of rats with AMI by upregulating microRNA-24 (148) (Figure 3). MSC-EVs loaded with miR-25-3p can target pro-apoptotic genes (FasL and PTEN) and enhancer of zeste homologue 2, leading to decreased apoptosis in CMs and reduced inflammation in both in vivo and in vitro MI models (149). SOX6, part of the SOXD group, can amplify LPS-triggered apoptosis in CMs by stimulating the Bcl-2 family pathway (150). UCMSC-EVs can prevent CMs apoptosis and alleviate myocardial injury post-MI by transferring miR-19a to target SOX6, subsequently activating AKT and suppressing Jun N-terminal kinase 3 (JNK3)/caspase-3 activation (151).
Sun et al. have found that miR-221-3p derived from Aged MSC-EVs attenuated the function of angiogenesis and promoted the survival of CMs. Upregulation of miR-221-3p in aged MSCs improved their ability of angiogenesis, proliferation and migration, and reduced apoptosis via the PTEN/AKT pathway (152). Furthermore, Zhang et al. have indicated that EVs derived from young MSCs can enhance the activity of aged MSCs and improve their myocardial repair function by transferring miR-136 and downregulating apoptotic peptidase-activating factor (153). BMMSC-EVs carrying itchy E3 ubiquitin ligase can mediate ubiquitination of apoptosis signal-regulated kinase-1, leading to the inhibition of CMs apoptosis and improved myocardial injury post-AMI (154). EVs derived from UCMSCs overexpressing MIF (MIF-EVs) exert cardioprotective effects, such as the promotion of angiogenesis, inhibition of apoptosis, alleviation of cardiac fibrosis, and preservation of heart function. MIF-EVs exert their biological effects through miR-133a-3p and the subsequent activation of the AKT signaling cascade (155). MSC-EVs also contain molecules that exert destructive effects. Low miR-153-3p expression in MSC-EVs significantly boosted the activation of the angiopoietin-1/VEGF/VEGFR2/PI3 K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway, which inhibited apoptosis in ECs and CMs while enhancing angiogenesis in an oxygen-glucose deprivation model (156). Circular RNA (circRNA) is a kind of ncRNA, involving in the development of CVD. Tian et al. demonstrated that EVs originating from circRNA_0002113-deficient BMMSCs could decrease H9C2 cell apoptosis caused by H/R and mitigate MI by by sponging miR-188-3p to regulate RUNX1 nuclear translocation. Specifically, the circRNA_0002113/miR-188-3p/RUNX1 axis mediated apoptosis by regulating the USP7/p53 pathway both in vitro and in vivo (157). CircRNA 0001273 in UCMSC-EVs can remarkably reduce myocardial cell apoptosis in ischemic environment and promote MI repair (158). Accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in CMs, a condition referred to as ER stress, can cause apoptosis and fibrosis (159). Zhang et al. have found that UCMSC-EVs alleviated ER stress-induced apoptosis in H9C2 cells subjected to H/R by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway (160). Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is crucial for controlling cell proliferation and apoptosis. Fu et al. have found that miR-338 in MSC-EVs can inhibit CMs apoptosis in MI model rats by regulating the MAP3K2/JNK signaling pathway, thereby substantially improving cardiac function (161).
Reportedly, BMMSC-EVs carrying overexpressed miR-301 could reduce infarct area and improve cardiac function in rats with MI by inhibiting myocardial autophagy compared with BMMSC-EVs group (162) (Figure 3). The role of p53 in autophagy is contingent upon its subcellular localization in the nucleus or cytoplasm (163). Xiao et al. have demonstrated that the benefits of MSCs transplantation post-MI can be attributed to the improved autophagic flux. The mechanism of MSC-induced autophagic inhibition involves the transfer of miR-125b-5p from MSC-EVs to native cells, where it interferes with p53/B-cell lymphoma 2-interacting protein 3 signaling (164). Compared with healthy individuals, patients with AMI exhibit elevated serum levels of miR-93-5p and inflammatory factors. In vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that miR-93-5p in ADMSC-EVs can alleviate heart damage after MI by targeting autophagy-related protein 7-mediated autophagy and TLR4-mediated inflammation (165). The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a negative regulator of autophagy. MiR-29c derived from BMMSC-EVs can target PTEN to activate the AKT/mTOR pathway, ultimately inhibiting CMs autophagy after I/R injury (166).
4.4.2 Reducing pyroptosis
Pyroptosis, a proinflammatory programmed cell death process, is characterized by the disruption of cell integrity and the release of inflammatory cytokines. In a mouse model of AMI, pyroptosis was triggered within 24 h. Preventing pyroptosis has been demonstrated to significantly decrease infarct size and enhance heart performance (167). Sirt1 has been discovered to inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Mao et al. have demonstrated that the lncRNA KLF3-AS1 acts as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-138-5p, which regulates the expression of Sirt1. In vitro and in vivo experiments have shown that lncRNA KLF3-AS1 within MSC-EVs can modulate Sirt1, thereby preventing cell pyroptosis and reducing MI progression by functioning as a ceRNA to sponge miR-138-5p (168) (Figure 3). Proteomic analysis conducted seven days after ligating the left coronary artery revealed that treatment with MSC-EVs could substantially reduce leukocyte accumulation in the infarct area and surrounding regions and decrease the expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX1), NLRP3 inflammasome, caspase-1, cleaved caspase-3, GSDMD, Bcl-2, and Bax, resulting in preservation of cardiac function (169). Liang et al. have reported that miR-100-5p in UCMSC-EVs suppresses the expression of Foxo3, inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and suppressing H/R-induced CMs pyroptosis (170). Yue and colleagues have uncovered that gasdermin D (GSDMD) is robustly expressed in H/R-exposed cardiac cells and I/R-injured myocardial tissues. The upregulation of GSDMD promoted H/R-induced cardiac cell pyroptosis. Further analysis revealed that GSDMD is a miR-182-5p target. Administration of MSC-EVs carrying miR-182-5p attenuated GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis and inflammation induced by H/R, improved cardiac function, reduced MI, and decreased inflammation and pyroptosis in vivo (171).
4.4.3 Reducing other types of cell death
Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death, is marked by the buildup of ROS, disrupted iron balance, and lipid peroxidation. Divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), a Fe2+transporter, is known to be markedly elevated in AMI. Song et al. have showed that DMT1 is a target gene of miR-23a-3p.Human umbilical cord blood derived MSC-EVs reduce DMT1 levels through miR-23a-3p, thereby preventing ferroptosis and lessening heart damage, which is abolished in EVs with knocked down miR-23a-3p expression (172) (Figure 3). Recently, cuproptosis has been identified as a novel non-apoptotic cell death process triggered primarily by intracellular copper accumulation (173). A relationship between copper overload and ferroptosis has been reported (174). A recent study identified 19 differentially expressed genes related to both copper overload and ferroptosis (CFRGs) in healthy individuals and those with AMI. Further research has identified the upregulation of immune-related CFRGs (CXCL2, DDIT3, DUSP1, CDKN1A, TLR4, and STAT3) in both animal models and patients, suggesting the potential of these genes as early diagnostic biomarkers for AMI. This evidence also indicates the interplay between cuproptosis and ferroptosis pathways in the development of MI (175). Recently, wang et al. have proposed an innovative treatment strategy for MI using the circASXL1 signaling network, UCMSC-EVs effectively repairs infarcted myocardium by stimulating CMs cell-cycle reentry and cytokinesis in a circASXL1-dependent manner (176).
4.5 Ameliorating cardiac remodeling
MiR-671 in ADMSC-EVs can directly bind to TGF-β receptor 2 and prevent SMAD2 phosphorylation, leading to decreased cell apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis, thereby alleviating MI-like symptoms both in vitro and in vivo models (177) (Figure 3). Low levels of miR-212-5p expression were detected in clinical and pathological samples, as well as in animal models of MI-induced cardiac fibrosis. ADAMTS16, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif 16, was found to activate latent TGF-β, accentuating fibrosis and cardiac function of the pressure-overloaded heart (178). BMMSC-EVs containing miR-212-5p (179) and miR-29b-3p (15) have been demonstrated to prevent myocardial fibrosis caused by MI by suppressing the NLRC5/VEGF/TGF-β1/SMAD pathway and reducing ADAMTS16 respectively. P53 is a target gene of miR-223, UCMSC-EVs containing miR-223 reduced myocardial fibrosis and inflammation in MI rat models and accelerated angiogenesis of HUVECs through the p53/S100A9 axis (180). Moreover, MSC-EVs can act directly on CFs and reduce fibrotic scar formation in the ischemic heart by regulating the secretion of fibronectin and collagen (181).
Xiao et al. have reported that BMMSC-EVs can improve heart remodeling and function after MI by modulating the balance of the RAS, specifically by upregulating ACE2-Ang1-7-Mas and downregulating the ACE-AngII-AT1R pathway, promoting the conversion of AngII to Ang1-7. This ultimately reduces Ang II-mediated adverse effects on CMs (182). The suppression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) by tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP2) is essential in the remodeling process after MI. According to reports, UCMSC-EVs with high levels of TIMP2 improve heart performance by reducing oxidative stress and ECM remodeling, in part through the AKT/secreted frizzled-related protein 2 (Sfrp2) pathway (183). Compared with the use of EVs or MSCs alone, the combined delivery of EVs and MSCs (first IM injection of EVs, followed by transplantation of MSCs into the heart) further reduced the collagen area, enhanced neovascularization, reduced infarct size, and improved cardiac function. This may be attributed to EVs improving the microenvironment and facilitating the recruitment and retention of MSCs. The optimal time for continuous stem cell delivery appears to be the third day after EVs treatment (184). Likewise, the use of BMMSC-EVs as carriers to deliver exogenous miR-19a/19b to infarcted tissues combined with MSCs transplantation reduced cardiac fibrosis and substantially improved cardiac function in mice with MI (185). Recently, Tcf21 has been identified as a critical target for improving cardiac fibrosis. LncRNA-Tcf21 antisense RNA inducing demethylation (TARID) that enriched in UCMSC-EVs was identified to up-regulate Tcf21 expression. Formulated lncRNA-TARID-laden lipid nanoparticles up-regulated Tcf21 expression in EPDCs and improved cardiac function and histology after MI in vivo (186).
5 Effects improvement strategies of MSC-EVs
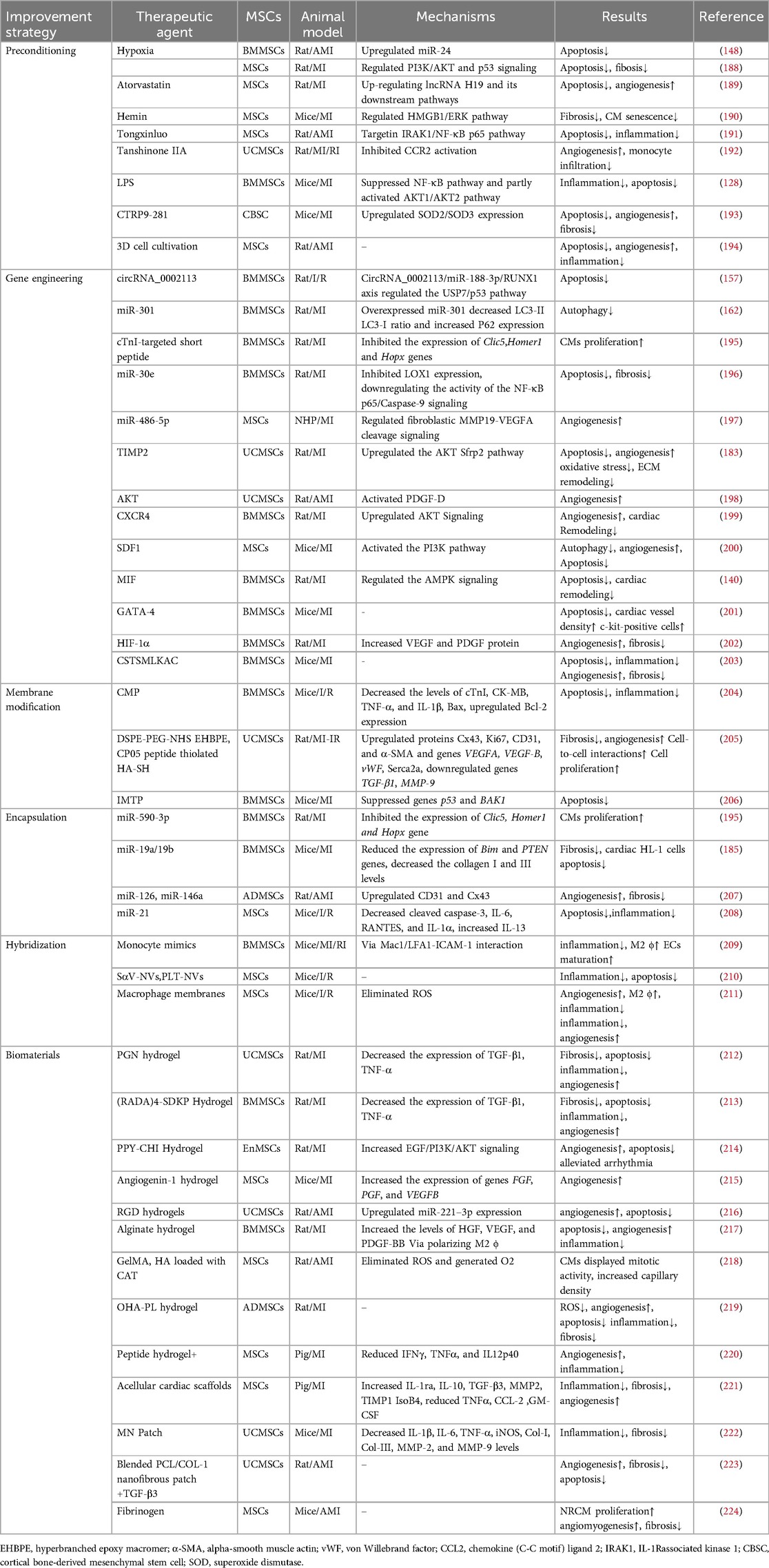
Despite the considerable therapeutic potential of natural MSC-EVs, limitations in their yield, targeting, on-demand delivery, and treatment feedback have hindered their widespread application (187). Therefore, it is important to improve the yield of EVs production and regulate their biological functions, current approaches including: preconditioning, gene engineering, membrane modification, encapsulation, hybridization and biomaterial-assisting (Table 1).
