- Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, School of Engineering and Digital Sciences, Nazarbayev University, Astana, Kazakhstan
This study investigates the engineering properties of sulfate-containing soils from Astana, Kazakhstan, with a focus on their physical, chemical, and water retention characteristics. Understanding the challenges posed by sulfate-rich soils is critical for developing effective stabilization methods, especially in regions with extreme climates. Initial soil characterization revealed that the soil is well-graded sand with silt (SW-SM), with significant sulfate content (8518.8 ppm) and salinity (18.45%). Advanced techniques, including ion chromatography (IC), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), identified the presence of sulfate minerals such as gypsum and anhydrite. The soil water characteristic curve (SWCC) demonstrated bimodal behavior, with distinct air entry values of 4.988 kPa for macropores and 1000 kPa for micropores, highlighting its complex water retention properties. Shrinkage tests, analyzed using a 3D scanner, revealed a hyperbolic drying curve, with a sharp void ratio reduction during the normal shrinkage phase and minimal changes during the residual phase. These results underscore the soil’s susceptibility to volumetric changes under varying moisture conditions. This comprehensive geotechnical characterization provides critical insights into the behavior of sulfate-rich soils and their implications for infrastructure stability. The findings emphasize the need for tailored engineering solutions to mitigate risks associated with sulfate-induced swelling and shrinkage, offering practical contributions to construction practices in sulfate-affected regions. Future research will explore stabilization strategies to enhance the mechanical performance and durability of these soils.
1 Introduction
Over the past few decades, problematic soils have become a significant global issue, severely impacting road infrastructure and environmental management. Traditionally, chemical treatment with various additives, including both conventional (Pandey and Rabbani, 2017; Mahmood et al., 2019; Brandl, 2021; Regasa et al., 2023; Ahmadullah and Chrysochoou, 2024) and non-conventional stabilizers (Mekonnen et al., 2022; Ale, 2023; Gidebo et al., 2023; Zivari et al., 2023) has been the primary method to address these challenges. However, certain soil conditions, particularly those containing sulfates, have exacerbated issues like road surface deformation and wear, especially when treated with calcium-based additives (Rollings et al., 1999; Harris et al., 2005).
Initially, these problems were attributed to soil swelling due to moisture variations, where the soil expands with water and contracts upon drying (National Academies of Sciences and Medicine, 2009). However, subsequent research revealed that sulfate heave plays a significant role in soil swelling and pavement damage. This phenomenon results from the reaction between calcium in stabilizers and sulfates or sulfides in the soil, forming ettringite—a mineral capable of expanding more than twice its original volume. The expansion creates stresses that exceed overburden pressure, leading to severe soil swelling and infrastructure damage (Puppala et al., 2018). Additionally, under specific conditions, such as the presence of carbonates and temperatures below 15°C, ettringite may transform into thaumasite, another expansive mineral that exacerbates heaving of road surfaces (Köhler et al., 2006).
Salinity further complicates the deformation and strength properties of frozen soils, particularly in cold regions. Sulfate minerals are especially impactful under freezing conditions. As soil water freezes, sulfate ions concentrate in the remaining unfrozen water, promoting the crystallization of sulfate minerals. This process generates both ice and mineral crystals, which can induce frost heave even in soils typically considered non-expansive (Harris et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2016). The degree of expansion in frozen sulfate soils depends on factors such as salt type and content, moisture levels, and temperature (Nguyen et al., 2010).
Several studies consistently show that low temperatures and high sulfate content exacerbate soil expansiveness. Freeze-thaw cycles in sulfate-rich soils often lead to significant reductions in strength and durability (Nguyen et al., 2010; Kutergin et al., 2012; Fang et al., 2018; Xiao et al., 2018). A recent study by Tang et al. (2020) introduced a predictive method for salt expansion, establishing a parabolic relationship between soil deformation and sulfate content. Furthermore, studies on the mechanical properties of frozen sulfate soils have consistently shown that their strength decreases as sulfate content increases (Nixon and Lem, 1984; Hivon and Sego, 1995; Hass et al., 2007; Kotov and Stanilovskaya, 2022). These findings highlight the significant risks sulfate-rich frozen soils pose to infrastructure, including roads and railways (Lai et al., 2016; Wan et al., 2017).
Addressing these challenges is especially critical in Kazakhstan, where cold climatic conditions and infrastructure stability are of paramount importance. Saline soils, particularly those rich in sulfates and chlorides, are widespread across Kazakhstan’s Central, Southern, and Western regions, encompassing desert steppes and deserts (Issanova et al., 2017). These areas experience significant salt accumulation due to the arid climate, with sulfates being more prevalent than chlorides in the semi-desert and dry steppe regions (Pashkov and Baybusinova, 2017). As a result, characterizing the engineering properties of sulfate-rich soils in Kazakhstan’s cold regions is crucial for ensuring the long-term stability of infrastructure.
This study investigates the engineering properties of sulfate-containing soils in Kazakhstan. The research begins by determining the physical properties of these soils through laboratory experiments. It then evaluates the soil water characteristic curve (SWCC) to assess water retention capacity, followed by shrinkage tests to describe the volume change characteristics of the soil. By providing a comprehensive analysis of these properties, the study contributes to the development of effective strategies for mitigating the risks posed by sulfate-rich soils in cold climates.
2 Geology of the region and geologic evolution of soil
Within this territory, three large geological-tectonic structures are identified, clearly isolated in space, and designated as engineering-geological regions of the first order: The orogenic belt of Kazakhstan, the Kazakh Shield, and the Turanian plate (Baitova, 2021). The Kazakh Shield stretches from the Alpine mountains of the Orogenic Belt of Kazakhstan in the south and southeast to the West Siberian Lowland in the north. Various Paleozoic structures are found in this area, including the Caledonian folds, which are particularly widespread. These Caledonian structures, part of the Ural-Siberian fold belt, occupy a significant part of the region under consideration and constitute the northern parts of folds extending from Central Asia to Kazakhstan and plunging under the loose cover of the West Siberian Lowland in the north. In addition, this territory contains large structures like the Kokchetav-North Tienshan system in the west and the Chingiz-Tarbagatai system in the east, which are anticlinal structures. The Hercynian Dzhungar-Balkhash mega synclinorium is located between them (Baitova, 2021).
About 60% of the territory of Kazakhstan is occupied by plains, and half of the country is covered by semi-deserts and deserts, particularly in the Turan lowland region (Danayev, 2008).
Kazakhstan experiences a distinctly continental climate with unevenly distributed precipitation. Evaporation rates are significantly higher than precipitation throughout most of Kazakhstan’s territory, except in mountainous regions (Issanova et al., 2017). The high aridity of the climate leads to increased groundwater evaporation, resulting in the accumulation of salt and soil salinization (Borovski, 1982). The climate has a great influence on the process of salt migration into soils.
