
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Built Environ., 13 March 2025
Sec. Earthquake Engineering
Volume 11 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2025.1559530
 Fateme Zamani1
Fateme Zamani1 Sayyed Hadi Alavi1
Sayyed Hadi Alavi1 Mohammadreza Mashayekhi1
Mohammadreza Mashayekhi1 Ehsan Noroozinejad Farsangi2*
Ehsan Noroozinejad Farsangi2* Ataallah Sadeghi-Movahhed3
Ataallah Sadeghi-Movahhed3 Ali Majdi4
Ali Majdi4The tuned mass damper is one of the most frequently employed structural control devices for mitigating dynamic vibrations in structures subjected to earthquake ground motions. Conventional tuned mass dampers require substantial mass to effectively reduce the structure’s vibration. However, implementing multiple-tuned mass dampers can also improve seismic performance while reducing the required mass. The dynamic characteristics of these devices play a critical role in enhancing the effectiveness of multiple-tuned mass dampers and the seismic performance of the structure. This study investigates the efficiency of double-tuned mass dampers and the optimization of their dynamic characteristics to minimize structural displacement and acceleration. The tuning process is carried out using a combination of Pareto front derived from seven multi-objective metaheuristic optimization algorithms with two objectives. The proposed methodology is applied to a 10-floor case study, using ground acceleration time histories to evaluate its seismic performance. To demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed method, the results are compared with those from a double-tuned mass damper system and an uncontrolled structure. The evaluation is carried out using seven earthquake ground motion records in addition to one benchmark record. The findings show that employing optimally tuned double-tuned mass dampers reduced acceleration by 30% and displacement by 50%. The numerical results confirmed that the proposed methodology effectively identifies the optimal double-tuned mass damper configuration under earthquake excitation.
In modern society, there is an increasing trend toward constructing large and complex structures for various economic and social reasons. These structures, characterized by significant height, lightweight materials, flexibility, and limited damping capacity, are particularly susceptible to vibrations. Vibrations adversely affect most engineering systems due to their destructive potential. Earthquakes, as one of the most hazardous natural disasters, pose a serious threat to these buildings by generating seismic vibrations (Wang et al., 2022). Other hand, seismic vibrations can cause asynchronous movements in adjacent buildings with insufficient separation, amplifying impact forces and significantly increasing the risk of severe structural damage a phenomenon known as structural pounding (Kamgar et al., 2025).
Structural vibration control is an effective and economical method for protecting buildings during earthquakes (Choi et al., 2023; Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2022; Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2023; Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2024a; Majdi et al., 2024). Numerous control strategies have been developed and implemented to improve the seismic performance of structures, especially to enhance the seismic performance of adjacent structures (Gattulli et al., 2019; Lin and Lin, 2021; Mazza and Labernarda, 2021; Majdi et al., 2023; Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2024b). Among these, the tuned mass damper (TMD) stands out as one of the most reliable devices, first proposed by Frahm (1909), to mitigate dynamic vibrations in structures subjected to seismic forces (Cao et al., 2019). A TMD system consists of a mass, a spring, and a dashpot. The fundamental principle of a TMD is to transfer vibrational energy from the primary structure to itself and dissipate it through a damping element. TMDs operate by adjusting their natural frequency to be close to the fundamental vibration frequency of the main structure, generating an antiphase resonance that absorbs and dissipates the disturbance energy (Lee et al., 2022; Zuo et al., 2021). These devices can be easily attached to the main structure without the need for serious changes to the main structure. The TMD is specifically tuned to a particular structural frequency, causing it to resonate out of phase with the structural motion when that frequency is excited. The parameters of the TMD, mass, stiffness, and damping coefficient, play a critical role in influencing the response of the primary structural system. Consequently, parameter optimization is a key design consideration for improving safety performance, as it directly impacts the reduction of structural vibrations such as displacements and acceleration.
Since the optimum parameters of a TMD are crucial for its effectiveness, determining these parameters is important (Cetin et al., 2019). However, identifying the optimal parameters is complex, particularly for damped systems. Two general approaches are commonly used to identify the optimal structural parameters for TMDs: analytical methods and optimization algorithms. Analytical methods rely on mathematical models and equations to predict the optimal parameters based on the characteristics of the structure and the expected loads. Thompson (1981) used a frequency locus method to obtain optimal damper parameters. Closed-form derived formulas for the design of TMDs subjected to lateral loads, such as wind and earthquake loadings, were proposed by Chang (1999). Lin et al. (2001) used an extended random decrement method to reduce the dynamic responses of a multi-degree-of-freedom system subjected to seismic loading. Yahyai et al. (2021) proposed a method for the optimal design of a structure equipped with TMD by minimizing the frequency response function of displacement.
Some studies have investigated the use of optimization algorithms in determining TMD parameters. In the optimization algorithms method, evolutionary techniques are commonly employed to iteratively search for the best parameters by improving potential solutions. Metaheuristic algorithms, such as genetic algorithm (Desu et al., 2006; Hadi and Arfiadi, 1998; Mohebbi et al., 2013; Singh et al., 2002), particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm (Leung and Zhang, 2009), harmony search algorithm (Bekdaş and Nigdeli, 2011) have been widely applied to tune TMD parameters. Notably, the first study in this field was presented by Hadi and Arfiadi (1998). Mashayekhi et al. (2023), used PSO, the whale optimization algorithm (WOA), and Hybrid PSO-WOA (HPW) algorithms to identify the optimal TMD parameters. Additionally, Farshidianfar and Soheili (2013) used the ant colony algorithm to optimize TMD parameters while considering soil-structure interaction effects, aiming to minimize the displacement and acceleration of high-rise building floors. The Ability of metaheuristic algorithms to handle nonlinear optimization problems and find near-optimal solutions makes them particularly suitable for tuning TMD parameters in complex structural systems.
In tall buildings, installing a single TMD can be challenging due to the significant space and mass required. While a TMD tuned to higher-mode vibrations can significantly impact the overall response of a tall building. Moreover, the performance of a single TMD is highly sensitive to variations in the natural frequency of the structure or the damping coefficient of the damper, which can lead to issues such as poor frequency tuning and suboptimal damping performance (Akhlagh Pasand and Zahrai, 2024; Steinbuch, 2011). To address these limitations, researchers have developed more advanced systems, such as damping-coupled TMDs, which consist of two mass units with slightly different natural frequencies coupled by a damping unit (Alnayhoum et al., 2023). Xu and Igusa (1992) introduced the concept of multiple TMD (MTMD). According to their study, an optimally designed MTMD can be more robust and efficient than a single optimally designed TMD with the same total mass, achieving greater reductions in structural responses (Chowdhury et al., 1987). Rahman et al. (2017) evaluated the performance of TMD and MTMD systems in a 10-floor building. Their findings indicated that MTMDs, when distributed across different stories, were more effective than TMDs. Similarly, Elias et al. (2017) studied the multimode seismic control of a 20-floor benchmark structure using MTMDs distributed according to the mode shapes. The study’s results demonstrated that this control method outperformed both single TMDs and MTMDs placed on the roof or distributed randomly. Fasil and Sajeeb (2019) introduced double-tuned mass dampers (DTMDs), capable of suppressing vibrations near the first and second natural frequencies of the structure. Their study showed that DTMDs provide superior performance in controlling floor displacements, accelerations, and base shear across a wider frequency bandwidth of the structure. Numerous studies have further demonstrated the impact of using MTMDs in various structures (Alnayhoum et al., 2023; Daniel and Lavan, 2014; Mohebbi et al., 2013).