5.1 Preconditioning
The production and therapeutic properties of EVs are markedly influenced by the tissue source, donor cells and culture conditions. Preconditioning can help engineering specific MSC-EVs. Preprocessing can be achieved by exposing MSCs to drugs, cytokines, physiological stresses. Specific treatments include atorvastatin, hemin, tongxinluo, tanshinone IIA, LPS, C1q-TNFα related protein-9 (CTRP9), hypoxia, and three-dimensional (3D) cell cultivation (188–194, 206, 225). Preconditioning typically moduate the secretome of MSCs with altered cytokines, chemokines, enzymes, or growth factors secretion, as well as influence the EVs synthesis process to enrich specific miRNA in MSC-EVs. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB is a potent mitogen of MSCs, enhancing the cardioprotection of MSCs by suppressing the expression of miR-320 (226). Moreover, miRNAs regulated by preconditioning also affect the survival of MSCs and function of MSC-EVs. Ischemic preconditioning can induce the expression of miR-107 in MSCs, thereby significantly improving transplanted MSCs in infarcted myocardium (227). Compared with normoxia-conditioned BMMSC-EVs, hypoxia-conditioned BMMSC-EVs exhibited elevated expression of miR-125b-5p (206) and miR-210 (188), which reportedly facilitate ischemic cardiac repair by reducing CMs apoptosis. Low oxygen levels triggered the production of HMGB1 in BMMSC-EVs, which promotes angiogenesis via JNK/HIF-1α signaling (228). Studies have shown that IFNγ and hypoxic pretreatment can induce partial changes in miRNA in EVs in a donor dependent manner, but their effects are far less important than their impact on protein content (229). Preprocessing is believed to overcome inter-donor variability in MSCs function. However, not all donors have similar responses to pretreatment initiation, indicating the need to test and optimize pretreatment for each individual indication, and careful selection of donors may be necessary in allogeneic therapy. In addition, attention should be paid to the degree of hypoxia. Moderate hypoxia (3%–5% O2) has been shown to stimulate MSCs proliferation (230). However, a sharp decrease in oxygen tension (<1%) potentiated a glycolytic metabolism and cell quiescence (230).
By simulating the physiological environment of tissue morphology and intercellular interactions in vivo, 3D cultures can influence the biogenesis and function of EVs (231). The two primary categories of 3D cultures are static (e.g., hydrogels and fiber scaffolds) and dynamic (e.g., perfusion bioreactors and microcarrier-based stirred bioreactors) (232). Cultivating UCMSCs in scalable microcarrier-based 3D cultures has been found to result in an approximately 20-fold increase in EVs production when compared with two-dimensional (2D) cultures. Moreover, the combination of tangential flow filtration and 3D cultures can further enhance the EVs yield by 7-fold, resulting in a 7-fold improvement in the transfer of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to neurons. This evidence demonstrates the synergistic enhancement in the EVs yield and transport properties (233). Furthermore, MSC-EVs obtained from 3D cultures were found to exhibit enhanced immunomodulatory potential, as evidenced by previous studies (234, 235). Furthermore, a hollow-fiber bioreactor-based 3D cultures system has been proven to considerably boost the production of MSC-EVs, resulting in robust cardioprotective effects in rats with AMI (194).
5.2 Gene engineering
Gene engineering can adjust the expression and release of EVs in MSCs, allowing for targeted delivery to specific tissues. Transduction of lentivirus, plasmid, and adenovirus vectors into parental cells are successful methods for selectively altering the composition of MSC-EVs (236). EVs released from BMMSCs overexpressing miR-30e can improve myocardial injury, inhibit myocardial cell apoptosis and cardiac fibrosis after MI in rats (196). In non-human primate (NHP) MI models, EVs produced by MSCs overexpressing miR-486-5p demonstrated substantial improvements in cardiac function and angiogenesis, with no increase in the incidence of arrhythmia-related complications (197). Hu etal. have demonstrated that EVs derived from MSCs overexpressing islet-1(ISL1) (ISL1-MSC-EVs) have the independent ability of EC-protective and pro-angiogenic and angiogenin-1 hydrogel can retain ISL1-MSC-EVs in ischemic heart, improving the survival and angiogenesis of ECs and promoting heart repair (215). GATA-4-expressing BMMSC-EVs can induce BMMSCs differentiation into CM-like cells, reduce hypoxia-induced CMs apoptosis, and improve myocardial function post-MI (201). Studies have shown that EVs from MSCs with overexpressing HIF-1α has been found to enhance neovascularization and suppress myocardial fibrosis in rats with MI (202). In a rat model of AMI, EVs secreted by MSCs overexpressing AKT showed higher levels of PDGF-D, which promoted post-MI angiogenesis and substantially improved cardiac function (198). Furthermore, PDGF could stimulate ADMSCs to secrete EVs carrying c-kit and stem cell factors, enhancing their angiogenic capacity (237). CXCR4, a G-protein-coupled receptor, in conjunction with stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α serves as a major regulator of stem/progenitor cell activities. CXCR4-enriched MSC-EVs have been found to reduce MI-induced cell death and promote angiogenesis by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway both in vitro and in vivo. This finding suggests that CXCR4 plays a pivotal role in angiogenesis (199). Moreover, overexpression of SDF1 in MSC-EVs suppressed autophagy of ischemic CMs and promoted microvascular production of ECs (200).
Genetic manipulation of parental cells represents a method to obtain engineered EVs with target characteristics by recombining functional peptides with EVs membrane proteins or lipid-binding proteins/peptides and displaying functional peptides on the EVs surface (238). Lysosome-associated membrane protein 2b (Lamp2b) is the most frequently used membrane protein for decorating EVs with targeting moieties. Wang et al. fused the ischemia-targeting peptide (IMTP) CSTSMLKAC with Lamp2b and introduced it into MSCs through lentivirus-based vector. This substantially enhanced the targeting ability of EVs to both hypoxia-injured H9C2 cells and the ischemic myocardium, thereby suppressing inflammation and CMs apoptosis, reducing infarct size, and improving cardiac function in mouse MI models (203). In terms of peptides that cannot be effectively displayed on the EVs surface upon fusion with Lamp2b, the introduction of a glycosylation sequence at a specific position in the engineered fusion protein may enhance stability (239). Based on the high levels of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) detected in the infarct area, Wang et al. expressed a cTnI-targeted short peptide on the surface of MSCs through gene transfection to obtain cTnI-targeted EVs. Furthermore, hsa-miR-590-3p was incorporated into cTnI-targeted EVs via electroporation. Upon intravenous administration, these EVs containing hsa-miR-590-3p localized to the infarct area along the cTnI concentration gradient and were endocytosed by CMs, thereby promoting CMs proliferation in the peri-infarct area and improving cardiac function (195).
5.3 Membrane modification
The membrane modification of EVs can be achieved through methods such as click chemistry and lipid insertion. Lipophilic components can be easily inserted into the membrane. Especially, distearoyl phosphoethanolamine (DSPE) can be embedded into the phospholipid bilayer, thereby anchoring the attached components to the EVs surface. In order to protect CM specific peptides (CMP, WLSEAGPVVTVRALRGTGSW) from degradation, Gu et al. modified CMP with covalently bound 1, 2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamineN-[hydroxysuccinimidyl (polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG-NHS), and then linked the PEG modified protein peptide to the EVs. Subsequently, the miR-302 mimic was loaded into the engineered EVs using electroporation technology. Compared with unmodified EVs, engineered EVs can be more effectively taken up by CMs, promote CMs proliferation in vitro, reduce CM apoptosis and inflammatory response, and improve cardiac function after myocardial I/R injury (204). Targeting peptides or fluorescent molecules can be decorated on EVs surface through the click chemistry with these groups. Zou et al. synthesized a hyperbranched epoxy macromer grafted with an aniline tetramer to cross-link thiolated hyaluronic acid and thiolated UCMSC-EVs anchoring a CP05 peptide via an epoxy/thiol “click” reaction. The resulting Gel@Exo systemcan significantly result in a prominent therapeutic effect on MI-I/R (205). Zhu et al. conjugated EVs with a IMTP by bio-orthogonal chemistry, which showed specific targeting to the ischemic area and exerted a significant cardioprotective effect post-MI (206).
5.4 Encapsulation of medicinal agents
The methods for EVs loading mainly include incubation, electroporation and permeabilization (240, 241). Suitable packaging methods can be selected based on the properties of the packaging molecules. Small molecules can be introduced into EVs through incubation or ultrasound assistance. Macromolecules need to enter EVs by electroporation. Sun etal. have demonstrated that curcumin transported via EVs remains more stable and achieves higher concentrations in the bloodstream (242). Wang et al. used electroporation to load miR-590-3p into EVs for systemic administration in animal models of MI (195). However, it is important to note that this method may induce the formation of siRNA aggregates, which can affect loading efficiency (243). In a mouse model with MI, the combination of EVs loaded with miR-19a/19b and MSCs transplantation significantly promoted the repair of infarcted heart (185). In addition, ADMSC-EVs can be an effective nanoshuttle for miR-126 and miR-146a (207). CD47 enables cells to evade clearance by macrophages through CD47-signal regulatory protein α binding. EVs were isolated from MSCs overexpressing CD47 (CD47-EVs) and then loaded with miR-21a via electroporation, resulting in electro CD47-EVs. Exogenous miR-21 was efficiently internalized into CMs, leading to inhibition of apoptosis, reduced inflammation, and improved cardiac function after myocardial I/R (208).
5.5 Hybridization
EVs can readily be fused with other types of exogenous lipid membrane structures by extrusion, filtration or freeze-thaw cycles methods (244). This fusion combines the advantages of liposomes and EVs, improving their circulation stability and drug delivery efficiency (245, 246). Distinct from the original EVs, a kind of hybrid EVs with liposomes can be used as delivery systems for larger cargoes, such as CRISPR/Cas9 (247), expanding the scope of applications of EVs as drug delivery systems. Zhang et al. modified MSC-EVs with monocyte membrane by an incubation-extrusion method, resulting in hybrid EVs with regenerative potential of stem cells and inflammatory targeting characteristics of monocytes. The interaction between macrophage receptor 1 (Mac1)/lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA1)-intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)-induced adhesion and transmigration at least partly levered the targeting efficiency. This modification markedly enhanced the homing efficiency of EVs in injured hearts and effectively alleviated myocardial I/R injury in mice (209). Recently, Lai et al. (210) developed genetically modified hybrid nanovesicles (hNVs) that include cell-derived nanovesicles with high-affinity SIRPα variants (SαV-NVs), MSC-EVs, and nanovesicles from platelets (PLT-NVs). SαV-NVs suppressed CD47-SIRPα interaction, promoting macrophage phagocytosis of dead cells. EVs components can alleviate inflammation. Furthermore, PLT-NVs provide hNVs the ability to evade immune surveillance and selectively target the infarct areas. The combined effects of hNVs notably improved the LVEF on day 21 in an I/R mouse model, offering a simple, safe, and robust strategy for boosting cardiac repair. The liposome-based cellular engineering method can be achieved by engineering parental cells with membrane fusogenic liposomes to equip EVs with various functional agents, including drugs, fluorophores and bio-orthogonal chemicals (248). Zhang et al. constructed a hybrid cell-derived EVs (N@MEVs) that was composed of MSCs and macrophage membranes encompassed MitoN, a ROS scavenger, to boost the healing of the heart. Fixing l-arginine within N@MEVs further enhanced the potential for delivery to injured cardiac tissues. This combination therapy has demonstrated synergistic effects on cardiac repair and regeneration, specifically via the regulation of M2 ϕ, promotion of angiogenesis, and reduction of DNA damage, thereby restarting CMs proliferation (211).
