- 1College of Energy and Power Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC, United States
- 3Key Laboratory of Novel Targets and Drug Study for Neural Repair of Zhejiang Province, School of Medicine, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou, China
Deep learning is progressively emerging as a vital tool for image reconstruction in light field microscopy. The present review provides a comprehensive examination of the latest advancements in light field image reconstruction techniques based on deep learning algorithms. First, the review briefly introduced the concept of light field and deep learning techniques. Following that, the application of deep learning in light field image reconstruction was discussed. Subsequently, we classified deep learning-based light field microscopy reconstruction algorithms into three types based on the contribution of deep learning, including fully deep learning-based method, deep learning enhanced raw light field image with numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction, and numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction with deep learning enhanced resolution, and comprehensively analyzed the features of each approach. Finally, we discussed several challenges, including deep neural approaches for increasing the accuracy of light field microscopy to predict temporal information, methods for obtaining light field training data, strategies for data enhancement using existing data, and the interpretability of deep neural networks.
1 Introduction
By simultaneously capturing combined signals from different depths of an entire volume in a single-camera-frame, light field microscopy (LFM) enables rapid spatial dynamic imaging (Levoy et al., 2006), and has developed into a valuable tool for structural and functional imaging of biological specimens. LFM usually necessitates computational volumetric reconstruction using traditional algorithms like refocusing (Dansereau et al., 2015; Jayaweera et al., 2020) or three-dimensional (3D) deconvolution (Broxton et al., 2013). However, conventional algorithms are limited by low efficiency and poor resolution, thereby hindering them for broader application of LFM. Therefore, the need to achieve high efficiency and high-resolution image reconstruction is crucial for the advance of LFM.
In recent years, deep learning has been widely used for variant applications, including image classification (Yu et al., 2022; Dosovitskiy, 2020; Foret et al., 2020), semantic segmentation (Wang et al., 2023; Srivastava and Sharma, 2024; Erisen, 2024), generation (Kim et al., 2023; Walton et al., 2022; Sadat et al., 2023), denoising (Zhou et al., 2020), restoration (Wan et al., 2022), super-resolution (Johnson et al., 2016; Ledig et al., 2017; Shi et al., 2016), depth estimation (Alhashim, 2018; Zhuang et al., 2022; Tateno et al., 2018) and image reconstruction (Drozdova et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024; Godard et al., 2017; Li et al., 2017; Liang et al., 2021; Quan et al., 2021; Schlemper et al., 2017). The use of deep learning algorithms has also boosted LFM (LeCun et al., 2015; Vizcaino et al., 2021a; Wang et al., 2021; Yi et al., 2023; Wagner et al., 2021). For instance, deep learning-based LFM has been applied to resolve the activity of motor neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans with single-cell resolution (Wang et al., 2021), to extract the calcium signal in the brains of 5-day-old transgenic zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae (Wagner et al., 2021), and to reconstruct the high-speed 3D voltage imaging in sparsely labeled dopaminergic neurons in the fruit fly brain (Lu et al., 2023).
This review first introduces light field acquisition methods, and explores the applicability of these methods in light field microimaging, then introduces the current application of deep learning in image processing technology and explores the feasibility of deep learning technology in light field microimaging reconstruction, and finally outlines the recent progress of deep learning-based reconstruction algorithms for LFM. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of deep learning-based LFM, focusing primarily on network architecture, reconstruction resolution, and running time to reveal current shortcomings, and future possibilities.
2 Light field and deep learning
2.1 Principle of light field imaging
In the field of 3D space, the light field serves as a comprehensive representation of all light rays existing in 3D space from any given point in any direction. The concept of the “Light Field” was first introduced by Alexander Gershun (Gershun, 1939), who proposed five-dimensional (5D) plenoptic function
Typically, there are three strategies to acquire light field information (Wu et al., 2017), multi-sensor capture (Figure 1A), time-sequential capture (Figure 1B), and multiplexed imaging (Figure 1C). Theoretically, all these three strategies aim to acquire light field information but the approaches they utilize to record light field information are totally different. Specifically, multi-sensor capture utilizes multiple cameras to concurrently capture light field, predominantly employing camera arrays (Lin et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2023; Gu et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2020). This approach can yield high spatial resolution imaging while capturing real-time information, but the total setup is complex and expensive. In time-sequential capture, a single camera is utilized to capture light field through a series of exposures. This method is known for being time-consuming and cannot provide real-time information (Li et al., 2014; Taguchi et al., 2010; Dansereau et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2022). On the other hand, multiplexed imaging involves the conversion of high-dimensional data into a more simplified two-dimensional (2D) image (Prevedel et al., 2014; Mignard-Debise, 2015; Kim et al., 2016; Vizcaino et al., 2021b; Orth and Crozier, 2012; Yang and Yuste, 2017; Fan et al., 2022) using a microlens array (MLA) positioned in the optical instrument’s intermediate image plane. By adopting this approach, the entire imaging system is significantly streamlined with easy operation. Consequently, light field camera and LFM developed based on the multiplexing principle are widely used in volumetric imaging. Particularly, LFM has demonstrated strong imaging ability in in-vivo imaging of heartbeat, blood flow, and neural activity, and has allowed 3D visualization of the spatial and temporal evolution patterns of the signals and the mechanisms behind biological processes.
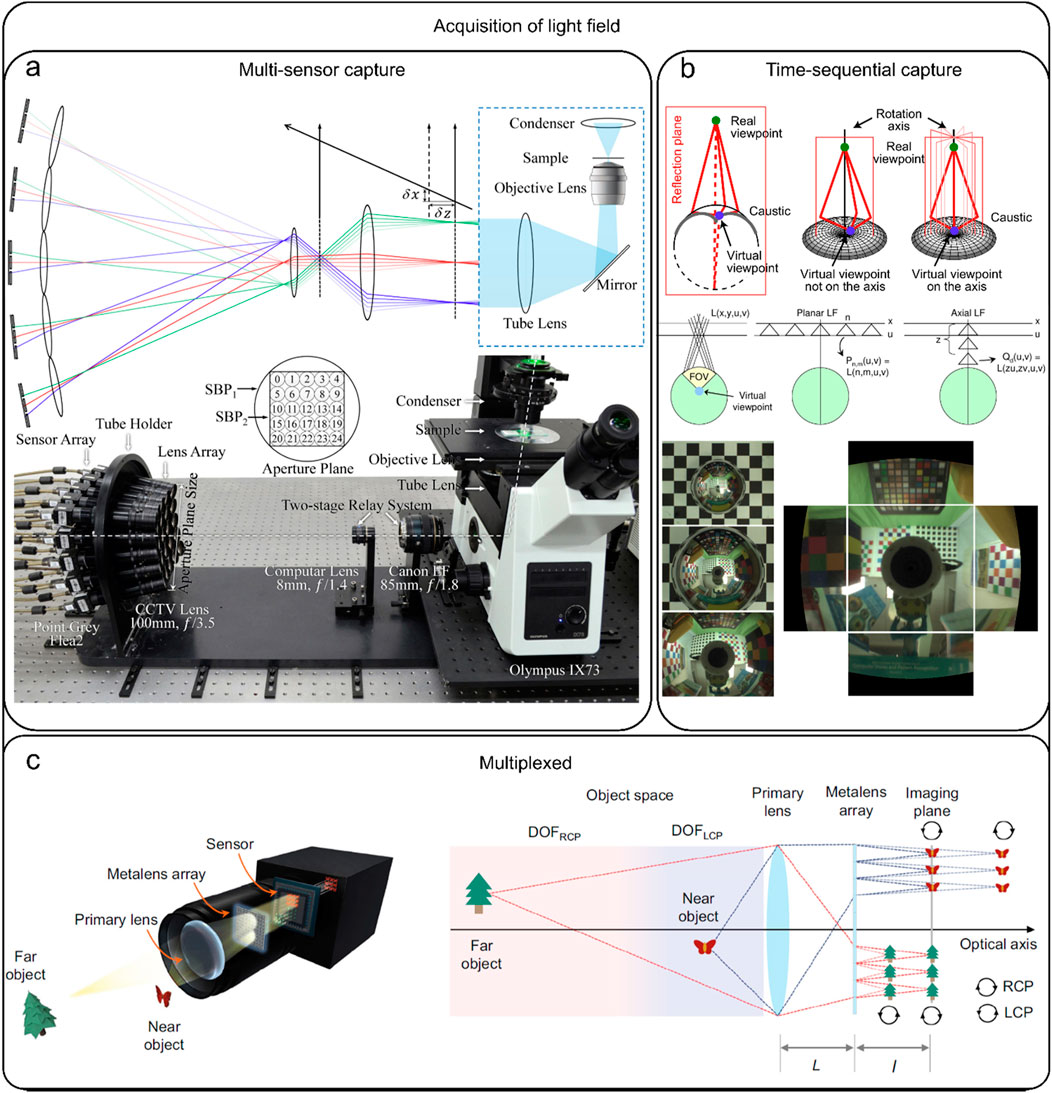
Figure 1. Acquisition of light field. (A) Multi-sensor capture: capturing the light field simultaneously using multiple cameras, most of which are camera arrays. [modified from (Lin et al., 2015)] (B) Time-sequential capture: capturing the light field using multiple exposures from a single camera, which is time-consuming. [modified from (Taguchi et al., 2010)] (C) Multiplexed capture: The process of mapping complex high-dimensional data into two-dimensional (2D) images. [modified from (Fan et al., 2022)].