The effectiveness of MTMD depends on their mass ratios, quantities, design frequencies, and arrangement. However, when MTMD are tuned to different structural modes, they can significantly enhance seismic performance (Kleingesinds and Lavan, 2022). The optimal design of MTMD is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness, as optimizing their parameters is inherently a multi-objective challenge, necessitating the use of multi-objective optimization approaches. Recent studies have addressed this challenge. For instance, Ok et al. (2008) proposed a multi-objective optimization-based design methodology for bi-TMDs to ensure robust seismic performance despite discrepancies between nominal and actual structural conditions. Lu et al. (2022) introduced a MTMD type with a broad frequency band for vibration attenuation and effective multi-mode control, aiming to mitigate vibrations in seismically excited high-rise buildings through multi-objective optimization. Similarly, Cao & Tran (2023) proposed a multi-objective design approach for bi-TMDs. However, no research has yet incorporated well-known metaheuristic optimization algorithms or evaluated their application for identifying the optimal parameters of MTMD in a multi-objective context.
In a recent study, a combination of multiple multi-objective optimization algorithms is utilized to identify the optimal parameters for TMD in a structure equipped with DTMDs. The innovative approach aimed at enhancing the efficiency and performance of the TMD system in mitigating seismic vibrations. This paper is organized as follows: After the introduction, section 2 introduces the concept of modeling DTMD. Section 3 provides the concept of multi-objective optimization algorithms. Section 4 presents the proposed methodology of this study. In Section 5, a parametric study is conducted on a frame equipped with DTMDs to absorb earthquake excitations, using a numerical example. In the next section, Section 6, the optimal parameters of DTMD are determined by solving its optimization problems for each optimization algorithm. Additionally, the effectiveness and robustness of the optimum DTMD are compared in Section 6. Finally, the conclusions drawn from this study are presented in Section 7.
In this section, the modeling of a structure equipped with DTMD is described in detail. In this paper, a DTMD is considered for mitigating a specific vibration mode of a multi-degree-of-freedom structure. The equations of motion for a structure are influenced by the placement of the tuned DTMD. Specifically, the structural equations of motion for a damped n-story shear frame, which is outfitted with a DTMD on its roof (Figure 1), and subjected to ground motion, can be formulated as shown in Equation 1. This equation is fundamental in understanding how the DTMD mitigates seismic responses by altering the natural frequencies and damping ratios of the primary structure.
Equation 1 incorporates the acceleration, velocity, and displacement vectors of the multi-degree-of-freedom system, denoted as
Equation 2 represents the mass matrix M, a diagonal matrix that includes the masses of the structure and the additional masses of the TMDs.
Equation 3 outlines the stiffness matrix K, accounting for the structural stiffness and the added stiffness from the TMDs.
Equation 4 describes the damping matrix C, which incorporates both the inherent damping of the structure and the additional damping provided by the TMDs.
The DTMD’s effect on the structure can be observed through the modifications in these matrices, specifically in how they adjust the system’s dynamic properties to minimize seismic responses.
In engineering design, decision-making often involves multiple criteria, such as cost, performance, and other factors that frequently conflict with one another. To address these challenges and find optimal solutions, multi-objective optimization methods can be used, as they effectively find suitable solutions that balance these competing factors (Coello et al., 2020). Multi-objective optimization involves the simultaneous optimization of several conflicting objective functions. This problem is generally formulated as follows:
Where x* is the vector of decision variables, n is the number of variables, k is the number of objective functions, m is the number of inequality constraints, p is the number of equality constraints, gi is the ith inequality constraints, hi indicates the ith equality constraints, and Li and Ui are the lower and upper boundaries of ith decision variable. In single-objective optimization, there exists a unique optimal solution due to the presence of a single objective function. However, in multi-objective optimization, a single best solution does not exist, as multiple conflicting objectives must be considered simultaneously. Instead, the solution to a multi-objective problem comprises a set of trade-off solutions that balance these competing objectives. The most widely used method in the literature for such comparisons is Pareto dominance, which is specifically defined for minimization problems according to Equation 6.
Where
Where S indicates a set of solutions and PS shows the Pareto solutions set. Equation 7 implies that within the Pareto-optimal solution set, no solution is dominated by any other. In other words, all solutions in this set are non-dominated. The primary objective of a multi-objective optimization algorithm is to identify this set. The fundamental concept in multi-objective optimization is the Pareto front. Each solution in the Pareto optimal set corresponds to a point in the objective function space forming a curve or surface known as the Pareto front.
Metaheuristic algorithms are inspired by natural processes and biological systems, serving as analogies that guide the design of efficient optimization techniques (Mashayekhi and Mosayyebi, 2023). These algorithms effectively explore and exploit search spaces, making them well-suited for solving complex multi-objective optimization problems. A typical metaheuristic optimization algorithm follows a structured procedure consisting of several key steps. The process begins with initialization, where a diverse set of candidate solutions is generated within the defined search space to ensure broad coverage and prevent premature convergence. The next phase, evaluation, assesses the fitness of each solution by computing its performance across multiple objective functions, identifying the most effective solutions. In the selection stage, high-quality solutions are chosen based on criteria such as fitness and diversity. Methods such as Pareto ranking and crowding distance are often employed to ensure an appropriate balance of solutions. During the regeneration phase, new solutions are generated through variation operators, facilitating the exploration and exploitation of new regions within the search space. The replacement step updates the population by selecting the best solutions from both the existing and newly generated ones. This phase also maintains an archive of non-dominated solutions that collectively represent the Pareto front. Finally, the termination phase is reached when a predefined stopping criterion is satisfied, such as the completion of a maximum number of iterations or the stabilization of the Pareto front. At this stage, the final Pareto front is produced, offering a representation of the optimized trade-offs between competing objectives. By effectively balancing exploration and exploitation, metaheuristic algorithms provide a powerful approach to solving multi-objective optimization problems, yielding robust and diverse solutions suitable for complex engineering applications.
Figure 2 provides a conceptual summary of the process and structural differences of the metaheuristic algorithms presented in the following sections. Although each algorithm has its own specific details, readers are encouraged to refer to the cited references for a more in-depth understanding.
The NSGA-II, developed by Deb et al. (2002), is a widely used multi-objective evolutionary algorithm designed to find a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions. The primary goal of NSGA-II is to identify non-dominated solutions that collectively form the Pareto front. The algorithm begins with the random generation of an initial population, followed by the evaluation of fitness functions. It employs a non-dominated sorting method to rank solutions based on Pareto dominance and calculates a crowding distance to assess the density of solutions within the same rank. Selection of parent solutions is performed using a binary tournament based on rank and crowding distance. Genetic operators such as crossover and mutation are then applied to generate new offspring. The parent and offspring populations are merged and sorted, and the best individuals are selected based on their rank and crowding distance to form the new population. This iterative process continues until termination criteria are met, ultimately yielding a set of high-quality, diverse solutions that represent the optimal trade-offs among the objectives. Through this method, NSGA-II effectively balances convergence and diversity, providing robust solutions for complex multi-objective optimization problems.
The MOPSO algorithm, introduced by (Coello et al., 2004), is a highly effective method for multi-objective optimization, known for its ability to cover the Pareto front of objective functions and achieve rapid convergence. This effectiveness stems from its mechanisms for leader selection and archive maintenance. The algorithm begins with the initialization of particles, assigning them random positions and velocities. Each particle’s fitness is then evaluated, and the optimal solutions are stored in an external archive. The personal best positions of the particles and the global best position among all particles are updated accordingly. A leader is selected from the archive using Roulette-wheel selection. Subsequently, particles’ velocities and positions are updated based on their personal best positions and the global best position. The archive is updated by retrieving non-dominated solutions, ensuring the retention of high-quality solutions. This iterative process continues until the algorithm converges or the maximum number of iterations is reached. Through these steps, MOPSO efficiently explores the solution space and maintains a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions, making it a competitive choice for solving complex multi-objective optimization problems.