5.6 Biomaterial-assisting
The therapeutic potential of MSC-EVs in cardiac repair has been constrained by limitations such as poor retention, brief biological half-life, necessity for repeated administration, and risk of secondary tissue damage (249). With the rapid development of biomaterials and tissue engineering, the combination of EVs with biomaterials can compensate for the shortcomings of EVs in specific applications of tissue repair. Injectable, biocompatible, hydrophilic, tunable, conductive, and compositionally versatile hydrogels serve as intriguing platforms for replicating cardiac ECM (250). In addition, hydrogels provide a controllable delivery system depending on the type of substrates used in their structures. Hydrogels can be used as injectable matrix for direct injection into injured myocardium and as myocardial patch placed on the surface of injured area. Polymer-based hydrogels infused with EVs, including hyaluronic acid (HA), gelatin, chitosan, silk, and alginate, are utilized to enhance cardiac healing (251). The use of hydrogels can enhance EVs stability and delivery to a specific injury site in a controlled and adjustable manner while enabling sustained in situ release.
Han et al. used a self-assembled peptide hydrogel (PGN hydrogel) to encapsulate UCMSC-EVs. Administering the EVs/PGN hydrogel mixture into the infarcted area improved cardiac function, as evidenced by a reduction in inflammation, fibrosis, and apoptosis, as well as an increase in angiogenesis (212). In rats with MI, cardiac function was improved after IM injection of MSC-EVs alone or in conjunction with (RADA)4-SDKP hydrogel (213). Following MI, scar formation in and around the infarction disrupts electrical signal propagation, leading to desynchronized cardiac activation and contraction (252). Conductive hydrogels have the potential to restore electrical impulse propagation during MI, preventing arrhythmias and protecting ventricular function (253, 254). Zou et al. formulated an injectable conductive hydrogel containing thiolated CP05 peptide to anchor UCMSC-EVs. The electrical activity of the hydrogel effectively improved the polarization of connexion 43 (Cx43) in cell-cell interactions, suppressing the risk of arrhythmias. In addition, the hydrogel enhanced EVs retention, consequently improving cardiac function and promoting vascular regeneration after I/R (205). Yan et al. developed an injectable hydrogel by incorporating EnMSC-EVs into polypyrrole chitosan (PPY-CHI). This synergistic combination of EVs and PPY-CHI improved cardiac function, as evidenced by the promotion of angiogenesis, inhibition of cell apoptosis, and resynchronization of electrical conduction (214). EVs from MSCs overexpressing HIF-1α can promote the angiogenesis and the apoptosis of CMs via upregulating the expression of miR-221-3p. RGD hydrogels can enhance the therapeutic efficacy of HIF-1α engineered MSC-EVs (216). IM injection the sodium alginate hydrogel incorporated with MSC-EVs enhanced the reparative potency of MSC-EVs in pro-angiogenesis, reducing fibrosis and improving cardiac function after MI (217). Recently, Wang et al. have discovered that MSC-EVs encapsulated gelatin methacryloyl/HA blended and oxygen releasing injectable hydrogel by CMs induction and vascularization in rat MI model (218). Ren etal. have demonstrated that an injectable ADMSC-EVs loaded HA-polylysine hydrogel for cardiac repair via modulating oxidative stress and the inflammatory microenvironment after MI (219).
Decellularized cardiac scaffold is a source of biological ECM derived from natural heart tissue, with conserved ECM structures and functional cardiac ECM components (255). The combination of MSC-EVs and decellularized heart tissue represents a hopeful tissue engineering approach, capable of locally administering MSC-EVs and boosting their therapeutic impact to recover cardiac function post-MI. Porcine heart adipose tissue-derived MSC-EVs (cATMSC-EVs) and peptide hydrogels were embedded in acellular porcine pericardial scaffolds for local myocardial delivery. Subsequently, the engineered scaffolds were administered to the ischemic myocardium of a pig model of MI. Six days after implantation, the designed scaffolds integrated into the infarcted heart tissue, resulting in an increase in vascular density and a reduction in macrophage and T-cell infiltration within the damaged myocardium (220). The same research group subsequently evaluated the long-term functional impact of cATMSC-EVs acellular cardiac scaffolds in a porcine MI model. The authors discovered that cATMSC-EVs enhanced post-MI right ventricular ejection fraction and ventricular dilation while also alleviating adverse cardiac remodeling. Remarkably, cATMSC-EVs also modulated the expression of inflammatory mediators and fibrosis modulators (221).
Cardiac patches provide an efficient method for administering treatments directly to the cardiac tissue. Yuan et al. designed a biocompatible gelatin-based microneedle (MN) patch loaded with UCMSC-EVs containing miRNA-29b mimics. The implantation of the MN patch into the infarcted hearts of mice resulted in increased EVs retention in the infarcted area, reducing inflammation, infarct size and fibrosis, and improving cardiac function (222). Guan et al. developed a blended polycaprolactone/type I collagen (PCL/COL-1) nanofibrous patch loaded with TGF-β3 and UCMSC-EVs (Exo@TGF-β3@NFs). Exo@TGF-β3/NFs upregulated genes involved in angiogenesis and mesenchymal differentiation in vitro. Four weeks post-transplantation, Exo@TGF-β3@NFs resulted in elevated LVEF and fraction shortening in vivo. Furthermore, Exo@TGF-β3@NFs could substantially reduce the size of MI, inhibit fibrosis, and increase scar thickness (223). Yao et al. designed and tested a minimally invasive EVs spray using MSC-EVs and biomaterials. In a mouse model of AMI, administration of this spray via thoracoscopy improved cardiac function, reduced fibrosis, and promoted endogenous angiomyogenesis in the post-MI heart. This delivery method was found to increase the retention of EVs and reduce surgical stress and inflammatory responses (224). Born et al. have demonstrated that MSC-EVs can be incorporated into a 3D-printed gelatin methacrylate (GelMA) hydrogel bioink while retaining their bioactivity. By increasing the crosslinker concentration, the initial burst release of EVs can be reduced during gelation (256).
6 Clinical trials of EVs in MI or I/R
Due to the inherent complexity of its mechanism of action, the application of EVs in the treatment of CVD has considerable appeal. EVs are being examined in clinical trials to assess their safety and efficacy as therapeutic agents. Nevertheless, clinical trials of EVs for cardiac indications are still in their early stages, and evidence supporting their clinical application in patients with MI or I/R is limited. As of August 2024, based on information from https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (Table 2). An ongoing trial (NCT05669144) is investigating the combined transplantation of mitochondria and administration of MSC-EVs in candidates for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. Patients in the experimental group will receive co-transplantation IM and IC injection of EVs (1 ml of EVs containing 100 μg of EVs) and mitochondria(1 ml of EVs containing 10 million mitochondria). Twenty patients will be recruited and the evaluation of the patient's recovery will be performed 1 month after the surgery. There are also some studies about EVs and MI or IR. A single-center study in the United States (NCT04327635) is aiming to assess the safety of purified EVs (PEP) derived from stored human blood in patients undergoing coronary stent implantation. Twelve patients who undergo PCI will be treated with a single dose of PEP within 20 min after stent placement or post-dilation. The study will conduct a one-year follow-up to evaluate the dose-limiting toxicity and maximum tolerated dose of PEP with increasing concentrations of EVs. In addition, the study plans to assess infarct size and EF, as well as monitor the alloimmune response. A French study (NCT05774509) plans to evaluate the safety and efficacy of three IVs of EVs-enriched secretome (20 × 10E9 particles/kg for each infusion) of CPCs in severely symptomatic patients with drug-refractory left ventricular dysfunction secondary to non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Another registered trial (NCT04127591) aims to determine the expression profile of miRNAs in peripheral blood EVs of patients with MI and investigate their relationship with MI. Furthermore, a multicenter observational prospective study (NCT06070974) plans to assess the potential of plasma EVs in identifying patients at a high risk of adverse remodeling following STEMI at an early stage. This could facilitate appropriate patient management and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Consecutive patients with STEMI will be enrolled three days after PCI to investigate the correlation between the EVs profile and the severity of MI. A Phase IV trial (NCT02931045) examined the concentrations of platelet EVs, c-reactive protein, IL-6, and elastase in patients after 6 months of antiplatelet therapy with ticagrelor or clopidogrel. The objective of this study is to identify an additional mechanism of the action of ticagrelor, which might contribute to the observed clinical benefits in patients treated with ticagrelor. Although the safety of cardiac or intravenous injections of EVs has been assessed in clinical trials, notable concerns regarding the safety and tolerability of repeated injections remain.
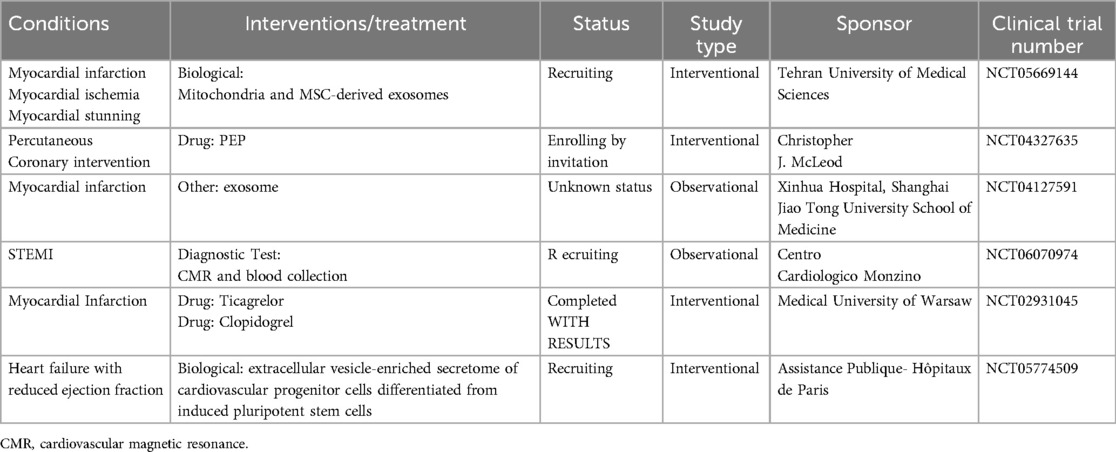
Table 2. Clinical trials of extracellular vesicles for cardiac indications (clinicalTrials.gov).
Compared with parental cells, MSC-EVs have several potential advantages: relative safety, because they cannot replicate and their smaller size allows them to pass through capillaries without clogging (257); low immunogenicity and easy to store, they can be stored at −20°C for up to 6 months without significant damage (258); they can transit physiological barriers, such as the blood-brain barrier (259). However, there are still several factors to be addressed for effective clinical translation, including production, isolation, dosage and administration method of MSC-EVs (260). In addition, although the safety of cardiac or intravenous injections of EVs has been assessed in clinical trials, notable concerns regarding the safety and tolerability of repeated injections remain. Improving the biological benefits of MSC-EVs by engineering parental cells or post-production EVs and improving the delivery of EVs by encapsulation in biomaterial to prolong their efficacy, which may help to promote their clinical translation.
7 Conclusions
Over the past decade, significant progress has been made in the understanding of the biology of EVs and their important role in cardiovascular pathology and physiology. As multifunctional carriers of molecular signals, EVs from cardiac cells can either transmit both protective and damaged signals in MI. Moreover, it has been well-recognised that MSC-EVs have great potential in the treatment of MI, potential mechanisms including promoting angiogenesis, mitigating inflammation and oxidative stress, inhibiting cell death and improving cardiac remodeling, typically indicating that EVs are as effective as their parental cells.