Saline soils are widely distributed across Kazakhstan, with salinization primarily of a sulfate and chloride-sulfate nature (Faizov, 1980). The country’s arid climate plays a pivotal role in this process, promoting salt accumulation through mechanisms such as surface and underground runoff and wind transport (Borovski, 1982). Arid regions constitute a significant portion of Kazakhstan’s landscape, covering approximately 29%–30% of leached soils and 37% of chernozems. These soils are characteristic of areas with limited precipitation and high evaporation rates, where salt buildup is intensified over time. The widespread presence of saline soils, particularly in the form of sulfate and chloride-sulfate complexes, highlights the importance of understanding their geological evolution to address the challenges they pose to infrastructure and agricultural practices.
Figure 1 shows the soil map of the Akmola region, Kazakhstan. The region is predominantly covered by (1) dark brown loamy soils, which have a balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay; (2) salty clays with high salt content and fine particles; (3) stratified soils with various textures, having different layers with varying compositions; and (4) argillaceous and heavy loamy soils with high sodium content, which are clay-rich and heavy, affecting their structure.
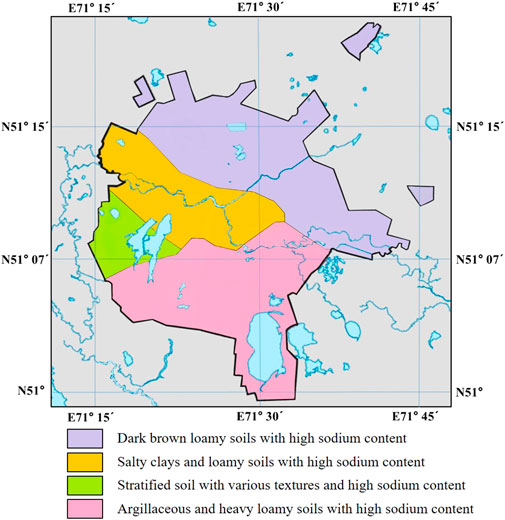
Figure 1. Soil map of Astana, Kazakhstan (modified from Uspanov et al., 1976).
3 Methodology
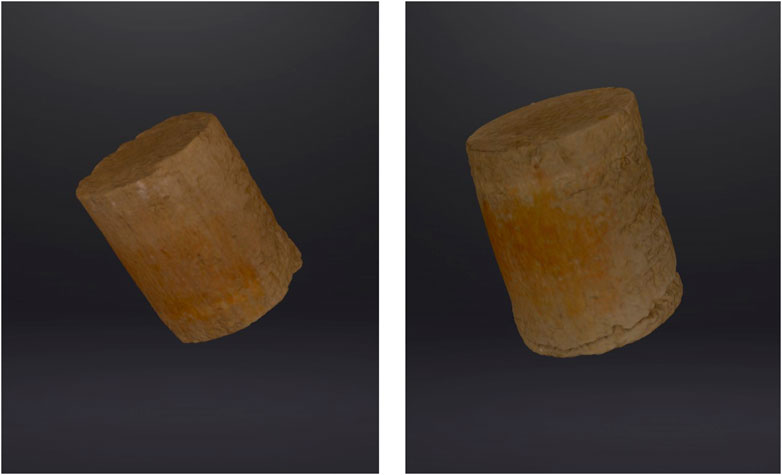
The soil samples were excavated from a construction site in Astana, Kazakhstan, at a 1.5–2.0 m depth. Figure 2 shows the soil from the site, where powdery, white efflorescence is visible on the soil’s surface.
3.1 Basic physical properties
A series of tests were conducted to determine its basic physical properties and comprehensively characterize the investigated soil for subsequent experimental analysis. Initially, sieve analysis and Atterberg limit tests were performed to classify the soil based on its grain size distribution and plasticity characteristics. Following this, the Standard Proctor test was employed to establish the soil’s maximum dry density and optimal moisture content. Additionally, specific gravity and shrinkage limit values were measured in accordance with ASTM standard test methods. These fundamental properties provide essential insights into the soil’s behavior and are crucial for guiding further experimental investigations.
3.2 Ion chromatography test
Ion chromatography (IC) is a reliable and effective technique for quantifying sulfate content in soils. In this study, IC was employed to measure the sulfate concentration in the soil samples. The process begins with the dissolution of sulfate compounds in a suitable solvent. A small aliquot of the dissolved sample is then introduced into the ion chromatography system. As the sample passes through ion exchange columns packed with inert materials like polyetheretherketone, various ions within the sample interact with the column resins. These interactions cause the ions to elute at different times, and conductivity detectors detect their presence. The concentration of sulfate ions is determined by comparing the conductivity of the sample solution to that of standard reference solutions used as the solvent for the sample and the baseline for calibration. A Dionex Ion Chromatography System (ICS) 6000 was utilized for this analysis, ensuring precise and accurate measurement of sulfate content in the soil samples.
3.3 X-ray fluorescence (XRF)
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) was employed to determine the elemental composition of the soil samples. In this technique, the soil sample is exposed to X-rays, which cause the atoms within the material to emit fluorescent X-rays at characteristic wavelengths. The specific oxides present in the soil can be identified by analyzing the energy and intensity of these emitted X-rays. For this study, the elemental analysis was performed using the Rigaku NEX CG, ensuring accurate detection of the various oxides within the soil matrix.
3.4 X-ray diffraction (XRD)
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was utilized to investigate the molecular structure and mineralogical composition of the soil. When a sample is subjected to X-rays, the scattered X-ray angles and intensities provide critical information regarding the arrangement of atoms in the soil. This data helps identify the minerals in the sample, complementing the elemental analysis obtained through XRF. The XRD analysis was carried out using the Rigaku SmartLab, allowing for precise characterization of the soil’s crystalline structure.
3.5 Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted gain a detailed understanding of the soil sample’s microstructure. The test was performed using the JEOL JSM IT200 (LA). Prior to imaging, the dried and powdered soil sample was coated with a thin layer of gold to enhance conductivity and improve image resolution. SEM provided high-resolution images that revealed the intricate microstructure of the soil, offering valuable insights when compared with the results obtained from XRD and XRF analyses.