The MOGOA, introduced by Mirjalili et al. (2018), extends the grasshopper optimization algorithm to effectively address multi-objective optimization problems. This algorithm emulates the behavior of grasshopper swarms, incorporating a modified comfort zone coefficient to balance exploration and exploitation effectively. The process begins with the random initialization of a population of grasshoppers. Each grasshopper’s fitness is evaluated, and the population is ranked using non-dominated sorting based on Pareto dominance. The crowding distance for each solution is then calculated to maintain diversity within the population. A target grasshopper is selected using Roulette-wheel selection. The movement of grasshoppers is simulated to explore the search space, guided by their positions relative to the target. The archive is updated to retain non-dominated solutions. This iterative process continues until convergence or a predefined number of iterations is reached. Through these steps, MOGOA efficiently searches the solution space, maintaining a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions, and ensuring robust performance in solving complex multi-objective optimization problems.
The MOGWO algorithm is an extension of the grey wolf optimization algorithm, inspired by the social hierarchy and hunting behavior of grey wolves (Kumar et al., 2019), as proposed by Mirjalili et al. (2016). The MOGWO starts with the random initialization of a population of grey wolves. Each wolf’s fitness is assessed, followed by non-dominated sorting to rank the wolves based on Pareto dominance. The crowding distance is calculated to maintain diversity among the solutions. The algorithm then identifies the leading wolves (alpha, beta, and delta) using Roulette-wheel selection based on their fitness. The positions of the wolves are updated by simulating the social leadership and encircling techniques observed in grey wolves, guided by the leading wolves. The archive is updated to store non-dominated solutions. This process repeats iteratively until the stopping criteria are met. Through these steps, MOGWO effectively explores the solution space and maintains a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions, demonstrating robust performance in solving complex multi-objective optimization problems.
The MOAVOA is a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the lifestyle of African vultures, initially developed to solve continuous optimization problems (Balakrishnan et al., 2022). Khodadadi et al. (2022a) extended this algorithm to address multi-objective optimization problems. The MOAVOA begins by generating an initial population of vultures randomly and assessing the fitness of each individual. Solutions are then sorted based on Pareto dominance, and crowding distances are calculated to ensure diversity among the solutions. The leading vultures are identified using Roulette-wheel selection based on their fitness. The positions of the vultures are updated using the leader positions and specific flight dynamics, simulating the vultures’ behavior in nature. An archive is maintained to store non-dominated solutions. This process is iteratively repeated until a predefined stopping condition is met. Through these steps, MOAVOA effectively explores the solution space, maintaining a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions and demonstrating robust performance in solving complex multi-objective optimization problems.
The MOALO is an extension of the single-objective ant lion optimization, designed to tackle multi-objective optimization problems. Inspired by the hunting mechanisms of ant lions in nature, MOALO was proposed by (Mirjalili et al., 2017) as a novel approach to address complex multi-objective challenges. The algorithm starts by randomly initializing a population of ant lions and evaluating their fitness. Solutions are ranked using Pareto dominance, and crowding distances are calculated to preserve diversity among the solutions. Elite and random ant lions are selected from the archive using Roulette-wheel selection. The algorithm then models the hunting behavior of ant lions, simulating the random walk of ants within the search space and normalizing it to ensure effective exploration. An archive is maintained to store non-dominated solutions, which is updated iteratively. This process continues until the termination criteria are met. Through these steps, MOALO effectively balances exploration and exploitation, maintaining a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions and demonstrating robust performance in solving complex multi-objective optimization problems.
The MOSPO algorithm is inspired by color theory, the color wheel, and color combination methods. Initially introduced as a single-objective algorithm by Kaveh et al. (2022) and later extended to handle multi-objective problems by Khodadadi et al. (2022b). MOSPO aims to find a balance of solutions using principles of color harmony. The algorithm begins by randomly generating an initial population of colors and evaluating their fitness. Solutions are ranked based on Pareto dominance, and crowding distances are calculated to maintain diversity within the population. Leading colors are selected from the archive using rank and crowding distance via Roulette-wheel selection. New colors are created by mixing existing ones to achieve a pleasing balance while preserving diversity. The archive is updated with non-dominated solutions, and the process is repeated iteratively until the termination conditions are met. By simulating the natural blending and balancing of colors, MOSPO effectively explores the solution space, ensuring a diverse set of Pareto-optimal solutions and demonstrating strong performance in solving complex multi-objective optimization problems.
Optimization is a systematic process that determines the values of design variables to identify the best set of options for minimizing or maximizing a specified objective function. The process of finding optimum values of DTMD parameters to minimize a structural response under certain conditions and constraints is an optimization problem. In this paper, a multi-objective optimization problem is addressed, as defined by Equation 8, with the aim of identifying a set of optimal designs known as Pareto optimal solutions for a frame equipped with a DTMD to mitigate vibrations effectively. The multi-objective optimization is particularly beneficial in vibration control as it enables balancing competing performance criteria, such as minimizing acceleration and displacement, which directly affect structural integrity (Islam et al., 2018). The primary objective in this study focuses on minimizing the displacement response of the top floor of the structure, denoted as f1(X), while the secondary objective aims to minimize the acceleration response of the same floor, represented as f2(X). These objectives are critical, as excessive acceleration can lead to discomfort for occupants and potential structural damage, whereas significant displacement may affect the stability and load-bearing capacity of the frame during seismic events (Joe et al., 2017).
Here, X represents the design set comprising the dynamic properties of the TMDs, such as mass, damping coefficient, and stiffness, while n denotes the number of design variables involved in the optimization process. The functions f1(X) and f2(X) quantify the displacement and acceleration of the roof floor, respectively. The consideration process of the optimization objectives will be elaborated upon in the following sections, highlighting a balance between minimizing vibrations and maintaining structural integrity. This study formulates a multi-objective optimization problem to identify the optimal combination of dynamic characteristics for TMDs, aiming to achieve the best trade-off between reducing roof floor acceleration and displacement. The methodology employed in this study consists of five main steps, systematically addressing the modeling, optimization, and evaluation of TMD configurations. These steps are as follows:
A) Modeling a frame equipped with DTMD in OpenSEES: The first step involves developing a numerical model of a structural frame equipped with a DTMD using OpenSEES (McKenna, 2011). This numerical model serves as the foundation for subsequent dynamic analyses and optimization.
B) Modification of DTMD dynamic characteristics using a randomly generated population in metaheuristic optimization algorithms: In this step, the dynamic properties of the DTMD (damping coefficient and stiffness) are iteratively adjusted using metaheuristic optimization algorithms to evaluate its effect on the structure’s vibrational behavior.
C) Performing dynamic time history analysis and recording structural responses: once a set of DTMD characteristics is considered from the random population of the optimization algorithm, dynamic time history analysis is performed to evaluate the effectiveness of a set of DTMD characteristics on structure. In this step, the acceleration and displacement of the structure are determined and recorded for each set of DTMD characteristics.
D) Iterative execution of steps B and C for each optimization algorithm: to ensure convergence and optimality; Steps B and C are repeated iteratively for each metaheuristic algorithm until a well-defined Pareto front is obtained. The optimization stops when reaching max iterations, meeting convergence criteria, or no further improvement occurs. The Pareto front identifies trade-offs that provide optimal DTMD design selection.
E) Comparing Pareto front curves and identifying optimal DTMD characteristics: after obtaining Pareto front solutions from different metaheuristic algorithms, a comparative analysis is performed to identify the best-performing DTMD characteristics. The Pareto fronts from different algorithms are compared to assess solution efficiency. A global Pareto front is formed by selecting the best solutions, ensuring an optimal DTMD design. The final design is chosen using weighting methods. Through this comparative process, the study arrives at well-optimized DTMD characteristics that offers the best trade-off between reducing vibrations.