However, there are still many challenges such as the isolation and characterization of clinical grade biological products EVs, scalable production, and batch standardization. Maldistribution of EVs within the body after systemic administration is also a challenge for achieving targeted drug delivery. In addition, despite preclinical studies on EVs demonstrating the apparent lack of immunotoxicity, immunological clearance remains largely unexplored. The rapidly growing EVs therapeutics and drug delivery systems requires an understanding of undesired immunogenicity, which is critical for the development of safe and efficient clinical products. The use of immortalized cell lines can minimize variability of EVs to improve the reproducibility of clinical outcomes. We know little about how cardiovascular pathophysiology changes the EVs biology, how EVs derived from different types of myocardial cells mediate intercellular communication in damaged myocardium and how MSC-EVs are designed to maximize their beneficial effects in the hypoxic/ischemic microenvironment. It is still unclear whether specific promotion or inhibition of EVs production will be beneficial for MI. The progress in these fields not only helps to reveal previously unknown mechanisms of CVDs, but also lead to new treatment methods to improve clinical outcomes. The development of technologies could provide novel insights into EVs biology and the clinical applications of MSC-EVs, paving the way for developing personalized precision medicine.
Author contributions
DQ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Visualization, Writing – original draft. JP: Validation, Writing – original draft. HH: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Major Projects of the Sichuan Provincial Health Commission (21ZD004) and the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province Project (2021YJ0208).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 update. Circulation. (2021) 143(8):e254–743. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950
2. Bouisset F, Ruidavets J-B, Dallongeville J, Moitry M, Montaye M, Biasch K, et al. Comparison of short- and long-term prognosis between ST-elevation and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. J Clin Med. (2021) 10(2):180. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020180
3. Christensen DM, Schjerning A-M, Smedegaard L, Charlot MG, Ravn PB, Ruwald AC, et al. Long-term mortality, cardiovascular events, and bleeding in stable patients 1 year after myocardial infarction: a Danish nationwide study. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(6):488–98. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac667
4. Pinto AR, Ilinykh A, Ivey MJ, Kuwabara JT, D’Antoni ML, Debuque R, et al. Revisiting cardiac cellular composition. Circ Res. (2016) 118(3):400–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307778
5. Cui M, Han Y, Yang J, Li G, Yang C. A narrative review of the research status of exosomes in cardiovascular disease. Ann Palliat Med. (2022) 11(1):363–77. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3364
6. Stewart MC, Stewart AA. Mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics, sources, and mechanisms of action. Vet Clin N Am Equine Pract. (2011) 27(2):243–61. doi: 10.1016/j.cveq.2011.06.004
7. Deans RJ, Moseley BA. Mesenchymal stem cells_ biology and potential clinical uses. Exp Hematol. (2000) 28(8):875–84. doi: 10.1016/S0301-472X(00)00482-3
8. McGinley LM, McMahon J, Stocca A, Duffy A, Flynn A, O'Toole D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell survival in the infarcted heart is enhanced by lentivirus vector-mediated heat shock protein 27 expression. Hum Gene Ther. (2013) 24(10):840–51. doi: 10.1089/hum.2011.009
9. Zangi L, Margalit R, Reich-Zeliger S, Bachar-Lustig E, Beilhack A, Negrin R, et al. Direct imaging of immune rejection and memory induction by allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. (2009) 27(11):2865–74. doi: 10.1002/stem.217
10. Cui L-l, Kerkelä E, Bakreen A, Nitzsche F, Andrzejewska A, Nowakowski A, et al. The cerebral embolism evoked by intra-arterial delivery of allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats is related to cell dose and infusion velocity. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2015) 6(1):11. doi: 10.1186/scrt544
11. Breitbach M, Bostani T, Roell W, Xia Y, Dewald O, Nygren JM, et al. Potential risks of bone marrow cell transplantation into infarcted hearts. Blood. (2007) 110(4):1362–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-063412
12. Madonna R, Van Laake LW, Davidson SM, Engel FB, Hausenloy DJ, Lecour S, et al. Position paper of the European Society of Cardiology working group cellular biology of the heart: cell-based therapies for myocardial repair and regeneration in ischemic heart disease and heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37(23):1789–98. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw113
13. Eleuteri S, Fierabracci A. Insights into the secretome of mesenchymal stem cells and its potential applications. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20(18):4597. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184597
14. Zou L, Ma X, Lin S, Wu B, Chen Y, Peng C. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect against myocardial infarction by promoting autophagy. Exp Ther Med. (2019) 18:2574–82. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7874
15. Zheng J, Zhang X, Cai W, Yang Y, Guo T, Li J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-29b-3p promotes angiogenesis and ventricular remodeling in rats with myocardial infarction by targeting ADAMTS16. Cardiovasc Toxicol. (2022) 22(8):689–700. doi: 10.1007/s12012-022-09745-7
16. Jeppesen DK, Fenix AM, Franklin JL, Higginbotham JN, Zhang Q, Zimmerman LJ, et al. Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell. (2019) 177(2):428–45.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.029
17. Jeppesen DK, Zhang Q, Franklin JL, Coffey RJ. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. (2023) 33(8):667–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.01.002
18. van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2018) 19(4):213–28. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.125
19. Ma L, Li Y, Peng J, Wu D, Zhao X, Cui Y, et al. Discovery of the migrasome, an organelle mediating release of cytoplasmic contents during cell migration. Cell Res. (2015) 25(1):24–38. doi: 10.1038/cr.2014.135
20. Melentijevic I, Toth ML, Arnold ML, Guasp RJ, Harinath G, Nguyen KC, et al. C. elegans neurons jettison protein aggregates and mitochondria under neurotoxic stress. Nature. (2017) 542 (7641):367–71. doi: 10.1038/nature21362
21. Jiao H, Jiang D, Hu X, Du W, Ji L, Yang Y, et al. Mitocytosis, a migrasome-mediated mitochondrial quality-control process. Cell. (2021) 184(11):2896–910.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.027
22. Zhang Q, Higginbotham JN, Jeppesen DK, Yang Y-P, Li W, McKinley ET, et al. Transfer of functional cargo in exomeres. Cell Rep. (2019) 27(3):940–54.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.009
23. Zhang Q, Jeppesen DK, Higginbotham JN, Graves-Deal R, Trinh VQ, Ramirez MA, et al. Supermeres are functional extracellular nanoparticles replete with disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat Cell Biol. (2021) 23(12):1240–54. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00805-8
24. Aheget H, Tristán-Manzano M, Mazini L, Cortijo-Gutierrez M, Galindo-Moreno P, Herrera C, et al. Exosome: a new player in translational nanomedicine. J Clin Med. (2020) 9(8):2380. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082380
25. Larios J, Mercier V, Roux A, Gruenberg J. ALIX- and ESCRT-III–dependent sorting of tetraspanins to exosomes. J Cell Biol. (2020) 219(3):1. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201904113
26. Marsh M, van Meer G. No ESCRTs for exosomes. Science. (2008) 319 (5867):1191–2. doi: 10.1126/science.1155750
27. Stuffers S, Sem Wegner C, Stenmark H, Brech A. Multivesicular endosome biogenesis in the absence of ESCRTs. Traffic. (2009) 10(7):925–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00920.x
28. Kamei N, Nishimura H, Matsumoto A, Asano R, Muranaka K, Fujita M, et al. Comparative study of commercial protocols for high recovery of high-purity mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle isolation and their efficient labeling with fluorescent dyes. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. (2021) 35:102396. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2021.102396
29. Mol EA, Goumans M-J, Doevendans PA, Sluijter JPG, Vader P. Higher functionality of extracellular vesicles isolated using size-exclusion chromatography compared to ultracentrifugation. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. (2017) 13(6):2061–5. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2017.03.011
30. Welsh JA, Goberdhan DCI, O'Driscoll L, Buzas EI, Blenkiron C, Bussolati B, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): from basic to advanced approaches. J Extracell Vesicles. (2024) 13(2):e12404. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12404
31. Bauzá-Martinez J, Heck AJR, Wu W. HLA-B and cysteinylated ligands distinguish the antigen presentation landscape of extracellular vesicles. Commun Biol. (2021) 4(1):825. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02364-y
32. Palviainen M, Saari H, Kärkkäinen O, Pekkinen J, Auriola S, Yliperttula M, et al. Metabolic signature of extracellular vesicles depends on the cell culture conditions. J Extracell Vesicles. (2019) 8(1):1596669. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1596669
33. Nabhan JF, Hu R, Oh RS, Cohen SN, Lu Q. Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2012) 109(11):4146–51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200448109
34. Wang Q, Yu J, Kadungure T, Beyene J, Zhang H, Lu Q. ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules. Nat Commun. (2018) 9(1):960. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03390-x
35. Sisirak V, Sally B, D’Agati V, Martinez-Ortiz W, Özçakar ZB, David J, et al. Digestion of chromatin in apoptotic cell microparticles prevents autoimmunity. Cell. (2016) 166(1):88–101. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.034
36. Huang Y, Zucker B, Zhang S, Elias S, Zhu Y, Chen H, et al. Migrasome formation is mediated by assembly of micron-scale tetraspanin macrodomains. Nat Cell Biol. (2019) 21(8):991–1002. doi: 10.1038/s41556-019-0367-5
37. Mathieu M, Névo N, Jouve M, Valenzuela JI, Maurin M, Verweij FJ, et al. Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9. Nat Commun. (2021) 12(1):4389. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24384-2
38. L. Ramos T, Sánchez-Abarca LI, Muntión S, Preciado S, Puig N, López-Ruano G, et al. MSC surface markers (CD44, CD73, and CD90) can identify human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles by conventional flow cytometry. Cell Commun Signaling. (2016) 14(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0124-8
39. Tóth EÁ, Turiák L, Visnovitz T, Cserép C, Mázló A, Sódar BW, et al. Formation of a protein corona on the surface of extracellular vesicles in blood plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. (2021) 10(11):e12140. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12140
40. Heidarzadeh M, Zarebkohan A, Rahbarghazi R, Sokullu E. Protein corona and exosomes: new challenges and prospects. Cell Commun Signal. (2023) 21(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01089-1
41. Buzas EI. Opportunities and challenges in studying the extracellular vesicle corona. Nat Cell Biol. (2022) 24(9):1322–5. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00983-z
42. Liam-Or R, Faruqu FN, Walters A, Han S, Xu L, Wang JT-W, et al. Cellular uptake and in vivo distribution of mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived extracellular vesicles are protein corona dependent. Nat Nanotechnol. (2024) 19(6):846–55. doi: 10.1038/s41565-023-01585-y
43. Shi M-m, Yang Q-y, Monsel A, Yan J-y, Dai C-x, Zhao J-y, et al. Preclinical efficacy and clinical safety of clinical-grade nebulized allogenic adipose mesenchymal stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. (2021) 10(10):e12134. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12134
44. de Abreu RC, Fernandes H, da Costa Martins PA, Sahoo S, Emanueli C, Ferreira L. Native and bioengineered extracellular vesicles for cardiovascular therapeutics. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2020) 17(11):685–97. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0389-5
45. Bertolino GM, Maumus M, Jorgensen C, Noël D. Recent advances in extracellular vesicle-based therapies using induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomedicines. (2022) 10(9):2281. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092281
46. Felekkis K, Touvana E, Stefanou C, Deltas C. microRNAs: a newly described class of encoded molecules that play a role in health and disease. Hippokratia. (2010) 14(4):236–40.21311629
47. Ribeiro-Rodrigues TM, Laundos TL, Pereira-Carvalho R, Batista-Almeida D, Pereira R, Coelho-Santos V, et al. Exosomes secreted by cardiomyocytes subjected to ischaemia promote cardiac angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. (2017) 113(11):1338–50. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx118
48. Geng T, Song Z-Y, Xing J-X, Wang B-X, Dai S-P, Xu Z-S. Exosome derived from coronary serum of patients with myocardial infarction promotes angiogenesis through the miRNA-143/IGF-IR pathway. Int J Nanomed. (2020) 15:2647–58. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S242908
49. Wang Y, Zhao R, Liu W, Wang Z, Rong J, Long X, et al. Exosomal circHIPK3 released from hypoxia-pretreated cardiomyocytes regulates oxidative damage in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via the miR-29a/IGF-1 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2019) 2019:1–28. doi: 10.1155/2019/7954657
50. Shyu KG, Wang BW, Fang WJ, Pan CM, Lin CM. Hyperbaric oxygen-induced long non-coding RNA MALAT1 exosomes suppress microRNA-92a expression in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24(22):12945–54. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15889
51. Gou L, Xue C, Tang X, Fang Z. Inhibition of exo-miR-19a-3p derived from cardiomyocytes promotes angiogenesis and improves heart function in mice with myocardial infarction via targeting HIF-1α. Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12(23):23609–18. doi: 10.18632/aging.103563