2.2 Light field image reconstruction benefits from deep learning
Light field reconstruction can be seen as a transformation between the raw light field image and the reconstructed volumetric image. Classical reconstruction methods address such transformations from a physical-optical perspective through display modeling, which can be classified into two categories: mathematical inversion and numerical inversion. Refocusing is a typical mathematical inversion method in light field reconstruction (Ng et al., 2005; Alain et al., 2019) and is based on an idealized mathematical model, that essentially superimposes and shifts sub-aperture images over the entire aperture range. During the reconstruction process, the difference between the actual situation and the mathematical model is magnified, and thus prone to image noises, and artifacts. Numerical inversion employs iterative reconstruction for various imaging modalities to introduce external a priori information, thereby greatly enriching the information available for reconstruction and improving the quality of the final image. One widely used numerical inversion method is Richardson-Lucy deconvolution which relies on the microscope’s point spread function and Poisson noise statistics assumption (Prevedel et al., 2014; Richardson, 1972). However, the accuracy of these classical reconstruction methods is restricted by the premises of their physical models. These methods are unable to capture the full statistical complexity of microscopic images, and thus can only reconstruct high-quality results in specific cases. In contrast, data-driven procedures, especially deep learning methods, rely on high-resolution data to optimize the reconstruction procedure, thereby usually offering better resolution than conventional algorithms. Consequently, deep learning-based methods allow high-resolution light field reconstruction. For instance, deep learning methods have enabled high-resolution LFM in the reconstruction of fluorescently labeled blood vessels in mouse brain slices (Vizcaino et al., 2021a), neuronal signals and analysis of the calcium activity patterns, four-dimensional dynamics of red blood cells and cardiomyocytes (Wang et al., 2021), continuous 3D observation of dynamic processes (Yi et al., 2023), and imaging of zebrafish (Oryzias latipes) embryos and zebrafish (D. rerio) larvae (Wagner et al., 2021).
Briefly, deep learning networks are primarily composed of various nonlinear parameterized processing modules that iteratively convert an input
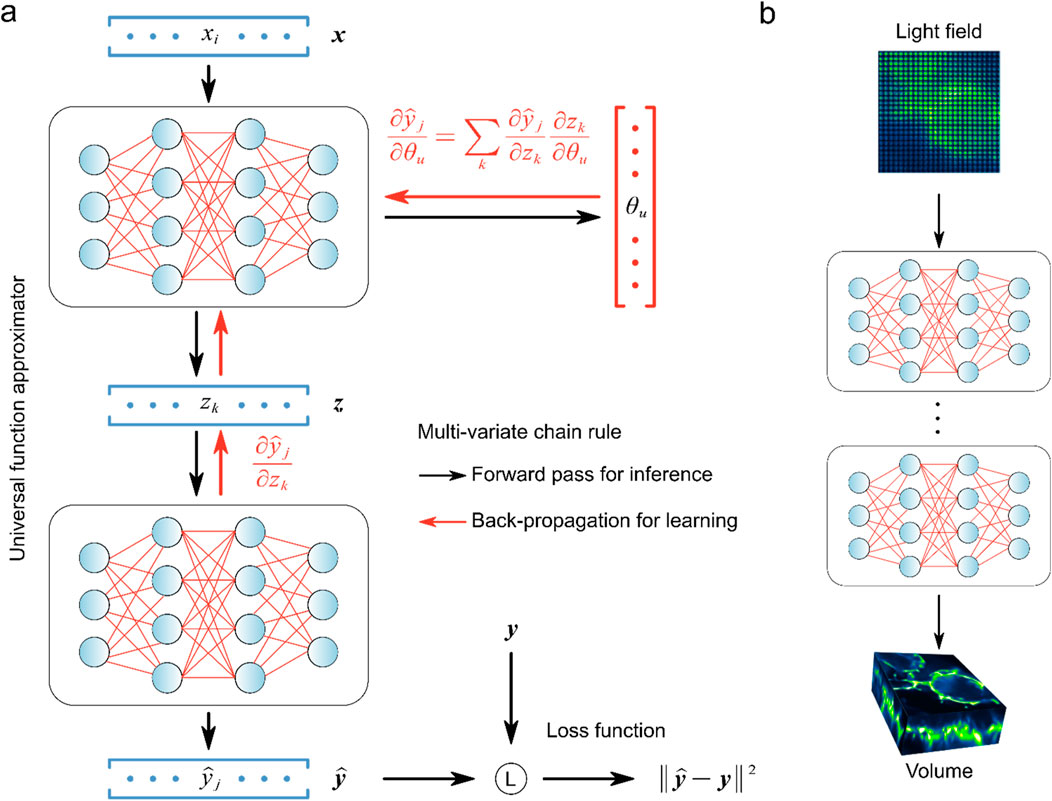
Figure 2. Universal function approximator and back-propagation were used to learn light field reconstruction. (A) Learning process of universal function approximator. (B) Multilayer neural networks and back-propagation were used to learn LFM direct reconstruction. [modified from (Lu et al., 2023)].
The trained network is the solver to compute volumetric images from the raw light field data, and directly impacts the quality of the reconstructed image. Typically, to ensure the network is fully optimized, high-resolution 3D images of the target samples are first acquired, which can be obtained from simulated data or experimental methods, such as confocal microscopy (Vizcaino et al., 2021a), selective plane illumination microscopy (SPIM) (Wagner et al., 2021) and light-sheet microscopy (Zhao et al., 2020). Using the wave optics model, these high-resolution volumetric images are projected into 2D light field images. In the network training process, the raw light field images serve as the initial input denoted as
3 Deep learning-based reconstruction algorithms for light field microscopy
Deep learning-based LFM image reconstruction has demonstrated superior resolution than conventional methods (Wang et al., 2021; Yi et al., 2023; Wagner et al., 2021), which allows researchers to observe finer structures, such as subcellular organelles or molecular complexes with greater clarity. The improved performance of deep learning-based methods originates from its upsampling design in the network, which can compensate for the reduced resolution of raw light field images when the volumetric information is encoded onto the 2D sensor. To attain high resolution and high efficiency, deep learning methods can also be integrated with numerical inversion strategy. Based on the combination of deep learning and numerical inversion methods, the current deep learning-based LFM algorithms can be subdivided into three categories: fully deep learning-based method (type I) (Figure 3A), deep learning enhanced raw light field image with numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction (type II) (Figure 3B), and numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction with deep learning enhanced volumetric data (type III) (Figure 3C).
