
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ERRATUM article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. , 11 February 2022
Sec. Biomaterials
Volume 10 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.862276
This article is part of the Research Topic Functional and Smart Biomaterials: Development and Application in Regenerative Medicine View all 18 articles
This article is an erratum on:
Gelatin/Polycaprolactone Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes: The Effect of Composition and Physicochemical Properties on Postoperative Cardiac Adhesion
by Wang, X., Xiang, L., Peng, Y., Dai, Z., Hu, Y., Pan, X., Zhou, X., Zhang, H., and Feng, B. (2021). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9:792893. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.792893
Due to a production error, the image used for Figure 8 was incorrect. Figure 6 was mistakenly duplicated and used in place of the correct image for Figure 8.
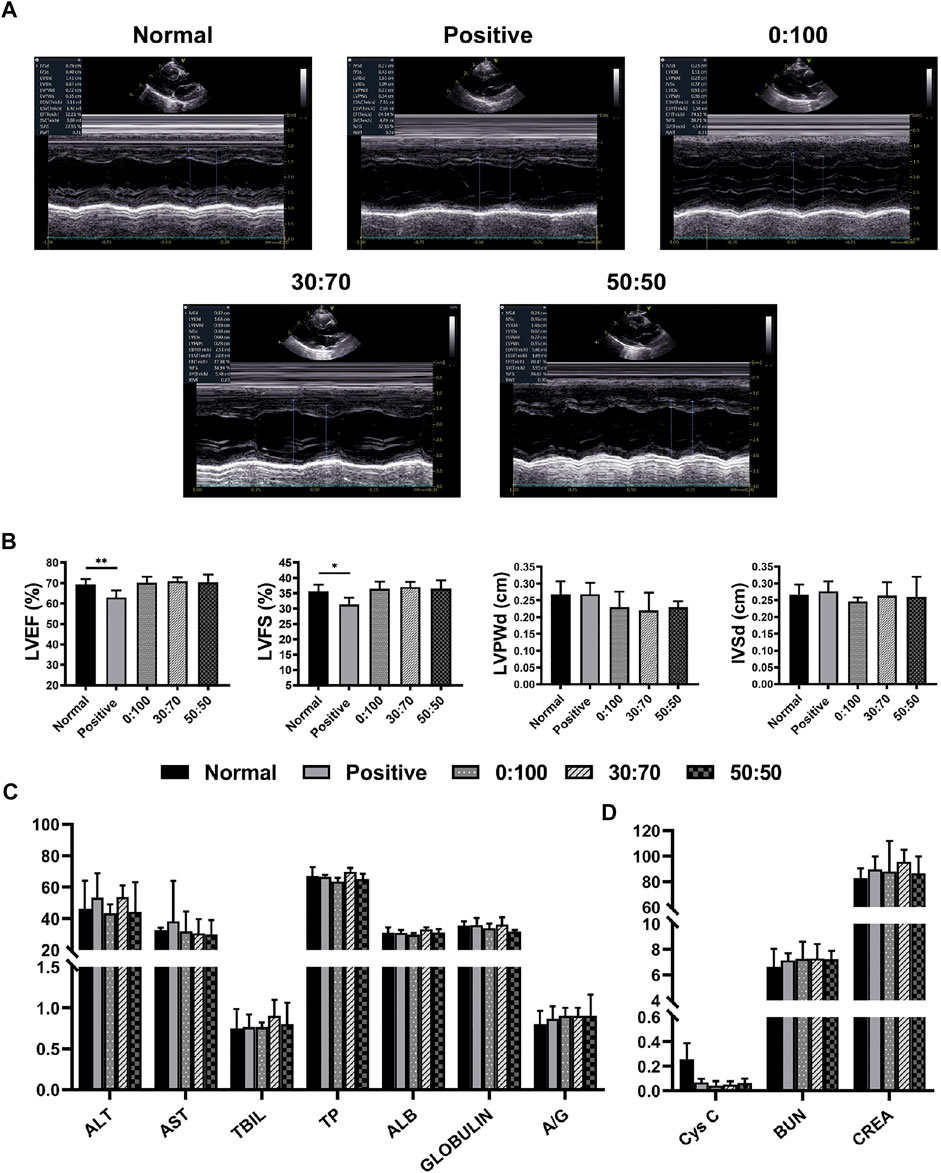
FIGURE 8. Three months after surgery (A) representative echocardiography images, (B) heart function and (C,D) liver/kidney function for normal and experimental groups. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
The correct Figure 8 appears below. The publisher apologizes for this mistake. The original version of this article has been updated.
Keywords: electrospinning, gelatin, polycaprolactone, postoperative adhesion, cardiac surgery
Citation: (2022) Erratum: Gelatin/Polycaprolactone Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes: The Effect of Composition and Physicochemical Properties on Postoperative Cardiac Adhesion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10:862276. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.862276
Received: 25 January 2022; Accepted: 25 January 2022;
Published: 11 February 2022.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2022 . This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Frontiers Production Office, cHJvZHVjdGlvbi5vZmZpY2VAZnJvbnRpZXJzaW4ub3Jn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.