3.6 Soil water characteristic curve (SWCC)
The Soil-Water Characteristic Curve (SWCC) was measured using two different methods: the Tempe cell and the WP4C, as shown in Figure 3. The Tempe cell, equipped with a 1 bar ceramic disc, was employed for precise measurements of soil-water behavior at relatively low pressures. Suction measurements were taken at 0.1, 5, 10, 20, 50, 75, and 100 kPa. The soil samples were prepared at the optimum water content and then compacted. Each test was continued until the sample’s weight stabilized, ensuring suction equalization within the soil. Prior to testing, the ceramic disc was submerged in the de-aired water to eliminate air bubbles, and the soil sample was fully saturated within the Tempe cell mold. The sample’s weight was closely monitored for each suction level, and once stabilized, the water content corresponding to that specific suction was calculated.
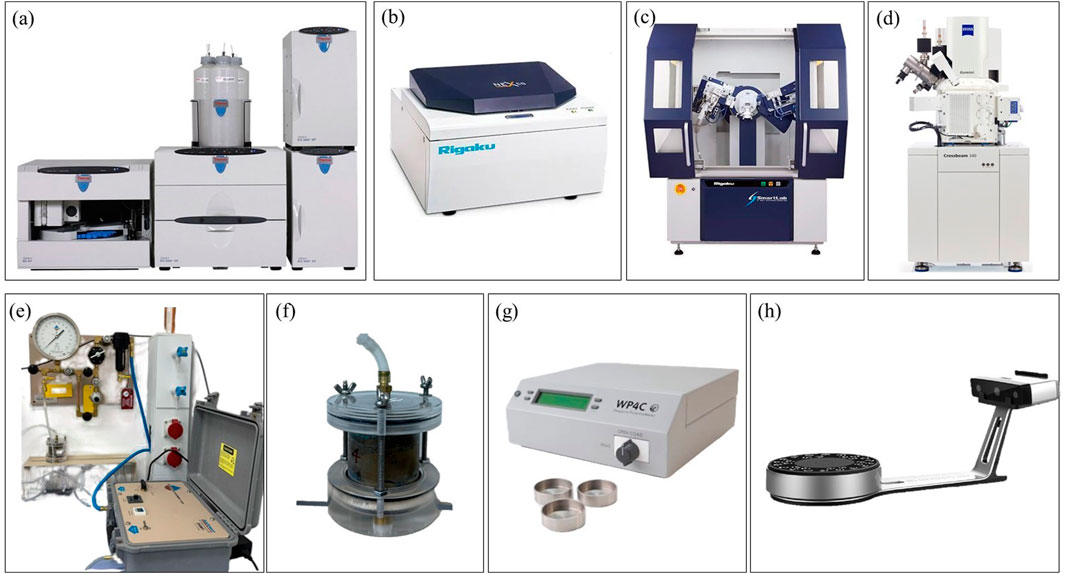

Figure 3. Experimental tests: (A) Dionex ICS; (B) Rigaku NEX CG-XRF; (C) Rigaku Smartlab-XRD; (D) SEM JEOL JSM IT200; (E) pressure controller system with automated air pump; (F) Tempe cell; (G) WP4C up to 300 MPa; (H) Einscan SP V2 3D scanner.
The WP4C was used to extend the measurement range up to 300 MPa, allowing the exploration of the soil’s water retention properties under higher pressures. To ensure accurate suction measurements, the WP4C sampling cup was filled halfway. The sample was oven-dried after each measurement, and a new suction value was recorded.
By utilizing both the Tempe cell and WP4C, a comprehensive understanding of the soil’s water retention behavior across a wide range of suction levels was achieved. These insights are crucial for geotechnical assessments and engineering applications.
3.7 Shrinkage test
The shrinkage test was conducted using the Einscan SP V2 3D scanner, known for its precise calibration, rapid scanning speeds, multiple alignment modes, and an accuracy of up to 0.05 mm. Before testing, the soil samples were fully saturated, then carefully extruded from their molds, and scanned to measure their initial volume post-extrusion. The samples were left to dry at room temperature, with their volume measured daily until completely dried. This process provided detailed insights into the volume change characteristics of the soil during drying, which are critical for understanding soil shrinkage behavior.
4 Results and discussions
4.1 Soil classification and physical properties
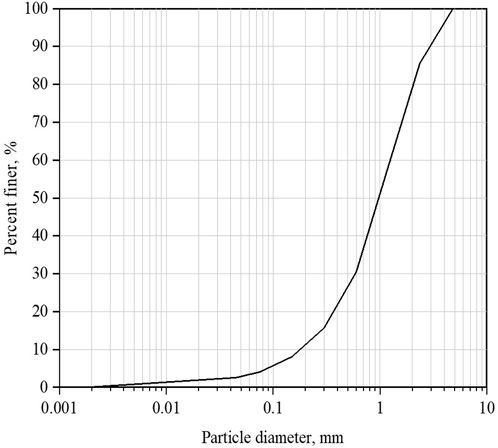
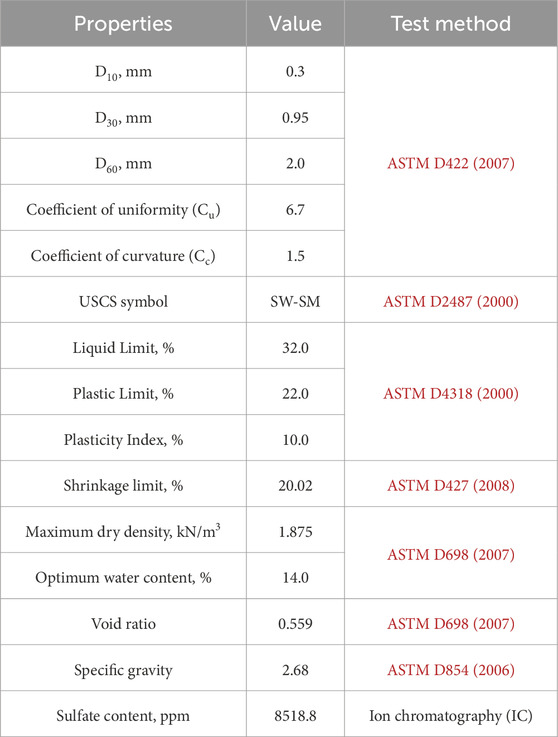
The primary physical soil properties of the soil were thoroughly investigated to ensure accurate classification. The grain size distribution (GSD) curve, obtained from the sieve analysis test, is presented in Figure 4, while Table 1 summarizes the detailed physical properties of the soil. The particle sizes corresponding to 10%, 30%, and 60% finer materials on the cumulative GSD curve were used to determine the coefficient of uniformity (cu) and coefficient of curvature (cc), which were found to be 6.7 and 1.5, respectively.
The Atterberg limits were determined, with a plastic limit (PL) of 22%, a liquid limit (LL) of 32%, and a plasticity index (PI) of 10%. Based on the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) and the results from Atterberg limit and sieve analysis tests, the soil was classified as well-graded sand with silt (SW-SM).