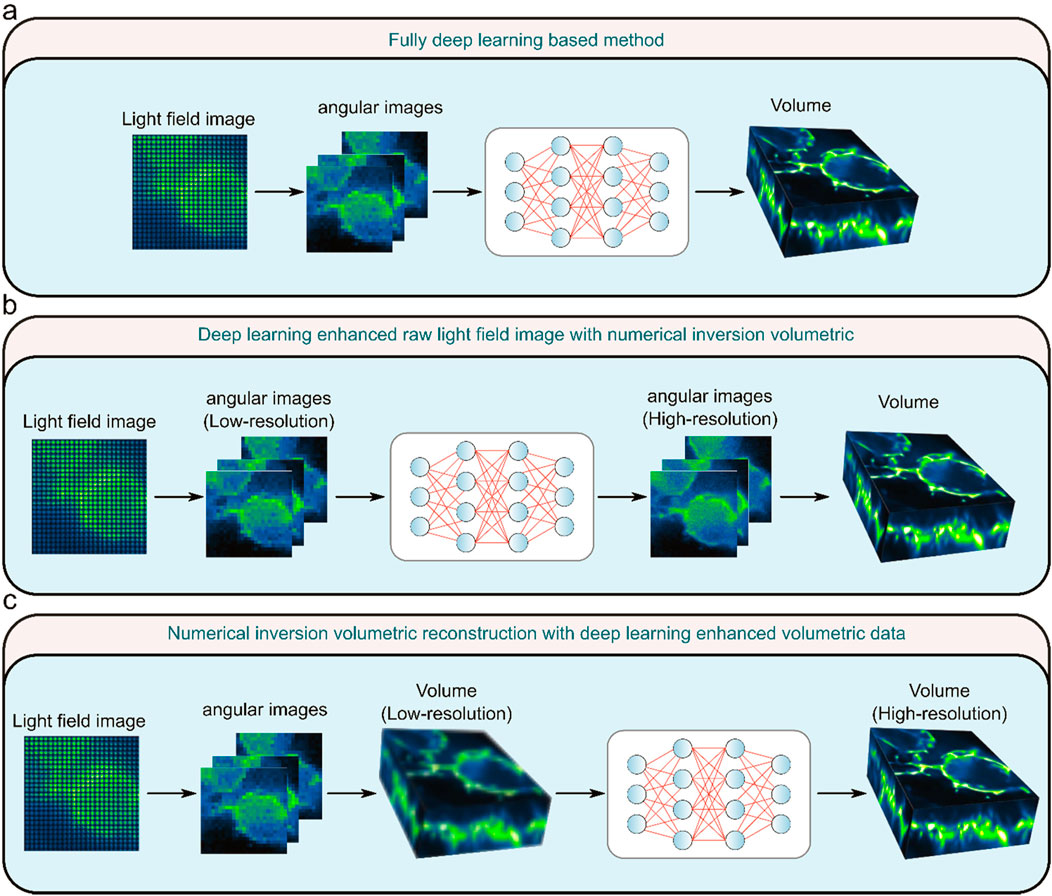
Figure 3. Three types of light field microscopy reconstruction methods. (A) Fully deep learning-based method. (B) Deep learning enhanced raw light field image with numerical inversion volumetric. (C) Numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction with deep learning enhanced volumetric data. [modified from (Lu et al., 2023)].
Type I method completely uses deep learning to reconstruct the raw light field image into a 3D volume. This network needs to accomplish both volumetric reconstruction and resolution improvement tasks simultaneously. The Type II method initially uses deep learning algorithms to elevate the resolution of the raw light field image, succeeded by a gradual reconstruction of the light field image through the utilization of numerical inversion methods. Type III method refers to the use of the numerical inversion method to iteratively reconstruct the light field image into poor 3D volume, and then use the deep learning method to transform the low-resolution volume into high-resolution volume. Specifically, the performance of these three types of methods varies depending on the structure of the variant. Type I methods use an end-to-end network, which has the advantage of being able to quickly reconstruct a volumetric image from a light field image as long as the network is appropriately trained, but is more difficult to train due to the complexity of the network. Compared to Type I methods, Type II and Type III methods have the advantage of better generalization, but the numerical inverse volumetric reconstruction in them requires iterative computation, resulting in less efficient reconstruction. The Type III method has a wider range of applications than the Type I and Type II methods, but the drawback is that false results that deviate too much from the real situation may occur. Each of these three types of methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, which need to be considered and weighed when applying them. In the future, type I methods may become the mainstream of real-time reconstruction of LFM, type II methods may become the mainstream of high-resolution reconstruction of LFM, and type III methods will be applied to a variety of 3D reconstruction in addition to LFM.
3.1 Type I: Fully deep learning-based method
The fully deep learning-based method is the most commonly used deep learning-based method for light field reconstruction (Figure 4). This approach uses the light field image as the input
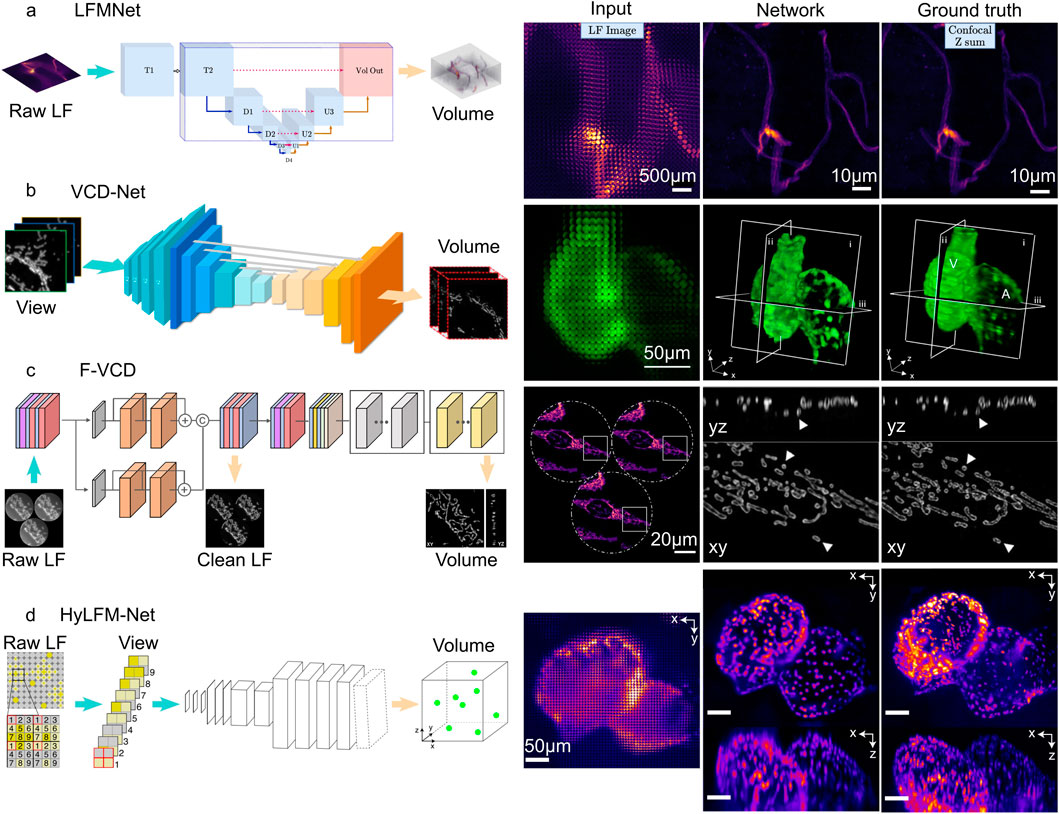
Figure 4. Fully deep learning-based method of light field microscopy. (A) LFMNet architecture (left), and the imaging result (right). Scale bars, 500
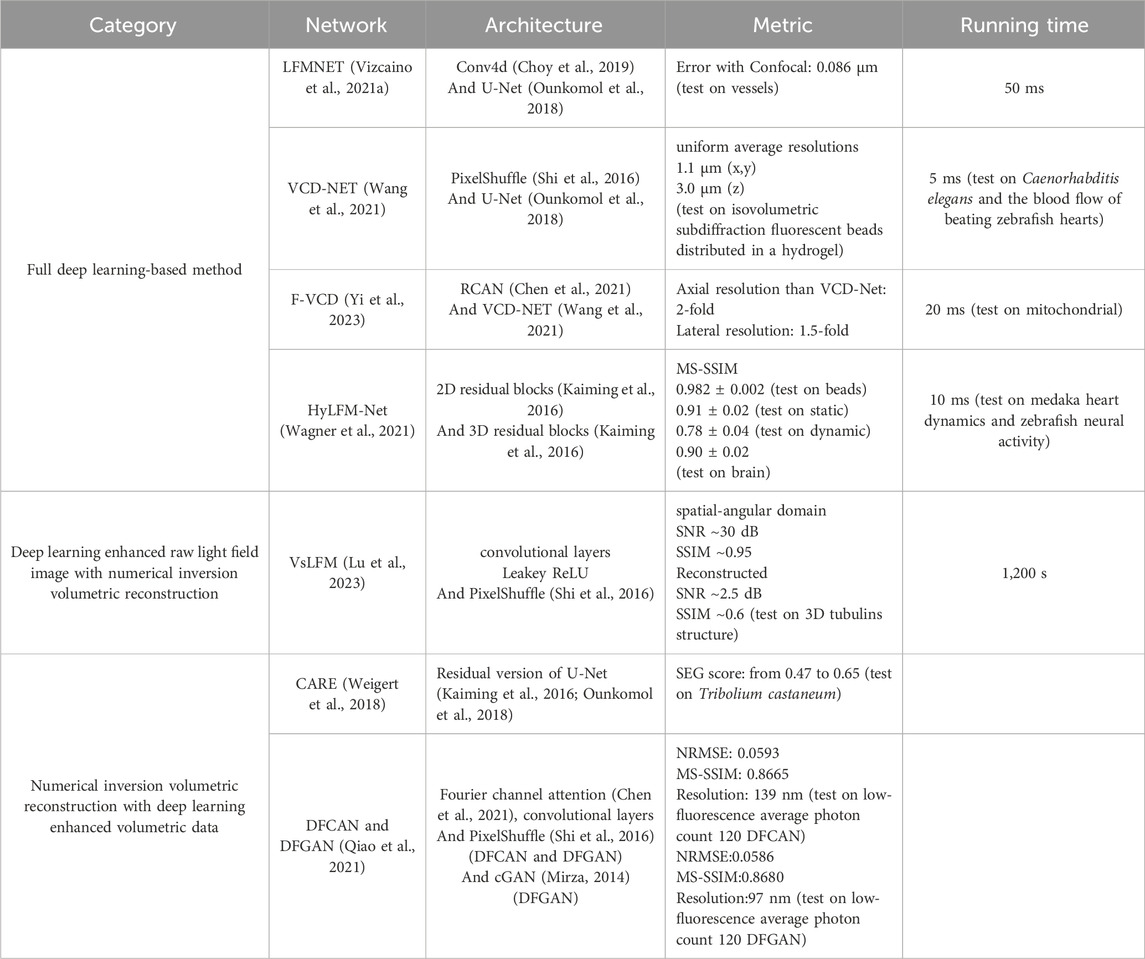
In these networks, LFMNet (Vizcaino et al., 2021a) is the earliest architecture, which adds an initial layer (Conv4d (Choy et al., 2019)) to the U-Net. This design produced a fully convolutional network with the first layer traversing each microlens and capturing its surrounding neighborhood. The resulting output is then transformed into a channel number that is equal to the depths that need to be reconstructed. Subsequently, the tensor enters the U-Net for feature extraction and 3D reconstruction. The LFMNet has been mainly validated on images of fluorescently labeled blood vessels in mouse brain slices and achieved reconstruction resolution
Following LFMNet, VCD-Net (Wang et al., 2021) was proposed, which adopts the cascaded convolutional layer design of the U-Net architecture, but differs from LFMNet in that the initial layer is no longer designed using Conv4d. Instead, the initial layer is transformed using SubPixel up-scaling (Shi et al., 2016) and a convolutional layer to reformat pixels in the input 2D light field raw image into different views, generating multi-channel outputs representing different depths. VCD-Net has performed single-cell resolution and up to 200 Hz volumetric imaging on the neuronal activity of moving C. elegans and the blood flow of beating zebrafish hearts, and has obtained uniform average resolutions within the range of the 1.1