52. Li H, Liao Y, Gao L, Zhuang T, Huang Z, Zhu H, et al. Coronary serum exosomes derived from patients with myocardial ischemia regulate angiogenesis through the miR-939-mediated nitric oxide signaling pathway. Theranostics. (2018) 8(8):2079–93. doi: 10.7150/thno.21895
53. Loyer X, Zlatanova I, Devue C, Yin M, Howangyin K-Y, Klaihmon P, et al. Intra-cardiac release of extracellular vesicles shapes inflammation following myocardial infarction. Circ Res. (2018) 123(1):100–6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311326
54. Chen C, Cai S, Wu M, Wang R, Liu M, Cao G, et al. Role of cardiomyocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-146a-5p in macrophage polarization and activation. Dis Markers. (2022) 2022:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2022/2948578
55. Sun S, Wu Y, Maimaitijiang A, Huang Q, Chen Q. Ferroptotic cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes promote cardiac macrophage M1 polarization during myocardial infarction. PeerJ. (2022) 10:e13717. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13717
56. Morelli MB, Shu J, Sardu C, Matarese A, Santulli G. Cardiosomal microRNAs are essential in post-infarction myofibroblast phenoconversion. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21(1):201. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010201
57. Guo Y, Bie Z-D, Li X. Hypoxic cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes regulate cardiac fibroblast activation, apoptosis, migration and ferroptosis through miR-208a/b. Gen Physiol Biophys. (2023) 42(02):149–58. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2022061
58. Wang X, Morelli MB, Matarese A, Sardu C, Santulli G. Cardiomyocyte-derived exosomal microRNA-92a mediates post-ischemic myofibroblast activation both in vitro and ex vivo. ESC Heart Fail. (2020) 7(1):285–9. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.12584
59. Kenneweg F, Bang C, Xiao K, Boulanger CM, Loyer X, Mazlan S, et al. Long noncoding RNA-enriched vesicles secreted by hypoxic cardiomyocytes drive cardiac fibrosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2019) 18:363–74. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.09.003
60. Xu Y, Wu A, Chen J, Song X, Chen M, Liu Q, et al. Limb-bud and heart (LBH) upregulation in cardiomyocytes under hypoxia promotes the activation of cardiac fibroblasts via exosome secretion. Mediat Inflamm. (2022) 2022:1–16. doi: 10.1155/2022/8939449
61. Wang L, Zhang J. Exosomal lncRNA AK139128 derived from hypoxic cardiomyocytes promotes apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation in cardiac fibroblasts. Int J Nanomed. (2020) 15:3363–76. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S240660
62. Li J, Salvador AM, Li G, Valkov N, Ziegler O, Yeri A, et al. Mir-30d regulates cardiac remodeling by intracellular and paracrine signaling. Circ Res. (2021) 128(1):e1–23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317244
63. Yang Y, Li Y, Chen X, Cheng X, Liao Y, Yu X. Exosomal transfer of miR-30a between cardiomyocytes regulates autophagy after hypoxia. J Mol Med. (2016) 94(6):711–24. doi: 10.1007/s00109-016-1387-2
64. Yu DW, Ge PP, Liu AL, Yu XY, Liu TT. HSP20-mediated cardiomyocyte exosomes improve cardiac function in mice with myocardial infarction by activating AKT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23(11):4873–81. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201906_18075
65. Jung J-H, Ikeda G, Tada Y, von Bornstädt D, Santoso MR, Wahlquist C, et al. miR-106a–363 cluster in extracellular vesicles promotes endogenous myocardial repair via Notch3 pathway in ischemic heart injury. Basic Res Cardiol. (2021) 116(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00858-8
66. Cheng M, Yang J, Zhao X, Zhang E, Zeng Q, Yu Y, et al. Circulating myocardial microRNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nat Commun. (2019) 10(1):959. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08895-7
67. Li Z, Huo X, Chen K, Yang F, Tan W, Zhang Q, et al. Profilin 2 and endothelial exosomal profilin 2 promote angiogenesis and myocardial infarction repair in mice. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:781753. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.781753
68. Yue Y, Wang C, Benedict C, Huang G, Truongcao M, Roy R, et al. Interleukin-10 deficiency alters endothelial progenitor cell–derived exosome reparative effect on myocardial repair via integrin-linked kinase enrichment. Circ Res. (2020) 126(3):315–29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315829
69. Wang H, Cao N, Spencer CI, Nie B, Ma T, Xu T, et al. Small molecules enable cardiac reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts with a single factor, Oct4. Cell Rep. (2014) 6(5):951–60. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.038
70. Jayawardena T, Mirotsou M, Dzau VJ. Direct Reprogramming of Cardiac Fibroblasts to Cardiomyocytes Using MicroRNAs. In: Stem Cell Transcriptional Networks. (2014) 1150:263–72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0512-6_18
71. Huang Y, Chen L, Feng Z, Chen W, Yan S, Yang R, et al. EPC-derived exosomal miR-1246 and miR-1290 regulate phenotypic changes of fibroblasts to endothelial cells to exert protective effects on myocardial infarction by targeting ELF5 and SP1. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.647763
72. Ke X, Yang R, Wu F, Wang X, Liang J, Hu X, et al. Exosomal miR-218–5p/miR-363–3p from endothelial progenitor cells ameliorate myocardial infarction by targeting the p53/JMY signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2021) 2021:1–23. doi: 10.1155/2021/5529430
73. Qiao S, Zhang W, Yin Y, Wei Z, Chen F, Zhao J, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from Krüppel-like factor 2-overexpressing endothelial cells attenuate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by preventing Ly6Chigh monocyte recruitment. Theranostics. (2020) 10(25):11562–79. doi: 10.7150/thno.45459
74. Su Q, Lv X-W, Xu Y-L, Cai R-P, Dai R-X, Yang X-H, et al. Exosomal LINC00174 derived from vascular endothelial cells attenuates myocardial I/R injury via p53-mediated autophagy and apoptosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2021) 23:1304–22. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.02.005
75. Ishigami S, Ohtsuki S, Tarui S, Ousaka D, Eitoku T, Kondo M, et al. Intracoronary autologous cardiac progenitor cell transfer in patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Circ Res. (2015) 116(4):653–64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.304671
76. Malliaras K, Makkar RR, Smith RR, Cheng K, Wu E, Bonow RO, et al. Intracoronary cardiosphere-derived cells after myocardial infarction: evidence for therapeutic regeneration in the final 1-year results of the CADUCEUS trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63(2):110–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.08.724
77. Barile L, Cervio E, Lionetti V, Milano G, Ciullo A, Biemmi V, et al. Cardioprotection by cardiac progenitor cell-secreted exosomes: role of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114(7):992–1005. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy055
78. Xiao J, Pan Y, Li XH, Yang XY, Feng YL, Tan HH, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7(6):e2277. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.181
79. Chen L, Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhang L, Shen C, Qin G, et al. Cardiac progenitor-derived exosomes protect ischemic myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2013) 431(3):566–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.015
80. Aguilar S, García-Olloqui P, Amigo-Morán L, Torán JL, López JA, Albericio G, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell exosomal miR-935 protects against oxidative stress. Cells. (2023) 12(18):2300. doi: 10.3390/cells12182300
81. Izarra A, Moscoso I, Levent E, Cañón S, Cerrada I, Díez-Juan A, et al. miR-133a enhances the protective capacity of cardiac progenitors cells after myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Rep. (2014) 3(6):1029–42. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.10.010
82. Barile L, Lionetti V, Cervio E, Matteucci M, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2014) 103(4):530–41. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu167
83. Vrijsen KR, Sluijter JPG, Schuchardt MWL, Van Balkom BWM, Noort WA, Chamuleau SAJ, et al. Cardiomyocyte progenitor cell-derived exosomes stimulate migration of endothelial cells. J Cell Mol Med. (2010) 14:1064–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01081.x
84. Youn S-W, Li Y, Kim Y-M, Sudhahar V, Abdelsaid K, Kim HW, et al. Modification of cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes by miR-322 provides protection against myocardial infarction through Nox2-dependent angiogenesis. Antioxidants. (2019) 8(1).
85. Gray WD, French KM, Ghosh-Choudhary S, Maxwell JT, Brown ME, Platt MO, et al. Identification of therapeutic covariant microRNA clusters in hypoxia-treated cardiac progenitor cell exosomes using systems biology. Circ Res. (2015) 116(2):255–63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.304360
86. Dougherty JA, Patel N, Kumar N, Rao SG, Angelos MG, Singh H, et al. Human cardiac progenitor cells enhance exosome release and promote angiogenesis under physoxia. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:130. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00130
87. Emmert MY, Burrello J, Wolint P, Hilbe M, Andriolo G, Balbi C, et al. Intracoronary delivery of extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells reduces infarct size in porcine acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2024) 45(9):728–32. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad636
88. Ibrahim AG-E, Cheng K, Marbán E. Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Rep. (2014) 2(5):606–19. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.04.006
89. Namazi H, Mohit E, Namazi I, Rajabi S, Samadian A, Hajizadeh-Saffar E, et al. Exosomes secreted by hypoxic cardiosphere-derived cells enhance tube formation and increase pro-angiogenic miRNA. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119(5):4150–60. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26621
90. Cambier L, de Couto G, Ibrahim A, Echavez AK, Valle J, Liu W, et al. Y RNA fragment in extracellular vesicles confers cardioprotection via modulation of IL-10 expression and secretion. EMBO Mol Med. (2017) 9(3):337–52. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606924
91. Mentkowski KI, Mursleen A, Snitzer JD, Euscher LM, Lang JK. CDC-derived extracellular vesicles reprogram inflammatory macrophages to an arginase 1-dependent proangiogenic phenotype. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2020) 318(6):H1447–60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00155.2020
92. de Couto G, Gallet R, Cambier L, Jaghatspanyan E, Makkar N, Dawkins JF, et al. Exosomal microRNA transfer into macrophages mediates cellular postconditioning. Circulation. (2017) 136(2):200–14. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024590
93. Tseliou E, Fouad J, Reich H, Slipczuk L, de Couto G, Aminzadeh M, et al. Fibroblasts rendered antifibrotic, antiapoptotic, and angiogenic by priming with cardiosphere-derived extracellular membrane vesicles. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2015) 66(6):599–611. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.05.068
94. Gallet R, Dawkins J, Valle J, Simsolo E, de Couto G, Middleton R, et al. Exosomes secreted by cardiosphere-derived cells reduce scarring, attenuate adverse remodelling, and improve function in acute and chronic porcine myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. (2016) 38:201–11. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw240
95. Dawkins JF, Ehdaie A, Rogers R, Soetkamp D, Valle J, Holm K, et al. Biological substrate modification suppresses ventricular arrhythmias in a porcine model of chronic ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. (2022) 43(22):2139–56. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac042
96. Liu S, Chen J, Shi J, Zhou W, Wang L, Fang W, et al. M1-like macrophage-derived exosomes suppress angiogenesis and exacerbate cardiac dysfunction in a myocardial infarction microenvironment. Basic Res Cardiol. (2020) 115(2):22. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-0781-7
97. Wang C, Zhang C, Liu L, A X, Chen B, Li Y, et al. Macrophage-derived mir-155-containing exosomes suppress fibroblast proliferation and promote fibroblast inflammation during cardiac injury. Mol Ther. (2017) 25(1):192–204. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.09.001
98. He X, Liu S, Zhang Z, Liu Q, Dong J, Lin Z, et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes inhibit cardiomyocyte proliferation through delivering miR-155. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2024) 24(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03893-0
99. Guo H, Li Z, Xiao B, Huang R. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote angiogenesis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biol Direct. (2024) 19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00485-y
100. Long R, Gao L, Li Y, Li G, Qin P, Wei Z, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry miR-1271-5p to alleviate cardiac injury in acute myocardial infarction through down-regulating SOX6. Mol Immunol. (2021) 136:26–35. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.05.006
101. Wang Y, Li C, Zhao R, Qiu Z, Shen C, Wang Z, et al. Circube3a from M2 macrophage-derived small extracellular vesicles mediates myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2021) 11(13):6315–33. doi: 10.7150/thno.52843
102. Luo H, Li X, Li T, Zhao L, He J, Zha L, et al. Exosomes/microvesicles microRNA-423-3p derived from cardiac fibroblasts mediates the cardioprotective effects of ischemic postconditionin. Cardiovasc Res. (2019) 115(7):1189–204. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy231
103. Liu N, Xie L, Xiao P, Chen X, Kong W, Lou Q, et al. Cardiac fibroblasts secrete exosome microRNA to suppress cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem. (2022) 477(4):1249–60. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04343-7