The shrinkage limit test, conducted in accordance with ASTM/427, (2008) revealed a shrinkage limit of 20.02%, indicating a low degree of expansion. Additionally, the Standard Proctor test results showed a maximum dry density of 1.875 kN/m³, an optimum water content of 14%, and a void ratio of 0.559.
The soil exhibited a powdery, white efflorescence on its surface, suggesting the presence of significant sulfate content, which was measured at 8518.8 ppm. According to Berger et al. (2001), soils with sulfate concentrations below 3000 ppm pose minimal risk, those between 3000 and 5,000 ppm represent a moderate risk, and concentrations between 5,000 and 8000 ppm are considered high risk. The high sulfate levels observed in this study place the soil in the high-risk category.
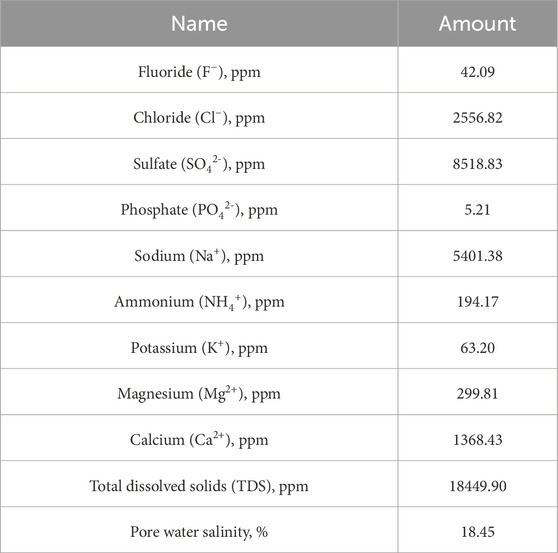
The pore water salinity, determined to be 18.45%, further indicates the presence of substantial dissolved salts (Table 2). Ion Chromatography (IC) analysis confirmed elevated concentrations of sulfate (8518.83 ppm), chloride (2,556.82 ppm), sodium (5,401.38 ppm), and calcium (1368.43 ppm). These high salinity levels suggest that the soil’s mechanical properties may be compromised by reduced cohesion and increased shrinkage and swelling. The combination of high sulfate content and elevated salinity underscores the necessity of selecting appropriate stabilization methods to mitigate potential adverse effects.
The geotechnical implications of high sulfate concentrations are significant. Soils rich in sulfates can undergo adverse chemical reactions when stabilized with calcium-based materials. These reactions often lead to the formation of expansive minerals, such as ettringite and thaumasite, which induce soil heave, pavement failures, and structural damage to foundations and critical infrastructure. The novelty of this study lies in its comprehensive characterization of high-risk sulfate soils, offering valuable insights into mitigation strategies to address these geotechnical challenges effectively.
4.2 Chemical and mineralogical composition
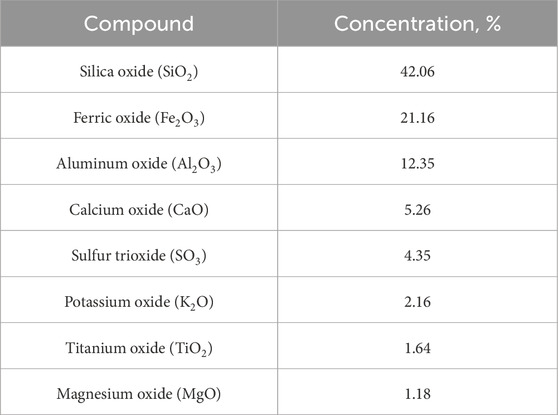
Following the determination of the basic physical properties, the chemical composition of the soil was analyzed using X-ray fluorescence (XRF). The primary oxides identified in the soil are presented in Table 3. This data provides insights into the chemical makeup of the soil, which significantly influences its geotechnical behavior.
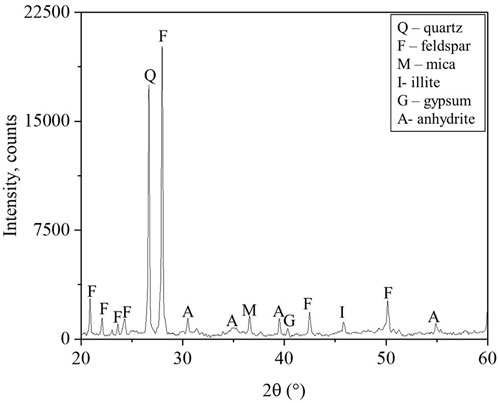
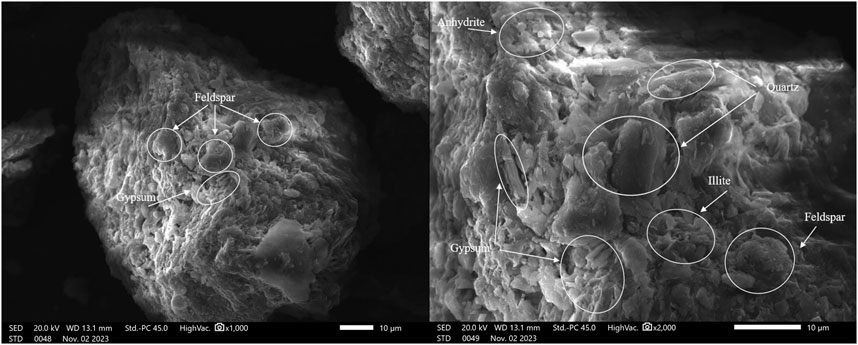
Building on the XRF analysis, an X-ray diffraction (XRD) graph was generated to identify the primary minerals present in the soil. As shown in Figure 5, the analysis revealed the presence of quartz, feldspar, mica, illite, gypsum, and anhydrite as the dominant minerals. These findings were further corroborated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images, displayed in Figure 6. In these images, quartz is visible as angular, prismatic crystals, feldspar appears in blocky and prismatic forms, illite is identified as fine-grained, flocculent particles, and gypsum is seen as elongated, tabular crystals with smooth cleavage planes. Anhydrite is recognized by its thick, blocky, prismatic structure. The presence of gypsum and anhydrite is particularly noteworthy, as these minerals are direct indicators of sulfate ions within the soil. Their presence aligns with findings by Puppala et al. (2003), who highlighted that these minerals are significant markers of elevated sulfate levels in soils. High sulfate concentrations often correlate with high salinity and present challenging geotechnical properties, such as expansive behavior and reduced stability.
This detailed chemical and mineralogical analysis provides a foundational understanding of the soil’s composition, enabling the identification of potential risks associated with its geotechnical applications. The observed mineralogy underscores the need for careful soil treatment strategies, especially when working in sulfate-rich environments prone to chemical reactivity and instability.