F-VCD (Yi et al., 2023) is proposed based on VCD-Net, so it provides improved reconstruction resolution, accuracy, and efficiency over VCD-Net. The F-VCD comprises two primary modules: the “F-Denoise” module and the “F-Reconstruction” module. The F-Denoise module introduces a viewing angle attention branch into the traditional RCAN network (Chen et al., 2021) to balance the influence of different viewing angles, to denoise raw light field images in a weighted way, because light field images from different viewing angles have different signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The F-Reconstruction module is based on VCD-Net but has added three dilated convolution blocks to the original U-Net coding blocks of VCD and replaced the normal convolution operation with a residual block. This increases the number of input channels and expands the lateral size of the extracted features. To prevent the loss of subtle signals in the optimization process of deep networks, adjustments have been made to the normalization layer and activation function, replacing them with instance normalization and LeakyRelu, respectively. The F-VCD has been mainly validated on live-cell imaging and fixed-cell imaging. In live-cell imaging, the F-VCD technique enabled the achievement of 3D super-resolution imaging with a resolution of approximately 180 nm × 180 nm × 400 nm and was able to capture the rapid motion and morphological changes of mitochondria within cells, including mitochondrial fusion, fission, and dynamic tubulation, at a rate of up to 50 Hz. In fixed-cell imaging, F-VCD significantly improved the spatial resolution and contrast, and reduced axial artifacts, enabling clear visualization of organelle structures such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Specifically, F-VCD improved the axial resolution from approximately 400 nm to approximately 320 nm and achieved a 2-fold increase in lateral and a 1.5-fold increase in axial resolution.
HyLFM-Net is different from the above methods. Instead of using a U-Net, HyLFM-Net (Wagner et al., 2021) consists of a series of residual blocks (Kaiming et al., 2016) and transposed convolutions. It converts the multi-channel 2D image to the axial spatial dimension after applying 2D residual blocks and transposed convolutions, resulting in a 3D image. This 3D image undergoes further processing through 3D residual blocks and is upsampled by transposed convolutions to ultimately obtain the reconstructed 3D volume. In the dynamic imaging of the 8-day-old zebrafish (O. latipes) embryonic heart, HyLFM-Net successfully imaged the dynamic of the zebrafish heart within a field of view of 350 × 300 × 150
The utilization of entirely deep learning-based approaches holds the potential to significantly reduce the presence of mosaic-like artifacts in the vicinity of the focal plane, a prevalent occurrence in LFD (Prevedel et al., 2014) and can accurately recover the signal even when the SNR of the raw image is low (Vizcaino et al., 2021a; Wang et al., 2021; Yi et al., 2023; Wagner et al., 2021). However, this approach has some drawbacks because the network simultaneously improves the resolution and spatial-angular of light field, which may increase the training workload and lead to structure missing and image artifacts. To improve this problem, it is necessary to improve the adaptability of the network structure and loss function to achieve satisfactory prediction results.
3.2 Type II: Deep learning enhanced raw light field image with numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction
Scanning LFM (sLFM) system (Morozov et al., 2002; Wu et al., 2021) improves the raw light field image quality through physical scanning to collect the 4D spatial-angular light distribution at near-diffraction-limited. However, sLFM usually requires a certain amount of time to scan the sample when acquiring the light field, and this spatial resolution improvement comes at the sacrifice of temporal resolution. To compensate for this deficiency, VsLFM (Lu et al., 2023) optimizes the scanning process using a deep learning model based on DAOSLIMIT (Wu et al., 2021).