104. Yaping XU, Guotian YIN, Dandan JIA, Jintao DOU, Xinyi LIU, Zhikun GUO. Fibroblast-derived exosomal miRNA-133 promotes cardiomyocyte-like differentiation. Acta Histochem. (2022) 124(6):151931. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2022.151931
105. Cosme J, Guo H, Hadipour-Lakmehsari S, Emili A, Gramolini AO. Hypoxia-induced changes in the fibroblast secretome, exosome, and whole-cell proteome using cultured, cardiac-derived cells isolated from neonatal mice. J Proteome Res. (2017) 16(8):2836–47. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00144
106. Papini G, Furini G, Matteucci M, Biemmi V, Casieri V, Di Lascio N, et al. Cardiomyocyte-targeting exosomes from sulforaphane-treated fibroblasts affords cardioprotection in infarcted rats. J Transl Med. (2023) 21(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04155-x
107. Liao Z, Chen Y, Duan C, Zhu K, Huang R, Zhao H, et al. Cardiac telocytes inhibit cardiac microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis through exosomal miRNA-21-5p-targeted cdip1 silencing to improve angiogenesis following myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2021) 11(1):268–91. doi: 10.7150/thno.47021
108. Yang J, Li Y, Xue F, Liu W, Zhang S. Exosomes derived from cardiac telocytes exert positive effects on endothelial cells. Am J Transl Res. (2017) 9(12):5375–87.29312490
109. del Campo CV, Liaw NY, Gunadasa-Rohling M, Matthaei M, Braga L, Kennedy T, et al. Regenerative potential of epicardium-derived extracellular vesicles mediated by conserved miRNA transfer. Cardiovasc Res. (2022) 118(2):597–611. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab054
110. Foglio E, Puddighinu G, Fasanaro P, D'Arcangelo D, Perrone GA, Mocini D, et al. Exosomal clusterin, identified in the pericardial fluid, improves myocardial performance following MI through epicardial activation, enhanced arteriogenesis and reduced apoptosis. Int J Cardiol. (2015) 197:333–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.008
111. Yang M, Liu X, Jiang M, Li J, Tang Y, Zhou L. Mir-543 in human mesenchymal stem cell–derived exosomes promotes cardiac microvascular endothelial cell angiogenesis after myocardial infarction through COL4A1. IUBMB Life. (2021) 73(7):927–40. doi: 10.1002/iub.2474
112. Wang T, Li T, Niu X, Hu L, Cheng J, Guo D, et al. ADSC-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial infarction injury by promoting miR-205-mediated cardiac angiogenesis. Biol Direct. (2023) 18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13062-023-00361-1
113. Wang K, Jiang Z, Webster KA, Chen J, Hu H, Zhou Y, et al. Enhanced cardioprotection by human endometrium mesenchymal stem cells driven by exosomal MicroRNA-21. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2017) 6(1):209–22. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0386
114. Ma T, Chen Y, Chen Y, Meng Q, Sun J, Shao L, et al. MicroRNA-132, delivered by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes, promote angiogenesis in myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. (2018) 2018:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2018/3290372
115. Wang N, Chen C, Yang D, Liao Q, Luo H, Wang X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles, via miR-210, improve infarcted cardiac function by promotion of angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2017) 1863:2085–92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.02.023
116. Xu H, Wang Z, Liu L, Zhang B, Li B. Exosomes derived from adipose tissue, bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood for cardioprotection after myocardial infarction. J Cell Biochem. (2020) 121(3):2089–102. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27399
117. Ju C, Shen Y, Ma G, Liu Y, Cai J, Kim I-m, et al. Transplantation of cardiac mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes repair in ischemic myocardium. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2018) 11(5):420–8. doi: 10.1007/s12265-018-9822-0
118. Takov K, He Z, Johnston HE, Timms JF, Guillot PV, Yellon DM, et al. Small extracellular vesicles secreted from human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stromal cells possess cardioprotective and promigratory potential. Basic Res Cardiol. (2020) 115(3):26. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-0785-3
119. Sun C, Li W, Li Y, Chen J, An H, Zeng G, et al. MiR-182-5p mediated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell attenuates inflammatory responses by targeting TLR4 in a mouse model of myocardial infraction. Immune Netw. (2022) 22(6):e49. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e49
120. Harris HE, Andersson U, Pisetsky DS. HMGB1: a multifunctional alarmin driving autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2012) 8(4):195–202. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.222
121. Wang S, Dong J, Li L, Wu R, Xu L, Ren Y, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-129-5p modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells represses ventricular remolding of mice with myocardial infarction. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. (2022) 16(2):177–87. doi: 10.1002/term.3268
122. Shi Y, Yang Y, Guo Q, Gao Q, Ding Y, Wang H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation in inflammatory environments and benefit cardioprotective effects. Stem Cells Dev. (2019) 28(12):799–811. doi: 10.1089/scd.2018.0242
123. Gutcher I, Becher B. APC-derived cytokines and T cell polarization in autoimmune inflammation. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117(5):1119–27. doi: 10.1172/JCI31720
124. Zhu D, Liu S, Huang K, Wang Z, Hu S, Li J, et al. Intrapericardial exosome therapy dampens cardiac injury via activating Foxo3. Circ Res. (2022) 131(10):e135–50. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321384
125. Yan X, Anzai A, Katsumata Y, Matsuhashi T, Ito K, Endo J, et al. Temporal dynamics of cardiac immune cell accumulation following acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2013) 62:24–35. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.04.023
126. Zhu F, Chen Y, Li J, Yang Z, Lin Y, Jiang B, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate myocardial infarction injury via miR-24-3p-promoted M2 macrophage polarization. Adv Biol. (2022) 6(11):e2200074. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200074
127. Deng S, zhou X, Ge Z, Song Y, Wang H, Liu X, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2019) 114:105564. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105564
128. Xu R, Zhang F, Chai R, Zhou W, Hu M, Liu B, et al. Exosomes derived from pro-inflammatory bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce inflammation and myocardial injury via mediating macrophage polarization. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23(11):7617–31. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14635
129. Domenis R, Cifù A, Quaglia S, Pistis C, Moretti M, Vicario A, et al. Pro inflammatory stimuli enhance the immunosuppressive functions of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Sci Rep. (2018) 8(1):13325. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31707-9
130. Hori M, Nishida K. Oxidative stress and left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2008) 81(3):457–64. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn335
131. Ide T, Tsutsui H, Hayashidani S, Kang D, Suematsu N, Nakamura K-i, et al. Mitochondrial DNA damage and dysfunction associated with oxidative stress in failing hearts after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. (2001) 88(5):529–35. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.88.5.529
132. Ibáñez B, Villena-Gutierrez R. Cardiac mitochondrial transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2021) 77(8):1089–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.01.017
133. Dutra Silva J, Su Y, Calfee CS, Delucchi KL, Weiss D, McAuley DF, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell extracellular vesicles rescue mitochondrial dysfunction and improve barrier integrity in clinically relevant models of ARDS. Eur Respir J. (2021) 58(1):2002978. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02978-2020
134. Zhang Y, Tan J, Miao Y, Zhang Q. The effect of extracellular vesicles on the regulation of mitochondria under hypoxia. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12(4):358. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03640-9
135. Zhao M, Liu S, Wang C, Wang Y, Wan M, Liu F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate mitochondrial damage and inflammation by stabilizing mitochondrial DNA. ACS Nano. (2021) 15(1):1519–38. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c08947
136. Zorova LD, Kovalchuk SI, Popkov VA, Chernikov VP, Zharikova AA, Khutornenko AA, et al. Do extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells contain functional mitochondria? Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(13):7408. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137408
137. Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal T, Junger W, et al. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature. (2010) 464(7285):104–7. doi: 10.1038/nature08780
138. Todkar K, Chikhi L, Desjardins V, El-Mortada F, Pépin G, Germain M. Selective packaging of mitochondrial proteins into extracellular vesicles prevents the release of mitochondrial DAMPs. Nat Commun. (2021) 12(1):1971. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21984-w
139. Dayawansa Nalin H, Gao X-M, White David A, Dart Anthony M, Du X-J. Role of MIF in myocardial ischaemia and infarction: insight from recent clinical and experimental findings. Clin Sci. (2014) 127(3):149–61. doi: 10.1042/CS20130828
140. Liu X, Li X, Zhu W, Zhang Y, Hong Y, Liang X, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing MIF enhance myocardial repair. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235(11):8010–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29456
141. Wang Y, Zhao R, Liu D, Deng W, Xu G, Liu W, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-214-enriched bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells regulate oxidative damage in cardiac stem cells by targeting CaMKII. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:1–21. doi: 10.1155/2018/4971261
142. de Almeida Oliveira Nathalia C, Neri Elida A, Silva Caio M, Valadão Iuri C, Fonseca-Alaniz Miriam H, Zogbi C, et al. Multicellular regulation of miR-196a-5p and miR-425-5 from adipose stem cell-derived exosomes and cardiac repair. Clin Sci. (2022) 136(17):1281–301. doi: 10.1042/CS20220216
143. Zhou F, Yang Y, Xing D. Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. FEBS J. (2011) 278(3):403–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07965.x
144. Maiuri MC, Criollo A, Kroemer G. Crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy within the beclin 1 interactome. EMBO J. (2010) 29(3):515–6. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.377
145. Dong Y, Chen H, Gao J, Liu Y, Li J, Wang J. Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. (2019) 136:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.09.001
146. Crow MT, Mani K, Nam Y-J, Kitsis RN. The mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ Res. (2004) 95(10):957–70. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000148632.35500.d9
147. Fan M, Zhang J, Zeng L, Wang D, Chen J, Xi X, et al. Non-coding RNA mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in heart disease. Heliyon. (2023) 9(5):e16246. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16246
148. Zhang CS, Shao K, Liu CW, Li CJ, Yu BT. Hypoxic preconditioning BMSCs-exosomes inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction by upregulating microRNA-24. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23(15):6691–9. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201908_18560
149. Peng Y, Zhao J-L, Peng Z-Y, Xu W-F, Yu G-L. Exosomal miR-25-3p from mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial infarction by targeting pro-apoptotic proteins and EZH2. Cell Death Dis. (2020) 11(5):317. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2545-6
150. Jia Z, Wang J, Shi Q, Liu S, Wang W, Tian Y, et al. SOX6 and PDCD4 enhance cardiomyocyte apoptosis through LPS-induced miR-499 inhibition. Apoptosis. (2016) 21(2):174–83. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1201-6
151. Huang L, Yang L, Ding Y, Jiang X, Xia Z, You Z. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes transfers microRNA-19a to protect cardiomyocytes from acute myocardial infarction by targeting SOX6. Cell Cycle. (2020) 19(3):339–53. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1711305
152. Sun L, Zhu W, Zhao P, Zhang J, Lu Y, Zhu Y, et al. Down-regulated exosomal MicroRNA-221-3p derived from senescent mesenchymal stem cells impairs heart repair. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:263. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00263
153. Zhang N, Zhu J, Ma Q, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Hu X, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord MSCs rejuvenate aged MSCs and enhance their functions for myocardial repair. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01782-9
154. Li X, Hu X, Chen Q, Jiang T. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying E3 ubiquitin ligase ITCH attenuated cardiomyocyte apoptosis by mediating apoptosis signal-regulated kinase-1. Pharmacogenet Genom. (2023) 33(6):117–25. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000499
155. Zhu W, Sun L, Zhao P, Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor facilitates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction through upregulating miR-133a-3p. J Nanobiotechnol. (2021) 19(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00808-5
156. Ning W, Li S, Yang W, Yang B, Xin C, Ping X, et al. Blocking exosomal miRNA-153-3p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates hypoxia-induced myocardial and microvascular damage by targeting the ANGPT1-mediated VEGF/PI3k/AKT/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal. (2021) 77:109812. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109812
157. Tian T, Li F, Chen R, Wang Z, Su X, Yang C. Therapeutic potential of exosomes derived from circRNA_0002113 lacking mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 9:779524. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.779524
158. Li CX, Song J, Li X, Zhang T, Li ZM. Circular RNA 0001273 in exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (UMSCs) in myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24(19):10086–95. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23228