By following these five steps, this study provides an optimization and analysis of the DTMD optimal design, along with a comparative evaluation across multiple optimization techniques. Figure 3 presents a graphical representation of the methodology employed in this study, clearly illustrating its various steps and providing a comprehensive overview of the approach.
This section presents a case study to evaluate the proposed methodology. It includes the specifications of the structural model, the earthquake excitation model, and the optimization variables. Further details are provided in the following subsections.
In this study, a 10-floor, two-dimensional shear frame model equipped with a DTMD on the roof floor is used to investigate the efficiency of the DTMD in reducing the structural response under earthquake excitation. The frame is modeled using OpenSEES (McKenna, 2011) and subjected to ground acceleration based on a time history model. The TMDs are typically installed on the upper floor of a frame, as this location corresponds to the point of maximum amplitude of the first mode shape, where the effects of vibrations are most pronounced (Ras, 2024). To ensure a comprehensive analysis, the structural properties of the frame are assumed to be identical across all floors. TMDs are typically designed to operate within a structure’s primary frequency range so that the response of the structure remains linear (Banerjee and Ghosh, 2020). On the other hand, standard design frameworks, such as ASCE 7-16, utilize linear response analysis for initial TMD design, making this approach suitable for preliminary evaluations (Haselton et al., 2017). In this study, the response of the structure is considered based on linear behavior due to the enhanced performance of optimization functions and other mentioned reasons.
The geometry and structural properties of the frame, along with the TMDs mass, are summarized in Table 1, which serves as a reference for the model parameters and their effects on dynamic performance. The linear members, including beams and columns, are modeled as elastic beam-column elements, which behave elastically. This approach allows for a rapid estimation of the structural behavior under dynamic loading conditions. The material used for the beam and column sections is assumed to be elastic. The floor damping is represented using a viscous material model with a damping coefficient c = 1.24 E+7
The DTMDs are strategically positioned at both ends of the beam on the roof floor, following the methodology proposed by Alibabaei Shahraki et al. (2023) as shown in Figure 4. For the TMDs, the masses are set to a constant, assumed to be approximately 30% of the floors mass, ensuring effective vibration mitigation. The schematic of model is presented in Figure 1.
The predominant natural period of the structure without TMDs is approximately 0.93 s. With the incorporation of TMDs, this period increases, with the extent of the increase depending on the dynamic properties of the TMD. Although the weight of the dampers was considered constant, other dynamic characteristics of the TMD must be considered and presented. These are presented in more detail below.
There are specific limitations to changing the mass of TMD such as space restrictions (Li, 2000), retrofitting challenges (Sun and Nagarajaiah, 2014), and installation (Li and Ni, 2007). Maintaining a constant mass minimizes material costs. Instead of adding expensive additional mass, optimizing stiffness and damping provides a more cost-effective solution with minimal structural modifications. Based on this consideration, the stiffness (Kdi) and damping coefficient (Cdi) of each TMD serve as the design variables in this study (four design variables). These characteristics are vital for enhancing the overall dynamic performance of the structure; however, practical constraints limit their values. To optimize efficiency, this study adopts the allowable values for the stiffness and damping coefficients as proposed by (Mashayekhi et al., 2023), which are detailed in Table 3.
However, the optimization problem is a frame with two TMDs, each with different values for stiffness and damping coefficient. Different values for these two parameters are the initial values in each metaheuristic algorithm, and then these values change based on the structure of the algorithm. After each change in the decision variables, a seismic analysis was performed to estimate the dynamic vibrations of the model. The details of the seismic analysis are provided below.
In this study, a specific earthquake excitation record is selected to optimize the stiffness and damping parameters of the TMDs, considering several reasons. First, it ensures an accurate evaluation of the structure’s performance under real conditions. Additionally, it simplifies calculations and enables a focused analysis of the structural response to a specific input, enhancing the efficiency of the optimization process. Finally, this approach serves as a foundation for more advanced analyses involving multiple earthquake records. Among the various methods for earthquake excitation modeling, time history analysis is regarded as one of the most effective, offering detailed insights into the dynamic behavior of structures under seismic loading (Greco et al., 2018). In this study, the El Centro ground motion data from the Imperial Valley, California earthquake, which occurred on 18 May 1940, is considered to simulate the ground shaking applied to the building. The El Centro earthquake is widely considered a significant historical benchmark due to its varied frequency contents (Figure 5B), and well-documented ground motion records, making it a standard reference for seismic analysis (Udwadia and Trifunac, 1973). The excitation data consists of 2830 points of acceleration values at a time interval of 0.02. The absolute peak ground acceleration in this record is 3.43 m/s2, as provided in Figure 5A. For an accurate seismic simulation, the building is assumed to be on soft soil (Type D), consistent with the El Centro earthquake record. The design spectrum from ASCE 41-17 (American Society of Civil Engineers, 2017) for the same soil type, with Ss = 0.7 and S1 = 0.36, is also considered to determine the spectral characteristics of the structure.
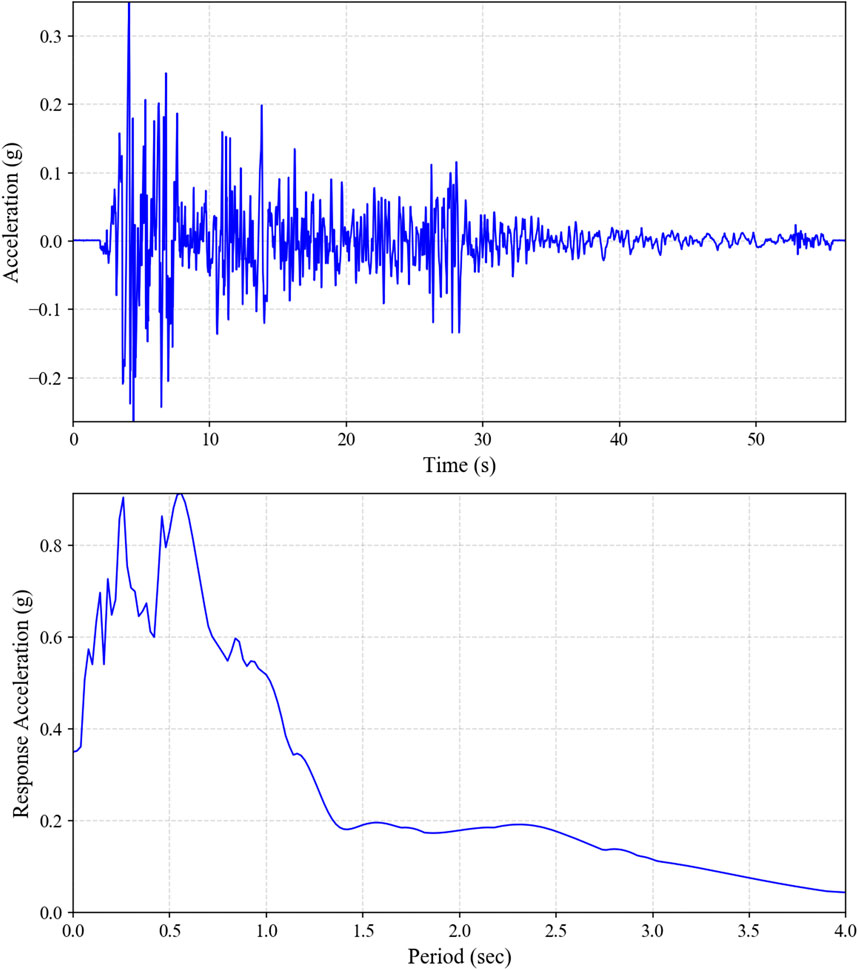
Figure 5. Earthquake of 1940 Imperial Valley used in seismic analysis of study, (A) acceleration time history, (B) response spectrum (5%).