After the light field’s resolution is increased, VsLFM is a typical network that is used for reconstruction. This process primarily uses deep learning to improve the raw light field image’s resolution. The subsequent reconstruction process necessitates the use of physical iterations to convert sample images from various angular views into volumetric images. To simulate the scanning process, VsLFM utilizes a supervised learning network (Vs-Net) to extract, interact, fuse and upsample spatial angle features. In network training, phase-dependent low-resolution angular data is used to learn physical priori relationships, and the high-resolution angular measurements produced by the sLFM are used as anticipated output. To rebuild 3D high-resolution volumes, iterative tomography is finally applied utilizing DAO on several angular views that are acquired by Vs-Net (Figure 5A). The subsequent reconstruction process requires the use of physical iterations to reconstruct the sample images from different viewpoints into volumetric images (Figure 5A). It is the improved resolution of the raw light field image that makes the imaging effect of VsLFM higher than that of the fully deep learning-based methods, especially in the localized details of specific depths where the image quality of VsLFM is close to ground truth.
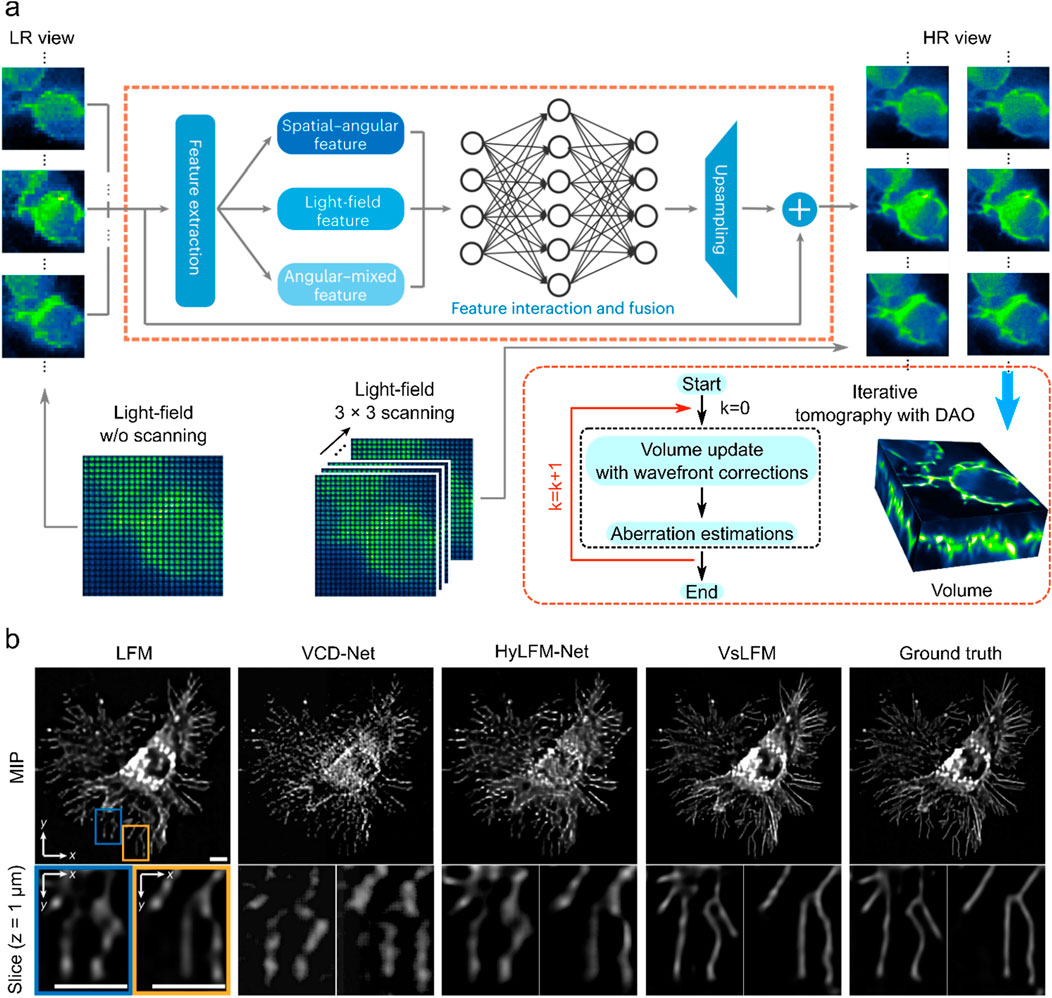
Figure 5. Deep learning enhanced raw light field image with numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction. (A) VsLFM schematic diagram. (B) Enhanced sections extracted from xy cross-sections at z = 1
VsLFM outperforms other methods such as LFM, VCD-Net, and HyLFM-Net on maximum intensity projection (MIP) images. VsLFM is able to obtain better resolution and contrast and performs well on both cell membrane-labeled and mitochondria-labeled samples (Figure 5B). In the numerical simulation of the synthesized 3D tubulins structure, the SNR of VsLFM in the spatial-angular domain is improved by about 15 dB and the SSIM is improved by 0.12. However, the increase in resolution involves physical iterations that can lead to time-consuming and poor reproducibility of the results. To address this issue, VsLFM has improved HyLFM-Net into HyLFM-A-Net to replace the physical iteration process with a deep neural network, which reduces the reconstruction of the whole process from 1,200 s to 11 s. The combination of Vs-Net and HyLFM-A-Net results in a deep neural network for mapping LF images to volumetric images. In contrast to the fully deep learning-based method, this approach is equivalent to tuning the network during the training process, so the complexity and redundancy of the model are much higher.
3.3 Type III: Numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction with deep learning enhanced volumetric data
It is widely acknowledged that conventional numerical iterative algorithms are unable to produce satisfactory reconstructions due to the presence of redundancy in the majority of light field datasets. Consequently, researchers are faced with the challenge of fully utilizing the redundancy (Dansereau et al., 2015; Jayaweera et al., 2020; Mihara et al., 2016). Moreover, real optical physics has many deviations from the model so the corresponding errors propagate during the reconstruction process can cause image noise, blurring, and artifacts. To obtain higher resolution light field reconstruction, the results are usually further post-processed after reconstruction by conventional iterative methods. It is on this premise that the deep learning-based post-processing networks CARE (Weigert et al., 2018) (Figure 6A), DFGAN and DFCAN (Qiao et al., 2021) (Figure 6B), have also been applied to LFM.
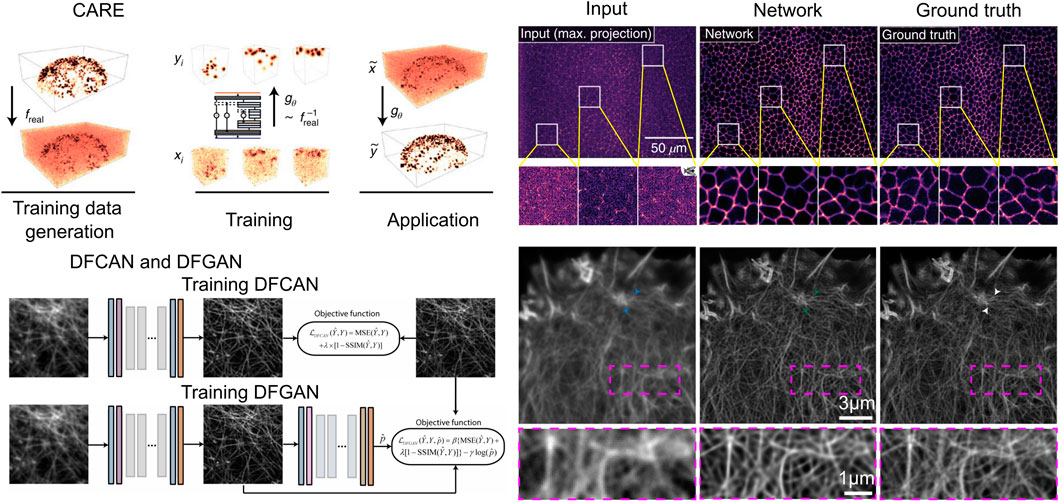
Figure 6. Numerical inversion volumetric reconstruction with deep learning enhanced volumetric data. (A) CARE architecture (left) and the imaging result (right). Scale bars, 50
CARE (Content-Aware Image Restoration) is a proposed method for LFM that utilizes machine learning techniques to enhance the quality of the acquired images. The primary objective of CARE is to develop a residual version of U-Net and train the network with a loss function mean square error (MSE). The CARE network can significantly improve the accuracy of cell nucleus segmentation with reduction in illumination dose, and has improved obvious segmentation accuracy (SEG) score from 0.47 in the original image to 0.65 in the CARE restored image. By leveraging machine-learned image computation, CARE networks can significantly improve image quality, making it easier to analyze biological samples.