159. Luo T, Kim JK, Chen B, Abdel-Latif A, Kitakaze M, Yan L. Attenuation of ER stress prevents post-infarction-induced cardiac rupture and remodeling by modulating both cardiac apoptosis and fibrosis. Chem-Biol Interact. (2015) 225:90–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.032
160. Zhang C, Wang H, Chan GCF, Zhou Y, Lai X, Lian M. Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells protect cardiac cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting endoplasmic Reticulum stress via activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Transplant. (2020) 29:096368972094567. doi: 10.1177/0963689720945677
161. Fu DL, Jiang H, Li CY, Gao T, Liu MR, Li HW. MicroRNA-338 in MSCs-derived exosomes inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24(19):10107–17. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23230
162. Li Y, Yang R, Guo B, Zhang H, Zhang H, Liu S, et al. Exosomal miR-301 derived from mesenchymal stem cells protects myocardial infarction by inhibiting myocardial autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 514(1):323–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.138
163. Crighton D, Wilkinson S, Ryan KM. DRAM links autophagy to p53 and programmed cell death. Autophagy. (2007) 3(1):72–4. doi: 10.4161/auto.3438
164. Xiao C, Wang K, Xu Y, Hu H, Zhang N, Wang Y, et al. Transplanted mesenchymal stem cells reduce autophagic flux in infarcted hearts via the exosomal transfer of miR-125b. Circ Res. (2018) 123(5):564–78. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312758
165. Liu J, Jiang M, Deng S, Lu J, Huang H, Zhang Y, et al. miR-93-5p-Containing exosomes treatment attenuates acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 11:103–15. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.01.010
166. Li T, Gu J, Yang O, Wang J, Wang Y, Kong J. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miRNA-29c decreases cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibition of excessive autophagy via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Circ J. (2020) 84(8):1304–11. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-19-1060
167. Liu W, Shen J, Li Y, Wu J, Luo X, Yu Y, et al. Pyroptosis inhibition improves the symptom of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12(10):852. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04143-3
168. Mao Q, Liang X-L, Zhang C-L, Pang Y-H, Lu Y-X. LncRNA KLF3-AS1 in human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes and myocardial infarction through miR-138-5p/Sirt1 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1522-4
169. Kore RA, Wang X, Ding Z, Griffin RJ, Tackett AJ, Mehta JL. MSC exosome-mediated cardioprotection in ischemic mouse heart comparative proteomics of infarct and peri-infarct areas. Mol Cell Biochem. (2021) 476(4):1691–704. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-04029-6
170. Liang C, Liu Y, Xu H, Huang J, Shen Y, Chen F, et al. Exosomes of human umbilical cord MSCs protect against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced pyroptosis of cardiomyocytes via the miRNA-100-5p/FOXO3/NLRP3 pathway. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2021) 8:615850. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.615850
171. Yue R, Lu S, Luo Y, Zeng J, Liang H, Qin D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-182-5p alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting GSDMD in mice. Cell Death Discov. (2022) 8(1):202. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00909-6
172. Song Y, Wang B, Zhu X, Hu J, Sun J, Xuan J, et al. Human umbilical cord blood–derived MSCs exosome attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in acute myocardial infarction mice. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2021) 37(1):51–64. doi: 10.1007/s10565-020-09530-8
173. Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. (2022) 375(6586):1254–61. doi: 10.1126/science.abf0529
174. Gao W, Huang Z, Duan J, Nice EC, Lin J, Huang C. Elesclomol induces copper-dependent ferroptosis in colorectal cancer cells via degradation of ATP7A. Mol Oncol. (2021) 15(12):3527–44. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13079
175. Miao M, Cao S, Tian Y, Liu D, Chen L, Chai Q, et al. Potential diagnostic biomarkers: 6 cuproptosis- and ferroptosis-related genes linking immune infiltration in acute myocardial infarction. Genes Immun. (2023) 24(4):159–70. doi: 10.1038/s41435-023-00209-8
176. Wang Y, Tu J, Wu W, Xu Y, Li Y, Pan X, et al. The orchestration of cell-cycle reentry and ribosome biogenesis network is critical for cardiac repair. Theranostics. (2024) 14(10):3927–44. doi: 10.7150/thno.96460
177. Wang X, Zhu Y, Wu C, Liu W, He Y, Yang Q. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carry MicroRNA-671 to alleviate myocardial infarction through inactivating the TGFBR2/Smad2 axis. Inflammation. (2021) 44(5):1815–30. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01460-9
178. Yao Y, Hu C, Song Q, Li Y, Da X, Yu Y, et al. ADAMTS16 activates latent TGF-beta, accentuating fibrosis and dysfunction of the pressure-overloaded heart. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 116(5):956–69. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz187
179. Wu Y, Peng W, Fang M, Wu M, Wu M. MSCs-derived extracellular vesicles carrying miR-212-5p alleviate myocardial infarction-induced cardiac fibrosis via NLRC5/VEGF/TGF-β1/SMAD axis. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. (2022) 15(2):302–16. doi: 10.1007/s12265-021-10156-2
180. Yang M, Liao M, Liu R, Zhang Q, Zhang S, He Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles loaded with miR-223 ameliorate myocardial infarction through P53/S100A9 axis. Genomics. (2022) 114(3):110319. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110319
181. Kore RA, Wang X, Henson JC, Ding Z, Jamshidi-Parsian A, Mehta JL. Proteomic basis of modulation of postischemic fibrosis by MSC exosomes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2021) 321(5):R639–54. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00124.2021
182. Xiao M, Zeng W, Wang J, Yao F, Peng Z, Liu G, et al. Exosomes protect against acute myocardial infarction in rats by regulating the renin-angiotensin system. Stem Cells Dev. (2021) 30(12):622–31. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0132
183. Ni J, Liu X, Yin Y, Zhang P, Xu Y-W, Liu Z. Exosomes derived from TIMP2-modified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance the repair effect in rat model with myocardial infarction possibly by the AKT/Sfrp2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2019) 2019:1–19. doi: 10.1155/2019/1958941
184. Huang P, Wang L, Li Q, Xu J, Xu J, Xiong Y, et al. Combinatorial treatment of acute myocardial infarction using stem cells and their derived exosomes resulted in improved heart performance. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1353-3
185. Wang S, Li L, Liu T, Jiang W, Hu X. miR-19a/19b-loaded exosomes in combination with mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a preclinical model of myocardial infarction. Regen Med. (2020) 15(6):1749–59. doi: 10.2217/rme-2019-0136
186. Zhu D, Liu S, Huang K, Li J, Mei X, Li Z, et al. Intrapericardial long non-coding RNA–Tcf21 antisense RNA inducing demethylation administration promotes cardiac repair. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(19):1748–60. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad114
187. Yamashita T, Takahashi Y, Takakura Y, Graduate SOPS, Kyoto U. Possibility of exosome-based therapeutics and challenges in production of exosomes eligible for therapeutic application. Biol Pharm Bull. (2018) 41(6):835–42. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00133
188. Cheng H, Chang S, Xu R, Chen L, Song X, Wu J, et al. Hypoxia-challenged MSC-derived exosomes deliver miR-210 to attenuate post-infarction cardiac apoptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01737-0
189. Huang P, Wang L, Li Q, Tian X, Xu J, Xu J, et al. Atorvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction via up-regulating long non-coding RNA H19. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 116(2):353–67. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz139
190. Zheng H, Liang X, Han Q, Shao Z, Zhang Y, Shi L, et al. Hemin enhances the cardioprotective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes against infarction via amelioration of cardiomyocyte senescence. J Nanobiotechnol. (2021) 19(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01077-y
191. Xiong Y, Tang R, Xu J, Jiang W, Gong Z, Zhang L, et al. Tongxinluo-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells facilitate cardiac repair via exosomal transfer of miR-146a-5p targeting IRAK1/NF-κB p65 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2022) 13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02969-y
192. Li S, Yang K, Cao W, Guo R, Liu Z, Zhang J, et al. Tanshinone IIA enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via up-regulating miR-223-5p. J Controlled Release. (2023) 358:13–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.04.014
193. Liu D, Gu G, Gan L, Yan W, Zhang Z, Yao P, et al. Identification of a CTRP9 C-terminal polypeptide capable of enhancing bone-derived mesenchymal stem cell cardioprotection through promoting angiogenic exosome production. Redox Biol. (2021) 41:101929. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101929
194. Sun L, Ji Y, Chi B, Xiao T, Li C, Yan X, et al. A 3D culture system improves the yield of MSCs-derived extracellular vesicles and enhances their therapeutic efficacy for heart repair. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 161:114557. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114557
195. Wang Y, Ding N, Guan G, Liu G, Huo D, Li Y, et al. Rapid delivery of hsa-miR-590-3p using targeted exosomes to treat acute myocardial infarction through regulation of the cell cycle. J Biomed Nanotechnol. (2018) 14(5):968–77. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2018.2493
196. Pu L, Kong X, Li H, He X. Exosomes released from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing microRNA-30e ameliorate heart failure in rats with myocardial infarction. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13(5):4007–25.34149995
197. Li Q, Xu Y, Lv K, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Xiao C, et al. Small extracellular vesicles containing miR-486-5p promote angiogenesis after myocardial infarction in mice and nonhuman primates. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 584(13):eabb0202. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abb0202
198. Ma J, Zhao Y, Sun L, Sun X, Zhao X, Sun X, et al. Exosomes derived from AKT-modified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac regeneration and promote angiogenesis via activating platelet-derived growth factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2017) 6(1):51–9. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2016-0038
199. Kang K, Ma R, Cai W, Huang W, Paul C, Liang J, et al. Exosomes secreted from CXCR4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote cardioprotection via AKT signaling pathway following myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. (2015) 2015:1–14. doi: 10.1155/2015/659890
200. Gong XH, Liu H, Wang SJ, Liang SW, Wang GG. Exosomes derived from SDF1-overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ischemic myocardial cell apoptosis and promote cardiac endothelial microvascular regeneration in mice with myocardial infarction. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234(8):13878–93. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28070
201. He J-G, Li H-R, Han J-X, Li B-B, Yan D, Li H-Y, et al. GATA-4-expressing mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction via secreted exosomes. Sci Rep. (2018) 8(1):9047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27435-9
202. Sun J, Shen H, Shao L, Teng X, Chen Y, Liu X, et al. HIF-1α overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes mediates cardioprotection in myocardial infarction by enhanced angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2020) 11(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01881-7
203. Wang X, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Meng Q, Yu Y, Sun J, et al. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. (2018) 7(15):e008737. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008737
204. Gu J, You J, Liang H, Zhan J, Gu X, Zhu Y. Engineered bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes loaded with miR302 through the cardiomyocyte specific peptide can reduce myocardial ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury. J Transl Med. (2024) 22(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04981-7
205. Zou Y, Li L, Li Y, Chen S, Xie X, Jin X, et al. Restoring cardiac functions after myocardial infarction–ischemia/reperfusion via an exosome anchoring conductive hydrogel. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2021) 13(48):56892–908. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c16481
206. Zhu L-P, Tian T, Wang J-Y, He J-N, Chen T, Pan M, et al. Hypoxia-elicited mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates cardiac repair through miR-125b-mediated prevention of cell death in myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2018) 8(22):6163–77. doi: 10.7150/thno.28021
207. Shafei S, Khanmohammadi M, Ghanbari H, Nooshabadi VT, Tafti SHA, Rabbani S, et al. Effectiveness of exosome mediated miR-126 and miR-146a delivery on cardiac tissue regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. (2022) 390(1):71–92. doi: 10.1007/s00441-022-03663-4
208. Wei Z, Chen Z, Zhao Y, Fan F, Xiong W, Song S, et al. Mononuclear phagocyte system blockade using extracellular vesicles modified with CD47 on membrane surface for myocardial infarction reperfusion injury treatment. Biomaterials. (2021) 275:121000. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121000
209. Zhang N, Song Y, Huang Z, Chen J, Tan H, Yang H, et al. Monocyte mimics improve mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle homing in a mouse MI/RI model. Biomaterials. (2020) 255:120168. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120168
210. Lai J, Pan Q, Chen G, Liu Y, Chen C, Pan Y, et al. Triple hybrid cellular nanovesicles promote cardiac repair after ischemic reperfusion. ACS Nano. (2024) 18(5):4443–55. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c10784