4.3 Soil water characteristic curve (SWCC)
The soil water characteristic curve (SWCC) visually represents the relationship between soil moisture and suction, which is vital for understanding the soil’s hydraulic properties that directly affect its stability and behavior. Key parameters of the SWCC include saturated water content, air entry value (AEV), inflection point, residual suction, and residual water content (Ito and Azam, 2013). These parameters are crucial for predicting how soil retains and releases water under various conditions. The AEV indicates the suction level at which air begins to enter soil pores, leading to desaturation.
Typically, the SWCC can be divided into three distinct zones: boundary effect, transition, and residual. The boundary effect zone occurs at low suction, where the soil remains nearly fully saturated, and the water content is relatively stable until the AEV is reached. The transition zone follows, marked by a rapid decline in water content as suction increases, signifying the progressive desaturation of soil pores. The residual zone is characterized by a much slower decrease in water content despite rising suction as the soil approaches its residual water content, which is largely retained by finer particles even under high suction conditions (Ito and Azam, 2013).
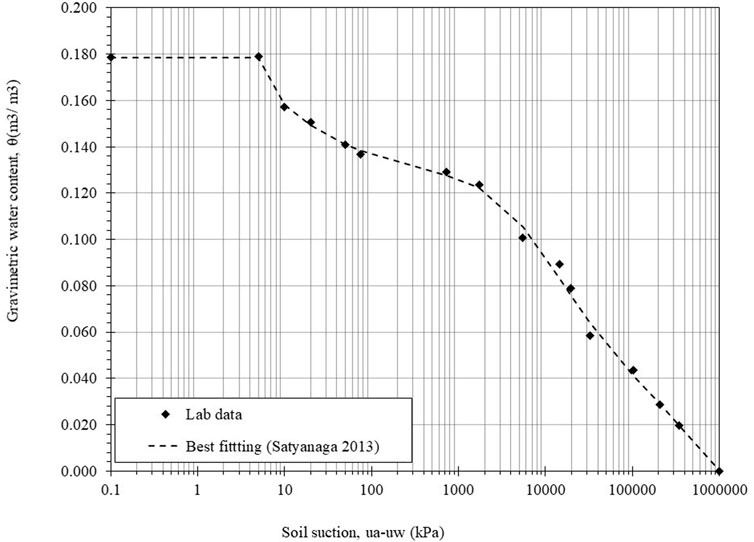
Figure 7 shows the relationship between gravimetric water content and soil suction, demonstrating a bimodal characteristic in the SWCC. The data from Tempe Cell and WP4C suggest that this curve is best modeled using a bimodal mathematical approach proposed by Satyanaga et al. (2022). This modeling approach accurately represents relevant physical parameters, including saturated water content, AEV, inflection points, and residual water content across varying moisture levels. These parameters are critical for understanding the moisture dynamics of sulfate-rich soils, as water availability governs the crystallization and hydration of sulfate minerals such as ettringite and gypsum.
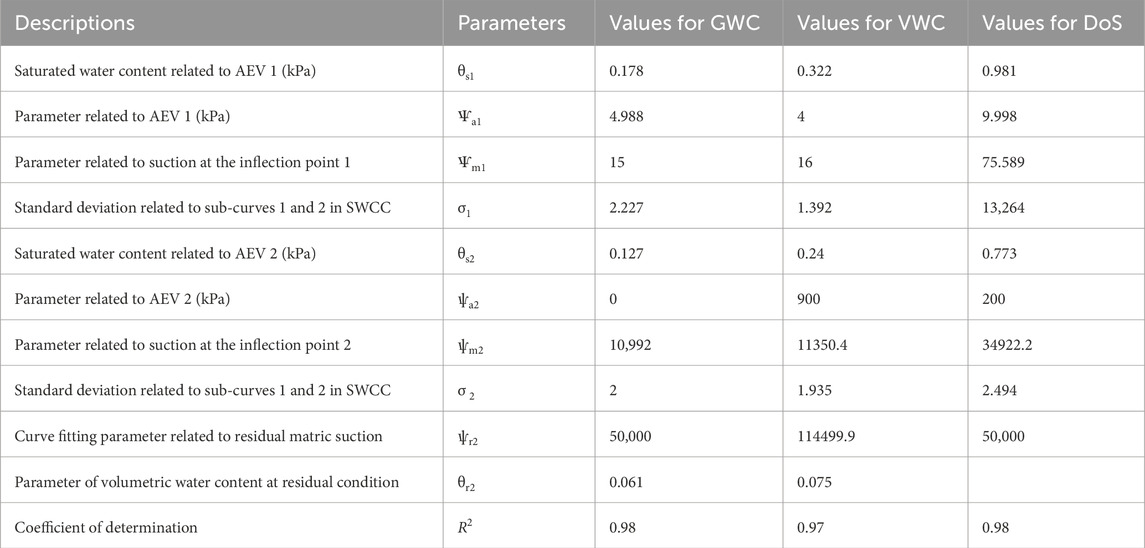
Table 4 summarizes the key physical attributes of the SWCC, including saturated and residual water content, residual suction, and the two air entry values (AEV1 and AEV2) identified through the optimal statistical method suggested by Satyanaga et al. (2013). The results indicate that the soil has a saturated gravimetric water content (θs1) of 0.178 with the first air entry (AEV1) at 4.988 kPa within macropores. The second air entry value (AEV2) occurs at 1000 kPa, associated with micropores, where the saturated gravimetric water content (θs2) decreases to 0.127. Initially, air enters the macropores at low suction levels, while higher suction is required for air entry into the micropores. This behavior aligns with findings by Ito and Azam (2013), who observed similar dual AEV patterns in vertisolic soils. These AEVs are of great importance in sulfate-rich soils. In sulfate-rich soils, these AEV thresholds are significant as they dictate water availability for sulfate hydration and the risk of sulfate precipitation, which can lead to heaving and cracking.