After CARE was proposed, networks for single-image super-resolution (SISR) have also been proposed, and the most representative of these networks are DFCAN and DFGAN. DFCAN consists of convolutional layers, and DFCAN is a deeper DFCAN, which consists of convolutional layers, residual groups, Fourier channel attention blocks, skip connections, and activation functions such as GELU. The DFGAN network is derived from a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN (Mirza, 2014)) framework applied to the DFCAN network. The generative model G of DFGAN is DFCAN, which mainly learns data distribution and image transformation. The discriminative model D is constructed based on the conventional CNN architecture, which consists of a convolutional layer activated by LeakyReLU and a fully connected layer activated by a sigmoid activation function. DFCAN and DFGAN validated the structures of clathrin-coated pits (CCPs), microtubules (MTs), and F-actin, and achieved good super-resolution reconstruction performance. Among them, in the case of 3-fold magnification, the quality of the reconstructed images is very close to the real super-resolution images, with the normalized root-mean-square error (NRMSE) below 0.1 on average. In addition, for the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) structure, due to the obvious aggregation caused by chemical fixation, the authors adopted real-time imaging and also obtained satisfactory reconstruction results.
This type of network can also be applied in other microscopy in fluorescent imaging, but it has certain drawbacks. For example, its performance could be compromised when handling samples with extremely complicated structures. In addition, widespread application in practical experiments may be limited by high-fidelity super-resolution information, especially when the network is applied in sample that contains structure absent from the training set. Moreover, this network is not ideal for intensity-based quantification, such as fluorescent substance counting, and cannot be used for all current image restoration challenges due to its nonlinear neural network prediction nature.
To better compare all the mentioned networks, we have summarized their structure and the performance of them in Table 1.
4 Challenges and opportunities
The existing reconstruction methods for LFM using deep learning are facing multiple challenges. Firstly, the current approaches are centered on predicting single frames, necessitating a refinement in ensuring accurate predictions for consecutive frames. Nonetheless, enhancing the forecast precision for continuous frames inevitably translates to an increase in computational burden, thereby escalating the requisites for advanced computational resources. Secondly, the scarcity of available LFM datasets poses a hindrance to fully harnessing these resources for achieving optimal outcomes. Lastly, the enigmatic nature of deep learning models presents a hurdle in enhancing the intelligibility of these intricate models.
4.1 Accuracy in predicting temporal information
Utilizing cutting-edge techniques in real-time data forecasting, researchers can accurately monitor the dynamic behaviors of numerous cells with precision in both the spatial and temporal domains, thereby enhancing comprehension of neuronal population activities (Prevedel et al., 2014; Hornik et al., 1989). Nonetheless, when applying deep learning methodologies to LFM, the conventional practice involves individual frame prediction, leading to potential inconsistencies in temporal coherence and the presence of artifacts over time intervals. To address this challenge effectively, it is crucial to explicitly account for temporal dynamics during data reconstruction by incorporating time-resolved data. While a straightforward approach involves treating time as an extra dimension within CNNs, such a method may not be viable for extensive networks managing prolonged correlations. An alternative and more efficient solution are to merge CNNs with advanced recurrent neural networks like convLSTM (Zhang and Zhang, 2024) and convGRU (Lagemann et al., 2021) architectures, which are specifically tailored for sequence prediction tasks. However, this integrated approach may demand more sophisticated hardware resources to ensure streamlined execution.
4.2 Hardware requirement
In the realm of deep learning for applications like LFM, the necessity for customized software frameworks to facilitate the manipulation and analysis of intricate neural networks is evident. A pivotal consideration in these advancements pertains to the evolving hardware prerequisites. As we all known, specialized graphics processors (GPUs) for training deep learning models underscores the criticality of hardware in expediting computational processes. The migration towards GPU utilization over conventional central processing units (CPUs) is essential for substantial gains in training speed, significantly reducing the training duration. This transition not only accelerates the pace of model refinement but also addresses the cost constraints associated with sophisticated hardware requirements. Looking ahead, the symbiotic relationship between software innovation and hardware optimization remains fundamental in shaping the trajectory of deep learning applications, paving the way for enhanced efficiencies and broader accessibility across research domains.
4.3 Better network structures and training strategies can reduce the need for datasets
Deep learning’s effectiveness is vitally dependent on the availability of training data. Inadequate training data will result in poor performance. However, a prevalent misperception is that deep learning requires an enormous amount of training samples. For example, VsLFM (Lu et al., 2023) training typically uses 5,000 paired spatial-angular patches, and VCD-Net (Wang et al., 2021) trains using 4,580 pairs of image patches, each with a light field image (176 × 176 pixels) and a volume (176 × 176 × 51 pixels). However, LFMNet (Vizcaino et al., 2021a) required 362 high-resolution images (1,287 × 1,287 pixels), whereas based on the U-Net architecture (Ounkomol et al., 2018) only used 40 images (1,500 × 1,500 pixels). It can be observed that different network architectures and training strategies can significantly reduce the size of the training dataset. The quality of the data and its relevance to the situation are likely more crucial. In order to advance further, LFM necessitates innovative experimental and computational approaches for the production of an increased quantity and quality of training data.
4.4 Strategies for obtaining a light field dataset and leveraging existing training data to enhance the dataset
Various strategies can be explored to acquire a comprehensive light field dataset. One avenue involves conducting specialized experiments tailored to capture the requisite images for training purposes. For instance, employing confocal microscopy and light field microscopy in tandem to capture pairs of high-quality volumetric images along with corresponding light field data from a stationary cell location can help validate LFM image reconstruction algorithm. Additionally, leveraging an in-depth understanding of the underlying physics governing light field propagation enables the utilization of forward model simulations to generate authentic images (Weigert et al., 2018; Nehme et al., 2018). Furthermore, the integration of neural networks presents a promising approach to dataset creation. Recent endeavors have focused on the development of cell generation models through adversarial generative techniques (Osokin et al., 2017; Goldsborough et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019), leading to the generation of synthetic images that can subsequently contribute to training reconstruction algorithms. Moreover, conventional approaches, such as data augmentation, present a feasible tactic for enriching datasets by creating diverse variations of existing images. This process involves employing methodologies like rotation, scaling, and manipulation of lighting conditions to expand the range of training samples available for model learning. An alternative efficacious approach involves the utilization of transfer learning (Zeiler and Fergus, 2014). By transferring knowledge from pre-trained models to new tasks, transfer learning enables the efficient utilization of learned features and representations, thereby enhancing the generalization capability and performance of the neural network on specific tasks. These techniques, rooted in the diversification of data and the strategic reuse of network knowledge, play pivotal roles in advancing the efficacy and adaptability of deep learning models across various domains and applications. By pretraining networks on extensive datasets sourced from different domains, transfer learning expedites convergence and enhances the generalization capabilities of the models (Weiss et al., 2016). This multifaceted approach holds significant promise for enriching the light field dataset and maximizing its efficacy in a research context.
4.5 Explainable/interpreting the deep neural network
The challenge of model interpretability emerges as a critical issue given the inherently opaque and enigmatic nature of deep neural networks (Zhang et al., 2018). To establish deep learning as a reliable component within LFM-based processes, it is important to explore the integration of conceptual frameworks and interactive graphical tools to elucidate the underlying rationale behind generating specific outcomes. Encouragingly, the field of computer vision has witnessed advancements in enhancing the interpretability of deep learning through various methodologies. These include delving into the essential components of input images for accurate predictions, scrutinizing the function of intermediate layers, analyzing the contributions of different module through ablation studies, constructing hierarchical explanatory graphs spanning across layers, and designing network architectures that prioritize interpretability. The adaptation of these techniques to the domain of light field imaging is deemed essential, calling for the development of specialized tools tailored to facilitate the interpretation of results. One potential avenue involves the creation of tools explicitly designed to explicate the rationale behind predicted outcomes, thereby fostering transparency and comprehension in the intricate mechanisms governing deep neural networks in LFM contexts.