After optimizing the structure using the specified earthquake record, additional optimization is conducted to assess the efficiency of the proposed method using multiple earthquake records representative of the seismic characteristics of the site of model. By incorporating a diverse set of ground motions, the effectiveness of the optimized TMD parameters is examined under varying seismic conditions. For this purpose, seven far-field ground motion records from FEMA P 695 (FEMA P 695, 2009)are selected, as listed in the Table 4. The selected ground motions are adjusted to make them compatible with the target spectrum using the spectral matching technique. These ground motion records are scaled to spectral acceleration proposed by ASCE 41-17 (American Society of Civil Engineers, 2017), as the target spectral acceleration by SeismoMatch (version 2025) program (Seismosoft, 2025). SeismoMatch adjusts ground motion records to match a target response spectrum using a wavelet-based algorithm. This method modifies the amplitude of frequency components in the time domain while preserving the original phase characteristics and duration. Figure 6 displays the original and scaled ground motion records. Additionally, Figure 7 presents the target design spectrum, along with the spectral acceleration of both the original and scaled ground motion records. Although the scaled ground motion record closely matches the target design spectrum, some discrepancies remain due to inherent differences, which are often unavoidable in real-world scenarios. The average error values for the spectrum of each record are presented in Table 5.
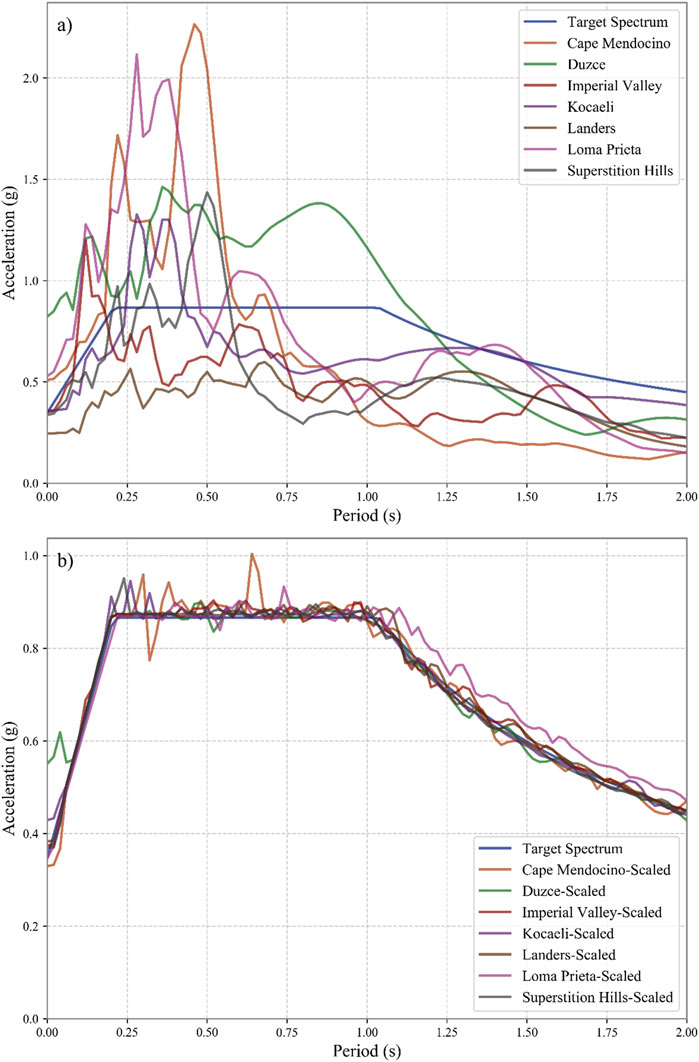
Figure 7. Spectral acceleration of the original and scaled ground motion records. (A) spectral acceleration of the original ground motion records, (B) spectral acceleration of the scaled ground motion records.
In this study, the dynamic characteristics of two TMDs installed in a 10-floor frame are analyzed to mitigate seismic vibrations. To achieve optimal tuning, seven distinct optimization algorithms are applied, refining the dampers’ parameters to enhance the frame’s dynamic response during seismic events. The results are divided into three key sections. In section (A), the dynamic properties of each TMD estimated by each optimization algorithm based on the El Centro ground motion record are presented, offering a comparative assessment of accuracy, convergence behavior, and computational efficiency. In section (B), the effectiveness of the optimized TMDs is assessed by comparing the seismic response of the building with and without dampers under identical earthquake conditions, using the El Centro ground motion record. In section (C), the dynamic characteristics of the TMDs are evaluated using seven scaled far-field earthquake ground motion records. Additionally, the structural responses with and without dampers are determined for each of these records. This comparison illustrates the extent to which the optimized TMDs improve structural resilience and reduce dynamic responses such as displacement and acceleration.
In optimization algorithms, iterating with varying decision variable values across multiple iterations is a common approach to gradually achieving improved solutions. Typically, the final iteration either yields a better solution or validates the trend observed in previous iterations. Various methods can be used to express the optimal solution. In this study, to address uncertainties in the optimization process, each algorithm was executed five times. For each algorithm, the Pareto front was generated during the final iteration of each run. For instance, Figure 8 displays the Pareto fronts generated by the NSGA-II algorithm over independent runs, while Figure 9 presents box plots of its competing objectives. The final Pareto front of each algorithm was determined by calculating the median front across the five Pareto fronts, providing a reliable set of optimal solutions. The optimal set of DTMD characteristics was then identified using a balanced weighting approach, a 50%–50% weighting scheme, to equally prioritize the minimization of displacement and acceleration. This evaluated optimal set of characteristics was considered the representative point on the final Pareto front that achieved the best-balanced trade-off between the two objectives. The details of the optimal DTMD characteristics are presented in Table 6.
In another part of the results, to implicitly assess the effect of DTMD and estimate their efficiency, particularly by utilizing their optimal characteristics, the acceleration and displacement responses of the frame are compared and evaluated under two conditions: A) with the implementation of DTMD (controlled frame), and B) without DTMD (uncontrolled frame). This comparison provides insight into the impact of DTMD on the overall structural performance.
The percentage decreases in the floor displacement and acceleration responses across the frame are presented in Table 7, 8 for the controlled and uncontrolled cases, respectively. Although the percentage decreases in displacement across different floors are relatively similar for each algorithm, the percentage decreases in acceleration are greater in the upper stories. The data clearly demonstrate significant reductions in both displacement and acceleration across all floors when the TMDs are implemented. Among the optimization algorithms, the NSGA-II achieved the highest reduction in mean floor displacement (47.69%), while the MOALO algorithm yielded the largest in mean floor acceleration reduction (30.67%).
Figure 10 provides additional insights into the comparative performance of the algorithms in reducing both floor displacement and acceleration. The numbers within the circular markers on each curve represent the floor levels of the structure, offering a clear visualization of how the performance of each algorithm varies across different structural heights. Notably, the greatest acceleration reduction occurs consistently at the 8th floor across all algorithms, while the floor with the highest displacement reduction varies among algorithms. All algorithms exhibit similar trends, clustering closely within a reduction range of 40%–50% for floor displacement and reaching up to 40% reduction in floor acceleration. However, while MOAVOA achieves the second-highest displacement reduction percentage in the lower floors, its effectiveness decreases in the upper floors. Among the algorithms, NSGA-II attains the most significant displacement reduction, ranging between 46% and 49%, while maintaining a consistent acceleration reduction of up to 40%. Overall, NSGA-II provides the best balance between displacement and acceleration reduction across all stories.