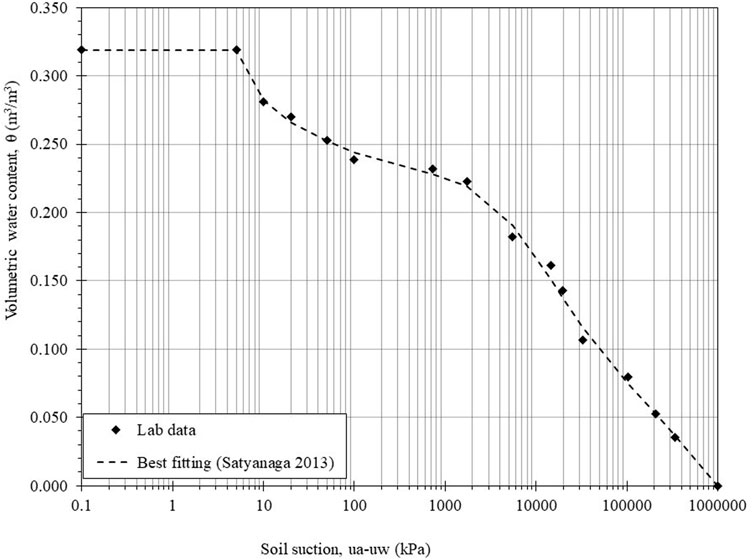
Figure 8 presents the SWCC, depicting the relationship between volumetric water content (VWC) and suction. Similar to the gravimetric water content (GWC) curve, the VWC curve exhibits bimodal characteristics and closely aligns with the equation proposed by Satyanaga et al. (2013). The relevant parameters for the SWCC are detailed in Table 4. The soil shows a saturated volumetric water content (θs1) of 0.322, with the first air entry (AEV1) at 40 kPa for macropores. The second air entry value (AEV2) is 900 kPa, with the micropore’s saturated volumetric water content (θs2) at 0.240. These AEV thresholds represent the transition from saturation to partial drainage in macro- and micropores, which governs moisture redistribution critical for sulfate hydration and associated swelling pressures.
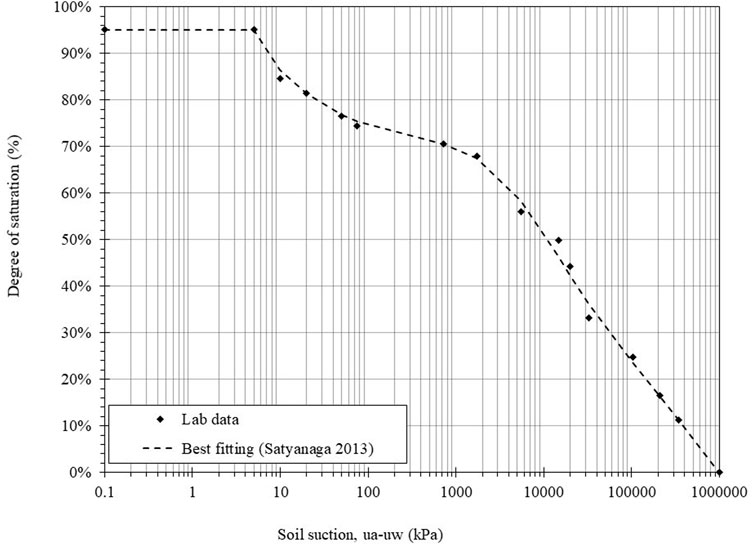
Figure 9 displays the SWCC in terms of the degree of saturation (DoS) and soil suction. Consistent with Figures 7, 8, the data reveal bimodal characteristics with a lower AEV of 9.998 kPa and a higher AEV of 200 kPa. The macropores are sufficiently drained when the DoS reaches 70%, while a higher suction of 1000 kPa is necessary to drain the micropores and facilitate air entry. This bimodal behavior highlights the dual pore structure of the soil, influencing water availability for sulfate reactions. For instance, macropores facilitate rapid water movement during wetting, while micropores serve as long-term water reservoirs that sustain sulfate hydration and associated swelling pressures under prolonged unsaturated conditions.
Understanding the SWCC is crucial for comprehending the behavior of sulfate-containing soils regarding water content and saturation levels. Gravimetric water content provides insights into water retention and drainage independent of volume changes. In contrast, volumetric water content is essential for predicting soil behavior under varying environmental conditions, including swelling and shrinkage tendencies. The degree of saturation offers a better understanding of how sulfate-containing soils’ volumes change with suction, highlighting the impact of moisture interaction. This comprehensive view allows for more accurate predictions and management of challenges associated with sulfate-rich soils in structural applications.
4.4 Shrinkage test
Figure 10 provides visual evidence of soil samples captured by the 3D scanner, illustrating the shrinkage test process. The shrinkage behavior follows a two-phase progression: an initial normal shrinkage phase characterized by rapid water loss and volume reduction, followed by a residual shrinkage phase where the drying rate slows significantly (Haines, 1923). During this phase, air infiltrates the micropores until the water content reaches zero and the void ratio stabilizes at a minimum value.
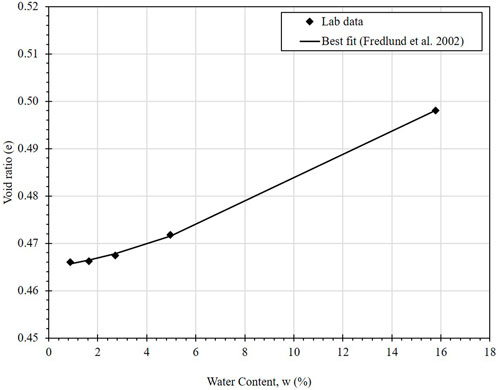
Figure 11 presents the shrinkage curve derived from 3-D scanning data. Soil samples were initially fully saturated and then allowed to dry at room temperature, with periodic volume measurements taken using the 3D scanner. The shrinkage curve exhibits a hyperbolic shape, reflecting the change in void ratio from 0.54 to 0.47. During the normal shrinkage phase, the void ratio decreases sharply as the soil loses water, with air entering larger voids. This phase aligns closely with the S = 100% curve, representing a fully saturated state where drainage primarily occurs through the soil matrix. The observed J-shaped shrinkage curve is consistent with the description provided by Ito and Azam (2013), where the swell-shrink path is described as having two distinct segments. Initially, the inclined segment follows the S = 100% curve, indicating the fully saturated state of the soil. The curve then transitions into a horizontal line at the void ratio corresponding to the soil’s shrinkage limit. This progression underscores the theoretical relationship between soil saturation and volume reduction during the shrinkage process.
The reliability of the 3D scanner in conducting shrinkage tests is confirmed by the alignment between volume measurements and established shrinkage curve models. Previous studies, such as Wong et al. (2018), demonstrated the scanner’s effectiveness in capturing precise volume changes during the shrinkage process. The shrinkage curve data were fitted using the equation proposed by Fredlund et al. (2002), which provides an optimal representation of shrinkage behavior (Figure 11). This equation highlights parameters such as ash, bsh, and csh, which represent the minimum void ratio, a variable related to the slope of the drying curve and curvature of the shrinkage curve, respectively.