4.6 Outlook for deep learning to microscale light field image reconstruction
Deep learning-based LFM is still in its nascent stage, but significant advancements have been achieved in leveraging deep learning techniques for this purpose. As we look forward, the future of deep learning-based LFM reconstruction may further highlight the utilization of expansive and high-quality big data sets to facilitate various forms of learning paradigms such as supervised, weakly supervised, self-supervised, or unsupervised learning. To promote broader adoption and enhancement of existing tools, as well as the development of novel ones, it is critical to create extensive datasets to meet the image analysis requirements of the broader life sciences data. These datasets should be publicly accessible, assisting skilled machine learning researchers to tackle biological challenges. It is evident that there are numerous unexplored applications awaiting discovery in this domain. It is hence advisable to simultaneously push forward the tool development and biological prediction processes, given that deep learning fundamentally thrives on data analysis.
Author contributions
BL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YZ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZZ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. DW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by Zhejiang Provincial Medical and Health Technology Project (Grant No. 2024KY246), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (NO. NS2023007), the Key Laboratory of Intake and Exhaust Technology, Ministry of Education (CEPE2024015).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alain, M., Aenchbacher, W., and Smolic, A. (2019). Interactive light field tilt-shift refocus with generalized shift-and-sum. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1910.04699.
Alhashim, I. (2018). High quality monocular depth estimation via transfer learning. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1812.11941.
Broxton, M., Grosenick, L., Yang, S., Cohen, N., Andalman, A., Deisseroth, K., et al. Wave optics theory and 3-D deconvolution for the light field microscope, Opt. Exp. 21 (21), 25418–25439. doi:10.1364/OE.21.0254182013).
Chen, J., Sasaki, H., Lai, H., Su, Y., Liu, J., Wu, Y., et al. (2021). Three-dimensional residual channel attention networks denoise and sharpen fluorescence microscopy image volumes. Nat. Methods 18 (6), 678–687.
Choy, C., Gwak, J., and Savarese, S. (2019). 4d spatio-temporal convnets: Minkowski convolutional neural networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 3075–3084.
Dansereau, D. G., Pizarro, O., and Williams, S. B. (2015). Linear volumetric focus for light field cameras. ACM Trans. Graph. 34 (2), 15-1.
Dansereau, D. G., Schuster, G., Ford, J., and Wetzstein, G. (2017). “A wide-field-of-view monocentric light field camera,” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 5048–5057.
Dosovitskiy, A. (2020). An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2010.11929.
Drozdova, M., Kinakh, V., Bait, O., Taran, O., Lastufka, E., Dessauges-Zavadsky, M., et al. (2024). Radio-astronomical image reconstruction with a conditional denoising diffusion model. Astronomy and Astrophysics 683, A105.
Erisen, S. (2024). SERNet-former: semantic segmentation by efficient residual network with attention-boosting gates and attention-fusion networks. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2401.15741.
Fan, Q., Xu, W., Hu, X., Zhu, W., Yue, T., Zhang, C., et al. (2022). Trilobite-inspired neural nanophotonic light-field camera with extreme depth-of-field. Nat. Comm., 13 (1), 2130.
Foret, P., Kleiner, A., Mobahi, H., and Neyshabur, B. (2020). Sharpness-aware minimization for efficiently improving generalization. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2010.01412.
Godard, C., Mac Aodha, O., and Brostow, G. J. (2017). “Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 270–279.
Goldsborough, P., Pawlowski, N., Caicedo, J. C., Singh, S., and Carpenter, A. E. (2017). CytoGAN: generative modeling of cell images. BioRxiv, 227645.
Gu, X., Fan, Z., Zhu, S., Dai, Z., Tan, F., and Tan, P. (2020). “Cascade cost volume for high-resolution multi-view stereo and stereo matching,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2495–2504.
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., and White, H. (1989). Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. 2 (5), 359–366.
Huang, F., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Wang, S., and Wu, X. (2023). Spectral clustering super-resolution imaging based on multispectral camera array. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 32, 1257–1271.
Jayaweera, S. S., Edussooriya, C. U., Wijenayake, C., Agathoklis, P., and Bruton, L. T. (2020). Multi-volumetric refocusing of light fields. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 28 31–35.
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., and Fei-Fei, L. (2016). “Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution,” in Computer vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016 (Springer), 694–711.
Kaiming, H., Xiangyu, Z., Shaoqing, R., and Jian, S. (2016). “Deep residual learning for image recognition,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Vol. 34, 770–778.
Kim, D., Lai, C. H., Liao, W. H., Murata, N., Takida, Y., Uesaka, T., et al. (2023). Consistency trajectory models: learning probability flow ode trajectory of diffusion. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2310.02279
Kim, J., Jeong, Y., Kim, H., Lee, C. K., Lee, B., Hong, J., et al. (2016). F-number matching method in light field microscopy using an elastic micro lens array. Opt. Lett., 41 (12), 2751–2754.
Kinga, D, and Adam, J. B. (2015). A method for stochastic optimization. International conference on learning representations (ICLR) 5, 6
Lagemann, C., Lagemann, K., Mukherjee, S., and Schröder, W. (2021). Deep recurrent optical flow learning for particle image velocimetry data. Nat. Mach. Intell. 3 (7), 641–651. doi:10.1038/s42256-021-00369-0
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature 521 (7553), 436–444. doi:10.1038/nature14539
Ledig, C., Theis, L., Huszár, F., Caballero, J., Cunningham, A., Acosta, A., et al. (2017). “Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 4681–4690.
Levoy, M., and Hanrahan, P. (2023). “Light field rendering,” in Seminal Graphics Papers: Pushing the Boundaries. Vol.2, 441–452.
Levoy, M., Ng, R., Adams, A., Footer, M., and Horowitz, M. (2006). “Light field microscopy”, in Acm siggraph 2006 papers, 924–934.
Li, J., Kaneko, A. M., and Fukushima, E. F. (2014). “Proposal of terrain mapping under extreme light conditions using direct stereo matching methods,” in 2014 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration, 153–158.
Li, Y., Fang, C., Yang, J., Wang, Z., Lu, X., and Yang, M. H. (2017). Universal style transfer via feature transforms. Advances in neural information processing systems 30.
Liang, J., Cao, J., Sun, G., Zhang, K., Van Gool, L., and Timofte, R. (2021). “Swinir: image restoration using swin transformer”, in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 1833–1844.
Lin, X., Wu, J., Zheng, G., and Dai, Q. (2015). Camera array based light field microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Exp. 6 (9), 3179–3189. doi:10.1364/boe.6.003179
Liu, C., Jiang, Z., Wang, X., Zheng, Y., Zheng, Y. W., and Wang, Q. H. (2022). Continuous optical zoom microscope with extended depth of field and 3D reconstruction. PhotoniX, 3 (1), 20.
Lu, Z., Liu, Y., Jin, M., Luo, X., Yue, H., Wang, Z., et al. (2023). Virtual-scanning light-field microscopy for robust snapshot high-resolution volumetric imaging. Nat. Methods 20 (5), 735–746.
Mignard-Debise, L., and Ihrke, I. (2015). “Light-field microscopy with a consumer light-field camera,” 2015 International Conference on 3D Vision, 335-343.
Mihara, H., Funatomi, T., Tanaka, K., Kubo, H., Mukaigawa, Y., and Nagahara, H. (2016). “4D light field segmentation with spatial and angular consistencies,” in 2016 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), 1–8.