Figure 11 illustrates the global Pareto front, derived by combining and analyzing the Pareto fronts of all algorithms, serving as a benchmark for evaluating algorithm performance. Local Pareto fronts are generated by individual optimization algorithms, while the global Pareto front is constructed by filtering out dominated solutions, retaining only the globally optimal trade-offs among competing objectives.
A more detailed analysis of the global Pareto front is provided in Figure 12, which shows the number of solutions contributed by each algorithm’s Pareto front to the global Pareto front. As depicted, NSGA-II contributes the highest number of optimal solutions, indicating its superior performance in optimizing the problem compared to the other algorithms. This dominance suggests that NSGA-II effectively balances competing objectives, resulting in a higher presence on the global Pareto front. Conversely, MOPSO has no contributions to the global Pareto front and resulted in producing the least-optimized solutions for the given problem.
Subsequently, a metaheuristic optimization algorithm was applied to optimize the structural model under seismic excitations. The objective of this work is to incorporate dynamic conditions while accounting for the spectral characteristics of structure. Since NSGA-II provided the most optimal solution in the previously discussed problem, the optimization process was conducted on seven distinct scale earthquake ground motion records to identify the best-performing design. The optimal solution was selected based on its ability to achieve the most balanced minimization of both roof acceleration and displacement. Table 9 presents the characteristics of the optimized DTMD, which achieved a well-balanced minimization of roof displacement and acceleration. After implementing these parameters in the DTMD, which was installed at the top of the frame, Figures 13B, 14B illustrate the distribution of maximum displacement and acceleration across the frame’s floors. Additionally, Figures 13A, 14A depict the percentage reduction in maximum floor displacement and acceleration achieved by equipping the frame with the DTMD compared to the unequipped frame.
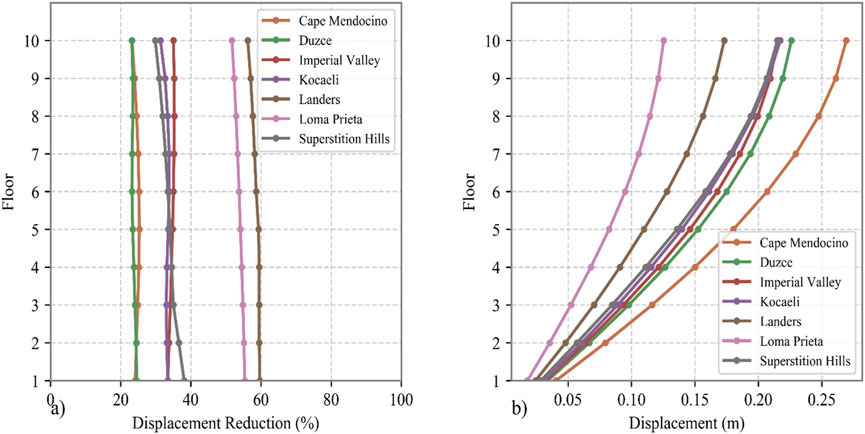
Figure 13. Response of frame under various scaled ground motion, (A) Displacement reduction, (B) Displacement.
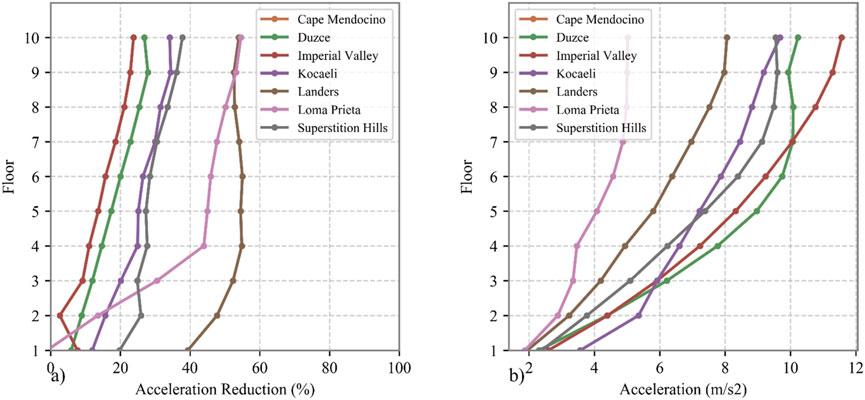
Figure 14. Response of frame under various scaled ground motion, (A) Acceleration reduction, (B) Acceleration.
This study investigated the optimization of DTMDs using seven metaheuristic algorithms to enhance seismic performance in a 10-floor shear frame structure, focusing on minimizing both displacement and acceleration responses under the seismic excitation of the El Centro earthquake and seven far-field ground motion records scaled to the design spectrum to account for the seismic conditions of the structural model. The study began with a detailed description of the modeling process and proceeded to estimate the dynamic characteristics of the DTMDs, providing a comprehensive framework for the optimization process. This study uses the global Pareto front as a benchmark for comparing the performance of the optimization algorithms. The global Pareto front is constructed by aggregating the Pareto fronts generated by individual algorithms and filtering out dominated solutions, thereby identifying the most optimal solutions across all methods. This approach provides a robust basis for evaluating and ranking algorithmic effectiveness in addressing multi-objective optimization problems.
Key findings demonstrate that optimally tuned DTMDs significantly enhance structural performance, achieving reductions in floor displacement by 40%–50% and floor acceleration by 2%–40%. These results underscore the effectiveness of DTMDs in mitigating seismic-induced vibrations and improving the safety and resilience of structures. Among the evaluated algorithms, NSGA-II consistently dominates other solutions, reaching the highest reduction in both story displacement and acceleration, demonstrating its ability to optimize displacement objectives effectively. Additionally, NSGA-II contributed the most solutions to the global Pareto front, indicating its superior capacity to balance competing objectives of displacement and acceleration reduction. In contrast, while MOSPO effectively reduced acceleration, it demonstrated limitations in minimizing displacement, resulting in a less balanced trade-off. MOAVOA performed well in the lower floors but showed a decline in displacement reduction efficiency in the upper floors compared to other algorithms. The clustering performance of MOALO, MOGOA, MOGWO, and MOPSO further demonstrated their robustness, consistently delivering solutions that achieve significant reductions in both objectives.
This study has certain limitations that should be acknowledged. All results are based on a single natural seismic ground motion record, which is a limitation of this study. In addition, the nonlinear behavior that causes changes in the stiffness of the structure against earthquakes has not been considered. Accordingly, for future research, it is suggested to evaluate the changes in the TMD to structure mass ratio and utilize nonlinear behavior for structure. This limitation may reduce the effectiveness of TMDs.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
FZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Software, Validation. SA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. EN: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AS-M: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
During the preparation of this work the first author used ChatGPT in order to improve readability and language. After using these tools, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Akhlagh Pasand, A., and Zahrai, S. M. (2024). Seismic control of tall buildings using vertically distributed multiple tuned mass dampers. Struct. Des. Tall Special Build. 33 (14), e2123. doi:10.1002/tal.2123
Alibabaei Shahraki, M., Kamgar, R., and Heidarzadeh, H. (2023). Damage-based design of multiple tuned mass dampers to improve the seismic performance of steel frame structures. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 173, 108062. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.108062
Alnayhoum, F., Bekdaş, G., Ni̇Gdeli̇, S. M., and Camara, I. K. (2023). Multiple tuned mass dampers and double tuned mass dampers for soft story structures: a comparative study. Eng. World 5, 167–174. doi:10.37394/232025.2023.5.19
American Society of Civil Engineers. (2017). ASCE/SEI 41-17: seismic evaluation and retrofit of existing buildings.