211. Zhang N, Fan M, Zhao Y, Hu X, Zhu Q, Jiao X, et al. Biomimetic and NOS-responsive nanomotor deeply delivery a combination of MSC-EV and mitochondrial ROS scavenger and promote heart repair and regeneration. Adv Sci. (2023) 10(21):e2301440. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301440
212. Han C, Zhou J, Liang C, Liu B, Pan X, Zhang Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes encapsulated in functional peptide hydrogels promote cardiac repair. Biomater Sci. (2019) 7(7):2920–33. doi: 10.1039/C9BM00101H
213. Firoozi S, Pahlavan S, Ghanian M-H, Rabbani S, Barekat M, Nazari A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alone or in conjunction with a SDKP-conjugated self-assembling peptide improve a rat model of myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2020) 524(4):903–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.009
214. Yan C, Wang X, Wang Q, Li H, Song H, Zhou J, et al. A novel conductive polypyrrole-chitosan hydrogel containing human endometrial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitated sustained release for cardiac repair. Adv Healthcare Mater. (2024) 13(10):e2304207. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202304207
215. Hu X, Ning X, Zhao Q, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Xie M, et al. Islet-1 mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome-incorporated angiogenin-1 hydrogel for enhanced acute myocardial infarction therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2022) 14(32):36289–303. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c04686
216. Wang Q, Zhang L, Sun Z, Chi B, Zou A, Mao L, et al. HIF-1α overexpression in mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-encapsulated arginine-glycine-aspartate (RGD) hydrogels boost therapeutic efficacy of cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Materials Today Bio. (2021) 12:100171. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100171
217. Lv K, Li Q, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Zhao J, et al. Incorporation of small extracellular vesicles in sodium alginate hydrogel as a novel therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. Theranostics. (2019) 9(24):7403–16. doi: 10.7150/thno.32637
218. Wang D, Zhang H, Chen Y, He J, Zhao L, Huang Y, et al. Improving therapeutic effects of exosomes encapsulated gelatin methacryloyl/hyaluronic acid blended and oxygen releasing injectable hydrogel by cardiomyocytes induction and vascularization in rat myocardial infarction model. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 271:132412. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132412
219. Ren Y, Wang W, Yu C, Wang Y, Qiu Y, Yue Z, et al. An injectable exosome-loaded hyaluronic acid-polylysine hydrogel for cardiac repair via modulating oxidative stress and the inflammatory microenvironment. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 275:133622. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133622
220. Monguió-Tortajada M, Prat-Vidal C, Moron-Font M, Clos-Sansalvador M, Calle A, Gastelurrutia P, et al. Local administration of porcine immunomodulatory, chemotactic and angiogenic extracellular vesicles using engineered cardiac scaffolds for myocardial infarction. Bioact Mater. (2021) 6(10):3314–27. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.02.026
221. Monguió-Tortajada M, Prat-Vidal C, Martínez-Falguera D, Teis A, Soler-Botija C, Courageux Y, et al. Acellular cardiac scaffolds enriched with MSC-derived extracellular vesicles limit ventricular remodelling and exert local and systemic immunomodulation in a myocardial infarction porcine model. Theranostics. (2022) 12(10):4656–70. doi: 10.7150/thno.72289
222. Yuan J, Yang H, Liu C, Shao L, Zhang H, Lu K, et al. Microneedle patch loaded with exosomes containing MicroRNA-29b prevents cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction. Adv Healthcare Mater. (2023) 12(13):e2202959. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202202959
223. Ping P, Guan S, Ning C, Yang T, Zhao Y, Zhang P, et al. Fabrication of blended nanofibrous cardiac patch transplanted with TGF-β3 and human umbilical cord MSCs-derived exosomes for potential cardiac regeneration after acute myocardial infarction. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. (2023) 54:102708. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2023.102708
224. Yao J, Huang K, Zhu D, Chen T, Jiang Y, Zhang J, et al. A minimally invasive exosome spray repairs heart after myocardial infarction. ACS Nano. (2021) 15(7):11099–111. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c00628
225. Liu H-Y, Yu L-F, Zhou T-G, Wang Y-D, Sun D-H, Chen H-R, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes inhibit H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte inflammation and oxidative stress via regulating miR-181a-5p/ATF2 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24(19):10069. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23224
226. Xu B, Luo Y, Liu Y, Li B-Y, Wang Y. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB enhances MSC-mediated cardioprotection via suppression of miR-320 expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2015) 308(9):H980–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00737.2014
227. Kim HW, Mallick F, Durrani S, Ashraf M, Jiang S, Haider KH. Concomitant activation of miR-107/PDCD10 and hypoxamir-210/Casp8ap2 and their role in cytoprotection during ischemic preconditioning of stem cells. Antioxid Redox Signaling. (2012) 17(8):1053–65. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4518
228. Gao W, He R, Ren J, Zhang W, Wang K, Zhu L, et al. Exosomal HMGB1 derived from hypoxia-conditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells increases angiogenesis via the JNK/HIF-1α pathway. FEBS Open Bio. (2021) 11(5):1364–73. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13142
229. Peltzer J, Lund K, Goriot M-E, Grosbot M, Lataillade J-J, Mauduit P, et al. Interferon-γ and hypoxia priming have limited effect on the miRNA landscape of human mesenchymal stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2020) 8:581436. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.581436
230. Moniz I, Ramalho-Santos J, Branco AF. Differential oxygen exposure modulates mesenchymal stem cell metabolism and proliferation through mTOR signaling. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23(7):3749. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073749
231. Casajuana Ester M, Day RM. Production and utility of extracellular vesicles with 3D culture methods. Pharmaceutics. (2023) 15(2):663. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020663
232. Johnston J, Stone T, Wang Y. Biomaterial-enabled 3D cell culture technologies for extracellular vesicle manufacturing. Biomater Sci. (2023) 11(12):4055–72. doi: 10.1039/D3BM00469D
233. Haraszti RA, Miller R, Stoppato M, Sere YY, Coles A, Didiot M-C, et al. Exosomes produced from 3D cultures of MSCs by tangential flow filtration show higher yield and improved activity. Mol Ther. (2018) 26(12):2838–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.015
234. Gobin J, Muradia G, Mehic J, Westwood C, Couvrette L, Stalker A, et al. Hollow-fiber bioreactor production of extracellular vesicles from human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells yields nanovesicles that mirrors the immuno-modulatory antigenic signature of the producer cell. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02190-3
235. Yuan X, Sun L, Jeske R, Nkosi D, York SB, Liu Y, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles by three-dimensional dynamic culture of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Extracell Vesicles. (2022) 11(6):e12235. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12235
236. Xi XM, Xia SJ, Lu R. Drug loading techniques for exosome-based drug delivery systems. Pharmazie. (2021) 76(2):61–7. doi: 10.1691/ph.2021.0128
237. Lopatina T, Bruno S, Tetta C, Kalinina N, Porta M, Camussi G. Platelet-derived growth factor regulates the secretion of extracellular vesicles by adipose mesenchymal stem cells and enhances their angiogenic potential. Cell Commun Signal. (2014) 12:26. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-26
238. Gaurav I, Thakur A, Iyaswamy A, Wang X, Chen X, Yang Z. Factors affecting extracellular vesicles based drug delivery systems. Molecules. (2021) 26(6):1544. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061544
239. Hung ME, Leonard JN. Stabilization of exosome-targeting peptides via engineered glycosylation. J Biol Chem. (2015) 290(13):8166–72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621383
240. Zeng H, Guo S, Ren X, Wu Z, Liu S, Yao X. Current strategies for exosome cargo loading and targeting delivery. Cells. (2023) 12(10):1416. doi: 10.3390/cells12101416
241. Mehryab F, Rabbani S, Shahhosseini S, Shekari F, Fatahi Y, Baharvand H, et al. Exosomes as a next-generation drug delivery system: an update on drug loading approaches, characterization, and clinical application challenges. Acta Biomater. (2020) 113:42–62. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.06.036
242. Sun D, Zhuang X, Xiang X, Liu Y, Zhang S, Liu C, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. (2010) 18(9):1606–14. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.105
243. Kooijmans SAA, Stremersch S, Braeckmans K, de Smedt SC, Hendrix A, Wood MJA, et al. Electroporation-induced siRNA precipitation obscures the efficiency of siRNA loading into extracellular vesicles. J Controlled Release. (2013) 172(1):229–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.08.014
244. Li S, Stöckl S, Lukas C, Herrmann M, Brochhausen C, König MA, et al. Curcumin-primed human BMSC-derived extracellular vesicles reverse IL-1β-induced catabolic responses of OA chondrocytes by upregulating miR-126-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2021) 12(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02317-6
245. Sato YT, Umezaki K, Sawada S, Mukai S-a, Sasaki Y, Harada N, et al. Engineering hybrid exosomes by membrane fusion with liposomes. Sci Rep. (2016) 6(1):21933. doi: 10.1038/srep21933
246. Piffoux M, Silva AKA, Wilhelm C, Gazeau F, Tareste D. Modification of extracellular vesicles by fusion with liposomes for the design of personalized biogenic drug delivery systems. ACS Nano. (2018) 12(7):6830–42. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b02053
247. Lin Y, Wu J, Gu W, Huang Y, Tong Z, Huang L, et al. Exosome–liposome hybrid nanoparticles deliver CRISPR/Cas9 system in MSCs. Adv Sci. (2018) 5(4):1700611. doi: 10.1002/advs.201700611
248. Lee J, Lee H, Goh U, Kim J, Jeong M, Lee J, et al. Cellular engineering with membrane fusogenic liposomes to produce functionalized extracellular vesicles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2016) 8(11):6790–5. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b01315
249. Zeng Y, Qiu Y, Jiang W, Shen J, Yao X, He X, et al. Biological features of extracellular vesicles and challenges. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2022) 10:816698. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.816698
250. Foster AA, Marquardt LM, Heilshorn SC. The diverse roles of hydrogel mechanics in injectable stem cell transplantation. Curr Opin Chem Eng. (2017) 15:15–23. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2016.11.003
251. Qasim M, Arunkumar P, Powell HM, Khan M. Current research trends and challenges in tissue engineering for mending broken hearts. Life Sci. (2019) 229:233–50. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.05.012
252. Ruschitzka F, Abraham WT, Singh JP, Bax JJ, Borer JS, Brugada J, et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy in heart failure with a narrow QRS complex. N Engl J Med. (2013) 369(15):1395–405. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1306687
253. Mihic A, Cui Z, Wu J, Vlacic G, Miyagi Y, Li S-H, et al. A conductive polymer hydrogel supports cell electrical signaling and improves cardiac function after implantation into myocardial infarct. Circulation. (2015) 132(8):772–84. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014937
254. Zhang C, Hsieh M-H, Wu S-Y, Li S-H, Wu J, Liu S-M, et al. A self-doping conductive polymer hydrogel that can restore electrical impulse propagation at myocardial infarct to prevent cardiac arrhythmia and preserve ventricular function. Biomaterials. (2020) 231:119672. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119672
255. Taylor DA, Sampaio LC, Ferdous Z, Gobin AS, Taite LJ. Decellularized matrices in regenerative medicine. Acta Biomater. (2018) 74:74–89. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.04.044
256. Born LJ, McLoughlin ST, Dutta D, Mahadik B, Jia X, Fisher JP, et al. Sustained released of bioactive mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles from 3D-printed gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. (2022) 110(6):1190–8. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.37362
257. Sun S-J, Wei R, Li F, Liao S-Y, Tse H-F. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes in cardiac regeneration and repair. Stem Cell Rep. (2021) 16(7):1662–73. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.05.003
258. Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2014) 15(3):4142–57. doi: 10.3390/ijms15034142
259. Cecchin R, Troyer Z, Witwer K, Morris KV. Extracellular vesicles: the next generation in gene therapy delivery. Mol Ther. (2023) 31(5):1225–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.021
Keywords: myocardial infarction, cardiac cells, cell-cell communication, mesenchymal stem cells, extracellular vesicles
Citation: Qin D, Wang X, Pu J and Hu H (2024) Cardiac cells and mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles: a potential therapeutic strategy for myocardial infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1493290. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1493290
Received: 8 September 2024; Accepted: 28 November 2024;
Published: 18 December 2024.
Edited by:
Zhichao Fan, UCONN Health, United StatesReviewed by:
Claudia Penna, University of Turin, ItalyGentaro Ikeda, Stanford University, United States
Copyright: © 2024 Qin, Wang, Pu and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Houxiang Hu, aGh4aWFuZ0Buc21jLmVkdS5jbg==
 Dan Qin1
Dan Qin1 Houxiang Hu
Houxiang Hu