The results highlight the ability of the shrinkage curve to provide a comprehensive understanding of soil behavior under varying moisture conditions. The alignment of experimental data with theoretical models not only validates the methodology but also emphasizes the implications of shrinkage behavior for soil stability and infrastructure resilience. These findings demonstrate the utility of advanced tools such as 3D scanners in accurately characterizing soil shrinkage, offering valuable insights for geotechnical applications involving moisture-sensitive soils.
5 Conclusion
This study comprehensively investigated the engineering properties of sulfate-containing soil from Astana, Kazakhstan, focusing on its physical, chemical, and water retention characteristics. The findings provide critical insights into the challenges posed by such soils in construction applications. The key findings of this research are summarized below.
- The soil was classified as well-graded sand with silt (SW-SM). The Atterberg limits revealed a liquid limit (LL) of 32%, a plastic limit (PL) of 22%, and a plasticity index (PI) of 10%. The shrinkage limit was 20.02%, while the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content were 1.875 kN/m³ and 14%, respectively.
- Chemical analysis of the soil revealed a high sulfate content of 8518.8 ppm, categorizing the soil as high-risk for sulfate heave. Mineralogical analysis using XRF, XRD, and SEM confirmed the presence of gypsum and anhydrite minerals, indicating elevated sulfate ion concentrations. These findings underscore the potential challenges posed by sulfate-induced expansion and instability in geotechnical applications.
- The SWCC demonstrated bimodal characteristics with two distinct air entry values (AEV): 4.988 kPa for macropores and 1000 kPa for micropores based on gravimetric water content. This bimodal behavior highlights the soil’s complex water retention properties, with significant implications for its stability and behavior under varying moisture conditions.
- The shrinkage behavior revealed a hyperbolic curve, characterized by a sharp reduction in the void ratio during the normal shrinkage phase, followed by a slower rate of volume change in the residual shrinkage phase. These findings highlight the dual-phase behavior of the soil during drying and its susceptibility to volumetric changes.
In conclusion, the high sulfate content and complex water retention properties of this soil present significant challenges for construction applications, particularly in terms of stability and durability. Understanding its physical, chemical, and hydraulic behavior is essential for developing effective stabilization and mitigation strategies. This study contributes valuable insights into the behavior of sulfate-rich soils and emphasizes the necessity of carefully considering their engineering applications. Building on these findings, future research will focus on evaluating the mechanical properties of sulfate-rich soils under the influence of various stabilizers. This will provide a deeper understanding of their effects on soil strength, shrinkage behavior, and long-term durability, ultimately informing more effective and sustainable construction practices in sulfate-affected regions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
NS: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. AS: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. JK: Supervision, Writing–review and editing. S-WM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Nazarbayev University, Faculty Development Competitive Research Grant Program (FDCRGP) Grant No. 20122022FD4115 and Collaborative Research Project (CRP) Grant No. 111024CRP2011. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of Nazarbayev University.
Acknowledgments
Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of Nazarbayev University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmadullah, T., and Chrysochoou, M. (2024). Relationship between strength development and pozzolanic reactions in lime stabilized kaolinite. Int. J. Geo-Engineering 15 (1), 11. doi:10.1186/s40703-024-00212-6
Ale, T. O. (2023). Improving the geotechnical properties of a Nigerian termite reworked soil using pretest drying conditions and sawdust ash. Int. J. Geo-Engineering 14 (1), 1. doi:10.1186/s40703-022-00178-3
ASTM/427 (2008). Test method for shrinkage factors of soils by the mercury method. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International.
ASTM/698 (2007). Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using standard effort (12 400 Ft-lbf/ft3 (600 KN-m/m3)), 1. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM international.
ASTM/D2487 (2000). Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (unified soil classification system), 4. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International, 249–260.
ASTM/D422 (2007). Standard test method for particle-size analysis of soils. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International.
ASTM/D4318 (2000). Standard test methods for liquid limit, plastic limit, and plasticity index of soils. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International.
ASTM/D854 (2006). Standard test methods for specific gravity of soil solids by water pycnometer. West Conshohocken, PA, USA: ASTM International.
Baitova, A. (2021). Features of engineering-geological properties of soils in Kazakhstan. Innovative Sci. Res. 2-1, 188–196.
Berger, E., Little, D., and Graves, R. (2001). Technical memorandum: guidelines for stabilization of soils containing sulfates. Arlington, VA: National Lime Association.
Borovski, V. M. (1982). Formation of saline soils and halogeochemical provinces of Kazakhstan. Almaty, Kazakhstan: Science.
Brandl, H. (2021). “Long-term behaviour of soils stabilised with lime and with cement,” in Geotechnics for developing africa. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 219–232.
Danayev, E. (2008). Feasibility of Wind Energy Development in Kazakhstan technical-economical analysis of wind farm construction in the Almaty region. Glasgow, Scotland, UK: Sc., University of Strathclyde.
Faizov, K. S. (1980). Soils of the desert zone of Kazakhstan. Almaty, Kazakhstan: Alma-Ata: Science.
Fredlund, M. D., Wilson, G. W., and Fredlund, D. G. (2022). Use of the grain-size distribution for estimation of the soil-water characteristic curve. Canad. Geotech. J. 39 (5), 1103–1117. doi:10.1139/t02-049
Fang, J., Li, X., Liu, J., Liu, C., Liu, Z., and Ji, Y. (2018). The crystallization and salt expansion characteristics of a silty clay. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 154, 63–73. doi:10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.06.009
Gidebo, F. A., Yasuhara, H., and Kinoshita, N. (2023). Stabilization of expansive soil with agricultural waste additives: a review. Int. J. Geo-Engineering 14 (1), 14. doi:10.1186/s40703-023-00194-x
Haines, W. B. (1923). The volume-changes associated with variations of water content in soil. J. Agric. Sci. 13 (3), 296–310. doi:10.1017/s0021859600003580
Harris, P., Sebesta, S., and von Holdt, J. (2005). “Sulfate heave on Texas Highways: reducing the odds of pavement failure,” in Proc. 2nd int. Symp. Treatment and recycling of materials for transport infrastructure TREMTI.