Balakrishnan, K., Dhanalakshmi, R., and Seetharaman, G. (2022). S-shaped and V-shaped binary African vulture optimization algorithm for feature selection. Expert Syst. 39 (10), e13079. doi:10.1111/exsy.13079
Banerjee, S., and Ghosh, A. D. (2020). Optimal design of tuned mass damper for base-excited structures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater Sci. Eng. 936, 012016. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/936/1/012016
Bekdaş, G., and Nigdeli, S. M. (2011). Estimating optimum parameters of tuned mass dampers using harmony search. Eng. Struct. 33 (9), 2716–2723. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.05.024
Cao, H. Q., and Tran, N.-A. (2023). Multi-objective optimal design of double tuned mass dampers for structural vibration control. Archive Appl. Mech. 93 (5), 2129–2144. doi:10.1007/s00419-023-02376-6
Cao, Z., Hua, X., Wen, Q., Chen, Z., and Niu, H. (2019). A state space technique for modal identification of coupled structure–tuned mass damper systems from vibration measurement. Adv. Struct. Eng. 22 (9), 2048–2060. doi:10.1177/1369433219829807
Cetin, H., Aydin, E., and Ozturk, B. (2019). Optimal design and distribution of viscous dampers for shear building structures under seismic excitations. Front. Built Environ. 5. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2019.00090
Chang, C. (1999). Mass dampers and their optimal designs for building vibration control. Eng. Struct. 21 (5), 454–463. doi:10.1016/s0141-0296(97)00213-7
Choi, J., Kang, D. S., Lee, M. G., Bae, S. G., Hong, T., Lee, D.-E., et al. (2023). Vibration safety evaluation model and sensor network-based monitoring system for coke drums in operation. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 22 (3), 1399–1412. doi:10.1080/13467581.2022.2085719
Chowdhury, A. H., Iwuchukwu, M. D., and Garske, J. J. (1987). The past and future of seismic effectiveness of tuned mass dampers. Struct. Control, 105–127. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-3525-9_7
Coello, C. A., González Brambila, S., Figueroa Gamboa, J., Castillo Tapia, M. G., and Hernández Gómez, R. (2020). Evolutionary multiobjective optimization: open research areas and some challenges lying ahead. Complex and Intelligent Syst. 6 (2), 221–236. doi:10.1007/s40747-019-0113-4
Coello, C. A. C., Pulido, G. T., and Lechuga, M. S. (2004). Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 8 (3), 256–279. doi:10.1109/tevc.2004.826067
Daniel, Y., and Lavan, O. (2014). Gradient based optimal seismic retrofitting of 3D irregular buildings using multiple tuned mass dampers. Comput. Struct. 139, 84–97. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2014.03.002
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., and Meyarivan, T. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6 (2), 182–197. doi:10.1109/4235.996017
Desu, N. B., Deb, S., and Dutta, A. (2006). Coupled tuned mass dampers for control of coupled vibrations in asymmetric buildings. Struct. Control Health Monit. Official J. Int. Assoc. Struct. Control Monit. Eur. Assoc. Control Struct. 13 (5), 897–916. doi:10.1002/stc.64
Elias, S., Matsagar, V., and Datta, T. K. (2017). Distributed multiple tuned mass dampers for wind response control of chimney with flexible foundation. Procedia Eng. 199, 1641–1646. doi:10.1016/j.proeng.2017.09.087
Farshidianfar, A., and Soheili, S. (2013). Ant colony optimization of tuned mass dampers for earthquake oscillations of high-rise structures including soil–structure interaction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 51, 14–22. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2013.04.002
Fasil, M., and Sajeeb, R. (2019). “Numerical investigation on the effectiveness of double tuned mass dampers in structural vibration control,”. Recent advances in structural engineering. Editors A. Rama Mohan Rao, and K. Ramanjaneyulu (Singapore: Springer), 2, 375–388. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-0365-4_32
Gattulli, V., Potenza, F., and Di Sabatino, U. (2019). Dissipative coupling for the seismic enhancement of adjacent structures. Eng. Struct. 199, 109520. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109520
Greco, F., Luciano, R., Serino, G., and Vaiana, N. (2018). A mixed explicit–implicit time integration approach for nonlinear analysis of base-isolated structures. Ann. Solid Struct. Mech. 10 (1–2), 17–29. doi:10.1007/s12356-017-0051-z
Hadi, M. N., and Arfiadi, Y. (1998). Optimum design of absorber for MDOF structures. J. Struct. Eng. 124 (11), 1272–1280. doi:10.1061/(asce)0733-9445(1998)124:11(1272)
Haselton, C. B., Baker, J. W., Stewart, J. P., Whittaker, A. S., Luco, N., Fry, A., et al. (2017). Response history analysis for the design of new buildings in the nehrp provisions and ASCE/SEI 7 Standard: Part I - overview and Specification of Ground Motions. Earthq. Spectra 33, 373–395. doi:10.1193/032114EQS039M
Islam, M. S., Do, J., and Kim, D. (2018). Multi-objective optimization of tmd for frame structure based on response surface methodology and weighted desirability function. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 22, 3015–3027. doi:10.1007/s12205-017-0387-2
Joe, Y. H., Son, H. M., and Hu, J. W. (2017). Behavioral performance evaluation of the moment-resisting frame models equipped with seismic damage mitigation systems. J. Earthq. Eng. Soc. Korea 21 (6), 311–322. doi:10.5000/EESK.2017.21.6.311
Kamgar, R., Dadkhah, M., Heidarzadeh, H., and Javanmardi, M. S. (2025). Utilizing tuned mass damper for reduction of seismic pounding between two adjacent buildings with different dynamic characteristics. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 188, 109036. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.109036
Kaveh, A., Talatahari, S., and Khodadadi, N. (2022). Stochastic paint optimizer: theory and application in civil engineering. Eng. Comput. 38, 1921–1952. doi:10.1007/s00366-020-01179-5
Khodadadi, N., Abualigah, L., and Mirjalili, S. (2022a). Multi-objective stochastic paint optimizer (MOSPO). Neural Comput. Appl. 34 (20), 18035–18058. doi:10.1007/s00521-022-07405-z
Khodadadi, N., Soleimanian Gharehchopogh, F., and Mirjalili, S. (2022b). MOAVOA: a new multi-objective artificial vultures optimization algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 34 (23), 20791–20829. doi:10.1007/s00521-022-07557-y
Kleingesinds, S., and Lavan, O. (2022). Bi-tuned semi-active TMDs: multi-hazard design for tall buildings using gradient-based optimization. Struct. Control Health Monit. 29 (3), 1–29. doi:10.1002/stc.2901
Kumar, A., Pant, S., Ram, M., and Chaube, S. (2019). Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer approach to the reliability-cost optimization of life support system in space capsule. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 10 (2), 276–284. doi:10.1007/s13198-019-00781-1
Lee, B.-H., Chen, C.-C., Chen, T.-W., Shiao, S.-Y., Jiang, C.-R., and Yeh, F.-Y. (2022). Enhancement of structural seismic performance of low-rise buildings using displacement-dependent tuned mass damper. Structures 37, 1119–1128. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2022.01.051
Leung, A. Y. T., and Zhang, H. (2009). Particle swarm optimization of tuned mass dampers. Eng. Struct. 31 (3), 715–728. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2008.11.017
Li, C. (2000). Performance of multiple tuned mass dampers for attenuating undesirable oscillations of structures under the ground acceleration. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 29, 1405–1421. doi:10.1002/1096-9845(200009)29:9<1405::AID-EQE976>3.0.CO;2-4
Li, H.-N., and Ni, X.-L. (2007). Optimization of non-uniformly distributed multiple tuned mass damper. J. Sound. Vib. 308, 80–97. doi:10.1016/j.jsv.2007.07.014
Lin, C.-C., Wang, J.-F., and Ueng, J.-M. (2001). Vibration control identification of seismically excited m.d.o.f. structure-ptmd systems. J. Sound Vib. 240 (1), 87–115. doi:10.1006/jsvi.2000.3188
Lin, X., and Lin, W. (2021). Optimal allocation and control of magnetorheological dampers for enhancing seismic performance of the adjacent structures using whale optimization algorithm. Shock Vib. 2021. doi:10.1155/2021/1218956
Lu, Z., Liu, X., Ma, N., and Zhou, M. (2022). Multi-objective optimization and seismic performance verification of multiple tuned impact dampers for nonlinear benchmark building. Structures 41, 1672–1686. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2022.05.101
Majdi, A., Mashayekhi, M., and Sadeghi-Movahhed, A. (2024). Effect of near-fault earthquake characteristics on seismic response of mid-rise structures with triple friction pendulum isolator. J. Rehabilitation Civ. Eng. 12 (1), 47–62. doi:10.22075/jrce.2023.30434.1845
Majdi, A., Sadeghi Movahhed, A., Mashayekhi, M., Zardari, S., Benjeddou, O., and De Domenico, D. (2023). On the influence of unexpected earthquake severity and dampers placement on isolated structures subjected to pounding using the modified endurance time method. Buildings 13 (5), 1278. doi:10.3390/buildings13051278
Mashayekhi, M., Shirpour, A., and Sadeghi, R. (2023). Finding optimum parameters of passive tuned mass damper by PSO, WOA, and hybrid PSO-WOA (HPW) algorithms. J. Soft Comput. Civ. Eng. 7 (4), 72–92. doi:10.22115/scce.2023.352340.1489
Mashayekhi, M. R., and Mosayyebi, S. (2023). A new hybrid Harris hawks optimization (HHO) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm for the design of castellated beams. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 24 (7), 2121–2139. doi:10.1007/s42107-023-00630-4
Mazza, F., and Labernarda, R. (2021). “Concave surface base-isolation system against seismic pounding of irregular adjacent buildings,” in 14th world congress in computational mechanics (WCCM), ECCOMAS congress 2020.