Morozov, O. G., Ovchinnikov, D. L., Akhtiamov, R. A., Zalyalov, R. G., Il’in, G. L., Pol'ski, Y. E., et al. (2002) “Two-frequency scanning LFM lidars: theory and applications,” in Remote sensing of clouds and the atmosphere VI Vol. 4539 (SPIE), 158–168. doi:10.1117/12.454435
Nehme, E., Weiss, L. E., Michaeli, T., and Shechtman, Y. (2018). Deep-STORM: super-resolution single-molecule microscopy by deep learning. Optica, 5, 458–464.
Ng, R., Levoy, M., Brédif, M., Duval, G., Horowitz, M., and Hanrahan, P. (2005). Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera. Stanford university.
Orth, A., and Crozier, K. (2012). Microscopy with microlens arrays: high throughput, high resolution and light-field imaging, Opt. Express 20 (12), 13522–13531. doi:10.1364/OE.20.0135222012).
Osokin, A., Chessel, A., Carazo Salas, R. E., and Vaggi, F. (2017). “GANs for biological image synthesis,” in Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2233–2242.
Ounkomol, C., Seshamani, S., Maleckar, M. M., Collman, F., and Johnson, G. R. (2018). Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy. Nat. Methods 15 (11), 917–920.
Prevedel, R., Yoon, Y. G., Hoffmann, M., Pak, N., Wetzstein, G., Kato, S., et al. (2014). Simultaneous whole-animal 3D imaging of neuronal activity using light-field microscopy, Nat. Methods 11 (7), 727–730. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2964
Qiao, C., Li, D., Guo, Y., Liu, C., Jiang, T., Dai, Q., et al. (2021). Evaluation and development of deep neural networks for image super-resolution in optical microscopy. Nat. Methods 18 (2), 194–202.
Quan, C., Zhou, J., Zhu, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, S., Liang, D., et al. (2021). Homotopic gradients of generative density priors for MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 40 (12), 3265–3278.
Rumelhart, D. E., Hinton, G. E., and Williams, R. J. (1986) . Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323 (6088), 533–536.
Sadat, S., Buhmann, J., Bradely, D., Hilliges, O., and Weber, R. M. (2023). CADS: Unleashing the diversity of diffusion models through condition-annealed sampling. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2310.17347.
Schlemper, J., Caballero, J., Hajnal, J. V., Price, A., and Rueckert, D. (2017). “A deep cascade of convolutional neural networks for MR image reconstruction,” in Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 25th International Conference, IPMI 2017, Boone, NC, June 25–30, 2017, 647–658.
Shi, W., Caballero, J., Huszár, F., Totz, J., Aitken, A. P., Bishop, R., et al. (2016). “Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 1874–1883.
Srivastava, S., and Sharma, G. (2024). “Omnivec: Learning robust representations with cross modal sharing,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, 1236–1248.
Taguchi, Y., Agrawal, A., Ramalingam, S., and Veeraraghavan, A. (2010). “ Axial light field for curved mirrors: Reflect your perspective, widen your view,” in 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 499–506.
Tateno, K., Navab, N., and Tombari, F. (2018). “ Distortion-aware convolutional filters for dense prediction in panoramic images,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (Munich, Germany: ECCV), 707–722.
Vizcaino, J. P., Saltarin, F., Belyaev, Y., Lyck, R., Lasser, T., and Favaro, P. (2021a) Learning to reconstruct confocal microscopy stacks from single light field images. IEEE transactions on computational imaging 7, 775–788.
Vizcaino, J. P., Wang, Z., Symvoulidis, P., Favaro, P., Guner-Ataman, B., Lasser, T., et al. (2021b). “Real-time light field 3D microscopy via sparsity-driven learned deconvolution,” in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), 1–11.
Wagner, N., Beuttenmueller, F., Norlin, N., Gierten, J., Boffi, J. C., Wittbrodt, J., et al. (2021). Deep learning-enhanced light-field imaging with continuous validation. Nat. Methods 18 (5), 557–563.
Walton, S., Hassani, A., Xu, X., Wang, Z., and Shi, H. (2022). Stylenat: giving each head a new perspective. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2211.05770.
Wan, Z., Zhang, B., Chen, D., Zhang, P., Wen, F., Liao, J., et al. (2022). Old photo restoration via deep latent space translation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 45 (2), 2071–2087.
Wang, P., Wang, S., Lin, J., Bai, S., Zhou, X., Zhou, J., et al. (2023). One-peace: Exploring one general representation model toward unlimited modalities. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2305.11172.
Wang, Z., Zhu, L., Zhang, H., Li, G., Yi, C., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Real-time volumetric reconstruction of biological dynamics with light-field microscopy and deep learning. Nat. methods 18 (5), 551–556. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2305.11172
Weigert, M., Schmidt, U., Boothe, T., Müller, A., Dibrov, A., Jain, A., et al. (2018). Content-aware image restoration: pushing the limits of fluorescence microscopy, Nat. Methods 15 (12), 1090–1097. doi:10.1038/s41592-018-0216-7
Weiss, K., Khoshgoftaar, T. M., and Wang, D. (2016). A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 3, 1–40.
Wu, G., Masia, B., Jarabo, A., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Dai, Q., et al. (2017). Light field image processing: An overview. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing 11 (7), 926–954.
Wu, J., Lu, Z., Jiang, D., Guo, Y., Qiao, H., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). Iterative tomography with digital adaptive optics permits hour-long intravital observation of 3D subcellular dynamics at millisecond scale. Cell 184 (12), 3318–3332.
Xu, H., and Zhang, J. (2020). “Aanet: Adaptive aggregation network for efficient stereo matching,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 1959–1968.
Yi, C., Zhu, L., Sun, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, M., Zhong, F., et al. (2023). Video-rate 3D imaging of living cells using Fourier view-channel-depth light field microscopy. Commun. Biol. 6 (1), 1259.
Yu, J., Wang, Z., Vasudevan, V., Yeung, L., Seyedhosseini, M., and Wu, Y. (2022). Contrastive captioners are image-text foundation models. arXiv preprint.
Yuan, H., Cai, L., Wang, Z., Hu, X., Zhang, S., and Ji, S. (2019). Computational modeling of cellular structures using conditional deep generative networks. Bioinformatics 35 (12), 2141–2149. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bty923
Zeiler, M. D. (2014). “Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks,” in European conference on computer vision/arXiv (Vol. 1311).
Zhang, C., Chen, Y., Fan, Z., Huang, Y., Weng, W., Ge, R., et al. (2024). TC-DiffRecon: texture coordination MRI reconstruction method based on diffusion model and modified MF-UNet method. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2402.11274.
Zhang, H., and Zhang, W. (2024). Application of GWO-attention-ConvLSTM model in customer churn prediction and satisfaction analysis in customer relationship management. Heliyon 10 (7), e37229. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37229
Zhang, Q., Wu, Y. N., and Zhu, S.-C. (2018). “ Interpretable convolutional neural networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 8827–8836.
Zhao, F., Zhu, L., Fang, C., Yu, T., Zhu, D., and Fei, P. (2020). Deep-learning super-resolution light-sheet add-on microscopy (Deep-SLAM) for easy isotropic volumetric imaging of large biological specimens. Biomed. Opt. Exp. 11 (12), 7273–7285.
Zhou, Y., Jiao, J., Huang, H., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Shi, H., et al. (2020). “When awgn-based denoiser meets real noises,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vol. 34 (07), 13074–13081. doi:10.1609/aaai.v34i07.7009
Keywords: deep learning, light field microscopy, light field imaging, high resolution, volumetric reconstruction
Citation: Lin B, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Zhu Z and Wang D (2024) Deep learning methods for high-resolution microscale light field image reconstruction: a survey. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12:1500270. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1500270
Received: 23 September 2024; Accepted: 30 October 2024;
Published: 18 November 2024.
Edited by:
Zetao Chen, Tianjin University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hao Dong, Zhejiang Lab, ChinaGuosen Xie, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Lin, Tian, Zhang, Zhu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Depeng Wang, ZGVwZW5nLndhbmdAbnVhYS5lZHUuY24=
 Bingzhi Lin
Bingzhi Lin Yuan Tian2
Yuan Tian2 Depeng Wang
Depeng Wang