Hass, H., Jagow-Klaff, R., and Wernecke, R. (2007). Influence of salinity on the strength of various frozen soils. Curr. Pract. Cold Regions Eng., 1–12. doi:10.1061/40836(210)40
Hivon, E., and Sego, D. (1995). Strength of frozen saline soils. Can. geotechnical J. 32 (2), 336–354. doi:10.1139/t95-034
Issanova, G., Abuduvayli, J., Mamutov, Z. U., Kaldybaev, A. A., Saparov, G. A., Bazarbaeva, T. A., et al. (2017). Saline soils and determination of the province of salt accumulation on the territory of Kazakhstan. Arid. Ecosyst. 7, 243–250. doi:10.1134/S2079096117040035
Ito, M., and Azam, S. (2013). Engineering properties of a vertisolic expansive soil deposit. Eng. Geol. 152 (1), 10–16. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.10.004
Köhler, S., Heinz, D., and Urbonas, L. (2006). Effect of ettringite on thaumasite formation. Cem. Concr. Res. 36 (4), 697–706. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2005.11.006
Kotov, P. I., and Stanilovskaya, J. Y. V. (2022). Predicting changes in the mechanical properties of frozen saline soils. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 26 (12), 5716–5728. doi:10.1080/19648189.2021.1916604
Kutergin, V., Kal’bergenov, R., Karpenko, F. S., Leonov, A. R., and Merzlyakov, V. P. (2012). Influence of salinity on rheologic and strength properties of frozen soils in Yamal. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 49, 105–110. doi:10.1007/s11204-012-9175-7
Lai, Y., Wan, X., and Zhang, M. (2016). An experimental study on the influence of cooling rates on salt expansion in sodium sulfate soils. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 124, 67–76. doi:10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.12.014
Mahmood, A., Hassan, R., and Fouad, A. (2019). “Effect of lime, cement, and lime-cement stabilisation on low to medium plasticity clayey soil,” in 2019 IEEE asia-pacific conference on computer science and data engineering (CSDE). Melbourne, Australia, 09-11 December 2019 (IEEE). doi:10.1109/CSDE48274.2019.9162384
Mekonnen, E., Amdie, Y., Etefa, H., Tefera, N., and Tafesse, M. (2022). Stabilization of expansive black cotton soil using bioenzymes produced by ureolytic bacteria. Int. J. Geo-Engineering 13 (1), 10. doi:10.1186/s40703-022-00175-6
National Academies of Sciences (2009). Recommended practice for stabilization of sulfate-rich subgrade soils. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press.
Nguyen, A., Sego, C., Arenson, U., and Biggar, W. (2010). “The dependence of strength and modulus of frozen saline sand on temperature, strain rate and salinity,” in Proceedings of the 63rd Canadian geotechnical conference. Calgary.
Nixon, J., and Lem, G. (1984). Creep and strength testing of frozen saline fine-grained soils. Can. geotechnical J. 21 (3), 518–529. doi:10.1139/t84-054
Pandey, A., and Rabbani, A. (2017). Stabilisation of pavement subgrade soil using lime and cement. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 4 (6), 5733–5735.
Pashkov, S., and Baybusinova, S. (2017). Natural and agrogene conditionality of soils fertility in northern Kazakhstan. Transbaik. State Univ. J. 23 (2), 16–27. doi:10.21209/2227-9245-2017-23-2-16-27
Puppala, A., Wattanasanticharoen, E., and Punthutaecha, K. (2003). Experimental evaluations of stabilisation methods for sulphate-rich expansive soils. Proc. Institution Civ. Engineers-Ground Improv. 7 (1), 25–35. doi:10.1680/grim.2003.7.1.25
Puppala, A. J., Talluri, N., Congress, S. S. C., and Gaily, A. (2018). Ettringite induced heaving in stabilized high sulfate soils. Innov. Infrastruct. Solutions 3, 72–12. doi:10.1007/s41062-018-0179-7
Regasa, H., Jothimani, M., and Oyda, Y. (2023). Subgrade soil stabilization using the Quicklime: a case study from Modjo-Hawassa highway, Central Ethiopia. Int. J. Geo-Engineering 14 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s40703-023-00197-8
Rollings, R. S., Burkes, J. P., and Rollings, M. P. (1999). Sulfate attack on cement-stabilized sand. J. geotechnical geoenvironmental Eng. 125 (5), 364–372. doi:10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(1999)125:5(364)
Satyanaga, A., Moon, S.-W., and Kim, R. (2022). Stability analyses of dual porosity soil slope. Geomechanics Eng. 28 (1), 77–87. doi:10.12989/gae.2022.28.1.077
Satyanaga, A., Rahardjo, H., Leong, E. C., and Wang, J. Y. (2013). Water characteristic curve of soil with bimodal grain-size distribution. Comput. Geotechnics 48, 51–61. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.09.008
Tang, R., Zhou, G., Wang, J., Zhao, G., Lai, Z., and Jiu, F. (2020). A new method for estimating salt expansion in saturated saline soils during cooling based on electrical conductivity. Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 170, 102943. doi:10.1016/j.coldregions.2019.102943
Uspanov, U. U., Evstifeev, Y. G., Storozhenko, D. M., Lobova, E. V., Kolkhozhayev, M. K., Kotin, N. I., et al. (1976). Institute of soil science of the academy of sciences of the Kazakh SSR. The map was compiled and prepared for publication by the scientific editorial and cartographic department of the main directorate of Geodesy and Cartography (GUHK). Editor L. M. Voronina Available at: www.etomesto.ru/map-kazakhstan_pochva-1976/
Wan, X., You, Z., Wen, H., and Crossley, W. (2017). An experimental study of salt expansion in sodium saline soils under transient conditions. J. Arid Land 9, 865–878. doi:10.1007/s40333-017-0029-z
Wong, J. M., Elwood, D., and Fredlund, D. G. (2018). Use of a 3D scanner for shrinkage curve tests. Canad. Geotech. J. doi:10.1139/cgj-2017-0700
Xiao, Z., Lai, Y., and Zhang, M. (2018). Study on the freezing temperature of saline soil. Acta Geotech. 13, 195–205. doi:10.1007/s11440-017-0537-1
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, K., and Pan, L. (2016). Natural saline soil salt-frost heave cold end step continuous cooling and experimental study on water and salt migration. Sci. Technol. Eng. 31, 051.
Keywords: sulfate-containing soils, soil-water characteristic curve, geotechnical characterization, microstructural analysis, shrinkage test
Citation: Sagidullina N, Satyanaga A, Kim J and Moon S-W (2025) Engineering behavior and geotechnical challenges of sulfate-rich soils in Astana. Front. Built Environ. 10:1504643. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2024.1504643
Received: 01 October 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 12 February 2025.
Edited by:
Siau Chen Chian, National University of Singapore, SingaporeReviewed by:
Małgorzata Jastrzębska, Silesian University of Technology, PolandSudhakar Rao, Retired, Bangalore, India
Copyright © 2025 Sagidullina, Satyanaga, Kim and Moon. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sung-Woo Moon, c3VuZy5tb29uQG51LmVkdS5reg==
†ORCID: Sung-Woo Moon, orcid.org/0000-0003-1164-8251
 Nazerke Sagidullina
Nazerke Sagidullina Alfrendo Satyanaga
Alfrendo Satyanaga Jong Kim
Jong Kim Sung-Woo Moon
Sung-Woo Moon