McKenna, F. (2011). OpenSees: a framework for earthquake engineering simulation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 13, 58–66. doi:10.1109/MCSE.2011.66
Mirjalili, S., Jangir, P., and Saremi, S. (2017). Multi-objective ant lion optimizer: a multi-objective optimization algorithm for solving engineering problems. Appl. Intell. 46 (1), 79–95. doi:10.1007/s10489-016-0825-8
Mirjalili, S., Saremi, S., Mirjalili, S. M., and Coelho, L. dos S. (2016). Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: a novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 47, 106–119. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.039
Mirjalili, S. Z., Mirjalili, S., Saremi, S., Faris, H., and Aljarah, I. (2018). Grasshopper optimization algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 48 (4), 805–820. doi:10.1007/s10489-017-1019-8
Mohebbi, M., Shakeri, K., Ghanbarpour, Y., and Majzoub, H. (2013). Designing optimal multiple tuned mass dampers using genetic algorithms (GAs) for mitigating the seismic response of structures. JVC/Journal Vib. Control 19 (4), 605–625. doi:10.1177/1077546311434520
Ok, S.-Y., Song, J., and Park, K.-S. (2008). Optimal performance design of bi-Tuned Mass Damper systems using multi-objective optimization. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 12 (5), 313–322. doi:10.1007/s12205-008-0313-8
Rahman, M. S., Hassan, M. K., Chang, S., and Kim, D. (2017). Adaptive multiple tuned mass dampers based on modal parameters for earthquake response reduction in multi-story buildings. Adv. Struct. Eng. 20 (9), 1375–1389. doi:10.1177/1369433216678863
Ras, A. (2024). Parametric investigation of tuned mass damper on metallic buildings response subjected to far-field and near-fault ground motions. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 25 (1), 413–425. doi:10.1007/s42107-023-00784-1
Sadeghi-Movahhed, A., Billah, A. H. M. M., Shirkhani, A., Mashayekhi, M., and Majdi, A. (2024a). Vulnerability assessment of tall isolated steel building under variable earthquake hazard levels using endurance time method. J. Struct. Integr. Maintenance 9 (1), 2314816. doi:10.1080/24705314.2024.2314816
Sadeghi-Movahhed, A., De Domenico, D., and Majdi, A. (2024b). Structural flexibility impact on pounding severity and seismic performance of adjacent isolated buildings. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 181, 108667. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.108667
Sadeghi Movahhed, A., Shirkhani, A., Zardari, S., Noroozinejad Farsangi, E., and Karimi Pour, A. (2023). Effective range of base isolation design parameters to improve structural performance under far and near-fault earthquakes. Adv. Struct. Eng. 26 (1), 52–71. doi:10.1177/13694332221119870
Sadeghi Movahhed, A., Zardari, S., and Şadoğlu, E. (2022). Seismic performance of a building base-isolated by TFP susceptible to pound with a surrounding moat wall. Earthquakes Struct. 23 (1), 723–736. doi:10.12989/eas.2022.23.1.087
Seismosoft (2025). SeismoMatch. Available online at: https://seismosoft.com/products/seismomatch/Tables.
Singh, M. P., Singh, S., and Moreschi, L. M. (2002). Tuned mass dampers for response control of torsional buildings. Earthq. Eng. and Struct. Dyn. 31 (4), 749–769. doi:10.1002/eqe.119
Steinbuch, R. (2011). Bionic optimisation of the earthquake resistance of high buildings by tuned mass dampers. J. Bionic Eng. 8 (3), 335–344. doi:10.1016/S1672-6529(11)60036-X
Sun, C., and Nagarajaiah, S. (2014). Study on semi-active tuned mass damper with variable damping and stiffness under seismic excitations. Struct. Control Health Monit. 21, 890–906. doi:10.1002/stc.1620
Thompson, A. G. (1981). Optimum tuning and damping of a dynamic vibration absorber applied to a force excited and damped primary system. J. Sound Vib. 77 (3), 403–415. doi:10.1016/S0022-460X(81)80176-9
Udwadia, F., and Trifunac, M. (1973). Comparison of earthquake and microtremor ground motions in El Centro, California. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 63 (4), 1227–1253. doi:10.1785/bssa0630041227
Wang, L., Shi, W., and Zhou, Y. (2022). Adaptive-passive tuned mass damper for structural aseismic protection including soil–structure interaction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 158, 107298. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2022.107298
Xu, K., and Igusa, T. (1992). Dynamic characteristics of multiple substructures with closely spaced frequencies. Earthq. Eng. and Struct. Dyn. 21 (12), 1059–1070. doi:10.1002/eqe.4290211203
Yahyai, M., Zebarjad, L., Head, M., and Shokouhian, M. (2021). Optimum parameters for large mass ratio TMDs using frequency response function. J. Earthq. Eng. 25 (10), 1–20. doi:10.1080/13632469.2019.1624228
Keywords: double tuned mass damper, seismic control, seismic response, multi-objective optimization, evolutionary algorithm, global Pareto front
Citation: Zamani F, Alavi SH, Mashayekhi M, Noroozinejad Farsangi E, Sadeghi-Movahhed A and Majdi A (2025) Optimum design of double tuned mass dampers using multiple metaheuristic multi-objective optimization algorithms under seismic excitation. Front. Built Environ. 11:1559530. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1559530
Received: 13 January 2025; Accepted: 11 February 2025;
Published: 13 March 2025.
Edited by:
Rosario Montuori, University of Salerno, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Zamani, Alavi, Mashayekhi, Noroozinejad Farsangi, Sadeghi-Movahhed and Majdi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ehsan Noroozinejad Farsangi, ZWhzYW4ubm9yb296aW5lamFkQHdlc3Rlcm5zeWRuZXkuZWR1LmF1
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.